⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
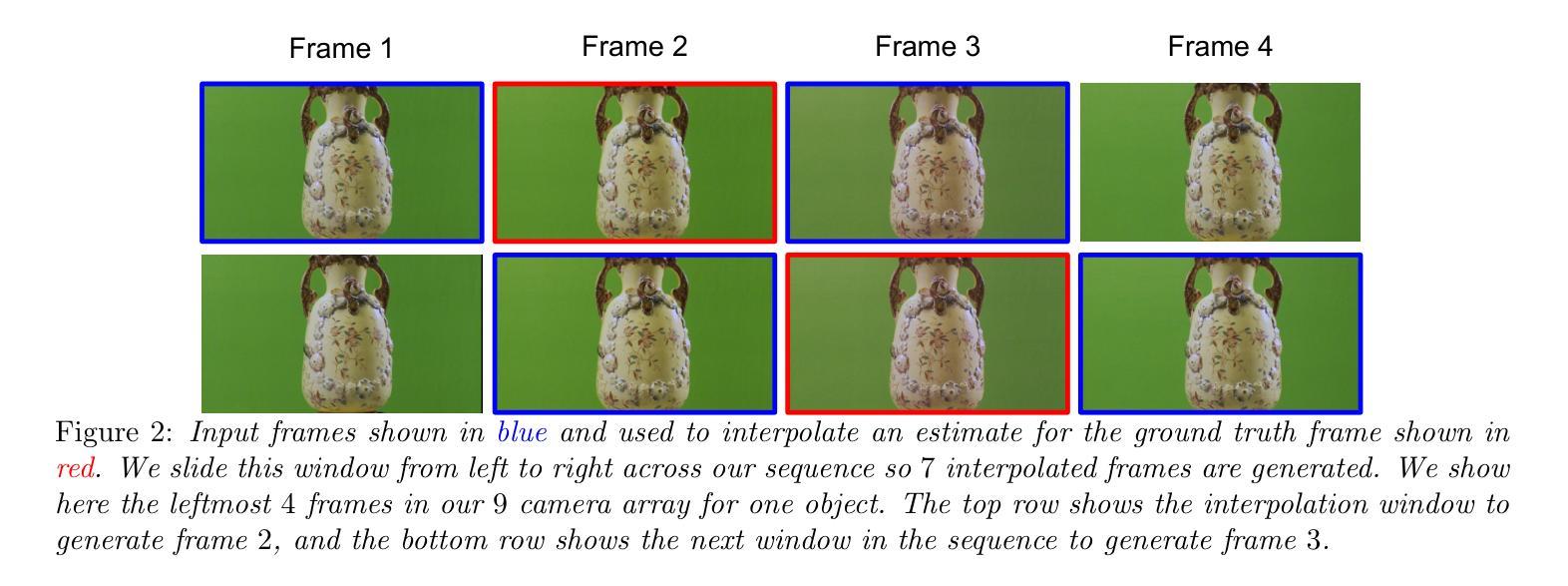
A new dataset and comparison for multi-camera frame synthesis
Authors:Conall Daly, Anil Kokaram
Many methods exist for frame synthesis in image sequences but can be broadly categorised into frame interpolation and view synthesis techniques. Fundamentally, both frame interpolation and view synthesis tackle the same task, interpolating a frame given surrounding frames in time or space. However, most frame interpolation datasets focus on temporal aspects with single cameras moving through time and space, while view synthesis datasets are typically biased toward stereoscopic depth estimation use cases. This makes direct comparison between view synthesis and frame interpolation methods challenging. In this paper, we develop a novel multi-camera dataset using a custom-built dense linear camera array to enable fair comparison between these approaches. We evaluate classical and deep learning frame interpolators against a view synthesis method (3D Gaussian Splatting) for the task of view in-betweening. Our results reveal that deep learning methods do not significantly outperform classical methods on real image data, with 3D Gaussian Splatting actually underperforming frame interpolators by as much as 3.5 dB PSNR. However, in synthetic scenes, the situation reverses – 3D Gaussian Splatting outperforms frame interpolation algorithms by almost 5 dB PSNR at a 95% confidence level.
关于图像序列中的帧合成方法存在许多,但大体上可归纳为帧插值和视图合成技术。从本质上讲,帧插值和视图合成解决的是同一任务,即在时间或空间上根据周围帧进行帧插值。然而,大多数帧插值数据集侧重于单个相机随时间在空间中的运动方面,而视图合成数据集通常偏向于立体深度估计的使用情况。这使得视图合成和帧插值方法之间的直接比较具有挑战性。在本文中,我们使用自定义的密集线性相机阵列开发了一个新型多相机数据集,以实现这些方法之间的公平比较。我们评估了经典和深度学习的帧插值器与视图合成方法(3D高斯拼贴)在视图中间任务上的表现。我们的结果表明,在真实图像数据上,深度学习方法并没有显著优于经典方法,3D高斯拼贴的实际表现甚至比帧插值器差3.5 dB PSNR。然而,在合成场景中情况恰恰相反——在95%的置信水平下,3D高斯拼贴比帧插值算法高出近5 dB PSNR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SPIE2025 - Applications of Digital Image Processing XLVIII accepted manuscript
Summary
本文介绍了图像序列中帧合成的两种方法:帧插值与视图合成。虽然两者都解决在给定周围帧的情况下内插帧的任务,但现有数据集大多侧重于时间方面的帧插值,而视图合成数据集则偏向于立体深度估计用例。为此,本文开发了一种使用自定义的密集线性相机阵列的多相机数据集,以便在这两种方法之间进行公平比较。评估结果显示,在真实图像数据上,深度学习方法并未显著优于经典方法,而3D高斯喷涂技术甚至比帧插值器性能差3.5 dB PSNR。但在合成场景中,情况逆转,3D高斯喷涂技术在95%的置信水平下比帧插补算法高出近5 dB PSNR。
