⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
Capabilities of GPT-5 on Multimodal Medical Reasoning
Authors:Shansong Wang, Mingzhe Hu, Qiang Li, Mojtaba Safari, Xiaofeng Yang
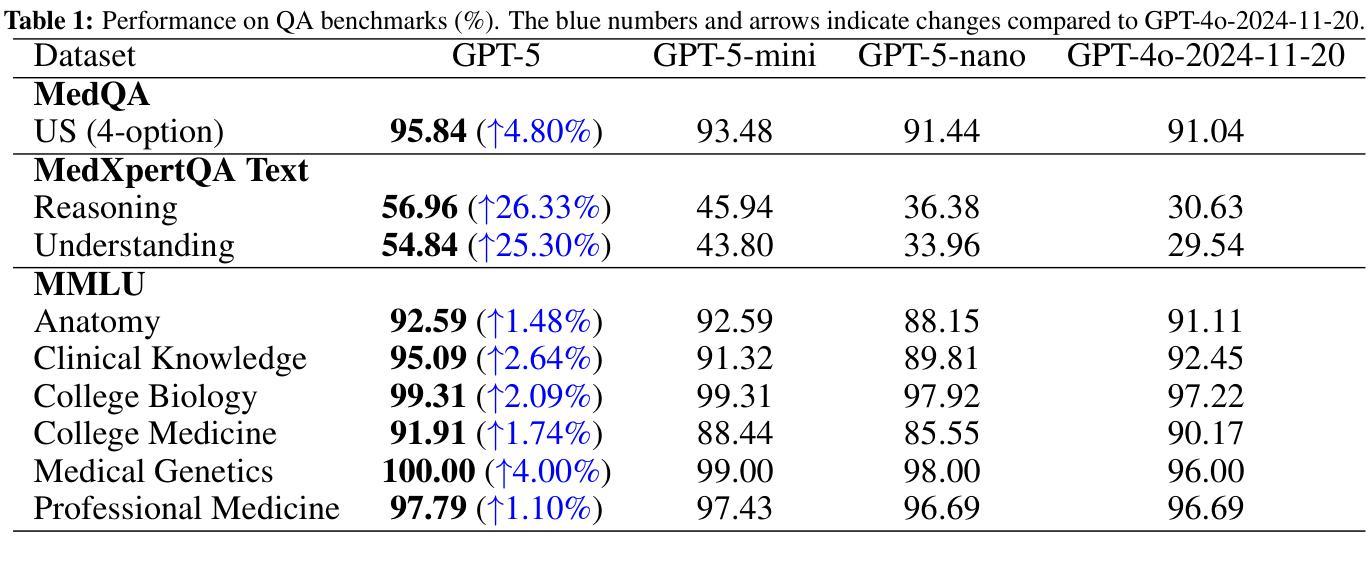
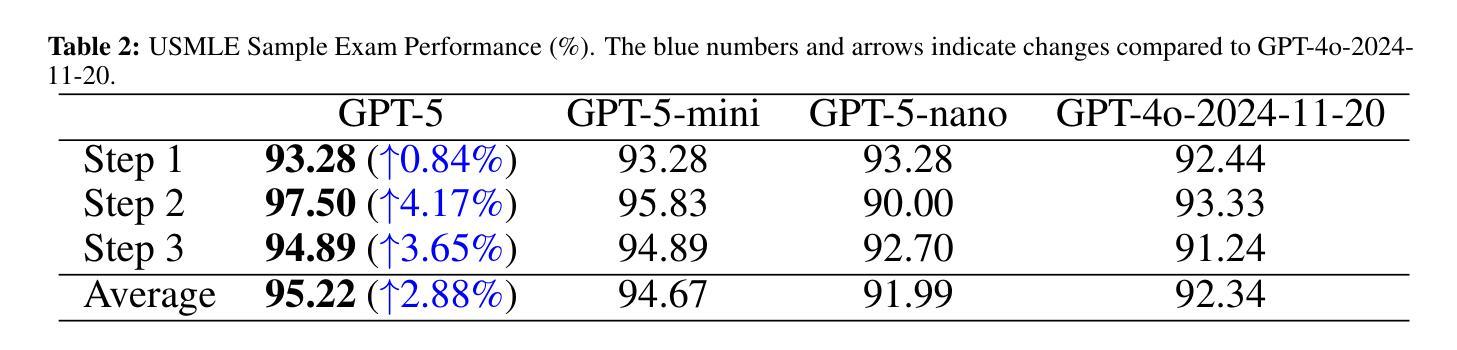
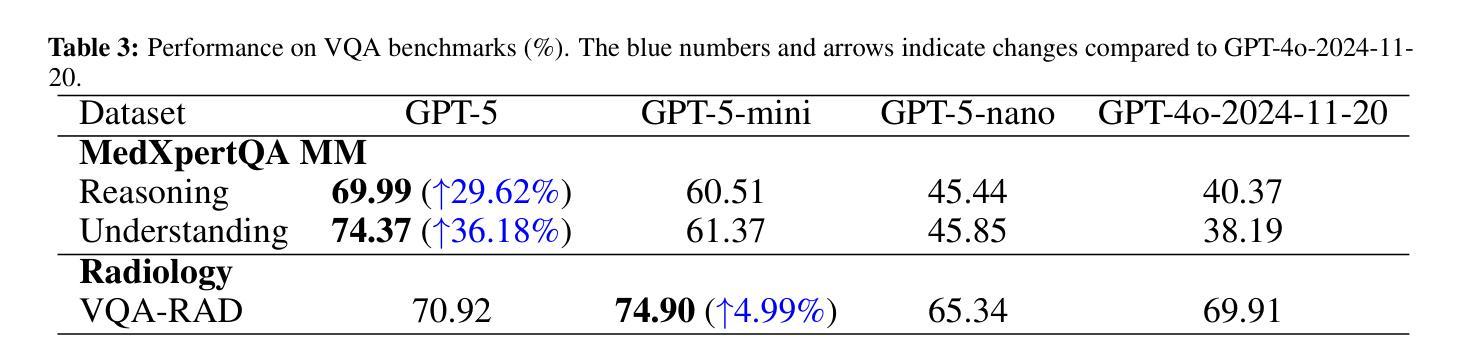
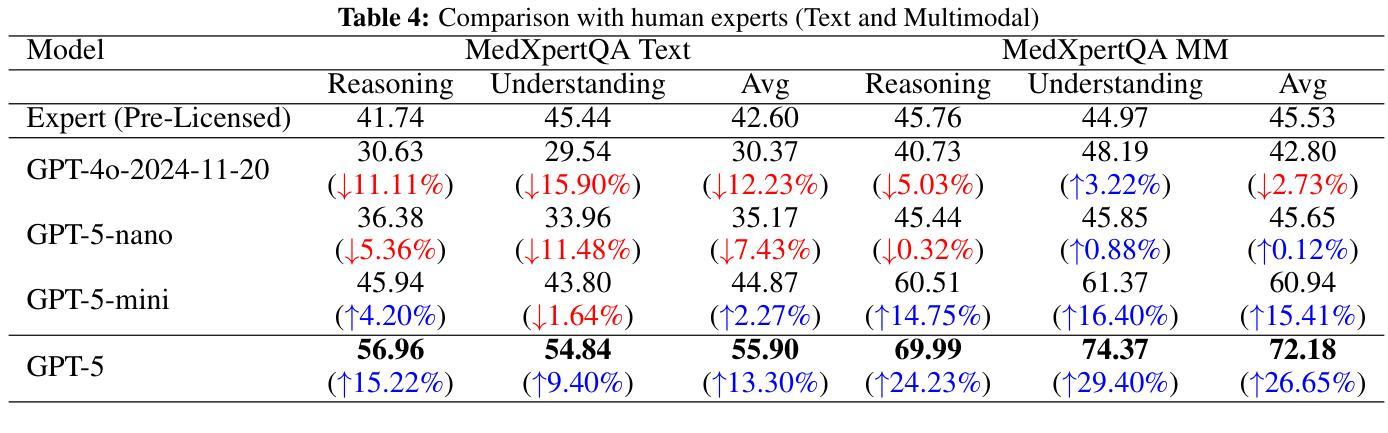
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled general-purpose systems to perform increasingly complex domain-specific reasoning without extensive fine-tuning. In the medical domain, decision-making often requires integrating heterogeneous information sources, including patient narratives, structured data, and medical images. This study positions GPT-5 as a generalist multimodal reasoner for medical decision support and systematically evaluates its zero-shot chain-of-thought reasoning performance on both text-based question answering and visual question answering tasks under a unified protocol. We benchmark GPT-5, GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano, and GPT-4o-2024-11-20 against standardized splits of MedQA, MedXpertQA (text and multimodal), MMLU medical subsets, USMLE self-assessment exams, and VQA-RAD. Results show that GPT-5 consistently outperforms all baselines, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy across all QA benchmarks and delivering substantial gains in multimodal reasoning. On MedXpertQA MM, GPT-5 improves reasoning and understanding scores by +29.62% and +36.18% over GPT-4o, respectively, and surpasses pre-licensed human experts by +24.23% in reasoning and +29.40% in understanding. In contrast, GPT-4o remains below human expert performance in most dimensions. A representative case study demonstrates GPT-5’s ability to integrate visual and textual cues into a coherent diagnostic reasoning chain, recommending appropriate high-stakes interventions. Our results show that, on these controlled multimodal reasoning benchmarks, GPT-5 moves from human-comparable to above human-expert performance. This improvement may substantially inform the design of future clinical decision-support systems.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进展使得通用系统能够在不需要广泛微调的情况下执行越来越复杂的特定领域推理。在医疗领域,决策制定通常需要整合异质的信息来源,包括患者叙述、结构化数据和医疗图像。本研究将GPT-5定位为通用的多模式推理机,用于医疗决策支持,并在统一协议下,系统评估其在基于文本的问题回答和视觉问题回答任务上的零射击链式思维推理性能。我们以MedQA、MedXpertQA(文本和多模态)、MMLU医疗子集、USMLE自我评估考试和VQA-RAD的标准分割数据为基准,对GPT-5、GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano和GPT-4o-2024-11-20进行了评估。结果表明,GPT-5持续优于所有基线,在所有的问答基准测试中达到最先进的准确性,并在多模态推理中实现了实质性的收益。在MedXpertQA MM上,GPT-5在推理和理解方面的得分分别比GPT-4o高出+29.62%和+36.18%,并且在推理和理解方面超越预先授权的专家+24.23%和+29.40%。相比之下,GPT-4o在大多数维度上仍低于人类专家的表现。一个具有代表性的案例研究展示了GPT-5将视觉和文本线索整合到连贯的诊断推理链中的能力,并推荐了适当的高风险干预措施。我们的结果表明,在这些受控的多模态推理基准测试中,GPT-5的表现从与人类相当提升到了超越人类专家的水平。这一改进可能会为未来的临床决策支持系统提供实质性的信息参考。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展使得通用系统能够在不需要广泛微调的情况下执行越来越复杂的领域特定推理。本研究将GPT-5定位为医疗决策支持的一般性多模式推理器,并系统地评估其在统一协议下的零射击链式思维推理性能。在基于文本和视觉的问题回答任务中,GPT-5在各种标准化分割的MedQA、MedXpertQA(文本和多模式)、MMLU医疗子集、USMLE自我评估考试和VQA-RAD上表现出色。结果证明GPT-5在所有问答基准测试中始终优于所有基线,实现了最先进的准确性,并在多模式推理方面取得了重大进展。在MedXpertQA MM上,GPT-5在推理和理解方面的得分分别比GPT-4o高出+29.62%和+36.18%,并且在推理和理解方面超越预先授权的人类专家分别高出+24.23%和+29.40%。相比之下,GPT-4o在大多数维度上仍低于人类专家的表现。一个典型的案例研究表明,GPT-5能够整合视觉和文本线索,形成连贯的诊断推理链,推荐适当的高风险干预措施。我们的结果表明,在这些受控的多模式推理基准测试中,GPT-5的表现已从人类相当的水平提升到了超越人类专家的水平。这一进步可能为未来的临床决策支持系统提供重要的设计参考。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可在无需广泛微调的情况下进行复杂的领域特定推理。
- GPT-5在医疗决策支持中表现出强大的多模式推理能力。
- GPT-5在各种标准化医疗问答基准测试中表现优异,超越其他基准和先前的研究。
- GPT-5在推理和理解方面的得分显著优于预先授权的人类专家。
- GPT-5能整合视觉和文本线索,形成连贯的诊断推理链。
- GPT-5的表现已从人类相当的水平提升到了超越人类专家的水平。
点此查看论文截图



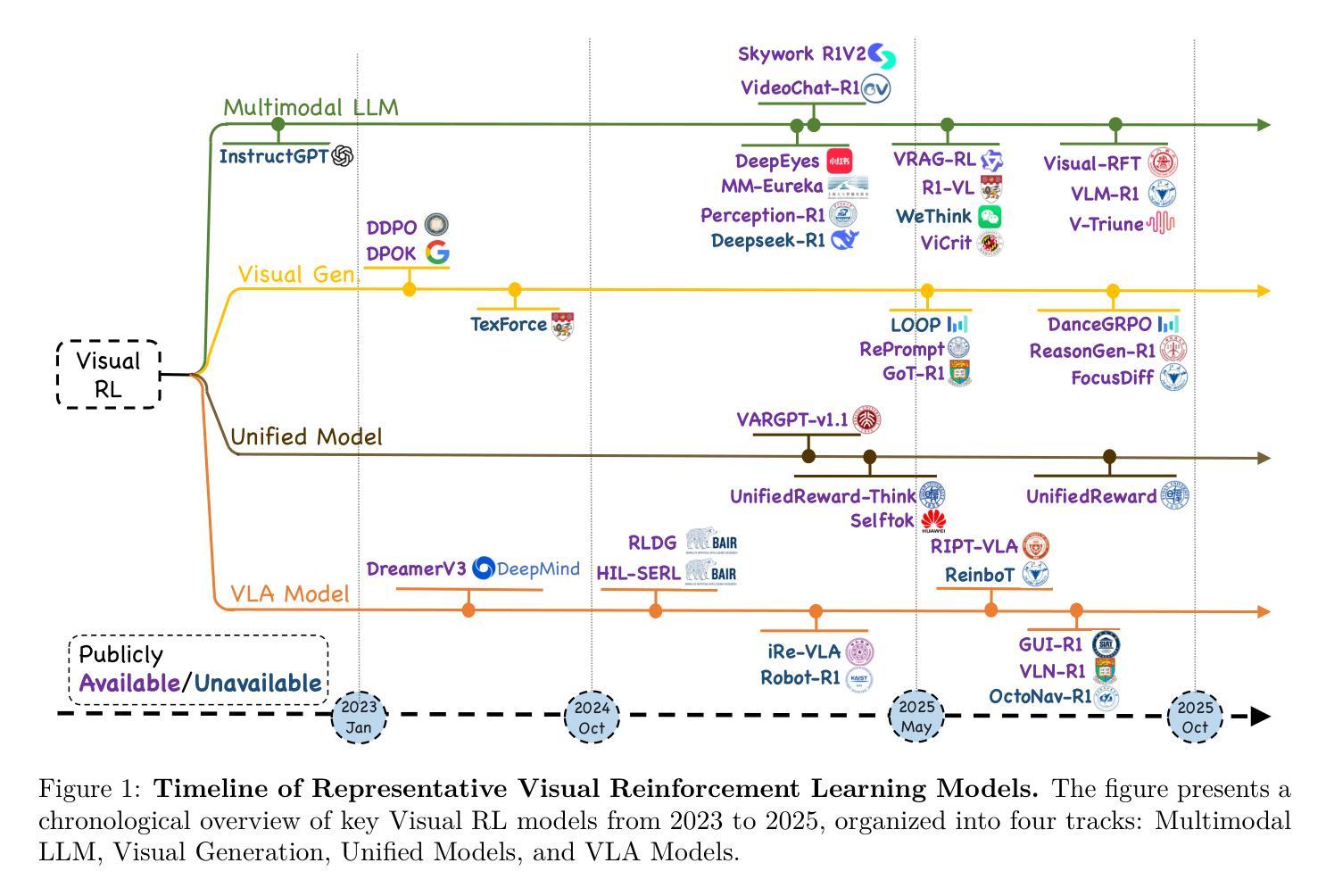
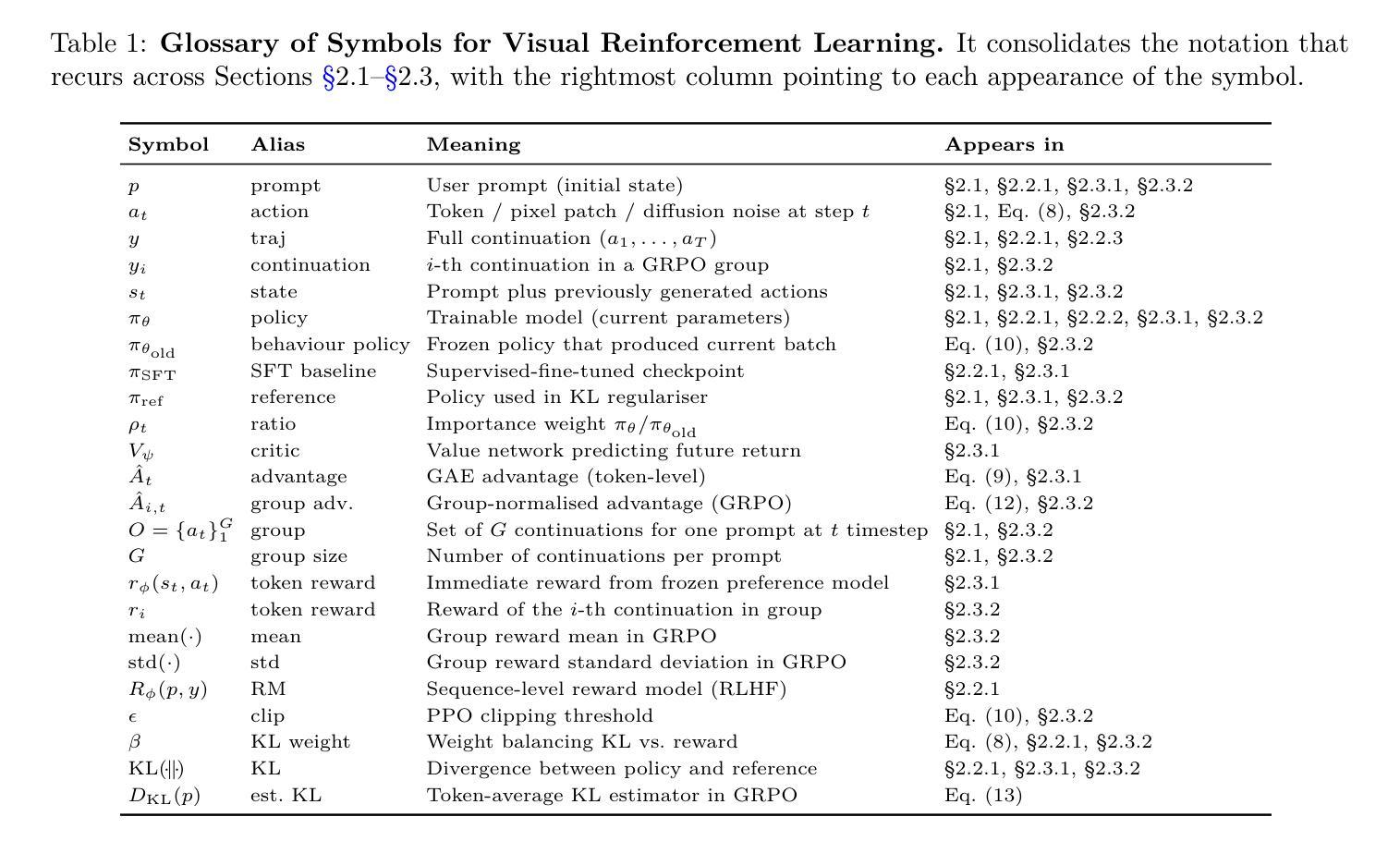
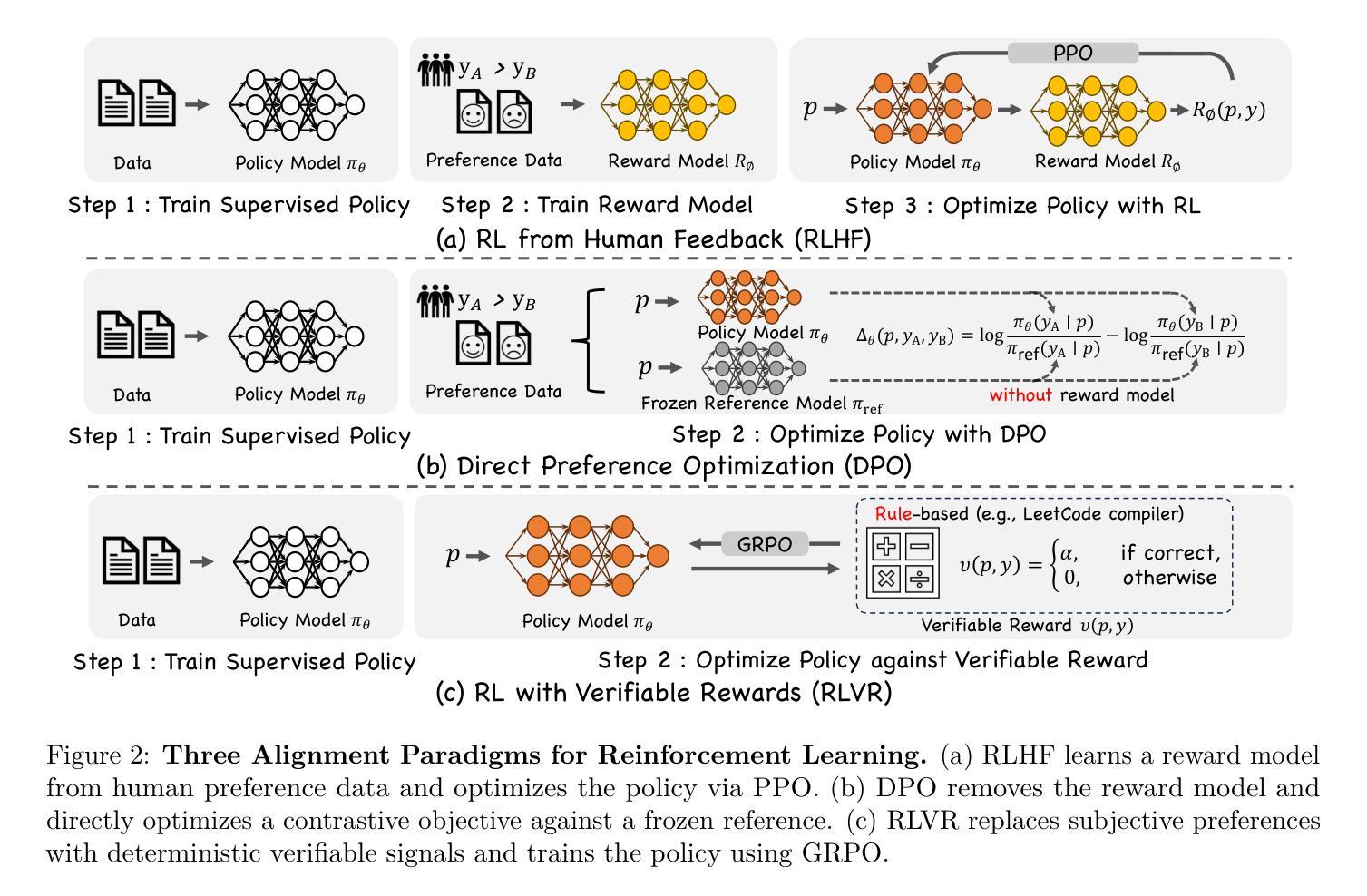
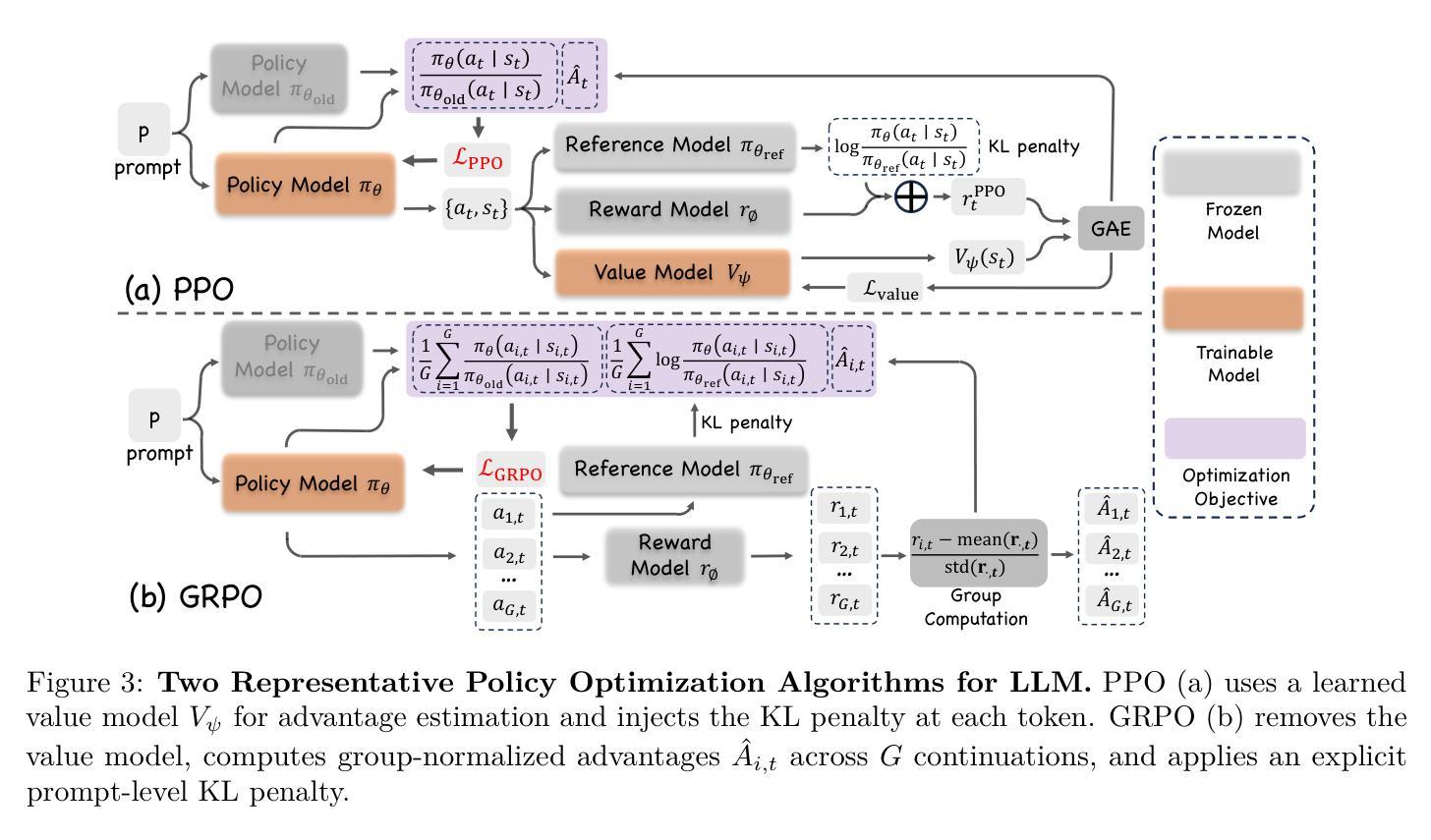
Reinforcement Learning in Vision: A Survey
Authors:Weijia Wu, Chen Gao, Joya Chen, Kevin Qinghong Lin, Qingwei Meng, Yiming Zhang, Yuke Qiu, Hong Zhou, Mike Zheng Shou
Recent advances at the intersection of reinforcement learning (RL) and visual intelligence have enabled agents that not only perceive complex visual scenes but also reason, generate, and act within them. This survey offers a critical and up-to-date synthesis of the field. We first formalize visual RL problems and trace the evolution of policy-optimization strategies from RLHF to verifiable reward paradigms, and from Proximal Policy Optimization to Group Relative Policy Optimization. We then organize more than 200 representative works into four thematic pillars: multi-modal large language models, visual generation, unified model frameworks, and vision-language-action models. For each pillar we examine algorithmic design, reward engineering, benchmark progress, and we distill trends such as curriculum-driven training, preference-aligned diffusion, and unified reward modeling. Finally, we review evaluation protocols spanning set-level fidelity, sample-level preference, and state-level stability, and we identify open challenges that include sample efficiency, generalization, and safe deployment. Our goal is to provide researchers and practitioners with a coherent map of the rapidly expanding landscape of visual RL and to highlight promising directions for future inquiry. Resources are available at: https://github.com/weijiawu/Awesome-Visual-Reinforcement-Learning.
最近,强化学习(RL)和视觉智能交叉领域的进展使得智能体不仅能够感知复杂的视觉场景,还能在这些场景中进行推理、生成和行动。这篇综述对该领域进行了批判性和最新的综合。我们首先正式提出视觉RL问题,并追踪从RLHF到可验证奖励范式,从近端策略优化到群组相对策略优化的策略优化策略的演变。然后,我们将超过200篇具有代表性的作品整理为四个主题支柱:多模态大型语言模型、视觉生成、统一模型框架和视觉语言行动模型。对于每个主题支柱,我们研究了算法设计、奖励工程、基准进展,并总结了趋势,如课程驱动训练、偏好对齐扩散和统一奖励建模。最后,我们回顾了包括集合级保真度、样本级偏好和状态级稳定性的评估协议,并确定了开放挑战,包括样本效率、概括和安全部署。我们的目标是为研究人员和实践者提供快速扩展的视觉RL景观的连贯地图,并突出未来探究的有希望的方向。资源可在:https://github.com/weijiawu/Awesome-Visual-Reinforcement-Learning找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages
Summary
强化学习与视觉智能的交叉融合为智能体提供了更高的能力,它们不仅能感知复杂的视觉场景,还能进行推理、生成和行动。这篇综述对该领域进行了最新、最重要的总结,从策略优化到四大主题支柱(多模态大型语言模型、视觉生成、统一模型框架和视觉语言行动模型),并对课程驱动训练等趋势进行了分析。文章的目的是为研究者和实践者提供视觉强化学习的最新研究地图,并指明未来研究的有前途方向。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习与视觉智能的融合让智能体具备更复杂的能力,如感知、推理、生成和行动。
- 综述文章系统总结了视觉强化学习领域的最新进展和重要成果。
- 文章详细描述了从策略优化到四大主题支柱(多模态大型语言模型等)的研究发展。
- 趋势分析包括课程驱动训练、偏好对齐扩散和统一奖励建模等。
- 综述涵盖了丰富的文献和前沿研究成果的组织和资源链接。
- 文章指出了开放挑战,如样本效率、泛化和安全部署等。
点此查看论文截图

