⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
Revisiting Efficient Semantic Segmentation: Learning Offsets for Better Spatial and Class Feature Alignment
Authors:Shi-Chen Zhang, Yunheng Li, Yu-Huan Wu, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng
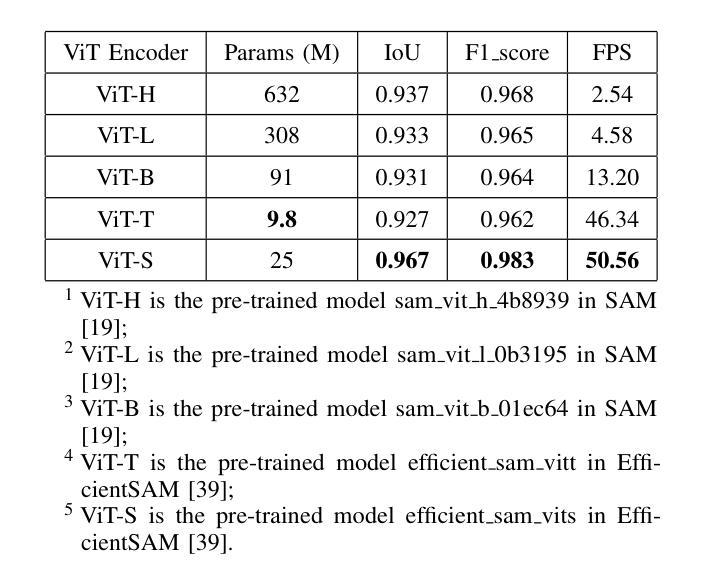
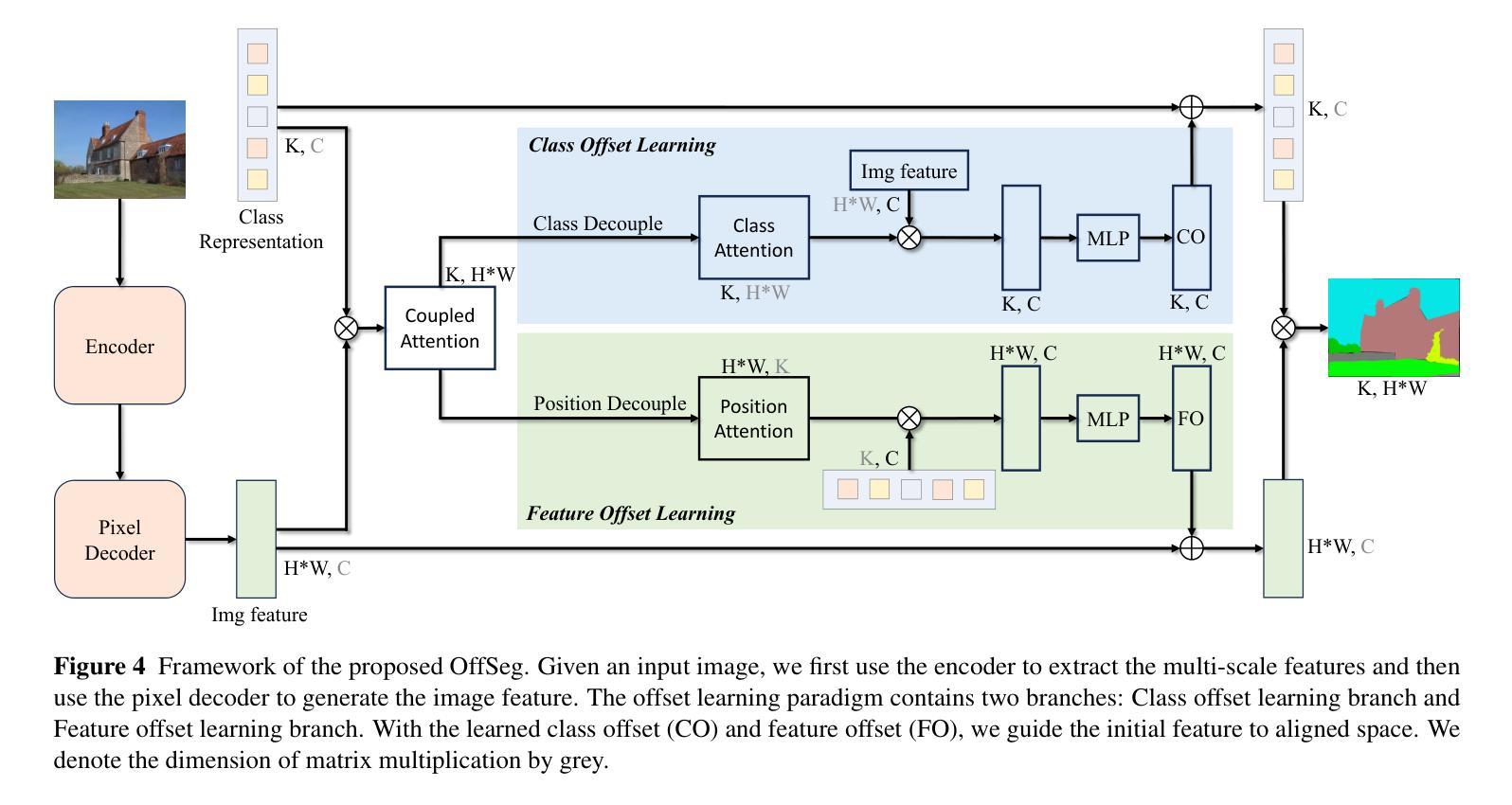
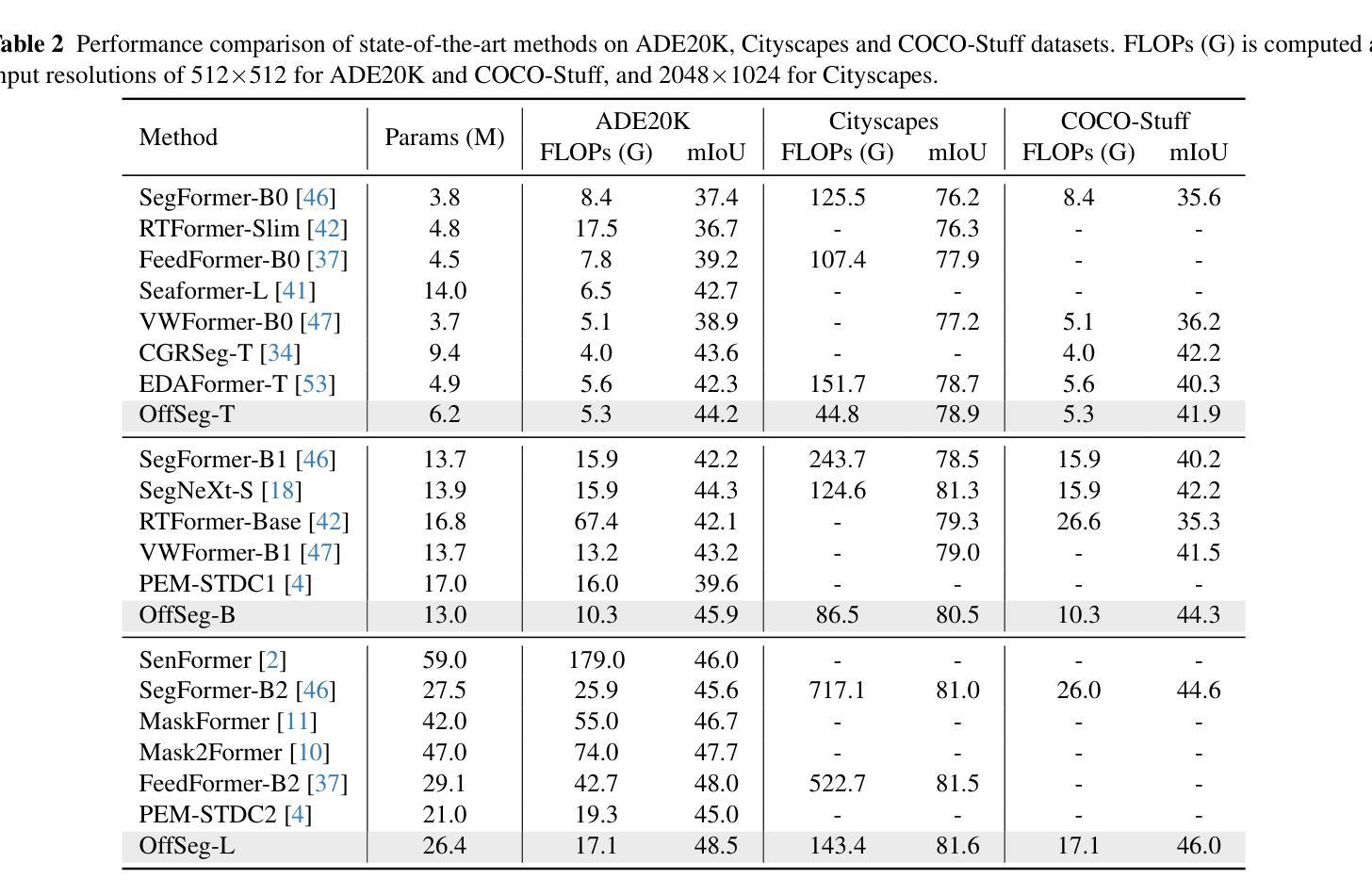
Semantic segmentation is fundamental to vision systems requiring pixel-level scene understanding, yet deploying it on resource-constrained devices demands efficient architectures. Although existing methods achieve real-time inference through lightweight designs, we reveal their inherent limitation: misalignment between class representations and image features caused by a per-pixel classification paradigm. With experimental analysis, we find that this paradigm results in a highly challenging assumption for efficient scenarios: Image pixel features should not vary for the same category in different images. To address this dilemma, we propose a coupled dual-branch offset learning paradigm that explicitly learns feature and class offsets to dynamically refine both class representations and spatial image features. Based on the proposed paradigm, we construct an efficient semantic segmentation network, OffSeg. Notably, the offset learning paradigm can be adopted to existing methods with no additional architectural changes. Extensive experiments on four datasets, including ADE20K, Cityscapes, COCO-Stuff-164K, and Pascal Context, demonstrate consistent improvements with negligible parameters. For instance, on the ADE20K dataset, our proposed offset learning paradigm improves SegFormer-B0, SegNeXt-T, and Mask2Former-Tiny by 2.7%, 1.9%, and 2.6% mIoU, respectively, with only 0.1-0.2M additional parameters required.
