⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
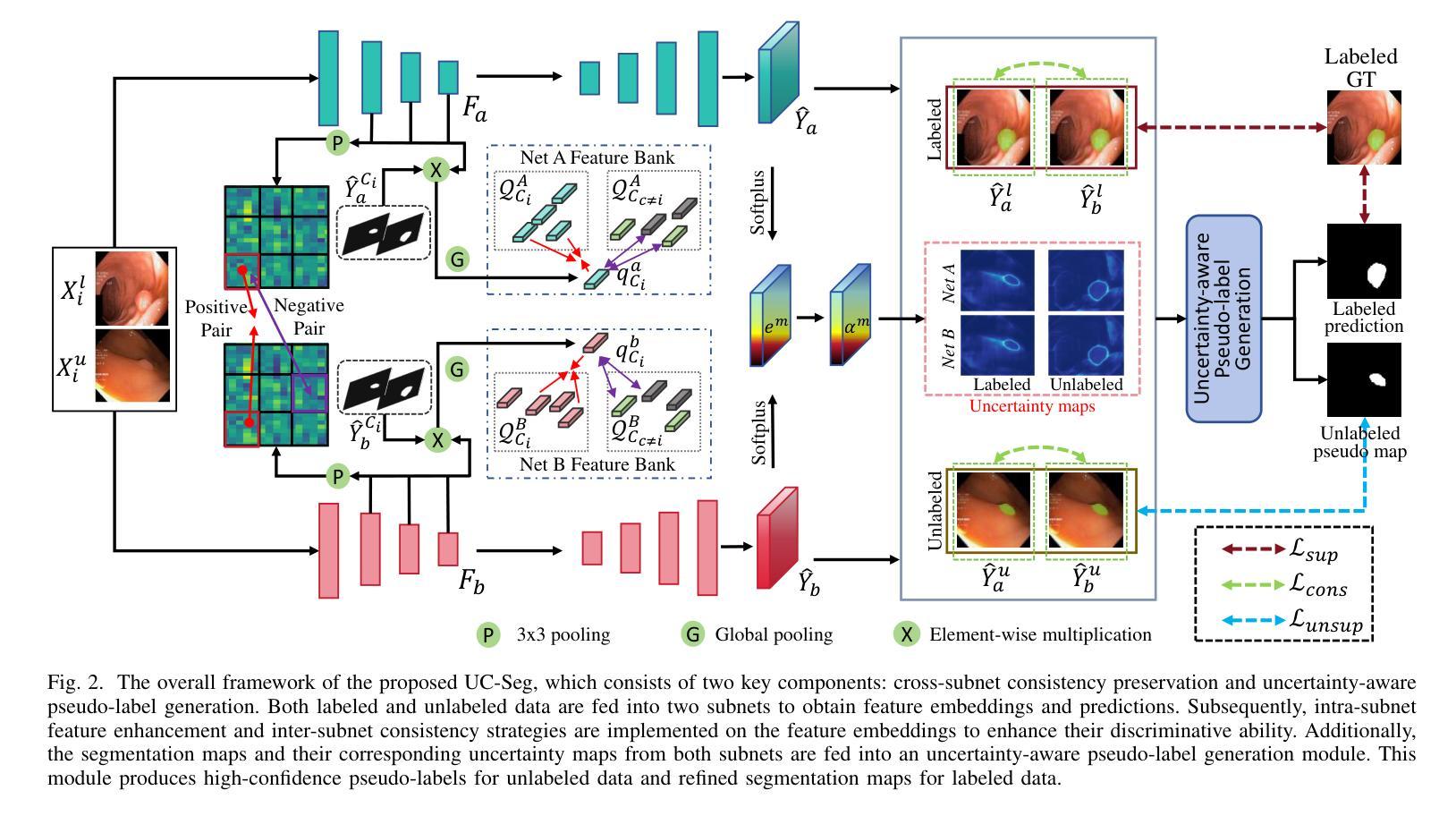
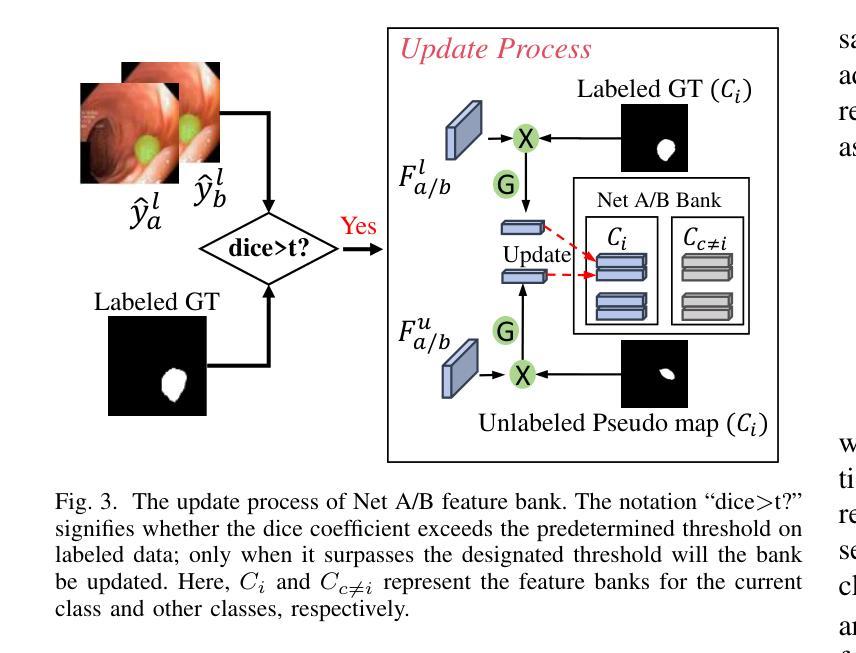
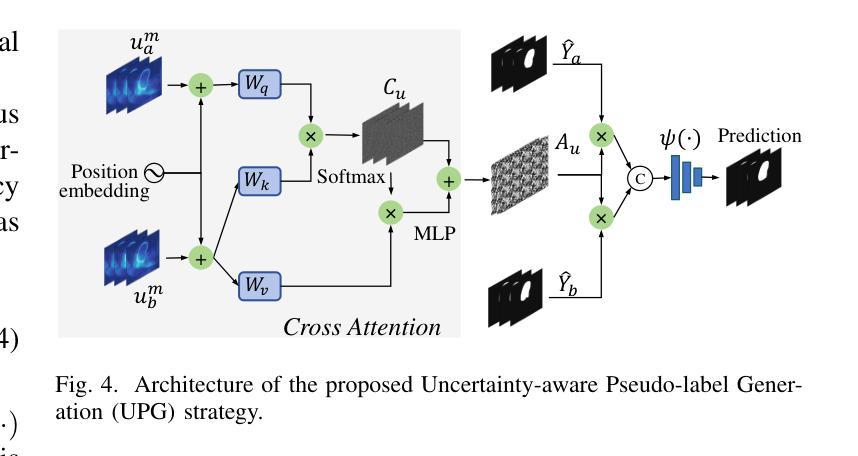
Uncertainty-aware Cross-training for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Kaiwen Huang, Tao Zhou, Huazhu Fu, Yizhe Zhang, Yi Zhou, Xiao-Jun Wu
Semi-supervised learning has gained considerable popularity in medical image segmentation tasks due to its capability to reduce reliance on expert-examined annotations. Several mean-teacher (MT) based semi-supervised methods utilize consistency regularization to effectively leverage valuable information from unlabeled data. However, these methods often heavily rely on the student model and overlook the potential impact of cognitive biases within the model. Furthermore, some methods employ co-training using pseudo-labels derived from different inputs, yet generating high-confidence pseudo-labels from perturbed inputs during training remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Cross-training framework for semi-supervised medical image Segmentation (UC-Seg). Our UC-Seg framework incorporates two distinct subnets to effectively explore and leverage the correlation between them, thereby mitigating cognitive biases within the model. Specifically, we present a Cross-subnet Consistency Preservation (CCP) strategy to enhance feature representation capability and ensure feature consistency across the two subnets. This strategy enables each subnet to correct its own biases and learn shared semantics from both labeled and unlabeled data. Additionally, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Pseudo-label Generation (UPG) component that leverages segmentation results and corresponding uncertainty maps from both subnets to generate high-confidence pseudo-labels. We extensively evaluate the proposed UC-Seg on various medical image segmentation tasks involving different modality images, such as MRI, CT, ultrasound, colonoscopy, and so on. The results demonstrate that our method achieves superior segmentation accuracy and generalization performance compared to other state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods. Our code will be released at https://github.com/taozh2017/UCSeg.
半监督学习在医学图像分割任务中因其减少依赖专家标注的能力而受到广泛关注。一些基于均值教师(MT)的半监督方法利用一致性正则化来有效挖掘未标注数据中的有价值信息。然而,这些方法通常严重依赖于学生模型,并忽略了模型内认知偏差的潜在影响。此外,一些方法使用从不同输入中派生出的伪标签进行协同训练,但在训练过程中从受扰输入生成高置信度的伪标签仍然是一个巨大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一个用于半监督医学图像分割的不确定性感知交叉训练框架(UC-Seg)。我们的UC-Seg框架结合了两个独立的子网,以有效地探索和利用它们之间的相关性,从而减轻模型内的认知偏差。具体来说,我们提出了一种跨子网一致性保留(CCP)策略,以提高特征表示能力,并确保两个子网之间的特征一致性。该策略使每个子网能够纠正自己的偏差,并从有标签和无标签数据中学习共享语义。此外,我们提出了一个不确定性感知伪标签生成(UPG)组件,它利用两个子网的分割结果和相应的不确定性图来生成高置信度的伪标签。我们在涉及不同模态图像(如MRI、CT、超声、结肠镜检查等)的各种医学图像分割任务上广泛评估了所提出的UC-Seg。结果表明,我们的方法与其他最先进的半监督方法相比,实现了更高的分割精度和泛化性能。我们的代码将在https://github.com/taozh2017/UCSeg上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures
摘要
本文提出一种半监督医学图像分割的新框架——不确定性感知交叉训练框架(UC-Seg)。该框架通过两个独立子网络进行探索与交互,降低模型内认知偏见的影响。文中提出交叉子网一致性保护策略(CCP),提高特征表征能力并确保跨子网的特征一致性,使每个子网能纠正自身偏见并从有标签和无标签数据中学习共享语义。同时,利用不确定性感知伪标签生成(UPG)组件,结合两个子网的分割结果和相应的不确定性地图,生成高信心伪标签。在涉及MRI、CT、超声、结肠镜等不同模态图像的医学图像分割任务上,UC-Seg表现出卓越的分割精度和泛化性能。
关键见解
- 半监督学习在医学图像分割任务中受到广泛关注,能够减少专家标注的依赖。
- 现有方法常依赖学生模型,忽视模型内认知偏见的影响。
- 本文提出UC-Seg框架,包含两个独立子网,提升特征表征能力并降低模型偏见。
- 引入CCP策略确保跨子网的特征一致性,提升分割性能。
- UPG组件结合两个子网的分割结果和不确定性地图,生成高信心伪标签。
- UC-Seg在不同模态医学图像分割任务上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

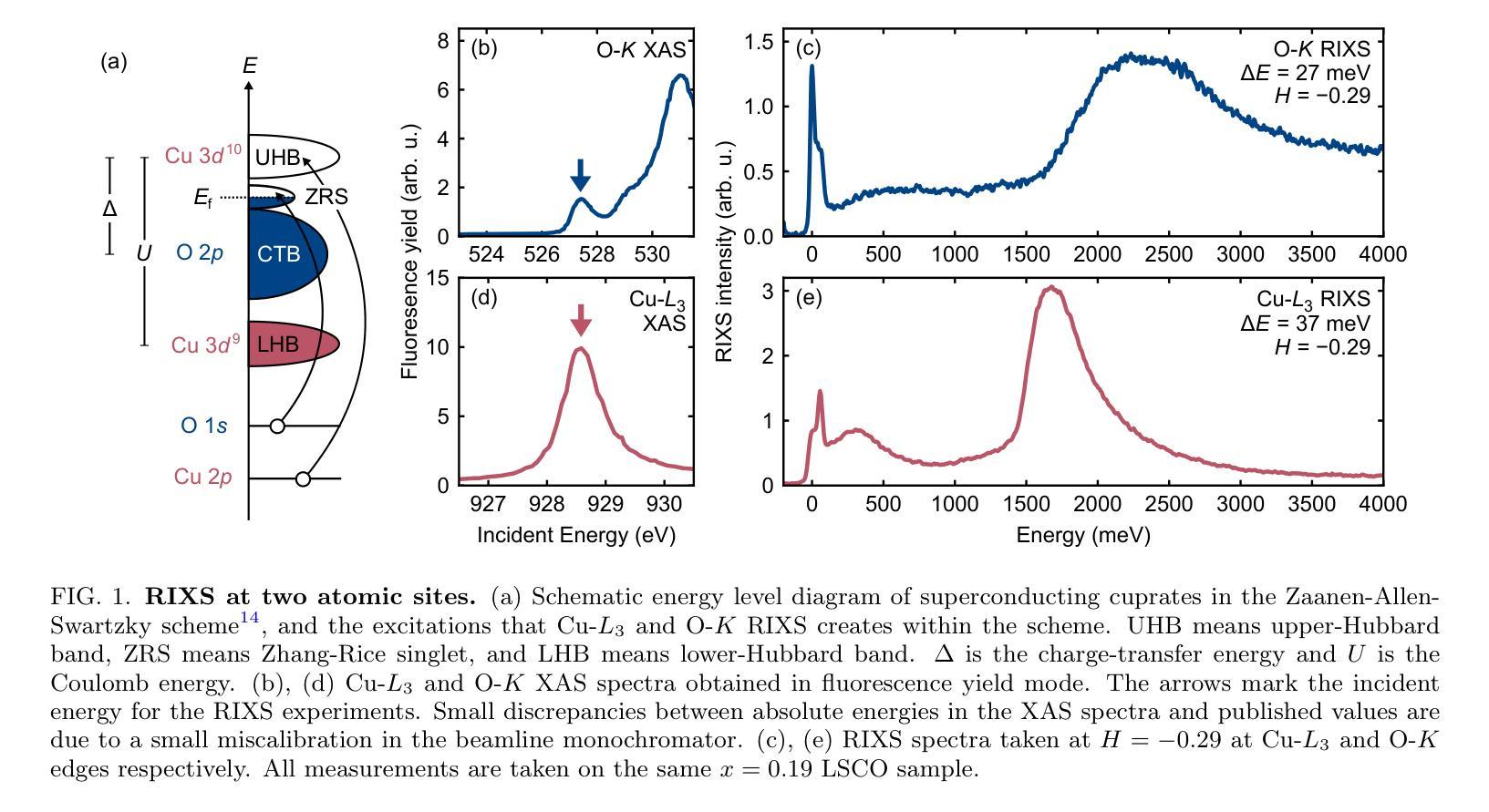
The doping evolution of the charge density wave and charge density fluctuations in La$_{2-x}$Sr$_x$CuO$_4$
Authors:Charles C. Tam, Mengze Zhu, Maud C. Barthélemy, Lauren J. Cane, Oliver J. Lipscombe, Stefano Agrestini, Jaewon Choi, Mirian Garcia-Fernandez, Ke-Jin Zhou, Stephen M. Hayden
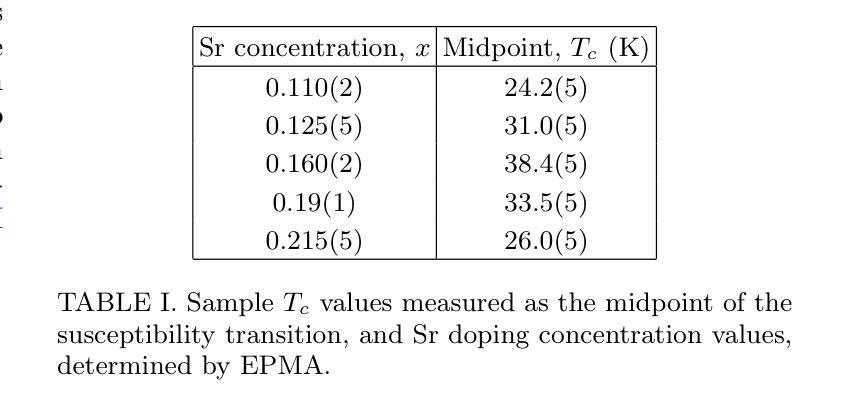
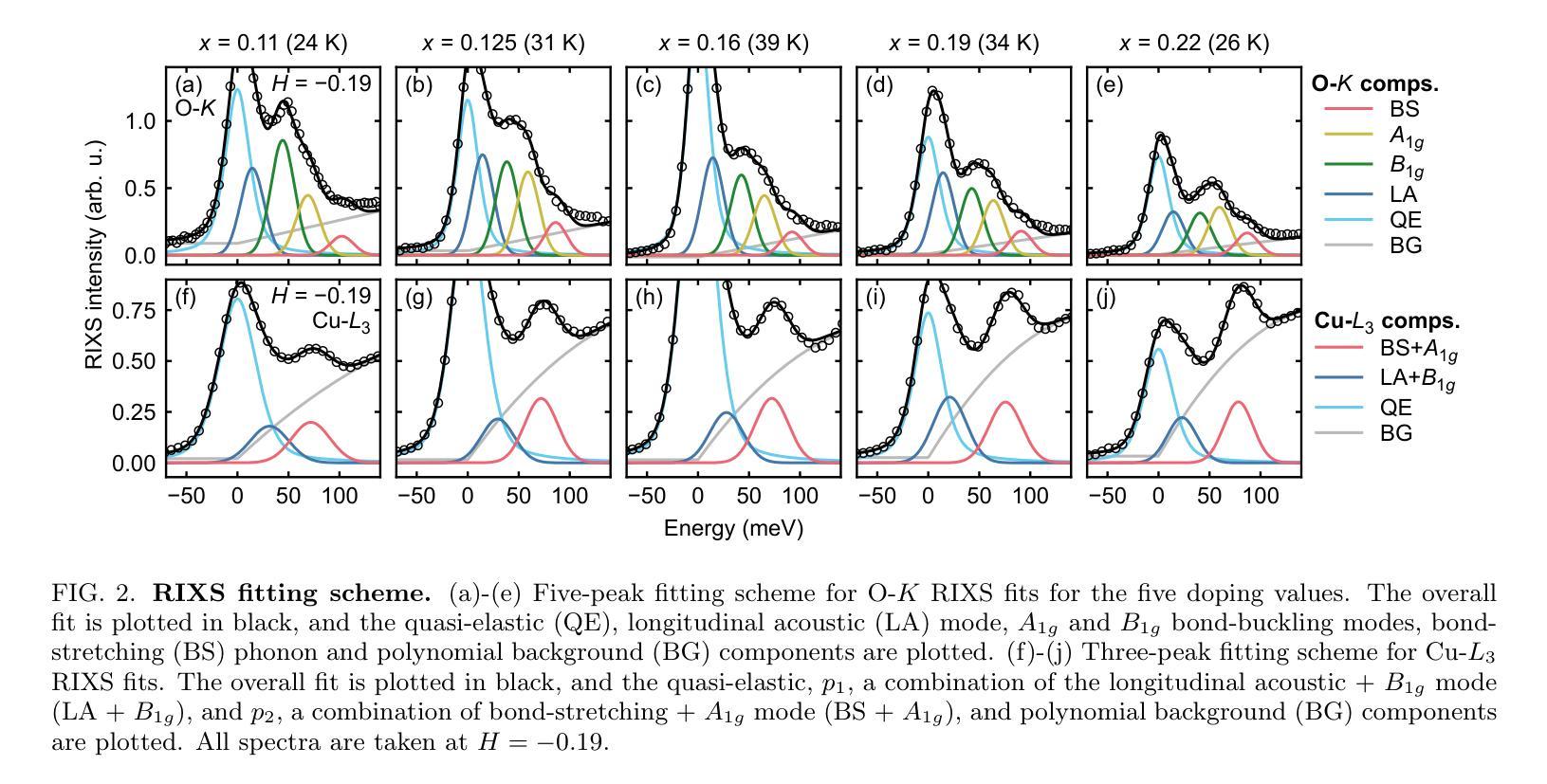
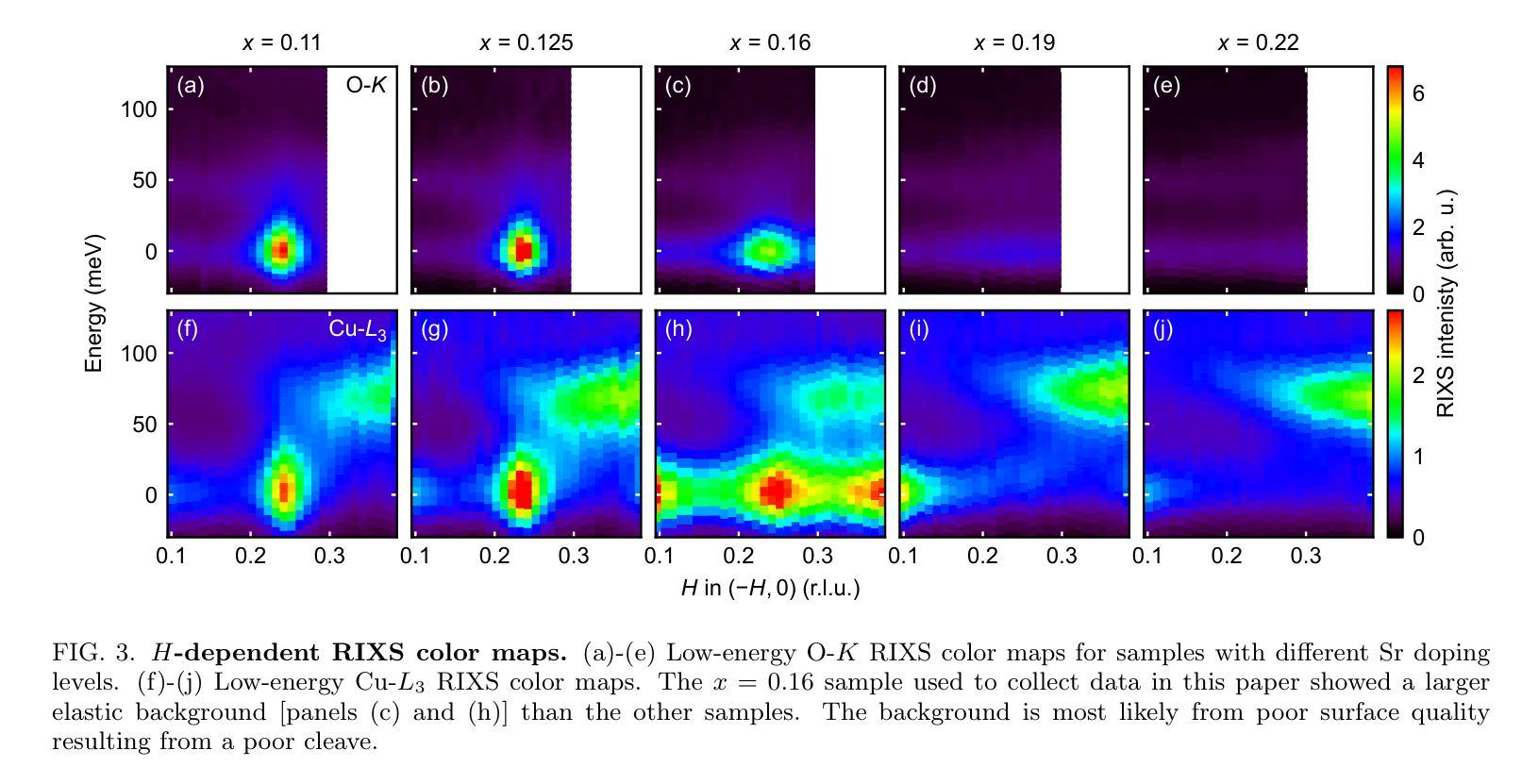
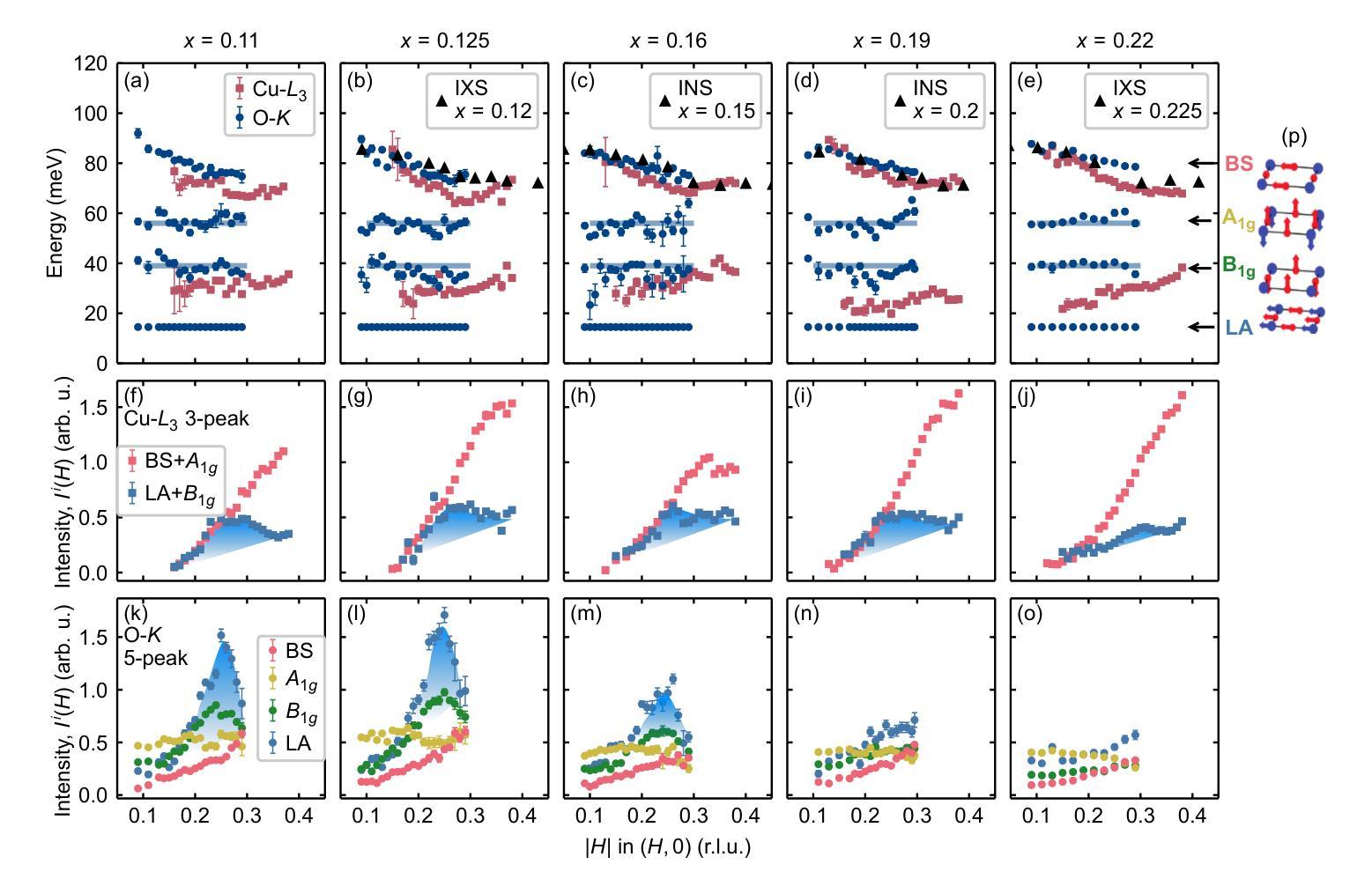
Cuprate superconductors show various collective charge correlations that are intimately connected with their electronic properties. In particular, charge order in the form of an incommensurate charge density wave (CDW) order with an in-plane wavevector $\delta_{\text{CDW}} \approx $ 0.23–0.35~r.l.u. appears to be universally present. In addition to CDW, dynamic charge density fluctuations (CDF) are also present with wavevectors comparable to $\delta_{\text{CDW}}$. CDFs are present up to $\sim300;$K and have relatively short correlation lengths of $\xi \sim 20$;\AA. Here we use Cu-$L_3$ and O-$K$ resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) to study the doping dependence of CDW and CDFs in La${2-x}$Sr$x$CuO$4$. We fit our data with (quasi)elastic peaks resulting from the CDW and up to four inelastic modes associated with oxygen phonons that can be strongly coupled to the CDFs. Our analysis allows us to separate the charge correlations into three components: the CDW with wavevector $\delta{4a-\text{CDW}} \approx 0.24$ and two CDF components with $\delta{4a-\text{CDF}} \approx 0.24$ and $\delta{3a-\text{CDF}} \approx 0.30$. We find that for $T \approx T_c$ the CDW coexists with the CDFs for dopings near $x=p \sim 1/8$. The $4a$-CDW disappears beyond $x=0.16$ and the $4a$-CDF beyond $x=0.19$, leaving only a weak $3a$-CDF at the highest doping studied, $x=0.22$. Our data suggest that low-energy charge fluctuations exist up to doping $x=0.19=p^{\star}$, where the pseudogap disappears, however, we find no evidence that they are associated with a quantum critical point.
在这篇文章中,研究了铜酸盐超导体中的集体电荷关联与电子特性之间的联系。特别地,以非公度电荷密度波(CDW)的形式出现的电荷序似乎普遍存在,其平面波矢量约为$\delta_{\text{CDW}} \approx 0.23–0.35$相对晶格单位。除了CDW之外,还存在动态电荷密度波动(CDF),其波矢量与$\delta_{\text{CDW}}$相当。CDF存在于高达$\sim300$K的温度下,并且具有相对较短的相干长度$\xi \sim 20$;\AA。在这里,我们使用Cu-$L_3$和O-$K$共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)来研究La${2-x}$Sr$x$CuO$4$中CDW和CDF的掺杂依赖性。我们的数据拟合了由CDW产生的(准)弹性峰以及与氧声子相关的四个非弹性模式,这些模式可以与CDF强烈耦合。我们的分析使我们能够将电荷关联分为三部分:具有波矢$\delta{4a-\text{CDW}} \approx 0.24$的CDW以及两个具有$\delta{4a-\text{CDF}} \approx 0.24$和$\delta{3a-\text{CDF}} \approx 0.30$的CDF成分。我们发现,在接近临界温度$T_c$时,对于掺杂接近$x=p \sim 1/8$的情况,CDW与CDF共存。当掺杂超过$x=0.16$时,$4a$-CDW消失,当掺杂超过$x=0.19$时,$4a$-CDF消失,只留下最高掺杂水平下的微弱$3a$-CDF。我们的数据表明,低能电荷波动存在于掺杂到$x=0.19=p^{\star}$的情况中,在那里伪间隙消失,然而我们没有发现它们与量子临界点相关的证据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用Cu-L3和O-K共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)研究La2-xSrxCuO4中电荷密度波(CDW)和电荷密度涨落(CDF)的掺杂依赖性。分析发现CDW和CDF在接近Tc温度时共存,且掺杂量接近x=p~1/8时尤为明显。CDF组分随掺杂量的变化而消失,但没有证据表明它们与量子临界点有关。
Key Takeaways
- Cuprate superconductors展现出集体电荷关联,与电子属性紧密相关。
- 存在一种称为电荷密度波(CDW)的现象,似乎普遍存在。
- 除了CDW,还存在动态电荷密度涨落(CDF),其波矢与CDW相当。
- 使用Cu-L3和O-K共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)研究La2-xSrxCuO4中的CDW和CDF的掺杂依赖性。
- CDW和CDF在接近临界温度Tc时共存,特定掺杂浓度下尤为明显。
- CDF组分随掺杂浓度的变化而消失。
- 没有证据表明CDF与量子临界点有关。
点此查看论文截图