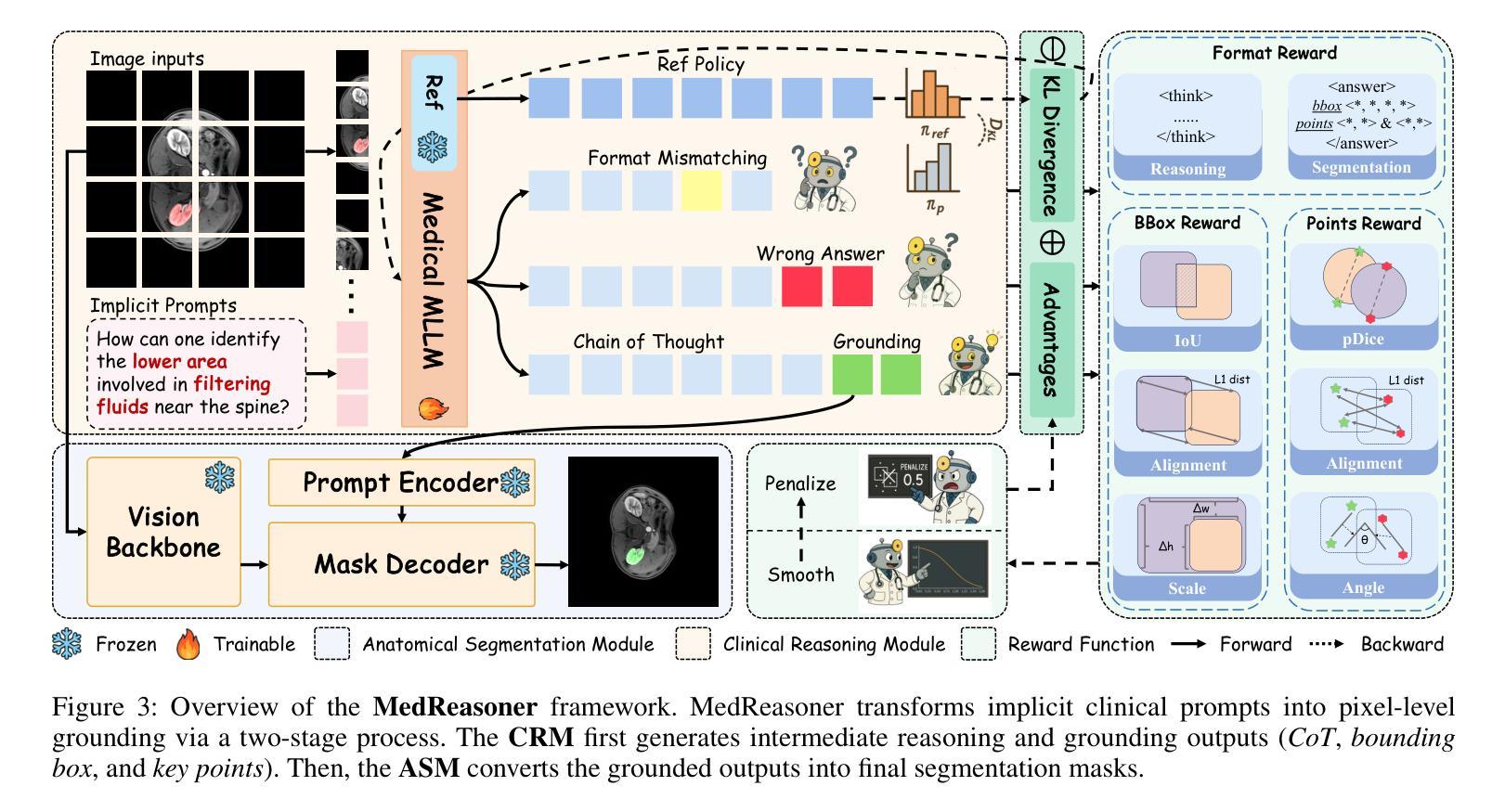
MedReasoner: Reinforcement Learning Drives Reasoning Grounding from Clinical Thought to Pixel-Level Precision
Authors:Zhonghao Yan, Muxi Diao, Yuxuan Yang, Jiayuan Xu, Kaizhou Zhang, Ruoyan Jing, Lele Yang, Yanxi Liu, Kongming Liang, Zhanyu Ma
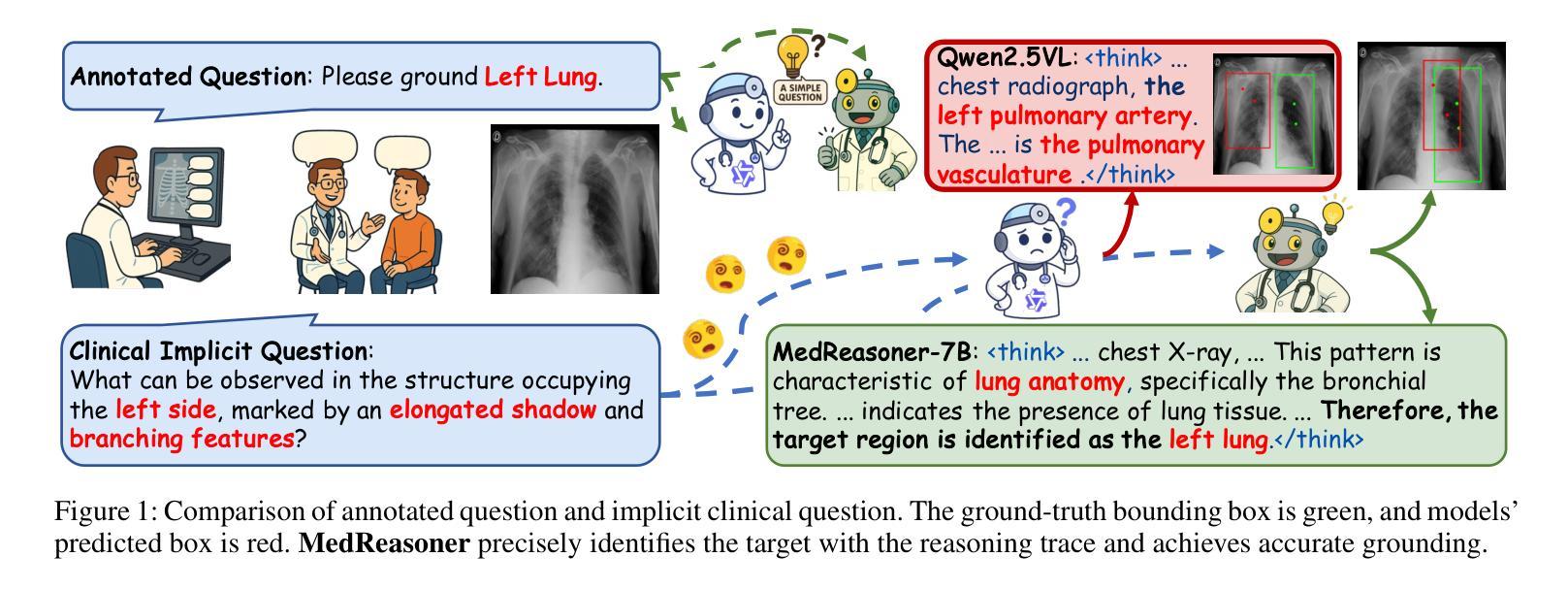
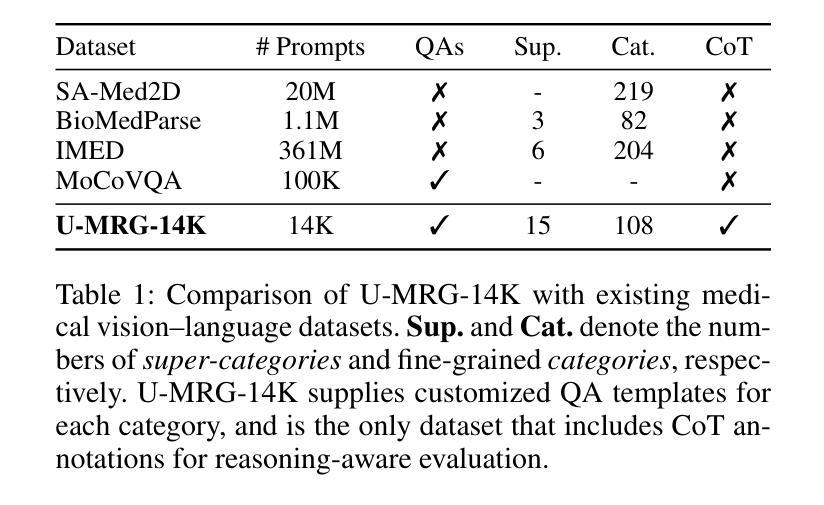
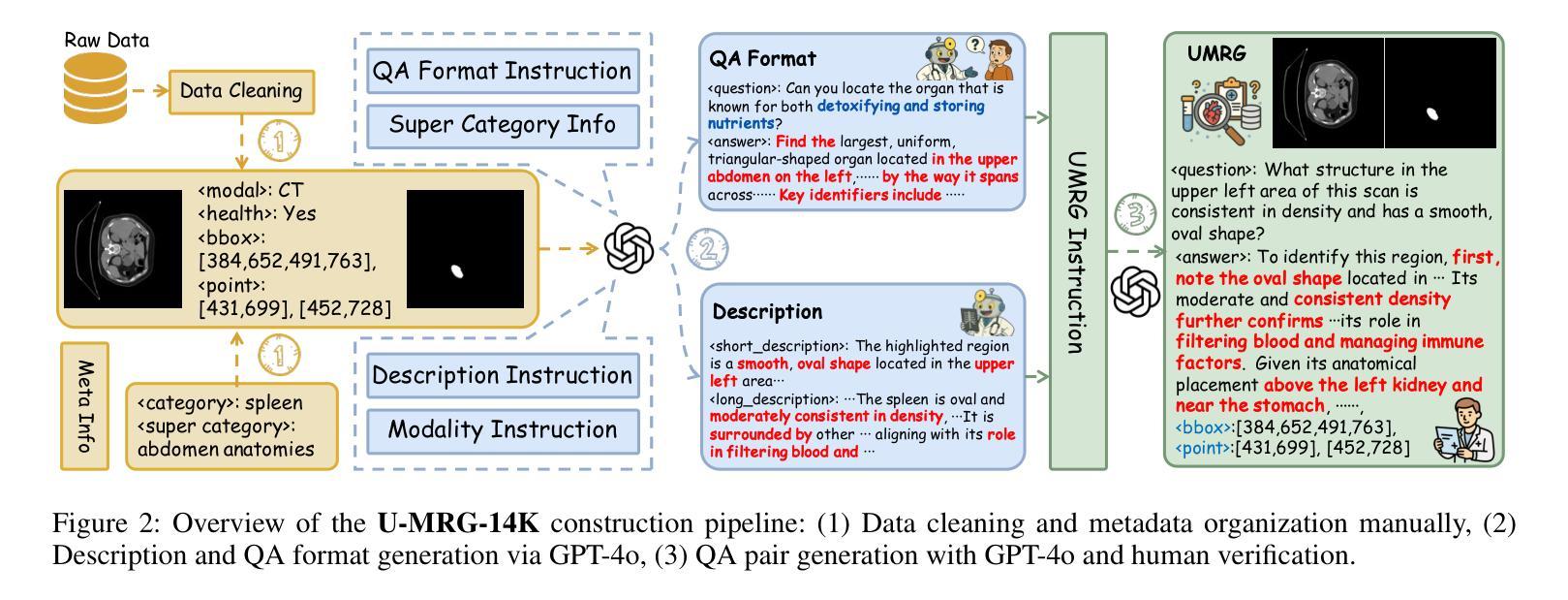
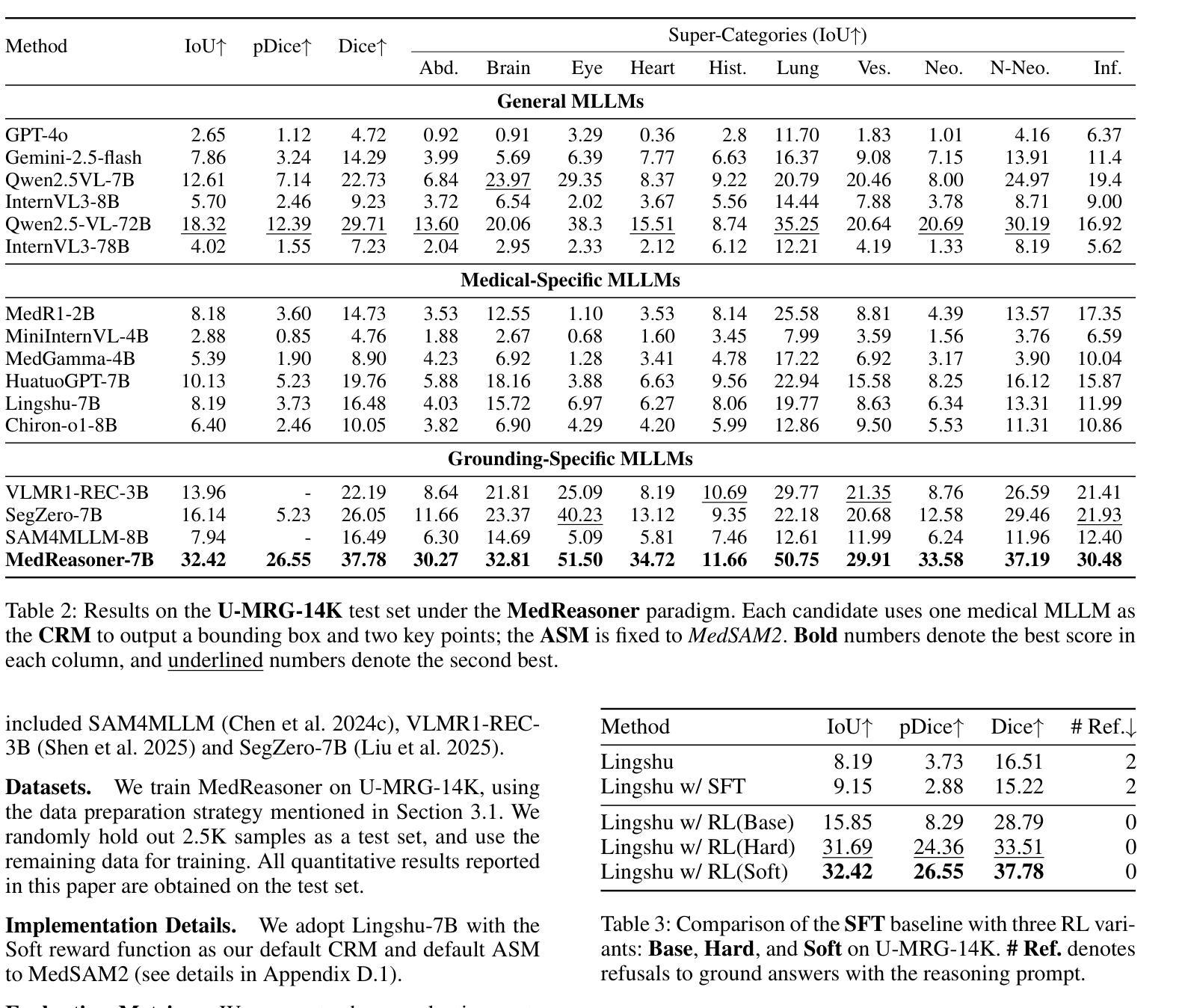
Accurately grounding regions of interest (ROIs) is critical for diagnosis and treatment planning in medical imaging. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) combine visual perception with natural language, current medical-grounding pipelines still rely on supervised fine-tuning with explicit spatial hints, making them ill-equipped to handle the implicit queries common in clinical practice. This work makes three core contributions. We first define Unified Medical Reasoning Grounding (UMRG), a novel vision-language task that demands clinical reasoning and pixel-level grounding. Second, we release U-MRG-14K, a dataset of 14K samples featuring pixel-level masks alongside implicit clinical queries and reasoning traces, spanning 10 modalities, 15 super-categories, and 108 specific categories. Finally, we introduce MedReasoner, a modular framework that distinctly separates reasoning from segmentation: an MLLM reasoner is optimized with reinforcement learning, while a frozen segmentation expert converts spatial prompts into masks, with alignment achieved through format and accuracy rewards. MedReasoner achieves state-of-the-art performance on U-MRG-14K and demonstrates strong generalization to unseen clinical queries, underscoring the significant promise of reinforcement learning for interpretable medical grounding.
在医学成像中,准确定位感兴趣区域(ROI)对于诊断和治疗计划的制定至关重要。虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了视觉感知与自然语言,但当前的医学定位流程仍然依赖于带有明确空间提示的监督微调,这使得它们难以应对临床实践中的隐式查询。本工作做出了三个核心贡献。首先,我们定义了统一医学推理定位(UMRG),这是一种新的视觉语言任务,需要临床推理和像素级定位。其次,我们发布了U-MRG-14K数据集,包含14K个样本,每个样本都有像素级掩膜、隐式临床查询和推理轨迹,涵盖10种模态、15个超类别和108个特定类别。最后,我们推出了MedReasoner,这是一个模块化框架,将推理与分割明确区分开来:MLLM推理器通过强化学习进行优化,而冻结的分割专家将空间提示转换为掩膜,通过格式和精度奖励实现对齐。MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K上达到了最先进的性能,并对未见过的临床查询表现出了强大的泛化能力,这突显了强化学习在可解释的医学定位中的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages
Summary
医学成像中的准确区域定位(ROIs)对于诊断和治疗计划至关重要。当前,医疗定位流程仍然依赖于带有明确空间提示的监督微调,无法处理临床实践中的隐含查询。本文定义了统一医学推理定位(UMRG)这一新颖的视觉语言任务,并发布U-MRG-14K数据集,包含跨越十种模态、十五个超级类别和一百零八种特定类别的隐性临床查询和推理痕迹的一万四千个样本。此外,还推出了MedReasoner模块化框架,将推理与分割分离,优化了强化学习下的MLLM推理器,将空间提示转换为掩膜。MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K上取得了最佳性能,并在未见过的临床查询上展示了强大的泛化能力。通过展现其在强化学习上的巨大潜力证明了技术重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 区域定位(ROIs)在医学成像中的诊断与治疗的角色是核心的。
- 当前医疗定位流程依赖监督微调及明确的空间提示,无法适应临床实践中的隐含查询需求。
- 统一医学推理定位(UMRG)定义了一种新的视觉语言任务,要求临床推理和像素级定位。
- U-MRG-14K数据集包含大量样本,涵盖多种模态、类别和临床查询及推理痕迹。
- MedReasoner模块化框架实现了推理与分割的分离,并采用强化学习优化MLLM推理器性能。
- MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K数据集上表现卓越,并在未见过的临床查询上展现了强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

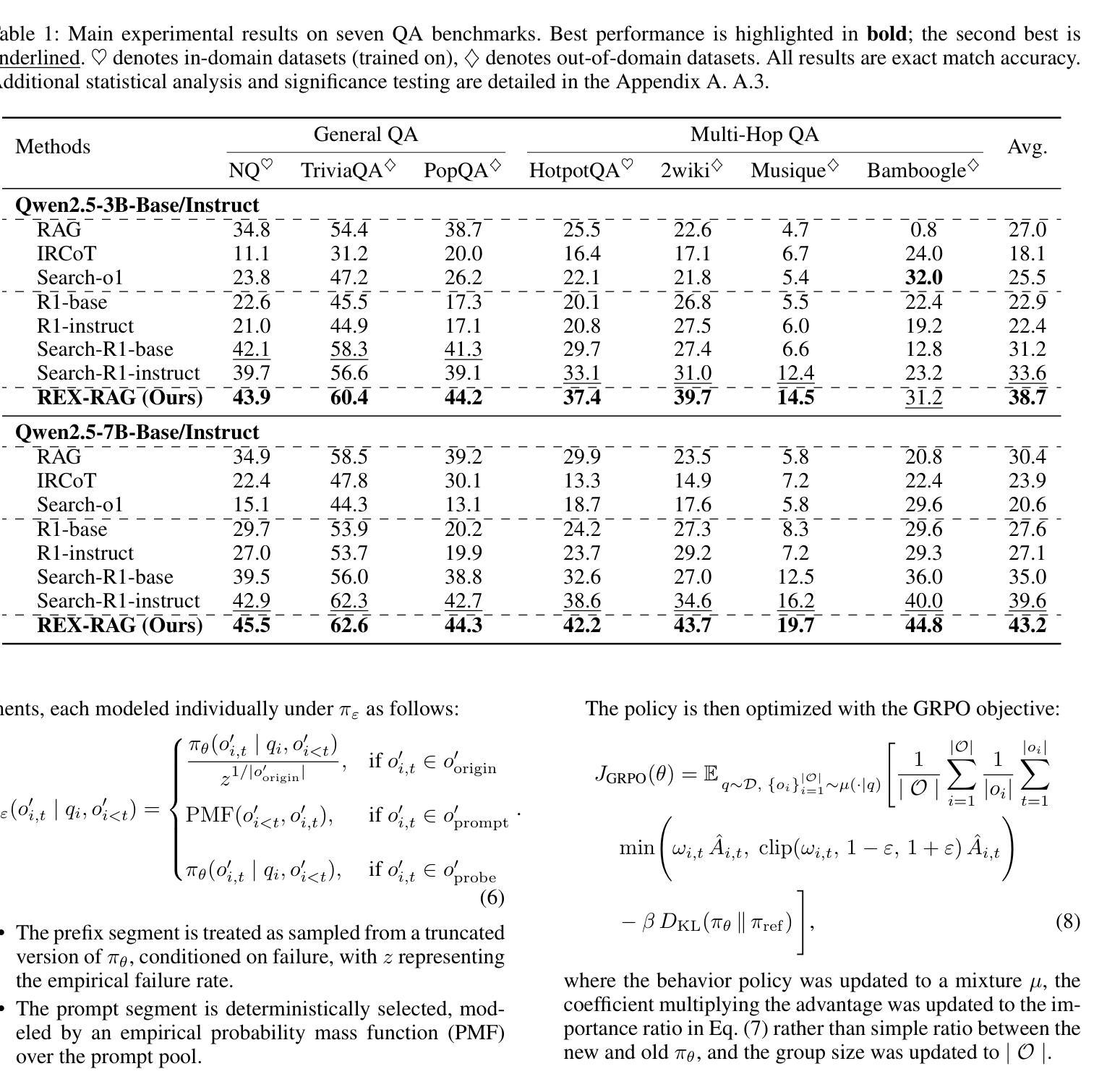
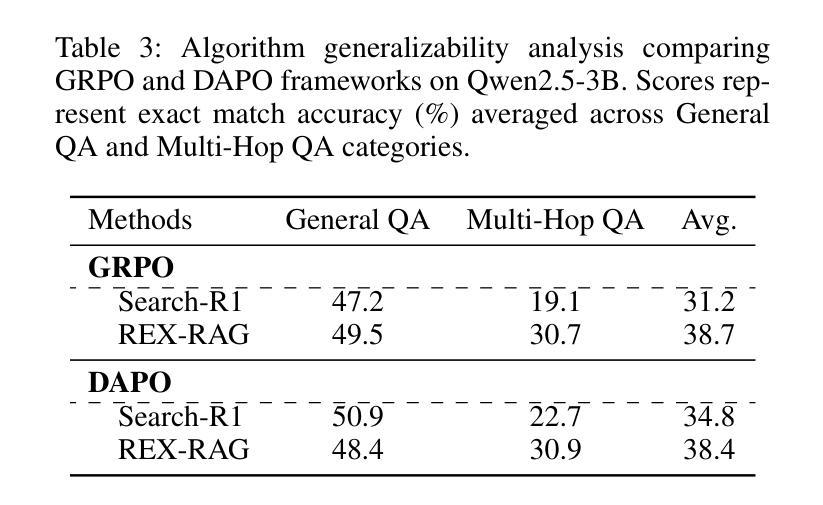
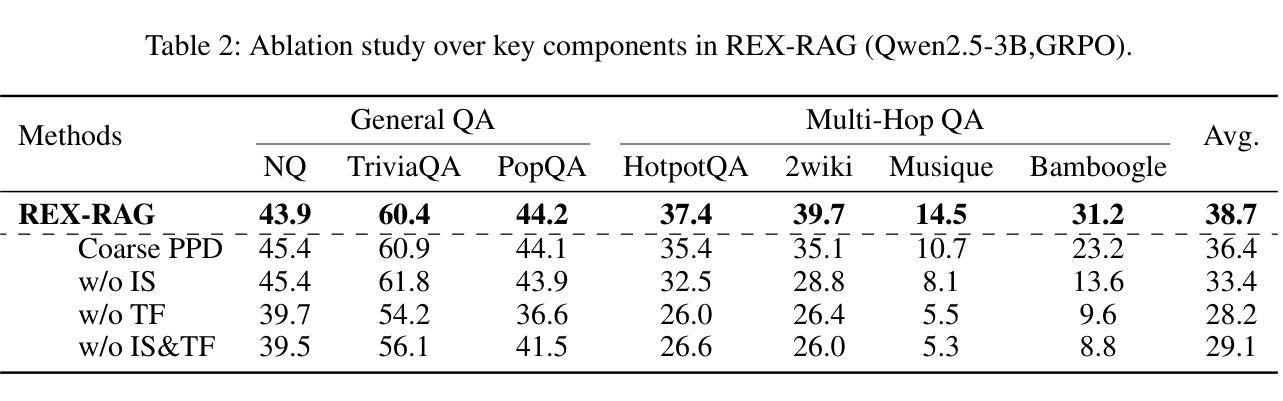
REX-RAG: Reasoning Exploration with Policy Correction in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Wentao Jiang, Xiang Feng, Zengmao Wang, Yong Luo, Pingbo Xu, Zhe Chen, Bo Du, Jing Zhang
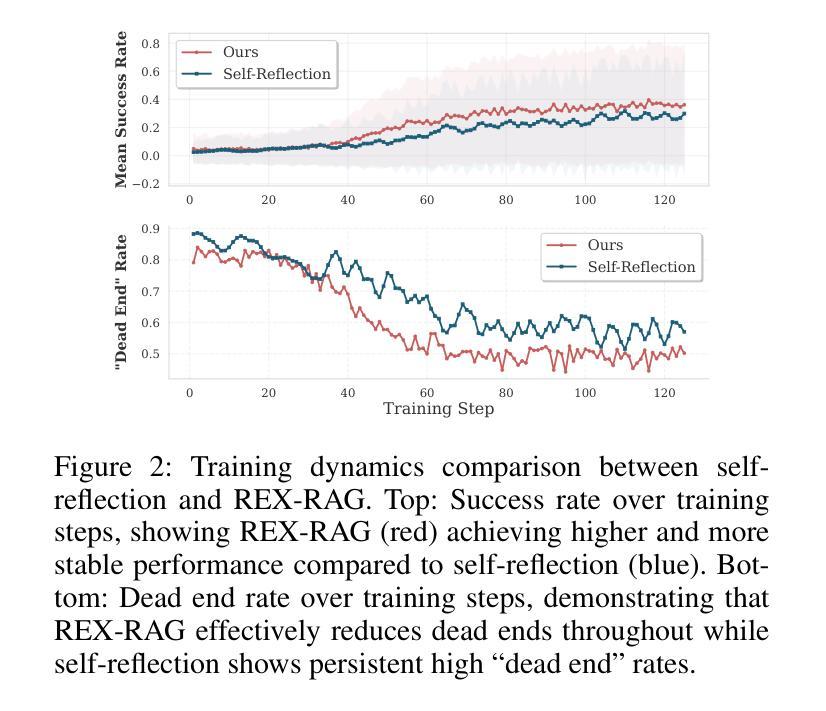
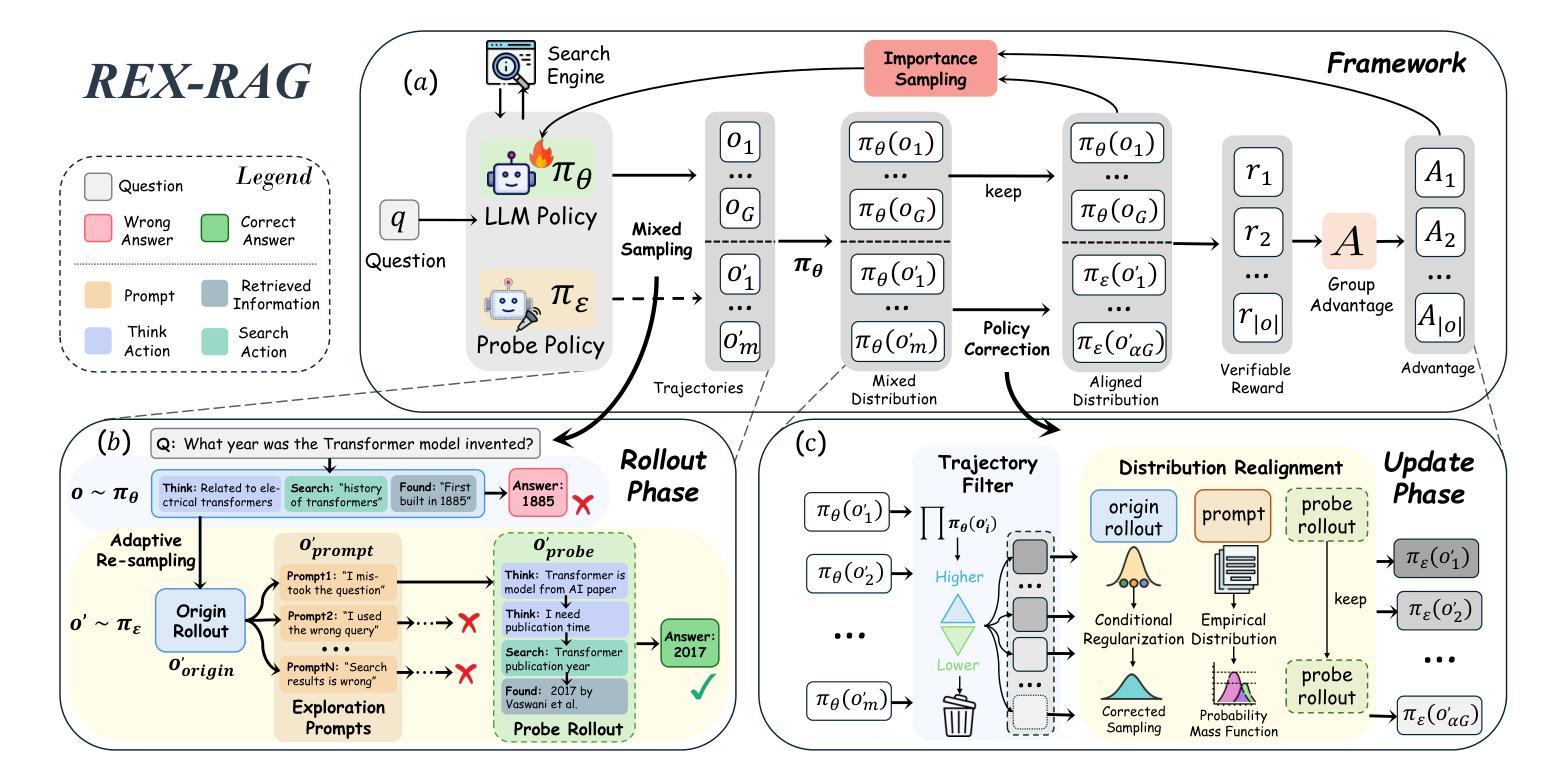
Reinforcement learning (RL) is emerging as a powerful paradigm for enabling large language models (LLMs) to perform complex reasoning tasks. Recent advances indicate that integrating RL with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) allows LLMs to dynamically incorporate external knowledge, leading to more informed and robust decision making. However, we identify a critical challenge during policy-driven trajectory sampling: LLMs are frequently trapped in unproductive reasoning paths, which we refer to as “dead ends”, committing to overconfident yet incorrect conclusions. This severely hampers exploration and undermines effective policy optimization. To address this challenge, we propose REX-RAG (Reasoning Exploration with Policy Correction in Retrieval-Augmented Generation), a novel framework that explores alternative reasoning paths while maintaining rigorous policy learning through principled distributional corrections. Our approach introduces two key innovations: (1) Mixed Sampling Strategy, which combines a novel probe sampling method with exploratory prompts to escape dead ends; and (2) Policy Correction Mechanism, which employs importance sampling to correct distribution shifts induced by mixed sampling, thereby mitigating gradient estimation bias. We evaluate it on seven question-answering benchmarks, and the experimental results show that REX-RAG achieves average performance gains of 5.1% on Qwen2.5-3B and 3.6% on Qwen2.5-7B over strong baselines, demonstrating competitive results across multiple datasets. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/MiliLab/REX-RAG.
强化学习(RL)正成为一种强大的范式,使大型语言模型(LLM)能够执行复杂的推理任务。最近的进展表明,将RL与检索增强生成(RAG)相结合,可以使LLM动态地融入外部知识,从而实现更加明智和稳健的决策。然而,我们在策略驱动的轨迹采样过程中发现了一个关键挑战:LLM经常陷入无结果的推理路径,我们称之为“死胡同”,导致过于自信的错误结论。这严重阻碍了探索并破坏了有效的策略优化。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了REX-RAG(检索增强生成中的带策略修正的推理探索),这是一种新的框架,在保持严谨的策略学习的情况下,探索替代的推理路径,并通过有原则的分布修正来进行策略修正。我们的方法引入了两个关键的创新点:(1)混合采样策略,它将一种新的探针采样方法与探索性提示相结合,以逃离死胡同;(2)策略修正机制,它采用重要性采样来纠正混合采样引起的分布偏移,从而减轻梯度估计偏差。我们在七个问答基准测试上对其实验评估,实验结果表明,在Qwen2.5-3B上REX-RAG平均性能提升5.1%,在Qwen2.5-7B上性能提升3.6%,相较于强大的基线模型表现出竞争力。相关代码已公开在https://github.com/MiliLab/REX-RAG。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 4 figures
Summary:强化学习正在成为使大型语言模型执行复杂推理任务的一种强大范式。将强化学习与检索增强生成相结合,可以动态地使语言模型融入外部知识,从而实现更加明智和稳健的决策。然而,策略驱动的轨迹采样面临一个挑战:语言模型经常陷入不产生效益的推理路径,即“死胡同”,导致过度自信的错误结论。为解决此问题,提出了REX-RAG框架,通过混合采样策略和策略校正机制,在检索增强生成中进行推理探索,同时保持严谨的策略学习。
Key Takeaways:
- 强化学习正在成为大型语言模型执行复杂推理任务的重要工具。
- 整合强化学习与检索增强生成,能让语言模型动态融入外部知识,提高决策质量。
- 策略驱动的轨迹采样在强化学习中存在挑战,语言模型易陷入不产生效益的推理路径。
- REX-RAG框架通过混合采样策略和策略校正机制解决此问题,实现推理探索与严谨的策略学习。
- REX-RAG的混合采样策略结合了新型探针采样方法和探索性提示,有助于逃离“死胡同”。
- REX-RAG的策略校正机制采用重要性采样,纠正由混合采样引起的分布偏移,减轻梯度估计偏差。
- 在七个问答基准测试上的评估显示,REX-RAG相较于强大的基准模型取得了平均性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