语义分割对于需要像素级场景理解的系统至关重要。然而,在资源受限的设备上部署它需要高效的架构。尽管现有方法通过轻型设计实现了实时推理,但我们也揭示了它们的固有局限性:由像素分类范式导致的类表示与图像特征之间的不匹配。通过实验分析,我们发现这种范式对高效场景提出了一个极具挑战性的假设:同一类别在不同图像中的像素特征不应有所变化。为了解决这一困境,我们提出了一种耦合的双分支偏移学习范式,该范式显式学习特征和类偏移以动态优化类表示和空间图像特征。基于这一范式,我们构建了一个高效的语义分割网络OffSeg。值得注意的是,偏移学习范式可以在无需额外架构更改的情况下应用于现有方法。在ADE20K、Cityscapes、COCO-Stuff-164K和Pascal Context等四个数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法实现了持续的改进,并且增加的参数微乎其微。例如,在ADE20K数据集上,我们提出的偏移学习范式将SegFormer-B0、SegNeXt-T和Mask2Former-Tiny的mIoU分别提高了2.7%、1.9%和2.6%,并且仅需要额外的0.1-0.2M参数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025. Project page: https://github.com/HVision-NKU/OffSeg
Summary
本文介绍了语义分割在视觉系统中的重要性,特别是在需要像素级场景理解的系统中的关键性。针对资源受限设备上部署语义分割时面临效率问题的挑战,本文揭示了现有方法的局限性,并提出了一种耦合的双分支偏移学习范式来解决这一问题。通过该范式,本文构建了一个高效的语义分割网络OffSeg,该网络可以在不增加额外架构改动的情况下对现有方法进行改进。实验结果表明,该范式在多个数据集上均实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在视觉系统中具有重要作用,特别是在需要像素级场景理解的系统中的应用十分关键。
- 现有方法在资源受限设备上部署语义分割时存在效率问题。
- 现有方法的局限性在于其分类模式导致的类表示与图像特征之间的不匹配。
- 提出了一种耦合的双分支偏移学习范式来解决上述问题,该范式可以动态地优化类表示和图像特征。
- 基于该范式构建了一个高效的语义分割网络OffSeg。
- Offset学习范式可以在不改变现有架构的前提下应用,实现性能的提升。
点此查看论文截图

Unified and Semantically Grounded Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xin Wang, Yin Guo, Jiamin Xia, Kaiyu Zhang, Niranjan Balu, Mahmud Mossa-Basha, Linda Shapiro, Chun Yuan
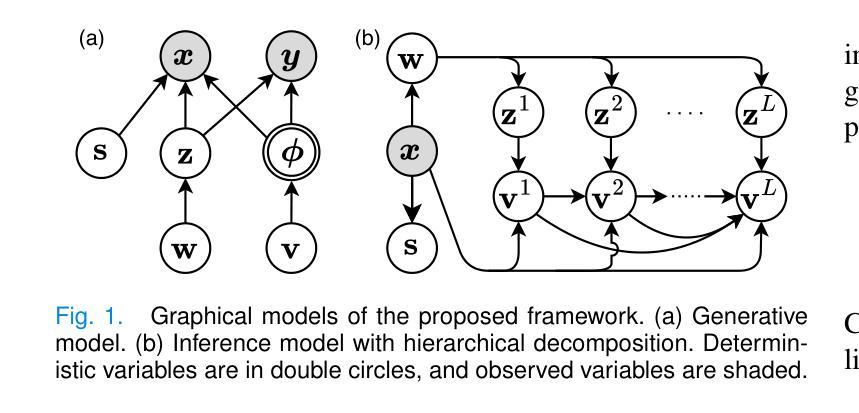
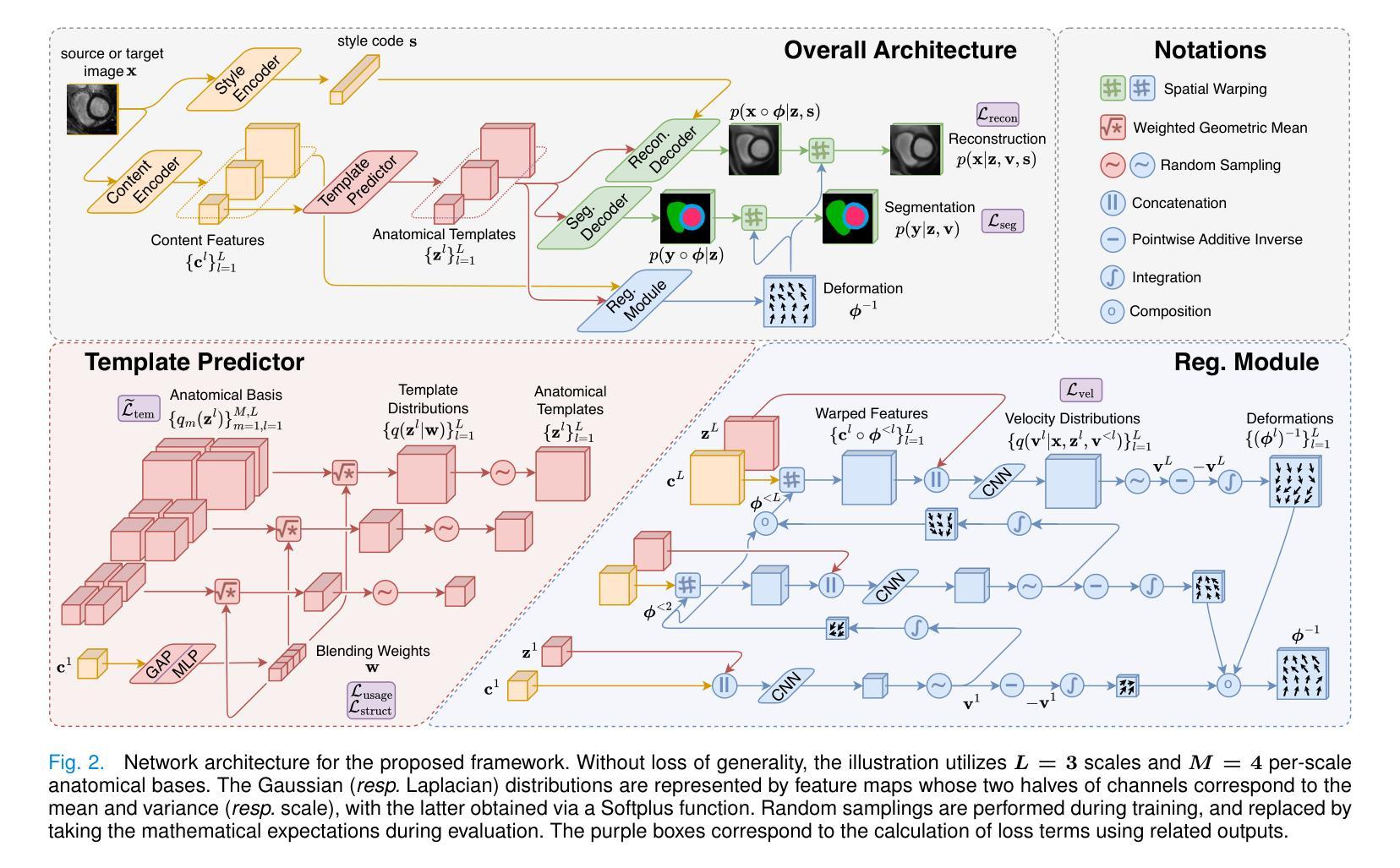
Most prior unsupervised domain adaptation approaches for medical image segmentation are narrowly tailored to either the source-accessible setting, where adaptation is guided by source-target alignment, or the source-free setting, which typically resorts to implicit supervision mechanisms such as pseudo-labeling and model distillation. This substantial divergence in methodological designs between the two settings reveals an inherent flaw: the lack of an explicit, structured construction of anatomical knowledge that naturally generalizes across domains and settings. To bridge this longstanding divide, we introduce a unified, semantically grounded framework that supports both source-accessible and source-free adaptation. Fundamentally distinct from all prior works, our framework’s adaptability emerges naturally as a direct consequence of the model architecture, without the need for any handcrafted adaptation strategies. Specifically, our model learns a domain-agnostic probabilistic manifold as a global space of anatomical regularities, mirroring how humans establish visual understanding. Thus, the structural content in each image can be interpreted as a canonical anatomy retrieved from the manifold and a spatial transformation capturing individual-specific geometry. This disentangled, interpretable formulation enables semantically meaningful prediction with intrinsic adaptability. Extensive experiments on challenging cardiac and abdominal datasets show that our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in both settings, with source-free performance closely approaching its source-accessible counterpart, a level of consistency rarely observed in prior works. Beyond quantitative improvement, we demonstrate strong interpretability of the proposed framework via manifold traversal for smooth shape manipulation.
