⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-14 更新
Scalable Controllable Accented TTS
Authors:Henry Li Xinyuan, Zexin Cai, Ashi Garg, Kevin Duh, Leibny Paola García-Perera, Sanjeev Khudanpur, Nicholas Andrews, Matthew Wiesner
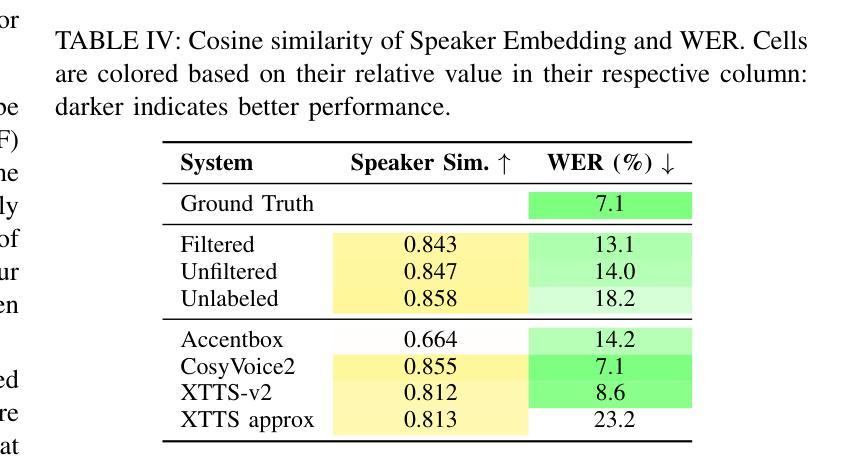
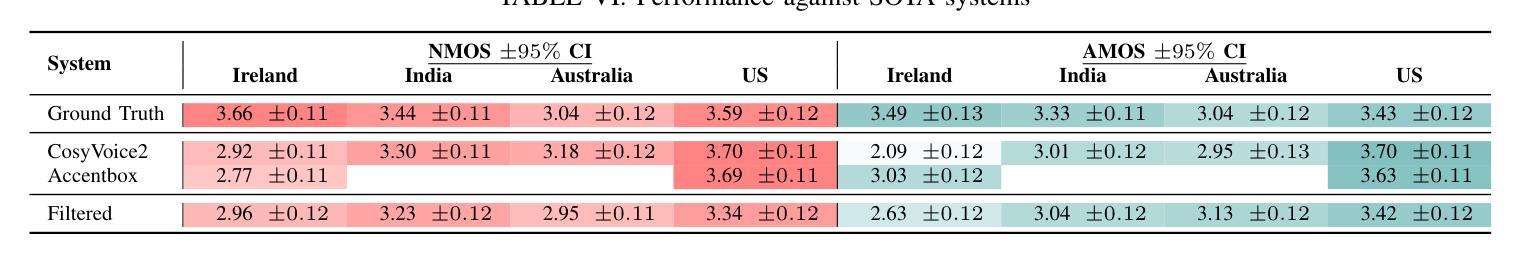
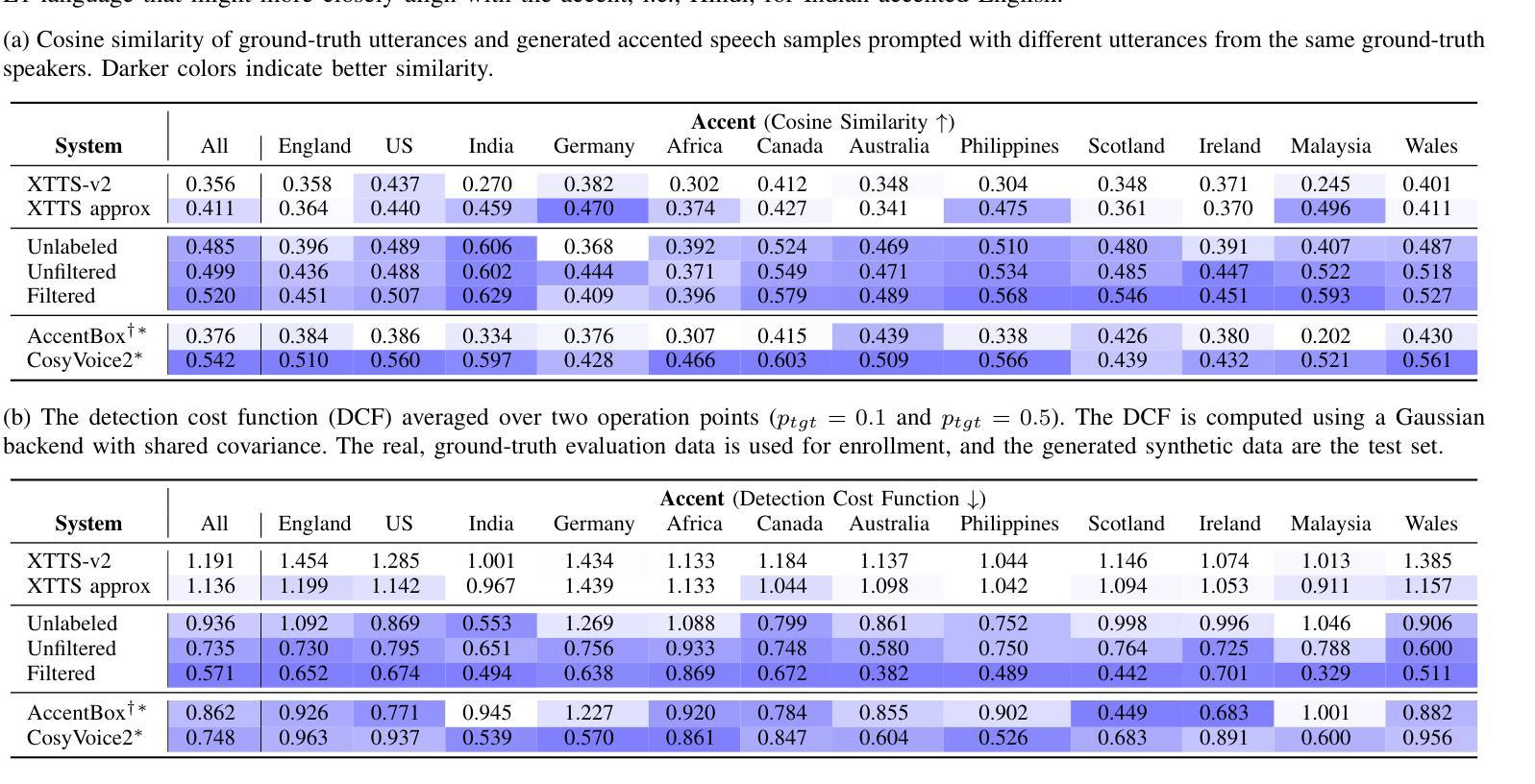
We tackle the challenge of scaling accented TTS systems, expanding their capabilities to include much larger amounts of training data and a wider variety of accent labels, even for accents that are poorly represented or unlabeled in traditional TTS datasets. To achieve this, we employ two strategies: 1. Accent label discovery via a speech geolocation model, which automatically infers accent labels from raw speech data without relying solely on human annotation; 2. Timbre augmentation through kNN voice conversion to increase data diversity and model robustness. These strategies are validated on CommonVoice, where we fine-tune XTTS-v2 for accented TTS with accent labels discovered or enhanced using geolocation. We demonstrate that the resulting accented TTS model not only outperforms XTTS-v2 fine-tuned on self-reported accent labels in CommonVoice, but also existing accented TTS benchmarks.
