⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-15 更新
Noise Hypernetworks: Amortizing Test-Time Compute in Diffusion Models
Authors:Luca Eyring, Shyamgopal Karthik, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Nataniel Ruiz, Zeynep Akata
The new paradigm of test-time scaling has yielded remarkable breakthroughs in Large Language Models (LLMs) (e.g. reasoning models) and in generative vision models, allowing models to allocate additional computation during inference to effectively tackle increasingly complex problems. Despite the improvements of this approach, an important limitation emerges: the substantial increase in computation time makes the process slow and impractical for many applications. Given the success of this paradigm and its growing usage, we seek to preserve its benefits while eschewing the inference overhead. In this work we propose one solution to the critical problem of integrating test-time scaling knowledge into a model during post-training. Specifically, we replace reward guided test-time noise optimization in diffusion models with a Noise Hypernetwork that modulates initial input noise. We propose a theoretically grounded framework for learning this reward-tilted distribution for distilled generators, through a tractable noise-space objective that maintains fidelity to the base model while optimizing for desired characteristics. We show that our approach recovers a substantial portion of the quality gains from explicit test-time optimization at a fraction of the computational cost. Code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/HyperNoise
测试时缩放的新范式在大型语言模型(如推理模型)和生成视觉模型方面取得了显著的突破,允许模型在推理过程中分配额外的计算来有效应对日益复杂的问题。尽管这种方法有所改进,但出现了一个重要局限性:计算时间的显著增加使得该过程对于许多应用而言变得缓慢且不切实际。考虑到这种范式的成功及其日益增长的用途,我们寻求在避免推理开销的同时保留其好处。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种在模型后训练期间将测试时缩放知识集成到模型中的关键问题的解决方案。具体来说,我们用噪声超网络取代了扩散模型中的奖励引导测试时间噪声优化,该超网络调制初始输入噪声。我们为蒸馏生成器学习这种奖励倾向分布提出了一个理论上的框架,通过一个可行的噪声空间目标来实现,该目标在保持对基础模型忠实性的同时优化所需特性。我们显示,我们的方法在较少的计算成本下恢复了大量来自显式测试时间优化的质量收益。代码可在https://github.com/ExplainableML/HyperNoise找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://noisehypernetworks.github.io/
Summary
新一代测试时间扩展模式在大规模语言模型(LLM)和生成视觉模型中取得了显著突破,允许模型在推理过程中分配额外的计算资源以应对日益复杂的问题。然而,计算时间的增加使得实际应用变得缓慢且不切实际。本研究提出了一种在模型后训练阶段集成测试时间扩展知识的解决方案。我们用一个噪声超网络取代了扩散模型中的奖励引导测试时间噪声优化,并提出了一个理论扎实的学习奖励倾斜分布的框架。该框架用于蒸馏生成器,通过一个可操作的噪声空间目标,在保持对基础模型保真度的同时优化所需特性。我们的方法能够在较低的计算成本下恢复大部分测试时间优化的质量收益。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间扩展模式在LLM和生成视觉模型中取得显著突破,允许模型应对复杂问题。
- 这种模式的一个关键限制是计算时间显著增加,使其在实际应用中变得不切实际。
- 研究提出了一种解决方案,即通过噪声超网络集成测试时间扩展知识。
- 该方法取代了扩散模型中的奖励引导测试时间噪声优化。
- 研究者提出了一个理论扎实的学习奖励倾斜分布的框架用于蒸馏生成器。
- 该框架通过噪声空间目标来优化所需特性并保持对基础模型的保真度。
点此查看论文截图


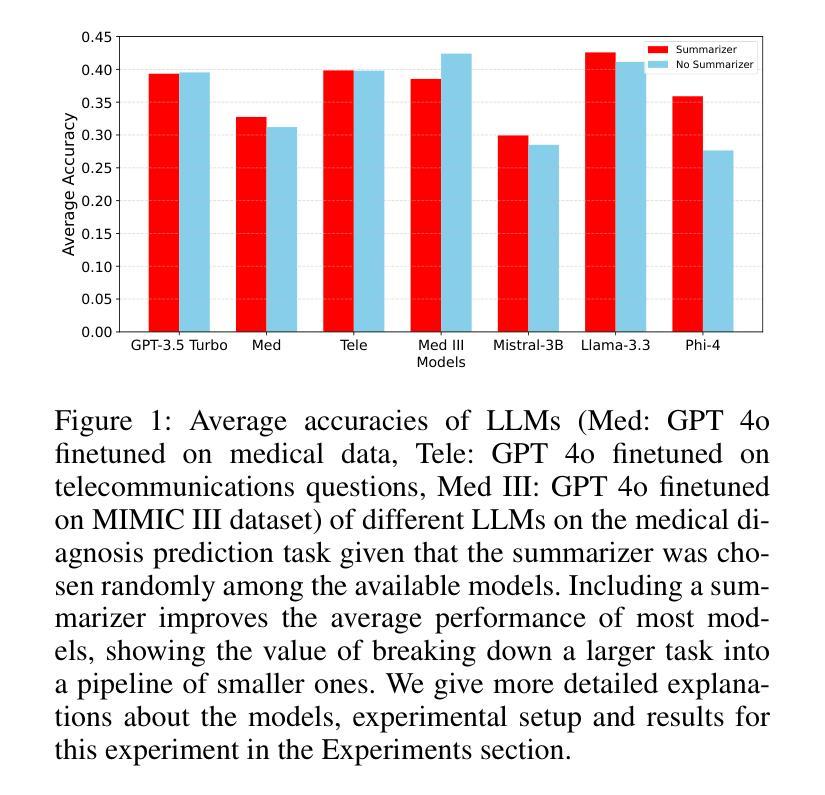
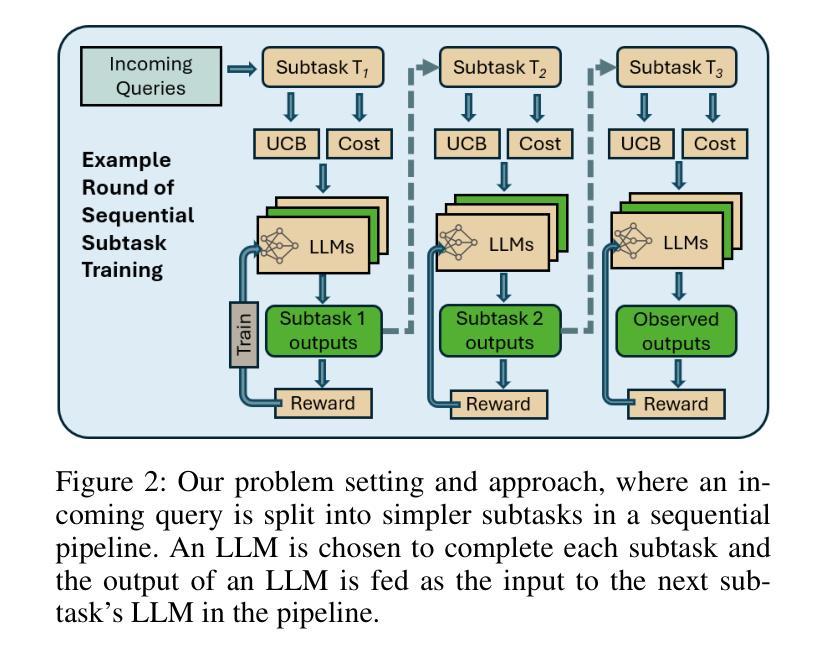
Neural Bandit Based Optimal LLM Selection for a Pipeline of Tasks
Authors:Baran Atalar, Eddie Zhang, Carlee Joe-Wong
With the increasing popularity of large language models (LLMs) for a variety of tasks, there has been a growing interest in strategies that can predict which out of a set of LLMs will yield a successful answer at low cost. This problem promises to become more and more relevant as providers like Microsoft allow users to easily create custom LLM “assistants” specialized to particular types of queries. However, some tasks (i.e., queries) may be too specialized and difficult for a single LLM to handle alone. These applications often benefit from breaking down the task into smaller subtasks, each of which can then be executed by a LLM expected to perform well on that specific subtask. For example, in extracting a diagnosis from medical records, one can first select an LLM to summarize the record, select another to validate the summary, and then select another, possibly different, LLM to extract the diagnosis from the summarized record. Unlike existing LLM selection or routing algorithms, this setting requires that we select a sequence of LLMs, with the output of each LLM feeding into the next and potentially influencing its success. Thus, unlike single LLM selection, the quality of each subtask’s output directly affects the inputs, and hence the cost and success rate, of downstream LLMs, creating complex performance dependencies that must be learned and accounted for during selection. We propose a neural contextual bandit-based algorithm that trains neural networks that model LLM success on each subtask in an online manner, thus learning to guide the LLM selections for the different subtasks, even in the absence of historical LLM performance data. Experiments on telecommunications question answering and medical diagnosis prediction datasets illustrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach compared to other LLM selection algorithms.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中的普及度越来越高,人们对于能够预测哪些LLM能够在低成本下产生成功答案的策略的兴趣也在增长。随着像微软这样的提供商让用户能够轻松创建针对特定类型查询的定制LLM“助理”,这个问题将变得越来越重要。然而,一些任务(即查询)可能过于专业化和复杂,单一LLM可能难以单独处理。这些应用程序通常受益于将任务分解成较小的子任务,每个子任务然后可以由一个在特定子任务上表现良好的LLM执行。例如,在从医疗记录中提取诊断信息时,可以先选择一个LLM来总结记录,再选择另一个来验证摘要,然后选择另一个可能是不同的LLM从摘要的记录中提取诊断信息。与现有的LLM选择或路由算法不同,此设置要求我们选择一个LLM序列,每个LLM的输出都会输入到下一个LLM中并可能影响其成功。因此,与单一LLM选择不同,每个子任务的输出直接影响输入,因此直接影响下游LLM的成本和成功率,产生复杂的性能依赖关系,必须在选择过程中学习和考虑。我们提出了一种基于神经网络上下文强盗算法的算法,该算法在线训练神经网络对每项任务的LLM成功率进行建模,从而学习为不同的子任务选择LLM,即使在没有历史LLM性能数据的情况下也是如此。在电信问答和医疗诊断预测数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法与其他LLM选择算法相比具有有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AAAI 2026
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中的普及引发了对其预测策略的兴趣,这些策略旨在以低成本预测哪些LLM能够成功完成任务。随着像微软这样的提供商允许用户轻松创建针对特定类型查询的自定义LLM“助手”,这个问题将变得越来越重要。针对某些复杂的任务,单独一个LLM可能难以处理。通过将这些任务分解为多个子任务并由适合的LLM执行,可以提高效率。本论文提出了一种基于神经上下文强盗算法的LLM选择方法,该方法可以在线建模每个子任务上LLM的成功率,从而指导不同子任务的LLM选择,即使在没有历史LLM性能数据的情况下也能有效工作。实验证明了该方法在电信问答和医疗诊断预测数据集上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs正在成为多种任务的热门选择,因此对预测其成功率的策略产生了兴趣。
- 随着LLM助手的普及,预测哪些LLM能成功完成任务的问题变得更为重要。
- 针对某些复杂的任务,单独一个LLM可能难以处理,将其分解为多个子任务可提高效率。
- 提出了一种基于神经上下文强盗算法的LLM选择方法,可以在线建模每个子任务上LLM的成功率。
- 该方法通过指导LLM选择来提高任务成功率并降低成本。
- 实验证明该方法在特定数据集上的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


Performance of GPT-5 Frontier Models in Ophthalmology Question Answering
Authors:Fares Antaki, David Mikhail, Daniel Milad, Danny A Mammo, Sumit Sharma, Sunil K Srivastava, Bing Yu Chen, Samir Touma, Mertcan Sevgi, Jonathan El-Khoury, Pearse A Keane, Qingyu Chen, Yih Chung Tham, Renaud Duval
Large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-5 integrate advanced reasoning capabilities that may improve performance on complex medical question-answering tasks. For this latest generation of reasoning models, the configurations that maximize both accuracy and cost-efficiency have yet to be established. We evaluated 12 configurations of OpenAI’s GPT-5 series (three model tiers across four reasoning effort settings) alongside o1-high, o3-high, and GPT-4o, using 260 closed-access multiple-choice questions from the American Academy of Ophthalmology Basic Clinical Science Course (BCSC) dataset. The primary outcome was multiple-choice accuracy; secondary outcomes included head-to-head ranking via a Bradley-Terry model, rationale quality assessment using a reference-anchored, pairwise LLM-as-a-judge framework, and analysis of accuracy-cost trade-offs using token-based cost estimates. GPT-5-high achieved the highest accuracy (0.965; 95% CI, 0.942-0.985), outperforming all GPT-5-nano variants (P < .001), o1-high (P = .04), and GPT-4o (P < .001), but not o3-high (0.958; 95% CI, 0.931-0.981). GPT-5-high ranked first in both accuracy (1.66x stronger than o3-high) and rationale quality (1.11x stronger than o3-high). Cost-accuracy analysis identified several GPT-5 configurations on the Pareto frontier, with GPT-5-mini-low offering the most favorable low-cost, high-performance balance. These results benchmark GPT-5 on a high-quality ophthalmology dataset, demonstrate the influence of reasoning effort on accuracy, and introduce an autograder framework for scalable evaluation of LLM-generated answers against reference standards in ophthalmology.
