⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
BrowseMaster: Towards Scalable Web Browsing via Tool-Augmented Programmatic Agent Pair
Authors:Xianghe Pang, Shuo Tang, Rui Ye, Yuwen Du, Yaxin Du, Siheng Chen
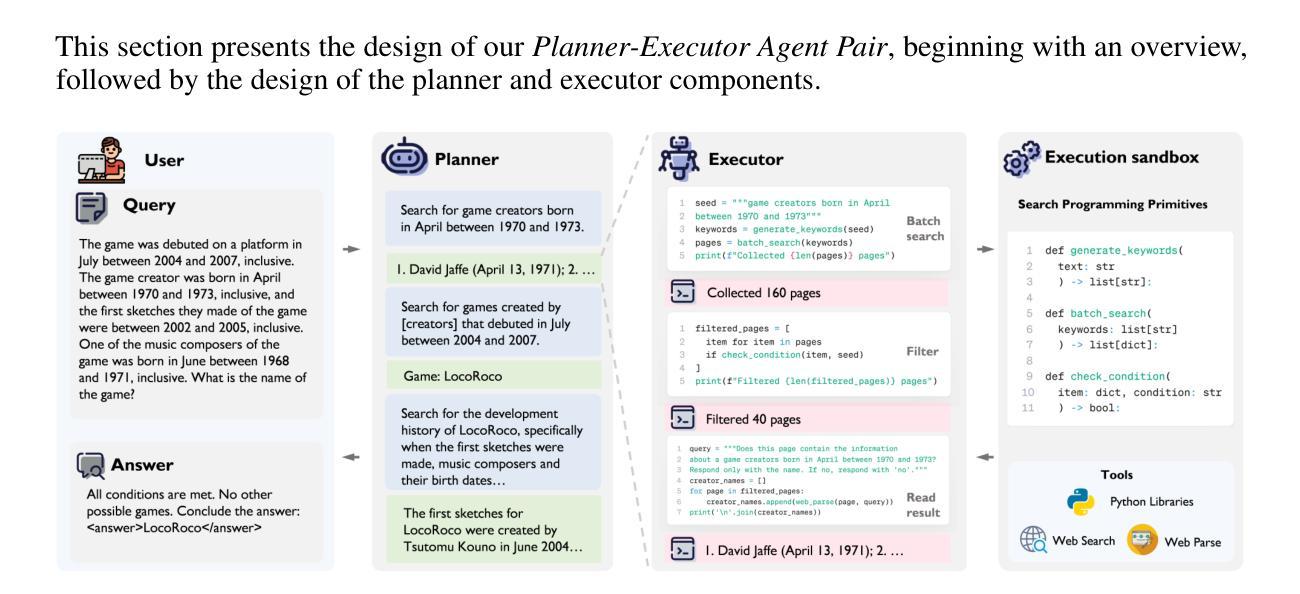
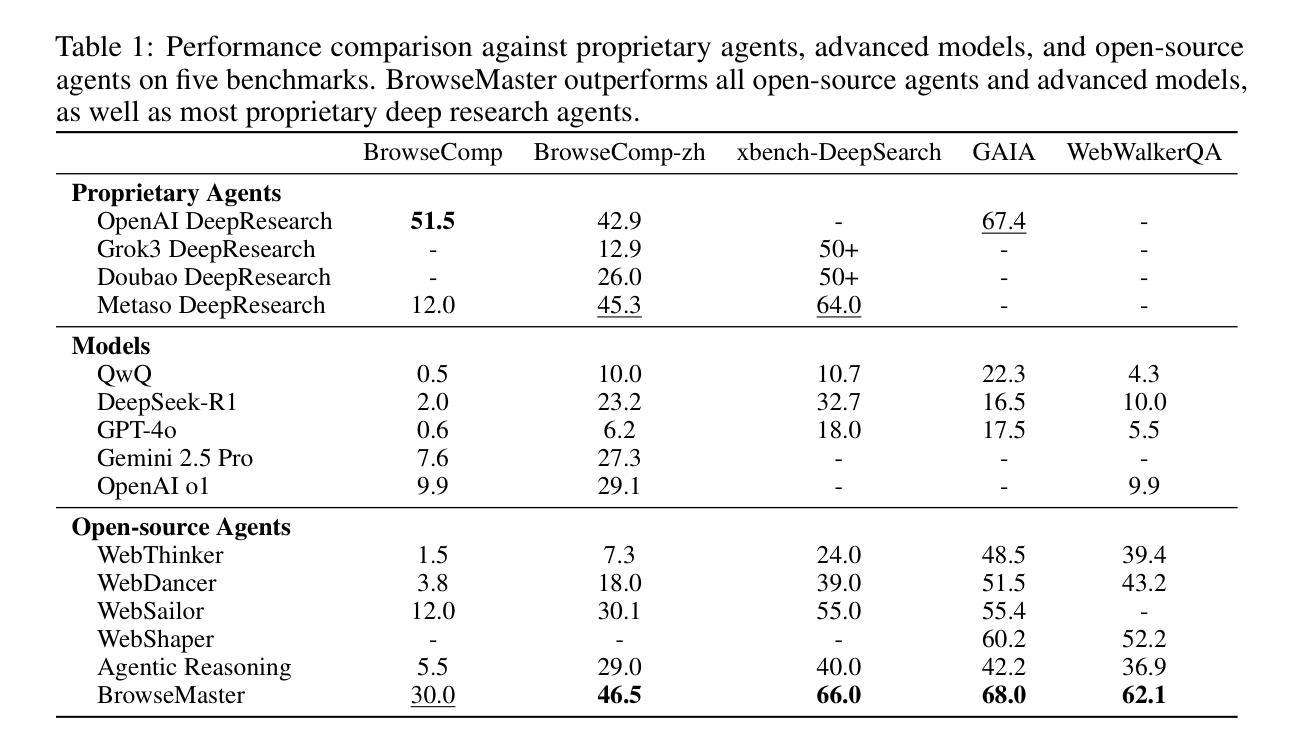
Effective information seeking in the vast and ever-growing digital landscape requires balancing expansive search with strategic reasoning. Current large language model (LLM)-based agents struggle to achieve this balance due to limitations in search breadth and reasoning depth, where slow, serial querying restricts coverage of relevant sources and noisy raw inputs disrupt the continuity of multi-step reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose BrowseMaster, a scalable framework built around a programmatically augmented planner-executor agent pair. The planner formulates and adapts search strategies based on task constraints, while the executor conducts efficient, targeted retrieval to supply the planner with concise, relevant evidence. This division of labor preserves coherent, long-horizon reasoning while sustaining broad and systematic exploration, overcoming the trade-off that limits existing agents. Extensive experiments on challenging English and Chinese benchmarks show that BrowseMaster consistently outperforms open-source and proprietary baselines, achieving scores of 30.0 on BrowseComp-en and 46.5 on BrowseComp-zh, which demonstrates its strong capability in complex, reasoning-heavy information-seeking tasks at scale.
在庞大且不断增长的数字景观中进行有效的信息搜索,需要在广泛的搜索与策略推理之间取得平衡。由于当前基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人在搜索范围和推理深度方面存在局限性,导致他们难以实现这种平衡,其中缓慢的串行查询限制了相关来源的覆盖,而嘈杂的原始输入破坏了多步骤推理的连续性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了BrowseMaster,这是一个围绕程序增强型规划器执行器代理对构建的可扩展框架。规划器根据任务约束制定并适应搜索策略,而执行者进行高效、有针对性的检索,为规划器提供简洁、相关的证据。这种分工保持了连贯、长远的推理,同时维持了广泛和有系统的探索,克服了限制现有代理人的权衡。在具有挑战性的英语和中文基准测试上的大量实验表明,BrowseMaster始终优于开源和专有基准测试,在BrowseComp-en上得分30.0,在BrowseComp-zh上得分46.5,这证明了其在复杂、重推理的大规模信息搜索任务中的强大能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在信息爆炸的数字时代,有效的信息搜索需要平衡广泛的搜索和策略性推理。当前的大型语言模型(LLM)代理由于搜索广度有限和推理深度不足而难以实现这种平衡。为解决这些问题,我们提出了BrowseMaster框架,该框架围绕可编程的增强型规划器执行器代理对构建而成。规划器根据任务约束制定和调整搜索策略,而执行器进行高效、有针对性的检索,为规划器提供简洁、相关的证据。这种分工合作既能保持连贯的长远推理又能维持广泛的系统性探索,突破了现有代理的限制。经大量英语和中文基准测试表明,BrowseMaster的性能持续优于开源和专有基线,在BrowseComp-en上的得分达到30.0,在BrowseComp-zh上的得分达到46.5,证明其在大规模复杂推理型信息搜索任务中的强大能力。
Key Takeaways
- 信息爆炸时代需要有效平衡广泛搜索和策略性推理。
- 当前LLM代理面临搜索广度与推理深度限制的挑战。
- BrowseMaster框架通过规划器与执行器的结合来解决这些问题。
- 规划器根据任务约束制定和调整搜索策略。
- 执行器进行高效、有针对性的检索,为规划器提供简洁证据。
- 这种分工合作实现连贯的长远推理与广泛的系统性探索。
点此查看论文截图

Complex Logical Instruction Generation
Authors:Mian Zhang, Shujian Liu, Sixun Dong, Ming Yin, Yebowen Hu, Xun Wang, Steven Ma, Song Wang, Sathish Reddy Indurthi, Haoyun Deng, Zhiyu Zoey Chen, Kaiqiang Song
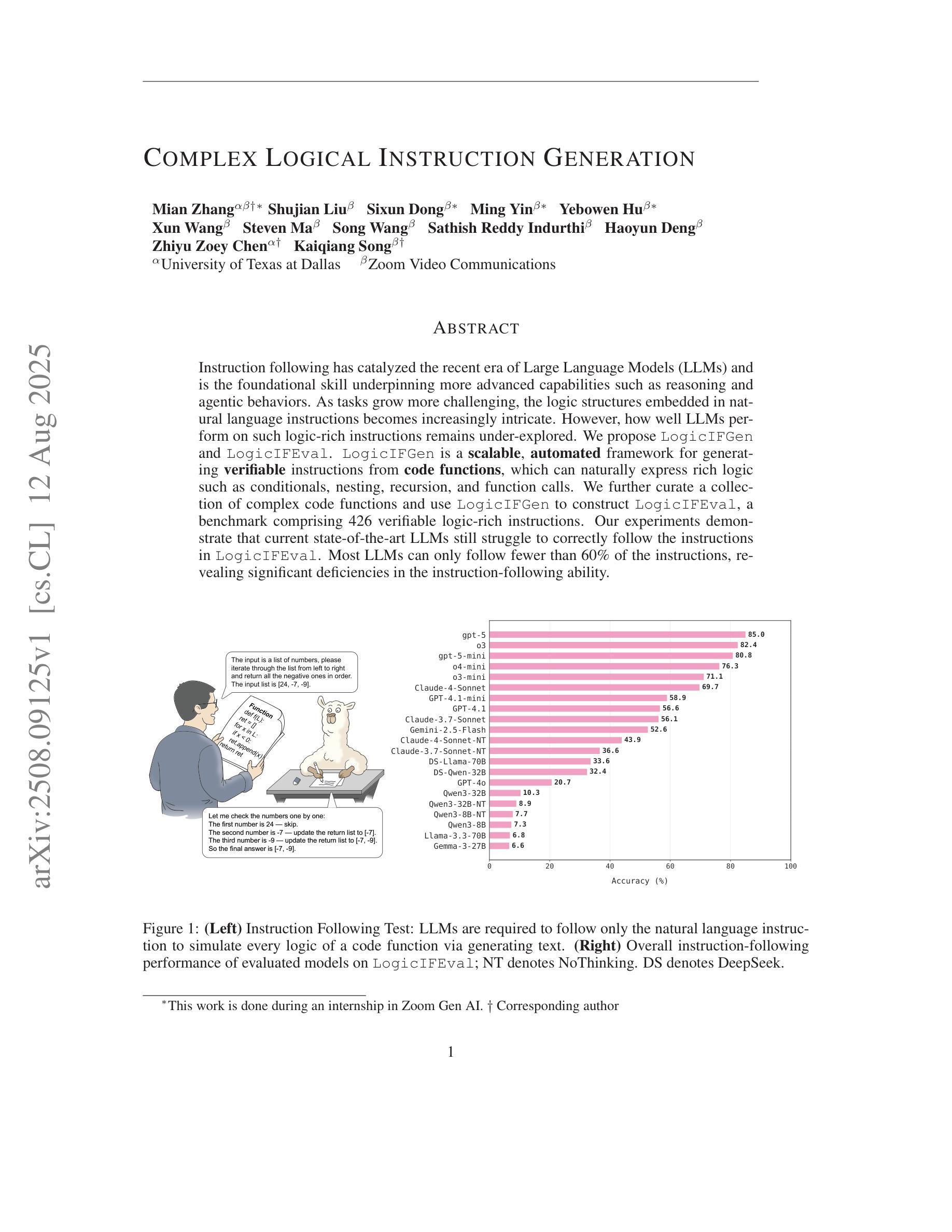
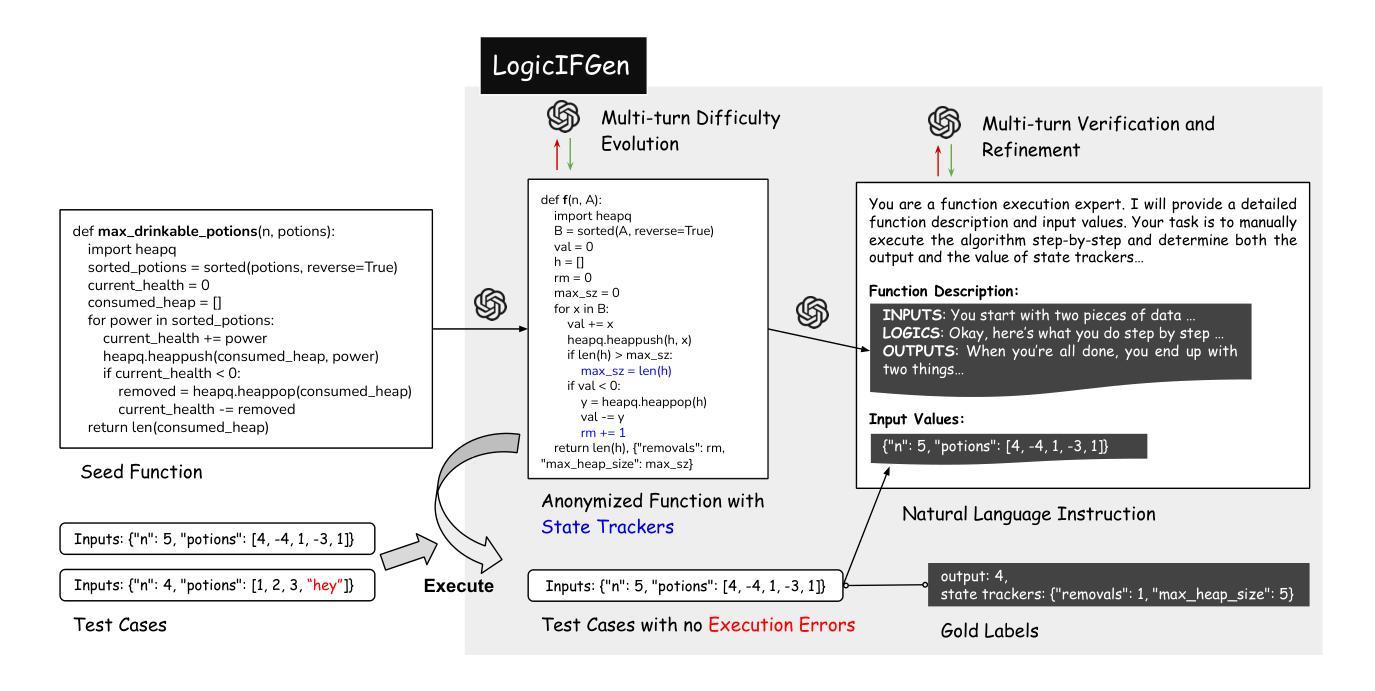
Instruction following has catalyzed the recent era of Large Language Models (LLMs) and is the foundational skill underpinning more advanced capabilities such as reasoning and agentic behaviors. As tasks grow more challenging, the logic structures embedded in natural language instructions becomes increasingly intricate. However, how well LLMs perform on such logic-rich instructions remains under-explored. We propose LogicIFGen and LogicIFEval. LogicIFGen is a scalable, automated framework for generating verifiable instructions from code functions, which can naturally express rich logic such as conditionals, nesting, recursion, and function calls. We further curate a collection of complex code functions and use LogicIFGen to construct LogicIFEval, a benchmark comprising 426 verifiable logic-rich instructions. Our experiments demonstrate that current state-of-the-art LLMs still struggle to correctly follow the instructions in LogicIFEval. Most LLMs can only follow fewer than 60% of the instructions, revealing significant deficiencies in the instruction-following ability. Code and Benchmark: https://github.com/mianzhang/LogicIF
接下来的指令已经催生了近期的大型语言模型(LLM)时代,并且是支撑推理和智能行为等更高级技能的基础。随着任务变得越来越具有挑战性,自然语言指令中嵌入的逻辑结构也变得越来越复杂。然而,LLM在逻辑丰富的指令上的表现如何仍有待探索。我们提出了LogicIFGen和LogicIFEval。LogicIFGen是一个可扩展的自动化框架,可以从代码函数中生成可验证的指令,它能够自然地表达丰富的逻辑,如条件、嵌套、递归和函数调用。我们还精心收集了一系列复杂的代码函数,并使用LogicIFGen构建了LogicIFEval,这是一个包含426个可验证的逻辑丰富指令的基准测试。我们的实验表明,当前最先进的LLM仍然难以正确遵循LogicIFEval中的指令。大多数LLM只能遵循不到60%的指令,这暴露了其在指令执行能力上的明显缺陷。代码和基准测试:https://github.com/mianzhang/LogicIF
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
LLM时代的指令跟随催生了一系列大型语言模型,这些模型具备推理和自主行为等高级能力的基础技能。随着任务难度增加,自然语言指令中的逻辑结构愈发复杂,但LLM在这些逻辑丰富指令上的表现尚待探索。本文提出LogicIFGen和LogicIFEval,前者是一个可规模化、自动化的框架,能从代码功能中生成可验证的指令,自然表达条件、嵌套、递归和函数调用等丰富逻辑;后者则是一个包含复杂代码功能的基准测试集,通过LogicIFGen生成逻辑丰富的可验证指令。实验表明,当前最先进的LLM在LogicIFEval中的指令跟随能力仍然不足,只能正确跟随不到60%的指令,显示出显著的缺陷。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在指令跟随方面具有重要作用。
- 随着任务难度的增加,自然语言指令中的逻辑结构愈发复杂。
- 当前LLM在逻辑丰富指令上的表现尚待探索。
- 提出了LogicIFGen框架,可以从代码功能中生成可验证的指令,支持表达丰富逻辑。
- 构建了LogicIFEval基准测试集,包含复杂代码功能的逻辑丰富指令。
- 实验显示当前最先进的LLM在LogicIFEval中的表现不佳,只能正确跟随少数指令。
点此查看论文截图
OdysseyBench: Evaluating LLM Agents on Long-Horizon Complex Office Application Workflows
Authors:Weixuan Wang, Dongge Han, Daniel Madrigal Diaz, Jin Xu, Victor Rühle, Saravan Rajmohan
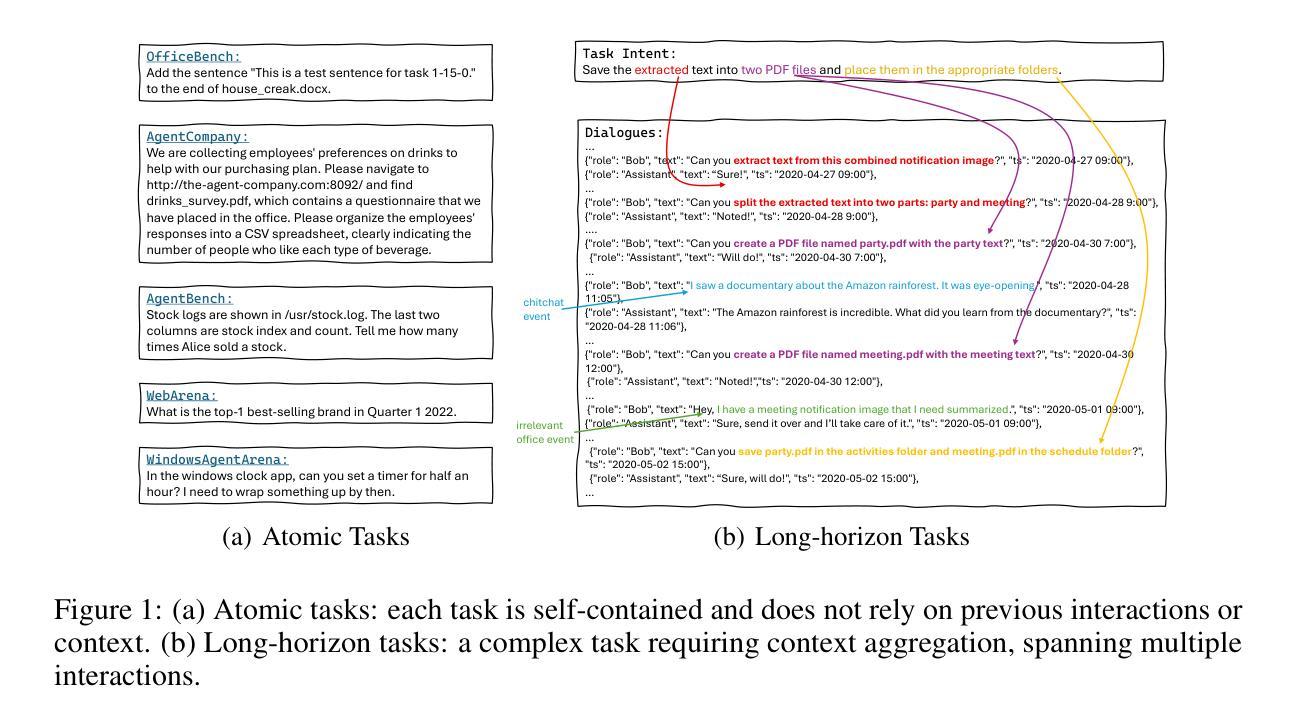
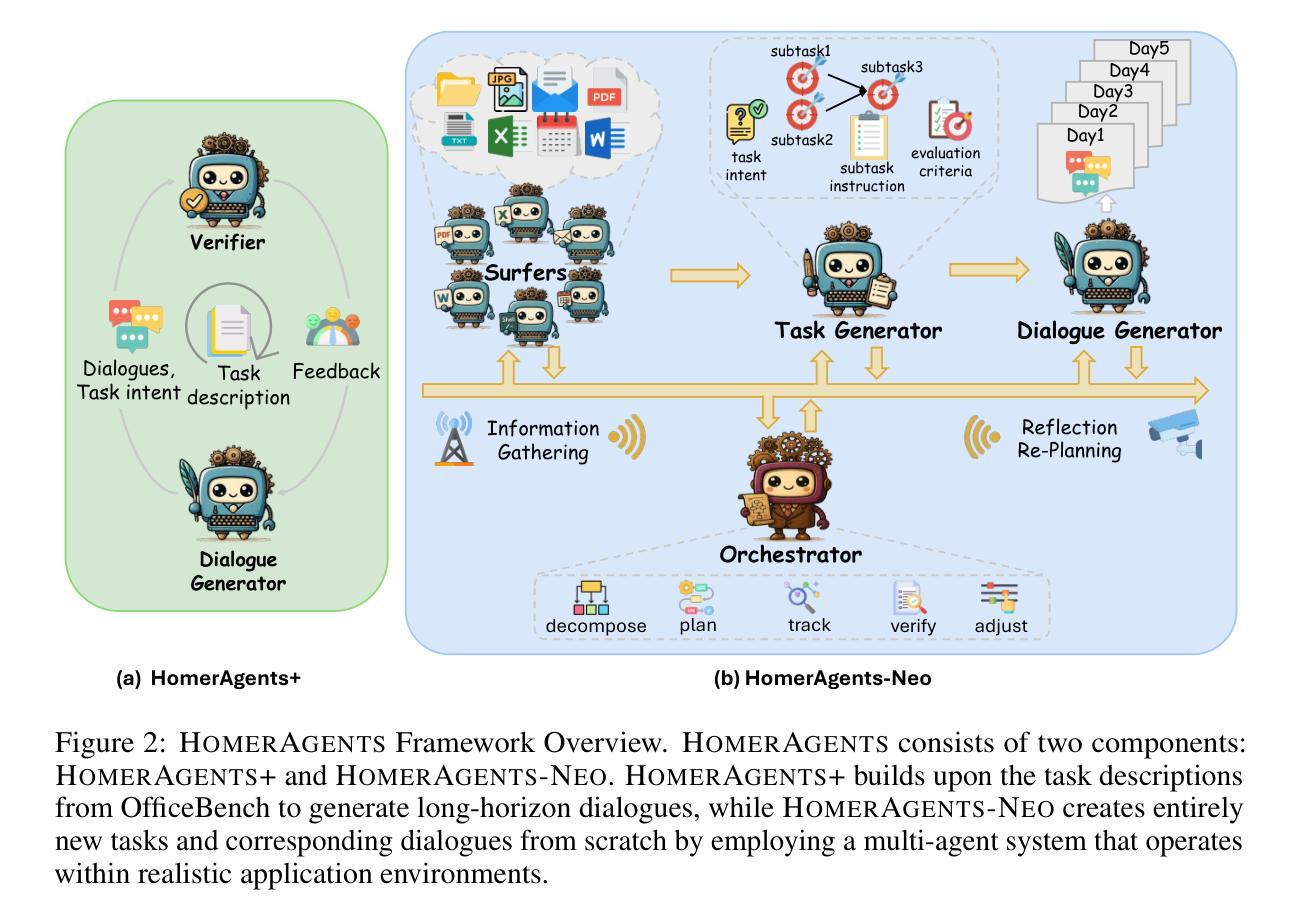
Autonomous agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications requiring complex, long-horizon workflows. However, existing benchmarks predominantly focus on atomic tasks that are self-contained and independent, failing to capture the long-term contextual dependencies and multi-interaction coordination required in realistic scenarios. To address this gap, we introduce OdysseyBench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM agents on long-horizon workflows across diverse office applications including Word, Excel, PDF, Email, and Calendar. Our benchmark comprises two complementary splits: OdysseyBench+ with 300 tasks derived from real-world use cases, and OdysseyBench-Neo with 302 newly synthesized complex tasks. Each task requires agent to identify essential information from long-horizon interaction histories and perform multi-step reasoning across various applications. To enable scalable benchmark creation, we propose HomerAgents, a multi-agent framework that automates the generation of long-horizon workflow benchmarks through systematic environment exploration, task generation, and dialogue synthesis. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates that OdysseyBench effectively challenges state-of-the-art LLM agents, providing more accurate assessment of their capabilities in complex, real-world contexts compared to existing atomic task benchmarks. We believe that OdysseyBench will serve as a valuable resource for advancing the development and evaluation of LLM agents in real-world productivity scenarios. In addition, we release OdysseyBench and HomerAgents to foster research along this line.
由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的自主导航代理越来越多地部署在需要复杂、长期工作流的现实应用中。然而,现有的基准测试主要集中在自我完善和独立的原子任务上,无法捕捉现实场景中所需的长期上下文依赖性和多交互协调。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了OdysseyBench,这是一个全面评估LLM代理在长期工作流方面性能的基准测试,涵盖多样化的办公应用,包括Word、Excel、PDF、电子邮件和日历。我们的基准测试包括两个互补的部分:OdysseyBench+,包含300个来自真实世界用例的任务;以及OdysseyBench-Neo,包含302个新合成的复杂任务。每个任务都要求代理从长期交互历史中识别关键信息,并在各种应用程序中进行多步骤推理。为了实现可扩展的基准测试创建,我们提出了HomerAgents,这是一个多代理框架,通过系统的环境探索、任务生成和对话合成,自动生成长期工作流基准测试。我们的广泛评估表明,OdysseyBench有效地挑战了最先进的LLM代理,与现有的原子任务基准测试相比,更能准确地评估它们在复杂现实环境中的能力。我们相信,OdysseyBench将成为推动和评估LLM代理在现实生产场景中的发展的宝贵资源。此外,我们发布OdysseyBench和HomerAgents以促进这一领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
引入OdysseyBench,一个全面评估LLM代理长期工作流程的基准测试,涵盖Word、Excel、PDF、Email和Calendar等多样化办公应用。该基准测试包含两个互补部分:OdysseyBench+和OdysseyBench-Neo,分别包含来自真实世界用例的300个任务和全新合成的302个复杂任务。每个任务要求代理识别长期交互历史中的关键信息,并在各种应用程序中进行多步骤推理。提出HomerAgents多代理框架,通过系统环境探索、任务生成和对话合成,实现长期工作流程基准测试的自动生成。OdysseyBench相比现有的原子任务基准测试,更有效地挑战了最先进的LLM代理,为复杂现实语境中评估其能力提供了更准确的评估。相信OdysseyBench将成为推动LLM代理在真实世界生产力场景中应用和发展的宝贵资源。
Key Takeaways:
- 引入OdysseyBench基准测试,用于评估LLM代理在涉及长期工作流程的复杂现实世界应用中的表现。
- OdysseyBench包含两个互补部分:OdysseyBench+和OdysseyBench-Neo,涵盖多种办公应用场景的实际任务和合成复杂任务。
- 每个任务需要代理识别长期交互历史中的关键信息,并在不同应用程序中进行多步骤推理。
- 提出HomerAgents多代理框架,实现长期工作流程基准测试的自动生成,包括环境探索、任务生成和对话合成等环节。
- OdysseyBench对现有LLM代理提出了有效挑战,相比原子任务基准测试能更准确地评估代理在复杂现实环境中的能力。
- OdysseyBench被认为是推动LLM代理在真实世界生产力场景中应用和发展的宝贵资源。
点此查看论文截图