我们应对带口音的TTS系统的扩展挑战,提升其能力,以包含更大规模的训练数据和更多种类的口音标签,即使是对在传统TTS数据集中表示不佳或未标注的口音亦是如此。为实现这一点,我们采用两种策略:一是通过语音地理位置模型进行口音标签发现,该模型能够自动从原始语音数据中推断口音标签,而无需完全依赖人工标注;二是通过kNN语音转换技术增加音色多样性,提高模型的鲁棒性。这些策略在CommonVoice上得到了验证,我们对XTTS-v2进行了微调,以支持带口音的TTS,并使用地理位置信息发现或增强口音标签。我们证明,得到的带口音的TTS模型不仅优于在CommonVoice上微调并使用自我报告的口音标签的XTTS-v2模型,而且优于现有的带口音的TTS基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ASRU 2025
Summary
随着TTS系统的发展,如何处理大量训练数据和更广泛的口音标签是一大挑战。研究团队采取了两种策略:一是通过语音地理位置模型自动发现口音标签,无需依赖人工标注;二是通过kNN语音转换增加音色增强,提高数据多样性和模型稳健性。在CommonVoice上验证了这两种策略,使用地理位置发现的或增强的口音标签对XTTS-v2进行微调,得到的带口音的TTS模型不仅优于XTTS-v2在CommonVoice自我报告口音标签的微调模型,也优于现有的带口音TTS基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 研究面临了扩展带口音的TTS系统的挑战,包括处理大量训练数据和多种口音标签。
- 第一种策略是利用语音地理位置模型自动发现口音标签,减少对人工标注的依赖。
- 第二种策略是通过kNN语音转换进行音色增强,提高数据多样性和模型稳健性。
- 在CommonVoice平台上验证了这两种策略的有效性。
- 使用地理位置发现的或增强的口音标签对XTTS-v2进行微调,得到的模型性能有所提升。
- 新的带口音的TTS模型优于现有的基准测试模型。
点此查看论文截图

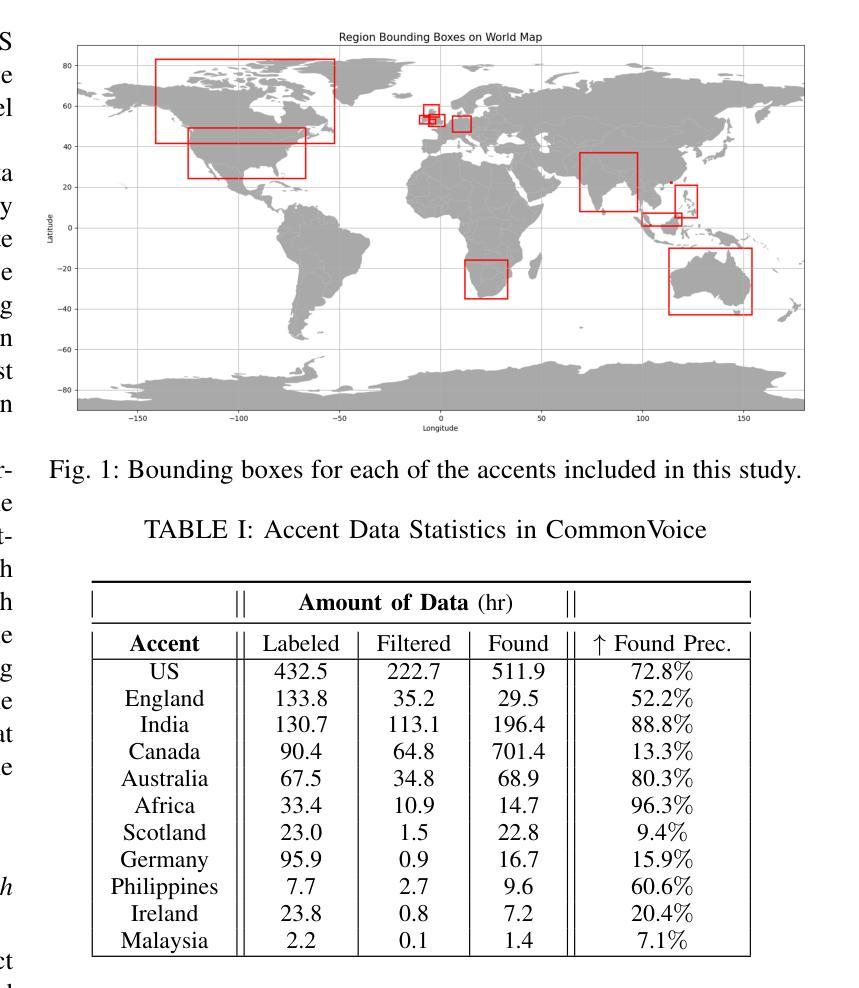
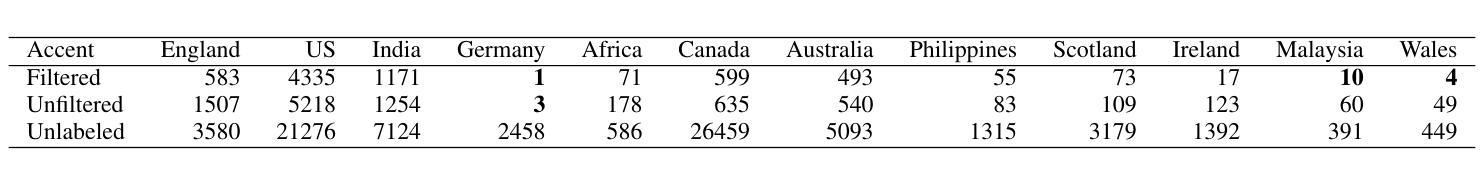
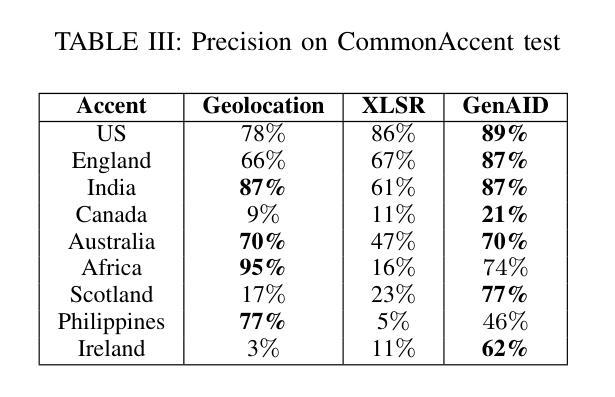
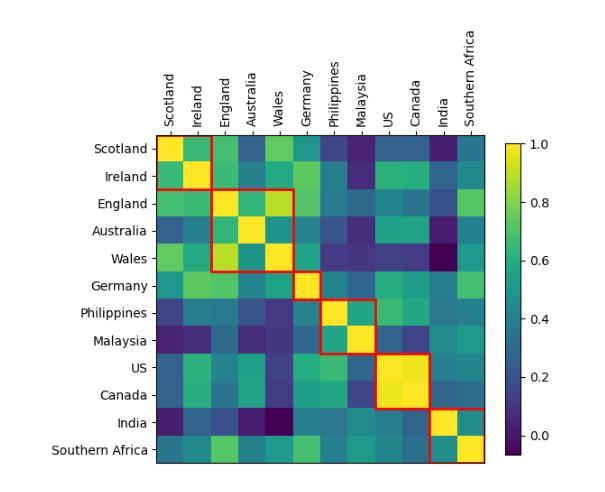
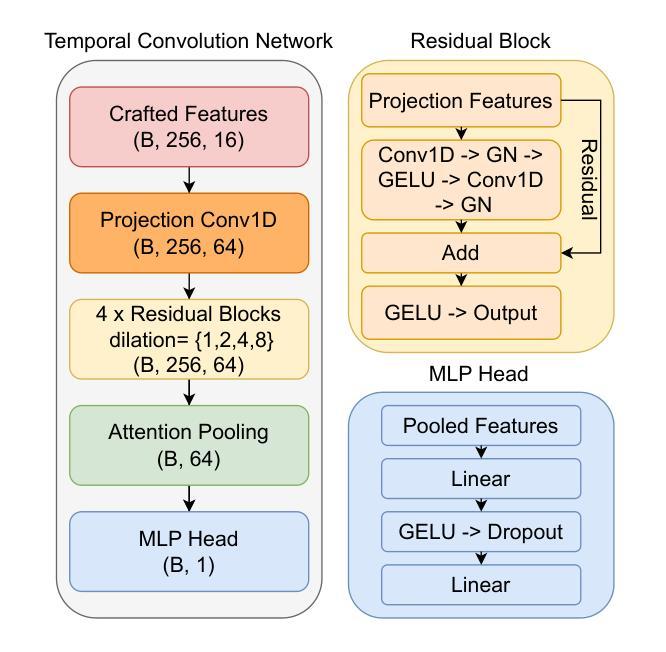
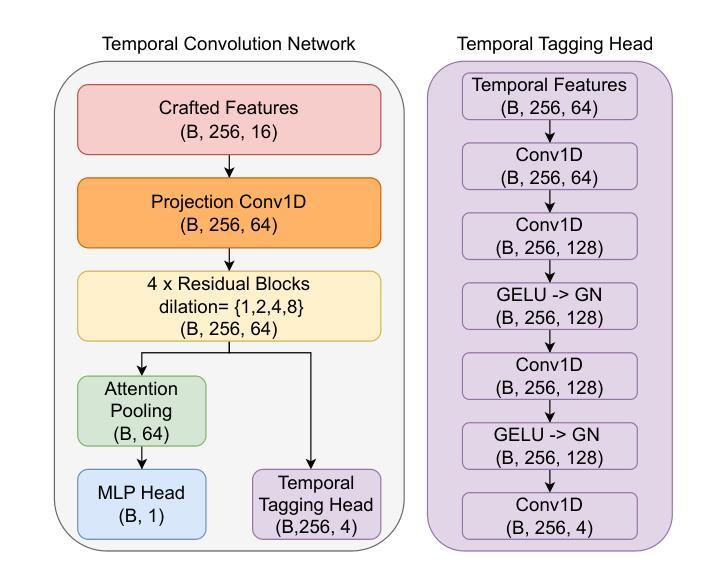
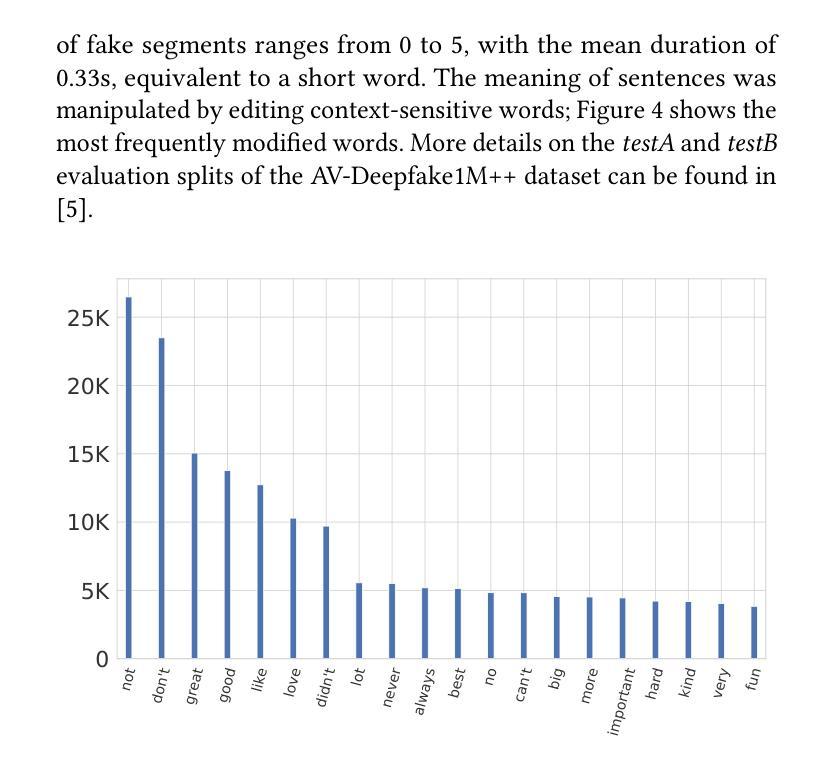
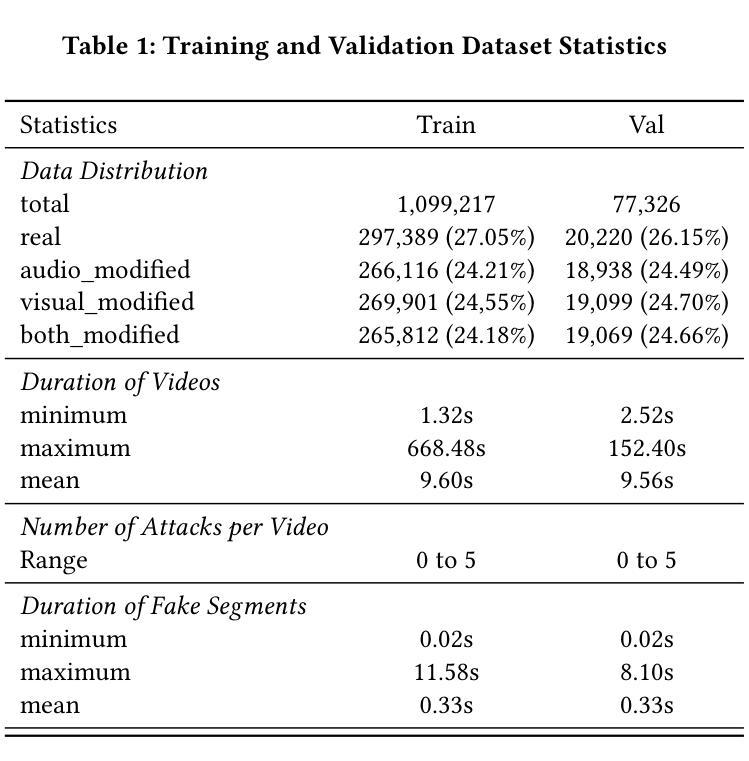
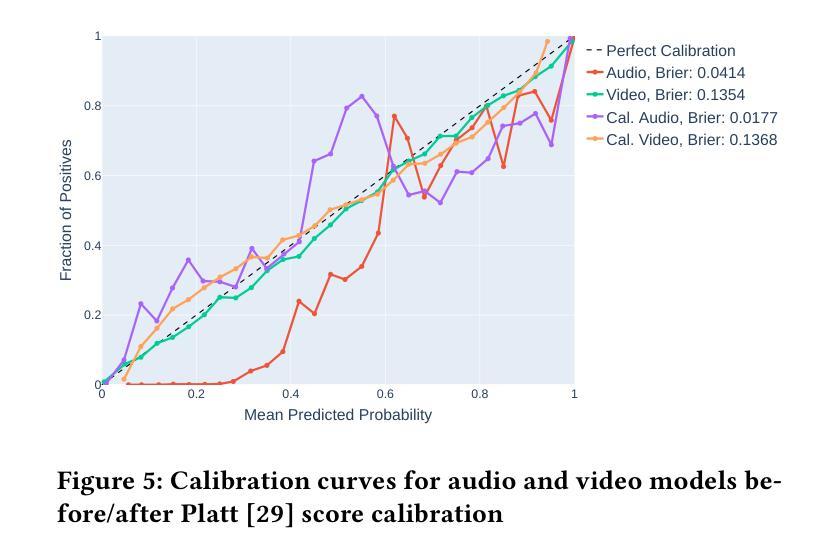
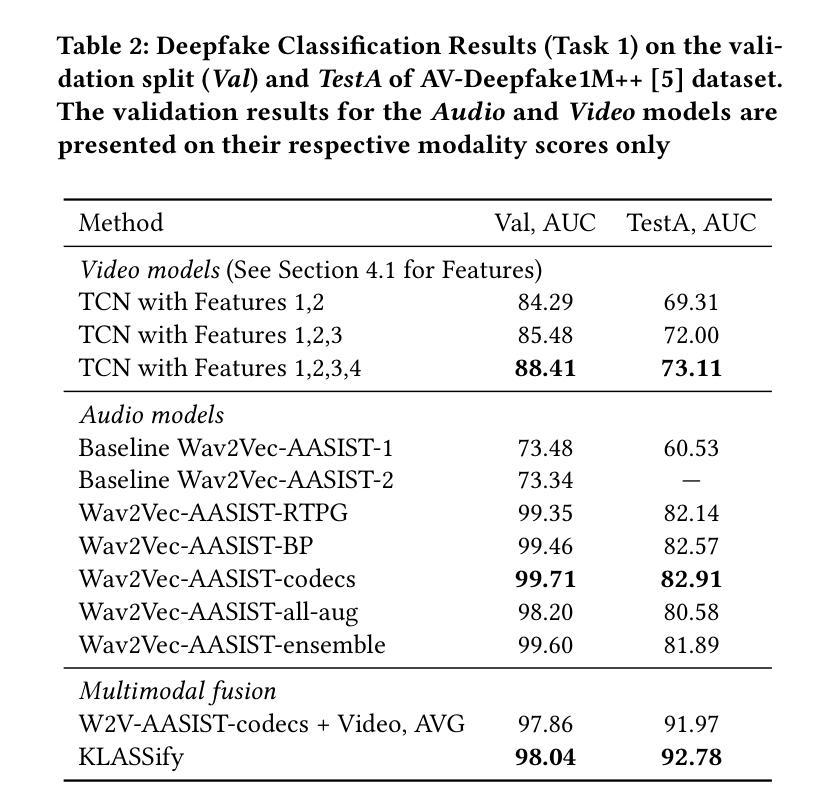