大型语言模型(LLM)如GPT-5集成了先进的推理能力,可能会提高在复杂医学问答任务上的性能。对于这一最新一代的推理模型,尚未确定能够最大化准确性和成本效益的配置。我们评估了OpenAI的GPT-5系列(四个推理努力设置中的三个模型层次)以及o1-high、o3-high和GPT-4o,使用美国眼科科学院基础临床科学课程(BCSC)数据集的260道封闭式多选题。主要结果是多选题的准确性;次要结果包括通过Bradley-Terry模型进行的头对头排名、使用参考锚定、成对的LLM作为法官框架的合理性质量评估,以及使用基于令牌的成本估算进行的准确性成本权衡分析。GPT-5-high的准确率最高(0.965;95%置信区间,0.942-0.985),优于所有GPT-5-nano变体(P < .001)、o1-high(P = .04)和GPT-4o(P < .001),但与o3-high(0.958;95%置信区间,0.931-0.981)无显著差异。GPT-5-high在准确性和合理性方面均排名第一(比o3-high高出1.66倍和1.11倍)。成本准确性分析确定了帕累托前沿的几个GPT-5配置,其中GPT-5-mini-low提供了最具成本效益、高性能平衡的方案。这些结果在眼科数据集上对GPT-5进行了基准测试,证明了推理努力对准确性的影响,并引入了一个自动评分框架,可规模化地评估LLM生成的答案与眼科领域的参考标准之间的对比情况。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)如GPT-5集成了先进的推理能力,可能提高复杂医学问答任务的性能。对于这一代推理模型,尚未建立既能最大化准确性又实现成本效益的配置。研究团队对OpenAI的GPT-5系列(三个模型层次,四种推理难度设置)以及o1-high、o3-high和GPT-4o进行了评估,使用了美国眼科科学院基础临床科学课程(BCSC)数据集的260道封闭多选题。主要结果是多项选择题准确率;次要结果包括基于Bradley-Terry模型的排名对比、利用参考锚定的成对LLM评判框架的合理性质量评估以及基于令牌成本的准确度成本权衡分析。GPT-5-high的准确率最高(0.965;95%置信区间,0.942-0.985),优于所有GPT-5-nano变种(P < .001)、o1-high(P = .04)和GPT-4o(P < .001),但与o3-high(0.958;95%置信区间,0.931-0.981)相当。GPT-5-high在准确率和合理性质量方面均排名第一(分别是o3的两倍和一点一一倍)。成本准确性分析确定了若干GPT-5配置位于帕累托前沿,其中GPT-5-mini-low提供了低成本和高性能之间的最佳平衡。该研究对GPT-5在眼科高质量数据集上的性能进行了基准测试,展示了推理难度对准确度的影响,并引入了一个自动评分框架,可针对眼科领域的参考标准对LLM生成的答案进行可规模化评估。
关键见解
- GPT-5在复杂医学问答任务上表现出优异的性能,特别是与之前的模型相比,如GPT-4o和o3系列模型。
- GPT-5系列的不同配置在准确性方面存在显著差异,其中GPT-5-high表现最佳。
- 除了准确性外,GPT-5系列模型在推理能力和答案合理性方面也表现出优势。
- 成本效益分析表明,GPT-5系列中存在一些具有高性价比的配置。
- GPT-5在眼科数据集上的性能评估为该领域的应用提供了重要参考。
- 推理难度对LLM的性能有影响,这意味着针对不同任务可能需要调整模型配置。
点此查看论文截图

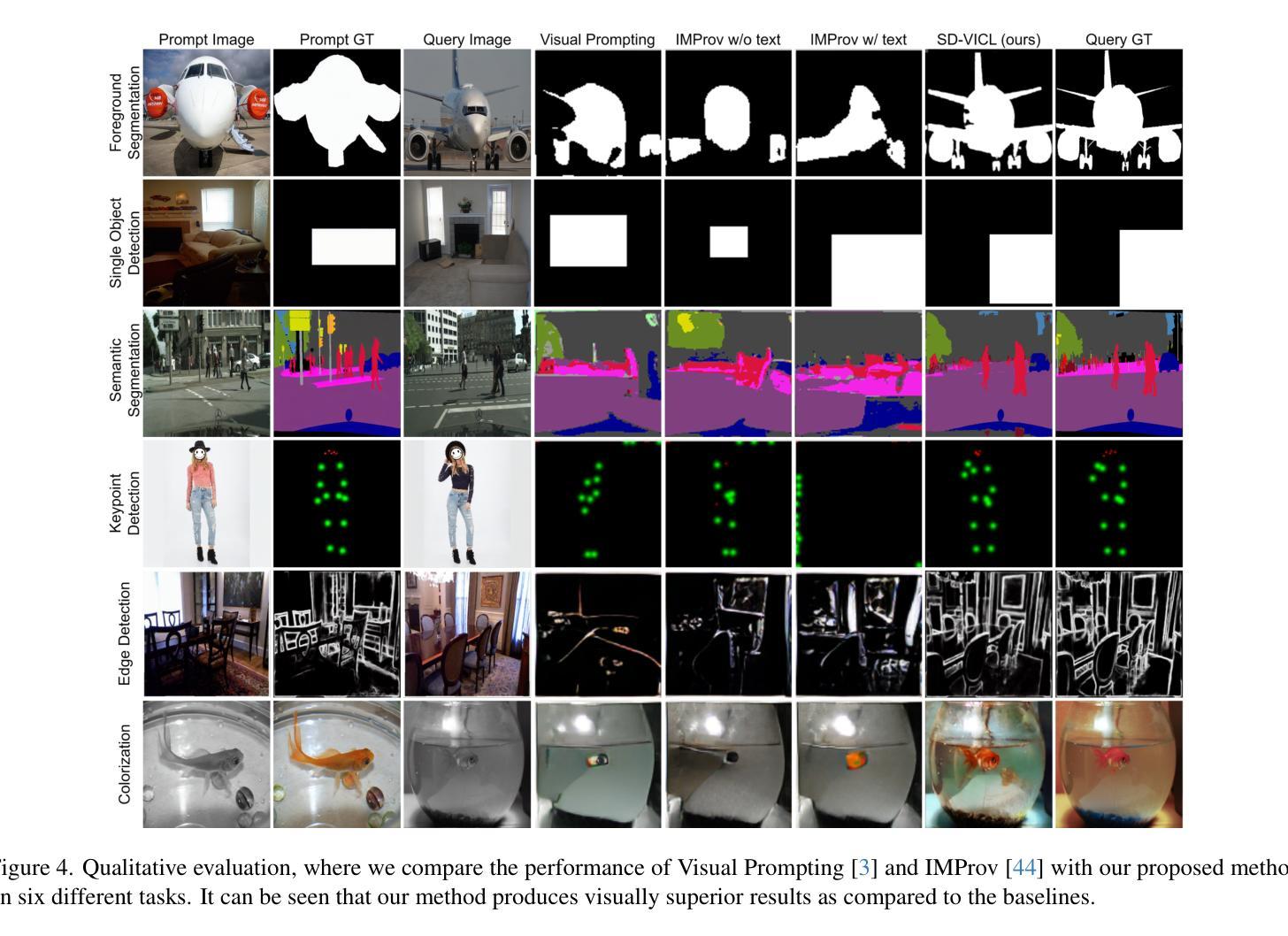
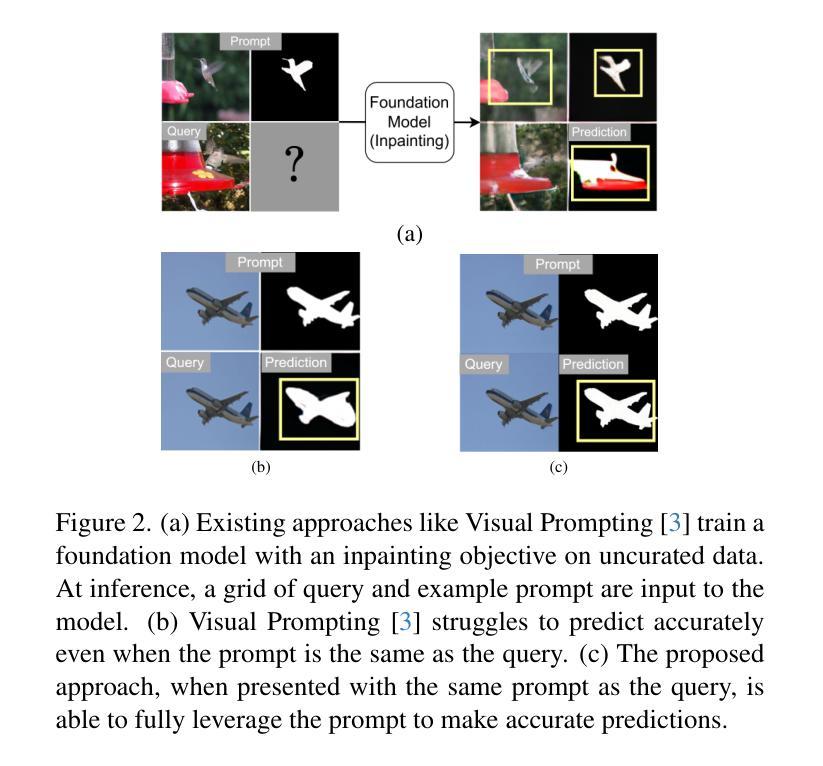
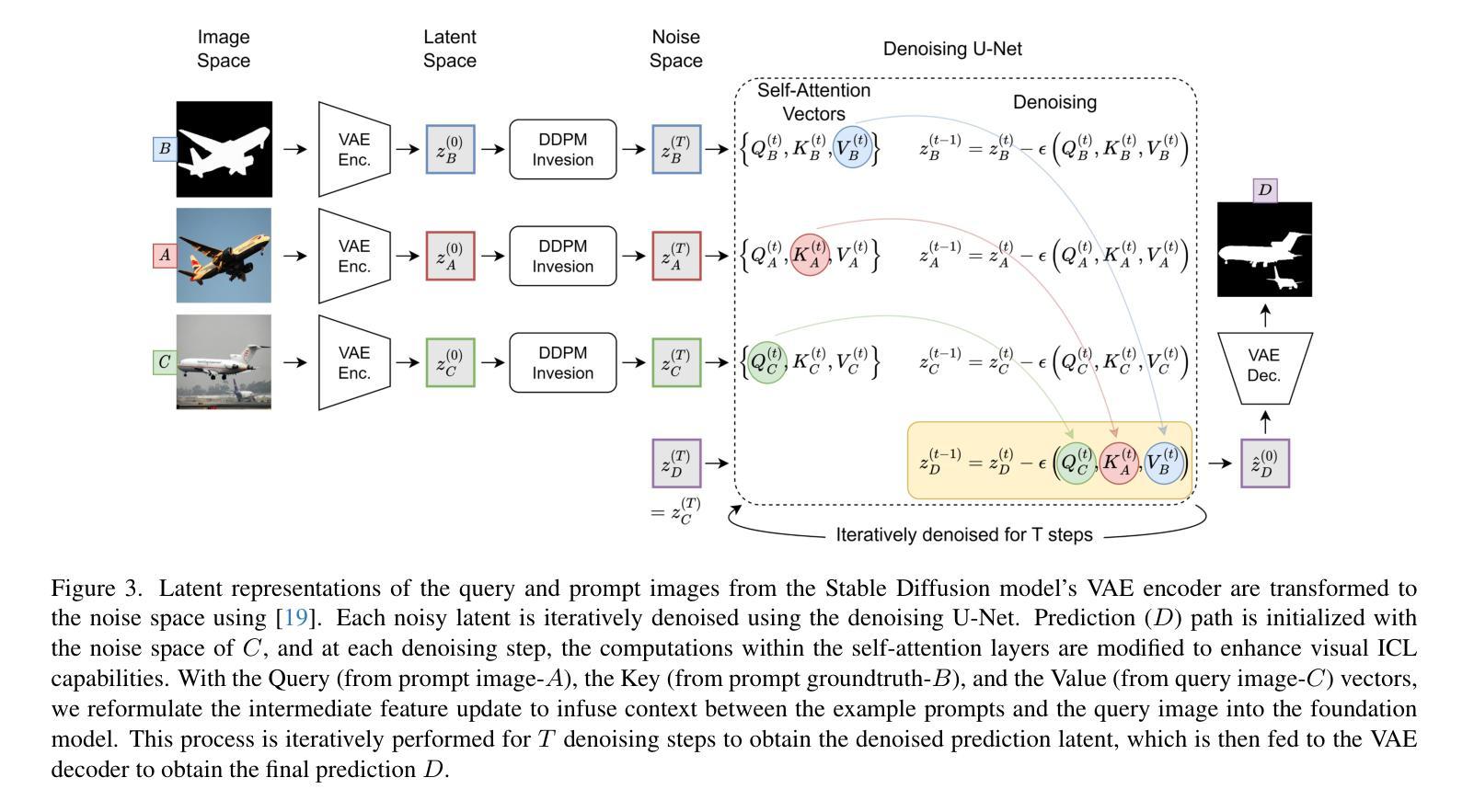
Stable Diffusion Models are Secretly Good at Visual In-Context Learning
Authors:Trevine Oorloff, Vishwanath Sindagi, Wele Gedara Chaminda Bandara, Ali Shafahi, Amin Ghiasi, Charan Prakash, Reza Ardekani
Large language models (LLM) in natural language processing (NLP) have demonstrated great potential for in-context learning (ICL) – the ability to leverage a few sets of example prompts to adapt to various tasks without having to explicitly update the model weights. ICL has recently been explored for computer vision tasks with promising early outcomes. These approaches involve specialized training and/or additional data that complicate the process and limit its generalizability. In this work, we show that off-the-shelf Stable Diffusion models can be repurposed for visual in-context learning (V-ICL). Specifically, we formulate an in-place attention re-computation within the self-attention layers of the Stable Diffusion architecture that explicitly incorporates context between the query and example prompts. Without any additional fine-tuning, we show that this repurposed Stable Diffusion model is able to adapt to six different tasks: foreground segmentation, single object detection, semantic segmentation, keypoint detection, edge detection, and colorization. For example, the proposed approach improves the mean intersection over union (mIoU) for the foreground segmentation task on Pascal-5i dataset by 8.9% and 3.2% over recent methods such as Visual Prompting and IMProv, respectively. Additionally, we show that the proposed method is able to effectively leverage multiple prompts through ensembling to infer the task better and further improve the performance.
在自然语言处理(NLP)中,大型语言模型(LLM)在上下文学习(ICL)方面表现出了巨大的潜力。上下文学习是指利用少量示例提示来适应各种任务,而无需明确更新模型权重。虽然最近已经开始探索计算机视觉任务的上下文学习并获得了有希望的早期成果,但这些方法涉及专门培训和/或额外数据,这增加了复杂性并限制了其普遍性。在这项工作中,我们展示了现成的Stable Diffusion模型可以用于视觉上下文学习(V-ICL)。具体来说,我们在Stable Diffusion架构的自注意力层内制定了即时注意力重新计算,该计算显式地结合了查询和示例提示之间的上下文。无需任何额外的微调,我们证明了这种重新设计的Stable Diffusion模型能够适应六种不同的任务:前景分割、单目标检测、语义分割、关键点检测、边缘检测和彩色化。例如,在Pascal-5i数据集上,所提出的方法在前景分割任务上的平均交并比(mIoU)提高了8.9%,相较于最近的Visual Prompting和IMProv方法分别提高了3.2%。此外,我们还表明,所提出的方法能够通过集成多个提示来更好地推断任务并进一步提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