Patient-Adaptive Focused Transmit Beamforming using Cognitive Ultrasound
Authors:Wessel L. van Nierop, Oisín Nolan, Tristan S. W. Stevens, Ruud J. G. van Sloun
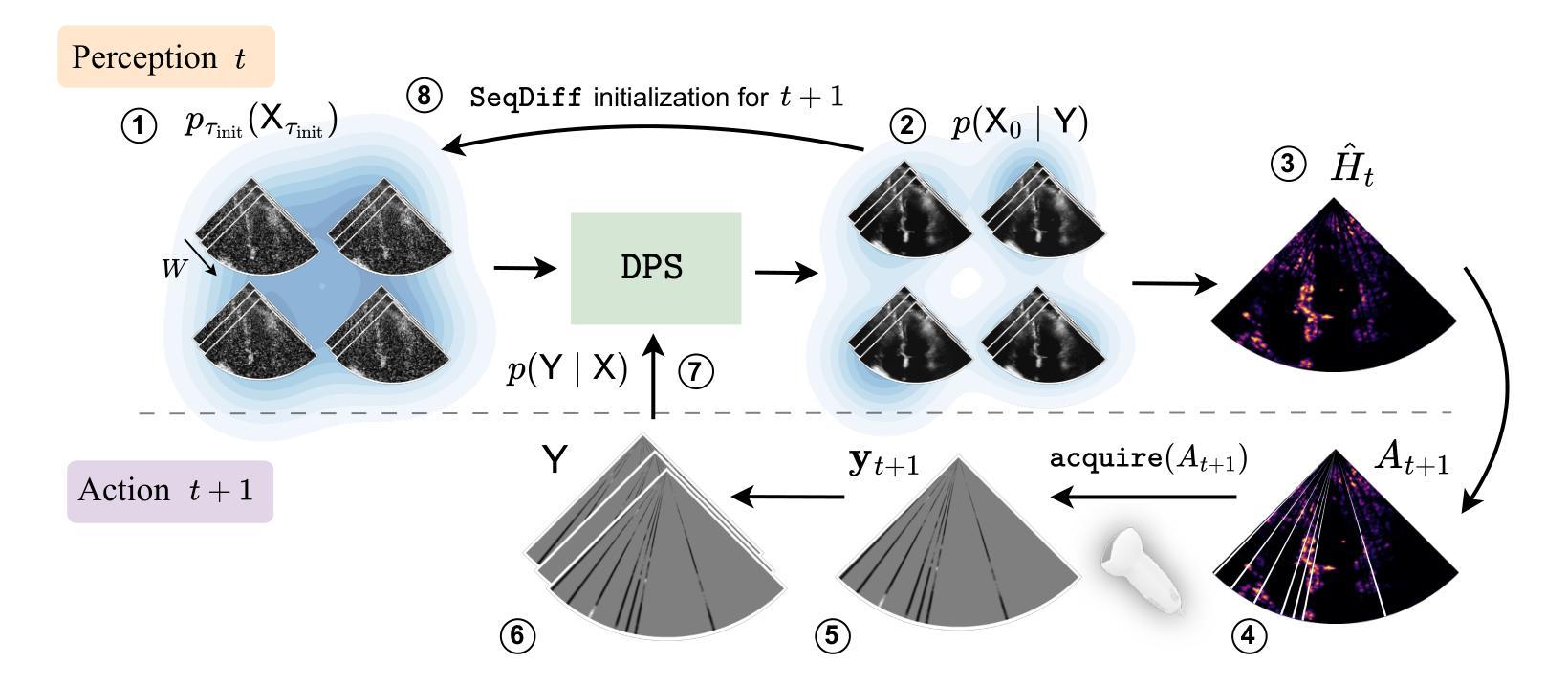
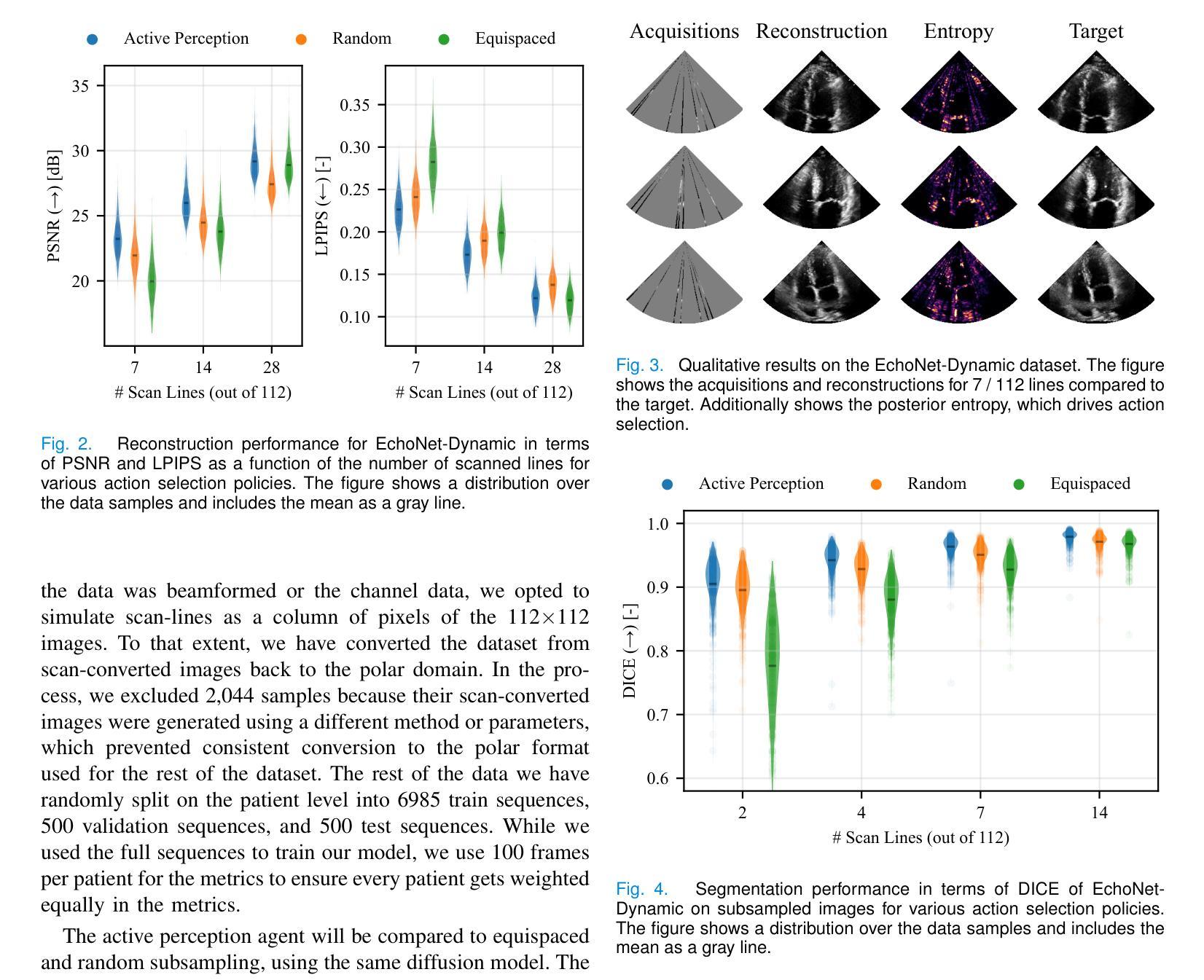
Focused transmit beamforming is the most commonly used acquisition scheme for echocardiograms, but suffers from relatively low frame rates, and in 3D, even lower volume rates. Fast imaging based on unfocused transmits has disadvantages such as motion decorrelation and limited harmonic imaging capabilities. This work introduces a patient-adaptive focused transmit scheme that has the ability to drastically reduce the number of transmits needed to produce a high-quality ultrasound image. The method relies on posterior sampling with a temporal diffusion model to perceive and reconstruct the anatomy based on partial observations, while subsequently taking an action to acquire the most informative transmits. This active perception modality outperforms random and equispaced subsampling on the 2D EchoNet-Dynamic dataset and a 3D Philips dataset, where we actively select focused elevation planes. Furthermore, we show it achieves better performance in terms of generalized contrast-to-noise ratio when compared to the same number of diverging waves transmits on three in-house echocardiograms. Additionally, we can estimate ejection fraction using only 2% of the total transmits and show that the method is robust to outlier patients. Finally, our method can be run in real-time on GPU accelerators from 2023. The code is publicly available at https://tue-bmd.github.io/ulsa/
聚焦发射波束形成是最常用的超声心动图采集方案,但其帧率相对较低,在3D中体积率更低。基于非聚焦发射的快速成像存在运动去相关和谐波成像能力有限等缺点。这项工作引入了一种病人自适应的聚焦发射方案,能够大大减少产生高质量超声图像所需要的发射次数。该方法依赖于后采样和时序扩散模型,根据部分观察来感知和重建结构,然后采取行动获取最具信息量的发射。这种主动感知模式在2D EchoNet-Dynamic数据集和3D飞利浦数据集上优于随机和等距子采样,我们主动选择聚焦的升降平面。此外,我们展示其在与三种内部超声心动图的相同发散波发射数量相比时,在广义对比度噪声比方面表现更好。另外,我们仅使用总发射次数的2%来估计射血分数,并证明该方法对于异常患者具有稳健性。最后,我们的方法可以在2023年的GPU加速器上实时运行。代码公开在https://tue-bmd.github.io/ulsa/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于自适应传输的超声成像技术能有效减少高质量超声图像所需的传输次数。该方法结合后采样和时序扩散模型,能重建器官结构,同时选择性获取信息最丰富的传输数据。该方法在二维和三维数据集上均表现优越,性能优于随机和均匀间隔采样技术。此外,该技术还具备实时运行能力,可在GPU加速器上实现。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像中常用的聚焦传输束形成技术存在帧率较低的问题,特别是在三维情况下体积率更低。
- 基于非聚焦传输的快速成像存在运动去相关和谐波成像能力受限的缺点。
- 新技术结合后采样和时序扩散模型,实现患者自适应的聚焦传输方案,能显著提高超声图像质量并减少必要的传输次数。
- 该技术在二维和三维数据集上的性能优于随机和均匀间隔子采样技术。
- 技术可实时运行,能在GPU加速器上实现高性能。估计喷射分数仅需使用总传输数据的2%。具备稳健性,能够适应不同的患者情况。
点此查看论文截图


Hierarchical Variable Importance with Statistical Control for Medical Data-Based Prediction
Authors:Joseph Paillard, Antoine Collas, Denis A. Engemann, Bertrand Thirion
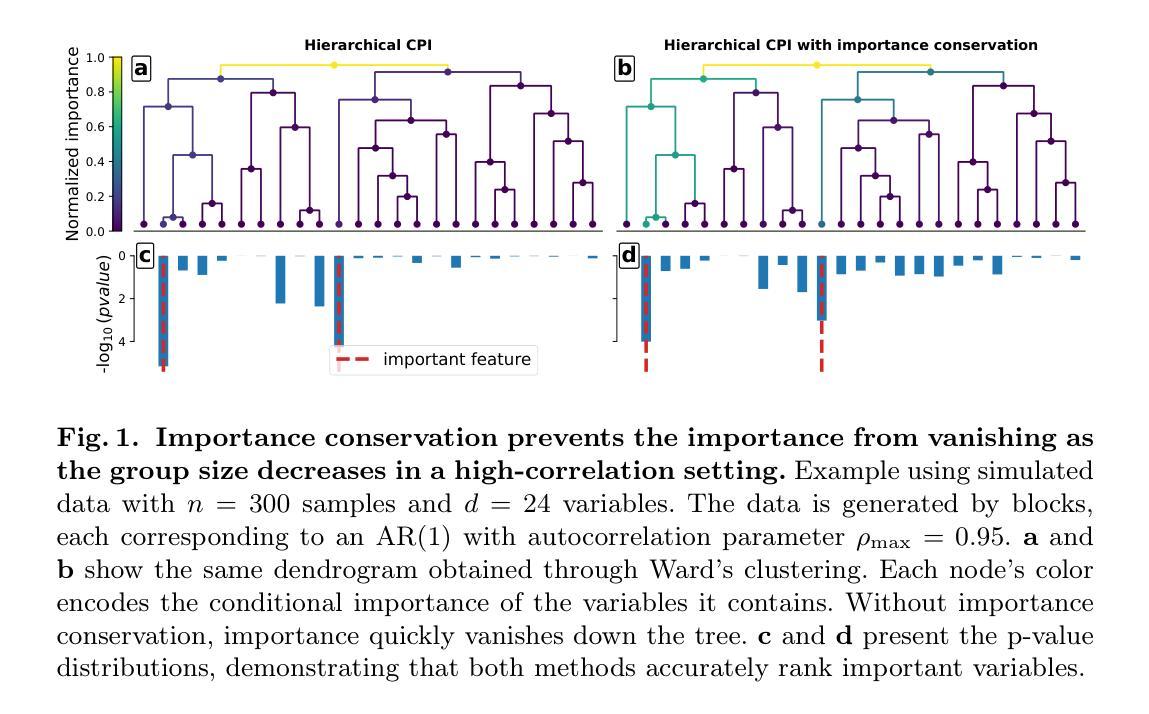
Recent advances in machine learning have greatly expanded the repertoire of predictive methods for medical imaging. However, the interpretability of complex models remains a challenge, which limits their utility in medical applications. Recently, model-agnostic methods have been proposed to measure conditional variable importance and accommodate complex non-linear models. However, they often lack power when dealing with highly correlated data, a common problem in medical imaging. We introduce Hierarchical-CPI, a model-agnostic variable importance measure that frames the inference problem as the discovery of groups of variables that are jointly predictive of the outcome. By exploring subgroups along a hierarchical tree, it remains computationally tractable, yet also enjoys explicit family-wise error rate control. Moreover, we address the issue of vanishing conditional importance under high correlation with a tree-based importance allocation mechanism. We benchmarked Hierarchical-CPI against state-of-the-art variable importance methods. Its effectiveness is demonstrated in two neuroimaging datasets: classifying dementia diagnoses from MRI data (ADNI dataset) and analyzing the Berger effect on EEG data (TDBRAIN dataset), identifying biologically plausible variables.
机器学习领域的最新进展极大地扩展了医学成像预测方法。然而,复杂模型的解释性仍然是一个挑战,这限制了它们在医学应用中的实用性。最近,一些模型无关的方法被提出来测量条件变量重要性并适应复杂的非线性模型。然而,在处理高度相关的数据时,它们往往缺乏效力,这在医学成像中是一个常见问题。我们介绍了Hierarchical-CPI,这是一种模型无关的变量重要性度量方法,它将推理问题表述为发现一组共同预测结果的变量。通过沿着层次树探索子组,它可以在计算上保持可行性,同时也享受明确的家族误差率控制。此外,我们解决了高相关性下条件重要性消失的问题,采用基于树的的重要性分配机制。我们将Hierarchical-CPI与最先进的变量重要性方法进行了比较。其在两个神经成像数据集上的有效性得到了验证:从MRI数据中分类痴呆诊断(ADNI数据集)和分析EEG数据的伯格效应(TDBRAIN数据集),识别出生物上合理的变量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习在医学成像预测方法上的最新进展大大扩展了预测方法的范围。然而,复杂模型的解释性仍是挑战,限制了其在医疗应用中的实用性。本文提出一种分层条件预测重要性(Hierarchical-CPI)模型,针对复杂非线性模型进行条件变量重要性度量,尤其适用于处理医学成像中常见的高相关性数据问题。通过分层树结构探索变量子组,该方法计算效率高且能控制家族误差率。此外,通过树状重要性分配机制解决高相关性下的条件重要性消失问题。在神经成像数据集上的实验表明,该方法在分类痴呆诊断和EEG数据伯格效应分析中的有效性,并能识别出具有生物学意义的变量。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习在医学成像预测方法上取得最新进展,但复杂模型的解释性仍是挑战。
- 现有模型在处理高相关性数据时的效能受限。
- 引入分层条件预测重要性(Hierarchical-CPI)模型,能有效处理复杂非线性模型和高相关性数据。
- Hierarchical-CPI通过将推理问题定位为发现联合预测结果的变量组来进行工作。
- Hierarchical-CPI通过分层树结构进行变量子组的探索,保持计算效率并控制家族误差率。
- Hierarchical-CPI通过树状重要性分配机制解决条件重要性在高相关性环境下的消失问题。
点此查看论文截图

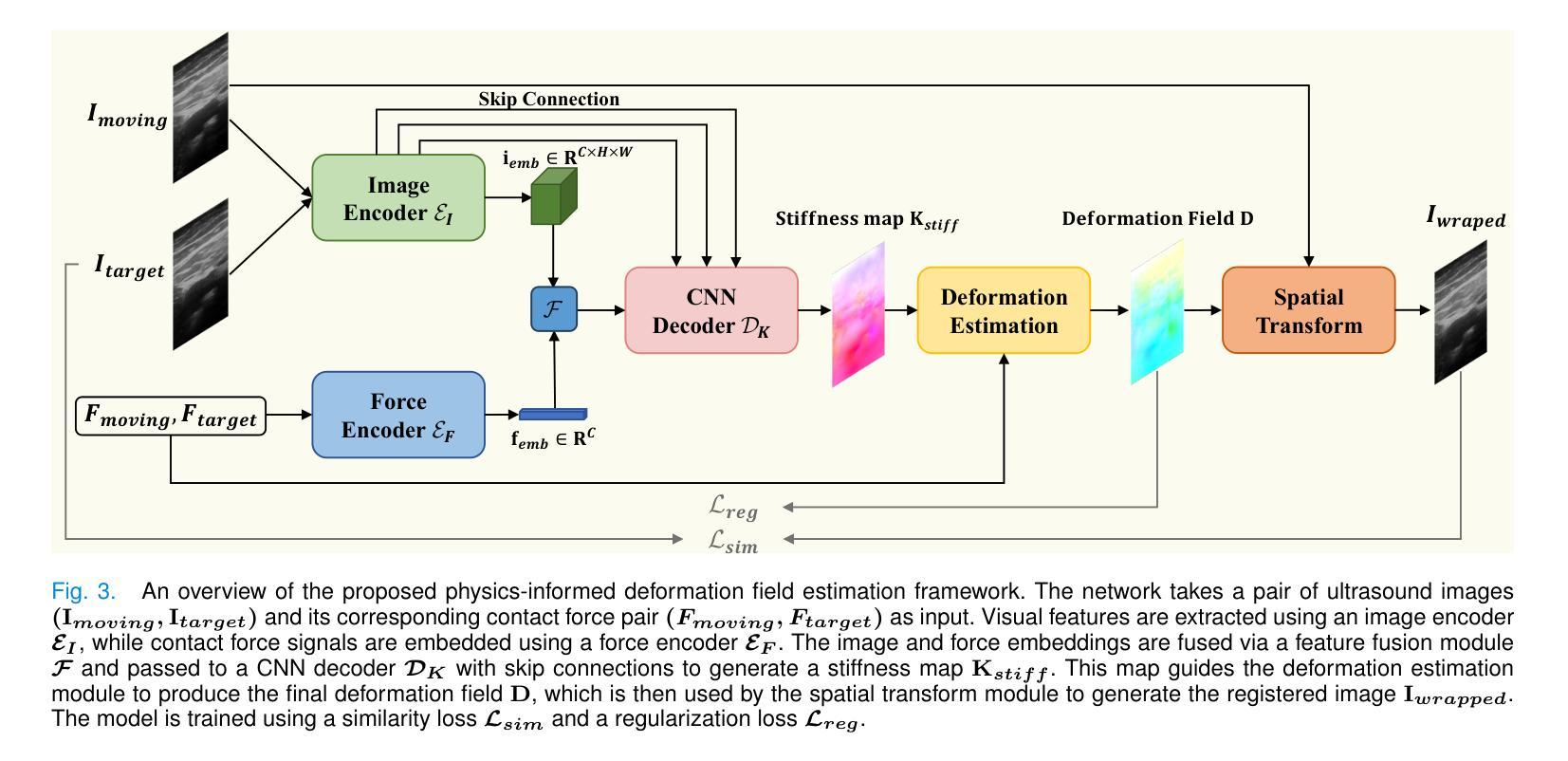
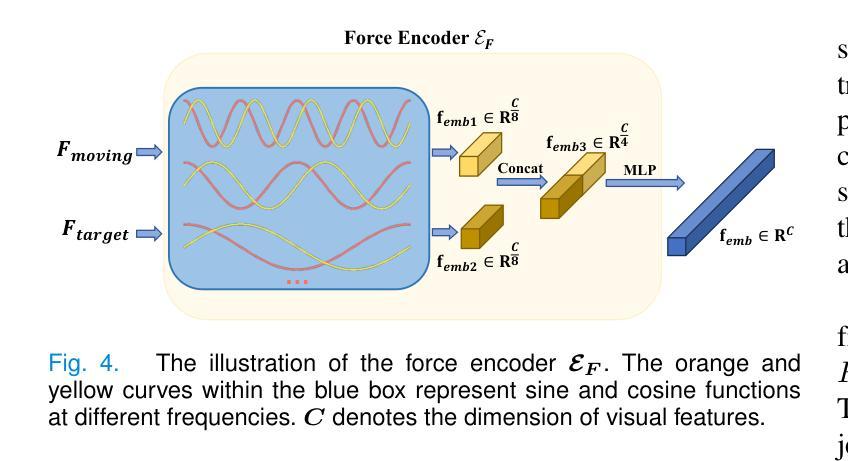
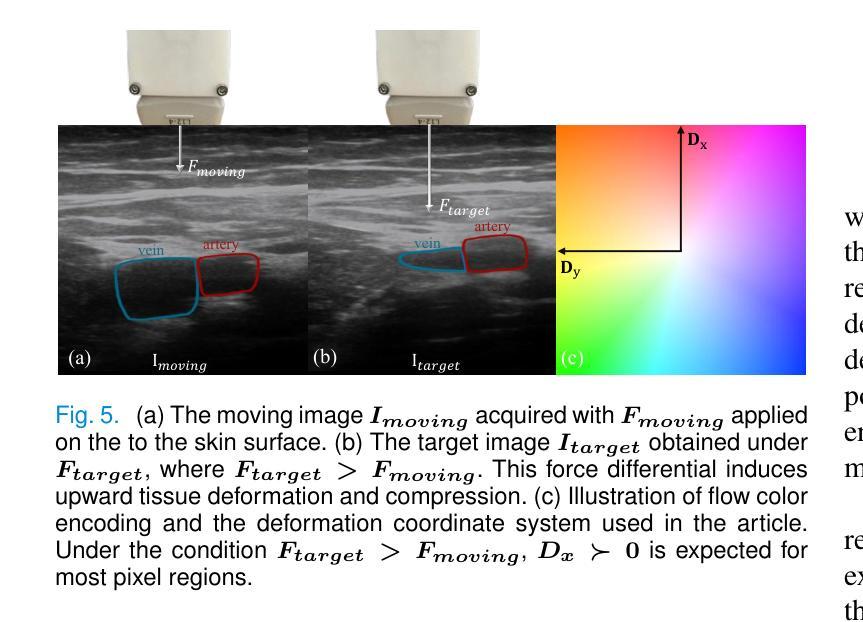
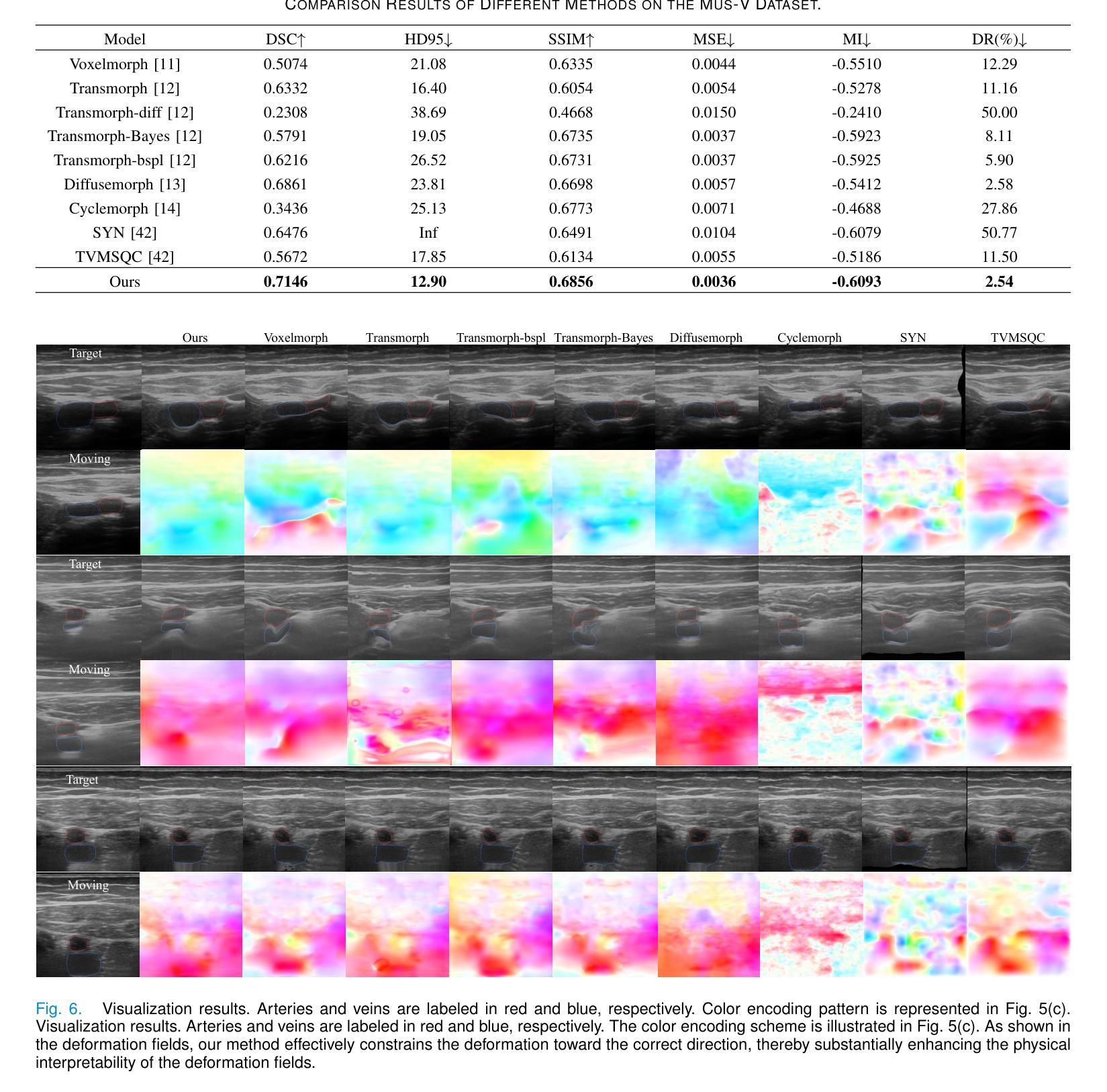
PADReg: Physics-Aware Deformable Registration Guided by Contact Force for Ultrasound Sequences
Authors:Yimeng Geng, Mingyang Zhao, Fan Xu, Guanglin Cao, Gaofeng Meng, Hongbin Liu
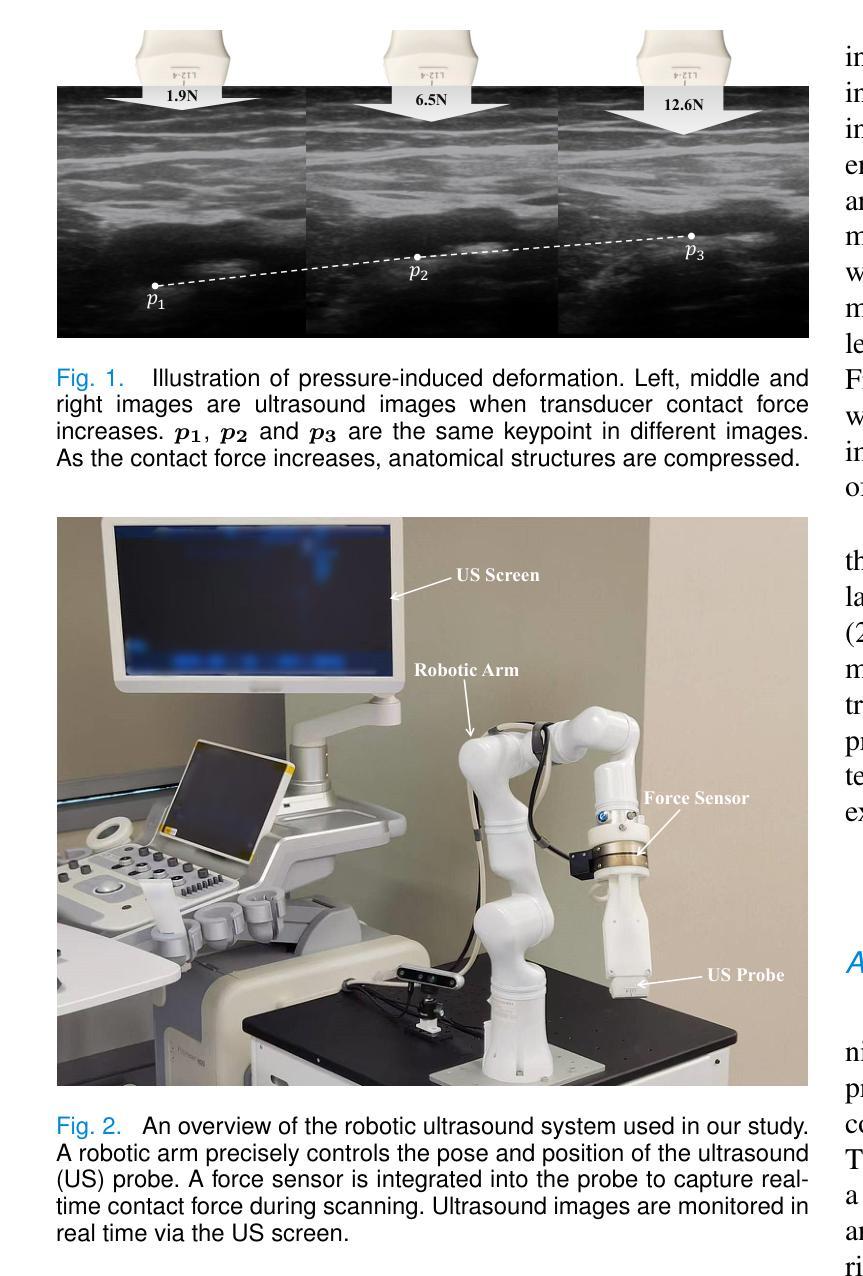
Ultrasound deformable registration estimates spatial transformations between pairs of deformed ultrasound images, which is crucial for capturing biomechanical properties and enhancing diagnostic accuracy in diseases such as thyroid nodules and breast cancer. However, ultrasound deformable registration remains highly challenging, especially under large deformation. The inherently low contrast, heavy noise and ambiguous tissue boundaries in ultrasound images severely hinder reliable feature extraction and correspondence matching. Existing methods often suffer from poor anatomical alignment and lack physical interpretability. To address the problem, we propose PADReg, a physics-aware deformable registration framework guided by contact force. PADReg leverages synchronized contact force measured by robotic ultrasound systems as a physical prior to constrain the registration. Specifically, instead of directly predicting deformation fields, we first construct a pixel-wise stiffness map utilizing the multi-modal information from contact force and ultrasound images. The stiffness map is then combined with force data to estimate a dense deformation field, through a lightweight physics-aware module inspired by Hooke’s law. This design enables PADReg to achieve physically plausible registration with better anatomical alignment than previous methods relying solely on image similarity. Experiments on in-vivo datasets demonstrate that it attains a HD95 of 12.90, which is 21.34% better than state-of-the-art methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/evelynskip/PADReg.
超声形变配准(Ultrasound deformable registration)是估计两个形变超声图像之间的空间变换的过程,这对捕捉甲状腺结节和乳腺癌等疾病的生物力学特性,提高诊断准确性至关重要。然而,超声形变配准仍然是一项艰巨的任务,特别是在大变形情况下。超声图像中固有的对比度低、噪声严重和组织边界模糊等问题严重阻碍了可靠的特征提取和对应关系匹配。现有方法通常存在解剖结构对齐不良和缺乏物理可解释性的问题。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了PADReg,这是一个受接触力引导的物理感知形变配准框架。PADReg利用机器人超声系统同步测量的接触力作为物理先验来约束配准过程。具体来说,我们不是直接预测变形场,而是首先利用接触力和超声图像的多模态信息构建像素级的刚度图。然后,将刚度图与力数据相结合,通过受Hooke定律启发的轻量化物理感知模块来估计密集的变形场。这种设计使PADReg能够实现物理上合理的配准,与仅依赖图像相似性的方法相比,达到更好的解剖结构对齐效果。在真实人体数据集上的实验表明,其实现了HD95为12.90,比最新方法提高了21.34%。源代码可在https://github.com/evelynskip/PADReg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文介绍了超声形变配准技术在医学图像领域的重要性,特别是在甲状腺结节和乳腺癌等疾病的诊断中。针对超声形变配准在大形变下面临的挑战,提出了一种结合接触力测量的物理感知形变配准框架PADReg。该框架通过构建像素级的刚度图来估计密集形变场,实现了具有物理合理性的配准,并获得了更好的解剖学对齐效果。
Key Takeaways
- 超声形变配准对于捕捉生物力学特性、提高甲状腺结节和乳腺癌等疾病的诊断准确性至关重要。
- 现有超声形变配准方法在大形变下面临挑战,主要由于超声图像中的低对比度、强噪声和模糊组织边界。
- PADReg框架利用接触力作为物理先验来约束配准,通过同步接触力测量增强了配准的准确性。
- PADReg通过构建像素级的刚度图并结合力数据来估计密集形变场,实现物理合理的配准。
- 与仅依赖图像相似性的方法相比,PADReg在解剖学对齐方面表现出更好的效果。
- 在实际数据集上的实验表明,PADReg达到了较高的配准精度,优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

