⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-13 更新
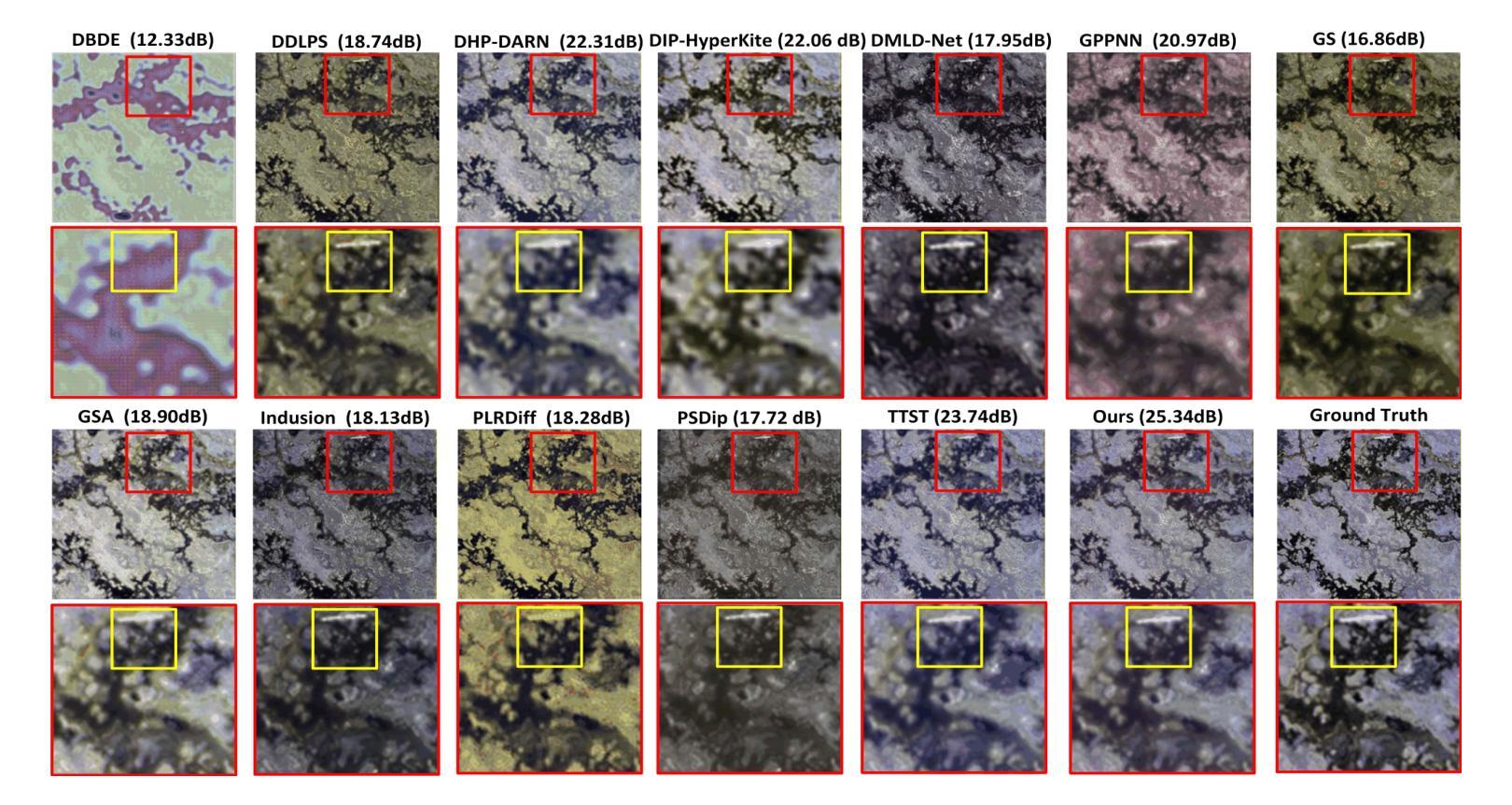
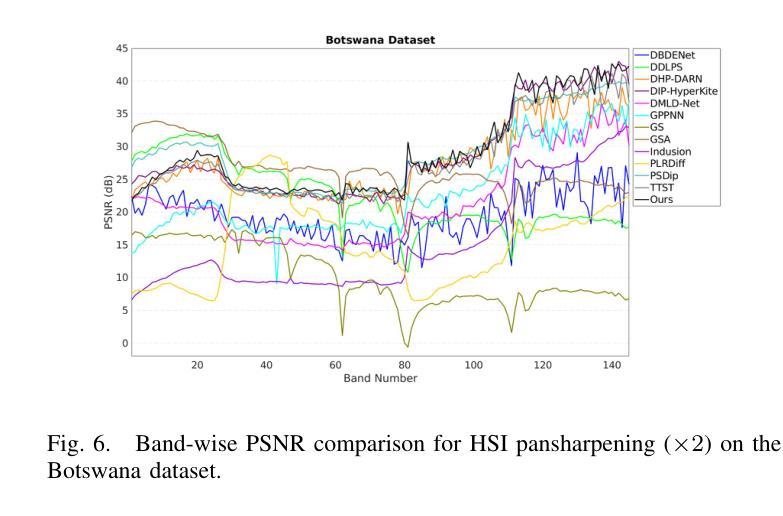
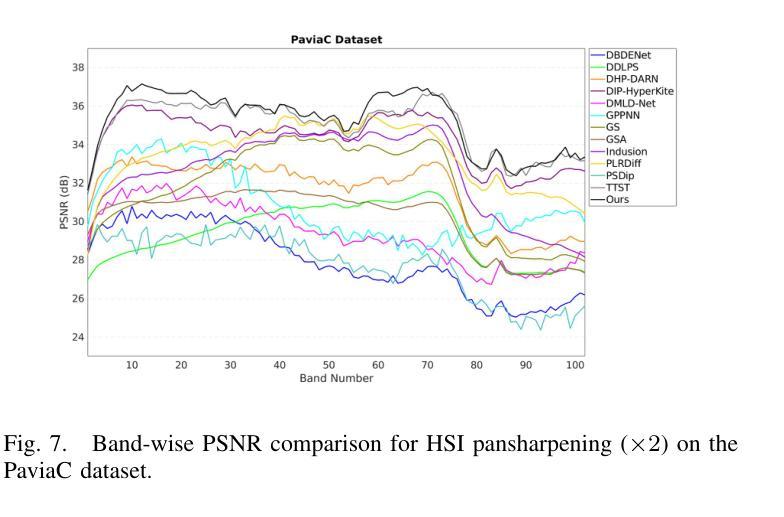
THAT: Token-wise High-frequency Augmentation Transformer for Hyperspectral Pansharpening
Authors:Hongkun Jin, Hongcheng Jiang, Zejun Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Jia Fu, Tingfeng Li, Kai Luo
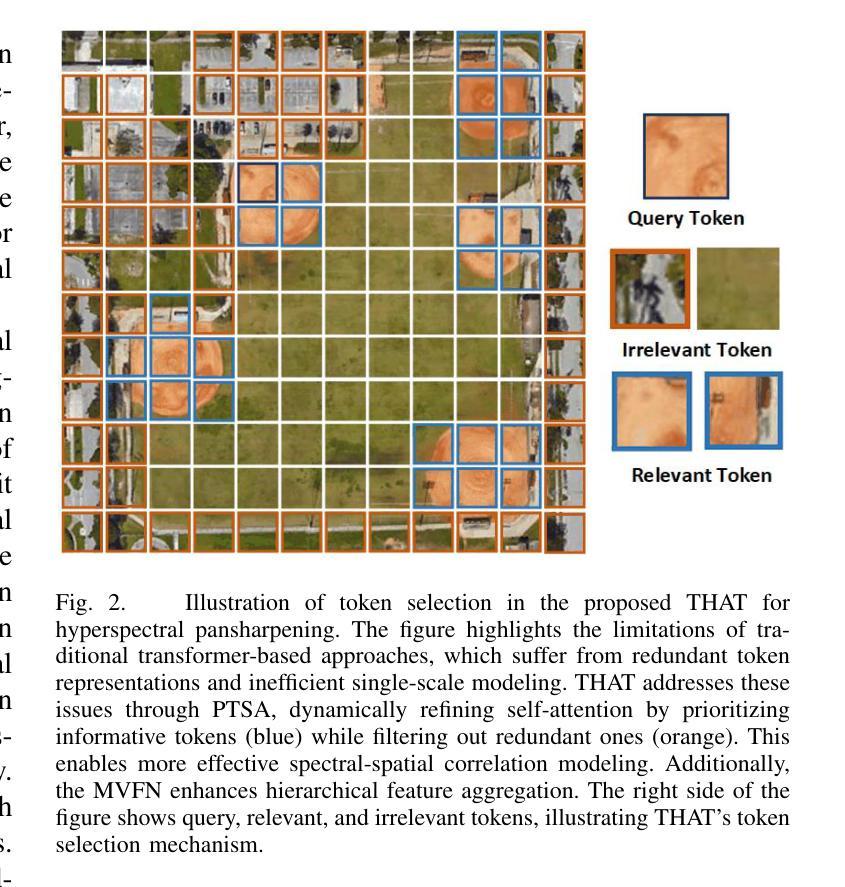
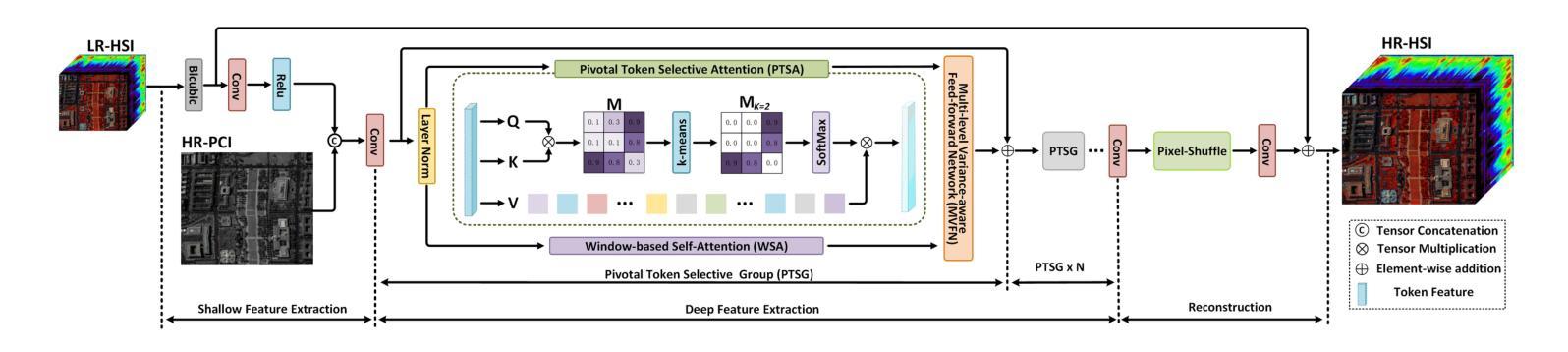
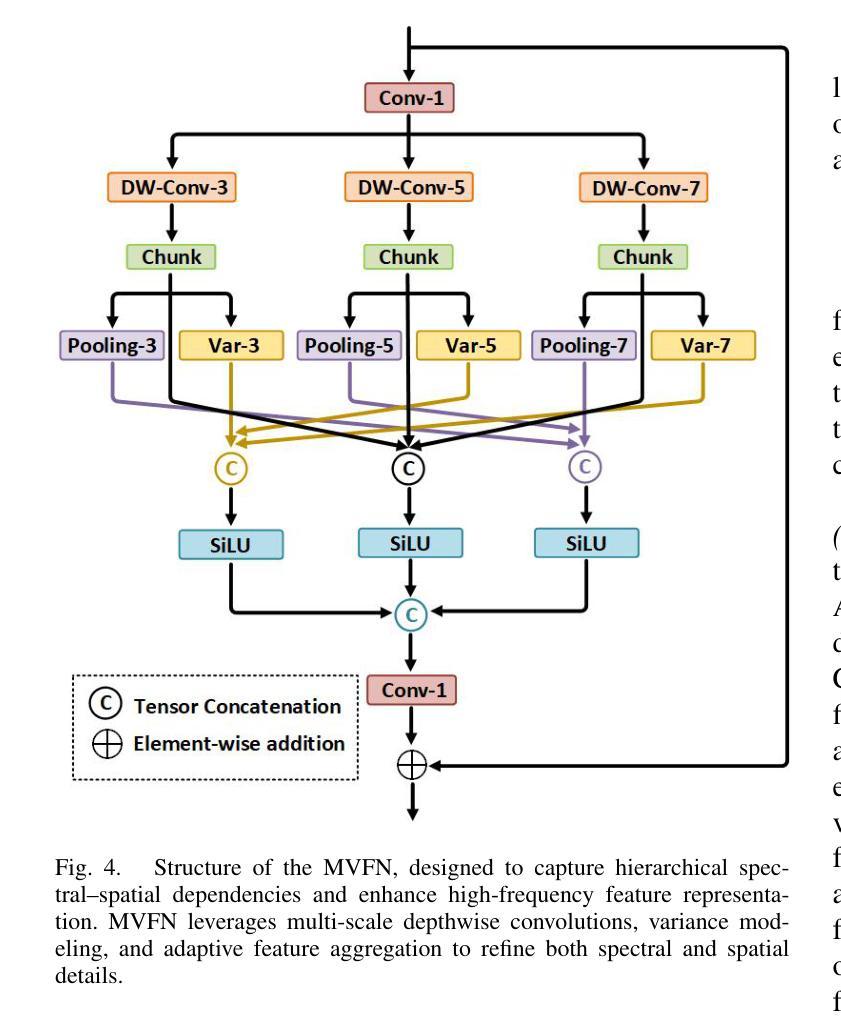
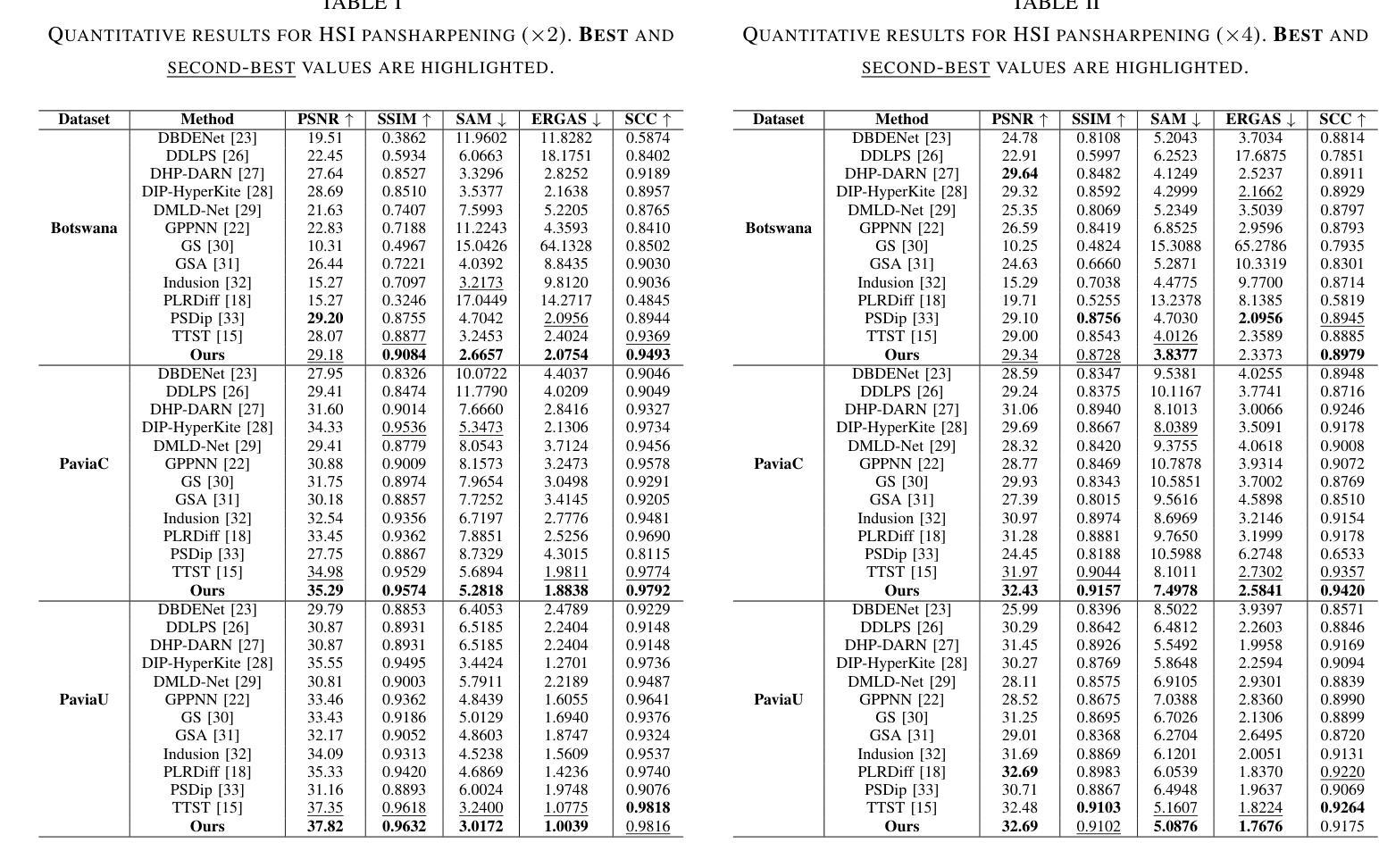
Transformer-based methods have demonstrated strong potential in hyperspectral pansharpening by modeling long-range dependencies. However, their effectiveness is often limited by redundant token representations and a lack of multi-scale feature modeling. Hyperspectral images exhibit intrinsic spectral priors (e.g., abundance sparsity) and spatial priors (e.g., non-local similarity), which are critical for accurate reconstruction. From a spectral-spatial perspective, Vision Transformers (ViTs) face two major limitations: they struggle to preserve high-frequency components–such as material edges and texture transitions–and suffer from attention dispersion across redundant tokens. These issues stem from the global self-attention mechanism, which tends to dilute high-frequency signals and overlook localized details. To address these challenges, we propose the Token-wise High-frequency Augmentation Transformer (THAT), a novel framework designed to enhance hyperspectral pansharpening through improved high-frequency feature representation and token selection. Specifically, THAT introduces: (1) Pivotal Token Selective Attention (PTSA) to prioritize informative tokens and suppress redundancy; (2) a Multi-level Variance-aware Feed-forward Network (MVFN) to enhance high-frequency detail learning. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that THAT achieves state-of-the-art performance with improved reconstruction quality and efficiency. The source code is available at https://github.com/kailuo93/THAT.
