⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
Training-Free Text-Guided Color Editing with Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Zixin Yin, Xili Dai, Ling-Hao Chen, Deyu Zhou, Jianan Wang, Duomin Wang, Gang Yu, Lionel M. Ni, Heung-Yeung Shum
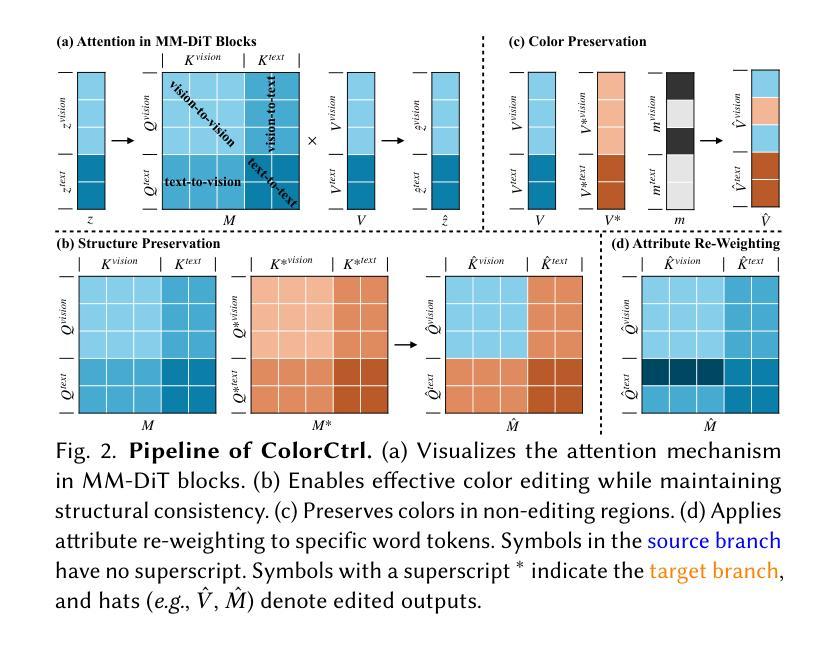
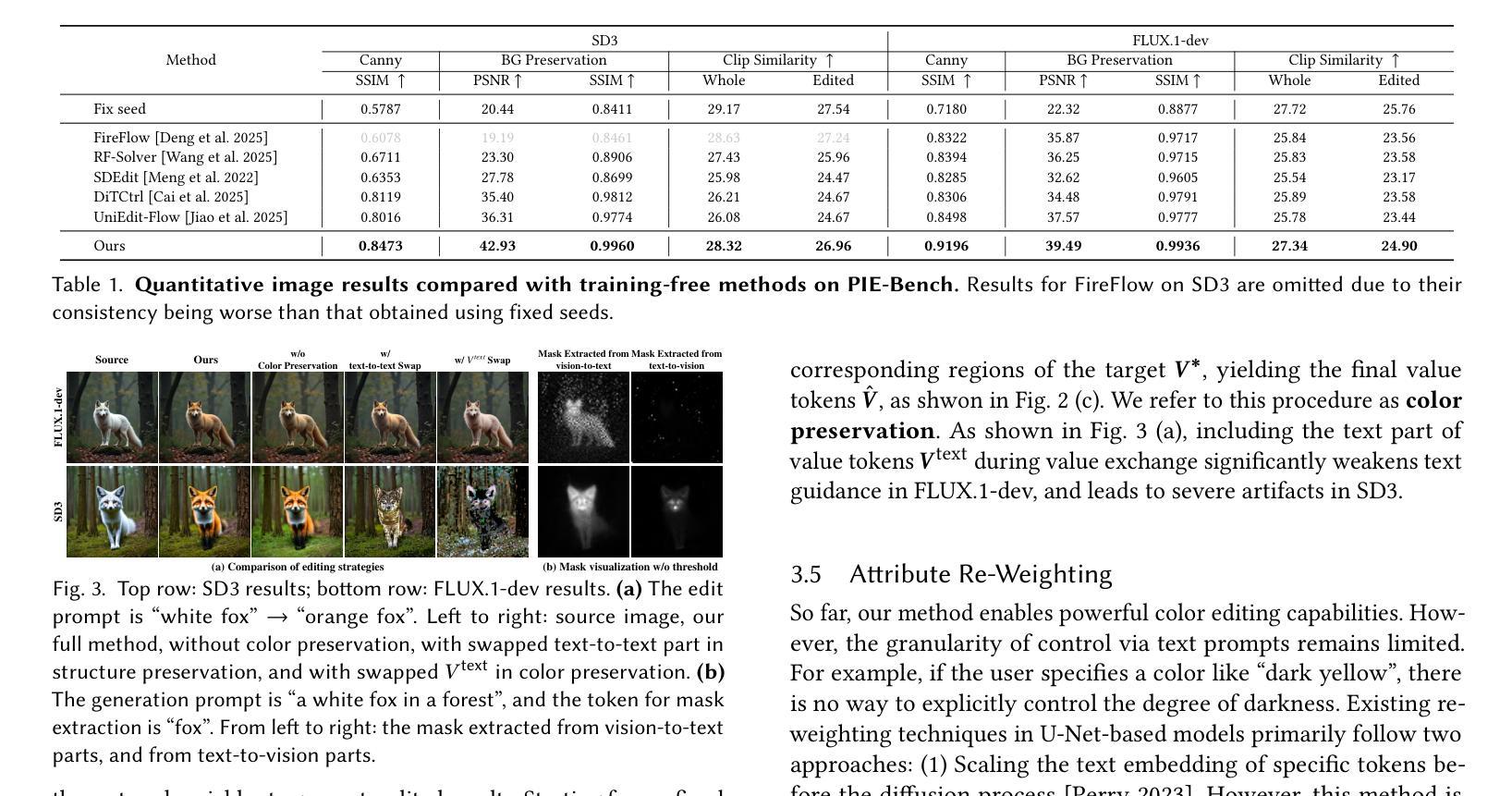
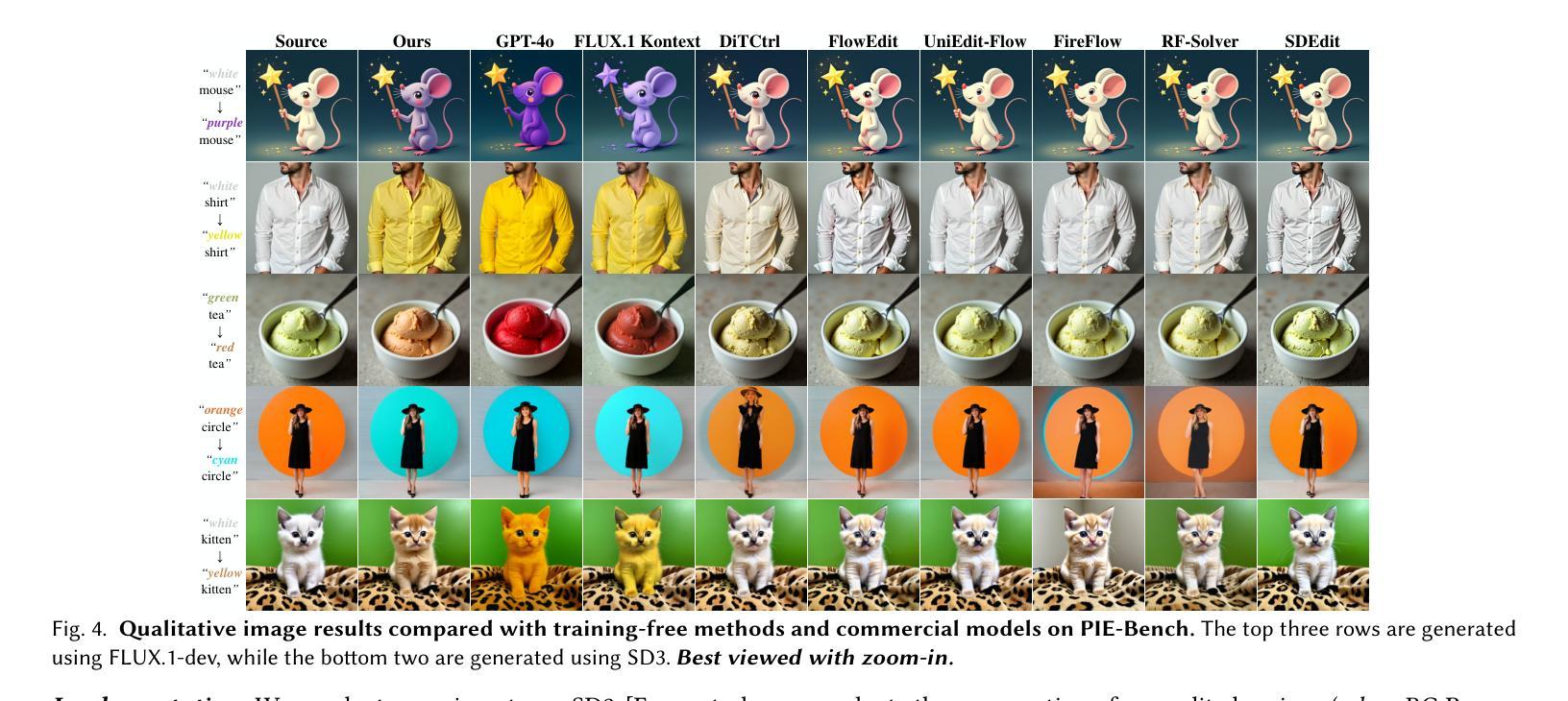
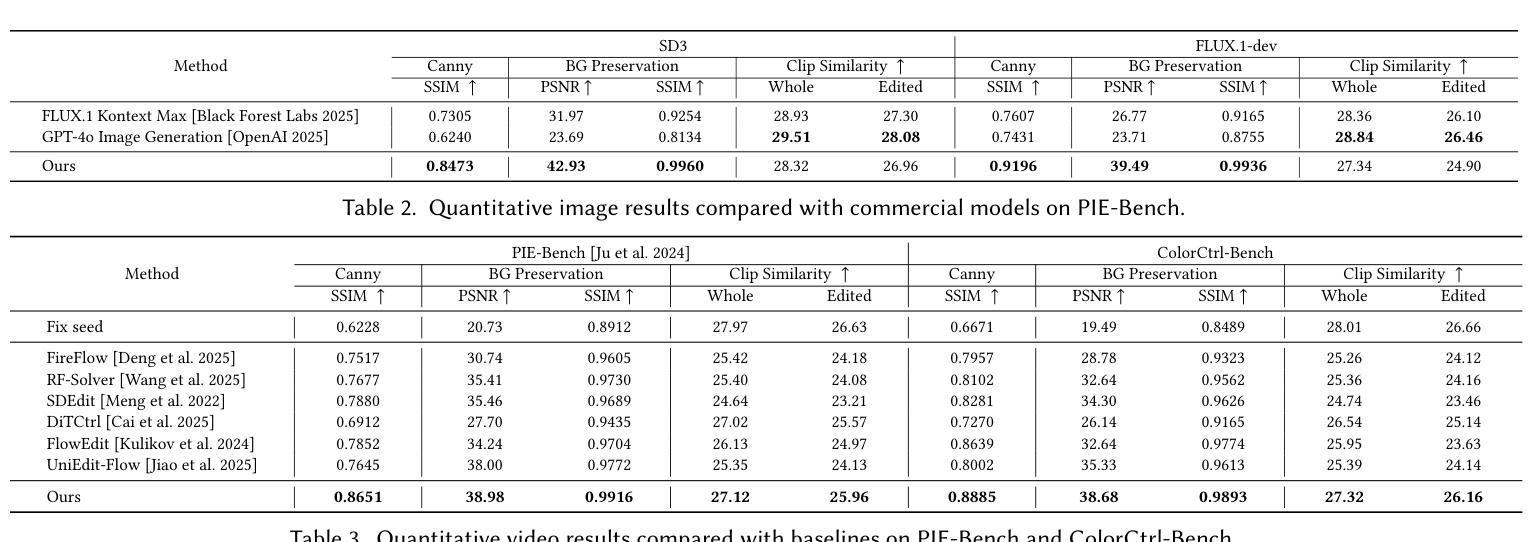
Text-guided color editing in images and videos is a fundamental yet unsolved problem, requiring fine-grained manipulation of color attributes, including albedo, light source color, and ambient lighting, while preserving physical consistency in geometry, material properties, and light-matter interactions. Existing training-free methods offer broad applicability across editing tasks but struggle with precise color control and often introduce visual inconsistency in both edited and non-edited regions. In this work, we present ColorCtrl, a training-free color editing method that leverages the attention mechanisms of modern Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiT). By disentangling structure and color through targeted manipulation of attention maps and value tokens, our method enables accurate and consistent color editing, along with word-level control of attribute intensity. Our method modifies only the intended regions specified by the prompt, leaving unrelated areas untouched. Extensive experiments on both SD3 and FLUX.1-dev demonstrate that ColorCtrl outperforms existing training-free approaches and achieves state-of-the-art performances in both edit quality and consistency. Furthermore, our method surpasses strong commercial models such as FLUX.1 Kontext Max and GPT-4o Image Generation in terms of consistency. When extended to video models like CogVideoX, our approach exhibits greater advantages, particularly in maintaining temporal coherence and editing stability. Finally, our method also generalizes to instruction-based editing diffusion models such as Step1X-Edit and FLUX.1 Kontext dev, further demonstrating its versatility.
文本中的图像和视频导向色彩编辑是一个基础但尚未解决的问题,它要求对色彩属性进行精细的操控,包括表面亮度、光源颜色和周围环境照明,同时保持几何结构、材质特性和光线物质交互的物理一致性。现有的无训练方法在编辑任务中具有广泛的应用性,但在精确色彩控制方面存在困难,并且在编辑和非编辑区域都引入了视觉不一致性。在这项工作中,我们提出了ColorCtrl,这是一种无训练的色彩编辑方法,它利用现代多模态扩散变压器(MM-DiT)的注意力机制。通过有针对性地操作注意力图和值令牌来分离结构和色彩,我们的方法能够实现精确且一致的颜色编辑,以及属性强度的词汇级控制。我们的方法仅修改提示指定的意图区域,而不影响无关区域。在SD3和FLUX.1-dev上的大量实验表明,ColorCtrl优于现有的无训练方法,并在编辑质量和一致性方面达到了最新水平。此外,我们的方法在一致性方面超越了强大的商业模型,如FLUX.1 Kontext Max和GPT-4o图像生成。当扩展到视频模型(如CogVideoX)时,我们的方法显示出更大的优势,特别是在保持时间连贯性和编辑稳定性方面。最后,我们的方法还适用于基于指令的编辑扩散模型(如Step1X-Edit和FLUX.1 Kontext dev),这进一步证明了其通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于无训练的多模态扩散Transformer(MM-DiT)的ColorCtrl颜色编辑方法。该方法通过操纵注意力图和值令牌来分离结构和颜色,实现了精确且一致的颜色编辑,并具备词语级别的属性强度控制。实验证明,ColorCtrl在编辑质量和一致性方面超越现有无训练方法,并在视频模型如CogVideoX上展现出更大的优势,特别是在保持时间连贯性和编辑稳定性方面。此外,ColorCtrl还适用于基于指令的编辑扩散模型,如Step1X-Edit和FLUX.1 Kontext dev,显示出其通用性。
Key Takeaways
- ColorCtrl是一种基于无训练的多模态扩散Transformer(MM-DiT)的颜色编辑方法。
- 通过操纵注意力图和值令牌,ColorCtrl实现了结构和颜色的分离。
- ColorCtrl实现了精确且一致的颜色编辑,具备词语级别的属性强度控制。
- 与现有无训练方法和商业模型相比,ColorCtrl在编辑质量和一致性方面表现出卓越性能。
- ColorCtrl在视频模型上的优势在于能够保持时间连贯性和编辑稳定性。
- ColorCtrl适用于基于指令的编辑扩散模型,显示出其通用性。
点此查看论文截图


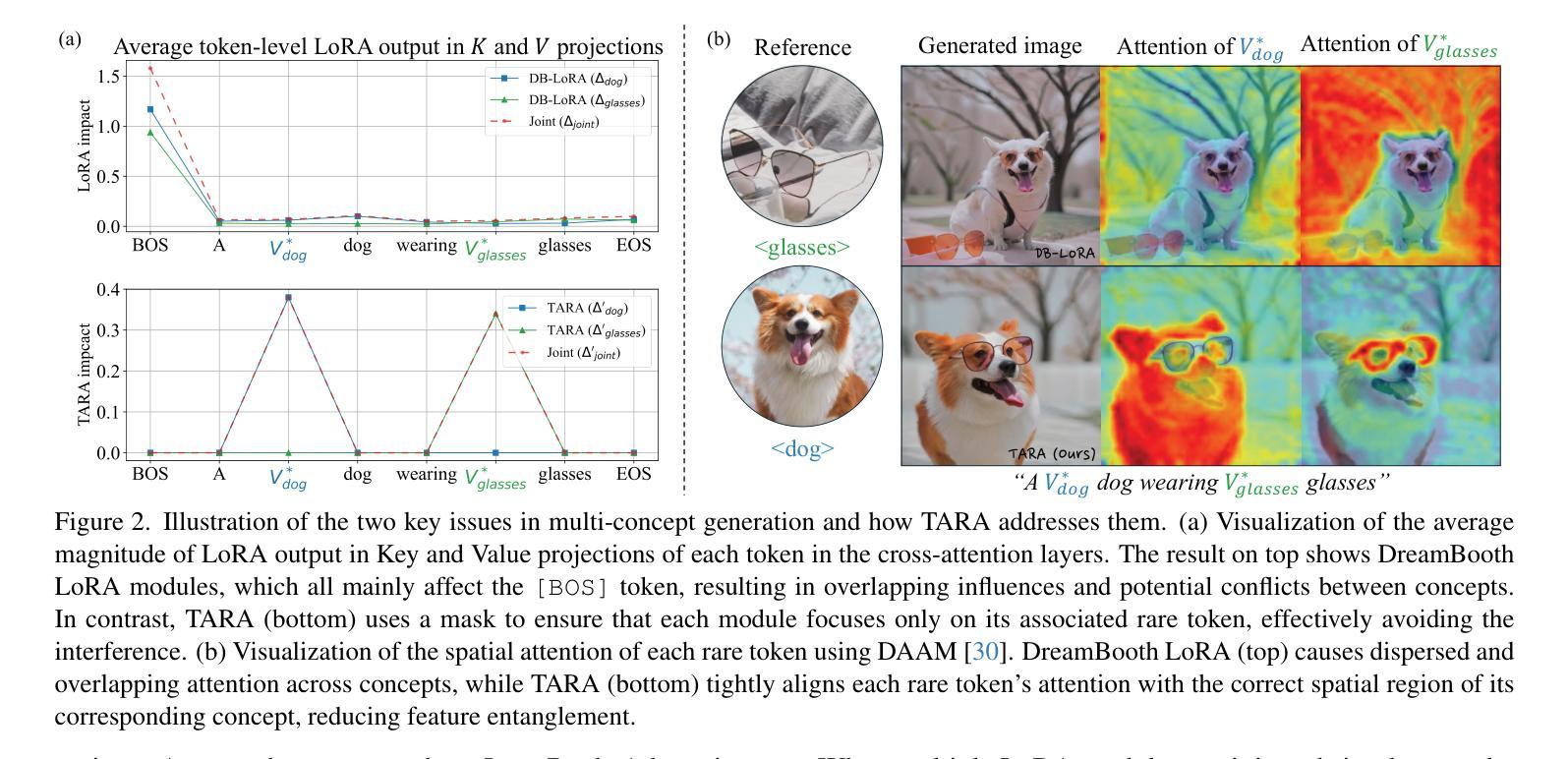
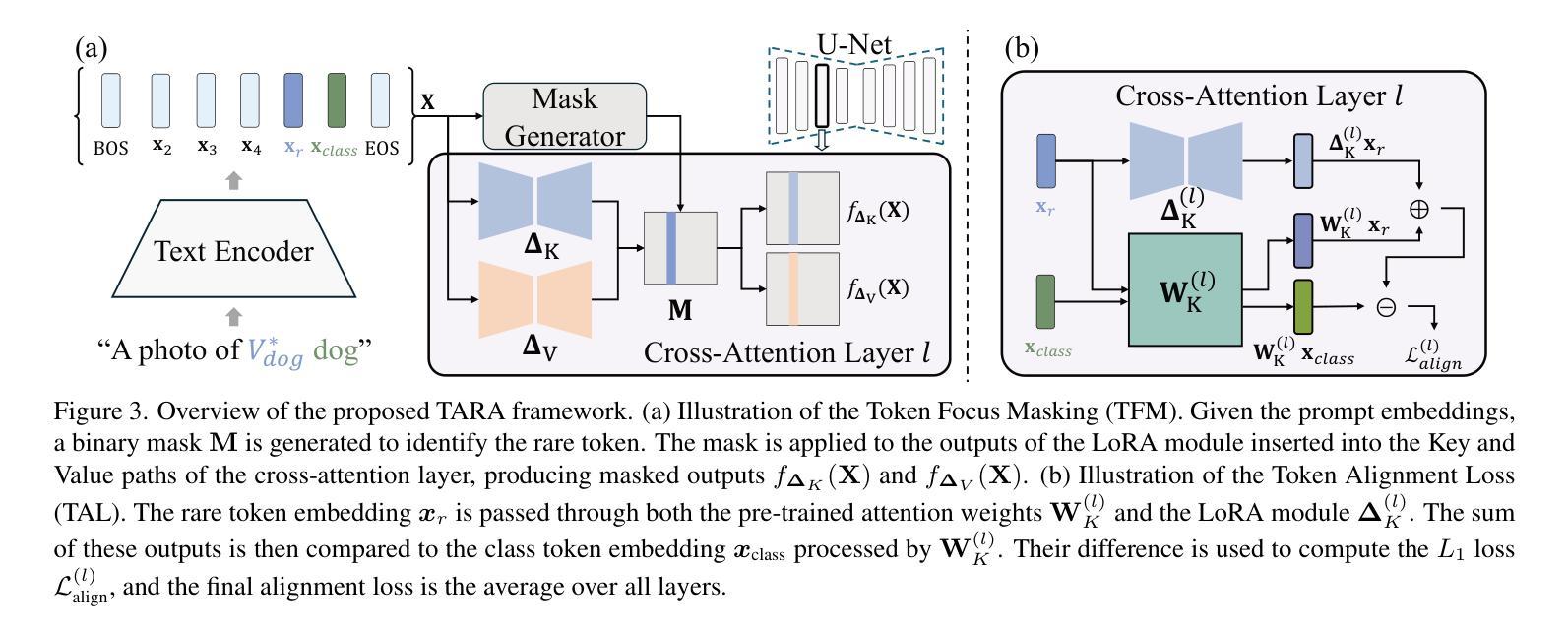
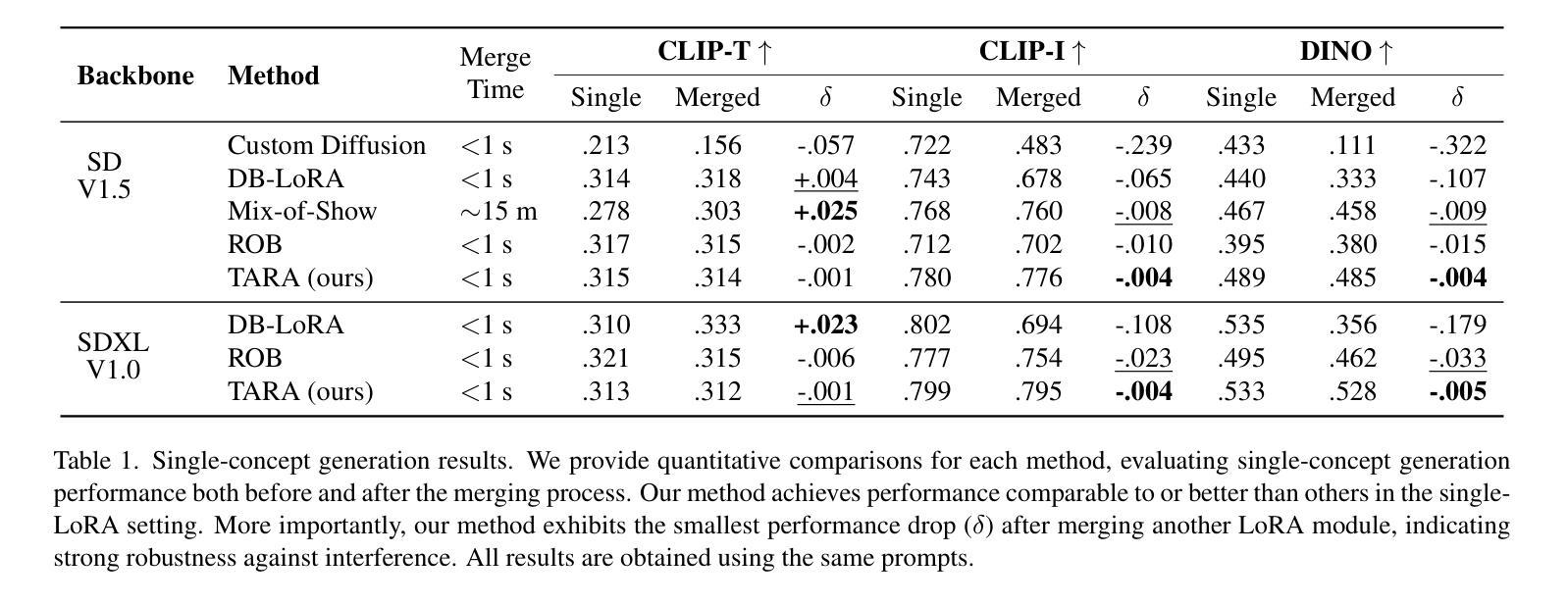
TARA: Token-Aware LoRA for Composable Personalization in Diffusion Models
Authors:Yuqi Peng, Lingtao Zheng, Yufeng Yang, Yi Huang, Mingfu Yan, Jianzhuang Liu, Shifeng Chen
Personalized text-to-image generation aims to synthesize novel images of a specific subject or style using only a few reference images. Recent methods based on Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) enable efficient single-concept customization by injecting lightweight, concept-specific adapters into pre-trained diffusion models. However, combining multiple LoRA modules for multi-concept generation often leads to identity missing and visual feature leakage. In this work, we identify two key issues behind these failures: (1) token-wise interference among different LoRA modules, and (2) spatial misalignment between the attention map of a rare token and its