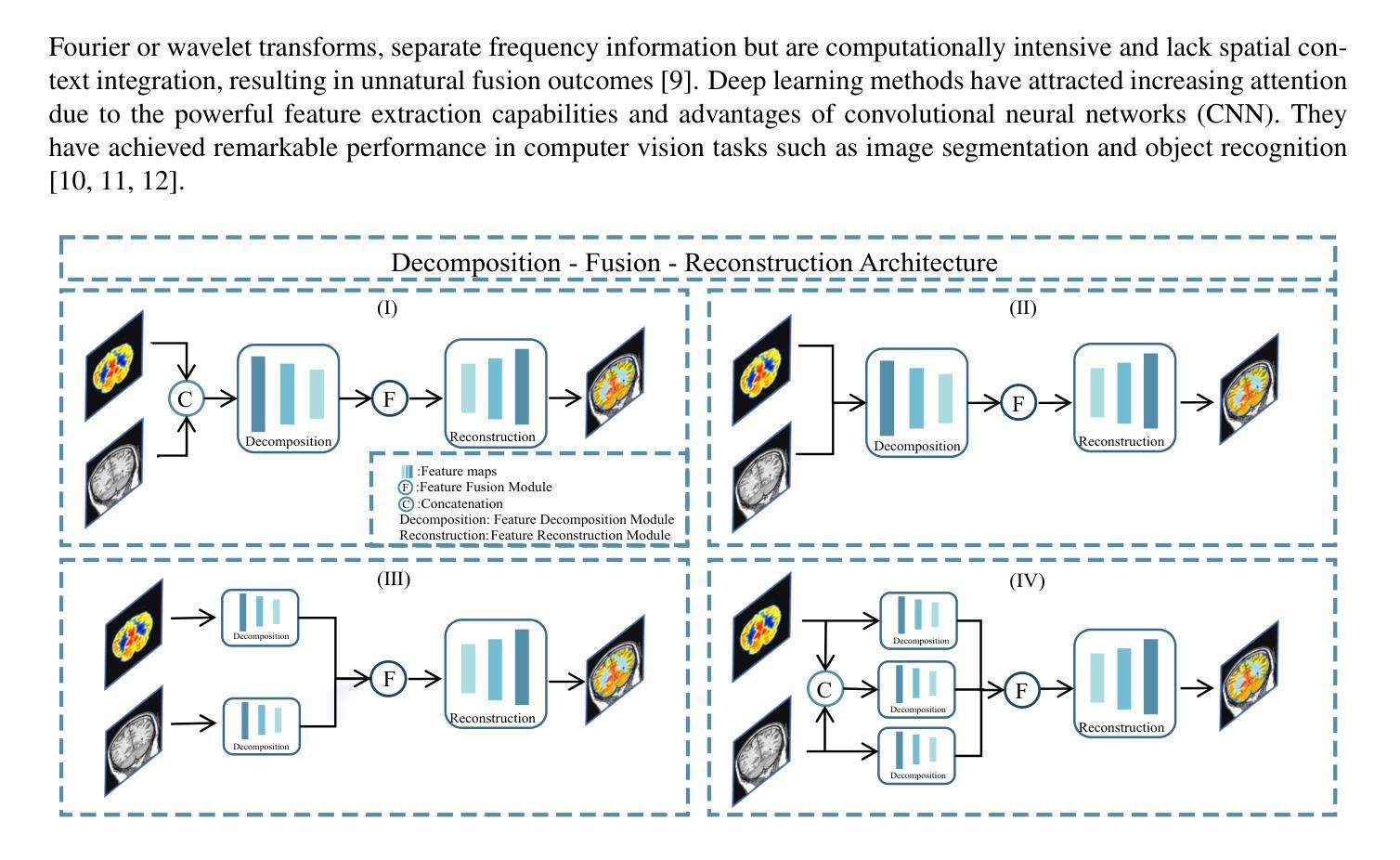
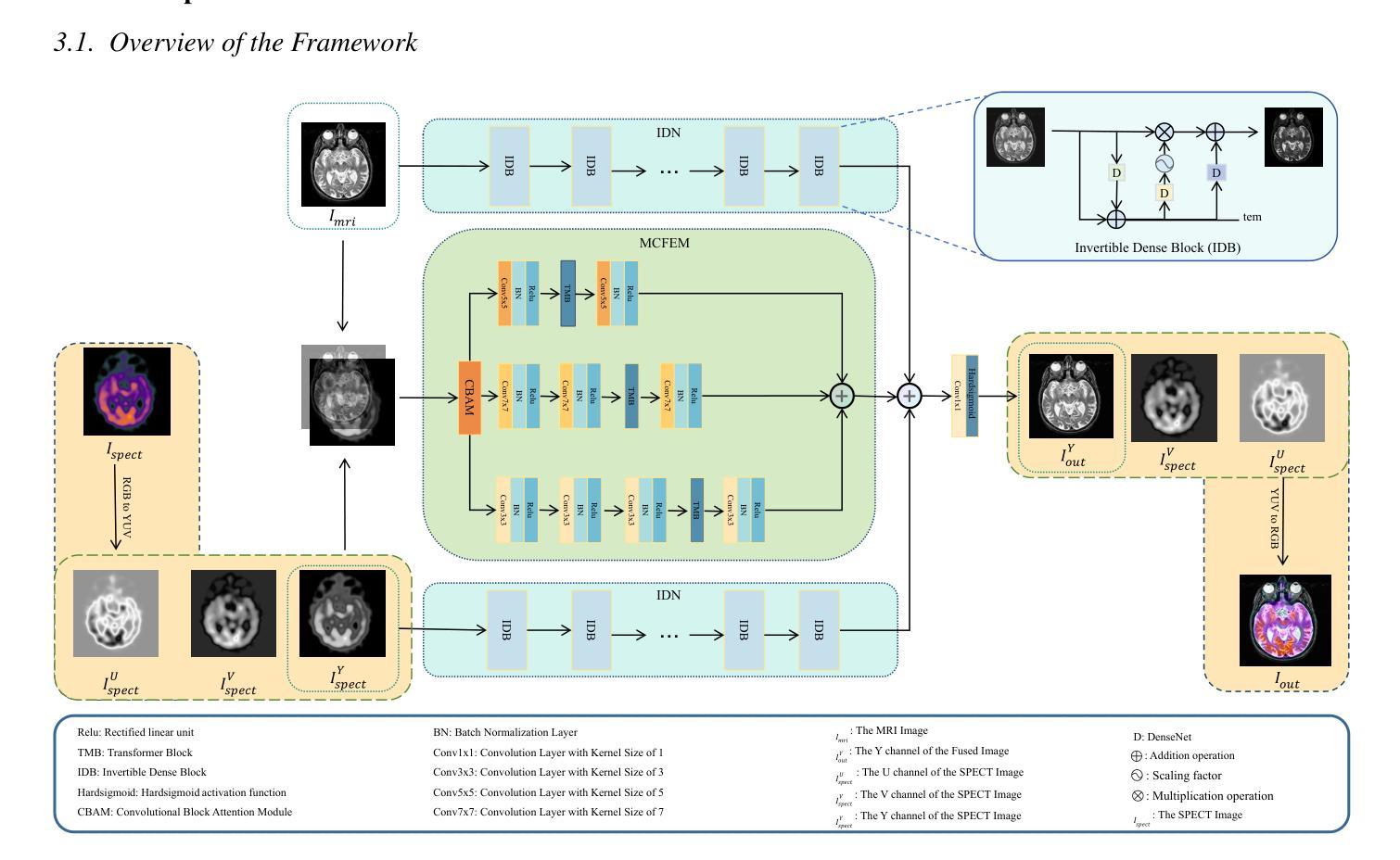
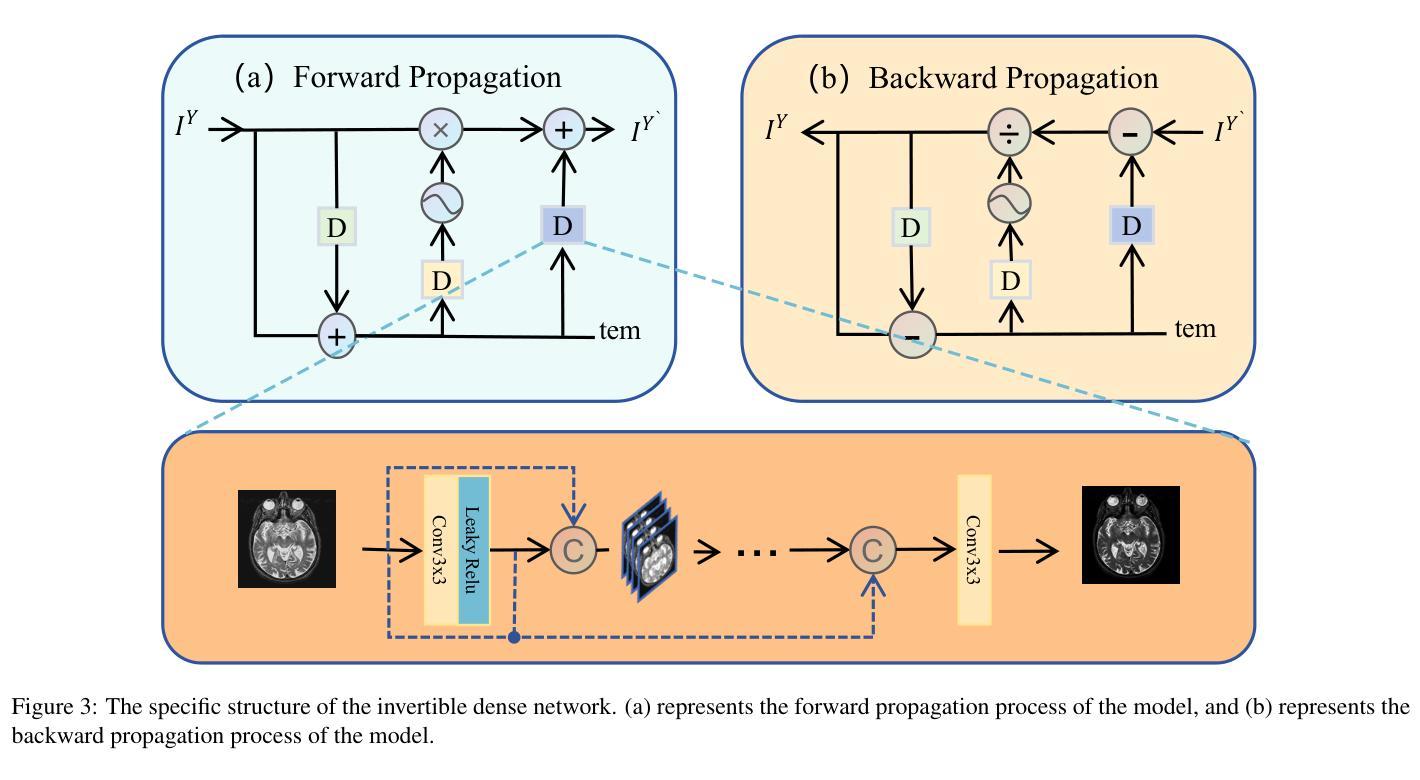
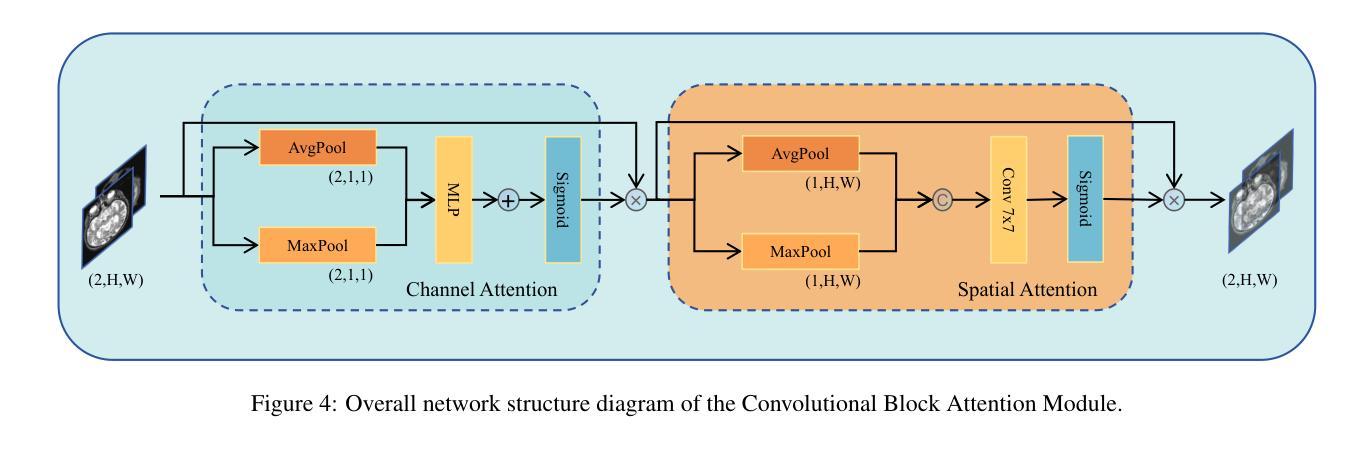
MMIF-AMIN: Adaptive Loss-Driven Multi-Scale Invertible Dense Network for Multimodal Medical Image Fusion
Authors:Tao Luo, Weihua Xu
Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) aims to integrate images from different modalities to produce a comprehensive image that enhances medical diagnosis by accurately depicting organ structures, tissue textures, and metabolic information. Capturing both the unique and complementary information across multiple modalities simultaneously is a key research challenge in MMIF. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a novel image fusion method, MMIF-AMIN, which features a new architecture that can effectively extract these unique and complementary features. Specifically, an Invertible Dense Network (IDN) is employed for lossless feature extraction from individual modalities. To extract complementary information between modalities, a Multi-scale Complementary Feature Extraction Module (MCFEM) is designed, which incorporates a hybrid attention mechanism, convolutional layers of varying sizes, and Transformers. An adaptive loss function is introduced to guide model learning, addressing the limitations of traditional manually-designed loss functions and enhancing the depth of data mining. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MMIF-AMIN outperforms nine state-of-the-art MMIF methods, delivering superior results in both quantitative and qualitative analyses. Ablation experiments confirm the effectiveness of each component of the proposed method. Additionally, extending MMIF-AMIN to other image fusion tasks also achieves promising performance.
多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)旨在将不同模态的图像进行融合,生成一幅全面的图像,该图像能准确地描绘出器官结构、组织纹理和代谢信息,从而提高医学诊断水平。在MMIF中,同时捕获多种模态的独有和互补信息是一项关键的研究挑战。为了应对这一挑战,本文提出了一种新的图像融合方法MMIF-AMIN,该方法具有能够有效提取这些独特和互补特征的新架构。具体来说,采用可逆密集网络(IDN)从各个模态进行无损特征提取。为了提取模态之间的互补信息,设计了一种多尺度互补特征提取模块(MCFEM),该模块结合了混合注意力机制、不同大小的卷积层和Transformer。引入自适应损失函数来指导模型学习,解决传统手动设计的损失函数的局限性,提高数据挖掘的深度。大量实验表明,MMIF-AMIN在定量和定性分析方面都优于九种最先进的MMIF方法,取得了优越的结果。消融实验证实了该方法各组成部分的有效性。此外,将MMIF-AMIN扩展到其他图像融合任务也取得了有前景的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures,conference
Summary
多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)旨在融合不同模态的图像,生成全面图像,准确描绘器官结构、组织纹理和代谢信息,提高医学诊断的准确性。本文提出一种新颖的MMIF方法MMIF-AMIN,采用新型架构有效提取独特和互补特征。使用Invertible Dense Network(IDN)进行无损特征提取,设计Multi-scale Complementary Feature Extraction Module(MCFEM)提取模态间的互补信息。引入自适应损失函数指导模型学习,解决传统手动设计损失函数的局限性,增强数据挖掘深度。实验证明MMIF-AMIN优于九种最新MMIF方法,在定量和定性分析中均表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像融合旨在提高医学诊断的准确性,通过融合不同模态的图像生成全面图像。
- MMIF-AMIN是一种新颖的医学图像融合方法,采用新型架构提取独特和互补特征。
- Invertible Dense Network(IDN)用于无损特征提取。
- Multi-scale Complementary Feature Extraction Module(MCFEM)设计用于提取模态间的互补信息。
- 引入自适应损失函数,解决传统损失函数的局限性,增强数据挖掘深度。
- MMIF-AMIN在实验中表现出优异性能,优于其他九种最新MMIF方法。
点此查看论文截图

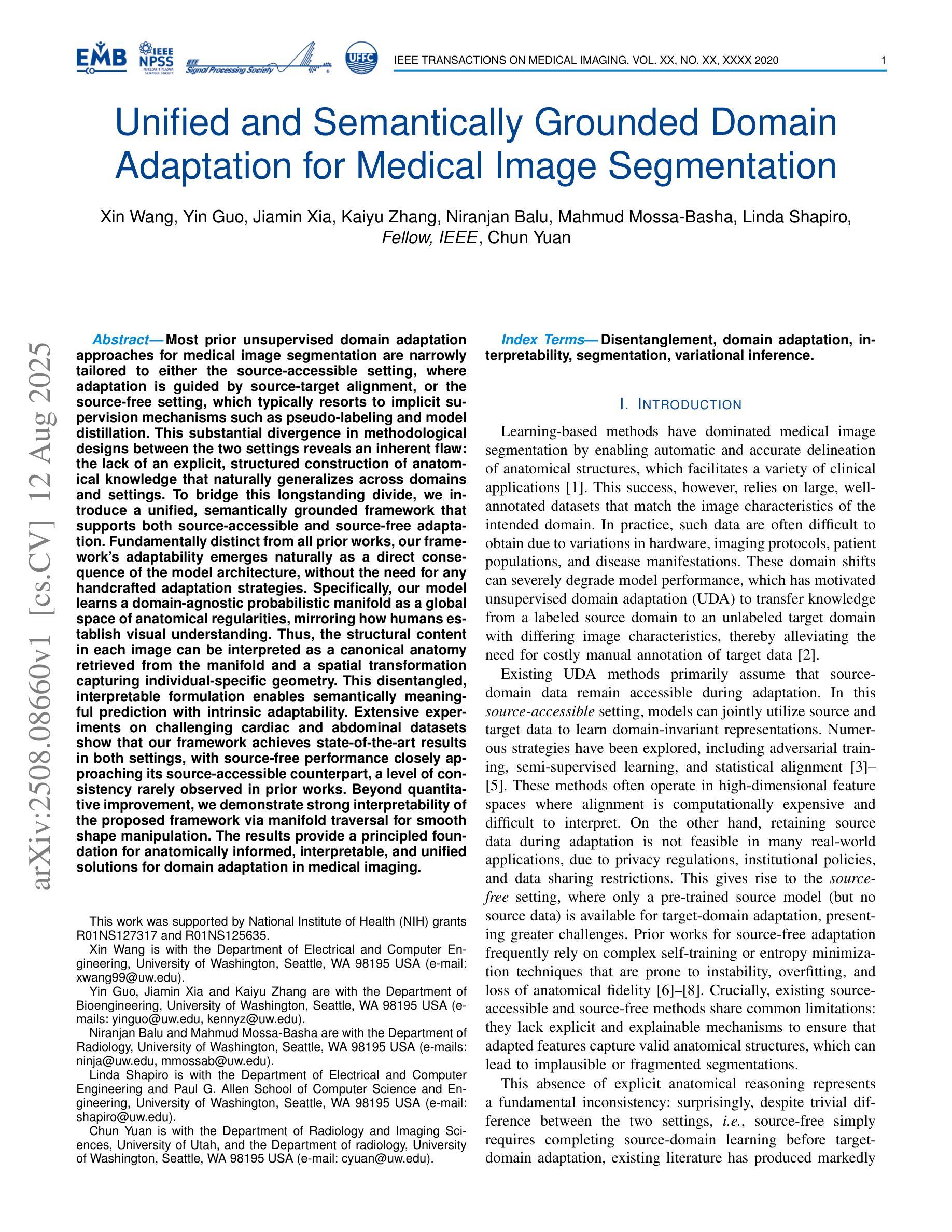
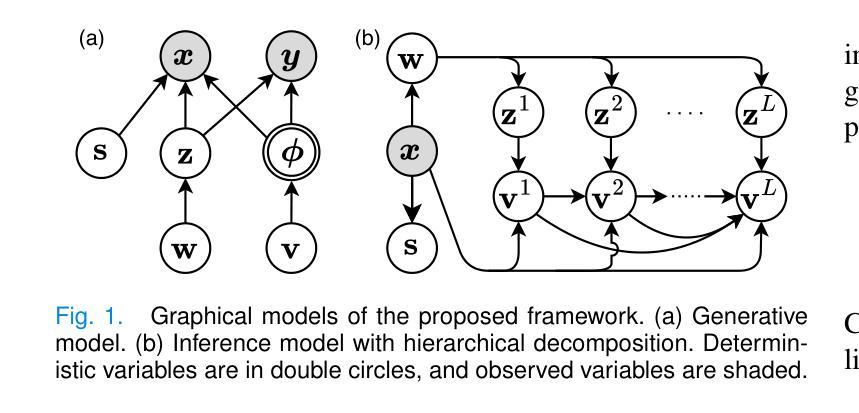
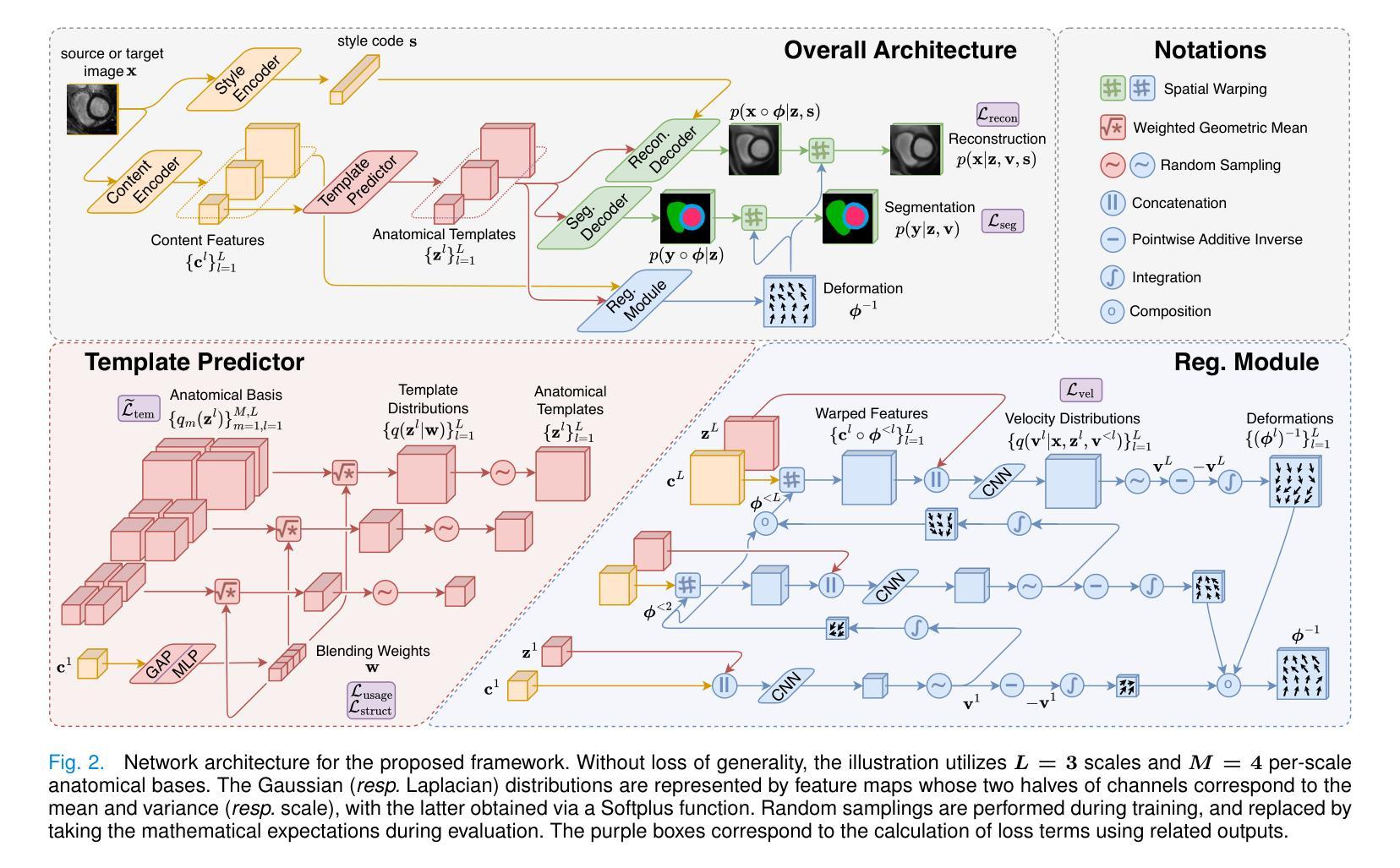
Unified and Semantically Grounded Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xin Wang, Yin Guo, Jiamin Xia, Kaiyu Zhang, Niranjan Balu, Mahmud Mossa-Basha, Linda Shapiro, Chun Yuan
Most prior unsupervised domain adaptation approaches for medical image segmentation are narrowly tailored to either the source-accessible setting, where adaptation is guided by source-target alignment, or the source-free setting, which typically resorts to implicit supervision mechanisms such as pseudo-labeling and model distillation. This substantial divergence in methodological designs between the two settings reveals an inherent flaw: the lack of an explicit, structured construction of anatomical knowledge that naturally generalizes across domains and settings. To bridge this longstanding divide, we introduce a unified, semantically grounded framework that supports both source-accessible and source-free adaptation. Fundamentally distinct from all prior works, our framework’s adaptability emerges naturally as a direct consequence of the model architecture, without the need for any handcrafted adaptation strategies. Specifically, our model learns a domain-agnostic probabilistic manifold as a global space of anatomical regularities, mirroring how humans establish visual understanding. Thus, the structural content in each image can be interpreted as a canonical anatomy retrieved from the manifold and a spatial transformation capturing individual-specific geometry. This disentangled, interpretable formulation enables semantically meaningful prediction with intrinsic adaptability. Extensive experiments on challenging cardiac and abdominal datasets show that our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in both settings, with source-free performance closely approaching its source-accessible counterpart, a level of consistency rarely observed in prior works. Beyond quantitative improvement, we demonstrate strong interpretability of the proposed framework via manifold traversal for smooth shape manipulation.
在医学图像分割中,大多数先前的无监督域自适应方法主要局限于源可访问设置,其中自适应由源目标对齐引导,或者无源的设定,这通常依赖于隐式监督机制,如伪标签和模型蒸馏。这两种设置之间在方法论设计上的巨大差异揭示了一个固有的缺陷:缺乏一个明确的结构化构建解剖知识,这种知识能在不同领域和设置中自然推广。为了弥合这一长期存在的分歧,我们引入了一个统一的、语义化的框架,支持源可访问和无源的适应。与所有先前的工作根本不同,我们框架的适应性是模型架构的直接结果,无需任何手工制定的适应策略。具体来说,我们的模型学习一个域无关的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,反映人类建立视觉理解的方式。因此,每个图像的结构内容可以被解释为从流形中检索的规范解剖结构和捕捉个体特定几何的空间变换。这种解耦、可解释的公式化实现了具有内在适应性的语义上有意义的预测。在具有挑战性的心脏和腹部数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的框架在这两种设置中均达到了最新水平的结果,无源的性能接近其源可访问的对应物,这在以前的工作中很少观察到的一致性。除了定量改进之外,我们还通过流形遍历进行平滑形状操纵来展示所提出框架的强大可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像分割的无监督域适应问题,现有方法主要分为源可访问设置和源自由设置两种,缺乏明确的结构化构建解剖知识。为此,我们提出了一种统一的语义框架,支持源可访问和源自由两种适应方式。我们的模型架构自然地产生了一种适应能力,无需手工制作适应策略。通过构建一个通用的解剖概率流形空间来体现人类理解视觉的方式,我们可以从流形中检索出结构内容作为标准解剖结构,并通过空间转换捕捉个体特定的几何形状。这种解释性的公式使得预测具有内在适应性和语义意义。实验证明,我们的框架在心脏和腹部数据集上均达到了领先水平,并且在源自由设置中实现了接近源可访问设置的表现一致性。此外,我们还通过流形遍历展示了该框架的强解释性,以实现平滑的形状操控。
Key Takeaways
- 现有医学图像分割的无监督域适应方法存在局限性,分为源可访问和源自由两种设置。缺乏通用的结构化解剖知识是其中的关键问题。为解决此问题,提出了一种统一的语义框架。
- 该框架构建了一个通用的解剖概率流形空间,反映人类理解视觉的方式。结构内容被解释为从流形中检索的标准解剖结构,同时通过空间转换捕捉个体特定的几何形状。这种结构使得预测具有内在适应性和语义意义。
点此查看论文截图
Boosting Generic Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation via Diverse Teaching and Label Propagation
Authors:Wei Li, Pengcheng Zhou, Linye Ma, Wenyi Zhao, Huihua Yang
Both limited annotation and domain shift are significant challenges frequently encountered in medical image segmentation, leading to derivative scenarios like semi-supervised medical (SSMIS), semi-supervised medical domain generalization (Semi-MDG) and unsupervised medical domain adaptation (UMDA). Conventional methods are generally tailored to specific tasks in isolation, the error accumulation hinders the effective utilization of unlabeled data and limits further improvements, resulting in suboptimal performance when these issues occur. In this paper, we aim to develop a generic framework that masters all three tasks. We found that the key to solving the problem lies in how to generate reliable pseudo labels for the unlabeled data in the presence of domain shift with labeled data and increasing the diversity of the model. To tackle this issue, we employ a Diverse Teaching and Label Propagation Network (DTLP-Net) to boosting the Generic Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. Our DTLP-Net involves a single student model and two diverse teacher models, which can generate reliable pseudo-labels for the student model. The first teacher model decouple the training process with labeled and unlabeled data, The second teacher is momentum-updated periodically, thus generating reliable yet divers pseudo-labels. To fully utilize the information within the data, we adopt inter-sample and intra-sample data augmentation to learn the global and local knowledge. In addition, to further capture the voxel-level correlations, we propose label propagation to enhance the model robust. We evaluate our proposed framework on five benchmark datasets for SSMIS, UMDA, and Semi-MDG tasks. The results showcase notable improvements compared to state-of-the-art methods across all five settings, indicating the potential of our framework to tackle more challenging SSL scenarios.
在医学图像分割中,有限的标注和领域偏移是经常遇到的重大挑战,这导致了诸如半监督医学(SSMIS)、半监督医学领域泛化(Semi-MDG)和无监督医学领域适应(UMDA)等衍生场景。传统的方法通常针对特定的任务进行定制,误差积累阻碍了未标注数据的有效利用,限制了进一步的改进。当这些问题发生时,性能往往达不到最优。本文旨在开发一个能够掌握所有三个任务(SSMIS、UMDA和Semi-MDG)的通用框架。我们发现解决问题的关键在于如何在存在领域偏移和有标注数据的情况下,为未标注数据生成可靠的伪标签,并增加模型的多样性。为了解决这个问题,我们采用了多样教学标签传播网络(DTLP-Net)来提升通用半监督医学图像分割的效果。我们的DTLP-Net包括一个学生模型和两个多样化的教师模型,可以为学生模型生成可靠的伪标签。第一个教师模型将标注和未标注数据的训练过程解耦;第二个教师模型定期更新动量,从而生成可靠且多样的伪标签。为了充分利用数据中的信息,我们采用了样本间和样本内的数据增强来学习全局和局部知识。此外,为了进一步捕捉体素级的关联,我们提出了标签传播以增强模型的稳健性。我们在五个基准数据集上评估了我们提出的框架在SSMIS、UMDA和Semi-MDG任务上的表现。结果显示,与最先进的方法相比,我们的框架在所有五个设置中都取得了显著的改进,这表明我们的框架在解决更具挑战性的SSL场景时具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对医学图像分割中常见的有限标注和领域偏移两大挑战,本文提出了一种通用的框架,能够应对半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)、半监督医学领域泛化(Semi-MDG)和无监督医学领域自适应(UMDA)等任务。该框架的关键在于如何在存在领域偏移且有标注数据的情况下,为无标注数据生成可靠的伪标签,并增加模型的多样性。为此,我们采用了多样教学标签传播网络(DTLP-Net)来提升通用半监督医学图像分割的效果。该网络包括一个学生模型和两个多样化的教师模型,能够为学生模型生成可靠的伪标签。通过样本间和样本内的数据增强,我们充分利用了数据中的信息,学习全局和局部知识。此外,为了进一步提高模型对像素级关系的捕捉能力,我们引入了标签传播技术。在五个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,与最新方法相比,我们的框架在所有五个设置中都取得了显著的改进,表明其解决更复杂的SSL场景的潜力。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割面临有限标注和领域偏移的挑战,导致半监督、无监督等衍生场景的出现。
- 现有方法往往针对特定任务设计,误差累积限制了无标注数据的利用和模型的进一步改进。
- 本文提出一个通用框架,能够应对多种任务,包括SSMIS、UMDA和Semi-MDG。
- 框架的关键在于生成可靠的伪标签和增加模型多样性,采用DTLP-Net网络实现。
- 通过样本间和样本内的数据增强以及标签传播技术,提高模型的性能和鲁棒性。
- 在五个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,该框架在多种设置下均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