Key Takeaways
- 帧插值和视图合成是图像序列中帧合成的两种主要方法,但现有数据集存在偏向,导致直接比较具有挑战性。
- 本文开发了一种新型多相机数据集,使用自定义密集线性相机阵列,以公平比较这两种方法。
- 在真实图像数据上,深度学习方法与经典方法的性能差异不大。
- 3D高斯喷涂技术在真实图像数据上的性能较差,与帧插值器相比可能低达3.5 dB PSNR。
- 在合成场景中,3D高斯喷涂技术的性能显著优于帧插补算法,差异近5 dB PSNR。
- 这种差异在95%的置信水平上是显著的。
点此查看论文截图

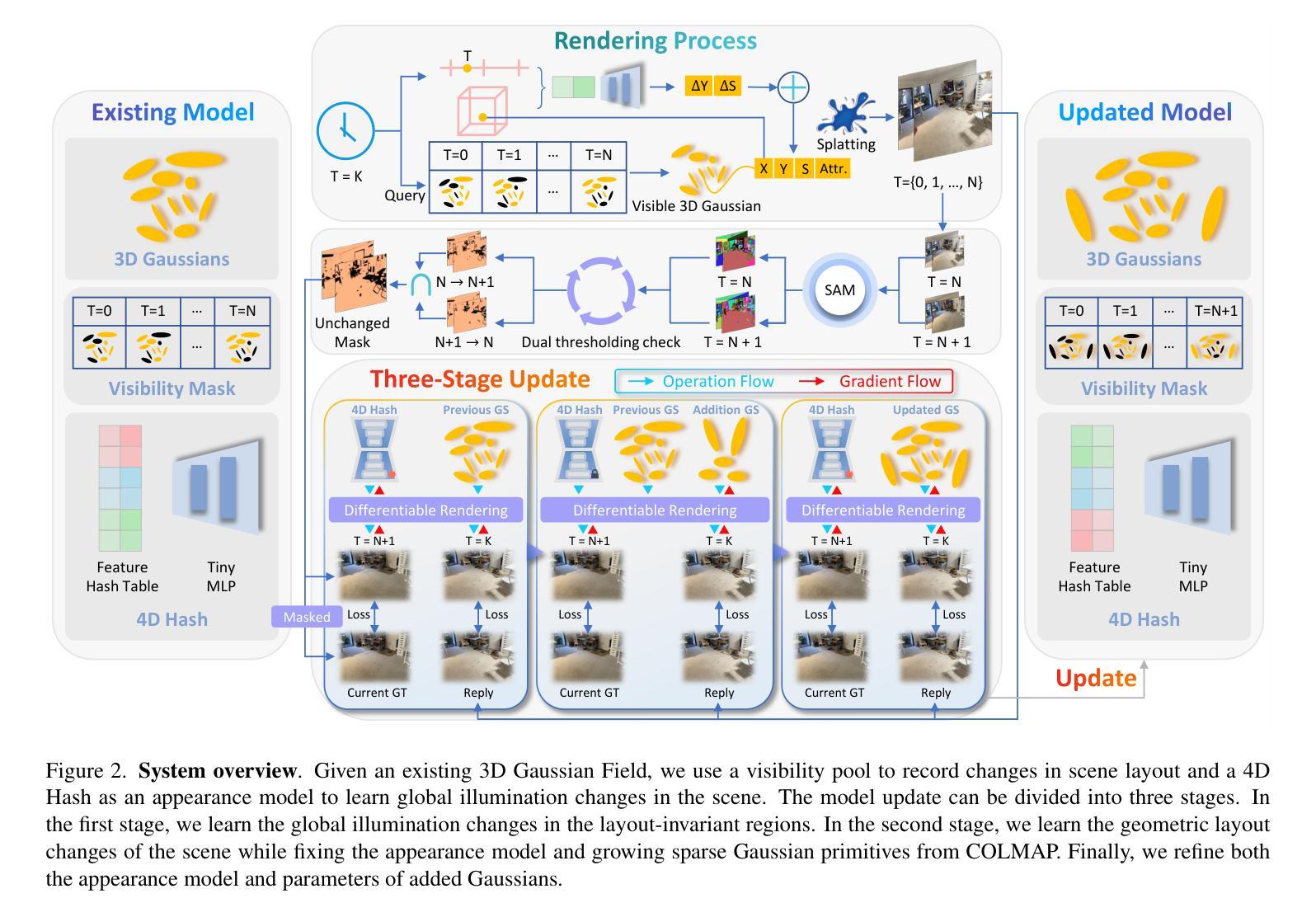
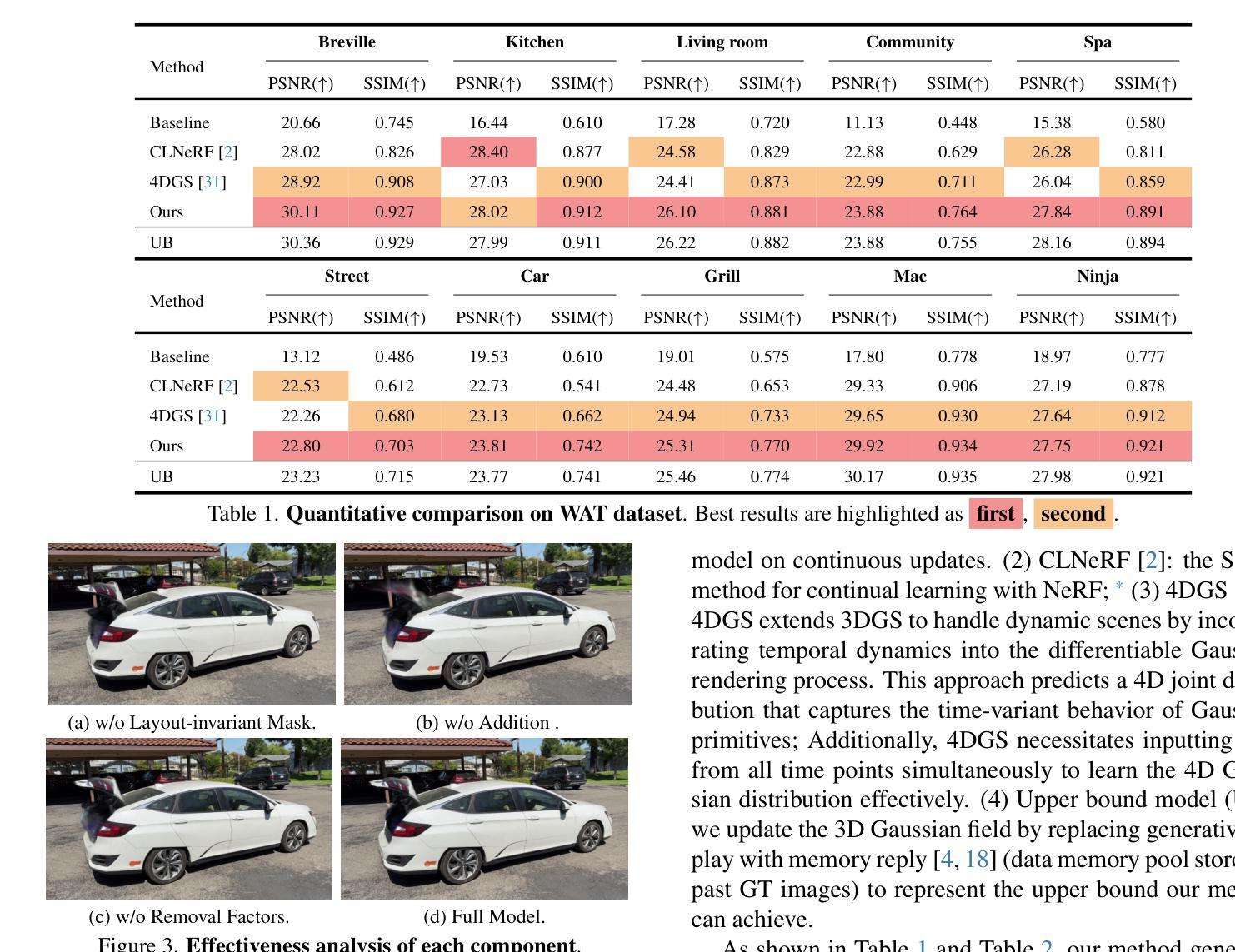
GaussianUpdate: Continual 3D Gaussian Splatting Update for Changing Environments
Authors:Lin Zeng, Boming Zhao, Jiarui Hu, Xujie Shen, Ziqiang Dang, Hujun Bao, Zhaopeng Cui
Novel view synthesis with neural models has advanced rapidly in recent years, yet adapting these models to scene changes remains an open problem. Existing methods are either labor-intensive, requiring extensive model retraining, or fail to capture detailed types of changes over time. In this paper, we present GaussianUpdate, a novel approach that combines 3D Gaussian representation with continual learning to address these challenges. Our method effectively updates the Gaussian radiance fields with current data while preserving information from past scenes. Unlike existing methods, GaussianUpdate explicitly models different types of changes through a novel multi-stage update strategy. Additionally, we introduce a visibility-aware continual learning approach with generative replay, enabling self-aware updating without the need to store images. The experiments on the benchmark dataset demonstrate our method achieves superior and real-time rendering with the capability of visualizing changes over different times
近年来,利用神经网络模型进行新型视图合成的研究进展迅速,然而,如何适应场景变化仍是亟待解决的问题。现有方法要么需要大量的人工进行模型重新训练,要么无法捕捉随时间变化的细节变化。在本文中,我们提出了GaussianUpdate,这是一种结合三维高斯表示和持续学习来解决这些挑战的新型方法。我们的方法可以有效地使用当前数据更新高斯辐射场,同时保留过去场景的信息。与现有方法不同,GaussianUpdate通过一种新型的多阶段更新策略来显式地模拟不同类型的场景变化。此外,我们引入了一种具有生成回放功能的可见性感知持续学习方法,实现了自我感知更新,无需存储图像。在基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法实现了具有实时渲染能力的卓越性能,能够可视化不同时间的变化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
神经网络模型在视图合成方面的应用近年来发展迅速,但在场景变化方面的适应性仍然是一个待解决的问题。现有方法要么需要大量的人工参与和模型重新训练,要么无法捕捉随时间变化的细节变化。本文提出了GaussianUpdate方法,它结合了三维高斯表示和持续学习技术,以应对这些挑战。该方法可以有效地更新当前数据的高斯辐射场,同时保留过去场景的信息。不同于现有方法,GaussianUpdate通过一种新的多阶段更新策略来显式地模拟不同类型的变化。此外,我们还引入了一种具有生成回放功能的可见性感知持续学习方法,实现了自我感知更新,无需存储图像。在基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法可实现先进且实时的渲染,能够可视化不同时间的变化。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络模型在视图合成领域发展迅速,但场景变化的适应性仍是问题。