corresponding concept-specific region. To address these issues, we propose Token-Aware LoRA (TARA), which introduces a token mask to explicitly constrain each module to focus on its associated rare token to avoid interference, and a training objective that encourages the spatial attention of a rare token to align with its concept region. Our method enables training-free multi-concept composition by directly injecting multiple independently trained TARA modules at inference time. Experimental results demonstrate that TARA enables efficient multi-concept inference and effectively preserving the visual identity of each concept by avoiding mutual interference between LoRA modules. The code and models are available at https://github.com/YuqiPeng77/TARA.
个性化文本到图像生成旨在使用少量参考图像合成特定主题或风格的全新图像。最近基于低秩适配(LoRA)的方法通过向预训练的扩散模型注入轻量级、概念特定的适配器,实现了高效的单概念定制。然而,为多概念生成组合多个LoRA模块通常会导致身份缺失和视觉特征泄露。在这项工作中,我们识别出这些失败背后的两个关键问题:(1)不同LoRA模块之间的标记级干扰;(2)稀有标记的注意力图与其对应的概念特定区域之间的空间不匹配。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Token感知LoRA(TARA),它引入了一个标记掩码来显式约束每个模块专注于其相关的稀有标记,以避免干扰,以及一个训练目标,鼓励稀有标记的空间注意力与其概念区域对齐。我们的方法通过在推理时间直接注入多个独立训练的TARA模块,实现了无需训练的多概念组合。实验结果表明,TARA能够实现高效的多概念推理,并有效地保留每个概念的身份特征,避免了LoRA模块之间的相互干扰。代码和模型可在https://github.com/YuqiPeng77/TARA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本生成的个性化图像合成方法通过使用少量参考图像合成特定主题或风格的图像。虽然现有的基于低秩适配(LoRA)的方法可以实现单一概念定制,但在多概念生成时会出现身份缺失和视觉特征泄露的问题。本研究针对这些问题提出了Token-Aware LoRA(TARA)方法,通过引入token掩码和训练目标来解决模块间的干扰和空间不匹配问题。TARA方法实现了无需训练的多概念组合,通过直接在推理时间注入多个独立训练的TARA模块,实现了高效的多概念推理,并有效保留了每个概念的视觉身份。
Key Takeaways
- 文本生成的个性化图像合成方法使用少量参考图像合成特定主题或风格的图像。
- 基于低秩适配(LoRA)的方法可实现单一概念定制,但在多概念生成时存在问题。
- 多概念生成失败的主要原因包括不同LoRA模块间的token-wise干扰和空间不匹配。
- TARA方法通过引入token掩码和训练目标来解决这些问题。
- TARA实现了无需训练的多概念组合,提高了多概念推理的效率。
- TARA能够保留每个概念的视觉身份,避免了相互干扰。
点此查看论文截图


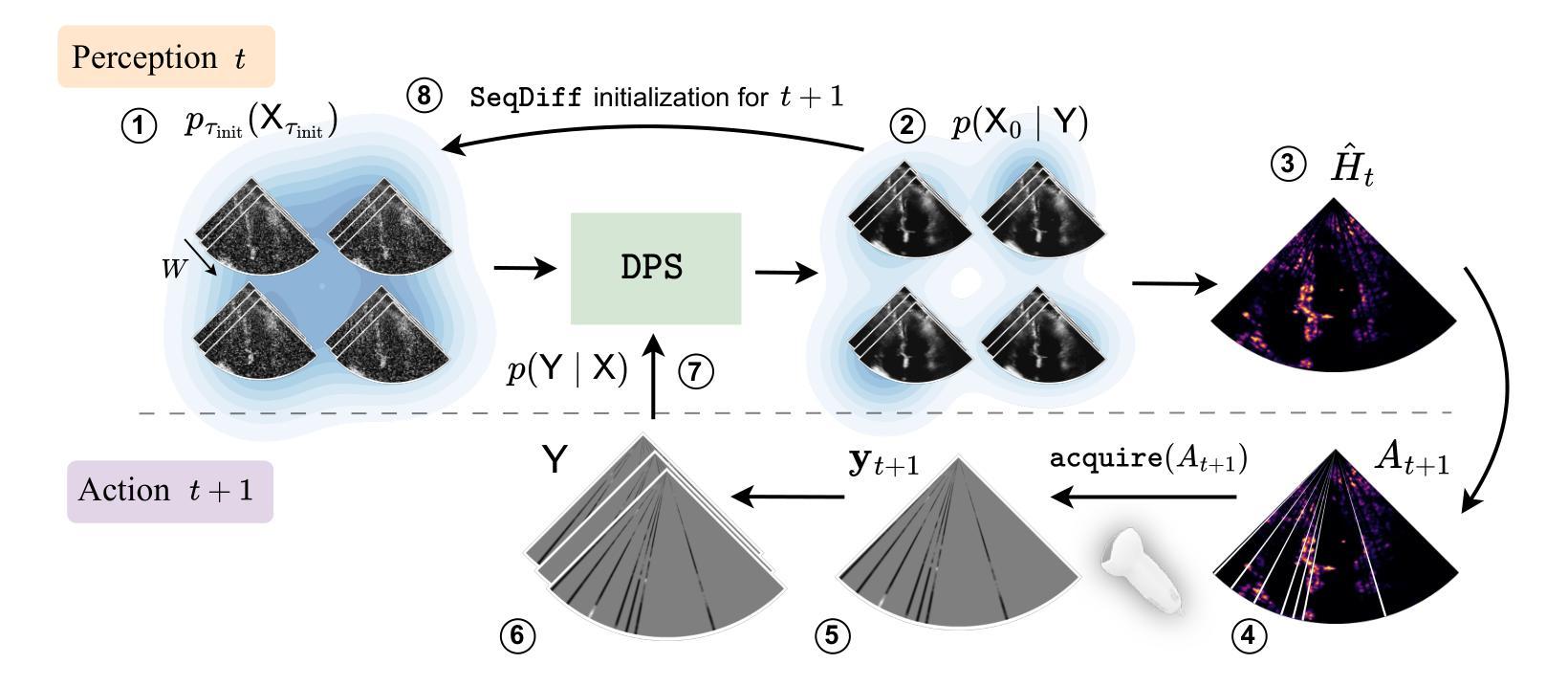
Patient-Adaptive Focused Transmit Beamforming using Cognitive Ultrasound
Authors:Wessel L. van Nierop, Oisín Nolan, Tristan S. W. Stevens, Ruud J. G. van Sloun
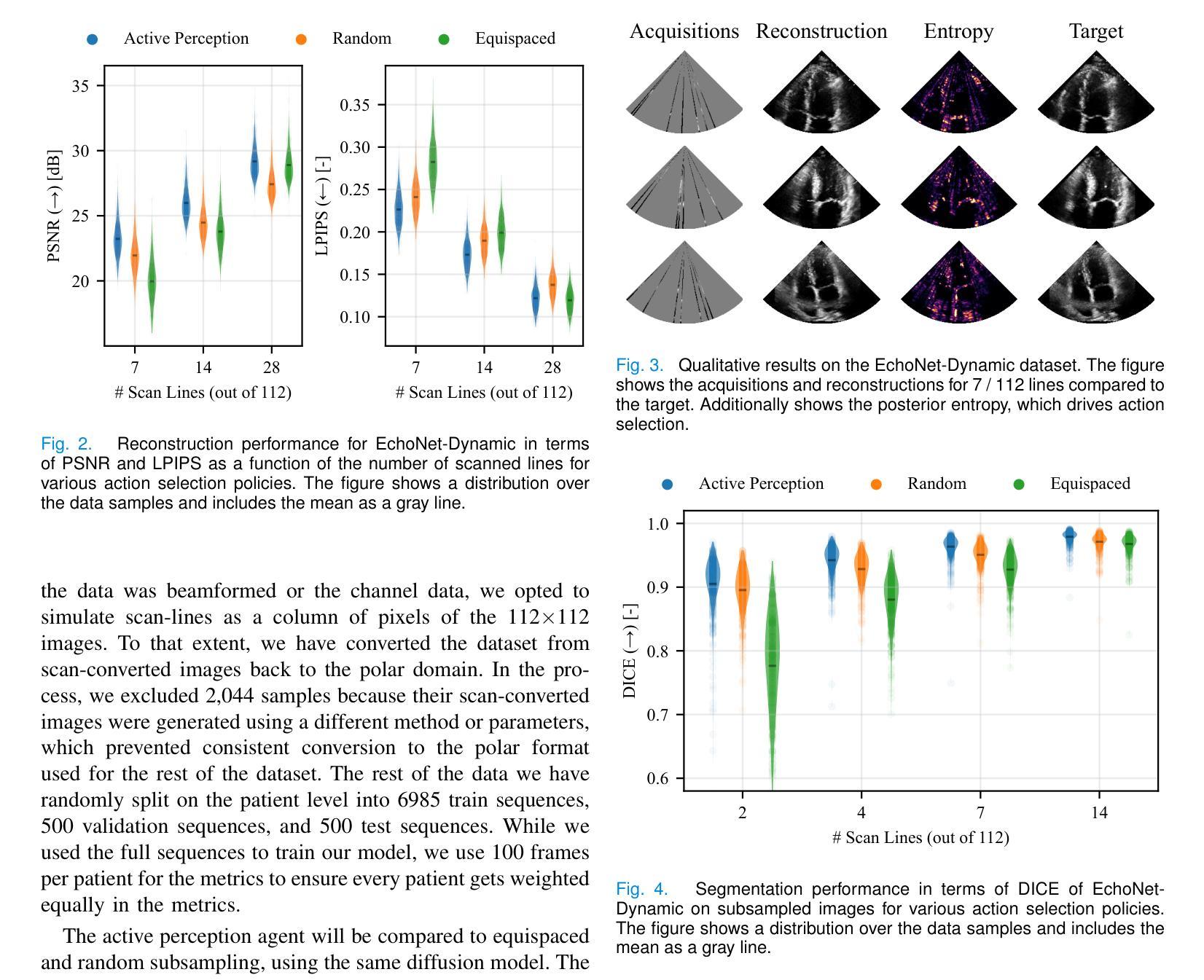
Focused transmit beamforming is the most commonly used acquisition scheme for echocardiograms, but suffers from relatively low frame rates, and in 3D, even lower volume rates. Fast imaging based on unfocused transmits has disadvantages such as motion decorrelation and limited harmonic imaging capabilities. This work introduces a patient-adaptive focused transmit scheme that has the ability to drastically reduce the number of transmits needed to produce a high-quality ultrasound image. The method relies on posterior sampling with a temporal diffusion model to perceive and reconstruct the anatomy based on partial observations, while subsequently taking an action to acquire the most informative transmits. This active perception modality outperforms random and equispaced subsampling on the 2D EchoNet-Dynamic dataset and a 3D Philips dataset, where we actively select focused elevation planes. Furthermore, we show it achieves better performance in terms of generalized contrast-to-noise ratio when compared to the same number of diverging waves transmits on three in-house echocardiograms. Additionally, we can estimate ejection fraction using only 2% of the total transmits and show that the method is robust to outlier patients. Finally, our method can be run in real-time on GPU accelerators from 2023. The code is publicly available at https://tue-bmd.github.io/ulsa/
聚焦发射波束形成是超声心动图最常用的采集方案,但其帧率较低,在三维情况下体积速率更低。基于非聚焦发射的快速成像存在运动去相关和谐波成像能力有限等缺点。这项工作引入了一种病人自适应的聚焦发射方案,能够大幅度减少产生高质量超声图像所需要的发射次数。该方法依赖于后采样和时序扩散模型,基于部分观察来感知和重建结构,然后采取行动获取最具信息量的发射。这种主动感知模式在EchoNet-Dynamic二维数据集和飞利浦三维数据集上优于随机和等距子采样,我们主动选择聚焦的仰角平面。此外,我们展示其在广义对比噪声比方面表现更好,在与三种内部超声心动图的发散波发射相同数量的情况下更是如此。此外,我们仅使用总发射次数的2%即可估算射血分数,并证明该方法对异常患者具有稳健性。最后,我们的方法可以在2023年的GPU加速器上实时运行。代码公开在https://tue-bmd.github.io/ulsa/上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种病人自适应的聚焦发射方案,该方案能够大大减少产生高质量超声图像所需的发射次数。该方法利用后采样和临时扩散模型来感知和重建结构,然后采取动作获取最具信息量的发射。此主动感知模式在2D EchoNet-Dynamic数据集和3D飞利浦数据集上表现出优于随机和等距子采样的性能,并能实现更好的广义对比噪声比。此外,该方法仅使用总发射量的2%即可估计射血分数,且对异常患者具有稳健性。该方法可在2023年的GPU加速器上实时运行。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的病人自适应聚焦发射方案,能够大幅度减少产生高质量超声图像所需的发射次数。
- 该方案利用后采样和临时扩散模型来感知和重建结构。