在之前的医学图像分割的无监督域适应方法中,大多数方法要么是针对可访问源数据的场景(其中自适应是由源-目标对齐引导的),要么是针对无源数据的场景(通常依赖于伪标签和模型蒸馏等隐式监督机制)。这两种设置之间在方法论设计上的巨大差异表明了一个内在缺陷:缺乏明确的结构化构造解剖知识,该知识可以自然地在不同的领域和环境中推广。为了弥补这一长期存在的分歧,我们引入了一个统一的、语义基础框架,支持源可访问和无源适应。从根本上讲,我们的框架的适应性是模型架构的直接结果,无需任何手工定制的自适应策略,这是与所有先前工作的根本区别。具体来说,我们的模型学习一个领域无关的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,这反映了人类如何建立视觉理解。因此,图像中的结构内容可以被解释为从流形中检索的典型解剖结构以及捕获个体特定几何的空间变换。这种解耦、可解释的表达实现了具有内在适应性的语义上有意义的预测。在具有挑战性的心脏和腹部数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在这两种环境中都达到了最先进的水平,无源的适应性能接近其可访问源的对应性能,这在以前的工作中很少观察到的一致性。除了定量改进之外,我们还通过流形遍历进行平滑形状操纵来展示所提出框架的强大可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出了一种统一、语义化的框架,支持源可访问和源自由适应两种情况下的医学图像分割的无监督域适应方法。该框架无需任何手工制定的适应策略,其适应性自然地来源于模型架构。通过学习和使用领域无关的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,该模型能够反映人类建立视觉理解的方式。在此基础上,图像的结构内容可以被解释为从流形中检索的典型解剖结构和捕捉个体特定几何的空间变换。这种解耦、可解释的表达实现了具有内在适应性的语义预测。在具有挑战性的心脏和腹部数据集上的实验表明,该框架在两种设置中都达到了最新水平的结果,其中源自由性能接近其源可访问的对应物,这在以前的工作中很少观察到。此外,通过流形遍历进行平滑形状操纵,展示了该框架的强大可解释性。
Key Takeaways:
- 医学图像分割的无监督域适应方法面临源可访问和源自由两大挑战。
- 当前方法缺乏明确的结构化解剖知识构建,导致难以适应不同域和设置。
- 提出一种统一、语义化的框架,支持源可访问和源自由两种设置下的医学图像分割。
- 框架无需手工制定的适应策略,其适应性来源于模型架构。
- 通过学习和使用领域无关的概率流形来反映人类建立视觉理解的方式。
- 实验表明,该框架在心脏和腹部数据集上达到最新水平的结果。
点此查看论文截图
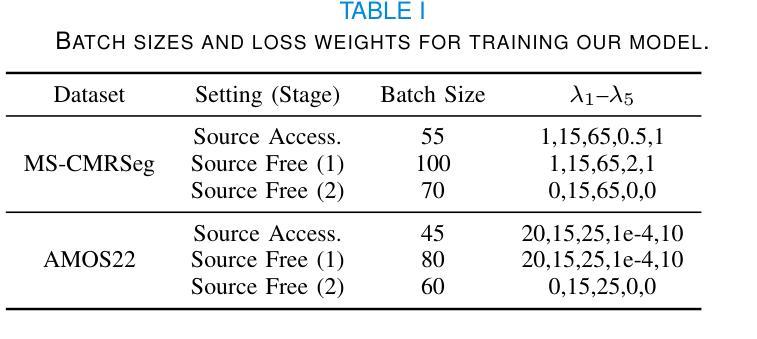