大型语言模型在自然语言处理领域展现出强大的上下文学习能力,即利用少量示例提示适应各种任务而无需显式更新模型权重。本研究展示了现成的Stable Diffusion模型可用于视觉上下文学习(V-ICL)。通过自我注意层内的即时注意力重新计算,明确结合了查询和示例提示之间的上下文。无需任何精细调整,该模型就能适应六种不同任务,并在Pascal-5i数据集上的前景分割任务提高了平均交并比(mIoU)8.9%和3.2%。此外,该方法能够通过集成多个提示来更好地推断任务并进一步提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自然语言处理中表现出强大的上下文学习能力。
- Stable Diffusion模型可用于视觉上下文学习(V-ICL)。
- 通过在自我注意层内进行即时注意力重新计算,Stable Diffusion模型能明确结合查询和示例提示之间的上下文。
- 无需精细调整,该模型就能适应多种任务,如前景分割、单目标检测等。
- 在Pascal-5i数据集上的前景分割任务,该模型的性能超过了最近的方法,如Visual Prompting和IMProv。
- 该方法能够通过集成多个提示来进一步改善性能。
点此查看论文截图


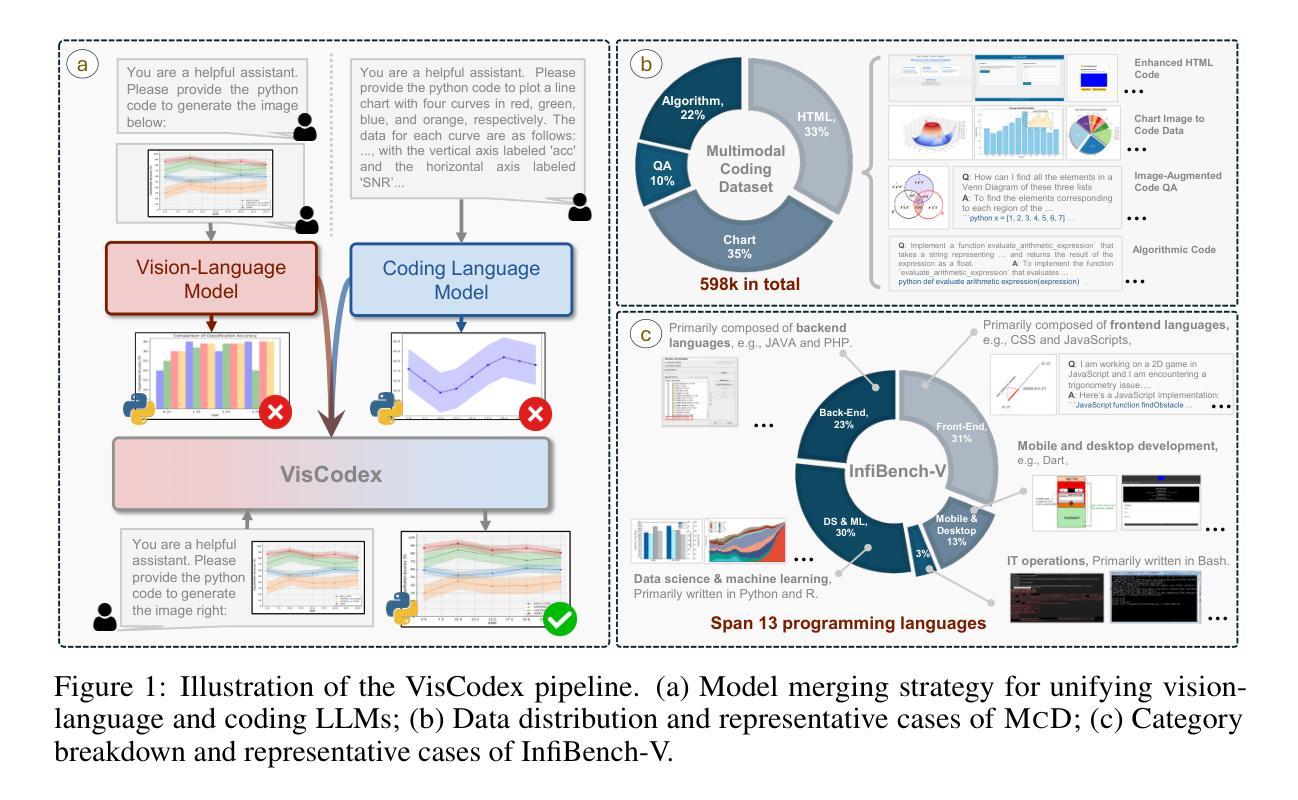
VisCodex: Unified Multimodal Code Generation via Merging Vision and Coding Models
Authors:Lingjie Jiang, Shaohan Huang, Xun Wu, Yixia Li, Dongdong Zhang, Furu Wei
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have significantly advanced the integration of visual and textual understanding. However, their ability to generate code from multimodal inputs remains limited. In this work, we introduce VisCodex, a unified framework that seamlessly merges vision and coding language models to empower MLLMs with strong multimodal code generation abilities. Leveraging a task vector-based model merging technique, we integrate a state-of-the-art coding LLM into a strong vision-language backbone, while preserving both visual comprehension and advanced coding skills. To support training and evaluation, we introduce the Multimodal Coding Dataset (MCD), a large-scale and diverse collection of 598k samples, including high-quality HTML code, chart image-code pairs, image-augmented StackOverflow QA, and algorithmic problems. Furthermore, we propose InfiBench-V, a novel and challenging benchmark specifically designed to assess models on visually-rich, real-world programming questions that demand a nuanced understanding of both textual and visual contexts. Extensive experiments show that VisCodex achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source MLLMs and approaches proprietary models like GPT-4o, highlighting the effectiveness of our model merging strategy and new datasets.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在视觉和文本理解的融合方面取得了显著进展。然而,它们从多模态输入生成代码的能力仍然有限。在这项工作中,我们引入了VisCodex,这是一个无缝融合视觉和编码语言模型的统一框架,使MLLM具备强大的多模态代码生成能力。我们采用基于任务向量的模型融合技术,将最先进的编码LLM集成到强大的视觉语言主干中,同时保留视觉理解和高级编码技能。为了支持和评估训练,我们推出了多模态编码数据集(MCD),这是一大规模且多样化的样本集合,包含59.8万个样本,包括高质量的HTML代码、图表图像代码对、图像增强的StackOverflow问答和算法问题。此外,我们还提出了InfiBench-V这一新型且具有挑战性的基准测试,专门用于评估模型在处理视觉丰富、现实世界编程问题上的能力,这些问题要求深刻理解和运用文本和视觉上下文。大量实验表明,VisCodex在开源MLLM中达到了最先进的性能,并接近专有模型如GPT-4o的性能,这凸显了我们模型融合策略和新数据集的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MLLMs通过VisCodex框架实现了视觉与编程语言模型的融合,提升了多模态代码生成能力。该框架采用任务向量模型融合技术,将先进的编程LLM融入强大的视觉语言主干网,同时保留视觉理解和高级编程技能。为支持和评估模型,引入了多模态编码数据集(MCD),并设立了InfiBench-V基准测试,以评估模型在视觉丰富的实际编程问题上的表现。实验表明,VisCodex在开源MLLMs中达到最佳性能,接近GPT-4o等专有模型,验证了模型融合策略和新型数据集的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs通过VisCodex框架实现了视觉与编程语言的融合。
- VisCodex采用任务向量模型融合技术,整合了先进的编程LLM和视觉语言主干网。
- 引入多模态编码数据集(MCD),支持VisCodex的训练和评估。
- MCD数据集包含高质量HTML代码、图表图像代码对、图像增强型StackOverflow问答和算法问题。
- 设立了InfiBench-V基准测试,用于评估模型在视觉丰富的编程问题上的性能。
- VisCodex在开源MLLMs中表现最佳,接近专有模型如GPT-4o。
点此查看论文截图

A Comprehensive Evaluation framework of Alignment Techniques for LLMs
Authors:Muneeza Azmat, Momin Abbas, Maysa Malfiza Garcia de Macedo, Marcelo Carpinette Grave, Luan Soares de Souza, Tiago Machado, Rogerio A de Paula, Raya Horesh, Yixin Chen, Heloisa Caroline de Souza Pereira Candello, Rebecka Nordenlow, Aminat Adebiyi