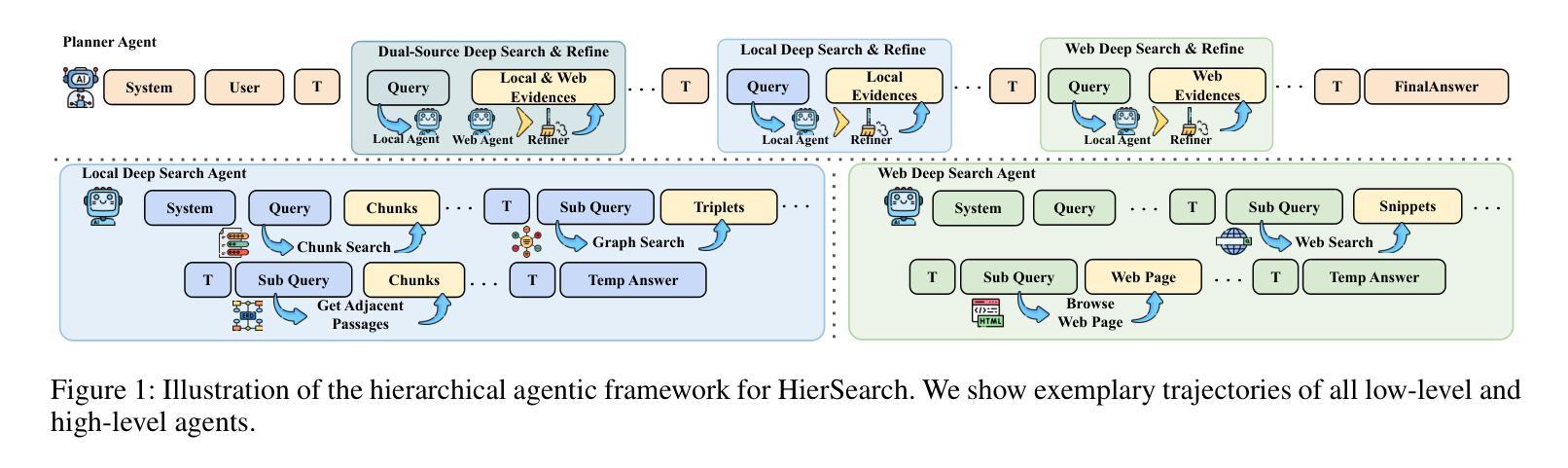
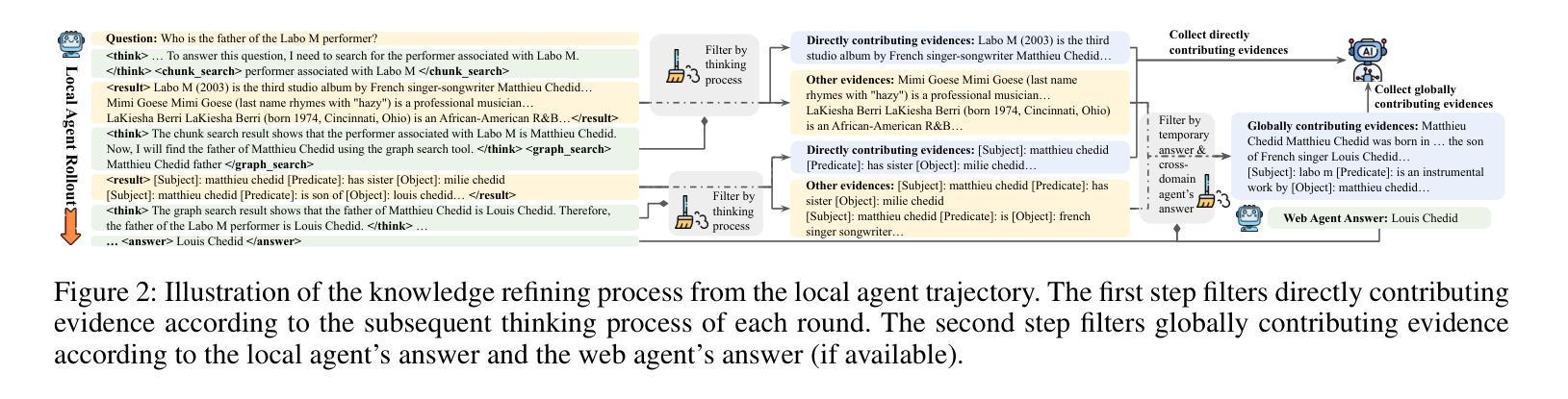
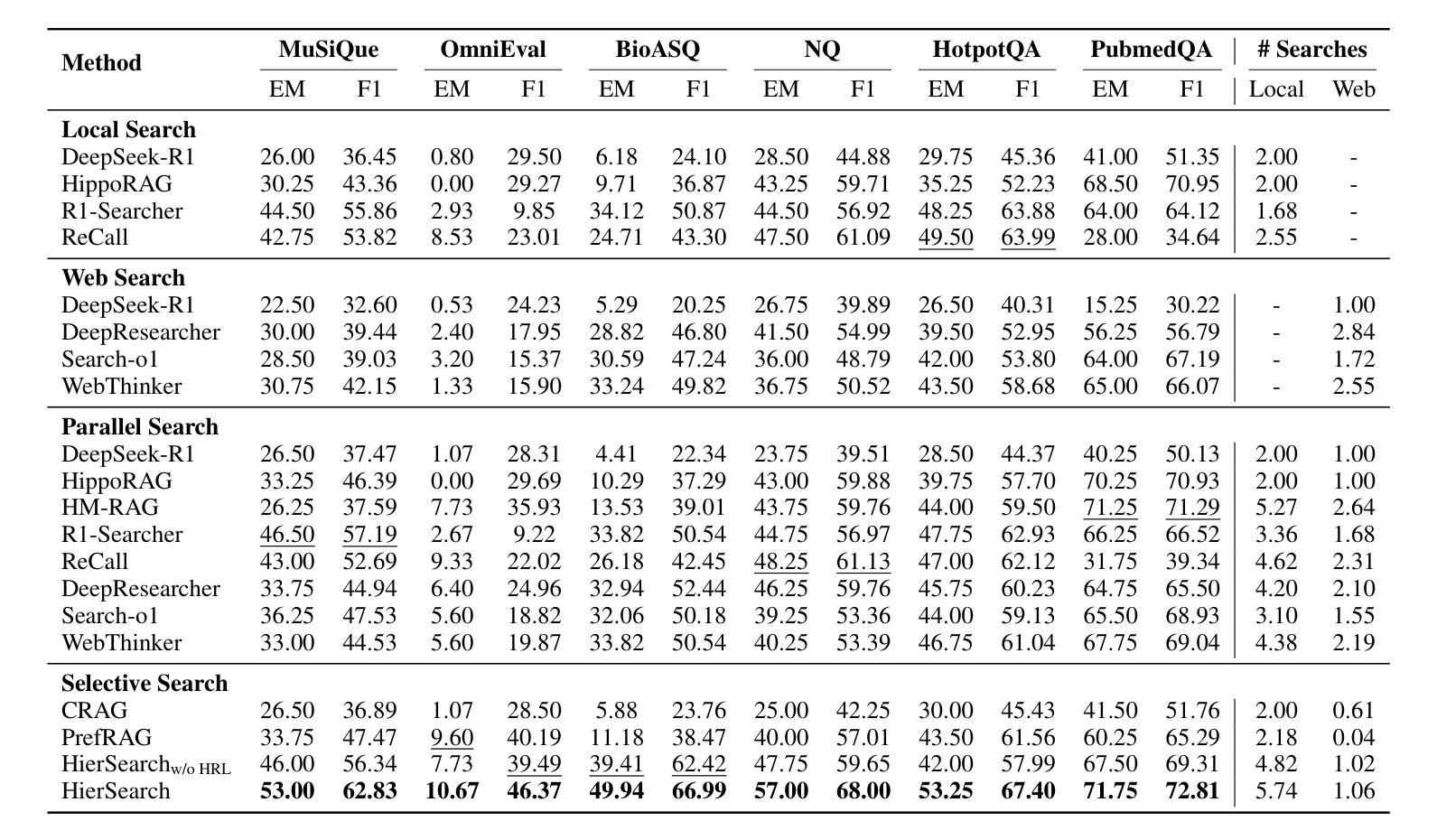
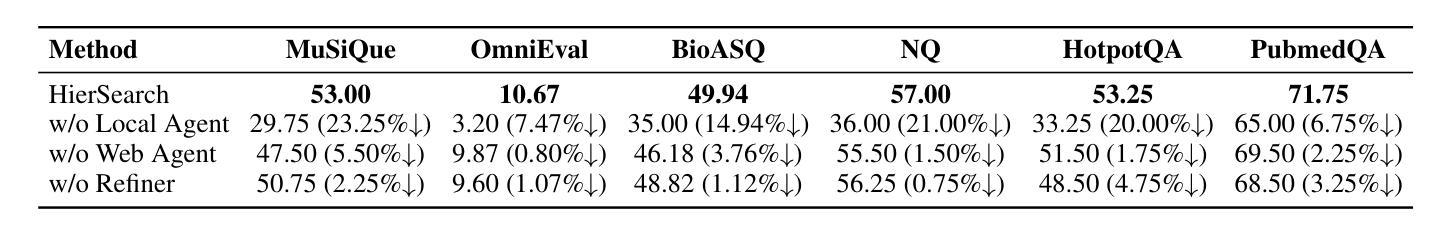
HierSearch: A Hierarchical Enterprise Deep Search Framework Integrating Local and Web Searches
Authors:Jiejun Tan, Zhicheng Dou, Yan Yu, Jiehan Cheng, Qiang Ju, Jian Xie, Ji-Rong Wen
Recently, large reasoning models have demonstrated strong mathematical and coding abilities, and deep search leverages their reasoning capabilities in challenging information retrieval tasks. Existing deep search works are generally limited to a single knowledge source, either local or the Web. However, enterprises often require private deep search systems that can leverage search tools over both local and the Web corpus. Simply training an agent equipped with multiple search tools using flat reinforcement learning (RL) is a straightforward idea, but it has problems such as low training data efficiency and poor mastery of complex tools. To address the above issue, we propose a hierarchical agentic deep search framework, HierSearch, trained with hierarchical RL. At the low level, a local deep search agent and a Web deep search agent are trained to retrieve evidence from their corresponding domains. At the high level, a planner agent coordinates low-level agents and provides the final answer. Moreover, to prevent direct answer copying and error propagation, we design a knowledge refiner that filters out hallucinations and irrelevant evidence returned by low-level agents. Experiments show that HierSearch achieves better performance compared to flat RL, and outperforms various deep search and multi-source retrieval-augmented generation baselines in six benchmarks across general, finance, and medical domains.
最近,大型推理模型展示了强大的数学和编码能力,深度搜索则在具有挑战性的信息检索任务中利用了这些推理能力。现有的深度搜索工作通常局限于单个知识源,无论是本地还是网络。然而,企业通常需要能够在本地和网络语料库上使用搜索工具的私人深度搜索系统。使用平面强化学习(RL)训练配备多种搜索工具的智能代理是一个直接的想法,但它存在训练数据效率低和难以掌握复杂工具等问题。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了使用分层强化学习训练的分层代理深度搜索框架HierSearch。在低级层面,本地深度搜索代理和网络深度搜索代理被训练从各自对应的领域检索证据。在高级层面,规划代理协调低级代理并提供最终答案。此外,为了防止直接答案复制和错误传播,我们设计了一个知识精炼器,可以过滤掉低级代理产生的幻觉和无关证据。实验表明,HierSearch在性能上优于平面RL,并且在通用、金融和医疗领域的六个基准测试中超越了各种深度搜索和多源检索增强生成基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code and datasets are available at https://github.com/plageon/HierSearch
Summary
大型推理模型展现出强大的数学与编码能力,并在信息检索任务中利用这些能力进行深度搜索。然而,现有深度搜索工作主要局限于单一知识源,难以同时运用本地及网络数据进行搜索。为解决企业需求中的私人深度搜索系统问题,研究者提出使用层次化的智能深度搜索框架——HierSearch,通过层次化强化学习进行训练。该框架在底层训练本地和网络深度搜索代理,以从相应领域检索证据;在高层设置规划代理进行协调并给出最终答案。此外,还设计了一个知识精炼器过滤掉底层代理产生的幻觉和无关证据。实验表明,HierSearch相较于平面强化学习有更好的性能表现,并在通用、金融和医学领域的六个基准测试中超越了各种深度搜索和多源检索增强生成基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型具备数学与编码能力,并在信息检索中展现深度搜索能力。
- 现有深度搜索主要依赖单一知识源,无法满足企业对本地和网络数据同时运用的需求。
- HierSearch框架使用层次化强化学习训练代理,实现本地和网络深度搜索。
- HierSearch在底层训练代理检索证据,高层规划代理进行协调并提供答案。
- 知识精炼器用于过滤底层代理产生的幻觉和无关证据。
- HierSearch相较于平面强化学习性能更优。
点此查看论文截图

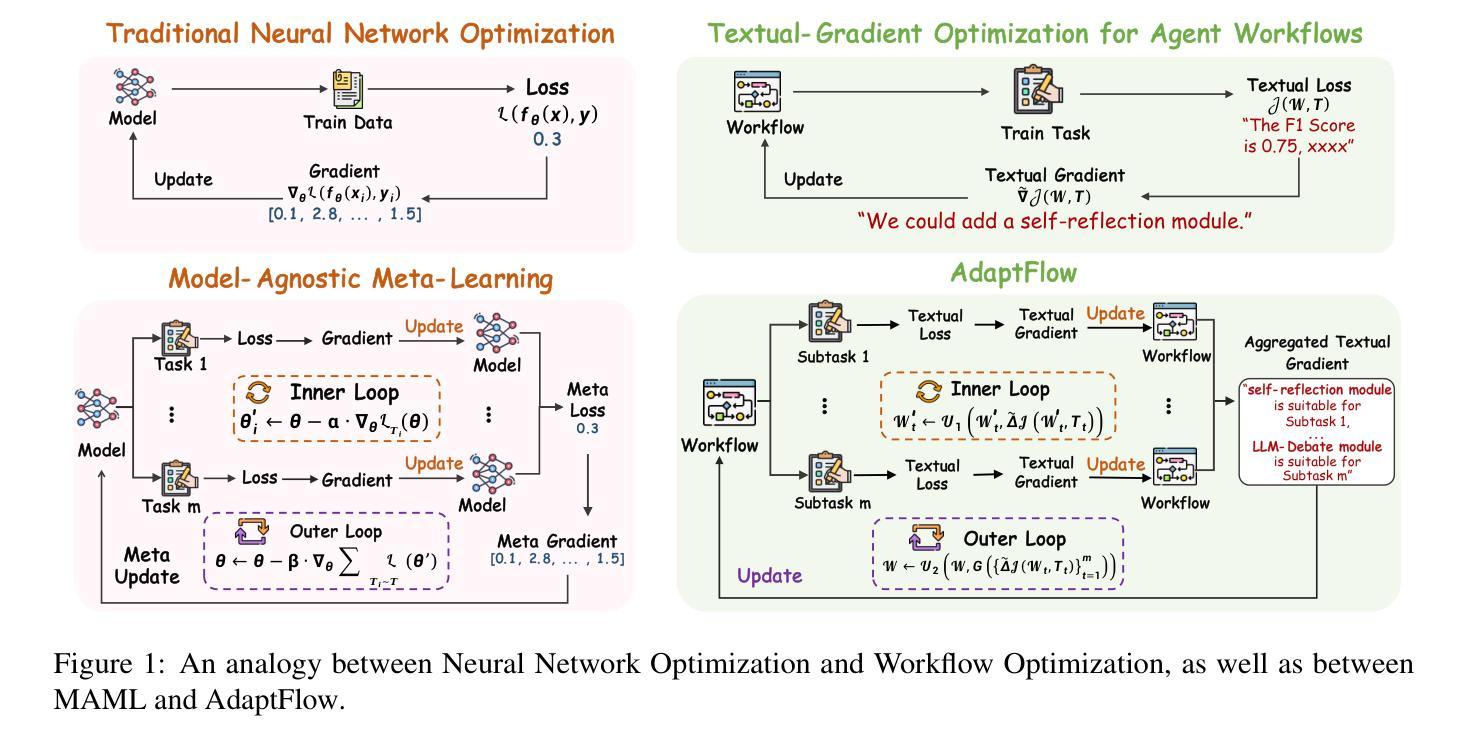
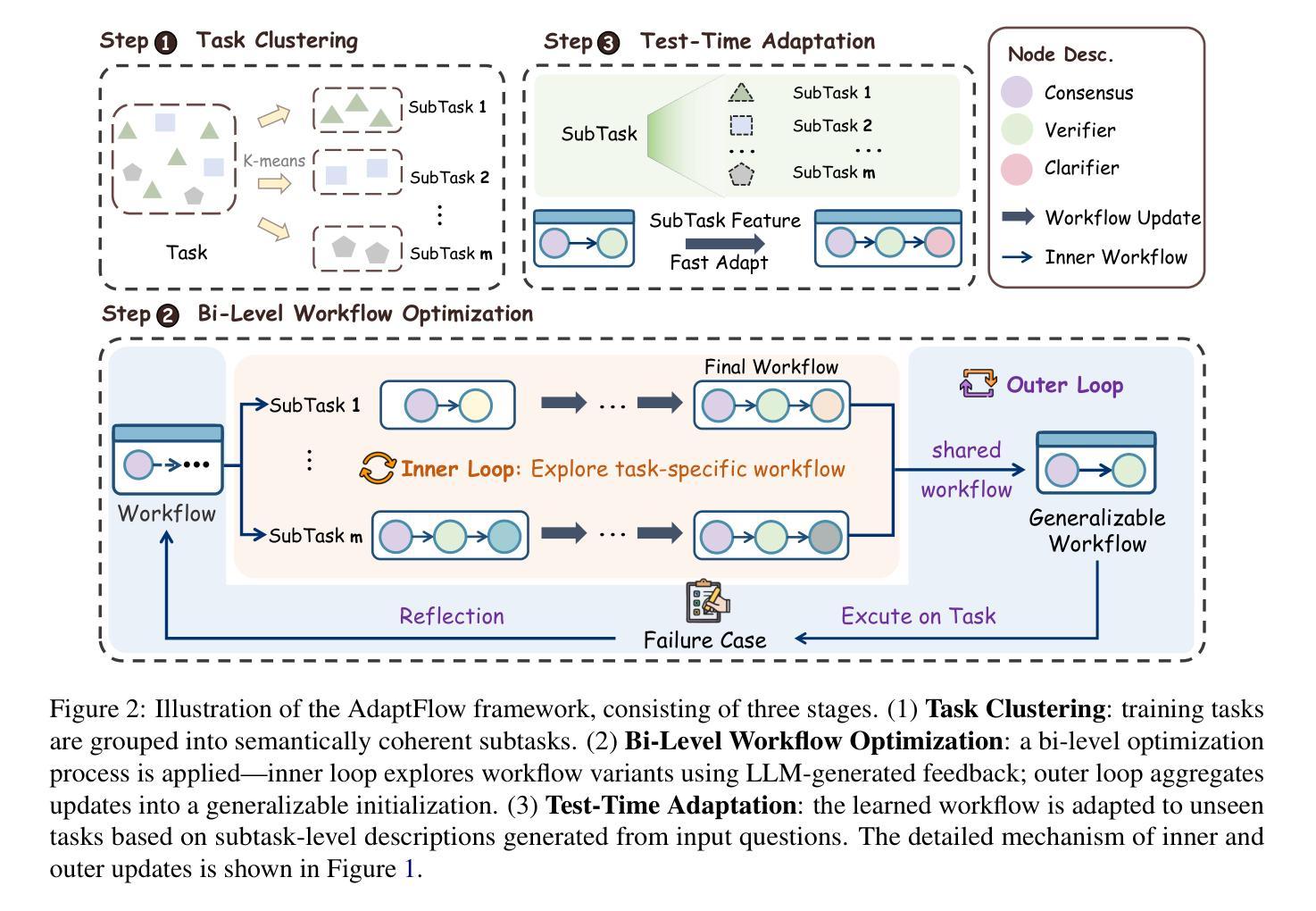
AdaptFlow: Adaptive Workflow Optimization via Meta-Learning
Authors:Runchuan Zhu, Bowen Jiang, Lingrui Mei, Fangkai Yang, Lu Wang, Haoxiang Gao, Fengshuo Bai, Pu Zhao, Qingwei Lin, Saravan Rajmohan, Dongmei Zhang
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in agentic workflows, which are structured sequences of LLM invocations intended to solve complex tasks. However, existing approaches often rely on static templates or manually designed workflows, which limit adaptability to diverse tasks and hinder scalability. We propose AdaptFlow, a natural language-based meta-learning framework inspired by model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML). AdaptFlow learns a generalizable workflow initialization that enables rapid subtask-level adaptation. It employs a bi-level optimization scheme: the inner loop refines the workflow for a specific subtask using LLM-generated feedback, while the outer loop updates the shared initialization to perform well across tasks. This setup allows AdaptFlow to generalize effectively to unseen tasks by adapting the initialized workflow through language-guided modifications. Evaluated across question answering, code generation, and mathematical reasoning benchmarks, AdaptFlow consistently outperforms both manually crafted and automatically searched baselines, achieving state-of-the-art results with strong generalization across tasks and models. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/microsoft/DKI_LLM/tree/AdaptFlow/AdaptFlow.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进展引发了人们对代理工作流的日益关注,代理工作流是由一系列LLM调用组成的结构化序列,旨在解决复杂任务。然而,现有方法通常依赖于静态模板或手动设计的工作流,这限制了它们对不同任务的适应性,并阻碍了可扩展性。我们提出了AdaptFlow,这是一个受模型无关元学习(MAML)启发的基于自然语言元学习框架。AdaptFlow学习一种可通用的工作流初始化方法,以加快特定子任务的适应性。它采用了一种两级优化方案:内循环利用LLM生成的反馈对特定子任务的工作流程进行精细化改进,而外循环则更新共享初始化设置以在任务之间表现良好。这种设置允许AdaptFlow通过语言指导的修改来适应初始化工作流,从而有效地推广到未见过的任务。在问答、代码生成和数学推理基准测试上进行了评估,AdaptFlow始终表现出色,不仅在手动设计和自动搜索的基准线上有所超越,而且在任务和模型之间实现了强大的泛化能力。源代码和数据在https://github.com/microsoft/DKI_LLM/tree/AdaptFlow/AdaptFlow上可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的最近进展引发了人们对代理工作流(agentic workflows)的浓厚兴趣。工作流是一系列LLM调用的结构化序列,旨在解决复杂任务。然而,现有方法往往依赖于静态模板或手动设计的工作流,这限制了其对各种任务的适应能力并阻碍其可扩展性。为此,我们提出了AdaptFlow,一个受模型不可知元学习(MAML)启发的自然语言驱动的元学习框架。AdaptFlow学习一种可通用的工作流初始化方案,以实现快速子任务级别的适应。它采用双层优化方案:内循环针对特定子任务优化工作流并使用LLM生成的反馈进行调整,而外循环更新共享初始化方案以实现跨任务的良好表现。这使得AdaptFlow能够有效地适应未见过的任务,并通过语言指导的修改来调整初始化工作流。在问答、代码生成和数学推理基准测试上进行的评估表明,AdaptFlow在手动设计和自动搜索的基准测试中都表现优异,实现了跨任务和模型的最佳结果。其源代码和数据在 https://github.com/microsoft/DKI_LLM/tree/AdaptFlow/AdaptFlow 上可供查阅。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进展推动了代理工作流(agentic workflows)的研究。
- 现有工作流方法主要依赖静态模板或手动设计,限制了其在多样任务中的适应性和可扩展性。
- AdaptFlow是一个自然语言驱动的元学习框架,旨在解决这一限制。
- AdaptFlow通过双层优化方案学习通用的工作流初始化,以实现快速子任务级别的适应。
- 该框架结合了内循环的特定子任务优化和外循环的跨任务表现优化。
- AdaptFlow能够适应未见过的任务,并通过语言指导修改初始化工作流。
点此查看论文截图


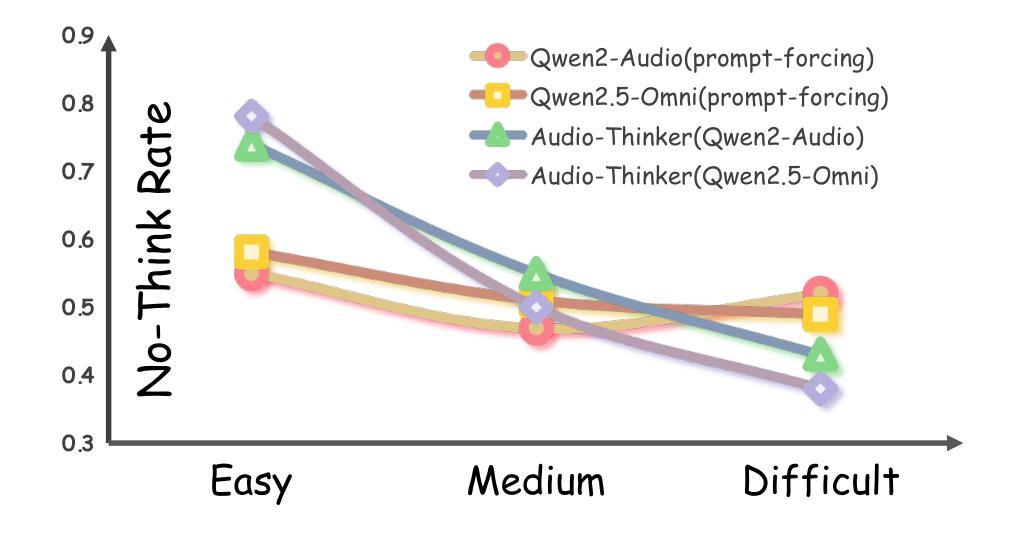
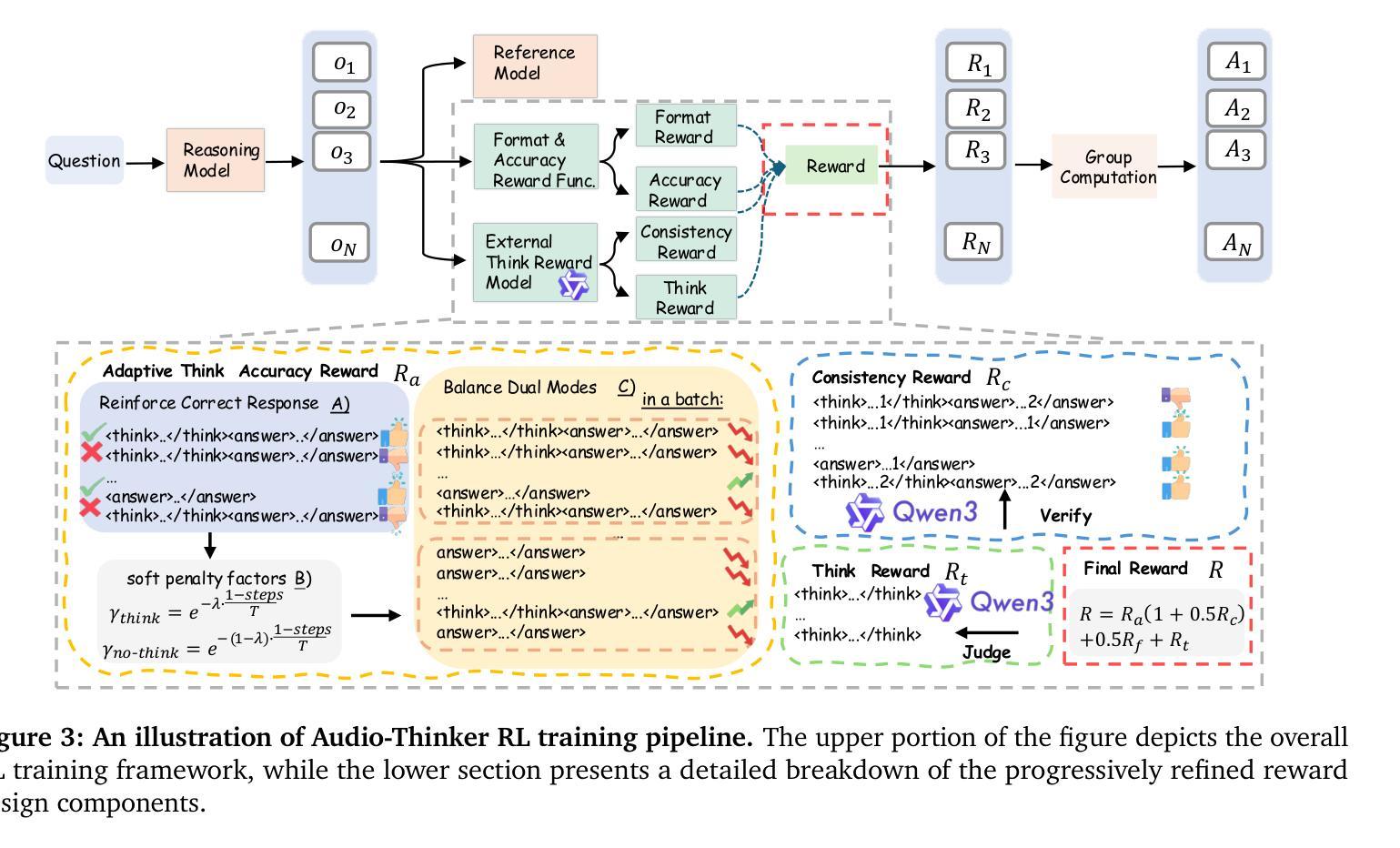
Audio-Thinker: Guiding Audio Language Model When and How to Think via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Shu Wu, Chenxing Li, Wenfu Wang, Hao Zhang, Hualei Wang, Meng Yu, Dong Yu
Recent advancements in large language models, multimodal large language models, and large audio language models (LALMs) have significantly improved their reasoning capabilities through reinforcement learning with rule-based rewards. However, the explicit reasoning process has yet to show significant benefits for audio question answering, and effectively leveraging deep reasoning remains an open challenge, with LALMs still falling short of human-level auditory-language reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose Audio-Thinker, a reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LALMs, with a focus on improving adaptability, consistency, and effectiveness. Our approach introduces an adaptive think accuracy reward, enabling the model to adjust its reasoning strategies based on task complexity dynamically. Furthermore, we incorporate an external reward model to evaluate the overall consistency and quality of the reasoning process, complemented by think-based rewards that help the model distinguish between valid and flawed reasoning paths during training. Experimental results demonstrate that our Audio-Thinker model outperforms existing reasoning-oriented LALMs across various benchmark tasks, exhibiting superior reasoning and generalization capabilities.
近期,大型语言模型、多模态大型语言模型和大型音频语言模型(LALM)的进步,通过基于规则的奖励进行强化学习,显著提升了其推理能力。然而,明确的推理过程在音频问答中尚未显示出显著的优势,有效利用深度推理仍然是一个开放性的挑战,LALM在音频语言推理方面仍未能达到人类水平。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了Audio-Thinker,这是一个旨在增强LALM推理能力的强化学习框架,重点关注适应性、一致性和有效性。我们的方法引入了一种自适应的思考准确性奖励,使模型能够基于任务的复杂性动态地调整其推理策略。此外,我们采用外部奖励模型来评估推理过程的整体一致性和质量,辅以基于思考的奖励,帮助模型在训练过程中区分有效的和错误的推理路径。实验结果表明,我们的Audio-Thinker模型在各种基准任务上优于现有的面向推理的LALM,表现出卓越的推理和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary:
随着大型语言模型、多模态大型语言模型和大型音频语言模型(LALM)的近期进展,通过基于规则的奖励进行强化学习,它们的推理能力已显著提高。然而,在音频问答方面,明确的推理过程尚未显示出显著优势,有效利用深度推理仍是开放挑战,LALM仍未能达到人类水平的听觉语言推理。为解决这个问题,我们提出了Audio-Thinker,一个旨在提高LALM推理能力的强化学习框架,重点改善适应性、一致性和有效性。通过引入自适应思考精度奖励,使模型能根据任务复杂度动态调整推理策略。此外,我们结合外部奖励模型来评估推理过程的一致性和质量,辅以基于思考的奖励,帮助模型在训练时区分有效的和错误的推理路径。实验结果表明,我们的Audio-Thinker模型在各项基准任务上优于现有的推理导向型LALM,展现出卓越的推理和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(包括音频语言模型)的推理能力通过强化学习得到显著提高。
- 在音频问答方面,明确推理过程尚未显现显著优势,且有效利用深度推理仍是挑战。
- 引入Audio-Thinker框架,旨在提高LALM的推理能力,特别是在适应性、一致性和有效性方面。
- Audio-Thinker采用自适应思考精度奖励,使模型能根据任务复杂度动态调整推理策略。
- 结合外部奖励模型评估推理过程的一致性和质量。
- 基于思考的奖励帮助模型区分有效和错误的推理路径。
点此查看论文截图

