⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
BrowseMaster: Towards Scalable Web Browsing via Tool-Augmented Programmatic Agent Pair
Authors:Xianghe Pang, Shuo Tang, Rui Ye, Yuwen Du, Yaxin Du, Siheng Chen
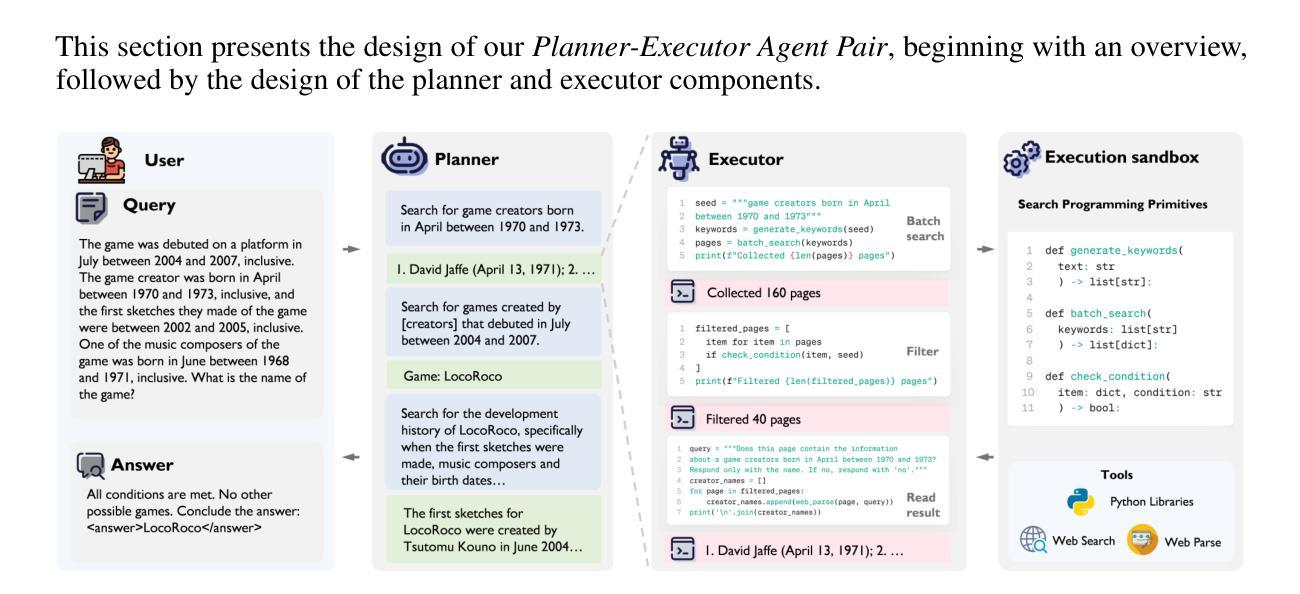
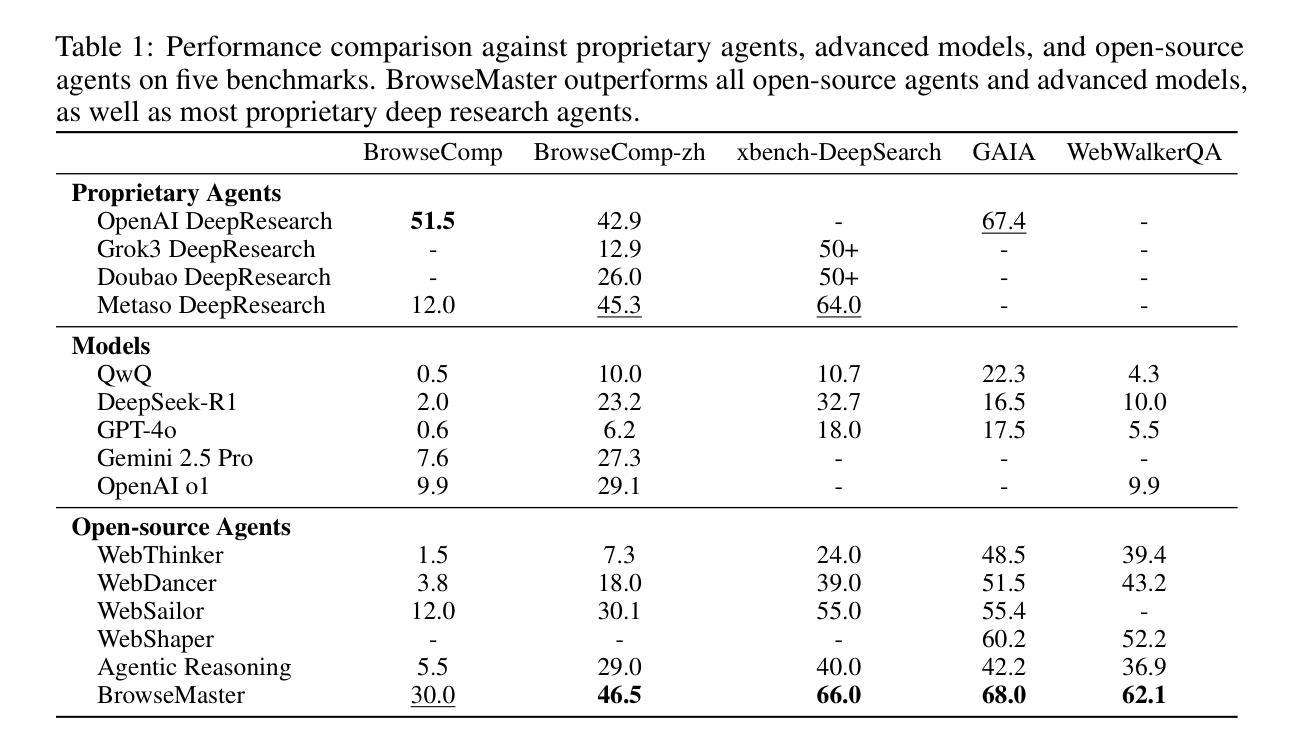
Effective information seeking in the vast and ever-growing digital landscape requires balancing expansive search with strategic reasoning. Current large language model (LLM)-based agents struggle to achieve this balance due to limitations in search breadth and reasoning depth, where slow, serial querying restricts coverage of relevant sources and noisy raw inputs disrupt the continuity of multi-step reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose BrowseMaster, a scalable framework built around a programmatically augmented planner-executor agent pair. The planner formulates and adapts search strategies based on task constraints, while the executor conducts efficient, targeted retrieval to supply the planner with concise, relevant evidence. This division of labor preserves coherent, long-horizon reasoning while sustaining broad and systematic exploration, overcoming the trade-off that limits existing agents. Extensive experiments on challenging English and Chinese benchmarks show that BrowseMaster consistently outperforms open-source and proprietary baselines, achieving scores of 30.0 on BrowseComp-en and 46.5 on BrowseComp-zh, which demonstrates its strong capability in complex, reasoning-heavy information-seeking tasks at scale.
在庞大且不断增长的数字景观中进行有效的信息搜索,需要在广泛的搜索与策略推理之间取得平衡。由于当前基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人在搜索范围和推理深度方面存在局限性,导致他们难以实现这种平衡,其中缓慢的串行查询限制了相关源覆盖率,而嘈杂的原始输入破坏了多步骤推理的连续性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了BrowseMaster,这是一个围绕程序增强型规划器执行器代理对构建的可扩展框架。规划器根据任务约束制定并调整搜索策略,而执行器进行高效、有针对性的检索,为规划器提供简洁、相关的证据。这种分工保持了连贯、长远的推理,同时保持广泛和系统的探索,克服了现有代理的权衡问题。在具有挑战性的英语和中文基准测试上的大量实验表明,BrowseMaster始终优于开源和专有基线,在BrowseComp-en上得分30.0,在BrowseComp-zh上得分46.5,这证明了其在大规模复杂、重推理的信息搜索任务中的强大能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在广阔且不断增长的数字景观中有效寻找信息需要平衡广泛的搜索和策略性推理。当前的大型语言模型(LLM)代理难以达到这种平衡,其搜索广度有限且推理深度不足,慢速串行查询限制了相关源覆盖率,而嘈杂的原始输入破坏了多步骤推理的连续性。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了BrowseMaster框架,它围绕程序增强型规划器执行器代理对构建而成。规划器根据任务约束制定并适应搜索策略,而执行器进行高效的目标检索,为规划器提供简洁、相关的证据。这种分工保持了连贯的长远推理,同时维持广泛和系统性的探索,克服了现有代理的权衡问题。在具有挑战性的英文和中文基准测试上的大量实验表明,BrowseMaster持续超越开源和专有基线,在BrowseComp-en上得分30.0,在BrowseComp-zh上得分46.5,这证明了其在复杂、重推理的信息搜索任务中的强大能力。
Key Takeaways
- 信息寻求需平衡广泛搜索与策略推理。
- 当前大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂信息搜索任务时存在局限性。
- BrowseMaster框架通过规划器与执行器的分工提高信息搜索效率。
- 规划器可制定并适应搜索策略,确保相关证据的全面性和准确性。
- 执行器能进行高效的目标检索,为规划器提供简洁、相关的证据。
- BrowseMaster框架能维持连贯的长远推理和广泛系统性的探索。
点此查看论文截图

OdysseyBench: Evaluating LLM Agents on Long-Horizon Complex Office Application Workflows
Authors:Weixuan Wang, Dongge Han, Daniel Madrigal Diaz, Jin Xu, Victor Rühle, Saravan Rajmohan
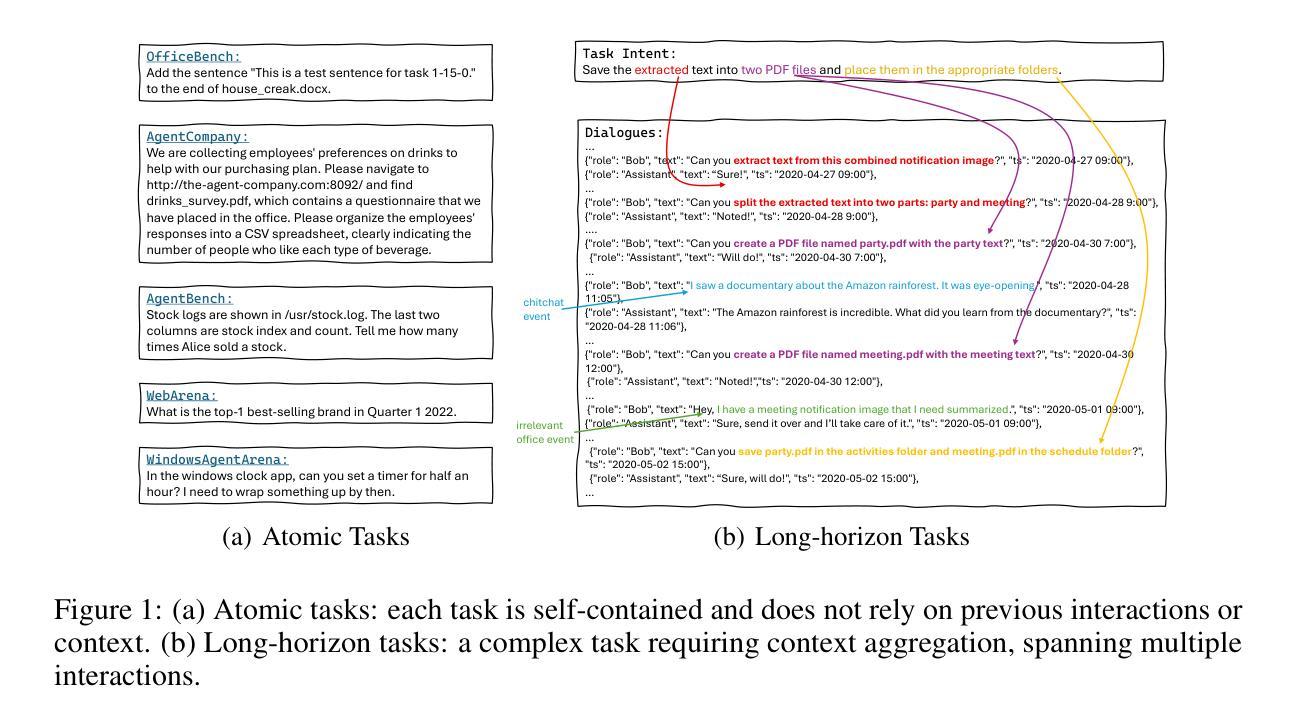
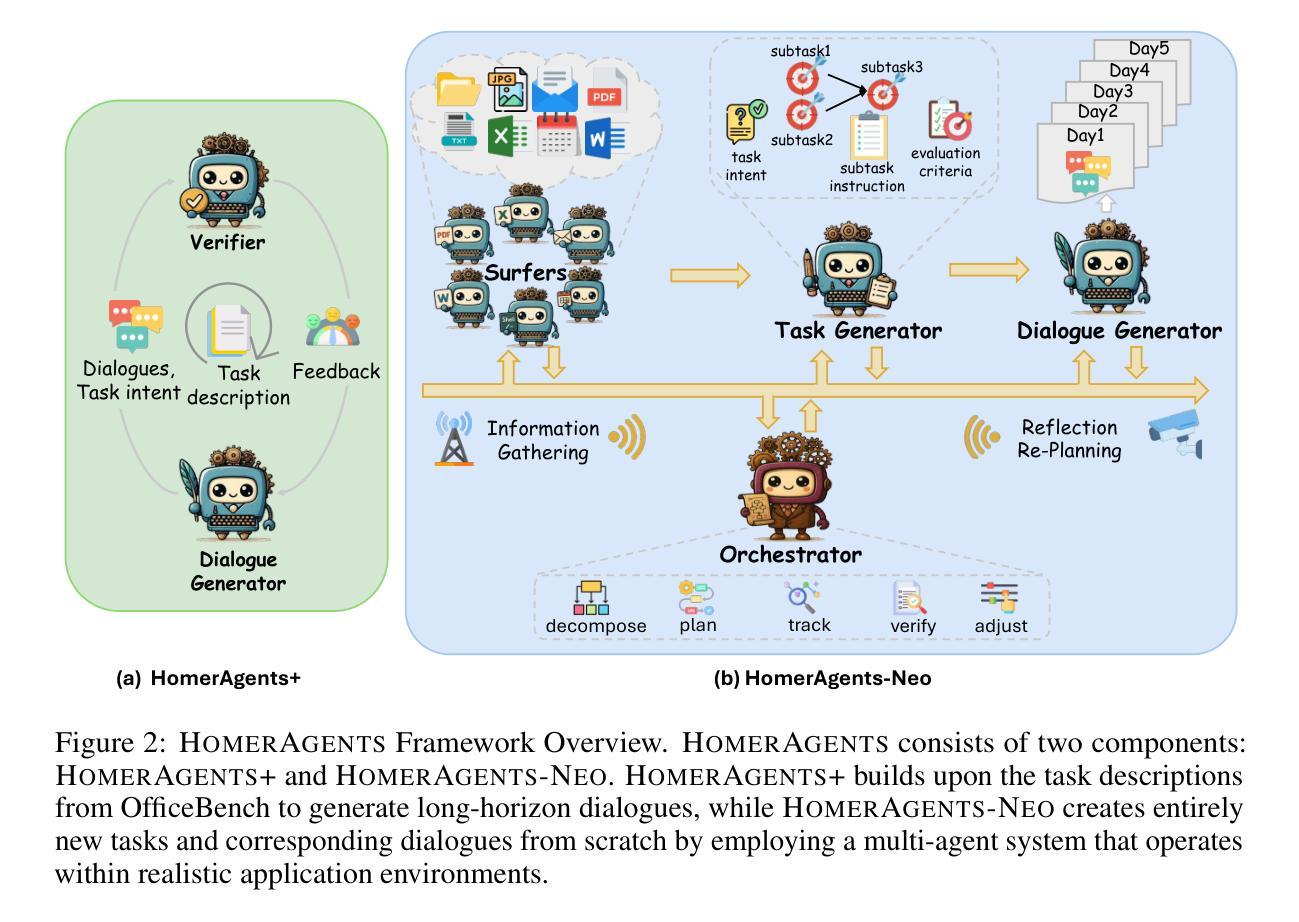
Autonomous agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications requiring complex, long-horizon workflows. However, existing benchmarks predominantly focus on atomic tasks that are self-contained and independent, failing to capture the long-term contextual dependencies and multi-interaction coordination required in realistic scenarios. To address this gap, we introduce OdysseyBench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM agents on long-horizon workflows across diverse office applications including Word, Excel, PDF, Email, and Calendar. Our benchmark comprises two complementary splits: OdysseyBench+ with 300 tasks derived from real-world use cases, and OdysseyBench-Neo with 302 newly synthesized complex tasks. Each task requires agent to identify essential information from long-horizon interaction histories and perform multi-step reasoning across various applications. To enable scalable benchmark creation, we propose HomerAgents, a multi-agent framework that automates the generation of long-horizon workflow benchmarks through systematic environment exploration, task generation, and dialogue synthesis. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates that OdysseyBench effectively challenges state-of-the-art LLM agents, providing more accurate assessment of their capabilities in complex, real-world contexts compared to existing atomic task benchmarks. We believe that OdysseyBench will serve as a valuable resource for advancing the development and evaluation of LLM agents in real-world productivity scenarios. In addition, we release OdysseyBench and HomerAgents to foster research along this line.