- 现有方法存在劳动密集或无法捕捉细节变化的问题。
- GaussianUpdate方法结合了三维高斯表示和持续学习技术。
- GaussianUpdate可以有效地更新当前数据的高斯辐射场并保留过去场景的信息。
- 多阶段更新策略显式地模拟不同类型的场景变化。
- 引入可见性感知持续学习方法,实现自我感知更新,无需存储图像。
点此查看论文截图

Communication Efficient Robotic Mixed Reality with Gaussian Splatting Cross-Layer Optimization
Authors:Chenxuan Liu, He Li, Zongze Li, Shuai Wang, Wei Xu, Kejiang Ye, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Chengzhong Xu
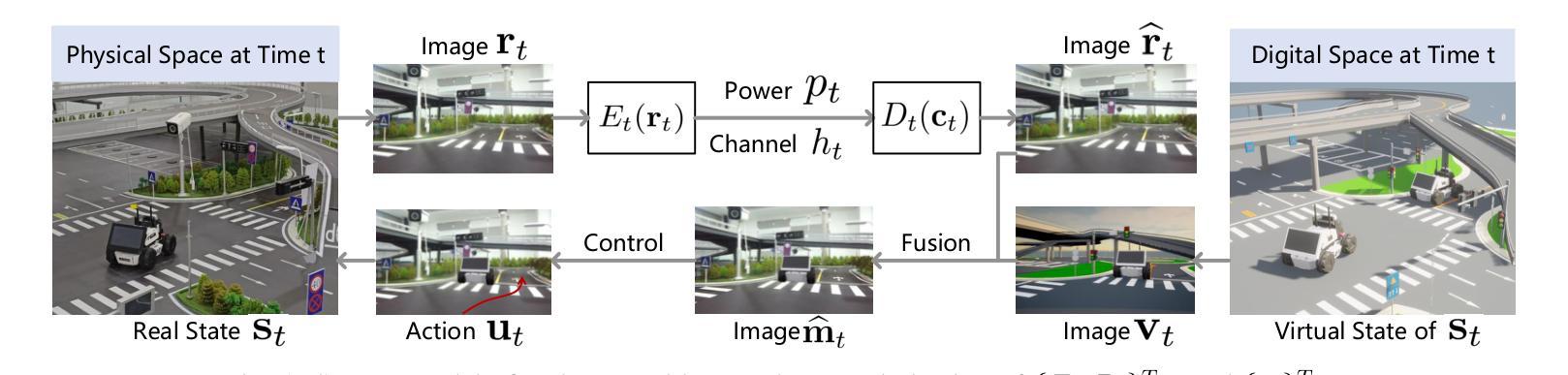
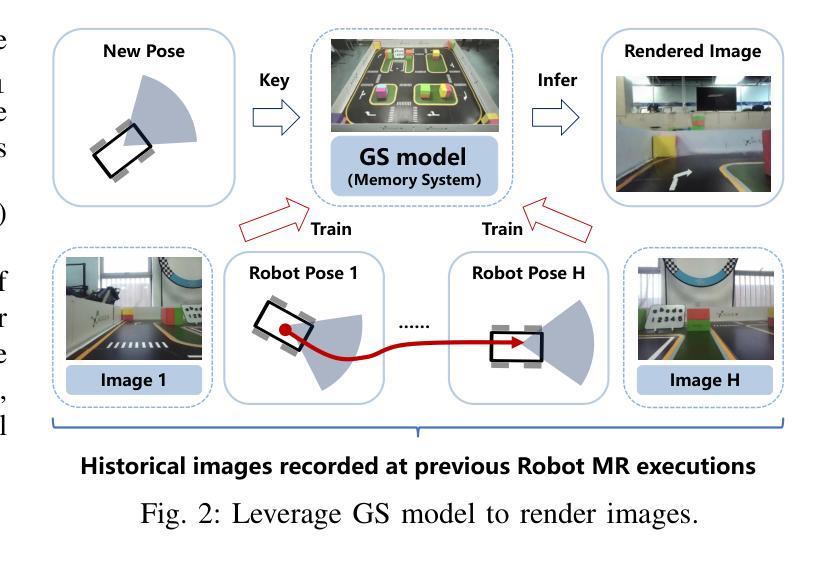
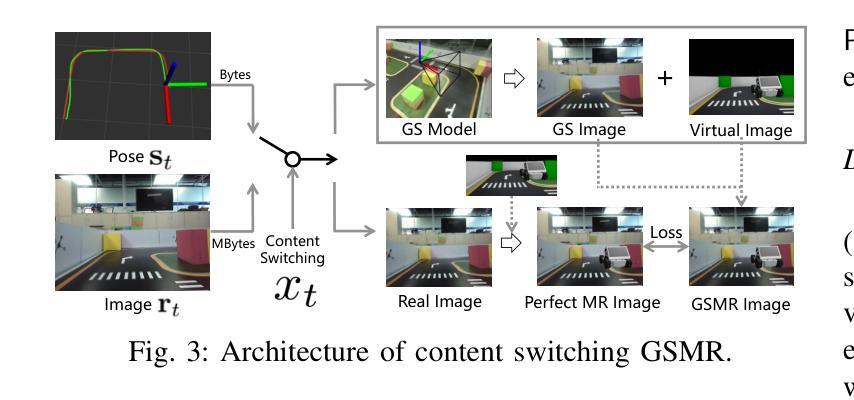
Realizing low-cost communication in robotic mixed reality (RoboMR) systems presents a challenge, due to the necessity of uploading high-resolution images through wireless channels. This paper proposes Gaussian splatting (GS) RoboMR (GSMR), which enables the simulator to opportunistically render a photo-realistic view from the robot’s pose by calling ``memory’’ from a GS model, thus reducing the need for excessive image uploads. However, the GS model may involve discrepancies compared to the actual environments. To this end, a GS cross-layer optimization (GSCLO) framework is further proposed, which jointly optimizes content switching (i.e., deciding whether to upload image or not) and power allocation (i.e., adjusting to content profiles) across different frames by minimizing a newly derived GSMR loss function. The GSCLO problem is addressed by an accelerated penalty optimization (APO) algorithm that reduces computational complexity by over $10$x compared to traditional branch-and-bound and search algorithms. Moreover, variants of GSCLO are presented to achieve robust, low-power, and multi-robot GSMR. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed GSMR paradigm and GSCLO method achieve significant improvements over existing benchmarks on both wheeled and legged robots in terms of diverse metrics in various scenarios. For the first time, it is found that RoboMR can be achieved with ultra-low communication costs, and mixture of data is useful for enhancing GS performance in dynamic scenarios.