基于Transformer的方法通过建模长距离依赖关系在超光谱锐化中显示出强大的潜力。然而,它们的有效性通常受到冗余令牌表示和多尺度特征建模缺乏的限制。超光谱图像表现出内在的谱先验(例如,丰度稀疏性)和空间先验(例如,非局部相似性),这对于准确重建至关重要。从谱-空间的角度来看,视觉Transformer(ViTs)面临两大局限:它们难以保留高频成分(如材料边缘和纹理过渡),并受到冗余令牌分散注意力的影响。这些问题源于全局自注意力机制,该机制往往稀释高频信号并忽略局部细节。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Token High频率增强Transformer(THAT),这是一个旨在通过改进的高频特征表示和令牌选择来提高超光谱锐化的新型框架。具体来说,THAT引入了:(1)关键令牌选择性注意力(PTSA)以优先处理信息丰富的令牌并抑制冗余;(2)多级方差感知前馈网络(MVFN)以增强高频细节学习。在标准基准测试上的实验表明,THAT实现了最先进的性能,提高了重建质量和效率。源代码可在https://github.com/kailuo93/THAT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to 2025 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC)
Summary
基于Transformer的方法在光谱高光谱锐化方面具有强大潜力,通过建模长距离依赖关系展现出了良好效果。然而,它们常常受限于冗余的符号表示和缺乏多尺度特征建模。高光谱图像具有固有的光谱先验(如丰度稀疏性)和空间先验(如非局部相似性),这对准确重建至关重要。针对光谱-空间视角,Vision Transformers(ViTs)面临两大局限:难以保留高频分量(如材料边缘和纹理过渡),以及受到冗余符号的注意力分散影响。为解决这些问题,我们提出了Token-wise High-frequency Augmentation Transformer(THAT)这一新型框架,通过改进高频特征表示和符号选择来提升高光谱锐化效果。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer方法在光谱高光谱锐化中具有潜力,但需解决冗余符号表示和多尺度特征建模的限制。
- 高光谱图像具有固有的光谱和空间先验,对准确重建至关重要。
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)在保留高频分量和处理冗余符号方面存在局限。
- 为解决这些问题,提出了THAT框架,包含PTSA和MVFN两大创新点。
- PTSA能优先处理信息丰富的符号并抑制冗余信息。
- MVFN增强了高频细节学习。
点此查看论文截图

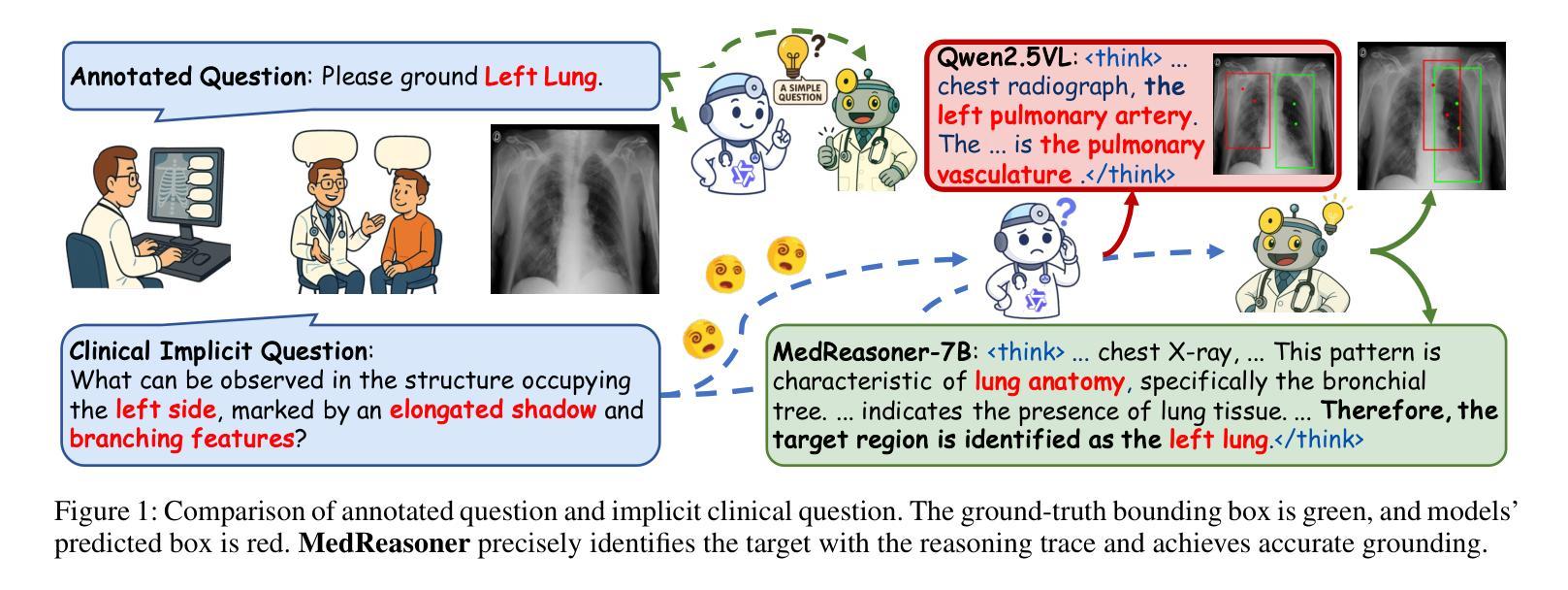
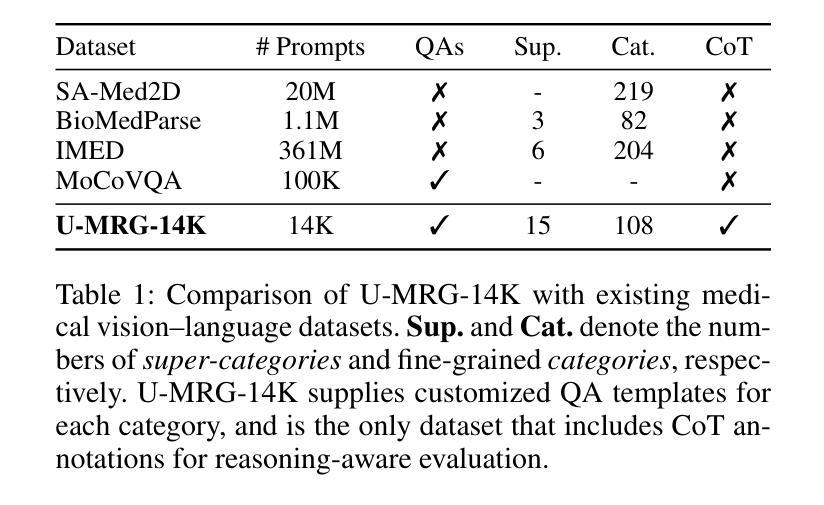
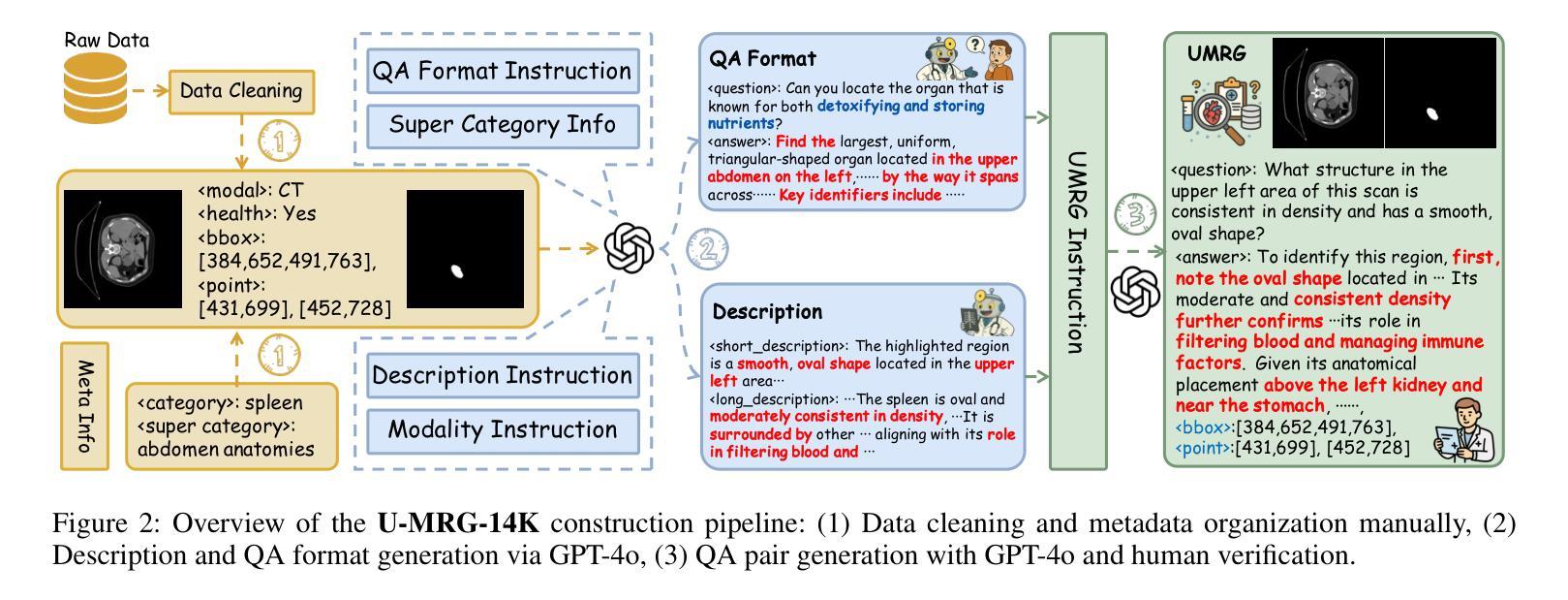
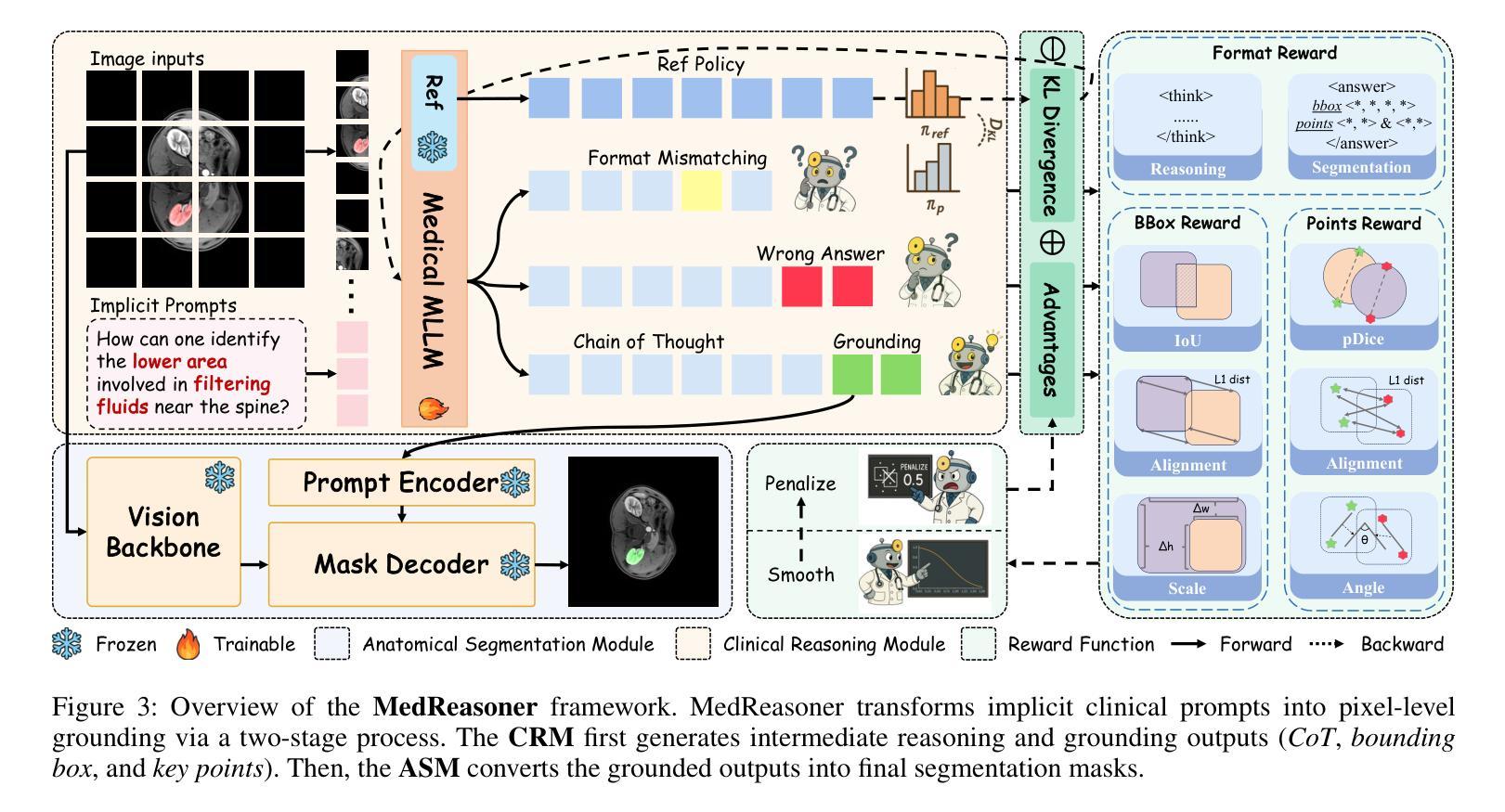
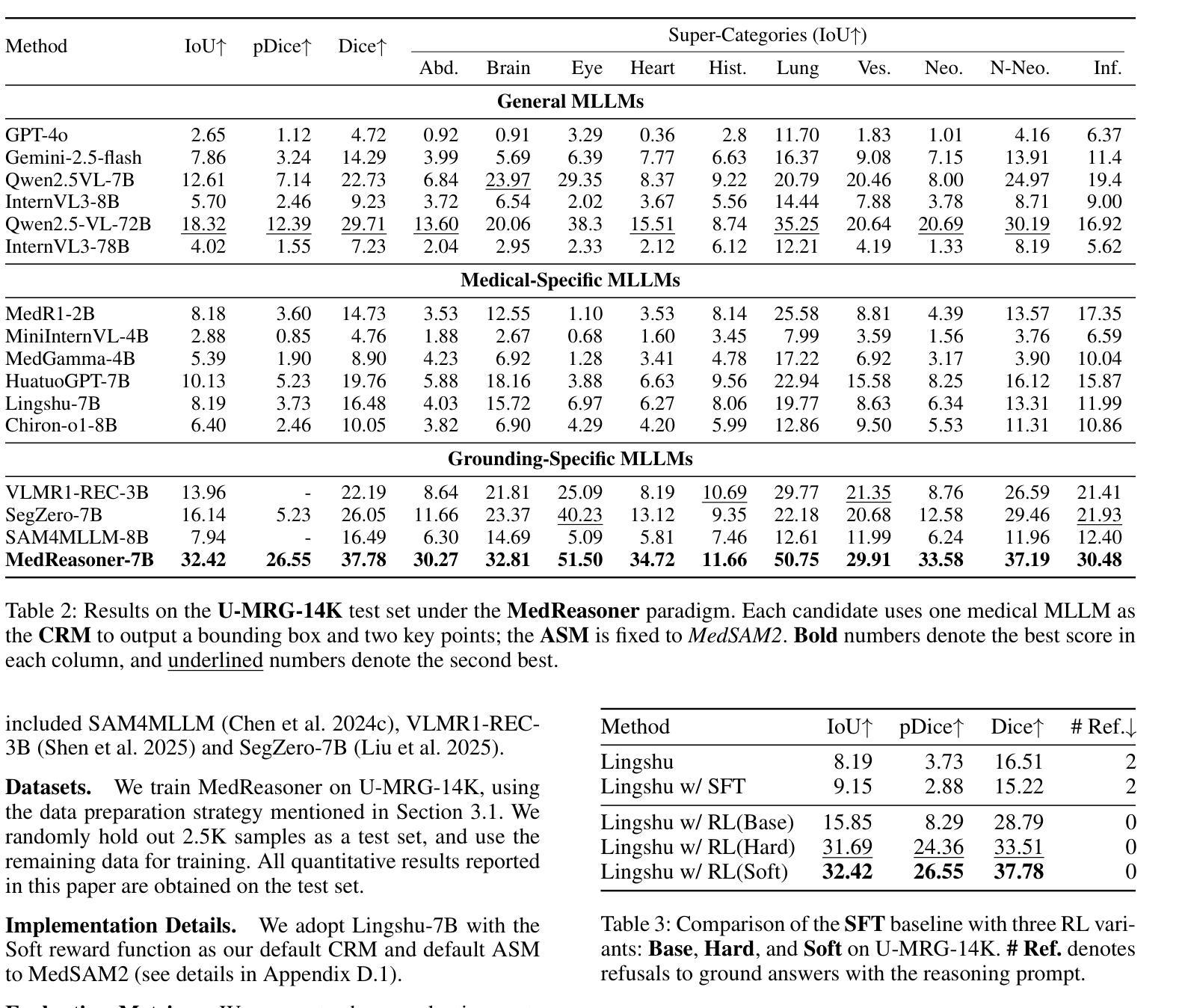
MedReasoner: Reinforcement Learning Drives Reasoning Grounding from Clinical Thought to Pixel-Level Precision
Authors:Zhonghao Yan, Muxi Diao, Yuxuan Yang, Jiayuan Xu, Kaizhou Zhang, Ruoyan Jing, Lele Yang, Yanxi Liu, Kongming Liang, Zhanyu Ma
Accurately grounding regions of interest (ROIs) is critical for diagnosis and treatment planning in medical imaging. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) combine visual perception with natural language, current medical-grounding pipelines still rely on supervised fine-tuning with explicit spatial hints, making them ill-equipped to handle the implicit queries common in clinical practice. This work makes three core contributions. We first define Unified Medical Reasoning Grounding (UMRG), a novel vision-language task that demands clinical reasoning and pixel-level grounding. Second, we release U-MRG-14K, a dataset of 14K samples featuring pixel-level masks alongside implicit