⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
MonoPartNeRF:Human Reconstruction from Monocular Video via Part-Based Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Yao Lu, Jiawei Li, Ming Jiang
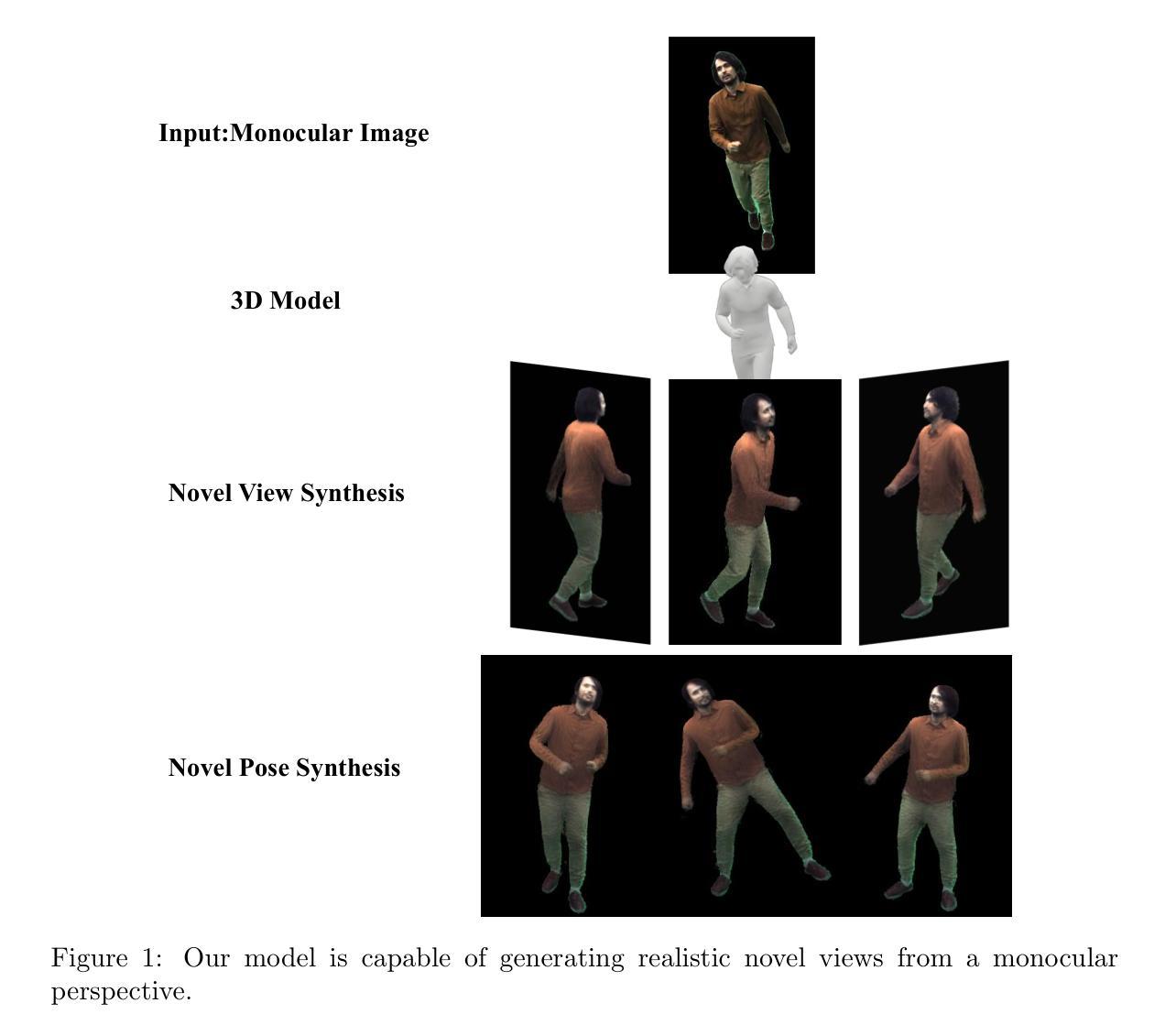
In recent years, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved remarkable progress in dynamic human reconstruction and rendering. Part-based rendering paradigms, guided by human segmentation, allow for flexible parameter allocation based on structural complexity, thereby enhancing representational efficiency. However, existing methods still struggle with complex pose variations, often producing unnatural transitions at part boundaries and failing to reconstruct occluded regions accurately in monocular settings. We propose MonoPartNeRF, a novel framework for monocular dynamic human rendering that ensures smooth transitions and robust occlusion recovery. First, we build a bidirectional deformation model that combines rigid and non-rigid transformations to establish a continuous, reversible mapping between observation and canonical spaces. Sampling points are projected into a parameterized surface-time space (u, v, t) to better capture non-rigid motion. A consistency loss further suppresses deformation-induced artifacts and discontinuities. We introduce a part-based pose embedding mechanism that decomposes global pose vectors into local joint embeddings based on body regions. This is combined with keyframe pose retrieval and