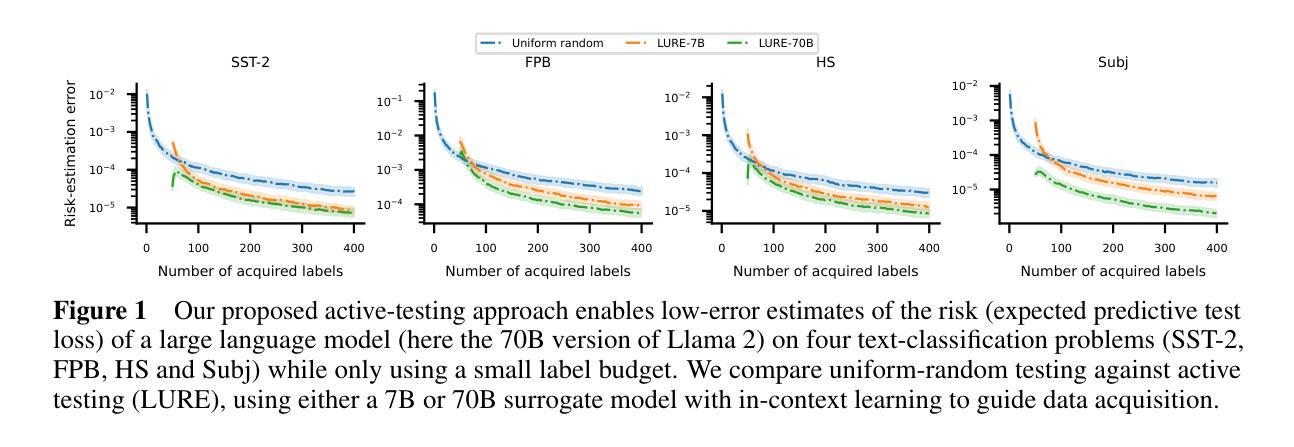
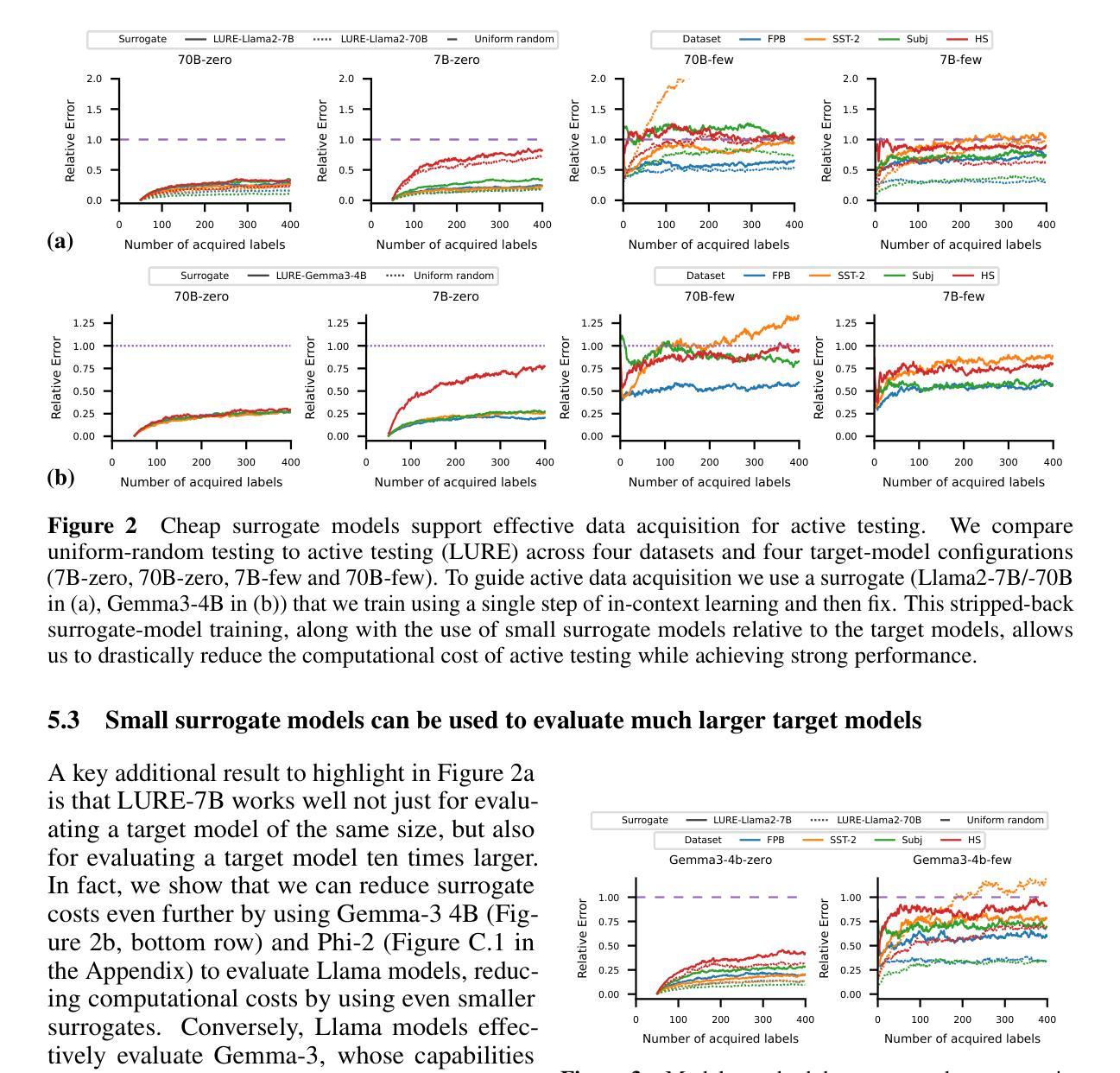
Scaling Up Active Testing to Large Language Models
Authors:Gabrielle Berrada, Jannik Kossen, Muhammed Razzak, Freddie Bickford Smith, Yarin Gal, Tom Rainforth
Active testing enables label-efficient evaluation of models through careful data acquisition. However, its significant computational costs have previously undermined its use for large models. We show how it can be successfully scaled up to the evaluation of large language models (LLMs). In particular we show that the surrogate model used to guide data acquisition can be constructed cheaply using in-context learning, does not require updating within an active-testing loop, and can be smaller than the target model. We even find we can make good data-acquisition decisions without computing predictions with the target model and further introduce a single-run error estimator to asses how well active testing is working on the fly. We find that our approach is able to more effectively evaluate LLM performance with less data than current standard practices.
主动测试能够通过精心收集数据,实现模型的高效评估。然而,其高昂的计算成本之前曾对大型模型的评估造成不利影响。我们展示了如何将其成功扩展到大型语言模型(LLM)的评估中。尤其要指出的是,用于指导数据收集的替代模型可以使用上下文学习来廉价构建,不需要在主动测试循环中进行更新,并且可以比目标模型更小。我们甚至发现,无需计算目标模型的预测值也能做出良好的数据采集决策,并引入了一种单次运行误差估计器,以实时评估主动测试的有效性。我们发现我们的方法能够在比当前标准实践更少的数据上更有效地评估LLM的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在积极测试(Active Testing)下,我们可以有效评估大型语言模型(LLM)的性能,同时通过精心选择数据实现标签的高效利用。虽然积极测试的计算成本较高,但我们展示了如何通过廉价地构建代理模型引导数据采集来实现其规模化扩展。我们的方法无需在主动测试循环中更新代理模型,而且代理模型可以小于目标模型。此外,我们甚至能够在不计算目标模型预测的情况下做出良好的数据采集决策,并引入单次运行误差估计器来实时评估积极测试的效果。研究发现,我们的方法能以较少的数据更有效地评估LLM的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 积极测试可用于有效评估LLM性能。
- 通过精心选择数据实现标签的高效利用。
- 利用廉价构建的代理模型进行数据采集扩展积极测试。
- 无需在主动测试循环中更新代理模型。
- 代理模型可以小于目标模型。
- 不计算目标模型预测也能做出良好的数据采集决策。
点此查看论文截图

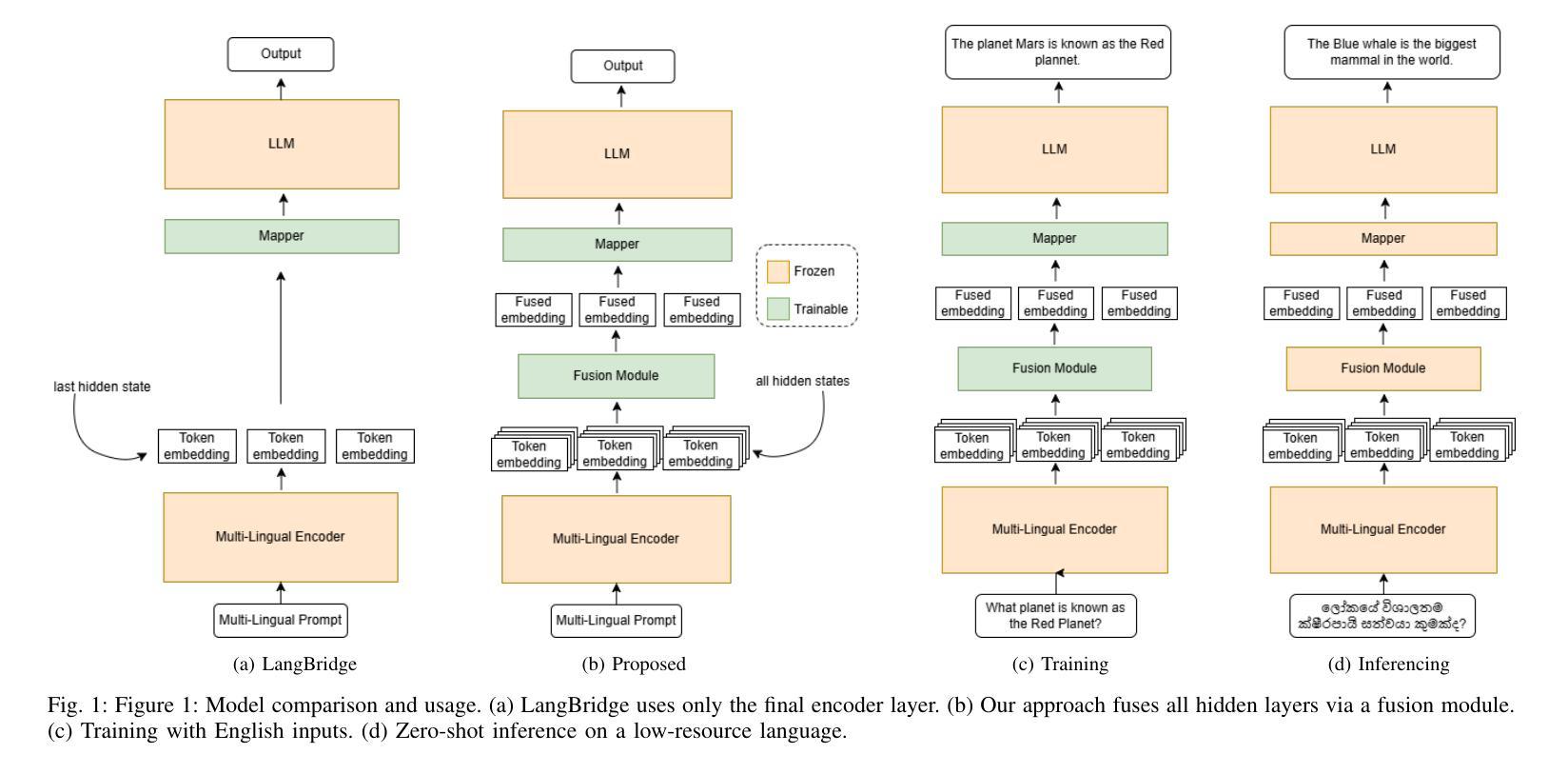
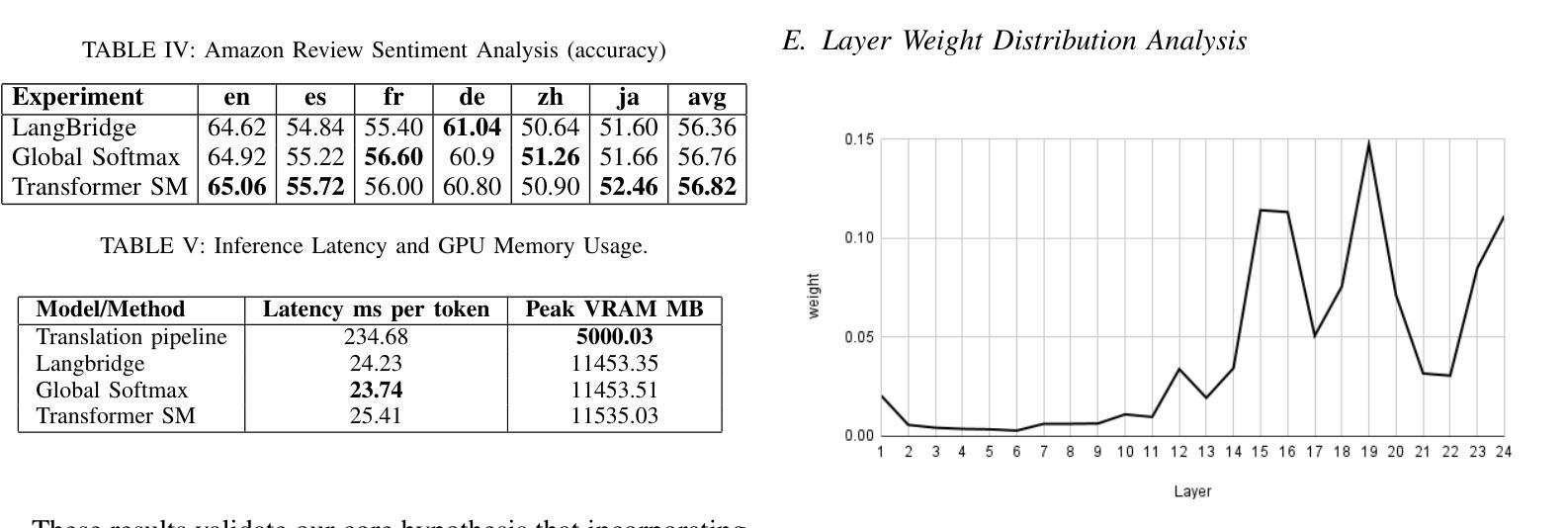
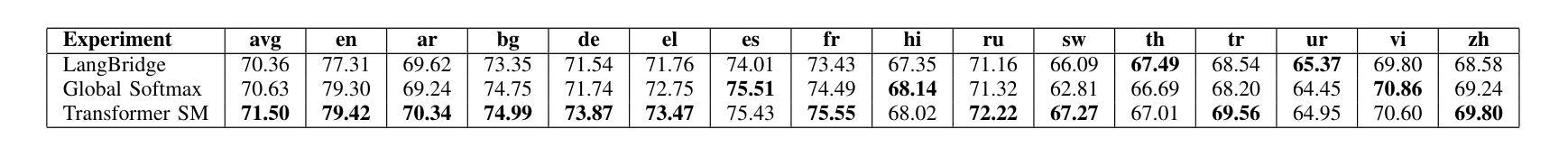
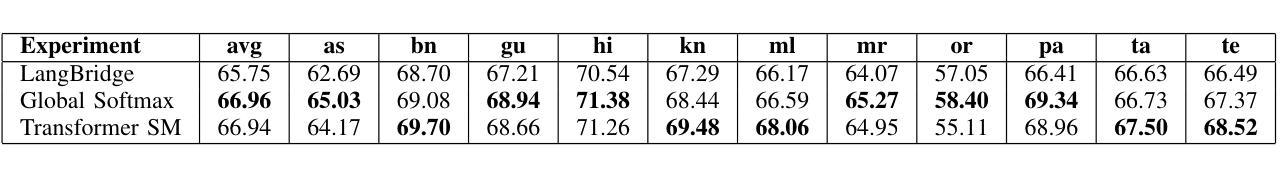
Utilizing Multilingual Encoders to Improve Large Language Models for Low-Resource Languages
Authors:Imalsha Puranegedara, Themira Chathumina, Nisal Ranathunga, Nisansa de Silva, Surangika Ranathunga, Mokanarangan Thayaparan
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in English, but their performance degrades significantly on low-resource languages (LRLs) due to English-centric training. While methods like LangBridge align LLMs with multilingual encoders such as the Massively Multilingual Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer (mT5), they typically use only the final encoder layer. We propose a novel architecture that fuses all intermediate layers, enriching the linguistic information passed to the LLM. Our approach features two strategies: (1) a Global Softmax weighting for overall layer importance, and (2) a Transformer Softmax model that learns token-specific weights. The fused representations are mapped into the LLM’s embedding space, enabling it to process multilingual inputs. The model is trained only on English data, without using any parallel or multilingual data. Evaluated on XNLI, IndicXNLI, Sinhala News Classification, and Amazon Reviews, our Transformer Softmax model significantly outperforms the LangBridge baseline. We observe strong performance gains in LRLs, improving Sinhala classification accuracy from 71.66% to 75.86% and achieving clear improvements across Indic languages such as Tamil, Bengali, and Malayalam. These specific gains contribute to an overall boost in average XNLI accuracy from 70.36% to 71.50%. This approach offers a scalable, data-efficient path toward more capable and equitable multilingual LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)在英语上表现出色,但由于以英语为中心的训练方式,它们在低资源语言(LRLs)上的性能会显著下降。虽然像LangBridge这样的方法可以将LLM与多语言编码器(如大规模多语言文本到文本转换转换器mT5)对齐,但它们通常只使用最终的编码器层。我们提出了一种融合所有中间层的新型架构,丰富传递给LLM的语言信息。我们的方法包括两种策略:(1)全局Softmax加权用于整体层重要性,(2)Transformer Softmax模型学习特定于令牌(token)的权重。融合的表示被映射到LLM的嵌入空间,使其能够处理多语言输入。该模型仅在英语数据上进行训练,无需使用任何平行或多语言数据。在XNLI、IndicXNLI、僧伽罗语新闻分类和亚马逊评论上的评估表明,我们的Transformer Softmax模型显著优于LangBridge基线。我们在低资源语言上观察到强大的性能提升,僧伽罗语分类准确率从71.66%提高到75.86%,以及在印度语言如泰米尔语、孟加拉语和马拉亚拉姆语等上实现明显的改进。这些特定改进有助于提高平均XNLI准确率从70.36%到71.50%。这种方法为构建更强大、更公平的多语言LLM提供了一条可扩展且数据高效的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)在多语种任务上的性能问题,并提出了一个融合多层信息的模型架构来解决这一问题。该架构使用全局Softmax权重和Transformer Softmax模型进行分层和令牌级融合,以增强传递给LLM的语言信息。模型仅在英语数据上进行训练,无需使用平行或多语种数据。在XNLI、IndicXNLI、僧伽罗语新闻分类和亚马逊评论等任务上,该模型显著优于LangBridge基线,特别是在低资源语言(LRLs)方面表现出强劲的性能提升。这提供了一种可扩展且数据高效的路径,朝着更强大和更均衡的多语种LLM发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理低资源语言(LRLs)时性能下降,主要由于它们以英语为中心的训练方式。
- 现有方法如LangBridge虽然尝试通过多语种编码器与LLM对接,但仅使用最终编码器层的信息。
- 提出的模型架构融合了所有中间层信息,通过全局Softmax权重和Transformer Softmax模型进行分层和令牌级融合。
- 融合后的表示映射到LLM的嵌入空间,使其能够处理多语种输入。
- 模型仅在英语数据上训练,无需平行或多语种数据。
- 在多个任务上,包括XNLI、IndicXNLI、僧伽罗语新闻分类和亚马逊评论等,新模型显著优于LangBridge基线,特别是在LRLs方面。
点此查看论文截图

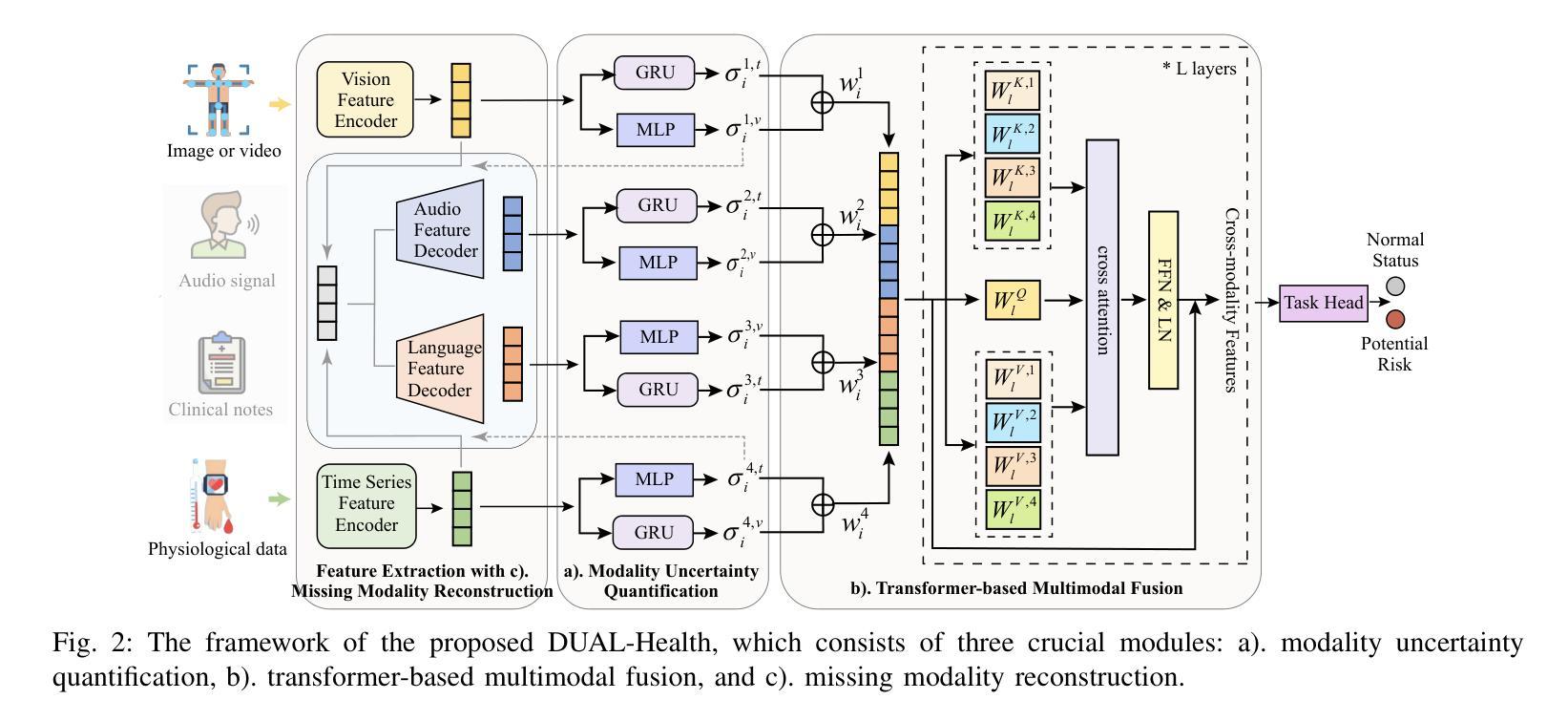
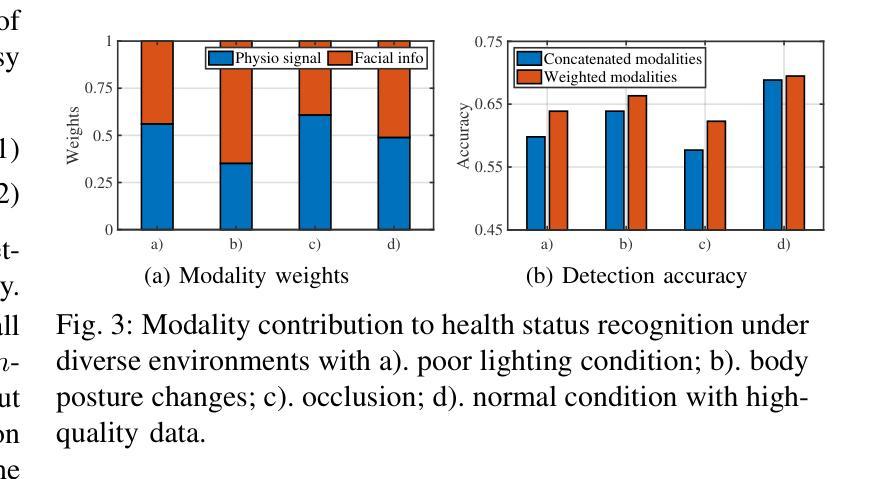
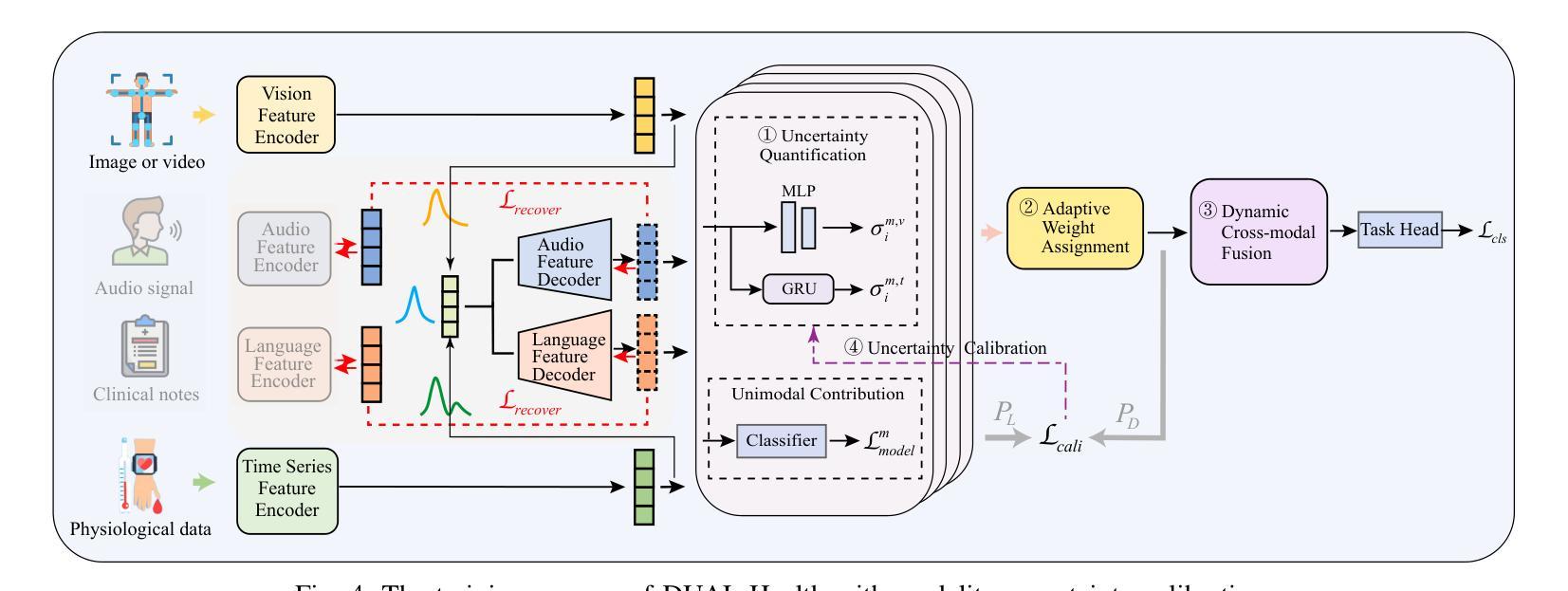
Dynamic Uncertainty-aware Multimodal Fusion for Outdoor Health Monitoring
Authors:Zihan Fang, Zheng Lin, Senkang Hu, Yihang Tao, Yiqin Deng, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fang
Outdoor health monitoring is essential to detect early abnormal health status for safeguarding human health and safety. Conventional outdoor monitoring relies on static multimodal deep learning frameworks, which requires extensive data training from scratch and fails to capture subtle health status changes. Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) emerge as a promising alternative, utilizing only small datasets to fine-tune pre-trained information-rich models for enabling powerful health status monitoring. Unfortunately, MLLM-based outdoor health monitoring also faces significant challenges: I) sensor data contains input noise stemming from sensor data acquisition and fluctuation noise caused by sudden changes in physiological signals due to dynamic outdoor environments, thus degrading the training performance; ii) current transformer based MLLMs struggle to achieve robust multimodal fusion, as they lack a design for fusing the noisy modality; iii) modalities with varying noise levels hinder accurate recovery of missing data from fluctuating distributions. To combat these challenges, we propose an uncertainty-aware multimodal fusion framework, named DUAL-Health, for outdoor health monitoring in dynamic and noisy environments. First, to assess the impact of noise, we accurately quantify modality uncertainty caused by input and fluctuation noise with current and temporal features. Second, to empower efficient muitimodal fusion with low-quality modalities,we customize the fusion weight for each modality based on quantified and calibrated uncertainty. Third, to enhance data recovery from fluctuating noisy modalities, we align modality distributions within a common semantic space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our DUAL-Health outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in detection accuracy and robustness.
户外健康监测对于及早发现异常健康状况以保障人类健康和安全至关重要。传统的户外监测依赖于静态多模态深度学习框架,需要从零开始的大量数据训练,并且无法捕捉到微妙的健康状况变化。多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为一种有前途的替代方案出现,它只利用小型数据集对预训练的信息丰富模型进行微调,以实现强大的健康状态监测。然而,基于MLLM的户外健康监测也面临重大挑战:一、传感器数据包含来自传感器数据获取的输入噪声和由动态室外环境引起的生理信号突变而产生的波动噪声,从而降低了训练性能;二、基于当前变换器的MLLMs难以实现稳健的多模态融合,因为它们缺乏融合噪声模态的设计;三、不同噪声水平的模态阻碍了从波动分布中准确恢复缺失数据。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种用于动态和噪声环境下户外健康监测的不确定性感知多模态融合框架,名为DUAL-Health。首先,为了评估噪声的影响,我们利用当前和时间特征准确量化由输入和波动噪声引起的模态不确定性。其次,为了赋能低质量模态的有效多模态融合,我们根据量化校准的不确定性为每个模态定制融合权重。第三,为了提高从波动噪声模态中恢复数据的能力,我们将模态分布对齐到公共语义空间。大量实验表明,我们的DUAL-Health在检测精度和稳健性方面优于最新基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了户外健康监测的重要性以及传统方法的局限性,提出了基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的户外健康监测方法。文章指出了MLLMs面临的挑战,如传感器数据的输入噪声、动态环境下的波动噪声、模态融合的不稳定性以及不同噪声水平模态的数据缺失问题。为应对这些挑战,提出了一种名为DUAL-Health的不确定性感知多模态融合框架,通过量化不确定性、定制融合权重以及对齐模态分布,提高了检测精度和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 户外健康监测对于及时发现人体健康状态异常具有重要意义。
- 传统户外监测方法依赖于静态多模态深度学习框架,存在需要大量数据训练、无法捕捉微妙健康状态变化的问题。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)利用小数据集微调预训练模型,为健康状态监测提供了有力支持。
- MLLM在户外健康监测中面临传感器数据输入噪声、动态环境下的波动噪声等挑战。
- DUAL-Health框架通过量化不确定性、定制融合权重和对齐模态分布,提高了检测精度和稳健性。
- 定量不确定性能有效评估噪声对监测结果的影响。
点此查看论文截图

