⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-15 更新
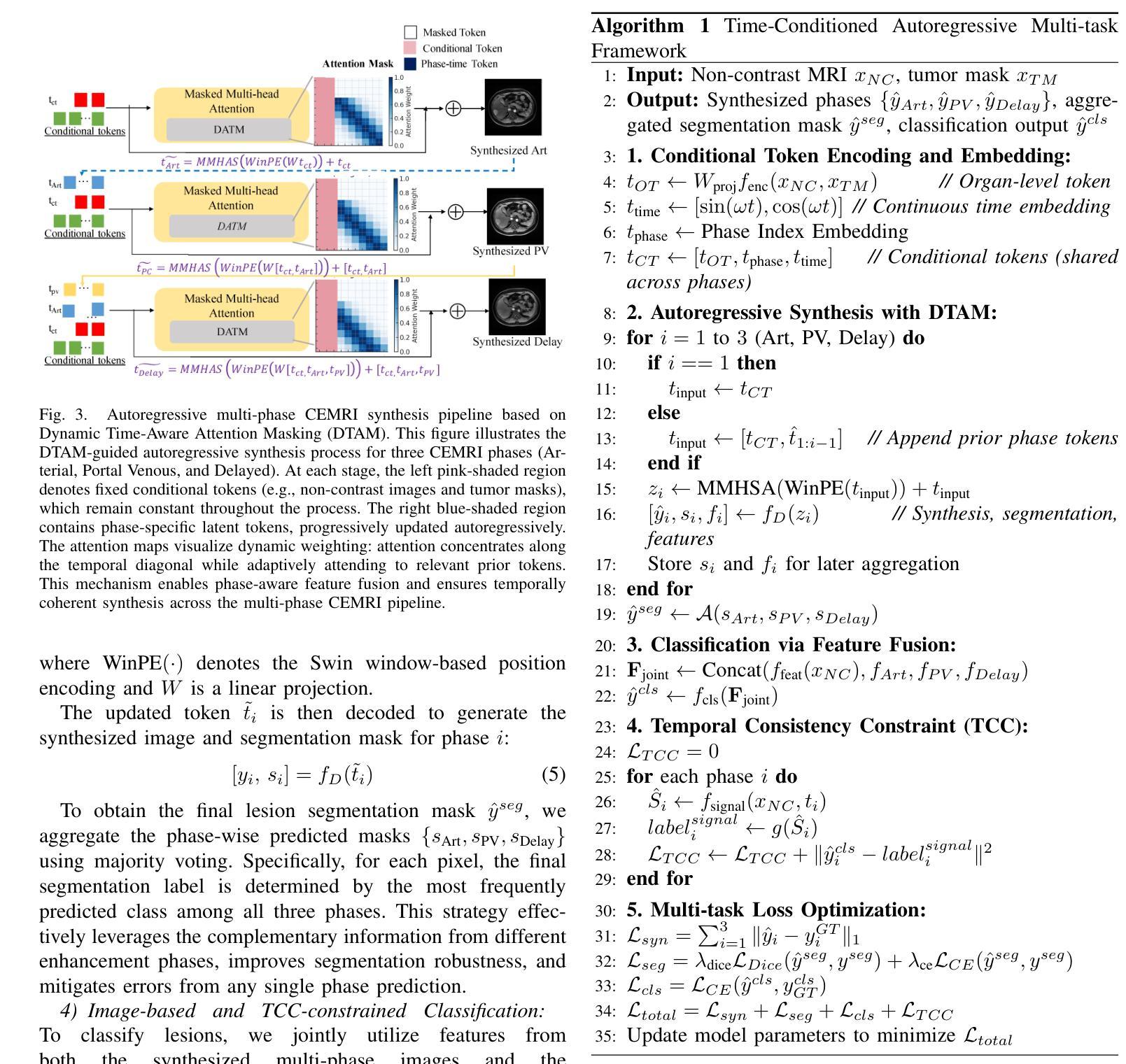
T-CACE: A Time-Conditioned Autoregressive Contrast Enhancement Multi-Task Framework for Contrast-Free Liver MRI Synthesis, Segmentation, and Diagnosis
Authors:Xiaojiao Xiao, Jianfeng Zhao, Qinmin Vivian Hu, Guanghui Wang
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a leading modality for the diagnosis of liver cancer, significantly improving the classification of the lesion and patient outcomes. However, traditional MRI faces challenges including risks from contrast agent (CA) administration, time-consuming manual assessment, and limited annotated datasets. To address these limitations, we propose a Time-Conditioned Autoregressive Contrast Enhancement (T-CACE) framework for synthesizing multi-phase contrast-enhanced MRI (CEMRI) directly from non-contrast MRI (NCMRI). T-CACE introduces three core innovations: a conditional token encoding (CTE) mechanism that unifies anatomical priors and temporal phase information into latent