clinical queries and reasoning traces, spanning 10 modalities, 15 super-categories, and 108 specific categories. Finally, we introduce MedReasoner, a modular framework that distinctly separates reasoning from segmentation: an MLLM reasoner is optimized with reinforcement learning, while a frozen segmentation expert converts spatial prompts into masks, with alignment achieved through format and accuracy rewards. MedReasoner achieves state-of-the-art performance on U-MRG-14K and demonstrates strong generalization to unseen clinical queries, underscoring the significant promise of reinforcement learning for interpretable medical grounding.
在医学成像中,准确地对感兴趣区域(ROI)进行定位对于诊断和治疗计划的制定至关重要。虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了视觉感知与自然语言,但当前的医学定位流程仍然依赖于具有明确空间提示的监督微调,这使得它们难以应对临床实践中的隐式查询。本文做出了三项核心贡献。首先,我们定义了统一医学推理定位(UMRG),这是一种新的视觉语言任务,需要临床推理和像素级定位。其次,我们发布了U-MRG-14K数据集,包含14K个样本,每个样本都有像素级掩膜、隐式临床查询和推理轨迹,涵盖10种模态、15种超级类别和108种特定类别。最后,我们推出了MedReasoner,这是一个模块化框架,将推理与分割区分开来:MLLM推理器通过强化学习进行优化,而冻结的分割专家将空间提示转换为掩膜,通过格式和精度奖励实现对齐。MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K上达到了最先进的性能,并对未见过的临床查询表现出了强大的泛化能力,这突显了强化学习在可解释的医学定位中的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages
Summary
本文提出了统一医学推理定位(UMRG)这一新型视觉语言任务,并发布了U-MRG-14K数据集和MedReasoner框架。UMRG要求临床推理和像素级定位。MedReasoner通过强化学习优化MLLM推理器,将空间提示转化为掩膜,实现格式和精度奖励对齐。该方法在U-MRG-14K上表现优异,并在未见过的临床查询上表现出良好的泛化能力,显示了强化学习在医学定位中的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了统一医学推理定位(UMRG)任务,结合了临床推理和像素级定位。
- 发布了U-MRG-14K数据集,包含14K样本,涵盖10种模态、15个超类别和108个具体类别的像素级掩膜和隐性临床查询及推理轨迹。
- 介绍了MedReasoner框架,将推理和分割任务分离,优化MLLM推理器通过强化学习。
- MedReasoner使用冻结的分割专家将空间提示转化为掩膜。
- MedReasoner在U-MRG-14K上表现优异。
- 该方法展示了对未见临床查询的强大泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

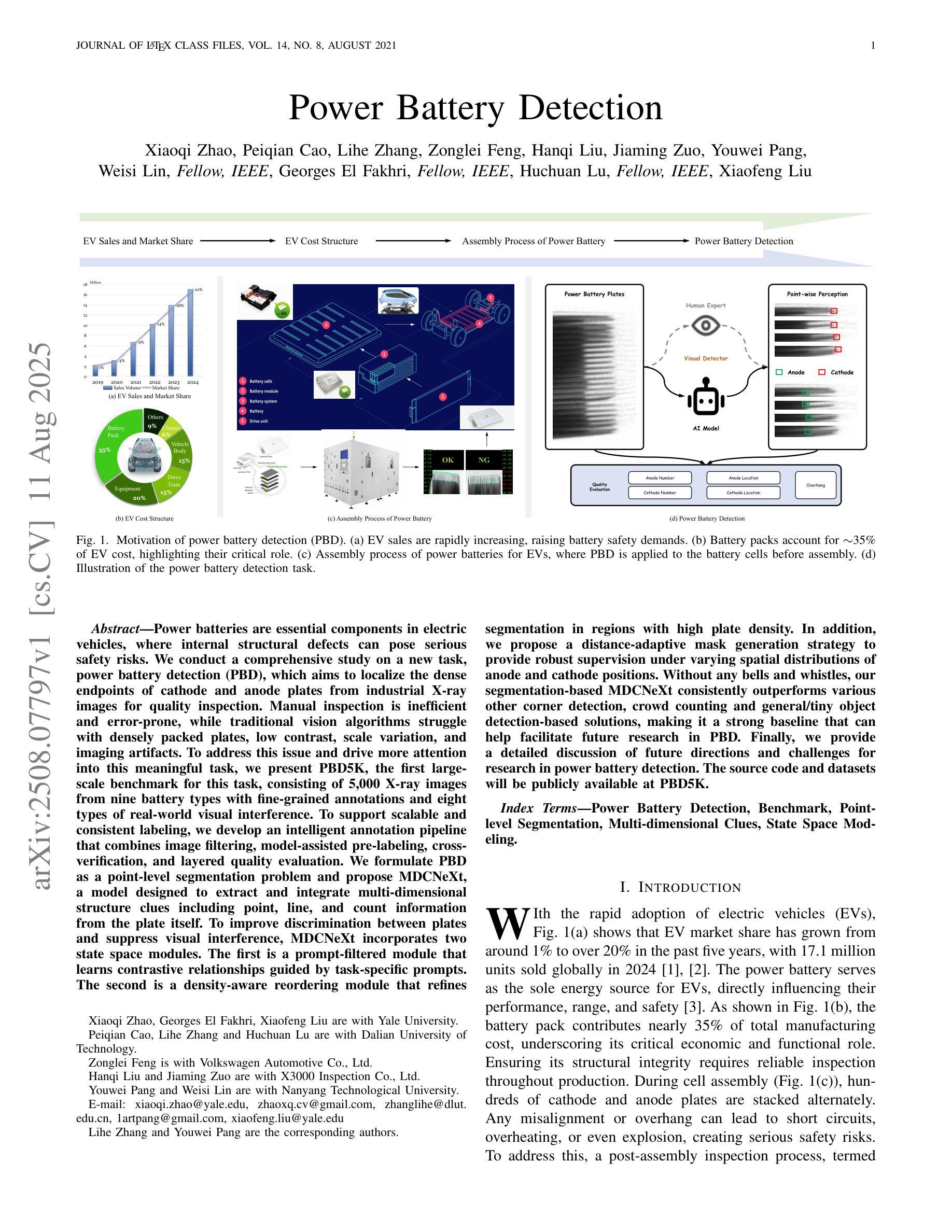
Power Battery Detection
Authors:Xiaoqi Zhao, Peiqian Cao, Lihe Zhang, Zonglei Feng, Hanqi Liu, Jiaming Zuo, Youwei Pang, Weisi Lin, Georges El Fakhri, Huchuan Lu, Xiaofeng Liu
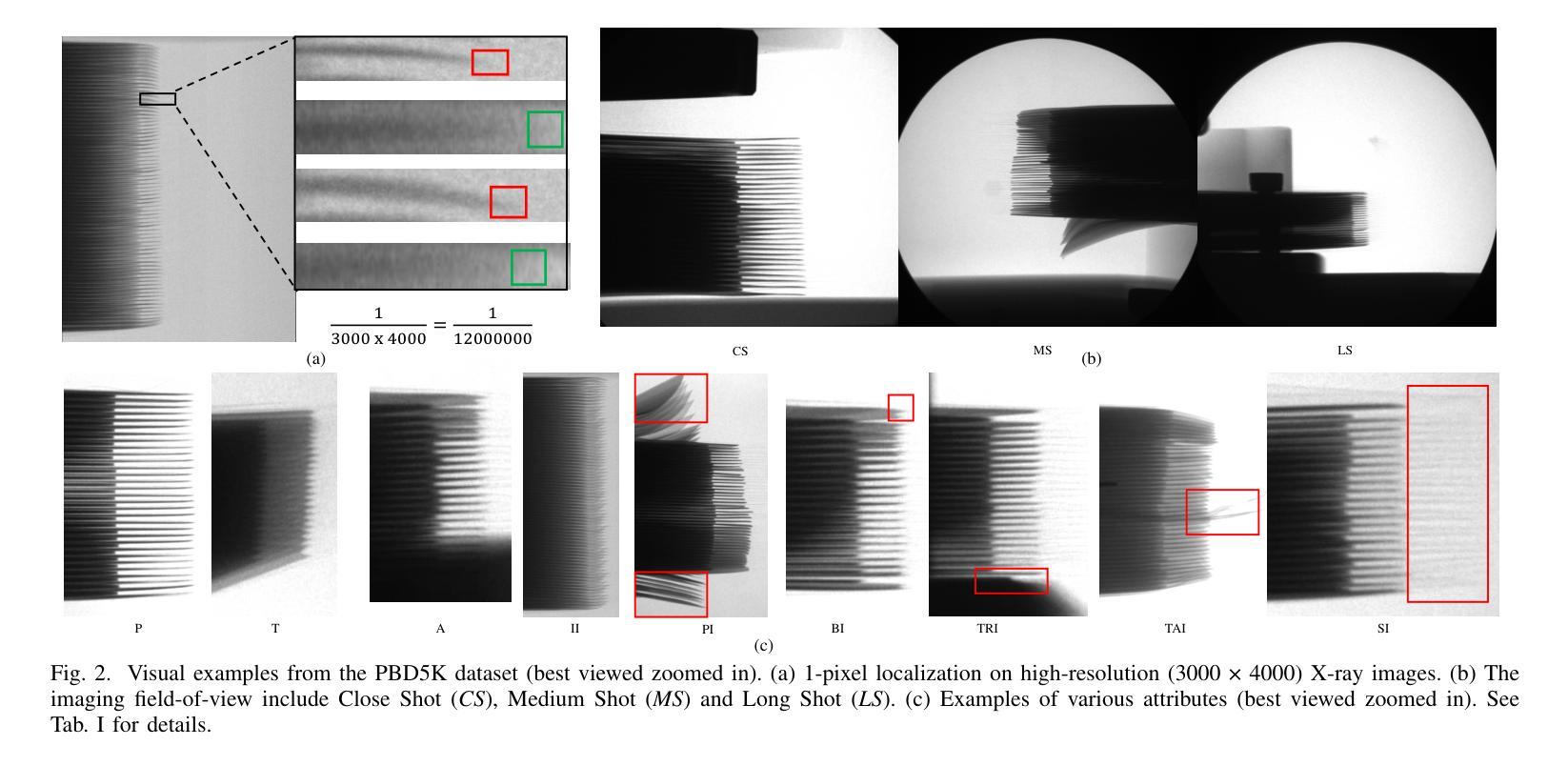
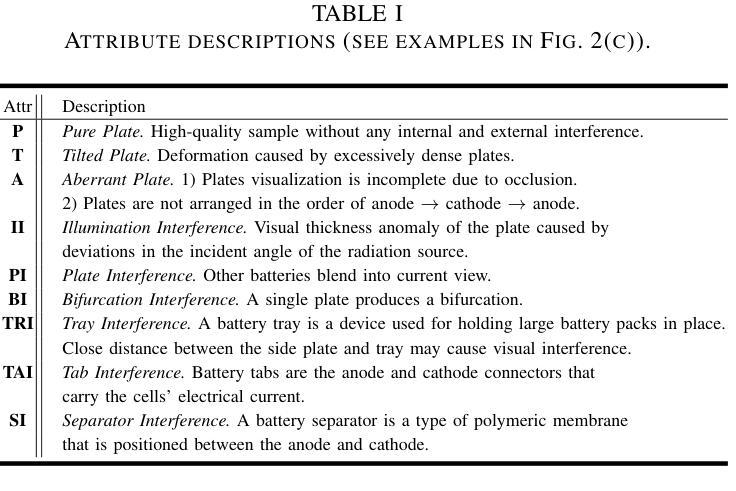
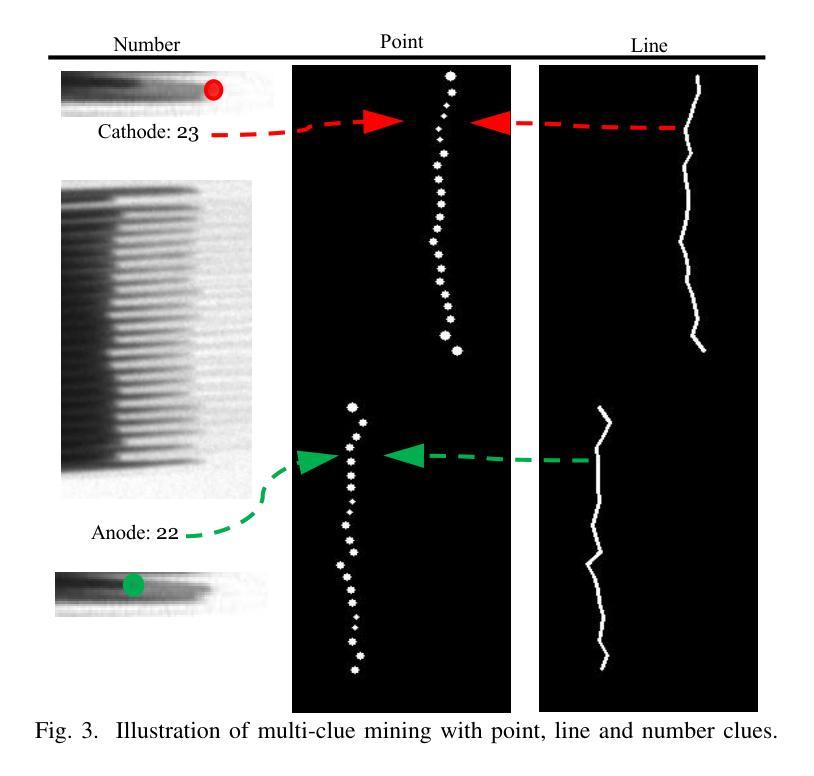
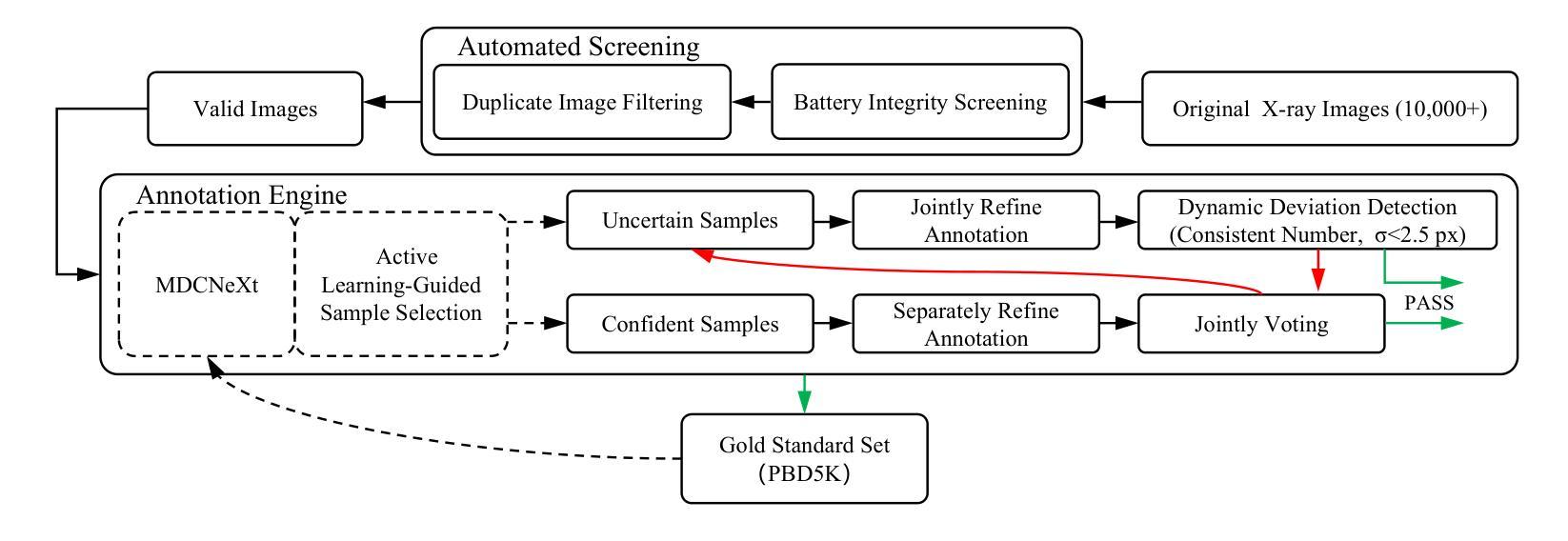
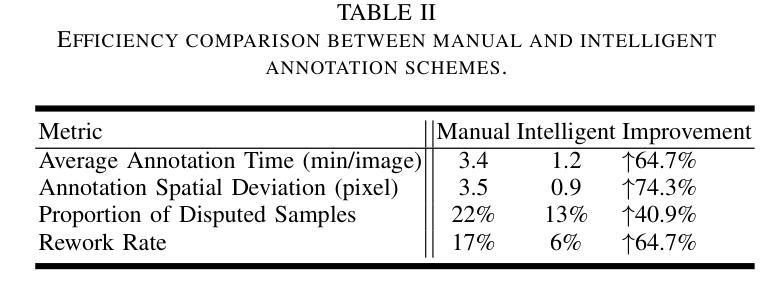