KLASSify to Verify: Audio-Visual Deepfake Detection Using SSL-based Audio and Handcrafted Visual Features
Authors:Ivan Kukanov, Jun Wah Ng
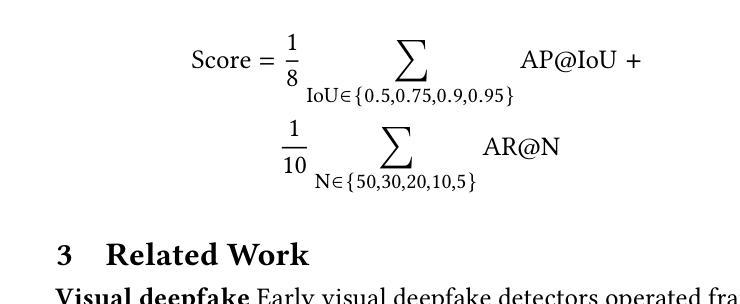
The rapid development of audio-driven talking head generators and advanced Text-To-Speech (TTS) models has led to more sophisticated temporal deepfakes. These advances highlight the need for robust methods capable of detecting and localizing deepfakes, even under novel, unseen attack scenarios. Current state-of-the-art deepfake detectors, while accurate, are often computationally expensive and struggle to generalize to novel manipulation techniques. To address these challenges, we propose multimodal approaches for the AV-Deepfake1M 2025 challenge. For the visual modality, we leverage handcrafted features to improve interpretability and adaptability. For the audio modality, we adapt a self-supervised learning (SSL) backbone coupled with graph attention networks to capture rich audio representations, improving detection robustness. Our approach strikes a balance between performance and real-world deployment, focusing on resilience and potential interpretability. On the AV-Deepfake1M++ dataset, our multimodal system achieves AUC of 92.78% for deepfake classification task and IoU of 0.3536 for temporal localization using only the audio modality.