representations; and a dynamic time-aware attention mask (DTAM) that adaptively modulates inter-phase information flow using a Gaussian-decayed attention mechanism, ensuring smooth and physiologically plausible transitions across phases. Furthermore, a constraint for temporal classification consistency (TCC) aligns the lesion classification output with the evolution of the physiological signal, further enhancing diagnostic reliability. Extensive experiments on two independent liver MRI datasets demonstrate that T-CACE outperforms state-of-the-art methods in image synthesis, segmentation, and lesion classification. This framework offers a clinically relevant and efficient alternative to traditional contrast-enhanced imaging, improving safety, diagnostic efficiency, and reliability for the assessment of liver lesion. The implementation of T-CACE is publicly available at: https://github.com/xiaojiao929/T-CACE.
磁共振成像(MRI)是诊断肝癌的主要手段,极大地提高了病变分类和患者治疗效果。然而,传统MRI面临着造影剂使用风险、耗时的人工评估以及标注数据集有限等挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于时间条件的自回归对比增强(T-CACE)框架,它能够直接从非对比增强MRI(NCMRI)合成多期对比增强MRI(CEMRI)。T-CACE有三个核心创新点:一种条件令牌编码(CTE)机制,它将解剖先验知识和时间相位信息统一为潜在表示;一个动态时间感知注意力掩模(DTAM),它使用高斯衰减注意力机制自适应地调节相间信息流,确保各相之间的平稳过渡并且符合生理规律。此外,一种时间分类一致性约束(TCC)使病变分类输出与生理信号的演变保持一致,进一步提高了诊断的可靠性。在两个独立的肝脏MRI数据集上的大量实验表明,T-CACE在图像合成、分割和病变分类方面均优于现有先进技术。该框架提供了一个与传统对比增强成像相关的、高效的替代方案,提高了安全性、诊断效率和肝脏病变评估的可靠性。T-CACE的实现可公开访问:https://github.com/xiaojiao929/T-CACE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对肝脏癌症诊断的磁共振成像(MRI)技术面临的挑战,如对比剂风险、耗时的人工评估和有限的标注数据集。为此,提出了一种时间条件自回归对比增强(T-CACE)框架,可从非对比MRI(NCMRI)直接合成多阶段对比增强MRI(CEMRI)。该框架引入三项核心创新:条件令牌编码(CTE)机制,统一解剖先验和时态相位信息到潜在表示;动态时间感知注意力掩膜(DTAM),使用高斯衰减注意力机制自适应调节阶段间信息流,确保平滑且符合生理的过渡;以及时间分类一致性约束(TCC),使病变分类输出与生理信号演变保持一致,进一步提高诊断可靠性。实验证明,T-CACE在图像合成、分割和病变分类方面优于现有方法,为传统对比增强成像提供了临床相关且高效的替代方案,提高了安全性、诊断效率和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 肝脏癌症诊断中MRI技术的局限性包括对比剂风险、耗时的手动评估和有限标注数据集。
- T-CACE框架通过合成多阶段对比增强MRI(CEMRI)直接从非对比MRI(NCMRI)进行改进。
- T-CACE引入三项核心创新:条件令牌编码、动态时间感知注意力掩膜和时间分类一致性约束。
- T-CACE在图像合成、分割和病变分类方面表现出优异性能,提高了诊断的可靠性、效率和安全性。
点此查看论文截图


