⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-15 更新
Beyond conventional vision: RGB-event fusion for robust object detection in dynamic traffic scenarios
Authors:Zhanwen Liu, Yujing Sun, Yang Wang, Nan Yang, Shengbo Eben Li, Xiangmo Zhao
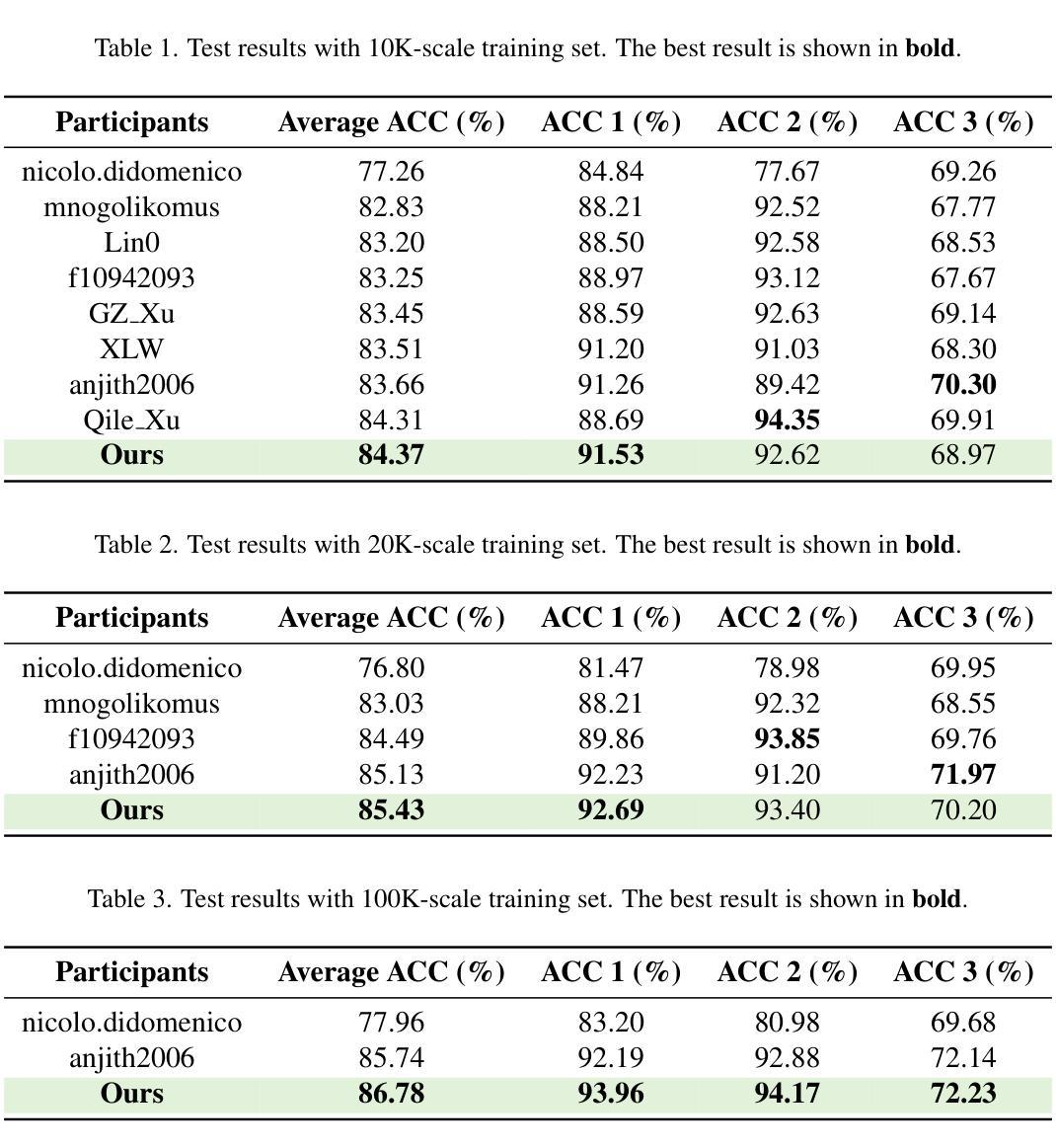
The dynamic range limitation of conventional RGB cameras reduces global contrast and causes loss of high-frequency details such as textures and edges in complex traffic environments (e.g., nighttime driving, tunnels), hindering discriminative feature extraction and degrading frame-based object detection. To address this, we integrate a bio-inspired event camera with an RGB camera to provide high dynamic range information and propose a motion cue fusion network (MCFNet), which achieves optimal spatiotemporal alignment and adaptive cross-modal feature fusion under challenging lighting. Specifically, an event correction module (ECM) temporally aligns asynchronous event streams with image frames via optical-flow-based warping, jointly optimized with the detection network to learn task-aware event representations. The event dynamic upsampling module (EDUM) enhances spatial resolution of event frames to match image structures, ensuring precise spatiotemporal alignment. The cross-modal mamba fusion module (CMM) uses adaptive feature fusion with a novel interlaced scanning mechanism, effectively integrating complementary information for robust detection. Experiments conducted on the DSEC-Det and PKU-DAVIS-SOD datasets demonstrate that MCFNet significantly outperforms existing methods in various poor lighting and fast moving traffic scenarios. Notably, on the DSEC-Det dataset, MCFNet achieves a remarkable improvement, surpassing the best existing methods by 7.4% in mAP50 and 1.7% in mAP metrics, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/Charm11492/MCFNet.
传统RGB相机的动态范围限制降低了全局对比度,导致在复杂的交通环境中(例如夜间驾驶、隧道内)高频细节(如纹理和边缘)的损失,阻碍了辨别特征提取和基于帧的对象检测。为了解决这个问题,我们将生物启发的事件相机与RGB相机相结合,提供高动态范围信息,并提出一种运动线索融合网络(MCFNet),该网络在具有挑战性的光照条件下实现了最佳时空对齐和自适应跨模态特征融合。具体而言,事件校正模块(ECM)通过基于光流的warp技术,对异步事件流进行时间对齐图像帧,并与检测网络联合优化,以学习任务感知事件表示。事件动态上采样模块(EDUM)提高了事件帧的空间分辨率,以匹配图像结构,确保精确的时空对齐。跨模态融合模块(CMM)采用自适应特征融合和新颖交织扫描机制,有效地集成了互补信息进行稳健检测。在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上进行的实验表明,MCFNet在各种光线不足和快速移动的交通场景中显著优于现有方法。值得注意的是,在DSEC-Det数据集上,MCFNet的改进非常显著,在mAP50和mAP指标上分别超过了现有最佳方法7.4%和1.7%。代码可用https://github.com/Charm11492/MCFNet访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
为了克服传统RGB相机动态范围限制带来的全球对比度降低和高频细节丢失问题,本研究结合了生物启发的事件相机和RGB相机,提供高动态范围信息,并提出一种运动线索融合网络(MCFNet)。通过事件校正模块(ECM)实现异步事件流与图像帧的时间对齐,并通过事件动态上采样模块(EDUM)提高事件帧的空间分辨率,以确保精确的时空对齐。跨模态融合模块(CMM)采用自适应特征融合和新型交错扫描机制,有效集成互补信息以实现稳健检测。在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上的实验表明,MCFNet在多种恶劣照明和快速交通场景中显著优于现有方法。特别是在DSEC-Det数据集上,其mAP50指标提高了7.4%,mAP指标提高了1.7%。代码已发布在https://github.com/Charm11492/MCFNet。
Key Takeaways:
- RGB相机的动态范围限制导致全球对比度和高频细节丢失,特别是在复杂交通环境中。
- 结合生物启发的事件相机来提供高动态范围信息是一个有效的解决方案。
- 提出的运动线索融合网络(MCFNet)能够实现异步事件流与图像帧的时空对齐。
- 事件校正模块(ECM)和事件动态上采样模块(EDUM)确保精确对齐。
- 跨模态融合模块(CMM)通过自适应特征融合和交错扫描机制集成互补信息。
- 在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上的实验验证了MCFNet的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

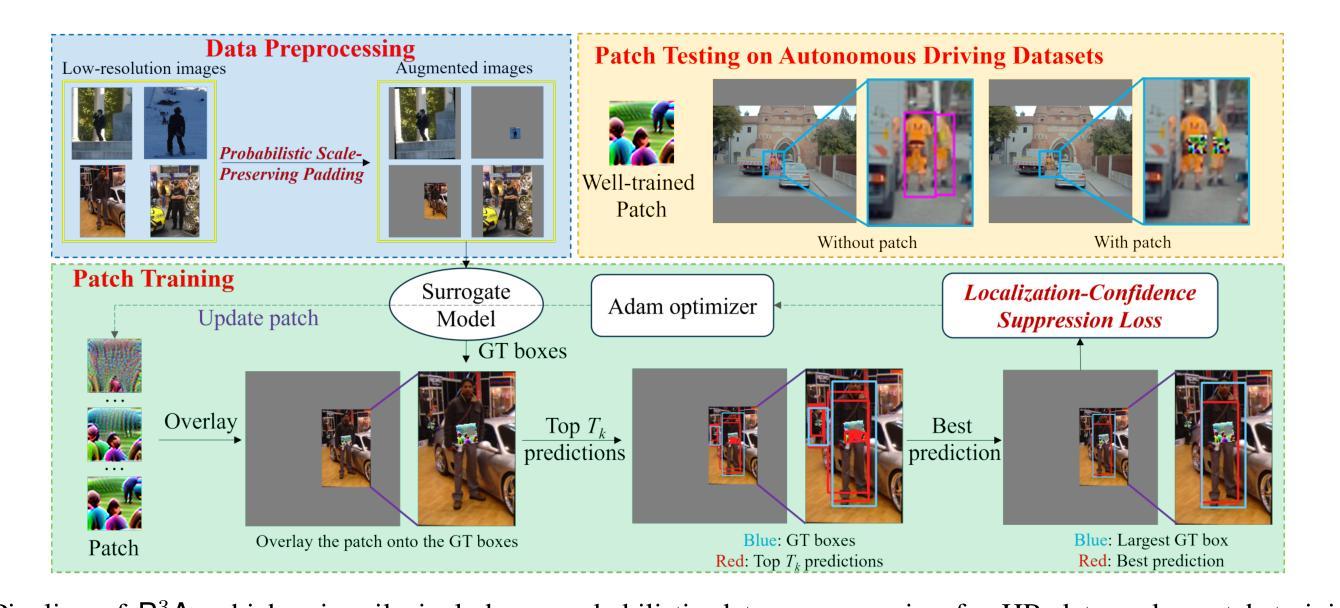
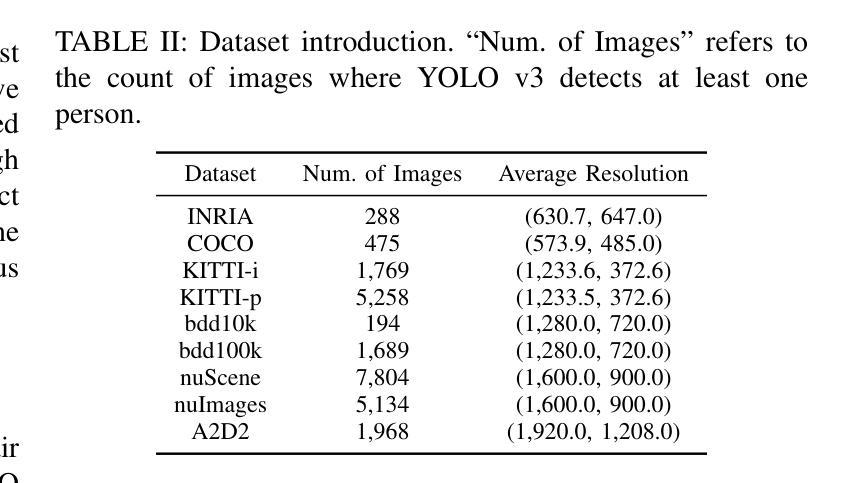
Towards Powerful and Practical Patch Attacks for 2D Object Detection in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Yuxin Cao, Yedi Zhang, Wentao He, Yifan Liao, Yan Xiao, Chang Li, Zhiyong Huang, Jin Song Dong
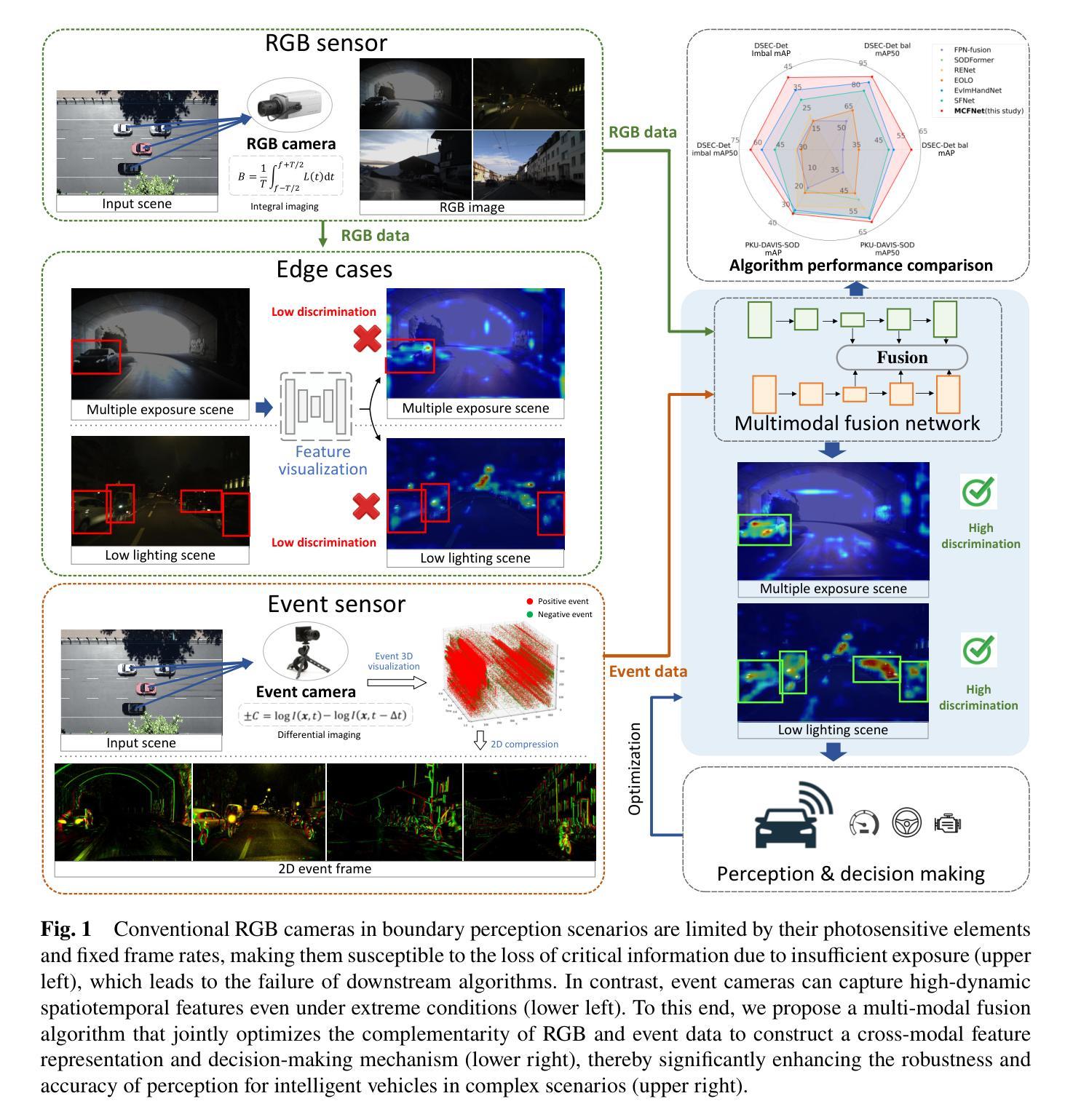
Learning-based autonomous driving systems remain critically vulnerable to adversarial patches, posing serious safety and security risks in their real-world deployment. Black-box attacks, notable for their high attack success rate without model knowledge, are especially concerning, with their transferability extensively studied to reduce computational costs compared to query-based attacks. Previous transferability-based black-box attacks typically adopt mean Average Precision (mAP) as the evaluation metric and design training loss accordingly. However, due to the presence of multiple detected bounding boxes and the relatively lenient Intersection over Union (IoU) thresholds, the attack effectiveness of these approaches is often overestimated, resulting in reduced success rates in practical attacking scenarios. Furthermore, patches trained on low-resolution data often fail to maintain effectiveness on high-resolution images, limiting their transferability to autonomous driving datasets. To fill this gap, we propose P$^3$A, a Powerful and Practical Patch Attack framework for 2D object detection in autonomous driving, specifically optimized for high-resolution datasets. First, we introduce a novel metric, Practical Attack Success Rate (PASR), to more accurately quantify attack effectiveness with greater relevance for pedestrian safety. Second, we present a tailored Localization-Confidence Suppression Loss (LCSL) to improve attack transferability under PASR. Finally, to maintain the transferability for high-resolution datasets, we further incorporate the Probabilistic Scale-Preserving Padding (PSPP) into the patch attack pipeline as a data preprocessing step. Extensive experiments show that P$^3$A outperforms state-of-the-art attacks on unseen models and unseen high-resolution datasets, both under the proposed practical IoU-based evaluation metric and the previous mAP-based metrics.