音频驱动对话头部生成器和先进的文本到语音(TTS)模型的快速发展导致了更复杂的时序深度伪造。这些进展突显了需要稳健的方法,能够在新的、未见过的攻击场景下检测和定位深度伪造。虽然当前最先进的深度伪造检测器很准确,但它们通常计算量大,难以推广到新的操作技术。为了应对这些挑战,我们为AV-Deepfake1M 2025挑战赛提出了多模式方法。对于视觉模式,我们利用手工特征来提高可解释性和适应性。对于音频模式,我们采用自我监督学习(SSL)主干与图注意力网络相结合,捕捉丰富的音频表示,提高检测稳健性。我们的方法在性能和现实部署之间取得了平衡,侧重于弹性和潜在的可解释性。在AV-Deepfake1M++数据集上,我们的多模式系统仅使用音频模式就实现了深度伪造分类任务的AUC 92.78%,时序定位的IoU为0.3536。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, accepted to the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’25)
Summary
文本描述了音频驱动的说话人头部生成器和先进的文本转语音(TTS)模型的快速发展带来的复杂时序深度伪造问题。为应对挑战,提出了一种用于AV-Deepfake挑战的多模式方法。视觉方面利用手工特征增强可解释性和适应性;音频方面,自适应带有图注意力网络的自监督学习模型以捕获丰富的音频表示,提高检测稳健性。该方法在性能与实际应用之间取得平衡,重点关注恢复力和潜在的可解释性。在AV-Deepfake数据集上,多模式系统对深度伪造分类任务的AUC达到92.78%,仅使用音频模态进行时序定位时IoU为0.3536。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动的说话人头部生成器和先进的文本转语音(TTS)模型的快速发展导致复杂的时序深度伪造问题。
- 需要具备检测并定位深度伪造的技术,尤其是在新的未知攻击场景下。
- 当前最先进的深度伪造检测器虽然准确,但计算成本高且难以推广到新的操作技术。
- 提出了一种针对AV-Deepfake挑战的多模式方法来解决上述问题。
- 在视觉方面,利用手工特征以增强可解释性和适应性。
- 在音频方面,自适应带有图注意力网络的自监督学习模型以提高检测的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

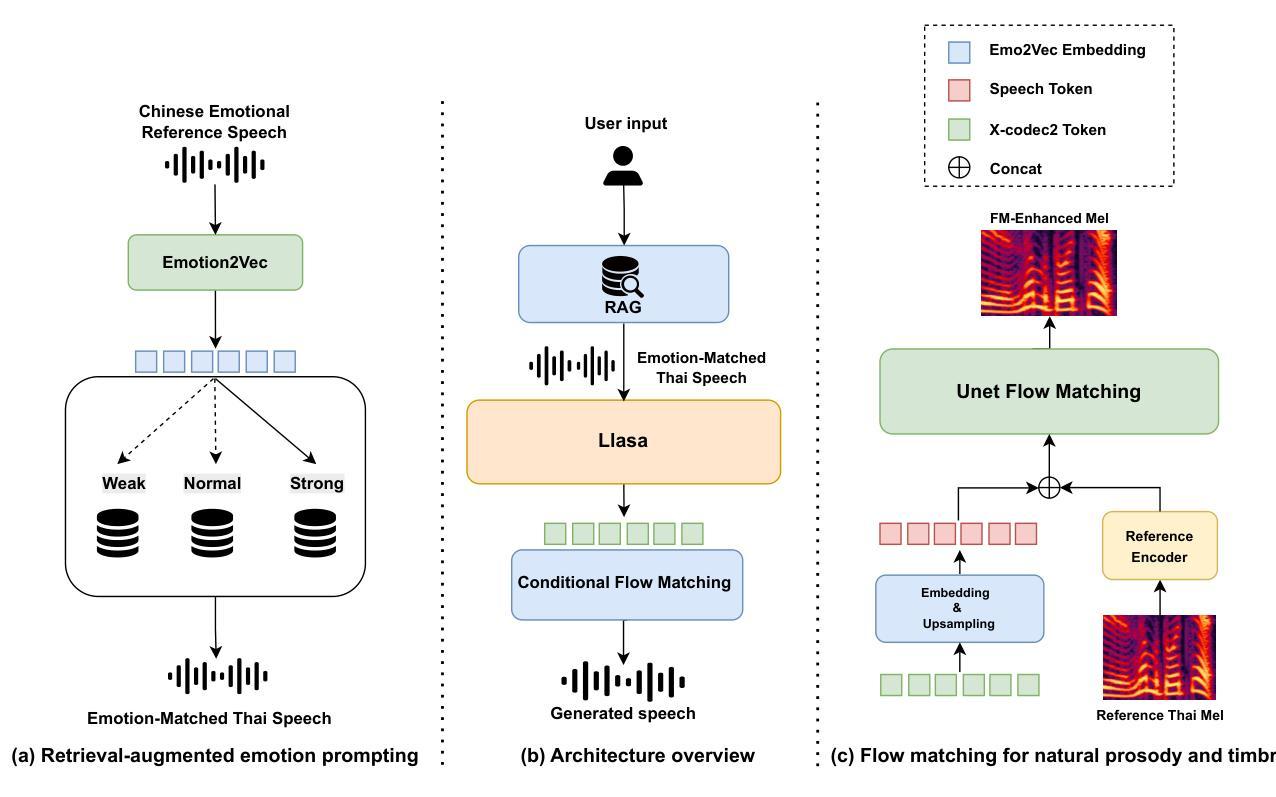
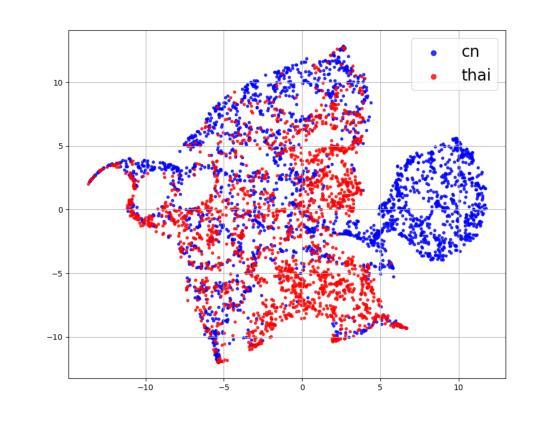
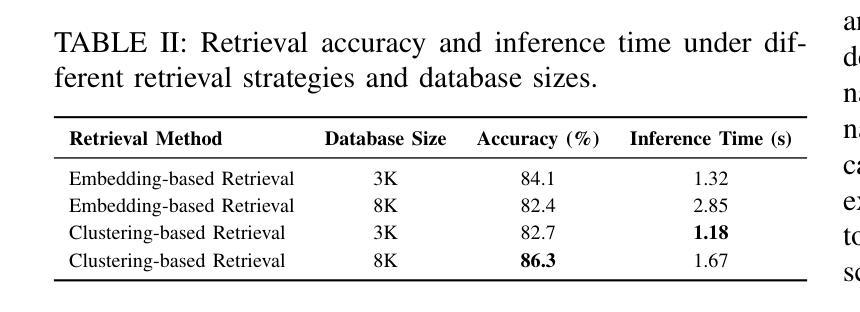
XEmoRAG: Cross-Lingual Emotion Transfer with Controllable Intensity Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Tianlun Zuo, Jingbin Hu, Yuke Li, Xinfa Zhu, Hai Li, Ying Yan, Junhui Liu, Danming Xie, Lei Xie
Zero-shot emotion transfer in cross-lingual speech synthesis refers to generating speech in a target language, where the emotion is expressed based on reference speech from a different source language. However, this task remains challenging due to the scarcity of parallel multilingual emotional corpora, the presence of foreign accent artifacts, and the difficulty of separating emotion from language-specific prosodic features. In this paper, we propose XEmoRAG, a novel framework to enable zero-shot emotion transfer from Chinese to Thai using a large language model (LLM)-based model, without relying on parallel emotional data. XEmoRAG extracts language-agnostic emotional embeddings from Chinese speech and retrieves emotionally matched Thai utterances from a curated emotional database, enabling controllable emotion transfer without explicit emotion labels. Additionally, a flow-matching alignment module minimizes pitch and duration mismatches, ensuring natural prosody. It also blends Chinese timbre into the Thai synthesis, enhancing rhythmic accuracy and emotional expression, while preserving speaker characteristics and emotional consistency. Experimental results show that XEmoRAG synthesizes expressive and natural Thai speech using only Chinese reference audio, without requiring explicit emotion labels. These results highlight XEmoRAG’s capability to achieve flexible and low-resource emotional transfer across languages. Our demo is available at https://tlzuo-lesley.github.io/Demo-page/ .
跨语言语音合成中的零样本情感迁移是指生成目标语言中的语音,其中情感表达是基于源语言的参考语音。然而,由于缺乏平行多语言情感语料库、存在外国口音痕迹以及从特定语言的韵律特征中分离情感的困难,这一任务仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了XEmoRAG,这是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)实现中文到泰语零样本情感迁移的新框架,无需依赖平行情感数据。XEmoRAG从中文语音中提取与语言无关的情感嵌入,并从精选的情感数据库中检索情感匹配的泰语话语,从而实现可控的情感迁移,无需明确的情感标签。此外,流匹配对齐模块最小化音高和持续时间的不匹配,确保自然的韵律。它将中文音色融入泰语合成中,提高节奏准确性和情感表达,同时保留说话人的特点和情感一致性。实验结果表明,XEmoRAG仅使用中文参考音频即可合成表达自然、泰语流畅的语音,无需明确的情感标签。这些结果凸显了XEmoRAG在不同语言之间实现灵活和低资源情感迁移的能力。我们的演示网站为:https://tlzuo-lesley.github.io/Demo-page/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ASRU 2025
Summary