As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into real-world applications, ensuring their outputs align with human values and safety standards has become critical. The field has developed diverse alignment approaches including traditional fine-tuning methods (RLHF, instruction tuning), post-hoc correction systems, and inference-time interventions, each with distinct advantages and limitations. However, the lack of unified evaluation frameworks makes it difficult to systematically compare these paradigms and guide deployment decisions. This paper introduces a multi-dimensional evaluation of alignment techniques for LLMs, a comprehensive evaluation framework that provides a systematic comparison across all major alignment paradigms. Our framework assesses methods along four key dimensions: alignment detection, alignment quality, computational efficiency, and robustness. Through experiments across diverse base models and alignment strategies, we demonstrate the utility of our framework in identifying strengths and limitations of current state-of-the-art models, providing valuable insights for future research directions.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在现实世界应用中的集成度越来越高,确保它们的输出与人类价值观和安全标准相一致已成为关键。该领域已经开发了多种对齐方法,包括传统的微调方法(RLHF、指令调整)、事后校正系统和推理时间干预,每种方法都有其独特的优势和局限性。然而,由于缺乏统一的评估框架,使得系统地比较这些范式并指导部署决策变得困难。本文介绍了大型语言模型对齐技术的多维度评估,这是一个全面的评估框架,为所有主要的对齐范式提供了系统的比较。我们的框架从四个关键维度评估方法:对齐检测、对齐质量、计算效率和稳健性。通过对不同基础模型和对齐策略的实验,我们证明了该框架在识别当前最先进模型的优点和局限性方面的实用性,为未来研究方向提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In submission
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)在现实世界应用中的集成度不断提高,确保其输出符合人类价值观和公共安全标准至关重要。本文介绍了一个对LLM对齐技术的多维度评估框架,该框架提供了一个跨所有主要对齐范式的系统比较。评估方法包括四个关键维度:对齐检测、对齐质量、计算效率和稳健性。通过实验,该框架证明了其识别当前最先进模型的优缺点并为未来的研究方向提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在现实应用中的集成度提高,需要确保输出符合人类价值观和公共安全标准。
- 目前存在多种LLM对齐方法,包括传统微调方法、事后校正系统和推理时间干预等,各有优势和局限。
- 缺乏统一的评估框架,难以系统地比较这些范式并做出部署决策。
- 论文引入了一个多维度评估LLM对齐技术的框架,涵盖对齐检测、对齐质量、计算效率和稳健性四个关键维度。
- 实验证明该框架能够识别当前最先进模型的优缺点。
- 该框架为未来的LLM对齐研究提供了有价值的指导方向。
点此查看论文截图


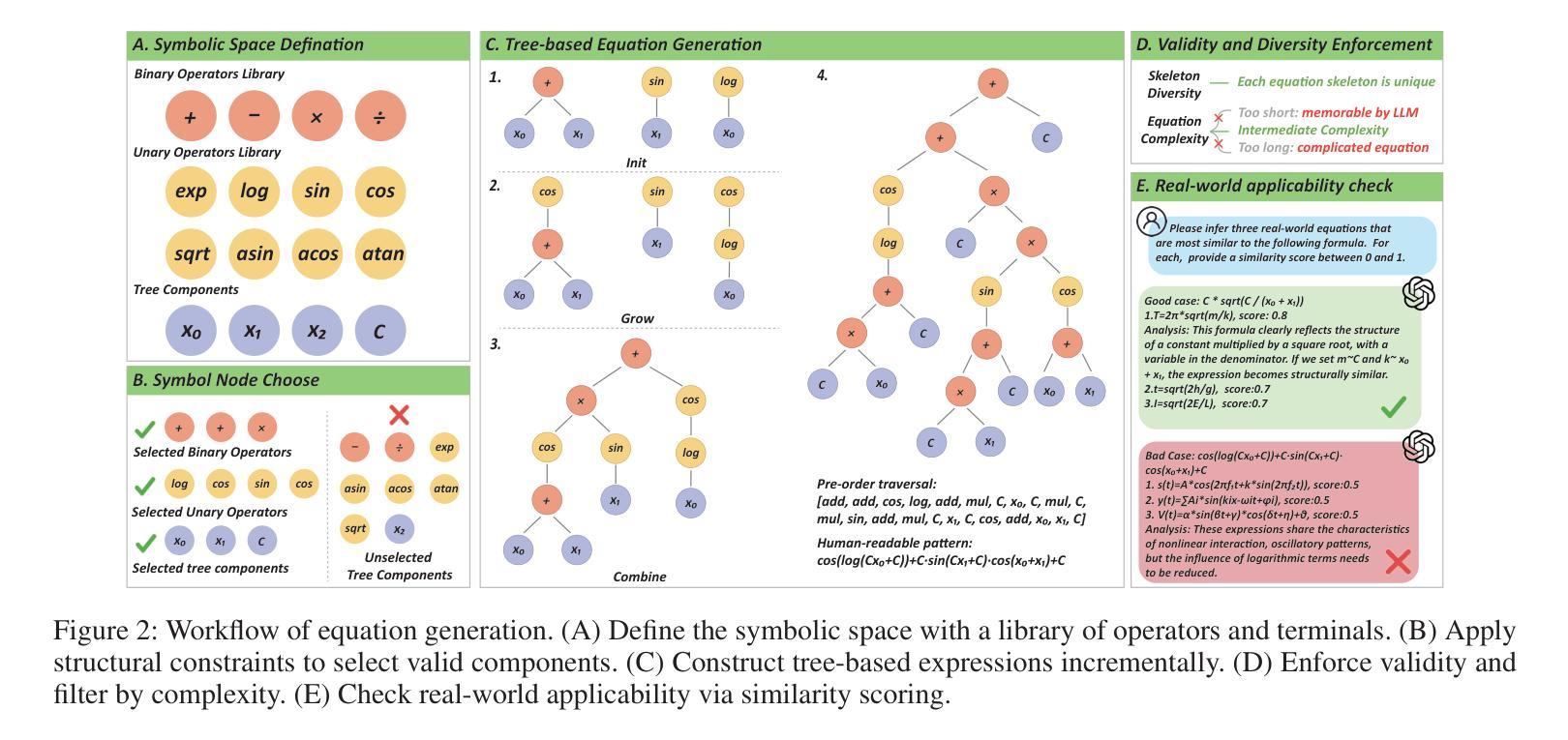
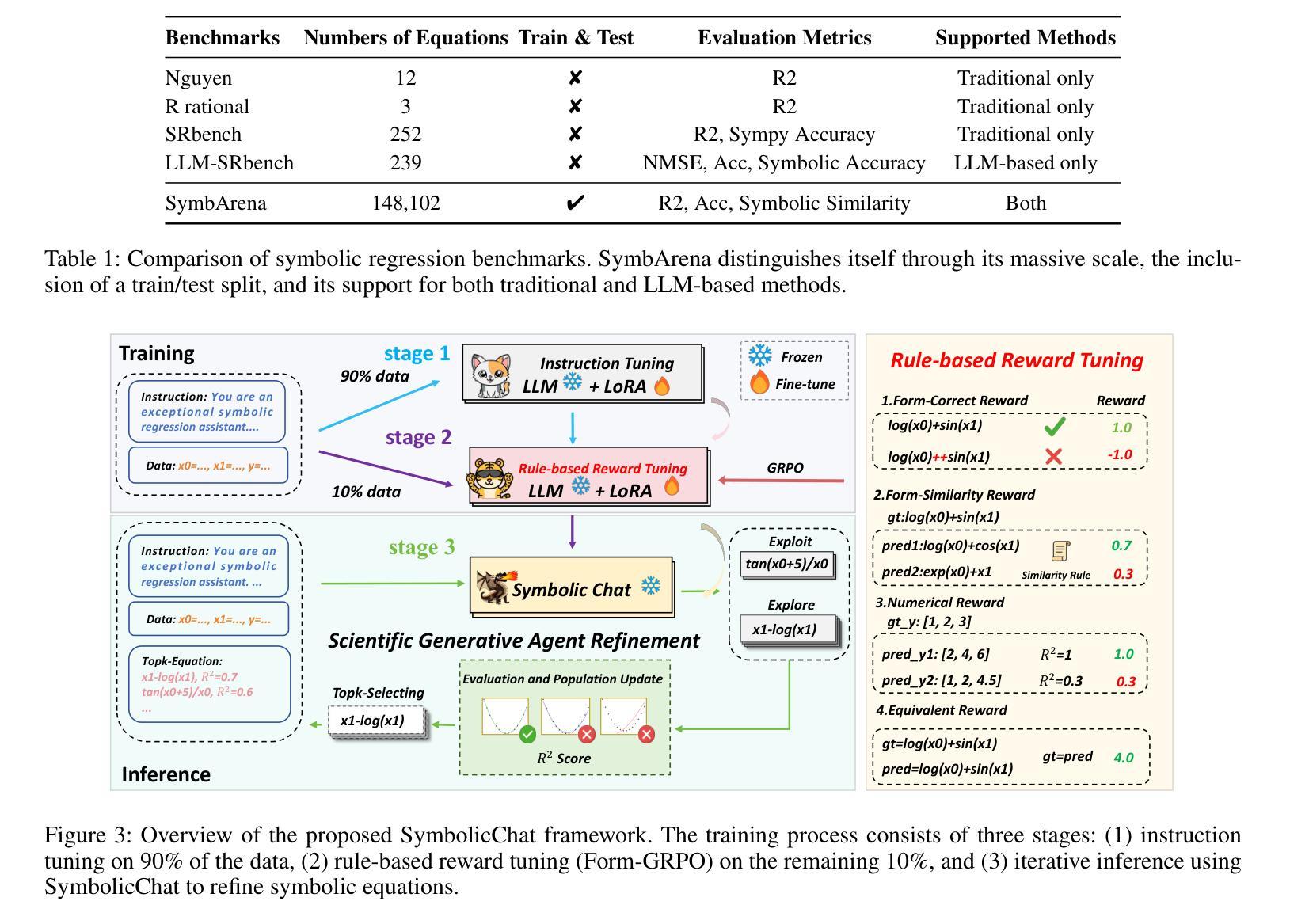
Finetuning Large Language Model as an Effective Symbolic Regressor
Authors:Yingfan Hua, Ruikun Li, Jun Yao, Guohang Zhuang, Shixiang Tang, Bin Liu, Wanli Ouyang, Yan Lu
Deriving governing equations from observational data, known as Symbolic Regression (SR), is a cornerstone of scientific discovery. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in this task by leveraging their vast cross-disciplinary scientific knowledge. However, existing LLM-based methods primarily rely on direct inference or prompt engineering, often requiring excessive inference iterations to converge on correct formulas or failing to treating complex equation targets. These limitations in effectiveness and generalization stem from an inherent tension between pre-trained LLMs’ proficiency in approximate reasoning and the high-precision demands of SR tasks. To bridge this gap, we propose to fine-tune LLMs for enhanced SR capability. Yet, the absence of dedicated datasets for SR-oriented fine-tuning remains a critical barrier. We thus introduce SymbArena, specifically engineered to optimize LLMs for SR. This benchmark comprises 148,102 diverse equations formulated as corpora of 1.83 billion tokens for LLM utilization, enabling effective training and inference. Further, SymbArena proposes a heuristics metric to precisely quantify form-level consistency, going beyond existing SR numerical-oriented evaluation strategies. With this benchmark, we explore mainstream LLM fine-tuning techniques for SR tasks and establish SymbolicChat, a simple yet effective LLM-based SR strong baseline. Experimental results validate SymbolicChat as the first LLM to exceed traditional numerical methods in both numerical precision and symbolic form accuracy, outperforming the second-best LLM baseline with improvements of 2-fold gains in R2 score and 8.37% in form-level consistency score.