基于学习的自动驾驶系统仍然极易受到对抗性补丁的攻击,这在其现实世界的部署中带来了严重的安全风险和隐患。黑盒攻击以其高攻击成功率且无需了解模型而备受关注,其可迁移性已被广泛研究以降低与查询攻击相比的计算成本。基于可迁移性的传统黑盒攻击通常采用平均精度均值(mAP)作为评估指标,并据此设计训练损失。然而,由于存在多个检测到的边界框和相对宽松的交集比例(IoU)阈值,这些方法的攻击效果往往被高估,导致在实际攻击场景中的成功率降低。此外,在自动驾驶数据集上,在低分辨率数据上训练的补丁往往无法在高分辨率图像上保持其有效性,限制了其可迁移性。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了P$^3$A,这是一个针对自动驾驶中二维对象检测的强大的实用补丁攻击框架,特别针对高分辨率数据集进行了优化。首先,我们引入了一个新的指标——实用攻击成功率(PASR),以更准确地衡量攻击效果,与行人安全更相关。其次,我们提出了一种定制的定位置信度抑制损失(LCSL),以提高PASR下的攻击可迁移性。最后,为了保持高分辨率数据集的可迁移性,我们将概率尺度保持填充(PSPP)作为补丁攻击流程的数据预处理步骤融入其中。大量实验表明,在提出的实用IoU评估指标和先前的mAP评估指标下,P$^3$A在未见过模型的未见高分辨率数据集上的表现均优于最新攻击方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文指出基于学习的自动驾驶系统受到对抗性补丁的威胁,存在安全性和稳健性问题。现有的基于迁移性的黑箱攻击方法采用平均精度(mAP)作为评估指标,但在实际攻击场景中效果被高估。为此,提出P$^3$A攻击框架,包括新型评估指标PASR、针对性设计损失函数LCSL及数据预处理步骤PSPP,以优化对高分辨率数据集的目标检测攻击效果。实验表明,P$^3$A在未见模型和未见高分辨率数据集上的表现优于现有攻击方法。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶系统面临对抗性补丁的威胁,存在安全性和稳健性问题。
- 现有黑箱攻击方法采用mAP作为评估指标,但在实际攻击场景中效果被高估。
- 提出P$^3$A攻击框架,包括新型评估指标PASR、针对性设计损失函数LCSL以及数据预处理步骤PSPP。
- P$^3$A优化了针对高分辨率数据集的目标检测攻击效果。
- P$^3$A在未见模型和未见高分辨率数据集上的表现优于现有攻击方法。
点此查看论文截图

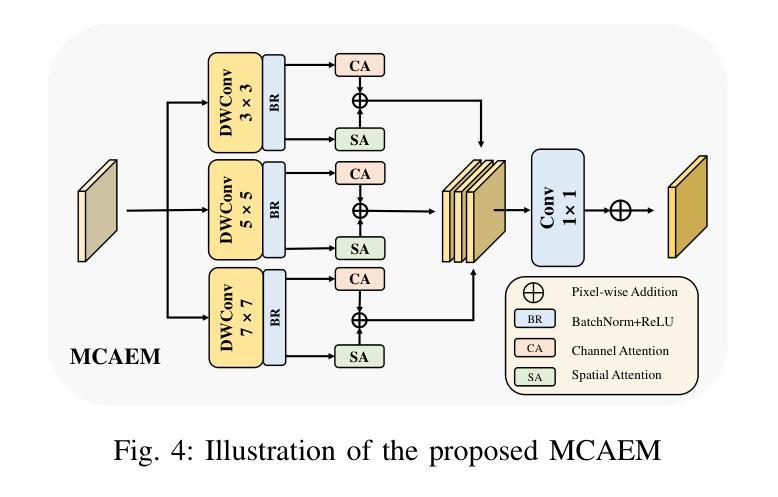
GCRPNet: Graph-Enhanced Contextual and Regional Perception Network For Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Mengyu Ren, Yutong Li, Hua Li, Runmin Cong, Sam Kwong
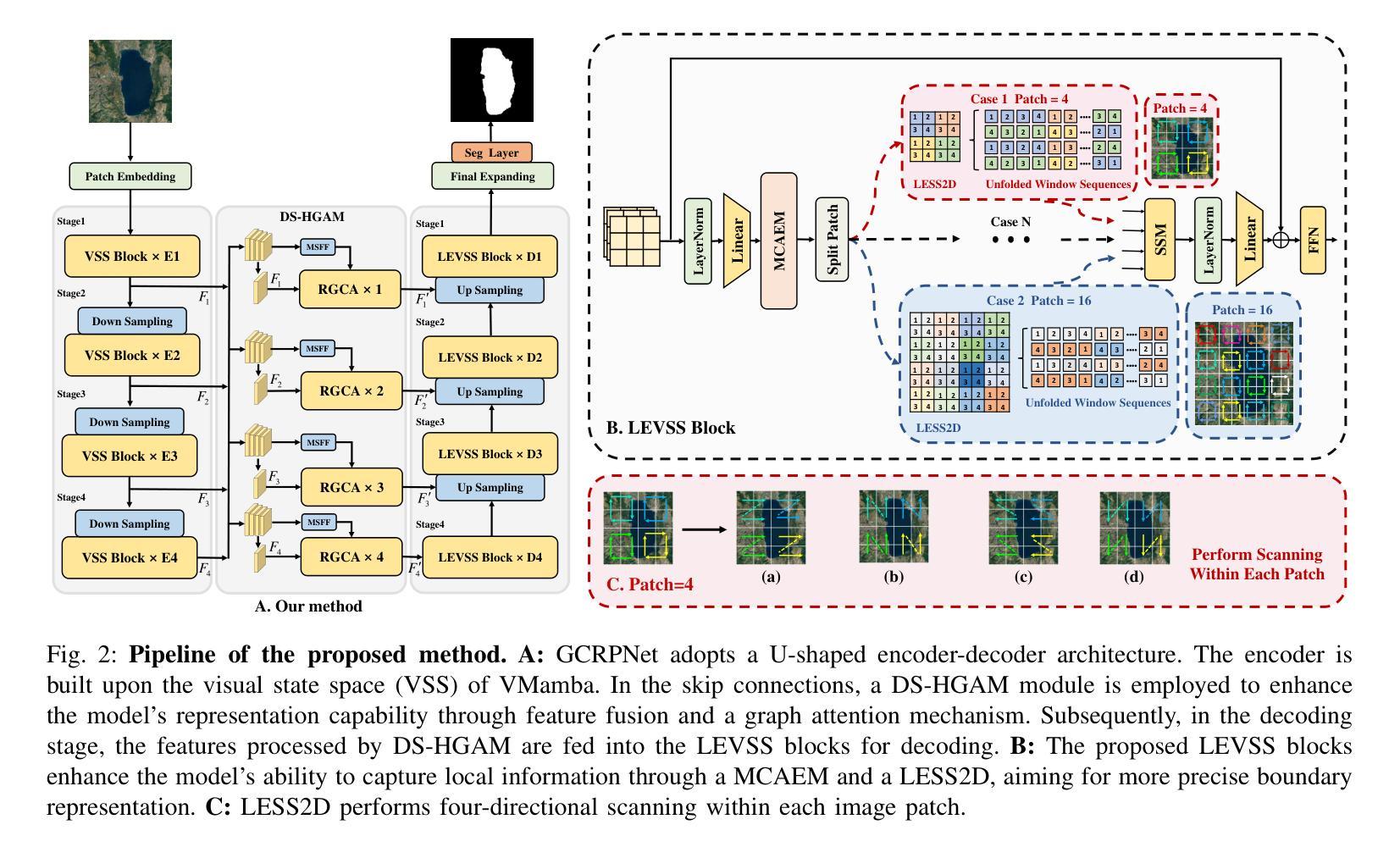
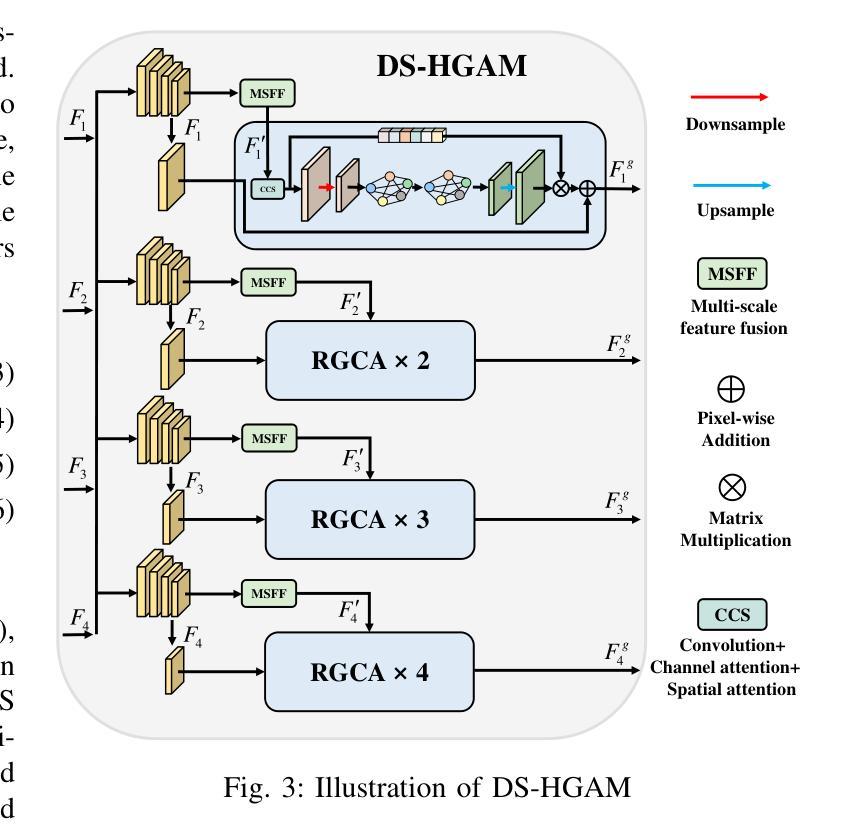
Salient object detection (SOD) in optical remote sensing images (ORSIs) faces numerous challenges, including significant variations in target scales and low contrast between targets and the background. Existing methods based on vision transformers (ViTs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) architectures aim to leverage both global and local features, but the difficulty in effectively integrating these heterogeneous features limits their overall performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a graph-enhanced contextual and regional perception network (GCRPNet), which builds upon the Mamba architecture to simultaneously capture long-range dependencies and enhance regional feature representation. Specifically, we employ the visual state space (VSS) encoder to extract multi-scale features. To further achieve deep guidance and enhancement of these features, we first design a difference-similarity guided hierarchical graph attention module (DS-HGAM). This module strengthens cross-layer interaction capabilities between features of different scales while enhancing the model’s structural perception,allowing it to distinguish between foreground and background more effectively. Then, we design the LEVSS block as the decoder of GCRPNet. This module integrates our proposed adaptive scanning strategy and multi-granularity collaborative attention enhancement module (MCAEM). It performs adaptive patch scanning on feature maps processed via multi-scale convolutions, thereby capturing rich local region information and enhancing Mamba’s local modeling capability. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating its effectiveness and superiority.