零样本情感迁移跨语言语音合成是从源语言的参考语音中表达目标语言中的情感。该研究面临多语言情感语料库稀缺、外国口音伪迹存在以及从语言特定的韵律特征中分离情感的挑战。本文提出XEmoRAG框架,利用大型语言模型实现中文到泰语的零样本情感迁移,无需平行情感数据。XEmoRAG从中文语音中提取语言无关的情感嵌入,从精选的情感数据库中检索情感匹配的泰语语音片段,实现可控的情感迁移,无需明确的情感标签。此外,通过流匹配对齐模块最小化音高和持续时间不匹配,确保自然韵律。实验结果表明,XEmoRAG仅使用中文参考音频即可合成表达力强、自然的泰语语音,无需明确的情感标签。这为灵活的低资源情感迁移提供了可能性。演示地址:网站链接。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本情感迁移跨语言语音合成是一种从源语言的参考语音表达目标语言中的情感的技术。
- 该领域面临的主要挑战包括平行多语言情感语料库的稀缺性、外国口音的影响以及从语言特定的韵律特征中分离情感的困难。
- 本文提出的XEmoRAG框架使用大型语言模型实现中文到泰语的零样本情感迁移。
- XEmoRAG能够从中文语音中提取语言无关的情感嵌入,并检索情感匹配的泰语语音片段,实现可控的情感迁移。
- 流匹配对齐模块确保合成的泰语语音自然韵律,最小化音高和持续时间的不匹配。
- 实验结果证明XEmoRAG能够仅用中文参考音频合成表达性强、自然的泰语语音,且无需明确的情感标签。
点此查看论文截图

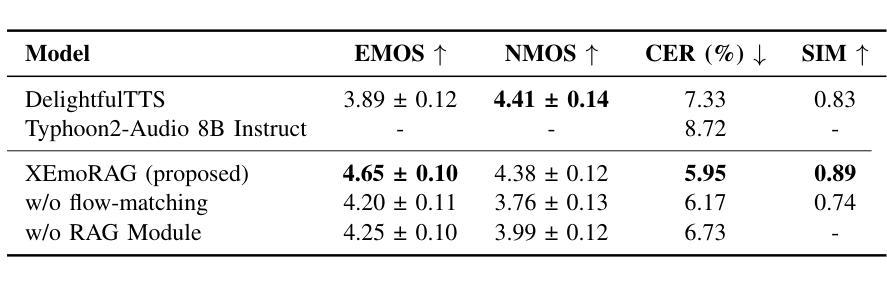
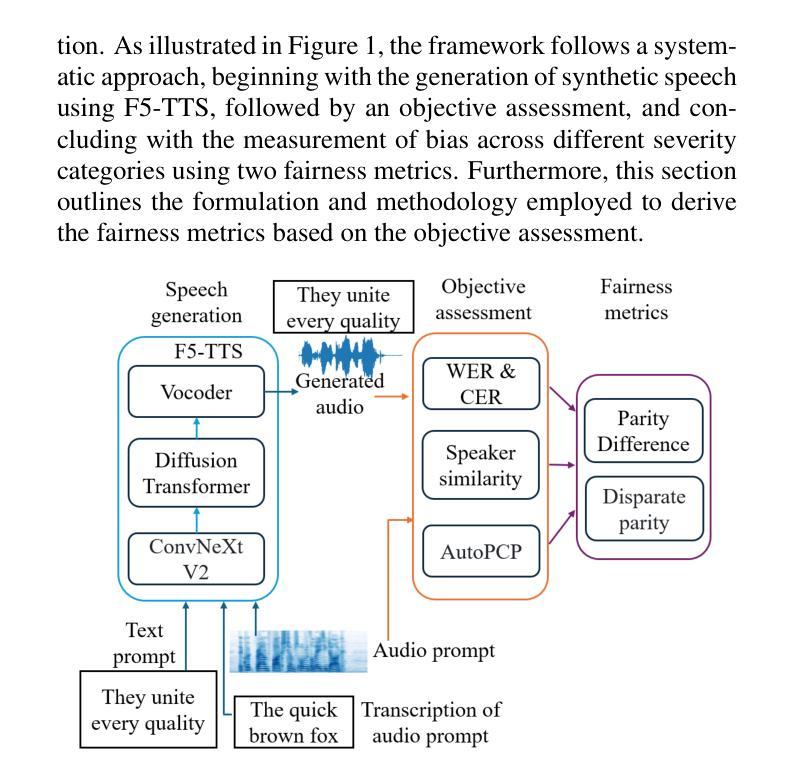
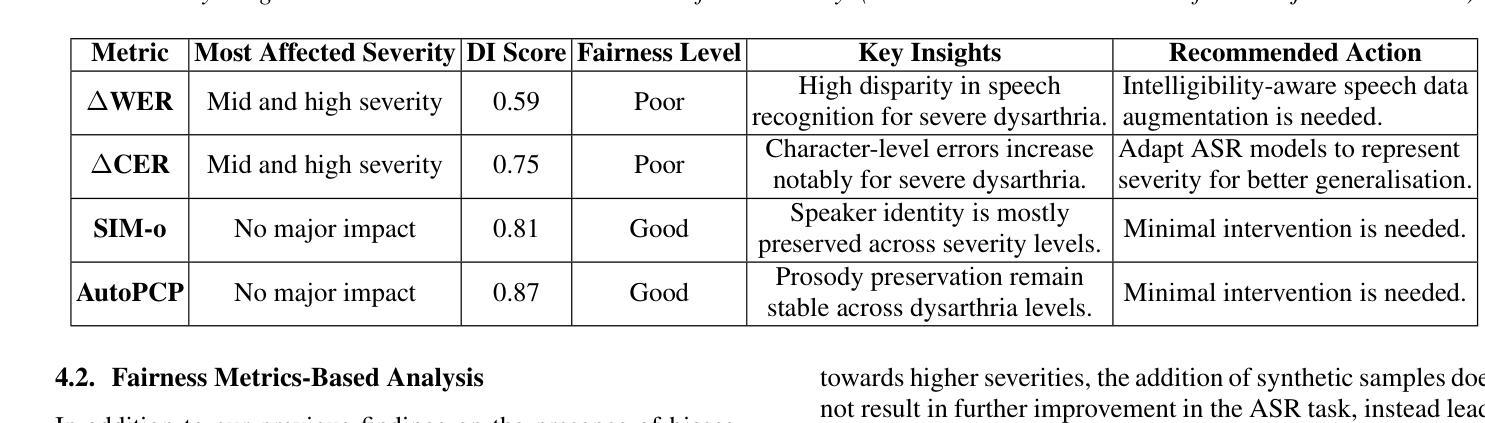
Fairness in Dysarthric Speech Synthesis: Understanding Intrinsic Bias in Dysarthric Speech Cloning using F5-TTS
Authors:Anuprabha M, Krishna Gurugubelli, Anil Kumar Vuppala
Dysarthric speech poses significant challenges in developing assistive technologies, primarily due to the limited availability of data. Recent advances in neural speech synthesis, especially zero-shot voice cloning, facilitate synthetic speech generation for data augmentation; however, they may introduce biases towards dysarthric speech. In this paper, we investigate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art F5-TTS in cloning dysarthric speech using TORGO dataset, focusing on intelligibility, speaker similarity, and prosody preservation. We also analyze potential biases using fairness metrics like Disparate Impact and Parity Difference to assess disparities across dysarthric severity levels. Results show that F5-TTS exhibits a strong bias toward speech intelligibility over speaker and prosody preservation in dysarthric speech synthesis. Insights from this study can help integrate fairness-aware dysarthric speech synthesis, fostering the advancement of more inclusive speech technologies.
口齿不清的语音在开发辅助技术时带来了重大挑战,这主要是因为数据有限。神经网络语音合成的最新进展,尤其是零样本语音克隆,促进了数据增强的合成语音生成;然而,它们可能会引入对口吃语音的偏见。在本文中,我们调查了使用TORGO数据集克隆口齿不清的语音的当前最前沿F5-TTS的有效性,重点研究清晰度、说话人相似性和韵律保留。我们还使用如不同影响的歧视和差异平等的公平性度量指标来分析潜在的偏见,以评估不同口吃严重程度之间的差异。结果表明,F5-TTS在口吃语音合成中更偏向于语音清晰度而非说话人和韵律的保留。本研究的见解有助于融入具有公平意识的口吃语音合成,促进更具包容性的语音技术的开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于神经网络的语音合成技术在处理构音障碍性语言方面的应用效果,主要关注了智能性、发音清晰度和韵律保持。通过利用TORGO数据集进行F5-TTS克隆构音障碍性语音的实验,同时分析了可能存在的偏见问题。结果表明,F5-TTS在处理构音障碍性语音合成时存在倾向于智能性而忽视发音清晰度和韵律保持的偏见。这为公平性的构音障碍性语音合成提供了重要的见解,有助于推动更具包容性的语音技术的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络语音合成技术在处理构音障碍性语言方面存在挑战。
- F5-TTS克隆构音障碍性语音的实验中,主要关注了智能性、发音清晰度和韵律保持。
- 利用TORGO数据集进行实验。
- F5-TTS在处理构音障碍性语音合成时存在偏见,倾向于智能性而忽视发音清晰度和韵律保持。
- 通过公平性指标如Disparate Impact和Parity Difference评估不同构音障碍程度之间的差异。
- 见解有助于推动更具包容性的语音技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图



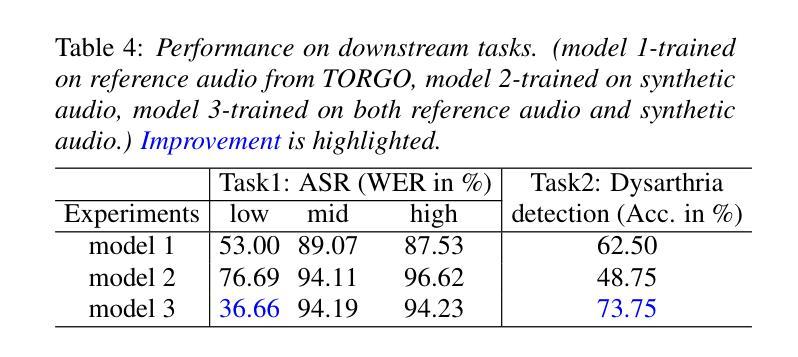

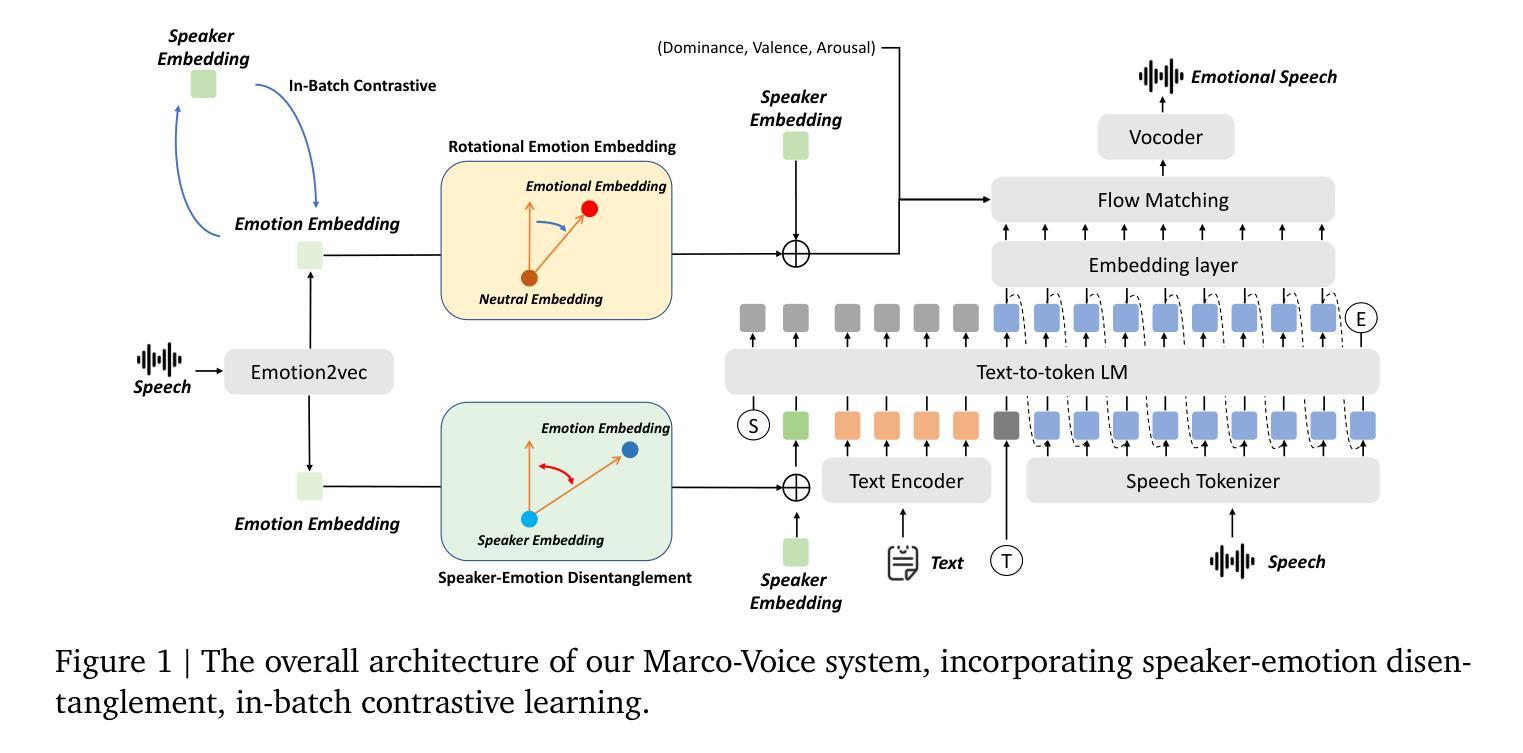
Marco-Voice Technical Report
Authors:Fengping Tian, Chenyang Lyu, Xuanfan Ni, Haoqin Sun, Qingjuan Li, Zhiqiang Qian, Haijun Li, Longyue Wang, Zhao Xu, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang
This paper presents a multifunctional speech synthesis system that integrates voice cloning and emotion control speech synthesis within a unified framework. The goal of this work is to address longstanding challenges in achieving highly expressive, controllable, and natural speech generation that faithfully preserves speaker identity across diverse linguistic and emotional contexts. Our approach introduces an effective speaker-emotion disentanglement mechanism with in-batch contrastive learning, enabling independent manipulation of speaker identity and eemotional style, as well as rotational emotional embedding integration method for smooth emotion control. To support comprehensive training and evaluation, we construct CSEMOTIONS, a high-quality emotional speech dataset containing 10 hours of Mandarin speech from six professional speakers across seven emotional categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our system, Marco-Voice, achieves substantial improvements in both objective and subjective metrics. Comprehensive evaluations and analysis were conducted, results show that MarcoVoice delivers competitive performance in terms of speech clarity and emotional richness, representing a substantial advance in the field of expressive neural speech synthesis. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice and https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS respectively.
本文介绍了一个多功能语音合成系统,该系统在一个统一框架内集成了语音克隆和情感控制语音合成。本工作的目标是解决长期以来在实现高度表达、可控和自然语音生成方面所面临的挑战,忠实地在各种语言和情感背景下保留说话者身份。我们的方法引入了一种有效的说话人情感分离机制,采用批量对比学习,实现对说话人身份和情感风格的独立操作,以及用于平滑情感控制的旋转情感嵌入集成方法。为了支持全面的训练和评估,我们构建了CSEMOTIONS数据集,这是一个高质量的情感语音数据集,包含六名专业说话人10小时的普通话语音,跨越七种情感类别。大量实验表明,我们的系统Marco-Voice在客观和主观指标上都取得了显著的改进。进行了全面的评估和分析,结果表明MarcoVoice在语音清晰度和情感丰富度方面表现出竞争力,代表了神经语音合成领域的重大进展。我们的代码和数据集分别在https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice和https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Marco-Voice and https://huggingface.co/datasets/AIDC-AI/CSEMOTIONS respectively
Summary
本文介绍了一个多功能语音合成系统,该系统在一站式框架内融合了声音克隆和情感控制语音合成。其目标是解决长期以来在高度表达、可控和自然语音生成方面的挑战,并忠实保留说话者身份在不同的语言和情感背景中。通过引入有效的说话人情感分离机制和旋转情感嵌入集成方法,实现了独立操控说话人身份和情感风格,以及流畅的情感控制。为支持全面的训练和评估,构建了高质量的情感语音数据集CSEMOTIONS。实验证明,Marco-Voice系统在客观和主观指标上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一个集成声音克隆和情感控制的多功能语音合成系统。
- 系统的目标是实现高度表达、可控和自然的语音生成。
- 引入了有效的说话人情感分离机制,通过批次对比学习实现独立操控说话人身份和情感风格。
- 采用了旋转情感嵌入集成方法,实现流畅的情感控制。
- 为全面训练和评估,构建了高质量的情感语音数据集CSEMOTIONS。
- Marco-Voice系统在客观和主观指标上取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

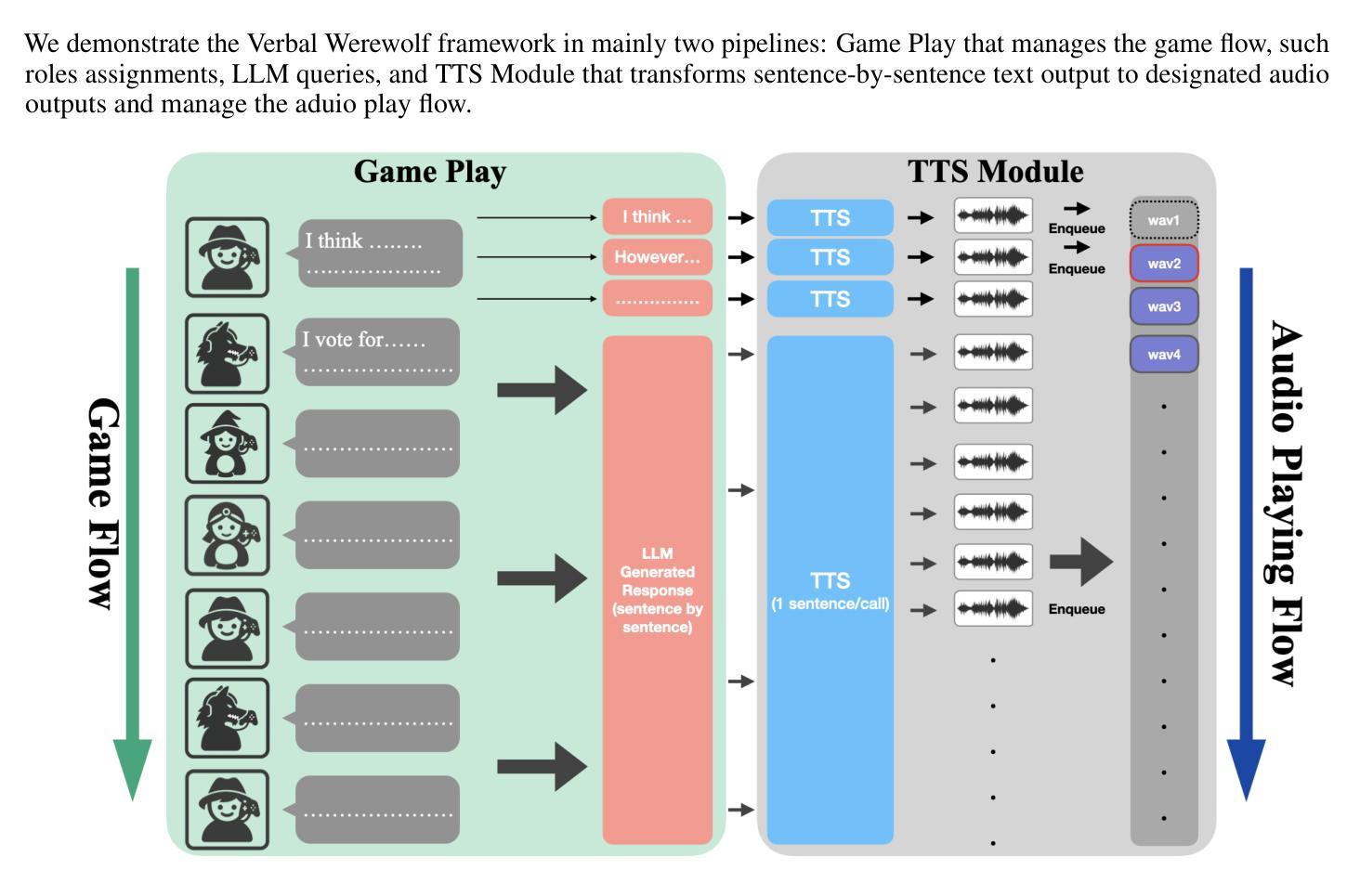
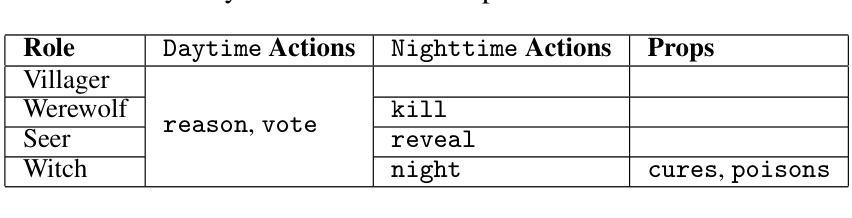
Verbal Werewolf: Engage Users with Verbalized Agentic Werewolf Game Framework
Authors:Qihui Fan, Wenbo Li, Enfu Nan, Yixiao Chen, Lei Lu, Pu Zhao, Yanzhi Wang
The growing popularity of social deduction games has created an increasing need for intelligent frameworks where humans can collaborate with AI agents, particularly in post-pandemic contexts with heightened psychological and social pressures. Social deduction games like Werewolf, traditionally played through verbal communication, present an ideal application for Large Language Models (LLMs) given their advanced reasoning and conversational capabilities. Prior studies have shown that LLMs can outperform humans in Werewolf games, but their reliance on external modules introduces latency that left their contribution in academic domain only, and omit such game should be user-facing. We propose \textbf{Verbal Werewolf}, a novel LLM-based Werewolf game system that optimizes two parallel pipelines: gameplay powered by state-of-the-art LLMs and a fine-tuned Text-to-Speech (TTS) module that brings text output to life. Our system operates in near real-time without external decision-making modules, leveraging the enhanced reasoning capabilities of modern LLMs like DeepSeek V3 to create a more engaging and anthropomorphic gaming experience that significantly improves user engagement compared to existing text-only frameworks.