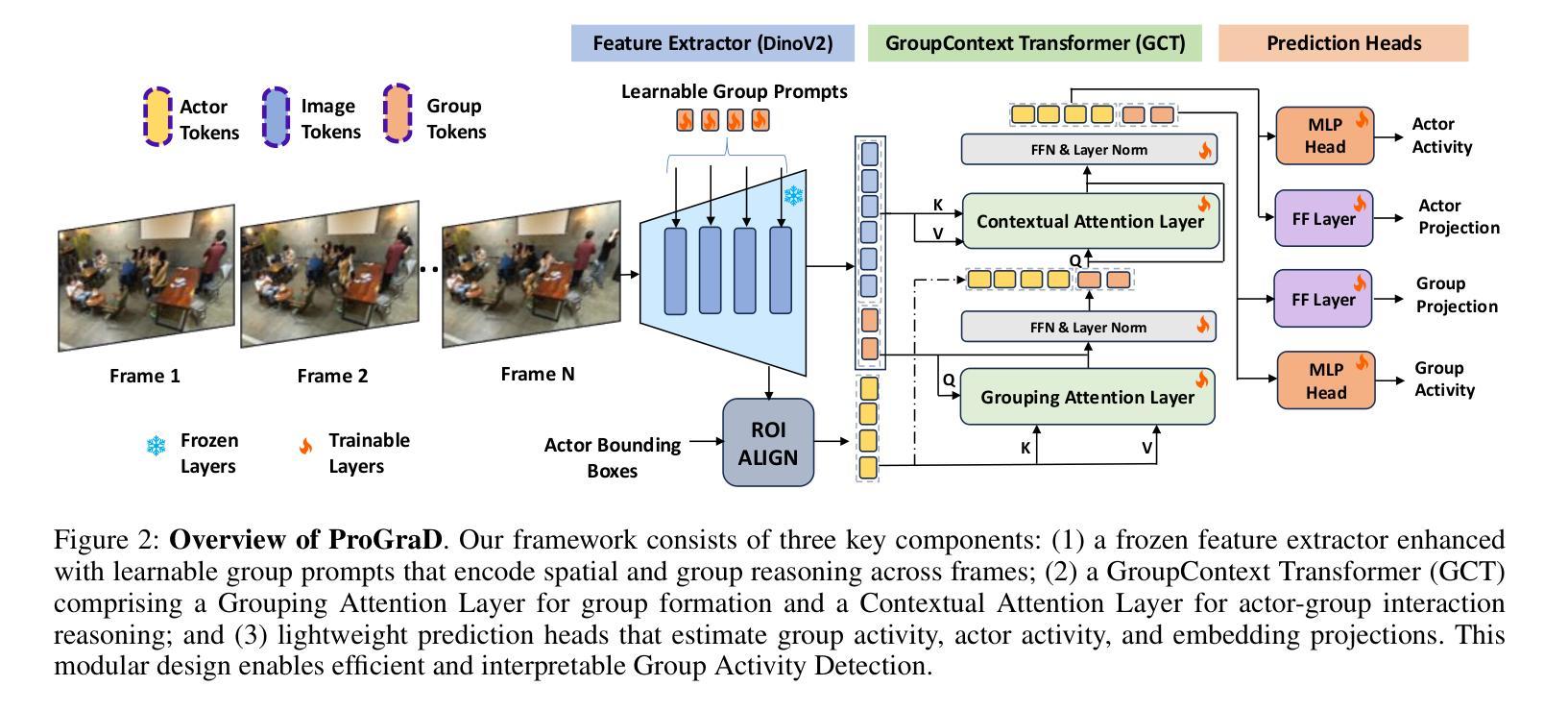
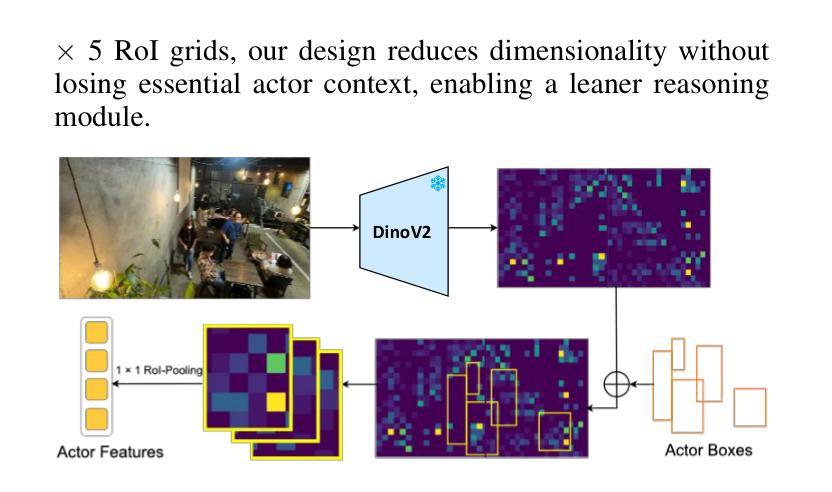
Prompt-Guided Relational Reasoning for Social Behavior Understanding with Vision Foundation Models
Authors:Thinesh Thiyakesan Ponbagavathi, Chengzheng Yang, Alina Roitberg
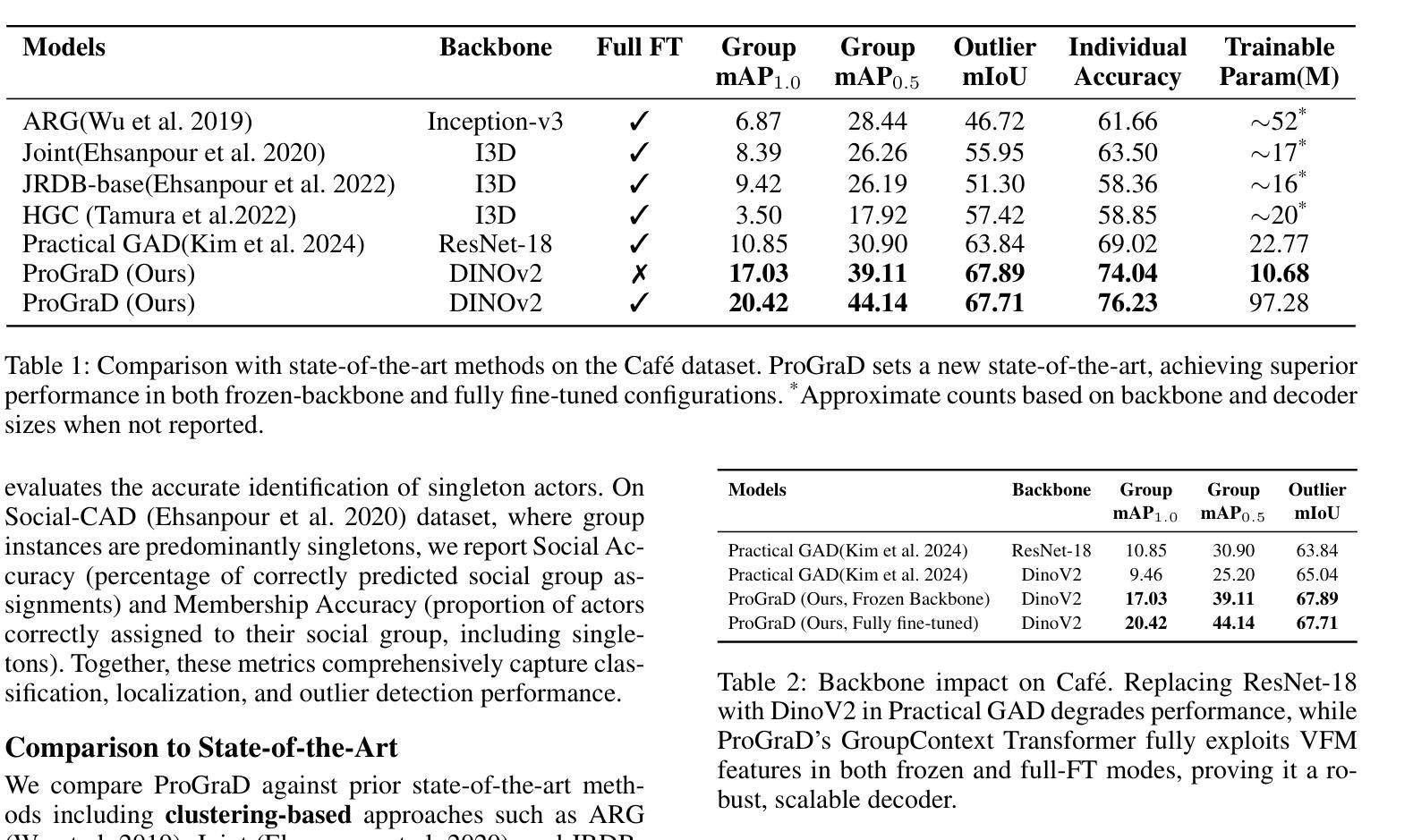
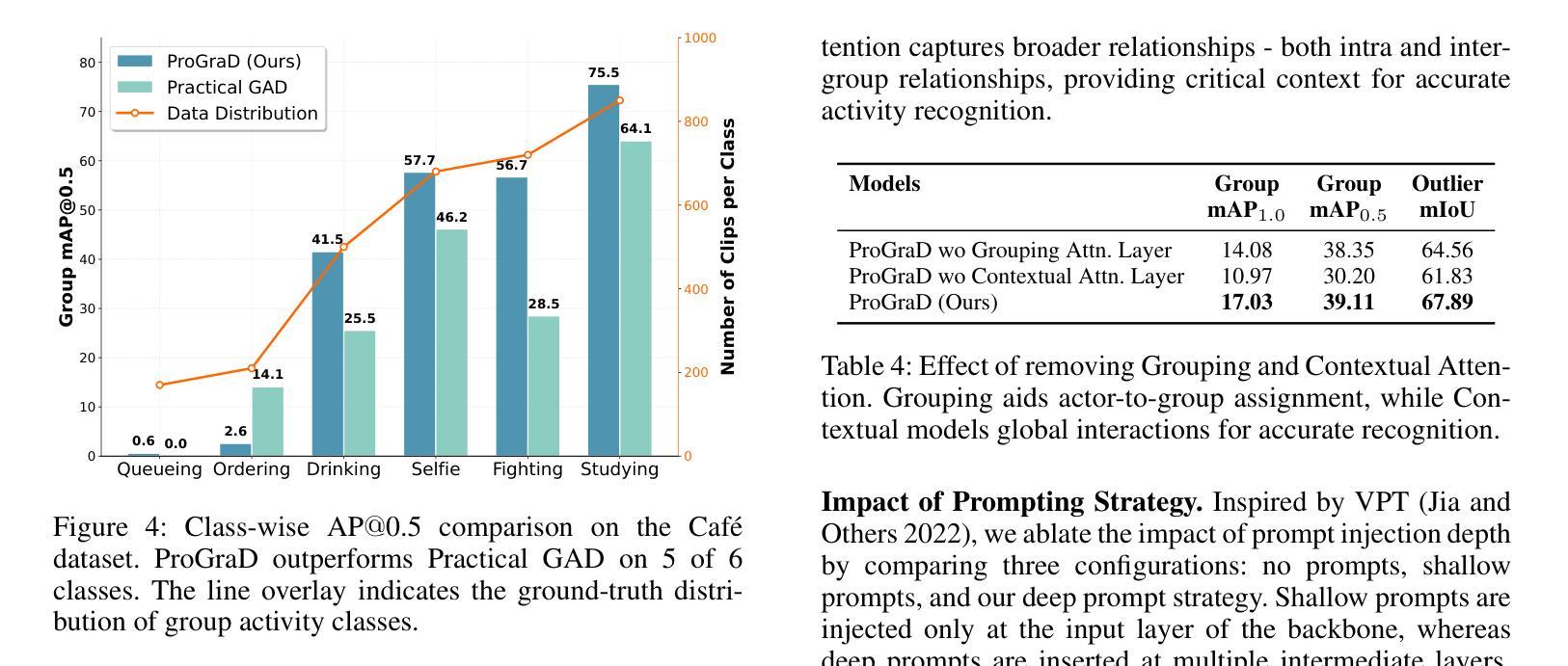
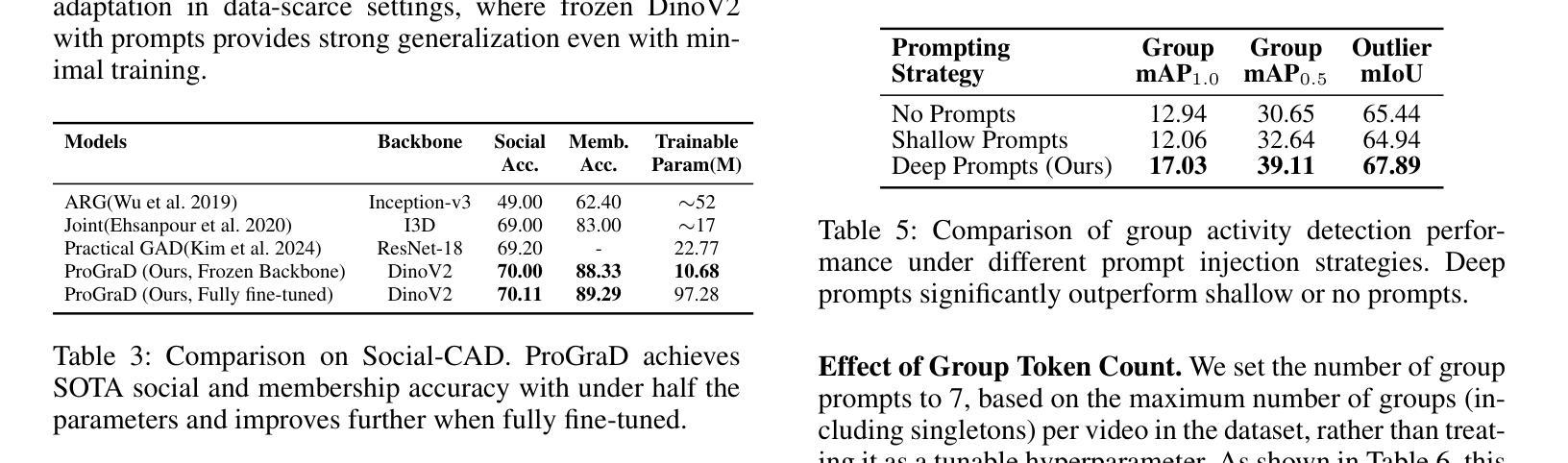
Group Activity Detection (GAD) involves recognizing social groups and their collective behaviors in videos. Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), like DinoV2, offer excellent features, but are pretrained primarily on object-centric data and remain underexplored for modeling group dynamics. While they are a promising alternative to highly task-specific GAD architectures that require full fine-tuning, our initial investigation reveals that simply swapping CNN backbones used in these methods with VFMs brings little gain, underscoring the need for structured, group-aware reasoning on top. We introduce Prompt-driven Group Activity Detection (ProGraD) – a method that bridges this gap through 1) learnable group prompts to guide the VFM attention toward social configurations, and 2) a lightweight two-layer GroupContext Transformer that infers actor-group associations and collective behavior. We evaluate our approach on two recent GAD benchmarks: Cafe, which features multiple concurrent social groups, and Social-CAD, which focuses on single-group interactions. While we surpass state-of-the-art in both settings, our method is especially effective in complex multi-group scenarios, where we yield a gain of 6.5% (Group mAP@1.0) and 8.2% (Group mAP@0.5) using only 10M trainable parameters. Furthermore, our experiments reveal that ProGraD produces interpretable attention maps, offering insights into actor-group reasoning. Code and models will be released.
群体活动检测(GAD)涉及识别视频中的社会群体及其集体行为。视觉基础模型(VFMs),如DinoV2,具有出色的功能,但主要是基于以对象为中心的数据进行预训练,并且在模拟群体动态方面仍然被较少研究。尽管它们是有前途的替代高度针对任务的GAD架构,这些架构需要全面微调,但我们的初步调查表明,仅仅用VFM替换这些方法中的CNN骨干所带来的收益甚微,这强调了需要在顶端进行结构化、群体感知推理的必要性。我们引入了Prompt驱动群体活动检测(ProGraD)——一种弥合这一鸿沟的方法,包括1)可学习的群体提示,引导VFM注意力关注社会配置,以及2)轻量级的两层组上下文转换器,推断演员-组关联和集体行为。我们在两个最新的GAD基准测试集上评估了我们的方法:Cafe,以多个并发社会群体为特色;以及Social-CAD,专注于单一群体互动。尽管我们在两种设置中都超越了最新技术状态,但我们的方法在复杂的多群体场景中尤其有效,仅使用10M个可训练参数就实现了群平均准确率提高6.5%(Group mAP@1.0)和8.2%(Group mAP@0.5)。此外,我们的实验表明,ProGraD产生可解释的关注图,为演员-组推理提供了深入见解。代码和模型将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
群体活动检测(GAD)旨在识别视频中的社交群体及其集体行为。虽然DinoV2等视觉基础模型(VFMs)具有出色的特征,但它们主要基于对象中心数据进行预训练,对于群体动态建模仍显不足。研究引入了一种名为Prompt驱动群体活动检测(ProGraD)的方法,通过可学习的群体提示和引导VFM注意力关注社交配置,以及一个轻量级的两层GroupContext Transformer来推断演员群体关联和集体行为。该方法在最近的GAD基准测试中表现优异,尤其在复杂的多元群组场景中优势明显,使用仅10M可训练参数便实现了显著的增益。此外,ProGraD产生的注意力地图具有可解释性,为演员群体推理提供了见解。
Key Takeaways:
- Group Activity Detection (GAD) 旨在识别视频中的社交群体及其行为。
- 视觉基础模型(VFMs)如DinoV2在GAD方面的应用尚待探索。
- 简单的将CNN骨干网络与VFMs替换对提升GAD效果有限,需要结构化的群体感知推理。
- ProGraD方法通过可学习的群体提示和GroupContext Transformer来优化VFM在GAD上的表现。
- ProGraD在多个GAD基准测试中表现优越,尤其在复杂多群组场景中效果突出。
- ProGraD仅使用10M可训练参数便实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

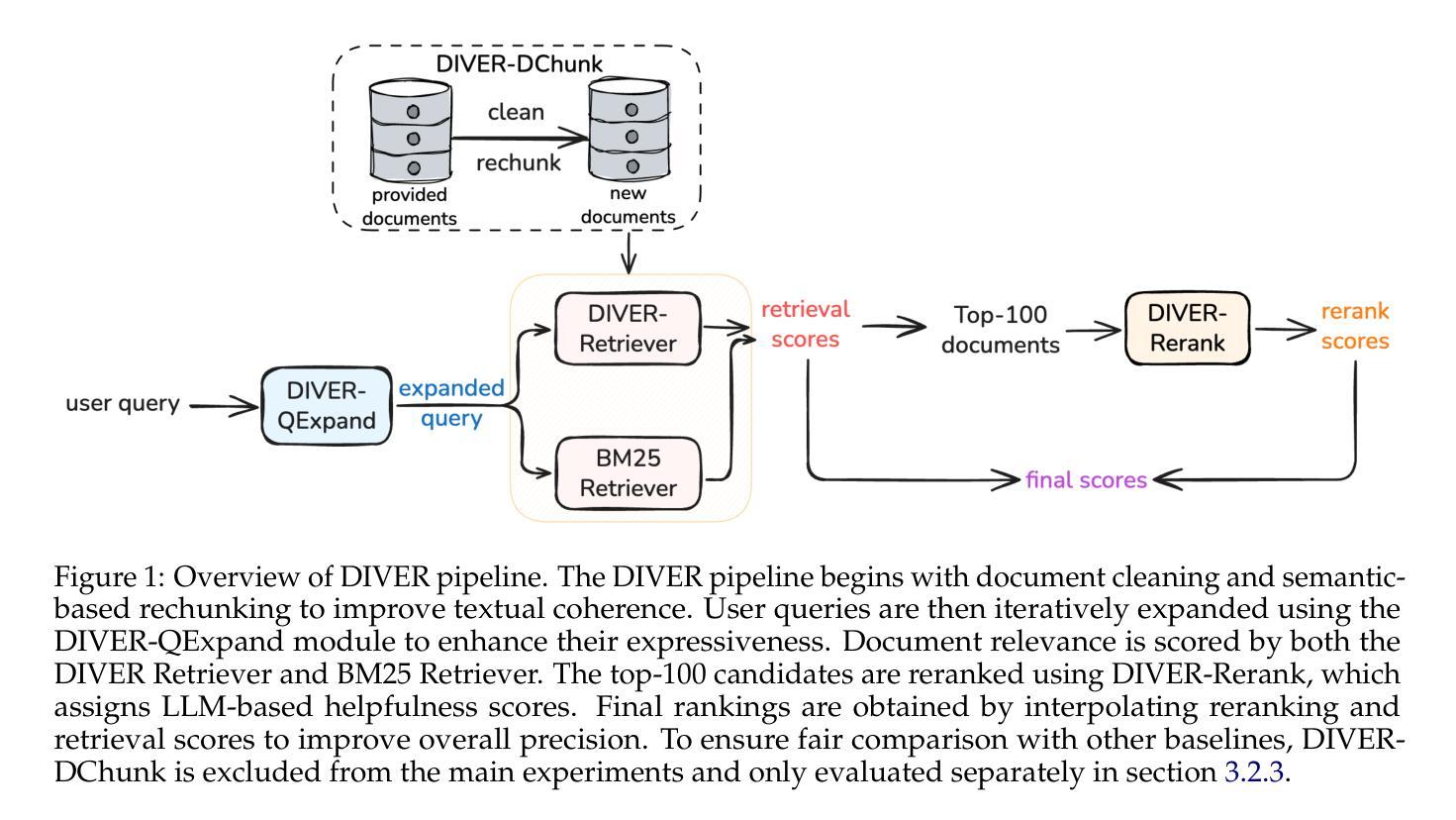
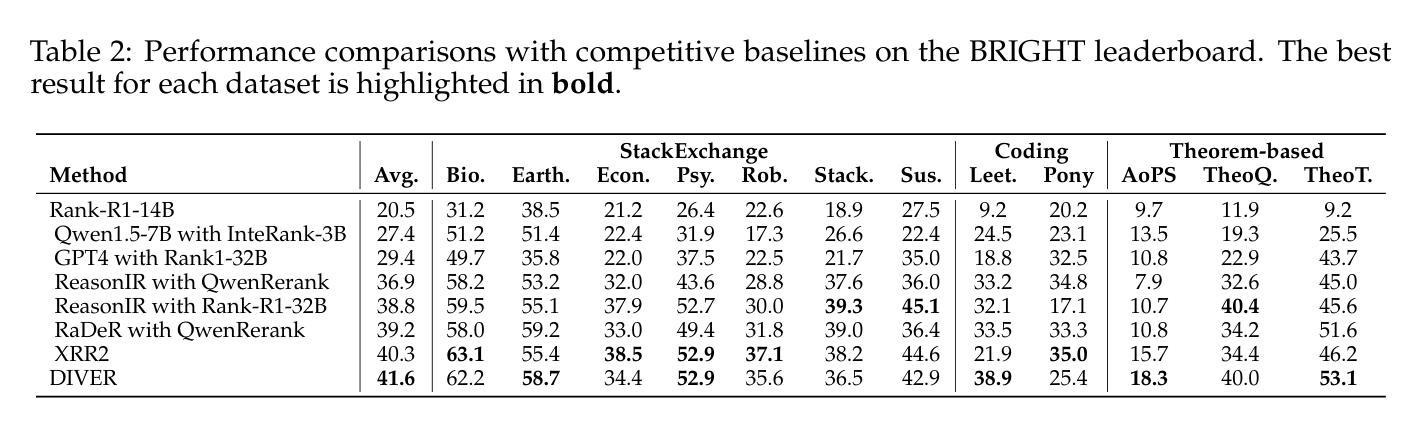
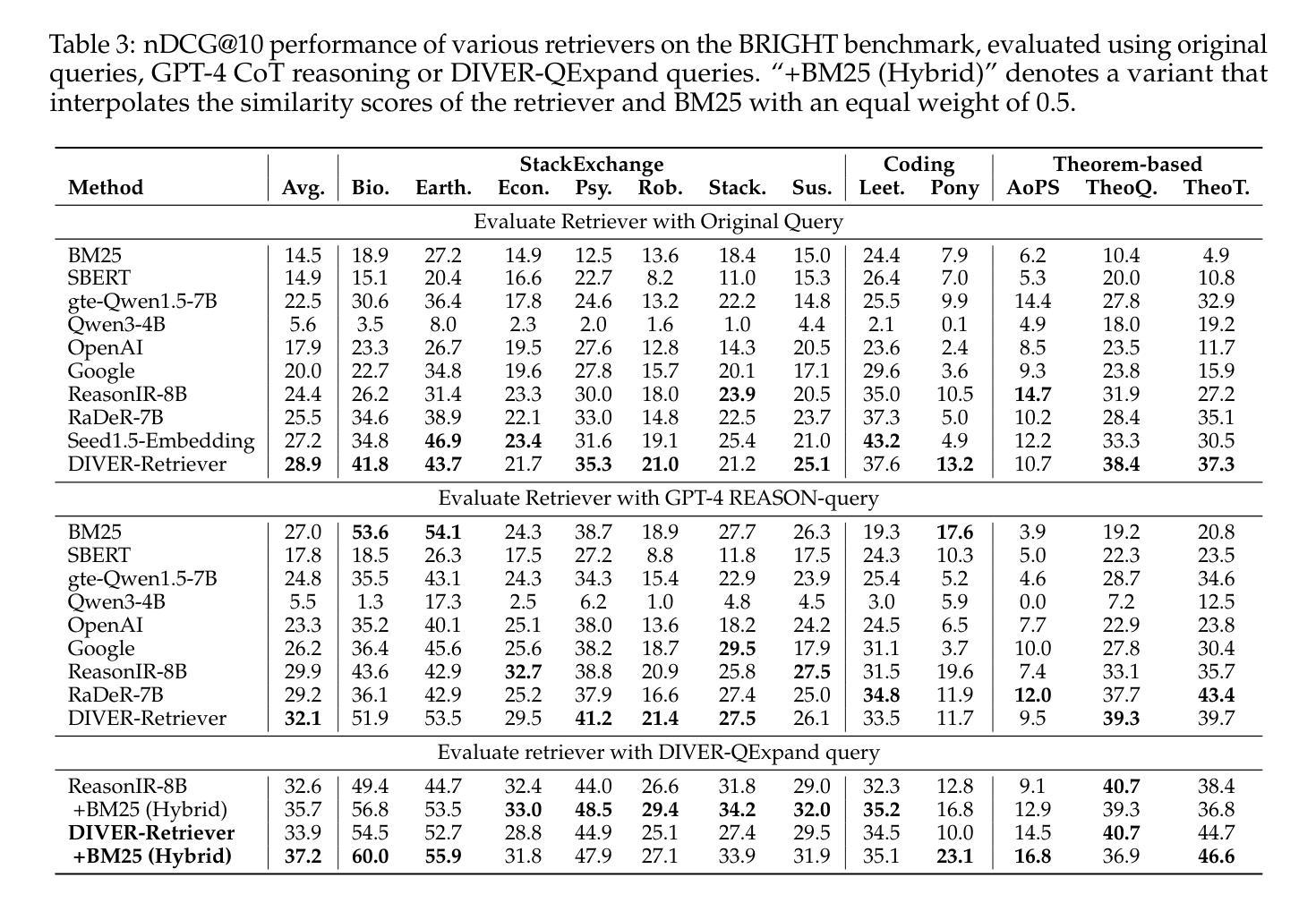
DIVER: A Multi-Stage Approach for Reasoning-intensive Information Retrieval
Authors:Meixiu Long, Duolin Sun, Dan Yang, Junjie Wang, Yue Shen, Jian Wang, Peng Wei, Jinjie Gu, Jiahai Wang
Retrieval-augmented generation has achieved strong performance on knowledge-intensive tasks where query-document relevance can be identified through direct lexical or semantic matches. However, many real-world queries involve abstract reasoning, analogical thinking, or multi-step inference, which existing retrievers often struggle to capture. To address this challenge, we present \textbf{DIVER}, a retrieval pipeline tailored for reasoning-intensive information retrieval. DIVER consists of four components: document processing to improve input quality, LLM-driven query expansion via iterative document interaction, a reasoning-enhanced retriever fine-tuned on synthetic multi-domain data with hard negatives, and a pointwise reranker that combines LLM-assigned helpfulness scores with retrieval scores. On the BRIGHT benchmark, DIVER achieves state-of-the-art nDCG@10 scores of 41.6 and 28.9 on original queries, consistently outperforming competitive reasoning-aware models. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of reasoning-aware retrieval strategies in complex real-world tasks. Our code and retrieval model will be released soon.
检索增强生成在知识密集型任务上表现强劲,其中通过直接词汇或语义匹配可以识别查询文档的相关性。然而,许多现实世界中的查询涉及抽象推理、类比思维或多步推理,现有检索器往往难以捕捉。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了针对推理密集型信息检索量身定制的DIVER检索管道。DIVER由四个组件构成:改进输入质量的文档处理,通过迭代文档交互驱动的LLM查询扩展,在合成多域数据上微调并带有硬阴性的推理增强检索器,以及结合LLM分配的有用性分数和检索分数的逐点重新排序器。在BRIGHT基准测试中,DIVER在原始查询上取得了最新的nDCG@10分数,分别为41.6和28.9,持续超越竞争性的推理感知模型。这些结果证明了推理感知检索策略在复杂现实世界任务中的有效性。我们的代码和检索模型很快就会发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对需要推理能力的信息检索任务而设计的检索管道DIVER。DIVER包含四个组件:改进输入质量的文档处理、通过迭代文档交互驱动LLM(大型语言模型)进行查询扩展、在合成多领域数据上进行微调且包含硬负样本的推理增强检索器以及结合LLM分配的帮助的得分与检索得分的逐点重排器。在BRIGHT基准测试上,DIVER在原始查询上取得了领先的nDCG@10得分,证明了其在复杂现实任务中推理感知检索策略的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 检索增强生成在知识密集型任务上的性能已经得到验证,但对于需要抽象推理、类比思维或多步推理的查询仍面临挑战。
- 为了解决这一挑战,提出了专为推理密集型信息检索设计的DIVER检索管道。
- DIVER包含四个主要组件,包括文档处理、LLM驱动的查询扩展、推理增强检索器以及逐点重排器。
- DIVER在BRIGHT基准测试上实现了最先进的nDCG@10得分,证明了其在复杂现实任务中的有效性。
- DIVER通过结合LLM的帮助的得分与检索得分,提高了检索的准确性和效率。
- DIVER的代码和检索模型将很快发布,为其他研究者使用和改进提供基础。
点此查看论文截图