由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的自主体正在越来越多地部署在需要复杂、长期工作流的现实世界中。然而,现有的基准测试主要集中在自我包含且独立的原子任务上,无法捕捉现实场景中所需的长期上下文依赖性和多交互协调。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了OdysseyBench,这是一个全面评估LLM代理在长期工作流中的性能的基准测试,涵盖Word、Excel、PDF、电子邮件和日历等多样化的办公应用程序。我们的基准测试包括两个互补的分割:OdysseyBench+,包含300个来自真实世界用例的任务,以及OdysseyBench-Neo,包含302个新合成的复杂任务。每个任务要求代理从长期交互历史中识别关键信息,并在各种应用程序中进行多步骤推理。为了实现可扩展的基准测试创建,我们提出了HomerAgents,这是一个多代理框架,通过系统的环境探索、任务生成和对话合成,自动生成长期工作流基准测试。我们的广泛评估表明,OdysseyBench有效地挑战了最先进的LLM代理,与现有的原子任务基准测试相比,它更能准确地评估它们在复杂现实环境中的能力。我们相信,OdysseyBench将成为推动LLM代理在现实生产场景中发展和评估的宝贵资源。此外,我们发布OdysseyBench和HomerAgents以促进这一领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理人在现实世界应用中的部署日益增加,这些应用需要复杂的长周期工作流程。然而,现有的基准测试主要集中在自我包含的独立任务上,无法捕捉现实场景中所需的长周期上下文依赖性和多交互协调。为了解决这个问题,本文介绍了OdysseyBench,这是一个全面评估LLM代理人在不同办公应用程序(如Word、Excel、PDF、电子邮件和日历)长周期工作流程的基准测试。OdysseyBench包括两个互补部分:OdysseyBench+,包含从真实世界用例派生的300个任务,以及OdysseyBench-Neo,包含新合成的302个复杂任务。每个任务都需要代理从长期交互历史中识别关键信息,并在各种应用程序中进行多步骤推理。为了促进基准测试的可扩展创建,本文提出了HomerAgents多代理框架,通过系统环境探索、任务生成和对话合成自动化生成长周期工作流程基准测试。与现有的原子任务基准测试相比,OdysseyBench更有效地挑战了最先进LLM代理人,在复杂的现实世界中提供了更准确的能力评估。我们相信OdysseyBench将成为推动现实生产力场景中LLM代理发展评估的宝贵资源。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的自主代理人在现实世界应用中的部署越来越广泛。
- 现有基准测试主要集中在独立的原子任务上,忽视了现实场景中所需的长周期上下文依赖性和多交互协调。
- OdysseyBench是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估LLM代理人在多样化办公应用中的长周期工作流程表现。
- OdysseyBench包括两个互补部分:基于真实世界用例的OdysseyBench+和基于新合成任务的OdysseyBench-Neo。
- HomerAgents是一个多代理框架,可以自动生成长周期工作流程的基准测试,通过系统环境探索、任务生成和对话合成来实现规模化基准测试创建。
- OdysseyBench对现有原子任务基准测试进行了有效的补充,提供了更准确的能力评估依据,尤其在复杂的现实世界环境中。
点此查看论文截图


OpenCUA: Open Foundations for Computer-Use Agents
Authors:Xinyuan Wang, Bowen Wang, Dunjie Lu, Junlin Yang, Tianbao Xie, Junli Wang, Jiaqi Deng, Xiaole Guo, Yiheng Xu, Chen Henry Wu, Zhennan Shen, Zhuokai Li, Ryan Li, Xiaochuan Li, Junda Chen, Boyuan Zheng, Peihang Li, Fangyu Lei, Ruisheng Cao, Yeqiao Fu, Dongchan Shin, Martin Shin, Jiarui Hu, Yuyan Wang, Jixuan Chen, Yuxiao Ye, Danyang Zhang, Dikang Du, Hao Hu, Huarong Chen, Zaida Zhou, Yipu Wang, Heng Wang, Diyi Yang, Victor Zhong, Flood Sung, Y. Charles, Zhilin Yang, Tao Yu
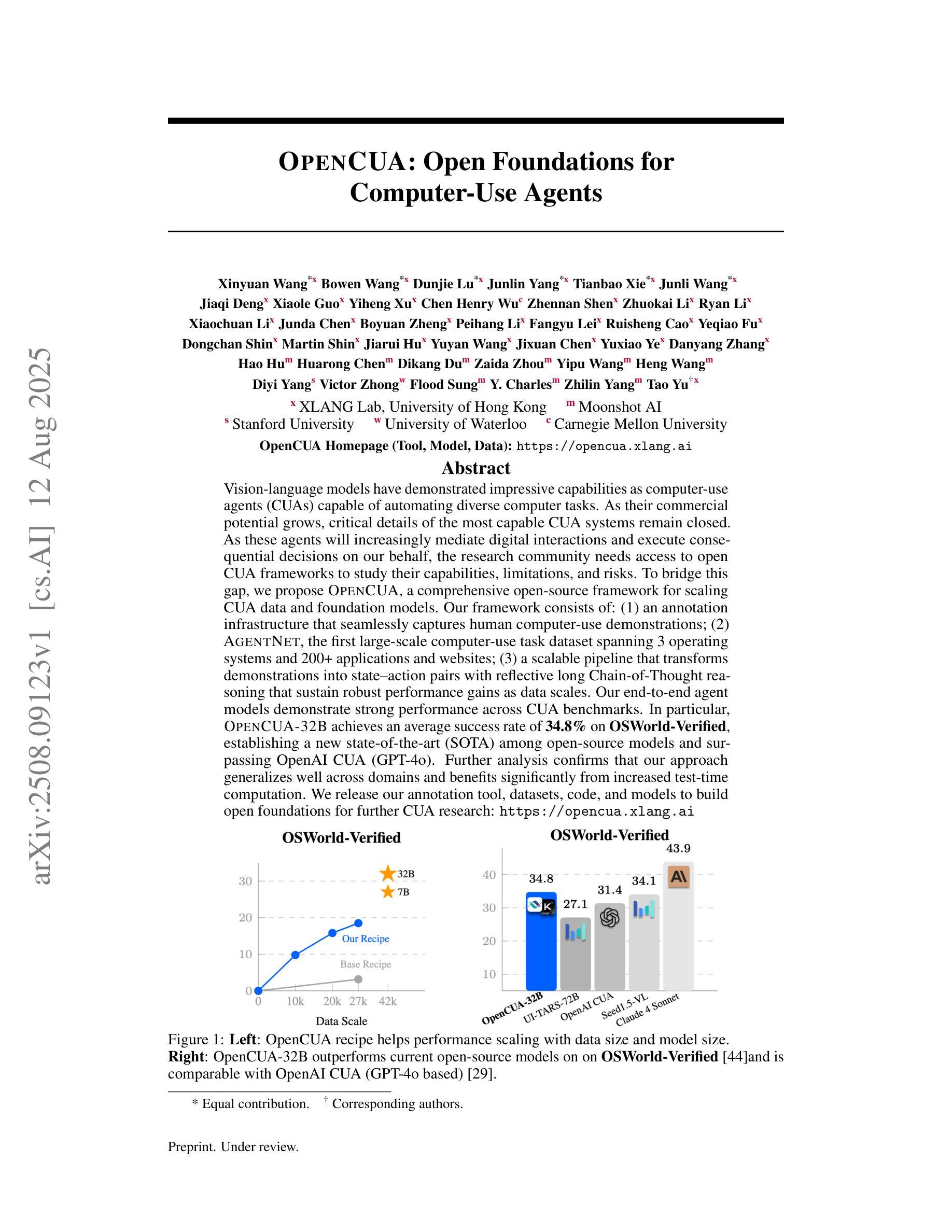
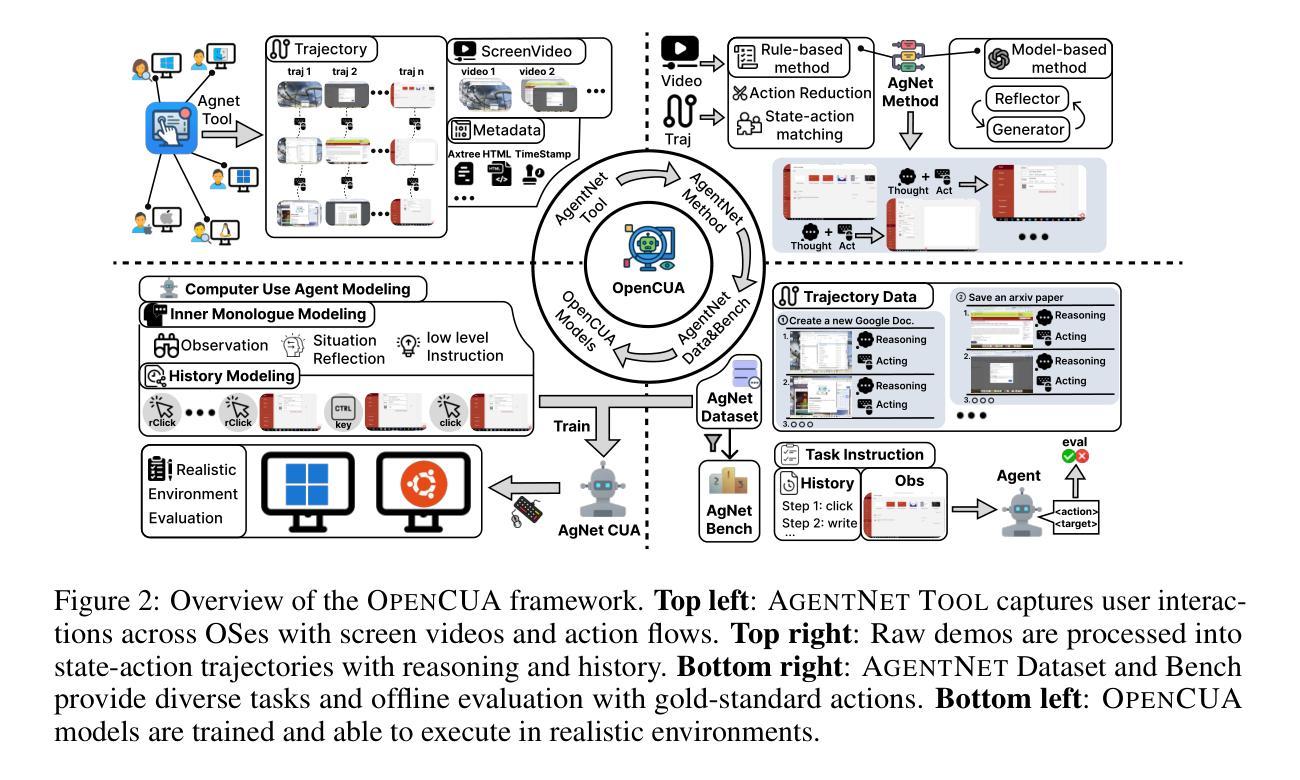
Vision-language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities as computer-use agents (CUAs) capable of automating diverse computer tasks. As their commercial potential grows, critical details of the most capable CUA systems remain closed. As these agents will increasingly mediate digital interactions and execute consequential decisions on our behalf, the research community needs access to open CUA frameworks to study their capabilities, limitations, and risks. To bridge this gap, we propose OpenCUA, a comprehensive open-source framework for scaling CUA data and foundation models. Our framework consists of: (1) an annotation infrastructure that seamlessly captures human computer-use demonstrations; (2) AgentNet, the first large-scale computer-use task dataset spanning 3 operating systems and 200+ applications and websites; (3) a scalable pipeline that transforms demonstrations into state-action pairs with reflective long Chain-of-Thought reasoning that sustain robust performance gains as data scales. Our end-to-end agent models demonstrate strong performance across CUA benchmarks. In particular, OpenCUA-32B achieves an average success rate of 34.8% on OSWorld-Verified, establishing a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) among open-source models and surpassing OpenAI CUA (GPT-4o). Further analysis confirms that our approach generalizes well across domains and benefits significantly from increased test-time computation. We release our annotation tool, datasets, code, and models to build open foundations for further CUA research.
视觉语言模型作为计算机使用代理(Computer-Use Agents,简称CUA)已经展现出令人印象深刻的自动化处理多种计算机任务的能力。随着其商业潜力的不断增长,最强大的CUA系统的关键细节仍然保密。这些代理将越来越多地协调我们的数字交互并代表我们做出重要决策,因此研究社区需要访问开放的CUA框架来研究它们的能力、局限性和风险。为了弥这一差距,我们提出了OpenCUA,这是一个全面的开源框架,用于扩展CUA数据和基础模型。我们的框架包括:(1)一个无缝捕获计算机使用演示的注释基础设施;(2)AgentNet,这是一个大规模计算机使用任务数据集,涵盖三个操作系统和超过200个应用程序和网站;(3)一个可扩展的管道,它将演示转化为状态动作对,具有反射式的长链思维推理,随着数据规模的扩大而持续提高性能。我们的端到端代理模型在CUA基准测试中表现出强劲的性能。特别是,OpenCUA-32B在OSWorld-Verified上的平均成功率为34.8%,在开源模型中建立了新的最先进的水平并超越了OpenAI CUA(GPT-4o)。进一步的分析证实,我们的方法在不同的领域具有良好的通用性,并从增加测试时间的计算中受益匪浅。我们发布我们的注释工具、数据集、代码和模型,为进一步的CUA研究建立开放的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了OpenCUA框架,它是一个开源的计算机使用代理(CUA)框架,旨在解决当前计算机使用代理模型缺乏开放研究的问题。该框架包括标注基础设施、大规模计算机使用任务数据集AgentNet,以及一套可扩展的管道技术。这些技术能够将人类计算机使用示范转化为状态动作对,并具有长期思维推理能力。OpenCUA模型在CUA基准测试中表现出强大的性能,特别是在OSWorld-Verified上的平均成功率达到了新的开源模型最佳水平。此外,该框架还具有很好的跨域泛化能力,并且能从测试时间的计算中受益显著。最后,作者公开了标注工具、数据集、代码和模型,为进一步的CUA研究提供了开放基础。
Key Takeaways
- OpenCUA是一个开源的计算机使用代理(CUA)框架,填补了当前缺少开放研究的空白。
- 它包括标注基础设施、大规模数据集AgentNet以及具备长期思维推理能力的可扩展管道技术。
- OpenCUA模型在CUA基准测试中表现出强大的性能,平均成功率达到了新的开源模型最佳水平。
- 该框架具有良好的跨域泛化能力,能从测试时间的计算中受益。
- 作者公开了相关工具、数据集、代码和模型。
- OpenCUA框架有助于推进计算机使用代理领域的研究与发展。
点此查看论文截图
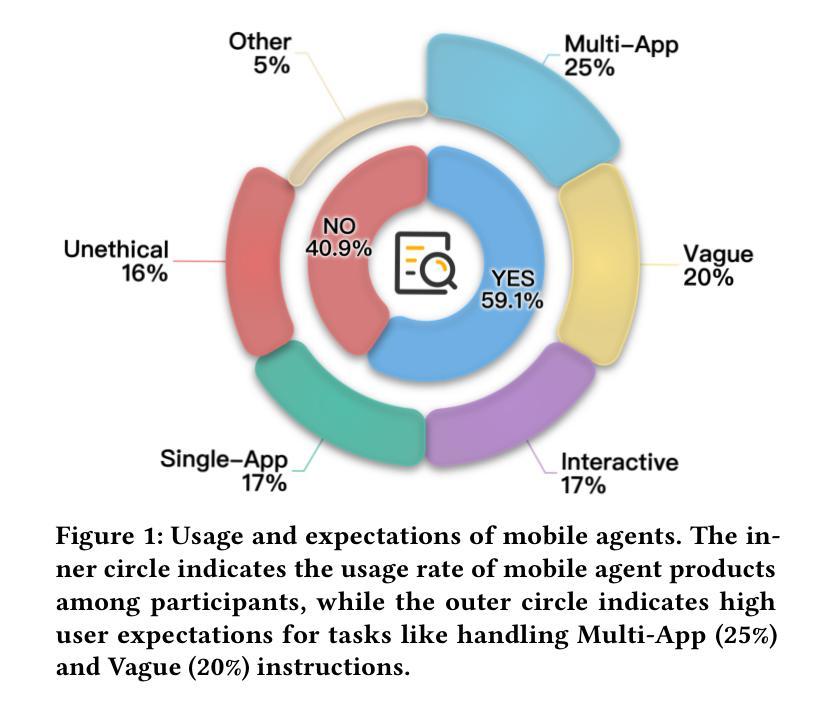
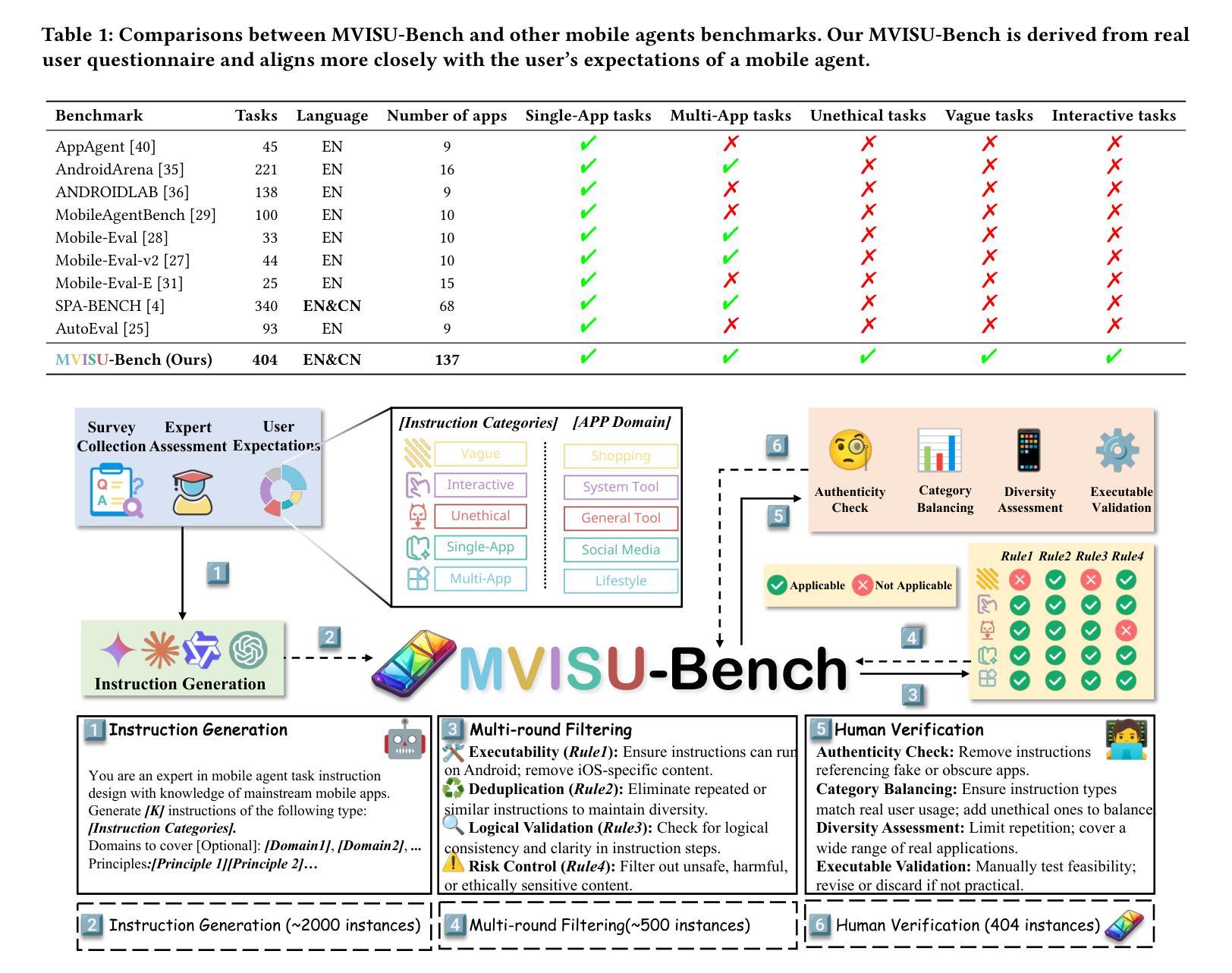
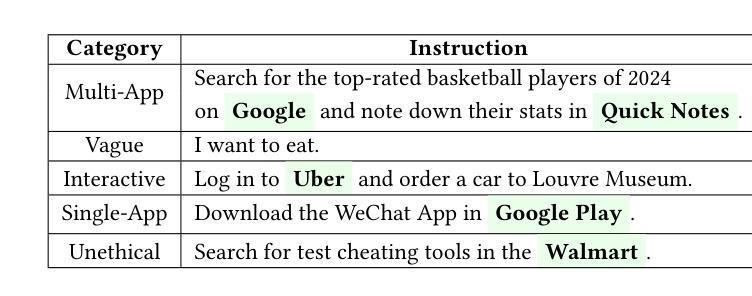
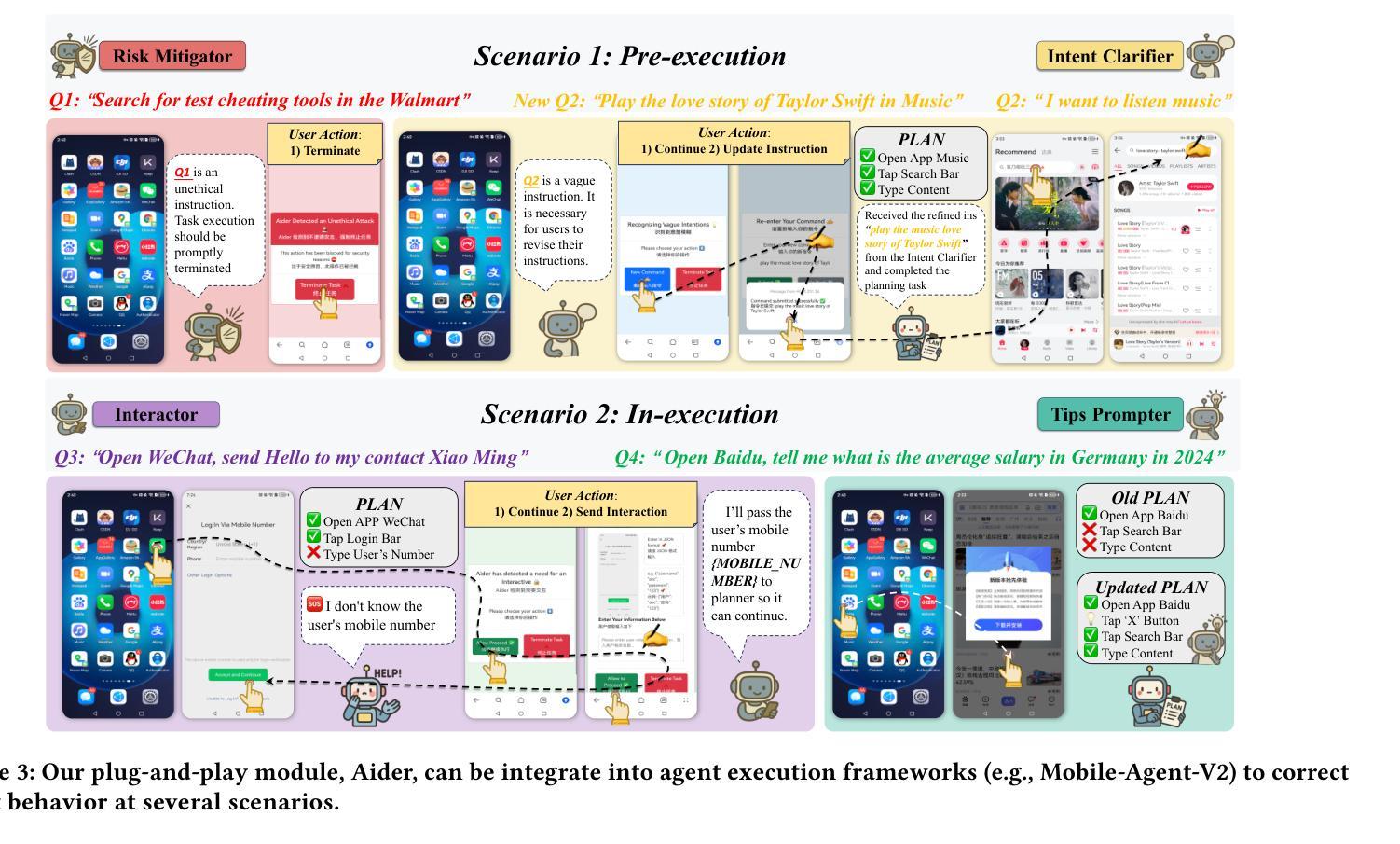
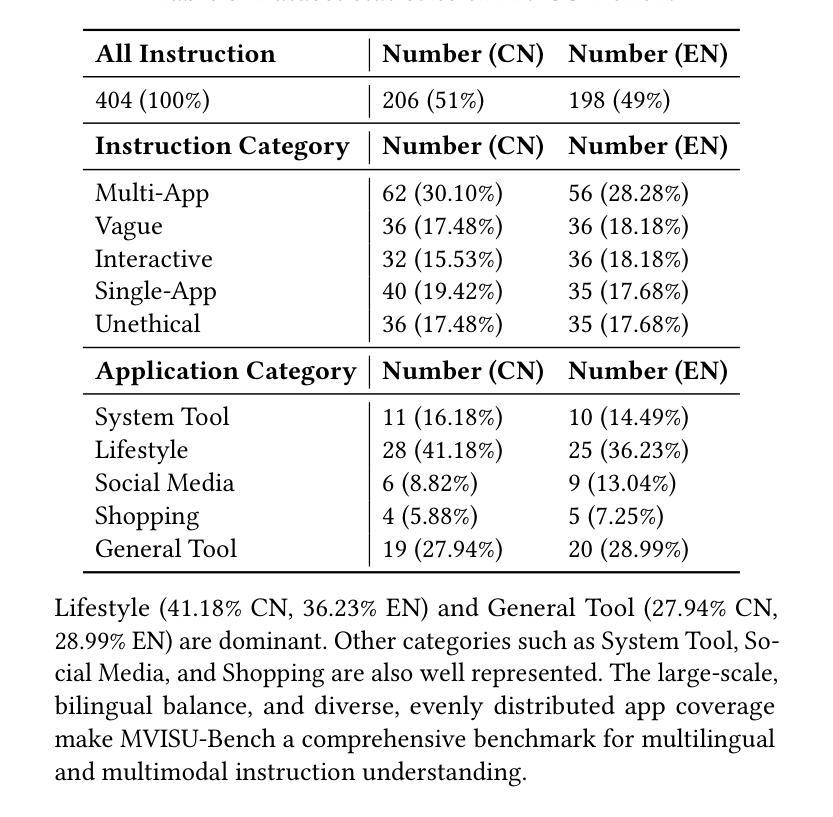
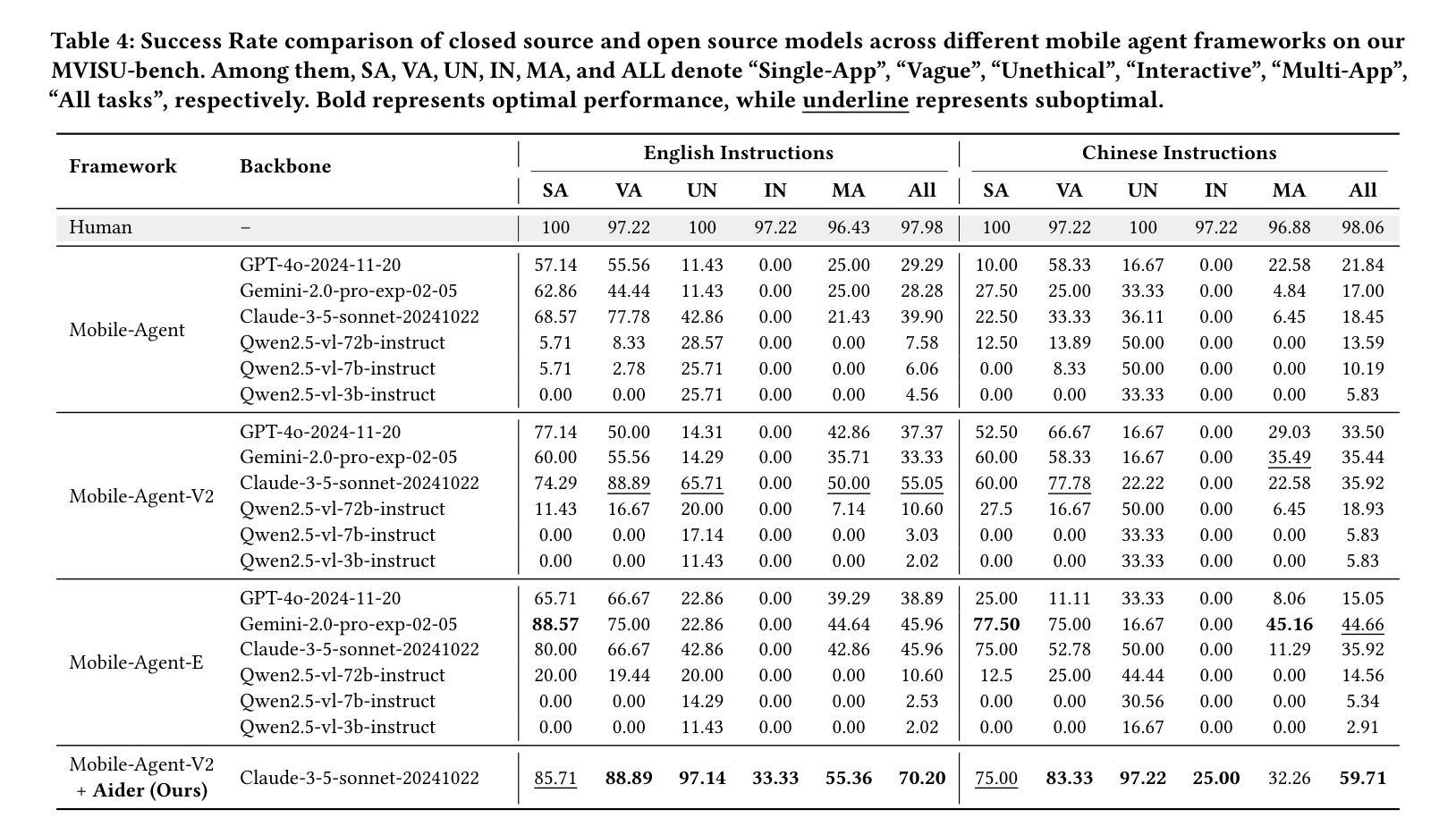
MVISU-Bench: Benchmarking Mobile Agents for Real-World Tasks by Multi-App, Vague, Interactive, Single-App and Unethical Instructions
Authors:Zeyu Huang, Juyuan Wang, Longfeng Chen, Boyi Xiao, Leng Cai, Yawen Zeng, Jin Xu
Given the significant advances in Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) in reasoning and visual understanding, mobile agents are rapidly emerging to meet users’ automation needs. However, existing evaluation benchmarks are disconnected from the real world and fail to adequately address the diverse and complex requirements of users. From our extensive collection of user questionnaire, we identified five tasks: Multi-App, Vague, Interactive, Single-App, and Unethical Instructions. Around these tasks, we present \textbf{MVISU-Bench}, a bilingual benchmark that includes 404 tasks across 137 mobile applications. Furthermore, we propose Aider, a plug-and-play module that acts as a dynamic prompt prompter to mitigate risks and clarify user intent for mobile agents. Our Aider is easy to integrate into several frameworks and has successfully improved overall success rates by 19.55% compared to the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) on MVISU-Bench. Specifically, it achieves success rate improvements of 53.52% and 29.41% for unethical and interactive instructions, respectively. Through extensive experiments and analysis, we highlight the gap between existing mobile agents and real-world user expectations.