从观测数据中推导出控制方程,被称为符号回归(SR),是科学发现的核心。大型语言模型(LLM)在此任务中表现出了巨大的潜力,它们能够利用跨学科的丰富科学知识。然而,现有的基于LLM的方法主要依赖于直接推理或提示工程,通常需要过多的推理迭代才能找到正确的公式,或者无法处理复杂的方程目标。这些有效性和泛化能力的局限性源于预训练LLM的近似推理能力与SR任务的高精度要求之间的内在矛盾。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出对LLM进行微调以增强其SR能力。然而,缺乏用于SR定向微调的专用数据集仍是关键障碍。因此,我们引入了SymbArena,它是专门为优化LLM进行SR而设计的。此基准测试包含148,102个多样化的方程,作为LLM利用的语料库,包含1.83亿个令牌,可实现有效的训练和推理。此外,SymbArena提出了一个启发式度量标准,可以精确地量化形式层面的一致性,超越了现有的SR数值导向评估策略。借助此基准测试,我们探索了针对SR任务的主流LLM微调技术,并建立了基于LLM的符号聊天简单有效的强基线。实验结果验证了符号聊天作为第一个超越传统数值方法的LLM,在数值精度和符号形式准确性方面都表现出色,相较于第二名LLM基准线,其在R2得分上提高了两倍的得分,在形式层面的一致性得分上提高了8.37%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于观测数据推导出的控制方程,即符号回归(SR),是科学发现的核心。大型语言模型(LLM)在这一任务中表现出了巨大的潜力,它们可以运用丰富的跨学科科学知识。然而,现有的LLM方法主要依赖于直接推理或提示工程,这通常需要过多的推理迭代来收敛到正确的公式,或者无法处理复杂的方程目标。这些在效果和泛化上的局限性源于预训练LLM的近似推理能力与SR任务的高精度要求之间的内在矛盾。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了对LLM进行微调以增强其SR能力的方法。然而,缺乏面向SR的专用数据集仍是实现这一目标的重大障碍。因此,我们引入了SymbArena,它是专门为优化LLM进行SR而设计的。该基准测试包含148,102个多样化的方程,作为LLM利用的语料库,包含约达到了庞大的1.83亿个标记符号。此外,SymbArena提出了一个启发式度量标准来精确量化形式级别的一致性,突破了现有的SR数值评估策略的限制。有了这个基准测试平台,我们探索了针对SR任务的主流LLM微调技术并建立了SymbolicChat模型,它是一个简单而有效的基于LLM的SR基线模型。实验结果验证了SymbolicChat作为首个超越传统数值方法的LLM模型的有效性,在数值精度和符号形式准确性方面都表现出色,相较于第二好的LLM基线模型在R²得分上提高了两倍并提高了形式一致性得分达8.37%。我们相信这个基准模型和平台将促进SR任务的进一步发展并推动相关领域的研究进步。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在符号回归(SR)任务中展现出巨大潜力,得益于其丰富的跨学科科学知识。
- 当前LLM方法在SR任务中主要面临过度迭代、处理复杂方程困难等问题。
- LLM的近似推理能力与SR任务的高精度需求之间存在矛盾,需要通过微调增强LLM的SR能力。
- 缺乏面向SR的专用数据集是限制LLM在SR任务上表现的关键障碍之一。
- 引入SymbArena基准测试平台,为优化LLM进行SR提供解决方案。该平台包含大量多样化的方程作为语料库,并提供了启发式度量标准来精确评估模型性能。
- 基于SymbArena平台建立的SymbolicChat模型在SR任务上表现出卓越性能,超越了传统数值方法。
点此查看论文截图

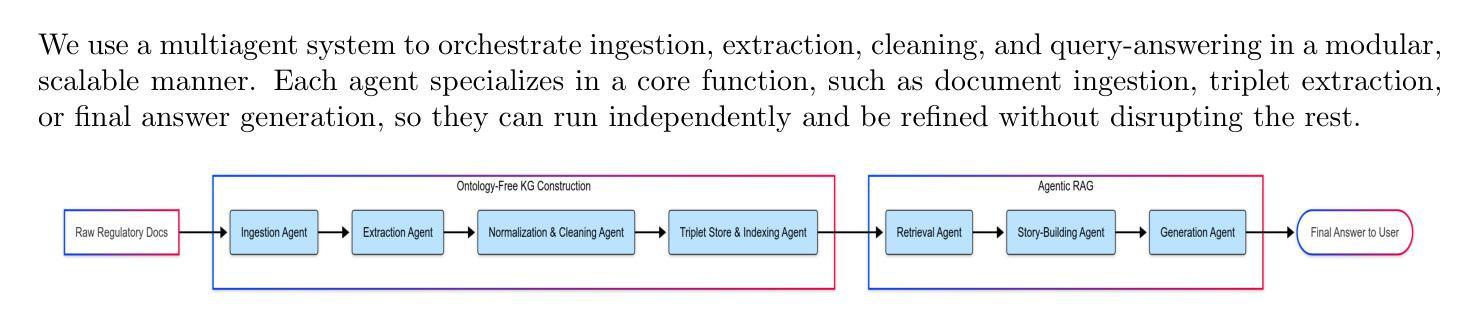
RAGulating Compliance: A Multi-Agent Knowledge Graph for Regulatory QA
Authors:Bhavik Agarwal, Hemant Sunil Jomraj, Simone Kaplunov, Jack Krolick, Viktoria Rojkova
Regulatory compliance question answering (QA) requires precise, verifiable information, and domain-specific expertise, posing challenges for Large Language Models (LLMs). In this work, we present a novel multi-agent framework that integrates a Knowledge Graph (KG) of Regulatory triplets with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to address these demands. First, agents build and maintain an ontology-free KG by extracting subject–predicate–object (SPO) triplets from regulatory documents and systematically cleaning, normalizing, deduplicating, and updating them. Second, these triplets are embedded and stored along with their corresponding textual sections and metadata in a single enriched vector database, allowing for both graph-based reasoning and efficient information retrieval. Third, an orchestrated agent pipeline leverages triplet-level retrieval for question answering, ensuring high semantic alignment between user queries and the factual “who-did-what-to-whom” core captured by the graph. Our hybrid system outperforms conventional methods in complex regulatory queries, ensuring factual correctness with embedded triplets, enabling traceability through a unified vector database, and enhancing understanding through subgraph visualization, providing a robust foundation for compliance-driven and broader audit-focused applications.