在机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统中实现低成本通信是一个挑战,因为需要通过无线信道上传高分辨率图像。本文提出了高斯斑点(GS)RoboMR(GSMR),它允许模拟器通过从GS模型中调用“内存”来随机呈现机器人的逼真视图,从而减少了过度图像上传的需求。然而,与实际情况相比,GS模型可能存在差异。为此,进一步提出了GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,该框架通过最小化新推导的GSMR损失函数来联合优化内容切换(即决定是否需要上传图像)和功率分配(即适应内容配置文件)。不同帧之间的GSCLO问题通过加速惩罚优化(APO)算法来解决,与传统的分支界定和搜索算法相比,该算法的计算复杂度降低了超过10倍。此外,还提出了GSCLO的变体,以实现稳健、低功耗和多机器人的GSMR。大量实验表明,在轮式机器人和步行机器人上,所提出的GSMR范式和GSCLO方法在多种场景下的各种指标方面均显著优于现有基准测试。首次发现RoboMR可以使用超低的通信成本来实现,并且数据的混合对于增强动态场景中的GS性能很有用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 18 figures, to appear in IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯点云技术(GS)的机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统,实现了低成本通信。该系统通过调用GS模型的“内存”来模拟渲染机器人姿态的逼真视图,减少了对大量图像上传的需求。为进一步减小与真实环境的差异,文章提出了GS跨层优化(GSLO)框架,联合优化内容切换和功率分配。通过加速惩罚优化算法解决GSLO问题,计算复杂度较传统方法降低了超过十倍。实验证明,该框架和方法在轮式和步行机器人上均显著优于现有基准测试,实现了超低通信成本的RoboMR,且混合数据在动态场景中有助于提升GS性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了基于高斯点云技术(GS)的机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统,实现了低成本通信。
- 系统通过调用GS模型的“内存”模拟渲染机器人姿态的视图,减少了图像上传的需求。
- 论文提出了GS跨层优化(GSLO)框架以减小与真实环境的差异,联合优化内容切换和功率分配。
- 采用加速惩罚优化算法解决GSLO问题,计算复杂度大幅降低。
- 实验证明,该框架和方法在多种机器人和场景下均显著优于现有技术。
- RobomR可以实现超低通信成本。
点此查看论文截图

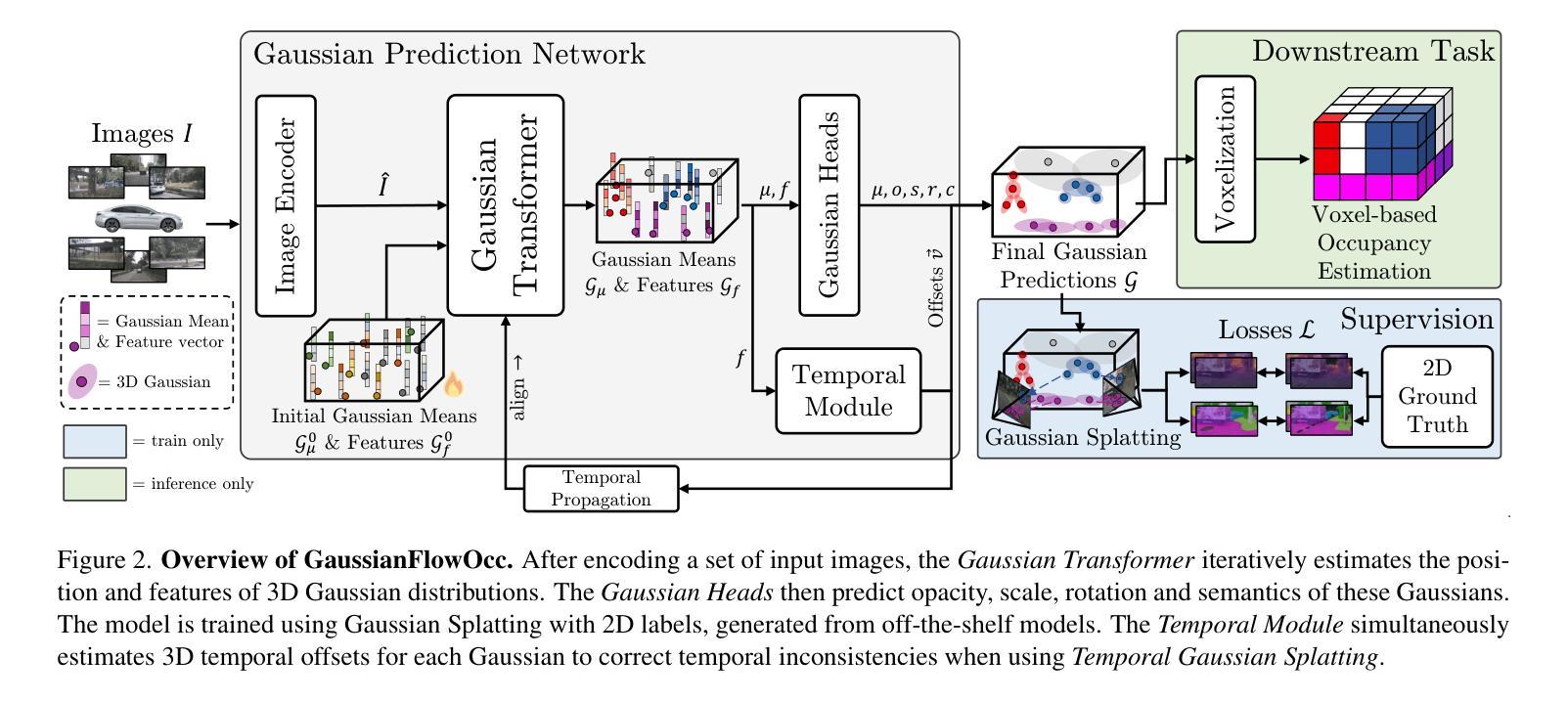
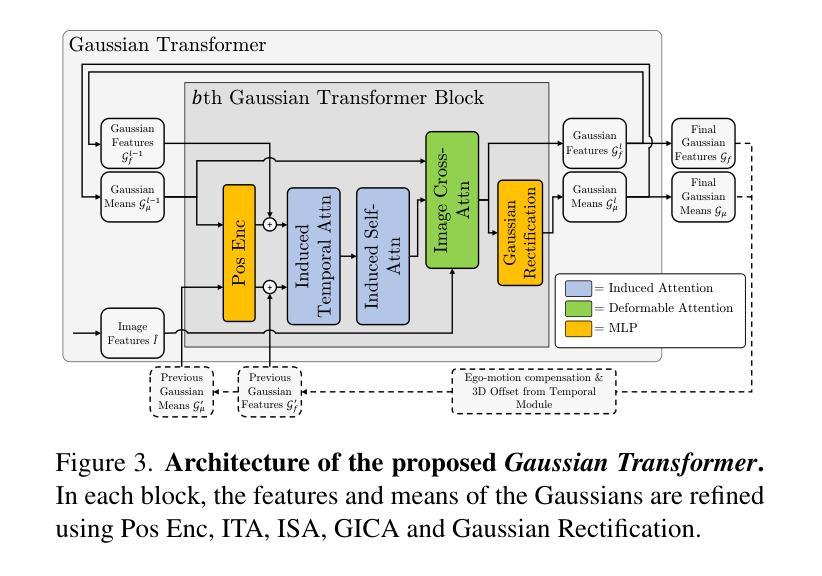
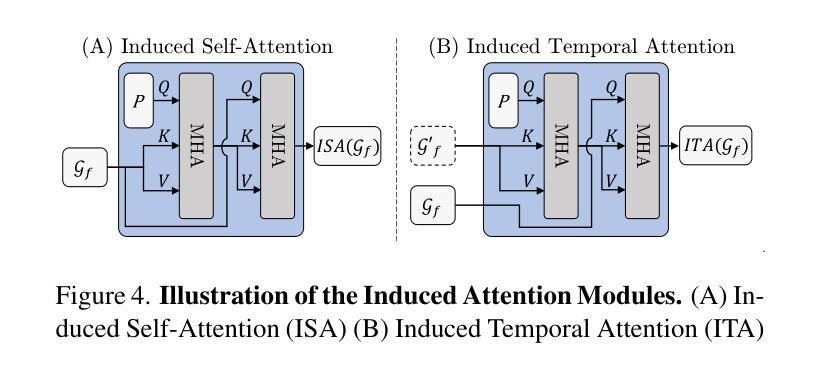
GaussianFlowOcc: Sparse and Weakly Supervised Occupancy Estimation using Gaussian Splatting and Temporal Flow
Authors:Simon Boeder, Fabian Gigengack, Benjamin Risse
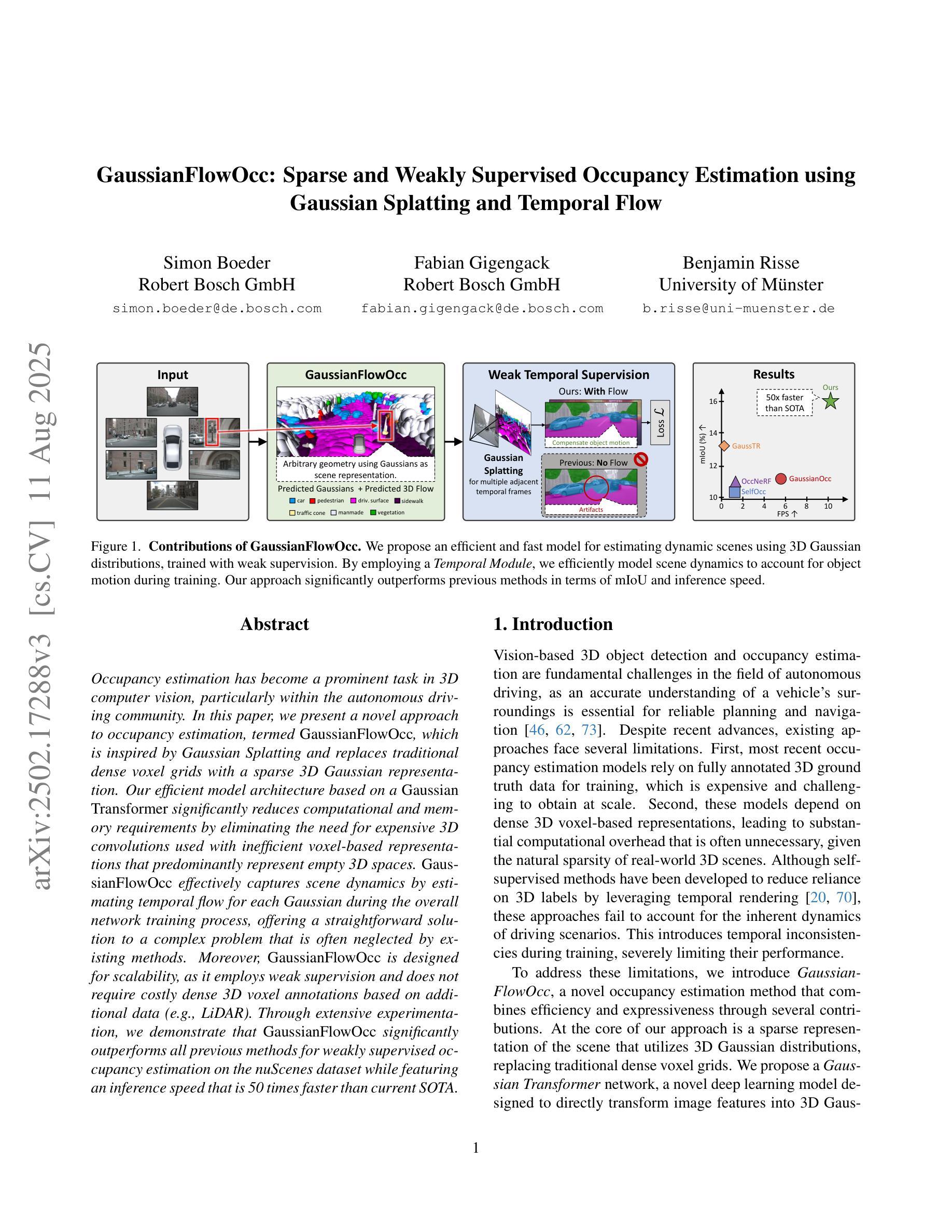
Occupancy estimation has become a prominent task in 3D computer vision, particularly within the autonomous driving community. In this paper, we present a novel approach to occupancy estimation, termed GaussianFlowOcc, which is inspired by Gaussian Splatting and replaces traditional dense voxel grids with a sparse 3D Gaussian representation. Our efficient model architecture based on a Gaussian Transformer