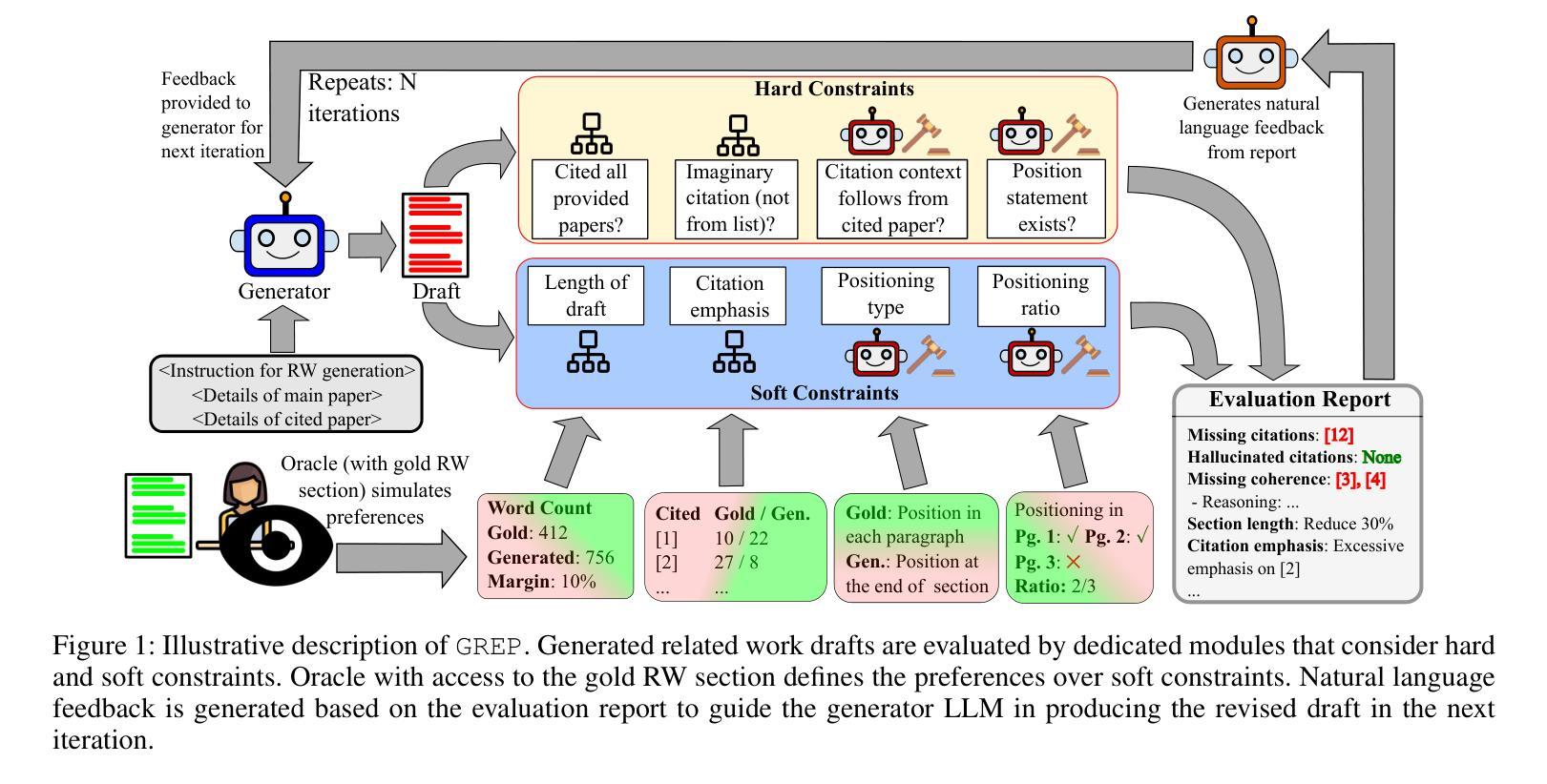
Expert Preference-based Evaluation of Automated Related Work Generation
Authors:Furkan Şahinuç, Subhabrata Dutta, Iryna Gurevych
Expert domain writing, such as scientific writing, typically demands extensive domain knowledge. Recent advances in LLMs show promising potential in reducing the expert workload. However, evaluating the quality of automatically generated scientific writing is a crucial open issue, as it requires knowledge of domain-specific evaluation criteria and the ability to discern expert preferences. Conventional automatic metrics and LLM-as-a-judge systems are insufficient to grasp expert preferences and domain-specific quality standards. To address this gap and support human-AI collaborative writing, we focus on related work generation, one of the most challenging scientific tasks, as an exemplar. We propose GREP, a multi-turn evaluation framework that integrates classical related work evaluation criteria with expert-specific preferences. Instead of assigning a single score, our framework decomposes the evaluation into fine-grained dimensions. This localized evaluation approach is further augmented with contrastive few-shot examples to provide detailed contextual guidance for the evaluation dimensions. The design principles allow our framework to deliver cardinal assessment of quality, which can facilitate better post-training compared to ordinal preference data. For better accessibility, we design two variants of GREP: a more precise variant with proprietary LLMs as evaluators, and a cheaper alternative with open-weight LLMs. Empirical investigation reveals that our framework is able to assess the quality of related work sections in a much more robust manner compared to standard LLM judges, reflects natural scenarios of scientific writing, and bears a strong correlation with the human expert assessment. We also observe that generations from state-of-the-art LLMs struggle to satisfy validation constraints of a suitable related work section. They (mostly) fail to improve based on feedback as well.
专业领域写作,如科学写作,通常需要广泛的专业知识。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步显示出减少专家工作量的潜力。然而,评估自动生成的科学写作的质量是一个关键的开放性问题,因为它需要了解特定领域的评估标准和识别专家偏好的能力。传统的自动指标和LLM作为评判系统的能力不足以把握专家偏好和特定领域的质量标准。为了弥补这一差距并支持人机协作写作,我们以相关工作生成这一最具挑战性的科学任务为例。我们提出了GREP,这是一个多轮评估框架,它将经典的相关工作评价标准与特定专家的偏好相结合。我们的框架不是赋予单一分数,而是将评估分解成精细的维度。这种局部评估方法与对比的少数案例相结合,为评估维度提供了详细的上下文指导。我们的设计原则使我们的框架能够提供质量的基数评估,这可以促进与排序偏好数据相比更好的后期训练。为了更容易访问,我们设计了GREP的两个变体:一个更精确的版本,使用专用的LLM作为评估器,和一个更便宜的版本,使用开放的LLM。实证研究结果表明,我们的框架能够更稳健地评估相关工作部分的质量,与标准LLM判断相比,它反映了科学写作的自然场景,并与人类专家评估具有很强的相关性。我们还观察到,来自最新LLM的生成在满足相关工作部分的验证约束方面存在困难。他们大多数不能根据反馈进行改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ukplab.github.io/arxiv2025-expert-eval-rw/
Summary
本文探讨了在科学写作领域,如何评估自动生成文本的质量。文章指出,现有的自动评估工具和LLM评判系统无法准确把握专家偏好和领域特定质量标准。为此,作者提出了一种新的多回合评估框架GREP,该框架结合了经典的相关工作评价标准与特定专家偏好。GREP通过细化评价标准,提供详细的上下文指导,更准确地评估文本质量。此外,文章还介绍了GREP的两种变体,一种使用专有LLM作为评估器,另一种使用开源LLM,以降低成本。实验表明,GREP框架能更稳健地评估相关工作部分的质量,与人类专家评估结果高度相关。
Key Takeaways
- 科学写作需要广泛的领域知识,LLMs的最近进展在减少专家工作量方面显示出潜力。
- 评估自动生成的科学写作的质量是一个重要但未解决的问题,需要了解领域特定的评估标准和专家偏好。
- 现有自动评估工具和LLM评判系统不足以把握专家偏好和领域特定标准。
- GREP是一个新的多回合评估框架,结合了经典的相关工作评价标准与特定专家偏好,进行精细化评价。
- GREP框架提供了详细的上下文指导,可以更准确地评估文本质量。
- 文章介绍了GREP的两种变体,一种使用专有LLM,另一种使用开源LLM以降低成本。
点此查看论文截图

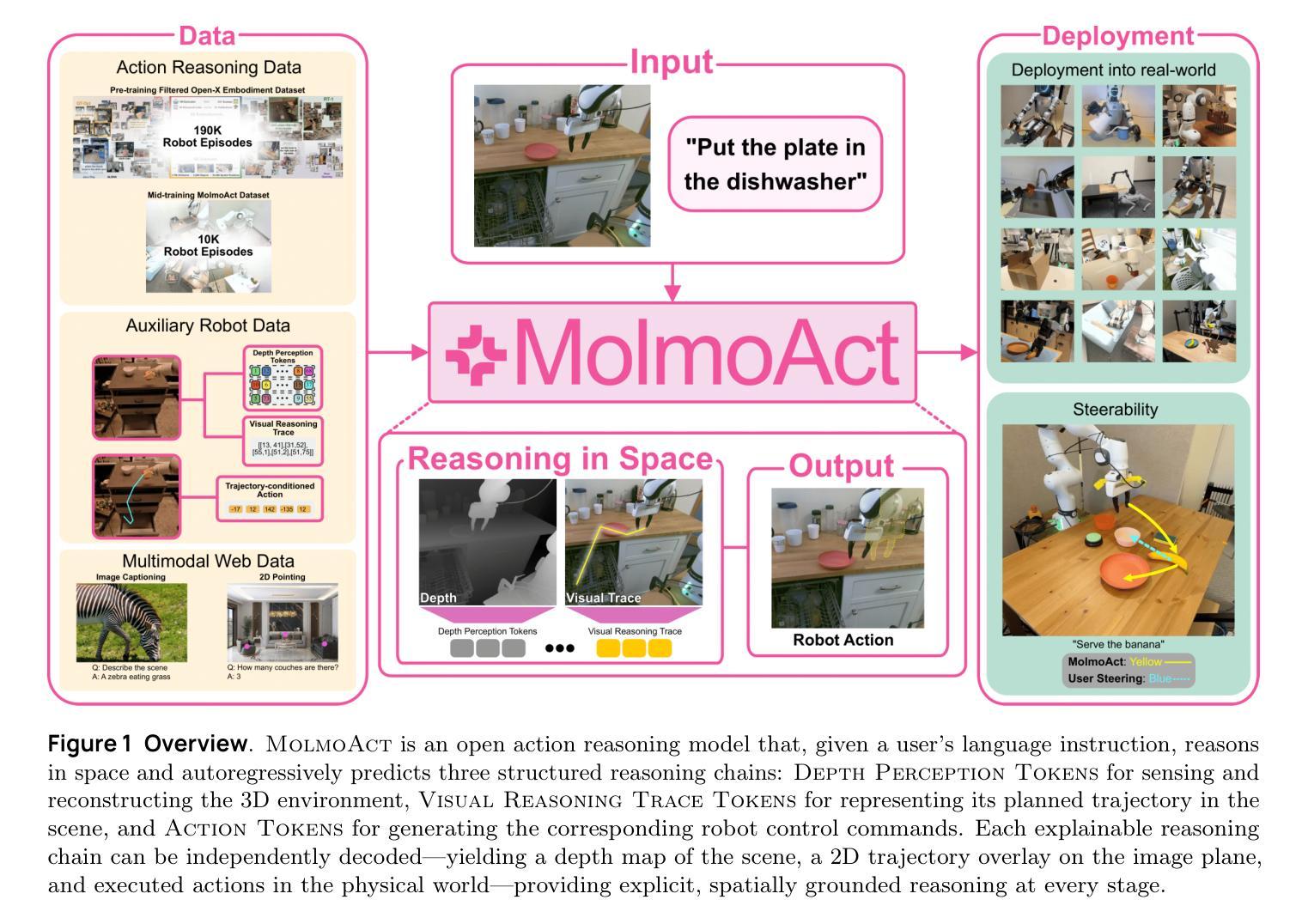
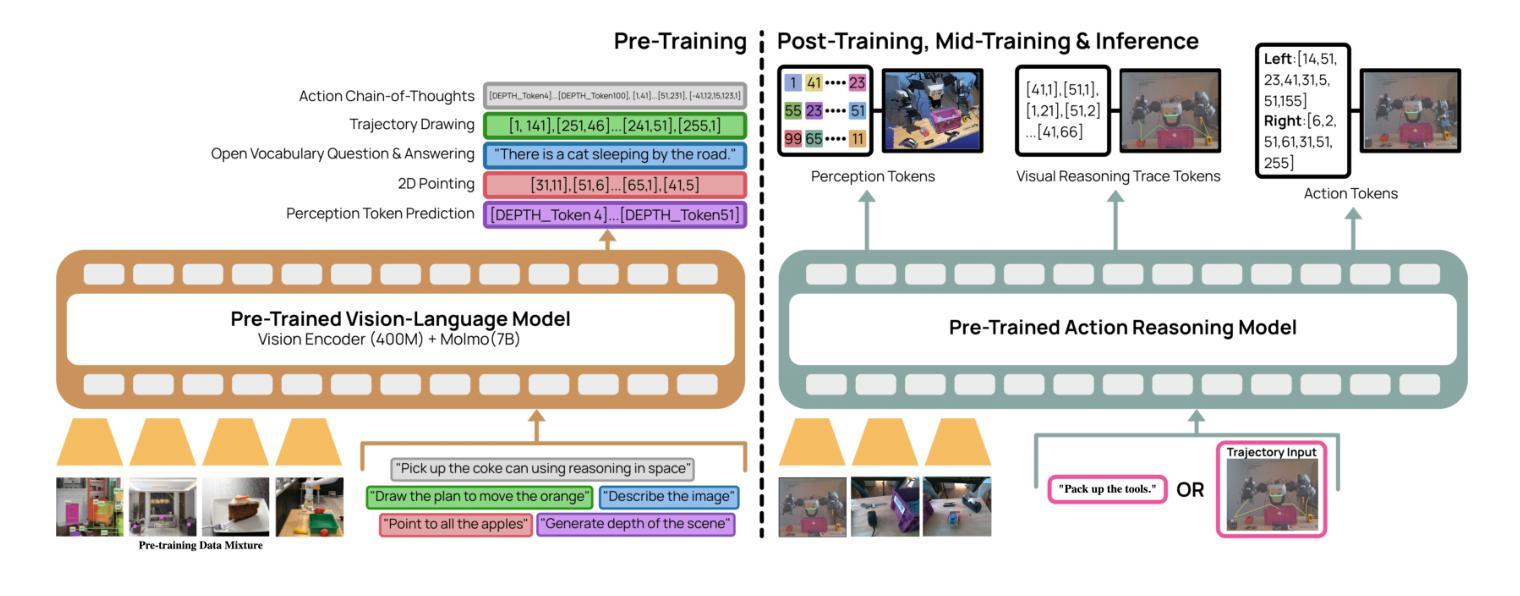
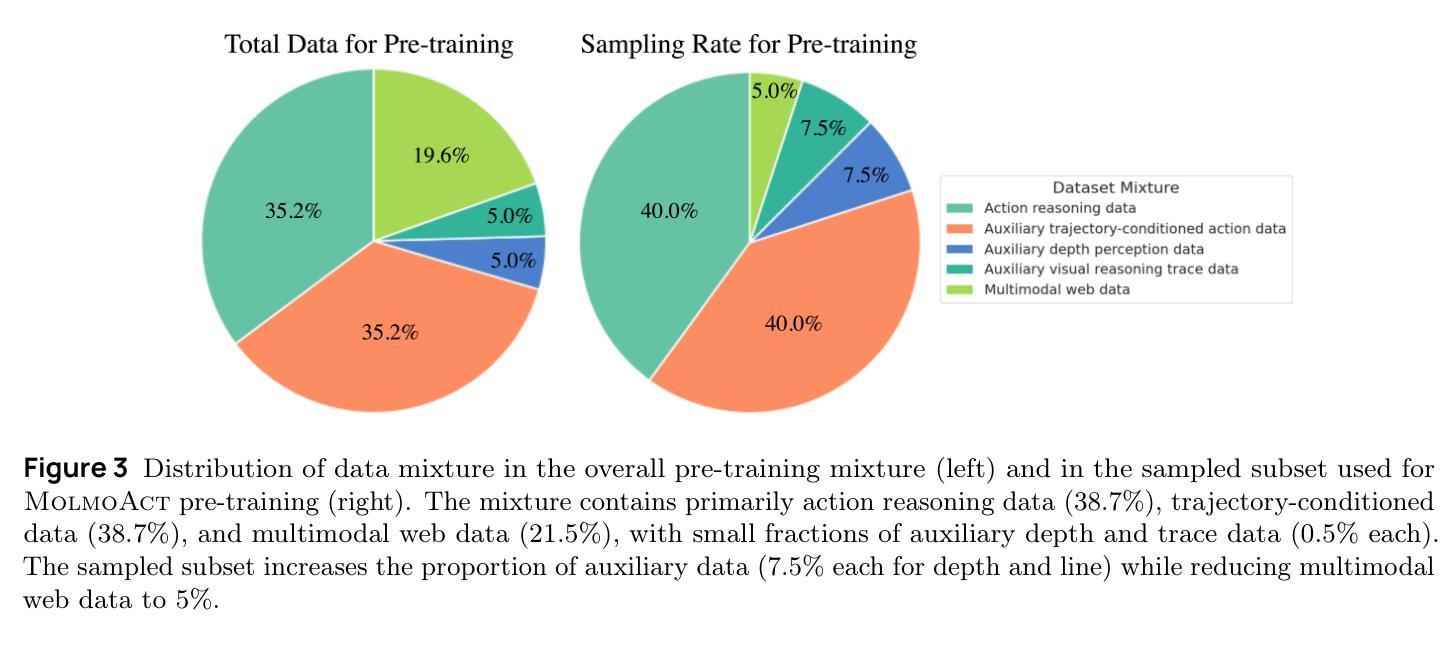
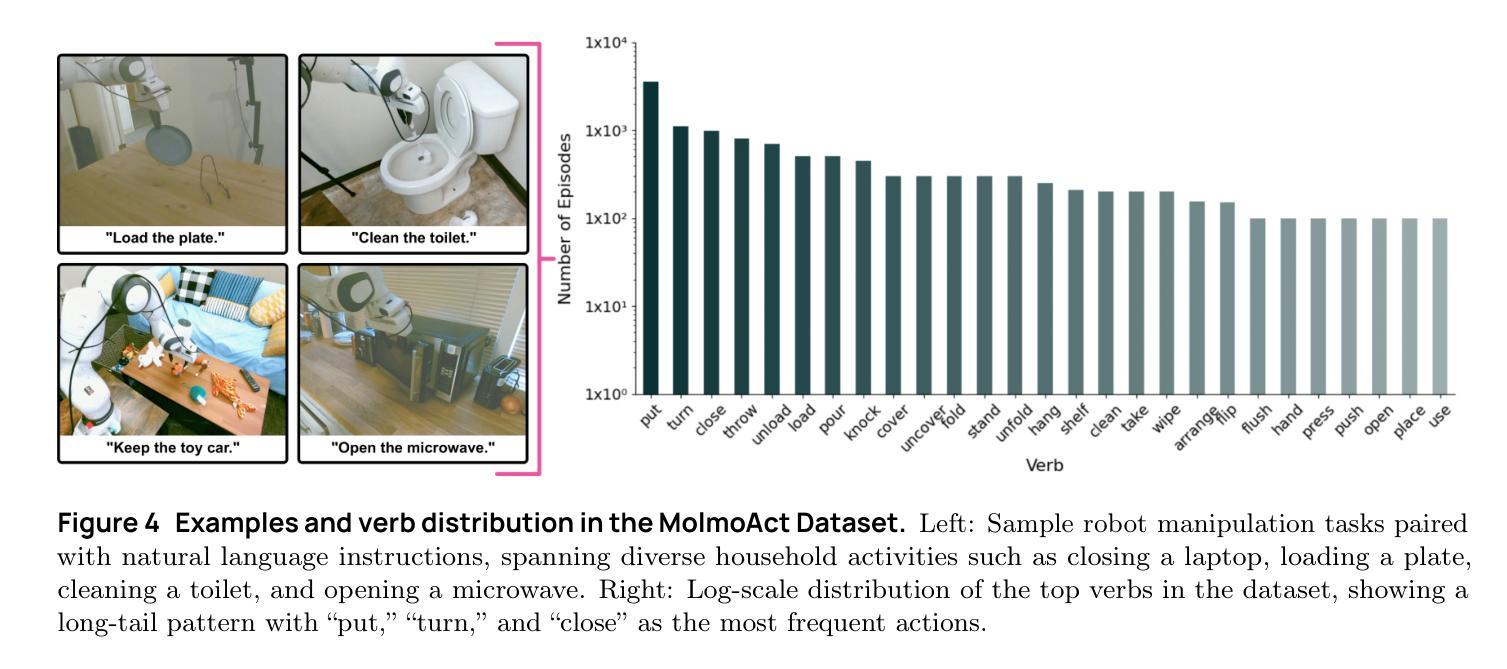
MolmoAct: Action Reasoning Models that can Reason in Space
Authors:Jason Lee, Jiafei Duan, Haoquan Fang, Yuquan Deng, Shuo Liu, Boyang Li, Bohan Fang, Jieyu Zhang, Yi Ru Wang, Sangho Lee, Winson Han, Wilbert Pumacay, Angelica Wu, Rose Hendrix, Karen Farley, Eli VanderBilt, Ali Farhadi, Dieter Fox, Ranjay Krishna
Reasoning is central to purposeful action, yet most robotic foundation models map perception and instructions directly to control, which limits adaptability, generalization, and semantic grounding. We introduce Action Reasoning Models (ARMs), a class of vision-language-action models that integrate perception, planning, and control through a structured three-stage pipeline. Our model, MolmoAct, encodes observations and instructions into depth-aware perception tokens, generates mid-level spatial plans as editable trajectory traces, and predicts precise low-level actions, enabling explainable and steerable behavior. MolmoAct-7B-D achieves strong performance across simulation and real-world settings: 70.5% zero-shot accuracy on SimplerEnv Visual Matching tasks, surpassing closed-source Pi-0 and GR00T N1; 86.6% average success on LIBERO, including an additional 6.3% gain over ThinkAct on long-horizon tasks; and in real-world fine-tuning, an additional 10% (single-arm) and an additional 22.7% (bimanual) task progression over Pi-0-FAST. It also outperforms baselines by an additional 23.3% on out-of-distribution generalization and achieves top human-preference scores for open-ended instruction following and trajectory steering. Furthermore, we release, for the first time, the MolmoAct Dataset – a mid-training robot dataset comprising over 10,000 high quality robot trajectories across diverse scenarios and tasks. Training with this dataset yields an average 5.5% improvement in general performance over the base model. We release all model weights, training code, our collected dataset, and our action reasoning dataset, establishing MolmoAct as both a state-of-the-art robotics foundation model and an open blueprint for building ARMs that transform perception into purposeful action through structured reasoning. Blogpost: https://allenai.org/blog/molmoact
推理是目标行动的核心,然而大多数机器人基础模型直接将感知和指令映射到控制上,这限制了适应性、泛化和语义基础。我们引入了行动推理模型(ARMs),这是一类融合感知、规划和控制的视觉语言行动模型,通过一个结构化的三阶段管道来实现。我们的模型MolmoAct将观察和指令编码为深度感知标记,生成可编辑的轨迹跟踪作为中级空间计划,并预测精确的低级行动,从而实现可解释和可引导的行为。MolmoAct-7B-D在模拟和真实环境设置中表现出强大的性能:在SimplerEnv视觉匹配任务上达到70.5%的零射击准确率,超越闭源Pi-0和GR00TN1;在LIBERO上平均成功率达到86.6%,其中长期任务较ThinkAct增加了额外的6.3%的优势;在真实世界的微调中,相较于Pi-0-FAST,单臂任务增加了额外的10%,双手动任务增加了额外的22.7%。此外,它还以额外的23.3%的优势超越基准线在超出分布泛化方面取得最佳表现,并且在开放式指令跟随和轨迹引导方面获得了最高的人类偏好分数。此外,我们首次发布MolmoAct数据集——一个中期训练机器人数据集,包含超过10,000条高质量机器人轨迹,涵盖各种场景和任务。使用该数据集进行训练相较于基础模型在整体性能上平均提高了5.5%。我们公开了所有模型权重、训练代码、收集的数据集以及我们的行动推理数据集,确立了MolmoAct作为最先进的机器人基础模型,并为建立通过结构化推理将感知转化为有目的行动的ARMs提供了一个开放的蓝图。博客文章:https://allenai.org/blog/molmoact
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Appendix on Blogpost: https://allenai.org/blog/molmoact
Summary
机器人动作推理模型(ARMs)是实现感知转化为有目的行动的关键。当前多数机器人基础模型直接将感知和指令映射到控制,这限制了其适应性、泛化和语义定位能力。为此,我们引入了动作推理模型(ARMs),这是一种融合感知、规划和控制的视觉语言动作模型。我们的模型MolmoAct通过结构化三阶段管道实现深度感知标记和指令编码、可编辑轨迹轨迹的空间规划以及精确的低层次动作预测,从而实现了可解释和可引导的行为。模型在模拟和真实环境下的表现优异,如在SimplerEnv视觉匹配任务上达到70.5%的零样本准确率,超越Pi-0和GR00T N1等封闭源代码模型;在LIBERO上平均成功率达到86.6%,在长周期任务上的提升幅度比ThinkAct高出6.3%;在真实世界微调中,相较于Pi-0-FAST模型,单臂任务进步幅度提高了额外的10%,双肢协同任务提高了额外的22.7%。此外,我们首次发布了MolmoAct数据集,这是一套包含超过一万条高质量机器人轨迹的中期训练数据集,涵盖各种场景和任务。使用此数据集进行训练相较于基础模型在总体上提升了平均5.5%的表现。我们的研究建立了一个兼具前沿水平的机器人基础模型MolmoAct,并为构建通过结构化推理将感知转化为有目的行动的ARMs提供了开放的蓝图。更多信息请参阅https://allenai.org/blog/molmoact。
Key Takeaways
- 动作推理模型(ARMs)在机器人领域是关键实现感知到动作转化的技术。
- 现有机器人基础模型直接映射感知和指令到控制,限制了适应性、泛化能力和语义定位。
- MolmoAct模型通过结构化三阶段管道实现深度感知和指令处理、空间规划和精确动作预测。
- MolmoAct在模拟和真实环境下表现优异,超越多个现有模型。
- 发布了MolmoAct数据集,包含多种场景和任务的高质量机器人轨迹。
- 使用MolmoAct数据集训练可提高模型整体表现。
点此查看论文截图