在光学遥感图像(ORSIs)中,显著目标检测(SOD)面临诸多挑战,包括目标尺度变化显著以及目标与背景之间的对比度低。现有的基于视觉变压器(ViTs)和卷积神经网络(CNNs)架构的方法旨在利用全局和局部特征,但有效整合这些异构特征的困难限制了它们的整体性能。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了图增强上下文和区域感知网络(GCRPNet),它基于Mamba架构,同时捕获长距离依赖关系并增强区域特征表示。具体来说,我们采用视觉状态空间(VSS)编码器提取多尺度特征。为了进一步实现这些特征的深度引导和增强,我们首先设计了一个差异相似性引导分层图注意力模块(DS-HGAM)。该模块增强了不同尺度特征之间的跨层交互能力,提高了模型的结构感知能力,使其更有效地区分前景和背景。然后,我们设计了LEVSS块作为GCRPNet的解码器。该模块结合了我们的自适应扫描策略和多粒度协同注意力增强模块(MCAEM)。它对经过多尺度卷积处理的特征图进行自适应斑块扫描,从而捕获丰富的局部区域信息,增强Mamba的局部建模能力。广泛的实验结果证明了所提出模型达到了最先进的性能,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
光遥感和对象检测中目标规模显著变化、目标背景对比度低的问题影响了研究的准确性。为解决这些挑战,研究者提出了基于Mamba架构的图增强上下文与区域感知网络(GCRPNet)。网络采用视觉状态空间(VSS)编码器提取多尺度特征,并采用差分相似度引导层次图注意力模块(DS-HGAM)进行特征融合与深层指导。此外,研究还设计了名为LEVSS的解码器块,集成自适应扫描策略和多重粒度协同注意力增强模块(MCAEM),提高局部建模能力。实验证明,该模型实现了卓越的性能,验证了其有效性和优越性。
关键见解
- 光遥感和对象检测面临诸多挑战,包括目标规模变化和背景对比度问题。
- 现有方法如ViTs和CNNs在集成全局和局部特征时存在困难。
- 提出的GCRPNet网络结合Mamba架构同时捕捉长期依赖关系并增强区域特征表示。
- 利用视觉状态空间编码器(VSS)进行多尺度特征提取。
- DS-HGAM模块增强不同尺度特征之间的跨层交互能力,提高模型的结构感知能力。
- LEVSS解码器块采用自适应扫描策略和MCAEM模块来捕捉丰富的局部区域信息,并增强Mamba的局部建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

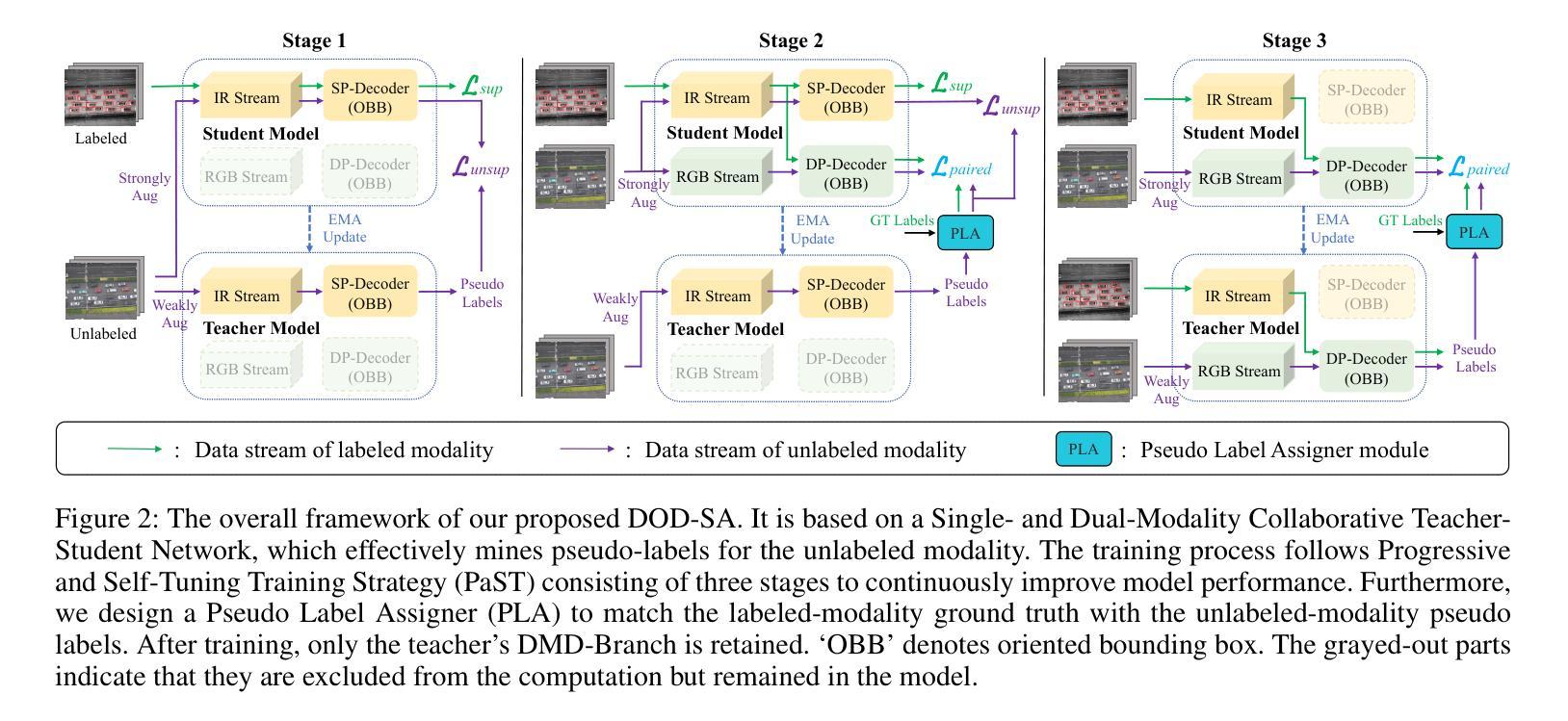
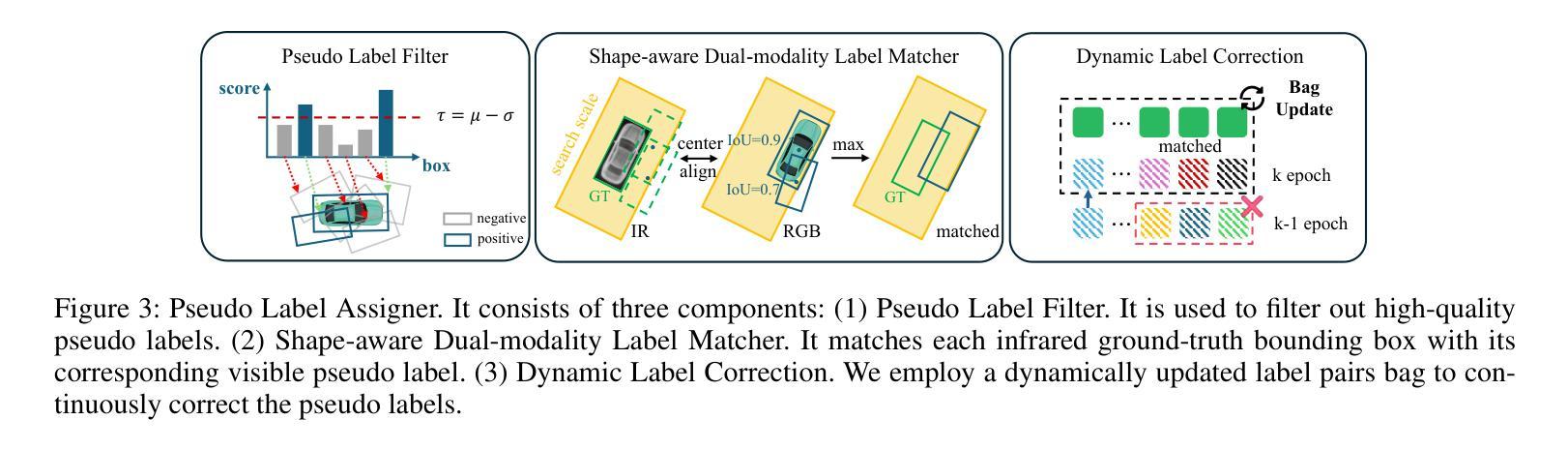
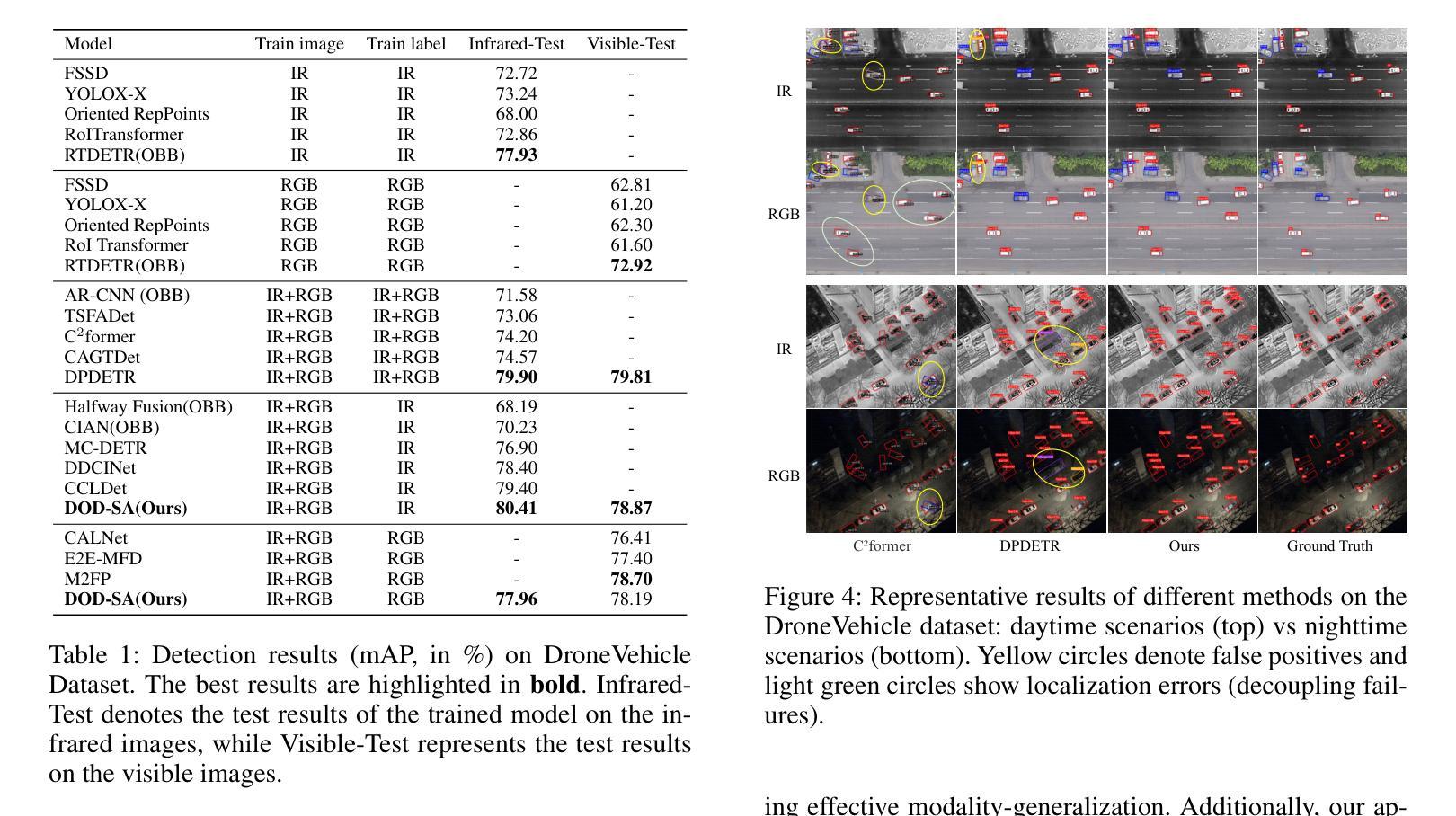
DOD-SA: Infrared-Visible Decoupled Object Detection with Single-Modality Annotations
Authors:Hang Jin, Chenqiang Gao, Junjie Guo, Fangcen Liu, Kanghui Tian, Qinyao Chang
Infrared-visible object detection has shown great potential in real-world applications, enabling robust all-day perception by leveraging the complementary information of infrared and visible images. However, existing methods typically require dual-modality annotations to output detection results for both modalities during prediction, which incurs high annotation costs. To address this challenge, we propose a novel infrared-visible Decoupled Object Detection framework with Single-modality Annotations, called DOD-SA. The architecture of DOD-SA is built upon a Single- and Dual-Modality Collaborative Teacher-Student Network (CoSD-TSNet), which consists of a single-modality branch (SM-Branch) and a dual-modality decoupled branch (DMD-Branch). The teacher model generates pseudo-labels for the unlabeled modality, simultaneously supporting the training of the student model. The collaborative design enables cross-modality knowledge transfer from the labeled modality to the unlabeled modality, and facilitates effective SM-to-DMD branch supervision. To further improve the decoupling ability of the model and the pseudo-label quality, we introduce a Progressive and Self-Tuning Training Strategy (PaST) that trains the model in three stages: (1) pretraining SM-Branch, (2) guiding the learning of DMD-Branch by SM-Branch, and (3) refining DMD-Branch. In addition, we design a Pseudo Label Assigner (PLA) to align and pair labels across modalities, explicitly addressing modality misalignment during training. Extensive experiments on the DroneVehicle dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA).