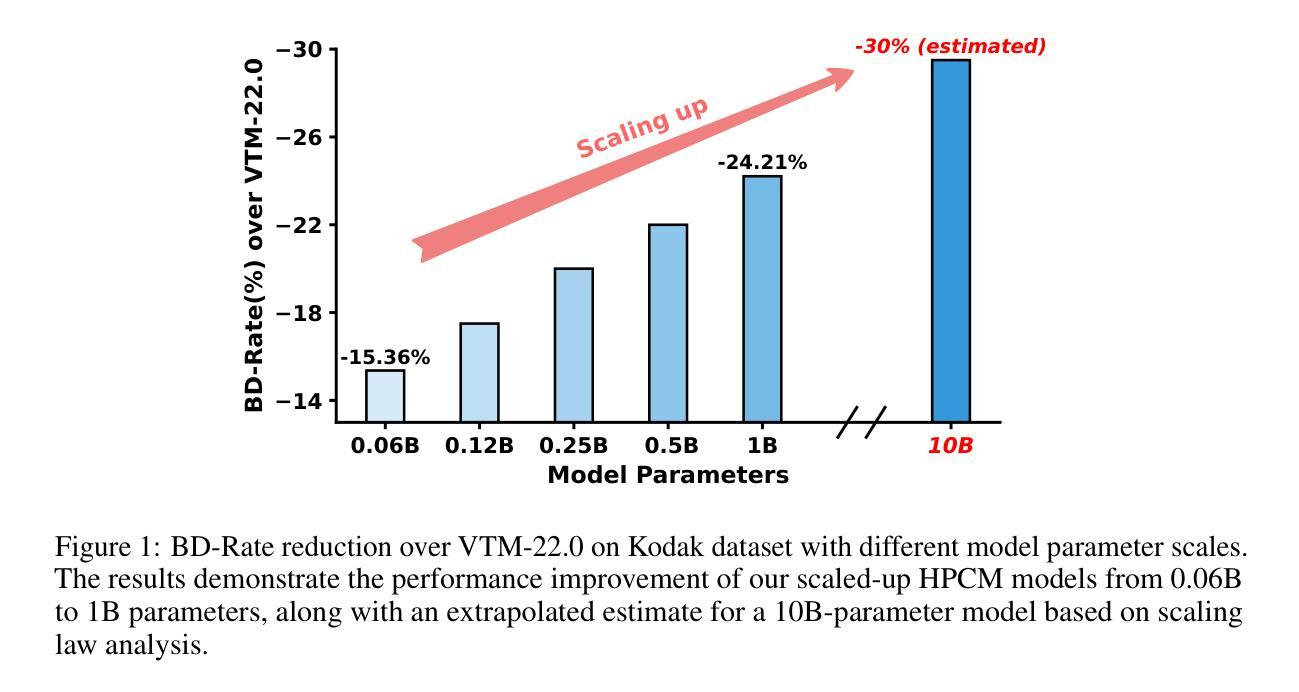
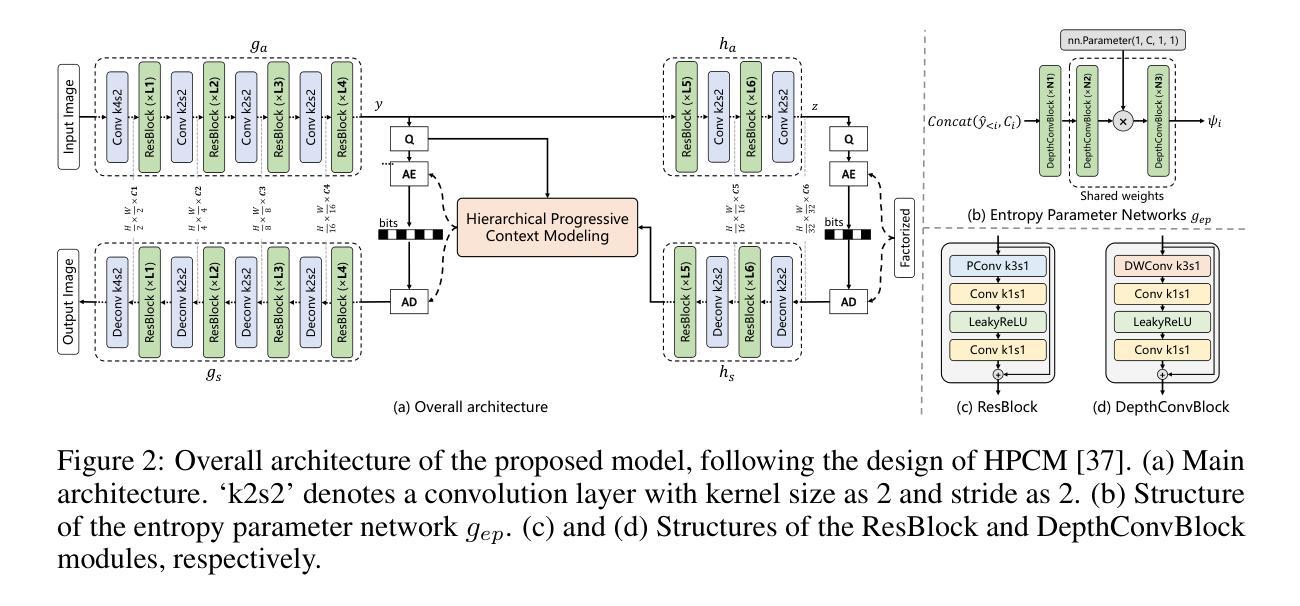
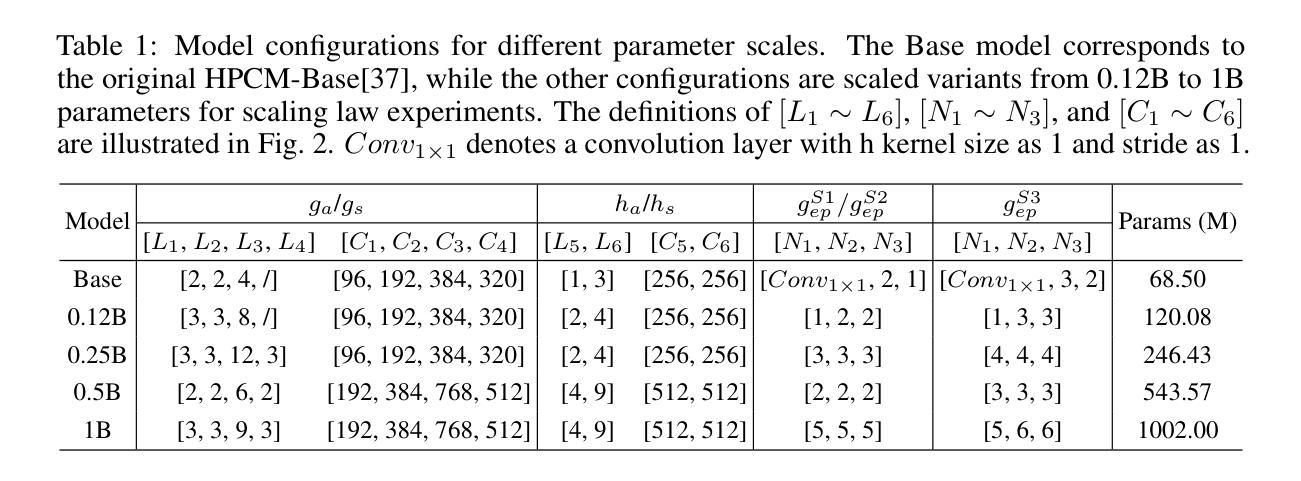
Scaling Learned Image Compression Models up to 1 Billion
Authors:Yuqi Li, Haotian Zhang, Li Li, Dong Liu, Feng Wu
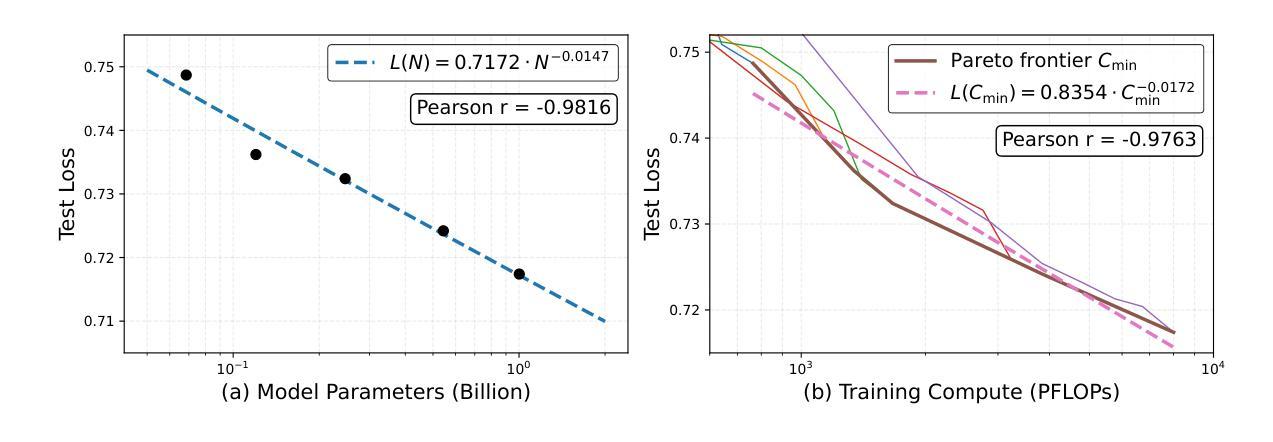
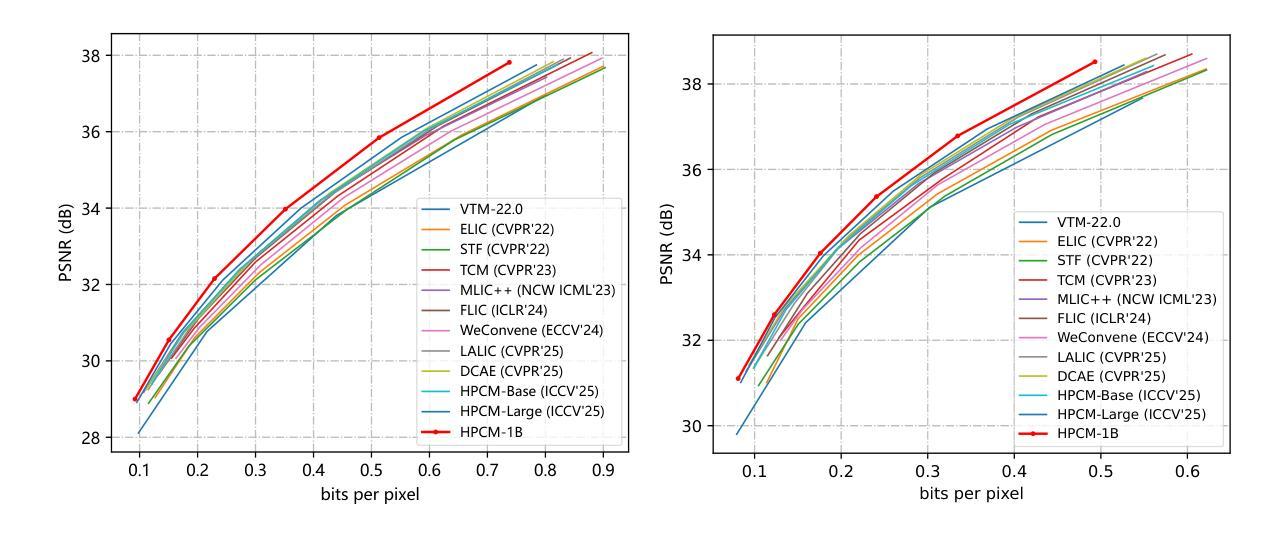
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) highlight a strong connection between intelligence and compression. Learned image compression, a fundamental task in modern data compression, has made significant progress in recent years. However, current models remain limited in scale, restricting their representation capacity, and how scaling model size influences compression performance remains unexplored. In this work, we present a pioneering study on scaling up learned image compression models and revealing the performance trends through scaling laws. Using the recent state-of-the-art HPCM model as baseline, we scale model parameters from 68.5 millions to 1 billion and fit power-law relations between test loss and key scaling variables, including model size and optimal training compute. The results reveal a scaling trend, enabling extrapolation to larger scale models. Experimental results demonstrate that the scaled-up HPCM-1B model achieves state-of-the-art rate-distortion performance. We hope this work inspires future exploration of large-scale compression models and deeper investigations into the connection between compression and intelligence.
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展突显了智能与压缩之间的强烈联系。现代数据压缩中的基本任务——学习图像压缩近年来取得了重大进展。然而,当前模型的规模仍然有限,限制了其表示能力,并且扩大模型规模如何影响压缩性能尚未得到探索。在这项工作中,我们对扩大学习图像压缩模型的规模进行了一项开创性研究,并通过规模定律揭示了性能趋势。我们以最新的最先进的HPCM模型为基准,将模型参数从6850万扩展到1亿,并在测试损失和关键缩放变量(包括模型大小和最佳训练计算)之间拟合幂律关系。结果揭示了缩放趋势,可实现向更大规模模型的推算。实验结果表明,扩展的HPCM-1B模型达到了最新的率失真性能标准。我们希望这项工作能激发对未来大规模压缩模型的探索,以及对压缩与智能之间联系的深入研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, technical report
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)的最新进展突显了智能与压缩之间的紧密联系。本研究首次探索了扩大图像压缩模型规模的趋势,并以最近的先进HPCM模型为基线,将其参数从68.5百万扩展到十亿规模。实验结果表明,通过模型规模的扩大,压缩性能得以提升,这为未来的大规模压缩模型探索提供了启示。本研究揭示的缩放趋势有望促进压缩与智能之间联系的深入研究。随着模型规模的扩大,其在测试损失上的表现展示出极大的潜力。期望此研究能为将来的压缩模型研究和模型规模对压缩性能的影响带来更深的理解和启发。在此基础上进一步扩展对大规模模型的探索,有望推动图像压缩技术的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 研究展示了如何通过扩大图像压缩模型的规模来提升性能。
- 以HPCM模型为基线,模型参数从数十百万扩展到十亿规模。
- 实验结果表明,随着模型规模的扩大,测试损失表现出特定的趋势。
- 通过揭示缩放趋势,研究为未来的大规模压缩模型探索提供了启示。
- 研究强调了模型规模在影响压缩性能方面的作用,并期望未来有更深入的研究。
点此查看论文截图

READER: Retrieval-Assisted Drafter for Efficient LLM Inference
Authors:Maxim Divilkovskiy, Vitaly Malygin, Sergey Zlobin, Sultan Isali, Vasily Kalugin, Stanislav Ilyushin, Nuriza Aitassova, Yi Fei, Zeng Weidi
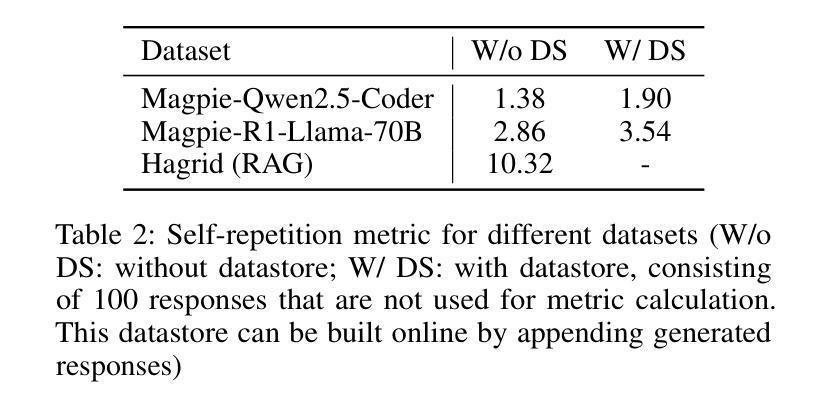
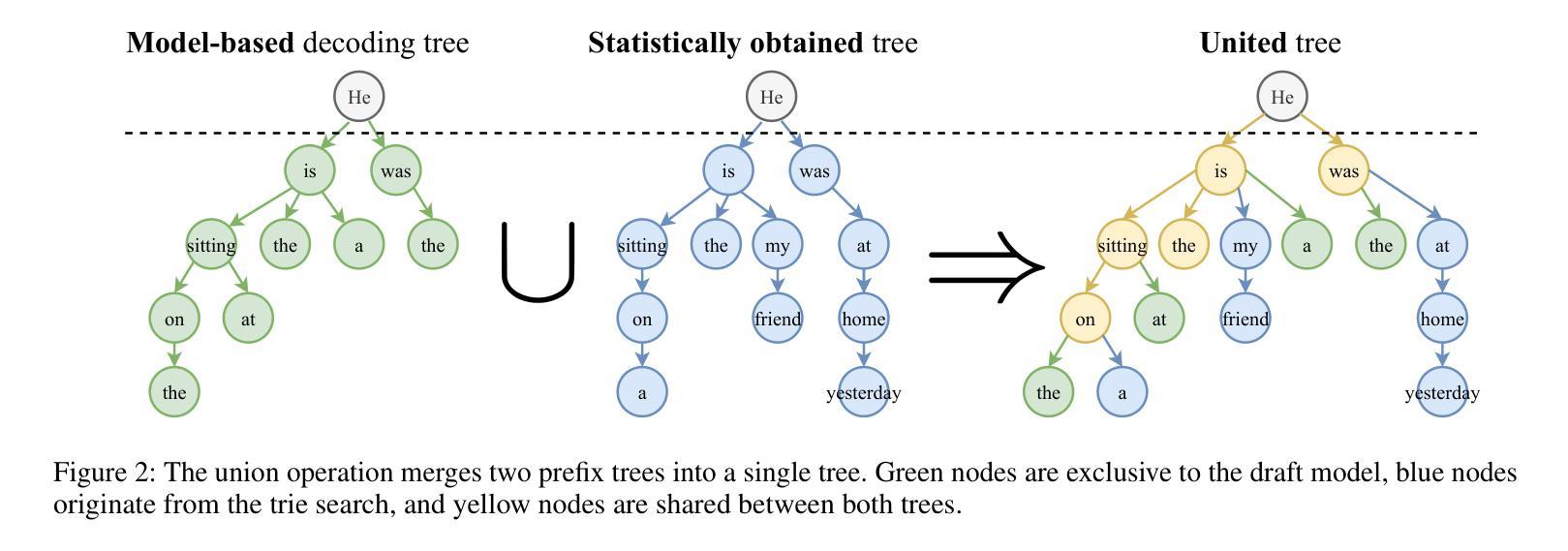
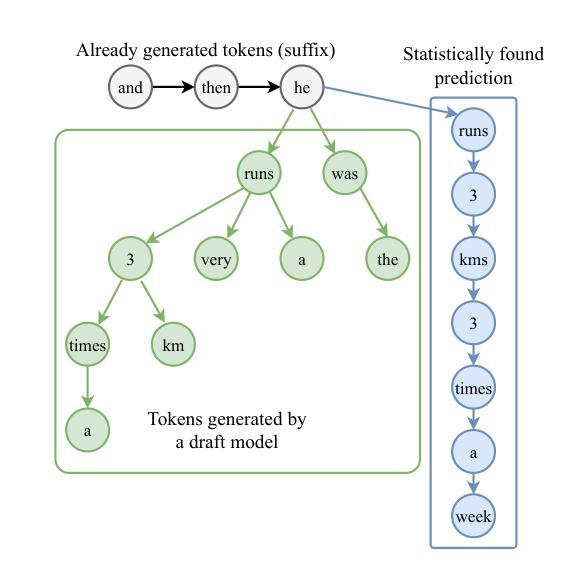
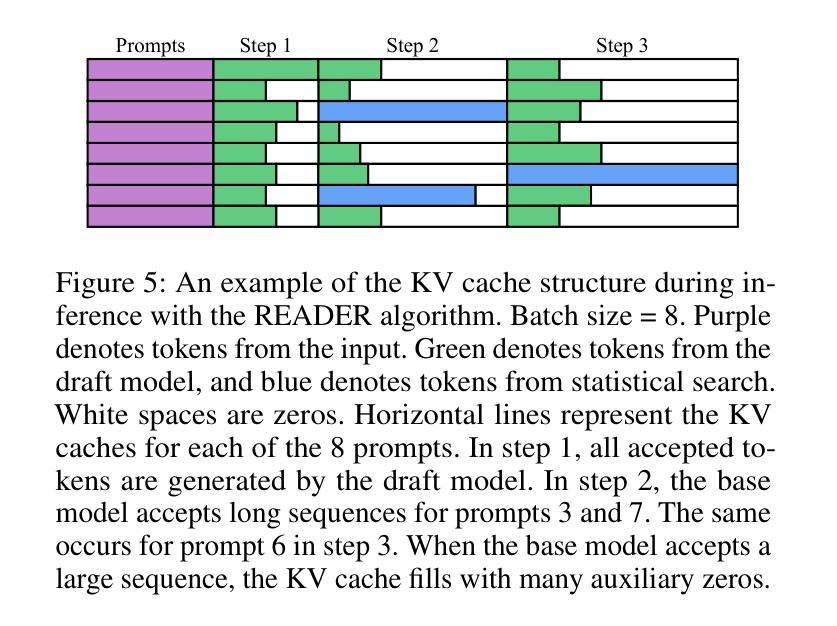
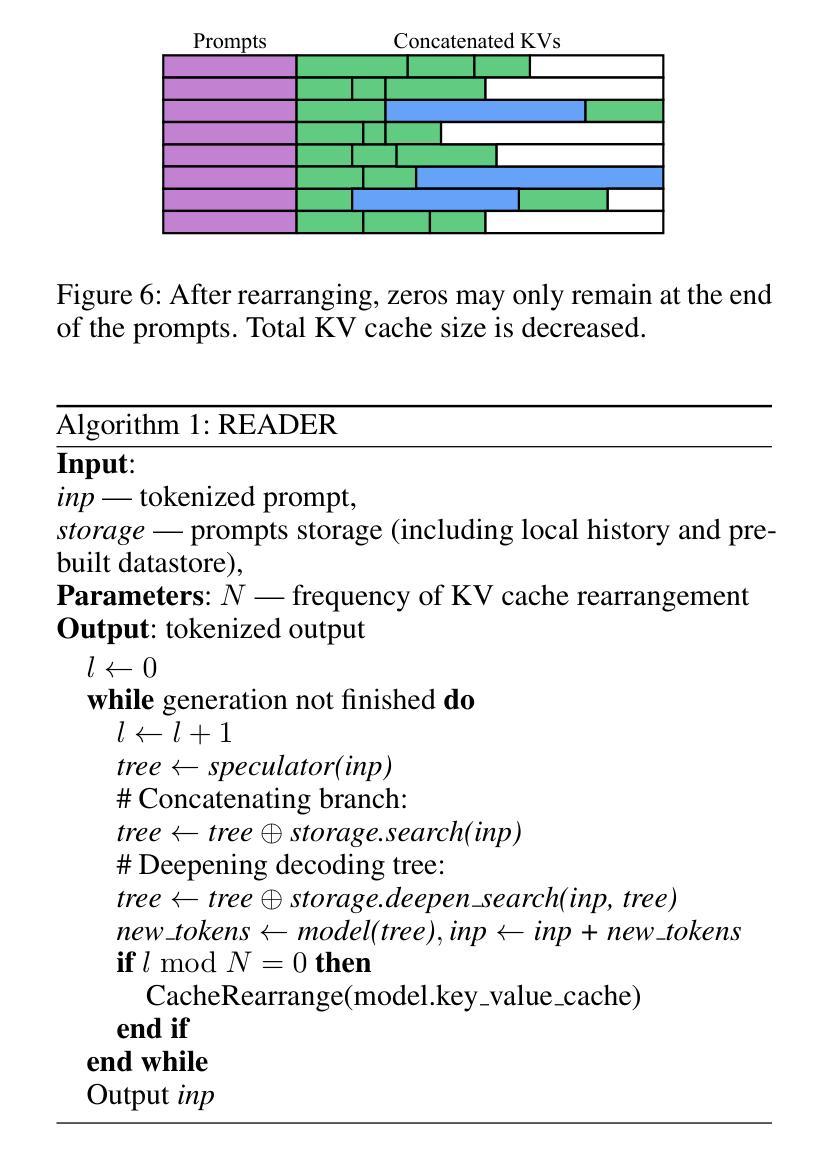
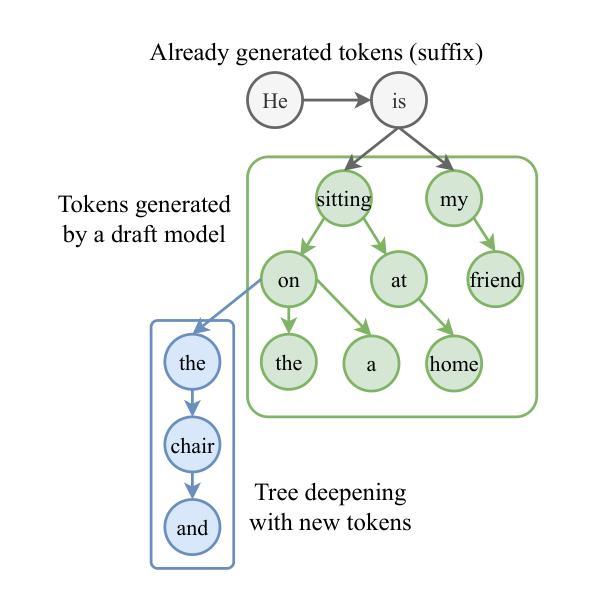
Large Language Models (LLMs) generate tokens autoregressively, with each token depending on the preceding context. This sequential nature makes the inference process inherently difficult to accelerate, posing a significant challenge for efficient deployment. In recent years, various methods have been proposed to address this issue, with the most effective approaches often involving the training of additional draft models. In this paper, we introduce READER (Retrieval-Assisted Drafter for Efficient LLM Inference), a novel lossless speculative decoding method that enhances model-based approaches by leveraging self-repetitions in the text. Our algorithm expands the speculative decoding tree using tokens obtained through statistical search. This work focuses on large batch sizes (>= 8), an underexplored yet important area for industrial applications. We also analyze the key-value (KV) cache size during speculative decoding and propose an optimization to improve performance for large batches. As a result, READER outperforms existing speculative decoding methods. Notably, READER requires no additional training and can reuse pre-trained speculator models, increasing the speedup by over 40%. Our method demonstrates particularly strong performance on search-based tasks, such as retrieval-augmented generation, where we achieve more than 10x speedup.
大型语言模型(LLM)采用自回归方式生成令牌,每个令牌都依赖于前面的上下文。这种序列性质使得推理过程本身难以加速,给有效部署带来了重大挑战。近年来,已经提出了各种方法来解决这个问题,最有效的方法通常涉及训练额外的草稿模型。在本文中,我们介绍了READER(用于高效LLM推理的检索辅助起草者),这是一种新的无损推测解码方法,它利用文本中的自我重复来增强基于模型的方法。我们的算法使用通过统计搜索获得的令牌来扩展推测解码树。我们的工作侧重于大批量(>= 8),这是工业应用方面鲜有研究但非常重要的领域。我们还分析了推测解码过程中的键值(KV)缓存大小,并提出了优化措施以提高大批量性能。因此,READER的性能优于现有的推测解码方法。值得注意的是,READER无需额外的训练,并能重用预训练的推测模型,提高了超过40%的加速性能。我们的方法在基于搜索的任务上表现特别出色,如在检索增强生成任务上,我们实现了超过10倍的加速。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)生成token的方式是自动回归的,每个token都依赖于前面的上下文。这种序列性质使得推理过程难以加速,对高效部署构成了重大挑战。本文提出了一种新型无损推测解码方法READER,它借助文本中的自我重复,通过统计搜索扩展推测解码树,增强了基于模型的方法。READER重点关注大批量数据(>= 8),这是工业应用中的一个被忽视但重要的领域。通过对推测解码过程中的键值(KV)缓存大小的分析,我们提出了优化方案以提高大批量数据的性能。READER表现优于现有推测解码方法,尤其在不需额外训练且可重用预训练推测模型的情况下,提速超过40%。在基于搜索的任务上,如增强检索生成任务中,我们实现了超过10倍的速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的推理过程由于序列生成特性而难以加速。
- READER是一种新型无损推测解码方法,利用文本中的自我重复来提高效率。
- READER通过统计搜索扩展推测解码树,无需额外训练。
- READER可重用预训练模型,提高速度。
- READER在大批量数据处理时表现出色,特别适用于工业应用。
- 通过分析键值(KV)缓存大小,优化了READER的性能。
点此查看论文截图