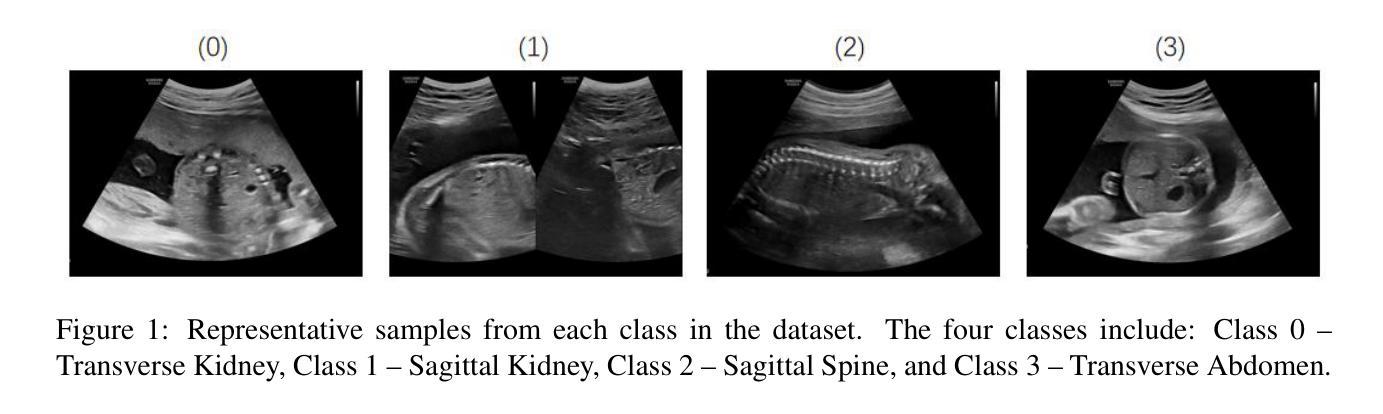
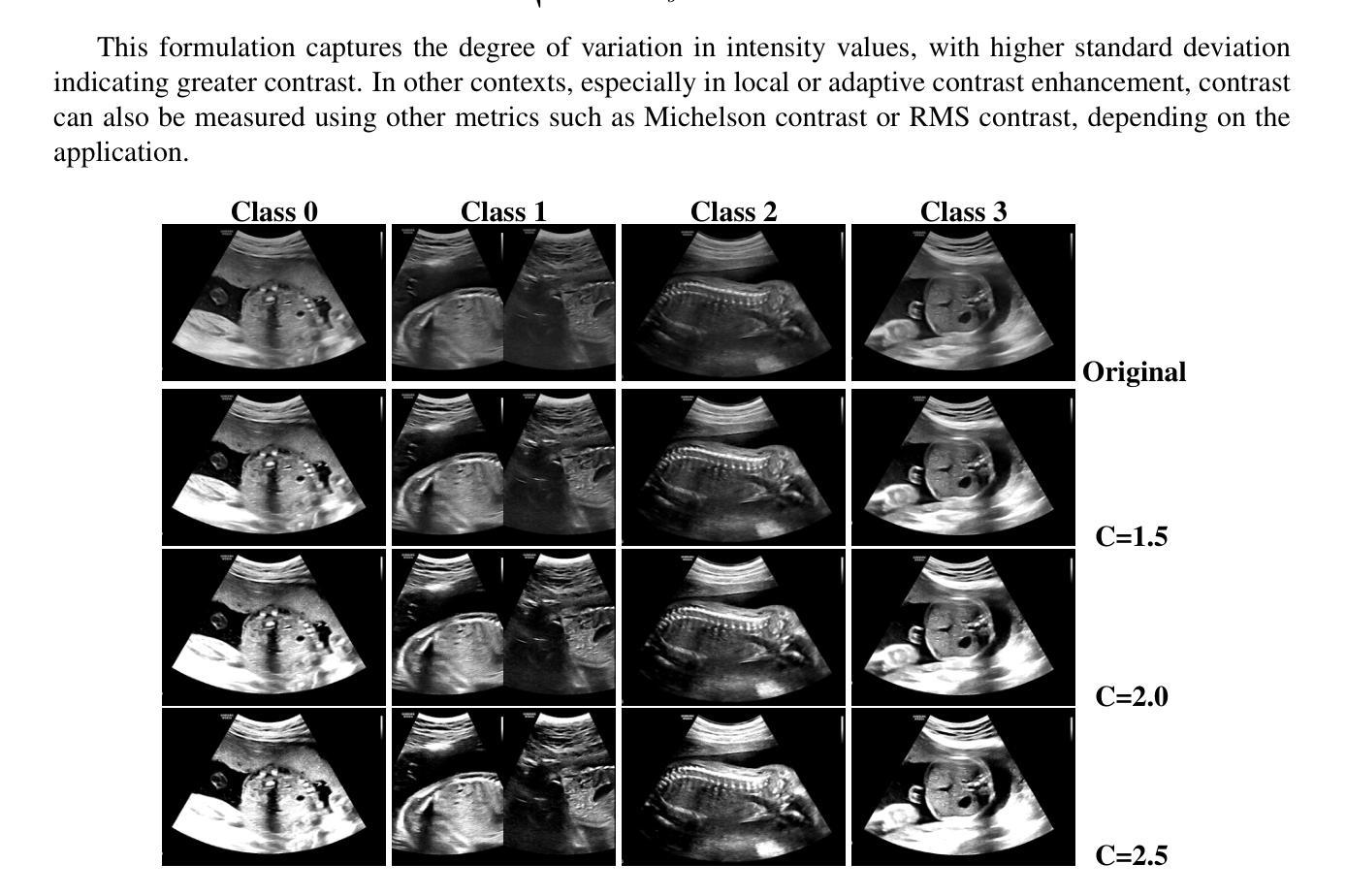
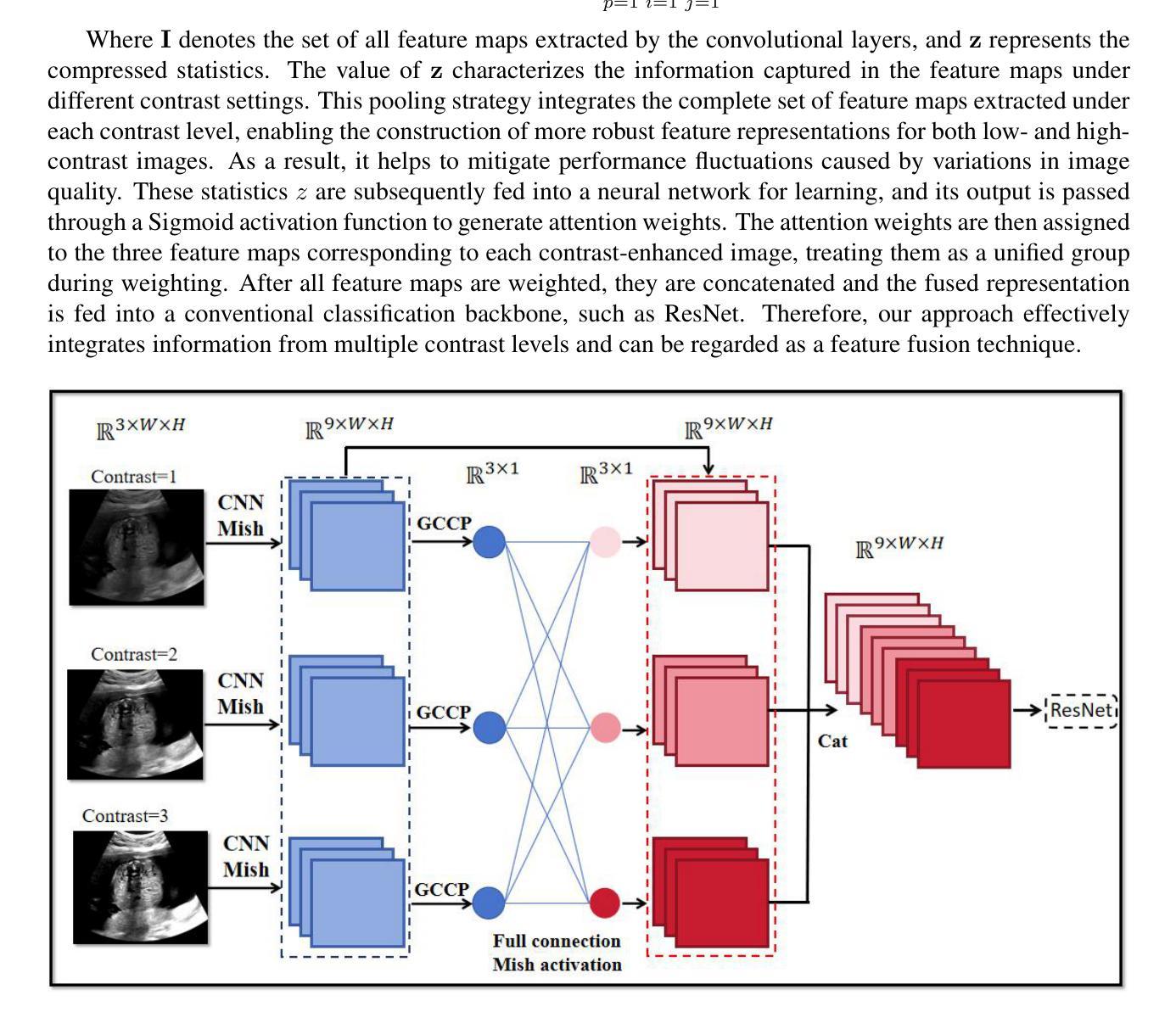
Multi-Contrast Fusion Module: An attention mechanism integrating multi-contrast features for fetal torso plane classification
Authors:Shengjun Zhu, Siyu Liu, Runqing Xiong, Liping Zheng, Duo Ma, Rongshang Chen, Jiaxin Cai
Purpose: Prenatal ultrasound is a key tool in evaluating fetal structural development and detecting abnormalities, contributing to reduced perinatal complications and improved neonatal survival. Accurate identification of standard fetal torso planes is essential for reliable assessment and personalized prenatal care. However, limitations such as low contrast and unclear texture details in ultrasound imaging pose significant challenges for fine-grained anatomical recognition. Methods: We propose a novel Multi-Contrast Fusion Module (MCFM) to enhance the model’s ability to extract detailed information from ultrasound images. MCFM operates exclusively on the lower layers of the neural network, directly processing raw ultrasound data. By assigning attention weights to image representations under different contrast conditions, the module enhances feature modeling while explicitly maintaining minimal parameter overhead. Results: The proposed MCFM was evaluated on a curated dataset of fetal torso plane ultrasound images. Experimental results demonstrate that MCFM substantially improves recognition performance, with a minimal increase in model complexity. The integration of multi-contrast attention enables the model to better capture subtle anatomical structures, contributing to higher classification accuracy and clinical reliability. Conclusions: Our method provides an effective solution for improving fetal torso plane recognition in ultrasound imaging. By enhancing feature representation through multi-contrast fusion, the proposed approach supports clinicians in achieving more accurate and consistent diagnoses, demonstrating strong potential for clinical adoption in prenatal screening. The codes are available at https://github.com/sysll/MCFM.