QueryCraft: Transformer-Guided Query Initialization for Enhanced Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Yuxiao Wang, Wolin Liang, Yu Lei, Weiying Xue, Nan Zhuang, Qi Liu
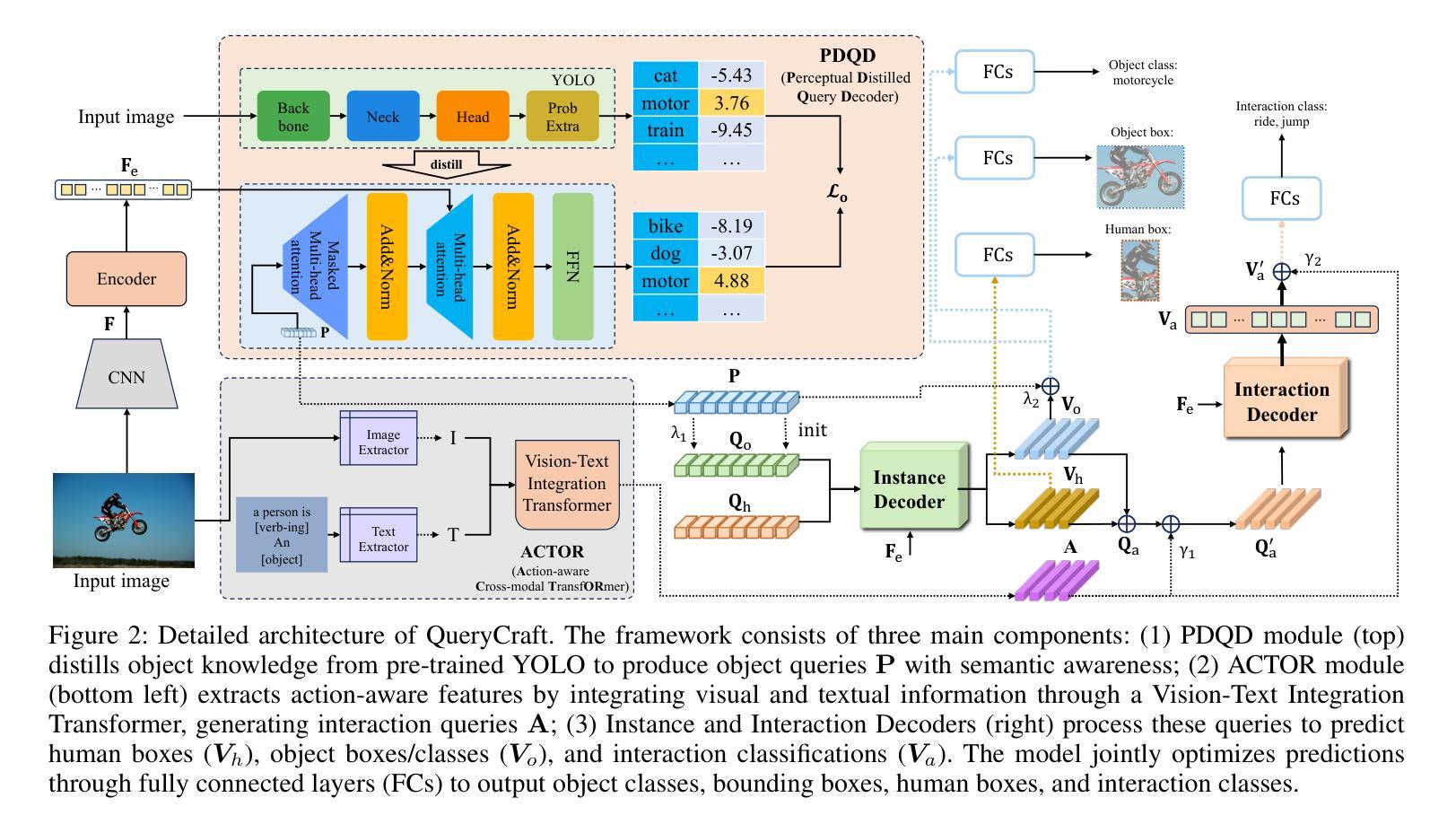
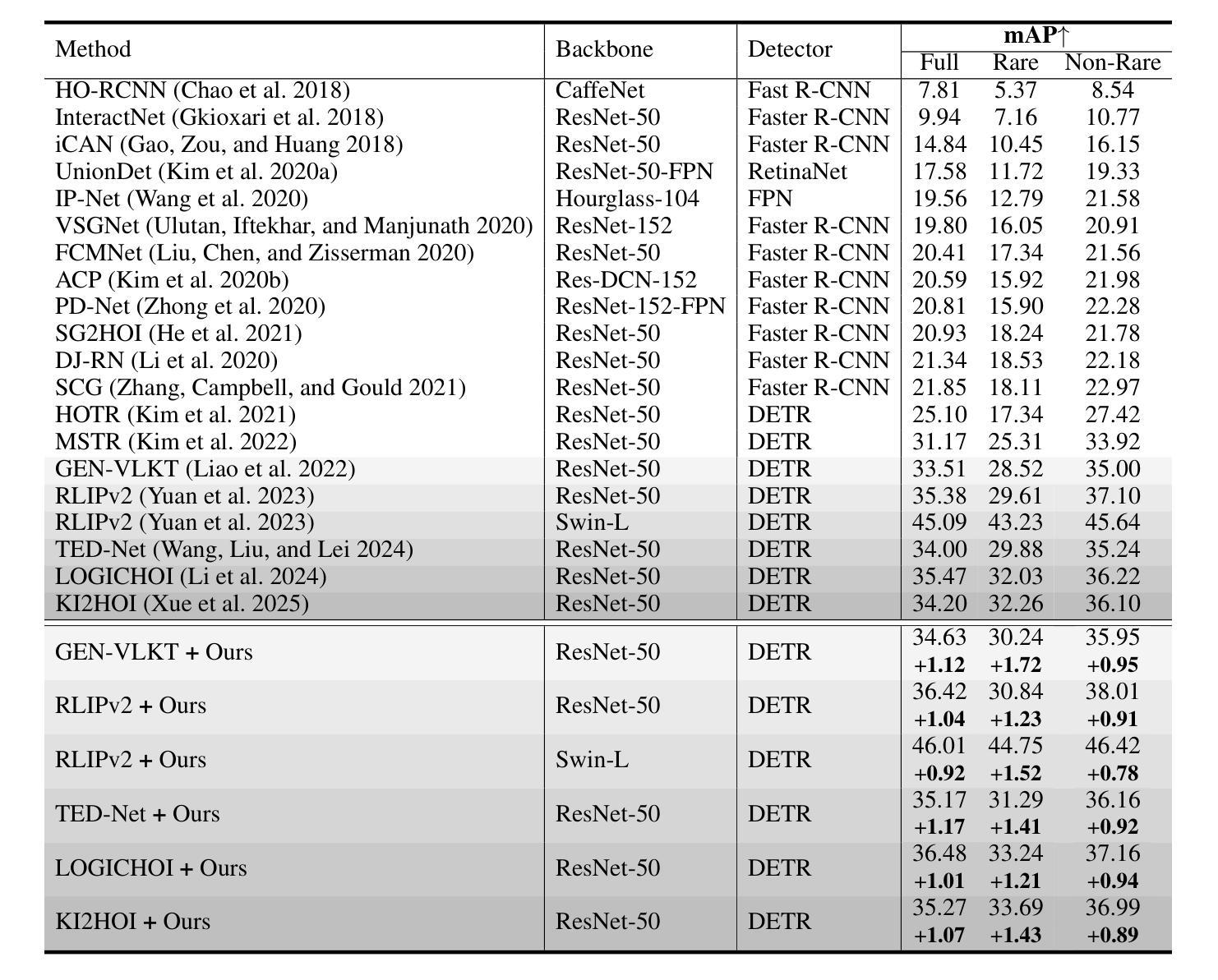
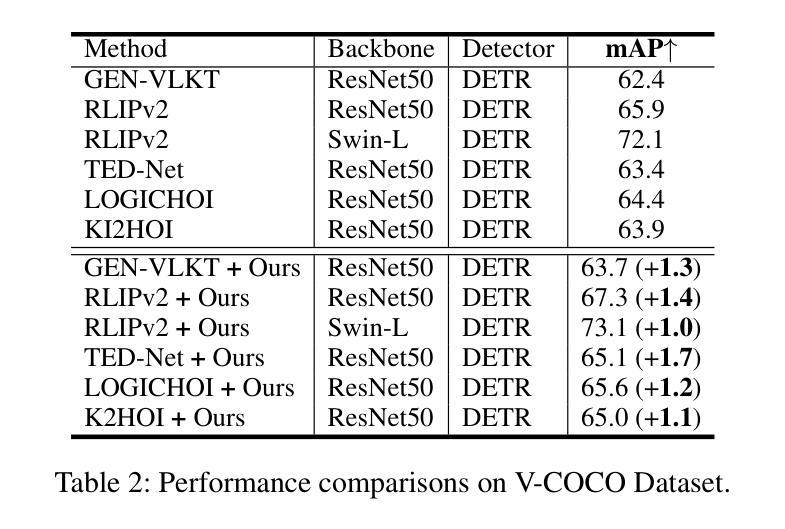
Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection aims to localize human-object pairs and recognize their interactions in images. Although DETR-based methods have recently emerged as the mainstream framework for HOI detection, they still suffer from a key limitation: Randomly initialized queries lack explicit semantics, leading to suboptimal detection performance. To address this challenge, we propose QueryCraft, a novel plug-and-play HOI detection framework that incorporates semantic priors and guided feature learning through transformer-based query initialization. Central to our approach is \textbf{ACTOR} (\textbf{A}ction-aware \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{T}ransf\textbf{OR}mer), a cross-modal Transformer encoder that jointly attends to visual regions and textual prompts to extract action-relevant features. Rather than merely aligning modalities, ACTOR leverages language-guided attention to infer interaction semantics and produce semantically meaningful query representations. To further enhance