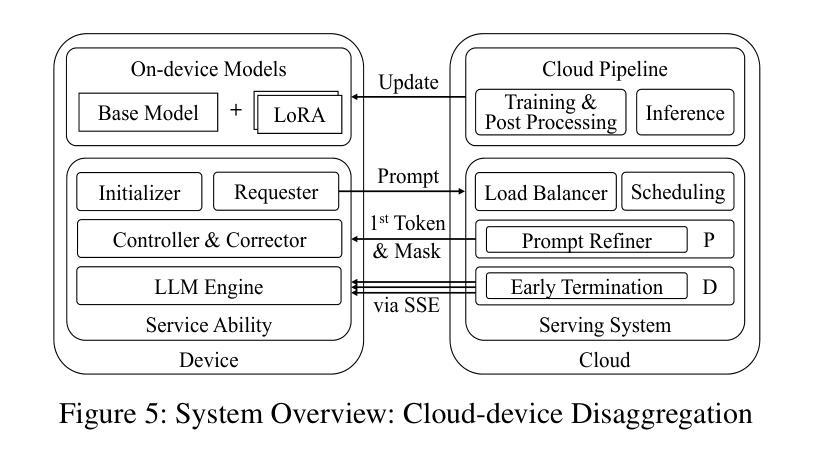
P/D-Device: Disaggregated Large Language Model between Cloud and Devices
Authors:Yibo Jin, Yixu Xu, Yue Chen, Chengbin Wang, Tao Wang, Jiaqi Huang, Rongfei Zhang, Yiming Dong, Yuting Yan, Ke Cheng, Yingjie Zhu, Shulan Wang, Qianqian Tang, Shuaishuai Meng, Guanxin Cheng, Ze Wang, Shuyan Miao, Ketao Wang, Wen Liu, Yifan Yang, Tong Zhang, Anran Wang, Chengzhou Lu, Tiantian Dong, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhe Wang, Hefei Guo, Hongjie Liu, Wei Lu, Zhengyong Zhang
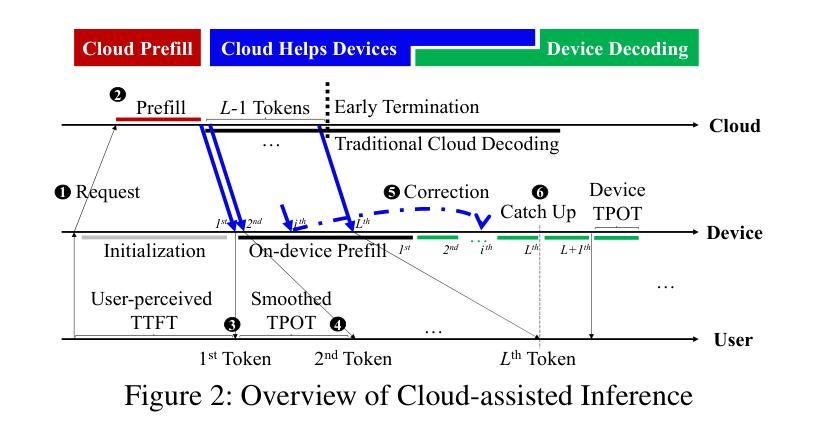
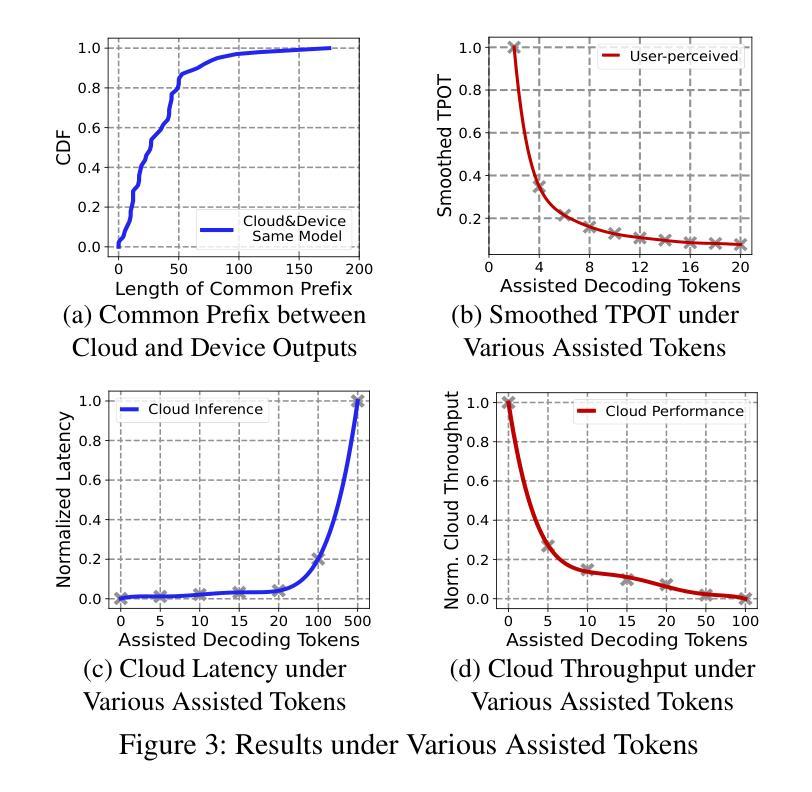
Serving disaggregated large language models has been widely adopted in industrial practice for enhanced performance. However, too many tokens generated in decoding phase, i.e., occupying the resources for a long time, essentially hamper the cloud from achieving a higher throughput. Meanwhile, due to limited on-device resources, the time to first token (TTFT), i.e., the latency of prefill phase, increases dramatically with the growth on prompt length. In order to concur with such a bottleneck on resources, i.e., long occupation in cloud and limited on-device computing capacity, we propose to separate large language model between cloud and devices. That is, the cloud helps a portion of the content for each device, only in its prefill phase. Specifically, after receiving the first token from the cloud, decoupling with its own prefill, the device responds to the user immediately for a lower TTFT. Then, the following tokens from cloud are presented via a speed controller for smoothed TPOT (the time per output token), until the device catches up with the progress. On-device prefill is then amortized using received tokens while the resource usage in cloud is controlled. Moreover, during cloud prefill, the prompt can be refined, using those intermediate data already generated, to further speed up on-device inference. We implement such a scheme P/D-Device, and confirm its superiority over other alternatives. We further propose an algorithm to decide the best settings. Real-trace experiments show that TTFT decreases at least 60%, maximum TPOT is about tens of milliseconds, and cloud throughput increases by up to 15x.
将大型语言模型拆分为多个部分进行服务在工业实践中已被广泛采用,以提高性能。然而,解码阶段生成的令牌过多,即长时间占用资源,本质上阻碍了云实现更高的吞吐量。同时,由于设备资源有限,首令牌生成时间(TTFT)随着提示长度的增加而急剧增加。为了应对云和设备资源瓶颈的问题,即长时间占用和有限的设备计算能力,我们提出在云和设备之间分离大型语言模型。也就是说,云仅在设备的预填充阶段帮助处理部分内容。具体来说,在接收到来自云的首个令牌后,设备脱离其自己的预填充阶段,立即响应用户请求以降低TTFT。然后,来自云的后续令牌通过速度控制器平滑地呈现,以降低每输出令牌的时间(TPOT),直到设备跟上进度。在收到令牌的同时使用设备的预填充进行摊销,同时控制云中的资源使用。此外,在云的预填充期间,可以使用已经生成的中间数据来优化提示,以进一步加快设备上的推理速度。我们实现了这种P/D-Device方案,并确认了其优于其他替代方案。我们还提出了一种算法来决定最佳设置。真实轨迹实验表明,TTFT至少减少了60%,最大TPOT约为几十毫秒,云的吞吐量提高了高达15倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于云计算的大型语言模型服务在实际应用中得到了广泛采用,但在解码阶段生成过多令牌,导致资源占用时间过长,限制了云服务的吞吐量。针对这一问题,我们提出了在云端和设备端分离大型语言模型的解决方案。云端负责为每个设备提供部分内容预填充服务,降低设备端响应时间。通过速度控制器平衡云和设备的处理进度,减少设备端和云端的资源消耗。实验证明,该方案显著提高了效率和性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型服务在实际应用中广泛采用,但存在解码阶段生成过多令牌的问题。
- 过多令牌生成导致资源占用时间长,限制了云服务的吞吐量。
- 提出在云端和设备端分离大型语言模型的解决方案,云端负责预填充服务以降低设备响应时间。
- 通过速度控制器平衡云和设备的处理进度。
- 实验结果显示,该方案显著提高设备响应时间、降低最大令牌处理时间和提高云服务吞吐量。
点此查看论文截图

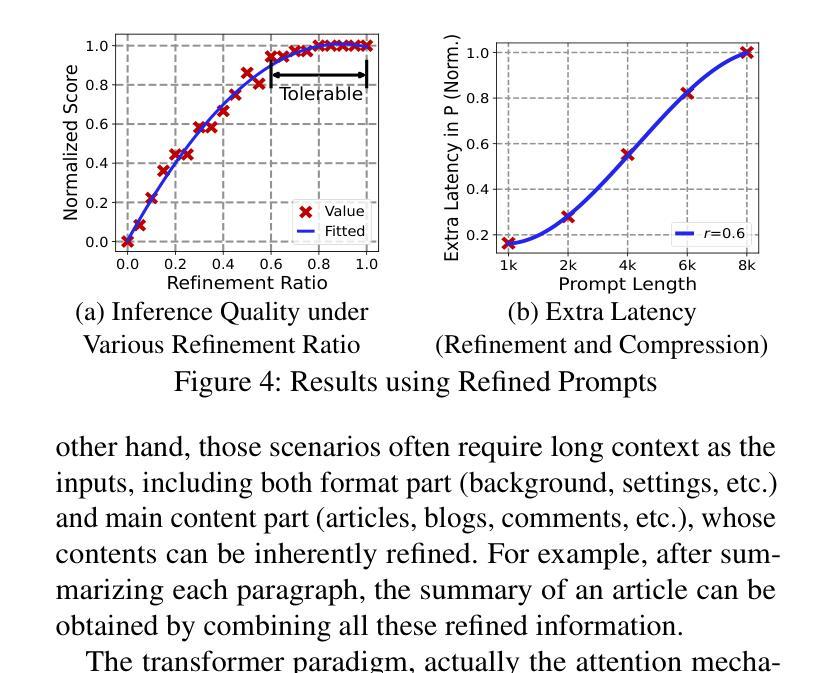
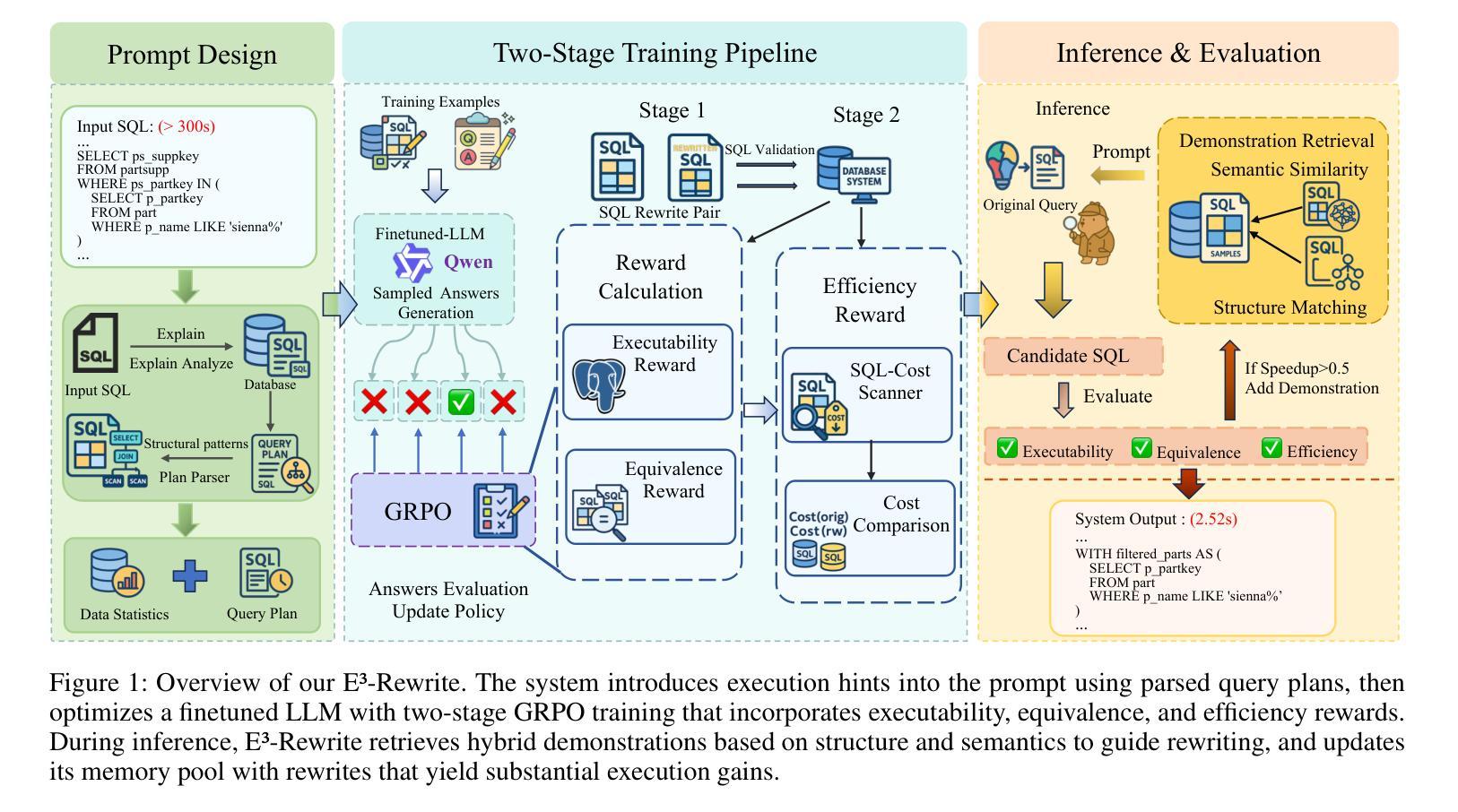
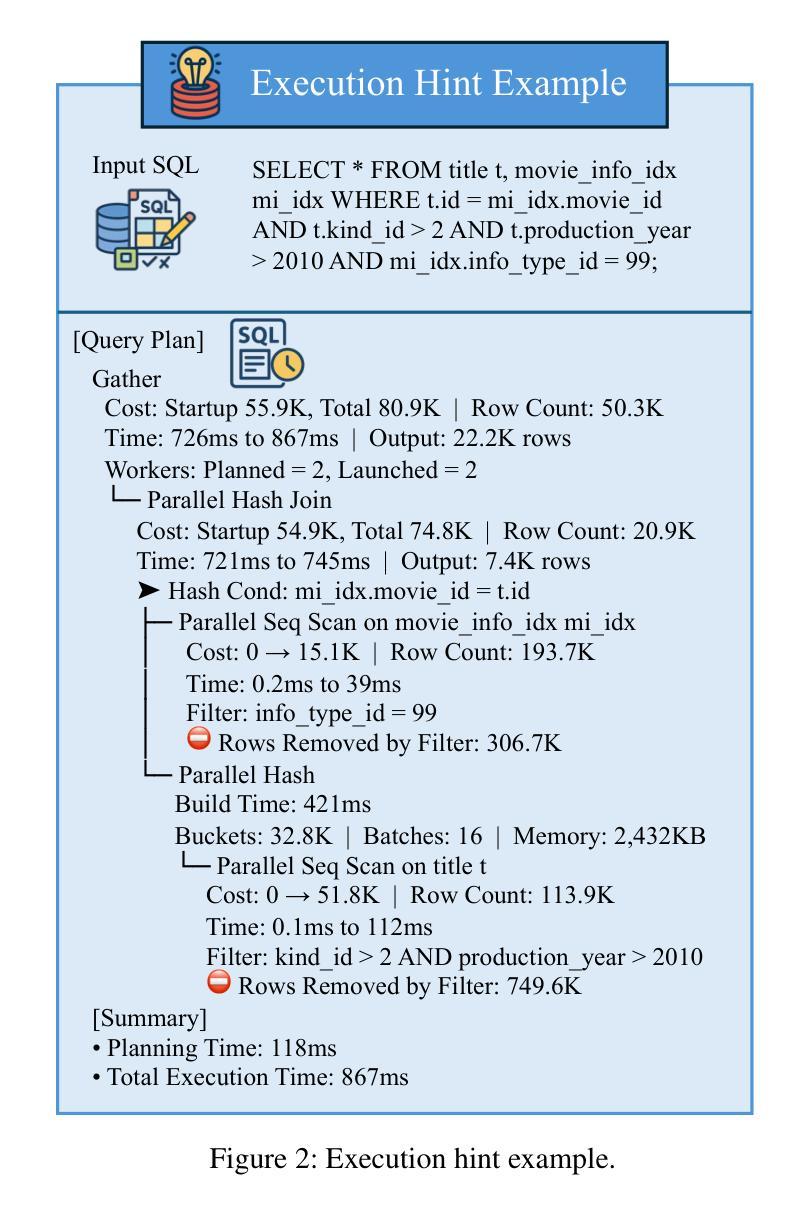
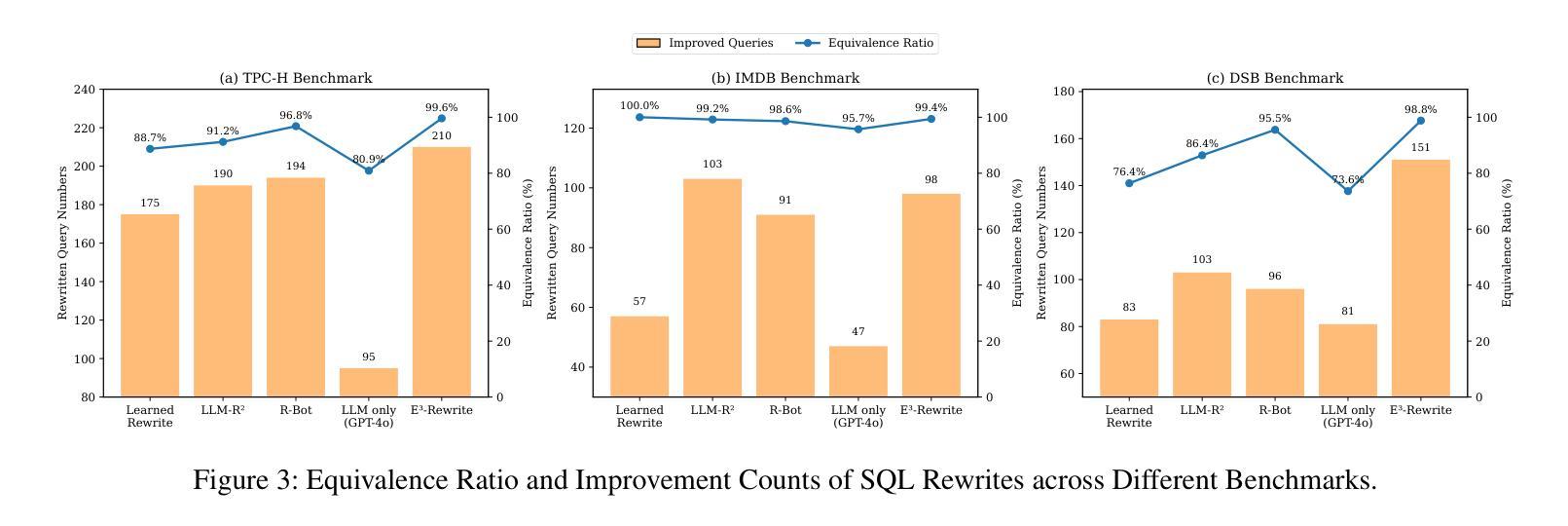
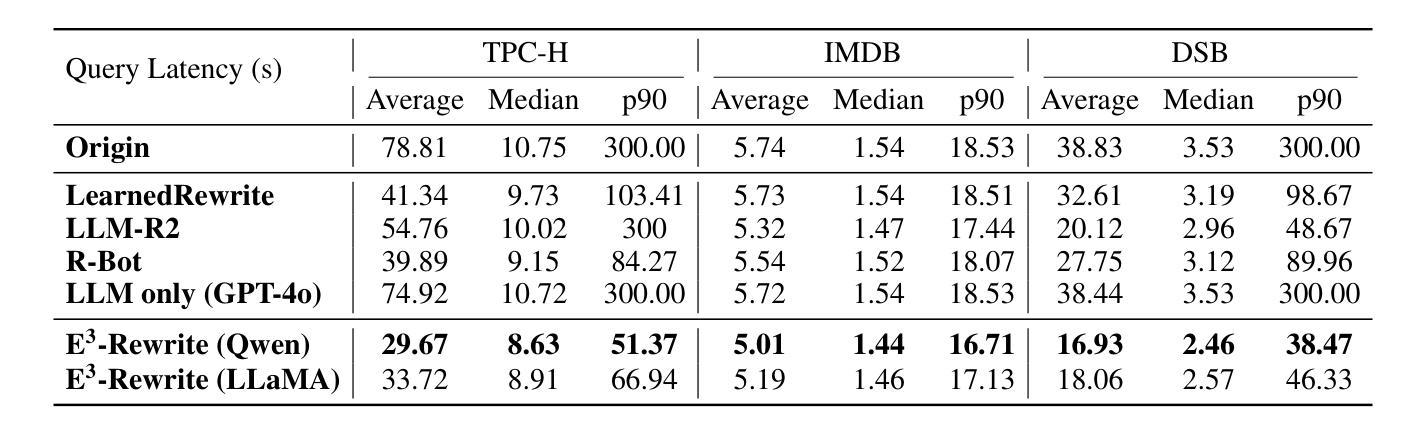
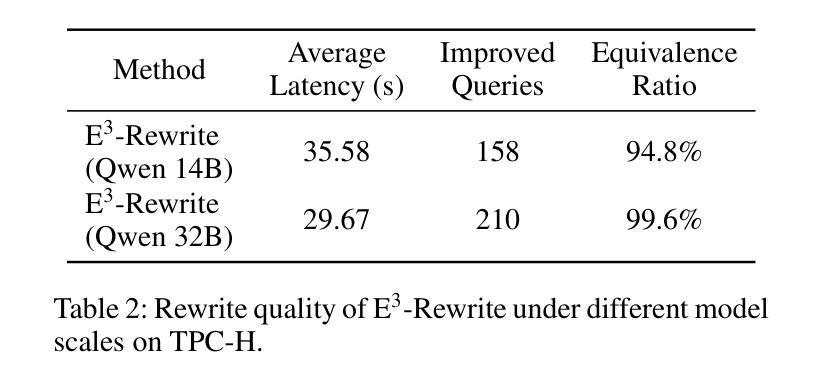
E3-Rewrite: Learning to Rewrite SQL for Executability, Equivalence,and Efficiency
Authors:Dongjie Xu, Yue Cui, Weijie Shi, Qingzhi Ma, Hanghui Guo, Jiaming Li, Yao Zhao, Ruiyuan Zhang, Shimin Di, Jia Zhu, Kai Zheng, Jiajie Xu
SQL query rewriting aims to reformulate a query into a more efficient form while preserving equivalence. Most existing methods rely on predefined rewrite rules. However, such rule-based approaches face fundamental limitations: (1) fixed rule sets generalize poorly to novel query patterns and struggle with complex queries; (2) a wide range of effective rewriting strategies cannot be fully captured by declarative rules. To overcome these issues, we propose using large language models (LLMs) to generate rewrites. LLMs can capture complex strategies, such as evaluation reordering and CTE rewriting. Despite this potential, directly applying LLMs often results in suboptimal or non-equivalent rewrites due to a lack of execution awareness and semantic grounding. To address these challenges, We present E3-Rewrite, an LLM-based SQL rewriting framework that produces executable, equivalent, and efficient queries. It integrates two core components: a context construction module and a reinforcement learning framework. First, the context module leverages execution plans and retrieved demonstrations to build bottleneck-aware prompts that guide inference-time rewriting. Second, we design a reward function targeting executability, equivalence, and efficiency, evaluated via syntax checks, equivalence verification, and cost estimation. Third, to ensure stable multi-objective learning, we adopt a staged curriculum that first emphasizes executability and equivalence, then gradually incorporates efficiency. Extensive experiments show that E3-Rewrite achieves up to a 25.6% reduction in query execution time compared to state-of-the-art methods across multiple SQL benchmarks. Moreover, it delivers up to 24.4% more successful rewrites, expanding coverage to complex queries that previous systems failed to handle.
SQL查询重写旨在将查询重新表述为更有效率的形式,同时保持等效性。现有的大多数方法都依赖于预定义的重写规则。然而,基于规则的方法面临根本性的局限:(1)固定规则集对新型查询模式泛化能力较差,难以应对复杂查询;(2)许多有效的重写策略无法被声明式规则完全捕获。为了克服这些问题,我们提议使用大型语言模型(LLM)来生成重写。LLM可以捕捉复杂的策略,如评估重排序和CTE重写。尽管有这一潜力,但直接应用LLM通常会导致由于缺乏对执行和语义基础知识的了解而产生非最优或非等效的重写。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了E3-Rewrite,一个基于LLM的SQL重写框架,能够生成可执行、等效且高效的查询。它整合了两个核心组件:一个上下文构建模块和一个强化学习框架。首先,上下文模块利用执行计划和检索到的示例来构建瓶颈感知提示,引导推理时间重写。其次,我们设计了一个奖励函数,以执行性、等效性和效率为目标,通过语法检查、等效性验证和成本评估进行评价。第三,为了确保稳定的多目标学习,我们采用了一种分阶段课程学习方法,首先强调执行性和等效性,然后逐渐融入效率考量。广泛的实验表明,与最新方法相比,E3-Rewrite在多个SQL基准测试上实现了最多达25.6%的查询执行时间减少。此外,它提供了最多达24.4%的更成功重写,扩展了对以前系统无法处理的复杂查询的覆盖范围。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
SQL查询重写旨在将查询转化为更高效的表达形式且保持原意不变。传统方法多依赖于预设的改写规则,但存在诸多局限:对新查询模式泛化能力弱,难以应对复杂查询;许多有效的改写策略无法被声明式规则完全捕捉。为克服这些问题,我们提议利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行改写。LLM能够捕捉复杂的策略,如评估重排序和CTE重写等。然而,直接应用LLM往往导致次优或非等效的改写结果,缺乏执行意识和语义基础。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个基于LLM的SQL重写框架E3-Rewrite,能够生成可执行的、等效的、高效的查询。它包含两个核心组件:上下文构建模块和强化学习框架。首先,上下文模块利用执行计划和检索到的示例来构建瓶颈感知提示,以引导推理时的重写。其次,我们设计了一个奖励函数,以执行性、等效性和高效性为目标,通过语法检查、等效验证和成本估算进行评价。再次,为确保稳定的多目标学习,我们采用分阶段课程学习的方法,首先强调执行性和等效性,然后逐渐融入高效性。大量实验表明,与最新方法相比,E3-Rewrite在多个SQL基准测试上实现了最多达25.6%的查询执行时间减少。此外,它还能进行更多达24.4%的成功改写,覆盖以前系统无法处理的复杂查询。
关键见解
- SQL查询重写旨在提高查询效率并保持语义不变。
- 传统规则方法面临对新查询模式和复杂查询的局限性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在SQL查询重写中具有捕捉复杂策略的能力。
- 直接应用LLM导致次优或非等效改写结果的问题。
- E3-Rewrite框架结合LLM和强化学习,生成可执行、等效和高效的SQL查询。
- E3-Rewrite通过上下文模块和奖励函数设计,能有效解决执行性、等效性和高效性问题。
点此查看论文截图