Power batteries are essential components in electric vehicles, where internal structural defects can pose serious safety risks. We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task, power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense endpoints of cathode and anode plates from industrial X-ray images for quality inspection. Manual inspection is inefficient and error-prone, while traditional vision algorithms struggle with densely packed plates, low contrast, scale variation, and imaging artifacts. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we present PBD5K, the first large-scale benchmark for this task, consisting of 5,000 X-ray images from nine battery types with fine-grained annotations and eight types of real-world visual interference. To support scalable and consistent labeling, we develop an intelligent annotation pipeline that combines image filtering, model-assisted pre-labeling, cross-verification, and layered quality evaluation. We formulate PBD as a point-level segmentation problem and propose MDCNeXt, a model designed to extract and integrate multi-dimensional structure clues including point, line, and count information from the plate itself. To improve discrimination between plates and suppress visual interference, MDCNeXt incorporates two state space modules. The first is a prompt-filtered module that learns contrastive relationships guided by task-specific prompts. The second is a density-aware reordering module that refines segmentation in regions with high plate density. In addition, we propose a distance-adaptive mask generation strategy to provide robust supervision under varying spatial distributions of anode and cathode positions. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD}{PBD5K}.
动力电池是电动汽车中的重要组成部分,其内部结构性缺陷可能带来严重的安全风险。我们对一项新的任务——动力电池检测(PBD)进行了深入研究,其目标是从工业X射线图像中定位阴极和阳极板的密集端点,以进行质量检测。人工检测效率低下且易出错,而传统视觉算法在密集排列的板材、低对比度、尺度变化和图像伪影方面面临挑战。为了解决这个问题并吸引更多注意力关注这项有意义的任务,我们推出了PBD5K,这是该任务的首个大规模基准测试,包含来自九种电池类型的5000张X射线图像,具有细粒度注释和八种现实世界的视觉干扰类型。为了支持可扩展和一致的标注,我们开发了一个智能标注管道,结合了图像过滤、模型辅助预标注、交叉验证和分层质量评估。我们将PBD制定为点级分割问题,并提出MDCNeXt模型,该模型旨在提取和整合包括点、线和计数信息在内的多维结构线索。为了提高板之间的辨别能力并抑制视觉干扰,MDCNeXt融入了两种状态空间模块。第一个是提示过滤模块,它学习在任务特定提示指导下对比关系。第二个是密度感知重新排序模块,它能在高板密度区域优化分割。此外,我们提出了一种距离自适应掩膜生成策略,以在阳极和阴极位置空间分布变化的情况下提供稳健的监督。源代码和数据集将在https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under submission to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (T-PAMI)
Summary
本文研究了电动车辆中重要组件动力电池的检测任务,提出了一种新的大规模基准数据集PBD5K,旨在从工业X射线图像中定位阴极和阳极板的密集端点以进行质量检测。文章还介绍了智能标注管道和一个名为MDCNeXt的模型,用于解决手动检测效率低下、传统视觉算法处理密集型电池板等问题。MDCNeXt可以提取并整合点、线和计数等多维度结构线索以提高精度并减少干扰。相关数据与源码将公开在链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了动力电池检测(PBD)的重要性及其所面临的挑战,如内部缺陷检测的安全风险。