监管合规问答(QA)需要准确、可验证的信息和特定领域的专业知识,这对大型语言模型(LLM)提出了挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的多代理框架,该框架将监管三元组的知识图谱(KG)与检索增强生成(RAG)相结合,以满足这些需求。首先,代理通过从监管文档中提取主体-谓语-宾语(SPO)三元组来构建和维护无本体知识图谱,并对其进行系统清理、规范化、去重和更新。其次,这些三元组被嵌入并与其相应的文本段落和元数据一起存储在一个单一的丰富向量数据库中,允许基于图推理和高效的信息检索。第三,协同代理管道利用三元组级别的检索来进行问答,确保用户查询与图中捕获的“谁做了哪些行为并影响了谁”的核心事实之间存在高度语义对齐。我们的混合系统在复杂的监管查询中优于传统方法,通过嵌入的三元组确保事实正确性,通过统一的向量数据库实现可追溯性,并通过子图可视化增强理解,为合规驱动和更广泛的审计重点应用提供了稳健的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在应对监管合规问题回答(QA)时面临精确信息和专业知识的挑战。本研究提出了一种新型多智能体框架,该框架结合了监管三元组的知识图谱(KG)与检索增强生成(RAG)技术来应对这些挑战。智能体通过从监管文档中提取主体-谓语-对象(SPO)三元组构建和维护无本体知识图谱,并进行清洗、归一化、去重和更新。这些三元组嵌入并与其相应的文本段落和元数据一起存储在单一的丰富向量数据库中,支持基于图的推理和高效的信息检索。最后,利用三元组级别的检索机制来回答用户的问题,确保用户查询与图谱中捕获的“谁对谁做了什么”核心事实之间的高度语义对齐。该混合系统优于传统方法,在复杂的监管查询中确保事实正确性、通过统一的向量数据库实现可追溯性,并通过子图可视化增强理解,为合规驱动和更广泛的审计重点应用提供了稳健的基础。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型多智能体框架,用于处理监管合规问题回答的挑战。
- 通过SPO三元组构建和维护知识图谱,以适应监管合规领域的需求。
- 丰富的向量数据库融合了知识图谱和文本数据,支持基于图的推理和信息检索。
- 利用三元组级别的检索机制来回答用户的问题,增强了语义对齐和事实准确性。
- 该系统通过子图可视化增强了理解,提高了复杂查询的处理能力。
- 保证了事实的正确性和可追溯性,优于传统的处理方法。
点此查看论文截图



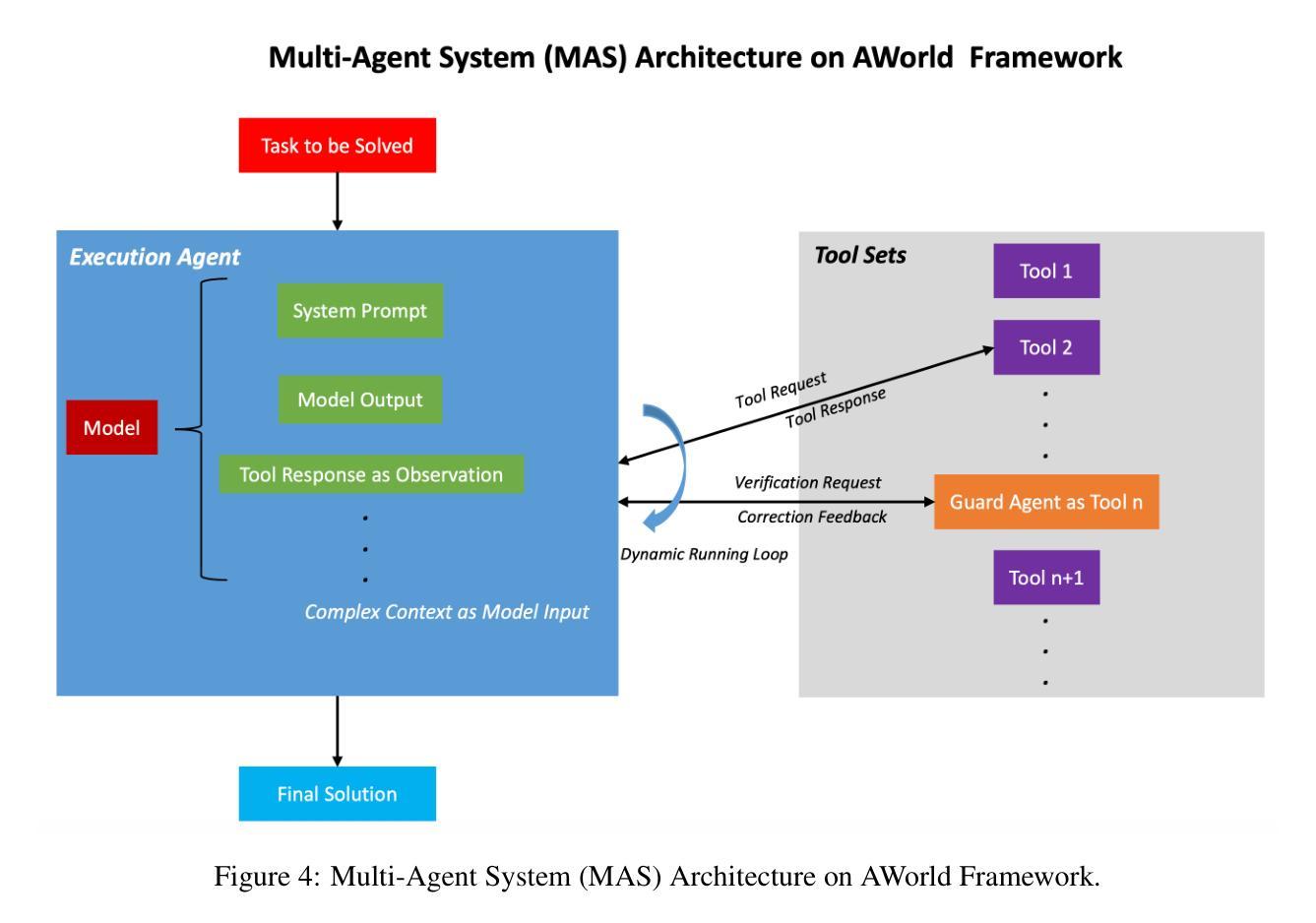
AWorld: Dynamic Multi-Agent System with Stable Maneuvering for Robust GAIA Problem Solving
Authors:Zhitian Xie, Qintong Wu, Chengyue Yu, Chenyi Zhuang, Jinjie Gu
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has empowered intelligent agents to leverage diverse external tools for solving complex real-world problems. However, as agents increasingly depend on multiple tools, they encounter new challenges: extended contexts from disparate sources and noisy or irrelevant tool outputs can undermine system reliability and accuracy. These challenges underscore the necessity for enhanced stability in agent-based systems. To address this, we introduce dynamic supervision and maneuvering mechanisms, constructing a robust and dynamic Multi-Agent System (MAS) architecture within the AWorld framework. In our approach, the Execution Agent invokes the Guard Agent at critical steps to verify and correct the reasoning process, effectively reducing errors arising from noise and bolstering problem-solving robustness. Extensive experiments on the GAIA test dataset reveal that our dynamic maneuvering mechanism significantly improves both the effectiveness and stability of solutions, outperforming single-agent system (SAS) and standard tool-augmented systems. As a result, our dynamic MAS system achieved first place among open-source projects on the prestigious GAIA leaderboard. These findings highlight the practical value of collaborative agent roles in developing more reliable and trustworthy intelligent systems.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展使得智能代理能够利用多种外部工具来解决复杂的现实世界问题。然而,随着代理越来越依赖多种工具,它们面临着新的挑战:来自不同来源的扩展上下文和嘈杂或无关的工具输出可能会破坏系统可靠性和准确性。这些挑战强调了提高基于代理的系统的稳定性的必要性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了动态监督和操作机制,在AWorld框架内构建了一个稳健且动态的多代理系统(MAS)架构。在我们的方法中,执行代理会在关键步骤调用守卫代理来验证和纠正推理过程,有效地减少了由噪声引起的错误,并增强了解决问题的稳健性。在GAIA测试数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的动态操作机制显著提高了解决方案的有效性和稳定性,优于单代理系统(SAS)和标准工具增强系统。因此,我们的动态MAS系统在著名的GAIA排行榜上获得了开源项目第一名。这些发现强调了协作代理角色在开发更可靠和可信的智能系统中的实际价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展使得智能代理能够利用多种外部工具解决复杂的现实世界问题。然而,随着代理越来越多地依赖多种工具,他们面临新的挑战:来自不同来源的扩展上下文和嘈杂或无关的工具输出会破坏系统可靠性和准确性。为解决这一问题,我们引入了动态监督机制和操控机制,在AWorld框架内构建了一个稳健且动态的多代理系统(MAS)架构。通过执行代理在关键步骤中调用防护代理进行验证和校正推理过程,我们有效地减少了由噪声引起的错误,增强了解决问题的稳健性。在GAIA测试数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的动态操控机制显著提高了解决方案的有效性和稳定性,优于单代理系统(SAS)和标准工具增强系统。因此,我们的动态MAS系统在著名的GAIA排行榜上获得了开源项目第一名。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)赋能智能代理利用多样外部工具解决复杂问题。