interpolation, along three orthogonal directions, to guide pose-aware feature sampling. A learnable appearance code is integrated via attention to model dynamic texture changes effectively. Experiments on the ZJU-MoCap and MonoCap datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms prior approaches under complex pose and occlusion conditions, achieving superior joint alignment, texture fidelity, and structural continuity.
近年来,神经辐射场(NeRF)在动态人体重建和渲染方面取得了显著的进展。基于人体分割的局部渲染范式,允许根据结构复杂性灵活地分配参数,从而提高表示效率。然而,现有方法仍然难以处理复杂的姿态变化,经常在部分边界处产生不自然的过渡,并且在单目设置下无法准确重建遮挡区域。我们提出了MonoPartNeRF,这是一种用于单目动态人体渲染的新型框架,可确保平滑过渡和稳健的遮挡恢复。首先,我们建立了一个双向变形模型,结合了刚性和非刚性变换,在观察空间和规范空间之间建立连续可逆的映射。采样点被投影到参数化的表面时间空间(u,v,t)中,以更好地捕捉非刚性运动。一致性损失进一步抑制了变形引起的伪影和不连续性。我们引入了一种基于部分的姿态嵌入机制,将全局姿态向量分解为基于身体区域的局部关节嵌入。这与关键帧姿态检索和沿三个正交方向的插值相结合,以指导姿态感知特征采样。通过注意力机制集成可学习的外观代码,以有效地模拟动态纹理变化。在ZJU-MoCap和MonoCap数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在复杂的姿态和遮挡条件下显著优于先前的方法,实现了优越的关节对齐、纹理保真和结构连续性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在动态人体重建和渲染方面取得了显著进展。现有的方法难以处理复杂的姿态变化,造成部分边界过渡不自然以及在单目环境下难以准确重建遮挡区域。为此,我们提出MonoPartNeRF框架,利用双向变形模型,实现平滑过渡和稳健的遮挡恢复。实验证明,我们的方法在复杂的姿态和遮挡条件下显著优于先前的方法,实现了更好的关节对齐、纹理保真和结构连续性。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在动态人体重建和渲染方面取得显著进展。
- 部分基于渲染的方法通过人体分割引导灵活参数分配,提高表达效率。
- 现有方法处理复杂姿态变化时存在挑战,如部分边界过渡不自然和遮挡区域重建不准确。
- MonoPartNeRF框架通过结合双向变形模型和基于部分的姿态嵌入机制解决这些问题。
- 双向变形模型建立观测与规范空间之间的连续可逆映射,更好地捕捉非刚性运动。
- 部分基于姿态的嵌入机制将全局姿态向量分解为基于身体区域的局部关节嵌入。
- 实验证明MonoPartNeRF在复杂姿态和遮挡条件下显著优于先前方法。
点此查看论文截图