- 提出大规模数据集PBD5K,包含多种电池类型的X射线图像及精细标注和真实世界视觉干扰类型。
- 为支持可扩展和一致的标注,开发了智能标注管道,包括图像过滤、模型辅助预标注、交叉验证和分层质量评估等功能。
- 将PBD任务定义为点级分割问题,并提出MDCNeXt模型来解决密集型电池板检测问题,整合多维度结构线索并引入两个状态空间模块来增强鉴别力和抑制视觉干扰。
点此查看论文截图
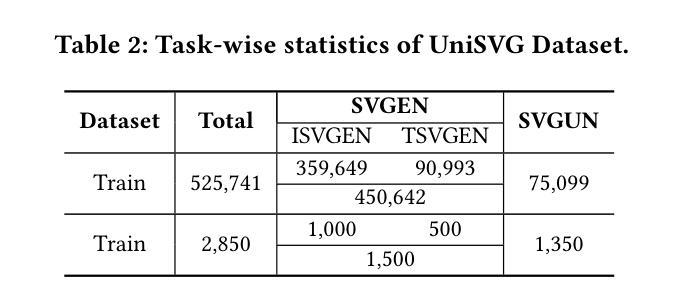
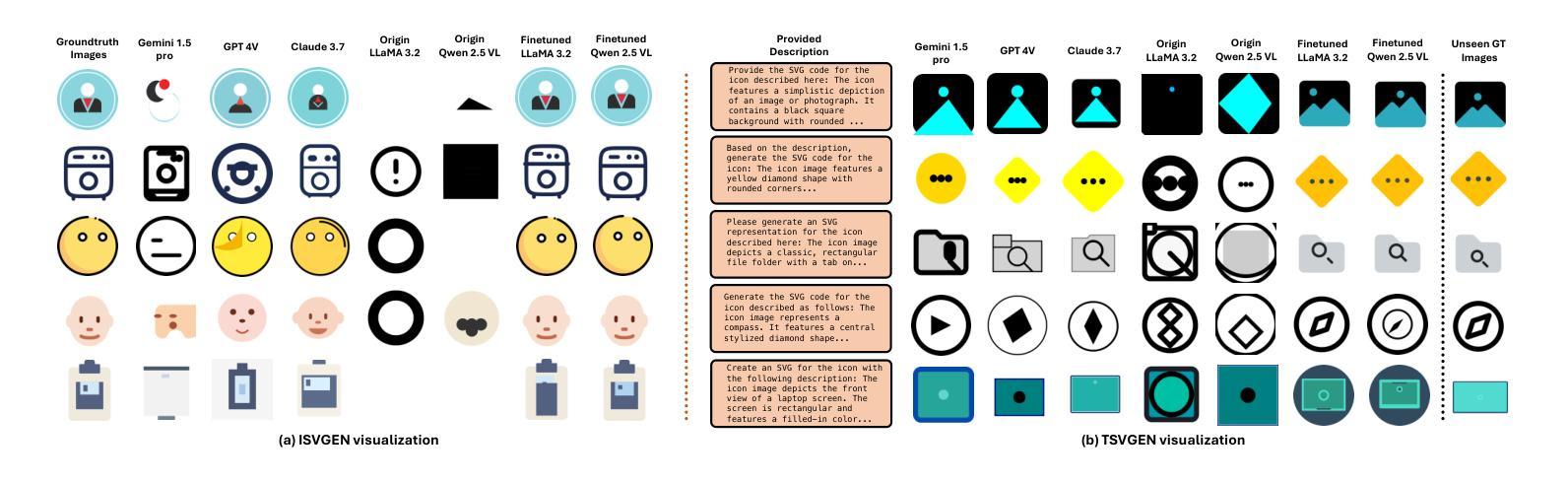
UniSVG: A Unified Dataset for Vector Graphic Understanding and Generation with Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Jinke Li, Jiarui Yu, Chenxing Wei, Hande Dong, Qiang Lin, Liangjing Yang, Zhicai Wang, Yanbin Hao
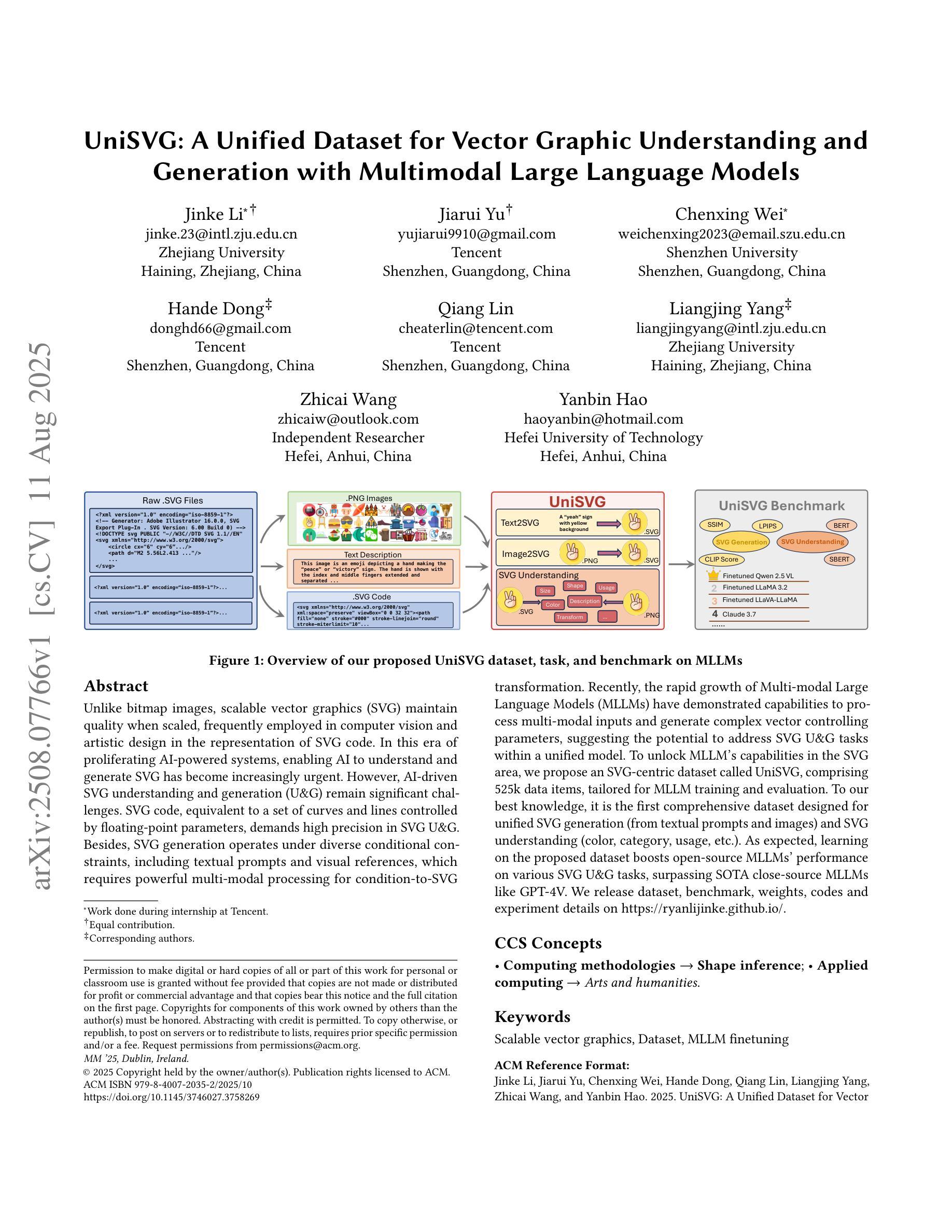
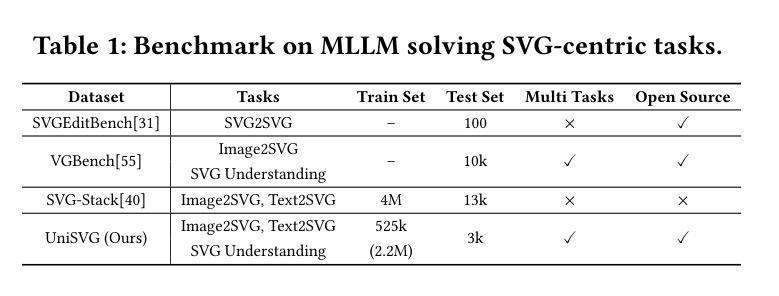
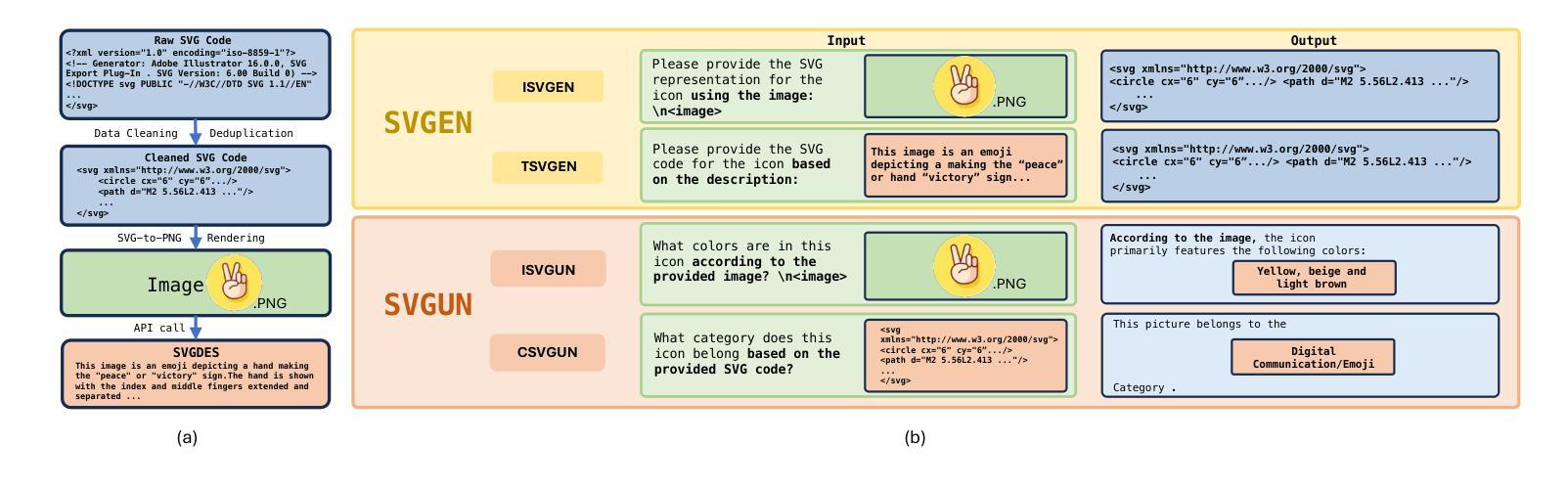
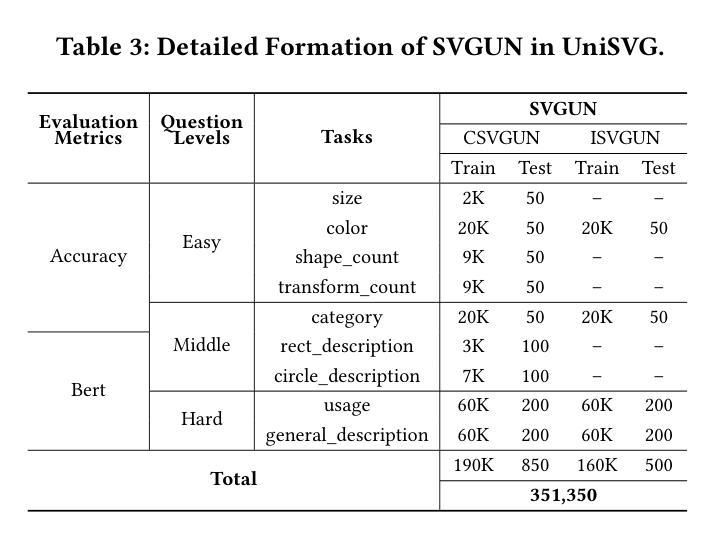
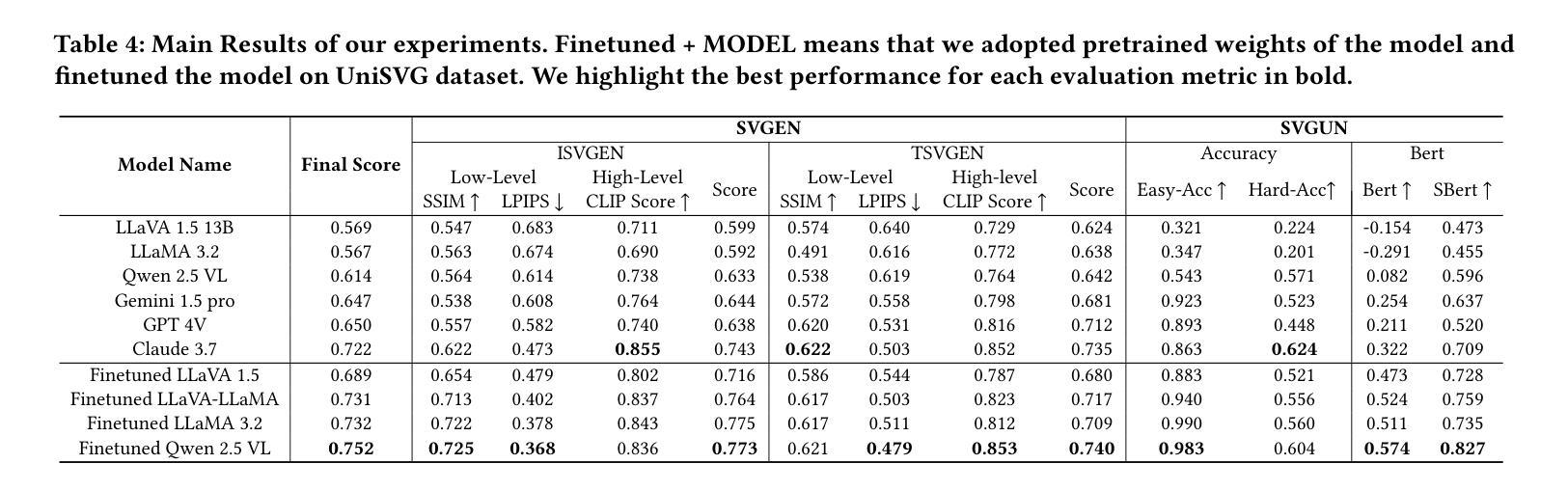
Unlike bitmap images, scalable vector graphics (SVG) maintain quality when scaled, frequently employed in computer vision and artistic design in the representation of SVG code. In this era of proliferating AI-powered systems, enabling AI to understand and generate SVG has become increasingly urgent. However, AI-driven SVG understanding and generation (U&G) remain significant challenges. SVG code, equivalent to a set of curves and lines controlled by floating-point parameters, demands high precision in SVG U&G. Besides, SVG generation operates under diverse conditional constraints, including textual prompts and visual references, which requires powerful multi-modal processing for condition-to-SVG transformation. Recently, the rapid growth of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated capabilities to process multi-modal inputs and generate complex vector controlling parameters, suggesting the potential to address SVG U&G tasks within a unified model. To unlock MLLM’s capabilities in the SVG area, we propose an SVG-centric dataset called UniSVG, comprising 525k data items, tailored for MLLM training and evaluation. To our best knowledge, it is the first comprehensive dataset designed for unified SVG generation (from textual prompts and images) and SVG understanding (color, category, usage, etc.). As expected, learning on the proposed dataset boosts open-source MLLMs’ performance on various SVG U&G tasks, surpassing SOTA close-source MLLMs like GPT-4V. We release dataset, benchmark, weights, codes and experiment details on https://ryanlijinke.github.io/.