目的:产前超声是评估胎儿结构发育和检测异常的关键工具,有助于减少围生期并发症,提高新生儿存活率。准确识别标准胎儿躯干平面对于可靠的评估和个性化的产前护理至关重要。然而,超声成像中对比度低和纹理细节不清晰等局限性给精细的解剖识别带来了重大挑战。方法:我们提出了一种新型的多对比度融合模块(MCFM),以增强模型从超声图像中提取详细信息的能力。MCFM仅在网络的下层运行,直接处理原始超声数据。通过在不同对比度条件下对图像表示分配注意力权重,该模块在显式保持最小参数开销的同时增强了特征建模。结果:所提出的MCFM在胎儿躯干平面超声图像的数据集上进行了评估。实验结果表明,MCFM在识别性能上有显著提高,且模型复杂度增加最小。多对比度注意力的集成使模型能够更好地捕捉微妙的解剖结构,从而提高分类精度和临床可靠性。结论:我们的方法为解决超声成像中胎儿躯干平面识别问题提供了有效解决方案。通过多对比度融合增强特征表示,所提出的方法支持临床医生实现更准确和一致的诊断,显示出在临床产前筛查中采用的强大潜力。相关代码可访问https://github.com/sysll/MCFM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Multi-Contrast Fusion Module(MCFM)的新方法,用于增强模型从超声波图像中提取详细信息的能力,从而提高对胎儿躯体平面的识别精度。该方法通过在不同对比度条件下对图像表示分配注意力权重,增强特征建模,同时保持较小的参数开销。实验结果表明,MCFM在胎儿躯体平面超声图像的数据集上显著提高识别性能,且模型复杂度增加较小。该方法有助于捕获微妙的解剖结构,提高分类精度和临床可靠性,为产前筛查的准确诊断提供了强有力的支持。
Key Takeaways
- 超声波是评估胎儿结构发育和检测异常的关键工具。
- 准确识别胎儿躯体平面对于可靠的评估和个性化产前护理至关重要。
- 提出的Multi-Contrast Fusion Module(MCFM)旨在增强模型从超声波图像中提取详细信息的能力。
- MCFM在神经网络的较低层级上运行,直接处理原始超声波数据。
- 通过在不同对比度条件下分配注意力权重,MCFM增强了特征建模。
- 实验结果表明,MCFM在胎儿躯体平面识别上显著提高识别性能。
点此查看论文截图

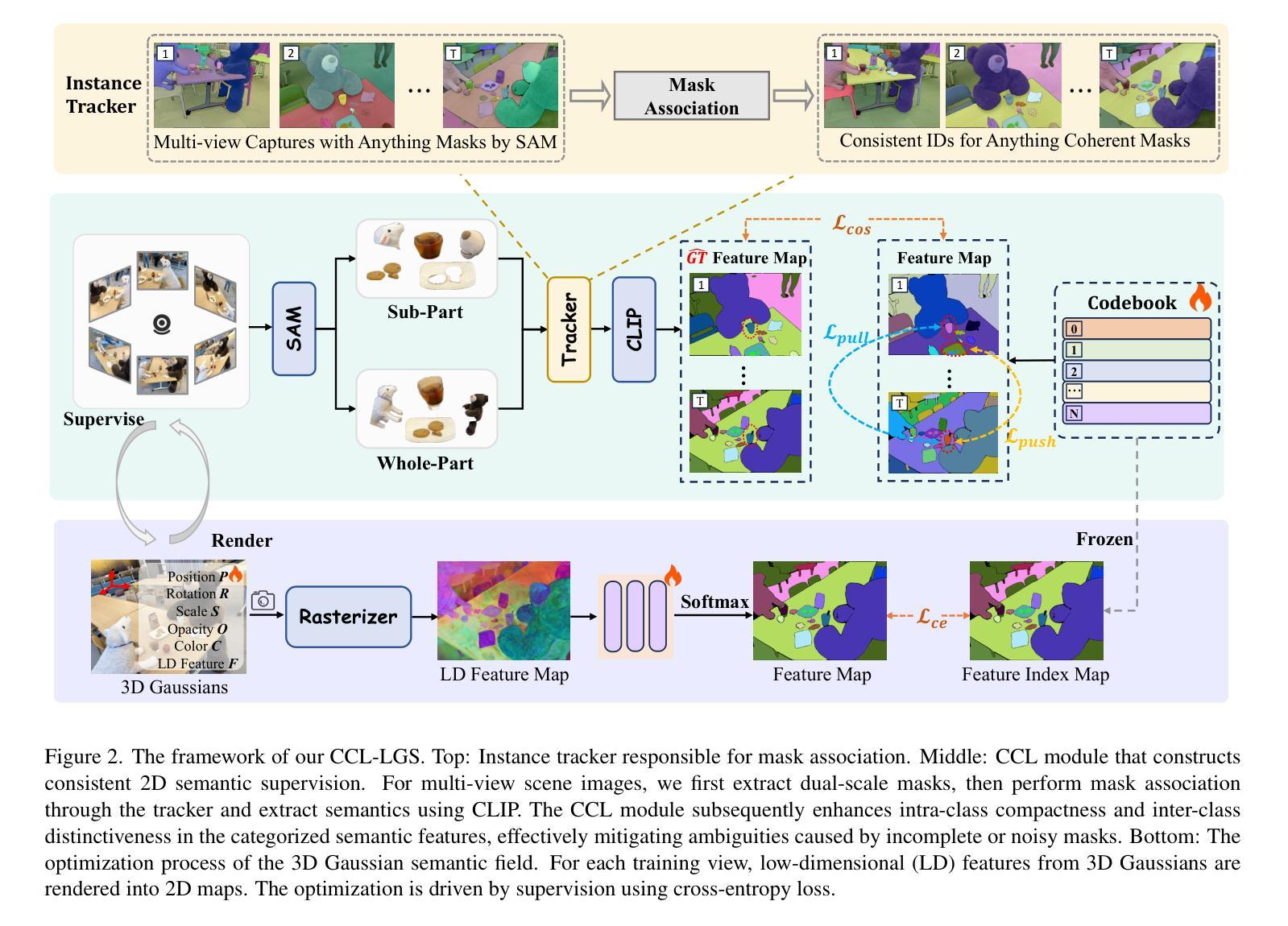
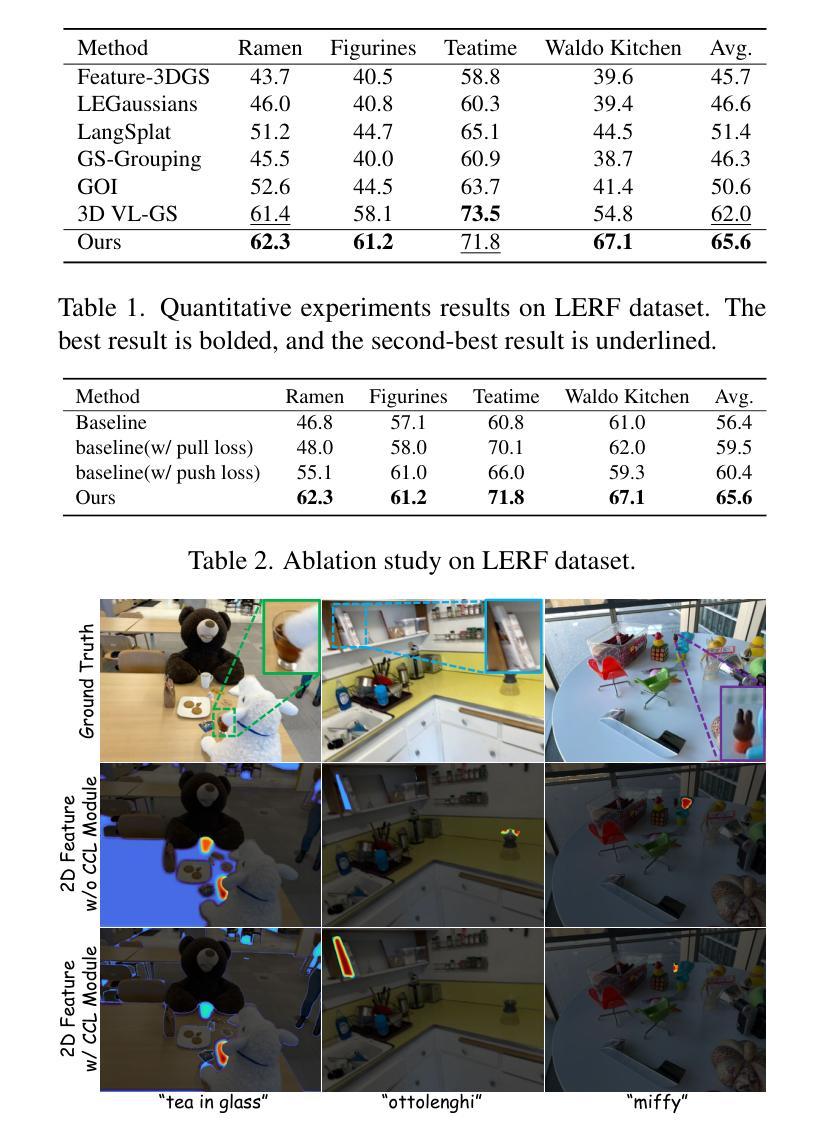
CCL-LGS: Contrastive Codebook Learning for 3D Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lei Tian, Xiaomin Li, Liqian Ma, Hao Yin, Zirui Zheng, Hefei Huang, Taiqing Li, Huchuan Lu, Xu Jia