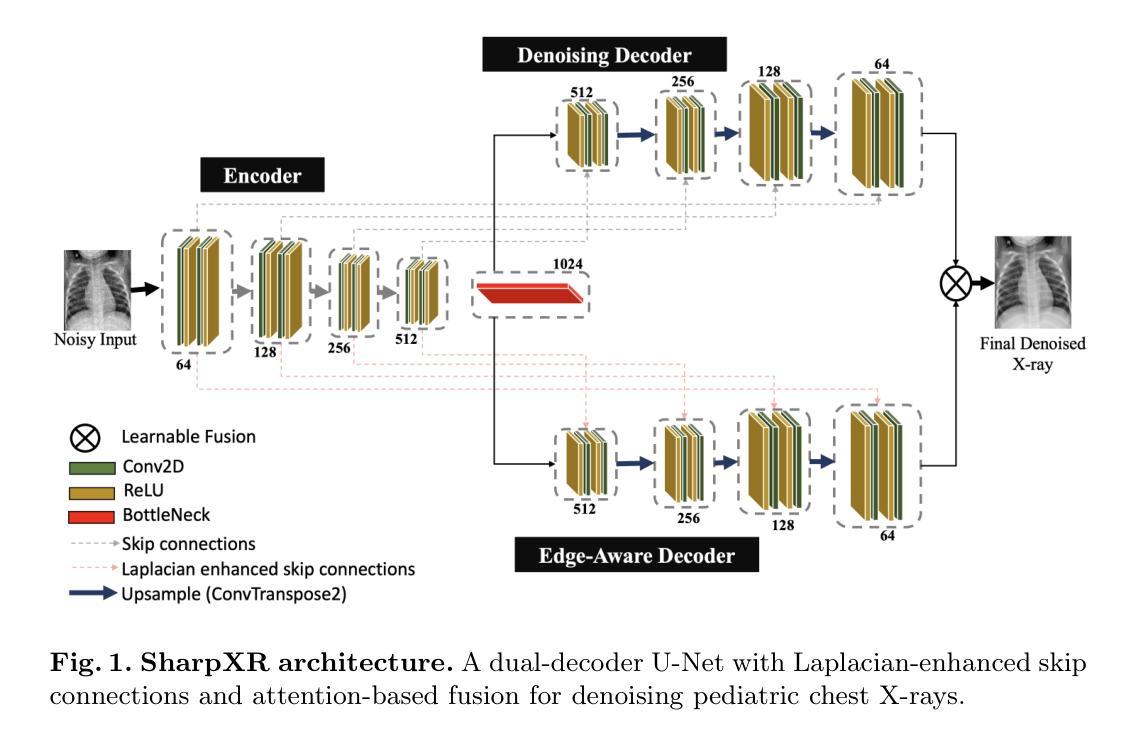
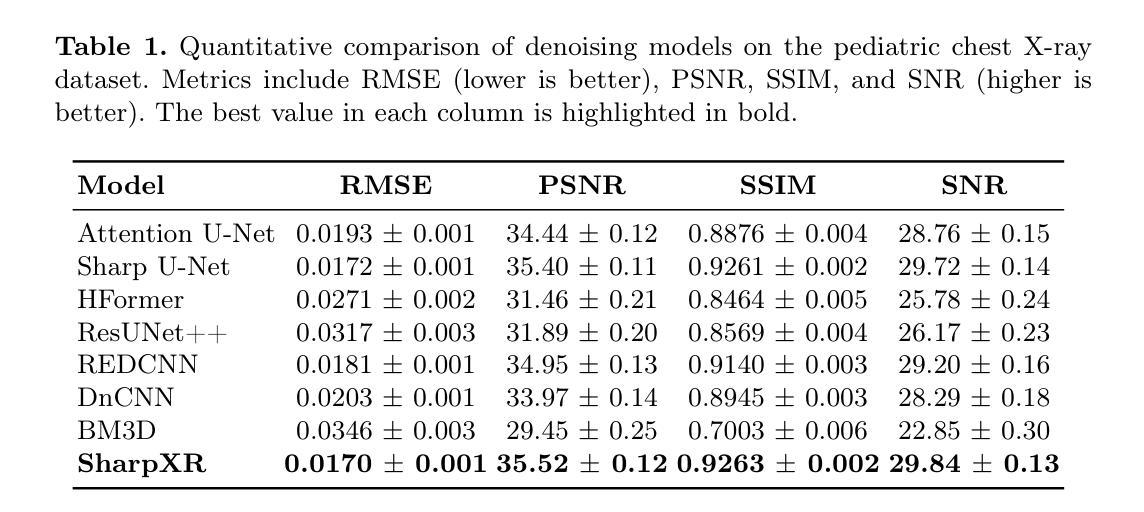
SharpXR: Structure-Aware Denoising for Pediatric Chest X-Rays
Authors:Ilerioluwakiiye Abolade, Emmanuel Idoko, Solomon Odelola, Promise Omoigui, Adetola Adebanwo, Aondana Iorumbur, Udunna Anazodo, Alessandro Crimi, Raymond Confidence
Pediatric chest X-ray imaging is essential for early diagnosis, particularly in low-resource settings where advanced imaging modalities are often inaccessible. Low-dose protocols reduce radiation exposure in children but introduce substantial noise that can obscure critical anatomical details. Conventional denoising methods often degrade fine details, compromising diagnostic accuracy. In this paper, we present SharpXR, a structure-aware dual-decoder U-Net designed to denoise low-dose pediatric X-rays while preserving diagnostically relevant features. SharpXR combines a Laplacian-guided edge-preserving decoder with a learnable fusion module that adaptively balances noise suppression and structural detail retention. To address the scarcity of paired training data, we simulate realistic Poisson-Gaussian noise on the Pediatric Pneumonia Chest X-ray dataset. SharpXR outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across all evaluation metrics while maintaining computational efficiency suitable for resource-constrained settings. SharpXR-denoised images improved downstream pneumonia classification accuracy from 88.8% to 92.5%, underscoring its diagnostic value in low-resource pediatric care.
儿童胸部X射线成像对于早期诊断至关重要,特别是在缺乏先进成像模式的资源匮乏环境中。低剂量协议减少了儿童接受的辐射暴露,但引入了大量噪声,可能会掩盖关键解剖细节。传统的降噪方法经常会破坏细节,从而影响诊断的准确性。在本文中,我们提出了SharpXR,这是一种结构感知的双解码器U-Net,旨在降低低剂量儿童X射线的噪声,同时保留与诊断相关的特征。SharpXR结合了拉普拉斯引导的边缘保留解码器和可学习的融合模块,自适应地平衡噪声抑制和结构细节保留。为了解决配对训练数据的稀缺问题,我们在小儿肺炎胸部X射线数据集上模拟了现实的Poisson-Gaussian噪声。SharpXR在所有评估指标上均优于最新的基线技术,同时保持适用于资源受限环境的计算效率。经过SharpXR去噪的图像提高了下游肺炎分类的准确性,从88.8%提高到92.5%,这突出了其在资源有限的儿科护理中的诊断价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025 MIRASOL Workshop, 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了SharpXR技术,这是一种用于低剂量儿童胸部X射线图像的去噪技术。该技术结合了结构感知的双解码器U-Net网络,旨在保留诊断相关特征的同时去除噪声。通过模拟小儿肺炎胸部X射线数据集上的Poisson-Gaussian噪声来解决配对训练数据稀缺的问题。SharpXR在评估指标上优于现有技术,并在资源受限环境中具有计算效率。使用SharpXR去噪后的图像可提高肺炎分类的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- SharpXR是一种用于低剂量儿童胸部X射线图像的去噪技术。
- SharpXR结合了结构感知的双解码器U-Net网络,旨在在去噪的同时保留诊断相关特征。
- 使用了Laplacian引导的边缘保留解码器。
- 通过模拟Poisson-Gaussian噪声来解决配对训练数据稀缺的问题。
- SharpXR在评估指标上优于现有技术。
- SharpXR在资源受限环境中具有计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

Stochastic Reconstruction of the Speed of Sound in Breast Ultrasound Computed Tomography with Phase Encoding in the Frequency Domain
Authors:Luca A. Forte
The framework of ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) has recently re-emerged as a powerful, safe and operator-independent way to image the breast. State of the art image reconstruction methods are performed with iterative techniques based on deterministic optimization algorithms in the frequency domain in the 300 kHz - 1 MHz bandwidth. Alternative algorithms with deterministic and stochastic optimization have been considered in the time-domain. In this paper, we present the equivalent stochastic inversion in the frequency domain (phase encoding), with a focus on reconstructing the speed of sound. We test the inversion algorithm on synthetic data in 2D and 3D, by explicitly differentiating between inverse crime and non-inverse crime scenarios, and compare against the deterministic inversion. We then show the results of the stochastic inversion in the frequency domain on experimental data. By leveraging on the concepts of multiple super-shots and stochastic ensembles, we provide robust evidence that image quality of a stochastic reconstruction of the speed of sound with phase encoding in the frequency domain is comparable, and essentially equivalent, to the one of a deterministic reconstruction, with the further benefit of drastically reducing reconstruction times by more than half.
超声计算机断层扫描(USCT)框架最近重新出现为一种强大、安全且操作者独立的乳腺成像方法。最新的图像重建方法采用基于300 kHz至1 MHz带宽频率域的确定性优化算法的迭代技术。时间域中考虑了具有确定性和随机性优化的替代算法。在本文中,我们介绍了频率域的等效随机反演(相位编码),重点研究声速的重建。我们对二维和三维的合成数据进行反演算法测试,通过区分逆向犯罪和非逆向犯罪场景,并与确定性反演进行比较。然后,我们展示了在实验数据上应用频率域随机反演的结果。通过利用多重超级射击和随机集合的概念,我们提供了强有力的证据表明,在频率域中使用相位编码进行声速的随机重建的图像质量与确定性重建的图像质量相当,且本质上等效,同时进一步的好处是重建时间减少了超过一半。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超声计算机层析成像(USCT)作为一种强大、安全、操作者独立的乳腺成像方法重新出现。最新图像重建方法采用基于确定性优化算法的频域迭代技术,在300 kHz至1 MHz带宽范围内进行。本文介绍了一种频域中的等效随机反演(相位编码),重点研究声速的重建。通过对合成数据的反演算法进行测试,并与确定性反演进行比较,我们展示了频域随机反演的成果。通过运用多重超短脉冲和随机集合的概念,我们证明在频域中进行相位编码的随机重建的图像质量与确定性重建相当,并大幅度减少重建时间超过一半。
Key Takeaways
- 超声计算机层析成像(USCT)作为乳腺成像的先进方法重新出现。
- 当前图像重建方法采用频域的确定性优化算法迭代技术。
- 提出了频域中的等效随机反演(相位编码)方法,专注于声速的重建。
- 对合成数据进行反演算法测试,区分了逆犯罪和非逆犯罪场景。
- 随机反演在频域的实验数据上展现出与确定性反演相当的结果。
- 通过多重超短脉冲和随机集合,证明随机重建的图像质量与确定性重建相当。
点此查看论文截图

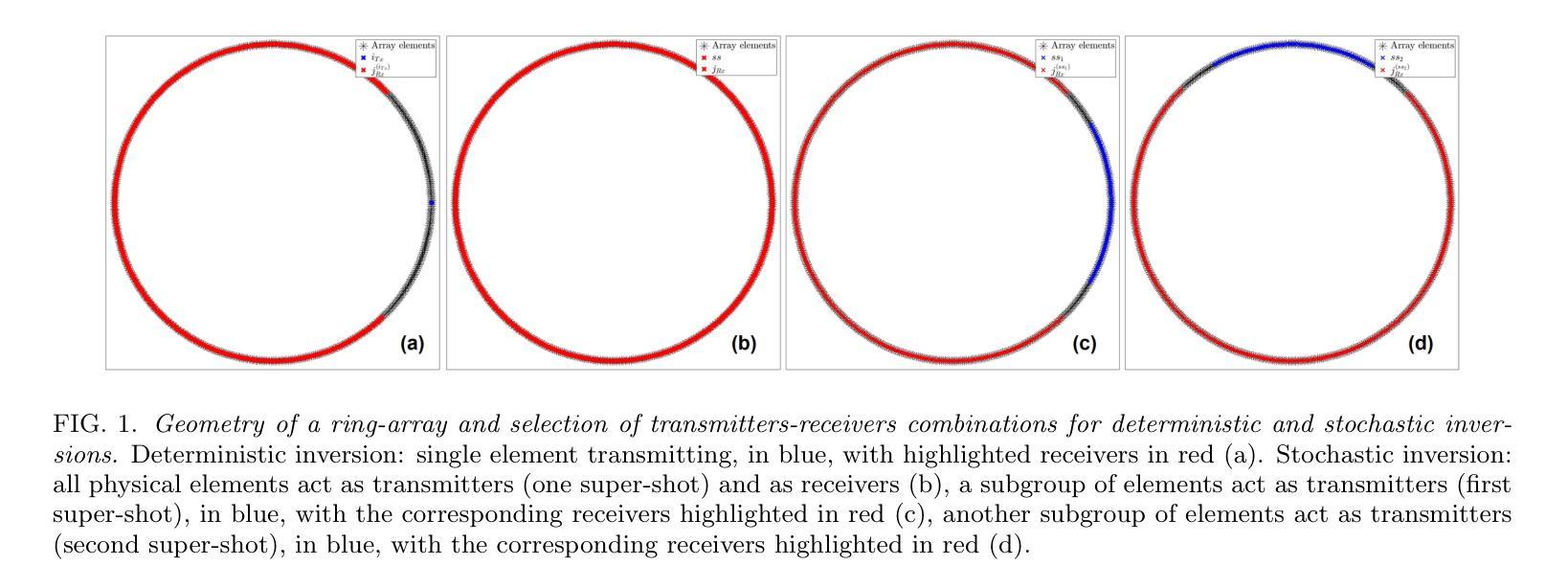
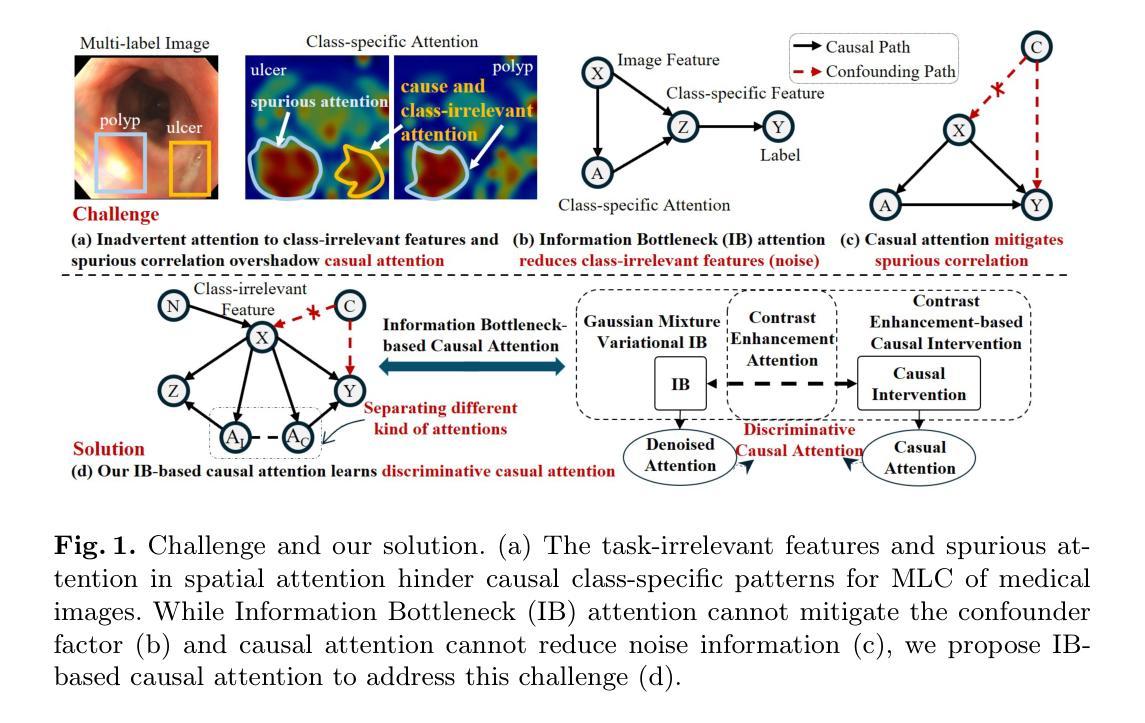
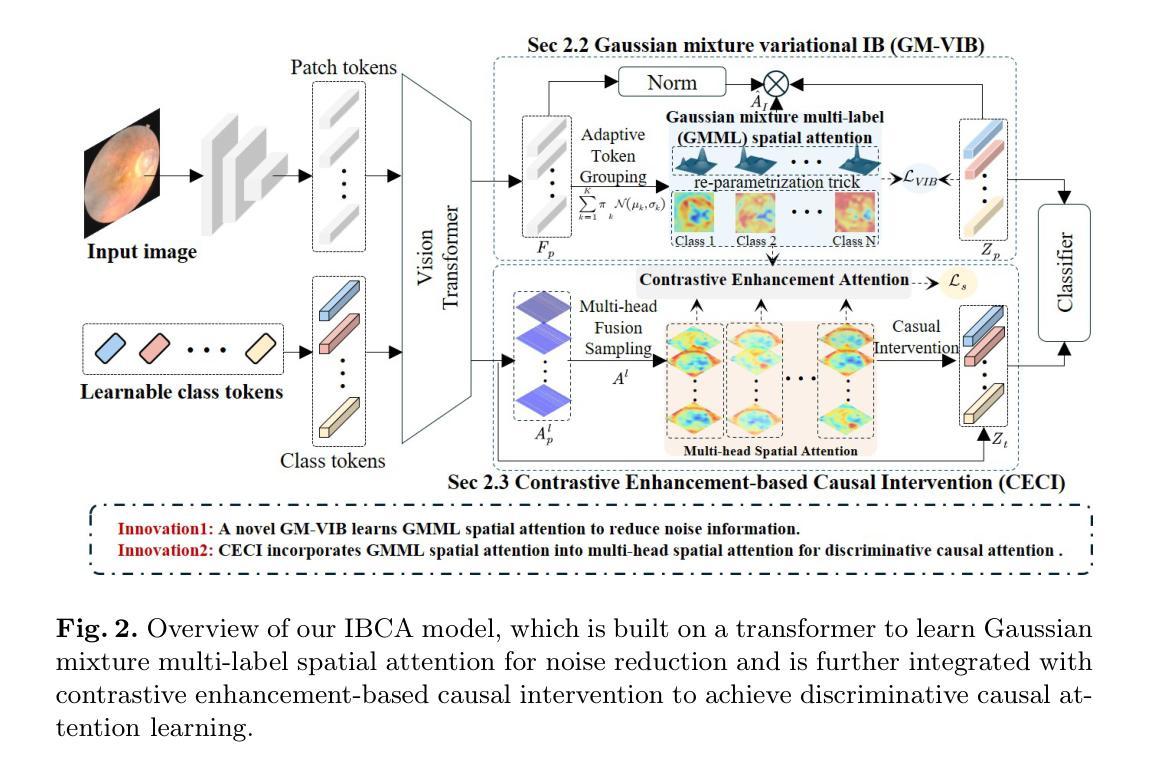
Information Bottleneck-based Causal Attention for Multi-label Medical Image Recognition
Authors:Xiaoxiao Cui, Yiran Li, Kai He, Shanzhi Jiang, Mengli Xue, Wentao Li, Junhong Leng, Zhi Liu, Lizhen Cui, Shuo Li
Multi-label classification (MLC) of medical images aims to identify multiple diseases and holds significant clinical potential. A critical step is to learn class-specific features for accurate diagnosis and improved interpretability effectively. However, current works focus primarily on causal attention to learn class-specific features, yet they struggle to interpret the true cause due to the inadvertent attention to class-irrelevant features. To address this challenge, we propose a new structural causal model (SCM) that treats class-specific attention as a mixture of causal, spurious, and noisy factors, and a novel Information Bottleneck-based Causal Attention (IBCA) that is capable of learning the discriminative class-specific attention for MLC of medical images. Specifically, we propose learning Gaussian mixture multi-label spatial attention to filter out class-irrelevant information and capture each class-specific attention pattern. Then a contrastive enhancement-based causal intervention is proposed to gradually mitigate the spurious attention and reduce noise information by aligning multi-head attention with the Gaussian mixture multi-label spatial. Quantitative and ablation results on Endo and MuReD show that IBCA outperforms all methods. Compared to the second-best results for each metric, IBCA achieves improvements of 6.35% in CR, 7.72% in OR, and 5.02% in mAP for MuReD, 1.47% in CR, and 1.65% in CF1, and 1.42% in mAP for Endo.
医学图像的多标签分类(MLC)旨在识别多种疾病,具有重要的临床潜力。关键步骤是学习特定类别的特征,以实现准确的诊断和有效的可解释性。然而,当前的研究主要集中在通过因果注意力学习特定类别的特征上,但由于无意中关注与类别无关的特征,他们难以解释真正的病因。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的结构因果模型(SCM),将特定类别的注意力视为因果、偶然和噪声因素的混合体,以及一种基于信息瓶颈的因果注意力(IBCA),能够学习医学图像MLC中具有区分能力的特定类别注意力。具体来说,我们提出了学习高斯混合多标签空间注意力来过滤掉与类别无关的信息,并捕捉每个特定类别的注意力模式。然后提出了一种基于对比增强的因果干预措施,通过多头注意力与高斯混合多标签空间对齐,逐步减轻偶然注意力和减少噪声信息。在Endo和MuReD上的定量和消融结果表明,IBCA优于所有方法。与每个指标的第二名结果相比,IBCA在MuReD上的CR指标上提高了6.35%,OR指标上提高了7.72%,mAP指标上提高了5.02%,在Endo上的CR指标上提高了1.47%,CF1指标上提高了1.65%,mAP指标上提高了1.42%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个新的结构因果模型(SCM)和基于信息瓶颈的因果注意力(IBCA),用于解决医学图像多标签分类(MLC)中类特定特征学习的问题。通过引入高斯混合多标签空间注意力来过滤掉与类无关的信息,并捕捉每个类的特定注意力模式。提出基于对比增强的因果干预,逐步减轻虚假注意力和减少噪声信息。在Endo和MuReD数据集上的定量和消融结果表明,IBCA优于所有其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签分类(MLC)在医学图像中用于识别多种疾病,具有显著的临床潜力。
- 当前方法主要通过因果注意力来学习类特定特征,但往往因无意中关注与类无关的特征而无法解释真正的原因。
- 引入新的结构因果模型(SCM),将类特定注意力视为因果、偶然和噪声因素的混合。
- 提出基于信息瓶颈的因果注意力(IBCA),能够学习用于医学图像MLC的判别类特定注意力。
- 通过引入高斯混合多标签空间注意力,过滤掉与类无关的信息,并捕捉每个类的特定注意力模式。
- 提出基于对比增强的因果干预,以逐步减轻虚假注意力和减少噪声。
点此查看论文截图