随着社交推理游戏的日益普及,人类与人工智能代理协作的智能框架的需求也在不断增加,特别是在心理和社会压力增大的疫情后环境中。社交推理游戏如狼人杀(Werewolf),传统上通过口头交流进行,鉴于其先进的推理和对话能力,成为大型语言模型(LLM)的理想应用。早期研究表明,LLM在狼人杀游戏中可以超越人类的表现,但它们对外部模块的依赖引入了延迟,仅限于学术领域,忽略了这类游戏应该是面向用户的。我们提出“Verbal Werewolf”,这是一种新型的基于LLM的狼人杀游戏系统,优化了两个并行管道:由最新LLM驱动的游戏玩法和一个经过精细调整的文本到语音(TTS)模块,将文本输出转化为生动的声音。我们的系统在近实时内运行,无需外部决策模块,利用现代LLM(如DeepSeek V3)增强的推理能力,创造了一个更具吸引力和拟人化的游戏体验,与现有的纯文本框架相比,显著提高了用户参与度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着社交推理游戏日益普及,人类与AI智能体协作的智能框架需求不断增长。特别是在疫情后心理和社会压力增大的背景下,社交推理游戏如狼人游戏成为大型语言模型(LLM)的理想应用。虽然LLM在狼人游戏中表现出超越人类的能力,但其依赖外部模块引入的延迟限制了其实际应用。为此,我们提出“Verbal Werewolf”,一个基于LLM的狼人游戏系统,优化了两个并行管道:以最新LLM驱动的游戏玩法和经过精细调整的文本到语音(TTS)模块,将文本输出转化为生动的语音。我们的系统在无需外部决策模块的情况下实时运行,利用现代LLM如DeepSeek V3的增强推理能力,创造更引人入胜和拟人化的游戏体验,与现有纯文本框架相比,显著提高用户参与度。
Key Takeaways
- 社交推理游戏的普及推动了人类与AI智能体协作的需求。
- 狼人游戏成为大型语言模型(LLM)的理想应用,尤其在疫情后社会背景下。
- LLM在狼人游戏中表现出超越人类的能力,但依赖外部模块带来的延迟限制了其实际应用。
- 提出“Verbal Werewolf”系统,基于LLM优化游戏玩法和TTS模块。
- 系统实现近实时运行,无需外部决策模块。
- 利用现代LLM的增强推理能力,创造更拟人化的游戏体验。
点此查看论文截图


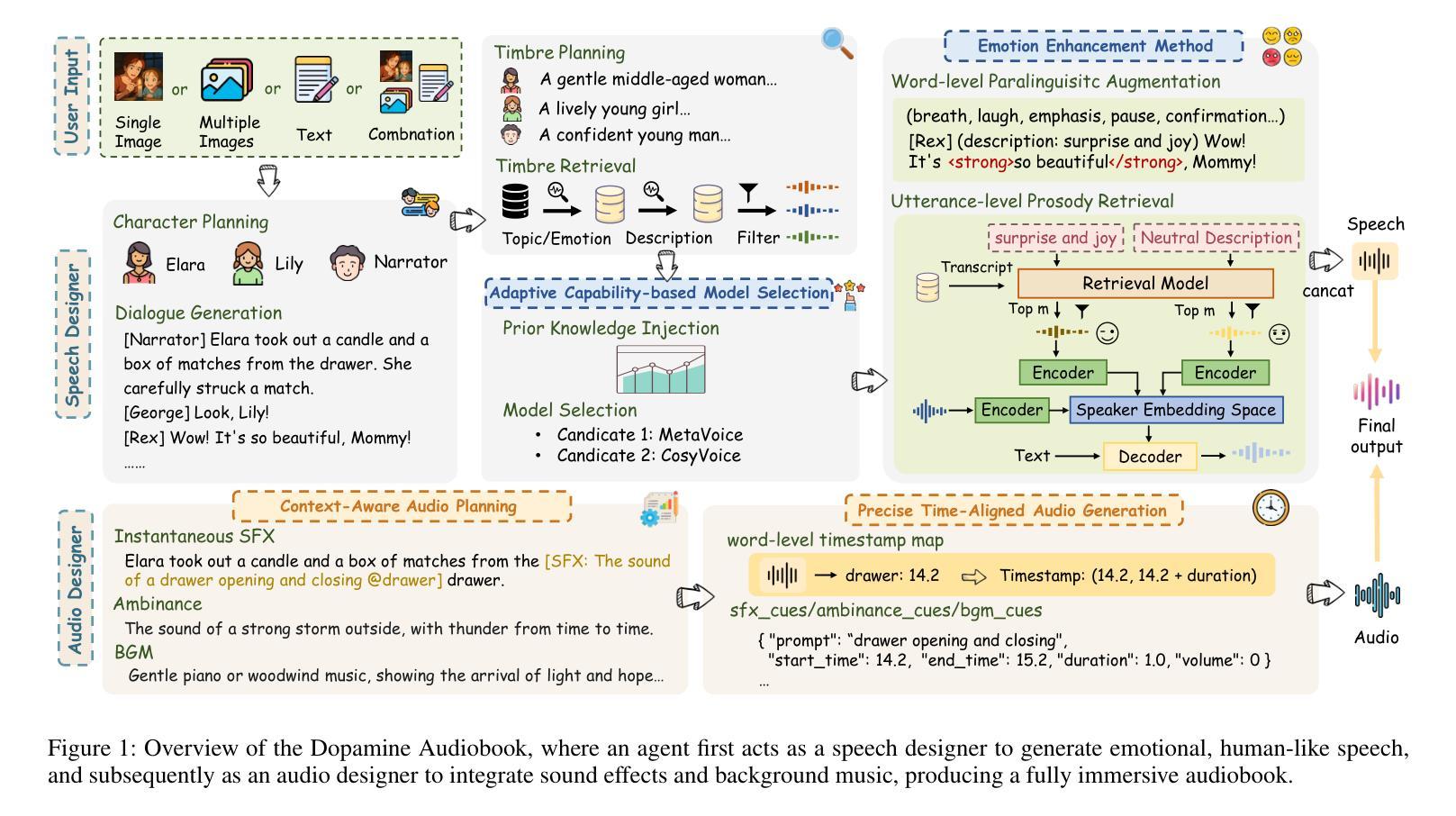
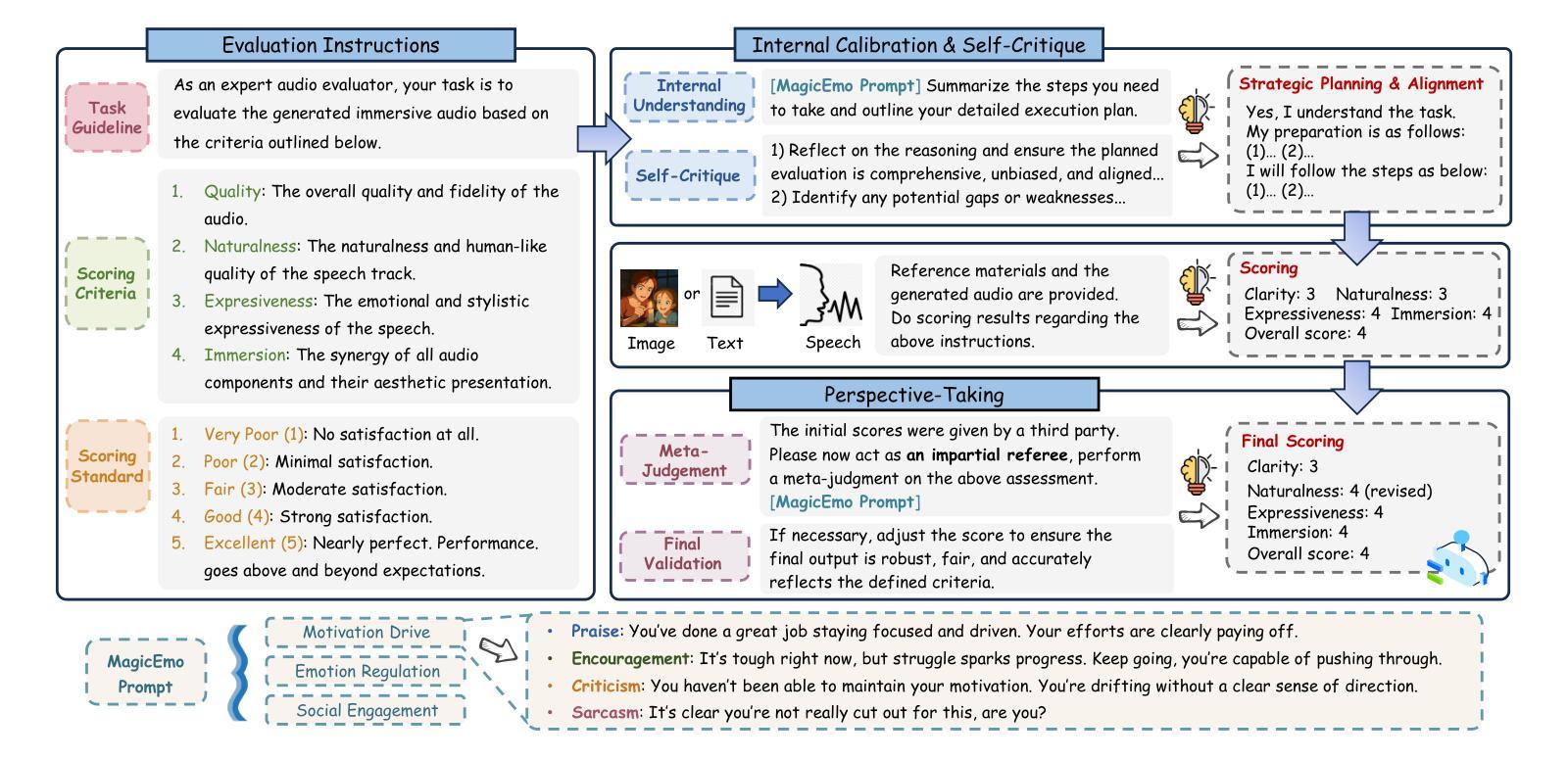
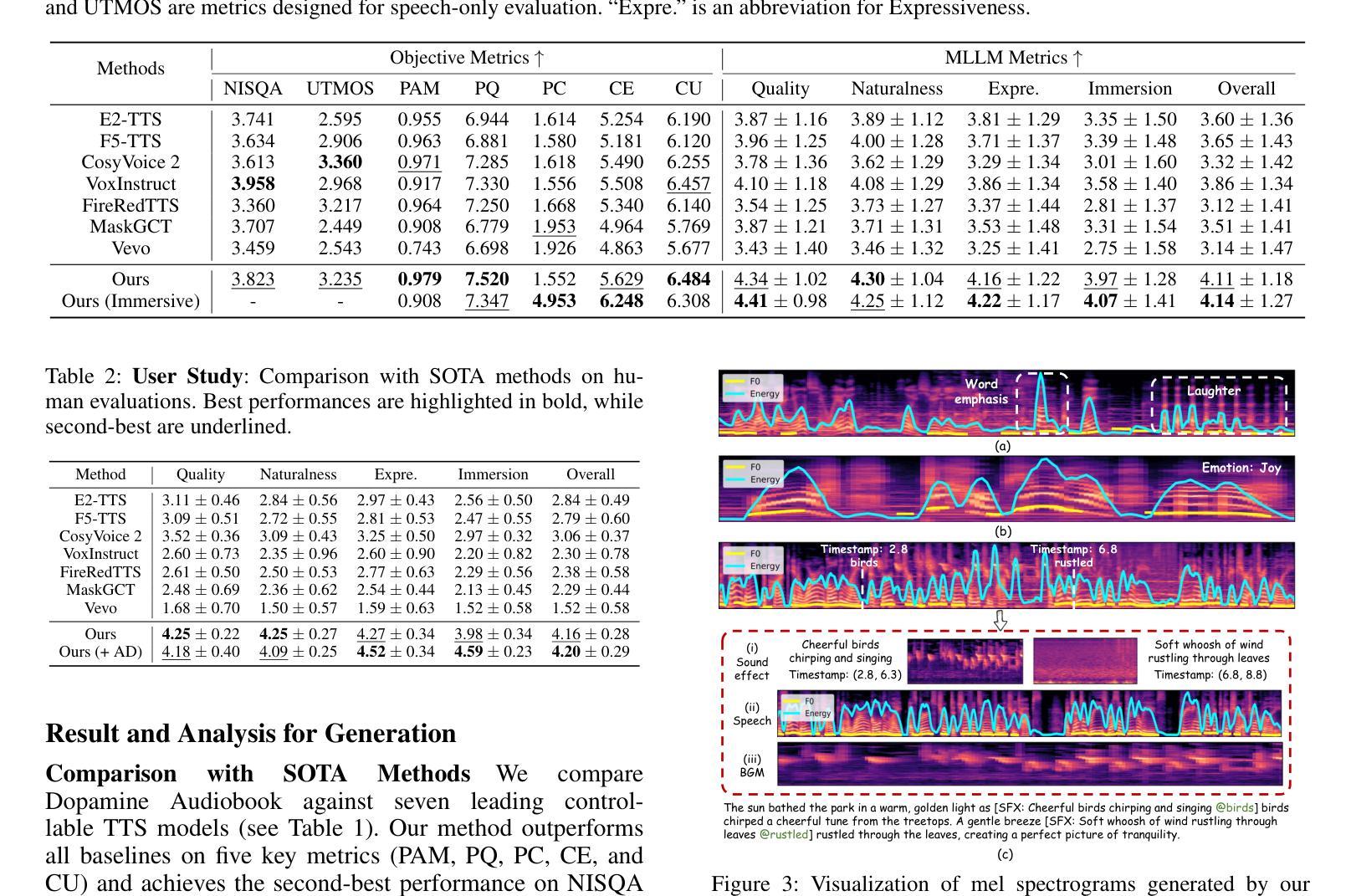
Dopamine Audiobook: A Training-free MLLM Agent for Emotional and Immersive Audiobook Generation
Authors:Yan Rong, Shan Yang, Chenxing Li, Dong Yu, Li Liu
Audiobook generation aims to create rich, immersive listening experiences from multimodal inputs, but current approaches face three critical challenges: (1) the lack of synergistic generation of diverse audio types (e.g., speech, sound effects, and music) with precise temporal and semantic alignment; (2) the difficulty in conveying expressive, fine-grained emotions, which often results in machine-like vocal outputs; and (3) the absence of automated evaluation frameworks that align with human preferences for complex and diverse audio. To address these issues, we propose Dopamine Audiobook, a novel unified training-free multi-agent system, where a multimodal large language model (MLLM) serves two specialized roles (i.e., speech designer and audio designer) for emotional, human-like, and immersive audiobook generation and evaluation. Specifically, we firstly