- 主动感知模式在2D和3D数据集上表现出优于随机和等距子采样的性能。
- 该方案在广义对比噪声比方面表现优秀。
- 仅使用少量发射即可估计射血分数。
- 该方案对异常患者具有稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


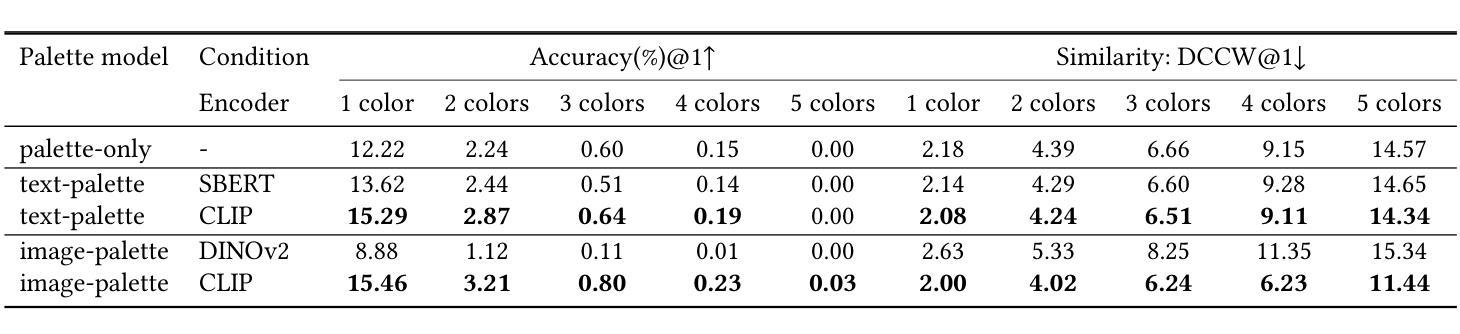
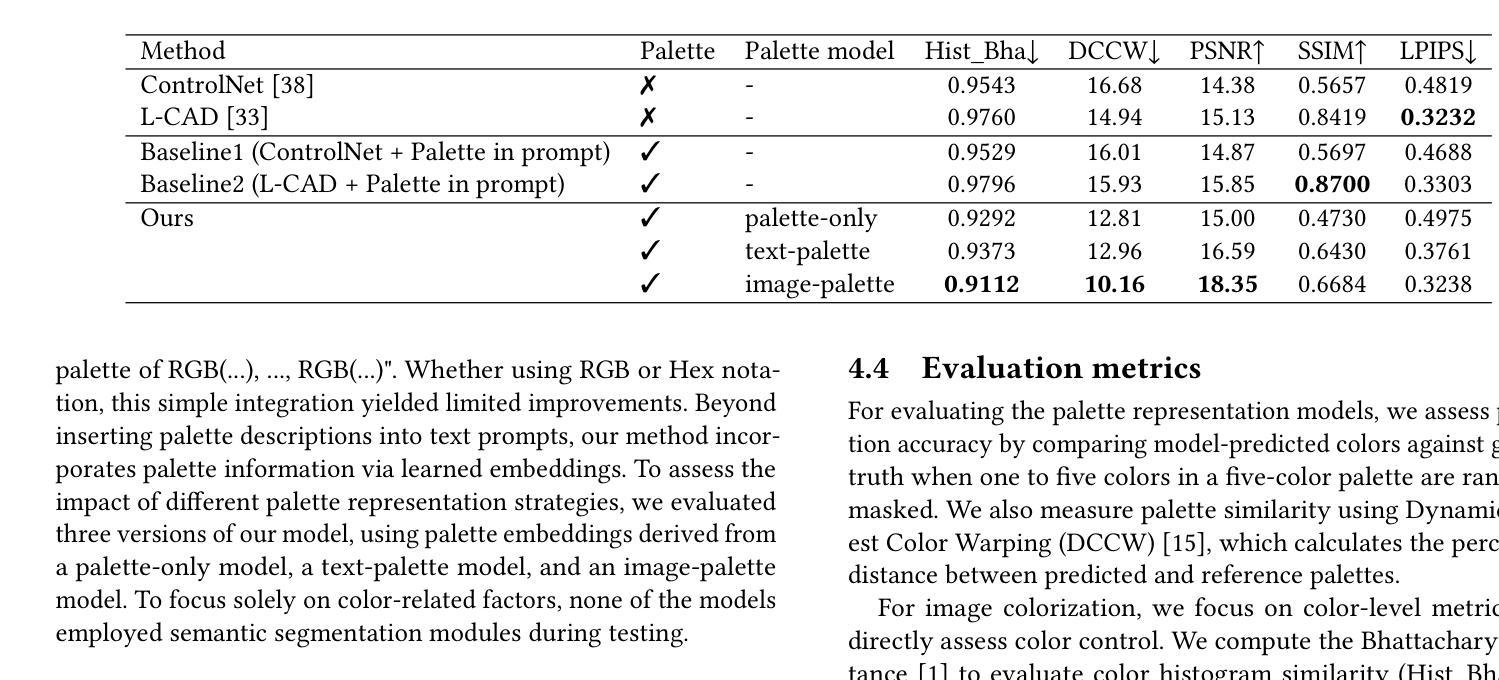
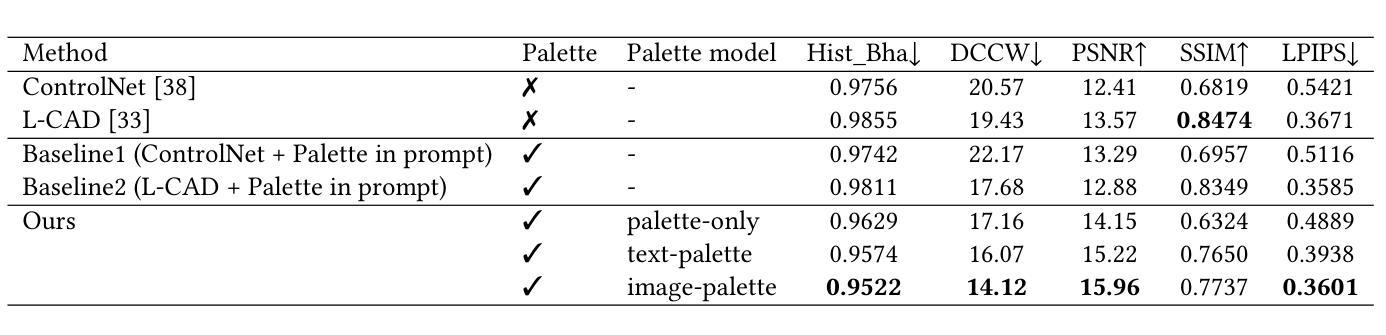
Exploring Palette based Color Guidance in Diffusion Models
Authors:Qianru Qiu, Jiafeng Mao, Xueting Wang
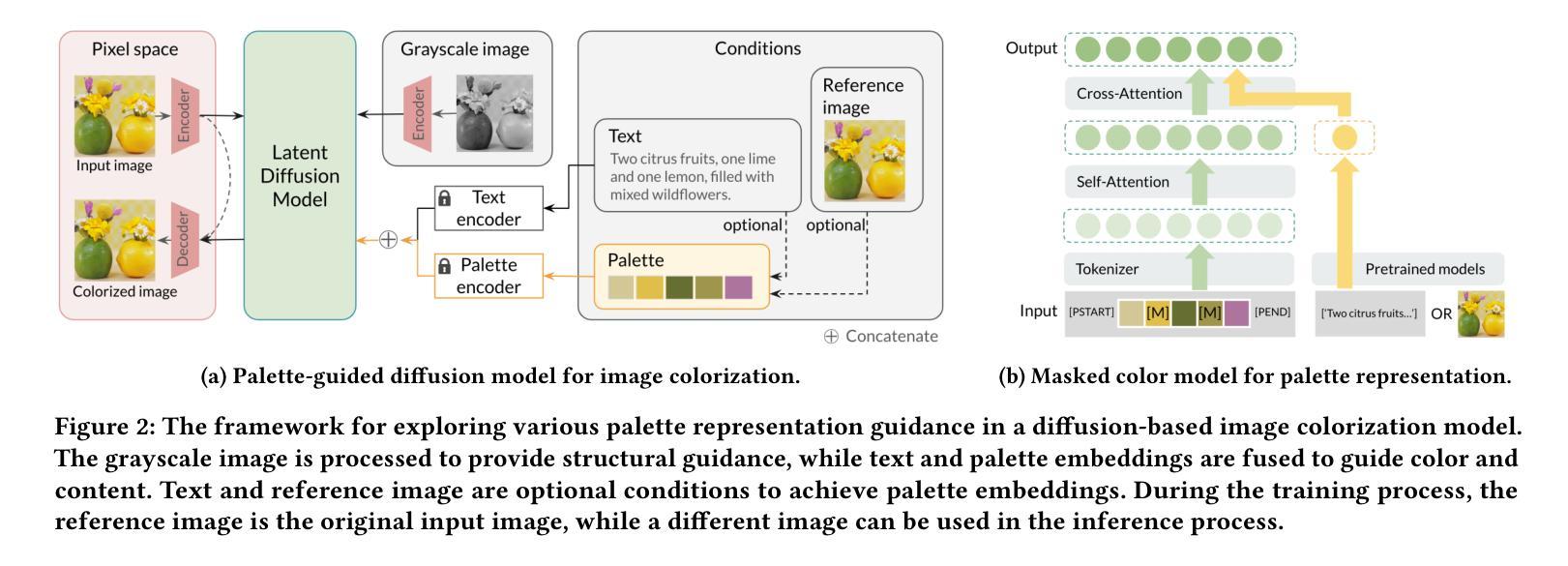
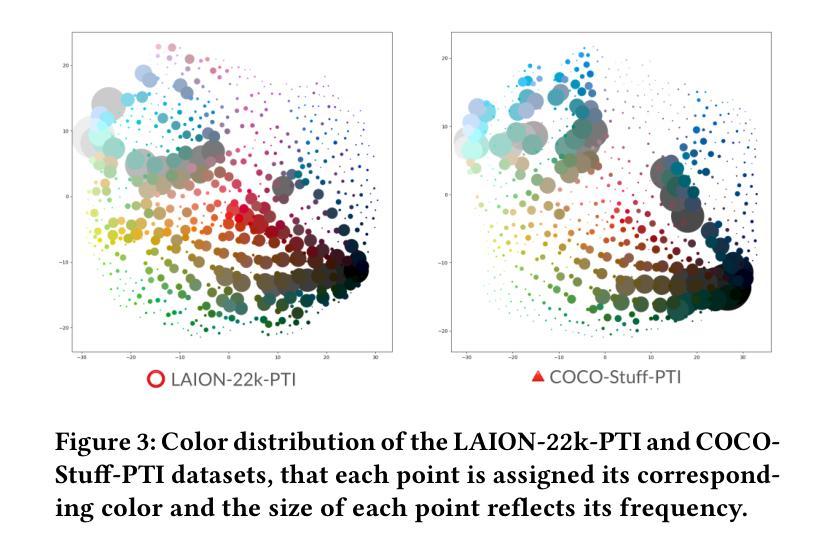
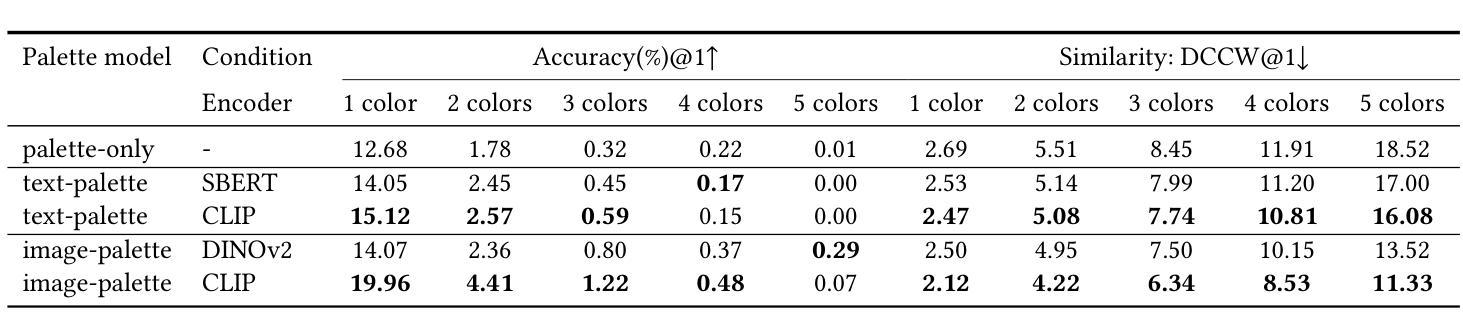
With the advent of diffusion models, Text-to-Image (T2I) generation has seen substantial advancements. Current T2I models allow users to specify object colors using linguistic color names, and some methods aim to personalize color-object association through prompt learning. However, existing models struggle to provide comprehensive control over the color schemes of an entire image, especially for background elements and less prominent objects not explicitly mentioned in prompts. This paper proposes a novel approach to enhance color scheme control by integrating color palettes as a separate guidance mechanism alongside prompt instructions. We investigate the effectiveness of palette guidance by exploring various palette representation methods within a diffusion-based image colorization framework. To facilitate this exploration, we construct specialized palette-text-image datasets and conduct extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses. Our results demonstrate that incorporating palette guidance significantly improves the model’s ability to generate images with desired color schemes, enabling a more controlled and refined colorization process.
随着扩散模型的出现,文本到图像(T2I)的生成技术取得了重大进展。当前的T2I模型允许用户使用语言中的颜色名称来指定对象颜色,一些方法旨在通过提示学习来实现颜色与对象的关联个性化。然而,现有模型在控制整个图像的颜色方案时遇到困难,尤其是对于背景元素和未明确提及的次要对象。本文提出了一种通过集成调色板作为独立于提示指令之外的指导机制来提高颜色方案控制的新方法。我们在基于扩散的图像彩色化框架内探索了各种调色板表示方法的有效性。为了促进这一探索,我们构建了专门的调色板-文本-图像数据集,并进行了广泛的定量和定性分析。结果表明,结合调色板指导可以显著提高模型生成具有所需颜色方案图像的能力,从而实现更可控和更精细的彩色化过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM 2025
Summary
随着扩散模型的出现,文本到图像(T2I)生成领域取得了重大进展。当前模型允许用户使用语言色彩名称指定对象颜色,但现有模型在控制整个图像的色彩方案上仍存在困难,特别是在背景元素和未明确提及的次要对象上。本文提出了一种通过集成色彩方案作为独立于提示指令的引导机制来提高色彩方案控制效果的新方法。通过探索基于扩散的图像着色框架中的不同色彩方案表示方法,我们调查了色彩方案指导的有效性。为了促进这一探索,我们构建了专门的色彩方案文本图像数据集,并进行了广泛的定量和定性分析。结果表明,引入色彩方案指导可以显著提高模型生成具有所需色彩方案的图像的能力,从而实现更可控和精细的着色过程。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成领域随着扩散模型的发展取得了重大进展。
- 当前模型允许用户使用语言指定对象颜色,但控制整个图像的色彩方案仍存在困难。
- 本文提出了一种通过集成色彩方案作为独立于提示指令的引导机制的新方法,以提高色彩方案的控制效果。
- 通过在基于扩散的图像着色框架中探索不同的色彩方案表示方法,调查了色彩方案指导的有效性。
- 为了促进探索,构建了专门的色彩方案文本图像数据集。
- 引入色彩方案指导可以显著提高模型生成具有所需色彩方案的图像的能力。
点此查看论文截图


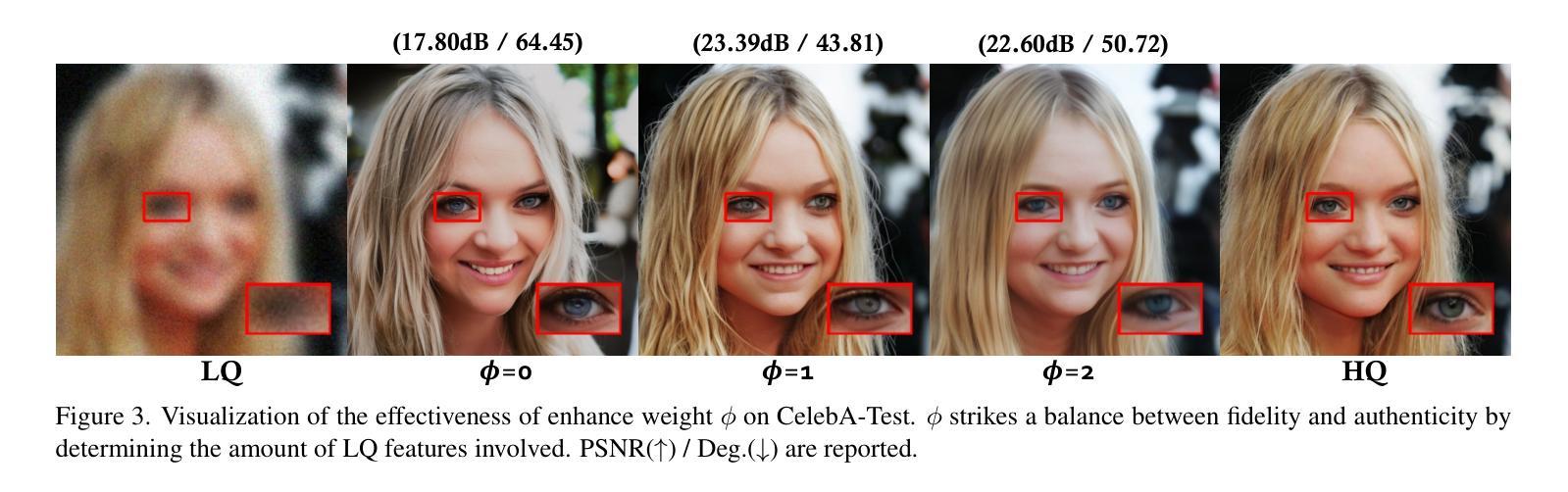
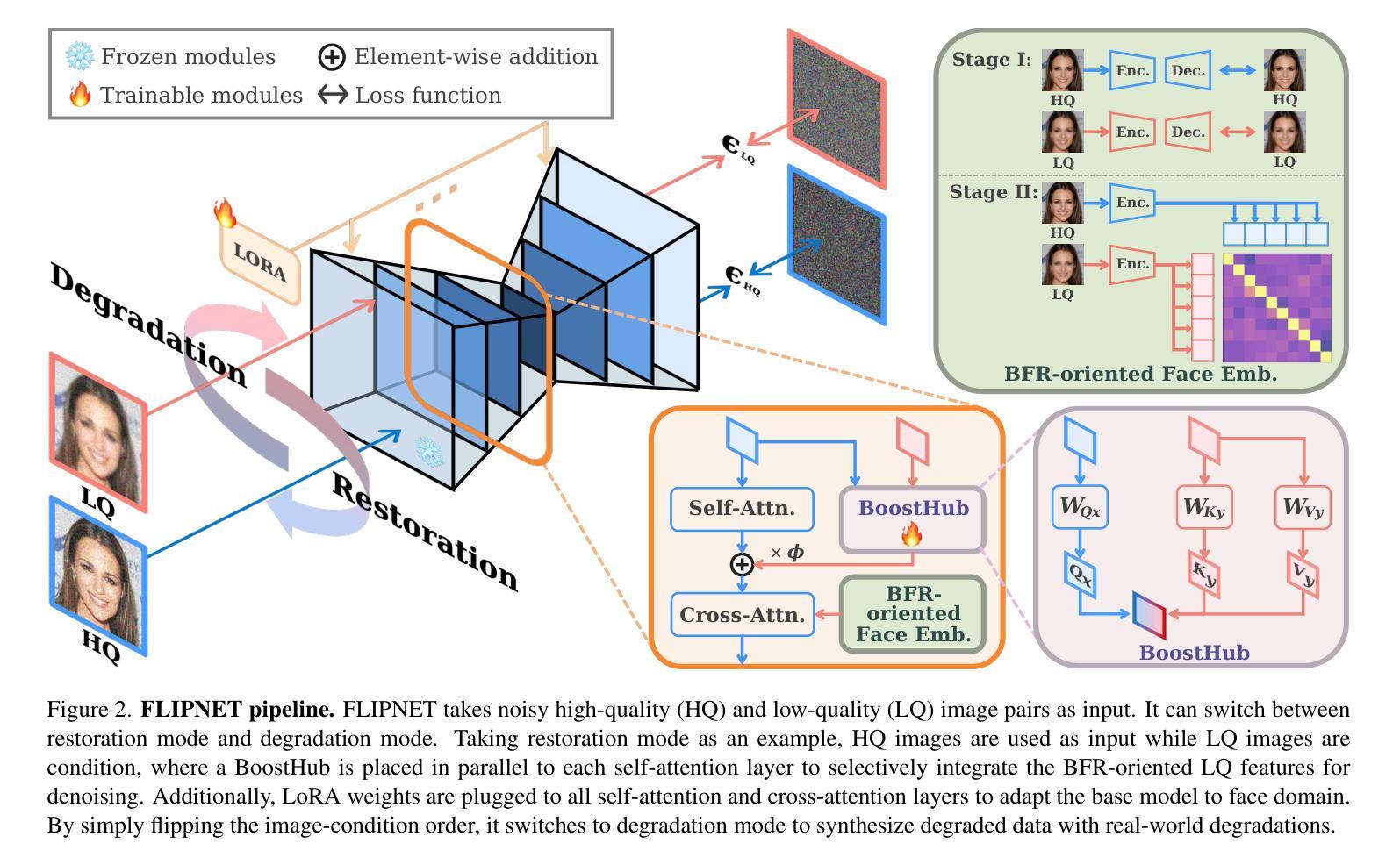
Unlocking the Potential of Diffusion Priors in Blind Face Restoration
Authors:Yunqi Miao, Zhiyu Qu, Mingqi Gao, Changrui Chen, Jifei Song, Jungong Han, Jiankang Deng
Although diffusion prior is rising as a powerful solution for blind face restoration (BFR), the inherent gap between the vanilla diffusion model and BFR settings hinders its seamless adaptation. The gap mainly stems from the discrepancy between 1) high-quality (HQ) and low-quality (LQ) images and 2) synthesized and real-world images. The vanilla diffusion model is trained on images with no or less degradations, whereas BFR handles moderately to severely degraded images. Additionally, LQ images used for training are synthesized by a naive degradation model with limited degradation patterns, which fails to simulate complex and unknown degradations in real-world scenarios. In this work, we use a unified network FLIPNET that switches between two modes to resolve specific gaps. In Restoration mode, the model gradually integrates BFR-oriented features and face embeddings from LQ images to achieve authentic and faithful face restoration. In Degradation mode, the model synthesizes real-world like degraded images based on the knowledge learned from real-world degradation datasets. Extensive evaluations on benchmark datasets show that our model 1) outperforms previous diffusion prior based BFR methods in terms of authenticity and fidelity, and 2) outperforms the naive degradation model in modeling the real-world degradations.