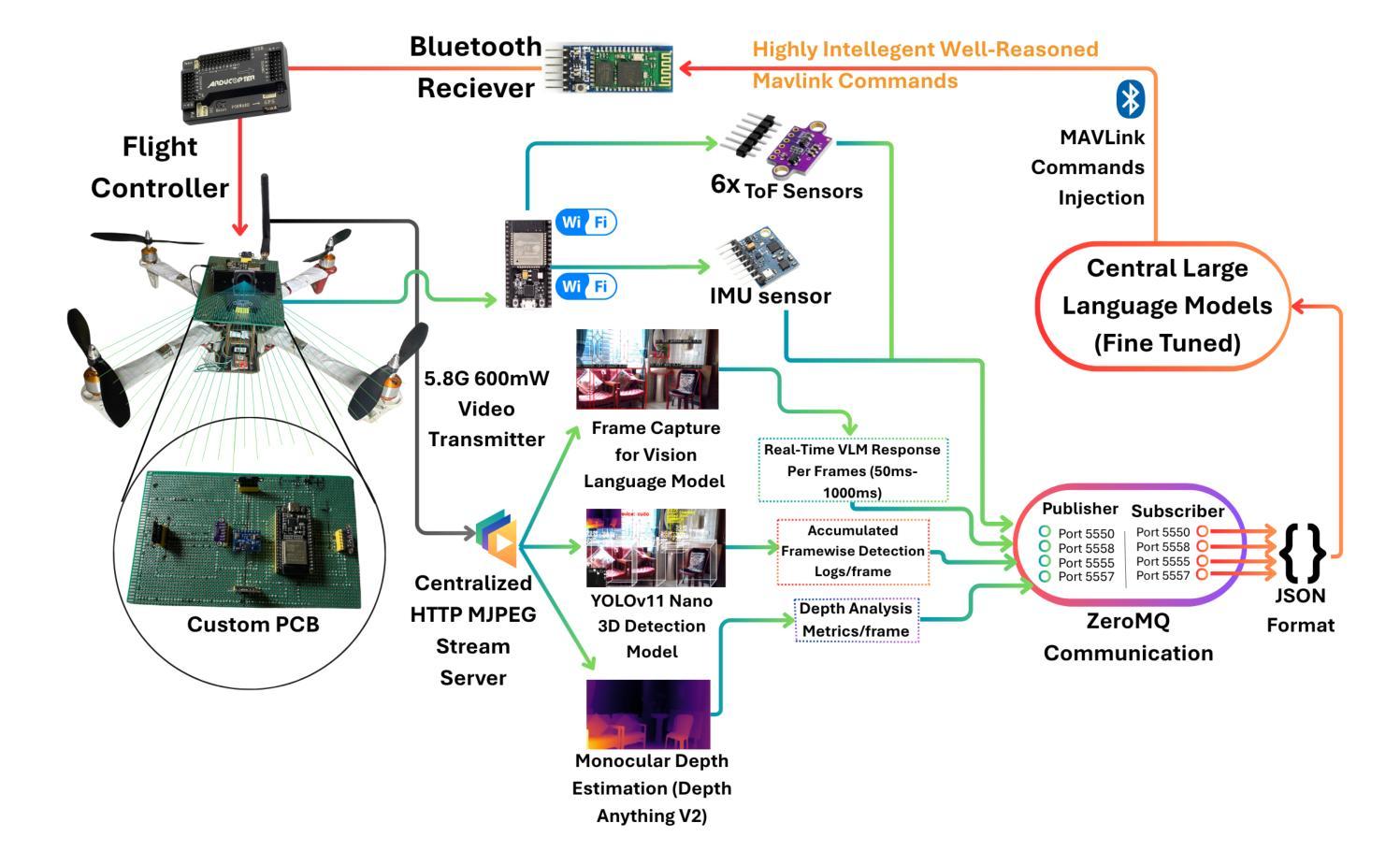
Autonomous Navigation of Cloud-Controlled Quadcopters in Confined Spaces Using Multi-Modal Perception and LLM-Driven High Semantic Reasoning
Authors:Shoaib Ahmmad, Zubayer Ahmed Aditto, Md Mehrab Hossain, Noushin Yeasmin, Shorower Hossain
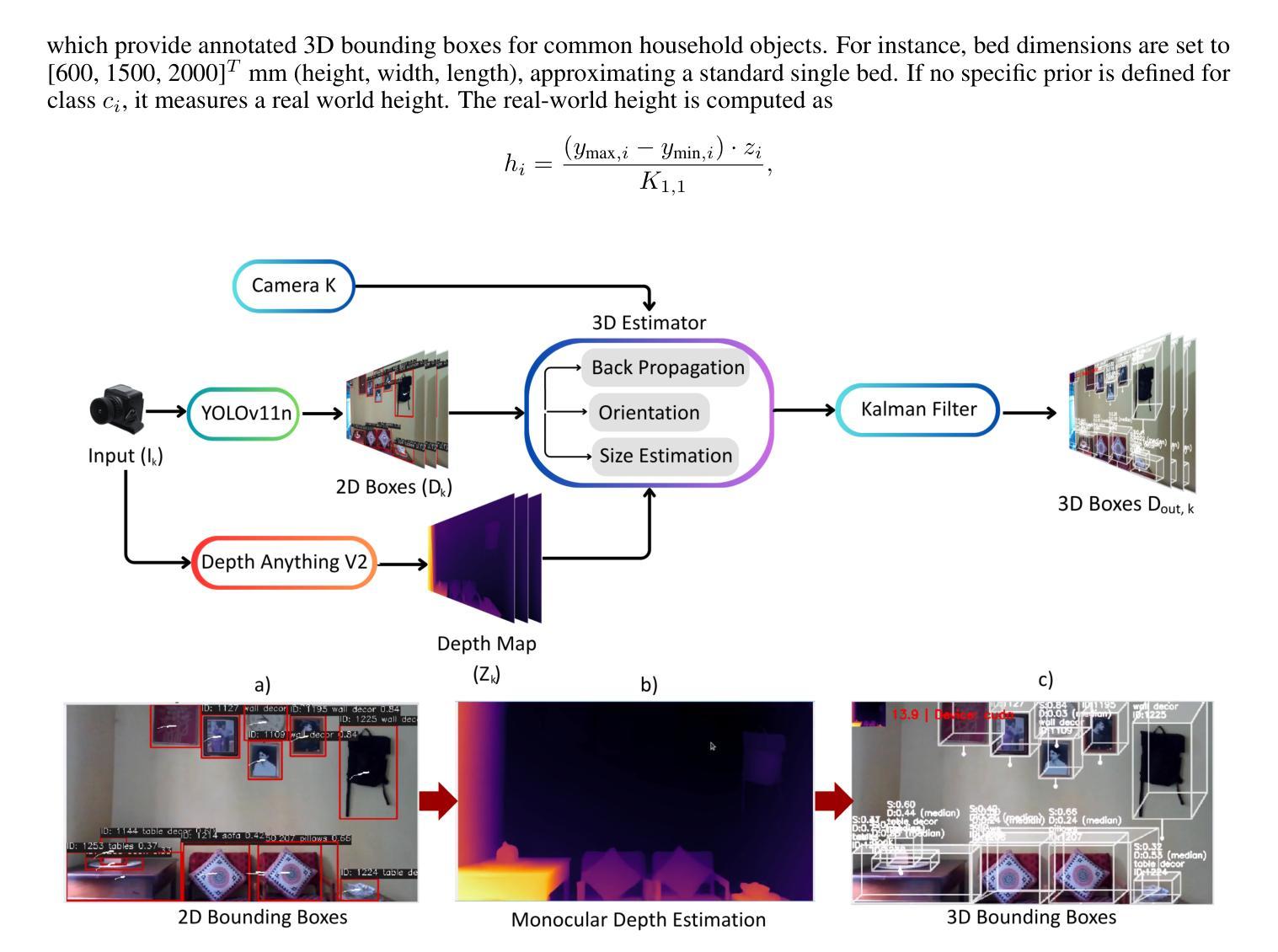
This paper introduces an advanced AI-driven perception system for autonomous quadcopter navigation in GPS-denied indoor environments. The proposed framework leverages cloud computing to offload computationally intensive tasks and incorporates a custom-designed printed circuit board (PCB) for efficient sensor data acquisition, enabling robust navigation in confined spaces. The system integrates YOLOv11 for object detection, Depth Anything V2 for monocular depth estimation, a PCB equipped with Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), and a cloud-based Large Language Model (LLM) for context-aware decision-making. A virtual safety envelope, enforced by calibrated sensor offsets, ensures collision avoidance, while a multithreaded architecture achieves low-latency processing. Enhanced spatial awareness is facilitated by 3D bounding box estimation with Kalman filtering. Experimental results in an indoor testbed demonstrate strong performance, with object detection achieving a mean Average Precision (mAP50) of 0.6, depth estimation Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 7.2 cm, only 16 safety envelope breaches across 42 trials over approximately 11 minutes, and end-to-end system latency below 1 second. This cloud-supported, high-intelligence framework serves as an auxiliary perception and navigation system, complementing state-of-the-art drone autonomy for GPS-denied confined spaces.
本文介绍了一种先进的AI驱动感知系统,用于GPS拒止的室内环境中的自主四轴飞行器导航。所提出的框架利用云计算来处理计算密集型任务,并采用定制设计的印刷电路板(PCB)进行高效传感器数据采集,从而在有限空间内实现稳健导航。该系统集成了YOLOv11进行目标检测、Depth Anything V2进行单目深度估计、配备飞行时间(ToF)传感器和惯性测量单元(IMU)的PCB,以及基于云的大型语言模型(LLM)进行上下文感知决策。通过校准的传感器偏移实施虚拟安全包络,以确保避免碰撞,同时多线程架构实现低延迟处理。通过卡尔曼滤波的3D边界框估计增强了空间感知能力。在室内测试平台上的实验结果表明,该系统性能强劲,目标检测平均精度(mAP50)达到0.6,深度估计平均绝对误差(MAE)为7.2厘米,在约11分钟的42次试验中只有16次安全包络违反,并且端到端系统延迟低于1秒。这一受云支持的高智能框架作为辅助感知和导航系统,补充了最新无人机在GPS拒止的封闭空间中的自主性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文介绍了一种用于GPS拒止室内环境中四轴飞行器自主导航的高级AI驱动感知系统。该系统利用云计算卸载计算密集型任务,采用定制印刷电路板进行高效传感器数据采集,并结合YOLOv11目标检测、Depth Anything V2单目深度估计等技术,实现室内环境中的稳健导航。通过飞行时间传感器和惯性测量装置的数据,结合云端大型语言模型进行语境决策,构建虚拟安全包络以实现避障。实验结果显示,该系统在室内测试环境中的表现强劲。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文描述了一种在GPS拒止室内环境中使用的先进AI驱动四轴飞行器感知系统。
- 系统利用云计算处理计算密集型任务,提升效率。
- 通过定制的印刷电路板实现高效传感器数据采集。
- 整合多种技术:YOLOv11目标检测、Depth Anything V2单目深度估计等。
- 结合飞行时间传感器和惯性测量装置数据,实现虚拟安全包络,确保避障。
- 通过云端大型语言模型进行语境决策。
点此查看论文截图

TAR-TVG: Enhancing VLMs with Timestamp Anchor-Constrained Reasoning for Temporal Video Grounding
Authors:Chaohong Guo, Xun Mo, Yongwei Nie, Xuemiao Xu, Chao Xu, Fei Yu, Chengjiang Long
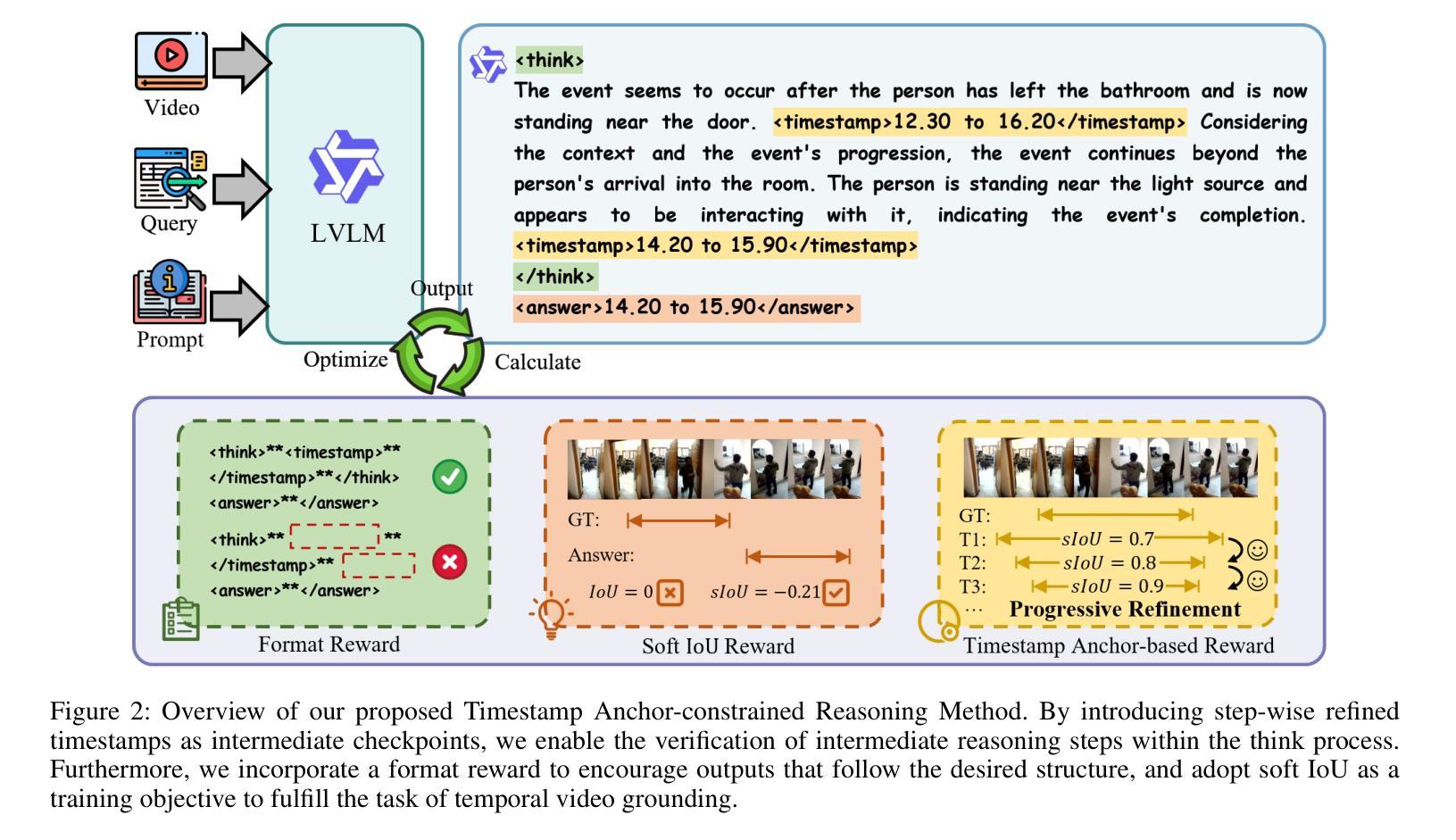
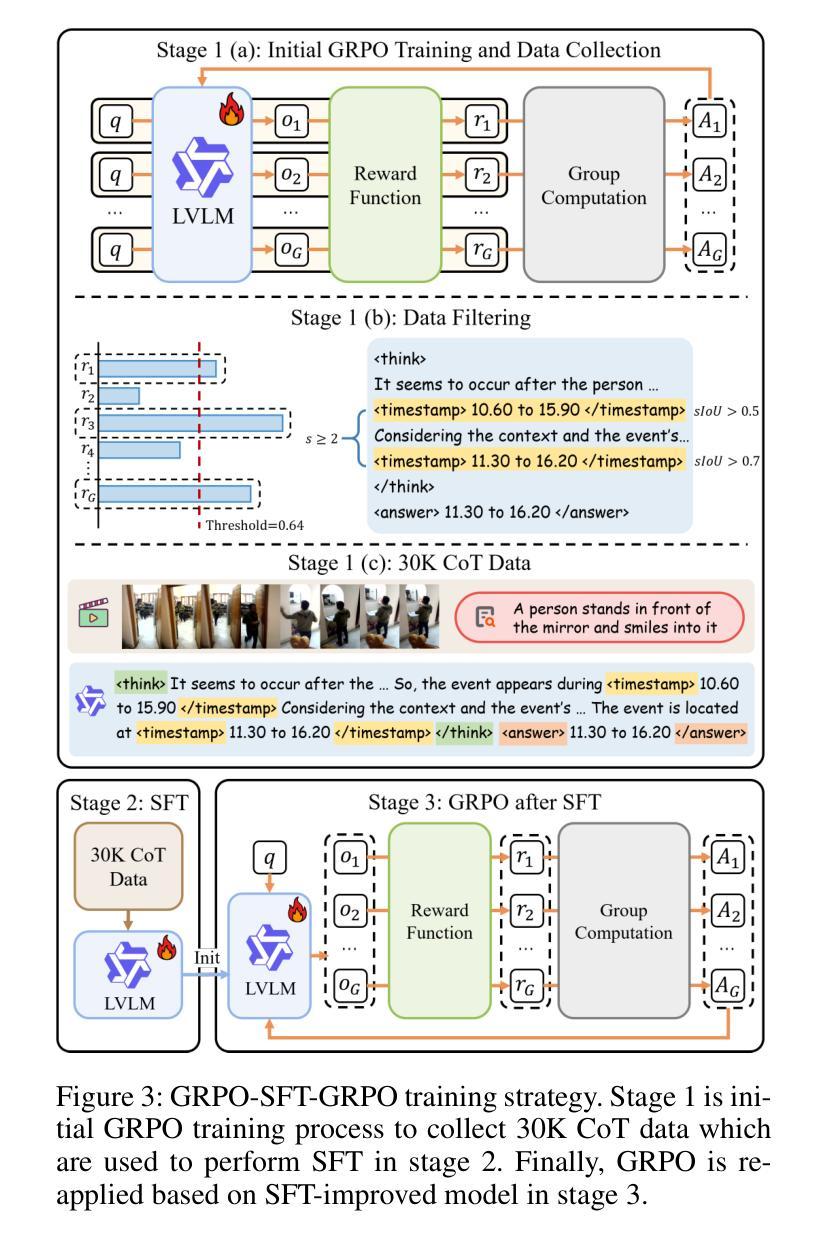
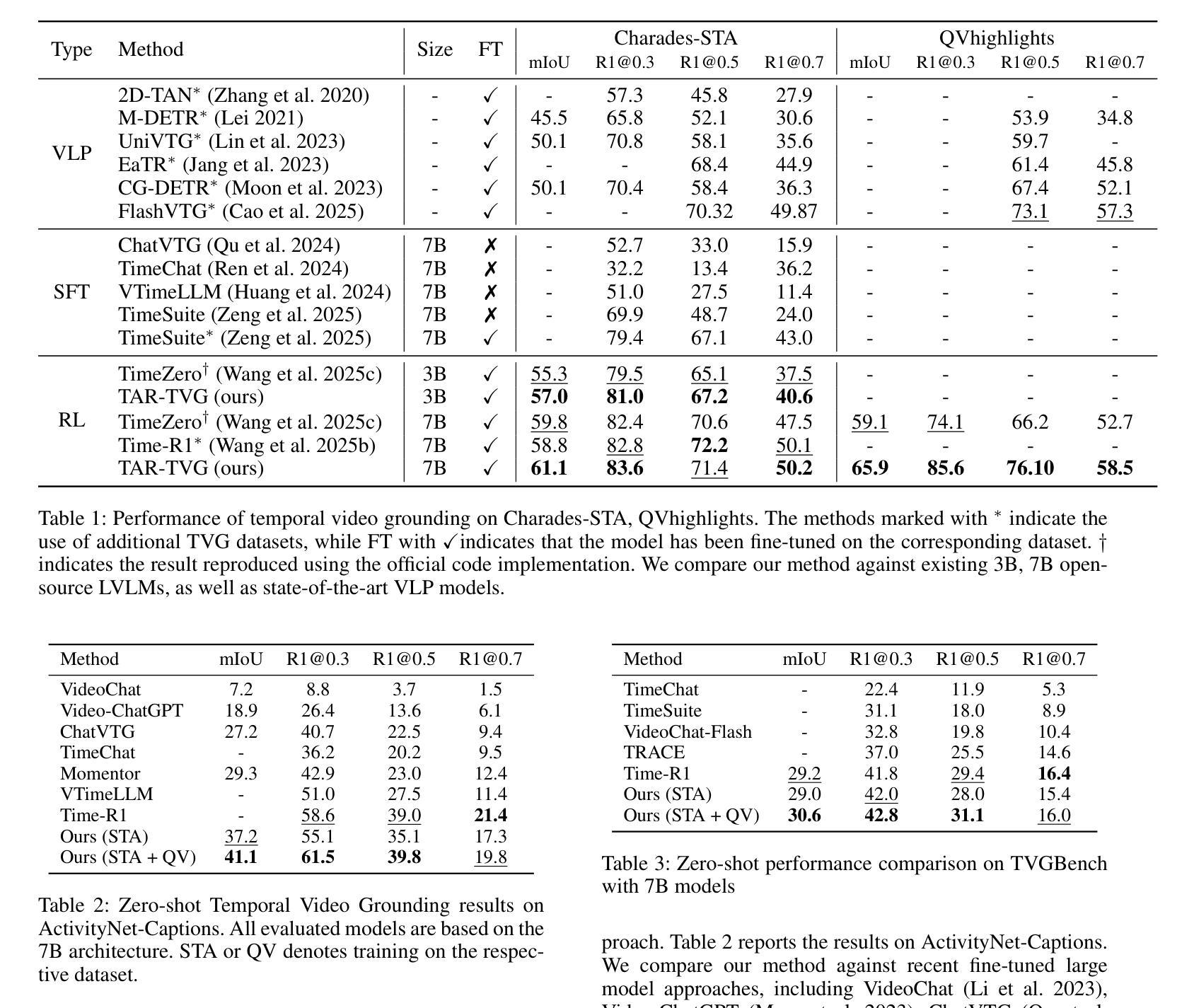
Temporal Video Grounding (TVG) aims to precisely localize video segments corresponding to natural language queries, which is a critical capability for long-form video understanding. Although existing reinforcement learning approaches encourage models to generate reasoning chains before predictions, they fail to explicitly constrain the reasoning process to ensure the quality of the final temporal predictions. To address this limitation, we propose Timestamp Anchor-constrained Reasoning for Temporal Video Grounding (TAR-TVG), a novel framework that introduces timestamp anchors within the reasoning process to enforce explicit supervision to the thought content. These anchors serve as intermediate verification points. More importantly, we require each reasoning step to produce increasingly accurate temporal estimations, thereby ensuring that the reasoning process contributes meaningfully to the final prediction. To address the challenge of low-probability anchor generation in models (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL-3B), we develop an efficient self-distillation training strategy: (1) initial GRPO training to collect 30K high-quality reasoning traces containing multiple timestamp anchors, (2) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on distilled data, and (3) final GRPO optimization on the SFT-enhanced model. This three-stage training strategy enables robust anchor generation while maintaining reasoning quality. Experiments show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance while producing interpretable, verifiable reasoning chains with progressively refined temporal estimations.
时序视频定位(TVG)旨在准确地对应自然语言查询定位视频片段,这对于长格式视频理解是一项关键能力。尽管现有的强化学习方法鼓励模型在预测前生成推理链,但它们未能显式约束推理过程以确保最终时序预测的质量。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了时序视频定位的时间戳锚点约束推理(TAR-TVG)新框架,该框架在推理过程中引入时间戳锚点,以强制执行对思想内容的显式监督。这些锚点充当中间验证点。更重要的是,我们要求每个推理步骤产生越来越准确的时序估计,从而确保推理过程对最终预测产生有意义的贡献。为了解决模型中低概率锚点生成的问题(例如Qwen2.5-VL-3B),我们开发了一种有效的自蒸馏训练策略:(1)初始GRPO训练以收集包含多个时间戳锚点的高质量推理轨迹3万条,(2)蒸馏数据的监督微调(SFT),(3)在SFT增强模型上进行最终的GRPO优化。这种三阶段的训练策略能够在保持推理质量的同时实现稳健的锚点生成。实验表明,我们的模型在产生可解释、可验证的推理链的同时,具有逐步改进的时序估计,实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了Temporal Video Grounding(TVG)的目标是通过自然语言查询精确定位视频段落。为解决现有强化学习方法的局限,提出了一种名为TAR-TVG的新框架,通过引入时间戳锚点来约束推理过程,确保最终时间预测的精准性。为应对模型低概率锚点生成的问题,开发了一种高效自蒸馏训练策略,包括初始GRPO训练收集高质量推理轨迹、监督微调(SFT)和最终GRPO优化。实验表明,该模型在产生可解释、可验证的推理链的同时,逐步优化时间估计,实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Temporal Video Grounding (TVG) 的目标是精确定位与自然语言查询相对应的视频段落。
- 现有强化学习方法在TVG中存在推理质量不高的问题。
- TAR-TVG框架通过引入时间戳锚点来约束推理过程,提高最终时间预测的质量。
- 时间戳锚点作为中间验证点,要求每个推理步骤产生越来越精确的时间估计。
- 模型面临低概率锚点生成的问题,需开发高效自蒸馏训练策略来解决。
- 自蒸馏训练策略包括三个阶段:初始GRPO训练、监督微调(SFT)和最终GRPO优化。
点此查看论文截图

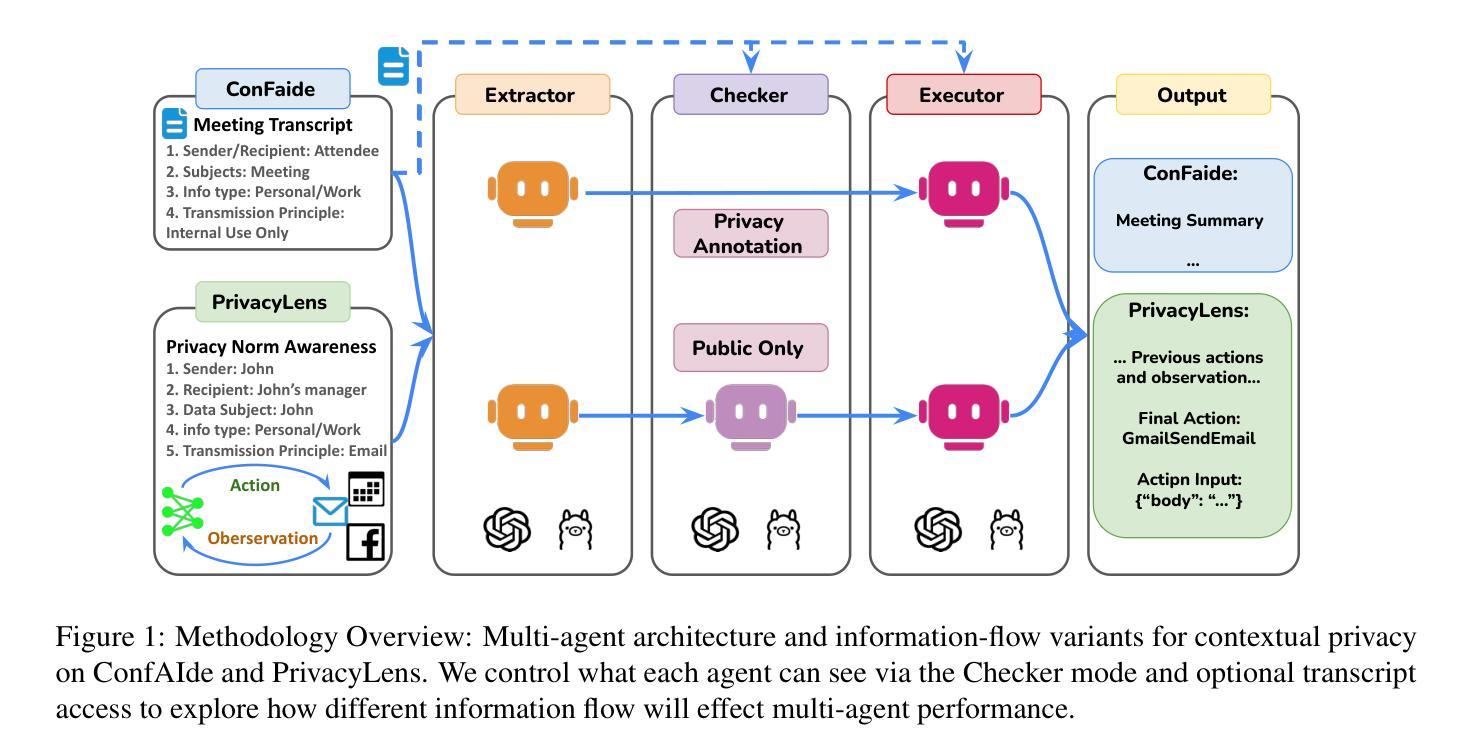
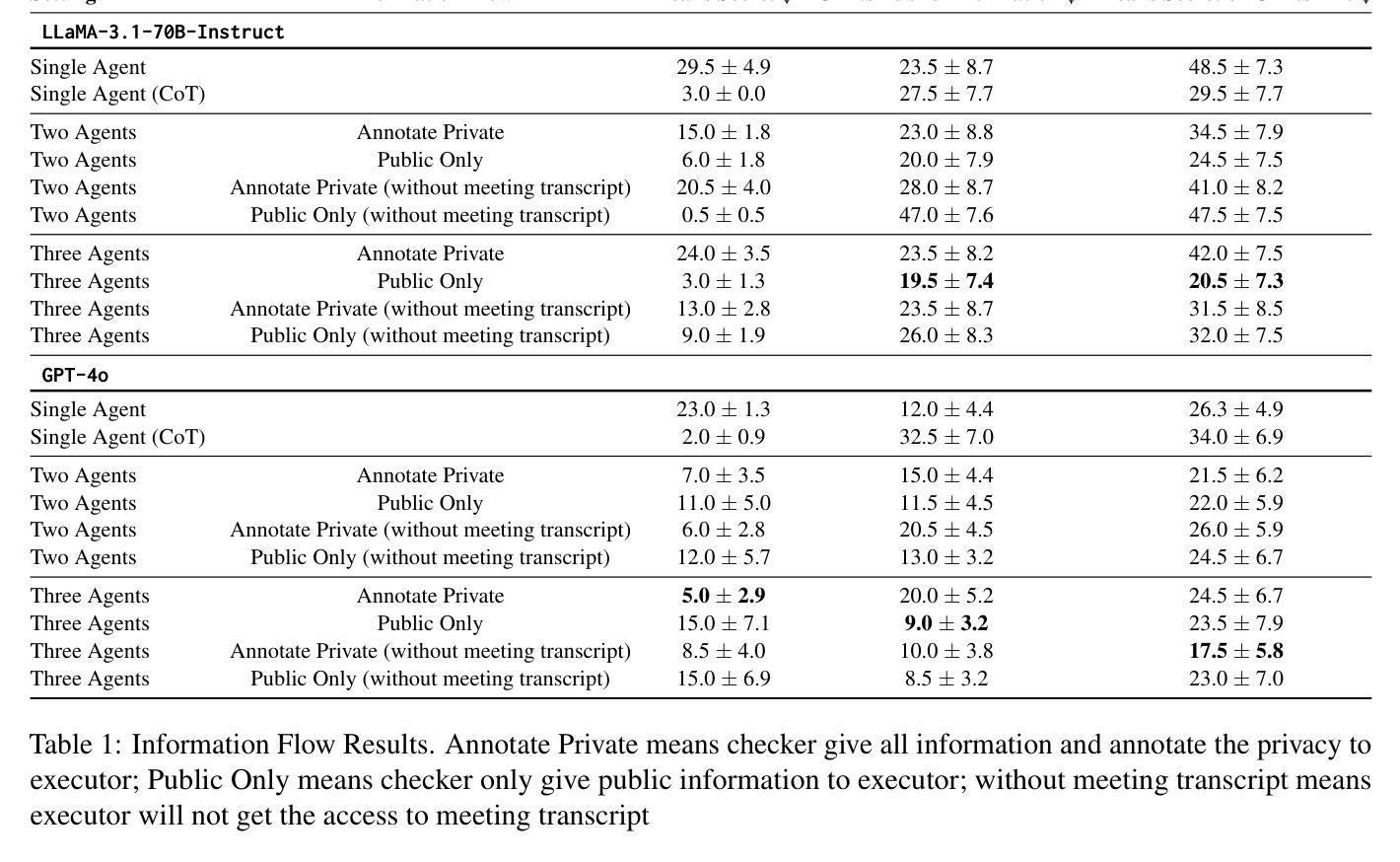
1-2-3 Check: Enhancing Contextual Privacy in LLM via Multi-Agent Reasoning
Authors:Wenkai Li, Liwen Sun, Zhenxiang Guan, Xuhui Zhou, Maarten Sap
Addressing contextual privacy concerns remains challenging in interactive settings where large language models (LLMs) process information from multiple sources (e.g., summarizing meetings with private and public information). We introduce a multi-agent framework that decomposes privacy reasoning into specialized subtasks (extraction, classification), reducing the information load on any single agent while enabling iterative validation and more reliable adherence to contextual privacy norms. To understand how privacy errors emerge and propagate, we conduct a systematic ablation over information-flow topologies, revealing when and why upstream detection mistakes cascade into downstream leakage. Experiments on the ConfAIde and PrivacyLens benchmark with several open-source and closed-sourced LLMs demonstrate that our best multi-agent configuration substantially reduces private information leakage (\textbf{18%} on ConfAIde and \textbf{19%} on PrivacyLens with GPT-4o) while preserving the fidelity of public content, outperforming single-agent baselines. These results highlight the promise of principled information-flow design in multi-agent systems for contextual privacy with LLMs.
在处理来自多个来源的信息(例如,总结包含私人信息和公共信息的会议)的语言模型时,如何在交互式环境中解决上下文隐私问题仍然是一个挑战。我们引入了一个多智能体框架,该框架将隐私推理分解成专门的子任务(提取、分类),从而减轻了任何单个智能体的信息负载,同时实现了迭代验证和更可靠地遵守上下文隐私规范。为了了解隐私错误是如何产生和传播的,我们对信息流拓扑进行了系统的切除研究,揭示了上游检测错误何时以及为何会级联成下游泄漏。在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上对多个开源和闭源的大型语言模型进行的实验表明,我们最好的多智能体配置大幅减少了私人信息的泄漏(在ConfAIde上减少了\textbf{18}%,在PrivacyLens上与GPT-4o一起减少了\textbf{19}%),同时保持了公共内容的保真度,超越了单智能体的基线。这些结果突显了在多智能体系统中进行有原则的信息流设计,利用大型语言模型进行上下文隐私的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对大型语言模型在处理来自多个源的上下文隐私信息时面临的挑战,提出了一种多代理框架。该框架将隐私推理分解为专门的子任务,减少单个代理的信息负载,同时实现迭代验证和更可靠地遵守上下文隐私规范。文章通过系统性地研究信息流动拓扑来了解隐私错误如何产生和扩散,揭示上游检测错误何时以及如何演变为下游泄露的原因。在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上的实验表明,最佳多代理配置能显著减少私人信息泄露,同时保持公共内容的保真度,优于单代理基线。这些结果突显了原则性信息流动设计在多代理系统与大型语言模型共同进行上下文隐私保护的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理来自多个源的上下文隐私信息时面临挑战。
- 提出了一种多代理框架,将隐私推理分解为专门的子任务,减少单个代理的信息负载。
- 通过研究信息流动拓扑来了解隐私错误如何产生和扩散。
- 揭示了上游检测错误如何演变为下游泄露的原因。
- 在ConfAIde和PrivacyLens基准测试上,多代理配置显著减少了私人信息泄露。
- 多代理配置在减少私人信息泄露的同时,保持了公共内容的保真度。
点此查看论文截图