与位图图像不同,可缩放矢量图形(SVG)在缩放时能保持质量不变,常被用于计算机视觉和艺术设计中的SVG代码表示。在这个AI系统日益增多的时代,让AI理解和生成SVG变得日益紧迫。然而,AI驱动的SVG理解和生成(U&G)仍然面临重大挑战。SVG代码相当于由浮点参数控制的曲线和线条集合,要求在SVG U&G中具有高精度。此外,SVG生成受到各种条件约束的影响,包括文本提示和视觉参考,这需要强大的多模态处理来实现条件到SVG的转换。最近,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的快速发展显示出处理多模态输入和生成复杂矢量控制参数的能力,表明有可能在统一模型中解决SVG U&G任务。为了解锁MLLM在SVG领域的潜力,我们提出了一个以SVG为中心的数据集,名为UniSVG,包含52.5万条数据项,专为MLLM训练和评估而设计。据我们所知,它是第一个为统一SVG生成(从文本提示和图像)和SVG理解(颜色、类别、用途等)而设计的综合数据集。正如预期的那样,在该数据集上进行学习提高了开源MLLM在各种SVG U&G任务上的性能,超越了最新专有MLLMs如GPT-4V等。我们在https://ryanlijinke.github.io/上发布了数据集、基准测试、权重、代码和实验细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACM MM 2025 Dataset Track
Summary
在AI驱动的系统不断普及的时代,可伸缩矢量图形(SVG)的理解与生成(U&G)成为重要的挑战。近期,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在处理多模态输入和生成复杂的矢量控制参数方面展现出潜力。为了解锁MLLM在SVG领域的潜力,提出了一种名为UniSVG的SVG专用数据集,包含52.5万项数据,适合用于MLLM的训练和评估,并期望能提高开源MLLM在各种SVG U&G任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- AI理解和生成SVG具有重要的挑战性和紧迫性。
- SVG代码需要高精度处理,且其生成受到多种条件约束。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)能够处理多模态输入并生成复杂的矢量控制参数。
- 提出了一个名为UniSVG的SVG专用数据集,用于MLLM的训练和评估。
- UniSVG数据集是首个统一SVG生成(从文本提示和图像)和SVG理解的综合数据集。
- 在UniSVG数据集上训练可以提高开源MLLM在多种SVG U&G任务上的性能。
点此查看论文截图
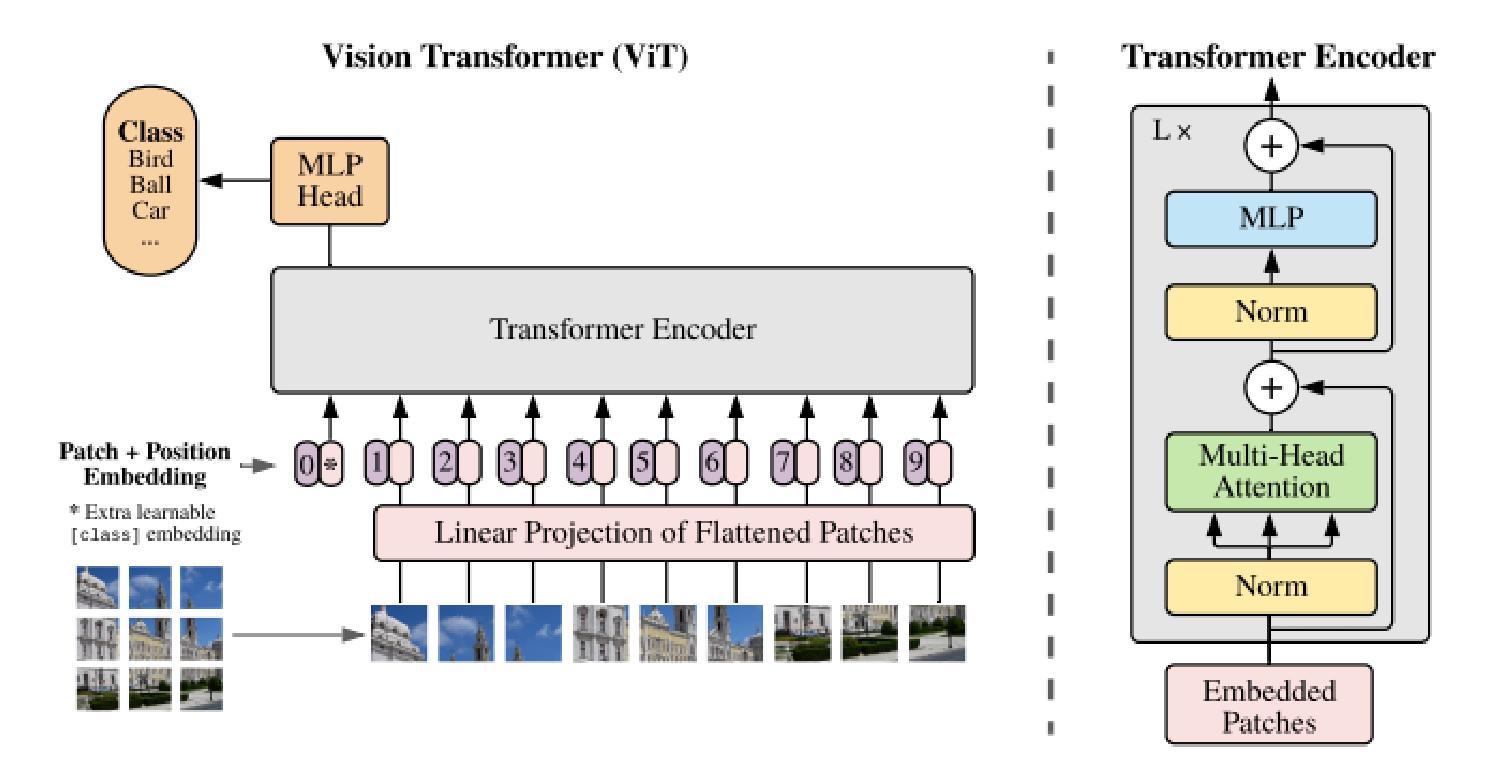
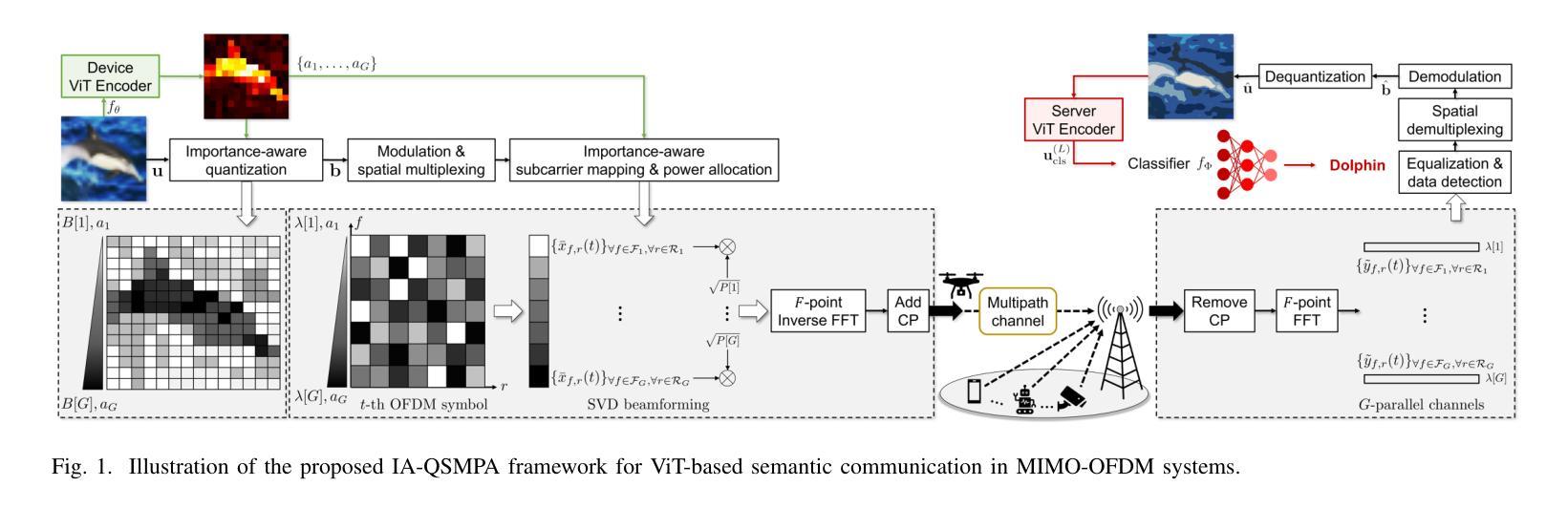
Importance-Aware Semantic Communication in MIMO-OFDM Systems Using Vision Transformer
Authors:Joohyuk Park, Yongjeong Oh, Jihun Park, Yo-Seb Jeon
This paper presents a novel importance-aware quantization, subcarrier mapping, and power allocation (IA-QSMPA) framework for semantic communication in multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) systems, empowered by a pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT). The proposed framework exploits attention-based importance extracted from a pretrained ViT to jointly optimize quantization levels, subcarrier mapping, and power allocation. Specifically, IA-QSMPA maps semantically important features to high-quality subchannels and allocates resources in accordance with their contribution to task performance and communication latency. To efficiently solve the resulting nonconvex optimization problem, a block coordinate descent algorithm is employed. The framework is further extended to operate under finite blocklength transmission, where communication errors may occur. In this setting, a segment-wise linear approximation of the channel dispersion penalty is introduced to enable efficient joint optimization under practical constraints. Simulation results on a multi-view image classification task using the MVP-N dataset demonstrate that IA-QSMPA significantly outperforms conventional methods in both ideal and finite blocklength transmission scenarios, achieving superior task performance and communication efficiency.
本文提出了一种基于预训练视觉转换器(ViT)的多输入多输出正交频分复用(MIMO-OFDM)系统中的语义通信的新型重要性感知量化、子载波映射和功率分配(IA-QSMPA)框架。该框架利用预训练的ViT的注意力机制提取的重要性,联合优化量化级别、子载波映射和功率分配。具体来说,IA-QSMPA将语义重要特征映射到高质量子通道上,并根据其对任务性能和通信延迟的贡献来分配资源。为了有效地解决由此产生的非凸优化问题,采用了块坐标下降算法。该框架进一步扩展到有限块长传输的情况下运行,在这种情况下可能会发生通信错误。在此设置中,引入了信道弥散罚分的分段线性近似,以在实用约束下实现有效的联合优化。使用MVP-N数据集进行的多视图图像分类任务的仿真结果表明,IA-QSMPA在理想和有限块长传输场景中均显著优于传统方法,实现了卓越的任务性能和通信效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于预训练Vision Transformer(ViT)的重要性感知量化、子载波映射和功率分配(IA-QSMPA)框架,用于MIMO-OFDM系统中的语义通信。该框架利用预训练ViT的注意力机制提取重要性,以联合优化量化级别、子载波映射和功率分配。IA-QSMPA将语义重要特征映射到高质量子通道,并根据其对任务性能和通信延迟的贡献分配资源。采用块坐标下降算法有效地解决了由此产生的非凸优化问题。该框架还扩展到有限块长传输情况下运行,在此情况下引入分段线性近似信道扩散惩罚,以在实用约束下实现有效的联合优化。模拟结果表明,在理想和有限块长传输场景下,IA-QSMPA在多视图图像分类任务上显著优于传统方法,实现了出色的任务性能和通信效率。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种基于预训练Vision Transformer(ViT)的IA-QSMPA框架,用于MIMO-OFDM系统中的语义通信。
- 该框架利用注意力机制提取重要性,并联合优化量化级别、子载波映射和功率分配。
- IA-QSMPA将语义重要特征映射到高质量子通道,并根据任务性能和通信延迟的贡献分配资源。
- 采用块坐标下降算法解决非凸优化问题。
- 框架扩展到有限块长传输情况,引入分段线性近似信道扩散惩罚以实现有效优化。
- 模拟结果表明,IA-QSMPA在理想和有限块长传输场景下均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图
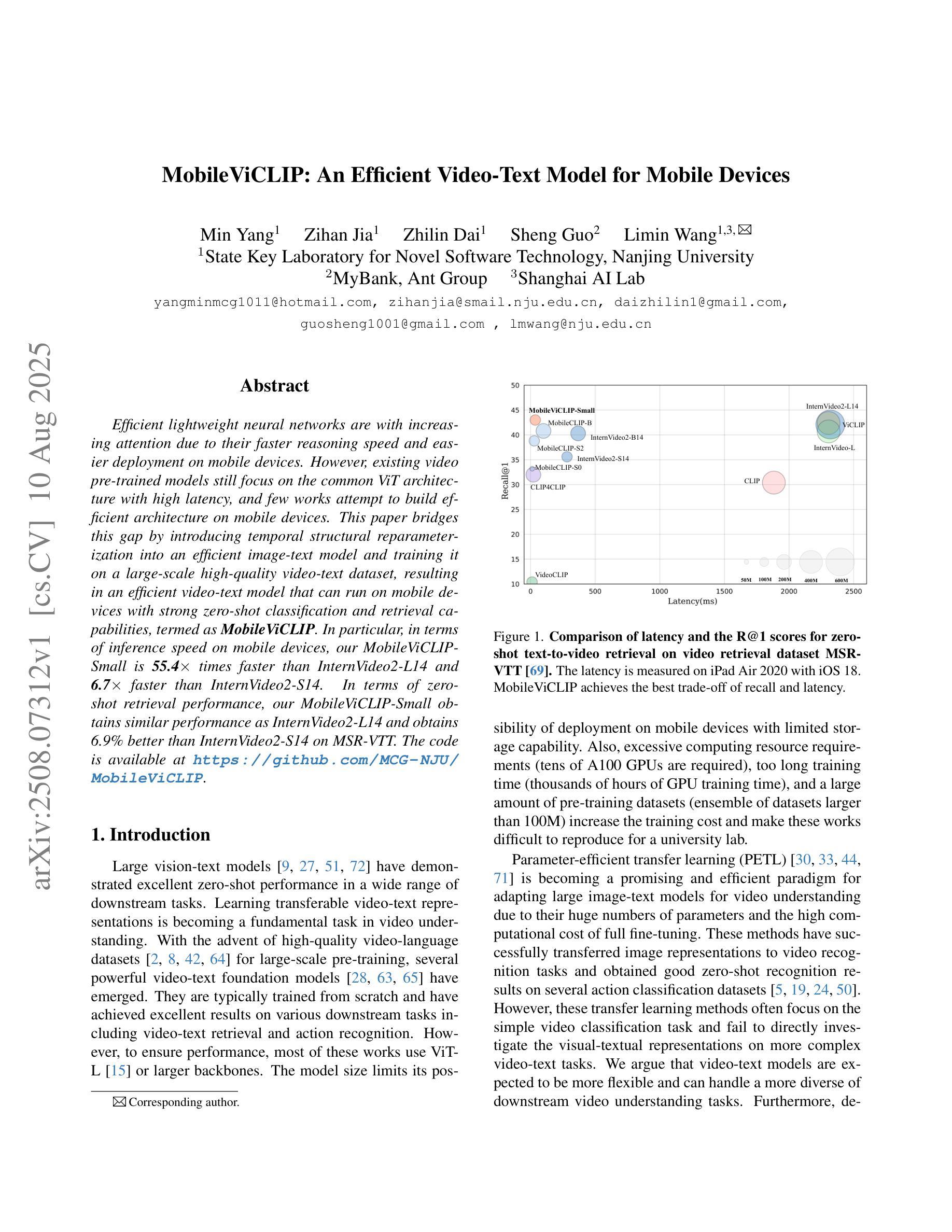
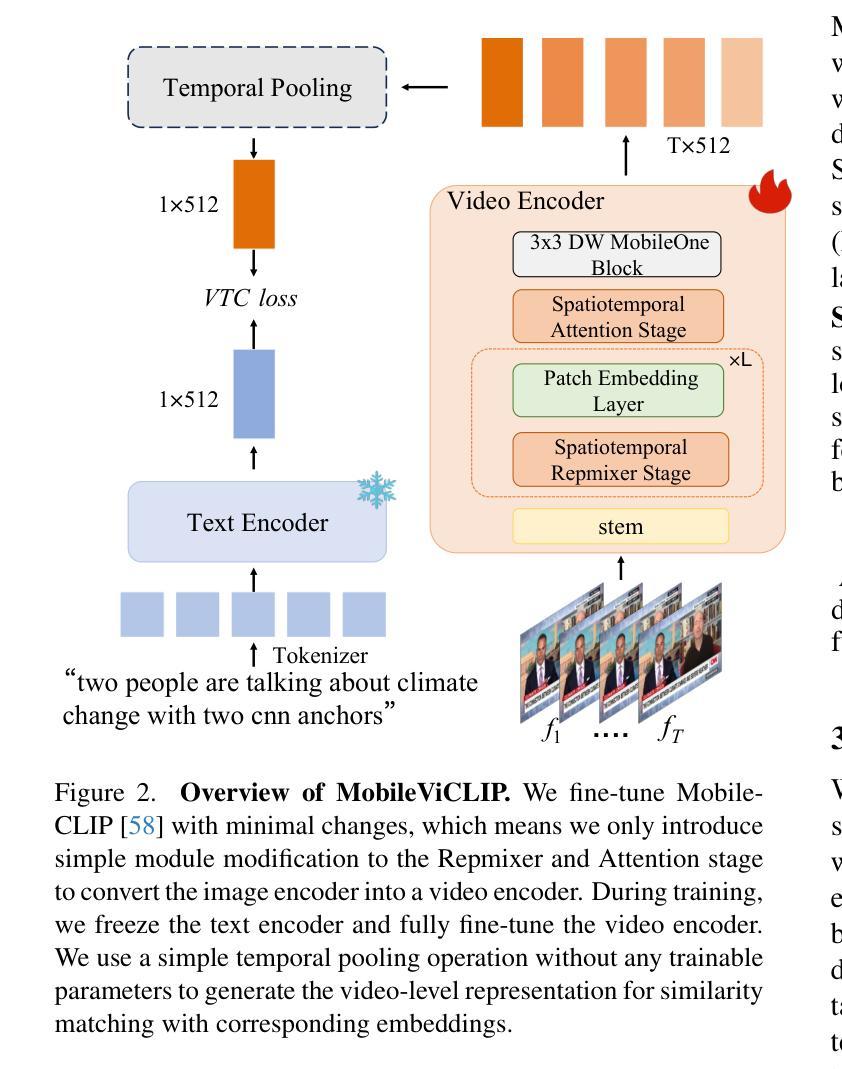
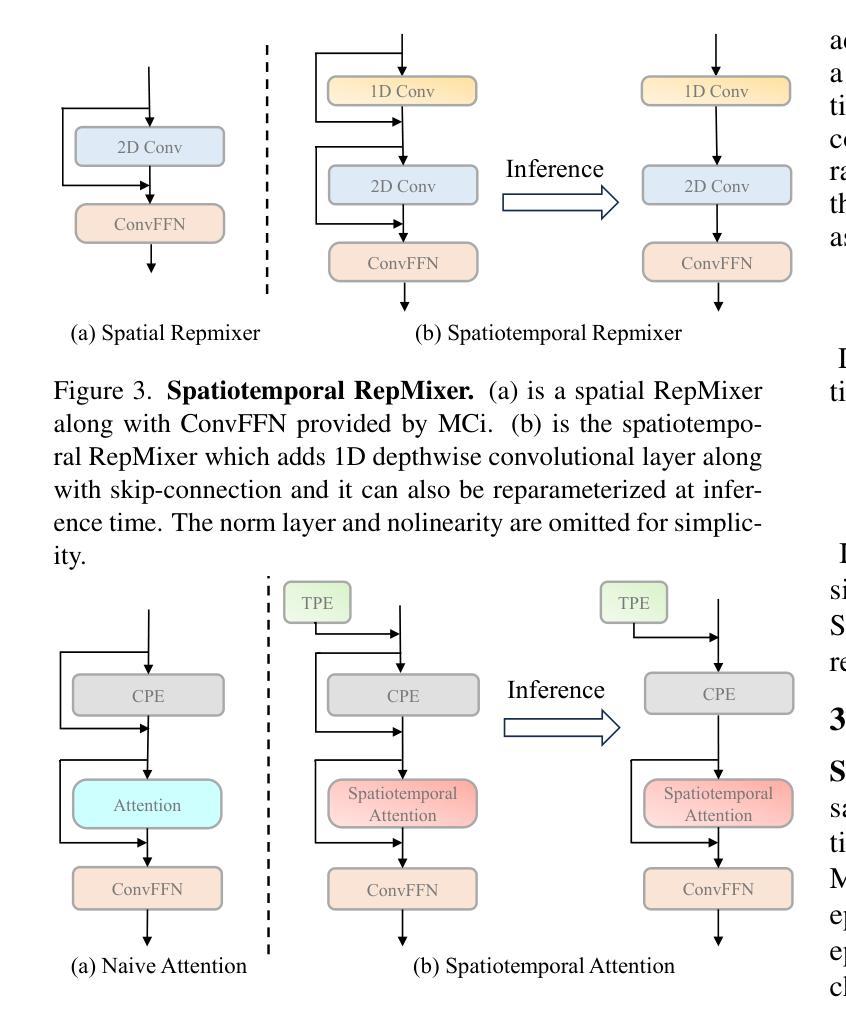
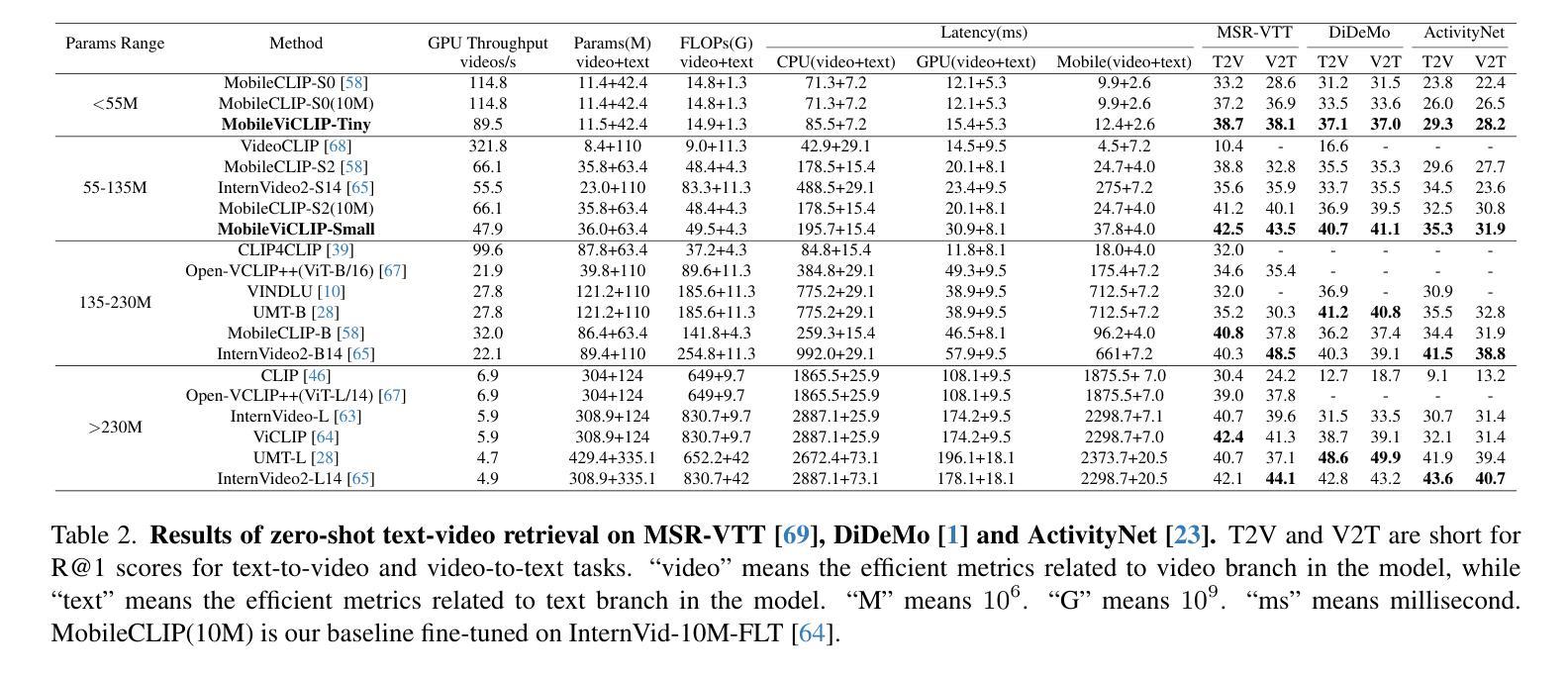
MobileViCLIP: An Efficient Video-Text Model for Mobile Devices
Authors:Min Yang, Zihan Jia, Zhilin Dai, Sheng Guo, Limin Wang