尽管扩散先验(diffusion prior)已经成为盲脸修复(BFR)的一种强大解决方案,但普通扩散模型与BFR设置之间的固有差距阻碍了其无缝适应。这一差距主要源于以下两点的不一致:1)高质量(HQ)与低质量(LQ)图像之间;2)合成图像与真实世界图像之间。普通扩散模型是在没有或较少退化的图像上进行训练的,而BFR则处理中度至重度退化的图像。此外,用于训练的低质量图像是由简单的退化模型合成的,具有有限的退化模式,无法模拟真实世界场景中的复杂和未知退化。在这项工作中,我们使用了一个统一网络FLIPNET,该网络可以在两种模式之间进行切换以解决特定的差距。在修复模式下,模型逐渐整合面向BFR的特征和人脸嵌入,从低质量图像中实现真实和忠诚的人脸修复。在退化模式下,模型基于从真实世界退化数据集中学习的知识,合成类似真实世界的退化图像。在基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型1)在真实性和保真度方面优于之前的基于扩散先验的BFR方法;2)在模拟真实世界退化方面优于简单的退化模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散先验虽然在盲脸修复(BFR)中展现出强大的解决方案潜力,但普通扩散模型与BFR设置之间存在固有差距,阻碍了其无缝适应。差距主要源于高质量(HQ)与低质量(LQ)图像、合成图像与真实世界图像之间的差异。普通扩散模型训练于无退化或较少退化的图像,而BFR处理中度至重度退化的图像。此外,用于训练的LQ图像由简单的退化模型合成,模拟的退化模式有限,无法模拟真实世界场景中的复杂和未知退化。本研究使用统一网络FLIPNET,可在两种模式之间切换以解决特定差距。修复模式下,模型逐渐融入面向BFR的特征和人脸嵌入自LQ图像,实现真实可信的人脸修复。退化模式下,模型基于从真实世界退化数据集中获得的知识,合成类似真实世界的退化图像。在基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型1)在真实性和保真度方面优于先前的扩散先验基于BFR的方法;2)在模拟真实世界退化方面优于简单的退化模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散先验在盲脸修复(BFR)中具有强大潜力,但存在与实际应用场景的差距。
- 差距主要源于高质量与低质量图像、合成与真实图像之间的差异。
- 普通扩散模型主要处理无退化或较少退化的图像,而BFR面临中度至重度退化图像的挑战。
- 现有退化模型无法充分模拟真实世界中的复杂和未知退化。
- FLIPNET网络通过两种模式解决上述问题:修复模式实现真实可信的人脸修复,退化模式合成类似真实世界的退化图像。
- 评估显示,FLIPNET在真实性和保真度方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图


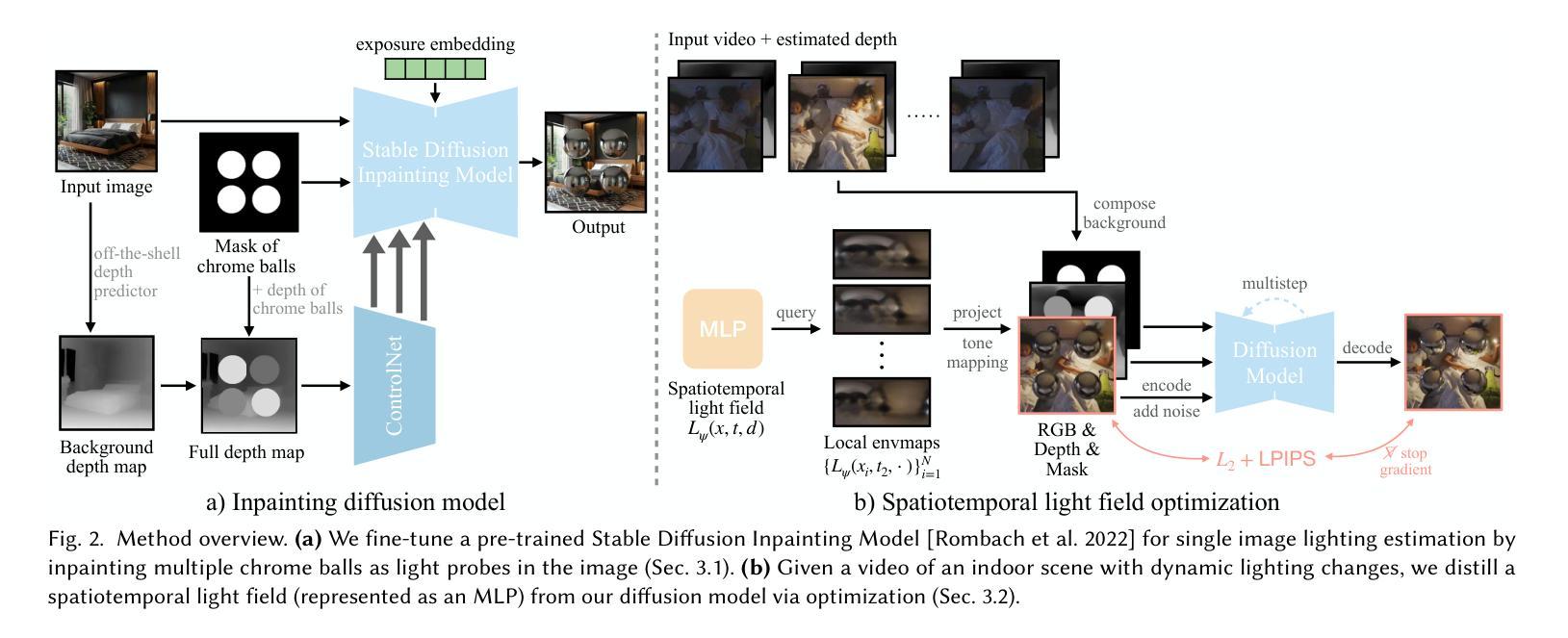
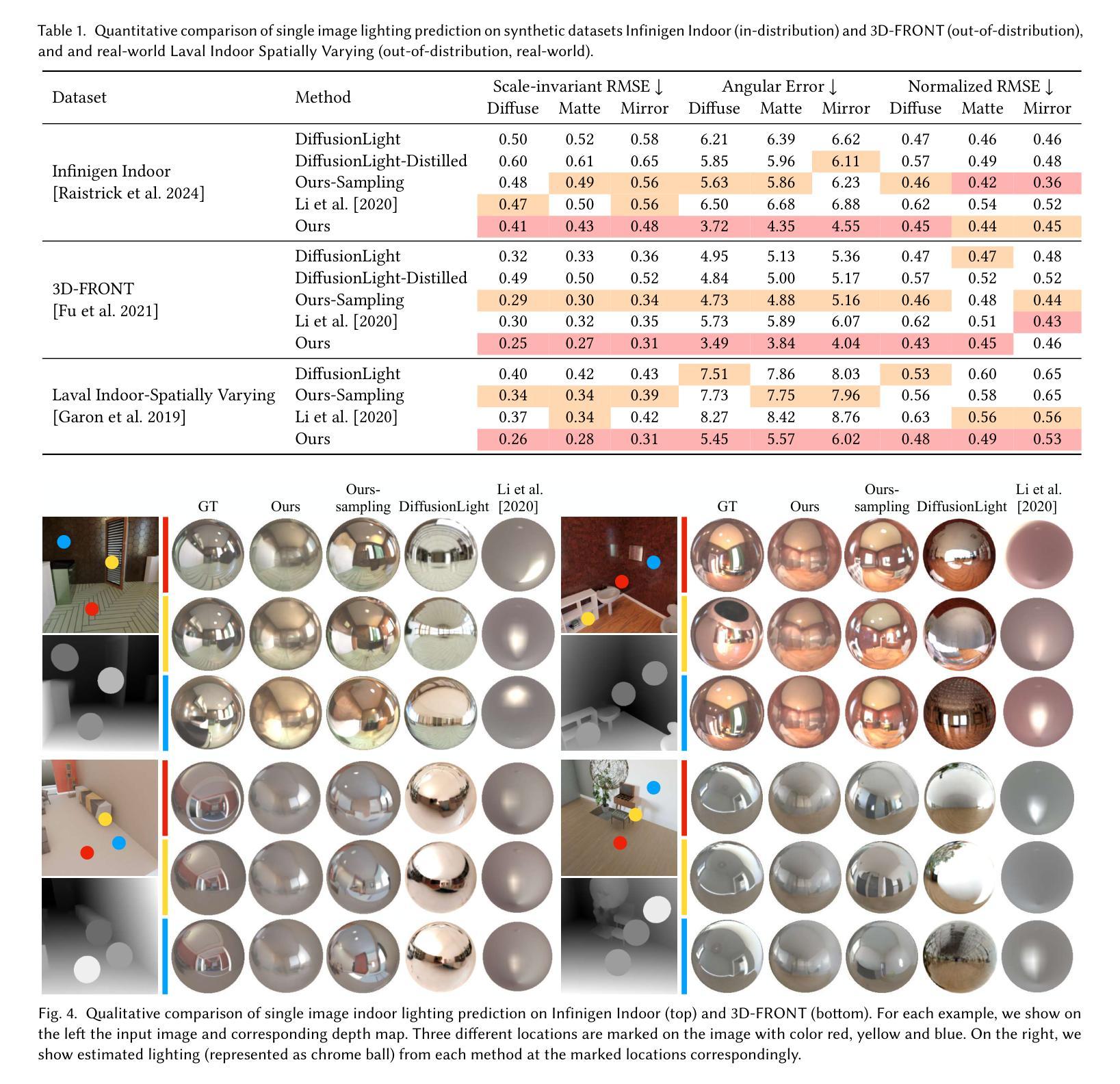
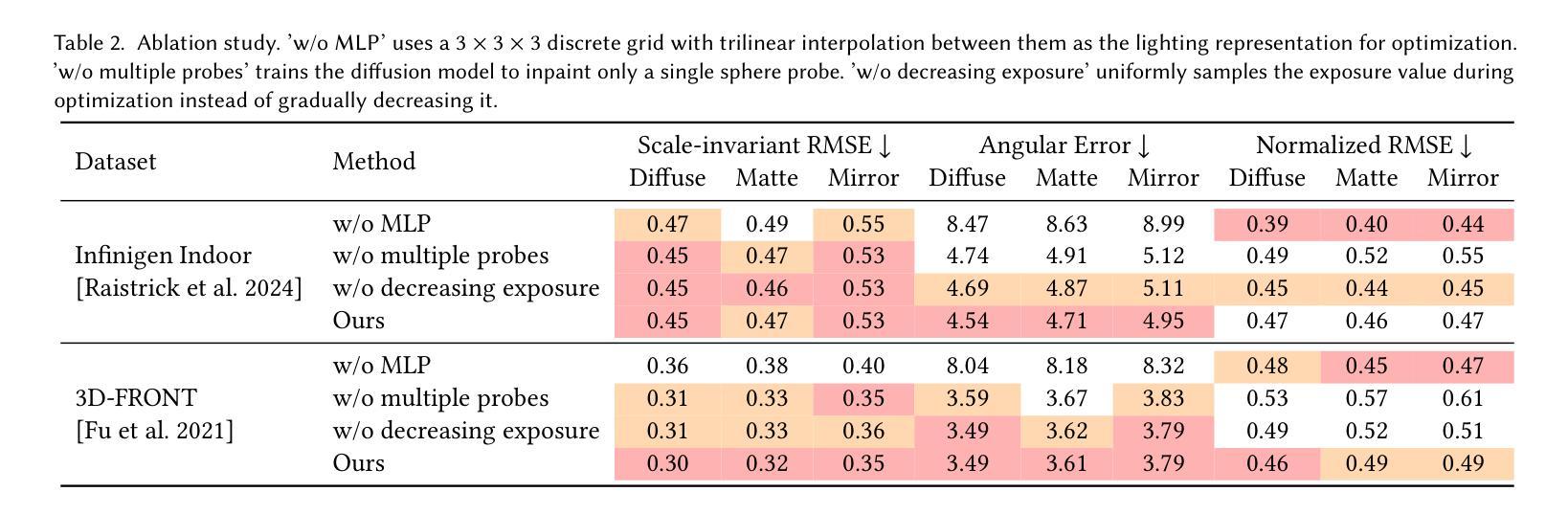
Spatiotemporally Consistent Indoor Lighting Estimation with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Mutian Tong, Rundi Wu, Changxi Zheng
Indoor lighting estimation from a single image or video remains a challenge due to its highly ill-posed nature, especially when the lighting condition of the scene varies spatially and temporally. We propose a method that estimates from an input video a continuous light field describing the spatiotemporally varying lighting of the scene. We leverage 2D diffusion priors for optimizing such light field represented as a MLP. To enable zero-shot generalization to in-the-wild scenes, we fine-tune a pre-trained image diffusion model to predict lighting at multiple locations by jointly inpainting multiple chrome balls as light probes. We evaluate our method on indoor lighting estimation from a single image or video and show superior performance over compared baselines. Most importantly, we highlight results on spatiotemporally consistent lighting estimation from in-the-wild videos, which is rarely demonstrated in previous works.