红外可见目标检测在现实世界的广泛应用已经展现出巨大的潜力,能够通过利用红外图像和可见光图像的互补信息来实现全天候的稳健感知。然而,现有的方法通常需要在预测时为两种模态都输出检测结果,这需要高昂的标注成本。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的红外可见解耦目标检测框架,该框架采用单模态标注方法,被称为DOD-SA(Decoupled Object Detection with Single-modality Annotations)。DOD-SA架构基于单模态和双模态协同教师学生网络(CoSD-TSNet),包括单模态分支(SM-Branch)和双模态解耦分支(DMD-Branch)。教师模型为未标记的模态生成伪标签,同时支持学生模型的训练。这种协同设计实现了跨模态知识从标记模态到未标记模态的转移,并促进了有效的SM到DMD分支监督。为了进一步提高模型的解耦能力和伪标签质量,我们引入了一种渐进式自调整训练策略(PaST),该策略将模型训练分为三个阶段:(1)预训练SM-Branch;(2)通过SM-Branch指导DMD-Branch的学习;(3)优化DMD-Branch。此外,我们设计了一个伪标签分配器(PLA)来对齐和配对跨模态的标签,明确解决训练过程中的模态不匹配问题。在DroneVehicle数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于当前最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures
Summary
红外可见目标检测在现实应用中有巨大潜力,通过利用红外和可见光图像的互补信息实现全天候感知。针对现有方法需要双模态标注的问题,我们提出一种基于单模态标注的红外可见解耦目标检测框架DOD-SA。其架构基于单模态和双模态协同的教师学生网络CoSD-TSNet,包括单模态分支SM-Branch和双模态解耦分支DMD-Branch。教师模型为无标签模态生成伪标签,支持学生模型的训练。通过协同设计实现跨模态知识转移,促进SM到DMD分支的有效监督。为提高模型的解耦能力和伪标签质量,我们引入了渐进式自我调整训练策略PaST,分三阶段训练模型。此外,设计伪标签分配器PLA以对齐和配对跨模态标签,解决训练过程中的模态不匹配问题。在DroneVehicle数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 红外可见目标检测能利用红外和可见光图像的互补信息,实现全天候感知,具有现实应用潜力。
- 现有方法需要双模态标注,导致高标注成本,本文提出基于单模态标注的红外可见解耦目标检测框架DOD-SA以解决这个问题。
- DOD-SA架构包含单模态分支SM-Branch和双模态解耦分支DMD-Branch,以及教师学生网络CoSD-TSNet。
- 教师模型为无标签模态生成伪标签,支持学生模型的训练,实现跨模态知识转移和有效监督。
- 引入渐进式自我调整训练策略PaST,分三阶段提高模型的解耦能力和伪标签质量。
- 设计伪标签分配器PLA以解决训练过程中的模态不匹配问题。
点此查看论文截图

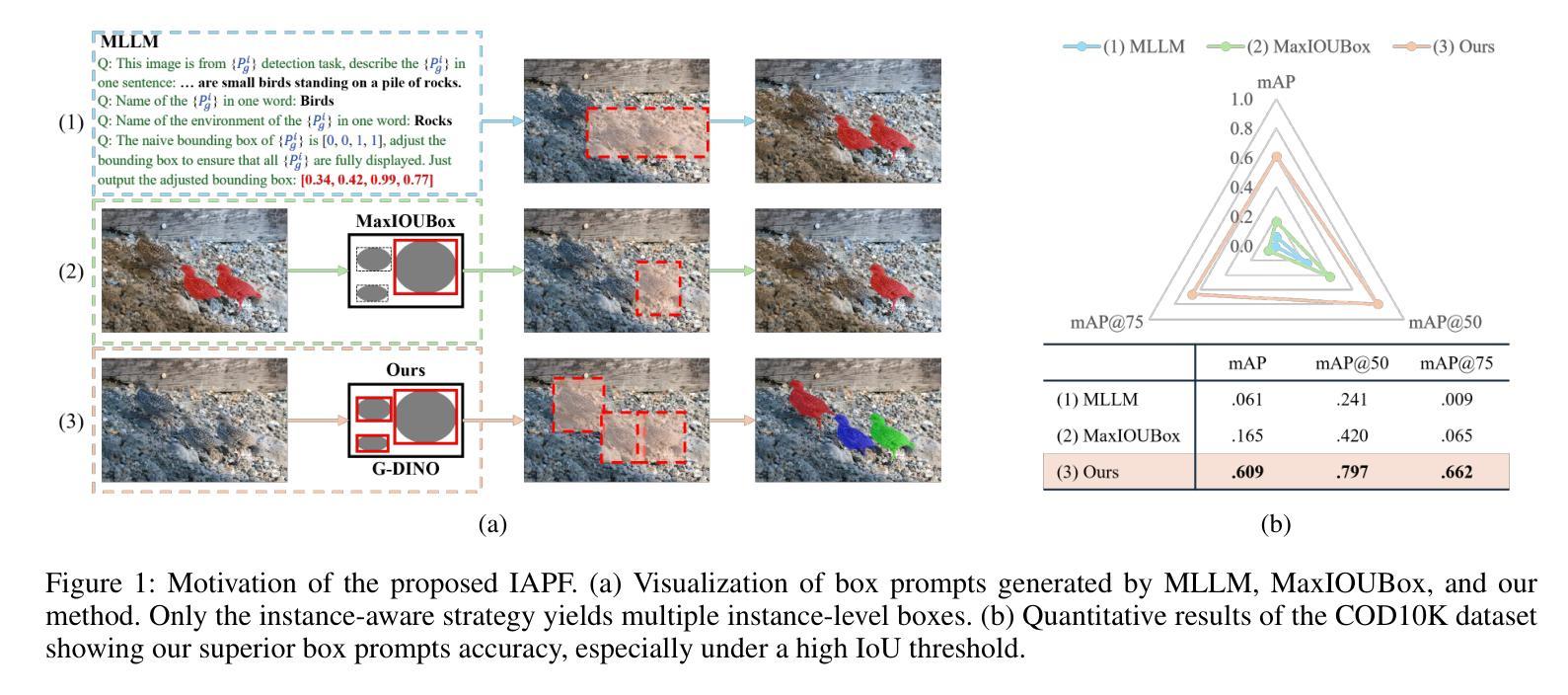
A Simple yet Powerful Instance-Aware Prompting Framework for Training-free Camouflaged Object Segmentation
Authors:Chao Yin, Jide Li, Xiaoqiang Li
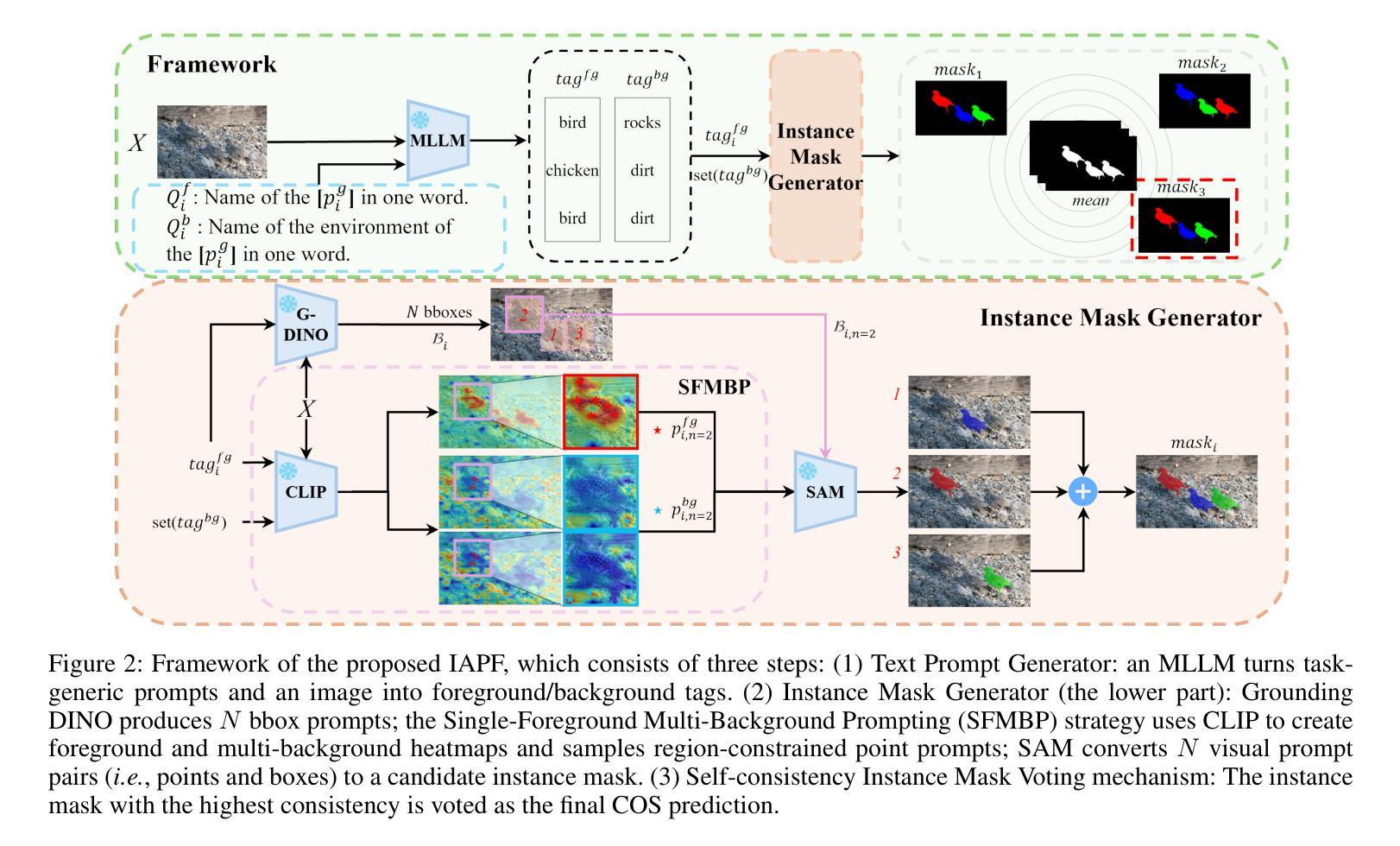
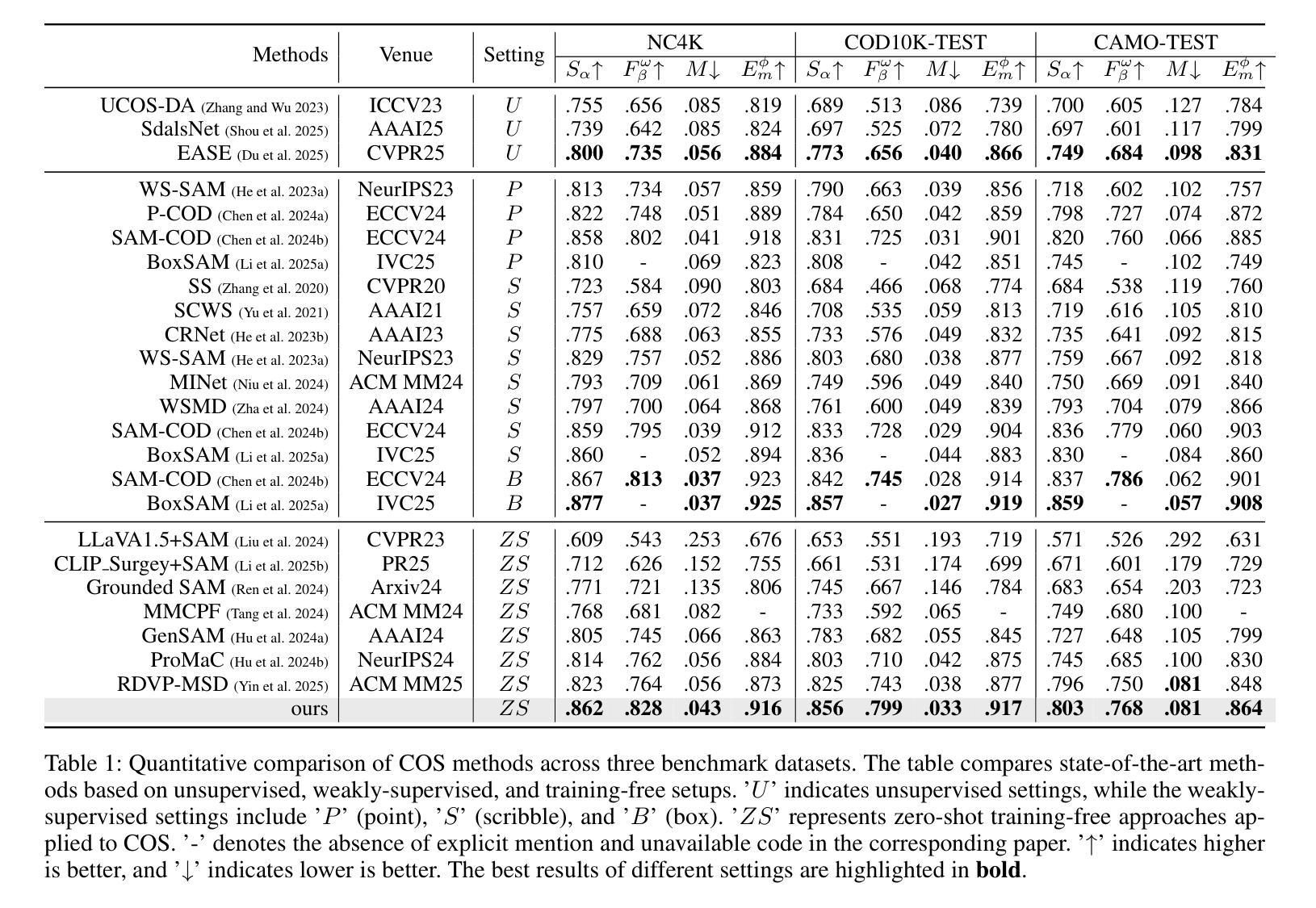
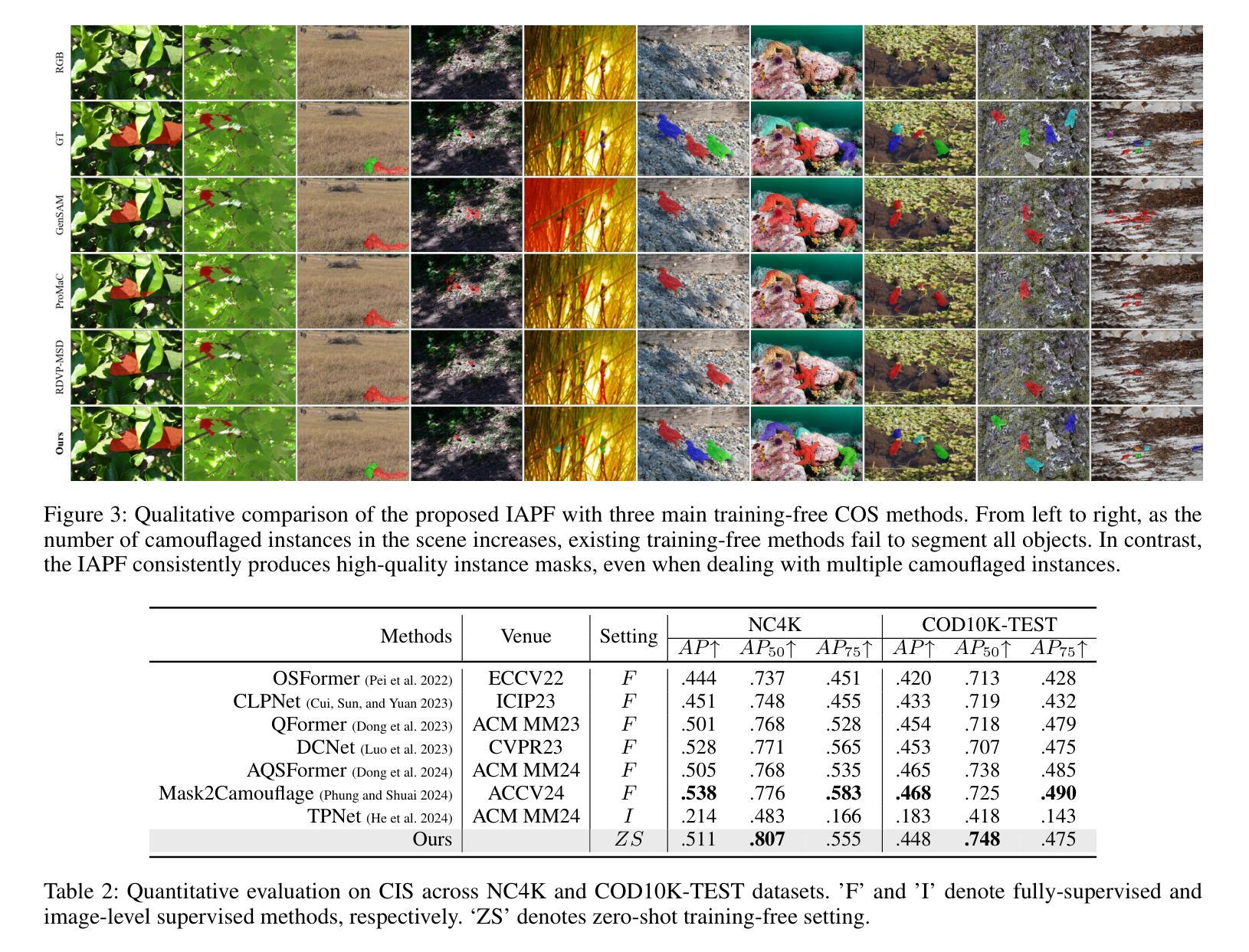