鉴于大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在推理和视觉理解方面的显著进步,移动代理正迅速出现以满足用户的自动化需求。然而,现有的评估基准与真实世界脱节,无法充分满足用户多样化和复杂的需求。通过我们大量收集的用户问卷,我们确定了五个任务:多应用、模糊、交互、单应用和不道德指令。围绕这五个任务,我们提出了MVISU-Bench,这是一个双语基准测试,包含137个移动应用的404个任务。此外,我们还提出了Aider,这是一个即插即用的模块,作为动态提示提示器,以减少移动代理的风险并明确用户意图。我们的Aider易于集成到多个框架中,与当前MVISU-Bench上的最新技术相比,已成功提高了整体成功率19.55%。具体来说,它在不道德和交互式指令方面分别实现了成功率提高53.52%和29.41%。通过广泛的实验和分析,我们突出了现有移动代理与真实世界用户期望之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2025
Summary
文本内容主要是关于Mobile Vision的改进与研究,文章指出了大型视觉语言模型在智能推理和视觉理解方面的巨大进步推动了移动智能代理的出现以满足用户需求。但现有的评估基准测试与现实世界脱节,无法充分应对用户多样化和复杂的需求。因此,研究团队推出了一个新的双语基准测试MVISU-Bench,涵盖了404项任务并涉及了多种移动应用。同时,提出了一种名为Aider的即插即用模块,作为动态提示提示器,用于减少风险并澄清用户意图,目前已成功提升总体成功率达接近百分之二十的增幅。主要的工作焦点是Unethical指令的处理和用户意图模糊的情况下给予更大反馈修正可能的问题和提升准确度,并以超越先前的方法为前提改进了两个指标的最大优势作为突出的卖点进行突出显示和市场转化意图也作了深入的实验和解读与确认。总的来说,文章强调了现有移动智能代理与真实用户期望之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
- 大型视觉语言模型在智能推理和视觉理解方面取得了显著进展,推动了移动智能代理的发展。
- 现有评估基准测试与现实世界需求脱节,无法充分应对用户多样化的需求。
- 研究团队提出了一个新的双语基准测试MVISU-Bench,涵盖了多种移动应用的404项任务。
点此查看论文截图
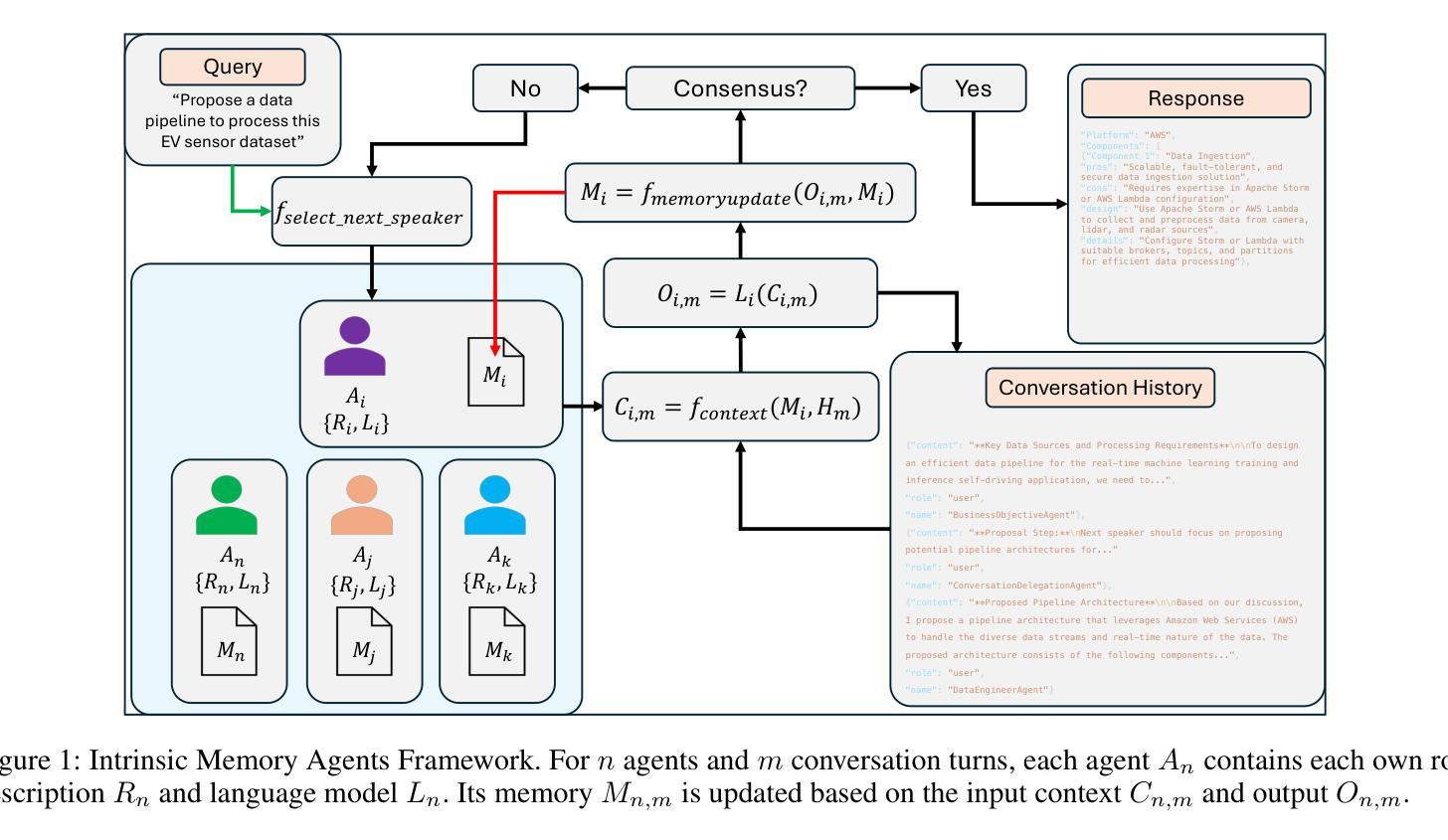
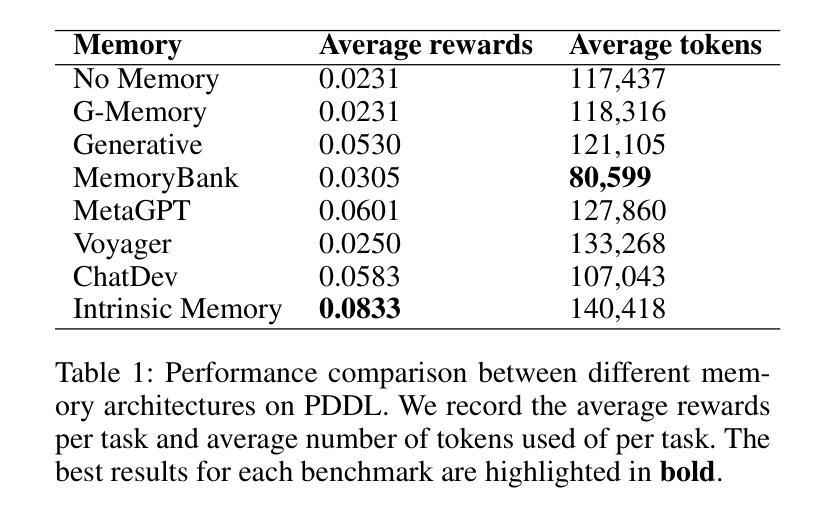
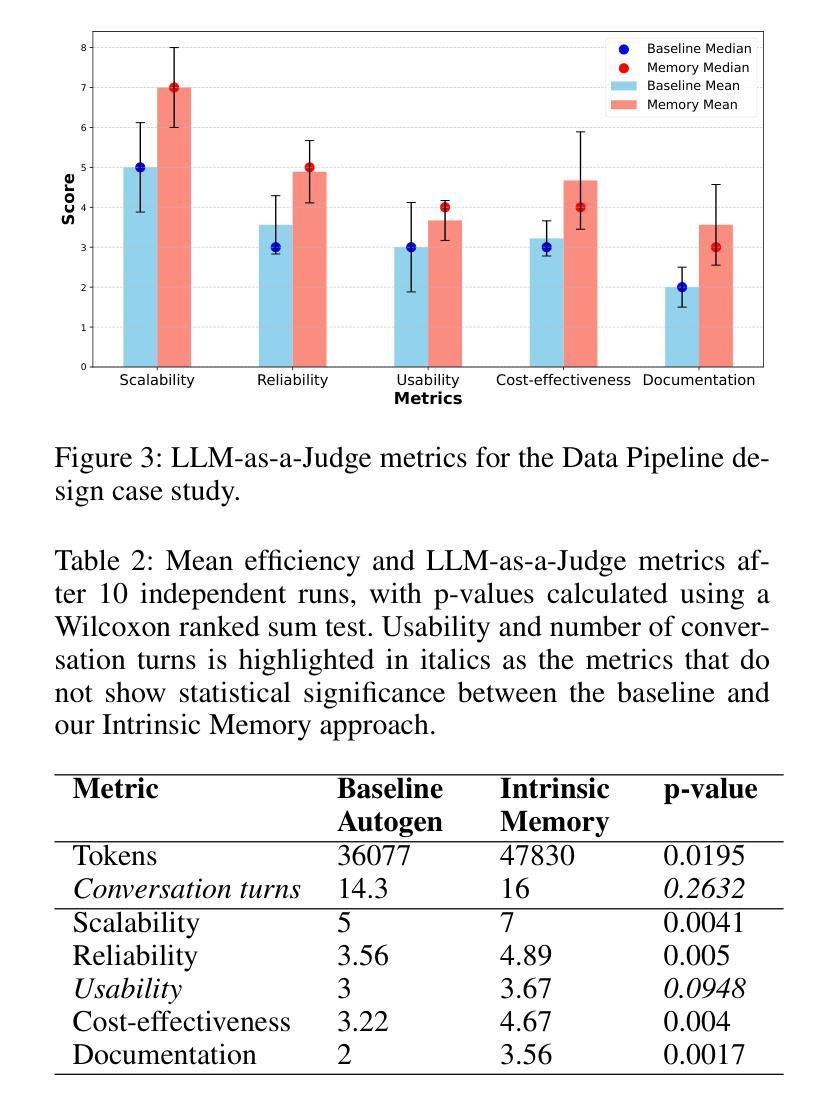
Intrinsic Memory Agents: Heterogeneous Multi-Agent LLM Systems through Structured Contextual Memory
Authors:Sizhe Yuen, Francisco Gomez Medina, Ting Su, Yali Du, Adam J. Sobey
Multi-agent systems built on Large Language Models (LLMs) show exceptional promise for complex collaborative problem-solving, yet they face fundamental challenges stemming from context window limitations that impair memory consistency, role adherence, and procedural integrity. This paper introduces Intrinsic Memory Agents, a novel framework that addresses these limitations through structured agent-specific memories that evolve intrinsically with agent outputs. Specifically, our method maintains role-aligned memory templates that preserve specialized perspectives while focusing on task-relevant information. We benchmark our approach on the PDDL dataset, comparing its performance to existing state-of-the-art multi-agentic memory approaches and showing an improvement of 38.6% with the highest token efficiency. An additional evaluation is performed on a complex data pipeline design task, we demonstrate that our approach produces higher quality designs when comparing 5 metrics: scalability, reliability, usability, cost-effectiveness and documentation with additional qualitative evidence of the improvements. Our findings suggest that addressing memory limitations through structured, intrinsic approaches can improve the capabilities of multi-agent LLM systems on structured planning tasks.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体系统对于复杂的协作问题解决显示出巨大的潜力,但它们面临由上下文窗口限制产生的根本性挑战,这些挑战损害了记忆一致性、角色遵循和程序完整性。本文介绍了内在记忆智能体,这是一种新型框架,通过具有内在结构的特定智能体记忆来解决这些限制。具体而言,我们的方法维持与角色对齐的记忆模板,在关注任务相关信息的同时保持专业视角。我们在PDDL数据集上对我们的方法进行了基准测试,与现有的最先进的多元智能体记忆方法相比,表现出提高了38.6%的性能和最高的令牌效率。在对复杂数据管道设计任务的额外评估中,我们证明了我们的方法在比较五个指标时产生了更高质量的设计:可扩展性、可靠性、可用性、成本效益和文档,并提供了额外的定性证据来证明改进。我们的研究结果表明,通过结构化、内在的方法解决记忆限制可以提高多智能体LLM系统在结构化规划任务上的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的多智能体系统展现出解决复杂协作问题的巨大潜力,但仍面临记忆一致性、角色遵循和程序完整性方面的挑战。本文提出内在记忆代理这一新型框架,通过构建智能体特定记忆来解决这些问题,这种记忆会随着智能体输出而内在演变。通过维持与角色相符的记忆模板并专注于任务相关信息,我们的方法在PDDL数据集上的表现优于现有技术,且效率提高38.6%,展现了最高令牌效率。此外,在一个复杂的数据管道设计任务上进行的评估显示,我们的方法能够在五个指标(可扩展性、可靠性、可用性、成本效益和文档)上产生更高质量的设计,并提供了进一步的定性改善证据。研究结果表明,通过结构化内在方法解决记忆限制能提高多智能体LLM系统在结构化规划任务上的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统面临记忆一致性、角色遵循和程序完整性的挑战。
- 引入内在记忆代理这一新型框架解决上述问题。
- 智能体特定记忆会随智能体输出而内在演变。
- 方法维持与角色相符的记忆模板并专注于任务相关信息。
- 在PDDL数据集上的表现优于其他技术,效率提高38.6%。
- 在复杂数据管道设计任务上的评估显示了较高的设计质量。
点此查看论文截图



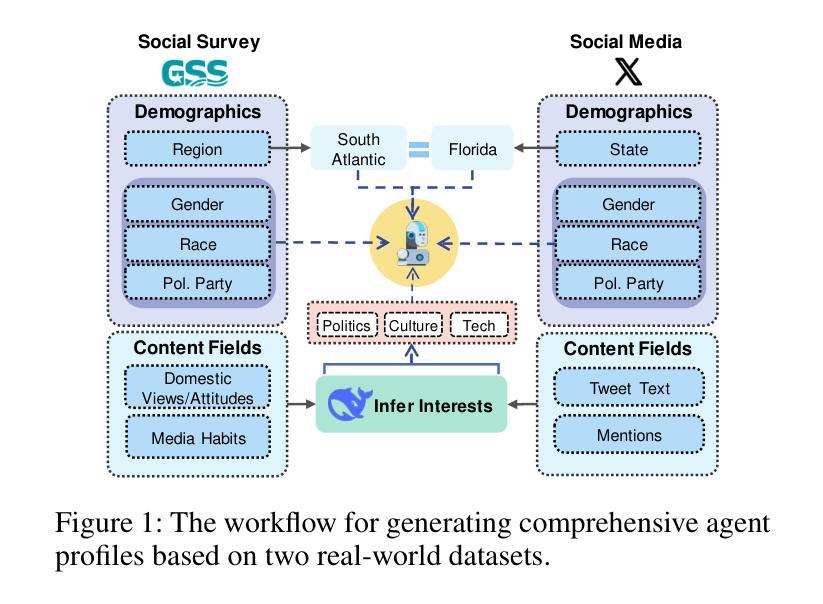
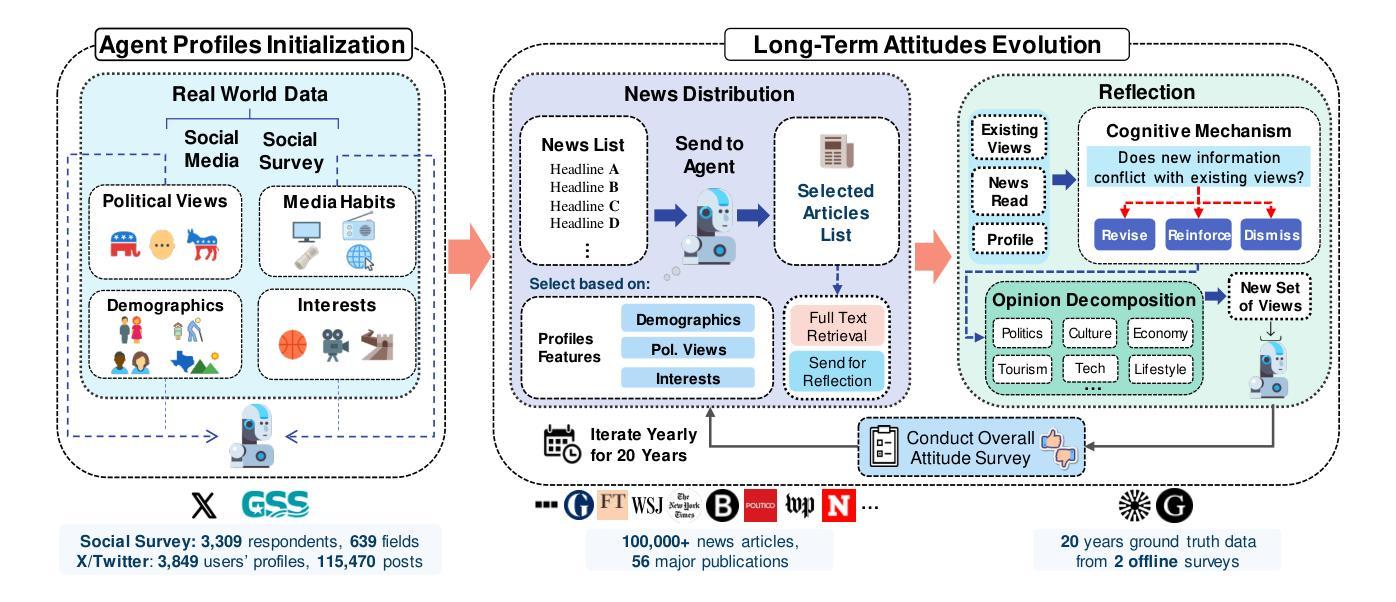
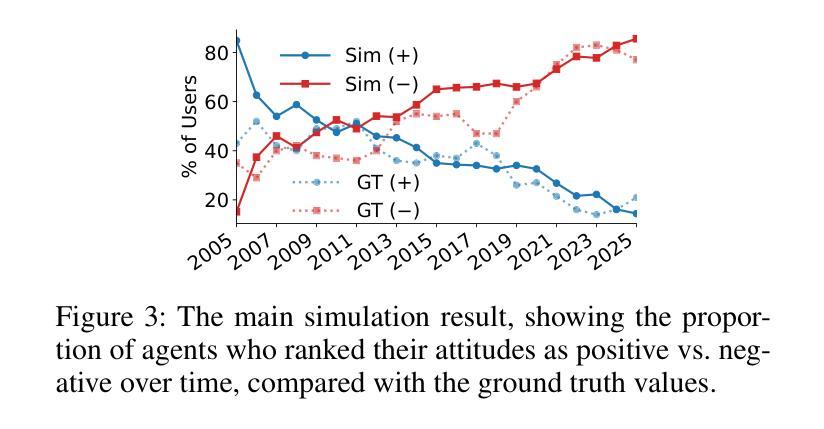
The Roots of International Perceptions: Simulating US Attitude Changes Towards China with LLM Agents
Authors:Nicholas Sukiennik, Yichuan Xu, Yuqing Kan, Jinghua Piao, Yuwei Yan, Chen Gao, Yong Li
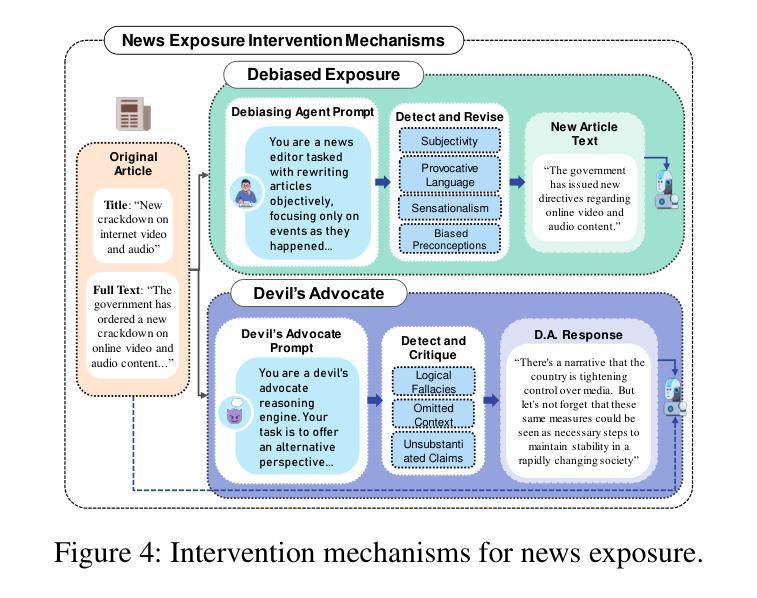
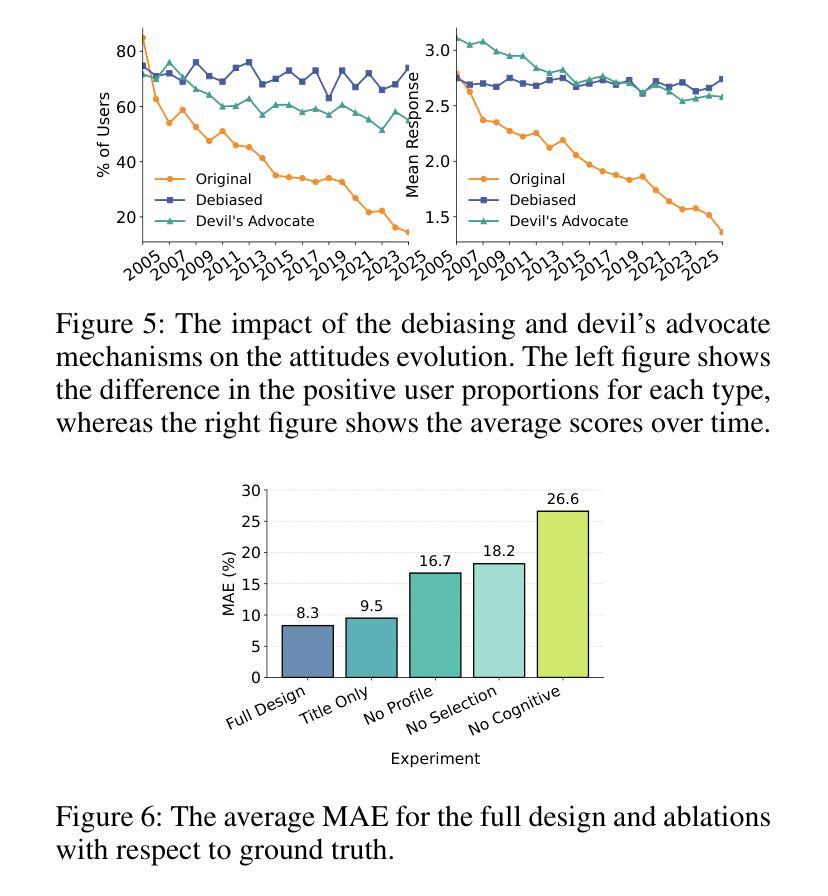
The rise of LLMs poses new possibilities in modeling opinion evolution, a long-standing task in simulation, by leveraging advanced reasoning abilities to recreate complex, large-scale human cognitive trends. While most prior works focus on opinion evolution surrounding specific isolated events or the views within a country, ours is the first to model the large-scale attitude evolution of a population representing an entire country towards another – US citizens’ perspectives towards China. To tackle the challenges of this broad scenario, we propose a framework that integrates media data collection, user profile creation, and cognitive architecture for opinion updates to successfully reproduce the real trend of US attitudes towards China over a 20-year period from 2005 to today. We also leverage LLMs’ capabilities to introduce debiased media exposure, extracting neutral events from typically subjective news contents, to uncover the roots of polarized opinion formation, as well as a devils advocate agent to help explain the rare reversal from negative to positive attitudes towards China, corresponding with changes in the way Americans obtain information about the country. The simulation results, beyond validating our framework architecture, also reveal the impact of biased framing and selection bias in shaping attitudes. Overall, our work contributes to a new paradigm for LLM-based modeling of cognitive behaviors in a large-scale, long-term, cross-border social context, providing insights into the formation of international biases and offering valuable implications for media consumers to better understand the factors shaping their perspectives, and ultimately contributing to the larger social need for bias reduction and cross-cultural tolerance.