从单张图像或视频中估计室内照明仍然是一个挑战,因为其高度不适定的性质,尤其是当场景的光线条件在空间和时间上变化时。我们提出了一种方法,可以从输入视频中估计一个连续的灯光场,描述场景的空间和时间变化照明。我们利用二维扩散先验来优化表示为多层感知机的光场。为了实现对自然场景的零样本泛化,我们通过联合填充多个作为光探针的镀铬球来微调预训练的图像扩散模型,以预测多个位置的照明。我们在从单张图像或视频估计室内照明方面评估了我们的方法,并显示出优于对比基准的性能。最重要的是,我们强调了从自然视频中估计时空一致照明的结果,这在以前的工作中很少展示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages. Accepted by SIGGRAPH 2025 as Conference Paper
Summary
本文提出了一种从输入视频中估计场景时空变化照明的方法。利用二维扩散先验优化表示为多层感知机的光场,并通过微调预训练的图像扩散模型,以联合填充多个铬球作为光探针,实现对场景中多个位置的照明预测。在室内外照明估计中表现出卓越性能,特别是在对野外视频的时空一致性照明估计方面,优于现有工作。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决了从单一图像或视频中估计室内照明的问题,特别是当场景照明在空间和时间上变化时。
- 提出了一种连续光场估计方法,该方法从输入视频中描述场景的时空变化照明。
- 利用二维扩散先验优化光场的表示,该光场被表示为多层感知机(MLP)。
- 通过微调预训练的图像扩散模型,实现对多个位置的照明预测。
- 通过联合填充多个铬球作为光探针,增强了模型的预测能力。
- 在室内外照明估计方面表现出卓越性能,尤其是在对野外视频的照明估计方面。
点此查看论文截图


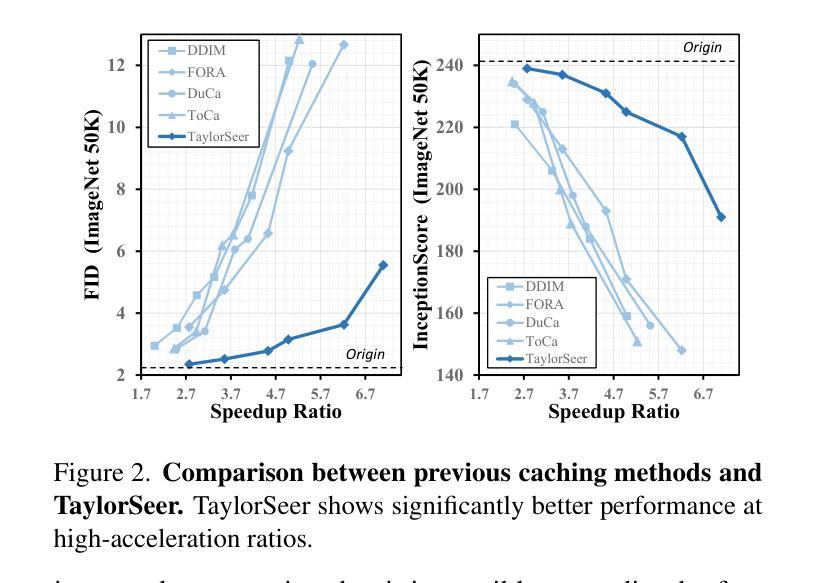
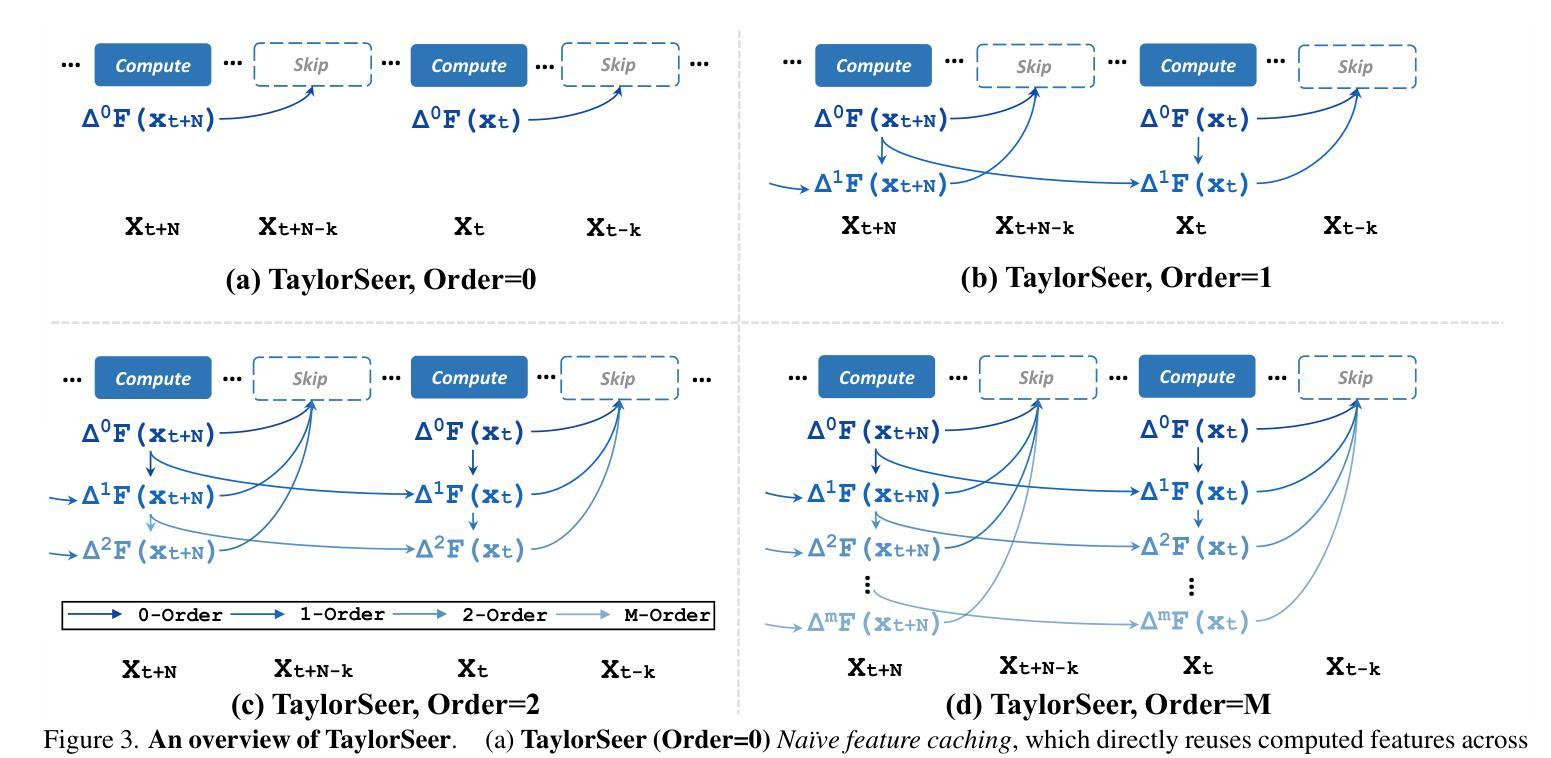
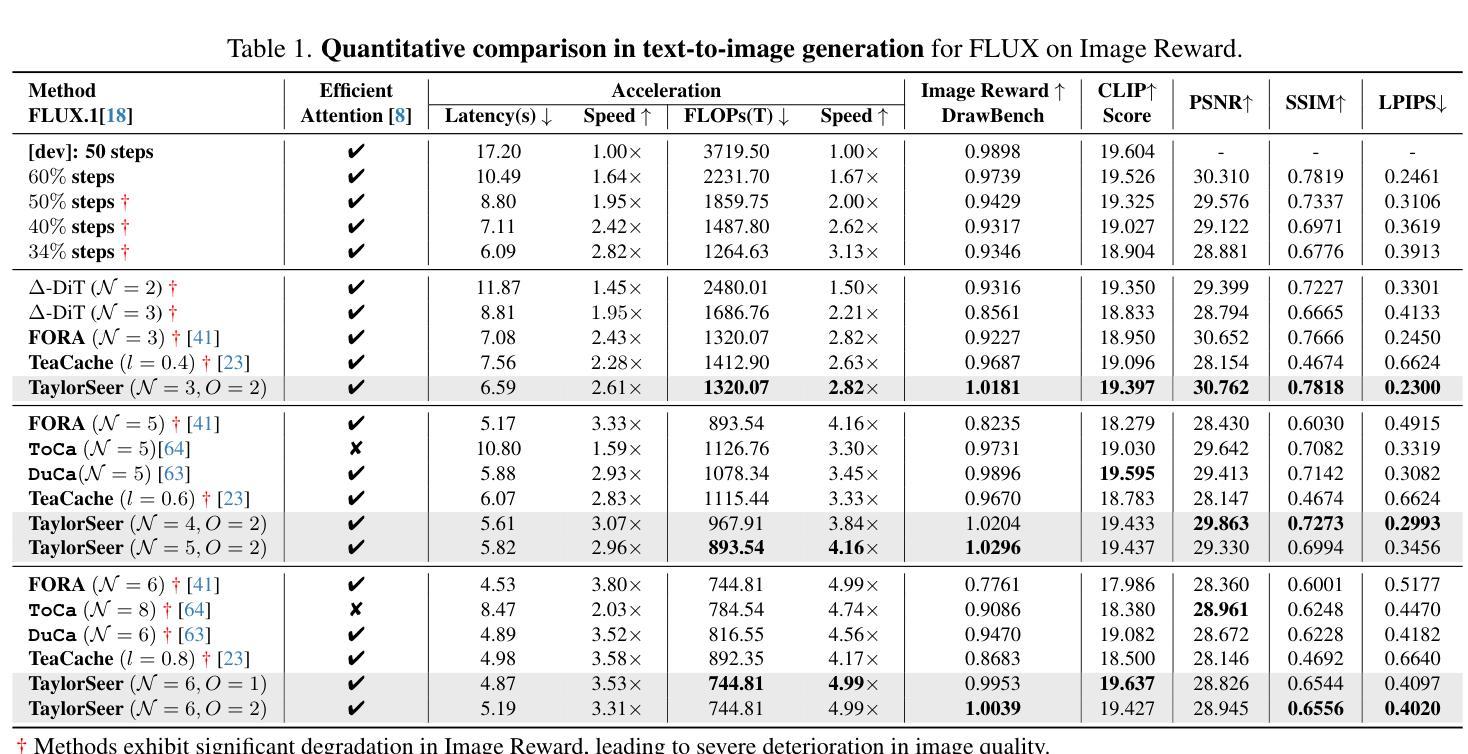
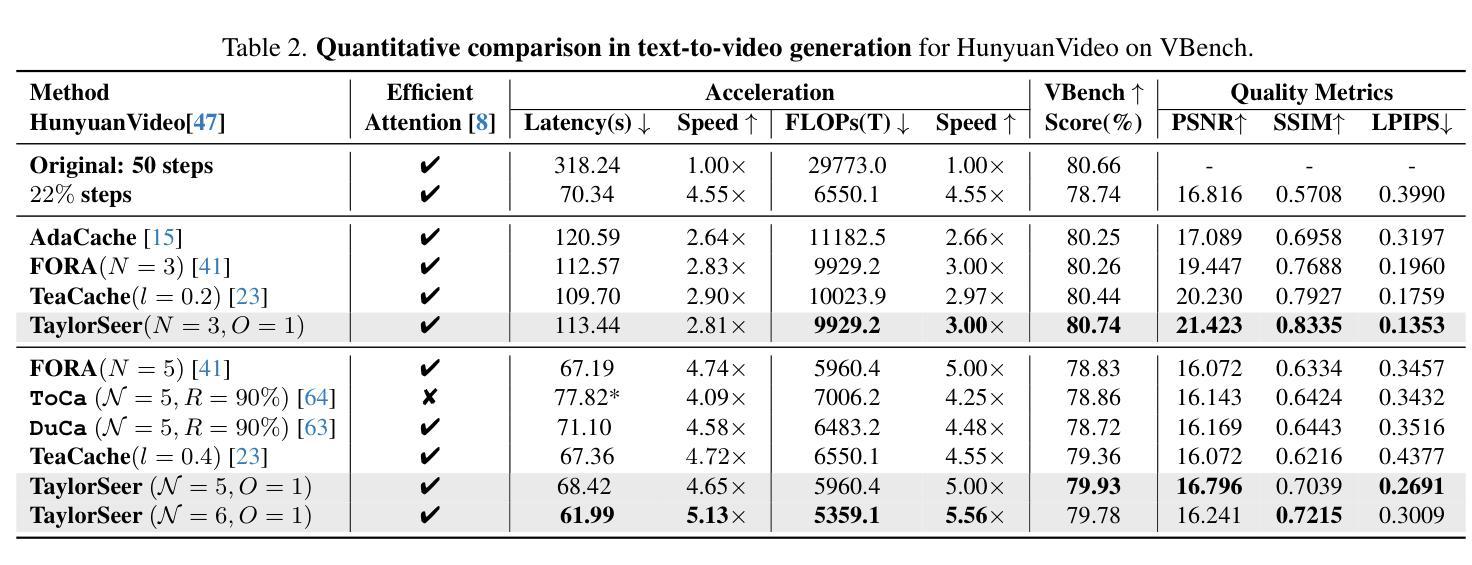
From Reusing to Forecasting: Accelerating Diffusion Models with TaylorSeers
Authors:Jiacheng Liu, Chang Zou, Yuanhuiyi Lyu, Junjie Chen, Linfeng Zhang
Diffusion Transformers (DiT) have revolutionized high-fidelity image and video synthesis, yet their computational demands remain prohibitive for real-time applications. To solve this problem, feature caching has been proposed to accelerate diffusion models by caching the features in the previous timesteps and then reusing them in the following timesteps. However, at timesteps with significant intervals, the feature similarity in diffusion models decreases substantially, leading to a pronounced increase in errors introduced by feature caching, significantly harming the generation quality. To solve this problem, we propose TaylorSeer, which firstly shows that features of diffusion models at future timesteps can be predicted based on their values at previous timesteps. Based on the fact that features change slowly and continuously across timesteps, TaylorSeer employs a differential method to approximate the higher-order derivatives of features and predict features in future timesteps with Taylor series expansion. Extensive experiments demonstrate its significant effectiveness in both image and video synthesis, especially in high acceleration ratios. For instance, it achieves an almost lossless acceleration of 4.99$\times$ on FLUX and 5.00$\times$ on HunyuanVideo without additional training. On DiT, it achieves $3.41$ lower FID compared with previous SOTA at $4.53$$\times$ acceleration. %Our code is provided in the supplementary materials and will be made publicly available on GitHub. Our codes have been released in Github:https://github.com/Shenyi-Z/TaylorSeer
扩散Transformer(DiT)已经实现了高保真图像和视频合成的革命性进展,但其计算需求仍然对于实时应用来说是巨大的。为了解决这一问题,提出了特征缓存来加速扩散模型,通过缓存前面时间步的特征并在后续时间步中重复使用它们。然而,在间隔时间较长的时间步中,扩散模型中的特征相似性会大幅下降,导致由特征缓存引入的错误显著增加,从而严重损害生成质量。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了TaylorSeer。它首先表明,扩散模型在未来时间步的特征可以基于它们在以前时间步的值进行预测。基于特征随时间步变化缓慢且连续的事实,TaylorSeer采用微分方法近似特征的高阶导数,并使用泰勒级数展开预测未来时间步的特征。大量实验证明,它在图像和视频合成中都取得了显著的有效性,特别是在高加速比的情况下。例如,它在FLUX和HunyuanVideo上实现了近乎无损的4.99×和5.00×的加速,无需额外的训练。在DiT上,与之前的最佳性能相比,它在加速4.53×的情况下实现了3.41更低的FID。我们的代码已作为补充材料提供,并将公开在GitHub上发布。我们的代码已发布在GitHub上:https://github.com/Shenyi-Z/TaylorSeer 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 14 figures; Accepted by ICCV2025; Mainly focus on feature caching for diffusion transformers acceleration
Summary
本文介绍了Diffusion Transformers(DiT)在高保真图像和视频合成中的革命性进展,但其计算需求仍然很大,不适用于实时应用。为解决这一问题,研究者提出了特征缓存来加速扩散模型,但在时间间隔较大的时刻,特征相似性会降低,导致特征缓存引入的错误增加,严重影响生成质量。针对这一问题,本文提出了TaylorSeer方法。该方法基于扩散模型在先前时刻的特征值来预测未来时刻的特征,并采用泰勒级数展开式进行预测。实验证明,该方法在图像和视频合成中效果显著,尤其在高速加速下表现更优秀。例如,在FLUX和HunyuanVideo上实现了近乎无损的加速,同时在DiT上实现了较低的FID得分。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Transformers (DiT) 已实现高保真图像和视频合成的重大突破。
- 特征缓存被提出以加速扩散模型,但在时间间隔大的时刻会出现问题。
- TaylorSeer方法利用先前时刻的特征预测未来时刻的特征。
- TaylorSeer采用微分法计算特征的高阶导数进行预测。
- 实验证明TaylorSeer在图像和视频合成中效果显著。
- TaylorSeer在高速加速下表现优秀,实现了近乎无损的加速。
点此查看论文截图

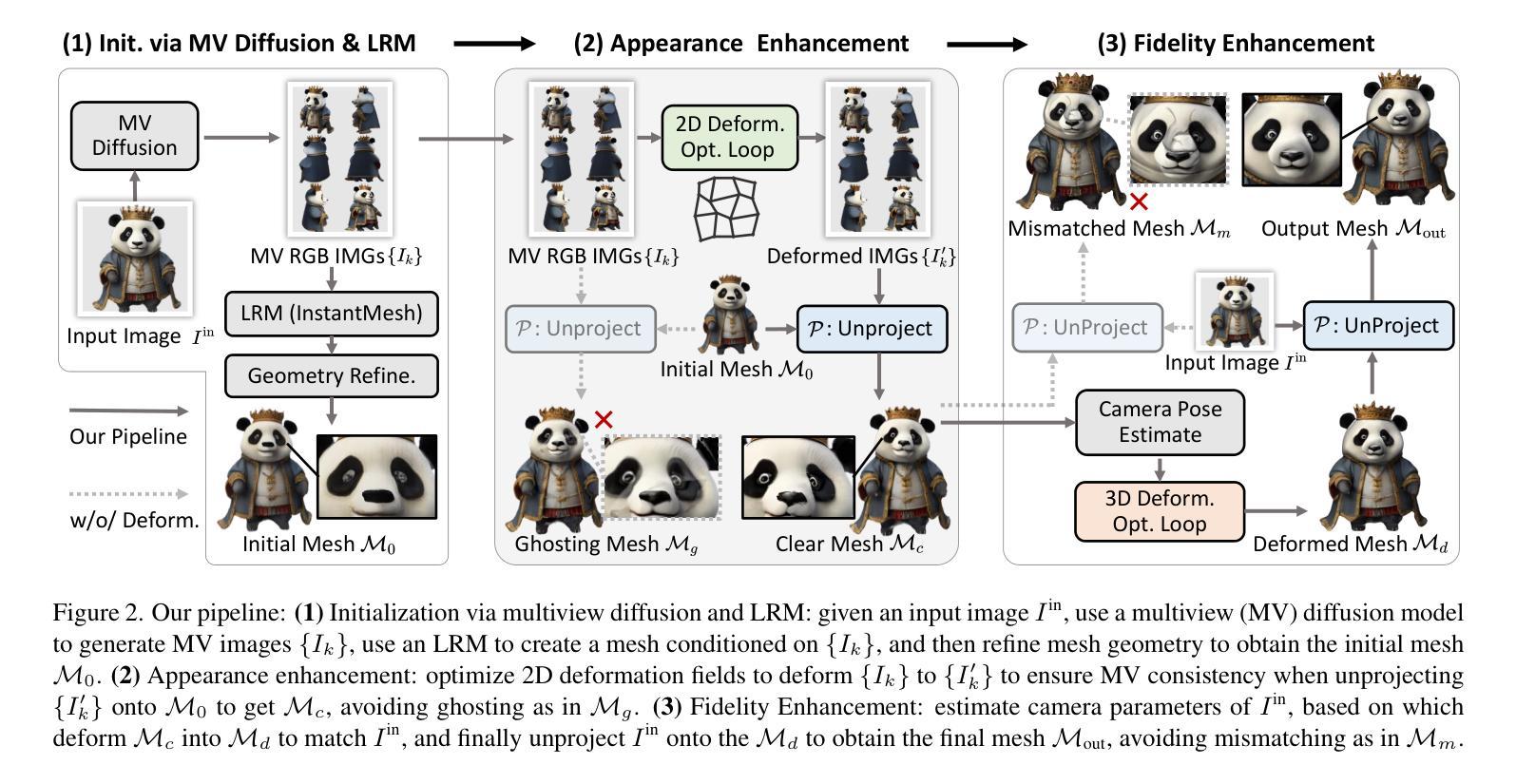
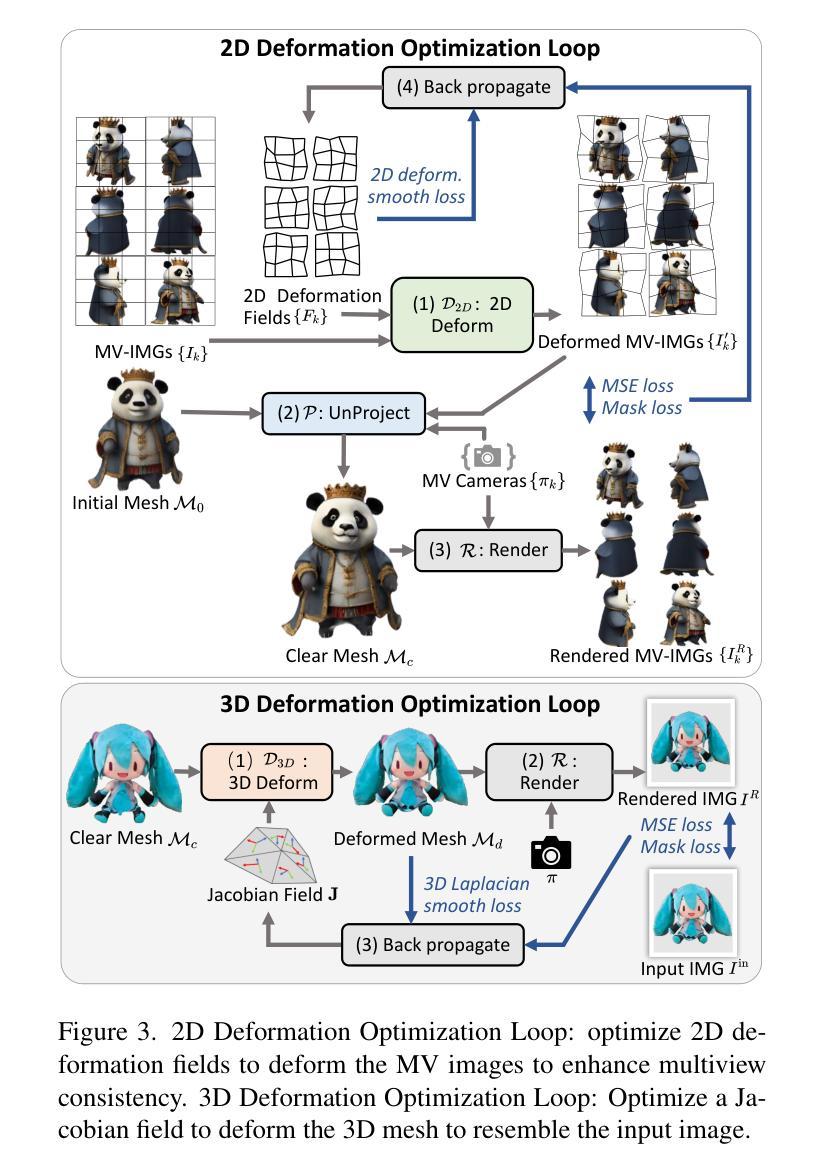
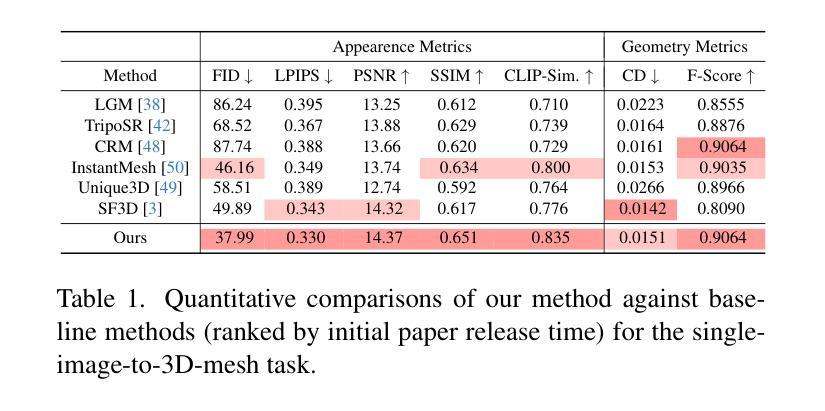