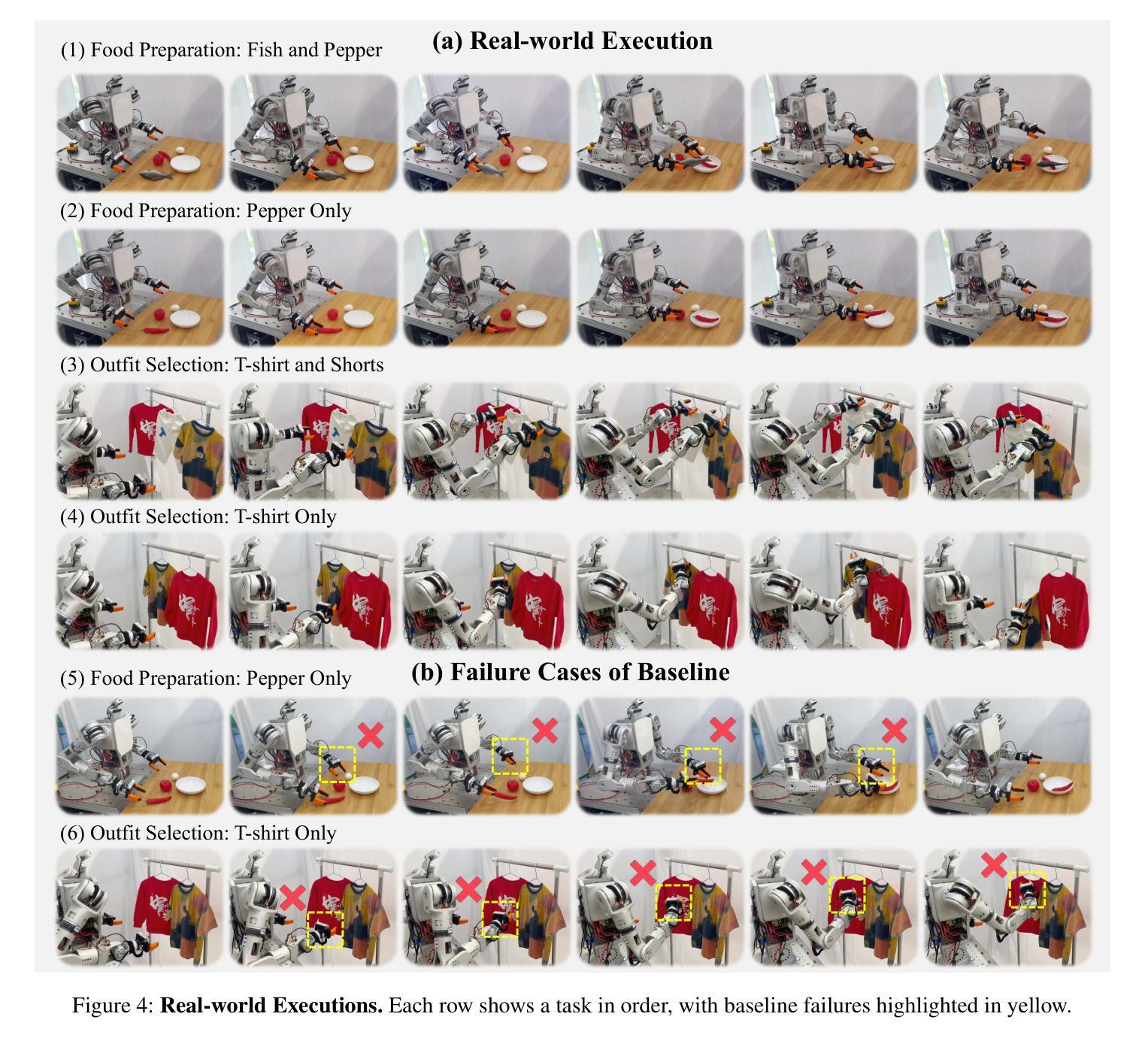
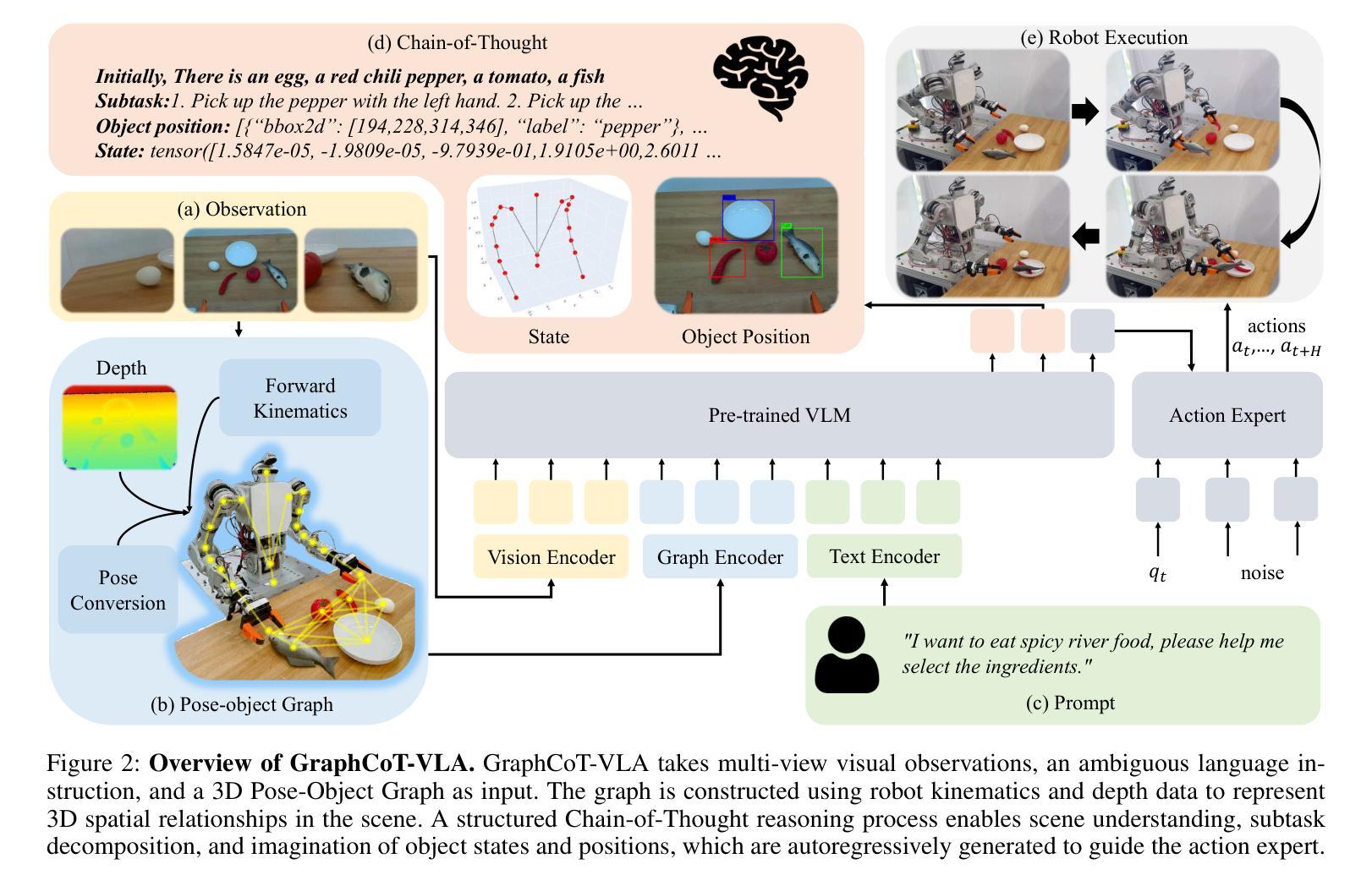
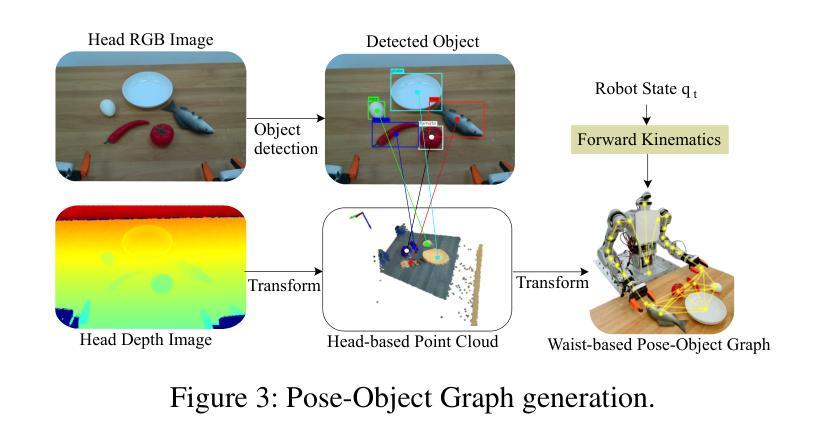
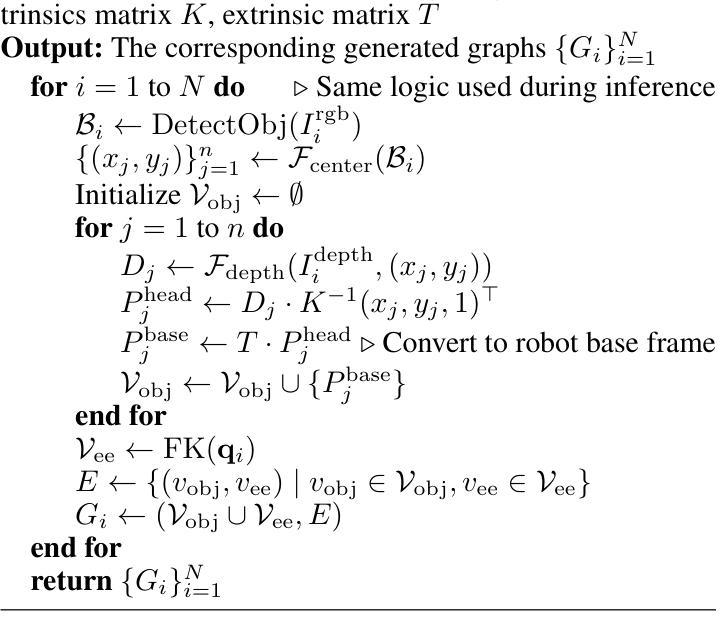
GraphCoT-VLA: A 3D Spatial-Aware Reasoning Vision-Language-Action Model for Robotic Manipulation with Ambiguous Instructions
Authors:Helong Huang, Min Cen, Kai Tan, Xingyue Quan, Guowei Huang, Hong Zhang
Vision-language-action models have emerged as a crucial paradigm in robotic manipulation. However, existing VLA models exhibit notable limitations in handling ambiguous language instructions and unknown environmental states. Furthermore, their perception is largely constrained to static two-dimensional observations, lacking the capability to model three-dimensional interactions between the robot and its environment. To address these challenges, this paper proposes GraphCoT-VLA, an efficient end-to-end model. To enhance the model’s ability to interpret ambiguous instructions and improve task planning, we design a structured Chain-of-Thought reasoning module that integrates high-level task understanding and planning, failed task feedback, and low-level imaginative reasoning about future object positions and robot actions. Additionally, we construct a real-time updatable 3D Pose-Object graph, which captures the spatial configuration of robot joints and the topological relationships between objects in 3D space, enabling the model to better understand and manipulate their interactions. We further integrates a dropout hybrid reasoning strategy to achieve efficient control outputs. Experimental results across multiple real-world robotic tasks demonstrate that GraphCoT-VLA significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of task success rate and response speed, exhibiting strong generalization and robustness in open environments and under uncertain instructions.
视觉语言动作模型已经成为机器人操作中的关键范式。然而,现有的VLA模型在处理模糊的语音指令和未知的环境状态时存在明显的局限性。此外,它们的感知主要局限于静态的二维观察,缺乏机器人与其环境之间三维交互的建模能力。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了GraphCoT-VLA这一高效的端到端模型。为了增强模型对模糊指令的解读能力和任务规划能力,我们设计了一种结构化的思维链推理模块,该模块融合了高级任务理解和规划、任务失败反馈以及关于未来物体位置和机器人动作的底层推理想象。此外,我们构建了一个可实时更新的三维姿态物体图,捕捉机器人关节的空间配置以及物体在三维空间中的拓扑关系,使模型能够更好地理解和操作物体间的交互。我们还采用了一种混合推理策略来实现有效的控制输出。在多个真实世界机器人任务上的实验结果表明,GraphCoT-VLA在任务成功率和响应速度方面显著优于现有方法,在开放环境和不确定指令下表现出强大的泛化能力和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于视觉-语言-动作模型的机器人操作技术中,GraphCoT-VLA模型能有效解决现有模型在处理模糊语言指令和未知环境状态方面的局限性。该模型通过设计结构化思维链(Chain-of-Thought)推理模块,提升对模糊指令的解读和任务规划能力。此外,还构建了可实时更新的三维姿态物体图(3D Pose-Object graph),能捕捉机器人关节的空间配置和物体间的拓扑关系,从而提升模型对物体交互的理解和操作能力。实验结果证明,GraphCoT-VLA在多个真实机器人任务中显著优于现有方法,任务成功率和响应速度均有显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 现有Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型在处理模糊语言指令和未知环境状态方面存在局限性。
- GraphCoT-VLA模型通过设计结构化思维链(Chain-of-Thought)推理模块,提升对模糊指令的解读和任务规划能力。
- GraphCoT-VLA构建了可实时更新的三维姿态物体图(3D Pose-Object graph),能捕捉机器人关节的空间配置和物体间的拓扑关系。
- 模型具备更好的物体交互理解和操作能力。
- GraphCoT-VLA在多个真实机器人任务中表现优异,任务成功率和响应速度均有显著提升。
- GraphCoT-VLA模型通过整合高层次的任务理解和规划、失败任务反馈以及未来物体位置和机器人动作的低位想象推理,提高了性能。
点此查看论文截图

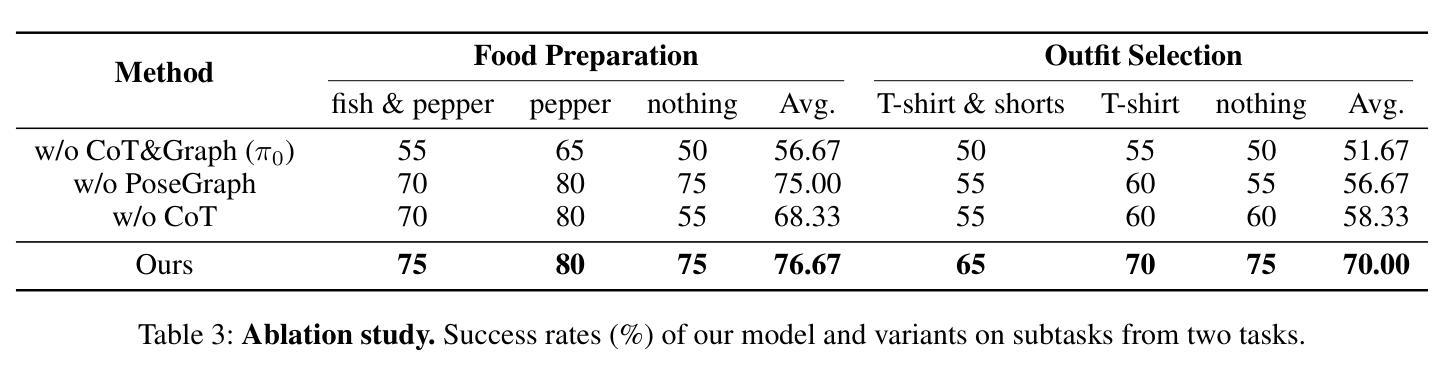

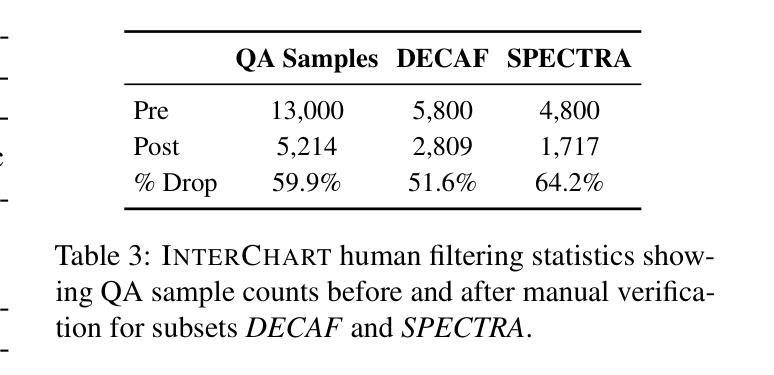
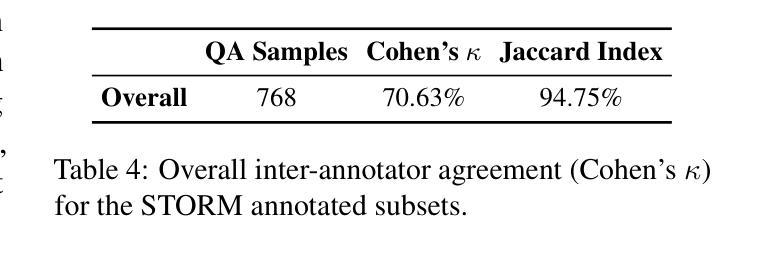
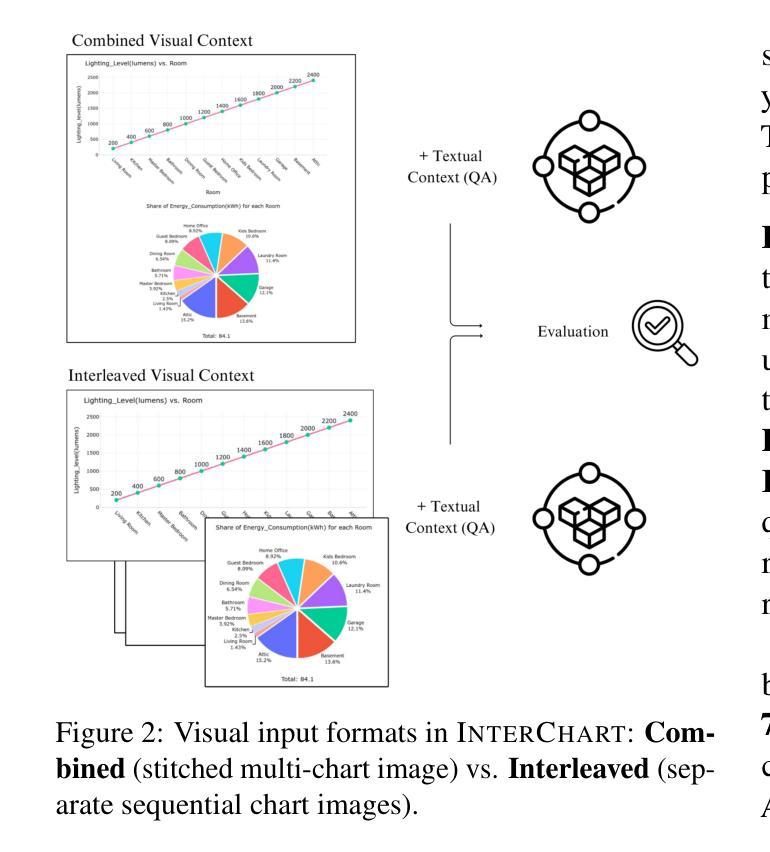
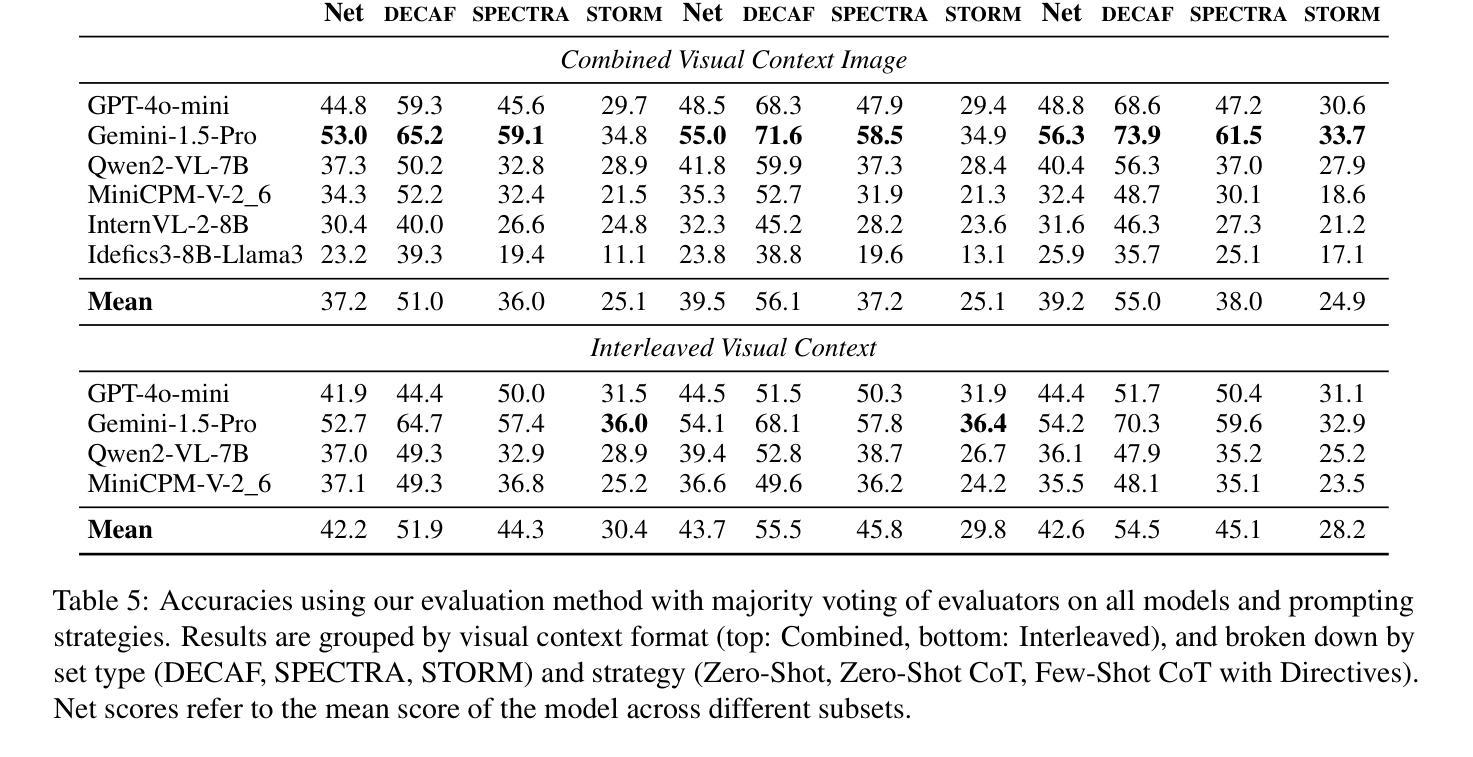
InterChart: Benchmarking Visual Reasoning Across Decomposed and Distributed Chart Information
Authors:Anirudh Iyengar Kaniyar Narayana Iyengar, Srija Mukhopadhyay, Adnan Qidwai, Shubhankar Singh, Dan Roth, Vivek Gupta
We introduce InterChart, a diagnostic benchmark that evaluates how well vision-language models (VLMs) reason across multiple related charts, a task central to real-world applications such as scientific reporting, financial analysis, and public policy dashboards. Unlike prior benchmarks focusing on isolated, visually uniform charts, InterChart challenges models with diverse question types ranging from entity inference and trend correlation to numerical estimation and abstract multi-step reasoning grounded in 2-3 thematically or structurally related charts. We organize the benchmark into three tiers of increasing difficulty: (1) factual reasoning over individual charts, (2) integrative analysis across synthetically aligned chart sets, and (3) semantic inference over visually complex, real-world chart pairs. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art open and closed-source VLMs reveals consistent and steep accuracy declines as chart complexity increases. We find that models perform better when we decompose multi-entity charts into simpler visual units, underscoring their struggles with cross-chart integration. By exposing these systematic limitations, InterChart provides a rigorous framework for advancing multimodal reasoning in complex, multi-visual environments.
我们介绍了InterChart,这是一个诊断基准测试,用于评估视觉语言模型(VLM)在多张相关图表上的推理能力。这一任务是现实世界应用(如科学报告、金融分析和公共政策仪表板)的核心。与以往侧重于孤立、视觉统一的图表的基准测试不同,InterChart通过多样的问题类型(如实体推理、趋势相关性、数值估算和基于两三个主题或结构上相关图表的抽象多步骤推理等)来挑战模型。我们将基准测试分为三个难度递增的层次:(1)单个图表的推理,(2)合成图表集的综合分析,(3)视觉上复杂、真实世界的图表对的语义推理。我们对最新开源和闭源的VLM评估显示,随着图表复杂性的增加,准确性持续且急剧下降。我们发现,当我们将多实体图表分解为更简单的视觉单元时,模型的性能更好,这突出了它们在跨图表整合方面的困难。通过揭示这些系统局限,InterChart为复杂多视觉环境中多模式推理的进步提供了严格框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures, 12 tables. Benchmark dataset and evaluation code will be publicly made available
Summary:
我们介绍了InterChart这一诊断基准测试,它旨在评估视觉语言模型在多张相关图表上的推理能力。该测试涵盖多种类型的图表问题,包括实体推断、趋势关联、数值估算和基于两到三张主题或结构上相关图表的抽象多步骤推理等。基准测试分为三个难度递增的层次:个人图表的推理能力、合成图表集的整合分析以及视觉复杂图表对的语义推理能力。对最先进的开放和封闭源代码视觉语言模型的评估显示,随着图表复杂性的增加,准确性持续且急剧下降。我们发现将多实体图表分解为更简单的视觉单元可以提高模型的性能,突显出跨图表整合方面的困难。通过揭示这些系统性局限,InterChart为复杂多视觉环境中的多模态推理提供了一个严格的框架。
Key Takeaways:
- InterChart是一个旨在评估视觉语言模型在多张相关图表上推理能力的诊断基准测试。
- 它涵盖了多种类型的图表问题,包括实体推断、趋势关联等。
- 基准测试分为三个层次,难度递增。
- 随着图表复杂性的增加,现有模型的准确性急剧下降。
- 将多实体图表分解为更简单的视觉单元可以提高模型的性能。
- InterChart揭示了跨图表整合方面的困难。
点此查看论文截图

Klear-Reasoner: Advancing Reasoning Capability via Gradient-Preserving Clipping Policy Optimization
Authors:Zhenpeng Su, Leiyu Pan, Xue Bai, Dening Liu, Guanting Dong, Jiaming Huang, Wenping Hu, Guorui Zhou
We present Klear-Reasoner, a model with long reasoning capabilities that demonstrates careful deliberation during problem solving, achieving outstanding performance across multiple benchmarks. Although there are already many excellent works related to inference models in the current community, there are still many problems with reproducing high-performance inference models due to incomplete disclosure of training details. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the reasoning model, covering the entire post-training workflow from data preparation and long Chain-of-Thought supervised fine-tuning (long CoT SFT) to reinforcement learning (RL), along with detailed ablation studies for each experimental component. For SFT data, our experiments show that a small number of high-quality data sources are more effective than a large number of diverse data sources, and that difficult samples can achieve better results without accuracy filtering. In addition, we investigate two key issues with current clipping mechanisms in RL: Clipping suppresses critical exploration signals and ignores suboptimal trajectories. To address these challenges, we propose Gradient-Preserving clipping Policy Optimization (GPPO) that gently backpropagates gradients from clipped tokens. GPPO not only enhances the model’s exploration capacity but also improves its efficiency in learning from negative samples. Klear-Reasoner exhibits exceptional reasoning abilities in mathematics and programming, scoring 90.5% on AIME 2024, 83.2% on AIME 2025, 66.0% on LiveCodeBench V5 and 58.1% on LiveCodeBench V6.
我们推出了Klear-Reasoner,这是一款具有长期推理能力的模型,在解决问题时展现出谨慎的考虑,并在多个基准测试中表现出卓越的性能。尽管当前社区已经有很多与推理模型相关的优秀作品,但由于培训细节披露不完整,因此重现高性能推理模型仍然存在许多问题。本报告对推理模型进行了深入分析,涵盖了从数据准备和长链思维监督微调(long CoT SFT)到强化学习(RL)的整个训练后工作流程,并对每个实验组件进行了详细的消融研究。对于SFT数据,我们的实验表明,少数高质量的数据源比大量多样的数据源更有效,而且困难样本可以在无需精度过滤的情况下实现更好的结果。此外,我们研究了当前强化学习中的裁剪机制的两个关键问题:裁剪会抑制关键探索信号并忽略次优轨迹。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了梯度保持裁剪策略优化(GPPO),该优化能温和地反向传播被裁剪令牌的梯度。GPPO不仅提高了模型的探索能力,而且提高了其从负样本中学习的效率。Klear-Reasoner在数学和编程方面展现出卓越的推理能力,在AIME 2024上得分90.5%,在AIME 2025上得分83.2%,在LiveCodeBench V5上得分66.0%,在LiveCodeBench V6上得分58.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Klear-Reasoner模型的深入研究,该模型具备出色的长期推理能力,并在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能。报告详细分析了推理模型,从头开始介绍了数据准备和长期思维链监督精细调整(long CoT SFT)到强化学习(RL)的整个训练流程,并对每个实验组件进行了详细的消融研究。实验表明,少量高质量数据源比大量多样化数据源更有效,且困难样本无需过滤即可获得更好的结果。针对当前RL中裁剪机制的两个关键问题,提出了梯度保留裁剪策略优化(GPPO)方法,该方法可温和地反向传播被裁剪令牌的梯度。GPPO不仅提高了模型的探索能力,还提高了其从负样本中学习的效率。Klear-Reasoner在数学和编程方面展现出非凡的推理能力,在AIME 2024、AIME 2025和LiveCodeBench V5/V6等考试中取得显著成绩。
Key Takeaways
- Klear-Reasoner是一个具有长期推理能力的模型,在多个基准测试中表现卓越。
- 报告提供了从数据准备到强化学习的全面训练流程分析。
- 实验显示少量高质量数据源比大量多样化数据源更有效。
- 困难样本无需过滤即可获得更好的结果。
- 针对RL中的裁剪机制问题,提出了GPPO方法以提高模型的探索能力和从负样本中学习效率。
- Klear-Reasoner在数学和编程方面展现出非凡的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