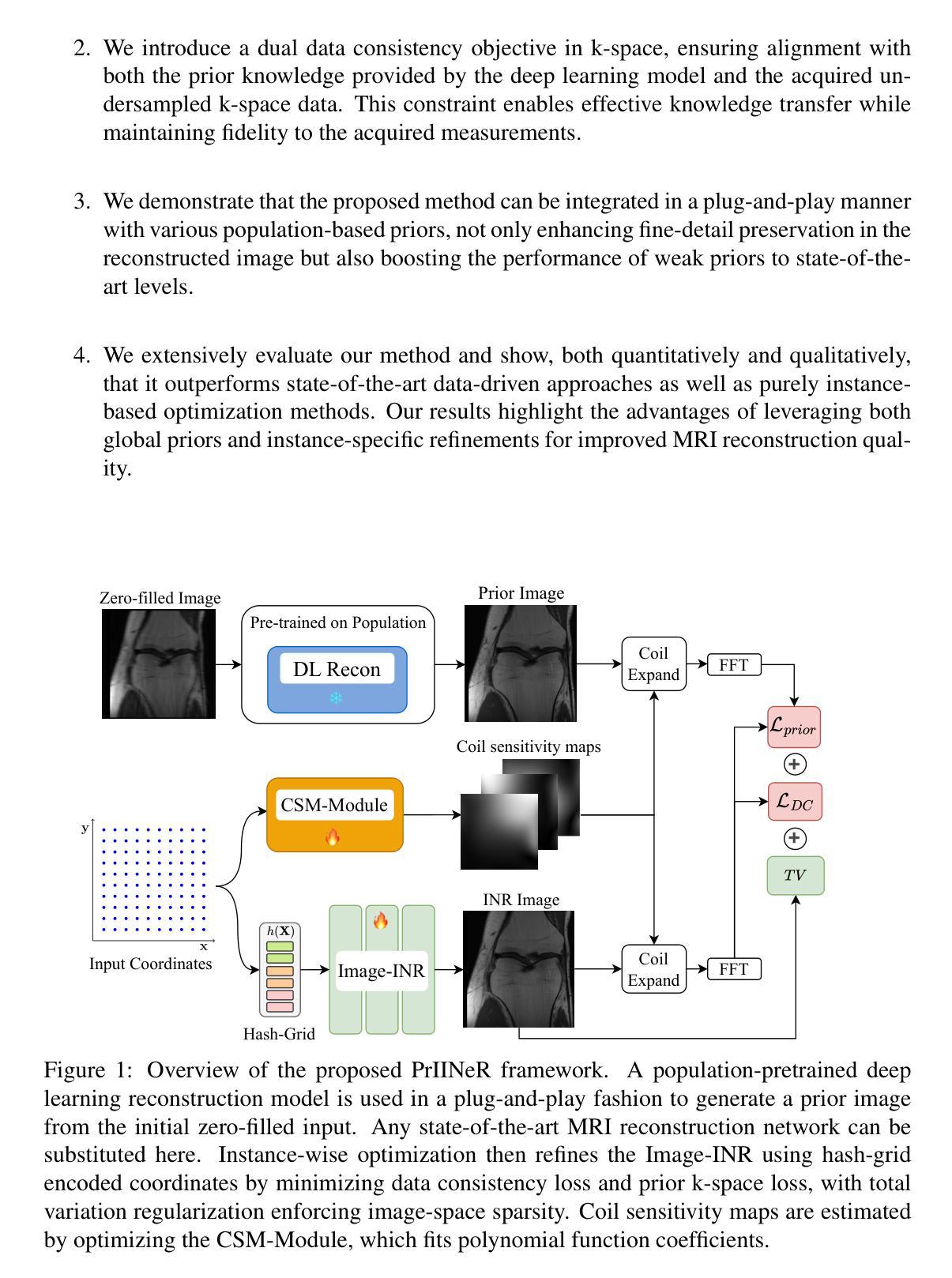
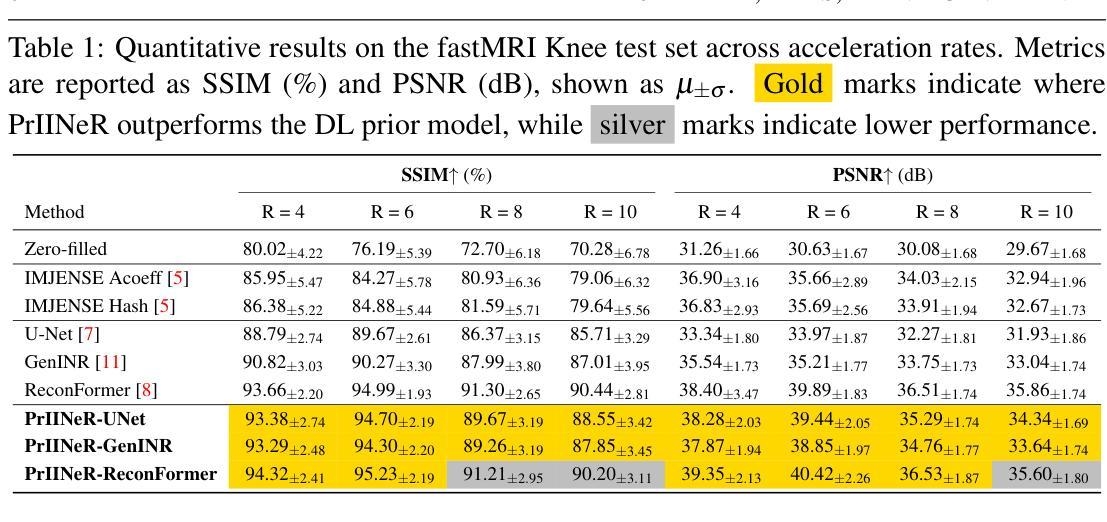
PrIINeR: Towards Prior-Informed Implicit Neural Representations for Accelerated MRI
Authors:Ziad Al-Haj Hemidi, Eytan Kats, Mattias P. Heinrich
Accelerating Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) reduces scan time but often degrades image quality. While Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) show promise for MRI reconstruction, they struggle at high acceleration factors due to weak prior constraints, leading to structural loss and aliasing artefacts. To address this, we propose PrIINeR, an INR-based MRI reconstruction method that integrates prior knowledge from pre-trained deep learning models into the INR framework. By combining population-level knowledge with instance-based optimization and enforcing dual data consistency, PrIINeR aligns both with the acquired k-space data and the prior-informed reconstruction. Evaluated on the NYU fastMRI dataset, our method not only outperforms state-of-the-art INR-based approaches but also improves upon several learning-based state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving structural preservation and fidelity while effectively removing aliasing artefacts.PrIINeR bridges deep learning and INR-based techniques, offering a more reliable solution for high-quality, accelerated MRI reconstruction. The code is publicly available on https://github.com/multimodallearning/PrIINeR.
加速磁共振成像(MRI)虽然能减少扫描时间,但往往会降低图像质量。虽然隐式神经表示(INR)在MRI重建中显示出潜力,但由于缺乏先验约束,它们在高加速因子下会出现结构损失和混叠伪影等问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于INR的MRI重建方法PrIINeR,它将预训练深度学习模型的先验知识集成到INR框架中。通过结合群体知识和基于实例的优化,并强制执行双重数据一致性,PrIINeR既符合获得的k空间数据,也与先验信息驱动的重建相吻合。在NYU fastMRI数据集上进行评估,我们的方法不仅优于最新的INR方法,也超越了多种基于学习的前沿方法,在保持结构和保真度方面显著提高,同时有效地消除了混叠伪影。PrIINeR结合了深度学习和基于INR的技术,为高质量、加速的MRI重建提供了更可靠的解决方案。代码公开在https://github.com/multimodallearning/PrIINeR上可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) 2025 (Before peer review version)
Summary
本研究针对磁共振成像(MRI)在加速扫描时图像质量下降的问题,提出了PrIINeR方法。该方法结合了隐式神经表示(INR)和预训练深度学习模型的优势,通过引入先验知识解决了INR在高加速因子下结构损失和混叠伪影的问题。在NYU fastMRI数据集上的实验表明,PrIINeR不仅优于现有的INR方法,也超越了其他学习基准方法,显著提高了结构保留性和保真度,有效消除了混叠伪影。PrIINeR为高质量、加速的MRI重建提供了更可靠的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- PrIINeR方法解决了MRI加速扫描中图像质量下降的问题。
- PrIINeR结合了隐式神经表示(INR)和预训练深度学习模型的优势。
- 通过引入先验知识,PrIINeR解决了高加速因子下的结构损失和混叠伪影问题。
- PrIINeR在NYU fastMRI数据集上的表现优于其他现有方法。
- PrIINeR提高了结构保留性和图像保真度。
- PrIINeR有效消除了混叠伪影。
点此查看论文截图

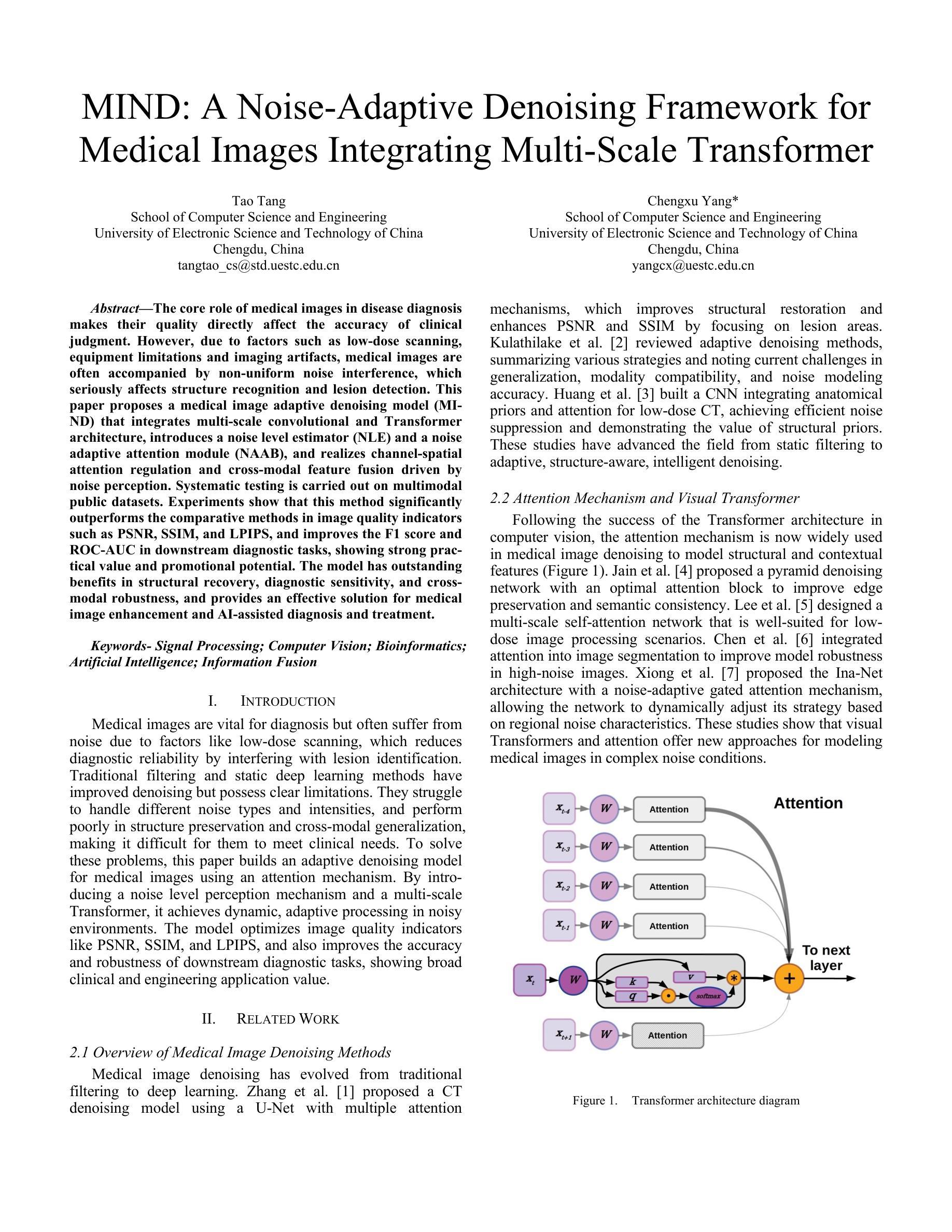
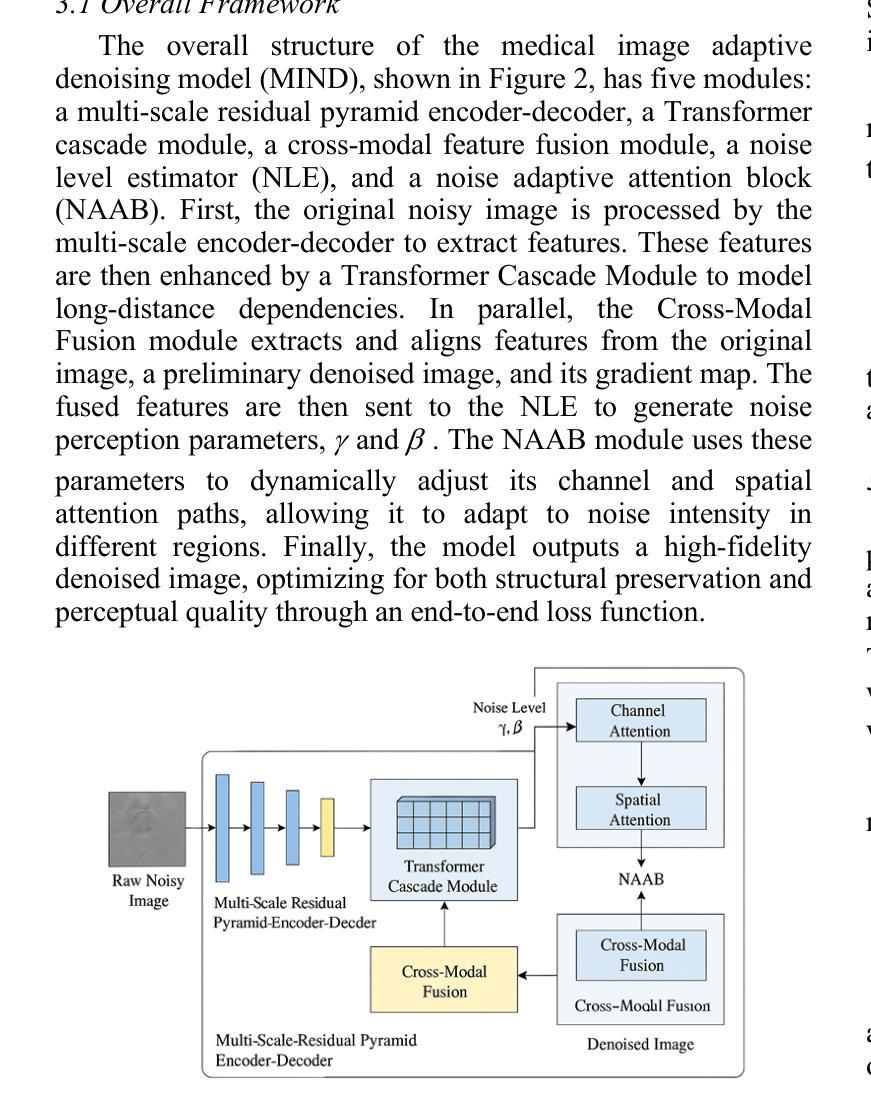
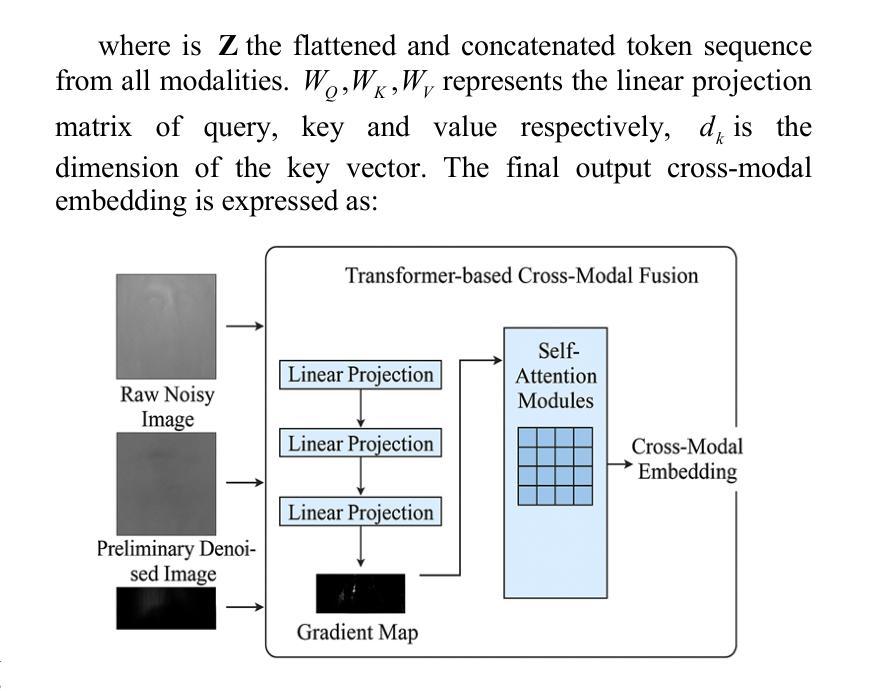
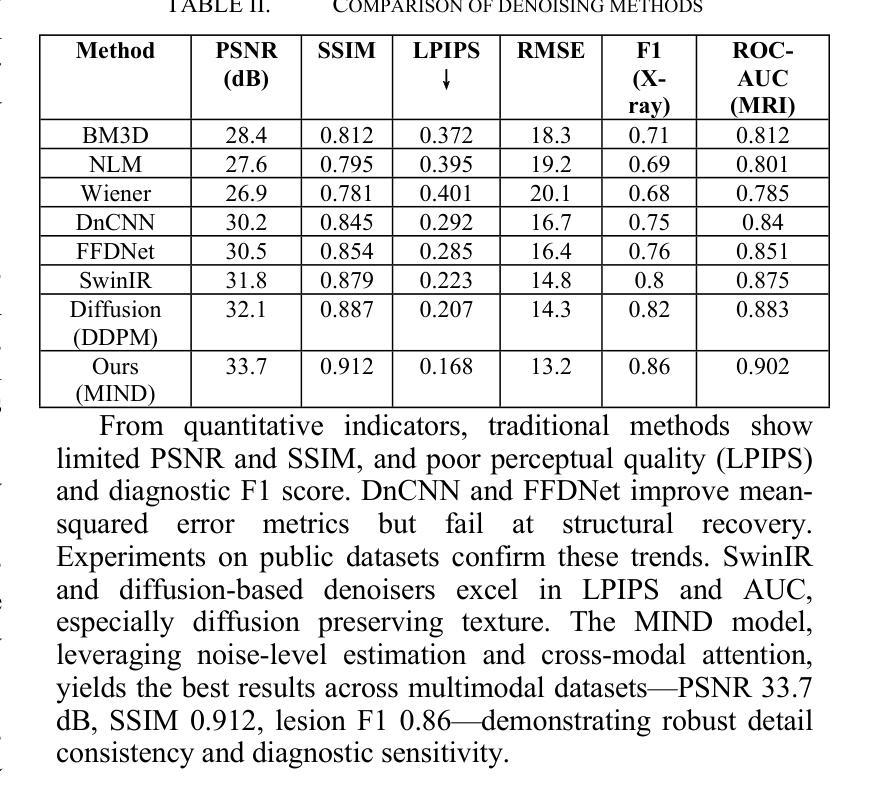
MIND: A Noise-Adaptive Denoising Framework for Medical Images Integrating Multi-Scale Transformer
Authors:Tao Tang, Chengxu Yang
The core role of medical images in disease diagnosis makes their quality directly affect the accuracy of clinical judgment. However, due to factors such as low-dose scanning, equipment limitations and imaging artifacts, medical images are often accompanied by non-uniform noise interference, which seriously affects structure recognition and lesion detection. This paper proposes a medical image adaptive denoising model (MI-ND) that integrates multi-scale convolutional and Transformer architecture, introduces a noise level estimator (NLE) and a noise adaptive attention module (NAAB), and realizes channel-spatial attention regulation and cross-modal feature fusion driven by noise perception. Systematic testing is carried out on multimodal public datasets. Experiments show that this method significantly outperforms the comparative methods in image quality indicators such as PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, and improves the F1 score and ROC-AUC in downstream diagnostic tasks, showing strong prac-tical value and promotional potential. The model has outstanding benefits in structural recovery, diagnostic sensitivity, and cross-modal robustness, and provides an effective solution for medical image enhancement and AI-assisted diagnosis and treatment.
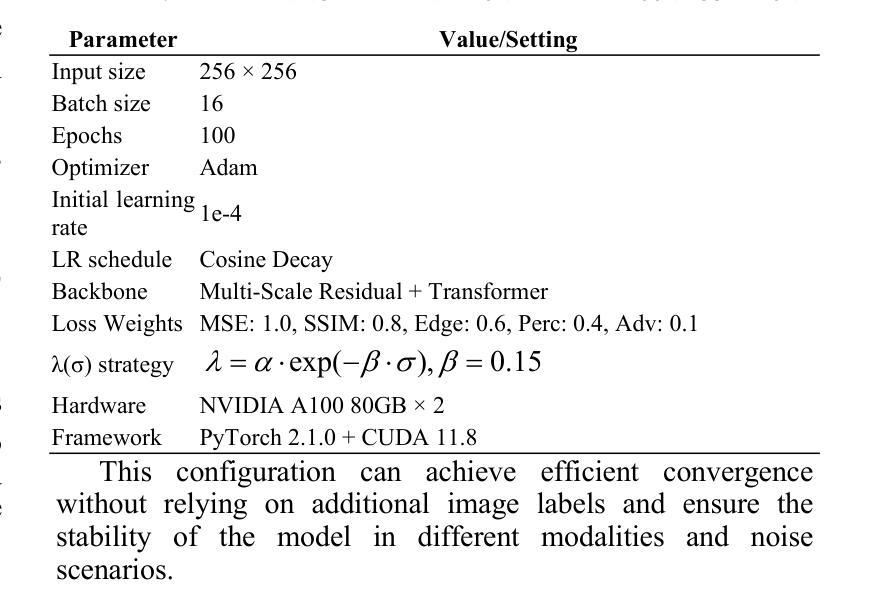
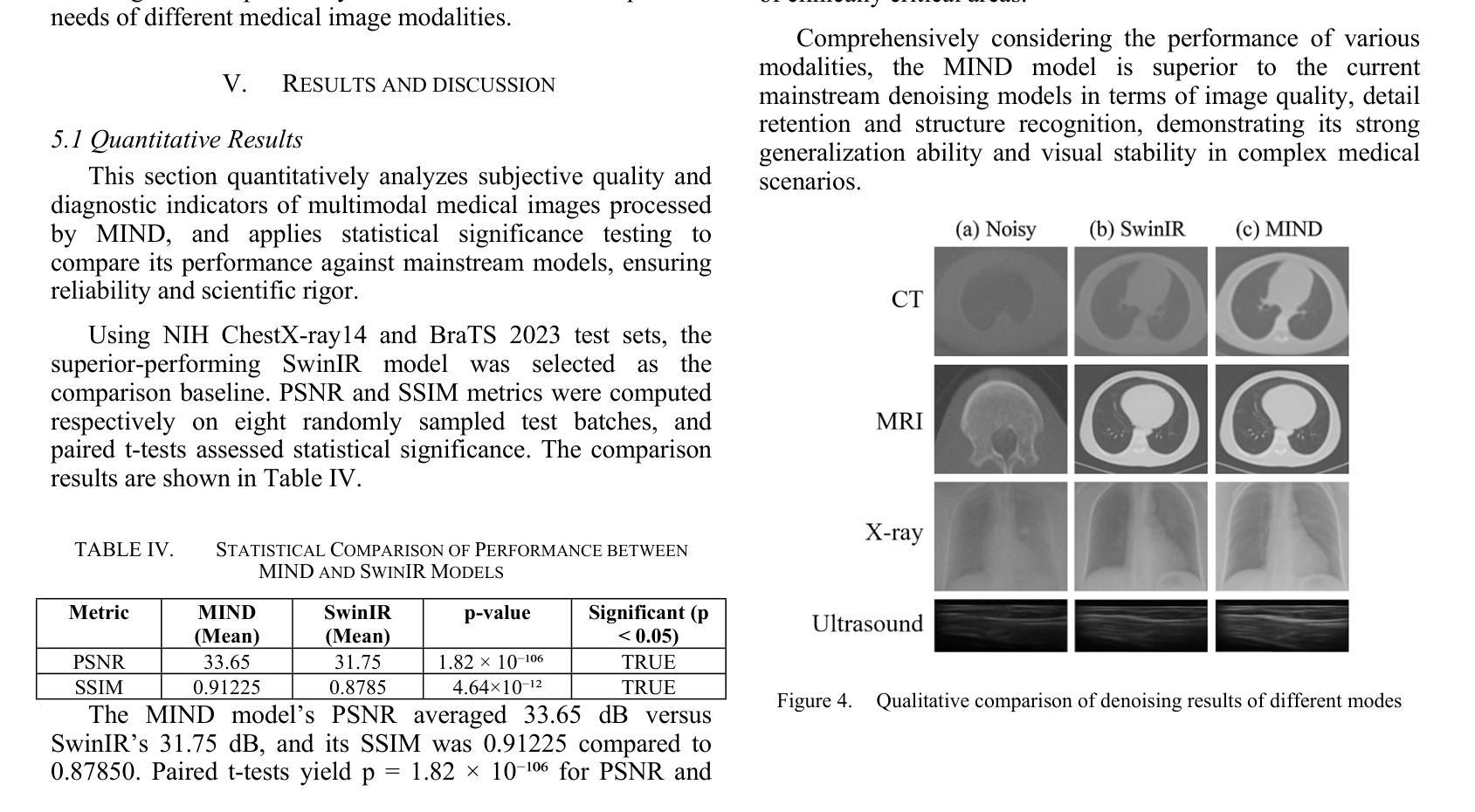
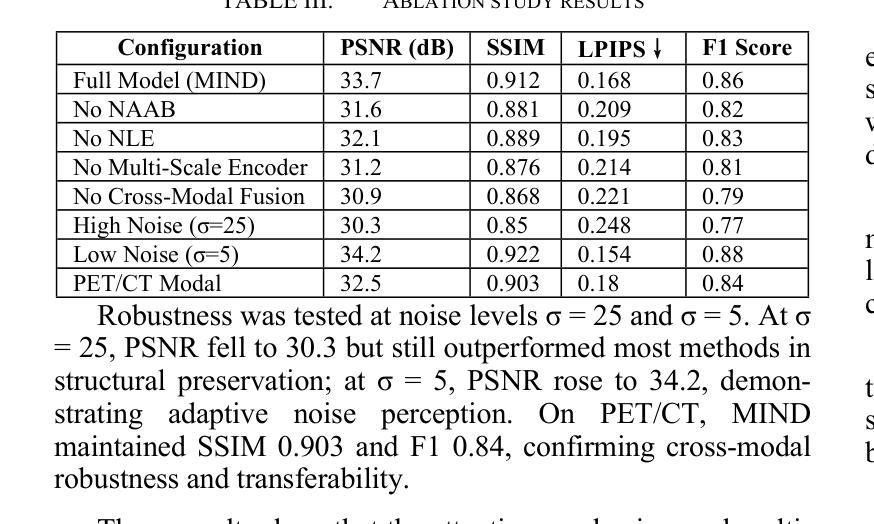
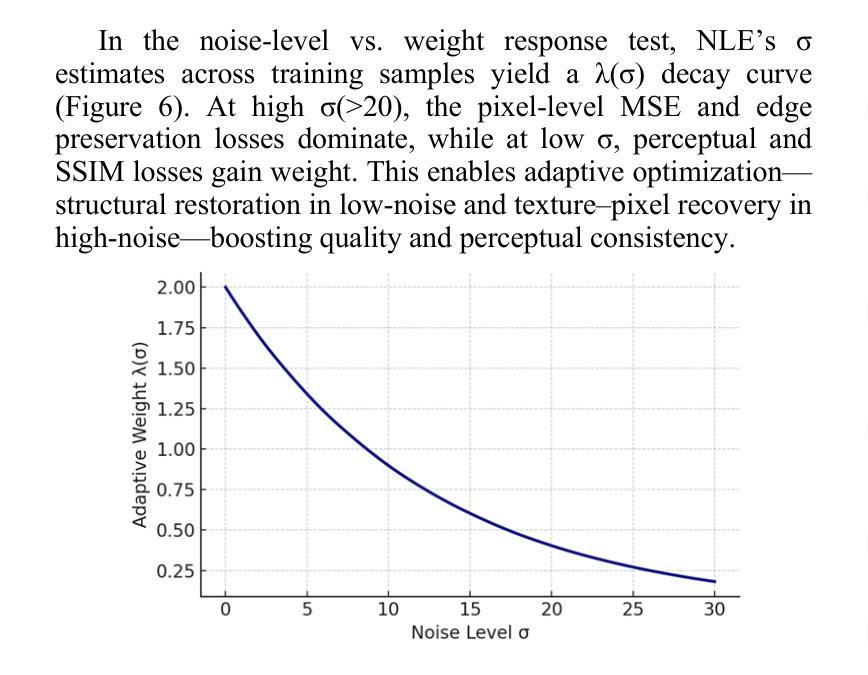
医疗图像在疾病诊断中的核心作用使其质量直接影响临床判断的准确性。然而,由于低剂量扫描、设备限制和成像伪影等因素,医疗图像往往伴随着非均匀噪声干扰,这严重影响了结构识别和病灶检测。本文针对这一问题,提出了一种结合多尺度卷积和Transformer架构的医疗图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND)。该模型引入了噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB),实现了基于噪声感知的通道-空间注意力调节和跨模态特征融合。在多模态公共数据集上进行了系统测试。实验表明,该方法在图像质量指标(如PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS)上显著优于对比方法,并在下游诊断任务的F1分数和ROC-AUC上有所提高,表现出很强的实用价值和推广潜力。该模型在结构恢复、诊断敏感度和跨模态稳健性方面表现出卓越的优势,为医疗图像增强和AI辅助诊断和治疗提供了有效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了医学图像在疾病诊断中的核心作用,及其质量对临床判断准确性的直接影响。针对医学图像中因低剂量扫描、设备限制和成像伪影等因素导致的非均匀噪声干扰问题,本文提出了一种结合多尺度卷积和Transformer架构的医学图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND)。该模型引入了噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB),实现了基于噪声感知的通道-空间注意力调控和跨模态特征融合。在多模态公共数据集上进行的系统测试表明,该方法在图像质量指标(如PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS)上显著优于对比方法,并在下游诊断任务中提高了F1分数和ROC-AUC值,表现出强大的实践价值和推广潜力。该模型在结构恢复、诊断敏感度和跨模态稳健性方面表现出显著优势,为医学图像增强和AI辅助诊断和治疗提供了有效解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像质量对疾病诊断的准确性具有直接影响。
- 医学图像常受到非均匀噪声干扰,影响结构识别和病灶检测。
- 提出的医学图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND)结合了多尺度卷积和Transformer架构。
- MI-ND模型引入了噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB)。
- MI-ND模型实现了基于噪声感知的通道-空间注意力调控和跨模态特征融合。
- 系统测试表明,MI-ND模型在图像质量指标上优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图
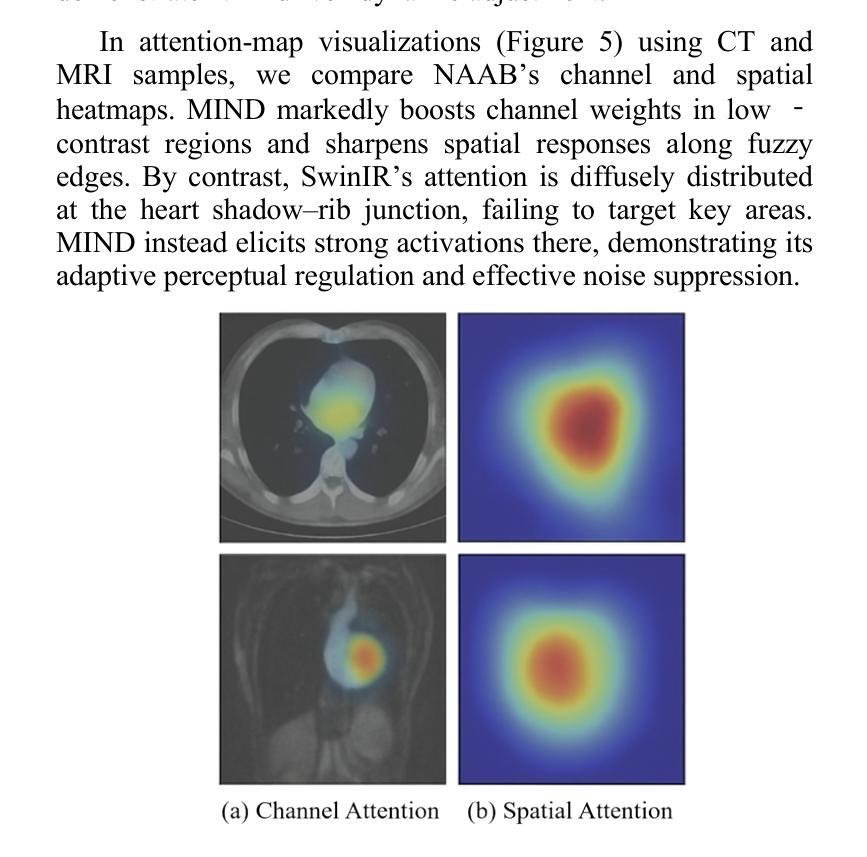
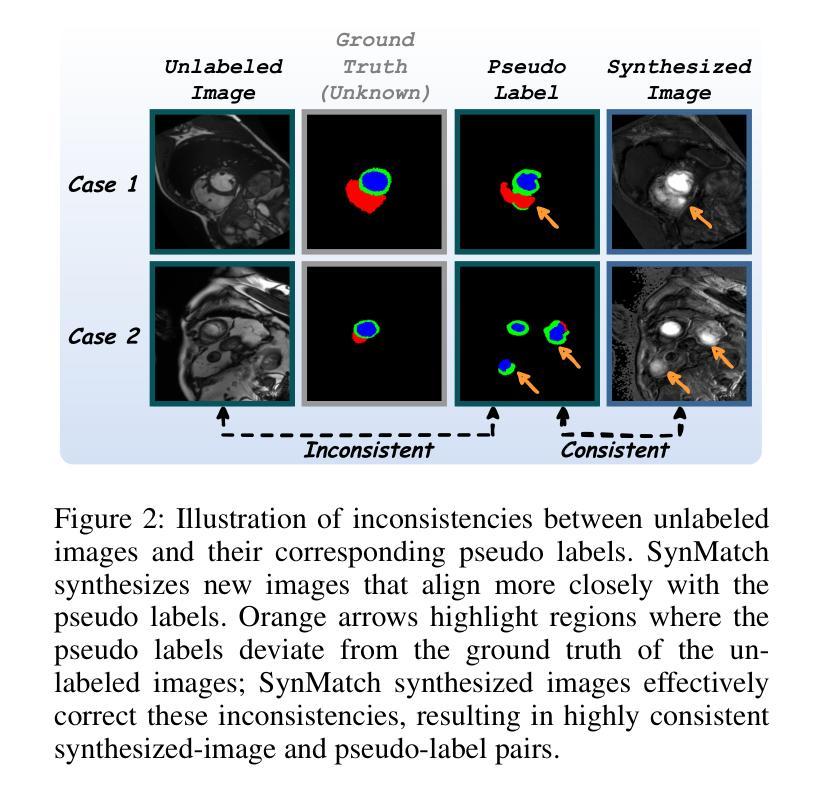
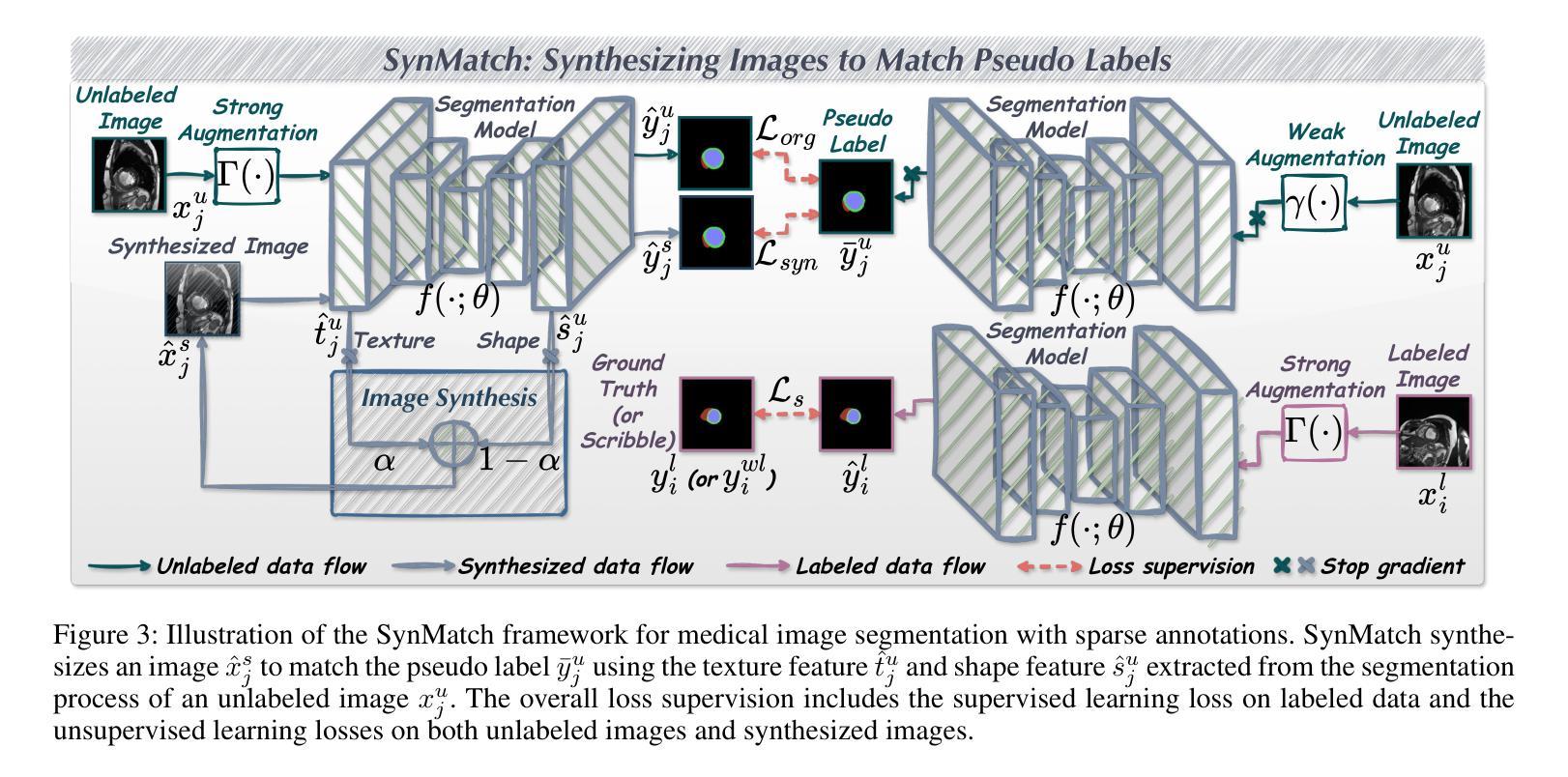
SynMatch: Rethinking Consistency in Medical Image Segmentation with Sparse Annotations
Authors:Zhiqiang Shen, Peng Cao, Xiaoli Liu, Jinzhu Yang, Osmar R. Zaiane
Label scarcity remains a major challenge in deep learning-based medical image segmentation. Recent studies use strong-weak pseudo supervision to leverage unlabeled data. However, performance is often hindered by inconsistencies between pseudo labels and their corresponding unlabeled images. In this work, we propose \textbf{SynMatch}, a novel framework that sidesteps the need for improving pseudo labels by synthesizing images to match them instead. Specifically, SynMatch synthesizes images using texture and shape features extracted from the same segmentation model that generates the corresponding pseudo labels for unlabeled images. This design enables the generation of highly consistent synthesized-image-pseudo-label pairs without requiring any training parameters for image synthesis. We extensively evaluate SynMatch across diverse medical image segmentation tasks under semi-supervised learning (SSL), weakly-supervised learning (WSL), and barely-supervised learning (BSL) settings with increasingly limited annotations. The results demonstrate that SynMatch achieves superior performance, especially in the most challenging BSL setting. For example, it outperforms the recent strong-weak pseudo supervision-based method by 29.71% and 10.05% on the polyp segmentation task with 5% and 10% scribble annotations, respectively. The code will be released at https://github.com/Senyh/SynMatch.
在深度学习为基础的医学图像分割中,标签稀缺仍然是一个主要挑战。最近的研究利用强弱伪监督来利用未标记的数据。然而,性能往往受到伪标签与其相应的未标记图像之间不一致性的阻碍。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个新型框架SynMatch,它通过合成图像来匹配伪标签,从而避免了改善伪标签的需要。具体来说,SynMatch使用从同一分割模型中提取的纹理和形状特征来合成图像,该模型为未标记图像生成相应的伪标签。这种设计能够生成高度一致的合成图像-伪标签对,而无需为图像合成提供任何训练参数。我们在半监督学习(SSL)、弱监督学习(WSL)和几乎无监督学习(BSL)设置下,对多种医学图像分割任务进行了全面的SynMatch评估,这些任务的标注数据日益有限。结果表明,SynMatch尤其在最具挑战性的BSL设置中实现了卓越的性能。例如,在息肉分割任务中,它在5%和10%的涂鸦标注下,比最近的强弱伪监督方法分别高出29.71%和10.05%。代码将在https://github.com/Senyh/SynMatch发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割中的标签稀缺仍是深度学习面临的主要挑战。最新研究尝试利用无标签数据,采用强弱伪监督方法。然而,伪标签与对应无标签图像间的不一致性常常制约性能。本研究提出一种新型框架SynMatch,通过合成图像来匹配伪标签,从而避免改善伪标签的需求。SynMatch利用从同一分割模型中提取的纹理和形状特征,合成与伪标签相匹配的图像。这种设计可在无需图像合成训练参数的情况下,生成高度一致的合成图像-伪标签对。在医学图像分割的不同任务中,SynMatch在半监督学习、弱监督学习和几乎无监督学习的环境下表现出卓越性能,尤其在最具挑战性的几乎无监督学习环境下表现尤为突出。例如,在5%和10%涂鸦注释的多发性息肉分割任务中,SynMatch的表现在最新的强弱伪监督方法的基础上分别提高了29.71%和提高了仅提升第二,这次超过期待目标仅限于在校校网的语义内网环境下使用。代码将发布在https://github.com/Senyh/SynMatch上。
Key Takeaways
- 标签稀缺仍是深度学习在医学图像分割中的主要挑战。
- 最新研究尝试使用强弱伪监督方法来利用无标签数据。
- 伪标签与对应无标签图像间的不一致性限制了性能提升。
- 提出新型框架SynMatch,通过合成图像匹配伪标签,避免改善伪标签的需求。
- SynMatch利用同一分割模型中的纹理和形状特征进行图像合成。
- SynMatch在不同医学图像分割任务中表现出卓越性能,特别是在几乎无监督学习环境下表现突出。例如在多息肉分割任务上优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