object-level query quality, we introduce a \textbf{P}erceptual \textbf{D}istilled \textbf{Q}uery \textbf{D}ecoder (\textbf{PDQD}), which distills object category awareness from a pre-trained detector to serve as object query initiation. This dual-branch query initialization enables the model to generate more interpretable and effective queries for HOI detection. Extensive experiments on HICO-Det and V-COCO benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and strong generalization. Code will be released upon publication.
人类与物体交互(HOI)检测旨在定位图像中的人与物体的配对,并识别它们的交互。尽管基于DETR的方法最近已成为HOI检测的主流框架,但它们仍存在关键局限性:随机初始化的查询缺乏明确的语义,导致检测性能不佳。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了QueryCraft,这是一种新型的即插即用HOI检测框架,它通过基于变压器的查询初始化,结合了语义先验知识和导向特征学习。我们的方法的核心是动作感知跨模态转换器(ACTOR),这是一种跨模态变压器编码器,能够共同关注视觉区域和文本提示,以提取与动作相关的特征。ACTOR不仅对齐不同的模态,还利用语言引导注意力来推断交互语义并产生语义上有意义的查询表示。为了进一步提高对象级别的查询质量,我们引入了感知蒸馏查询解码器(PDQD),它从预训练的检测器中提炼出物体类别意识,作为物体查询的初始化。这种双分支查询初始化使模型能够为HOI检测生成更具可解释性和有效的查询。在HICO-Det和V-COCO基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。代码将在发布时公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出一种基于语义先验和引导特征学习的HOI检测框架QueryCraft,解决了DETR方法中的查询语义不明确问题。通过引入ACTOR(动作感知跨模态Transformer编码器)和PDQD(感知蒸馏查询解码器)来提取动作相关特征并初始化对象查询,提高模型性能。在HICO-Det和V-COCO数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到领先水平并具有良好泛化能力。