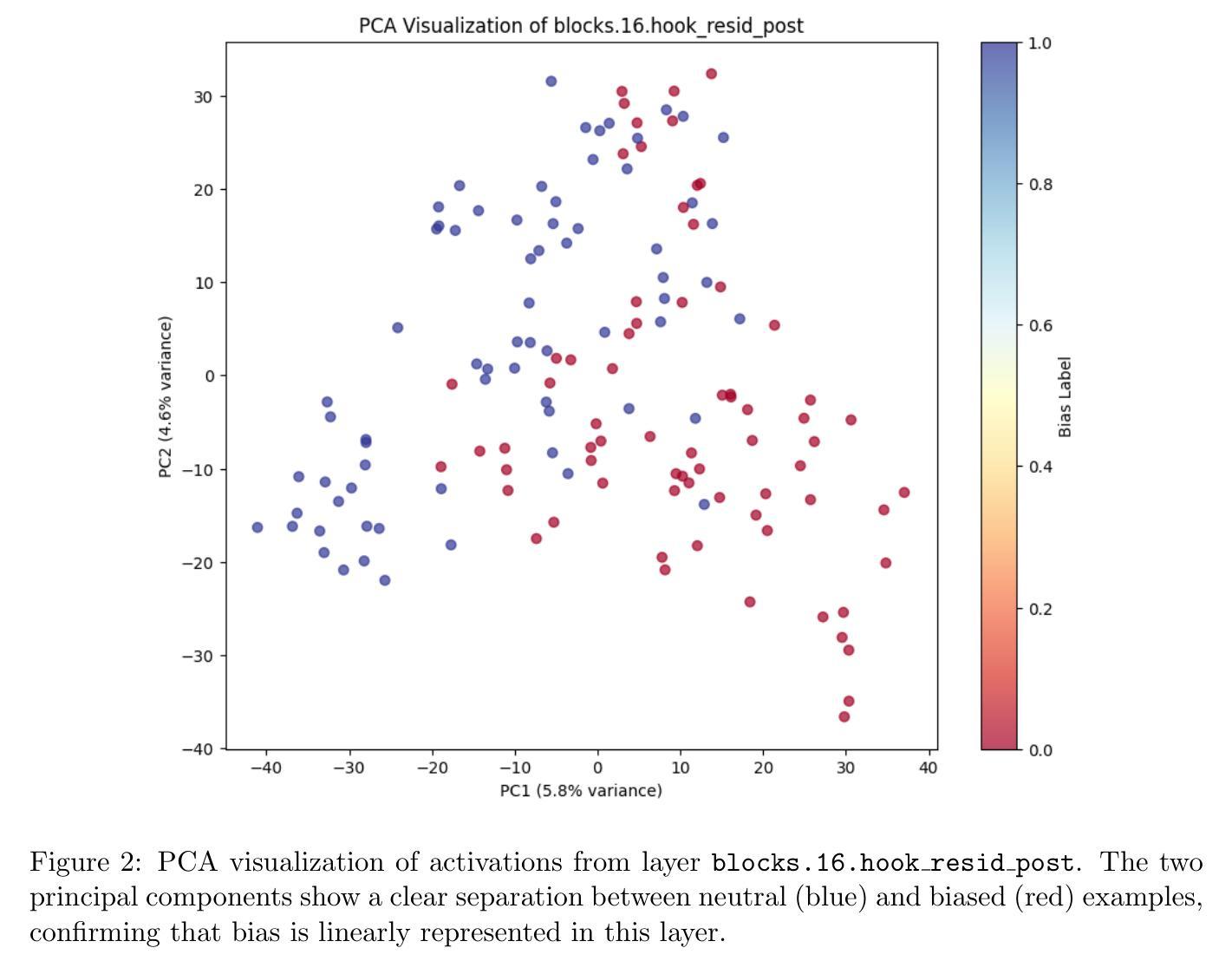
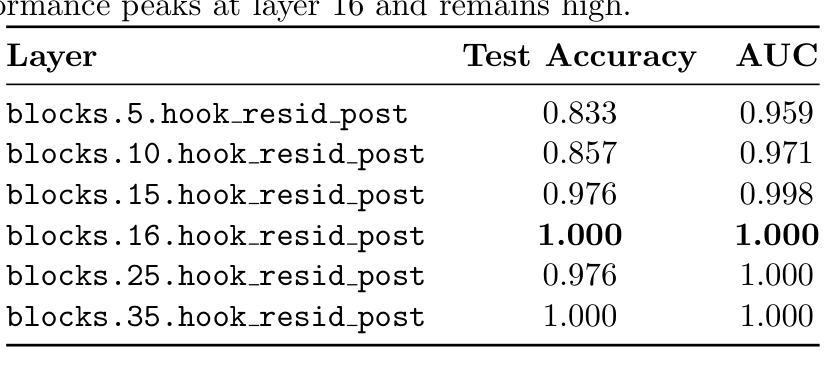
Activation Steering for Bias Mitigation: An Interpretable Approach to Safer LLMs
Authors:Shivam Dubey
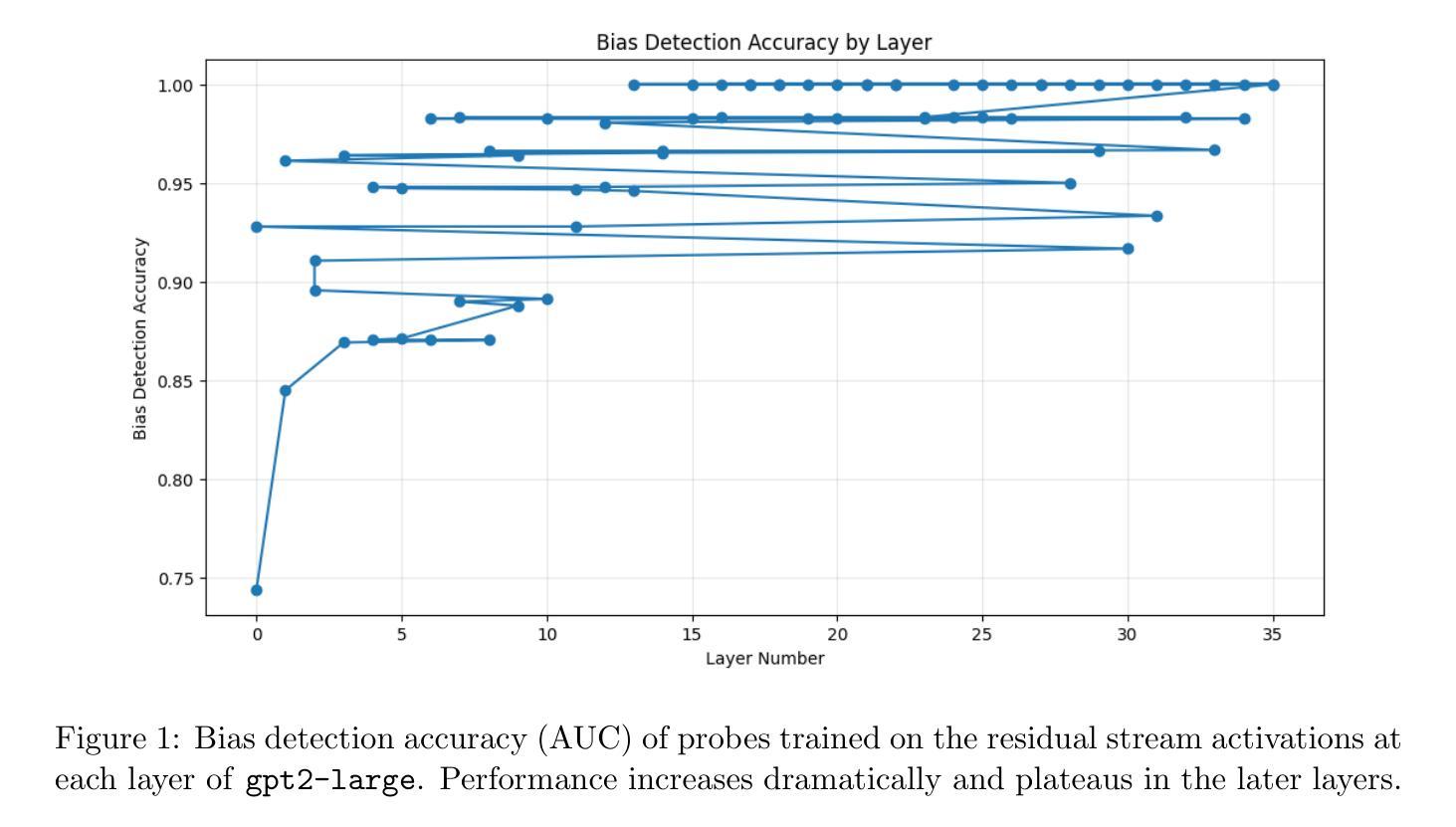
As large language models (LLMs) become more integrated into societal systems, the risk of them perpetuating and amplifying harmful biases becomes a critical safety concern. Traditional methods for mitigating bias often rely on data filtering or post-hoc output moderation, which treat the model as an opaque black box. In this work, we introduce a complete, end-to-end system that uses techniques from mechanistic interpretability to both identify and actively mitigate bias directly within a model’s internal workings. Our method involves two primary stages. First, we train linear “probes” on the internal activations of a model to detect the latent representations of various biases (e.g., gender, race, age). Our experiments on \texttt{gpt2-large} demonstrate that these probes can identify biased content with near-perfect accuracy, revealing that bias representations become most salient in the model’s later layers. Second, we leverage these findings to compute “steering vectors” by contrasting the model’s activation patterns for biased and neutral statements. By adding these vectors during inference, we can actively steer the model’s generative process away from producing harmful, stereotypical, or biased content in real-time. We demonstrate the efficacy of this activation steering technique, showing that it successfully alters biased completions toward more neutral alternatives. We present our work as a robust and reproducible system that offers a more direct and interpretable approach to building safer and more accountable LLMs.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在社会系统中得到更深入的集成,它们可能传播和放大有害偏见的风险成为了一个关键的安全问题。传统的减轻偏见的方法通常依赖于数据过滤或事后输出调解,这些方法将模型视为一个不透明的黑箱。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个完整、端到端的系统,该系统使用来自机械解释性的技术来识别和主动减轻模型内部工作中存在的偏见。我们的方法涉及两个阶段。首先,我们在模型的内部激活上训练线性“探针”,以检测各种偏见(如性别、种族、年龄等)的潜在表示。我们在
gpt2-large上的实验表明,这些探针可以近乎完美地识别出有偏见的内容,揭示出偏见表示在模型的较深层中变得最为突出。其次,我们利用这些发现,通过对比模型对带有偏见和中性陈述的激活模式来计算“转向向量”。通过在推理过程中添加这些向量,我们可以实时地主动引导模型的生成过程,避免产生有害的、刻板的或有偏见的内容。我们证明了激活转向技术的有效性,表明它成功地改变了有偏见的完成内容,使其更加中立。我们提出的是一个稳健且可复制的系统,它提供了一种更直接和可解释的方法,用于构建更安全、更负责任的大型语言模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在社会系统中的集成愈发普及,因此潜在的对社会产生偏见和加剧放大有害偏见的担忧与日俱增。以往解决偏见问题的策略主要依赖于数据过滤或事后输出调节方法,但这些方法未充分关注模型的内部运作过程,使得模型像黑箱一样难以理解和控制。本研究介绍了一种端到端的系统,采用机械解释性技术直接识别并缓解模型内部存在的偏见。首先,通过对模型内部激活状态进行训练来探测各种偏见的潜在表征。实验显示这些探测器可以近乎完美地识别出有偏见的言论,并发现偏见信息在模型的深层结构中最为突出。其次,通过对比有偏见和无偏见语句的激活模式,计算出所谓的“引导向量”。在推理过程中引入这些向量,可以实时引导模型生成过程避免产生有害的刻板印象或偏见内容。研究证明了这种激活引导技术的有效性,即通过该方法可以将偏向性的结论引向更为中立的方向。本研究提供了一个稳健和可复制的系统框架,为构建更安全、更负责任的大型语言模型提供了更直接和可解释的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在社会系统中的应用引发了对偏见风险的关注。
- 传统方法处理偏见问题存在局限性,无法充分解释模型的内部运作过程。
- 本研究介绍了一种端到端的系统来直接识别和缓解模型内部的偏见。
- 通过训练线性探测器来探测模型的内部激活状态,可识别偏见言论的潜在表征。实验证明这些探测器可以近乎完美地识别偏见内容。
- 揭示偏见信息在模型的深层结构中最为突出。
- 通过对比有偏见和无偏见语句的激活模式计算引导向量,实时引导模型避免生成有害的刻板印象或偏见内容。
点此查看论文截图


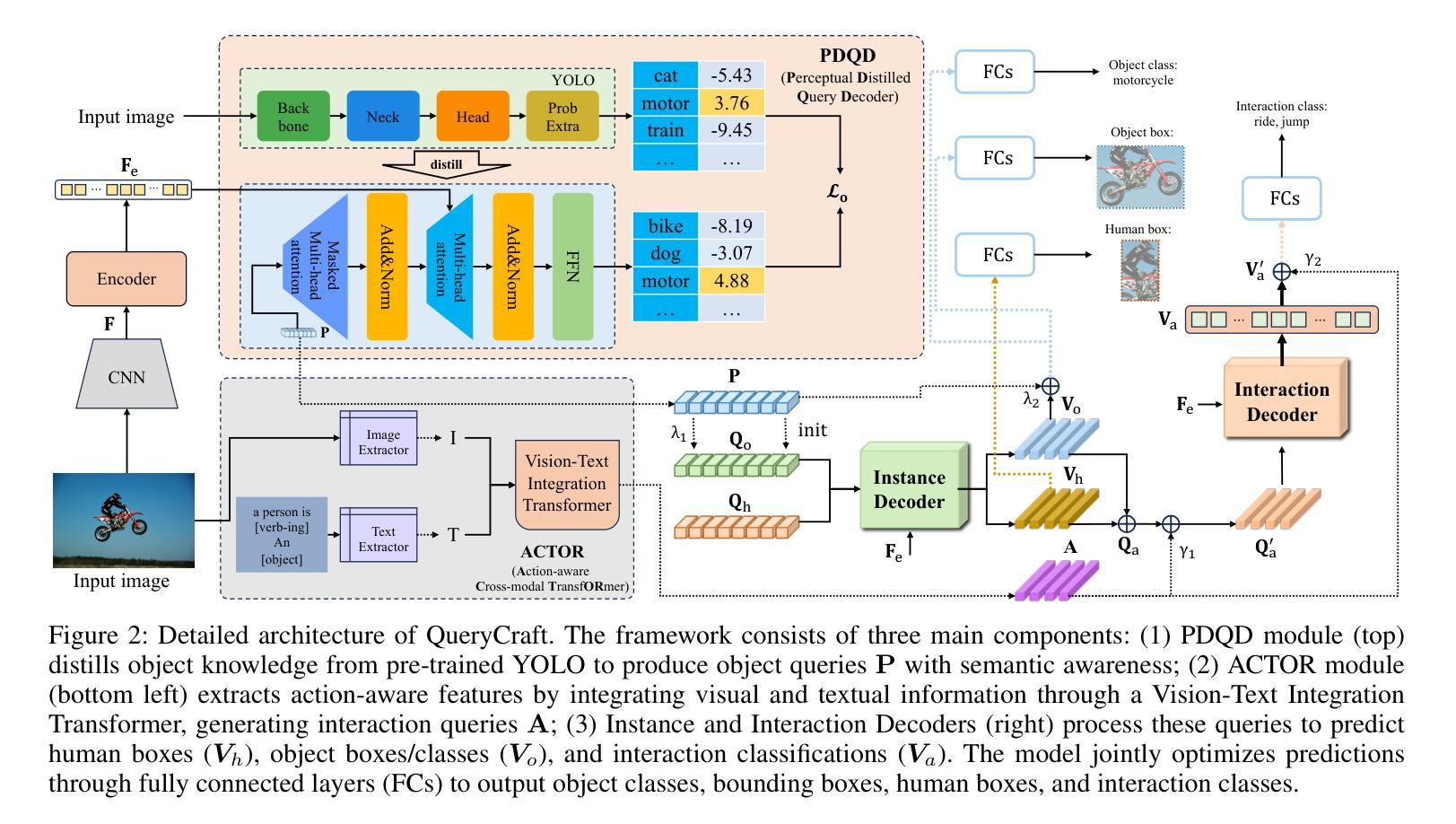
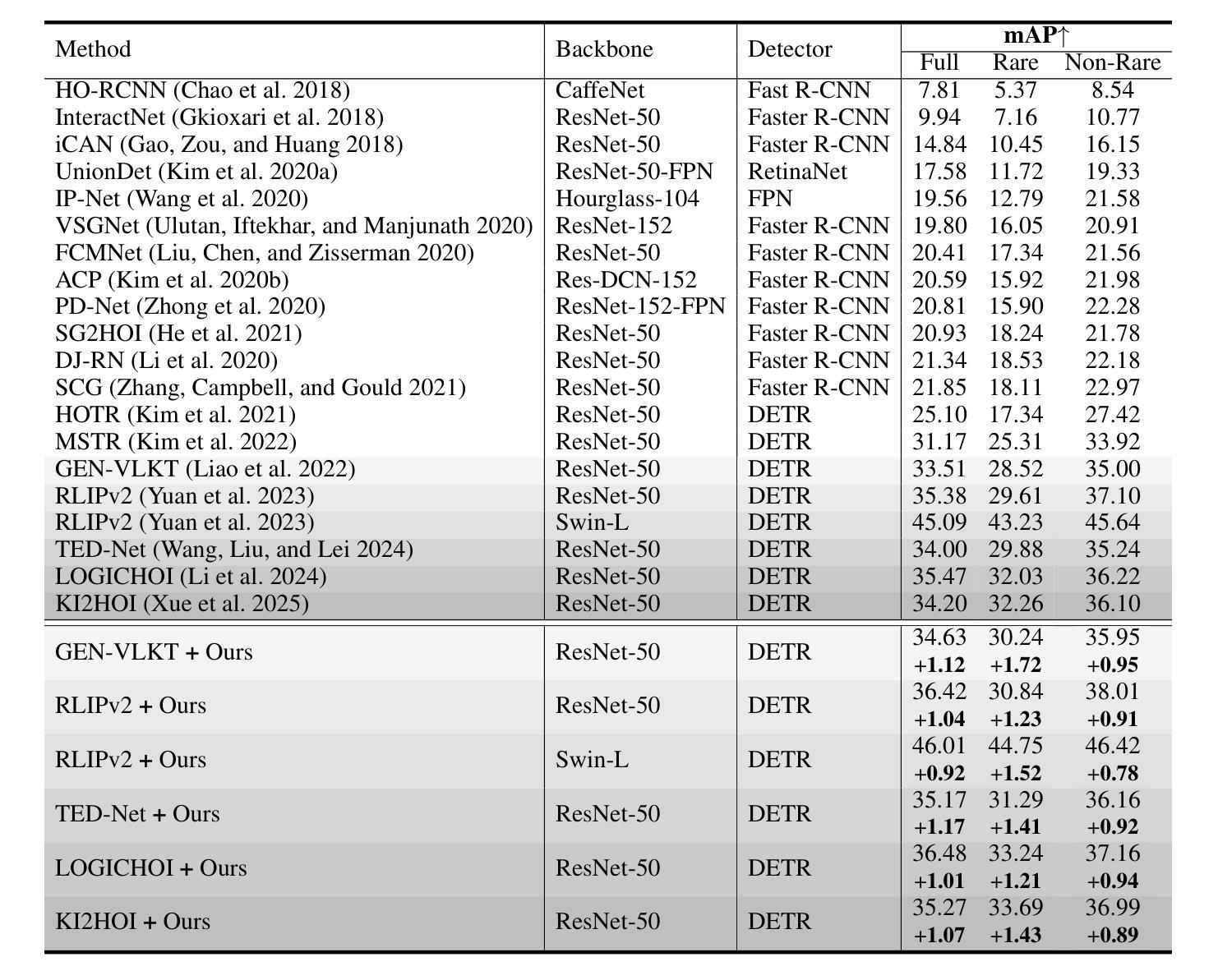
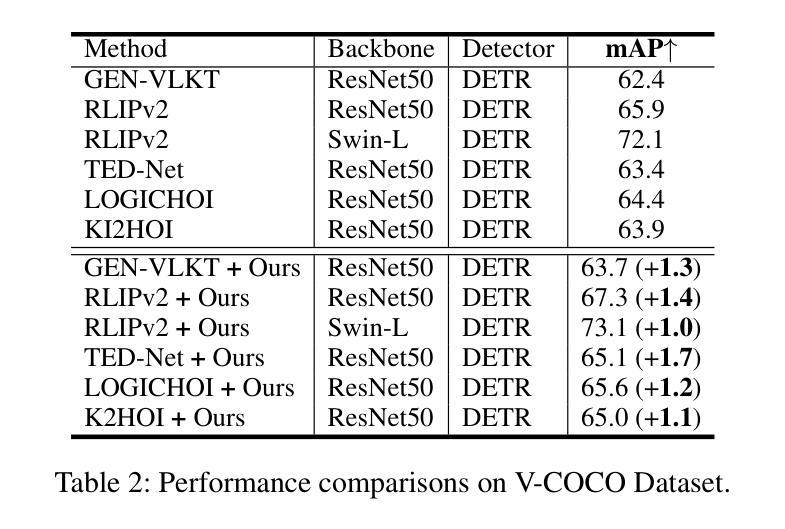
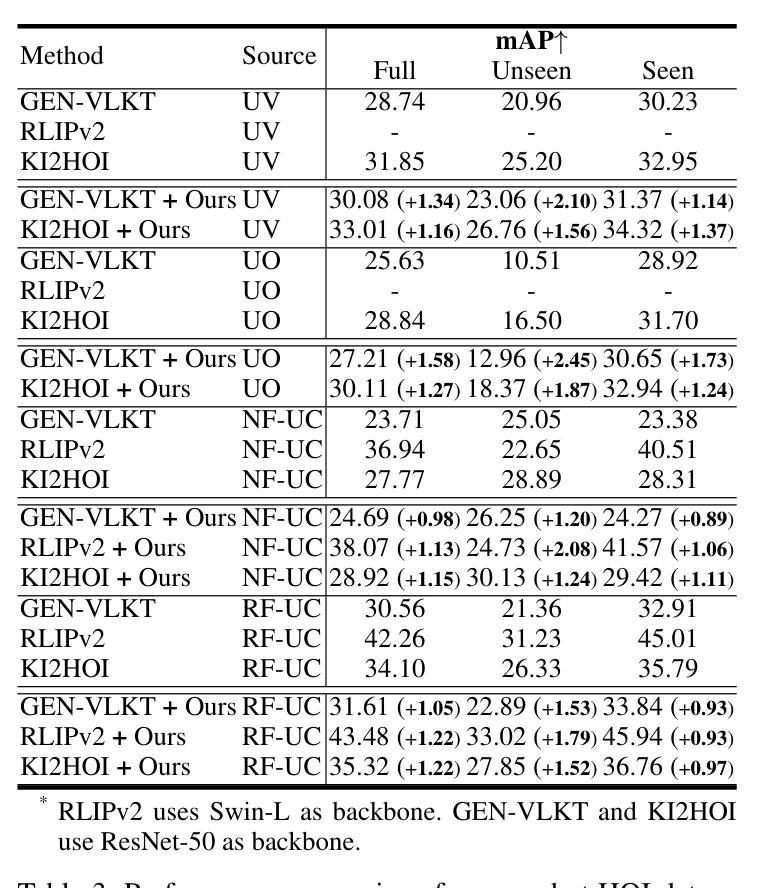
QueryCraft: Transformer-Guided Query Initialization for Enhanced Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Yuxiao Wang, Wolin Liang, Yu Lei, Weiying Xue, Nan Zhuang, Qi Liu
Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection aims to localize human-object pairs and recognize their interactions in images. Although DETR-based methods have recently emerged as the mainstream framework for HOI detection, they still suffer from a key limitation: Randomly initialized queries lack explicit semantics, leading to suboptimal detection performance. To address this challenge, we propose QueryCraft, a novel plug-and-play HOI detection framework that incorporates semantic priors and guided feature learning through transformer-based query initialization. Central to our approach is \textbf{ACTOR} (\textbf{A}ction-aware \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{T}ransf\textbf{OR}mer), a cross-modal Transformer encoder that jointly attends to visual regions and textual prompts to extract action-relevant features. Rather than merely aligning modalities, ACTOR leverages language-guided attention to infer interaction semantics and produce semantically meaningful query representations. To further enhance object-level query quality, we introduce a \textbf{P}erceptual \textbf{D}istilled \textbf{Q}uery \textbf{D}ecoder (\textbf{PDQD}), which distills object category awareness from a pre-trained detector to serve as object query initiation. This dual-branch query initialization enables the model to generate more interpretable and effective queries for HOI detection. Extensive experiments on HICO-Det and V-COCO benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and strong generalization. Code will be released upon publication.
人类物体交互(HOI)检测旨在定位图像中的人-物体对并识别其交互。尽管基于DETR的方法已经逐渐成为HOI检测的主流框架,但它们仍然存在一个关键局限性:随机初始化的查询缺乏明确的语义,导致检测性能不佳。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了QueryCraft,这是一个新的即插即用的人机交互检测框架,它通过基于变压器的查询初始化,结合了语义先验知识和引导特征学习。我们的方法的核心是动作感知跨模态转换器(ACTOR),这是一种跨模态变压器编码器,能够共同关注视觉区域和文本提示,以提取与动作相关的特征。ACTOR不仅对齐不同模态,还利用语言引导注意力来推断交互语义并产生语义上有意义的查询表示。为了进一步提高了对象级别的查询质量,我们引入了感知蒸馏查询解码器(PDQD),它从预训练的检测器中提炼出物体类别意识,作为物体查询的初始化。这种双分支查询初始化使模型能够生成更具解释性和有效性的查询,用于HOI检测。在HICO-Det和V-COCO基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能和强大的泛化能力。代码将在出版时发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于语义先验和引导特征学习的HOI检测框架QueryCraft,通过初始化的查询来识别图像中的人与物体的交互。核心方法是利用跨模态Transformer编码器ACTOR,它关注视觉区域和文本提示,提取动作相关特征,通过语言引导注意力推断交互语义并产生语义上有意义的查询表示。为提高对象级别查询质量,引入了感知蒸馏查询解码器PDQD,从预训练检测器中蒸馏出物体类别意识用于对象查询启动。双分支查询初始化使模型生成更可解释和有效的查询进行HOI检测。在HICO-Det和V-COCO基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- QueryCraft是一种新型的HOI检测框架,旨在解决DETR方法中随机初始化查询语义不明确的问题。
- ACTOR是跨模态Transformer编码器,关注视觉区域和文本提示以提取动作相关特征,并通过语言引导注意力推断交互语义。
- PDQD解码器用于提高对象级别查询质量,通过从预训练检测器中蒸馏物体类别意识来初始化对象查询。
- 双分支查询初始化生成更可解释和有效的查询进行HOI检测。
点此查看论文截图