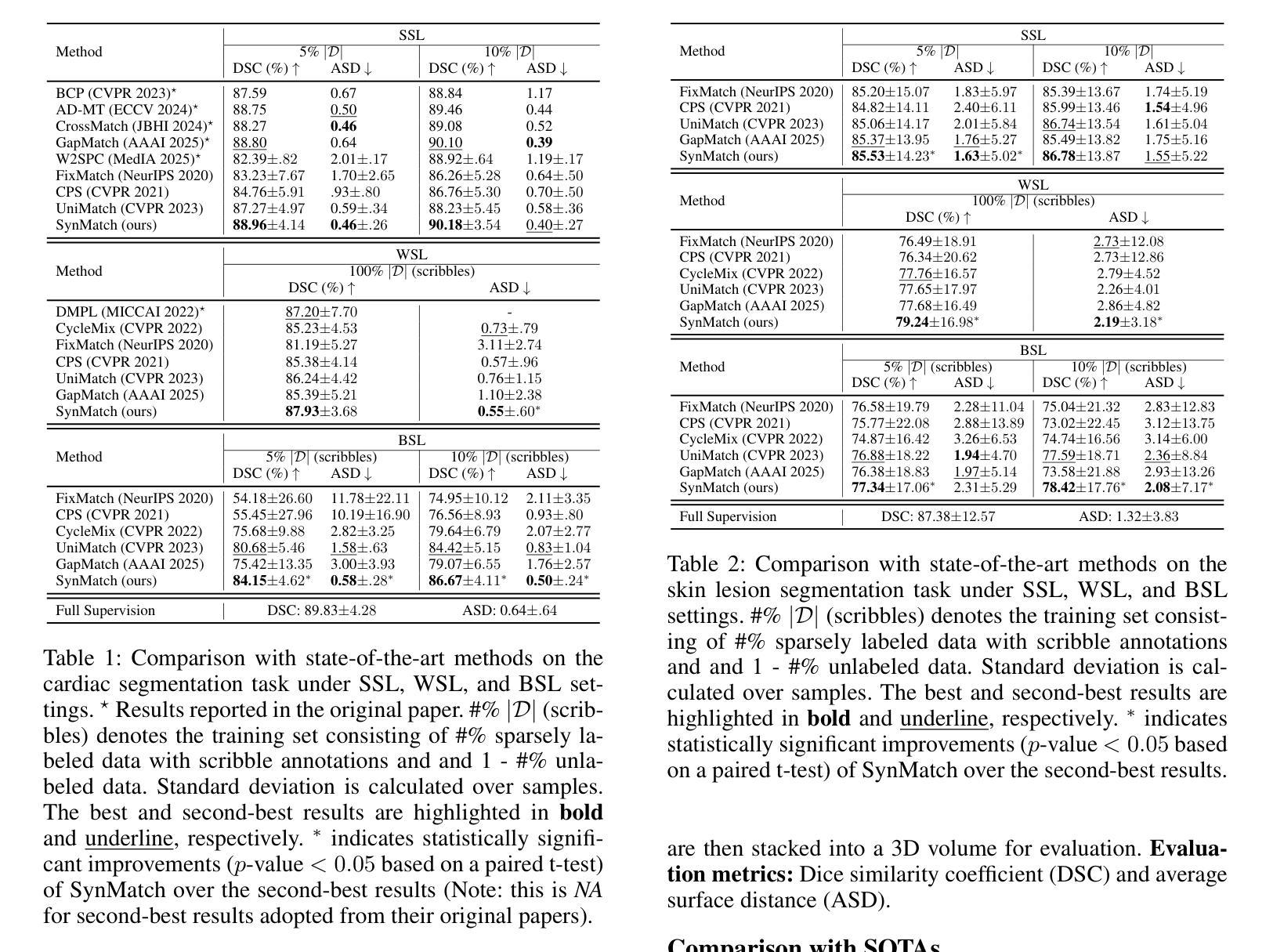
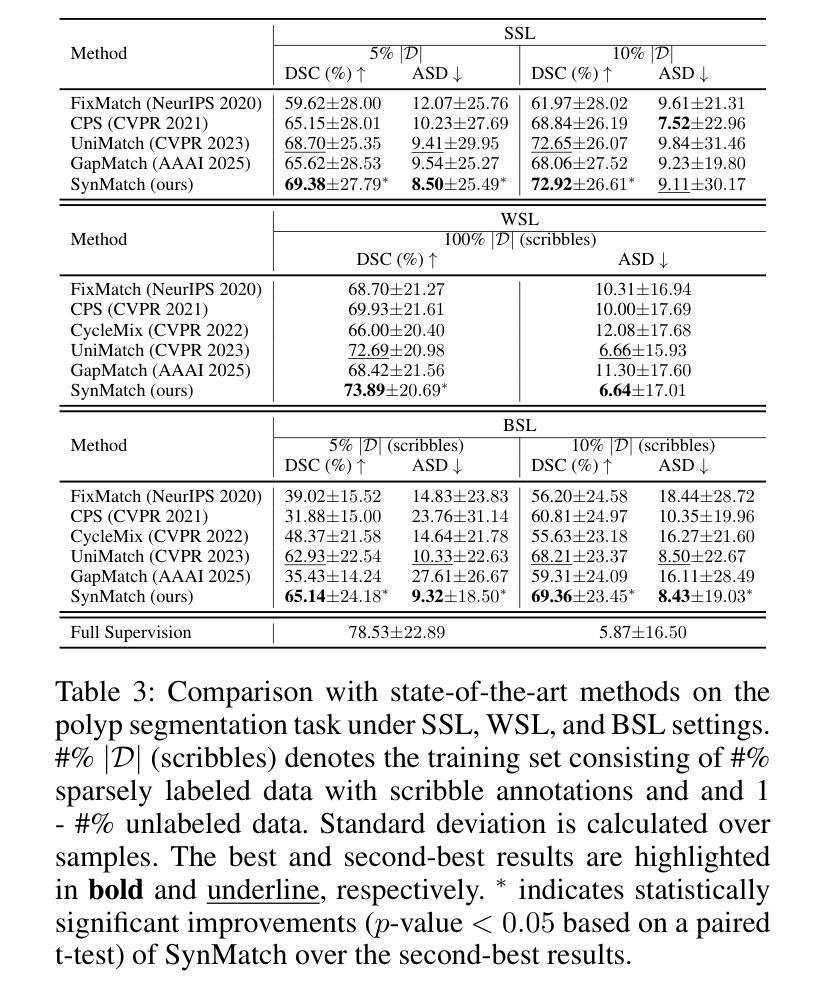
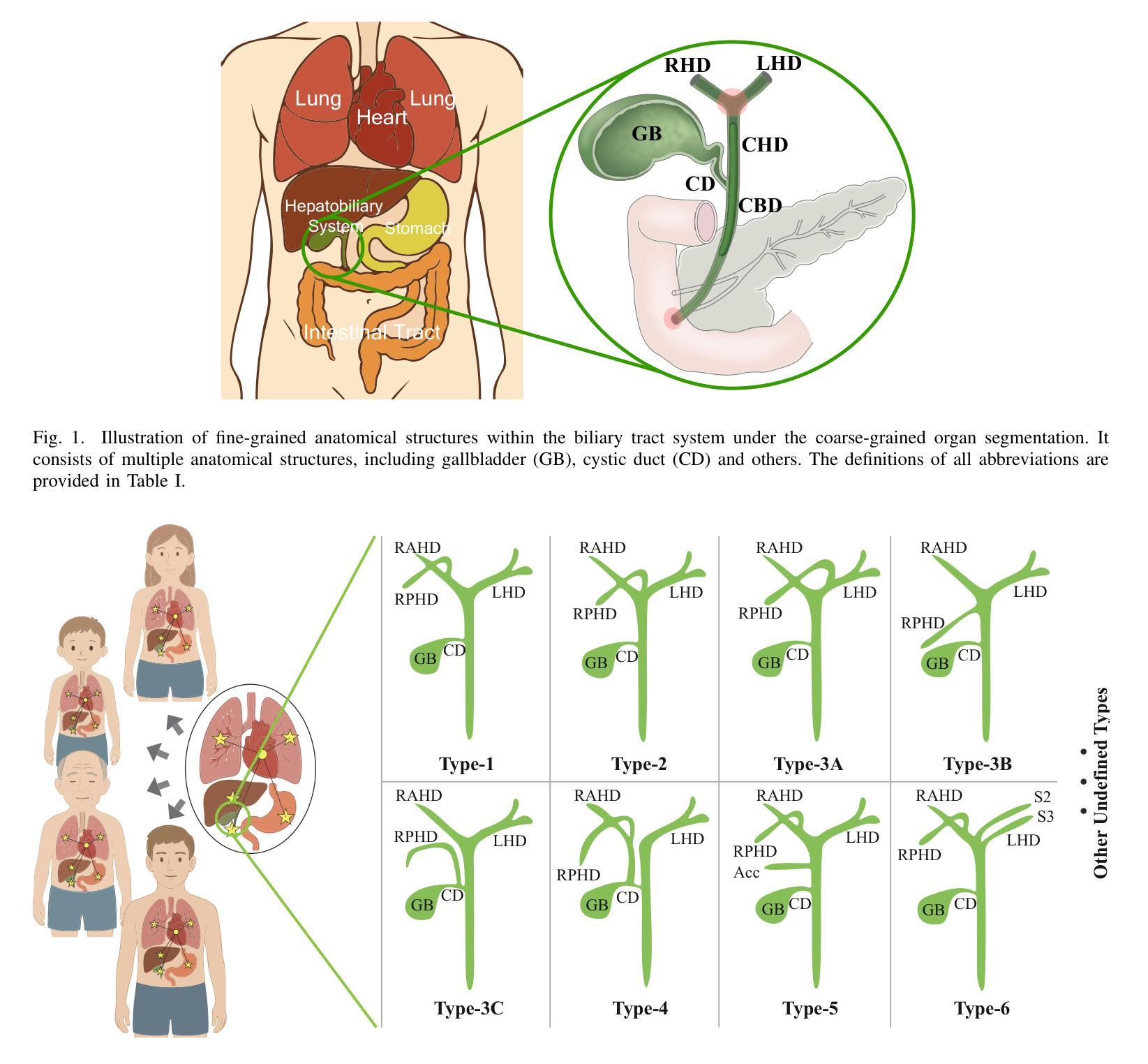
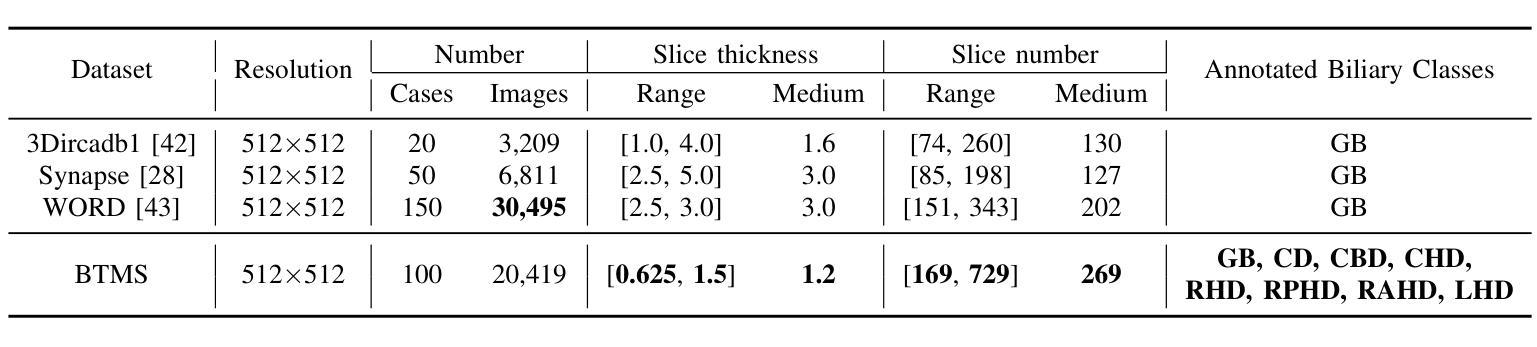
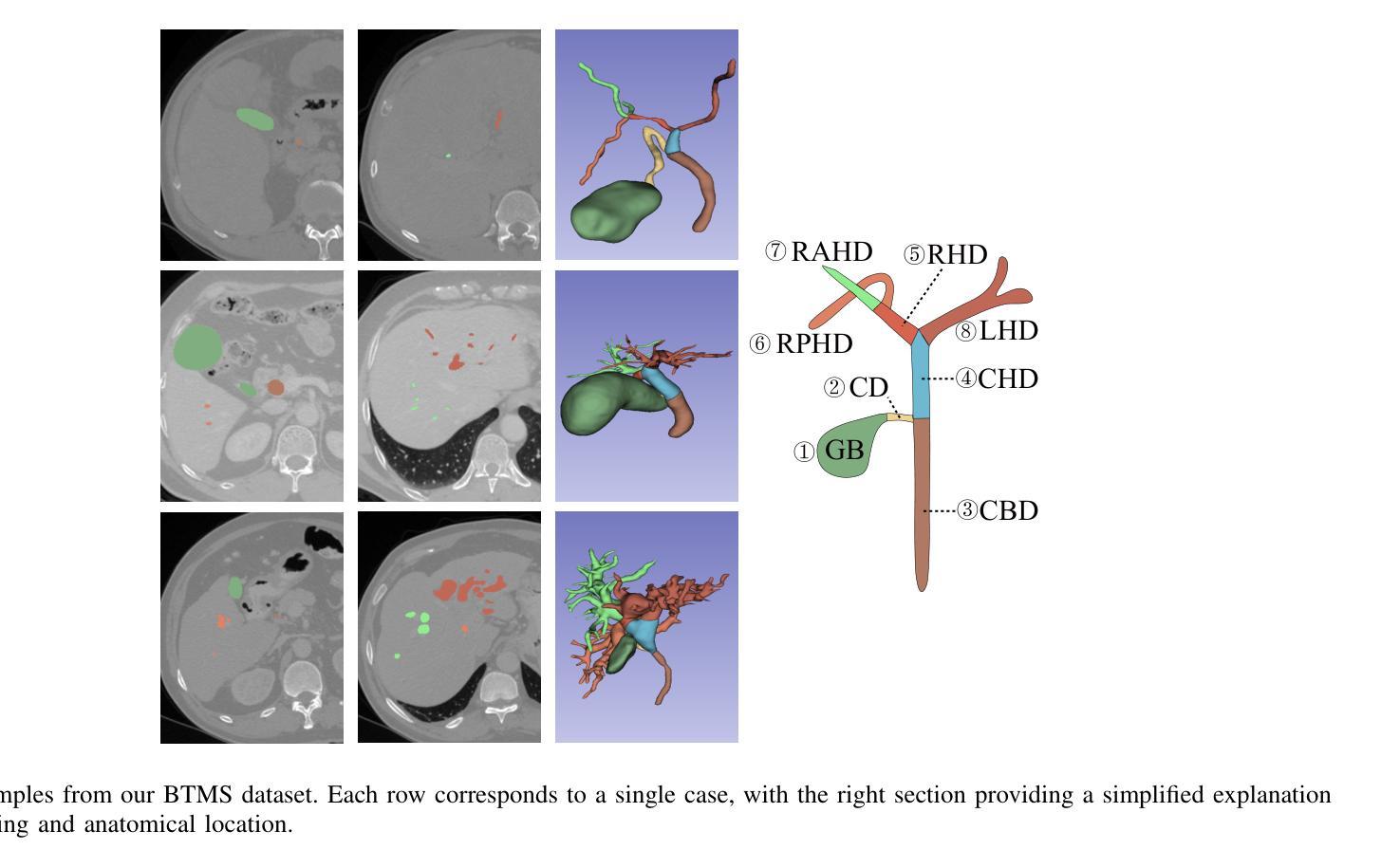
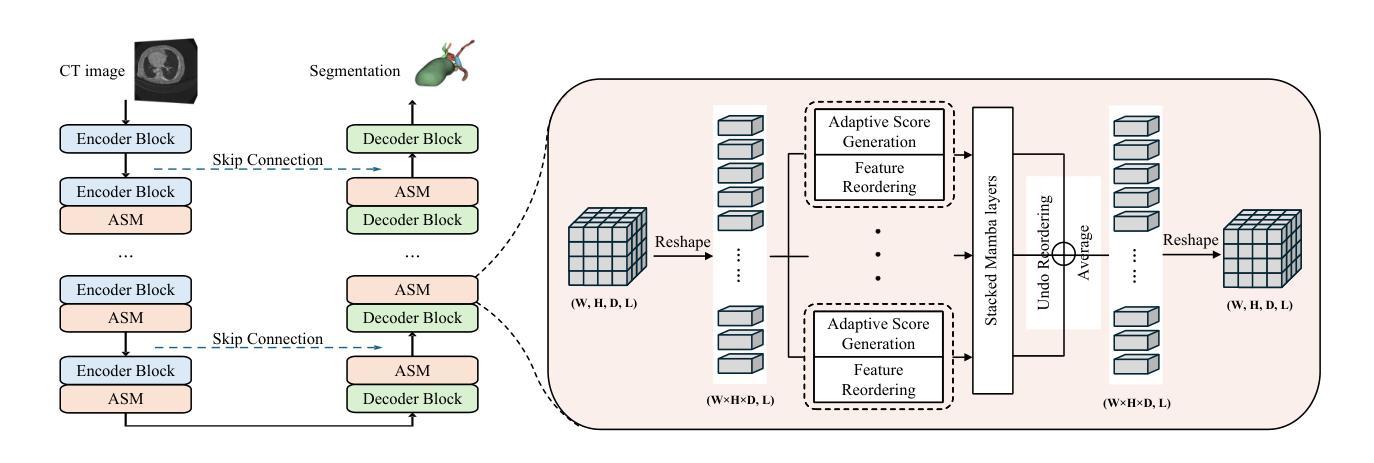
ASM-UNet: Adaptive Scan Mamba Integrating Group Commonalities and Individual Variations for Fine-Grained Segmentation
Authors:Bo Wang, Mengyuan Xu, Yue Yan, Yuqun Yang, Kechen Shu, Wei Ping, Xu Tang, Wei Jiang, Zheng You
Precise lesion resection depends on accurately identifying fine-grained anatomical structures. While many coarse-grained segmentation (CGS) methods have been successful in large-scale segmentation (e.g., organs), they fall short in clinical scenarios requiring fine-grained segmentation (FGS), which remains challenging due to frequent individual variations in small-scale anatomical structures. Although recent Mamba-based models have advanced medical image segmentation, they often rely on fixed manually-defined scanning orders, which limit their adaptability to individual variations in FGS. To address this, we propose ASM-UNet, a novel Mamba-based architecture for FGS. It introduces adaptive scan scores to dynamically guide the scanning order, generated by combining group-level commonalities and individual-level variations. Experiments on two public datasets (ACDC and Synapse) and a newly proposed challenging biliary tract FGS dataset, namely BTMS, demonstrate that ASM-UNet achieves superior performance in both CGS and FGS tasks. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/YqunYang/ASM-UNet.
精确的病变切除依赖于对精细解剖结构的准确识别。虽然许多粗粒度分割(CGS)方法在大规模分割(如器官)中取得了成功,但在临床场景中需要进行精细粒度分割(FGS)时,它们就显得力不从心。由于小尺度解剖结构的个体变异频繁,精细粒度分割仍然是一个挑战。尽管最近的基于Mamba的模型在医学图像分割方面取得了进展,但它们通常依赖于固定的手动定义的扫描顺序,这限制了它们对精细粒度分割中个体差异的适应性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了ASM-UNet,这是一种基于Mamba的新型精细粒度分割架构。它引入了自适应扫描得分来动态引导扫描顺序,该得分是通过结合群组级别的共性以及个体级别的变化生成的。在两个公共数据集(ACDC和Synapse)以及新提出的具有挑战性的胆道精细粒度分割数据集BTMS上的实验表明,ASM-UNet在粗粒度分割和精细粒度分割任务中都实现了卓越的性能。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/YqunYang/ASM-UNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于Mamba的新型架构ASM-UNet,用于精细粒度分割(FGS)。该架构引入自适应扫描得分来动态指导扫描顺序,该得分结合了群体级别共性及个体级别差异。在ACDC、Synapse两个公开数据集及新提出的具有挑战性的胆道精细分割数据集BTMS上的实验表明,ASM-UNet在粗细粒度分割任务中都表现出卓越性能。
要点掌握
- 精细粒度分割(FGS)在临床场景中非常重要,因为它涉及到小尺度解剖结构的精确识别。
- 传统粗粒度分割(CGS)方法在大规模分割中成功,但在FGS中因个体变异而受限。
- Mamba模型虽在医学图像分割中有进展,但固定扫描顺序限制了其适应个体变异的能力。
- ASM-UNet是一种新型Mamba架构,引入自适应扫描得分来动态调整扫描顺序。
- 自适应扫描得分结合了群体级别共性及个体级别差异。
- 在多个公开数据集上的实验证明了ASM-UNet在粗细粒度分割任务中的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