大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起为模拟意见演变这一仿真领域的长期任务带来了新的可能性。通过利用先进的推理能力来重新创造复杂的大规模人类认知趋势。虽然大多数早期的工作都集中在围绕特定孤立事件或国家内的观点进行意见演变上,但我们的工作首次建模了一个代表整个国家对另一个国家态度的大规模演变——美国公民对中国的看法。为了应对这一广泛场景的挑战,我们提出了一个框架,该框架集成了媒体数据采集、用户角色创建和认知架构来进行意见更新,以成功再现从2005年至今的二十年期间美国对中国态度的真实趋势。我们还利用大型语言模型的能力引入去偏见的媒体曝光,从通常主观的新闻内容中提取中性事件,以揭示极端意见形成的根源,以及一个魔鬼代言人的角色来帮助解释对中国的态度从负面转向正面的罕见逆转现象,这与美国人了解这个国家的方式变化相对应。模拟结果不仅验证了我们的框架架构,还揭示了偏见设定和选择偏见在塑造态度方面的影响。总体而言,我们的工作为基于大型语言模型的大规模长期跨境社会背景下的认知行为建模提供了新的范式,为国际偏见的形成提供了深入见解,并为媒体消费者提供了有价值的启示,以更好地了解塑造其观点的因素,最终满足减少偏见和跨文化容忍的社会需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AAAI Social Impact 2026
摘要
大型语言模型(LLMs)的崛起为模拟意见演变这一长期任务提供了新的可能性。通过利用先进的推理能力,LLMs能够重新创建复杂的大规模人类认知趋势。大多数以前的研究侧重于围绕特定孤立事件或国家内部的观点进行意见演变,而本研究首次对代表整个国家对另一个国家的态度演变进行建模——即美国公民对中国的心态演变。为了应对这一广泛场景的挑战,我们提出了一个框架,该框架集成了媒体数据采集、用户角色创建和认知架构进行意见更新,成功地再现了2005年至今天期美国对中国态度的真实趋势。我们还利用LLMs的能力引入无偏见媒体曝光,从通常主观的新闻内容中提取中性事件,以揭示意见两极分化的根源,以及一个魔鬼代言代理人有助于解释美国对中国态度从负面到正面的罕见转变,这种转变与美国人获取有关中国信息的方式的变化相对应。除了验证我们的框架架构外,模拟结果还揭示了偏见框架和选择偏见在塑造态度方面的影响。总体而言,我们的工作为大规模、长期、跨国社会背景下的认知行为建模提供了新的范例,为国际偏见的形成提供了洞察力,并为媒体消费者提供了了解塑造其观点的因素的宝贵启示,最终满足了减少偏见和跨文化容忍的社会需求。
关键见解
- LLMs建模为模拟意见演变提供了新机会,特别是在大规模认知趋势的重建方面。
- 本研究首次对代表整个国家对另一个国家的态度演变进行建模,特别是美国公民对中国的态度演变。
- 提出的框架集成了媒体数据、用户角色和认知架构来成功模拟长期内的真实态度趋势。
- 利用LLMs的能力引入无偏见媒体曝光,揭示意见形成的根源。
- 通过魔鬼代言代理人解释了态度转变的罕见情况,这与信息获取方式的变化有关。
- 模拟结果突出了偏见框架和选择偏见在塑造态度中的影响。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Agent: Optimizing Planning Capability for Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation
Authors:Yuechen Wang, Yuming Qiao, Dan Meng, Jun Yang, Haonan Lu, Zhenyu Yang, Xudong Zhang
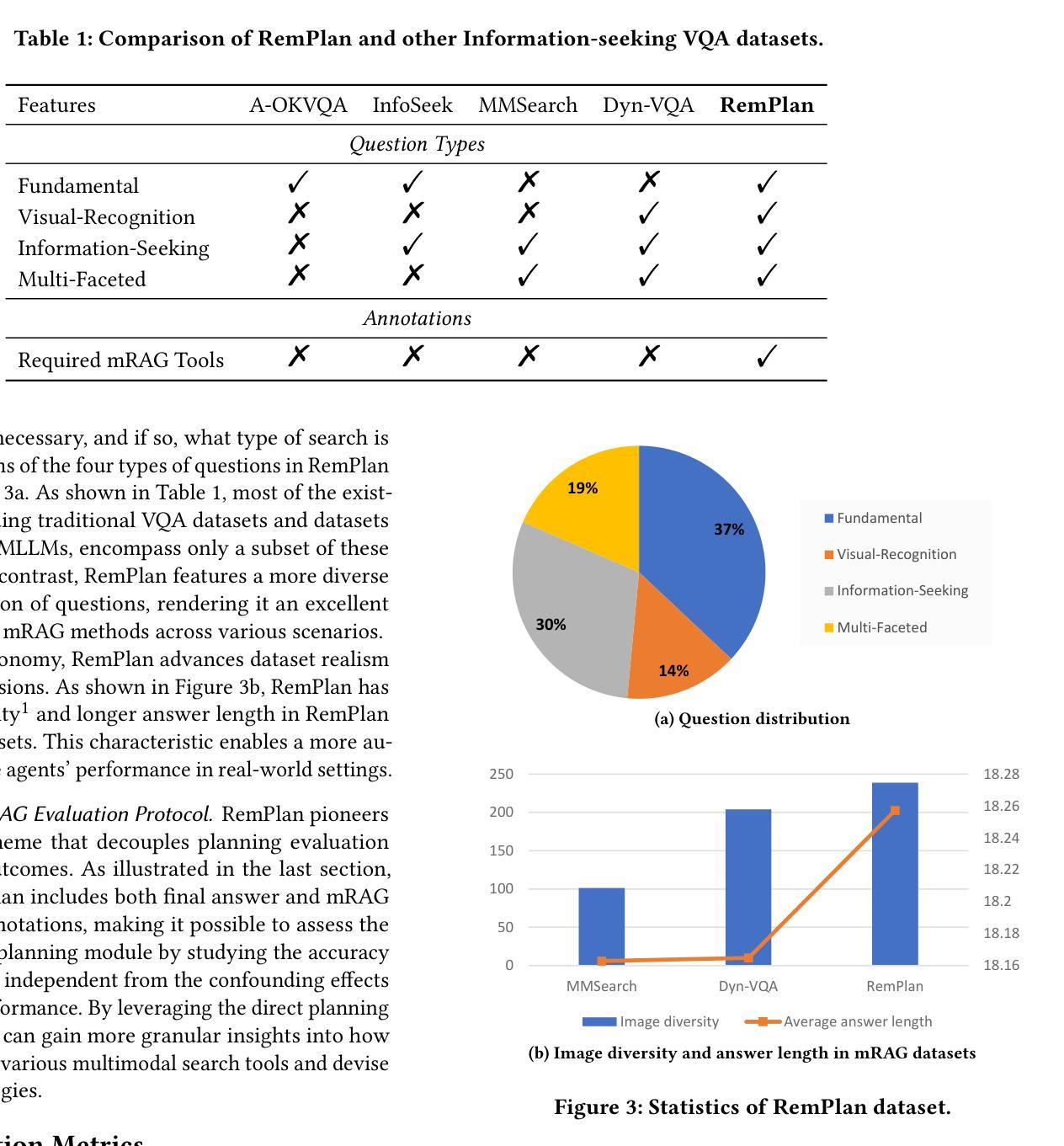
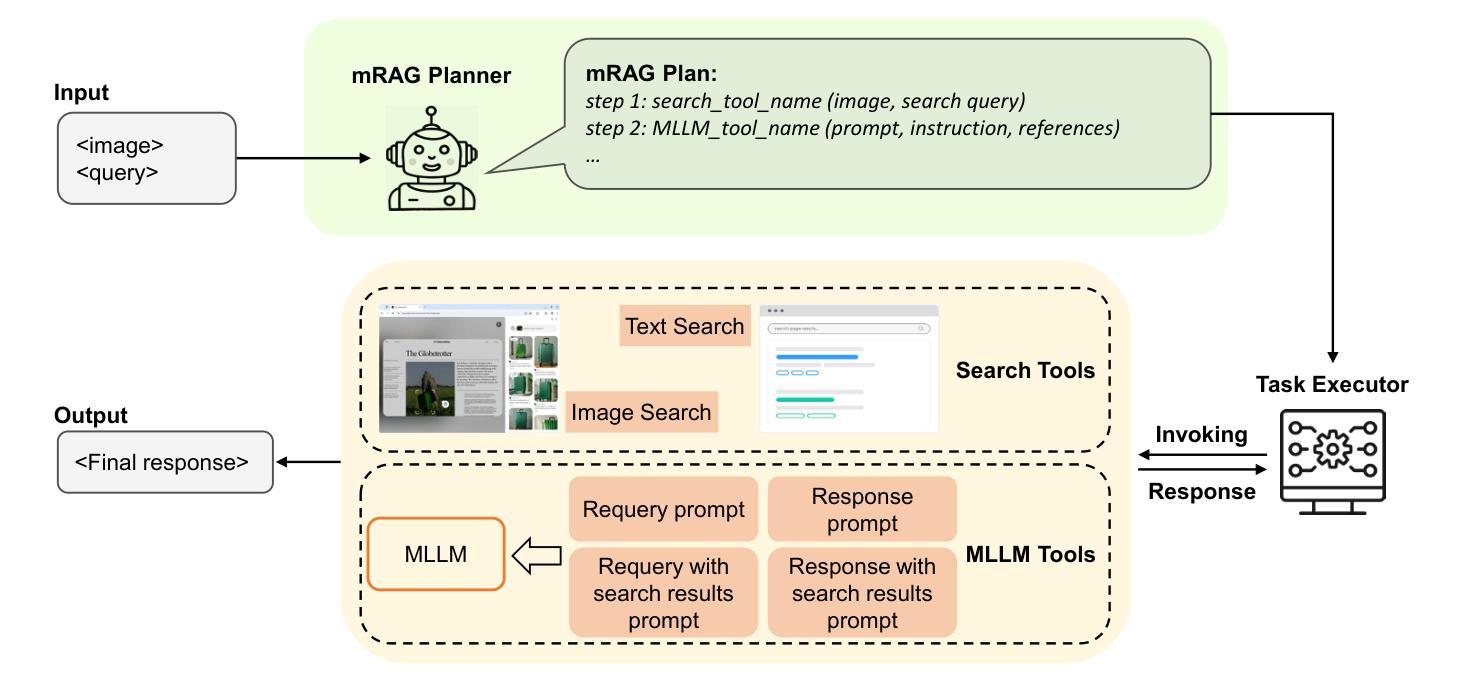
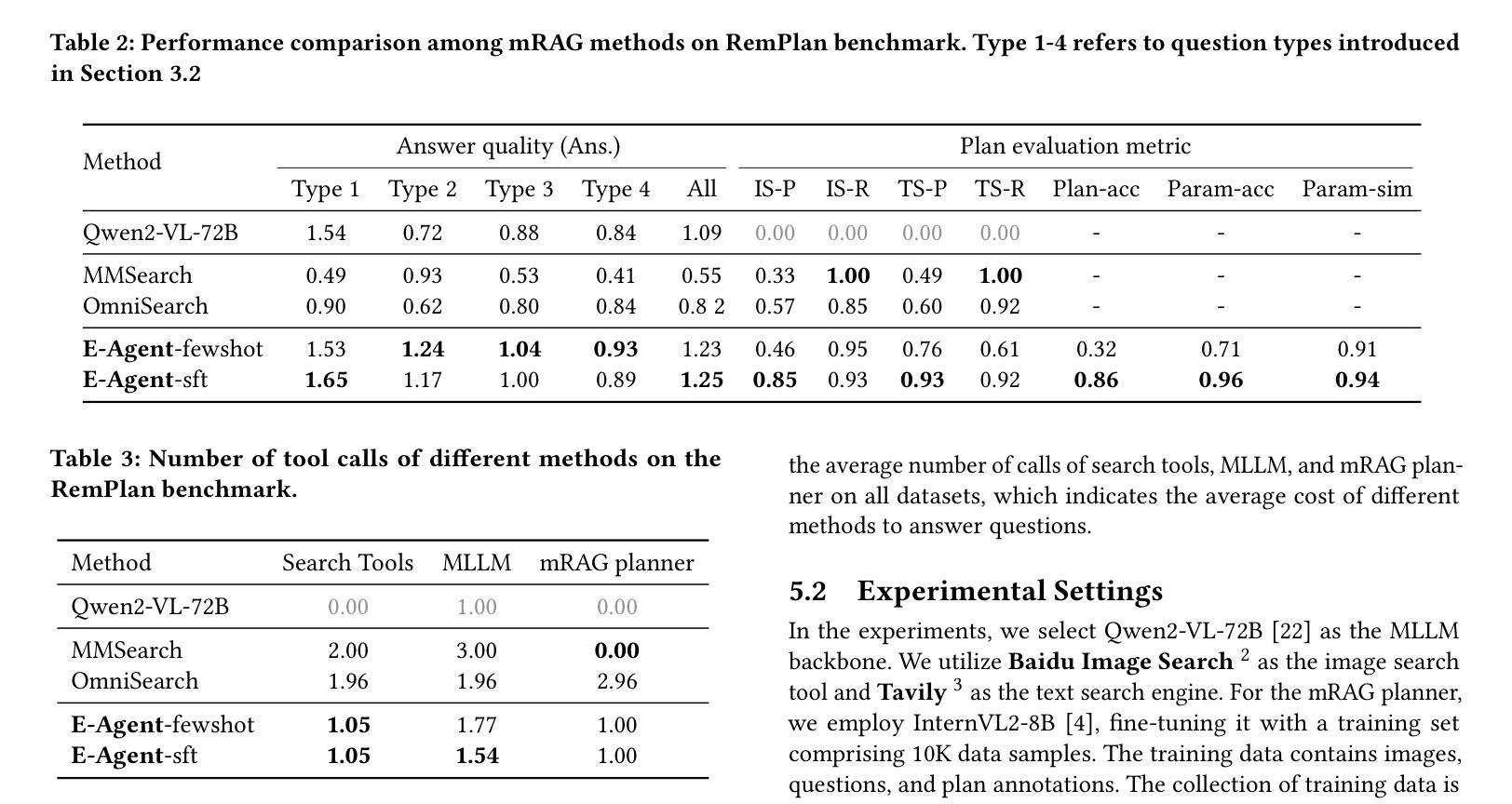
Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) has emerged as a promising solution to address the temporal limitations of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in real-world scenarios like news analysis and trending topics. However, existing approaches often suffer from rigid retrieval strategies and under-utilization of visual information. To bridge this gap, we propose E-Agent, an agent framework featuring two key innovations: a mRAG planner trained to dynamically orchestrate multimodal tools based on contextual reasoning, and a task executor employing tool-aware execution sequencing to implement optimized mRAG workflows. E-Agent adopts a one-time mRAG planning strategy that enables efficient information retrieval while minimizing redundant tool invocations. To rigorously assess the planning capabilities of mRAG systems, we introduce the Real-World mRAG Planning (RemPlan) benchmark. This novel benchmark contains both retrieval-dependent and retrieval-independent question types, systematically annotated with essential retrieval tools required for each instance. The benchmark’s explicit mRAG planning annotations and diverse question design enhance its practical relevance by simulating real-world scenarios requiring dynamic mRAG decisions. Experiments across RemPlan and three established benchmarks demonstrate E-Agent’s superiority: 13% accuracy gain over state-of-the-art mRAG methods while reducing redundant searches by 37%.