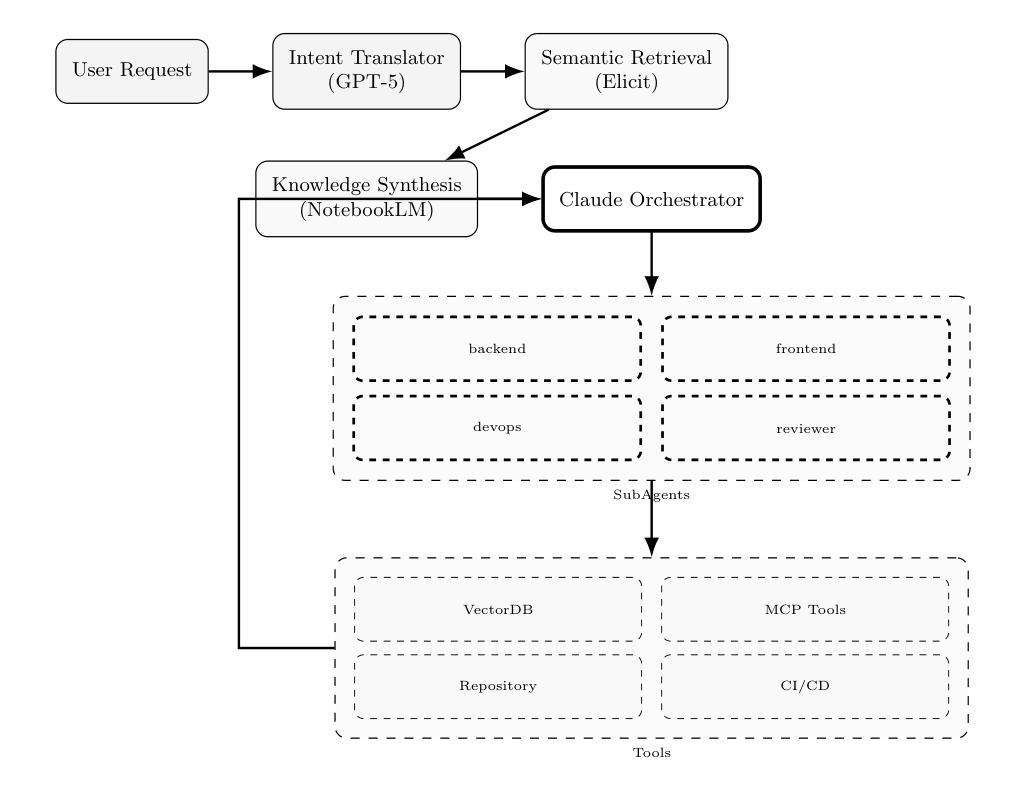
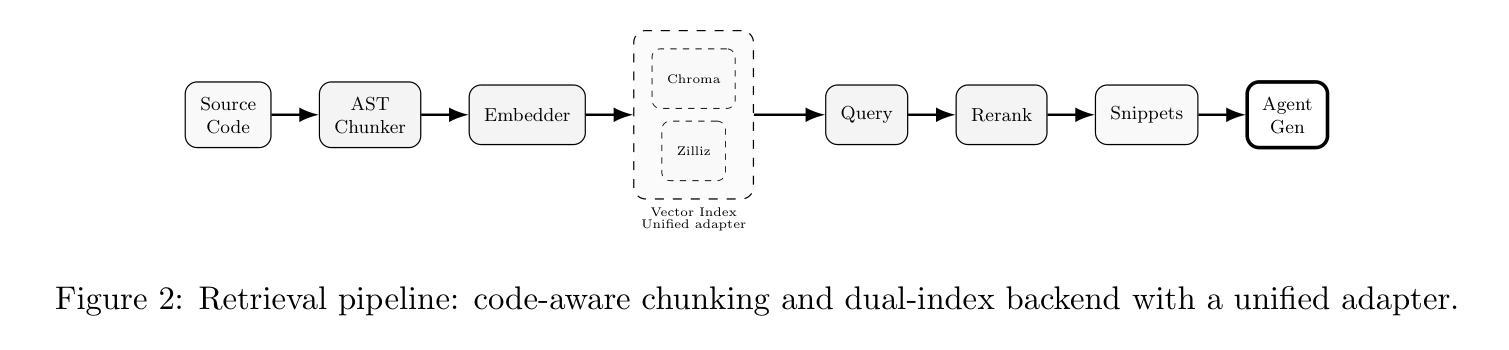
Context Engineering for Multi-Agent LLM Code Assistants Using Elicit, NotebookLM, ChatGPT, and Claude Code
Authors:Muhammad Haseeb
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automating code generation and software engineering tasks, yet they often struggle with complex, multi-file projects due to context limitations and knowledge gaps. We propose a novel context engineering workflow that combines multiple AI components: an Intent Translator (GPT-5) for clarifying user requirements, an Elicit-powered semantic literature retrieval for injecting domain knowledge, NotebookLM-based document synthesis for contextual understanding, and a Claude Code multi-agent system for code generation and validation. Our integrated approach leverages intent clarification, retrieval-augmented generation, and specialized sub-agents orchestrated via Claude’s agent framework. We demonstrate that this method significantly improves the accuracy and reliability of code assistants in real-world repositories, yielding higher single-shot success rates and better adherence to project context than baseline single-agent approaches. Qualitative results on a large Next.js codebase show the multi-agent system effectively plans, edits, and tests complex features with minimal human intervention. We compare our system with recent frameworks like CodePlan, MASAI, and HyperAgent, highlighting how targeted context injection and agent role decomposition lead to state-of-the-art performance. Finally, we discuss the implications for deploying LLM-based coding assistants in production, along with lessons learned on context management and future research directions.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化代码生成和软件工程任务方面展现出巨大潜力,但由于上下文限制和知识差距,它们在处理复杂的多文件项目时常常遇到困难。我们提出了一种结合多个AI组件的新型上下文工程工作流程:使用GPT-5意图翻译器来明确用户需求,利用Elicit增强的语义文献检索来注入领域知识,使用NotebookLM基于文档的合成进行上下文理解,以及使用Claude Code多智能体系统进行代码生成和验证。我们的综合方法利用意图澄清、检索增强生成和通过Claude的代理框架协调的专门子代理。我们证明,该方法显著提高了真实世界存储库中代码助手的准确性和可靠性,与基线单代理方法相比,单次成功率和项目上下文的遵循度更高。在大型Next.js代码库上的定性结果证明了多智能体系统能够有效地规划、编辑和测试复杂功能,几乎无需人工干预。我们将我们的系统与最近的CodePlan、MASAI和HyperAgent等框架进行了比较,重点介绍了如何通过有针对性的上下文注入和智能体角色分解来实现最新性能。最后,我们讨论了在生产环境中部署基于LLM的编码助手的含义,以及在上下文管理方面的经验教训和未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures, research paper on multi-agent LLM systems for code generation
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化代码生成和软件工程任务中展现出潜力,但在处理复杂多文件项目时面临语境限制和知识鸿沟的挑战。本研究提出了一种结合多种AI组件的新型语境工程流程,包括意图翻译器(GPT-5)、Elicit驱动的语义文献检索、NotebookLM基础的文档合成以及Claude Code多智能体系统进行代码生成和验证。该方法通过意图澄清、检索增强生成和通过Claude的智能体框架协调的专业子智能体,显著提高了代码助手的准确性和可靠性,实现了更高的单次成功率,更好地适应了项目语境。在Next.js代码库的大规模定性结果中,显示了多智能体系统能够有效地规划、编辑和测试复杂功能,几乎无需人工干预。最后,本文讨论了将LLM基于的编码助手用于生产的影响,以及关于语境管理和未来研究方向的经验教训。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在自动化代码生成和软件工程任务中具有潜力,但在处理复杂多文件项目时存在局限。
- 提出了一种新型语境工程流程,结合多种AI组件以提高代码助手的准确性和可靠性。
- 通过意图澄清、检索增强生成和专用子智能体协调,实现了更高的单次成功率和更好的项目语境适应性。
- 多智能体系统在Next.js代码库的大规模测试中表现出色,能够有效规划、编辑和测试复杂功能。
- 与CodePlan、MASAI和HyperAgent等框架相比,本系统的针对性语境注入和智能体角色分解达到了最新性能。
- 讨论了将LLM用于生产的影响,强调了部署时的潜在挑战和机会。
点此查看论文截图

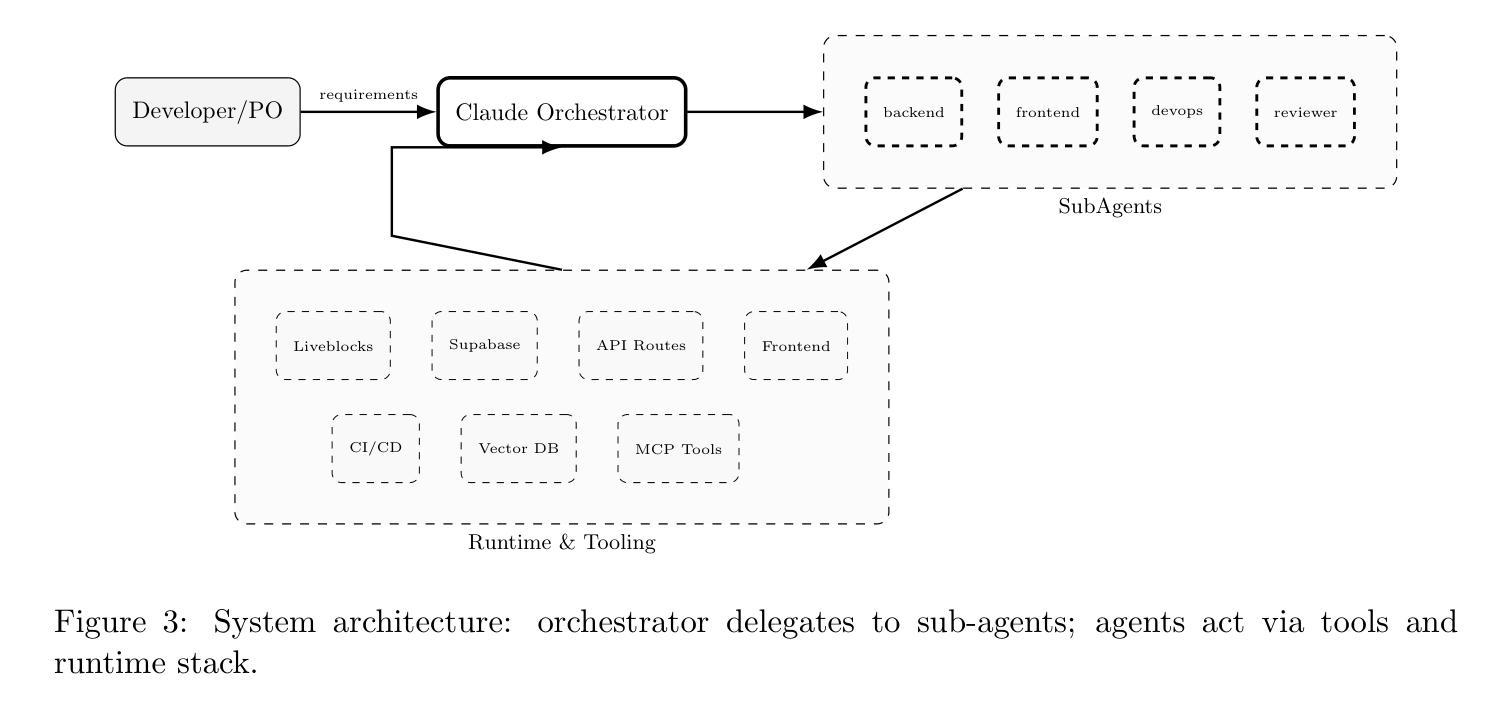
Grounding Multilingual Multimodal LLMs With Cultural Knowledge
Authors:Jean de Dieu Nyandwi, Yueqi Song, Simran Khanuja, Graham Neubig
Multimodal Large Language Models excel in high-resource settings, but often misinterpret long-tail cultural entities and underperform in low-resource languages. To address this gap, we propose a data-centric approach that directly grounds MLLMs in cultural knowledge. Leveraging a large scale knowledge graph from Wikidata, we collect images that represent culturally significant entities, and generate synthetic multilingual visual question answering data. The resulting dataset, CulturalGround, comprises 22 million high-quality, culturally-rich VQA pairs spanning 42 countries and 39 languages. We train an open-source MLLM CulturalPangea on CulturalGround, interleaving standard multilingual instruction-tuning data to preserve general abilities. CulturalPangea achieves state-of-the-art performance among open models on various culture-focused multilingual multimodal benchmarks, outperforming prior models by an average of 5.0 without degrading results on mainstream vision-language tasks. Our findings show that our targeted, culturally grounded approach could substantially narrow the cultural gap in MLLMs and offer a practical path towards globally inclusive multimodal systems.
多模态大型语言模型在高资源环境中表现出色,但常常误解长尾文化实体并在低资源语言中表现不佳。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种以数据为中心的方法,该方法直接将多模态大型语言模型根植于文化知识中。我们利用来自维基百科的大规模知识图谱,收集代表文化重要实体的图像,并生成合成多语言视觉问答数据。所得数据集CulturalGround包含2200万高质量、文化丰富的问答对,涵盖42个国家和39种语言。我们在CulturalGround上训练开源多模态大型语言模型CulturalPangea,同时交织标准的多语言指令微调数据以保留其一般能力。CulturalPangea在各种以文化为重点的多语言多模态基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,相较于先前的模型,平均性能提高了5.0%,同时在主流视觉语言任务上的结果并未降低。我们的研究结果表明,我们针对性、以文化为基础的方法可以大幅度缩小多模态大型语言模型中的文化差距,并为实现全球包容性多模态系统提供实际路径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模多模态语言模型在高资源环境下表现出色,但在长尾文化实体方面常常误解,并且在低资源语言环境下表现不佳。为弥补这一差距,本研究提出了一种以数据为中心的方法,直接以文化为基础对多模态语言模型进行训练。通过利用维基百科的大规模知识图谱收集代表文化重要实体的图像,并生成合成多语言视觉问答数据。所构建的CulturalGround数据集包含跨越42个国家和39种语言的22亿高质量、文化丰富的问答对。训练出的开源多模态语言模型CulturalPangea在多种面向文化的多语言多模态基准测试中达到了先进水平,平均优于现有模型5.0%,同时在主流视觉语言任务上未出现性能下降。研究结果表明,有针对性的文化基础方法能够显著缩小多模态语言模型中的文化差距,并为全球包容性多模态系统提供了实际的发展路径。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大规模语言模型在高资源环境下表现良好,但在处理长尾文化实体和低资源语言时存在不足。
- 提出了以数据为中心的方法,利用维基百科知识图谱和图像数据来丰富多模态语言模型的文化知识。
- 构建了CulturalGround数据集,包含跨越多个国家和语言的丰富文化视觉问答对。
- 训练出的开源多模态语言模型CulturalPangea在多种文化相关的基准测试中表现优异,显著优于现有模型。
- CulturalPangea模型在保持主流视觉语言任务性能的同时,提高了在文化领域的表现。
- 研究显示,有针对性的文化基础方法有助于缩小多模态语言模型中的文化差距。
点此查看论文截图