- 智能代理在依赖多工具时面临上下文扩展和工具输出噪声的挑战。
- 需要增强代理系统的稳定性以应对这些挑战。
- 引入动态监督机制和操控机制,构建稳健和动态的多代理系统(MAS)架构。
- 执行代理通过调用防护代理验证和校正推理过程,提高系统稳健性。
- 在GAIA测试数据集上的实验表明,动态操控机制提高解决方案的有效性和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

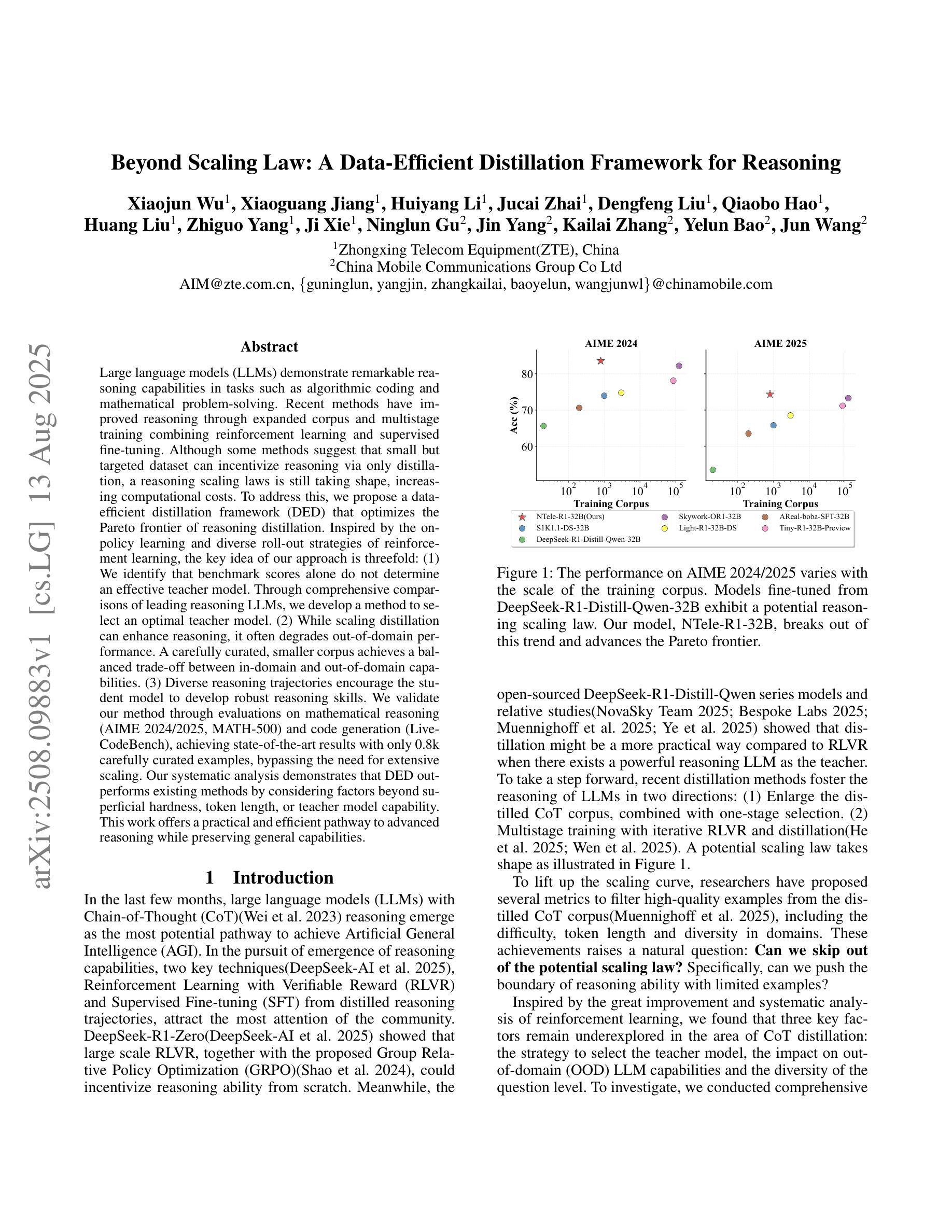
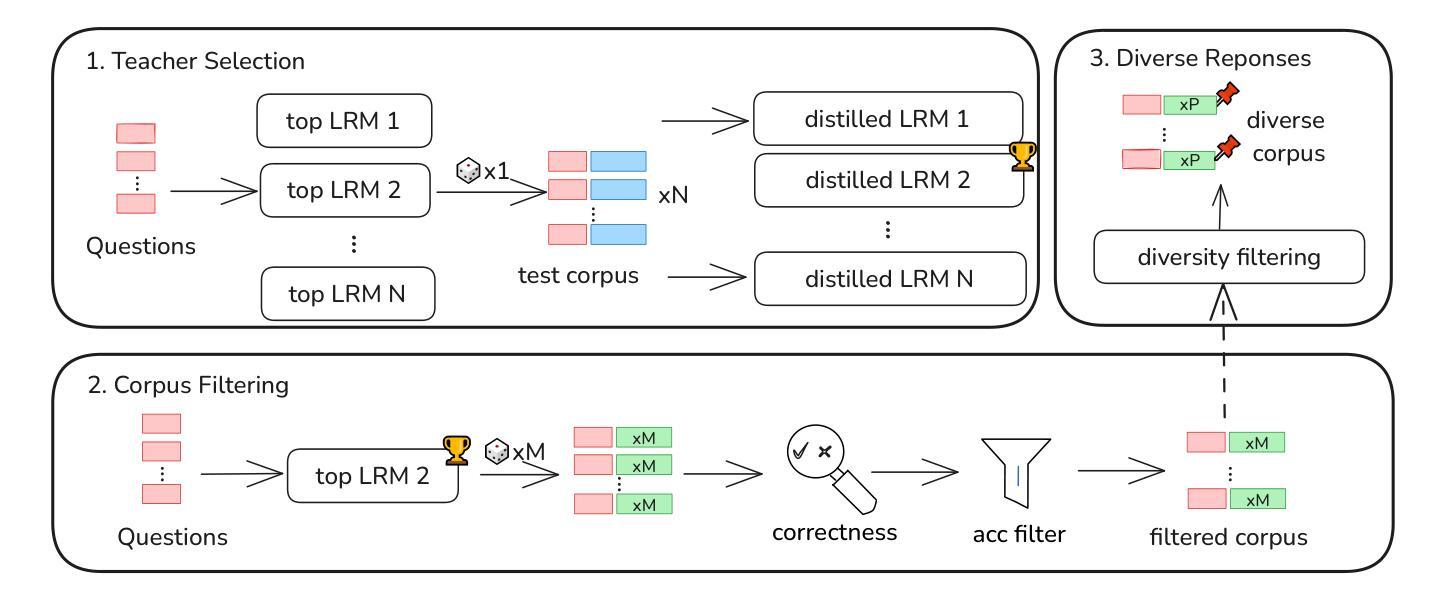
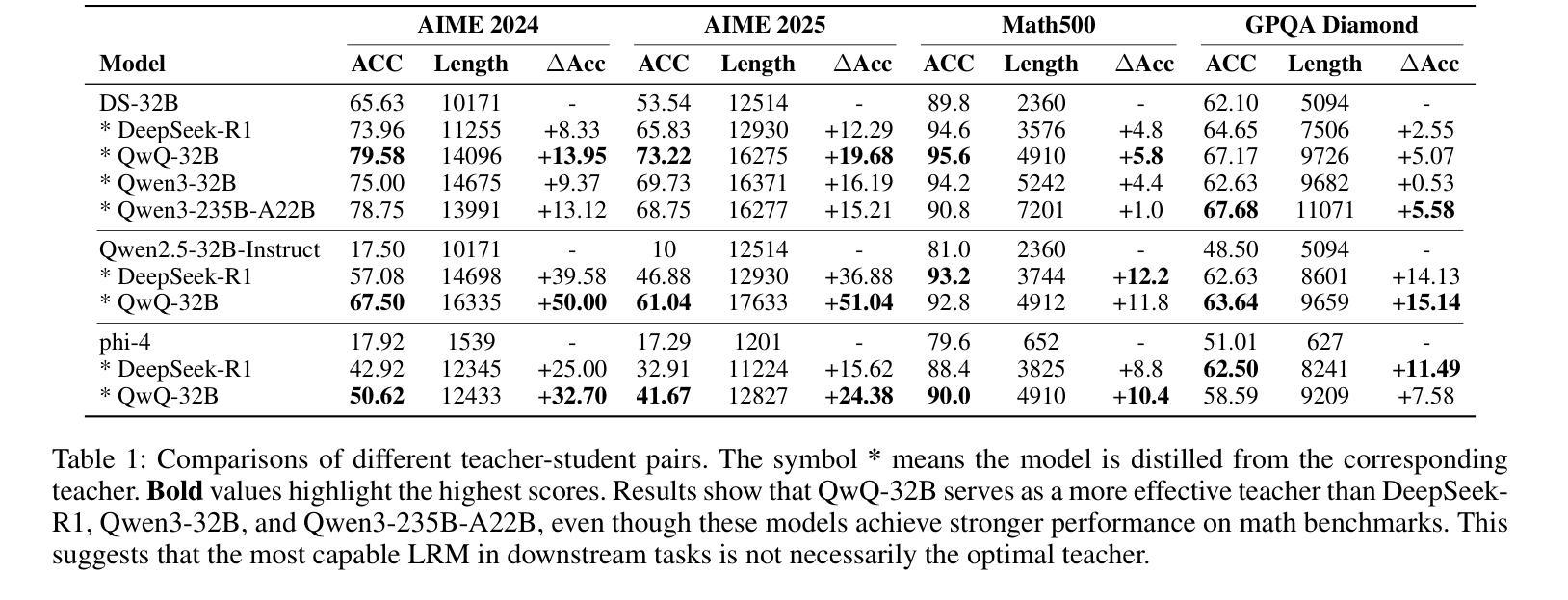
Beyond Scaling Law: A Data-Efficient Distillation Framework for Reasoning
Authors:Xiaojun Wu, Xiaoguang Jiang, Huiyang Li, Jucai Zhai, Dengfeng Liu, Qiaobo Hao, Huang Liu, Zhiguo Yang, Ji Xie, Ninglun Gu, Jin Yang, Kailai Zhang, Yelun Bao, Jun Wang
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable reasoning capabilities in tasks such as algorithmic coding and mathematical problem-solving. Recent methods have improved reasoning through expanded corpus and multistage training combining reinforcement learning and supervised fine-tuning. Although some methods suggest that small but targeted dataset can incentivize reasoning via only distillation, a reasoning scaling laws is still taking shape, increasing computational costs. To address this, we propose a data-efficient distillation framework (DED) that optimizes the Pareto frontier of reasoning distillation. Inspired by the on-policy learning and diverse roll-out strategies of reinforcement learning, the key idea of our approach is threefold: (1) We identify that benchmark scores alone do not determine an effective teacher model. Through comprehensive comparisons of leading reasoning LLMs, we develop a method to select an optimal teacher model. (2) While scaling distillation can enhance reasoning, it often degrades out-of-domain performance. A carefully curated, smaller corpus achieves a balanced trade-off between in-domain and out-of-domain capabilities. (3) Diverse reasoning trajectories encourage the student model to develop robust reasoning skills. We validate our method through evaluations on mathematical reasoning (AIME 2024/2025, MATH-500) and code generation (LiveCodeBench), achieving state-of-the-art results with only 0.8k carefully curated examples, bypassing the need for extensive scaling. Our systematic analysis demonstrates that DED outperforms existing methods by considering factors beyond superficial hardness, token length, or teacher model capability. This work offers a practical and efficient pathway to advanced reasoning while preserving general capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)在算法编码和数学问题解决等任务中展现出卓越的逻辑推理能力。最近的方法通过扩大语料库和结合强化学习与监督微调的多阶段训练来改善推理能力。尽管一些方法认为,小规模但有针对性的数据集可以通过仅通过蒸馏来激励推理,但推理规模法则仍在形成中,增加了计算成本。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一个数据高效蒸馏框架(DED),该框架优化了推理蒸馏的帕累托边界。我们的方法受到强化学习的基于策略的学习和多样化滚动策略启发,其关键思想包括三个方面:(1)我们发现仅通过基准分数并不能确定有效的教师模型。通过对领先的推理型LLM的全面比较,我们开发了一种选择最佳教师模型的方法。(2)虽然扩大蒸馏规模可以增强推理能力,但它往往会降低域外性能。一个精心挑选的小型语料库能够在域内和域外能力之间实现平衡。