Camouflaged Object Segmentation (COS) remains highly challenging due to the intrinsic visual similarity between target objects and their surroundings. While training-based COS methods achieve good performance, their performance degrades rapidly with increased annotation sparsity. To circumvent this limitation, recent studies have explored training-free COS methods, leveraging the Segment Anything Model (SAM) by automatically generating visual prompts from a single task-generic prompt (\textit{e.g.}, “\textit{camouflaged animal}”) uniformly applied across all test images. However, these methods typically produce only semantic-level visual prompts, causing SAM to output coarse semantic masks and thus failing to handle scenarios with multiple discrete camouflaged instances effectively. To address this critical limitation, we propose a simple yet powerful \textbf{I}nstance-\textbf{A}ware \textbf{P}rompting \textbf{F}ramework (IAPF), the first training-free COS pipeline that explicitly converts a task-generic prompt into fine-grained instance masks. Specifically, the IAPF comprises three steps: (1) Text Prompt Generator, utilizing task-generic queries to prompt a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) for generating image-specific foreground and background tags; (2) \textbf{Instance Mask Generator}, leveraging Grounding DINO to produce precise instance-level bounding box prompts, alongside the proposed Single-Foreground Multi-Background Prompting strategy to sample region-constrained point prompts within each box, enabling SAM to yield a candidate instance mask; (3) Self-consistency Instance Mask Voting, which selects the final COS prediction by identifying the candidate mask most consistent across multiple candidate instance masks. Extensive evaluations on standard COS benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed IAPF significantly surpasses existing state-of-the-art training-free COS methods.