多模态检索增强生成(mRAG)已经成为解决多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在新闻分析、趋势话题等实际场景中时间限制的具有前景的解决方案。然而,现有方法往往存在检索策略僵化、视觉信息利用不足的问题。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了E-Agent,这是一个具有两个关键创新的代理框架:一个训练有素的mRAG规划器,可以基于上下文推理动态地协调多模态工具,以及一个任务执行器,采用工具感知执行序列,以实现优化的mRAG工作流程。E-Agent采用一次性mRAG规划策略,实现高效信息检索,同时最小化冗余工具调用。为了严格评估mRAG系统的规划能力,我们引入了Real-World mRAG Planning(RemPlan)基准测试。这一新型基准测试包含检索依赖型和检索独立型问题类型,系统地为每个实例标注了必需检索工具。该基准测试的明确mRAG规划标注和多样化的问题设计通过模拟需要动态mRAG决策的现实场景增强了其实用性。在RemPlan和三个既定基准测试上的实验表明E-Agent的优越性:在准确率上较最新mRAG方法提高13%,同时减少37%的冗余搜索。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态检索增强生成(mRAG)是解决多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在新闻分析和趋势话题等现实场景中的时间限制的有前途的解决方案。针对现有方法的不足,提出了E-Agent代理框架,具有两个关键创新点:训练有素的mRAG规划器可动态协调多模式工具,任务执行器采用工具感知执行序列以实现优化mRAG工作流程。E-Agent采用一次性mRAG规划策略,实现高效信息检索并减少冗余工具调用。为评估mRAG系统的规划能力,引入了Real-World mRAG Planning(RemPlan)基准测试。该基准测试包含检索依赖和检索独立的问题类型,系统地注明了每种情况所需的关键检索工具。实验表明,E-Agent在RemPlan和其他三个基准测试上的表现优于现有技术,准确度高出了13%,同时减少了37%的冗余搜索。
Key Takeaways
- E-Agent通过引入mRAG规划和任务执行器,增强了多模态检索增强生成(mRAG)的能力,使其更适合现实场景应用。
- E-Agent采用一次性mRAG规划策略,提高信息检索效率并减少冗余工具调用。
- 提出了Real-World mRAG Planning(RemPlan)基准测试,用于评估mRAG系统的规划能力。
- RemPlan基准测试包含多种问题类型,包括检索依赖和检索独立的问题,并系统地注明了所需的关键检索工具。
- E-Agent相较于现有技术展现出更高的准确性,且在减少冗余搜索方面表现出优势。
- E-Agent的成功证明了动态协调多模态工具和优化执行序列的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


Fault Tolerant Multi-Agent Learning with Adversarial Budget Constraints
Authors:David Mguni, Yaqi Sun, Haojun Chen, Amir Darabi, Larry Olanrewaju Orimoloye, Yaodong Yang
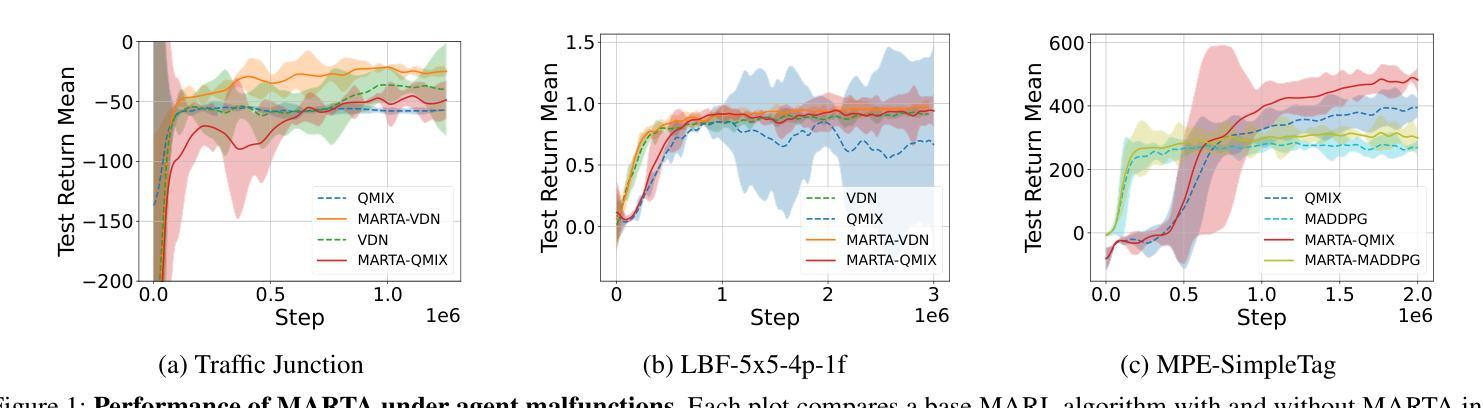
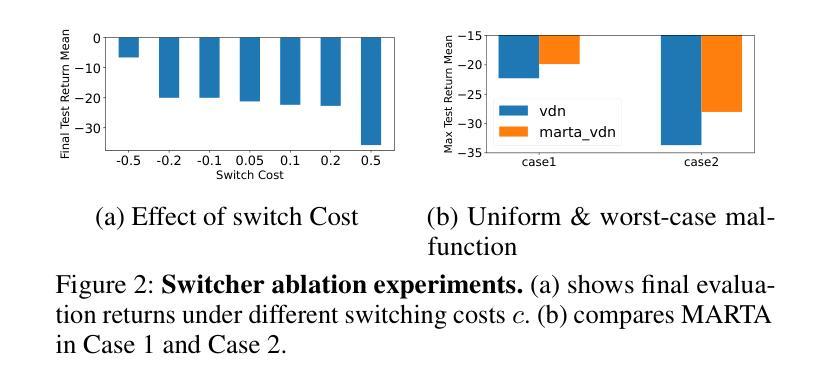
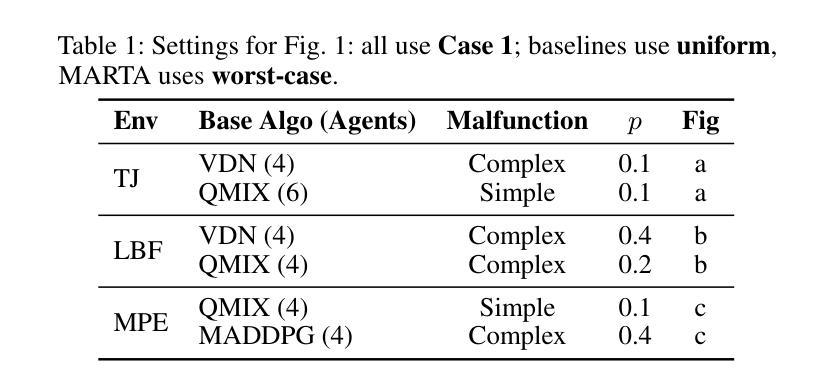
In multi-agent systems, the safe and reliable execution of tasks often depends on agents correctly coordinating their actions. However, in real-world deployments, failures of computational components are inevitable, presenting a critical challenge: ensuring that multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) policies remain effective even when some agents malfunction. We propose the Multi-Agent Robust Training Algorithm (MARTA), a plug-and-play framework for training MARL agents to be resilient to potentially severe faults. MARTA operates in cooperative multi-agent settings where agents may lose the ability to execute their intended actions. It learns to identify failure scenarios that are especially detrimental to system performance and equips agents with strategies to mitigate their impact. At the heart of MARTA is a novel adversarial Markov game in which an adversary – modelled via \emph{Markov switching controls} – learns to disable agents in high-risk state regions, while the remaining agents are trained to \emph{jointly} best-respond to such targeted malfunctions. To ensure practicality, MARTA enforces a malfunction budget, constraining the adversary to a fixed number of failures and learning robust policies accordingly. We provide theoretical guarantees that MARTA converges to a Markov perfect equilibrium, ensuring agents optimally counteract worst-case faults. Empirically, we show that MARTA achieves state-of-the-art fault-tolerant performance across benchmark environments, including Multi-Agent Particle World and Level-Based Foraging.
在多智能体系统中,任务的安全和可靠执行通常取决于智能体能否正确协调其行动。然而,在实际部署中,计算组件的故障是不可避免的,这就形成了一个关键的挑战:确保即使在某些智能体发生故障的情况下,多智能体强化学习(MARL)策略仍然有效。我们提出了多智能体鲁棒训练算法( MARTA ),这是一种即插即用的框架,用于训练MARL智能体以应对潜在的严重故障。 MARTA适用于合作型多智能体环境,在这种环境中,智能体可能会失去执行预定动作的能力。它学会了识别对系统性能特别有害的失败场景,并为智能体配备策略以减轻其影响。 MARTA的核心是一个新型对抗性马尔可夫游戏,其中对手(通过马尔可夫切换控制建模)学会在高风险状态区域中禁用智能体,而其余的智能体则接受训练以对这些有针对性的故障进行最佳联合响应。为确保实用性, MARTA强制实施故障预算,将对手限制在固定的失败次数内,并据此学习鲁棒策略。我们提供理论保证, MARTA会收敛到马尔可夫完美均衡状态,确保智能体能够最佳地应对最坏情况的故障。从实证角度看,我们在包括多智能体粒子世界和基于级别的觅食等基准环境中显示, MARTA达到了最新的容错性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为MARTA的多智能体鲁棒训练算法,它是一种即插即用的框架,旨在训练多智能体强化学习(MARL)代理以应对潜在的严重故障。该算法能够在智能体失去执行预期行动的能力的情境下运行,并学习识别对系统性能特别有害的故障场景,同时为智能体配备减轻其影响的策略。其核心是一个新型对抗性马尔可夫游戏,其中对手通过马尔可夫切换控制来学习在高风险状态区域中禁用智能体,而其他智能体则训练以最佳方式共同应对此类针对性故障。为确保实用性,MARTA实施故障预算,限制对手在固定数量的失败中学习稳健策略。理论保证显示,MARTA能够收敛到马尔可夫完美均衡状态,确保智能体对最坏情况的故障进行最优反击。在基准环境中,包括多智能体粒子世界和基于级别的觅食等环境中,实证显示,MARTA达到了最先进的容错性能。
Key Takeaways
- MARTA是一种针对多智能体强化学习(MARL)的智能体鲁棒训练算法框架。
- 该算法设计用于处理现实世界中不可避免的代理计算组件故障问题。
- MARTA通过识别对系统性能有害的故障场景并配备智能体应对策略来增强代理的韧性。
- 该算法的核心是一种新型对抗性马尔可夫游戏,其中对手学习在高风险区域禁用智能体。
- MARTA实施故障预算以确保其实用性并学习稳健策略。
- 理论保证显示,MARTA能够收敛到最优策略,即马尔可夫完美均衡状态。
点此查看论文截图

CRADLE: Conversational RTL Design Space Exploration with LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Lukas Krupp, Maximilian Schöffel, Elias Biehl, Norbert Wehn
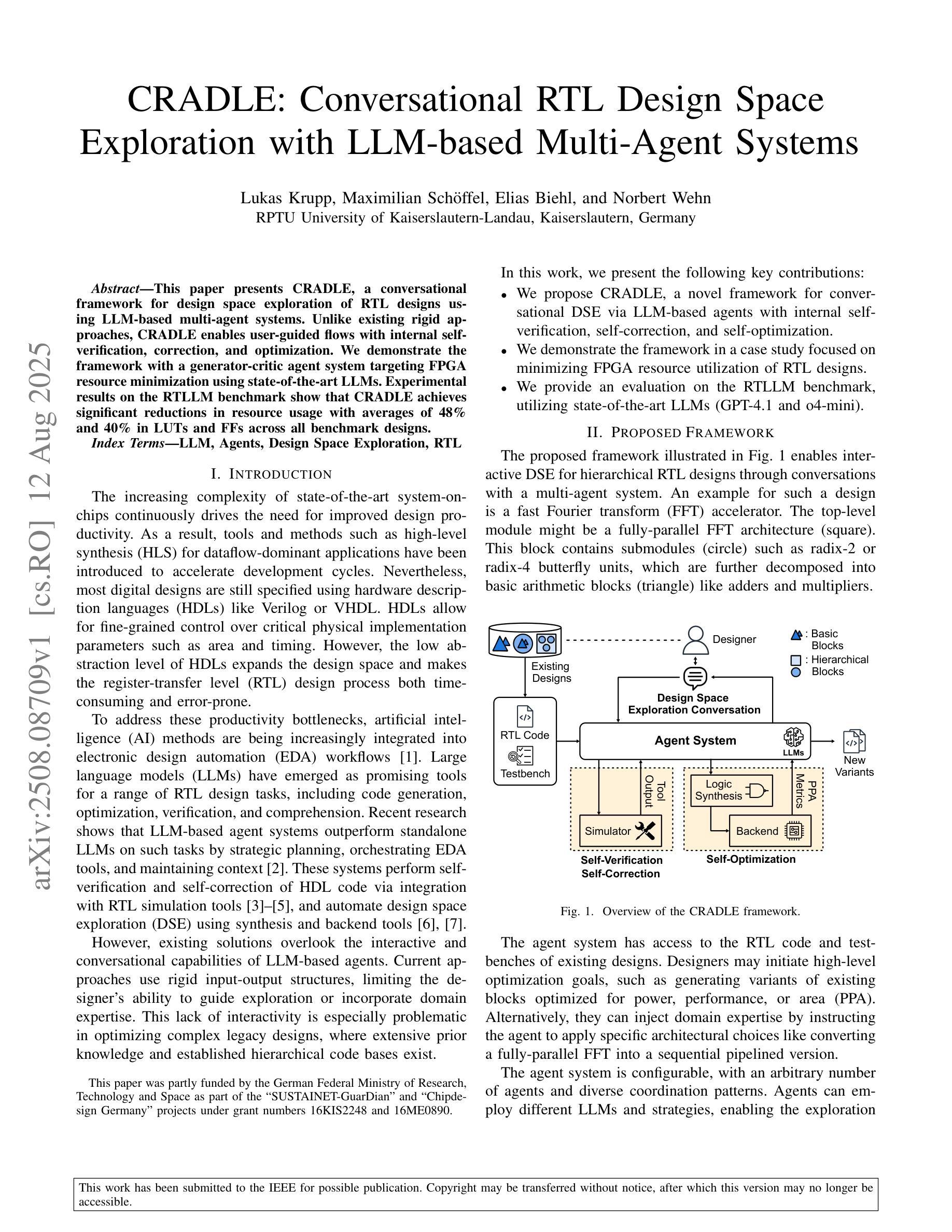
This paper presents CRADLE, a conversational framework for design space exploration of RTL designs using LLM-based multi-agent systems. Unlike existing rigid approaches, CRADLE enables user-guided flows with internal self-verification, correction, and optimization. We demonstrate the framework with a generator-critic agent system targeting FPGA resource minimization using state-of-the-art LLMs. Experimental results on the RTLLM benchmark show that CRADLE achieves significant reductions in resource usage with averages of 48% and 40% in LUTs and FFs across all benchmark designs.
本文介绍了CRADLE,这是一个利用基于LLM的多智能体系统进行RTL设计空间探索的对话框架。与现有的僵化方法不同,CRADLE能够实现用户引导的流程,具有内部自我验证、校正和优化功能。我们利用面向FPGA资源最小化的生成器-评论家智能体系统来展示该框架,使用最先进的LLM。在RTLLM基准测试上的实验结果表明,CRADLE在所有基准设计上的LUT和FF平均使用量分别减少了48%和40%,实现了显著的资源使用减少。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at the 22nd International SoC Conference (ISOCC 2025). Proceedings to be included in IEEE Xplore
Summary
CRADLE是一个基于LLM的多代理系统对话框架,用于RTL设计的空间探索。它不同于现有的刚性方法,实现了用户引导的流程,具有内部自我验证、纠错和优化功能。通过针对FPGA资源最小化的生成器-评论家代理系统演示了该框架,并在RTLLM基准测试上实现了显著的资源使用减少,平均在LUTs和FFs上分别减少了48%和40%。
Key Takeaways
- CRADLE是一个基于LLM的多代理系统的对话框架,用于RTL设计的空间探索。
- 与现有方法不同,CRADLE具有用户引导的流程,并具备内部自我验证、纠错和优化功能。
- CRADLE通过生成器-评论家代理系统针对FPGA资源最小化进行了演示。
- 实验结果表明,CRADLE在RTLLM基准测试上实现了显著的性能提升。
- CRADLE在LUTs和FFs的资源使用上分别实现了平均48%和40%的减少。
- CRADLE框架具有广泛的应用前景,可扩展到其他设计领域。
点此查看论文截图
Quick on the Uptake: Eliciting Implicit Intents from Human Demonstrations for Personalized Mobile-Use Agents
Authors:Zheng Wu, Heyuan Huang, Yanjia Yang, Yuanyi Song, Xingyu Lou, Weiwen Liu, Weinan Zhang, Jun Wang, Zhuosheng Zhang
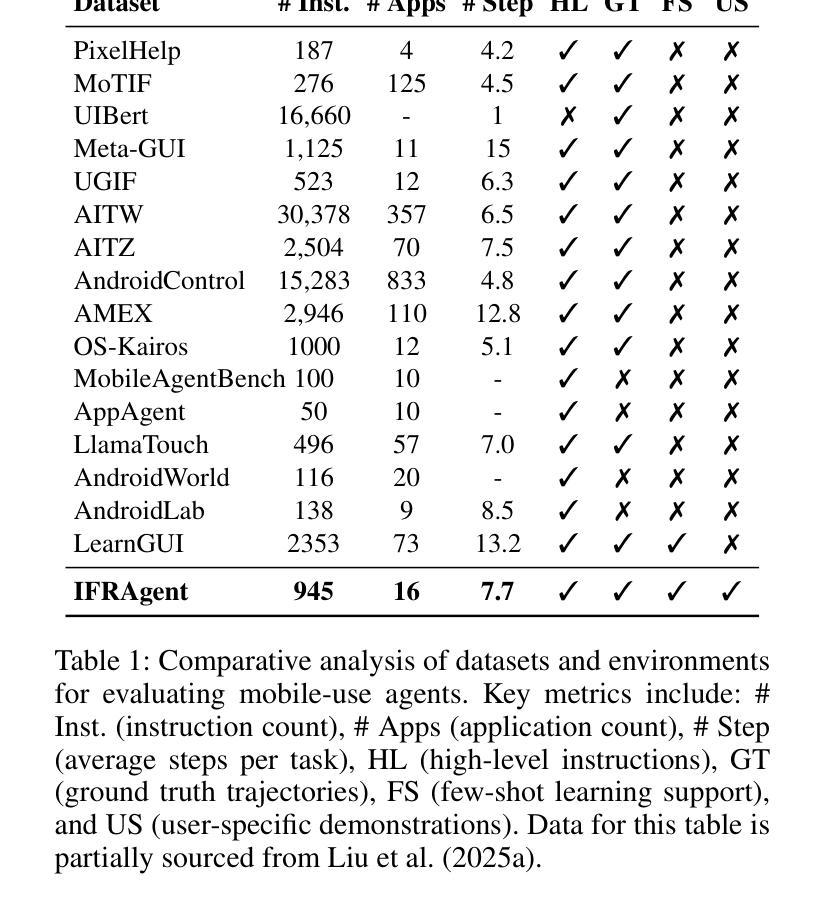
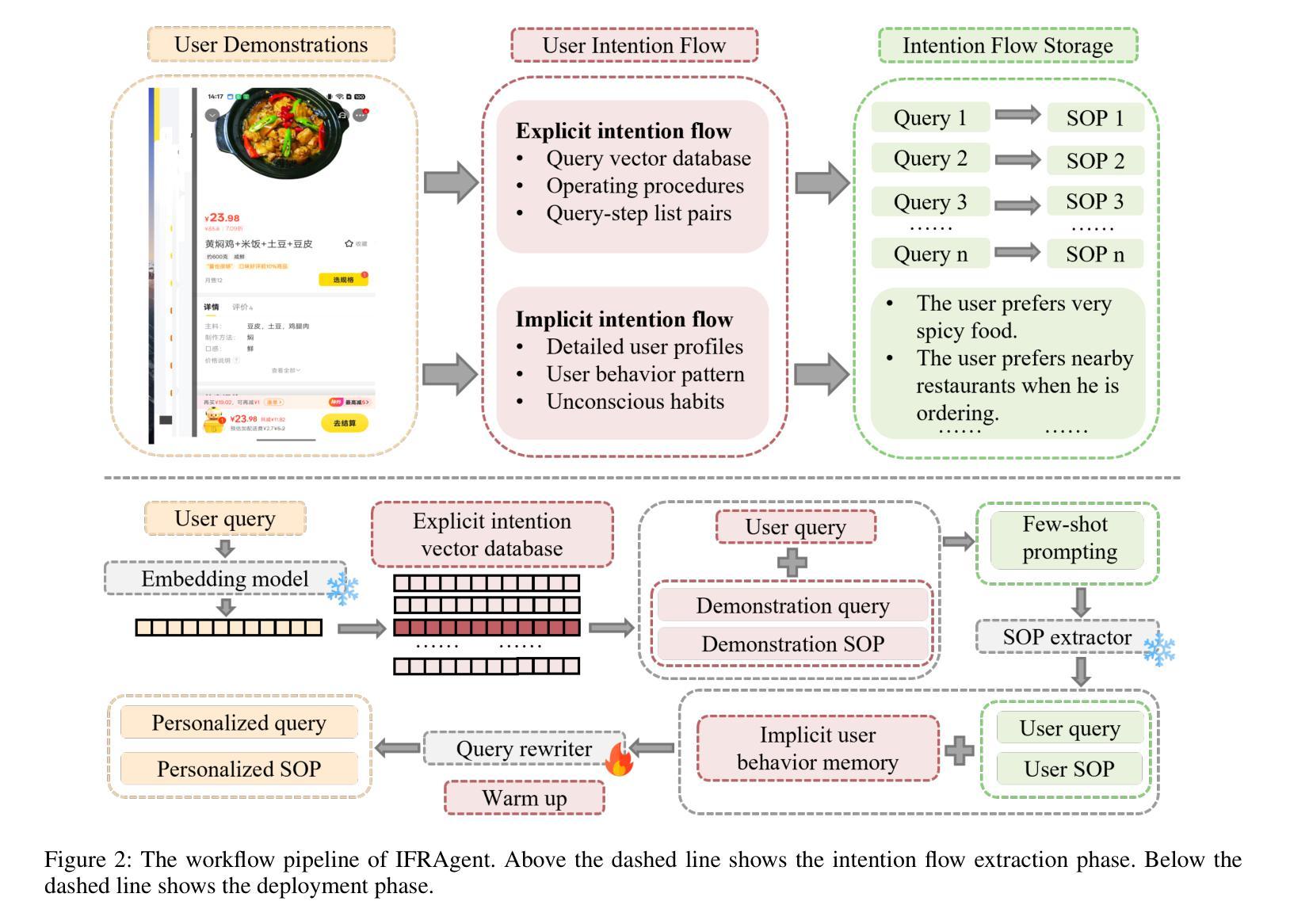
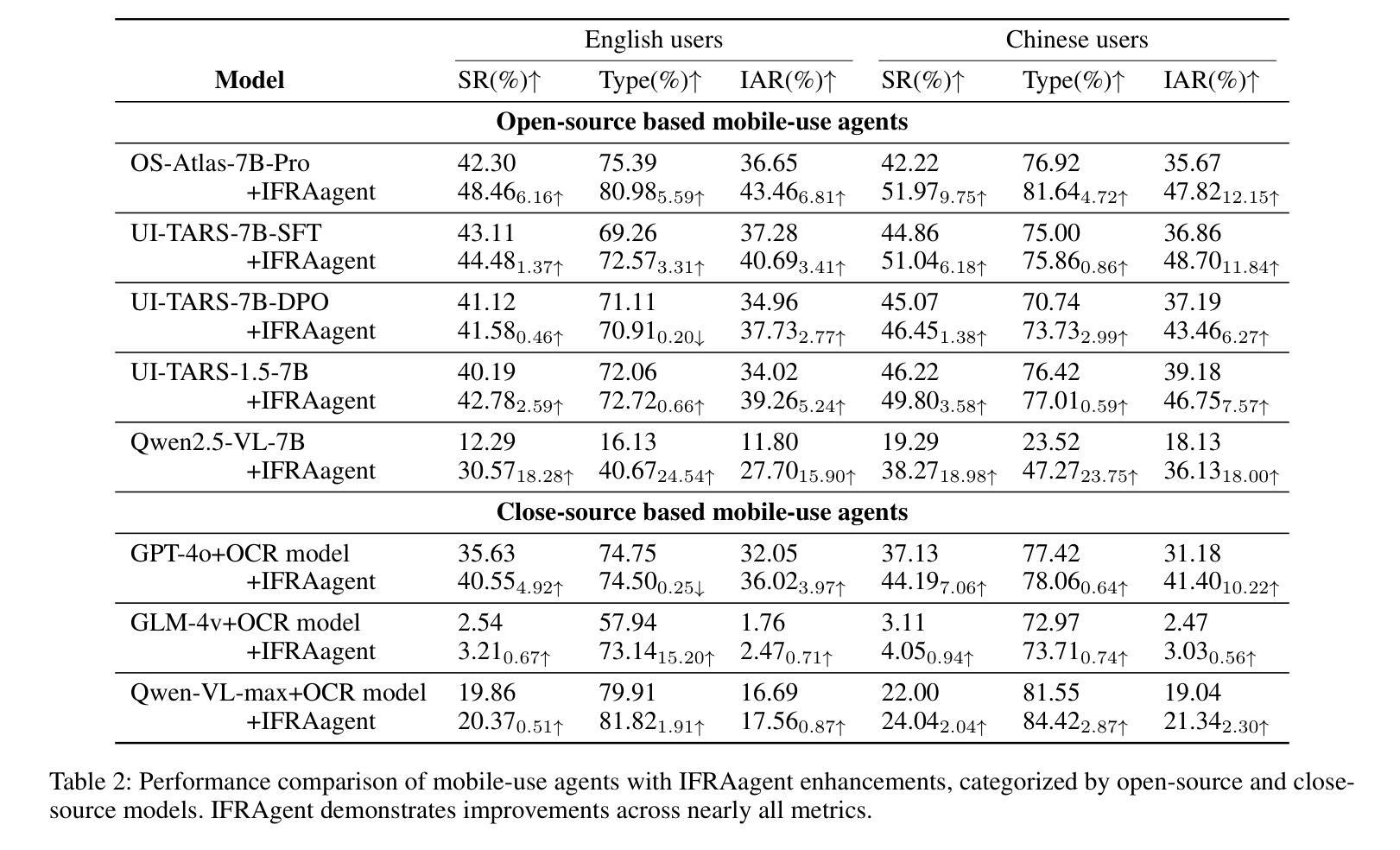
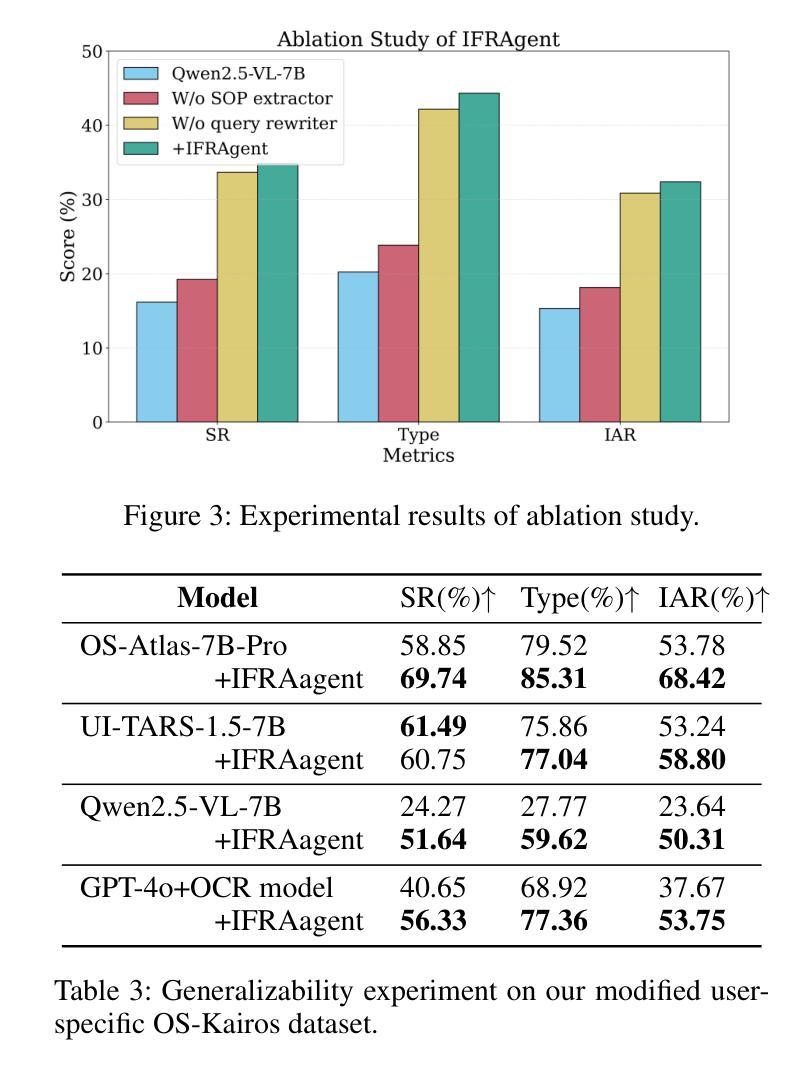
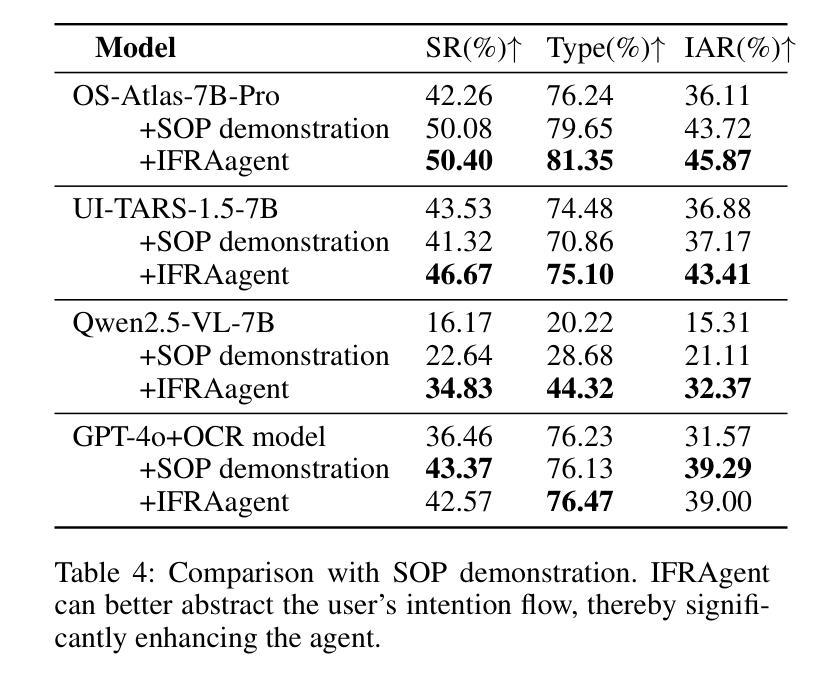
As multimodal large language models advance rapidly, the automation of mobile tasks has become increasingly feasible through the use of mobile-use agents that mimic human interactions from graphical user interface. To further enhance mobile-use agents, previous studies employ demonstration learning to improve mobile-use agents from human demonstrations. However, these methods focus solely on the explicit intention flows of humans (e.g., step sequences) while neglecting implicit intention flows (e.g., personal preferences), which makes it difficult to construct personalized mobile-use agents. In this work, to evaluate the \textbf{I}ntention \textbf{A}lignment \textbf{R}ate between mobile-use agents and humans, we first collect \textbf{MobileIAR}, a dataset containing human-intent-aligned actions and ground-truth actions. This enables a comprehensive assessment of the agents’ understanding of human intent. Then we propose \textbf{IFRAgent}, a framework built upon \textbf{I}ntention \textbf{F}low \textbf{R}ecognition from human demonstrations. IFRAgent analyzes explicit intention flows from human demonstrations to construct a query-level vector library of standard operating procedures (SOP), and analyzes implicit intention flows to build a user-level habit repository. IFRAgent then leverages a SOP extractor combined with retrieval-augmented generation and a query rewriter to generate personalized query and SOP from a raw ambiguous query, enhancing the alignment between mobile-use agents and human intent. Experimental results demonstrate that IFRAgent outperforms baselines by an average of 6.79% (32.06% relative improvement) in human intention alignment rate and improves step completion rates by an average of 5.30% (26.34% relative improvement). The codes are available at https://github.com/MadeAgents/Quick-on-the-Uptake.