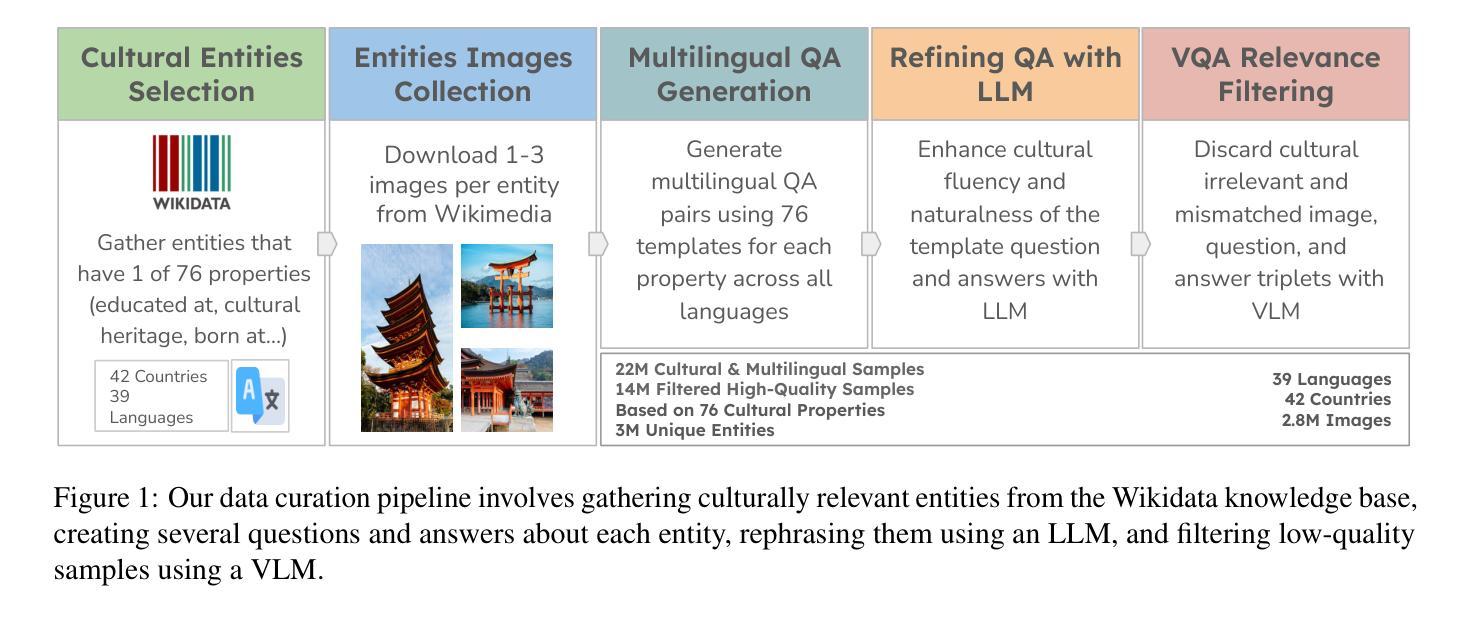
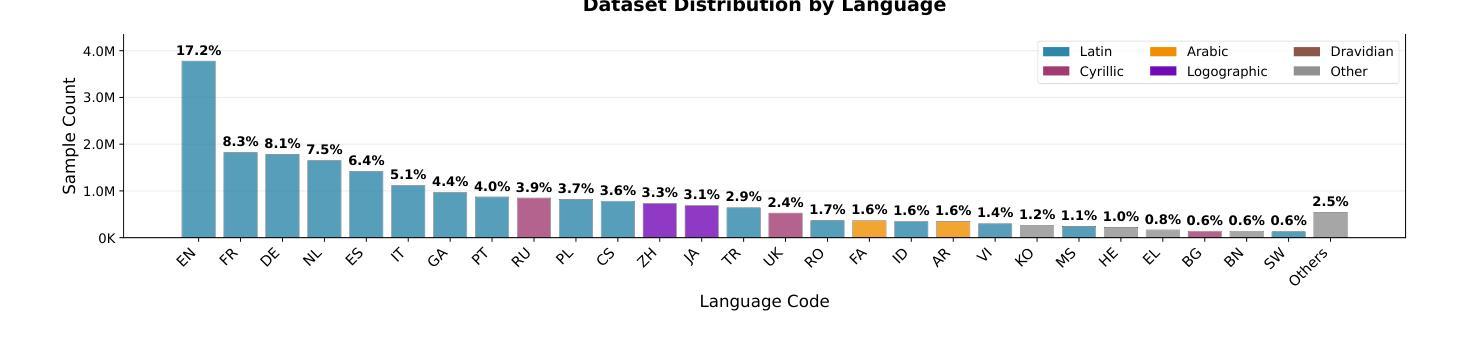
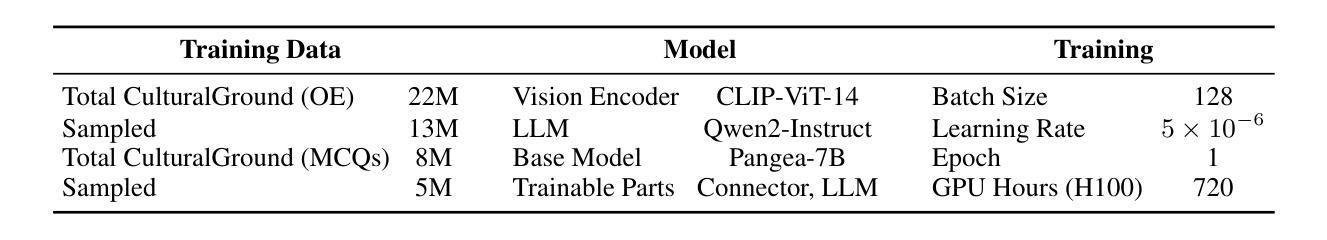
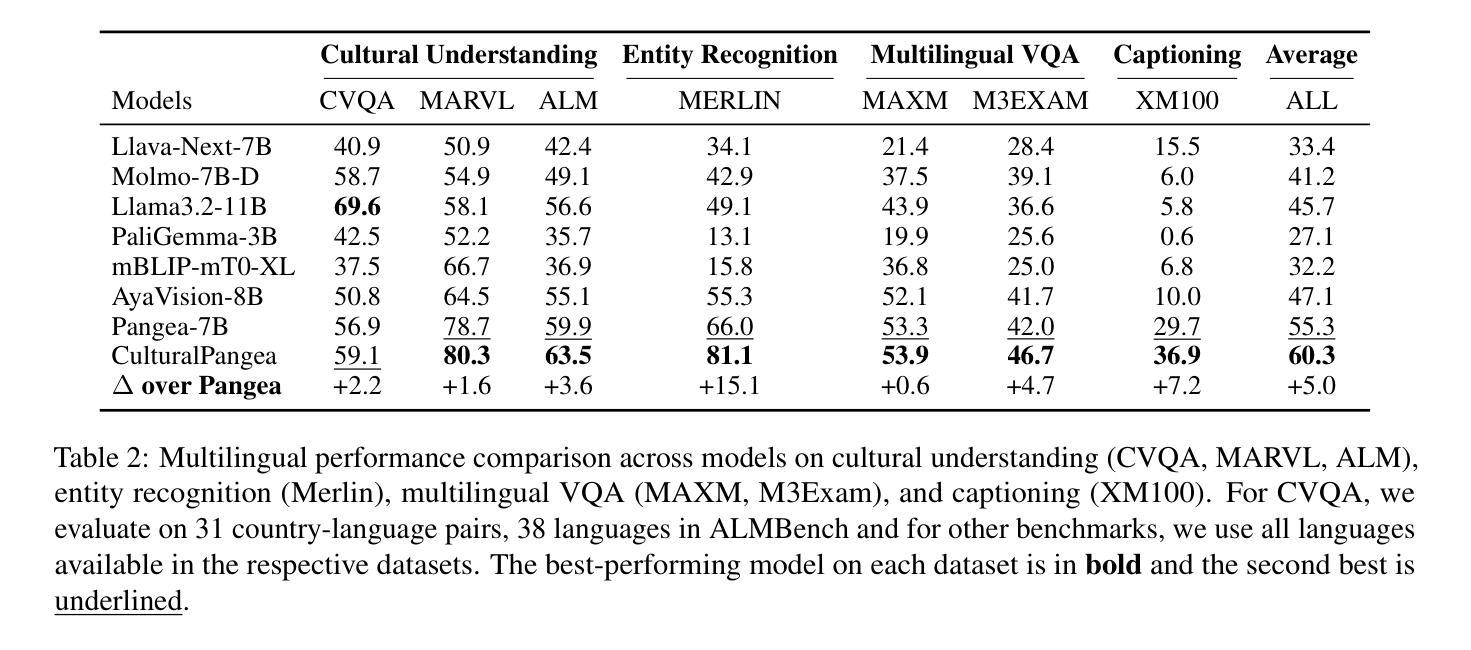
Technical Report: Full-Stack Fine-Tuning for the Q Programming Language
Authors:Brendan R. Hogan, Will Brown, Adel Boyarsky, Anderson Schneider, Yuriy Nevmyvaka
Even though large language models are becoming increasingly capable, it is still unreasonable to expect them to excel at tasks that are under-represented on the Internet. Leveraging LLMs for specialized applications, particularly in niche programming languages and private domains, remains challenging and largely unsolved. In this work, we address this gap by presenting a comprehensive, open-source approach for adapting LLMs to the Q programming language, a popular tool in quantitative finance that is much less present on the Internet compared to Python, C, Java, and other ``mainstream” languages and is therefore not a strong suit of general-purpose AI models. We introduce a new Leetcode style evaluation dataset for Q, benchmark major frontier models on the dataset, then do pretraining, supervised fine tuning, and reinforcement learning to train a suite of reasoning and non-reasoning models based on the Qwen-2.5 series, spanning five parameter sizes (1.5B, 3B, 7B, 14B, 32B). Our best model achieves a pass@1 accuracy of 59 percent on our Q benchmark, surpassing the best-performing frontier model, Claude Opus-4 by 29.5 percent. Additionally, all models, even our 1.5B model, outperform GPT-4.1 on this task. In addition to releasing models, code, and data, we provide a detailed blueprint for dataset construction, model pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning. Our methodology is broadly applicable, and we discuss how these techniques can be extended to other tasks, including those where evaluation may rely on soft or subjective signals.
尽管大型语言模型的能力越来越强,但期望它们在互联网上表现不足的任务上表现出色仍然不合理。将大型语言模型应用于专业应用程序,特别是在小众编程语言和私有领域,仍然存在挑战且尚未完全解决。在这项工作中,我们通过提出一种适应Q编程语言的全面开源方法来解决这一差距。Q是量化金融中流行的工具,与Python、C、Java等“主流”语言相比,其在互联网上的存在度较低,因此不是通用AI模型的强项。我们为Q语言引入了一个新的Leetcode风格评估数据集,在该数据集上评估了主要的前沿模型,然后进行预训练、有监督微调以及强化学习,基于Qwen-2.5系列训练了一套推理和非推理模型,涵盖五种参数大小(1.5B、3B、7B、14B、32B)。我们最好的模型在我们的Q基准测试中达到了59%的pass@1准确率,比最佳性能的前沿模型Claude Opus-4高出29.5%。此外,所有模型,即使是我们最小的1.5B模型,在此任务上的表现也优于GPT-4.1。除了发布模型、代码和数据外,我们还提供了关于数据集构建、模型预训练、有监督微调以及强化学习的详细蓝图。我们的方法是普遍适用的,我们讨论了如何将这些技术扩展到其他任务,包括那些可能依赖于软或主观信号的评估任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然在许多任务上表现出强大的能力,但在代表性不足的网络任务上仍有局限性。特别是在小众编程语言和私有领域的应用中,运用LLM仍存在挑战且尚未完全解决。本研究旨在解决这一缺口,提出了一种针对Q编程语言的开源适应方法。Q是定量金融领域的流行工具,相较于Python、C、Java等主流语言,其在互联网上的存在较少,也是通用AI模型的薄弱环节。研究构建了针对Q语言的Leetcode风格评估数据集,对前沿模型进行基准测试,并采用预训练、监督微调、强化学习等方法,基于Qwen-2.5系列训练了一套推理和非推理模型,参数规模包括五种(1.5B、3B、7B、14B、32B)。最佳模型在Q基准测试上的pass@1准确率达到了59%,比最佳前沿模型Claude Opus-4高出29.5%。此外,所有模型,包括最小的1.5B模型,在此任务上的表现都优于GPT-4.1。除了发布模型、代码和数据外,还提供了详细的数据集构建、模型预训练、监督微调和强化学习的蓝图。此方法具有广泛的应用性,并探讨了如何将这些技术扩展到其他任务,包括那些可能依赖于软性指标或主观信号的评估任务。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在代表性不足的网络任务上表现仍有局限,特别是在小众编程语言和私有领域的应用中。
- 针对Q编程语言(在定量金融领域流行但互联网上较少涉及)的研究填补了LLM在该领域的空白。
- 研究构建了针对Q语言的Leetcode风格评估数据集,为模型性能评估提供了基准。
- 通过预训练、监督微调、强化学习等技术,训练了基于Qwen-2.5系列的推理和非推理模型,参数规模多样。
- 最佳模型在Q基准测试上的准确率超过现有最佳前沿模型,表现优异。
- 所有评估的模型在任务表现上均优于GPT-4.1。
点此查看论文截图
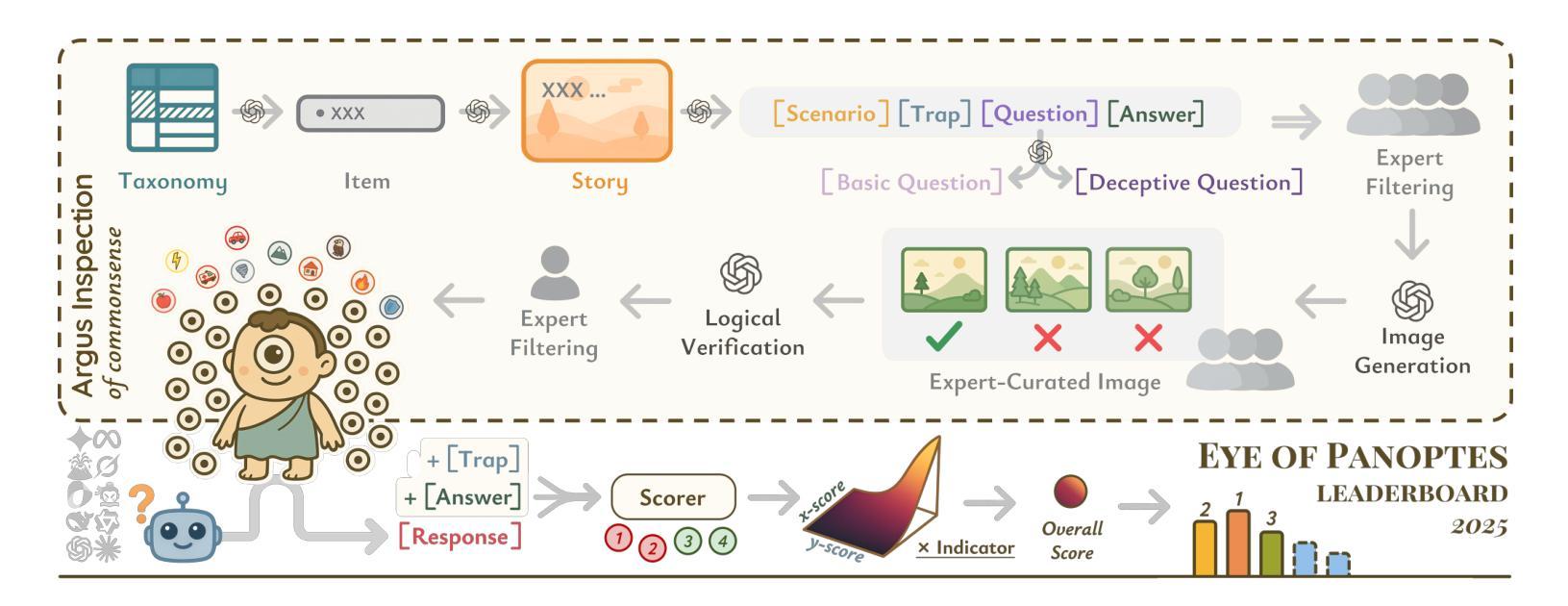
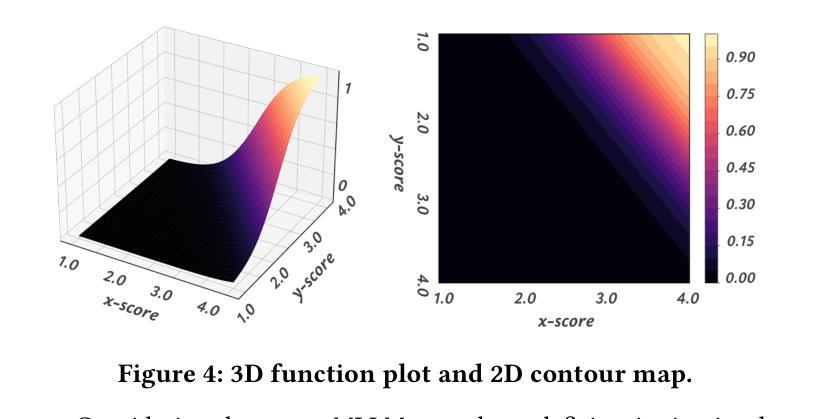
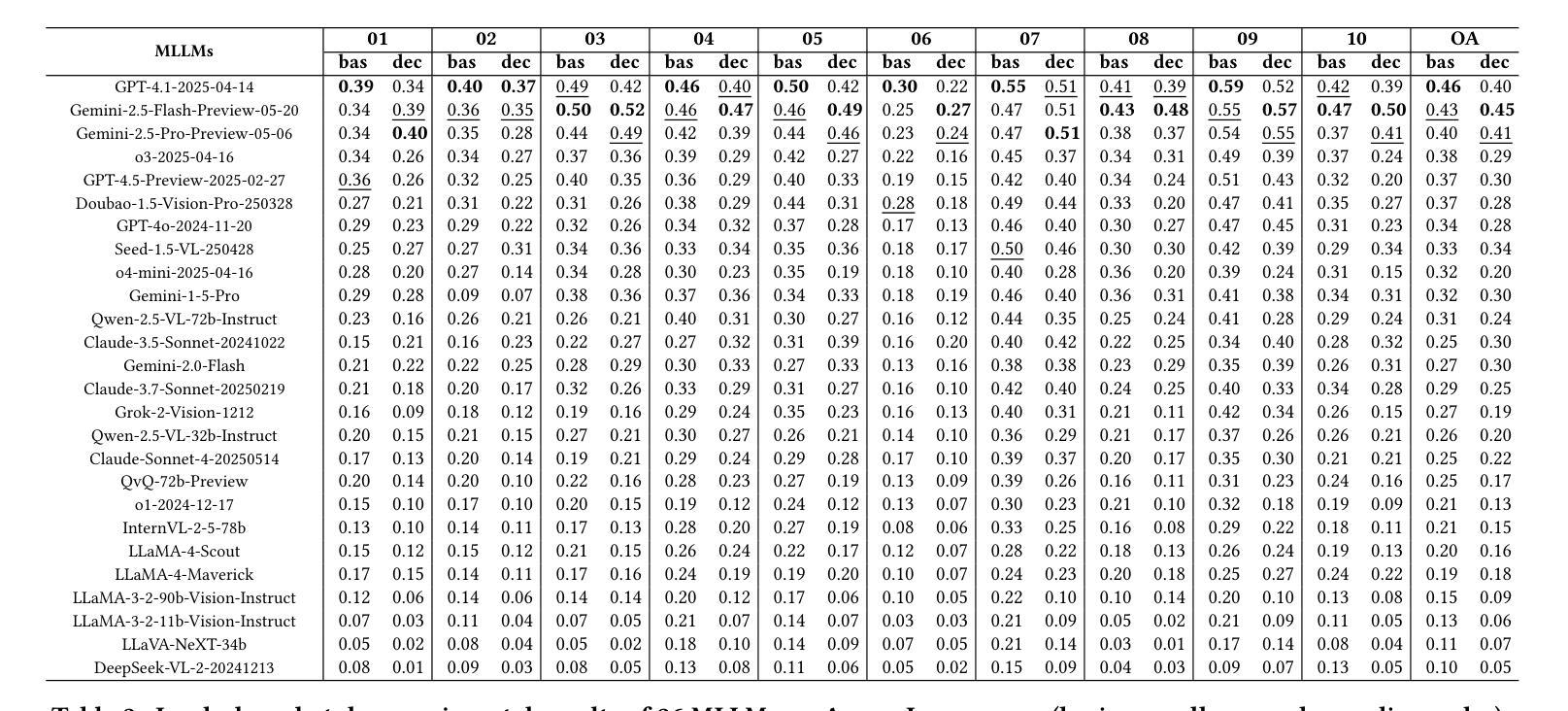
Argus Inspection: Do Multimodal Large Language Models Possess the Eye of Panoptes?
Authors:Yang Yao, Lingyu Li, Jiaxin Song, Chiyu Chen, Zhenqi He, Yixu Wang, Xin Wang, Tianle Gu, Jie Li, Yan Teng, Yingchun Wang
As Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) continue to evolve, their cognitive and reasoning capabilities have seen remarkable progress. However, challenges in visual fine-grained perception and commonsense causal inference persist. This paper introduces Argus Inspection, a multimodal benchmark with two levels of difficulty, emphasizing detailed visual recognition while incorporating real-world commonsense understanding to evaluate causal reasoning abilities. Expanding on it, we present the Eye of Panoptes framework, which integrates a binary parametric Sigmoid metric with an indicator function, enabling a more holistic evaluation of MLLMs’ responses in opinion-based reasoning tasks. Experiments conducted on 26 mainstream MLLMs reveal that the highest performance in visual fine-grained reasoning reaches only 0.46, highlighting considerable potential for enhancement. Our research offers valuable perspectives for the continued refinement of MLLMs.
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的不断发展,其认知和推理能力已经取得了显著的进步。然而,在精细视觉感知和常识推理方面仍存在挑战。本文介绍了Argus Inspection,这是一个多模态基准测试,具有两个难度级别,强调详细的视觉识别,同时结合现实世界常识理解来评估因果推理能力。在此基础上,我们提出了Panoptes之眼框架,该框架将二元参数Sigmoid度量与指示函数相结合,能够在基于意见推理任务中对MLLMs的响应进行更全面的评估。对26个主流MLLMs进行的实验表明,精细视觉推理的最高性能仅达到0.46,凸显了巨大的提升潜力。我们的研究为MLLMs的持续改进提供了宝贵的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的不断发展,其认知和推理能力取得了显著的进步。然而,在精细视觉感知和常识推理方面仍存在挑战。本文介绍了Argus Inspection多模态基准测试,包括两个难度级别,强调详细的视觉识别,同时结合现实世界常识理解来评估因果推理能力。此外,还推出了Panoptes框架的Eye,该框架结合了二元参数Sigmoid指标和指示函数,能够更全面地评估MLLMs在基于意见推理任务中的表现。对主流MLLM的实验表明,精细视觉推理的最高性能仅为0.46,显示出巨大的改进潜力。本研究为MLLM的持续改进提供了宝贵的视角。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在认知和推理能力方面取得显著进步。
- Argus Inspection多模态基准测试强调视觉精细感知和常识推理能力的评估。
- Argus Inspection包含两个难度级别,旨在全面评价MLLMs的性能。
- Eye of Panoptes框架能够更全面地评估MLLMs在基于意见推理任务中的表现。
- 现有MLLM在视觉精细推理方面的性能有待提高,存在巨大的改进空间。
- Sigmoid指标与指示函数的结合为评估MLLMs提供了更有效的方法。
点此查看论文截图



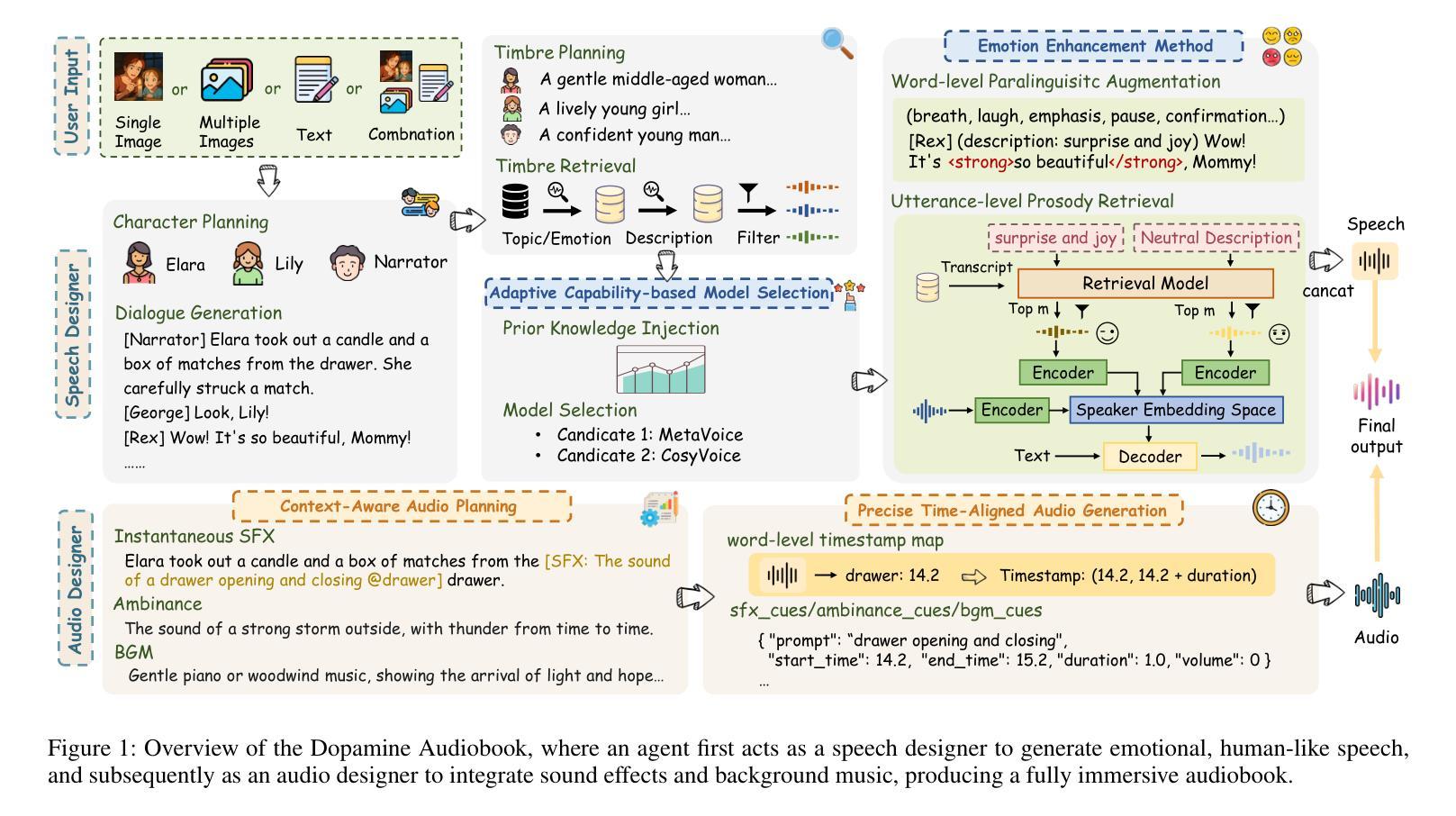
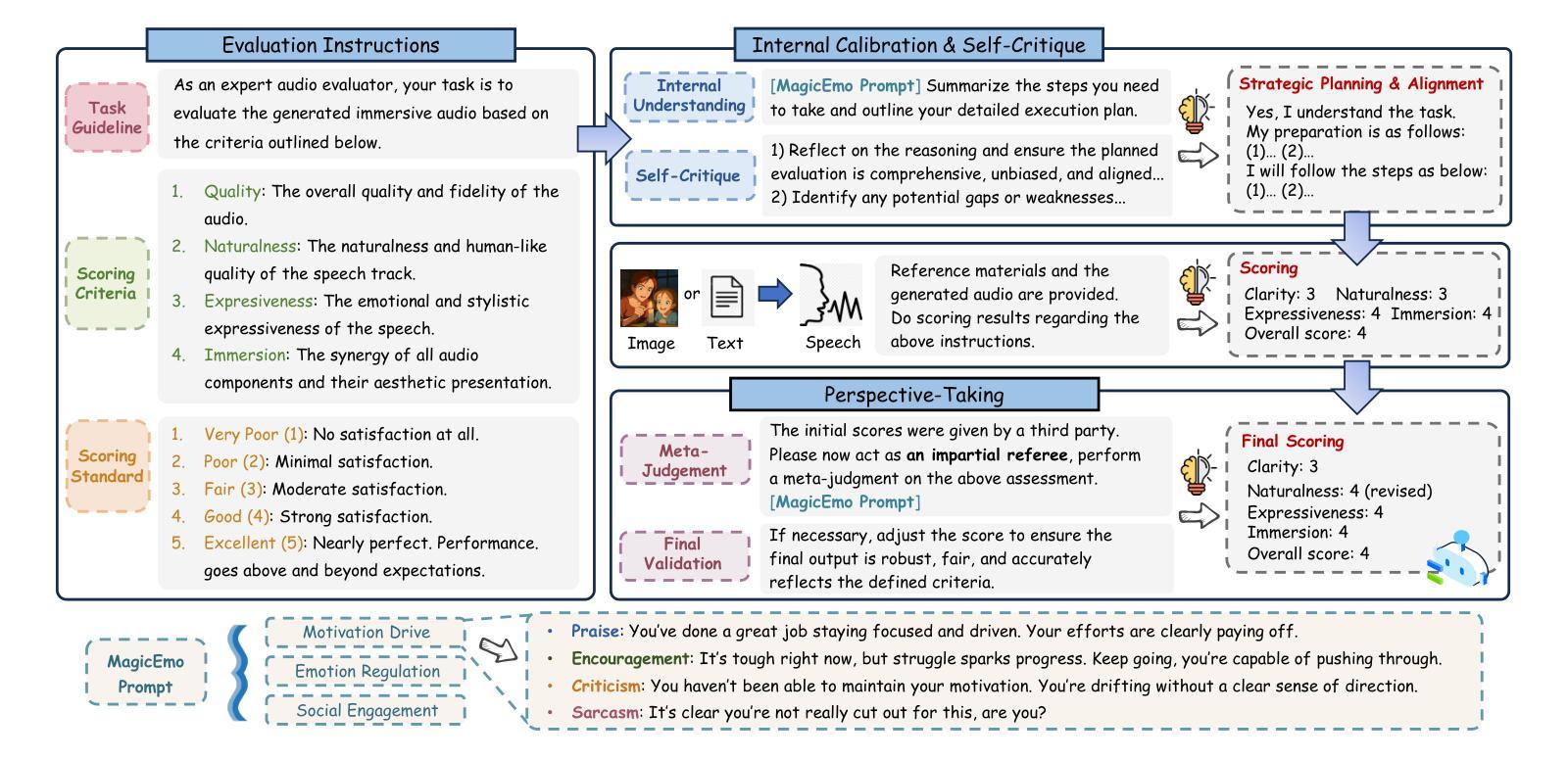
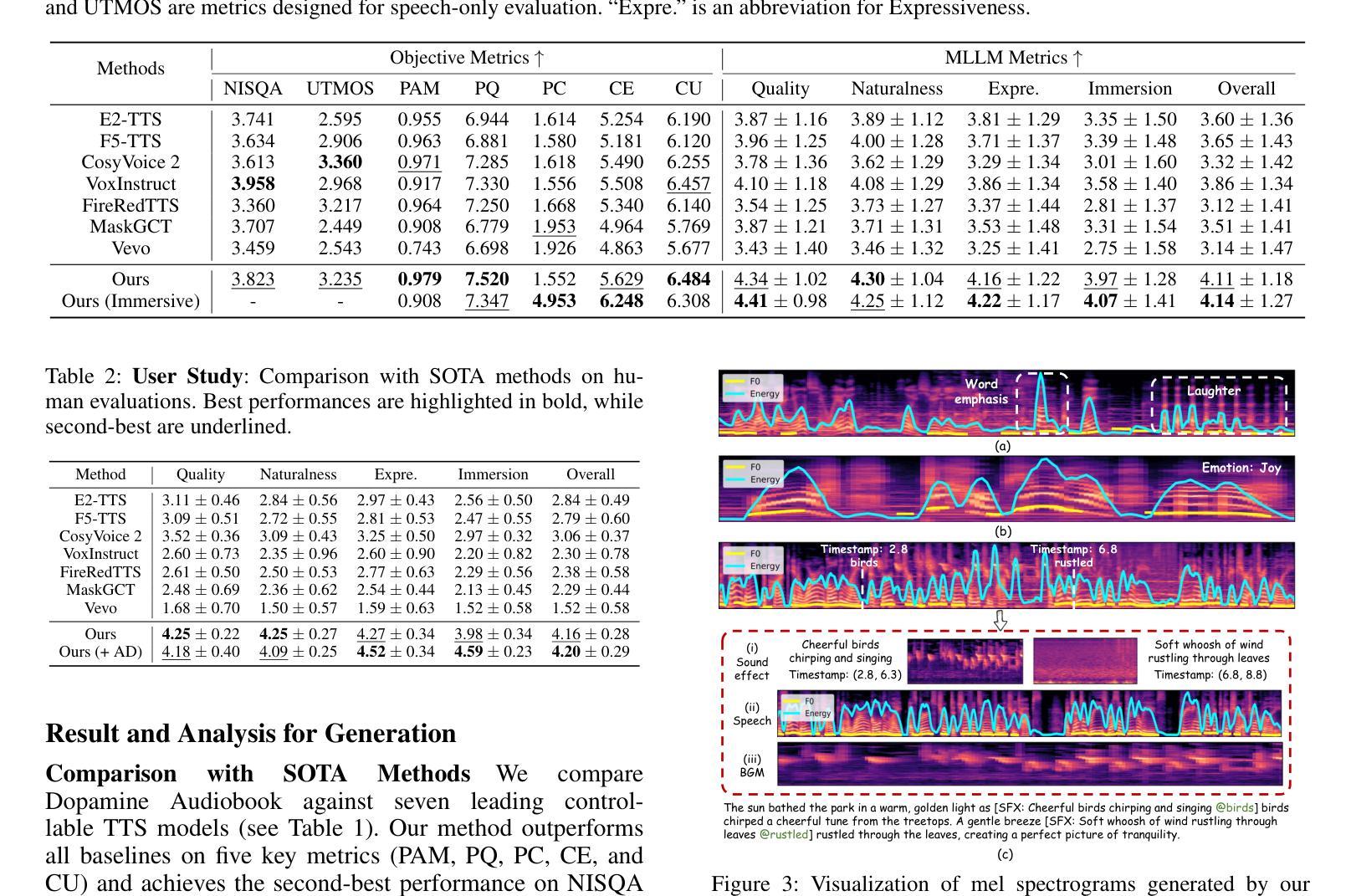
Dopamine Audiobook: A Training-free MLLM Agent for Emotional and Immersive Audiobook Generation
Authors:Yan Rong, Shan Yang, Chenxing Li, Dong Yu, Li Liu
Audiobook generation aims to create rich, immersive listening experiences from multimodal inputs, but current approaches face three critical challenges: (1) the lack of synergistic generation of diverse audio types (e.g., speech, sound effects, and music) with precise temporal and semantic alignment; (2) the difficulty in conveying expressive, fine-grained emotions, which often results in machine-like vocal outputs; and (3) the absence of automated evaluation frameworks that align with human preferences for complex and diverse audio. To address these issues, we propose Dopamine Audiobook, a novel unified training-free multi-agent system, where a multimodal large language model (MLLM) serves two specialized roles (i.e., speech designer and audio designer) for emotional, human-like, and immersive audiobook generation and evaluation. Specifically, we firstly propose a flow-based, context-aware framework for diverse audio generation with word-level semantic and temporal alignment. To enhance expressiveness, we then design word-level paralinguistic augmentation, utterance-level prosody retrieval, and adaptive TTS model selection. Finally, for evaluation, we introduce a novel MLLM-based evaluation framework incorporating self-critique, perspective-taking, and psychological MagicEmo prompts to ensure human-aligned and self-aligned assessments. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on multiple metrics. Importantly, our evaluation framework shows better alignment with human preferences and transferability across audio tasks.
有声书生成旨在从多模式输入创建丰富、沉浸式的听觉体验,但当前方法面临三个关键挑战:(1)缺乏协同生成具有精确时间和语义对齐的多种音频类型(如语音、音效和音乐);(2)表达细腻情感的困难,这往往导致机器般的语音输出;(3)缺乏与复杂和多样音频的人类偏好相符的自动化评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了多巴胺有声书,这是一个新型的统一、无需训练的多智能体系统,其中多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)扮演两个专业角色(即语音设计师和音频设计师),用于情感化、人性化、沉浸式有声书的生成和评估。具体来说,我们首先提出了一个基于流的、上下文感知的框架,用于具有单词级语义和时间对齐的多样音频生成。为了提高表达力,然后我们设计了单词级副语言增强、句子级语调检索和自适应TTS模型选择。最后,在评估方面,我们引入了一个基于MLLM的评估框架,结合自我批评、换位思考和心理MagicEmo提示,确保人类和自我的评估对齐。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个指标上达到了最新技术水平。重要的是,我们的评估框架显示出更好的与人类偏好对齐的能力,并在音频任务之间具有可转移性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了音频书生成面临的挑战,包括音频类型协同生成不足、表达精细情绪困难和缺乏与人类偏好对齐的自动评估框架。为解决这些问题,提出一种名为多巴胺音频书的统一无训练多智能体系统,采用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)担任语音设计师和音频设计师两个角色,实现情感丰富、人性化、沉浸式音频书生成和评估。提出基于流的上下文感知框架进行多样化音频生成,实现词级语义和时间对齐。设计词级语言修辞增强、句子级语调检索和自适应语音合成模型选择以增强表现力。引入基于MLLM的评估框架进行自评、换位思考和心理MagicEmo提示,确保与人类偏好和自我对齐的评估。实验结果显示,该方法在多个指标上达到最新水平,评估框架更好地与人类偏好对齐并适用于各种音频任务。
关键见解
- 音频书生成面临三大挑战:音频类型协同生成不足、表达精细情绪困难和缺乏与人类偏好对齐的自动评估框架。
- 提出一种统一的无训练多智能体系统——多巴胺音频书,解决上述问题。
- 利用多模态大型语言模型担任语音设计师和音频设计师角色,实现情感丰富、人性化、沉浸式音频书的生成。
- 提出基于流的上下文感知框架进行多样化音频生成,确保词级语义和时间对齐。
- 通过设计词级语言修辞增强、句子级语调检索和自适应语音合成模型选择,增强音频表达力。
- 引入基于MLLM的评估框架,包括自评、换位思考和心理提示,确保评估与人类偏好和自我对齐。
点此查看论文截图