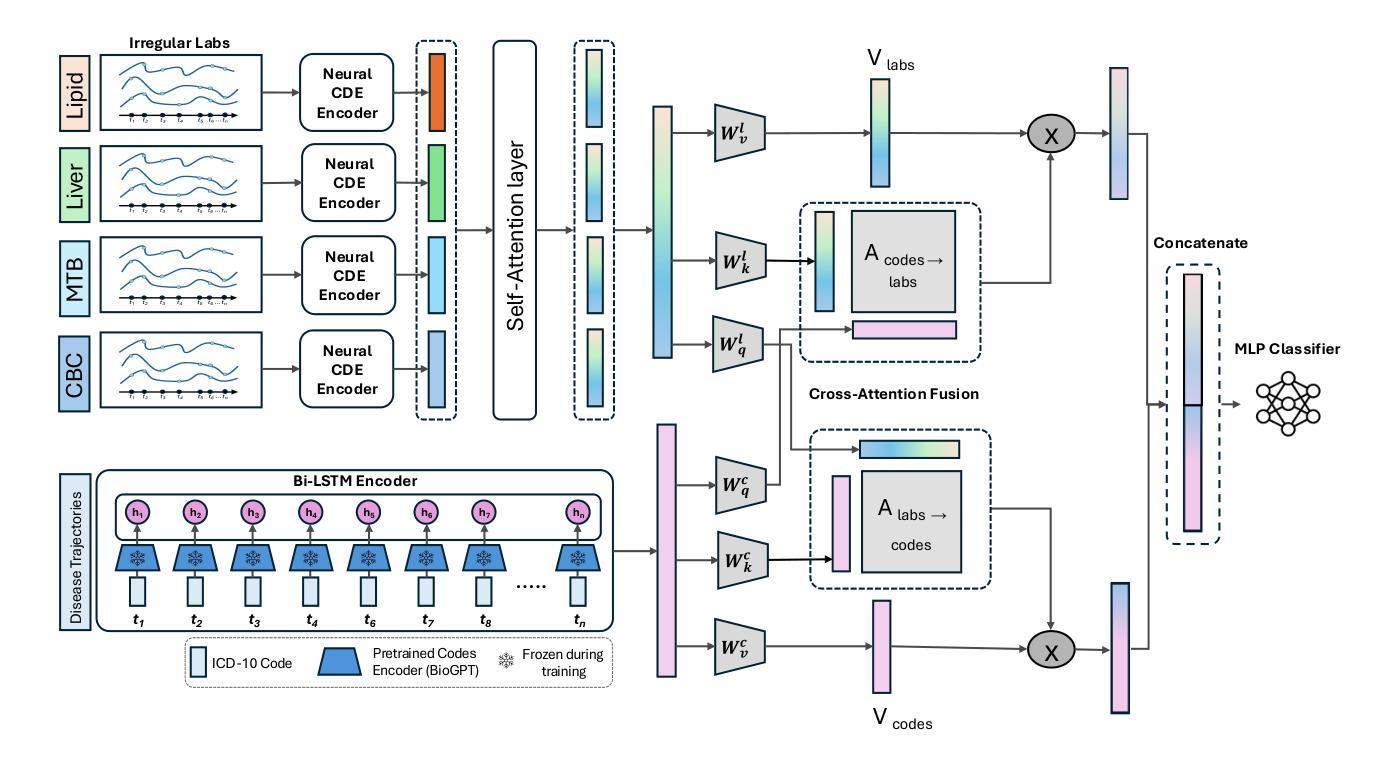
Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer Using Multimodal Learning on Electronic Health Record
Authors:Mosbah Aouad, Anirudh Choudhary, Awais Farooq, Steven Nevers, Lusine Demirkhanyan, Bhrandon Harris, Suguna Pappu, Christopher Gondi, Ravishankar Iyer
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest cancers, and early detection remains a major clinical challenge due to the absence of specific symptoms and reliable biomarkers. In this work, we propose a new multimodal approach that integrates longitudinal diagnosis code histories and routinely collected laboratory measurements from electronic health records to detect PDAC up to one year prior to clinical diagnosis. Our method combines neural controlled differential equations to model irregular lab time series, pretrained language models and recurrent networks to learn diagnosis code trajectory representations, and cross-attention mechanisms to capture interactions between the two modalities. We develop and evaluate our approach on a real-world dataset of nearly 4,700 patients and achieve significant improvements in AUC ranging from 6.5% to 15.5% over state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, our model identifies diagnosis codes and laboratory panels associated with elevated PDAC risk, including both established and new biomarkers. Our code is available at https://github.com/MosbahAouad/EarlyPDAC-MML.
胰腺癌导管腺癌(PDAC)是最致命的癌症之一,由于缺少特定症状和可靠生物标志物,早期检测仍是临床上的一个主要挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的多模式方法,该方法结合了纵向诊断代码历史和电子健康记录中常规收集的实验室测量值,可在临床诊断前一年检测到PDAC。我们的方法结合了神经控制微分方程来模拟不规则的实验室时间序列数据、预训练的语言模型和循环网络来学习诊断代码轨迹表示,以及交叉注意机制来捕捉两种模式之间的交互。我们在包含近4700名患者的真实世界数据集上开发和评估了我们的方法,与最先进的方法相比,AUC有6.5%至15.5%的显著提高。此外,我们的模型还确定了与胰腺癌风险增加相关的诊断代码和实验室检测板,包括已知和新生物标志物。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/MosbahAouad/EarlyPDAC-MML 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的多模式方法,通过整合纵向诊断代码历史和电子健康记录中常规收集的实验室测量数据,可在临床确诊前一年预测胰腺癌。该方法使用神经网络控制微分方程对不规则实验室时间序列进行建模,利用预训练的语言模型和循环网络学习诊断代码轨迹表示,并通过交叉注意力机制捕捉两种模式之间的交互。在接近4700名患者的真实数据集上,该方法较最新技术取得了AUC值提高6.5%至15.5%的显著成果。此外,该模型还确定了与胰腺癌风险升高的诊断代码和实验室检测板,包括已知和新生物标志物。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的多模式方法用于胰腺癌早期检测。
- 结合纵向诊断代码历史和实验室测量数据,可在临床确诊前一年进行预测。
- 使用神经网络控制微分方程对不规则实验室时间序列进行建模。
- 利用预训练的语言模型和循环网络学习诊断代码轨迹表示。
- 通过交叉注意力机制捕捉诊断代码和实验室数据之间的交互。
- 在真实数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法较现有技术有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

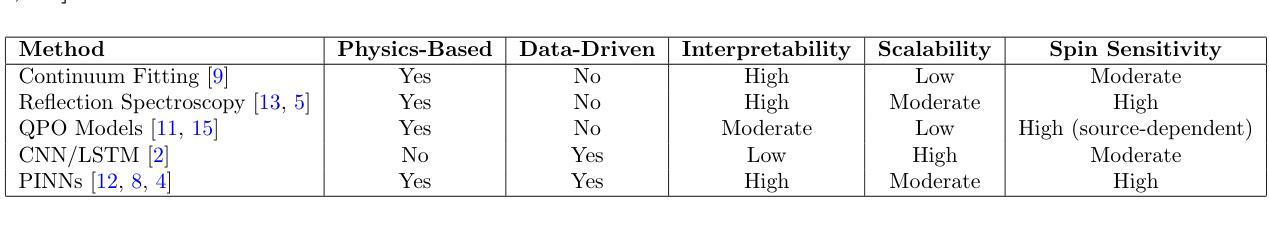
Hybrid Approaches for Black Hole Spin Estimation: From Classical Spectroscopy to Physics-Informed Machine Learning
Authors:Stella Menziltsidou
The measurement of black hole spin is considered one of the key problems in relativistic astrophysics. Existing methods, such as continuum fitting, X-ray reflection spectroscopy and quasi-periodic oscillation analysis, have systematic limitations in accuracy, interpretability and scalability. In this work, a hybrid approach is proposed in which theoretical models based on the Teukolsky formalism are integrated with Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs). A PINN model is developed to solve the linearized spin problem in the scalar case, with physical constraints directly embedded into the training process. Annotated data are not required; instead, the model is trained using the differential operator and boundary conditions as supervision. It is demonstrated that the PINN converges reliably, with residual loss values below 1e-7 and a root mean squared error (RMSE) of the order of 1e-6 (final approx 5.4 x 1e-8). Benchmarking results indicate that the proposed method outperforms both classical and data-driven machine learning approaches in terms of AUC and sensitivity, while also exhibiting superior interpretability, generalizability and adherence to physical principles, with moderate computational cost. Potential extensions include integration with general relativistic magnetohydrodynamics (GRMHD) solvers and application to real observational data. These findings support the viability of physics-based machine learning as a robust framework for accurate and interpretable black hole spin estimation.
黑洞自转测量被认为是相对论天体物理学中的关键问题之一。现有的方法,如连续谱拟合、X射线反射光谱学和准周期振荡分析,在准确性、可解释性和可扩展性方面存在系统局限性。在这项工作中,提出了一种混合方法,该方法结合了基于Teukolsky形式的理论模型与物理信息神经网络(PINN)。开发了一个PINN模型来解决标量情况下的线性化自转问题,物理约束直接嵌入到训练过程中。不需要注释数据;相反,该模型使用微分算子和边界条件作为监督进行训练。结果表明,PINN收敛可靠,残差损失值低于1e-7,均方根误差(RMSE)约为1e-6(最终近似为5.4 x 1e-8)。基准测试结果表明,该方法在AUC和敏感性方面优于经典的和数据驱动的机器学习方法,同时表现出更好的可解释性、通用性和对物理原则的遵循,计算成本适中。潜在扩展包括与广义相对论磁流体动力学(GRMHD)求解器集成以及应用于真实观测数据。这些发现支持了基于物理的机器学习作为一个稳健框架,用于准确和可解释的黑洞自转估计。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables, 4 equations
Summary
本研究提出了基于Teukolsky形式和物理信息神经网络(PINN)的混合方法来测量黑洞自转。开发了一个PINN模型解决标量情况下的线性自转问题,将物理约束直接嵌入训练过程。研究结果表明,该方法具有较高的准确性和可靠性,在基准测试中表现优于传统和基于数据驱动的机器学习算法。
Key Takeaways
- 黑洞自转测量是相对论天体物理学中的关键问题之一。
- 现有方法如连续谱拟合、X射线反射光谱学和准周期振荡分析在准确性、可解释性和可扩展性方面存在系统局限性。
- 本研究提出了基于Teukolsky形式和物理信息神经网络(PINN)的混合方法。
- 开发了一个PINN模型来解决标量情况下的线性自转问题,将物理约束直接嵌入训练过程。
- 该模型不需要注释数据,而是使用微分算子和边界条件作为监督进行训练。
- 研究结果表明,该方法具有较高的准确性和可靠性,优于传统和基于数据的机器学习算法。
- 该方法具有潜在的应用价值,例如与广义相对论磁流体动力学(GRMHD)求解器集成,并应用于实际观测数据。
点此查看论文截图