Key Takeaways:
- HOI检测主要关注人类与物体的交互作用。
- QueryCraft解决了DETR方法查询语义不明确的问题,提升了HOI检测的准确性。
- 提出ACTOR(动作感知跨模态Transformer编码器),结合了视觉区域和文本提示,提取动作相关特征。
- PDQD(感知蒸馏查询解码器)用于提高对象级别查询质量,通过预训练检测器蒸馏物体类别意识作为对象查询的初始值。
- 模型具有强泛化能力,在HICO-Det和V-COCO数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

DriveIndia: An Object Detection Dataset for Diverse Indian Traffic Scenes
Authors:Rishav Kumar, D. Santhosh Reddy, P. Rajalakshmi
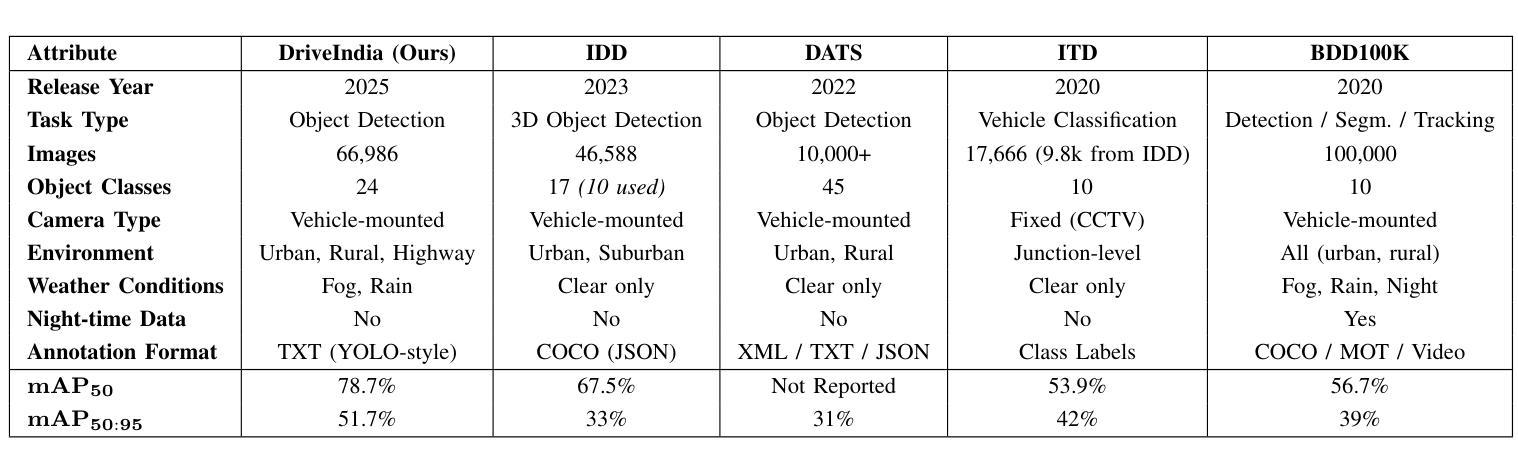
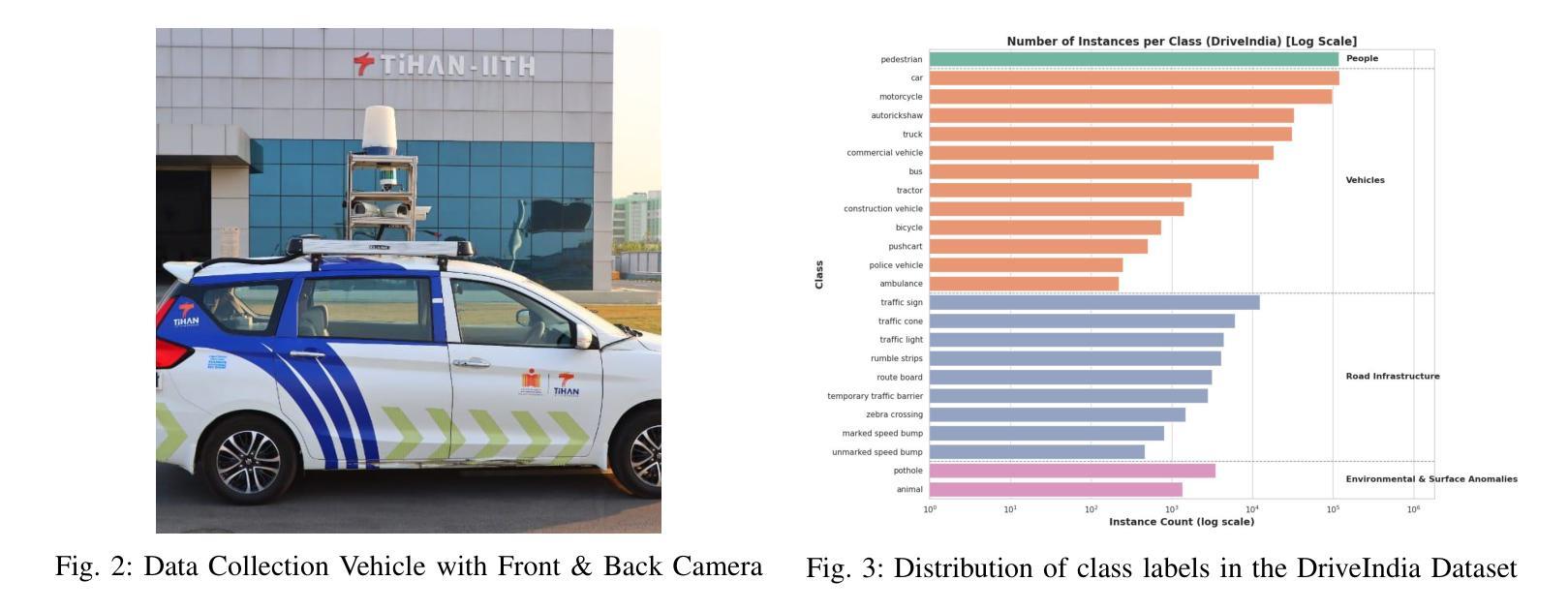
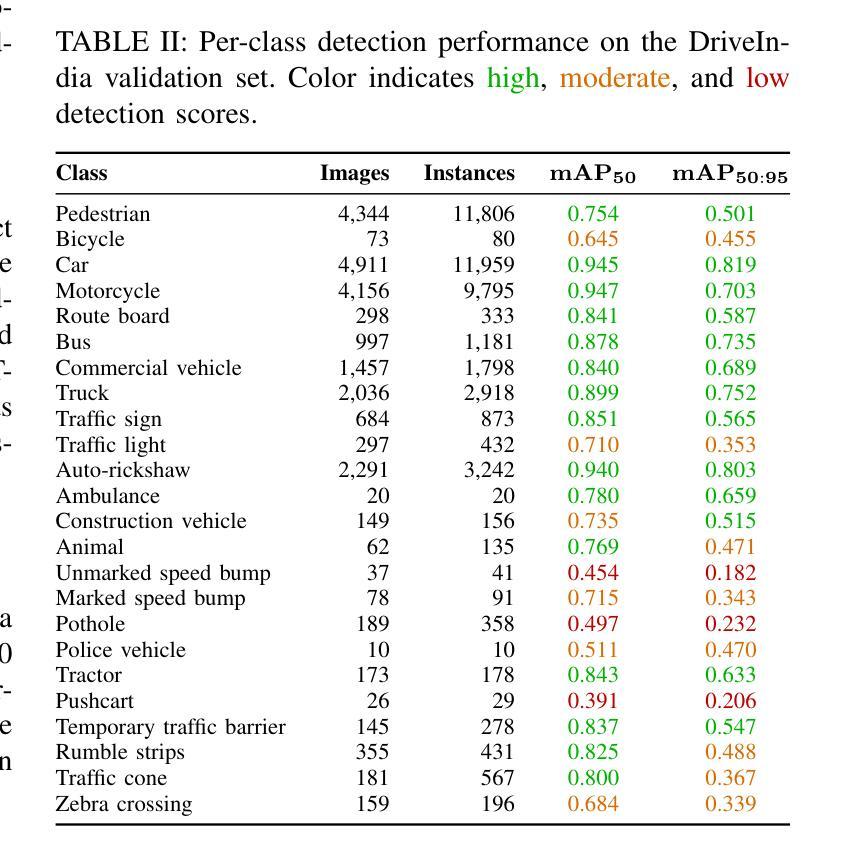
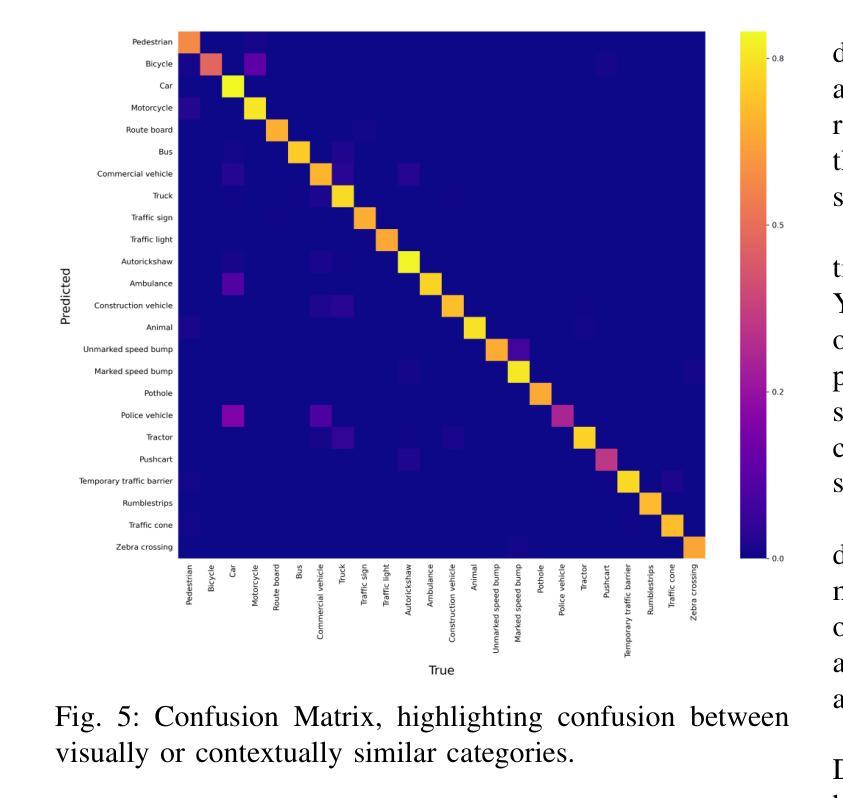
We introduce DriveIndia, a large-scale object detection dataset purpose-built to capture the complexity and unpredictability of Indian traffic environments. The dataset contains 66,986 high-resolution images annotated in YOLO format across 24 traffic-relevant object categories, encompassing diverse conditions such as varied weather (fog, rain), illumination changes, heterogeneous road infrastructure, and dense, mixed traffic patterns and collected over 120+ hours and covering 3,400+ kilometers across urban, rural, and highway routes. DriveIndia offers a comprehensive benchmark for real-world autonomous driving challenges. We provide baseline results using state-of-the-art YOLO family models, with