significantly reduces computational and memory requirements by eliminating the need for expensive 3D convolutions used with inefficient voxel-based representations that predominantly represent empty 3D spaces. GaussianFlowOcc effectively captures scene dynamics by estimating temporal flow for each Gaussian during the overall network training process, offering a straightforward solution to a complex problem that is often neglected by existing methods. Moreover, GaussianFlowOcc is designed for scalability, as it employs weak supervision and does not require costly dense 3D voxel annotations based on additional data (e.g., LiDAR). Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that GaussianFlowOcc significantly outperforms all previous methods for weakly supervised occupancy estimation on the nuScenes dataset while featuring an inference speed that is 50 times faster than current SOTA.
场景中的物体占有率估计在三维计算机视觉中已经成为一项重要任务,特别是在自动驾驶领域。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的占有率估计方法,称为GaussianFlowOcc。该方法受到高斯涂抹(Gaussian Splatting)的启发,用稀疏的三维高斯表示替换了传统的密集体素网格。我们基于高斯变换器的有效模型架构,通过消除主要代表空三维空间的低效体素表示所需的高昂的三维卷积,大大减少了计算和内存需求。GaussianFlowOcc通过在整个网络训练过程中估计每个高斯的时间流来有效地捕捉场景动态,为解决现有方法经常忽略的复杂问题提供了直接解决方案。此外,GaussianFlowOcc具有可扩展性设计,因为它采用弱监督,无需基于其他数据(如激光雷达)的昂贵密集三维体素注释。通过广泛的实验,我们证明GaussianFlowOcc在nuScenes数据集上的弱监督占有率估计方面大大优于所有之前的方法,同时其推理速度比当前最佳方法快50倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新颖的占用率估计方法,称为GaussianFlowOcc。该方法受到高斯涂抹技术的启发,采用稀疏的3D高斯表示替代传统的密集体素网格。基于高斯变换器的有效模型架构大大减少了计算和内存需求,因为它消除了需要使用昂贵的3D卷积和基于体素的表示方法,后者主要代表空的3D空间。GaussianFlowOcc通过在网络训练过程中估计每个高斯的时间流来有效地捕捉场景动态,为常被现有方法忽视的一个复杂问题提供了简单的解决方案。此外,GaussianFlowOcc设计用于可扩展性,它采用弱监督,无需基于额外数据(如激光雷达)的昂贵密集3D体素注释。通过广泛的实验,我们证明GaussianFlowOcc在nuScenes数据集上的弱监督占用率估计方面显著优于所有之前的方法,同时其推理速度比当前的最佳方法快50倍。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianFlowOcc是一种用于占用率估计的新型方法,基于稀疏的3D高斯表示。
- 该方法受到高斯涂抹技术的启发,并采用了基于高斯变换器的有效模型架构。
- GaussianFlowOcc通过估计场景动态的时间流来解决复杂问题。
- 与传统方法相比,GaussianFlowOcc大大减少了计算和内存需求。