AR-VRM: Imitating Human Motions for Visual Robot Manipulation with Analogical Reasoning
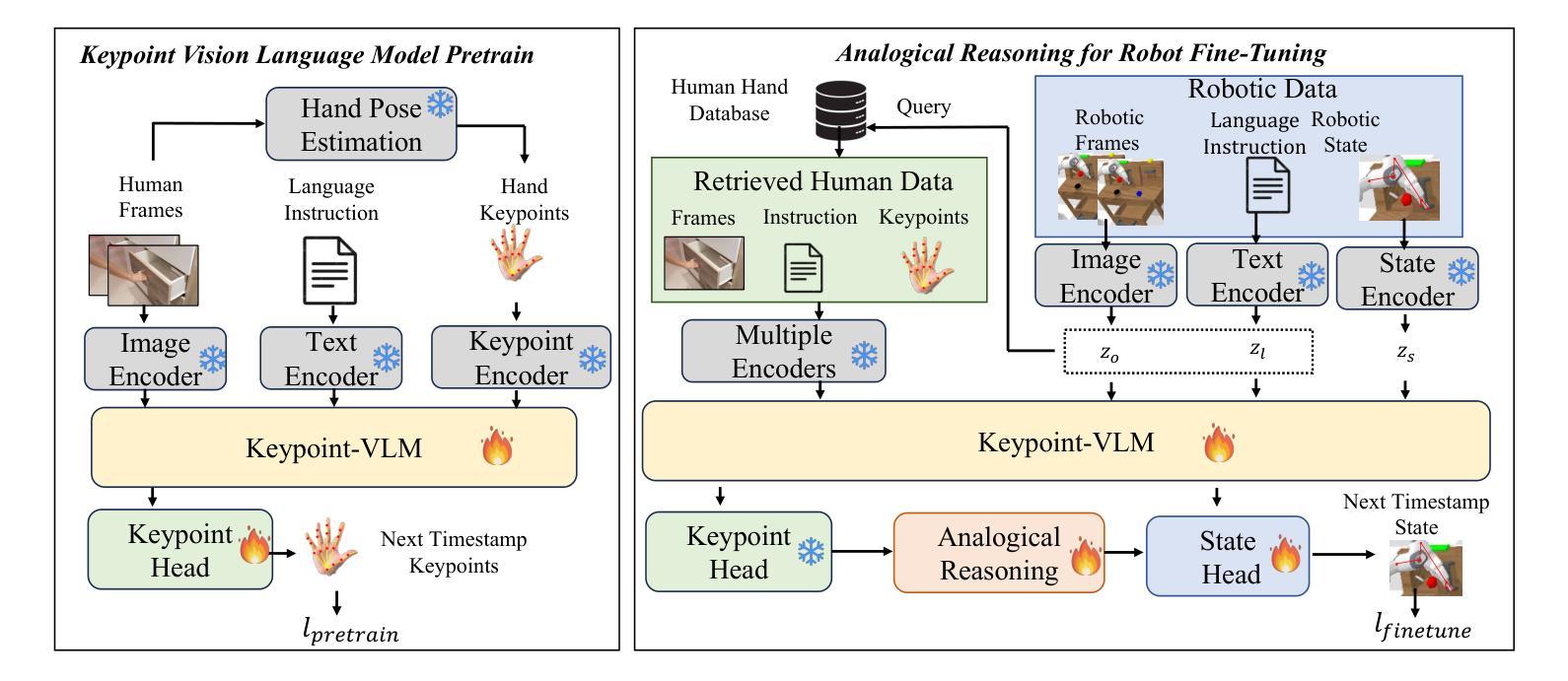
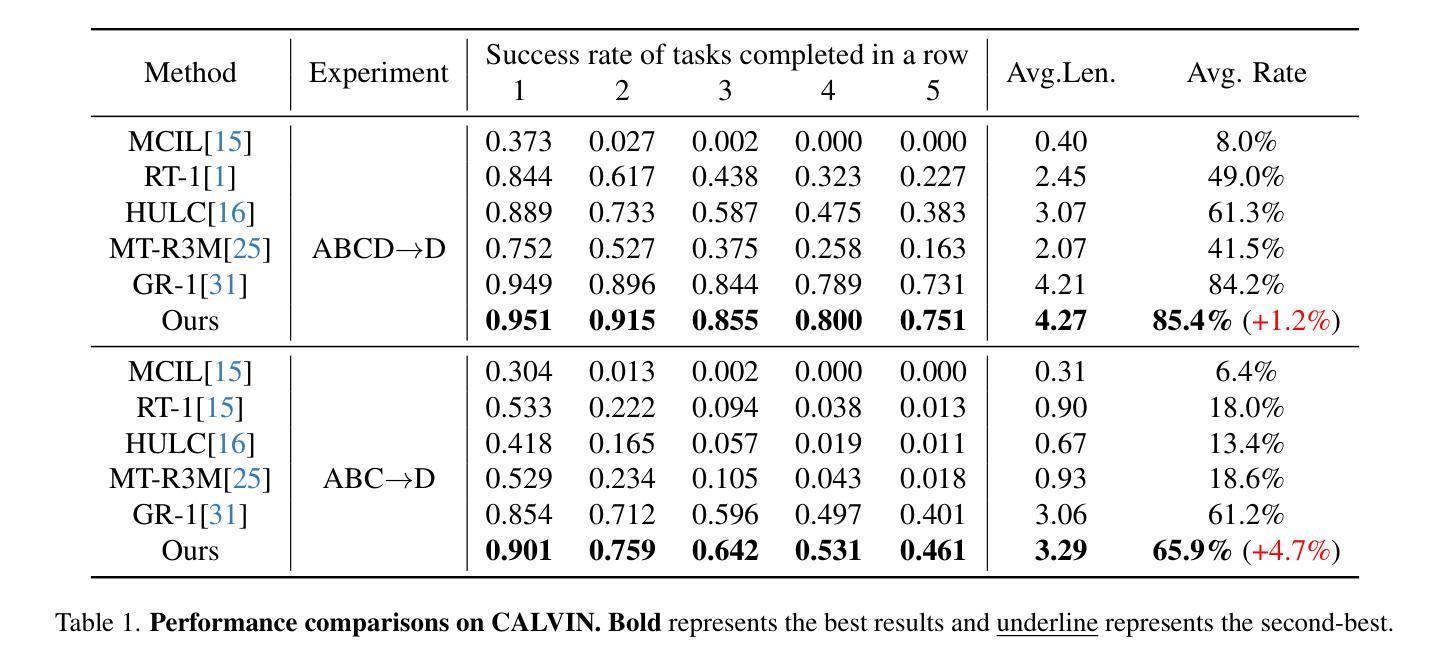
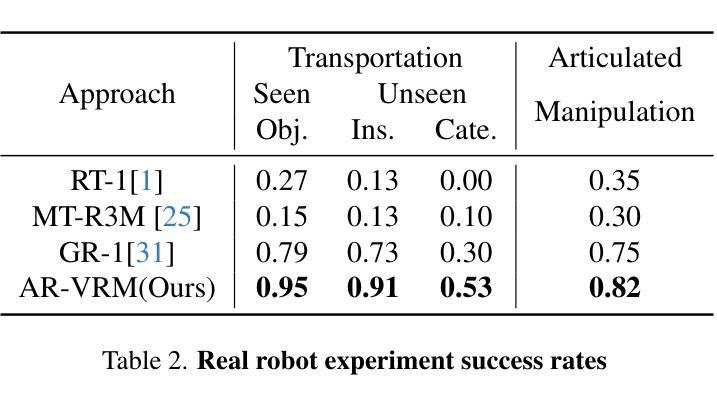
Authors:Dejie Yang, Zijing Zhao, Yang Liu
Visual Robot Manipulation (VRM) aims to enable a robot to follow natural language instructions based on robot states and visual observations, and therefore requires costly multi-modal data. To compensate for the deficiency of robot data, existing approaches have employed vision-language pretraining with large-scale data. However, they either utilize web data that differs from robotic tasks, or train the model in an implicit way (e.g., predicting future frames at the pixel level), thus showing limited generalization ability under insufficient robot data. In this paper, we propose to learn from large-scale human action video datasets in an explicit way (i.e., imitating human actions from hand keypoints), introducing Visual Robot Manipulation with Analogical Reasoning (AR-VRM). To acquire action knowledge explicitly from human action videos, we propose a keypoint Vision-Language Model (VLM) pretraining scheme, enabling the VLM to learn human action knowledge and directly predict human hand keypoints. During fine-tuning on robot data, to facilitate the robotic arm in imitating the action patterns of human motions, we first retrieve human action videos that perform similar manipulation tasks and have similar historical observations , and then learn the Analogical Reasoning (AR) map between human hand keypoints and robot components. Taking advantage of focusing on action keypoints instead of irrelevant visual cues, our method achieves leading performance on the CALVIN benchmark {and real-world experiments}. In few-shot scenarios, our AR-VRM outperforms previous methods by large margins , underscoring the effectiveness of explicitly imitating human actions under data scarcity.
视觉机器人操控(VRM)的目标是使机器人能够根据机器人状态和视觉观察来执行自然语言指令,因此需要昂贵的多模式数据。为了弥补机器人数据的不足,现有方法已经采用了大规模数据的视觉语言预训练。然而,它们要么使用与机器人任务不同的网络数据,要么以隐式方式训练模型(例如,在像素级别预测未来帧),因此在机器人数据不足的情况下,显示出有限的泛化能力。在本文中,我们提出以明确的方式从大规模人类行为视频数据集中进行学习(即通过手关键点模仿人类行为),引入类比推理视觉机器人操控(AR-VRM)。为了从人类行为视频中明确获取行动知识,我们提出了一种关键点视觉语言模型(VLM)预训练方案,使VLM能够学习人类行为知识并直接预测人类手关键点。在机器人数据上进行微调时,为了促进机械臂模仿人类运动的行为模式,我们首先检索执行类似操控任务并具有相似历史观察记录的人类行为视频,然后学习人类手关键点和机器人组件之间的类比推理(AR)映射。通过关注动作关键点而不是无关的视觉线索,我们的方法在CALVIN基准测试{和真实世界实验}中取得了领先的成绩。在少数场景的情况下,我们的AR-VRM大幅超越了以前的方法,突显了在数据稀缺情况下明确模仿人类动作的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
视觉机器人操控(VRM)旨在使机器人能够根据机器人状态与视觉观察来执行自然语言指令,因此需依赖昂贵的多模态数据。为弥补机器人数据的不足,现有方法采用视觉语言预训练结合大规模数据的方式。然而,它们使用与机器人任务不同的网络数据或采用隐式训练方法(如预测未来帧像素级别),在机器人数据不足时表现出有限的泛化能力。本文提出从大规模人类动作视频数据集中显式学习的方法(即根据手部关键点模仿人类动作),引入具有类比推理(AR)的视觉机器人操控(AR-VRM)。我们从人类动作视频中显式获取动作知识,并提出一种关键点视觉语言模型(VLM)的预训练方案,使VLM能够学习人类动作知识并直接预测人手关键点。在机器人数据上进行微调时,为帮助机械臂模仿人类动作模式,我们首先检索执行类似操控任务并具有相似历史观察记录的人类动作视频,然后学习人手关键点与机器人组件之间的类比推理(AR)映射。通过关注动作关键点而非无关的视觉线索,我们的方法在CALVIN基准测试和真实世界实验中取得了领先的表现。在少量场景数据下,我们的AR-VRM较之前的方法有较大优势,突显了在数据稀缺时显式模仿人类动作的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- VRM需要多模态数据来使机器人根据自然语言指令执行操作。
- 现有方法使用网络数据与机器人任务不同或隐式训练模型,导致泛化能力受限。
- 本文提出从大规模人类动作视频数据中显式学习的方法,即AR-VRM。
- 通过关键点VLM预训练方案,模型能够学习人类动作知识并预测手部关键点。
- 在微调阶段,利用类比推理(AR)映射机器人与人类的动作模式。
- 方法专注于动作关键点而非无关视觉线索,在基准测试和真实世界实验中表现领先。
点此查看论文截图

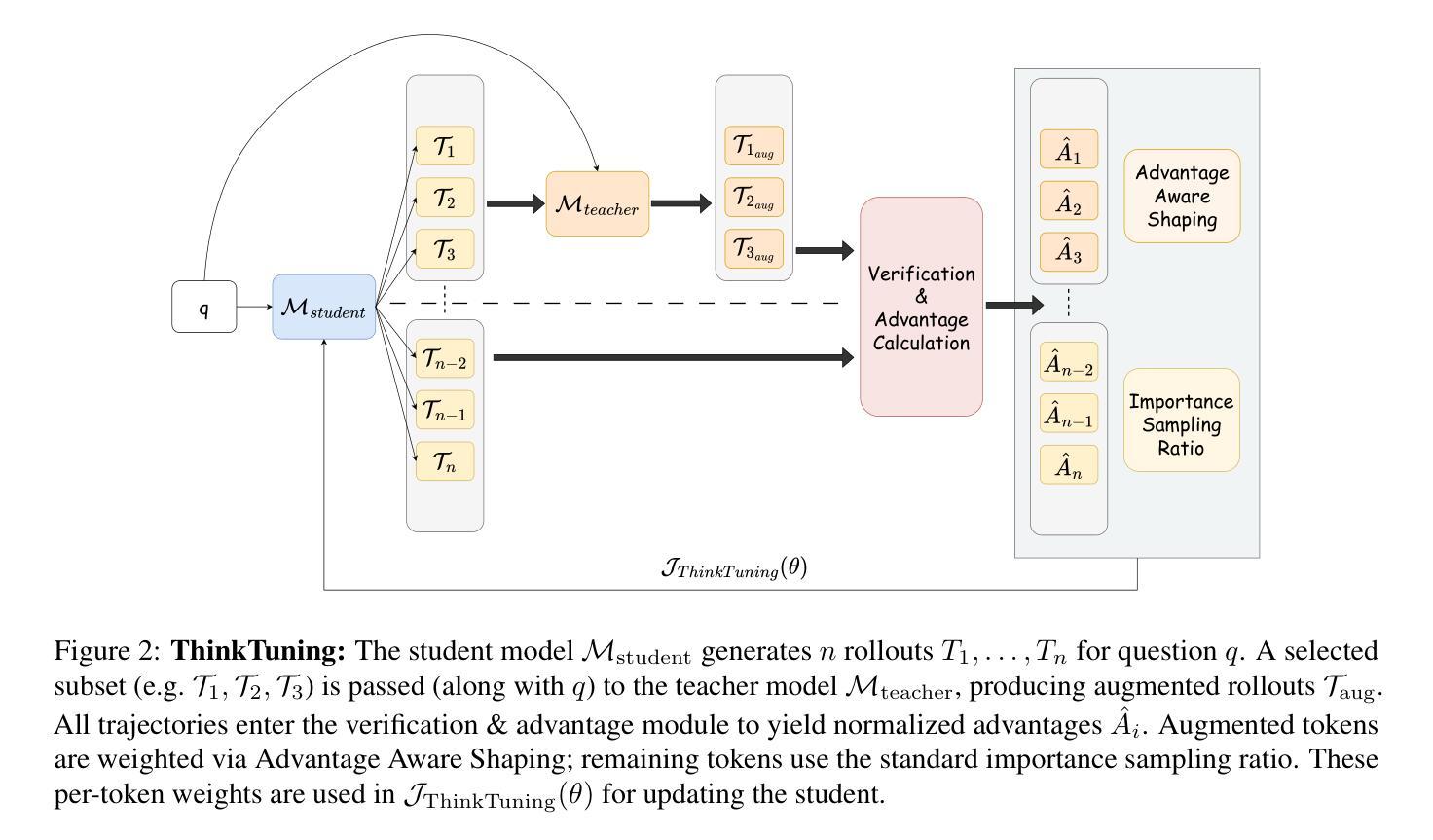
ThinkTuning: Instilling Cognitive Reflections without Distillation
Authors:Aswin RRV, Jacob Dineen, Divij Handa, Md Nayem Uddin, Mihir Parmar, Chitta Baral, Ben Zhou
Recent advances in test-time scaling have led to the emergence of thinking LLMs that exhibit self-reflective behaviors and multi-step reasoning. While RL drives this self-improvement paradigm, a recent study (Gandhi et al., 2025) shows that RL alone does not truly instill these new reasoning abilities - it merely draws out behaviors already present in the base models. This raises a question: How can we train the models that don’t exhibit such thinking behavior to develop it in the first place? To this end, we propose ThinkTuning, a GRPO-based interactive training approach where we augment the rollouts of a student model with the guidance from a teacher model. A simple idea from classroom practice inspires our method: a teacher poses a problem, lets the student try an answer, then gives corrective feedback – enough to point the mind in the right direction and then show the solution. Each piece of feedback reshapes the student’s thoughts, leading them to arrive at the correct solution. Similarly, we find that this type of implicit supervision through feedback from a teacher model of the same size improves the reasoning capabilities of the student model. In particular, on average, our method shows a 3.85% improvement over zero-shot baselines across benchmarks, and on MATH-500, AIME and GPQA-Diamond it shows 2.08%, 2.23% and 3.99% improvements over the vanilla-GRPO baseline. Source code is available at https://github.com/3rdAT/ThinkTuning.
最近测试时间缩放方面的进展催生出了展现自我反思行为和多步推理的思考型大型语言模型(LLMs)。虽然强化学习(RL)推动了这种自我改进的模式,但最近的一项研究(甘地等人,2025)表明,仅依靠RL并不能真正赋予这些新的推理能力——它只是激发出基础模型中已经存在的行为。这就提出了一个问题:如何训练那些原本不具备这种思考行为的模型,让它们首先具备这种能力呢?为此,我们提出了ThinkTuning,这是一种基于GRPO的交互式训练方法,我们借助教师模型的指导来增强学生模型的滚动输出。我们的方法灵感来自于课堂实践的简单想法:教师提出问题,让学生尝试回答,然后给出纠正反馈——足以指出正确的方向并展示解决方案。每一份反馈都会重塑学生的思路,引导他们找到正确的答案。同样,我们发现,通过教师模型的反馈进行这种隐式监督,可以提高学生模型的推理能力。特别是,我们的方法在所有基准测试上的平均表现比零基准线高出3.85%,在MATH-500、AIME和GPQA-Diamond上的表现则分别比基础GRPO高出2.08%、2.23%和3.99%。源代码可在https://github.com/3rdAT/ThinkTuning获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
本文介绍了最新测试时间缩放技术的进步,使得大型语言模型展现出自我反思行为和跨多步骤的推理能力。虽然强化学习驱动了这种自我改进的模式,但研究表明仅靠强化学习并不能真正赋予模型这些新的推理能力,而只是激发模型中已有的能力。为此,本文提出了ThinkTuning方法,这是一种基于GRPO的交互式训练方法,通过教师模型的指导来增强学生模型的rollout。该方法受到课堂实践的启发,通过教师提出问题、学生尝试回答、教师提供纠正反馈的方式,逐步引导学生找到正确答案。类似地,本文发现来自相同规模教师模型的反馈能提高学生的推理能力。实验结果显示,该方法在多个基准测试上平均比零基准高出3.85%,并在MATH-500、AIME和GPQA-Diamond上分别实现了2.08%、2.23%和3.99%的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间缩放技术的最新进展导致大型语言模型展现出自我反思行为和跨多步骤推理能力。
- 强化学习虽在这种自我改进模式中起关键作用,但单独使用并不能真正赋予模型新的推理能力。
- ThinkTuning方法是一种基于GRPO的交互式训练方法,通过教师模型的指导来增强学生模型的性能。
- ThinkTuning方法受到课堂实践的启发,通过教师与学生的互动来提高学生的推理能力。
- 教师模型的反馈能够重塑学生模型的想法,并引导其找到正确的解决方案。
- ThinkTuning方法在多个基准测试上实现了显著的改进,平均高于零基准3.85%。
点此查看论文截图

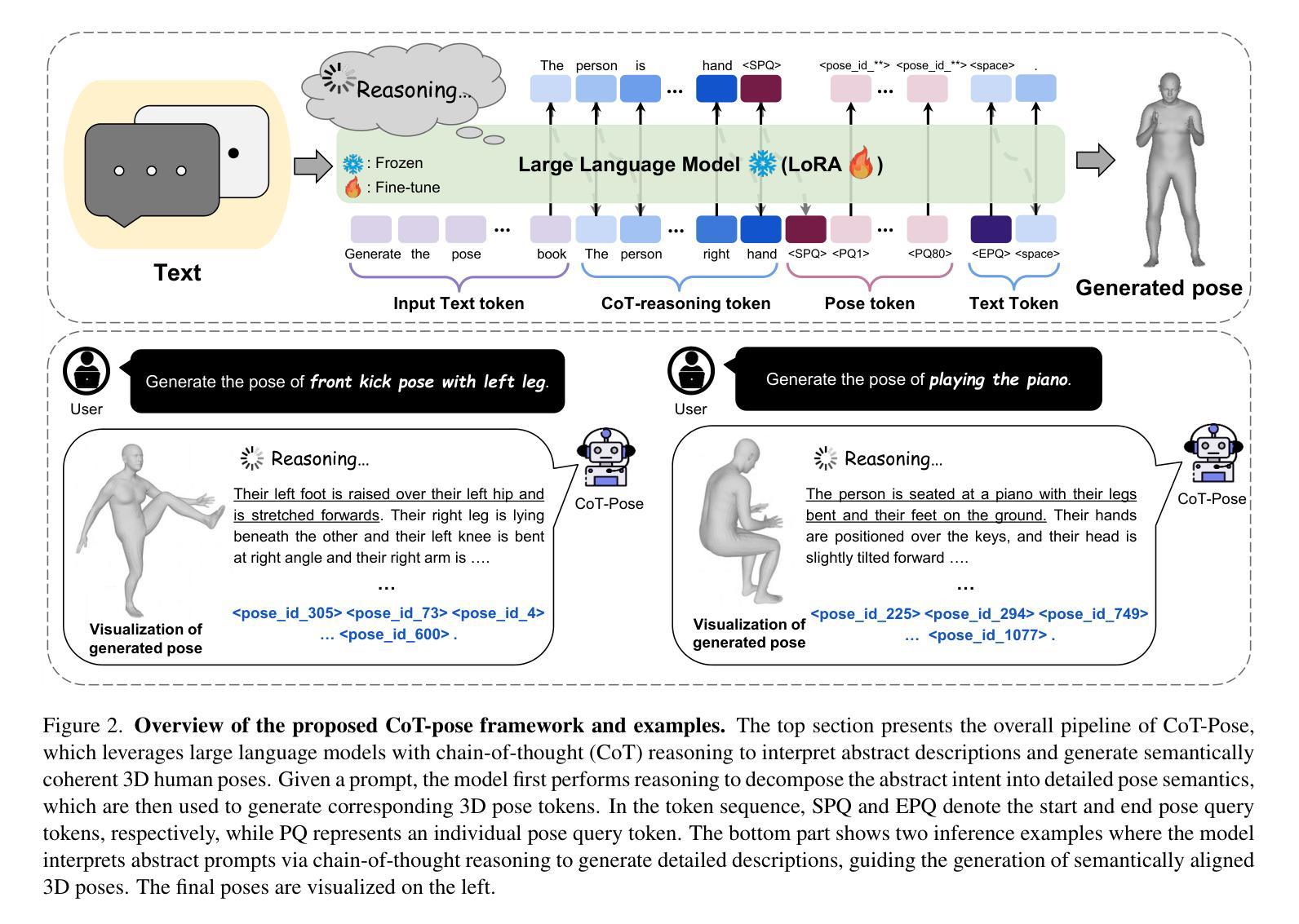
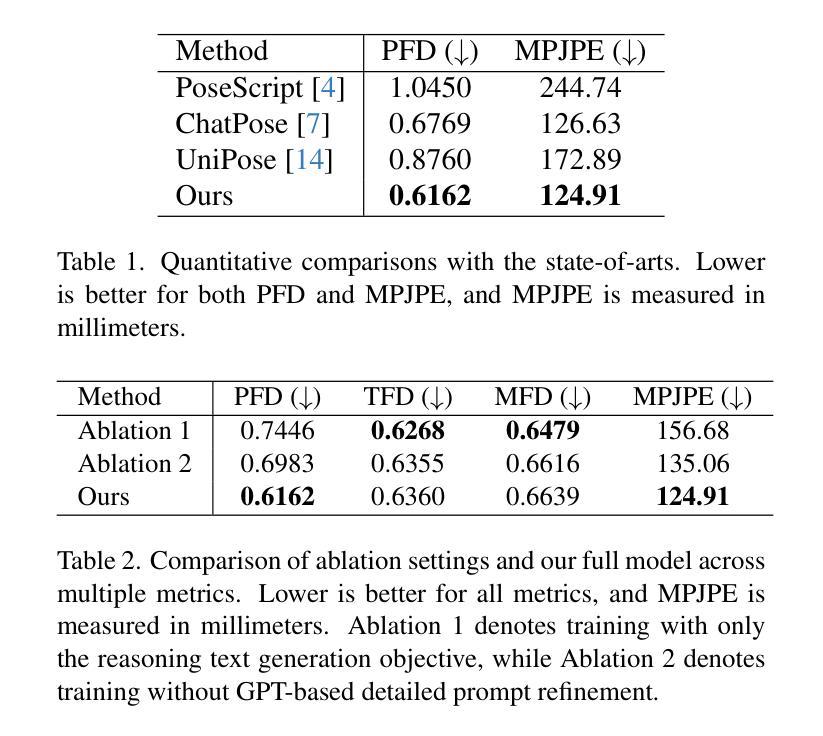
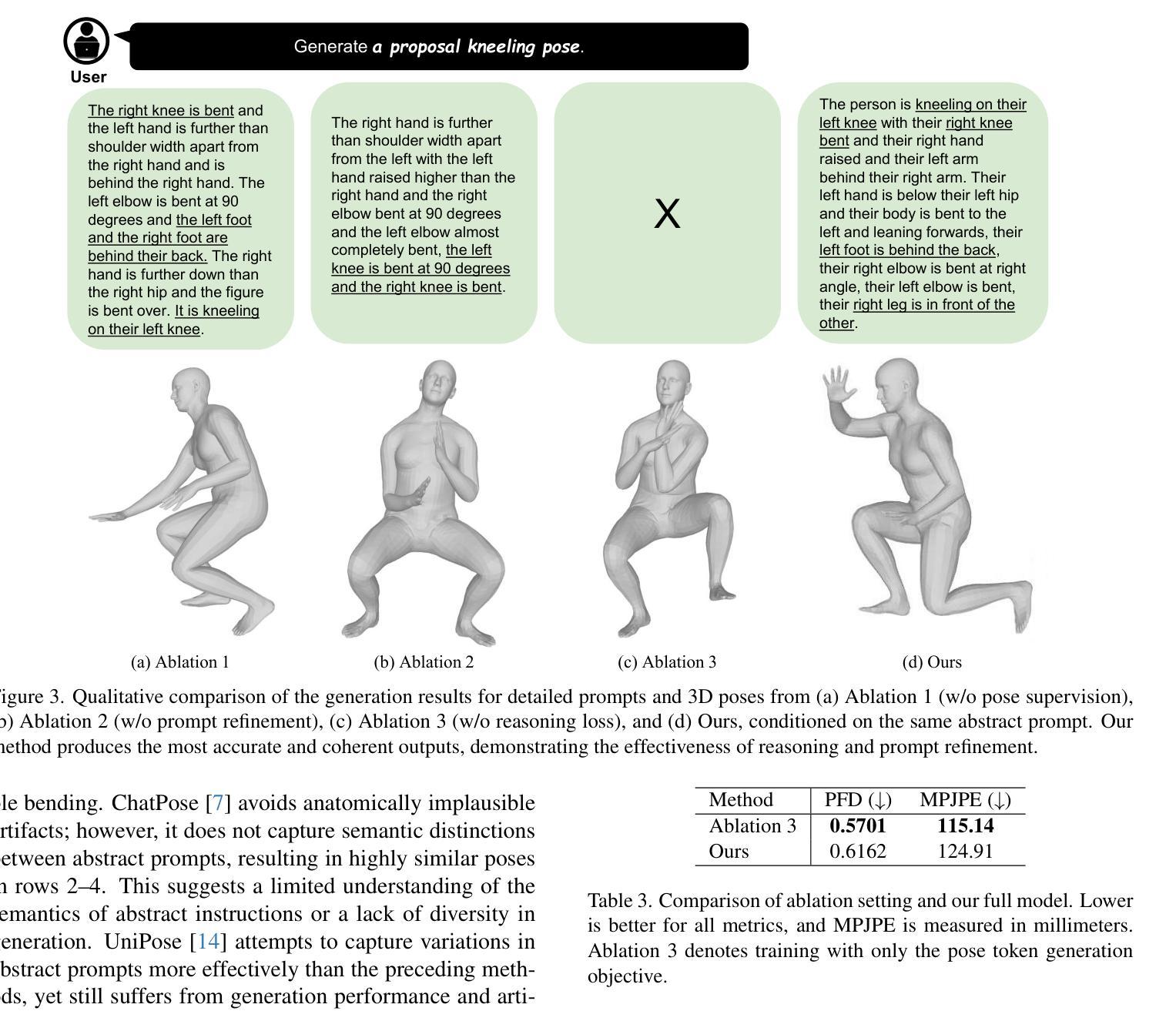
CoT-Pose: Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for 3D Pose Generation from Abstract Prompts
Authors:Junuk Cha, Jihyeon Kim
Recent advances in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) and chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning have led to significant progress in image and text generation tasks. However, the field of 3D human pose generation still faces critical limitations. Most existing text-to-pose models rely heavily on detailed (low-level) prompts that explicitly describe joint configurations. In contrast, humans tend to communicate actions and intentions using abstract (high-level) language. This mismatch results in a practical challenge for deploying pose generation systems in real-world scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel framework that incorporates CoT reasoning into the pose generation process, enabling the interpretation of abstract prompts into accurate 3D human poses. We further propose a data synthesis pipeline that automatically generates triplets of abstract prompts, detailed prompts, and corresponding 3D poses for training process. Experimental results demonstrate that our reasoning-enhanced model, CoT-Pose, can effectively generate plausible and semantically aligned poses from abstract textual inputs. This work highlights the importance of high-level understanding in pose generation and opens new directions for reasoning-enhanced approach for human pose generation.
近年来,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和思维链(CoT)推理的进展在图像和文本生成任务方面取得了显著进展。然而,在3D人体姿态生成领域,仍然存在关键性局限。大多数现有的文本到姿态模型严重依赖于详细描述关节配置的低位提示。相比之下,人类倾向于使用抽象(高级)语言来交流动作和意图。这种不匹配为在实际场景中部署姿态生成系统带来了实际挑战。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一个将思维链推理融入姿态生成过程的新框架,该框架能够将抽象提示解释为准确可靠的3D人体姿态。我们还提出了一个数据合成管道,该管道能够自动生成抽象提示、详细提示和相应的3D姿态的三元组,用于训练过程。实验结果表明,我们增强的推理模型CoT-Pose可以有效地从抽象的文本输入中生成合理且语义对齐的姿态。这项工作强调了高级理解在姿态生成中的重要性,并为增强推理方法在人类姿态生成领域开辟了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCVW’25
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)和思维链(CoT)推理在图像和文本生成任务中的最新进展。然而,在3D人体姿态生成领域仍存在关键限制。大多数现有的文本到姿态模型依赖于详细的低级别提示来描述关节配置。与之相反,人类倾向于使用抽象的高级语言来表达动作和意图。为了弥补这一差距,本文提出了一种结合CoT推理的新型框架,使抽象提示能够转化为准确的3D人体姿态。此外,还提出了一种数据合成管道,可自动生成抽象提示、详细提示和相应的3D姿态用于训练过程。实验结果表明,增强型推理模型CoT-Pose可以有效地从抽象文本输入中生成合理且语义对齐的姿态。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型和思维链推理在图像和文本生成任务中有显著进展。
- 3D人体姿态生成领域仍面临依赖低级别提示的局限性。
- 人类使用高级语言来表达动作和意图,而现有模型通常依赖低级别提示。
- 提出了一种结合思维链推理的新型框架,用于从抽象提示生成准确的3D人体姿态。
- 引入了一种数据合成管道,自动生成用于训练的数据。
- 实验证明,增强型推理模型CoT-Pose能从抽象文本输入中生成合理且语义对齐的姿态。
点此查看论文截图