Recent advances in 3D reconstruction techniques and vision-language models have fueled significant progress in 3D semantic understanding, a capability critical to robotics, autonomous driving, and virtual/augmented reality. However, methods that rely on 2D priors are prone to a critical challenge: cross-view semantic inconsistencies induced by occlusion, image blur, and view-dependent variations. These inconsistencies, when propagated via projection supervision, deteriorate the quality of 3D Gaussian semantic fields and introduce artifacts in the rendered outputs. To mitigate this limitation, we propose CCL-LGS, a novel framework that enforces view-consistent semantic supervision by integrating multi-view semantic cues. Specifically, our approach first employs a zero-shot tracker to align a set of SAM-generated 2D masks and reliably identify their corresponding categories. Next, we utilize CLIP to extract robust semantic encodings across views. Finally, our Contrastive Codebook Learning (CCL) module distills discriminative semantic features by enforcing intra-class compactness and inter-class distinctiveness. In contrast to previous methods that directly apply CLIP to imperfect masks, our framework explicitly resolves semantic conflicts while preserving category discriminability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCL-LGS outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. Our project page is available at https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/.
最近,三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的进步推动了三维语义理解能力的显著发展,这对机器人技术、自动驾驶和虚拟/增强现实至关重要。然而,依赖二维先验的方法面临一个关键挑战:由遮挡、图像模糊和视角依赖变化引起的跨视图语义不一致性。这些不一致性通过投影监督传播时,会恶化三维高斯语义场的品质,并在渲染输出中引入伪影。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了CCL-LGS这一新型框架,它通过整合多视图语义线索来实施视图一致的语义监督。具体来说,我们的方法首先采用零样本跟踪器来对齐一组由SAM生成的二维掩膜,并可靠地识别出它们对应的类别。然后,我们使用CLIP来提取跨视图的稳健语义编码。最后,我们的对比代码本学习(CCL)模块通过执行类内紧凑性和类间区分性的强化来提炼出判别性语义特征。与之前直接应用于不完美掩膜的方法不同,我们的框架能够显式解决语义冲突,同时保留类别可分辨性。大量实验表明,CCL-LGS优于以前的最先进方法。我们的项目页面可在https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
随着三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的发展,三维语义理解在机器人、自动驾驶、虚拟现实等领域取得重要进展。然而,依赖二维先验的方法面临跨视图语义不一致的挑战。本文提出CCL-LGS框架,通过集成多视图语义线索来强制执行视图一致的语义监督。实验表明,CCL-LGS优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的进步推动了三维语义理解的发展。
- 依赖二维先验的方法面临跨视图语义不一致的挑战,这会影响三维高斯语义场的质量和渲染输出。
- CCL-LGS框架通过集成多视图语义线索来强制执行视图一致的语义监督。
- CCL-LGS采用零样本跟踪器对齐SAM生成的二维掩膜并识别其对应的类别。
- CLIP被用来提取跨视图的稳健语义编码。
- 对比编码本学习(CCL)模块通过执行类内紧凑性和类间区分性来提炼判别性语义特征。
点此查看论文截图