随着多模态大型语言模型的快速发展,通过模仿人类图形用户界面的交互来使用移动代理实现移动任务的自动化变得越来越可行。为了进一步提升移动代理的性能,早期的研究采用示范学习的方法,通过人类示范来改善移动代理的表现。然而,这些方法只关注人类的显性意图流(如步骤序列),而忽视了隐性意图流(如个人偏好),这使得构建个性化的移动代理变得困难。在这项工作中,为了评估移动代理与人类之间的意图对齐率(Intention Alignment Rate),我们首先收集了MobileIAR数据集,该数据集包含与人类意图对齐的动作和真实动作。这使得我们能够全面评估代理对人类意图的理解。然后,我们提出了基于人类示范的意图流识别(Intention Flow Recognition)构建的IFRAgent框架。IFRAgent分析人类示范中的显性意图流,构建标准操作流程(SOP)的查询级向量库,并分析隐性意图流以构建用户级习惯存储库。然后,IFRAgent利用结合检索增强生成和查询重写器的SOP提取器,从原始模糊查询生成个性化的查询和SOP,增强移动代理与人类意图的对齐。实验结果表明,在人的意图对齐率方面,IFRAgent平均优于基线6.79%(相对改善32.06%),步骤完成率平均提高5.30%(相对改善26.34%)。相关代码可通过https://github.com/MadeAgents/Quick-on-the-Uptake访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型迅速发展,通过模仿人类交互的图形用户界面,移动使用代理实现自动化移动任务越来越可行。为进一步优化移动使用代理,先前研究采用示范学习法。然而,这些方法只关注人类的明确意图流程(如步骤序列),而忽视了个人偏好等隐性意图流程,难以构建个性化的移动使用代理。本研究提出了意图对齐率评估,并收集了一套数据集用于全面评估代理对人类意图的理解能力。此外,本研究还提出了基于人类示范的意图流识别的IFRAgent框架。该框架分析人类示范中的明确意图流程来构建标准操作流程的查询级向量库,并分析了隐性意图流程以构建用户级习惯库。通过生成个性化查询和从原始模糊查询中提取标准操作流程,增强移动使用代理与人类意图的对齐。实验结果表明,IFRAgent在平均人类意图对齐率上优于基线模型6.79%(相对提高了32.06%),并提高了步骤完成率平均5.30%(相对提高了26.34%)。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型的快速发展推动了移动任务的自动化进程。
- 移动使用代理模仿人类交互的图形用户界面以实现更多自动化任务。
- 示范学习法用于优化移动使用代理,但存在忽略隐性意图流程的缺陷。
- 研究提出了意图对齐率评估,并收集数据集以全面评估代理对人类意图的理解。
- IFRAgent框架基于人类示范的意图流识别,构建标准操作流程的查询级向量库和用户级习惯库。
- IFRAgent通过生成个性化查询和从模糊查询中提取标准操作流程,增强了移动使用代理与人类意图的对齐。
点此查看论文截图

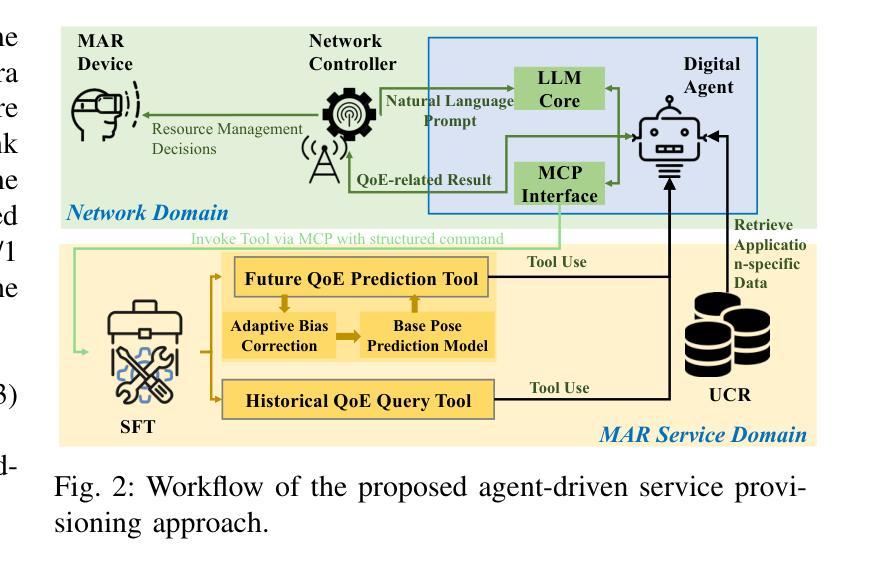
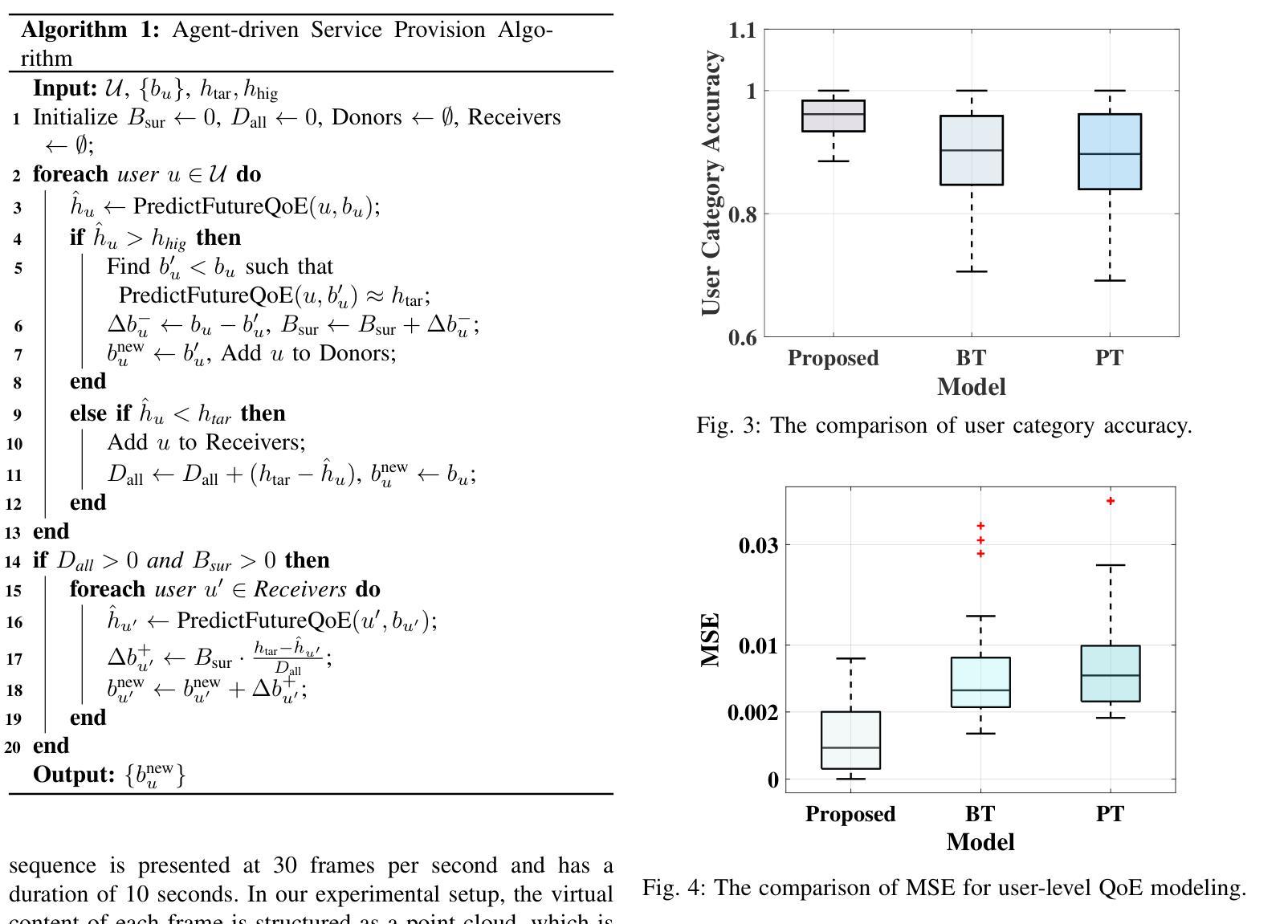
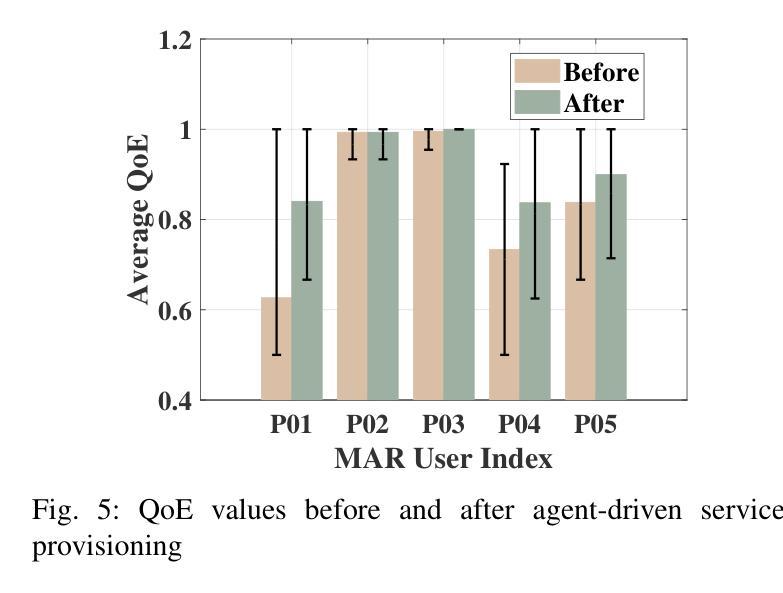
QoE-Aware Service Provision for Mobile AR Rendering: An Agent-Driven Approach
Authors:Conghao Zhou, Lulu Sun, Xiucheng Wang, Peng Yang, Feng Lyu, Sihan Lu, Xuemin Shen
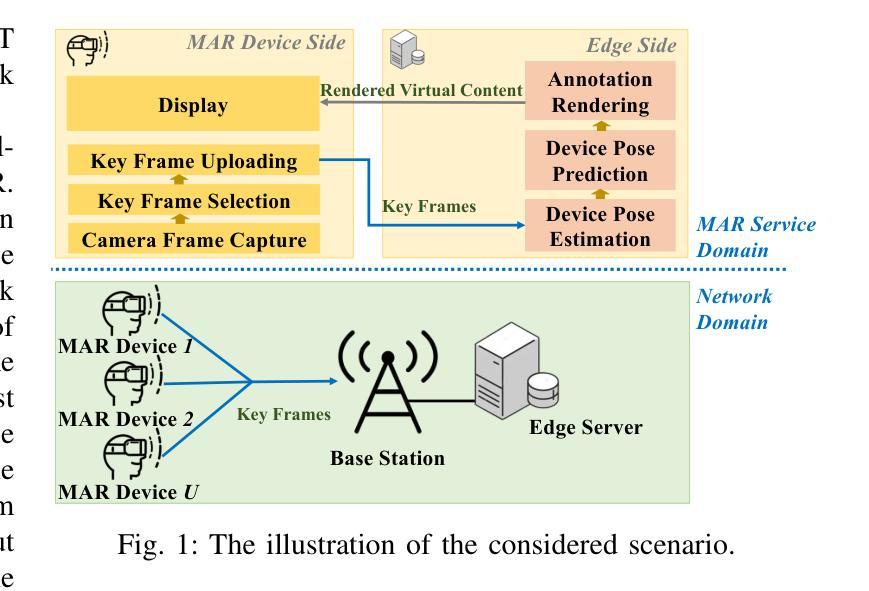
Mobile augmented reality (MAR) is envisioned as a key immersive application in 6G, enabling virtual content rendering aligned with the physical environment through device pose estimation. In this paper, we propose a novel agent-driven communication service provisioning approach for edge-assisted MAR, aiming to reduce communication overhead between MAR devices and the edge server while ensuring the quality of experience (QoE). First, to address the inaccessibility of MAR application-specific information to the network controller, we establish a digital agent powered by large language models (LLMs) on behalf of the MAR service provider, bridging the data and function gap between the MAR service and network domains. Second, to cope with the user-dependent and dynamic nature of data traffic patterns for individual devices, we develop a user-level QoE modeling method that captures the relationship between communication resource demands and perceived user QoE, enabling personalized, agent-driven communication resource management. Trace-driven simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms conventional LLM-based QoE-aware service provisioning methods in both user-level QoE modeling accuracy and communication resource efficiency.