- GaussianFlowOcc采用弱监督,无需昂贵的密集3D体素注释。
- 在nuScenes数据集上,GaussianFlowOcc在弱监督占用率估计方面表现出显著的优势。
点此查看论文截图
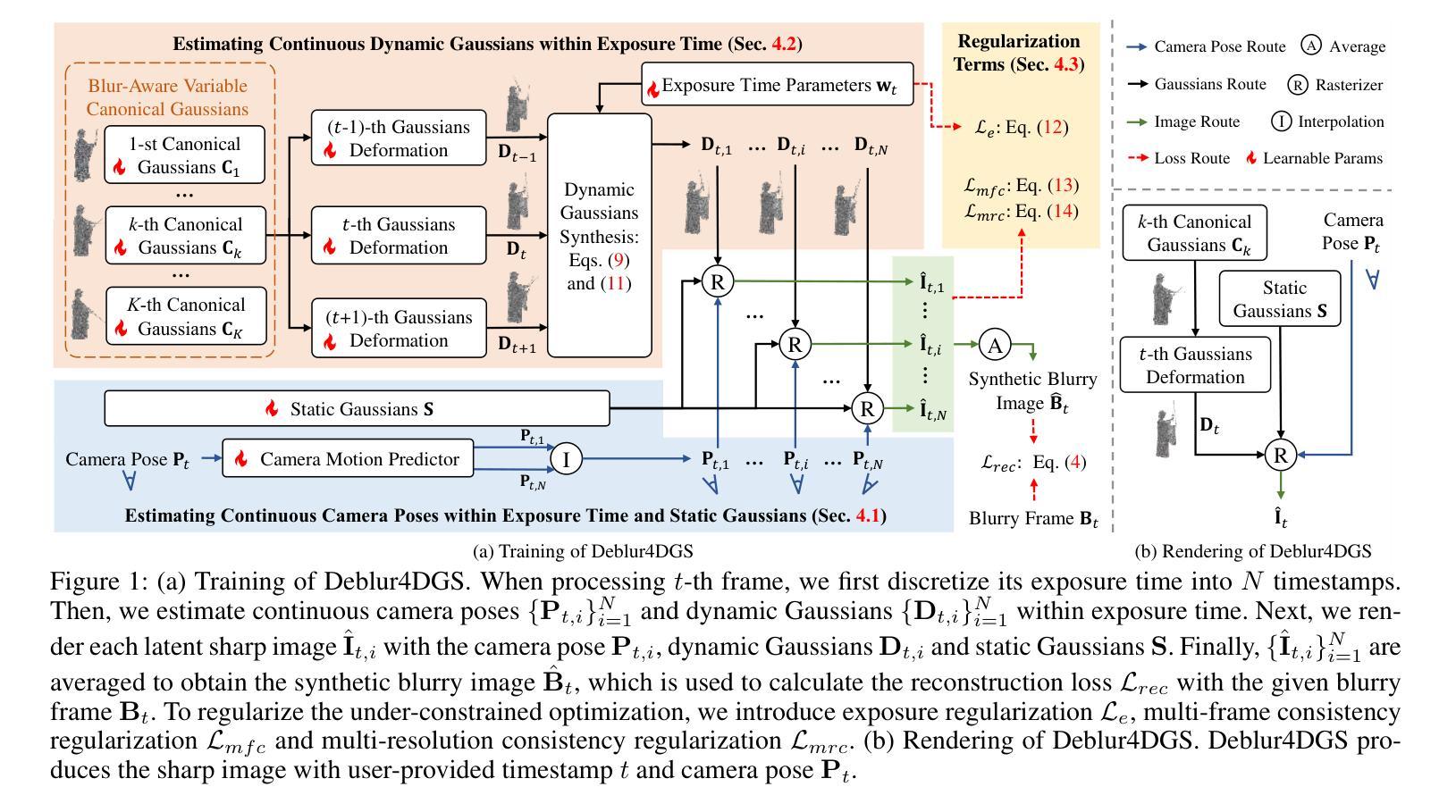
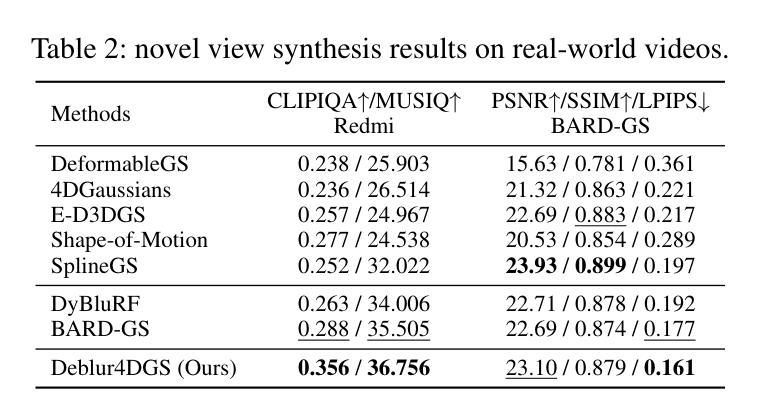
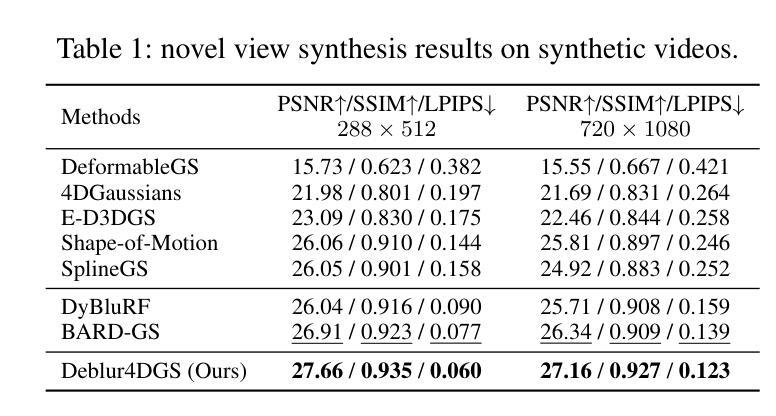
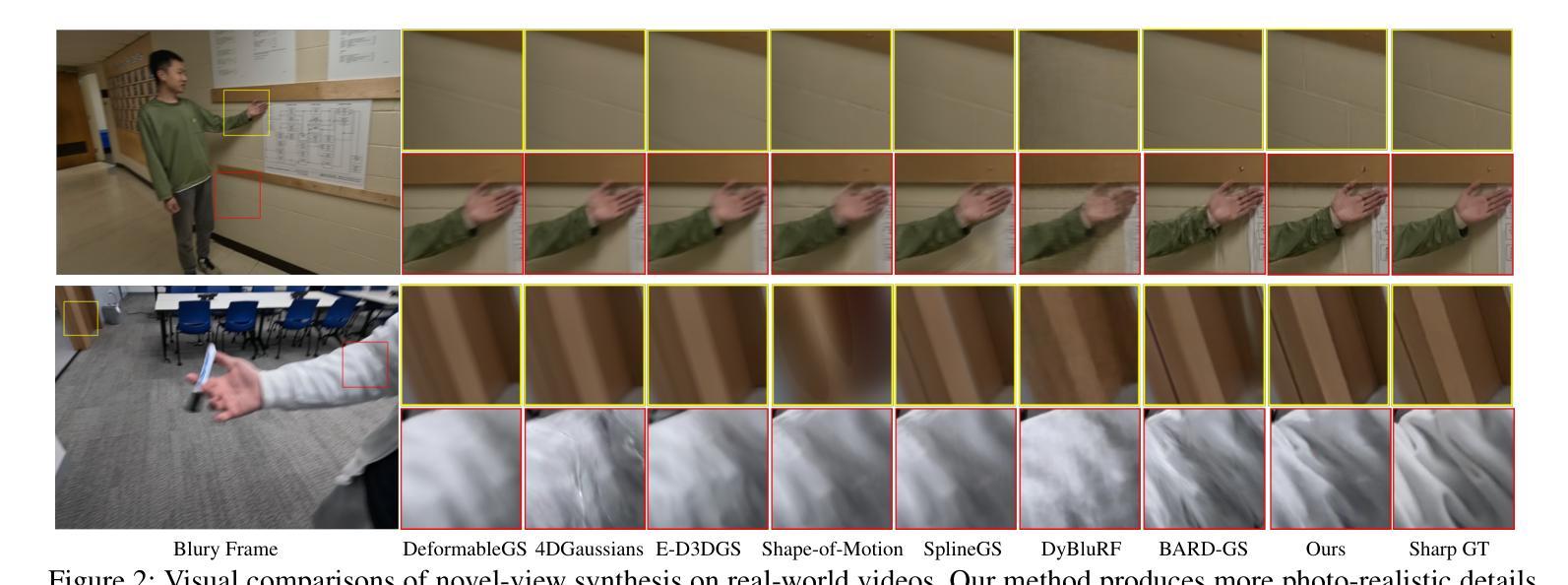
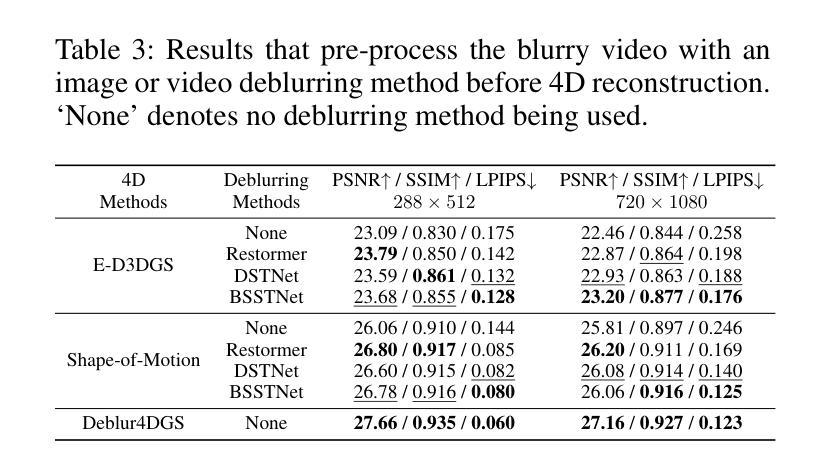
Deblur4DGS: 4D Gaussian Splatting from Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Renlong Wu, Zhilu Zhang, Mingyang Chen, Zifei Yan, Wangmeng Zuo
Recent 4D reconstruction methods have yielded impressive results but rely on sharp videos as supervision. However, motion blur often occurs in videos due to camera shake and object movement, while existing methods render blurry results when using such videos for reconstructing 4D models. Although a few approaches attempted to address the problem, they struggled to produce high-quality results, due to the inaccuracy in estimating continuous dynamic representations within the exposure time. Encouraged by recent works in 3D motion trajectory modeling using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), we take 3DGS as the scene representation manner, and propose Deblur4DGS to reconstruct a high-quality 4D model from blurry monocular video. Specifically, we transform continuous dynamic representations estimation within an exposure time into the exposure time estimation. Moreover, we introduce the exposure regularization term, multi-frame, and multi-resolution consistency regularization term to avoid trivial solutions. Furthermore, to better represent objects with large motion, we suggest blur-aware variable canonical Gaussians. Beyond novel-view synthesis, Deblur4DGS can be applied to improve blurry video from multiple perspectives, including deblurring, frame interpolation, and video stabilization. Extensive experiments in both synthetic and real-world data on the above four tasks show that Deblur4DGS outperforms state-of-the-art 4D reconstruction methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS.