Efficient lightweight neural networks are with increasing attention due to their faster reasoning speed and easier deployment on mobile devices. However, existing video pre-trained models still focus on the common ViT architecture with high latency, and few works attempt to build efficient architecture on mobile devices. This paper bridges this gap by introducing temporal structural reparameterization into an efficient image-text model and training it on a large-scale high-quality video-text dataset, resulting in an efficient video-text model that can run on mobile devices with strong zero-shot classification and retrieval capabilities, termed as MobileViCLIP. In particular, in terms of inference speed on mobile devices, our MobileViCLIP-Small is 55.4x times faster than InternVideo2-L14 and 6.7x faster than InternVideo2-S14. In terms of zero-shot retrieval performance, our MobileViCLIP-Small obtains similar performance as InternVideo2-L14 and obtains 6.9% better than InternVideo2-S14 on MSR-VTT. The code is available at https://github.com/MCG-NJU/MobileViCLIP.
高效轻量级神经网络因其更快的推理速度和在移动设备上的更容易部署而受到越来越多的关注。然而,现有的视频预训练模型仍然主要关注高延迟的通用ViT架构,很少有工作尝试在移动设备上构建高效架构。本文通过引入时间结构重参数化到一个高效的图像文本模型中,并在大规模高质量的视频文本数据集上进行训练,从而填补了这一空白。这导致了一个能在移动设备上运行的高效视频文本模型,具有强烈的零样本分类和检索能力,被称为MobileViCLIP。特别地,在移动设备上的推理速度方面,我们的MobileViCLIP-Small是InternVideo2-L14的55.4倍,比InternVideo2-S14快6.7倍。在零样本检索性能方面,我们的MobileViCLIP-Small与InternVideo2-L14表现相似,并在MSR-VTT上比InternVideo2-S14高出6.9%。代码可在https://github.com/MCG-NJU/MobileViCLIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出一种高效的视频文本模型MobileViCLIP,通过引入时间结构重参数化,在大型高质量视频文本数据集上训练,可在移动设备上运行,具有强大的零样本分类和检索能力。MobileViCLIP-Small在推理速度和零样本检索性能上表现优异,相较于其他模型有更快的推理速度和更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究解决了现有视频预训练模型主要集中在高延迟的通用ViT架构上,而针对移动设备的高效架构研究较少的问题。
- 通过引入时间结构重参数化,提出了一种高效的视频文本模型MobileViCLIP。
- MobileViCLIP可在移动设备上运行,具有强大的零样本分类和检索能力。
- MobileViCLIP-Small在推理速度上相较于其他模型有显著优势,例如,它的推理速度是InternVideo2-L14的55.4倍,是InternVideo2-S14的6.7倍。
- 在零样本检索性能方面,MobileViCLIP-Small的表现优异,相较于InternVideo2-L14表现相当,并在MSR-VTT上比InternVideo2-S14高出6.9%。
- 该模型的代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和进一步改进。
点此查看论文截图
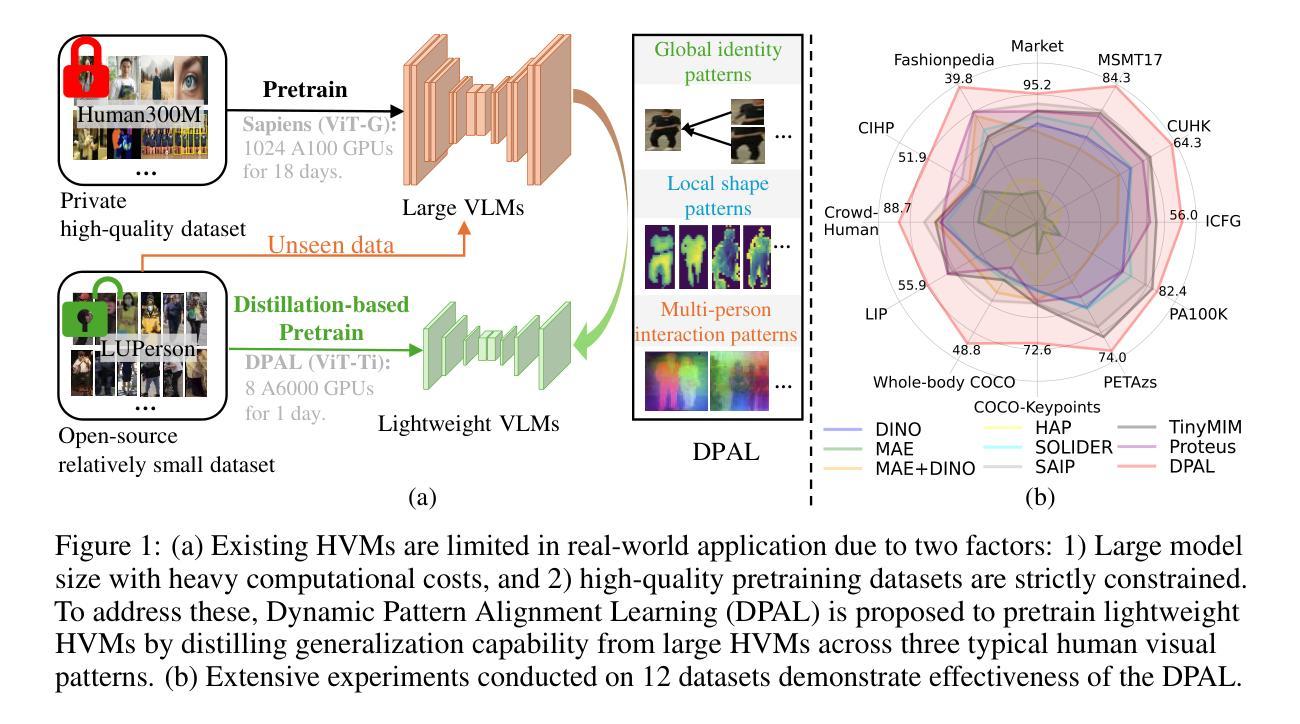
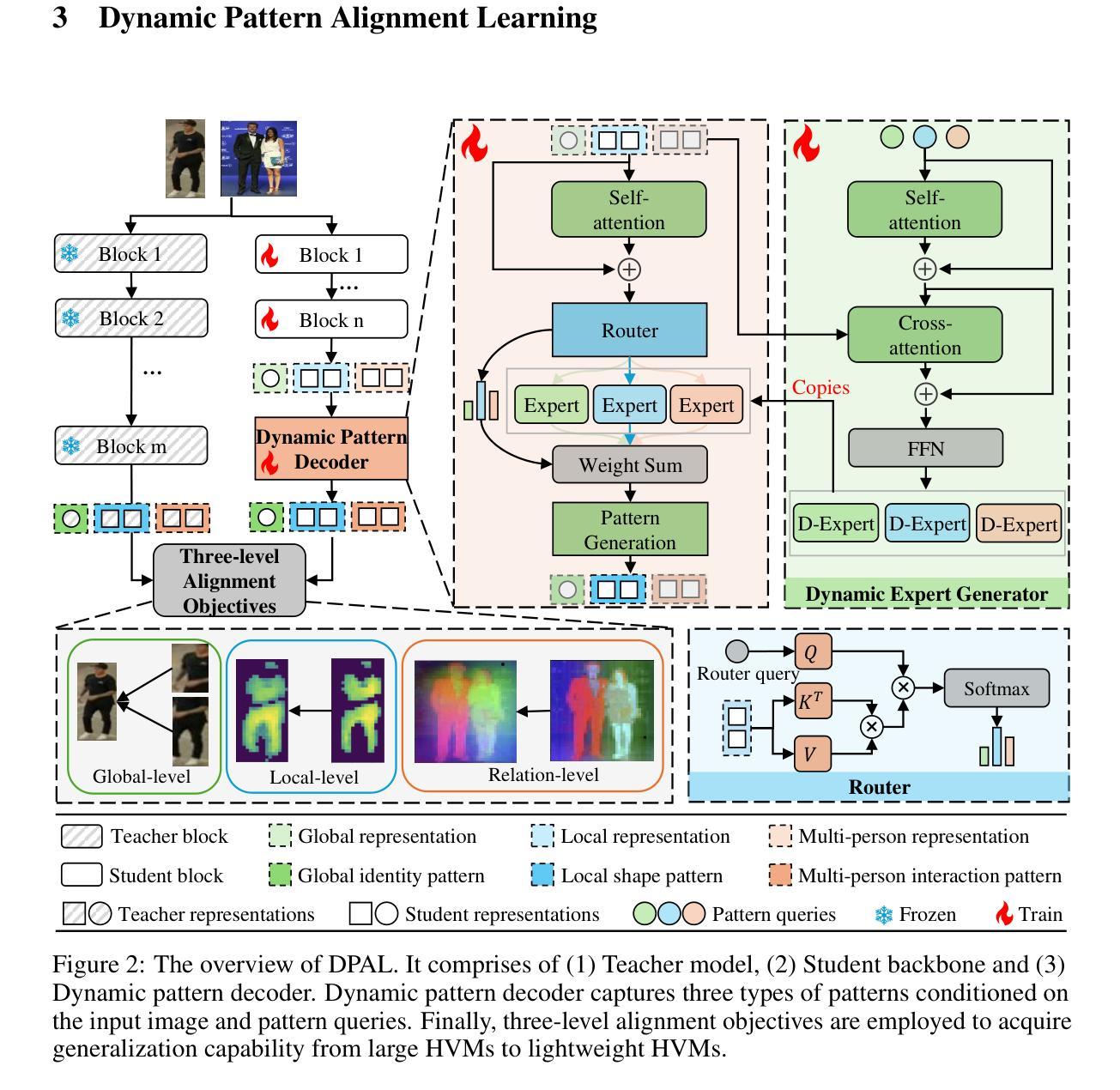
Dynamic Pattern Alignment Learning for Pretraining Lightweight Human-Centric Vision Models
Authors:Xuanhan Wang, Huimin Deng, Ke Liu, Jun Wang, Lianli Gao, Jingkuan Song
Human-centric vision models (HVMs) have achieved remarkable generalization due to large-scale pretraining on massive person images. However, their dependence on large neural architectures and the restricted accessibility of pretraining data significantly limits their practicality in real-world applications. To address this limitation, we propose Dynamic Pattern Alignment Learning (DPAL), a novel distillation-based pretraining framework that efficiently trains lightweight HVMs to acquire strong generalization from large HVMs. In particular, human-centric visual perception are highly dependent on three typical visual patterns, including global identity pattern, local shape pattern and multi-person interaction pattern. To achieve generalizable lightweight HVMs, we firstly design a dynamic pattern decoder (D-PaDe), acting as a dynamic Mixture of Expert (MoE) model. It incorporates three specialized experts dedicated to adaptively extract typical visual patterns, conditioned on both input image and pattern queries. And then, we present three levels of alignment objectives, which aims to minimize generalization gap between lightweight HVMs and large HVMs at global image level, local pixel level, and instance relation level. With these two deliberate designs, the DPAL effectively guides lightweight model to learn all typical human visual patterns from large HVMs, which can generalize to various human-centric vision tasks. Extensive experiments conducted on 15 challenging datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the DPAL. Remarkably, when employing PATH-B as the teacher, DPAL-ViT/Ti (5M parameters) achieves surprising generalizability similar to existing large HVMs such as PATH-B (84M) and Sapiens-L (307M), and outperforms previous distillation-based pretraining methods including Proteus-ViT/Ti (5M) and TinyMiM-ViT/Ti (5M) by a large margin.