隐蔽物体分割(COS)仍然是一项巨大的挑战,因为目标物体与其周围环境之间具有固有的视觉相似性。基于训练的方法在COS上取得了良好的效果,但随着标注稀疏度的增加,它们的性能迅速下降。为了克服这一局限性,最近的研究探讨了无训练COS方法,利用无训练分割模型(SAM)自动从单一任务通用提示生成视觉提示(例如,“隐蔽动物”),并统一应用于所有测试图像。然而,这些方法通常只产生语义级别的视觉提示,导致SAM输出粗略的语义掩码,因此无法有效地处理具有多个离散隐蔽实例的场景。为了解决这一关键局限性,我们提出了一种简单而强大的实例感知提示框架(IAPF),这是第一个无训练的COS管道,它将任务通用提示明确转换为精细的实例掩码。具体来说,IAPF包含三个步骤:(1)文本提示生成器,利用任务通用查询来提示多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)生成图像特定的前景和背景标签;(2)实例掩码生成器,利用接地DINO生成精确实例级别的边界框提示,以及提出的单前景多背景提示策略在每个框内采样区域约束点提示,使SAM能够产生候选实例掩码;(3)自一致性实例掩码投票,通过识别多个候选实例掩码中最一致的候选掩码来选择最终的COS预测。在标准COS基准测试上的广泛评估表明,所提出的IAPF显著超越了现有的最先进的无训练COS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
本文介绍了针对伪装目标分割(COS)任务的一种无训练方法。针对现有方法仅产生语义级视觉提示,无法有效处理多个离散伪装实例的问题,提出了一种新的实例感知提示框架(IAPF)。该框架通过文本提示生成器生成特定图像的标签,利用接地DINO产生精确的实例级边界框提示,并采用单前景多背景提示策略,最后通过自我一致的实例掩膜投票选择最佳COS预测。在标准COS基准测试上的评估表明,IAPF显著优于现有的无训练COS方法。
Key Takeaways
- 伪装目标分割(COS)面临视觉相似性的挑战。
- 训练基于的COS方法性能在标注稀疏时迅速下降。
- 现有无训练COS方法通常只产生语义级视觉提示。
- 提出了一种新的实例感知提示框架(IAPF)来解决上述问题。
- IAPF包含文本提示生成器、实例掩膜生成器和自我一致的实例掩膜投票三个步骤。
- IAPF利用多模态大语言模型(MLLM)和接地DINO技术。
点此查看论文截图

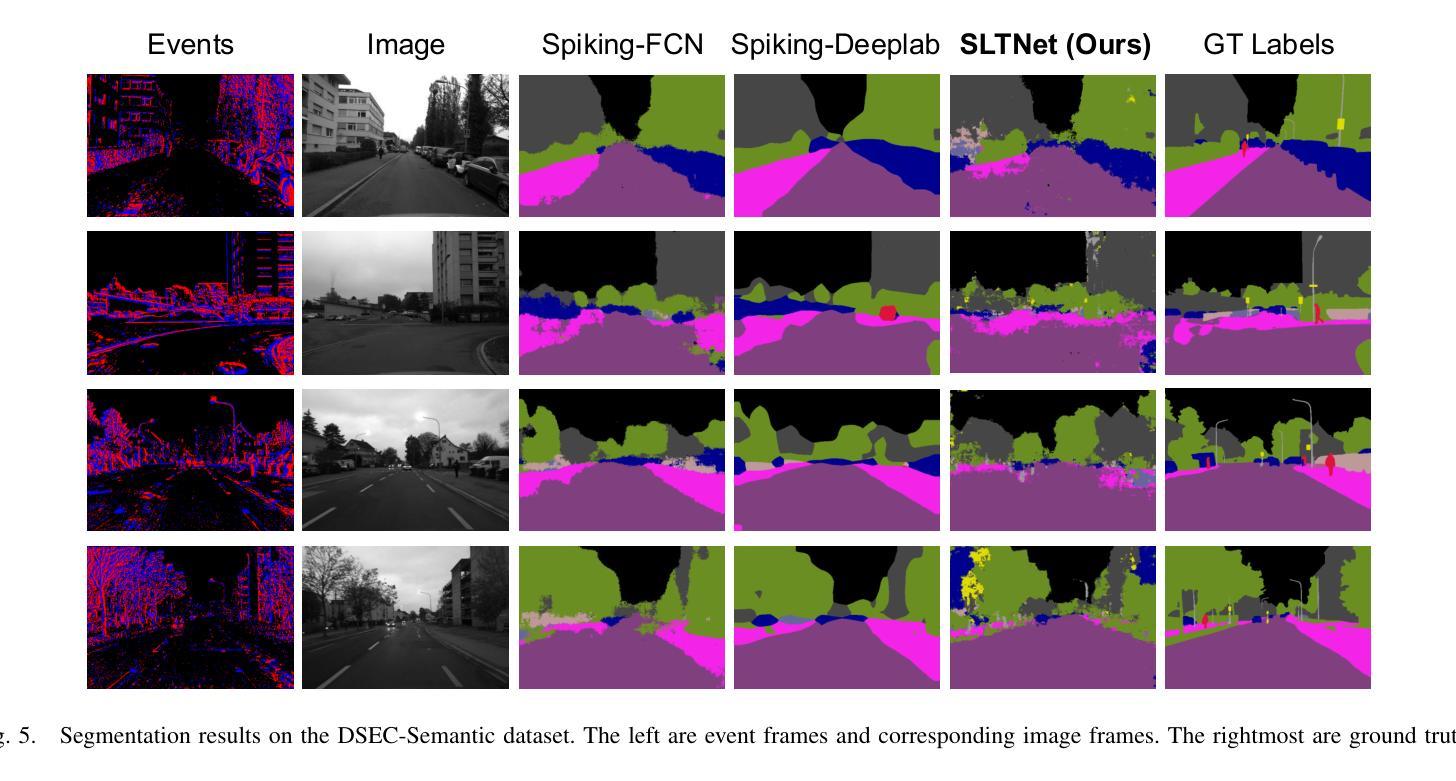
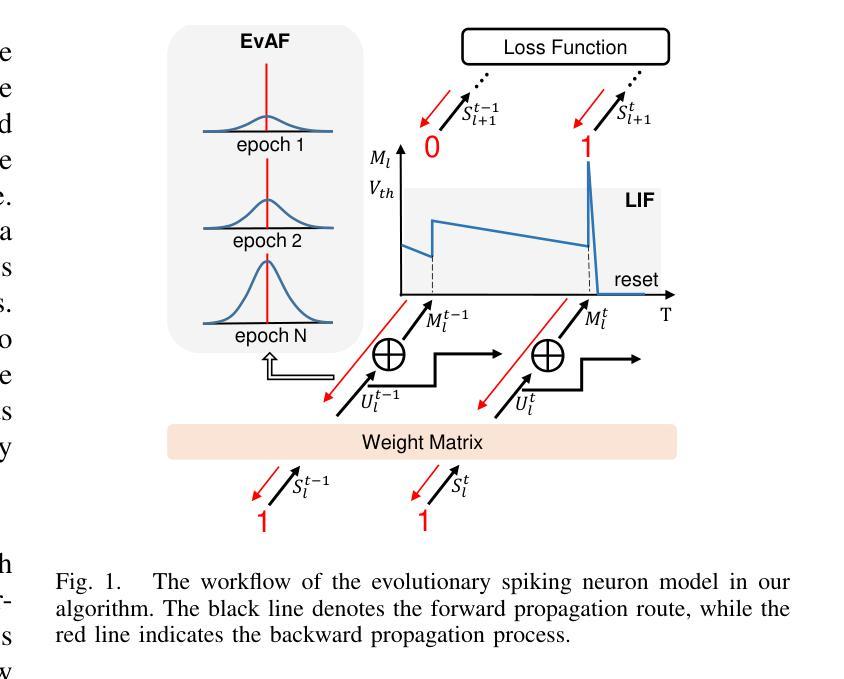
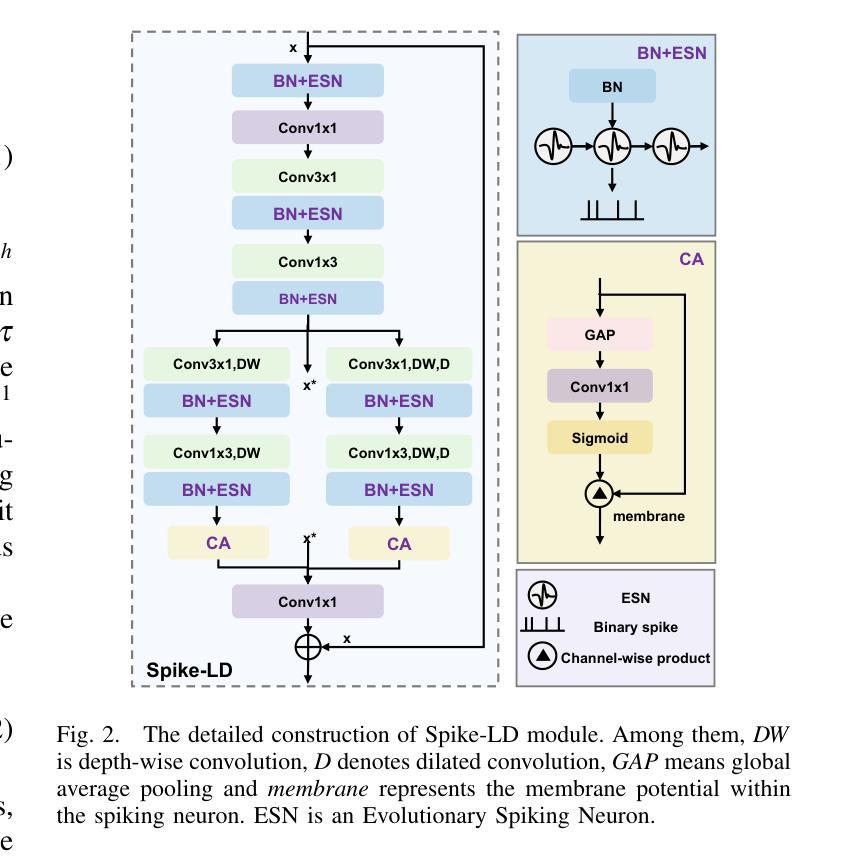
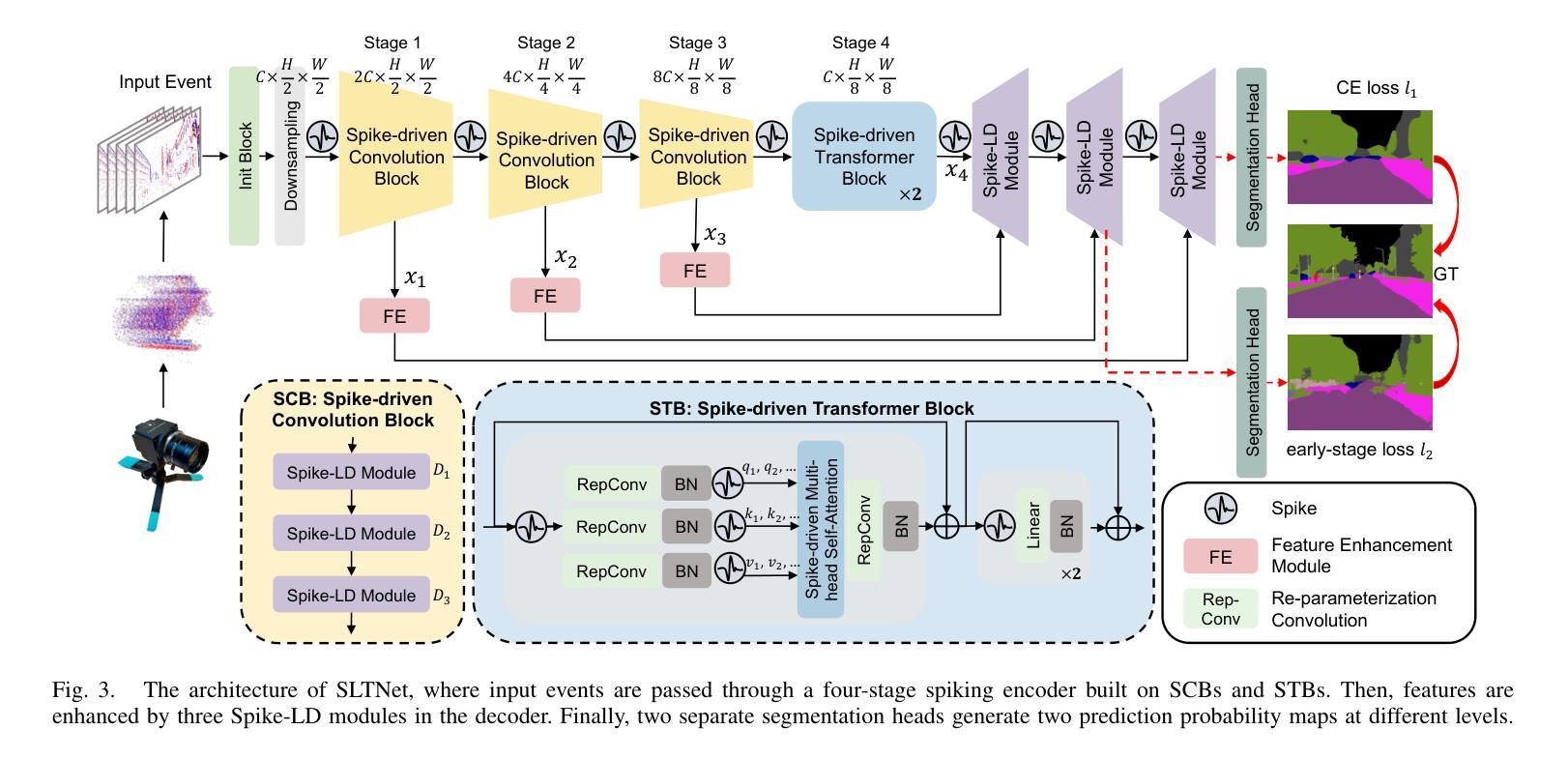
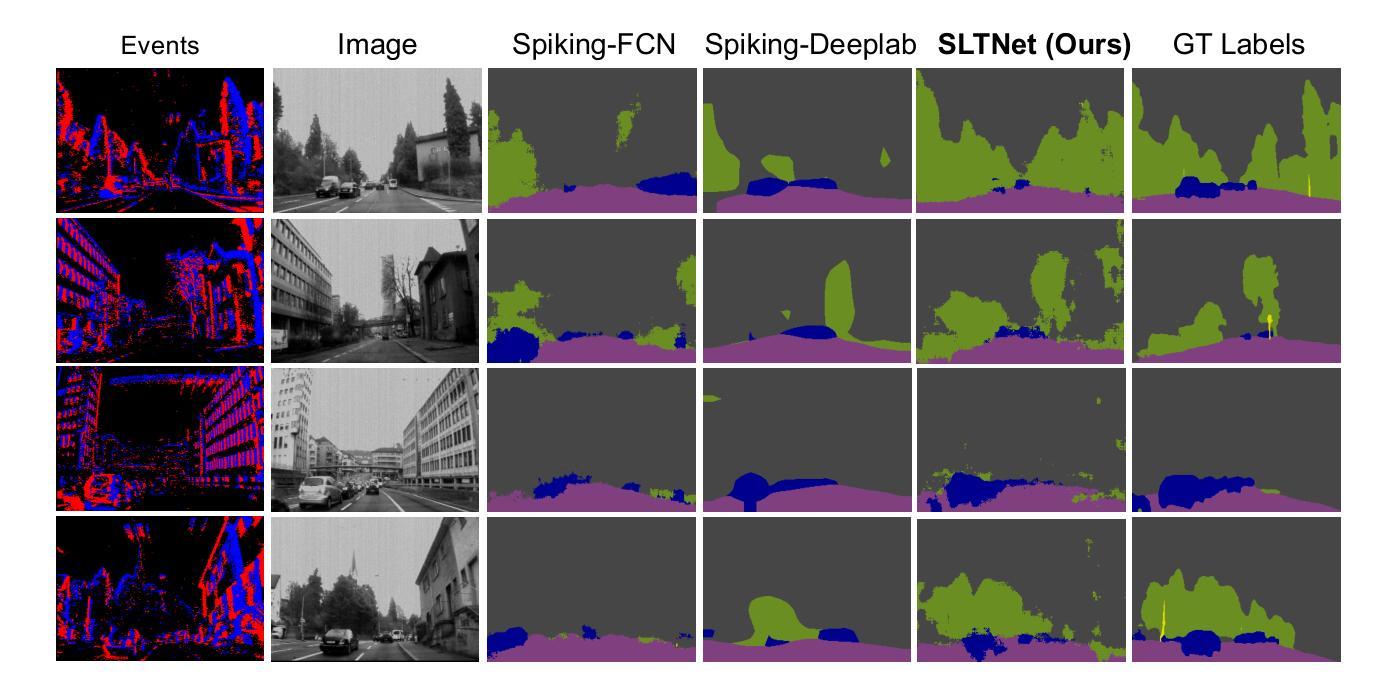
SLTNet: Efficient Event-based Semantic Segmentation with Spike-driven Lightweight Transformer-based Networks
Authors:Xianlei Long, Xiaxin Zhu, Fangming Guo, Wanyi Zhang, Qingyi Gu, Chao Chen, Fuqiang Gu
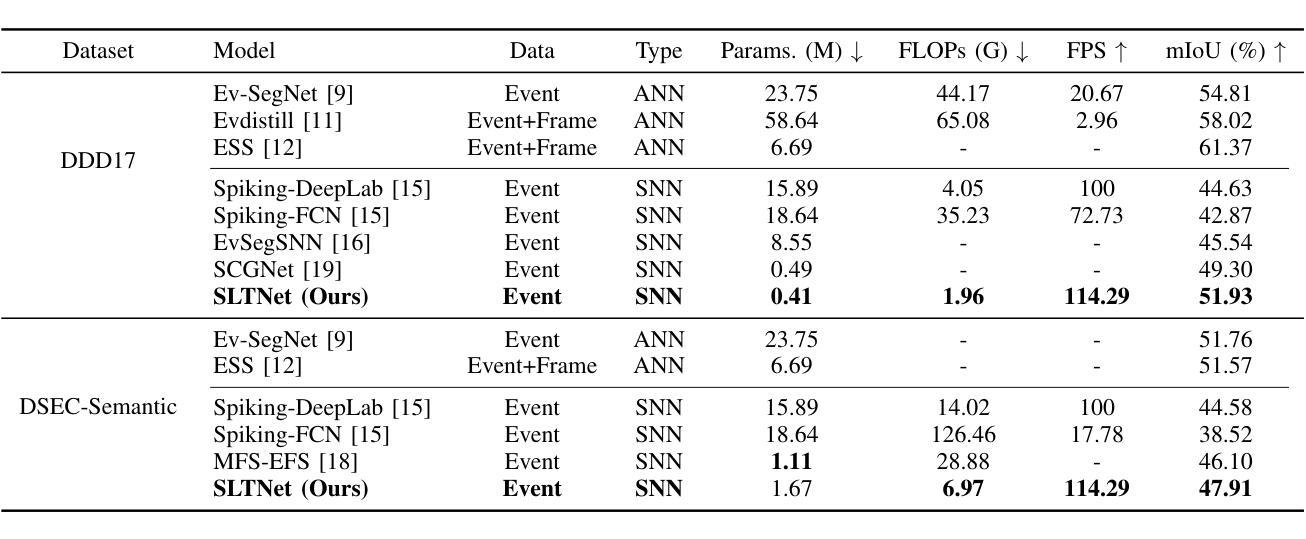
Event-based semantic segmentation has great potential in autonomous driving and robotics due to the advantages of event cameras, such as high dynamic range, low latency, and low power cost. Unfortunately, current artificial neural network (ANN)-based segmentation methods suffer from high computational demands, the requirements for image frames, and massive energy consumption, limiting their efficiency and application on resource-constrained edge/mobile platforms. To address these problems, we introduce SLTNet, a spike-driven lightweight transformer-based network designed for event-based semantic segmentation. Specifically, SLTNet is built on efficient spike-driven convolution blocks (SCBs) to extract rich semantic features while reducing