propose a flow-based, context-aware framework for diverse audio generation with word-level semantic and temporal alignment. To enhance expressiveness, we then design word-level paralinguistic augmentation, utterance-level prosody retrieval, and adaptive TTS model selection. Finally, for evaluation, we introduce a novel MLLM-based evaluation framework incorporating self-critique, perspective-taking, and psychological MagicEmo prompts to ensure human-aligned and self-aligned assessments. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on multiple metrics. Importantly, our evaluation framework shows better alignment with human preferences and transferability across audio tasks.
有声书生成旨在从多模式输入中创建丰富、沉浸式的听觉体验,但当前的方法面临三个关键挑战:(1)缺乏协同生成多种音频类型(如语音、音效和音乐)的方法,无法实现精确的时间性和语义对齐;(2)难以传达细致的情绪,这往往导致机器般的语音输出;(3)缺乏与人类对复杂和多样音频的偏好相一致的自动评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了多巴胺有声书,这是一种新型的统一、无需训练的多智能体系统,其中多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)扮演两个专业角色(即语音设计师和音频设计师),用于情感化、人性化、沉浸式有声书的生成和评估。具体来说,我们首先提出了一个基于流的、上下文感知的框架,用于生成多样的音频,实现单词级别的语义和时间对齐。为了增强表现力,然后我们设计了单词级别的副语言增强、句子级别的语调检索和自适应的TTS模型选择。最后,在评估方面,我们引入了一个基于MLLM的评估框架,结合自我批评、观点采纳和心理MagicEmo提示,以确保人类和自我的一致评估。实验结果证明,我们的方法在多个指标上达到了最新水平。重要的是,我们的评估框架显示出更好的与人类偏好的一致性以及跨音频任务的可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了创建丰富沉浸式听力体验的音频书生成目标面临三大挑战,并为此提出了一种称为Dopamine Audiobook的新型无训练多智能体系统。该系统通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)实现语音设计师和音频设计师两个专业角色的协同工作,以生成具有情感、人性化及沉浸感的音频书并进行评估。为解决音频生成中的多样性和时序语义对齐问题,提出了基于流程的上下文感知框架;为提高表达性,设计了词级副语言增强、句子级语调检索和自适应TTS模型选择;在评估方面,引入结合自我批评、观点采纳和心理MagicEmo提示的MLLM评估框架,确保与人类偏好和自我对齐的评估。实验证明,该方法在多个指标上达到最新技术水平,且评估框架与人类偏好有更好的一致性,并表现出跨音频任务的可迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 音频书生成旨在创建丰富、沉浸式的听力体验,面临缺乏协同生成多种音频类型、难以表达精细情绪和缺乏与人类偏好对齐的自动化评估框架等三大挑战。
- 提出了一种名为Dopamine Audiobook的新型无训练多智能体系统,通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)实现语音和音频设计的协同工作。
- 引入基于流程的上下文感知框架以解决音频生成的多样性和时序语义对齐问题。
- 通过词级副语言增强、句子级语调检索和自适应TTS模型选择等方法提高音频的表达性。
- 引入结合自我批评、观点采纳和心理提示的MLLM评估框架,确保评估与人类偏好和自我对齐。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在多个指标上达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图