人类为中心的视觉模型(HVMs)由于大规模预训练在大量人像上的应用,已经实现了显著的泛化。然而,它们对大型神经网络架构的依赖以及预训练数据获取的限制,显著限制了它们在现实世界应用中的实用性。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了动态模式对齐学习(DPAL)这种基于蒸馏的预训练框架,它能有效地训练轻量级HVMs,从大型HVMs中获得强大的泛化能力。特别是,人类为中心的视觉感知高度依赖于三种典型的视觉模式,包括全局身份模式、局部形状模式和多人物交互模式。为了实现可泛化的轻量级HVMs,我们首先设计了一个动态模式解码器(D-PaDe),它作为一个动态的混合专家(MoE)模型。它结合了三个专业专家,旨在根据输入图像和模式查询自适应地提取典型视觉模式。然后,我们提出了三个级别的对齐目标,旨在最小化轻量级HVMs和大型HVMs在全局图像级别、局部像素级别和实例关系级别的泛化差距。通过这两个精心设计,DPAL有效地引导轻量级模型从大型HVMs学习所有典型的人类视觉模式,可以泛化到各种以人类为中心的视觉任务。在15个具有挑战性的数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了DPAL的有效性。值得一提的是,当使用PATH-B作为教师时,DPAL-ViT/Ti(5M参数)实现了与现有大型HVMs(如PATH-B(84M)和Sapiens-L(307M))相似的惊人泛化能力,并大大超越了之前的基于蒸馏的预训练方法,包括Proteus-ViT/Ti(5M)和TinyMiM-ViT/Ti(5M)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对人中心视觉模型(HVMs)在实际应用中的局限性,提出动态模式对齐学习(DPAL)框架。通过设计动态模式解码器(D-PaDe)和三个层次的对齐目标,实现从小型模型向大型HVMs的有效学习,提高了轻型HVMs的通用性。在多个数据集上的实验验证了DPAL的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 人中心视觉模型(HVMs)通过大规模预训练实现显著泛化,但受限于大型神经网络架构和预训练数据可访问性,在现实世界应用中的实用性受限。
- 提出动态模式对齐学习(DPAL)框架,旨在训练轻量级的人中心视觉模型(HVMs),使其从大型HVMs中有效获取强大的泛化能力。
- DPAL框架包含动态模式解码器(D-PaDe),它作为动态混合专家(MoE)模型,能够自适应地提取典型视觉模式。
- 引入三个层次的对齐目标,以最小化轻量级HVMs和大型HVMs之间的泛化差距,包括全局图像级别、局部像素级别和实例关系级别。
- DPAL框架能够引导轻型模型从大型HVMs学习所有人类典型的视觉模式,并可以泛化到各种人中心视觉任务。
- 在15个具有挑战性的数据集上进行的实验验证了DPAL的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

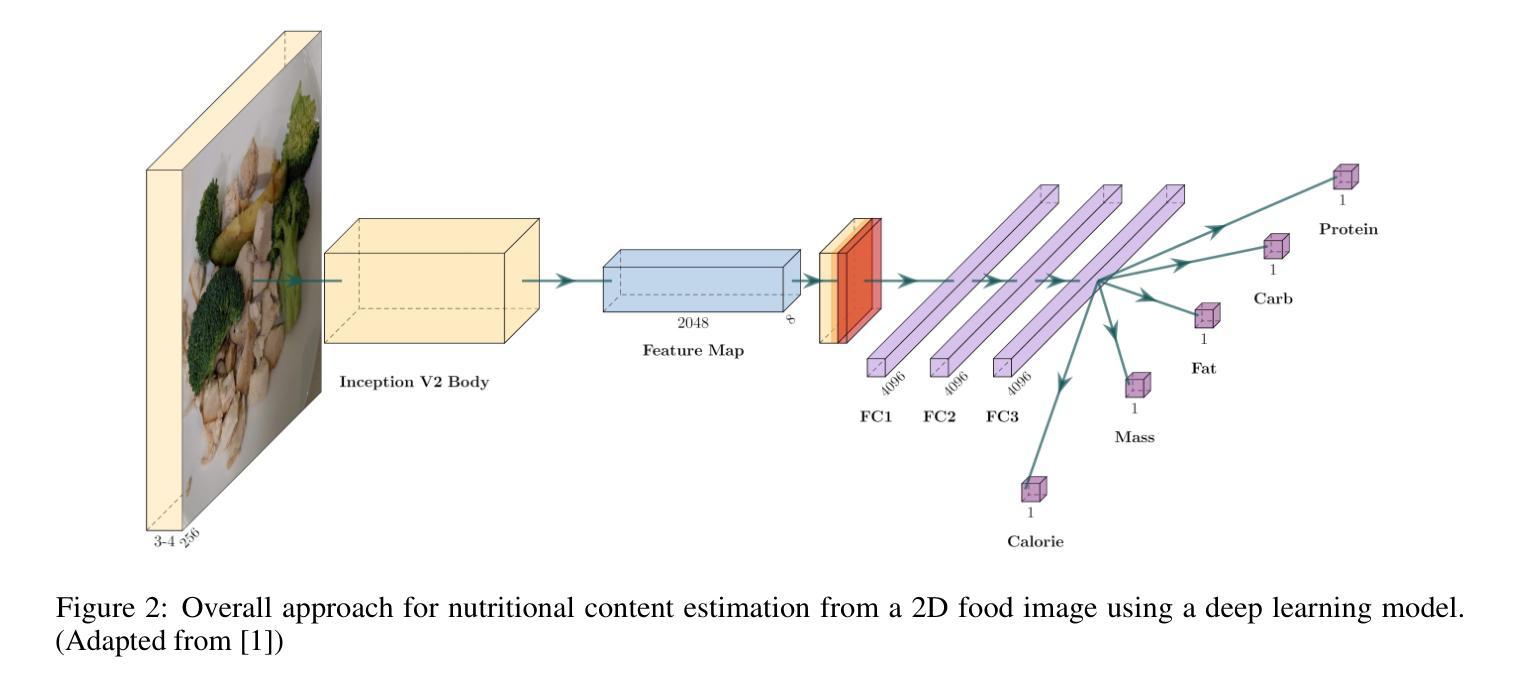
Investigating the Impact of Large-Scale Pre-training on Nutritional Content Estimation from 2D Images
Authors:Michele Andrade, Guilherme A. L. Silva, Valéria Santos, Gladston Moreira, Eduardo Luz
Estimating the nutritional content of food from images is a critical task with significant implications for health and dietary monitoring. This is challenging, especially when relying solely on 2D images, due to the variability in food presentation, lighting, and the inherent difficulty in inferring volume and mass without depth information. Furthermore, reproducibility in this domain is hampered by the reliance of state-of-the-art methods on proprietary datasets for large-scale pre-training. In this paper, we investigate the impact of large-scale pre-training datasets on the performance of deep learning models for nutritional estimation using only 2D images. We fine-tune and evaluate Vision Transformer (ViT) models pre-trained on two large public datasets, ImageNet and COYO, comparing their performance against baseline CNN models (InceptionV2 and ResNet-50) and a state-of-the-art method pre-trained on the proprietary JFT-300M dataset. We conduct extensive experiments on the Nutrition5k dataset, a large-scale collection of real-world food plates with high-precision nutritional annotations. Our evaluation using Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAE%) reveals that models pre-trained on JFT-300M significantly outperform those pre-trained on public datasets. Unexpectedly, the model pre-trained on the massive COYO dataset performs worse than the model pre-trained on ImageNet for this specific regression task, refuting our initial hypothesis. Our analysis provides quantitative evidence highlighting the critical role of pre-training dataset characteristics, including scale, domain relevance, and curation quality, for effective transfer learning in 2D nutritional estimation.
从图像估算食品的营养成分是健康与饮食监测中具有重要意义的任务。这是一项挑战,尤其是仅依赖2D图像时,由于食品展示、光照的多样性以及缺乏深度信息导致推断体积和质量的固有困难。此外,该领域的可重复性受到阻碍,因为最先进的方法依赖于大规模预训练的专有数据集。在本文中,我们研究了大规模预训练数据集对仅使用2D图像进行营养估算的深度学习模型性能的影响。我们微调并评估了在ImageNet和COYO两个大型公共数据集上预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,将其性能与基线CNN模型(InceptionV2和ResNet-50)以及一种在专有JFT-300M数据集上预训练的最新方法进行比较。我们在Nutrition5k数据集上进行了大量实验,该数据集是现实世界食品盘的大量集合,具有高精度营养注释。我们使用平均绝对误差(MAE)和平均绝对百分比误差(MAE%)进行评估,结果显示在JFT-300M上预训练的模型显著优于在公共数据集上预训练的模型。出乎意料的是,在大量COYO数据集上预训练的模型在此特定回归任务上的表现不如在ImageNet上预训练的模型,这与我们最初的假设相悖。我们的分析提供了定量证据,突出显示了预训练数据集特征(包括规模、领域相关性和筛选质量)在2D营养估算中的有效迁移学习中的关键作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
摘要
本文研究了大规模预训练数据集对仅使用2D图像进行营养估算的深度学习模型性能的影响。通过微调并在Nutrition5k数据集上评估预训练于ImageNet和COYO的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型,与基准CNN模型(InceptionV2和ResNet-50)以及预训练于专有JFT-300M数据集的最先进方法进行比较。实验结果表明,预训练于JFT-300M的模型显著优于预训练于公开数据集的模型。意外的是,预训练于大规模COYO数据集的模型在此特定回归任务上的表现不如预训练于ImageNet的模型,这反驳了我们的初步假设。分析提供了定量证据,突出显示了预训练数据集特性,包括规模、领域相关性和编纂质量,在2D营养估算中的有效迁移学习方面的关键作用。
关键见解
- 营养图像估算具有健康与饮食监测的重大意义,但面临食品展示、光照、体积和质量推断的难题。
- 使用Vision Transformer (ViT)模型进行深度学习,研究大规模预训练数据集对营养估算性能的影响。
- 对比了预训练于ImageNet和COYO的ViT模型,以及与基准CNN模型的性能。
- 预训练于JFT-300M的模型表现最佳,显示预训练数据集规模、领域相关性和编纂质量的重要性。
- COYO数据集在特定回归任务上的表现不如ImageNet,这出乎预料并反驳了初始假设。
- 定量证据表明,预训练数据集特性对有效迁移学习在营养估算中的关键作用。
点此查看论文截图