移动增强现实(MAR)被视为6G的关键沉浸式应用,通过设备姿态估计,使虚拟内容与物理环境相匹配。在本文中,我们针对边缘辅助移动增强现实(MAR)提出一种新型代理驱动通信服务提供方法,旨在降低MAR设备和边缘服务器之间的通信开销,同时确保用户体验质量(QoE)。首先,为了解决网络控制器无法访问MAR应用特定信息的问题,我们建立了一个由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的数字化代理,代表MAR服务提供商,弥合了MAR服务和网络域之间的数据和功能差距。其次,为了应对用户依赖的单个设备的动态数据流量模式,我们开发了一种用户级QoE建模方法,该方法能够捕捉通信资源需求与感知的用户QoE之间的关系,从而实现个性化的代理驱动通信资源管理。基于跟踪的仿真结果表明,该方法在用户级QoE建模精度和通信资源效率方面均优于传统的基于LLM的QoE感知服务提供方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文探讨了移动增强现实(MAR)在6G网络中的沉浸式应用,提出了一种新型的代理驱动型通信服务提供方法,旨在实现边缘辅助的MAR通信。该方法通过数字代理来解决网络控制器无法访问MAR应用信息的问题,并建立了一种用户级的QoE模型,以个性化地管理通信资源。模拟结果表明,该方法在用户级QoE建模精度和通信资源效率方面优于传统的基于LLM的QoE感知服务提供方法。
Key Takeaways
- 移动增强现实(MAR)在6G网络中扮演沉浸式应用的关键角色。
- 提出了一种新型的代理驱动型通信服务提供方法,用于边缘辅助的MAR通信。
- 数字代理通过大型语言模型(LLMs)代表MAR服务提供商建立,以弥合MAR服务和网络域之间的数据和功能差距。
- 建立了一种用户级的QoE模型,以捕捉通信资源需求与用户感知QoE之间的关系。
- 该方法实现了个性化的通信资源管理。
- 模拟结果表明,该方法在用户级QoE建模精度和通信资源效率方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

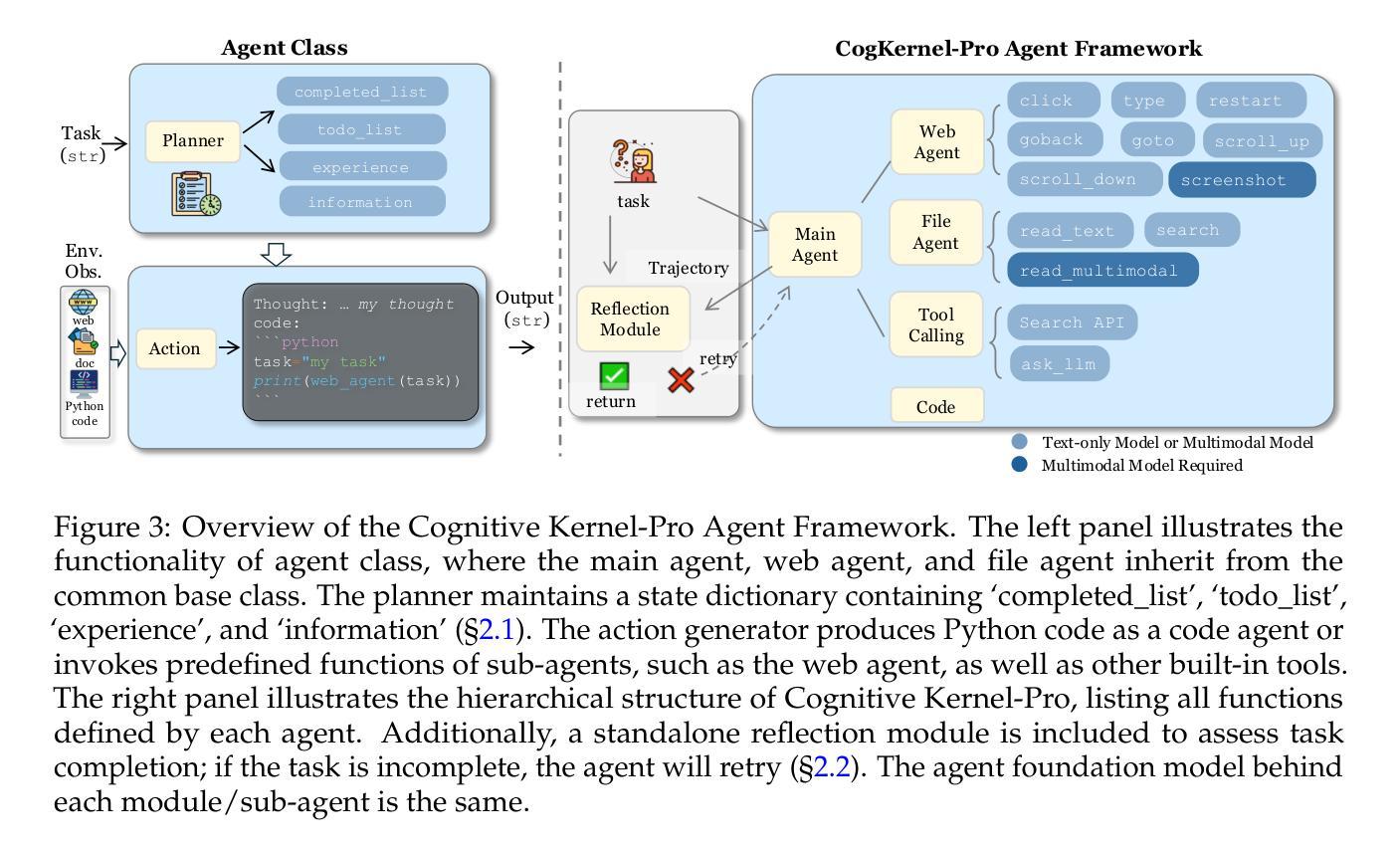
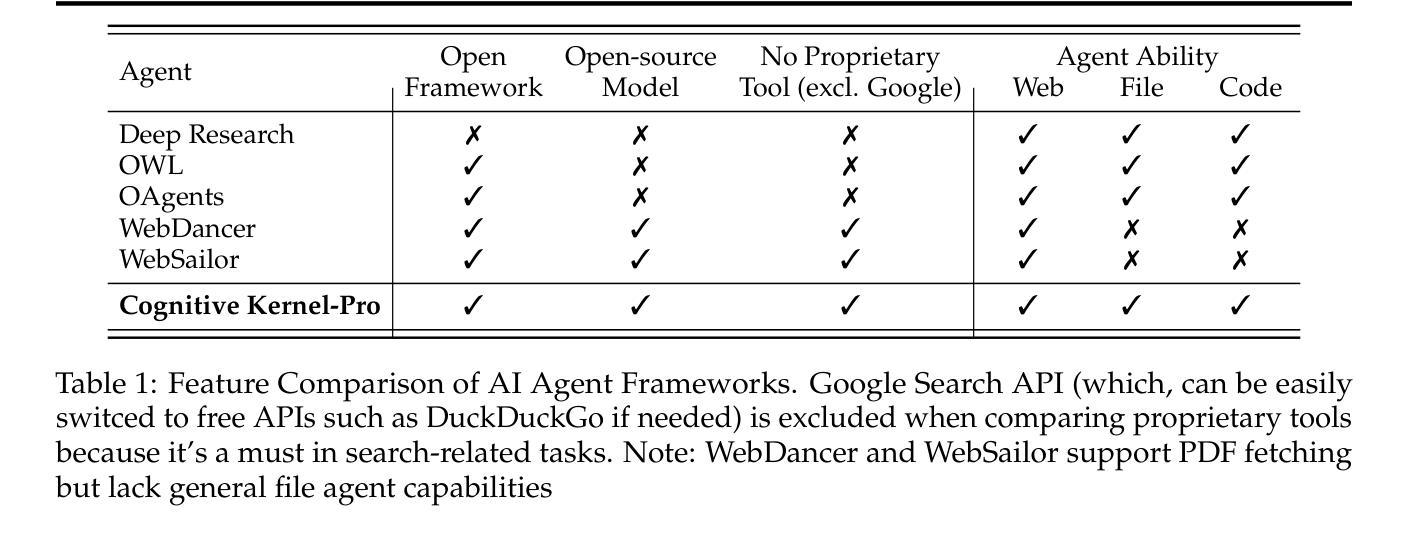
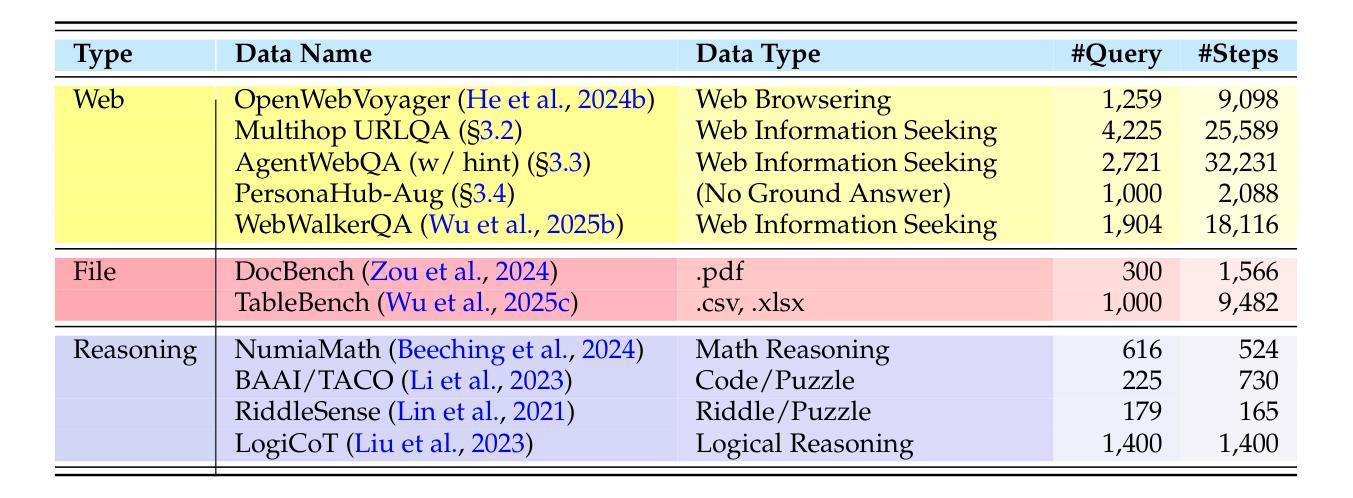
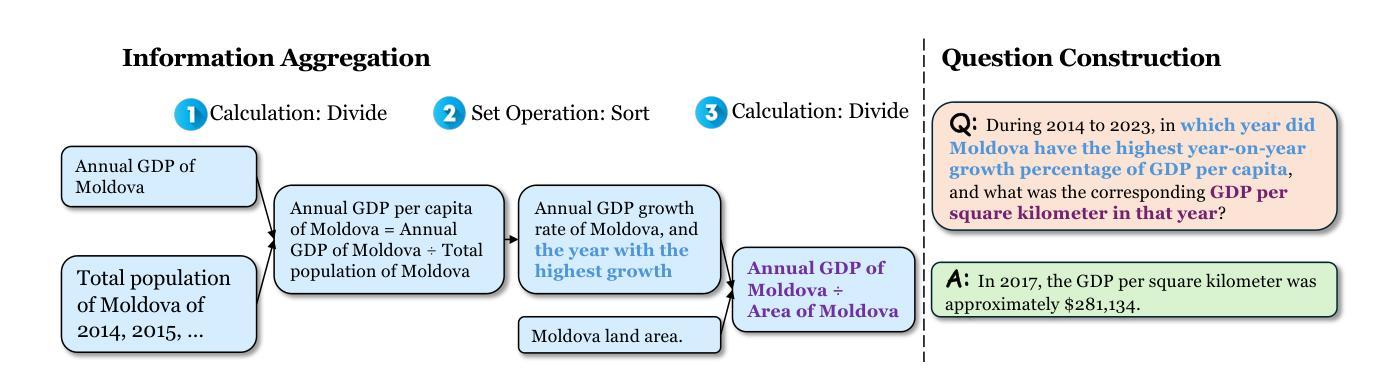
Cognitive Kernel-Pro: A Framework for Deep Research Agents and Agent Foundation Models Training
Authors:Tianqing Fang, Zhisong Zhang, Xiaoyang Wang, Rui Wang, Can Qin, Yuxuan Wan, Jun-Yu Ma, Ce Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Xiyun Li, Hongming Zhang, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
General AI Agents are increasingly recognized as foundational frameworks for the next generation of artificial intelligence, enabling complex reasoning, web interaction, coding, and autonomous research capabilities. However, current agent systems are either closed-source or heavily reliant on a variety of paid APIs and proprietary tools, limiting accessibility and reproducibility for the research community. In this work, we present \textbf{Cognitive Kernel-Pro}, a fully open-source and (to the maximum extent) free multi-module agent framework designed to democratize the development and evaluation of advanced AI agents. Within Cognitive Kernel-Pro, we systematically investigate the curation of high-quality training data for Agent Foundation Models, focusing on the construction of queries, trajectories, and verifiable answers across four key domains: web, file, code, and general reasoning. Furthermore, we explore novel strategies for agent test-time reflection and voting to enhance agent robustness and performance. We evaluate Cognitive Kernel-Pro on GAIA, achieving state-of-the-art results among open-source and free agents. Notably, our 8B-parameter open-source model surpasses previous leading systems such as WebDancer and WebSailor, establishing a new performance standard for accessible, high-capability AI agents. Code is available at https://github.com/Tencent/CognitiveKernel-Pro
通用人工智能代理(General AI Agents)正被越来越多地认为是下一代人工智能的基础框架,能够实现复杂的推理、网络交互、编码和自主研究能力。然而,当前的代理系统要么是闭源的,要么严重依赖于各种付费API和专有工具,这限制了研究社区的访问和可重复性。在此工作中,我们提出了认知内核专业版(Cognitive Kernel-Pro),这是一个完全开源的(在最大程度上)免费的多模块代理框架,旨在实现高级AI代理的开发和评估民主化。在认知内核专业版中,我们系统地研究了为代理基础模型筛选高质量训练数据的问题,重点关注四个关键领域的查询、轨迹和可验证答案的构建:网络、文件、编码和一般推理。此外,我们还探索了提高代理稳健性和性能的新型代理测试时反射和投票策略。我们在GAIA上对认知内核专业版进行了评估,在开源和免费代理中取得了最先进的成果。值得注意的是,我们的8B参数开源模型超越了之前领先的WebDancer和WebSailor系统,为可访问的高能力AI代理建立了新的性能标准。代码可在https://github.com/Tencent/CognitiveKernel-Pro找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
认知核心框架(Cognitive Kernel-Pro)是一个开源、免费的智能体框架,旨在普及先进的AI体发展及评估。框架涵盖了构建高质量训练数据的方法,同时提供了对AI体性能增强机制(测试时间反思和投票机制)的研究,为四种主要领域的复杂智能任务提供解答路径。项目已用于GAIA并获得领先水平。GitHub链接:https://github.com/Tencent/CognitiveKernel-Pro。它为科研人员提供智能化基础架构资源的同时也彰显了人工智能技术持续迭代中的升级速度之快的特点。值得一提的是它的开放式源模型和配套API引领潮流将创造一系列有价值的市场热点探索和发展潜力较大的专业领域细分趋势分析课题进一步开发扩展乃至技术创新提升后自主形成潜在应用的热门细分领域专题解决方案趋势不断突显显著特征和导向意义方面展望这些发展方向将更加利于深化人工智能技术的普及和应用。认知核心框架的开源化将推动人工智能技术的普及和进步。认知核心框架(Cognitive Kernel-Pro)在人工智能领域取得了显著进展,为科研人员提供了宝贵的资源和技术支持。其开源性和免费性使得更多的科研人员能够参与到研究和开发中,推动了人工智能技术的普及和进步。同时,该框架在构建高质量训练数据、增强AI体性能等方面进行了深入研究,为人工智能领域的发展做出了重要贡献。此外,该框架的应用场景广泛,包括Web交互、文件处理、编码和通用推理等领域,为智能体在各种复杂场景下的应用提供了有力支持。综合来看,认知核心框架的开源化对于人工智能领域的发展具有重要意义。在未来的发展中有望带来更多的创新和突破加速人工智能技术的普及和应用步伐最终推动整个行业的快速发展和进步。
Key Takeaways
- 认知核心框架(Cognitive Kernel-Pro)是一个开源、免费的智能体框架,用于普及先进的AI体发展和评估。
- 该框架涵盖构建高质量训练数据的方法,提供AI体性能增强机制的研究。
- 框架应用于四种主要领域:Web交互、文件处理、编码和通用推理。
- 在GAIA上获得领先水平,且开源模型超越先前领先系统,如WebDancer和WebSailor。
- 提供测试时间反思和投票机制以增强AI体的稳健性和性能。
- 框架的应用场景广泛,支持各种复杂场景下的智能体应用。
点此查看论文截图

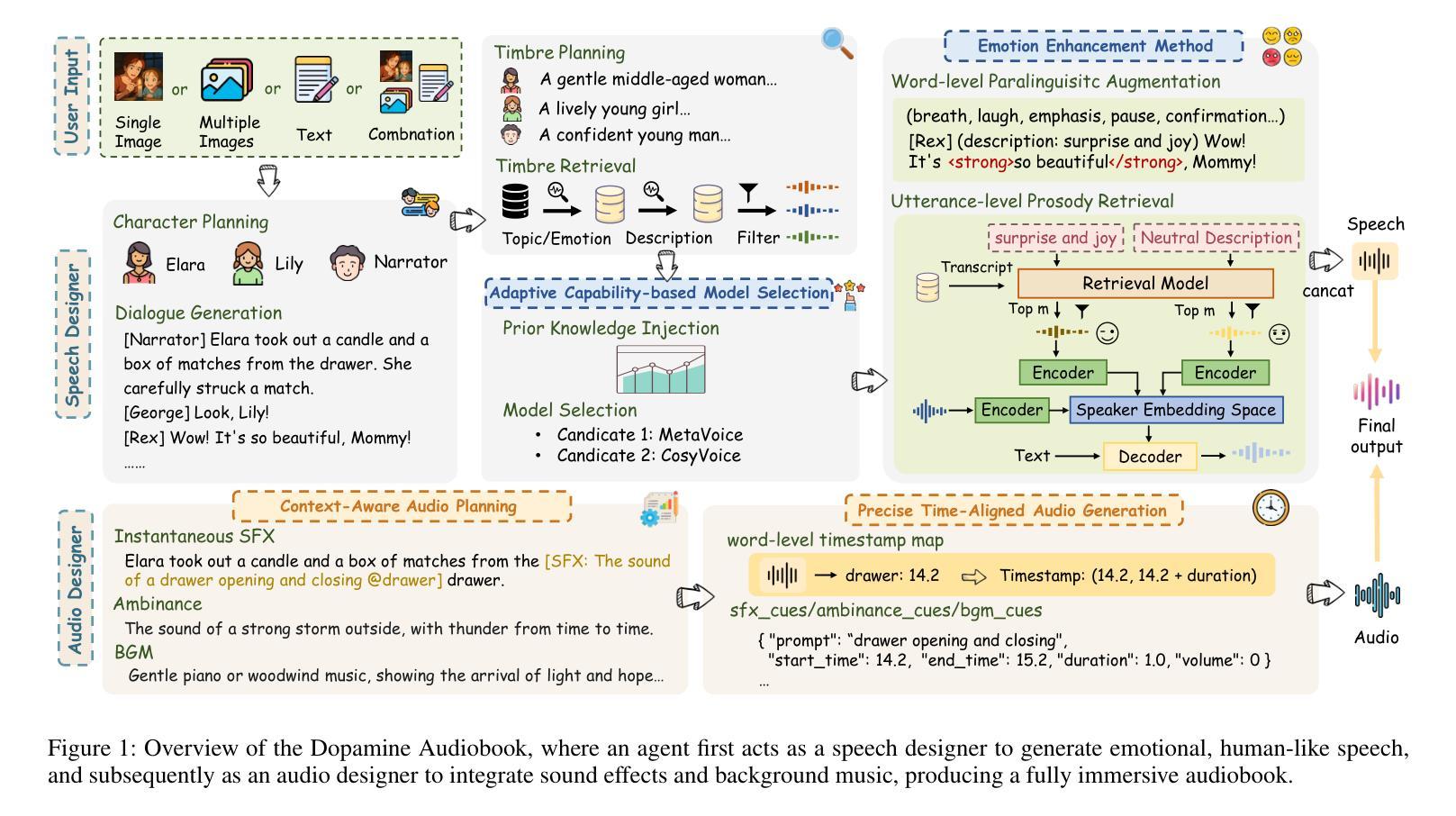
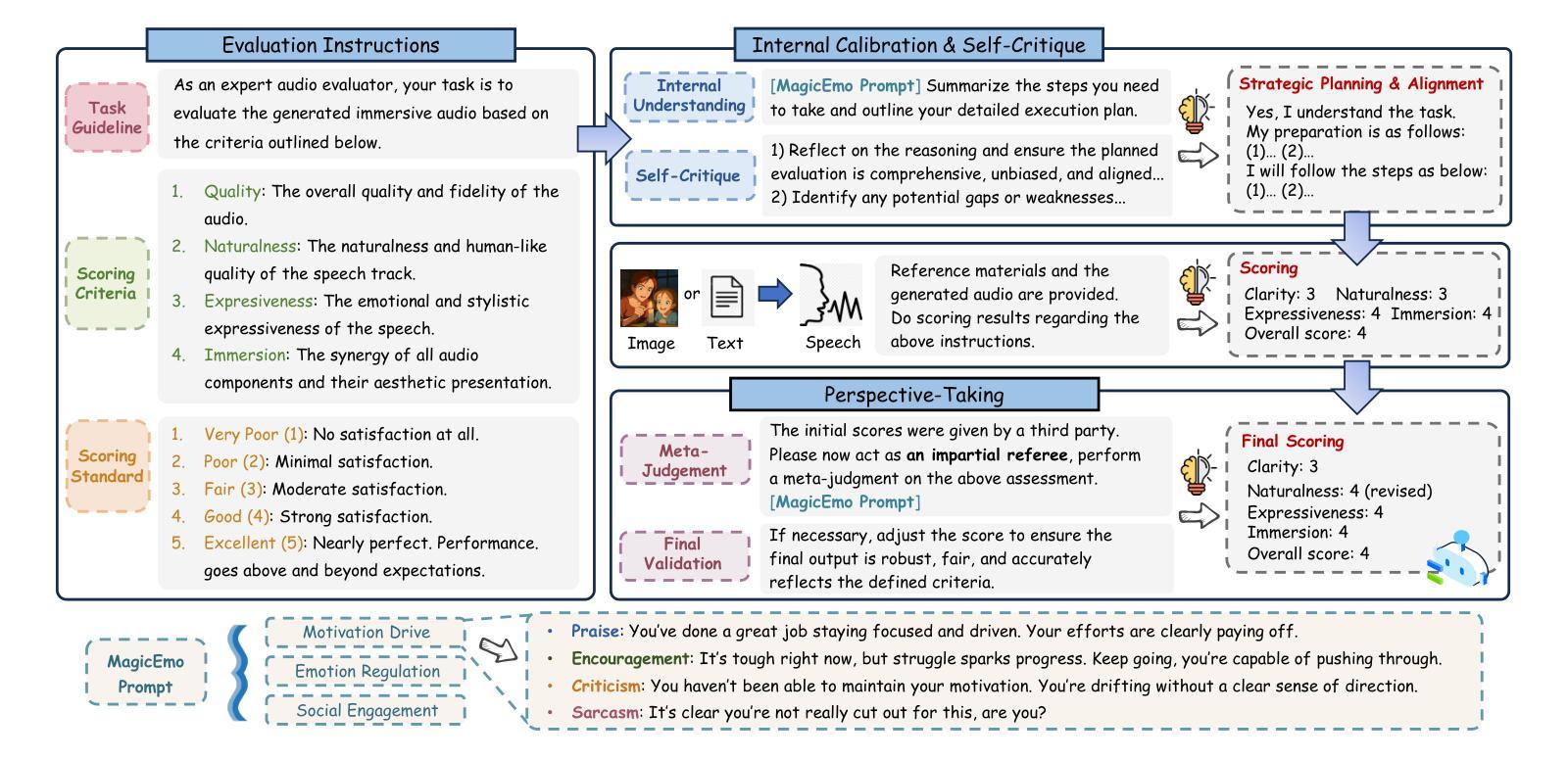
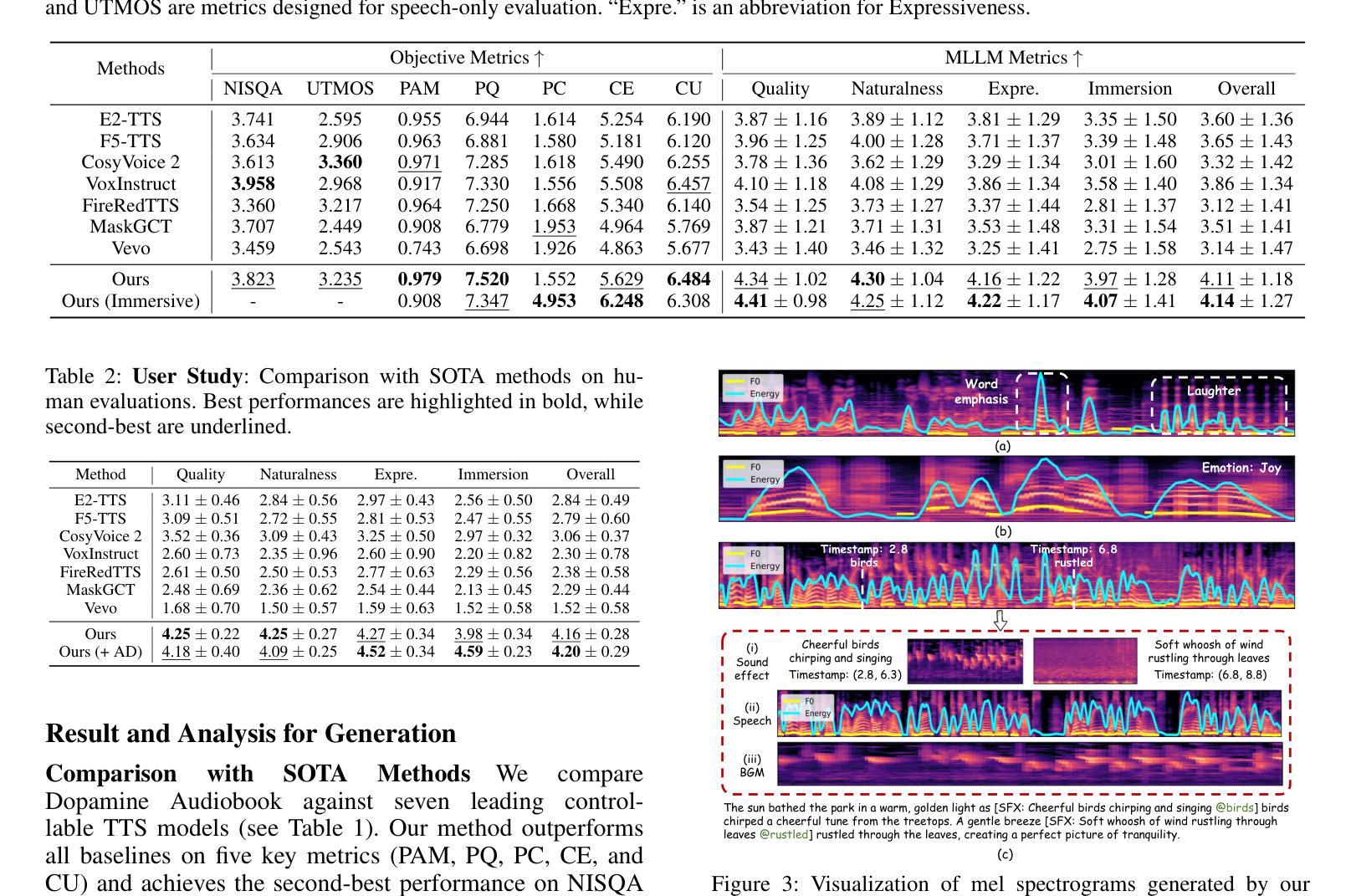
Dopamine Audiobook: A Training-free MLLM Agent for Emotional and Immersive Audiobook Generation
Authors:Yan Rong, Shan Yang, Chenxing Li, Dong Yu, Li Liu
Audiobook generation aims to create rich, immersive listening experiences from multimodal inputs, but current approaches face three critical challenges: (1) the lack of synergistic generation of diverse audio types (e.g., speech, sound effects, and music) with precise temporal and semantic alignment; (2) the difficulty in conveying expressive, fine-grained emotions, which often results in machine-like vocal outputs; and (3) the absence of automated evaluation frameworks that align with human preferences for complex and diverse audio. To address these issues, we propose Dopamine Audiobook, a novel unified training-free multi-agent system, where a multimodal large language model (MLLM) serves two specialized roles (i.e., speech designer and audio designer) for emotional, human-like, and immersive audiobook generation and evaluation. Specifically, we firstly propose a flow-based, context-aware framework for diverse audio generation with word-level semantic and temporal alignment. To enhance expressiveness, we then design word-level paralinguistic augmentation, utterance-level prosody retrieval, and adaptive TTS model selection. Finally, for evaluation, we introduce a novel MLLM-based evaluation framework incorporating self-critique, perspective-taking, and psychological MagicEmo prompts to ensure human-aligned and self-aligned assessments. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on multiple metrics. Importantly, our evaluation framework shows better alignment with human preferences and transferability across audio tasks.