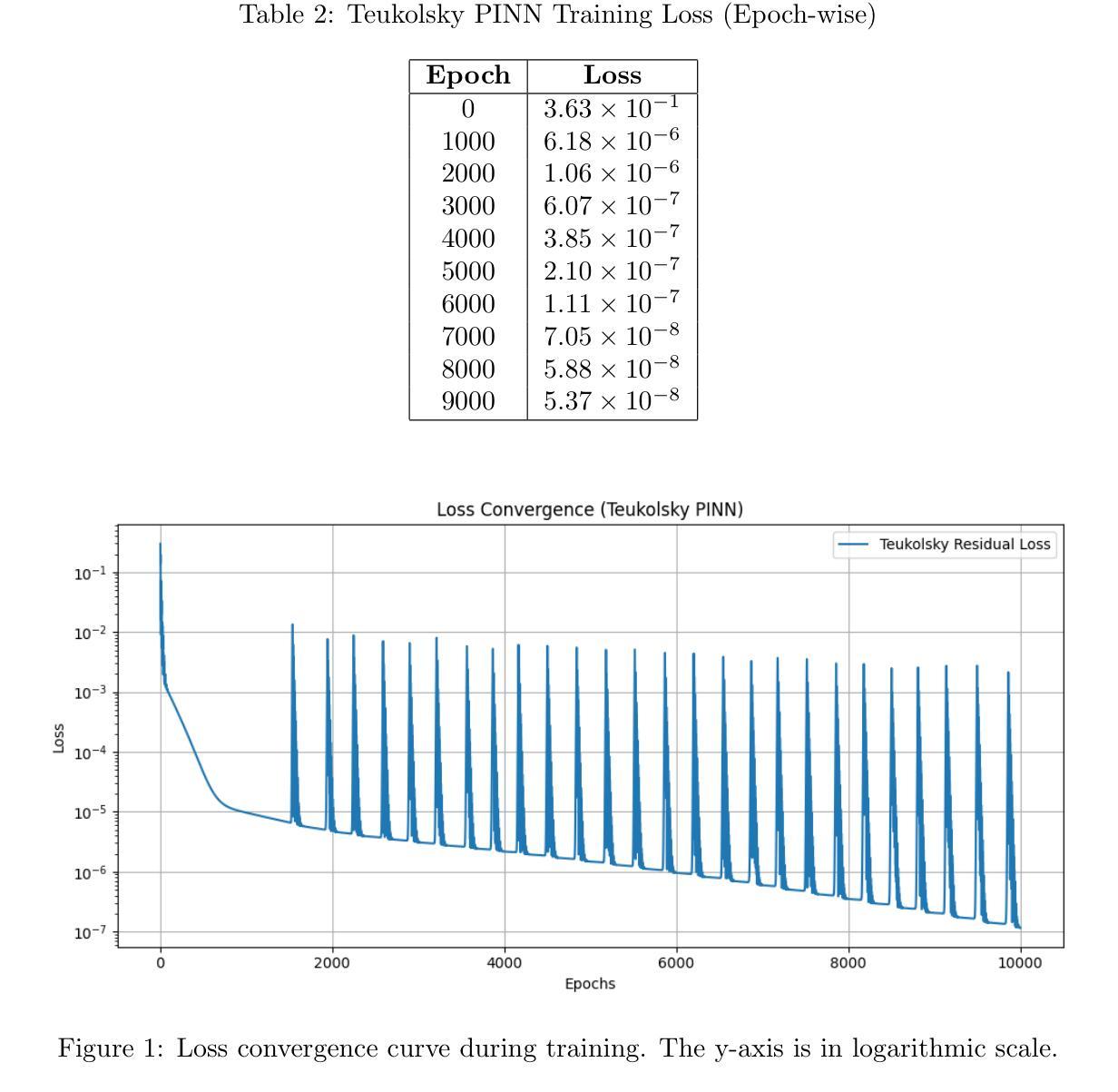
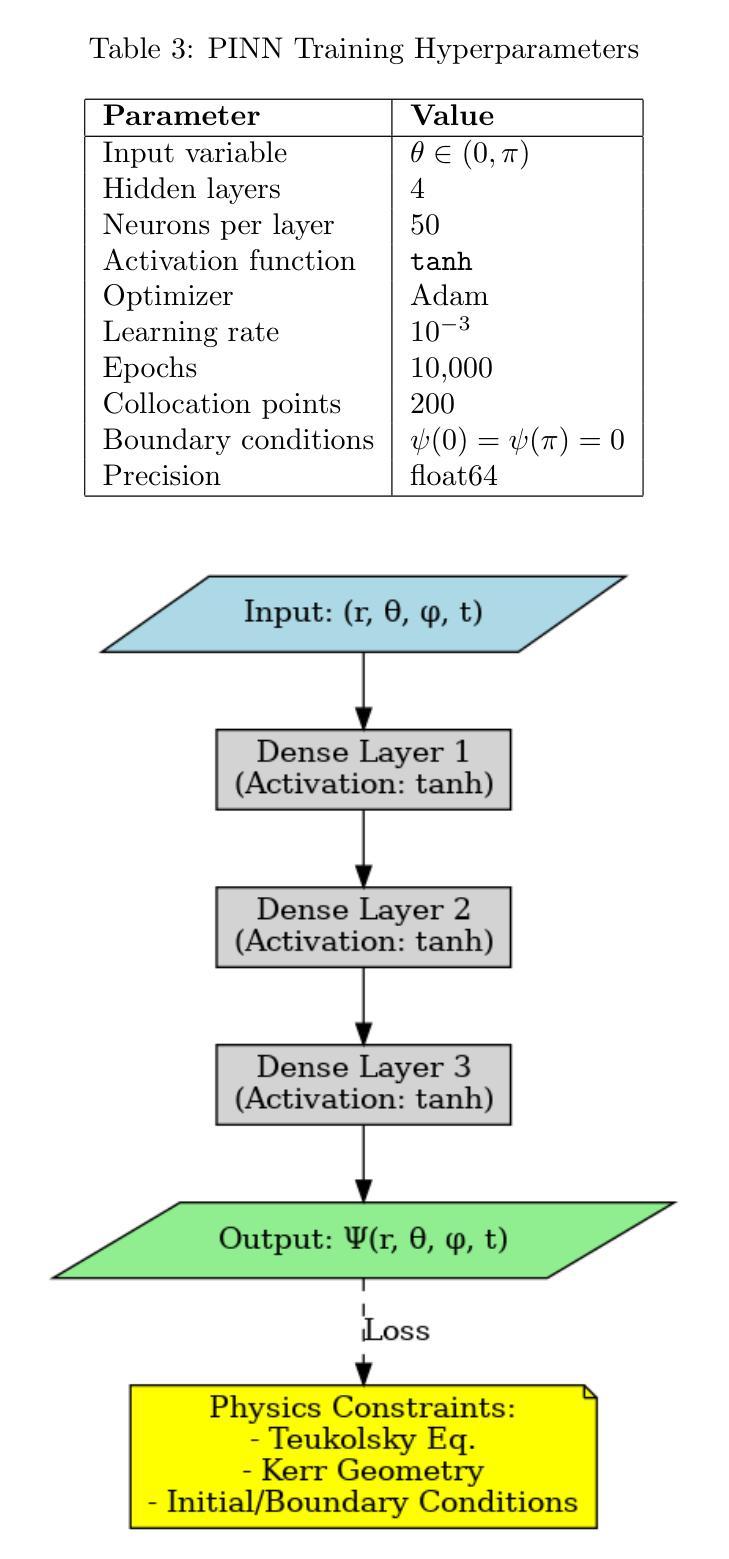
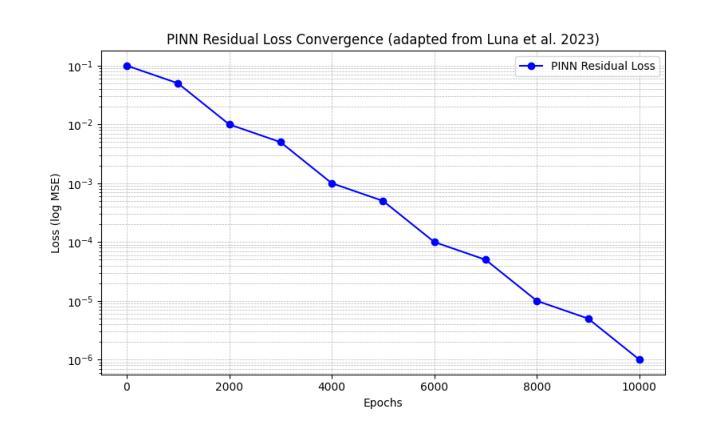
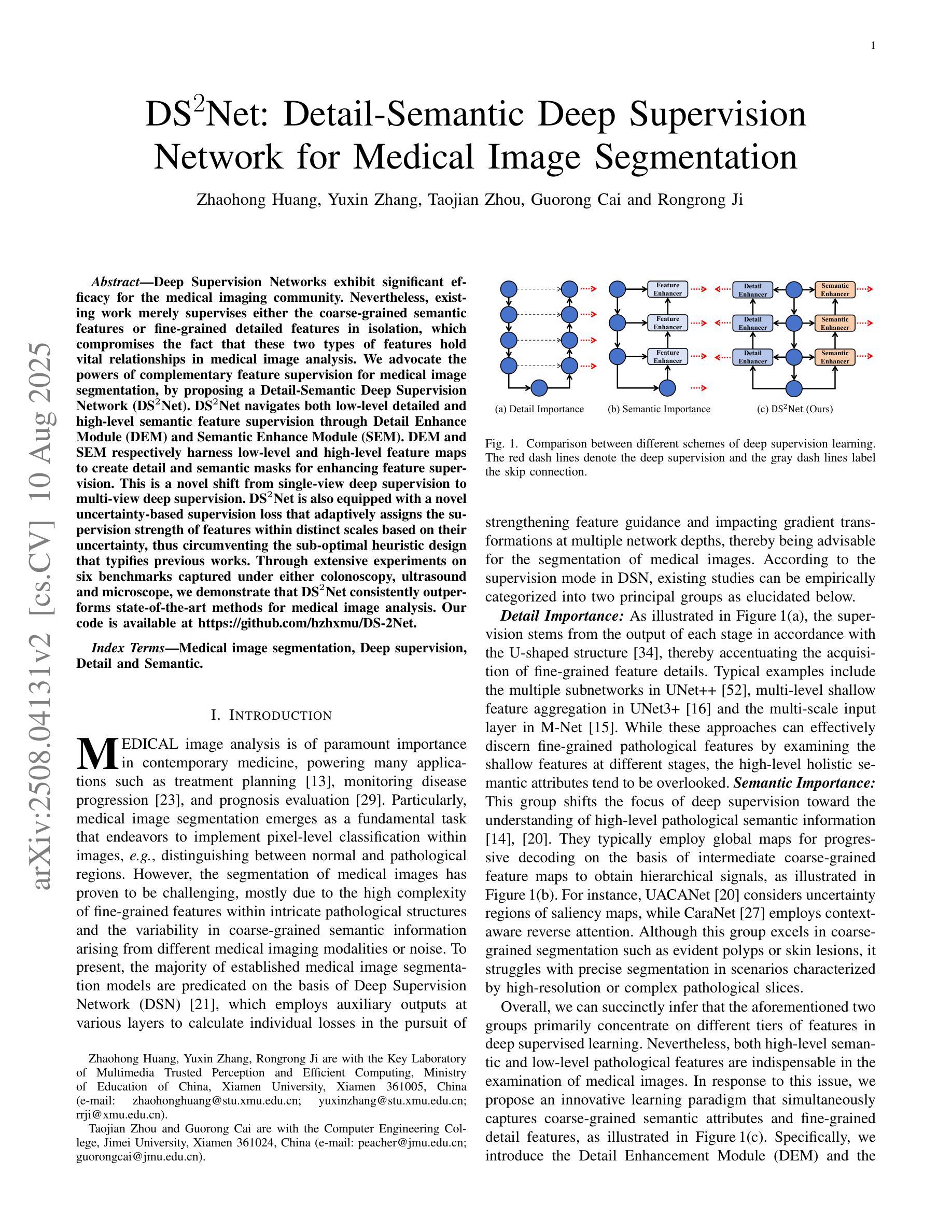
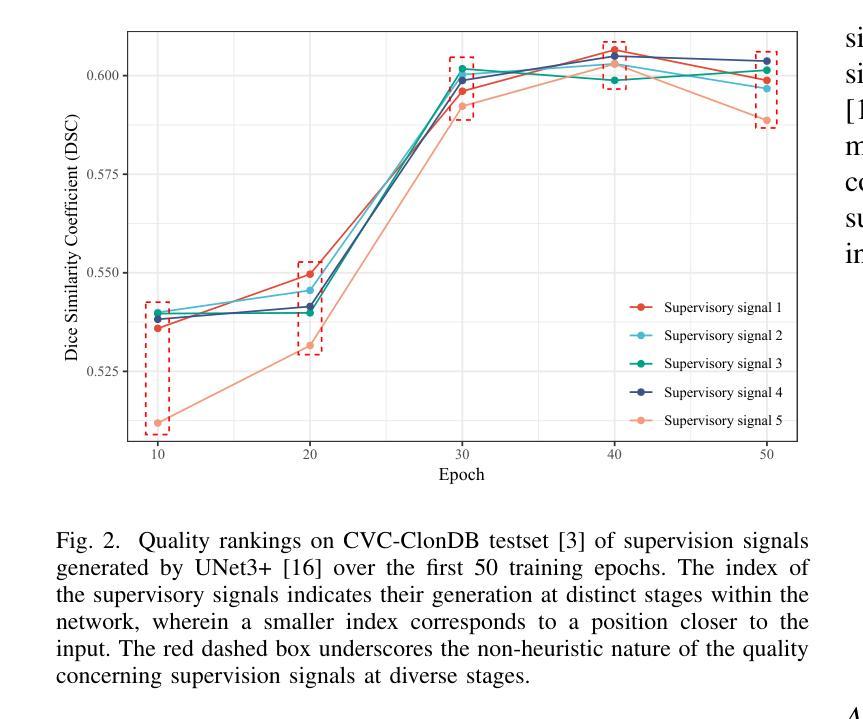
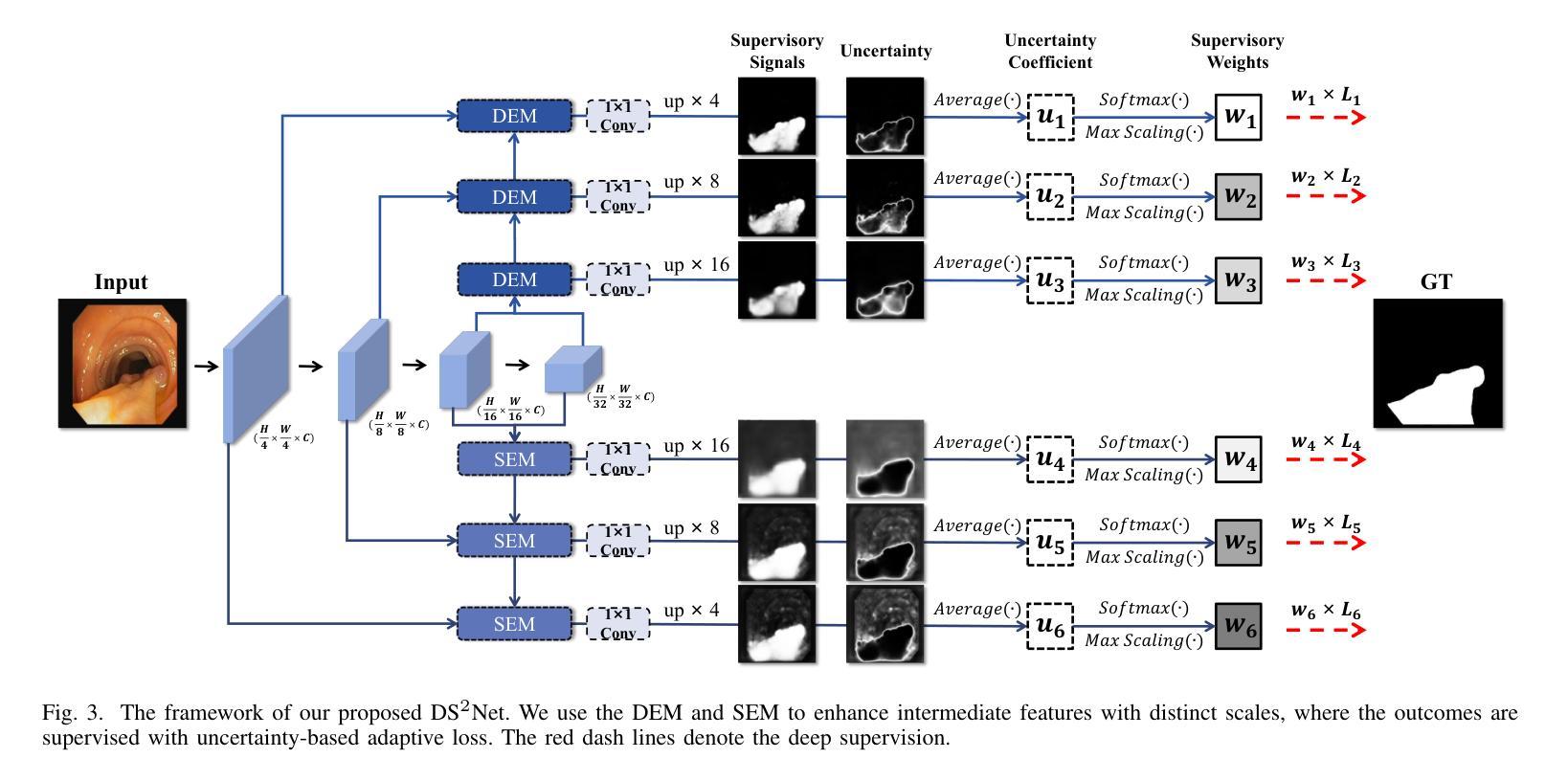
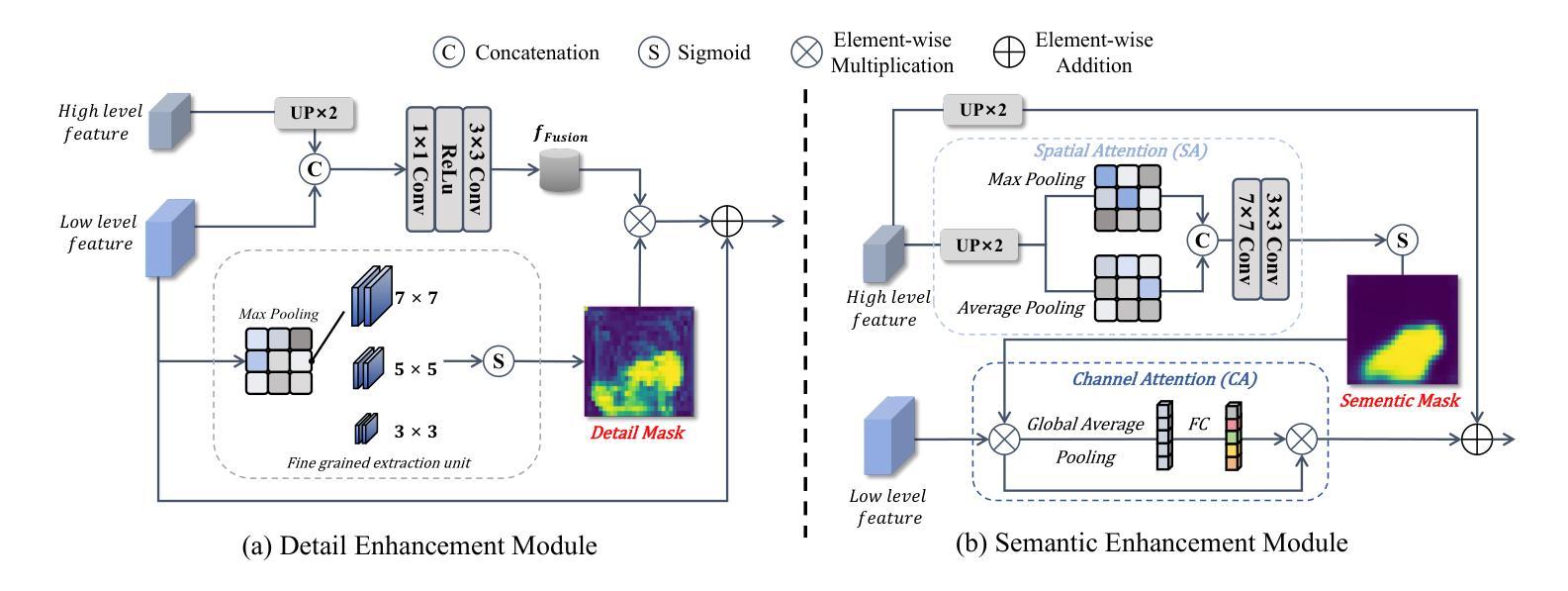
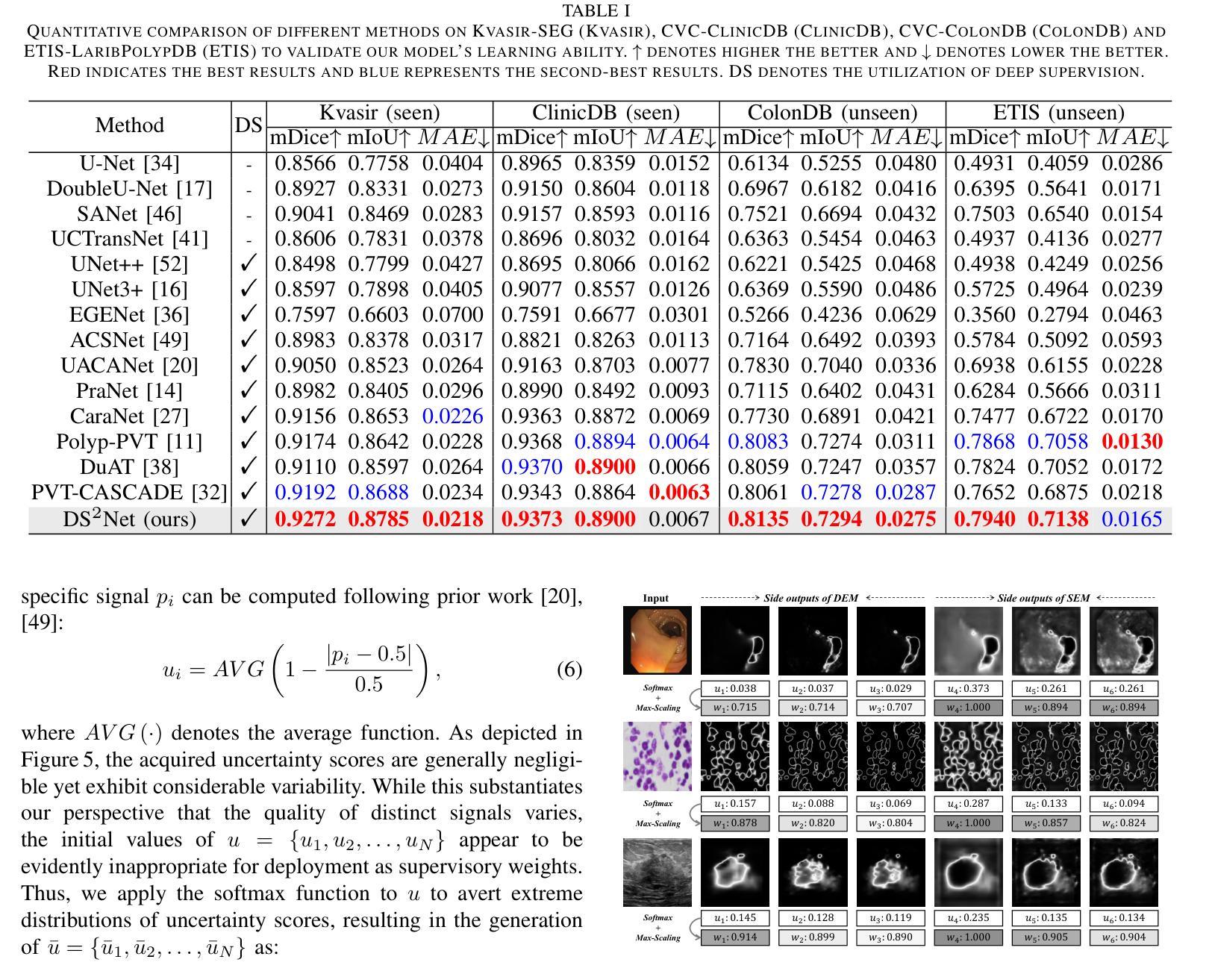
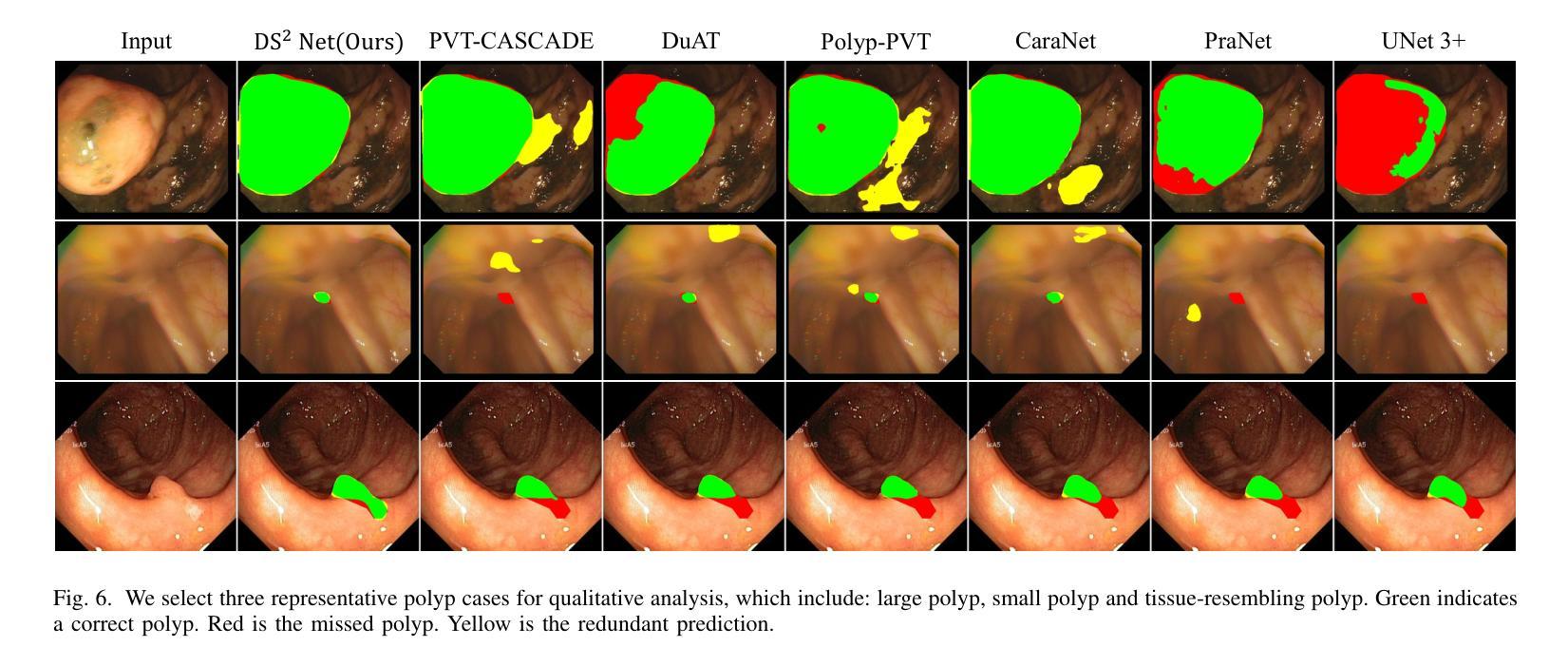
DS$^2$Net: Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhaohong Huang, Yuxin Zhang, Taojian Zhou, Guorong Cai, Rongrong Ji
Deep Supervision Networks exhibit significant efficacy for the medical imaging community. Nevertheless, existing work merely supervises either the coarse-grained semantic features or fine-grained detailed features in isolation, which compromises the fact that these two types of features hold vital relationships in medical image analysis. We advocate the powers of complementary feature supervision for medical image segmentation, by proposing a Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network (DS$^2$Net). DS$^2$Net navigates both low-level detailed and high-level semantic feature supervision through Detail Enhance Module (DEM) and Semantic Enhance Module (SEM). DEM and SEM respectively harness low-level and high-level feature maps to create detail and semantic masks for enhancing feature supervision. This is a novel shift from single-view deep supervision to multi-view deep supervision. DS$^2$Net is also equipped with a novel uncertainty-based supervision loss that adaptively assigns the supervision strength of features within distinct scales based on their uncertainty, thus circumventing the sub-optimal heuristic design that typifies previous works. Through extensive experiments on six benchmarks captured under either colonoscopy, ultrasound and microscope, we demonstrate that DS$^2$Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for medical image analysis.
深度监督网络对医学影像界具有显著效果。然而,现有的工作仅仅单独监督粗粒度的语义特征或细粒度的详细特征,忽略了这两种特征在医学图像分析中具有重要关系的事实。我们提出通过细节语义深度监督网络(DS$^2$Net)进行医学图像分割的互补特征监督。DS$^2$Net通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)导航低级别的详细特征和高级别的语义特征监督。DEM和SEM分别利用低级别和高级别的特征图创建细节和语义掩膜,以增强特征监督。这是一种从单视图深度监督到多视图深度监督的新转变。DS$^2$Net还配备了一种新型基于不确定性的监督损失,该损失可以根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度内特征的监督强度,从而避免了以前工作中典型的次优启发式设计。通过在结肠镜、超声和显微镜下采集的六个基准测试集上进行广泛实验,我们证明了DS$^2$Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度监督网络在医学成像领域表现出显著的效果。现有工作通常只监督粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征,忽略了两者之间的关系。我们提出了一种细节语义深度监督网络(DS^2Net),通过细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)进行互补特征监督。DS^2Net还配备了一种基于不确定性监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应地分配不同尺度的特征监督强度。在六个基准测试上的实验表明,DS^2Net在医学图像分析方面始终优于最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度监督网络在医学成像领域具有显著效果。
- 现有工作主要监督粗粒度语义特征或细粒度详细特征,忽略了它们之间的关系。
- 细节语义深度监督网络(DS^2Net)结合了细节增强模块(DEM)和语义增强模块(SEM)进行互补特征监督。
- DS^2Net从单视图深度监督转向多视图深度监督。
- DS^2Net配备了一种基于不确定性的监督损失,根据特征的不确定性自适应分配监督强度。
- DS^2Net在多个基准测试上表现优异,始终优于现有最先进的医学图像分析方法。
点此查看论文截图
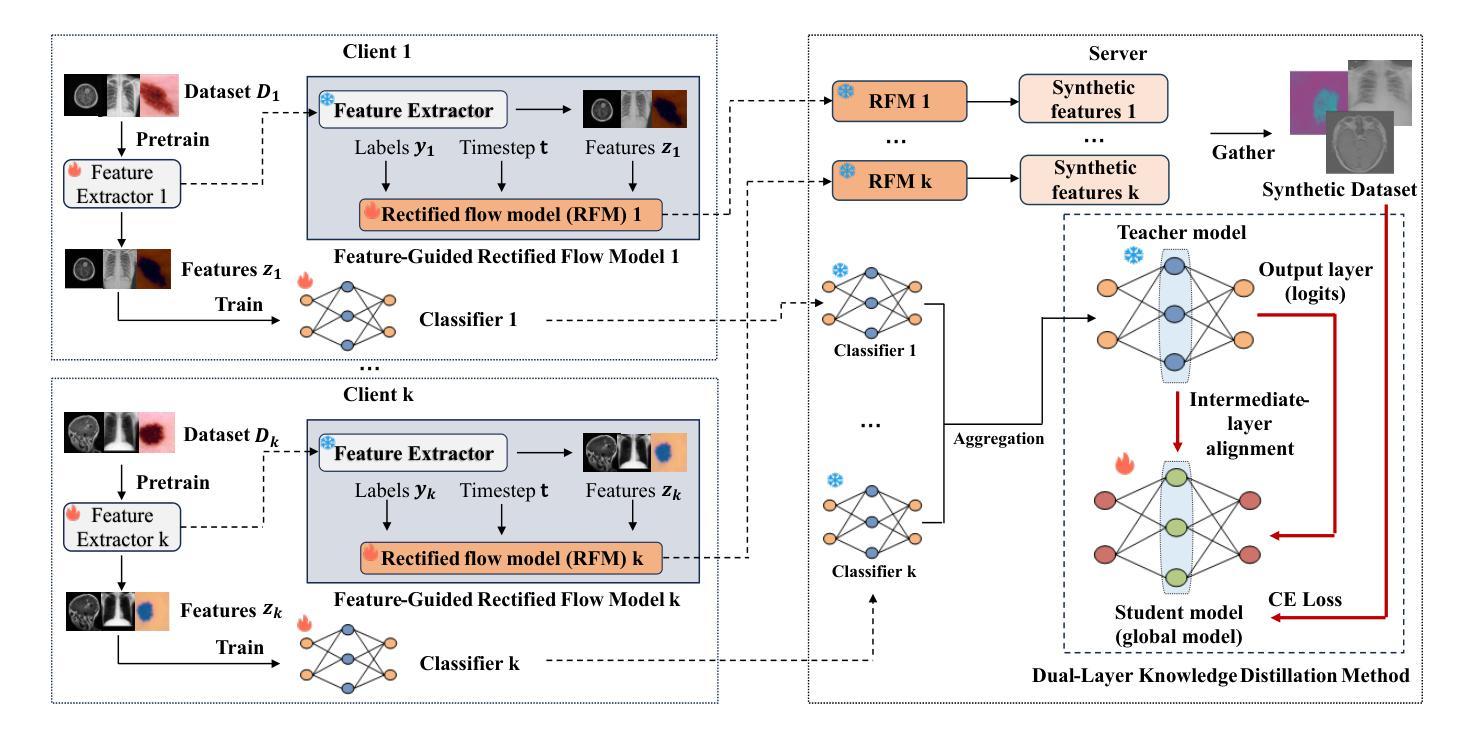
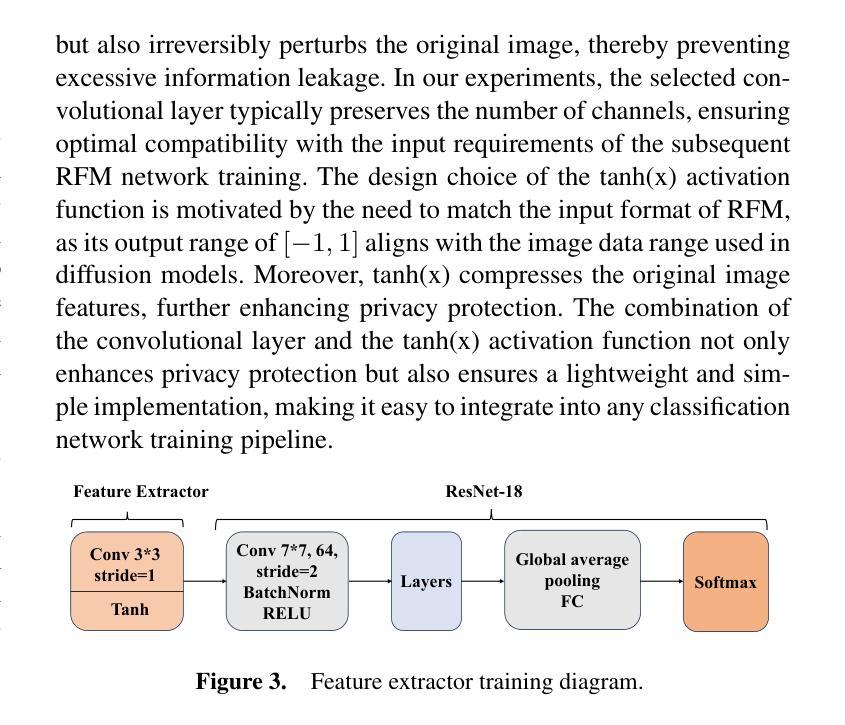
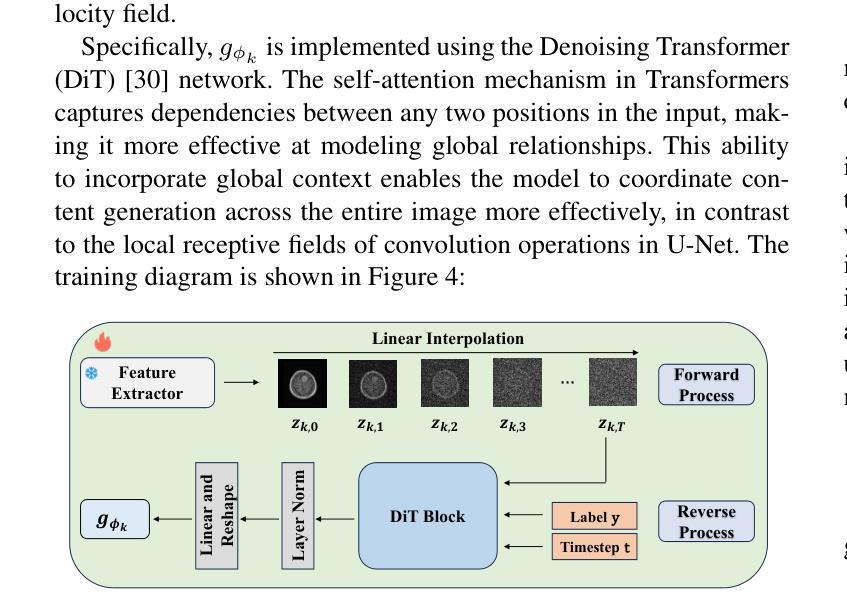
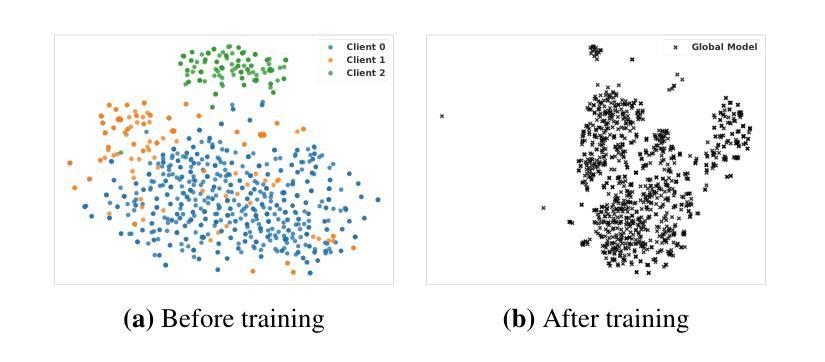
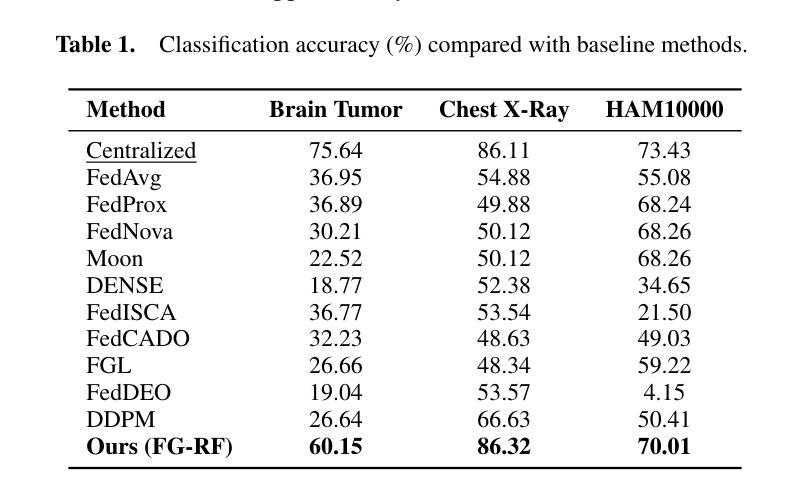
A New One-Shot Federated Learning Framework for Medical Imaging Classification with Feature-Guided Rectified Flow and Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Yufei Ma, Hanwen Zhang, Qiya Yang, Guibo Luo, Yuesheng Zhu
In multi-center scenarios, One-Shot Federated Learning (OSFL) has attracted increasing attention due to its low communication overhead, requiring only a single round of transmission. However, existing generative model-based OSFL methods suffer from low training efficiency and potential privacy leakage in the healthcare domain. Additionally, achieving convergence within a single round of model aggregation is challenging under non-Independent and Identically Distributed (non-IID) data. To address these challenges, in this paper a modified OSFL framework is proposed, in which a new Feature-Guided Rectified Flow Model (FG-RF) and Dual-Layer Knowledge Distillation (DLKD) aggregation method are developed. FG-RF on the client side accelerates generative modeling in medical imaging scenarios while preserving privacy by synthesizing feature-level images rather than pixel-level images. To handle non-IID distributions, DLKD enables the global student model to simultaneously mimic the output logits and align the intermediate-layer features of client-side teacher models during aggregation. Experimental results on three non-IID medical imaging datasets show that our new framework and method outperform multi-round federated learning approaches, achieving up to 21.73% improvement, and exceeds the baseline FedISCA by an average of 21.75%. Furthermore, our experiments demonstrate that feature-level synthetic images significantly reduce privacy leakage risks compared to pixel-level synthetic images. The code is available at https://github.com/LMIAPC/one-shot-fl-medical.
在多中心场景中,由于只需一轮传输,一次联邦学习(OSFL)因其低通信开销而备受关注。然而,现有的基于生成模型的OSFL方法存在训练效率低下和医疗保健领域潜在隐私泄露的问题。此外,在非独立同分布(non-IID)数据下,在单次模型聚合中实现收敛是一个挑战。针对这些挑战,本文提出了一种改进的OSFL框架,其中开发了一种新的特征引导校正流模型(FG-RF)和双层知识蒸馏(DLKD)聚合方法。客户端的FG-RF加速医学成像场景中的生成建模,通过合成特征级图像而不是像素级图像来保留隐私。为了处理非IID分布,DLKD使全局学生模型能够在聚合过程中同时模仿输出逻辑和与客户端教师模型的中间层特征对齐。在三个非IID医学成像数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的新框架和方法优于多轮联邦学习方法,实现了高达21.73%的改进,并且比基线FedISCA平均高出21.75%。此外,我们的实验表明,与像素级合成图像相比,特征级合成图像显著降低了隐私泄露风险。代码可在https://github.com/LMIAPC/one-shot-fl-medical找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECAI 2025
摘要
本论文提出了一种改进的一次性联邦学习框架,针对医疗影像场景,通过特征引导修正流模型和双层知识蒸馏聚合方法,解决现有生成模型存在的训练效率低和隐私泄露问题。特征引导修正流模型在客户端加速生成模型,合成特征级图像以保留隐私。双层知识蒸馏解决了非独立同分布数据的聚合问题。实验结果显示,新方法在非独立同分布的医学影像数据集上表现优于多轮联邦学习,并降低了隐私泄露风险。
关键见解
- 论文引入了一种新的单次联邦学习框架来解决多中心场景下的问题,特别是针对医疗影像的处理。
- 提出了特征引导修正流模型(FG-RF),在客户端加速生成模型,并通过合成特征级图像来保留隐私。
- 引入双层知识蒸馏(DLKD)方法以解决非独立同分布(non-IID)数据的聚合挑战。
- 实验证明,新的框架和方法在三个非独立同分布的医学影像数据集上的表现优于多轮联邦学习,平均提升达21.75%。
- 特征级合成图像相较于像素级合成图像,显著降低了隐私泄露风险。
- 论文提供了实验代码,可供进一步研究和应用。
- 该框架对一次性联邦学习在医疗影像领域的应用具有潜在的推动作用。
点此查看论文截图

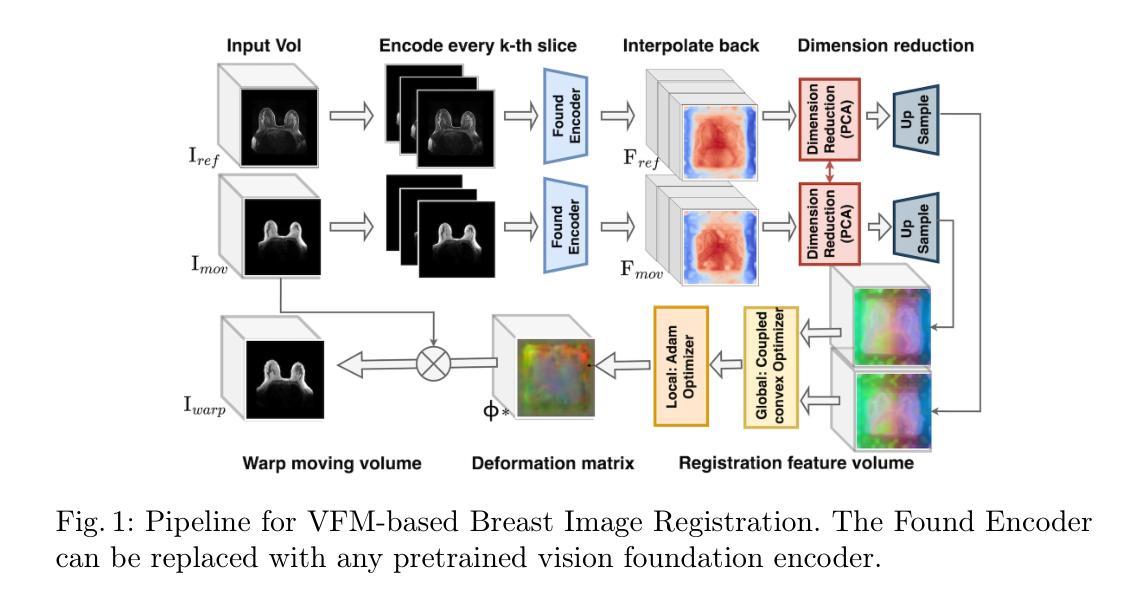
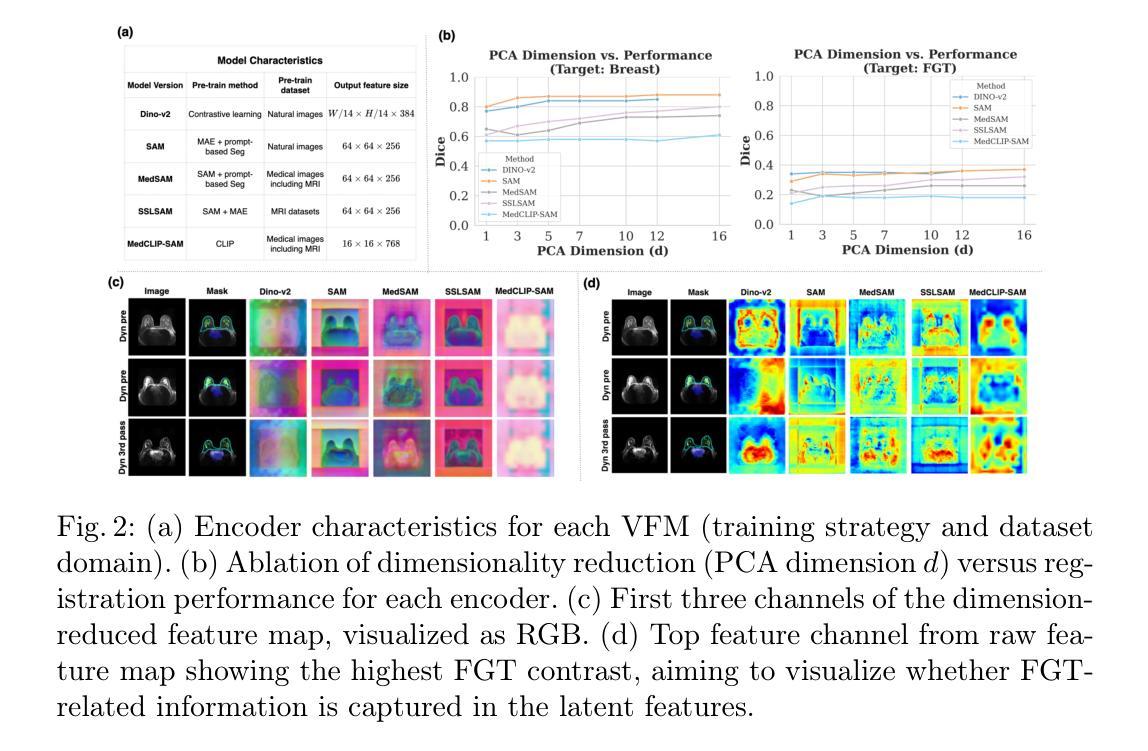
Are Vision Foundation Models Ready for Out-of-the-Box Medical Image Registration?
Authors:Hanxue Gu, Yaqian Chen, Nicholas Konz, Qihang Li, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Foundation models, pre-trained on large image datasets and capable of capturing rich feature representations, have recently shown potential for zero-shot image registration. However, their performance has mostly been tested in the context of rigid or less complex structures, such as the brain or abdominal organs, and it remains unclear whether these models can handle more challenging, deformable anatomy. Breast MRI registration is particularly difficult due to significant anatomical variation between patients, deformation caused by patient positioning, and the presence of thin and complex internal structure of fibroglandular tissue, where accurate alignment is crucial. Whether foundation model-based registration algorithms can address this level of complexity remains an open question. In this study, we provide a comprehensive evaluation of foundation model-based registration algorithms for breast MRI. We assess five pre-trained encoders, including DINO-v2, SAM, MedSAM, SSLSAM, and MedCLIP, across four key breast registration tasks that capture variations in different years and dates, sequences, modalities, and patient disease status (lesion versus no lesion). Our results show that foundation model-based algorithms such as SAM outperform traditional registration baselines for overall breast alignment, especially under large domain shifts, but struggle with capturing fine details of fibroglandular tissue. Interestingly, additional pre-training or fine-tuning on medical or breast-specific images in MedSAM and SSLSAM, does not improve registration performance and may even decrease it in some cases. Further work is needed to understand how domain-specific training influences registration and to explore targeted strategies that improve both global alignment and fine structure accuracy. We also publicly release our code at \href{https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/Foundation-based-reg}{Github}.
基于大型图像数据集进行预训练的模型,能够捕获丰富的特征表示,最近在零样本图像注册中显示出潜力。然而,它们的性能大多是在刚性或较简单的结构背景下测试的,如大脑或腹部器官,尚不清楚这些模型是否能处理更具挑战性的、可变形的结构。乳房MRI注册特别困难,因为患者之间存在重大的解剖变异、由患者定位引起的变形,以及纤维腺体组织的薄而复杂的内部结构,准确对齐是关键的。基于模型的注册算法是否能应对这种复杂程度仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在这项研究中,我们对基于模型的乳房MRI注册算法进行了全面评估。我们评估了五种预训练的编码器,包括DINO-v2、SAM、MedSAM、SSLSAM和MedCLIP,涵盖了四个关键的乳房注册任务,这些任务捕捉了不同年份和日期的变化、序列、模态和患者的疾病状态(病变与非病变)。我们的结果表明,基于模型的算法,如SAM,在总体乳房对齐方面优于传统注册基线,特别是在大域偏移的情况下,但在捕捉纤维腺体组织的细节方面存在困难。有趣的是,在MedSAM和SSLSAM中对医疗或乳房特定图像进行额外的预训练或微调,并不会改善注册性能,甚至在某些情况下会降低性能。需要进一步的工作来理解域特定训练对注册的影响,并探索旨在提高全局对齐和精细结构准确性的策略。我们的代码已公开发布在Github上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 3 figures, 9 pages
Summary
本文研究了基于基础模型的图像配准算法在乳腺MRI图像配准中的应用。实验评估了五种预训练编码器在四项乳腺配准任务上的性能,发现基于基础模型的算法如SAM在整体乳腺对齐方面表现优于传统配准基线,但在捕捉乳腺组织的细节方面存在困难。此外,对于特定医学或乳腺图像的预训练或微调并不一定能提高配准性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基础模型在零样本图像配准中显示出潜力,尤其是用于处理复杂、可变形结构的图像。
- 乳腺MRI配准面临患者间解剖结构差异、患者定位引起的变形以及纤维腺体组织内部复杂结构等挑战。
- 研究评估了五种预训练编码器在乳腺MRI配准中的性能,涉及四项关键任务。
- 基于基础模型的算法如SAM在整体乳腺对齐方面优于传统方法,但在精细结构准确性方面存在挑战。
- 特定医学或乳腺图像的预训练或微调不一定会提高配准性能,甚至可能降低性能。
- 需要进一步了解领域特定训练对配准的影响。
点此查看论文截图