Fancy123: One Image to High-Quality 3D Mesh Generation via Plug-and-Play Deformation
Authors:Qiao Yu, Xianzhi Li, Yuan Tang, Xu Han, Long Hu, Yixue Hao, Min Chen
Generating 3D meshes from a single image is an important but ill-posed task. Existing methods mainly adopt 2D multiview diffusion models to generate intermediate multiview images, and use the Large Reconstruction Model (LRM) to create the final meshes. However, the multiview images exhibit local inconsistencies, and the meshes often lack fidelity to the input image or look blurry. We propose Fancy123, featuring two enhancement modules and an unprojection operation to address the above three issues, respectively. The appearance enhancement module deforms the 2D multiview images to realign misaligned pixels for better multiview consistency. The fidelity enhancement module deforms the 3D mesh to match the input image. The unprojection of the input image and deformed multiview images onto LRM’s generated mesh ensures high clarity, discarding LRM’s predicted blurry-looking mesh colors. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments verify Fancy123’s SoTA performance with significant improvement. Also, the two enhancement modules are plug-and-play and work at inference time, allowing seamless integration into various existing single-image-to-3D methods. Code at: https://github.com/YuQiao0303/Fancy123
从单一图像生成3D网格是一项重要但不适定的任务。现有方法主要采用2D多视角扩散模型生成中间多视角图像,并使用大型重建模型(LRM)创建最终的网格。然而,多视角图像存在局部不一致性,网格往往对输入图像的保真度不足或看起来模糊。我们提出Fancy123,它包含两个增强模块和一个反投影操作,分别解决上述三个问题。外观增强模块对2D多视角图像进行变形,以对齐错位像素,实现更好的多视角一致性。保真度增强模块对3D网格进行变形,以匹配输入图像。将输入图像和反投影后的多视角图像投影到LRM生成的网格上,确保高清晰度,摒弃LRM预测的模糊网格颜色。大量的定性和定量实验验证了Fancy123的最佳性能,并实现了显著的提升。此外,两个增强模块即插即用,可在推理阶段工作,可无缝集成到各种现有的单图像到3D的方法中。代码地址:https://github.com/YuQiao0303/Fancy123
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
基于现有技术生成单幅图像的三维网格是一项重要但难以解决的问题。现有方法主要采用二维多视角扩散模型生成中间多视角图像,并使用大型重建模型(LRM)创建最终网格。然而,多视角图像存在局部不一致性,网格往往缺乏与输入图像的保真度或看起来模糊。为此,我们提出了Fancy123方案,包括两个增强模块和一个反向投影操作。外观增强模块对二维多视角图像进行变形,以对齐错位像素,提高多视角一致性。保真度增强模块对三维网格进行变形,以匹配输入图像。将输入图像和变形的多视角图像投影到LRM生成的网格上,确保高清晰度,并摒弃LRM预测的模糊网格颜色。广泛的定性和定量实验验证了Fancy123的最佳性能,并实现了显著改进。此外,两个增强模块即插即用,可在推理过程中无缝集成到各种现有的单图像到三维转换方法中。代码已发布在:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 生成单幅图像的三维网格是一项重要且具有挑战的任务。
- 当前方法依赖二维多视角扩散模型和大型重建模型(LRM)。
- 多视角图像存在局部不一致性,且生成的网格常常模糊或与输入图像不匹配。
- Fancy123通过引入两个增强模块和一个反向投影操作来解决上述问题。
- 外观增强模块提高多视角一致性,而保真度增强模块确保网格与输入图像匹配。
- 通过将图像和变形后的多视角图像投影到LRM网格上,实现高清晰度输出。
点此查看论文截图

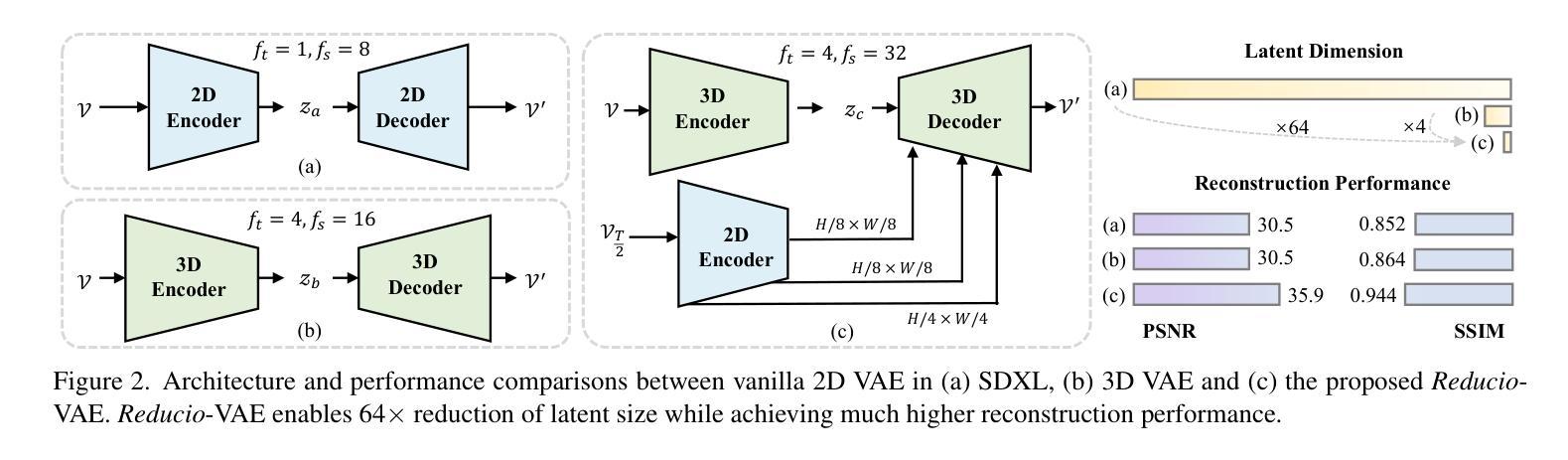
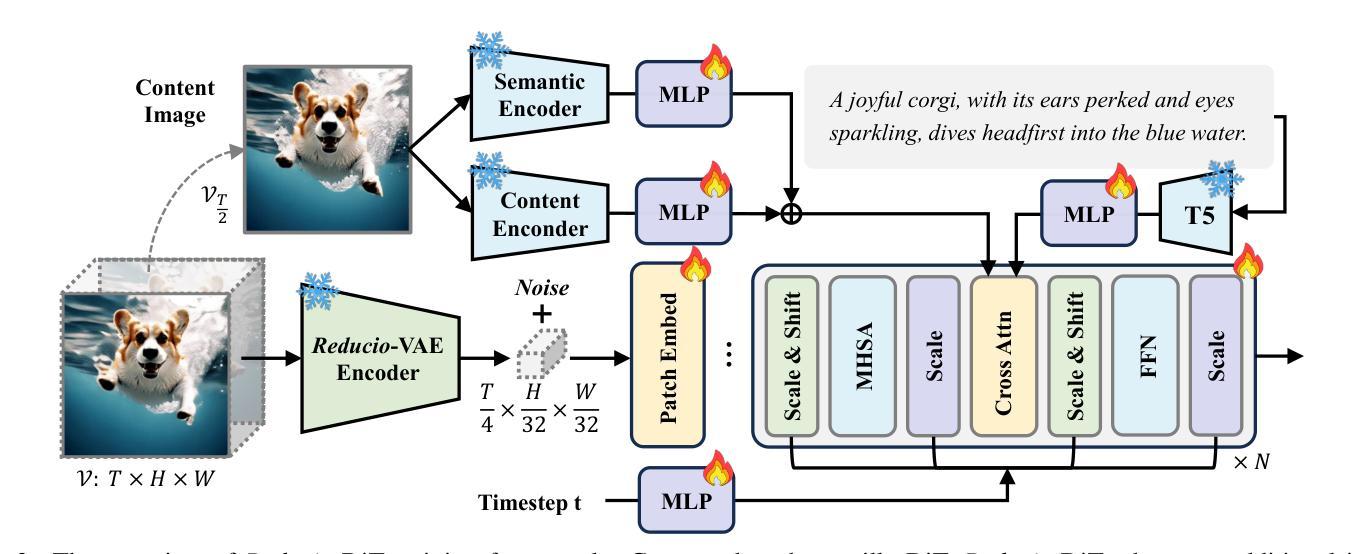
REDUCIO! Generating 1K Video within 16 Seconds using Extremely Compressed Motion Latents
Authors:Rui Tian, Qi Dai, Jianmin Bao, Kai Qiu, Yifan Yang, Chong Luo, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang
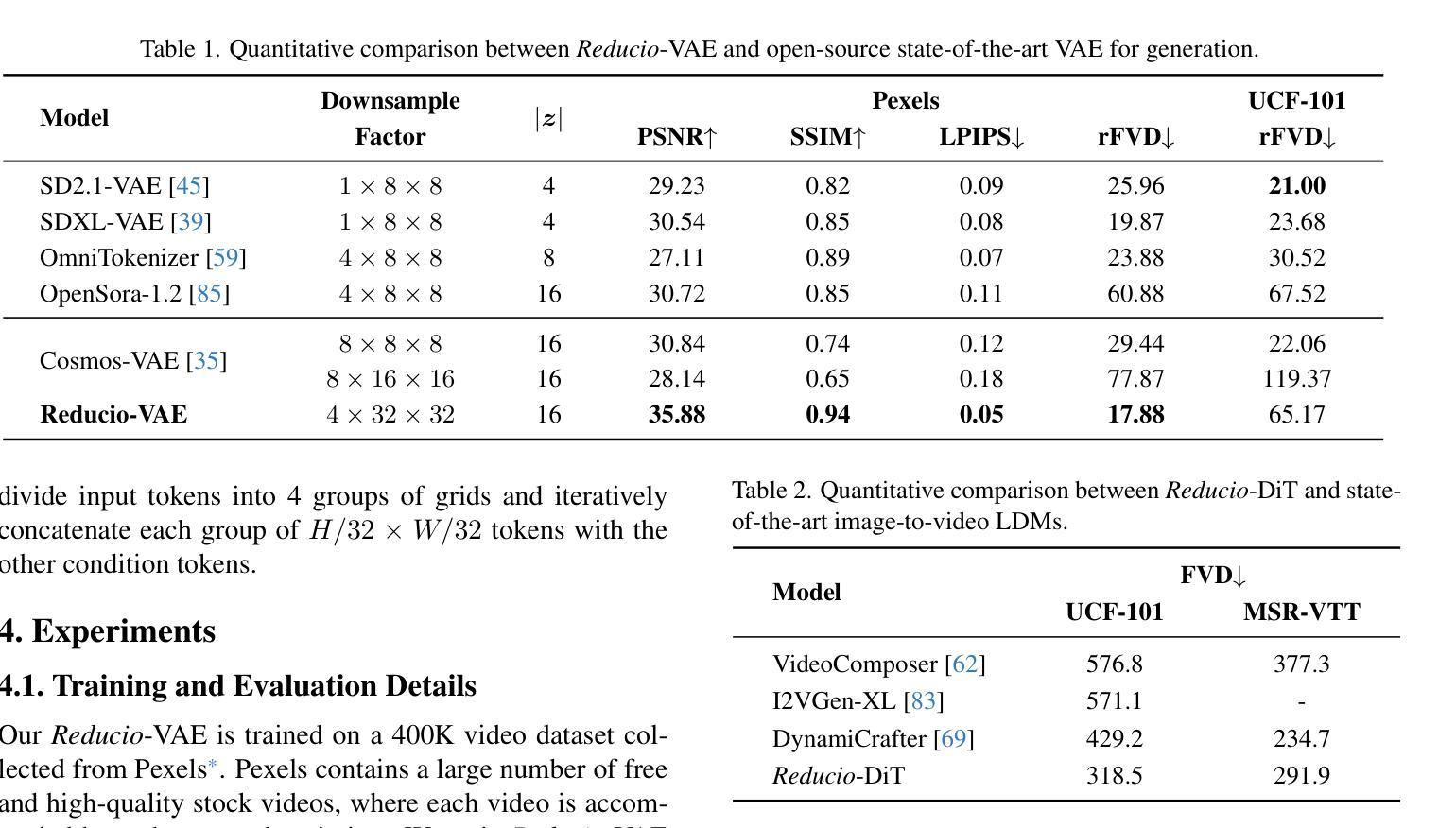
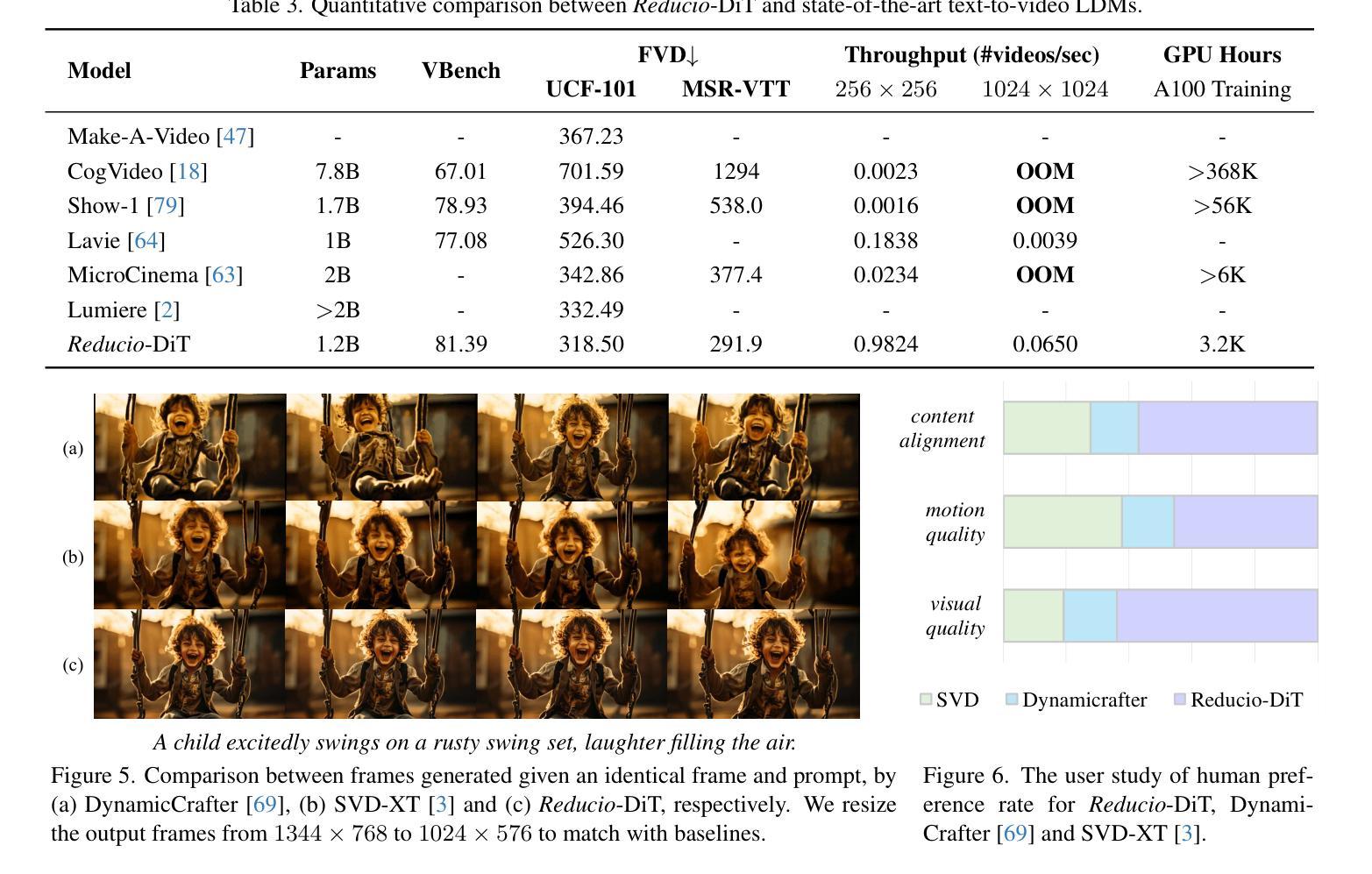
Commercial video generation models have exhibited realistic, high-fidelity results but are still restricted to limited access. One crucial obstacle for large-scale applications is the expensive training and inference cost. In this paper, we argue that videos contain significantly more redundant information than images, allowing them to be encoded with very few motion latents. Towards this goal, we design an image-conditioned VAE that projects videos into extremely compressed latent space and decode them based on content images. This magic Reducio charm enables 64x reduction of latents compared to a common 2D VAE, without sacrificing the quality. Building upon Reducio-VAE, we can train diffusion models for high-resolution video generation efficiently. Specifically, we adopt a two-stage generation paradigm, first generating a condition image via text-to-image generation, followed by text-image-to-video generation with the proposed Reducio-DiT. Extensive experiments show that our model achieves strong performance in evaluation. More importantly, our method significantly boosts the training and inference efficiency of video LDMs. Reducio-DiT is trained in just 3.2K A100 GPU hours in total and can generate a 16-frame 1024$\times$1024 video clip within 15.5 seconds on a single A100 GPU. Code released at https://github.com/microsoft/Reducio-VAE .