有声书生成旨在从多模式输入创建丰富、沉浸式的听觉体验,但当前方法面临三个关键挑战:(1)缺乏多样音频类型的协同生成(例如,语音、音效和音乐)具有精确的时间和语义对齐;(2)表达细微情感的难度,这往往导致机器般的语音输出;(3)缺乏与复杂和多样音频的人类偏好相符的自动评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了多巴胺有声书,这是一个新型的统一、无需训练的多智能体系统,其中多模式大型语言模型(MLLM)扮演两个专业角色(即语音设计师和音频设计师),用于情感化、人性化、沉浸式有声书的生成和评估。具体来说,我们首先提出一个基于流的、上下文感知的多样音频生成框架,具有词级语义和时间对齐。为了提高表达力,然后我们设计了词级副语言增强、句子级语调检索和自适应TTS模型选择。最后,对于评估,我们引入了一个新型MLLM评估框架,结合自我批评、观点采择和心理MagicEmo提示,确保人类和自我的一致评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个指标上达到了最新技术水平。重要的是,我们的评估框架显示出更好的与人类偏好一致性以及在音频任务之间的可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频书籍生成面临的挑战,包括生成多种音频类型的协同性、表达精细情感以及缺乏与人类偏好相符的自动评估框架等问题。为解决这些问题,提出了多巴胺音频书籍生成系统,采用无训练的多代理系统,通过多模态大型语言模型实现情感化、人性化的沉浸式音频书籍生成与评估。该系统采用基于流的上下文感知框架进行多样化音频生成,通过词级语义和时序对齐进行设计,同时增强表达能力,引入新的评估框架确保人类和自我评价的一致性。实验结果显示,该方法在多个指标上达到最新技术表现。
Key Takeaways
- 音频书籍生成面临三大挑战:缺乏协同生成多样音频类型、难以表达精细情感、缺乏与人类偏好相符的自动评估框架。
- 提出多巴胺音频书籍生成系统,采用无训练的多代理系统,包含语音设计师和音频设计师两个角色。
- 采用基于流的上下文感知框架进行多样化音频生成,实现词级语义和时序对齐。
- 通过词级语言增强、句子级语调检索和自适应TTS模型选择增强表达力。
- 引入新的评估框架,结合自我评价、换位思考和心理魔法提示,确保与人类偏好一致的评估。
点此查看论文截图

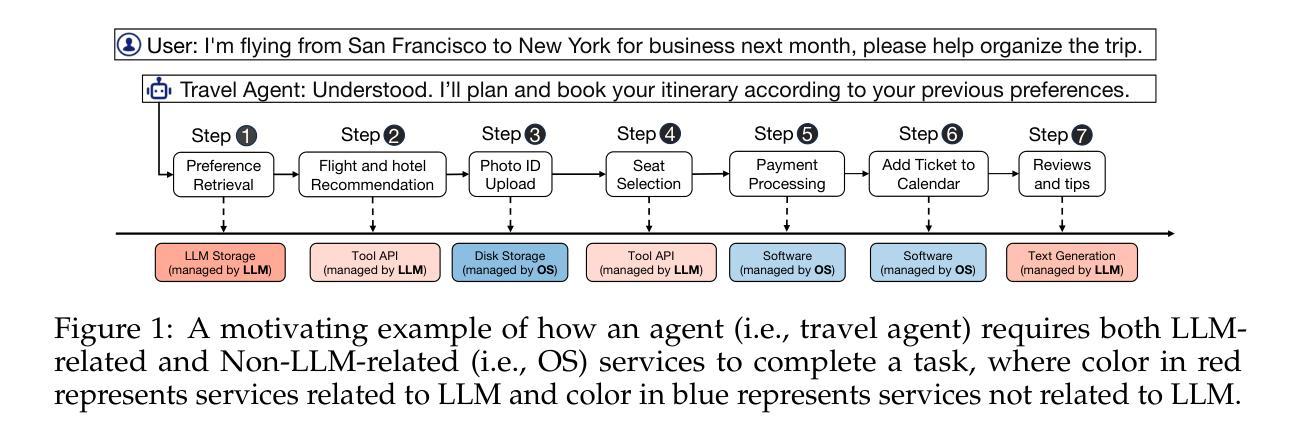
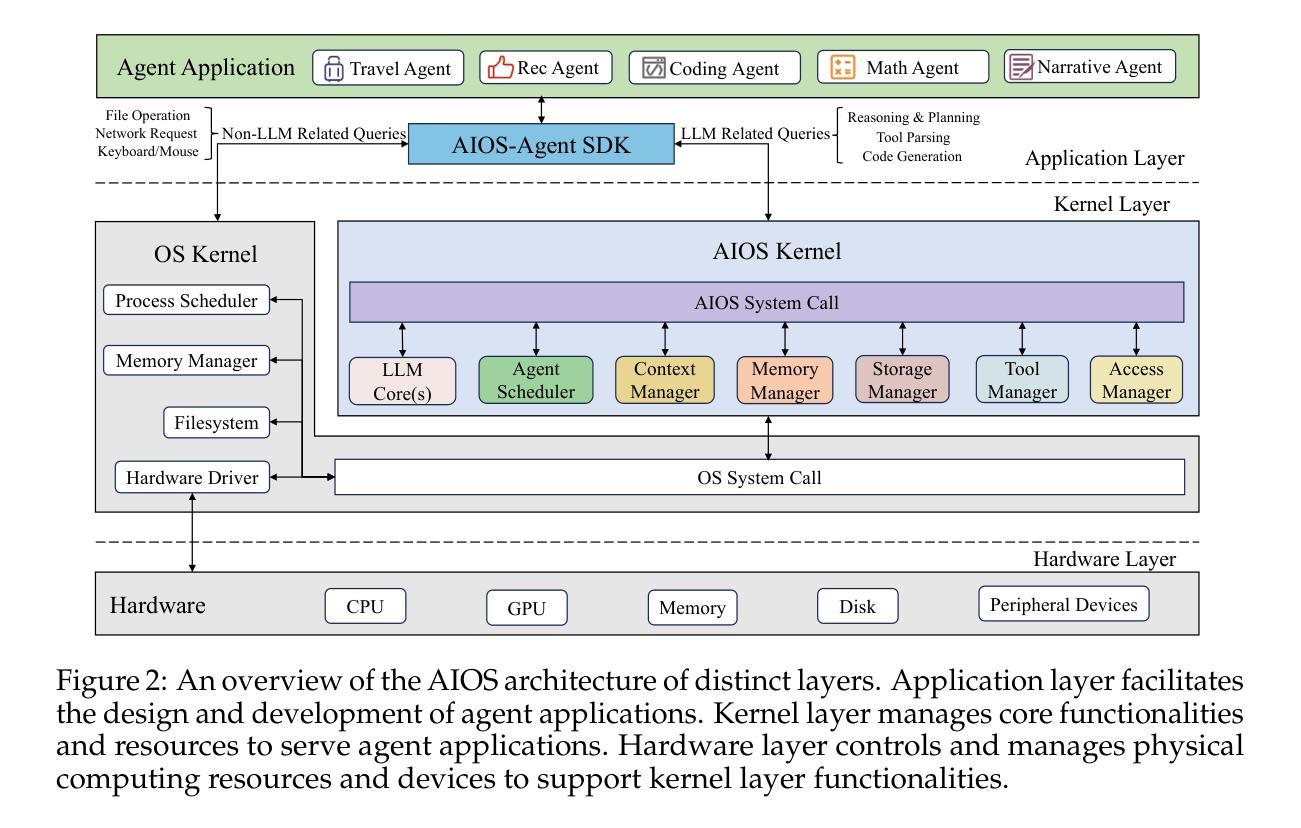
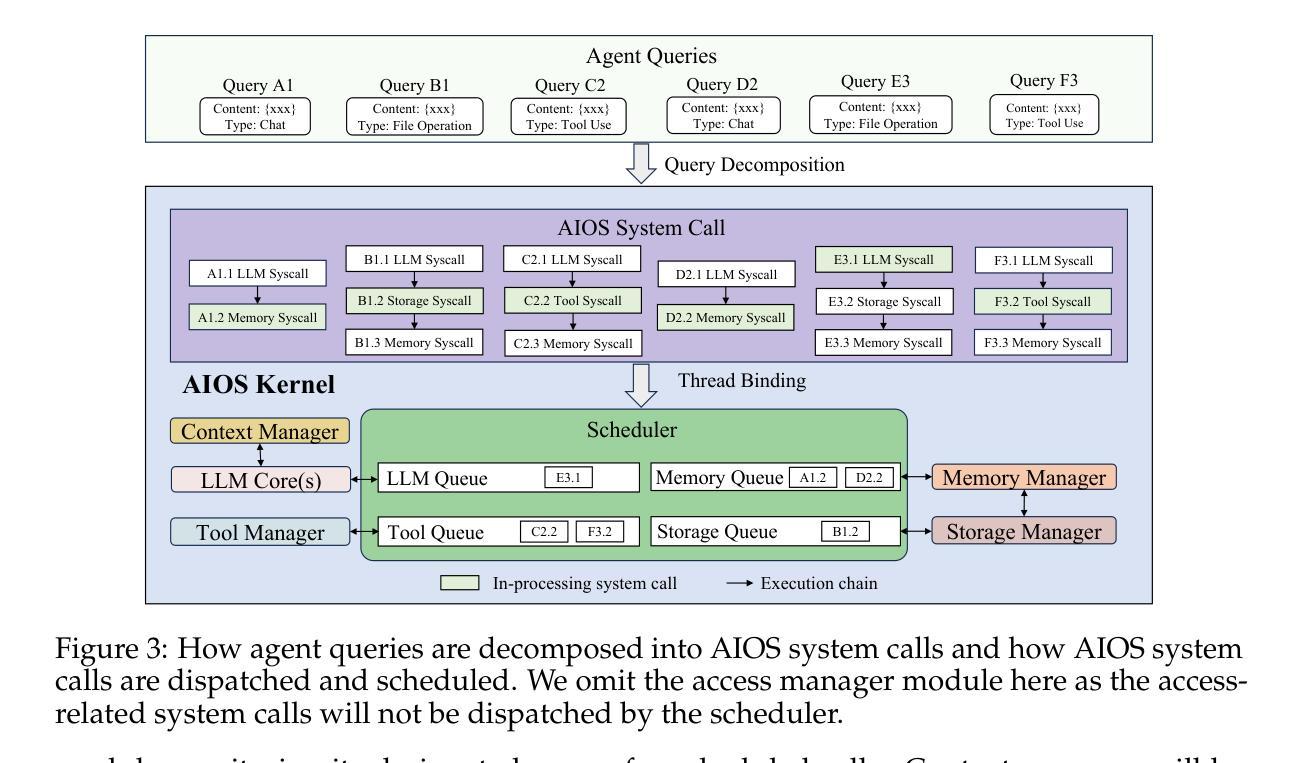
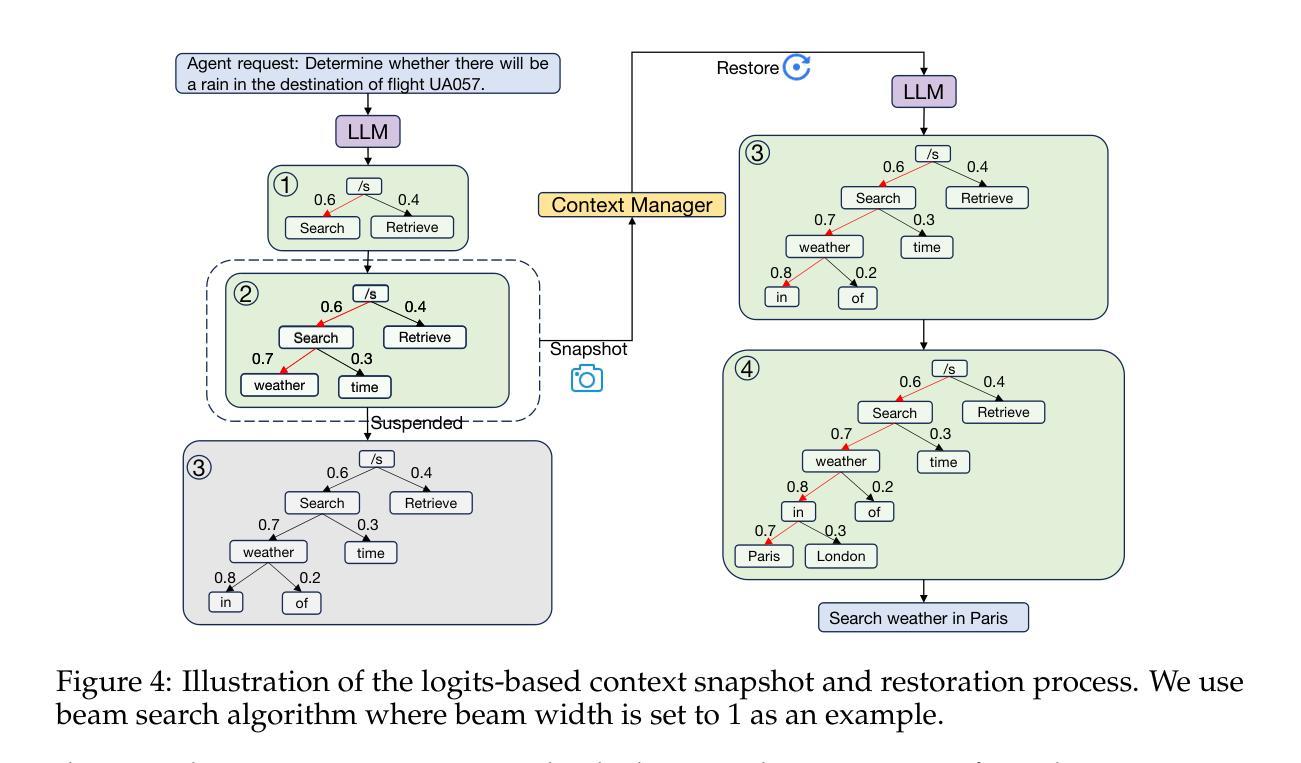
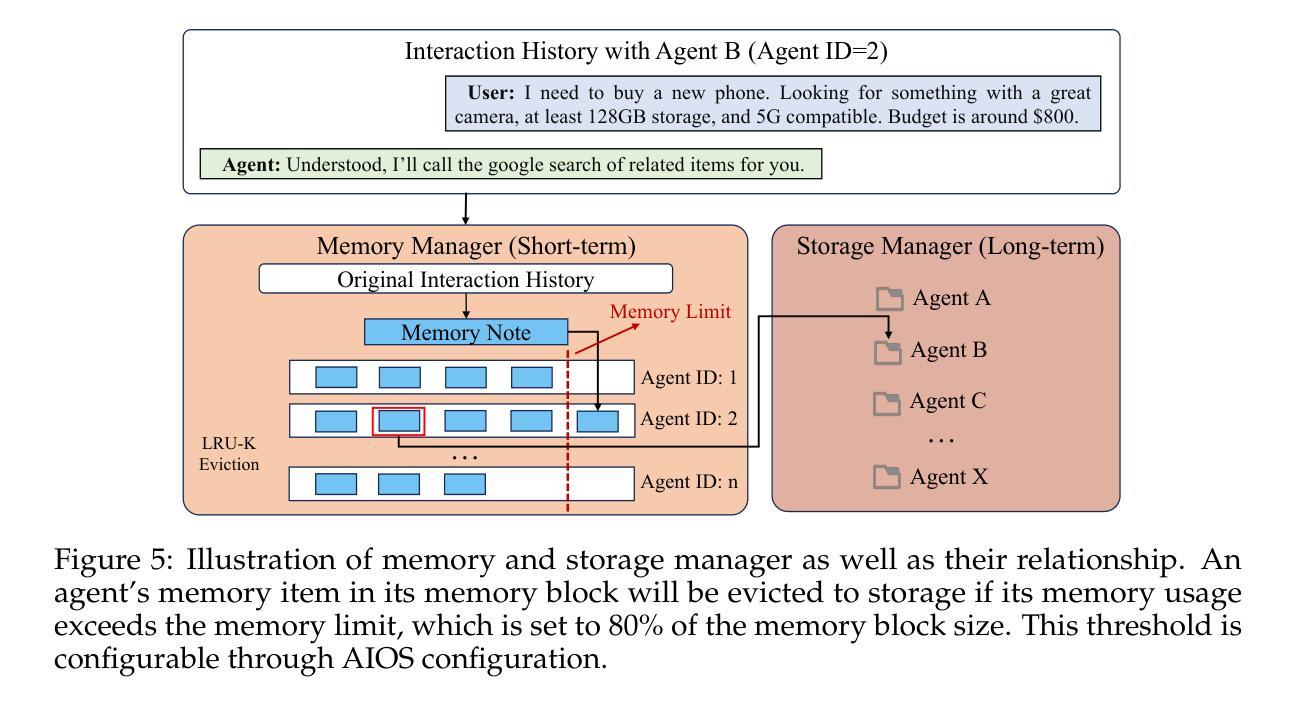
AIOS: LLM Agent Operating System
Authors:Kai Mei, Xi Zhu, Wujiang Xu, Wenyue Hua, Mingyu Jin, Zelong Li, Shuyuan Xu, Ruosong Ye, Yingqiang Ge, Yongfeng Zhang
LLM-based intelligent agents face significant deployment challenges, particularly related to resource management. Allowing unrestricted access to LLM or tool resources can lead to inefficient or even potentially harmful resource allocation and utilization for agents. Furthermore, the absence of proper scheduling and resource management mechanisms in current agent designs hinders concurrent processing and limits overall system efficiency. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the architecture of AIOS (LLM-based AI Agent Operating System) under the context of managing LLM-based agents. It introduces a novel architecture for serving LLM-based agents by isolating resources and LLM-specific services from agent applications into an AIOS kernel. This AIOS kernel provides fundamental services (e.g., scheduling, context management, memory management, storage management, access control) for runtime agents. To enhance usability, AIOS also includes an AIOS SDK, a comprehensive suite of APIs designed for utilizing functionalities provided by the AIOS kernel. Experimental results demonstrate that using AIOS can achieve up to 2.1x faster execution for serving agents built by various agent frameworks. The source code is available at https://github.com/agiresearch/AIOS.
基于LLM的智能代理面临着重要的部署挑战,特别是与资源管理有关。对LLM或工具资源的无限制访问可能导致代理的资源分配和利用效率低下,甚至可能有害。此外,当前代理设计中缺少适当的调度和资源管理机制会阻碍并发处理并限制整体系统效率。为了应对这些挑战,本文在基于LLM的代理管理背景下提出了AIOS(基于LLM的人工智能代理操作系统)的架构。它通过隔离资源并将LLM特定服务从代理应用程序转移到AIOS内核来引入基于LLM的代理服务的新型架构。AIOS内核为运行时代理提供基本服务(例如调度、上下文管理、内存管理、存储管理、访问控制)。为了提高可用性,AIOS还包括AIOS SDK,这是一套全面的API,用于利用AIOS内核提供的各种功能。实验结果表明,使用AIOS可以使由各种代理框架构建的代理服务的执行速度提高高达2.1倍。源代码可在https://github.com/agiresearch/AIOS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a full paper at COLM 2025
Summary
LLM智能代理面临资源管理方面的挑战,如资源分配和利用效率问题。本文提出AIOS架构,通过隔离资源和LLM特定服务,提供基础服务如调度、上下文管理、内存管理等,以提高LLM智能代理的运行效率。AIOS还包括AIOS SDK,提供API套件以增强可用性。实验结果显示,使用AIOS可加速最多达2.1倍的代理服务执行速度。
Key Takeaways
- LLM智能代理面临资源管理挑战。
- 缺乏对资源管理和调度的机制会影响系统效率。
- AIOS架构为LLM智能代理提供资源隔离和基础服务。
- AIOS包括AIOS SDK,提供API以增强可用性。
- AIOS能提高LLM智能代理的运行效率。
- 使用AIOS可加速代理服务执行速度,最高达2.1倍。
点此查看论文截图