虽然最近的4D重建方法取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但它们依赖于清晰视频作为监督。然而,由于相机抖动和物体移动,视频中的运动模糊经常发生,而现有方法在利用此类视频进行4D模型重建时会产生模糊的结果。尽管有一些方法试图解决这个问题,但由于在曝光时间内估计连续动态表示的不准确性,它们很难产生高质量的结果。受最近使用3D高斯描画(3DGS)进行3D运动轨迹建模的工作的启发,我们以3DGS作为场景表示方式,并提出Deblur4DGS从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量的4D模型。具体来说,我们将曝光时间内连续动态表示的估计转化为曝光时间估计。此外,我们引入了曝光正则化项、多帧和多分辨率一致性正则化项,以避免平凡解。为了进一步更好地表示大运动物体,我们建议使用模糊感知的可变规范高斯。除了新型视图合成,Deblur4DGS可以从多个角度提高模糊视频,包括去模糊、帧内插和视频稳定。在合成和真实数据对上述四个任务的广泛实验表明,Deblur4DGS优于最新的4D重建方法。相关代码可访问 https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS 了解更多。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
摘要
视频中的运动模糊问题在4D重建中是一大挑战。传统方法依赖清晰视频进行重建,但面对运动模糊时效果不佳。本研究利用3D高斯点云技术(3DGS)进行场景表示,提出Deblur4DGS方法,可从模糊的单视角视频重建高质量4D模型。通过估算曝光时间内的连续动态表示,结合曝光正则化项、多帧多分辨率一致性正则化项等,实现更佳结果。对于运动幅度较大的对象,我们引入了模糊感知的可变规范高斯。除了新颖视图合成外,Deblur4DGS还可应用于多种模糊视频改进任务,如去模糊、帧插值和视频稳定等。实验证明,Deblur4DGS在合成和真实数据上的效果优于现有主流方法。相关代码可通过https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS获取。
关键见解
- 4D重建方法在面对视频中的运动模糊问题时存在挑战。
- 本研究采用3D高斯点云技术(3DGS)作为场景表示方式。
- 提出Deblur4DGS方法,能够从模糊的单视角视频重建高质量的4D模型。
- 通过估算曝光时间内的连续动态表示来解决模糊问题。
- 引入曝光正则化项和多帧多分辨率一致性正则化项,进一步优化结果。
- 对于运动幅度大的对象,采用模糊感知的可变规范高斯进行更好表示。
点此查看论文截图

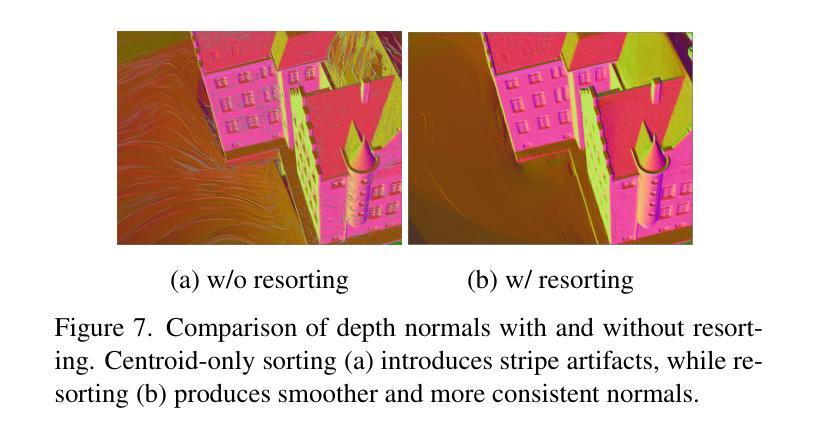
Quadratic Gaussian Splatting: High Quality Surface Reconstruction with Second-order Geometric Primitives
Authors:Ziyu Zhang, Binbin Huang, Hanqing Jiang, Liyang Zhou, Xiaojun Xiang, Shunhan Shen
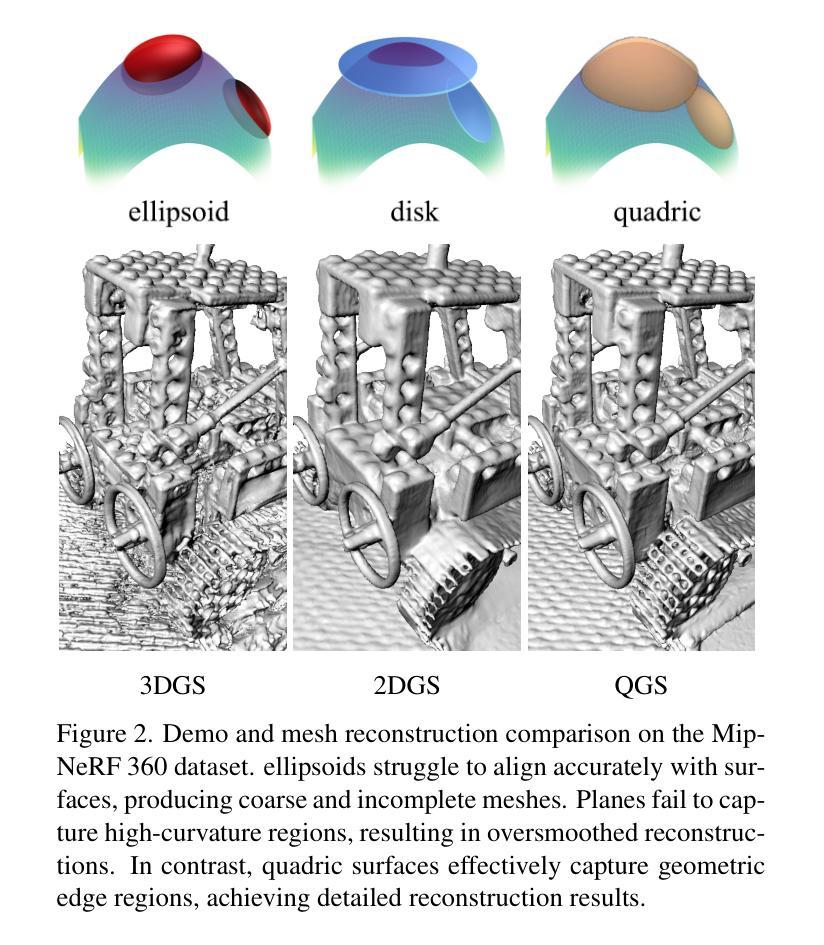
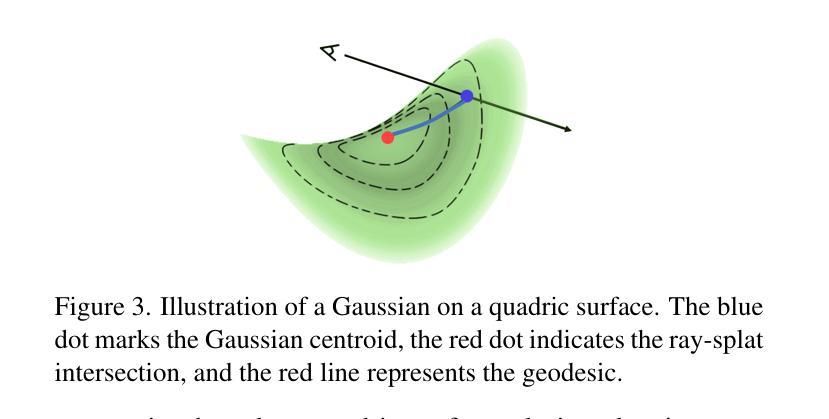
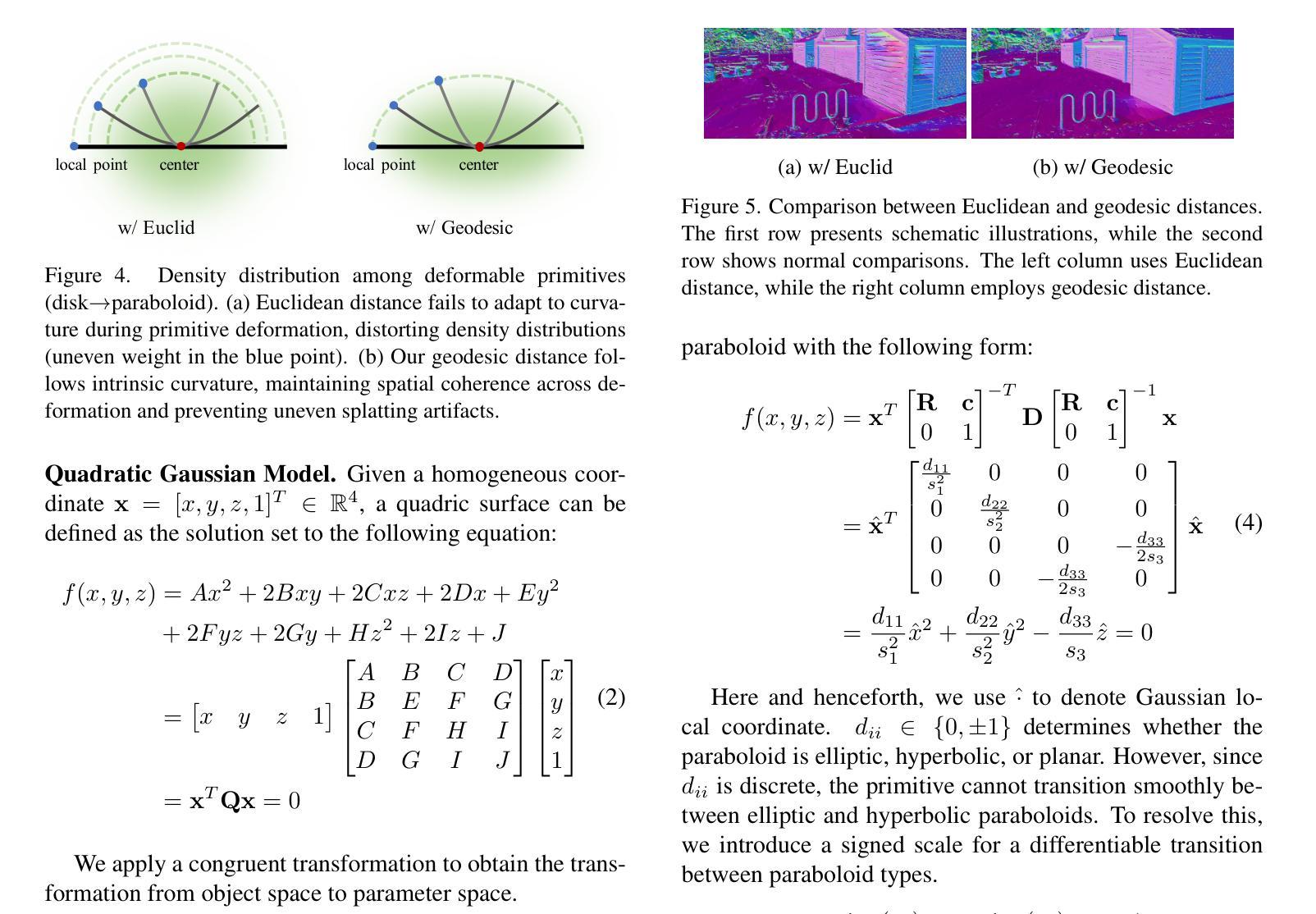
We propose Quadratic Gaussian Splatting (QGS), a novel representation that replaces static primitives with deformable quadric surfaces (e.g., ellipse, paraboloids) to capture intricate geometry. Unlike prior works that rely on Euclidean distance for primitive density modeling–a metric misaligned with surface geometry under deformation–QGS introduces geodesic distance-based density distributions. This innovation ensures that density weights adapt intrinsically to the primitive curvature, preserving