商业视频生成模型已经展现出逼真、高保真的结果,但仍然限于有限访问。大规模应用的一个关键障碍是训练和推理成本高。在本文中,我们认为视频包含比图像更多的冗余信息,因此可以用很少的动潜编码。为了达成这个目标,我们设计了一种基于图像条件的VAE(变分自编码器),它将视频投影到极压缩的潜在空间,并根据内容图像进行解码。这个神奇的Reducio咒语实现了与常见2D VAE相比的64倍潜空间减少,而不会牺牲质量。基于Reducio-VAE,我们可以有效地训练用于高分辨率视频生成的扩散模型。具体来说,我们采用两阶段生成范式,首先通过文本到图像生成条件图像,然后通过提出的Reducio-DiT进行文本图像到视频的生成。大量实验表明,我们的模型在评估中表现出强劲的性能。更重要的是,我们的方法显著提高了视频LDM的训练和推理效率。Reducio-DiT总共只需要3.2K个A100 GPU小时进行训练,并在单个A100 GPU上可以在15.5秒内生成一个16帧的1024x1024视频片段。代码已发布在https://github.com/microsoft/Reducio-VAE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV2025. Code available at https://github.com/microsoft/Reducio-VAE
Summary
视频生成模型虽能产生高保真结果,但训练与推理成本高昂,限制了其大规模应用。本文提出一种基于图像条件的VAE模型(Reducio-VAE),能将视频投影到高度压缩的潜在空间,并基于内容图像进行解码,实现了潜在空间的64倍缩减。在此基础上,本文训练了高效的扩散模型用于高分辨率视频生成。实验表明,该方法在评估中表现优异,显著提高了视频LDM的训练和推理效率。Reducio-DiT模型总训练时间仅为3.2K A100 GPU小时,可在单个A100 GPU上15.5秒内生成一个16帧的1024×1024视频片段。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了一种新的基于图像条件的VAE模型(Reducio-VAE),能有效压缩视频数据。
- Reducio-VAE实现了与常规2D VAE相比,潜在空间64倍的缩减,同时保证了视频质量。
- 基于Reducio-VAE,研究开发了高效的扩散模型用于视频生成。
- 该方法采用两阶段生成策略,先通过文本生成条件图像,再通过Reducio-DiT生成视频。
- 实验显示,该方法在评估中表现优异,并显著提高视频LDM的训练和推理效率。
- Reducio-DiT模型训练时间短,生成视频速度快。
点此查看论文截图


SynthVLM: Towards High-Quality and Efficient Synthesis of Image-Caption Datasets for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Zheng Liu, Hao Liang, Bozhou Li, Wentao Xiong, Chong Chen, Conghui He, Wentao Zhang, Bin Cui
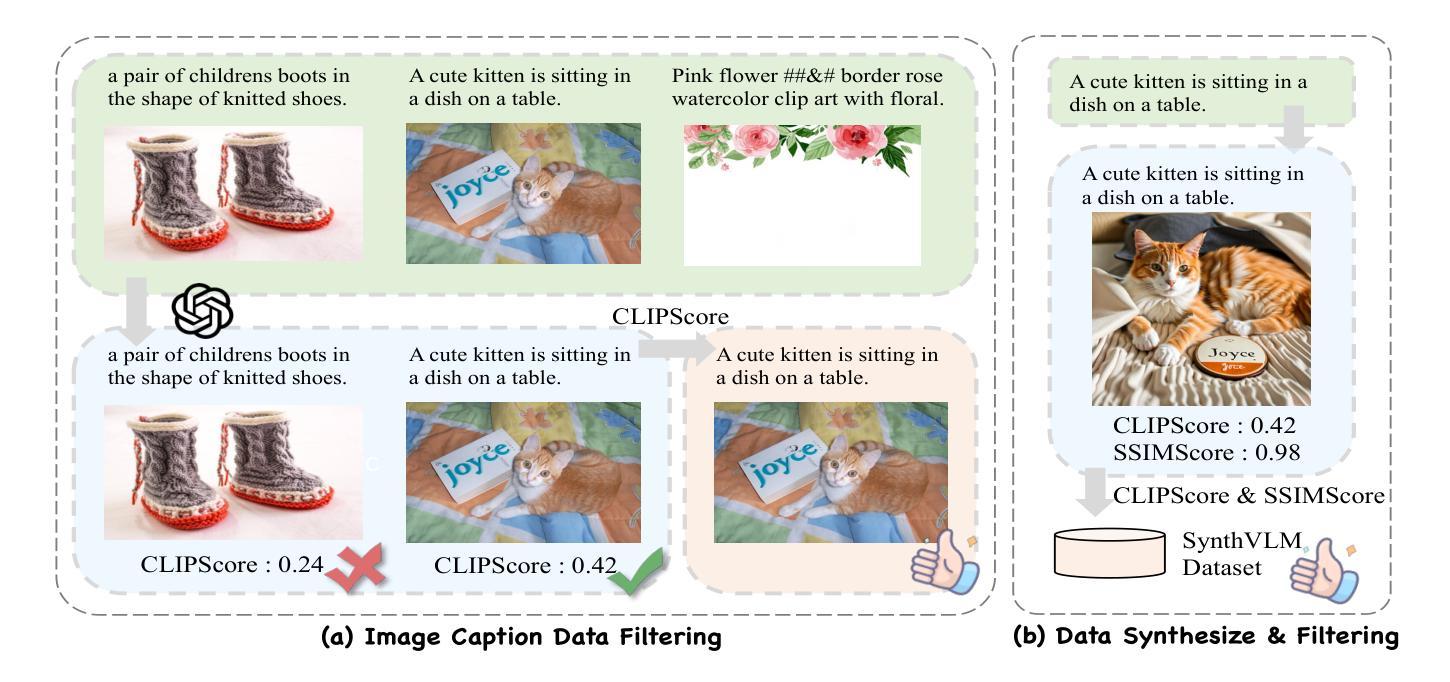
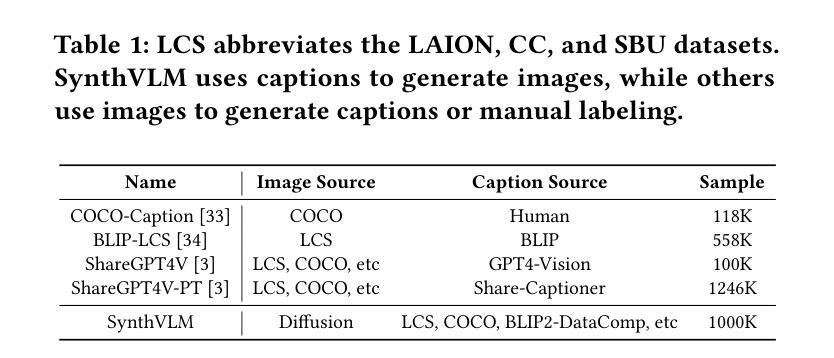
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently emerged, demonstrating remarkable vision-understanding capabilities. However, training these models requires large-scale datasets, which brings challenges related to efficiency, effectiveness, and quality of web data. In this paper, we introduce SynthVLM, a new data synthesis and curation method for generating image-caption pairs. Unlike traditional methods, where captions are generated from images, SynthVLM utilizes advanced diffusion models and high-quality captions to synthesize and select images from text captions, thereby creating precisely aligned image-text pairs. We further introduce SynthVLM-100K, a high-quality dataset consisting of 100K curated and synthesized image-caption pairs. In both model and human evaluations, SynthVLM-100K outperforms traditional real-world datasets. Leveraging this dataset, we develop a new family of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), SynthVLM-7B and SynthVLM-13B, which achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on various vision question-answering (VQA) tasks. Notably, our models outperform LLaVA across most metrics with only 18% pretrain data. Furthermore, SynthVLM-7B and SynthVLM-13B attain SOTA performance on the MMLU benchmark, demonstrating that the high-quality SynthVLM-100K dataset preserves language abilities.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近崭露头角,展现出卓越的视觉理解能力。然而,训练这些模型需要大规模数据集,这带来了与网页数据的效率、有效性和质量相关的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了SynthVLM,一种用于生成图像-字幕对的新数据合成和筛选方法。与传统的从图像生成字幕的方法不同,SynthVLM利用先进的扩散模型和高质量字幕,从文本字幕中合成并选择图像,从而创建精确对齐的图像文本对。我们还进一步介绍了SynthVLM-100K,这是一个高质量的数据集,包含10万个经过筛选和合成的图像-字幕对。在模型和人类评估中,SynthVLM-100K的表现都优于传统的现实世界数据集。利用这个数据集,我们开发了一系列新的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),包括SynthVLM-7B和SynthVLM-13B。它们在各种视觉问答(VQA)任务上达到了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,我们的模型在大多数指标上都优于LLaVA,并且只需要18%的预训练数据。此外,SynthVLM-7B和SynthVLM-13B在MMLU基准测试上也达到了最先进的性能,证明了高质量SynthVLM-100K数据集能够保留语言能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的数据合成与筛选方法——SynthVLM,用于生成图像-文字描述配对。该方法利用先进的扩散模型和高质量的文字描述来合成和筛选图像,创建精准对齐的图像-文字对。此外,还推出了SynthVLM-100K数据集,包含10万组高质量合成图像-文字描述对。基于此数据集,研发了新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)——SynthVLM-7B和SynthVLM-13B。这些模型在视觉问答任务上达到或超越了现有技术水平的性能表现,并且在仅使用18%的预训练数据的情况下,就已在多数指标上超越了LLaVA。同时,它们在MMLU基准测试上也取得了卓越表现,证明了SynthVLM-100K数据集的高质量。
Key Takeaways
- SynthVLM是一种新的数据合成与筛选方法,用于生成图像-文字描述配对。
- 该方法利用扩散模型和高质量文字描述进行图像合成和筛选。
- 推出了包含10万组高质量合成图像-文字描述对的数据集SynthVLM-100K。
- 基于SynthVLM-100K数据集,研发了新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)——SynthVLM-7B和SynthVLM-13B。
- 这些模型在视觉问答任务上达到或超越了现有技术水平。
- 在仅使用少量预训练数据的情况下,这些模型已超越LLaVA在多数指标上的表现。
点此查看论文截图


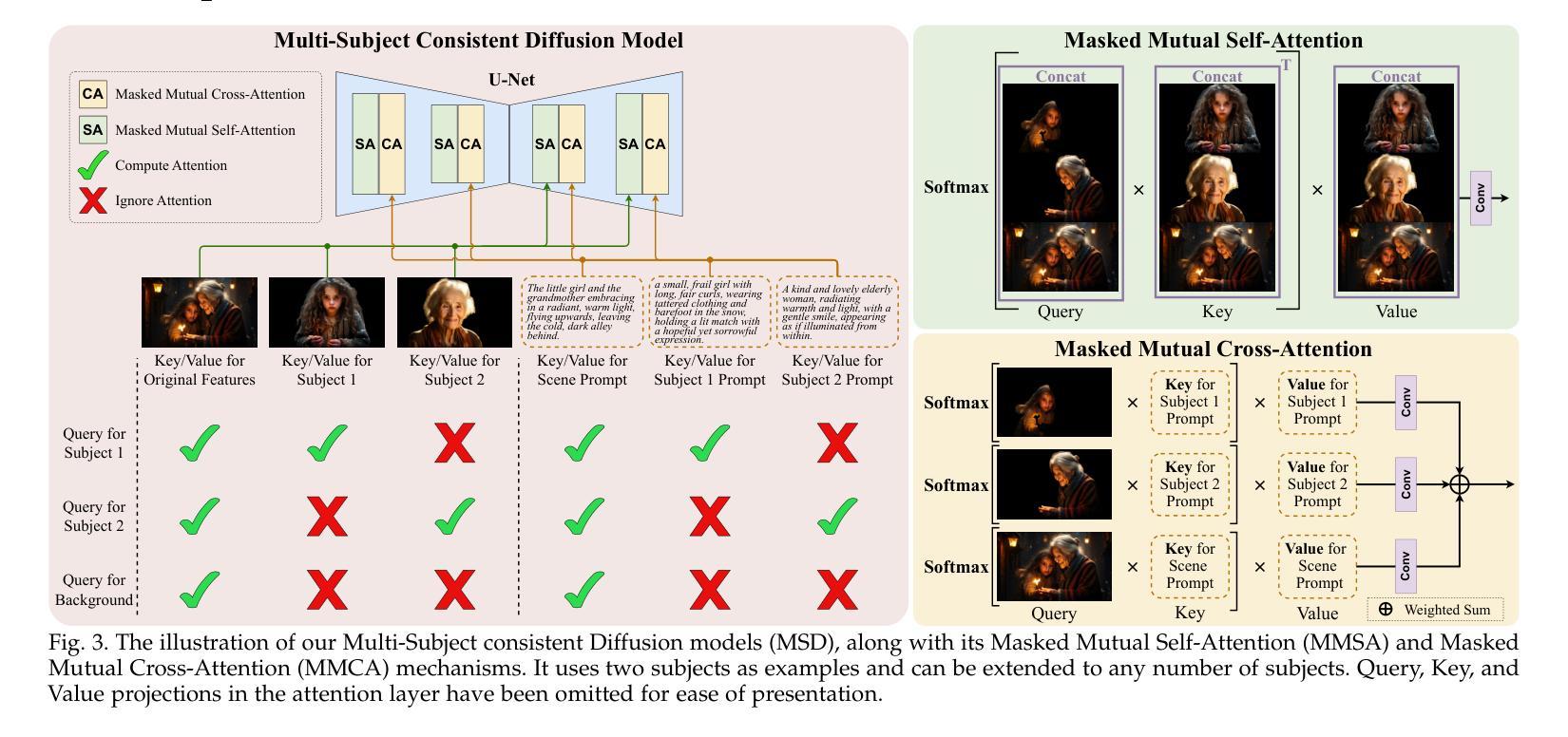
DreamStory: Open-Domain Story Visualization by LLM-Guided Multi-Subject Consistent Diffusion
Authors:Huiguo He, Huan Yang, Zixi Tuo, Yuan Zhou, Qiuyue Wang, Yuhang Zhang, Zeyu Liu, Wenhao Huang, Hongyang Chao, Jian Yin
Story visualization aims to create visually compelling images or videos corresponding to textual narratives. Despite recent advances in diffusion models yielding promising results, existing methods still struggle to create a coherent sequence of subject-consistent frames based solely on a story. To this end, we propose DreamStory, an automatic open-domain story visualization framework by leveraging the LLMs and a novel multi-subject consistent diffusion model. DreamStory consists of (1) an LLM acting as a story director and (2) an innovative Multi-Subject consistent Diffusion model (MSD) for generating consistent multi-subject across the images. First, DreamStory employs the LLM to generate descriptive prompts for subjects and scenes aligned with the story, annotating each scene’s subjects for subsequent subject-consistent generation. Second, DreamStory utilizes these detailed subject descriptions to create portraits of the subjects, with these portraits and their corresponding textual information serving as multimodal anchors (guidance). Finally, the MSD uses these multimodal anchors to generate story scenes with consistent multi-subject. Specifically, the MSD includes Masked Mutual Self-Attention (MMSA) and Masked Mutual Cross-Attention (MMCA) modules. MMSA and MMCA modules ensure appearance and semantic consistency with reference images and text, respectively. Both modules employ masking mechanisms to prevent subject blending. To validate our approach and promote progress in story visualization, we established a benchmark, DS-500, which can assess the overall performance of the story visualization framework, subject-identification accuracy, and the consistency of the generation model. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of DreamStory in both subjective and objective evaluations. Please visit our project homepage at https://dream-xyz.github.io/dreamstory.