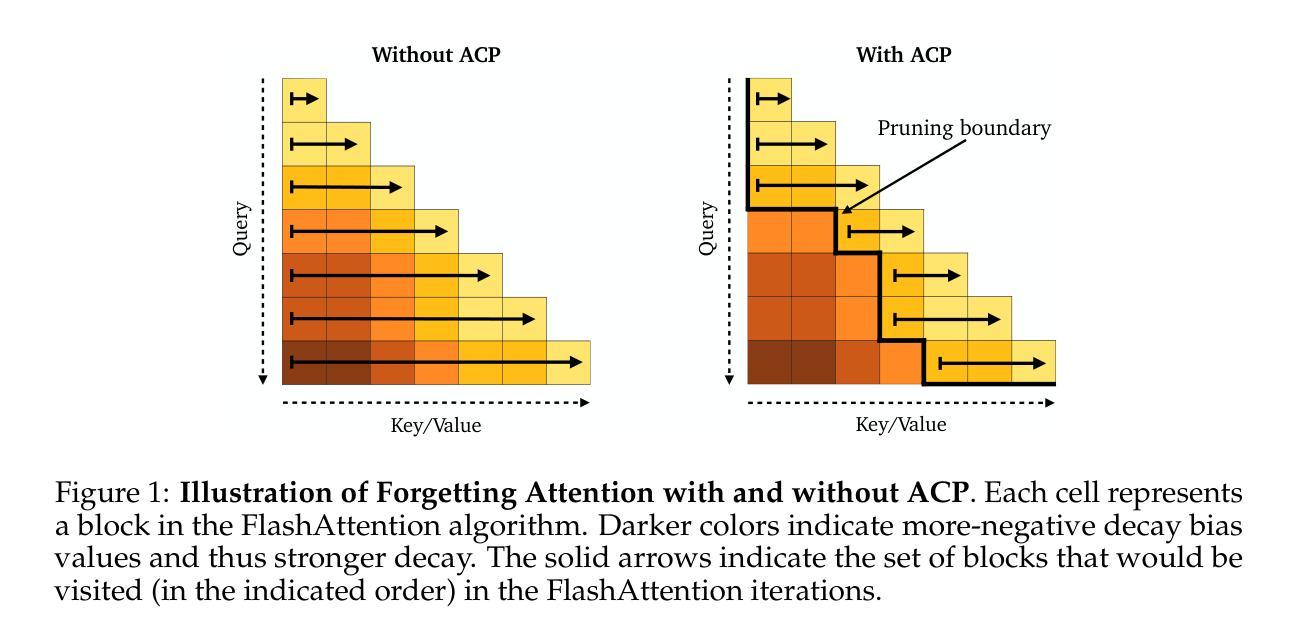
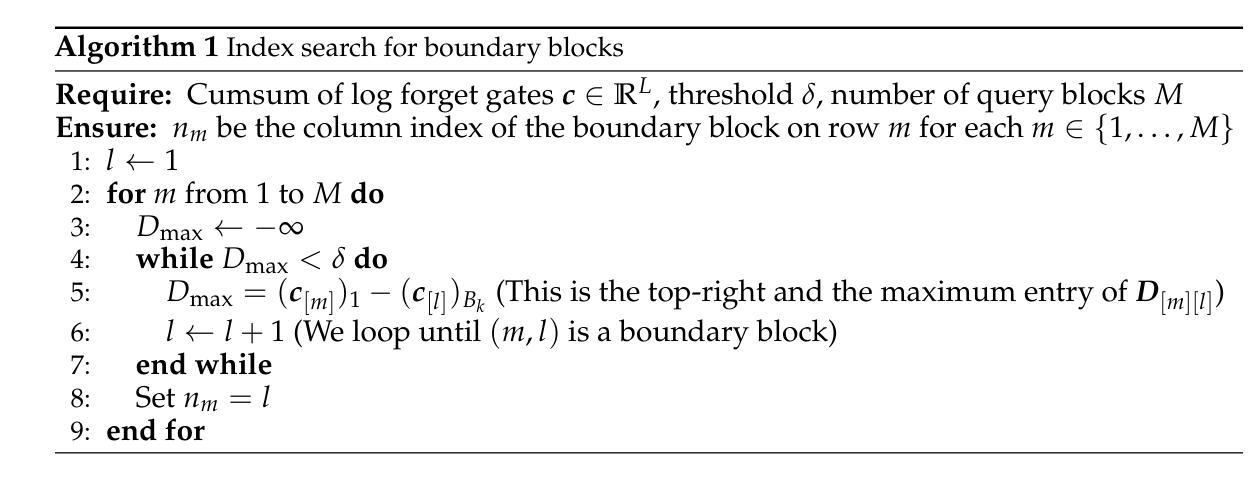
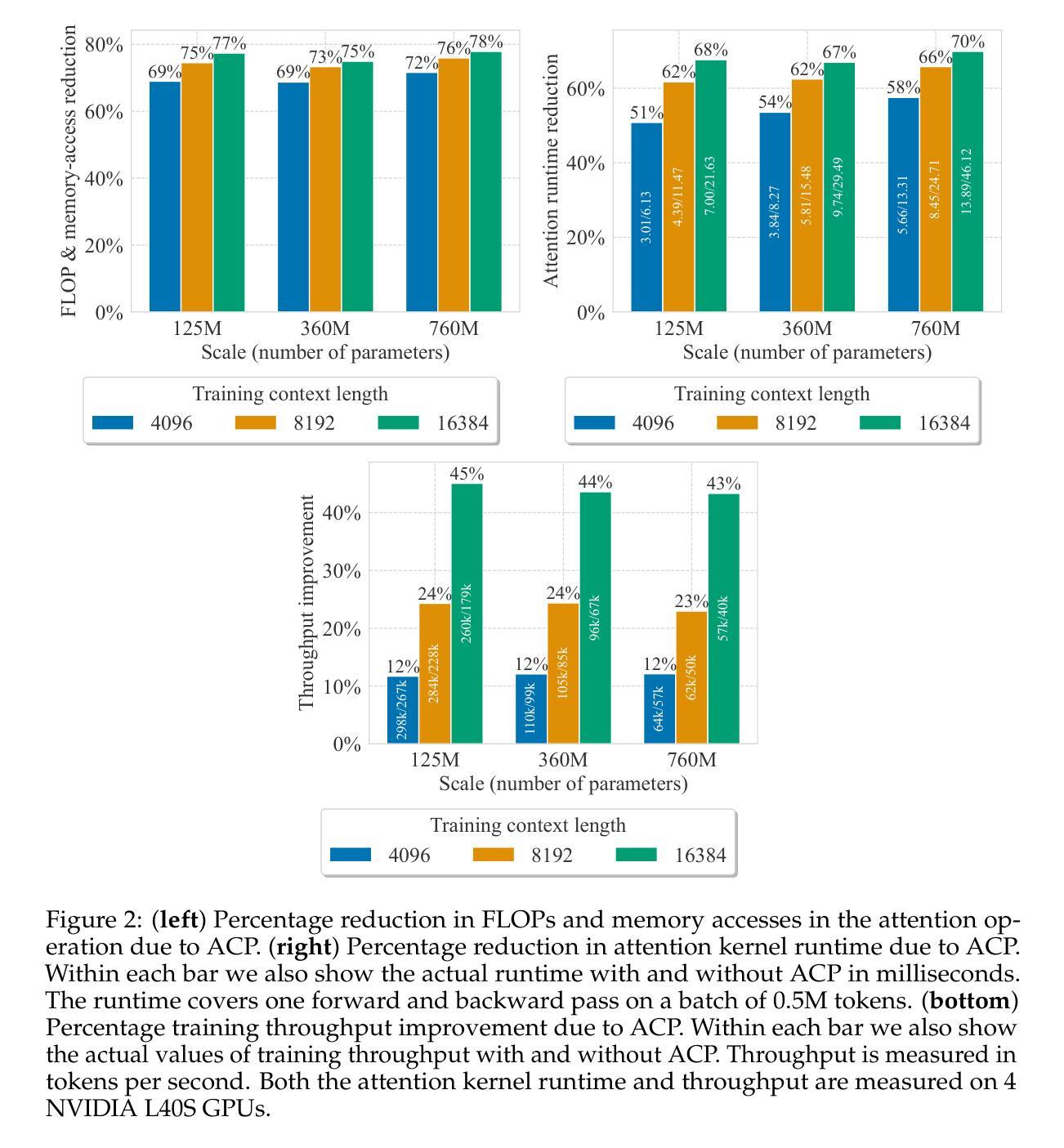
Adaptive Computation Pruning for the Forgetting Transformer
Authors:Zhixuan Lin, Johan Obando-Ceron, Xu Owen He, Aaron Courville
The recently proposed Forgetting Transformer (FoX) incorporates a forget gate into softmax attention and has shown consistently better or on-par performance compared to the standard RoPE-based Transformer. Notably, many attention heads in FoX tend to forget quickly, causing their output at each timestep to rely primarily on local context. Based on this observation, we propose Adaptive Computation Pruning (ACP) for FoX, a method that dynamically prunes computations involving input-output dependencies that are strongly decayed by the forget gate. In particular, our method performs provably safe pruning via a dynamically set pruning threshold that guarantees the pruned attention weights are negligible. We apply ACP to language model pretraining with FoX and show it consistently reduces the number of FLOPs and memory accesses in softmax attention by around 70% across different model sizes and context lengths, resulting in a roughly 50% to 70% reduction in attention runtime (or a 2-3$\times$ speedup) and a roughly 10% to 40% increase in end-to-end training throughput. Furthermore, longer context lengths yield greater computational savings. All these speed improvements are achieved without any performance degradation. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhixuan-lin/forgetting-transformer.
最近提出的遗忘转换器(FoX)将遗忘门纳入softmax注意力中,与基于RoPE的标准转换器相比,其性能一直表现更好或相当。值得注意的是,FoX中的许多注意力头倾向于快速遗忘,导致其在每个时间步的输出主要依赖于局部上下文。基于此观察,我们为FoX提出了自适应计算修剪(ACP)方法,该方法动态删除涉及由遗忘门强烈衰减的输入-输出依赖关系的计算。特别是,我们的方法通过动态设置的修剪阈值执行可证明的安全修剪,该阈值保证修剪的注意力权重可以忽略不计。我们将ACP应用于使用FoX的语言模型预训练,并显示它始终减少了softmax注意力中的FLOPs和内存访问量约70%,这适用于不同的模型大小和上下文长度。这导致注意力运行时间大致减少了50%到70%(或提高了2-3倍速度),并且端到端训练吞吐量提高了大约10%到40%。此外,较长的上下文长度会带来更大的计算节省。所有这些速度提升都是在没有任何性能下降的情况下实现的。我们的代码位于https://github.com/zhixuan-lin/forgetting-transformer。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at COLM 2025
Summary
近期提出的遗忘变压器(FoX)结合了遗忘门和softmax注意力机制,表现出优于或相当于基于RoPE的Transformer的性能。针对FoX中许多注意力头快速遗忘的特点,我们提出了自适应计算剪枝(ACP)方法。ACP通过动态设置的剪枝阈值,在保证被剪枝的注意力权重可以忽略不计的前提下进行安全剪枝。在预训练语言模型中应用ACP,可使softmax注意力的FLOPs和内存访问量减少约70%,注意力运行时间减少约50%至70%(或加速2-3倍),整体训练效率提高约10%至40%。在较长的上下文长度下,计算节省更为显著,且这些速度提升并未带来性能损失。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 遗忘变压器(FoX)结合了遗忘门和softmax注意力机制,展现出卓越性能。
- FoX中的许多注意力头存在快速遗忘现象,主要依赖局部上下文。
- 针对FoX提出了自适应计算剪枝(ACP)方法,可动态剪枝被遗忘门强烈衰减的输入输出依赖计算。
- ACP通过安全剪枝机制,在保证不影响模型性能的前提下,减少了计算量和内存访问。
- ACP在预训练语言模型中应用广泛,能显著减少注意力运算的FLOPs和内存需求。
- ACP能显著提升注意力运行速度和整体训练效率,加速比达到2-3倍。
点此查看论文截图

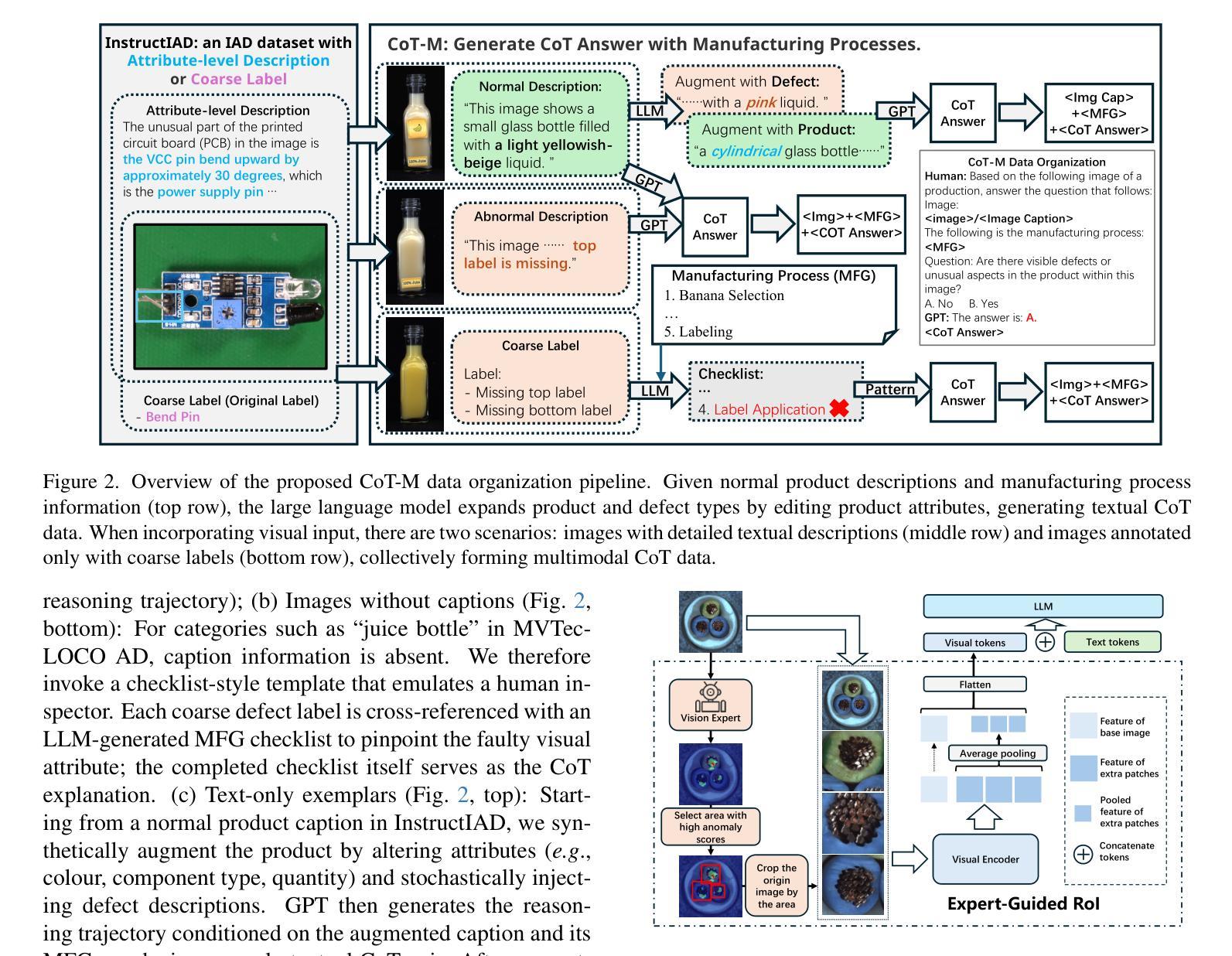
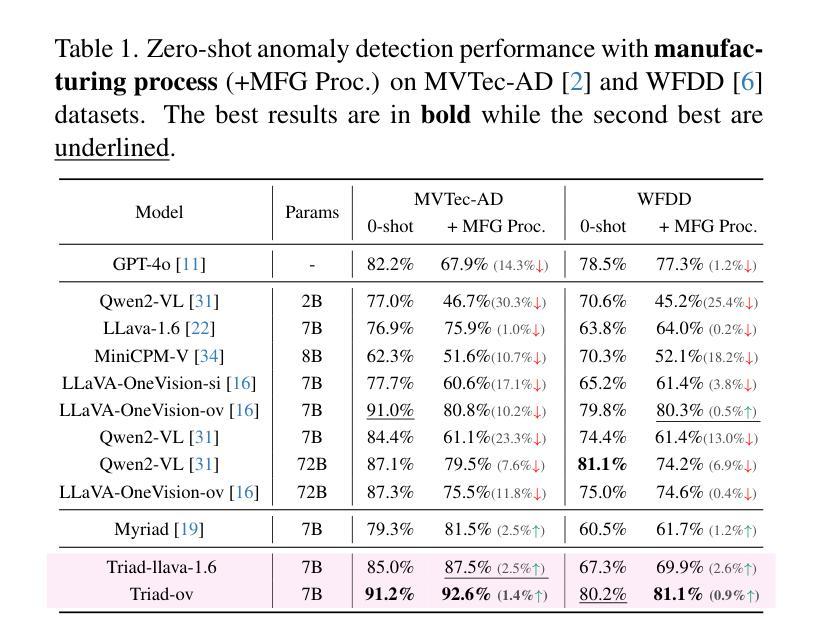
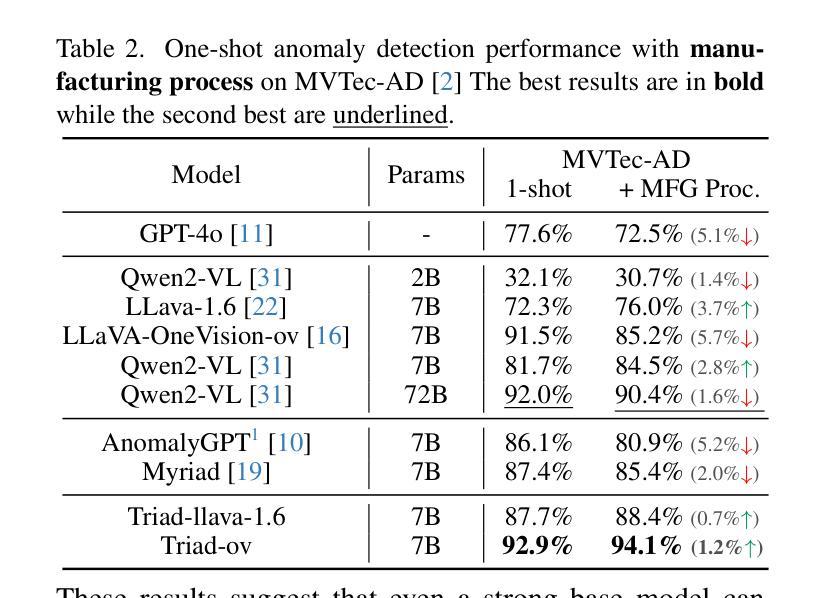
Triad: Empowering LMM-based Anomaly Detection with Vision Expert-guided Visual Tokenizer and Manufacturing Process
Authors:Yuanze Li, Shihao Yuan, Haolin Wang, Qizhang Li, Ming Liu, Chen Xu, Guangming Shi, Wangmeng Zuo
Although recent methods have tried to introduce large multimodal models (LMMs) into industrial anomaly detection (IAD), their generalization in the IAD field is far inferior to that for general purposes. We summarize the main reasons for this gap into two aspects. On one hand, general-purpose LMMs lack cognition of defects in the visual modality, thereby failing to sufficiently focus on defect areas. Therefore, we propose to modify the AnyRes structure of the LLaVA model, providing the potential anomalous areas identified by existing IAD models to the LMMs. On the other hand, existing methods mainly focus on identifying defects by learning defect patterns or comparing with normal samples, yet they fall short of understanding the causes of these defects. Considering that the generation of defects is closely related to the manufacturing process, we propose a manufacturing-driven IAD paradigm. An instruction-tuning dataset for IAD (InstructIAD) and a data organization approach for Chain-of-Thought with manufacturing (CoT-M) are designed to leverage the manufacturing process for IAD. Based on the above two modifications, we present Triad, a novel LMM-based method incorporating an expert-guided region-of-interest tokenizer and manufacturing process for industrial anomaly detection. Extensive experiments show that our Triad not only demonstrates competitive performance against current LMMs but also achieves further improved accuracy when equipped with manufacturing processes. Source code, training data, and pre-trained models will be publicly available at https://github.com/tzjtatata/Triad.
尽管最近的方法试图将大型多模态模型(LMM)引入工业异常检测(IAD),但它们在IAD领域的泛化能力远远落后于通用目的模型。我们总结了造成这种差距的主要原因有两点。一方面,通用LMM缺乏对视觉模态缺陷的认知,因此无法充分关注缺陷区域。因此,我们提出修改LLaVA模型的AnyRes结构,向LMM提供现有IAD模型识别的潜在异常区域。另一方面,现有方法主要侧重于通过学习缺陷模式或与正常样本进行比较来识别缺陷,但它们缺乏对缺陷原因的理解。考虑到缺陷的产生与制造过程密切相关,我们提出了以制造为核心的IAD范式。设计了用于IAD的指令调整数据集(InstructIAD)和用于与制造相关的思维链数据组织方法(CoT-M),以利用制造过程进行IAD。基于上述两项改进,我们提出了Triad,这是一种基于LMM的新方法,结合了专家引导的兴趣区域标记器和制造过程进行工业异常检测。大量实验表明,我们的Triad不仅在与当前LMM的竞争中表现出良好的性能,而且在配备制造过程后还实现了更高的准确性。源代码、训练数据和预训练模型将在https://github.com/tzjtatata/Triad上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:近期虽尝试将大型多模态模型(LMMs)引入工业异常检测(IAD),但在IAD领域的泛化能力较差。主要原因为一般用途的LMMs对视觉缺陷的认知不足,无法充分关注缺陷区域。为此,我们提出修改LLaVA模型的AnyRes结构,将现有IAD模型识别的潜在异常区域提供给LMMs。同时,现有方法主要通过学习缺陷模式或正常样本对比来识别缺陷,缺乏对缺陷原因的理解。考虑缺陷的产生与制造过程密切相关,我们提出制造驱动型IAD范式。设计了面向IAD的指令调整数据集InstructIAD和结合制造的Chain-of-Thought数据组织方法CoT-M。基于上述两项改进,我们提出了Triad新型LMM方法,结合专家引导的兴趣区域分词器和制造过程进行工业异常检测。实验表明,Triad不仅表现出对现有的竞争力水平高且具有优异的准确度提升效果。开源代码和模型可以在指定网址获取。
Key Takeaways:
- LMMs在IAD领域的泛化能力有待提高,主要原因是缺乏对视觉缺陷的认知。
- 提出修改LLaVA模型的AnyRes结构以整合潜在异常区域信息。
- 当前方法主要关注缺陷识别而非理解其成因。
- 考虑制造过程与缺陷生成的关系,提出制造驱动型IAD范式。
- 设计了InstructIAD数据集和CoT-M数据组织方法用于改进工业异常检测过程。
- 提出的Triad方法结合兴趣区域分词器和制造过程进行异常检测。
点此查看论文截图


X2I: Seamless Integration of Multimodal Understanding into Diffusion Transformer via Attention Distillation
Authors:Jian Ma, Qirong Peng, Xu Guo, Chen Chen, Haonan Lu, Zhenyu Yang
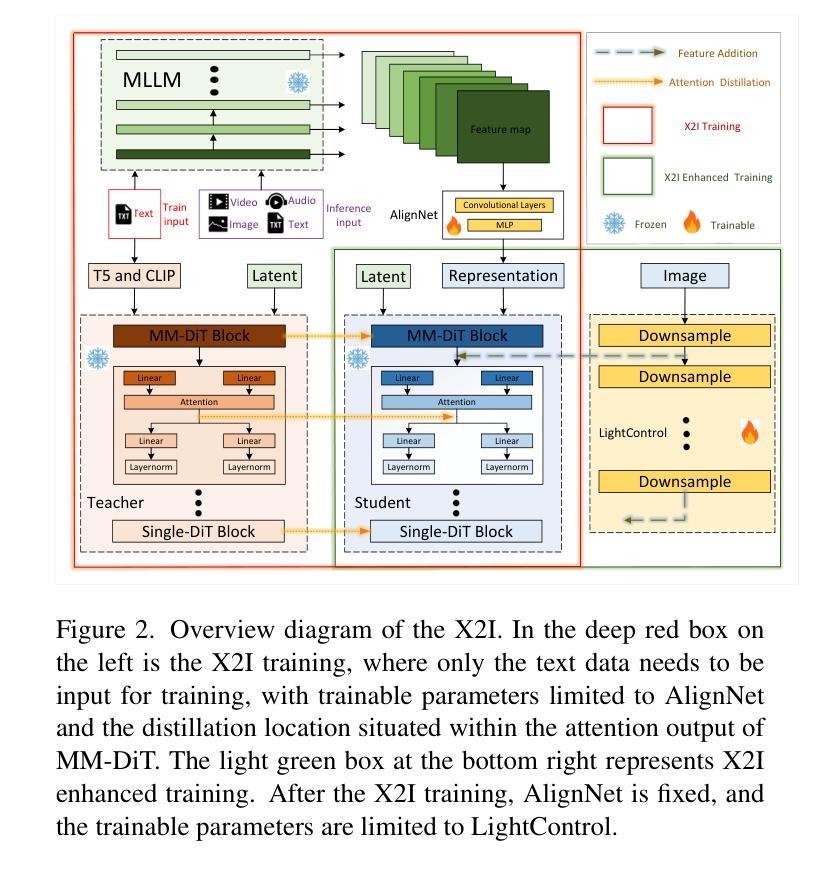
Text-to-image (T2I) models are well known for their ability to produce highly realistic images, while multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are renowned for their proficiency in understanding and integrating multiple modalities. However, currently there is no straightforward and efficient framework to transfer the multimodal comprehension abilities of MLLMs to T2I models to enable them to understand multimodal inputs. In this paper, we propose the X2I framework, which endows Diffusion Transformer (DiT) models with the capability to comprehend various modalities, including multilingual text, screenshot documents, images, videos, and audio. X2I is trained using merely 100K English corpus with 160 GPU hours. Building on the DiT teacher model, we adopt an innovative distillation method to extract the inference capabilities of the teacher model and design a lightweight AlignNet structure to serve as an intermediate bridge. Compared to the teacher model, X2I shows a decrease in performance degradation of less than 1% while gaining various multimodal understanding abilities, including multilingual to image, image to image, image-text to image, video to image, audio to image, and utilizing creative fusion to enhance imagery. Furthermore, it is applicable for LoRA training in the context of image-text to image generation, filling a void in the industry in this area. We further design a simple LightControl to enhance the fidelity of instructional image editing. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency, multifunctionality, and transferability of our X2I. The open-source code and checkpoints for X2I can be found at the following link: https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2I.
文本到图像(T2I)模型以其生成高度逼真的图像的能力而闻名,而多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)则以其在理解和融合多种模态方面的专长而著称。然而,目前没有一个简单有效的框架能将MLLM的多模态理解能力转移到T2I模型上,使其能够理解和处理多模态输入。在本文中,我们提出了X2I框架,该框架赋予了扩散变换器(DiT)模型理解各种模态的能力,包括多语言文本、截图文档、图像、视频和音频。X2I仅使用10万个英文语料库和16万个GPU小时进行训练。基于DiT教师模型,我们采用了一种创新的蒸馏方法,提取教师模型的推理能力,并设计了一个轻量级的AlignNet结构作为中间桥梁。与基础模型相比,X2I的性能下降幅度不到1%,同时获得了多种多模态理解能力,包括多语言到图像、图像到图像、图文到图像、视频到图像、音频到图像的能力,并利用创意融合增强图像效果。此外,它在图像文本到图像生成的LoRA训练方面表现出适用性,填补了行业中的一项空白。我们还设计了一个简单的LightControl,以提高指令性图像编辑的保真度。最后,大量实验证明了我们的X2I模型的有效性、高效性、多功能性和可迁移性。关于X2I的开源代码和检查点可在以下链接找到:https://github.com/OPPO-Mente-Lab/X2I。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
摘要
本文提出一种名为X2I的框架,旨在将多模态理解能力赋予Diffusion Transformer(DiT)模型,使其能够理解和生成多模态输入。该框架让DiT模型能够处理多种模态,包括多语言文本、截图文档、图像、视频和音频。通过使用仅100K的英文语料库和160 GPU小时的训练,X2I得以实现。基于DiT教师模型,采用创新蒸馏法提取其推理能力,并设计轻量级的AlignNet结构作为中间桥梁。相较于教师模型,X2I性能下降不到1%,同时获得了多种多模态理解能力。此外,它适用于图像文本生成领域的LoRA训练,填补了行业空白。为提升教学图像编辑的保真度,设计了一种简单的LightControl。大量实验证明了X2I的有效性、效率、多功能性和可迁移性。
关键见解
- X2I框架成功将多模态理解能力赋予Diffusion Transformer(DiT)模型。
- X2I能处理包括多语言文本、截图文档、图像、视频和音频在内的多种模态。
- 使用100K的英文语料库和160 GPU小时的训练实现了X2I。
- 创新蒸馏法用于提取DiT教师模型的推理能力。
- X2I性能与教师模型相比下降不到1%,同时获得了多种多模态理解能力。
- X2I适用于图像文本生成领域的LoRA训练,填补了行业空白。
- 简单的LightControl设计提升了教学图像编辑的保真度。
点此查看论文截图