consistency during shape changes (e.g., from planar disks to curved paraboloids). By solving geodesic distances in closed form on quadric surfaces, QGS enables surface-aware splatting, where a single primitive can represent complex curvature that previously required dozens of planar surfels, potentially reducing memory usage while maintaining efficient rendering via fast ray-quadric intersection. Experiments on DTU, Tanks and Temples, and MipNeRF360 datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art surface reconstruction, with QGS reducing geometric error (chamfer distance) by 33% over 2DGS and 27% over GOF on the DTU dataset. Crucially, QGS retains competitive appearance quality, bridging the gap between geometric precision and visual fidelity for applications like robotics and immersive reality.
我们提出了二次高斯摊铺(Quadratic Gaussian Splatting,简称QGS)这一新型表示方法,它用可变形的二次曲面(如椭圆、抛物线等)替代静态基本体素,以捕捉复杂的几何形状。不同于以往依赖欧几里得距离进行基本体素密度建模的工作——这一度量方式与变形下的表面几何结构不符——QGS引入了基于测地距离(geodesic distance)的密度分布。这一创新确保了密度权重能够内在地适应原始曲率,在形状变化(例如从平面圆盘到弯曲的抛物线)过程中保持一致性。通过在二次曲面上解决闭合形式的测地距离问题,QGS实现了表面感知摊铺,其中单个基本体素就能代表以前需要数十个平面surfels的复杂曲率,这在可能降低内存使用的同时,通过快速的射线与二次曲面求交算法,维持了高效的渲染效率。在DTU、Tanks and Temples以及MipNeRF360数据集上的实验证明了其最先进的三维重建能力,相较于二维GS,QGS在DTU数据集上将几何误差减少了33%,相较于GOF减少了27%。最重要的是,QGS保持了出色的外观质量,在机器人和沉浸式现实等应用中缩小了几何精度和视觉保真度之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16pages,18figures
Summary
二次高斯融合(Quadratic Gaussian Splatting,简称QGS)是一种新型几何表示方法,它采用可变形二次曲面(如椭圆、抛物线等)替代静态基本体素,以捕捉复杂几何结构。与依赖欧几里得距离进行基本密度建模的先前方法不同,QGS引入基于测地距离(geodesic distance)的密度分布。这一创新确保密度权重能够自适应基本曲面的曲率变化,从而在形状变化时保持一致性。通过解决二次曲面上的测地距离问题,QGS实现了表面感知融合(surface-aware splatting),单个基本体能代表复杂的曲面,从而可能减少内存使用并维持高效的渲染效率。实验结果表明,QGS在表面重建方面具有最佳性能,与二维高斯融合相比减少了33%的几何误差(使用测地距离作为评价指标),并且在机器人和沉浸式现实等应用中实现了几何精度与视觉逼真度之间的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- QGS使用可变形二次曲面替代静态基本体素,捕捉复杂几何结构。
- QGS引入基于测地距离的密度分布,确保密度权重适应基本曲面的曲率变化。
- QGS实现表面感知融合,单个基本体能代表复杂曲面,降低内存使用并提高渲染效率。
- QGS在表面重建方面表现最佳,与现有方法相比显著减少几何误差。
- QGS在机器人和沉浸式现实等应用中实现了几何精度与视觉逼真度之间的平衡。
- QGS方法解决了传统方法中欧式距离与曲面几何变形不匹配的问题。
点此查看论文截图