the top-performing variant achieving a mAP50 of 78.7%. Designed to support research in robust, generalizable object detection under uncertain road conditions, DriveIndia will be publicly available via the TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad dataset repository https://tihan.iith.ac.in/TiAND.html (Terrestrial Datasets -> Camera Dataset).
我们推出了DriveIndia数据集,这是一个专为捕捉印度交通环境的复杂性和不可预测性而构建的大规模物体检测数据集。该数据集包含66,986张高分辨率图像,采用YOLO格式进行标注,涵盖24个与交通相关的物体类别,涵盖多种条件,如多变的天气(雾、雨)、照明变化、异质的道路基础设施以及密集、混合的交通模式等,并在超过120小时内收集,覆盖城市、乡村和高速公路路线超过3,400公里。DriveIndia为现实世界自动驾驶挑战提供了全面的基准测试。我们使用最先进的YOLO家族模型提供基准结果,表现最佳的变体达到50%的平均准确度为78.7%。该数据集旨在支持在不确定道路条件下的稳健、通用物体检测研究,将通过TiHAN-印度理工学院海德拉巴数据集存储库公开可用:https://tihan.iith.ac.in/TiAND.html(陆地数据集->摄像机数据集)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ITSC 2025 Conference
Summary:
介绍了一个名为DriveIndia的大型目标检测数据集,专为捕捉印度交通环境的复杂性和不可预测性而设计。数据集包含6.6万多个高分辨率图像,以YOLO格式标注了涵盖各种条件下的不同对象类别。提供YOLO家族模型的基准结果,表现最佳变体达到了mAP50的78.7%。旨在为不确定道路条件下的稳健通用目标检测提供支持,可通过TiHAN-IIT Hyderabd数据集仓库公开访问。
Key Takeaways:
- DriveIndia是一个专为捕捉印度交通环境复杂性和不可预测性而构建的大型目标检测数据集。
- 数据集包含超过6.6万张高分辨率图像,标注了涵盖不同天气、照明条件以及多样化的道路基础设施的多个交通相关对象类别。
- 数据集收集了超过120小时,覆盖城市、乡村和高速公路路线超过三千公里的数据。
- DriveIndia为现实世界自动驾驶挑战提供了全面的基准测试。
- 使用最先进的YOLO家族模型提供了基准结果,其中表现最佳的模型达到了mAP50的78.7%。
- 数据集旨在支持不确定道路条件下的稳健通用目标检测研究。
点此查看论文截图