故事可视化旨在根据文本叙事创建具有视觉吸引力的图像或视频。尽管扩散模型领域最近的进展带来了充满希望的结果,但现有方法仍然难以仅根据故事来创建连贯且主题一致的画面序列。为此,我们提出了DreamStory,一个利用大型语言模型(LLM)和新型多主题一致扩散模型的自动开放域故事可视化框架。DreamStory包括(1)作为故事导演的大型语言模型(LLM)和(2)用于生成图像中一致多主题的创新多主题一致扩散模型(MSD)。首先,DreamStory使用LLM生成与故事对齐的主题和场景的描述性提示,并为每个场景的主题是进行标注,以便于后续的主题一致生成。其次,DreamStory利用这些详细的主题描述来创建主题人物的肖像,这些肖像及其相应的文本信息作为多模态锚点(指导)。最后,MSD使用这些多模态锚点来生成具有一致多主题的故事场景。具体来说,MSD包括Masked Mutual Self-Attention(MMSA)和Masked Mutual Cross-Attention(MMCA)模块。MMSA和MMCA模块分别确保与参考图像的外观和语义一致性。两个模块都使用屏蔽机制来防止主题混合。为了验证我们的方法和促进故事可视化领域的进展,我们建立了一个基准测试DS-500,它可以评估故事可视化框架的整体性能、主题识别准确性和生成模型的一致性。大量实验验证了DreamStory在主观和客观评估中的有效性。请访问我们的项目主页:https://dream-xyz.github.io/dreamstory。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TPAMI
Summary
针对故事可视化的问题,提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)和新型多主题一致扩散模型的自动开放域故事可视化框架DreamStory。DreamStory通过LLM生成与故事相符的描述性提示,为场景和主题提供注解,并利用这些描述创建人物肖像作为多模态锚点,指导后续生成。此外,还提出了多主题一致扩散模型(MSD),包括Masked Mutual Self-Attention (MMSA)和Masked Mutual Cross-Attention (MMCA)模块,确保图像和文本的一致性和参照性。最后建立了评估故事可视化框架性能的基准DS-500。
Key Takeaways
- DreamStory是一个结合LLM和新型多主题一致扩散模型的自动开放域故事可视化框架。
- LLM用于生成描述性提示,为故事场景和主题提供注解。
- 利用详细的主题描述创建人物肖像作为多模态锚点(指导生成)。
- MSD模型包括MMSA和MMCA模块,确保图像和文本的一致性和参照性。
- 建立了DS-500基准,用于评估故事可视化框架的性能、主题识别准确性和生成模型的一致性。
- DreamStory在主观和客观评估中均表现出有效性。
点此查看论文截图

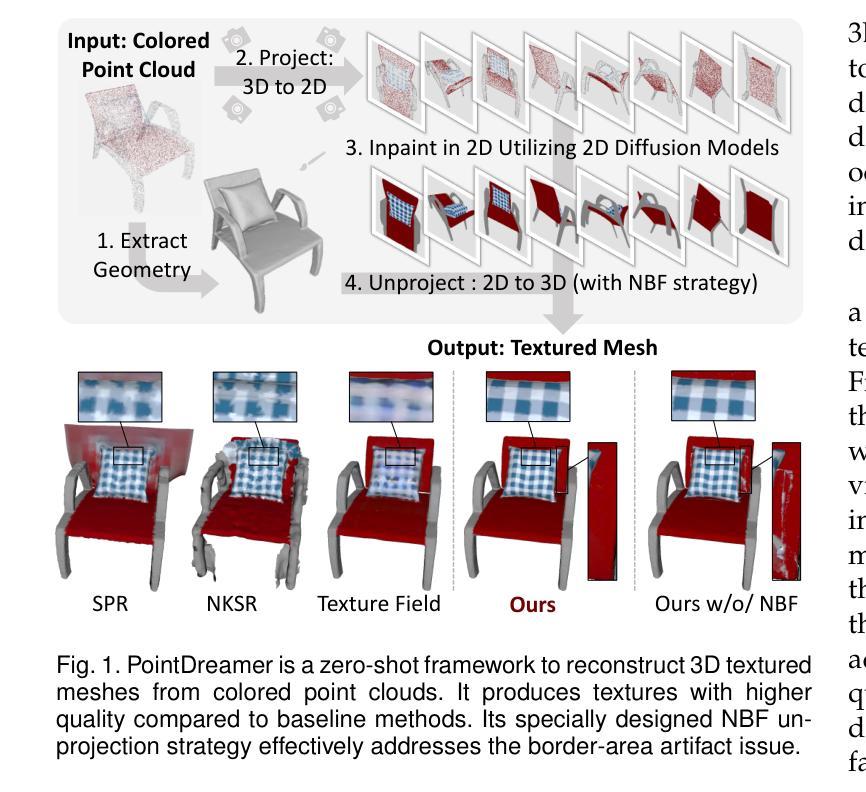
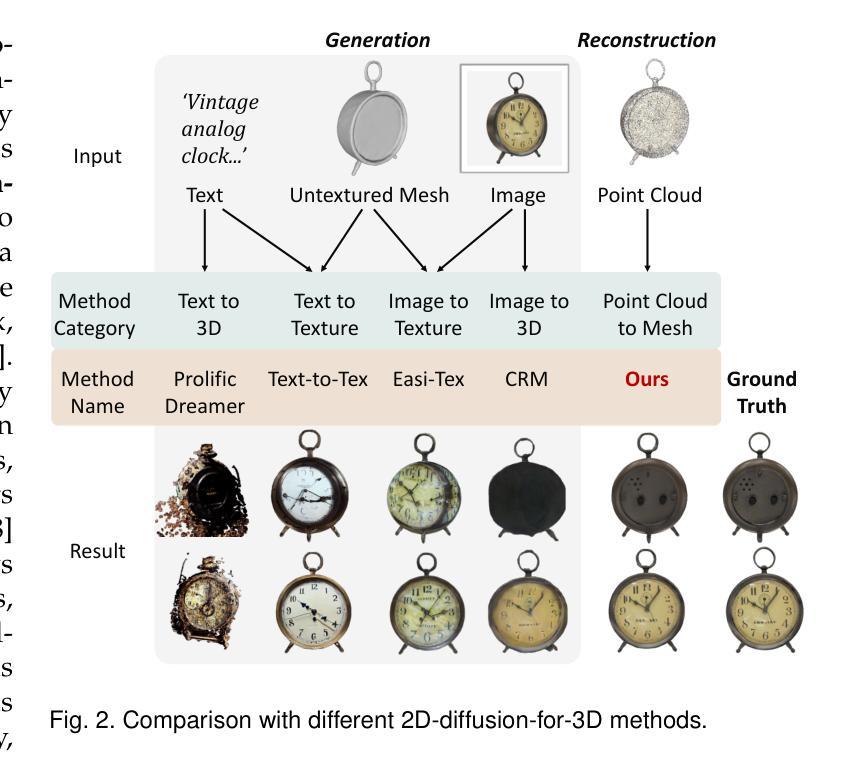
PointDreamer: Zero-shot 3D Textured Mesh Reconstruction from Colored Point Cloud
Authors:Qiao Yu, Xianzhi Li, Yuan Tang, Xu Han, Jinfeng Xu, Long Hu, Min Chen
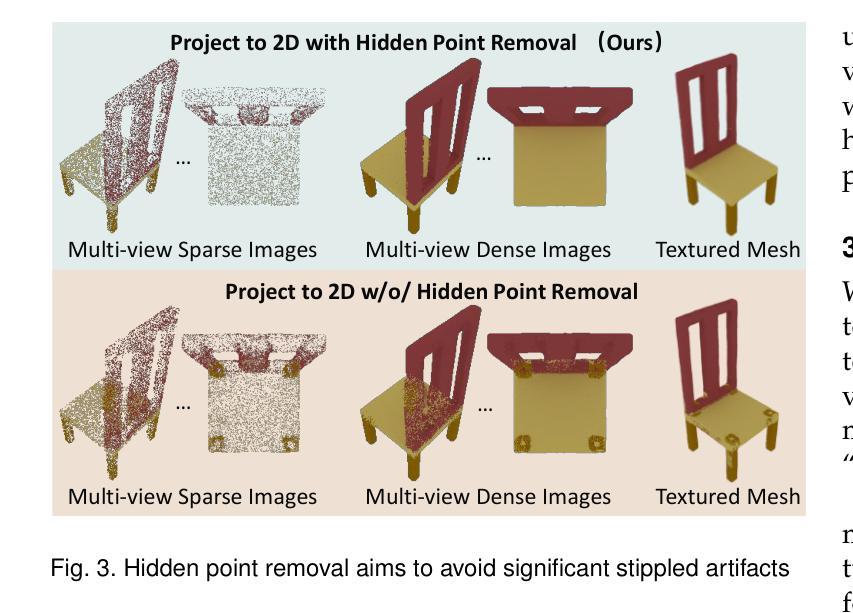
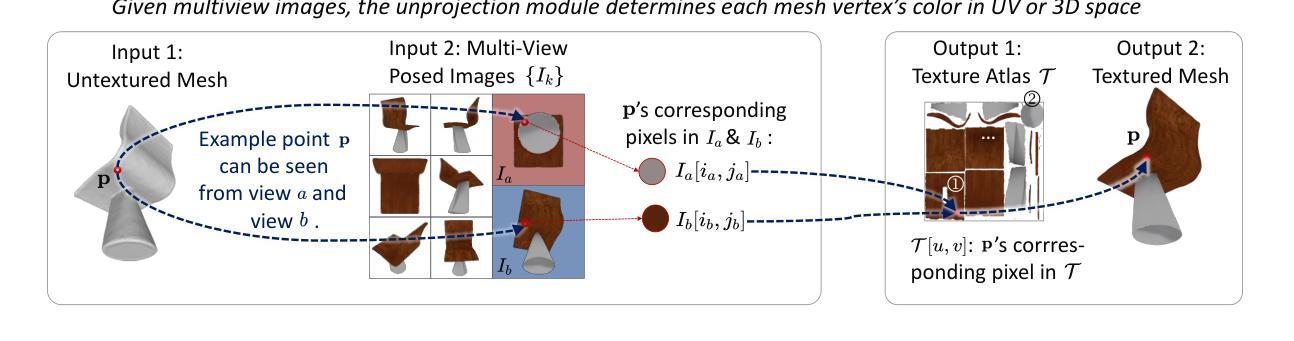
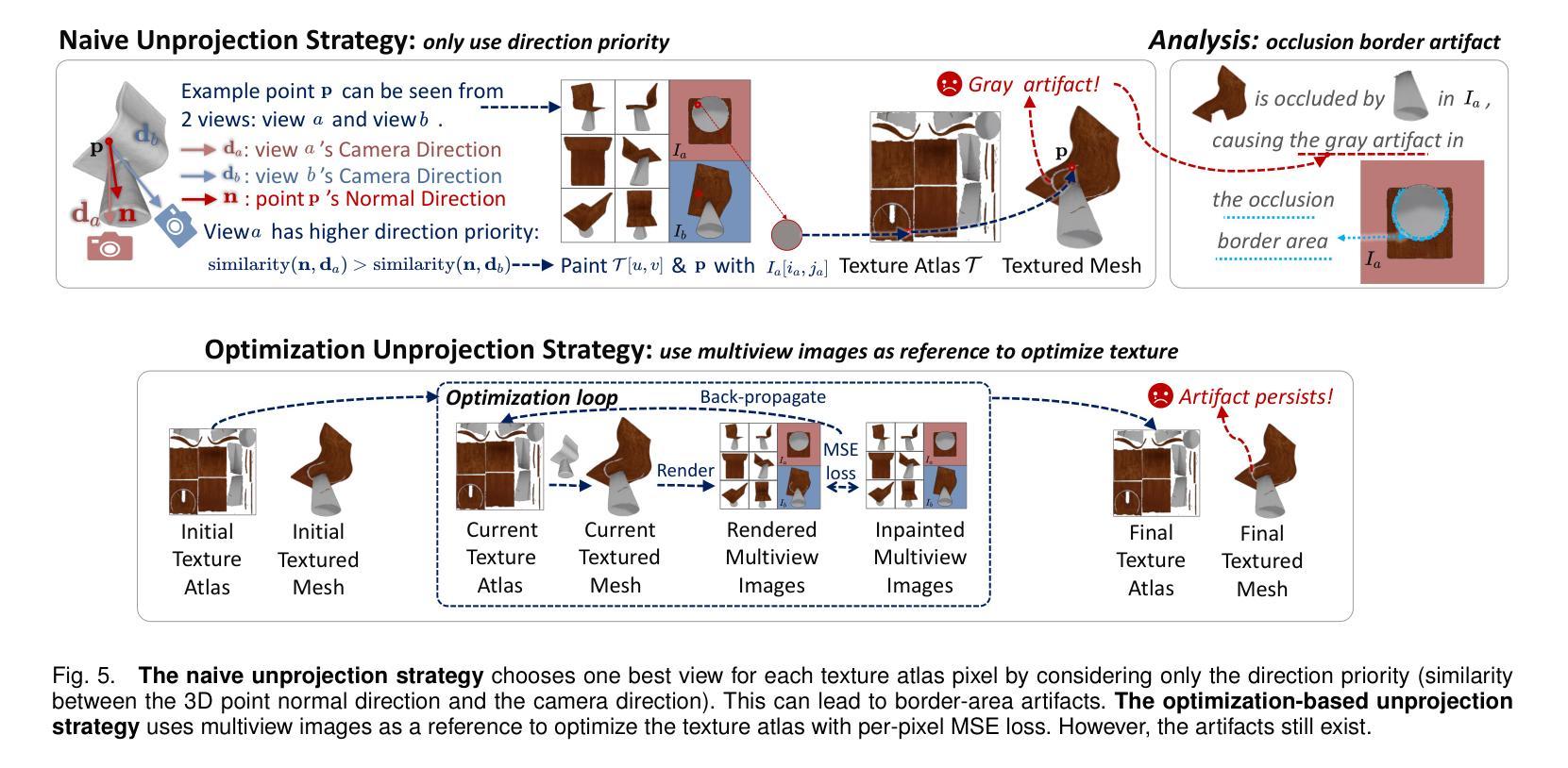
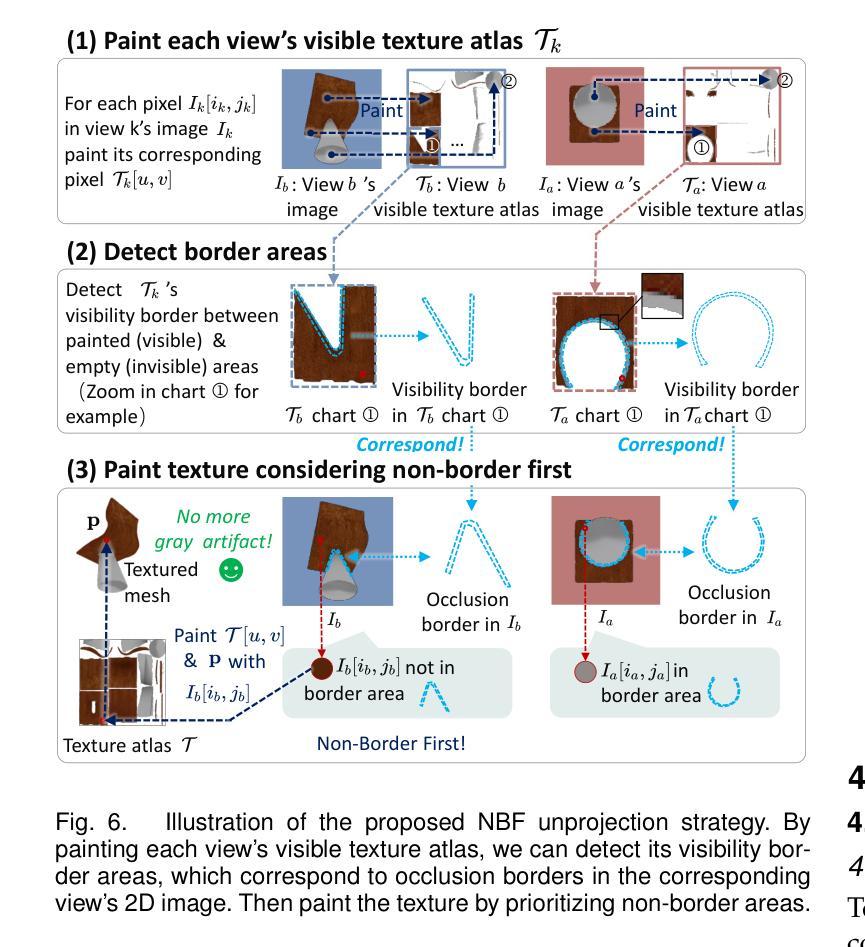
Faithfully reconstructing textured meshes is crucial for many applications. Compared to text or image modalities, leveraging 3D colored point clouds as input (colored-PC-to-mesh) offers inherent advantages in comprehensively and precisely replicating the target object’s 360{\deg} characteristics. While most existing colored-PC-to-mesh methods suffer from blurry textures or require hard-to-acquire 3D training data, we propose PointDreamer, a novel framework that harnesses 2D diffusion prior for superior texture quality. Crucially, unlike prior 2D-diffusion-for-3D works driven by text or image inputs, PointDreamer successfully adapts 2D diffusion models to 3D point cloud data by a novel project-inpaint-unproject pipeline. Specifically, it first projects the point cloud into sparse 2D images and then performs diffusion-based inpainting. After that, diverging from most existing 3D reconstruction or generation approaches that predict texture in 3D/UV space thus often yielding blurry texture, PointDreamer achieves high-quality texture by directly unprojecting the inpainted 2D images to the 3D mesh. Furthermore, we identify for the first time a typical kind of unprojection artifact appearing in occlusion borders, which is common in other multiview-image-to-3D pipelines but less-explored. To address this, we propose a novel solution named the Non-Border-First (NBF) unprojection strategy. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on various synthetic and real-scanned datasets demonstrate that PointDreamer, though zero-shot, exhibits SoTA performance (30% improvement on LPIPS score from 0.118 to 0.068), and is robust to noisy, sparse, or even incomplete input data. Code at: https://github.com/YuQiao0303/PointDreamer.
纹理网格的忠实重建对于许多应用至关重要。与文本或图像模式相比,利用三维彩色点云作为输入(彩色点云到网格)在全面和精确地复制目标对象的360°特征方面具有固有的优势。尽管大多数现有的彩色点云到网格的方法存在纹理模糊的问题,或者需要难以获取的三维训练数据,我们提出了PointDreamer,一个利用二维扩散先验来获得优质纹理的新框架。关键的是,不同于以往受文本或图像输入驱动的二维扩散到三维的工作,PointDreamer通过新颖的项目-填充-反项目管道成功地将二维扩散模型适应到三维点云数据。具体来说,它首先将点云投影到稀疏的二维图像上,然后进行基于扩散的填充。之后,不同于大多数现有的三维重建或生成方法,这些方法在三维/UV空间中进行纹理预测,因此通常会产生模糊的纹理,PointDreamer通过直接将填充的二维图像投影到三维网格上,实现了高质量的纹理。此外,我们首次发现了一种在遮挡边界中出现的典型投影伪影,这在其他多视图图像到三维的管道中很常见,但研究较少。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为非边界优先(NBF)的投影策略。在各种合成和真实扫描数据集上的大量定性和定量实验表明,PointDreamer虽然不是逐样本拍摄(zero-shot),但展现出了最先进的性能(在LPIPS得分上提高了30%,从0.118提高到0.068),并且对噪声、稀疏甚至不完整的数据具有稳健性。代码地址:https://github.com/YuQiao0303/PointDreamer。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为PointDreamer的新框架,用于从彩色点云重建纹理网格。该框架利用二维扩散先验实现高质量纹理,通过投影点云到稀疏二维图像进行扩散修复,然后直接投影修复后的二维图像到三维网格实现高质量纹理。此外,本文还解决了在遮挡边界中出现的投影伪影问题。实验证明,PointDreamer具有领先水平,并在多个数据集上展现出出色的性能。代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- PointDreamer是一个新型框架,可以从彩色点云重建高质量纹理网格。它利用了二维扩散先验来实现此目的。
- 该框架通过将点云投影到稀疏二维图像,并利用扩散模型进行修复来增强纹理质量。修复后的图像被直接投影到三维网格上。这不同于大多数在三维空间或UV空间预测纹理的方法,从而避免了模糊纹理的问题。
- 解决了一种新的投影伪影问题,特别是在遮挡边界处的问题。该问题在其他多视角图像到三维网格的转换过程中普遍存在,但鲜有研究涉及。为此,提出了非边界优先(NBF)投影策略来解决这一问题。
点此查看论文截图