the model’s parameters. Then, to enhance the long-range contextural feature interaction, we propose novel spike-driven transformer blocks (STBs) with binary mask operations. Based on these basic blocks, SLTNet employs a high-efficiency single-branch architecture while maintaining the low energy consumption of the Spiking Neural Network (SNN). Finally, extensive experiments on DDD17 and DSEC-Semantic datasets demonstrate that SLTNet outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) SNN-based methods by at most 9.06% and 9.39% mIoU, respectively, with extremely 4.58x lower energy consumption and 114 FPS inference speed. Our code is open-sourced and available at https://github.com/longxianlei/SLTNet-v1.0.
基于事件的语义分割在自动驾驶和机器人技术方面有着巨大的潜力,这是因为事件相机具有诸如高动态范围、低延迟和低成本等优势。然而,目前基于人工神经网络(ANN)的分割方法存在计算量大、对图像帧的要求高以及能耗巨大的问题,这在资源受限的边缘/移动平台上限制了其效率和应用。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了SLTNet,这是一个基于脉冲驱动轻量级变压器网络,为基于事件的语义分割而设计。具体而言,SLTNet建立在高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCB)上,以提取丰富的语义特征同时减少模型的参数。然后,为了增强长距离上下文特征的交互,我们提出了新颖的脉冲驱动变压器块(STB)带有二进制掩码操作。基于这些基本块,SLTNet采用高效的单分支架构,同时保持脉冲神经网络(SNN)的低能耗。最后,在DDD17和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的大量实验表明,SLTNet比最先进(SOTA)的基于SNN的方法最多高出9.06%和9.39%的mIoU,分别具有极低的4.58倍能耗和每秒114帧的推理速度。我们的代码是开源的,可以在https://github.com/longxianlei/SLTNet-v1.0获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IROS 2025 (2025 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems)
Summary
基于事件语义分割的方法在自动驾驶和机器人领域有巨大的潜力,但因现有基于人工神经网络(ANN)的分割方法计算量大、依赖图像帧及能耗高等问题,其在资源受限的边缘或移动平台上的应用受限。为此,我们提出SLTNet,一种基于脉冲驱动的轻量级Transformer网络,用于事件语义分割。其构建于高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCBs),减少了模型参数的同时提取丰富的语义特征。同时提出脉冲驱动Transformer块(STBs)增强长程上下文特征交互。基于这些基本块,SLTNet采用高效单分支架构,保持脉冲神经网络(SNN)的低能耗优势。在DDD17和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的实验表明,SLTNet较现有SNN方法最多提升9.06%和9.39%的mIoU指标,能耗降低4.58倍,推理速度达到每秒114帧。相关代码已开源并可通过链接获取。
Key Takeaways
- 事件语义分割在自动驾驶和机器人领域具有潜力。
- 当前基于ANN的分割方法存在计算量大、依赖图像帧和能耗高等问题。
- SLTNet是基于脉冲驱动的轻量级Transformer网络,用于事件语义分割。
- SLTNet利用高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCBs)提取语义特征并减少模型参数。
- 通过脉冲驱动Transformer块(STBs)增强长程上下文特征交互。
- SLTNet采用高效单分支架构并保持SNN的低能耗优势。
- 在DDD17和DSEC-Semantic数据集上,SLTNet性能优于现有SNN方法,并显著降低能耗。
点此查看论文截图