(3)多样化的推理轨迹鼓励学生模型发展稳健的推理技能。我们通过在数学推理(AIME 2024/2025,MATH-500)和代码生成(LiveCodeBench)方面的评估验证了我们的方法,仅使用0.8k个精心挑选的例子即可实现最新技术成果,无需大规模扩展。我们的系统分析表明,DED在考虑到超越表面难度、令牌长度或教师模型能力等因素时,其表现优于现有方法。这项工作提供了一个实用且高效的途径来实现高级推理,同时保留了一般能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在算法编码和数学问题解决等任务中展现出卓越的推理能力。通过扩大语料库和多阶段训练结合强化学习与监督微调的方法,提高了模型的推理能力。为解决推理规模法则带来的计算成本增加问题,提出了一种数据高效蒸馏框架(DED),优化了推理蒸馏的帕累托边界。该框架受到强化学习的策略启发,通过选择最佳教师模型、平衡语料库大小以及多样化推理轨迹,实现了在数学推理和代码生成任务上的最新成果,仅使用精心挑选的0.8k示例,无需大规模扩展。系统分析表明,DED在超越表面难度、令牌长度或教师模型能力等因素的情况下,表现出优于现有方法的性能。本研究提供了一个实用且高效的实现高级推理的途径,同时保留了通用能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型展现出强大的推理能力,特别是在算法编码和数学问题解决方面。
- 扩大语料库和多阶段训练结合强化学习和监督微调有助于提高模型的推理能力。
- 提出了数据高效蒸馏框架(DED)来解决计算成本增加的问题,优化推理蒸馏的帕累托边界。
- DED框架通过选择最佳教师模型、平衡语料库大小和多样化推理轨迹来实现优异性能。
- 在数学推理和代码生成任务上取得了最新成果,仅使用少量的精心挑选的示例。
- 系统分析表明,DED在多个因素中表现出优于现有方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图
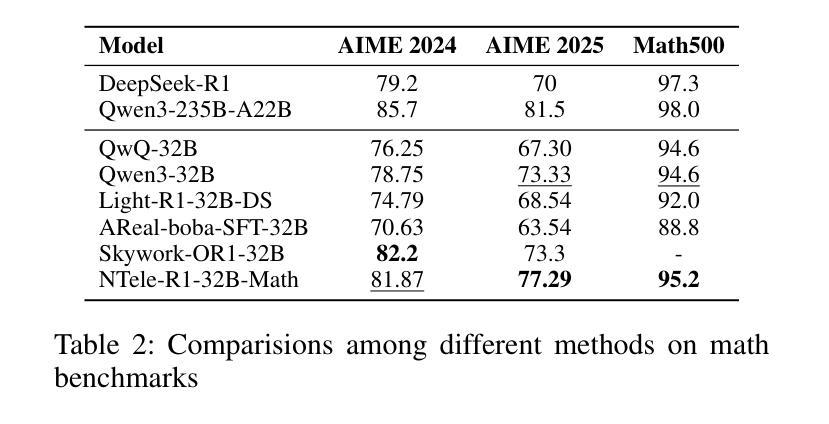
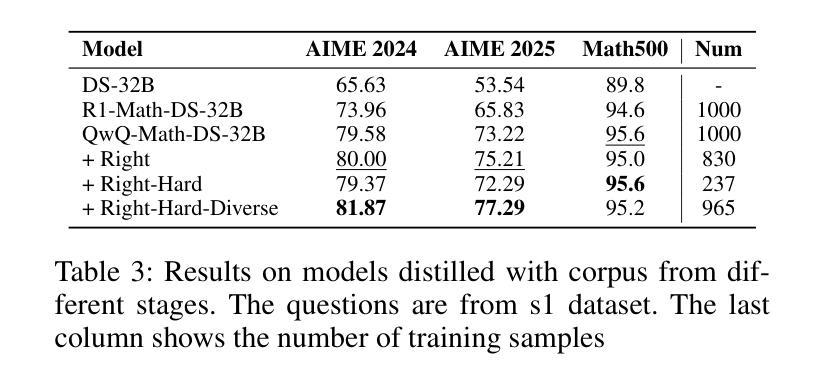
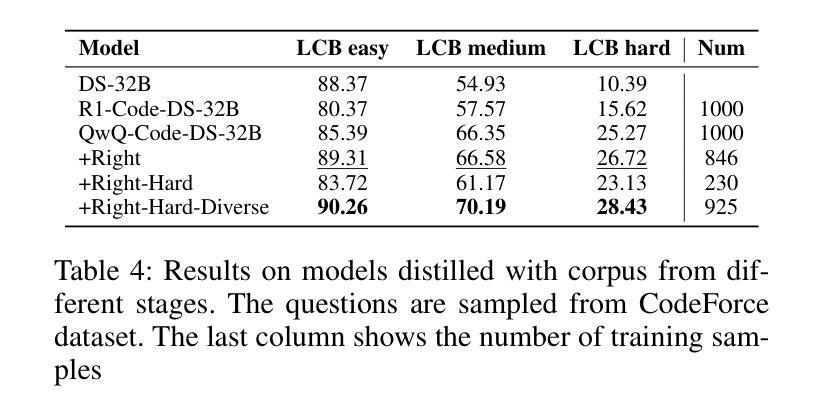
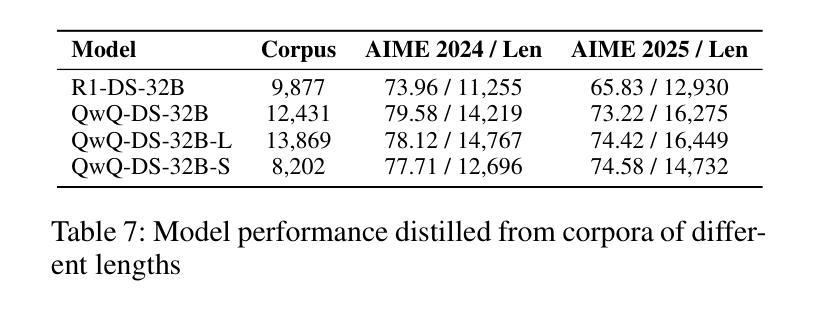
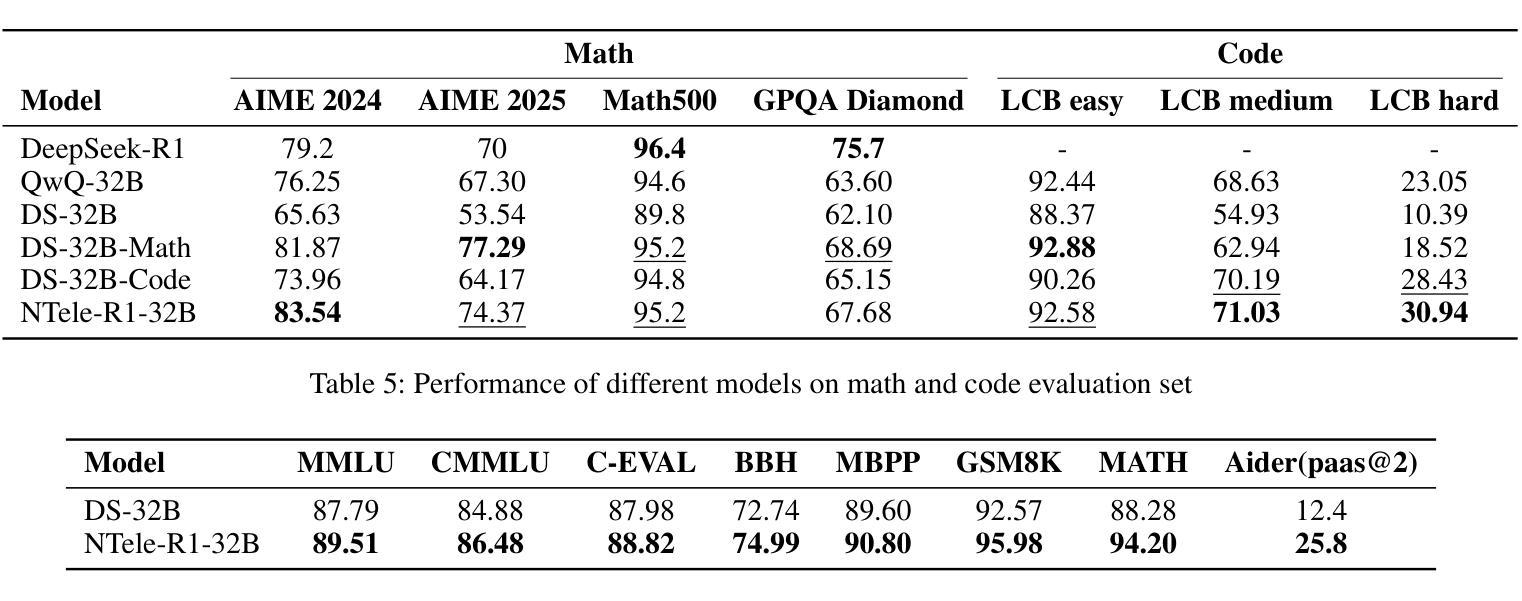
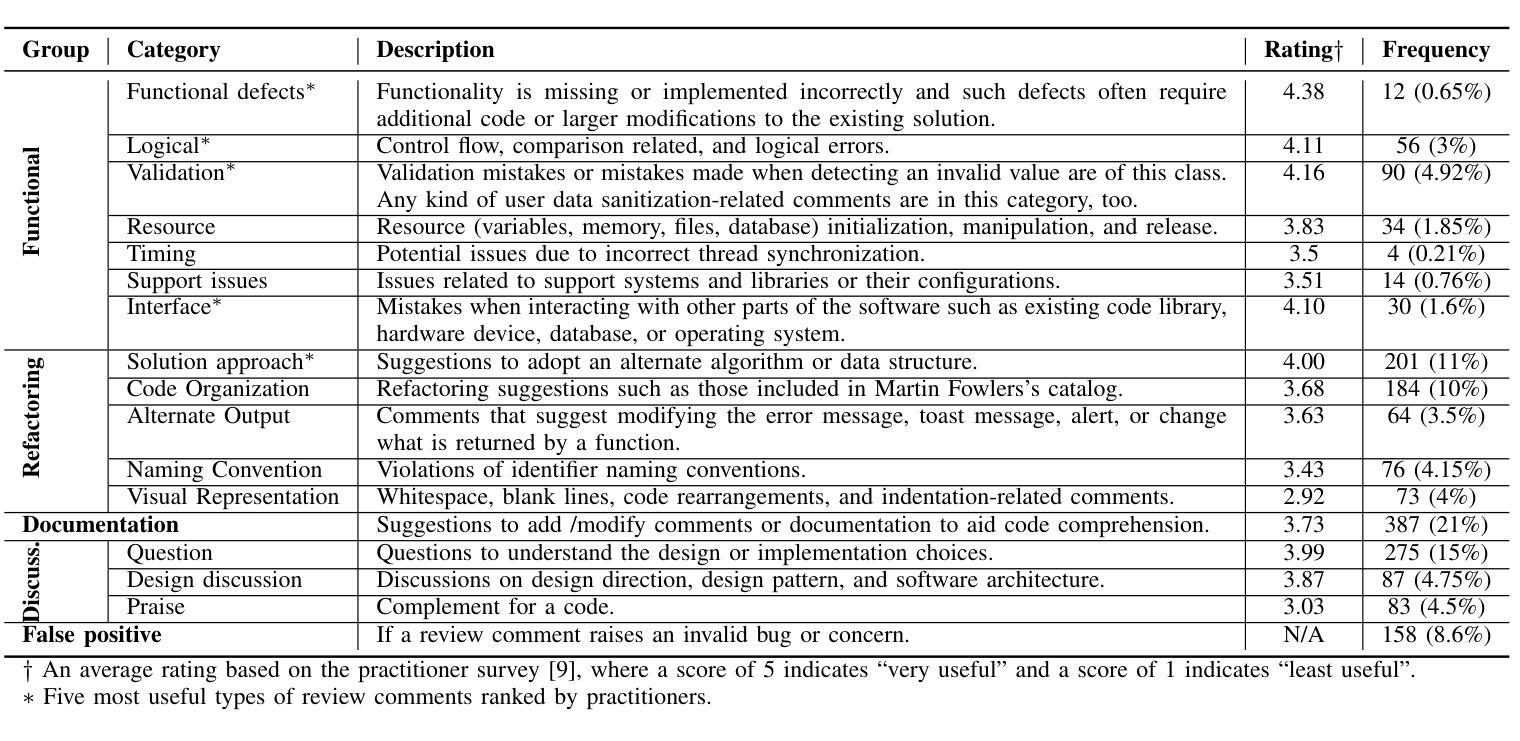
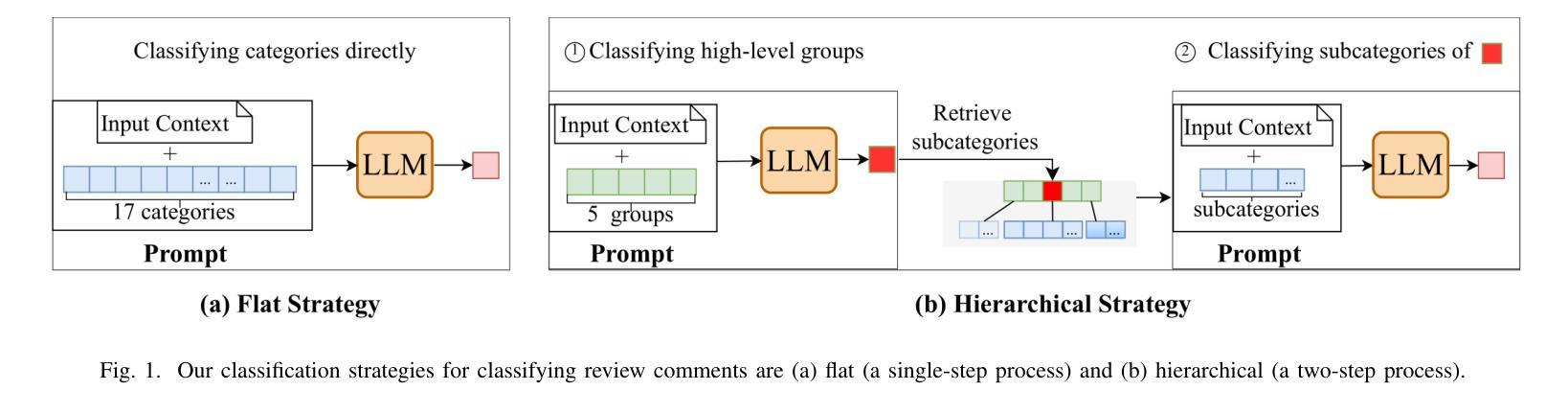
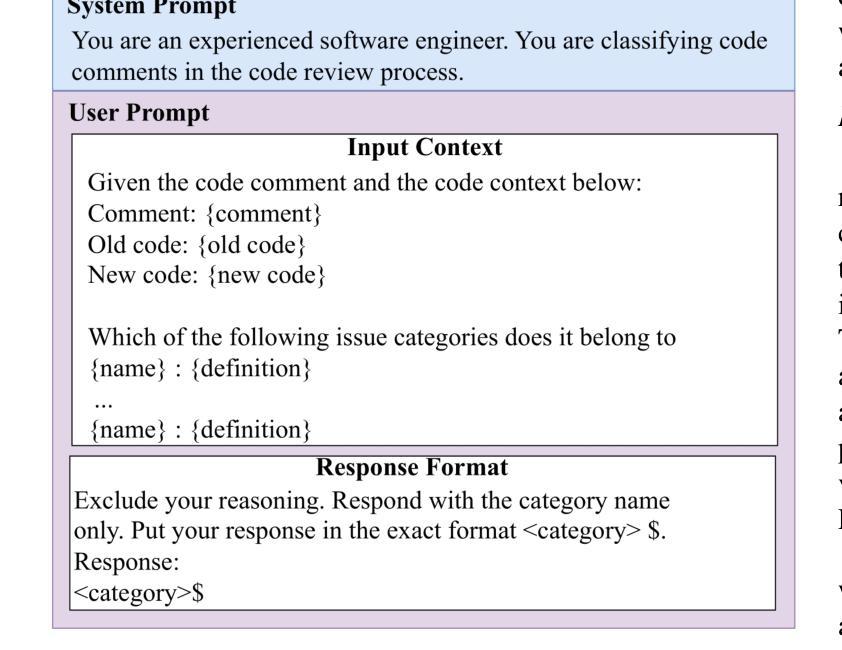
Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models in Fine-Grained Review Comment Classification
Authors:Linh Nguyen, Chunhua Liu, Hong Yi Lin, Patanamon Thongtanunam
Code review is a crucial practice in software development. As code review nowadays is lightweight, various issues can be identified, and sometimes, they can be trivial. Research has investigated automated approaches to classify review comments to gauge the effectiveness of code reviews. However, previous studies have primarily relied on supervised machine learning, which requires extensive manual annotation to train the models effectively. To address this limitation, we explore the potential of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to classify code review comments. We assess the performance of LLMs to classify 17 categories of code review comments. Our results show that LLMs can classify code review comments, outperforming the state-of-the-art approach using a trained deep learning model. In particular, LLMs achieve better accuracy in classifying the five most useful categories, which the state-of-the-art approach struggles with due to low training examples. Rather than relying solely on a specific small training data distribution, our results show that LLMs provide balanced performance across high- and low-frequency categories. These results suggest that the LLMs could offer a scalable solution for code review analytics to improve the effectiveness of the code review process.
代码审查是软件开发中的一项重要实践。由于现在的代码审查较为轻便,可以识别出各种问题,有时这些问题可能微不足道。已有研究探讨了自动分类审查评论的方法,以衡量代码审查的有效性。然而,之前的研究主要依赖于有监督的机器学习,这需要大量的手动注释来有效地训练模型。为了解决这一局限性,我们探索了使用大型语言模型(LLM)对代码审查评论进行分类的潜力。我们评估了LLM对17类代码审查评论进行分类的性能。我们的结果表明,LLM能够分类代码审查评论,并且优于使用训练好的深度学习模型的最先进方法。特别是,LLM在分类五种最有益的类别时达到了更高的准确性,由于训练实例较少,最先进的方法在这些类别上遇到了困难。与仅依赖于特定的少量训练数据分布不同,我们的结果表明,LLM在高频和低频类别之间提供了平衡的性能。这些结果表明,LLM可能为代码审查分析提供可扩展的解决方案,以提高代码审查过程的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2025 IEEE International Conference on Source Code Analysis & Manipulation (SCAM)
Summary
代码审查是软件开发中的重要环节。当前,尽管代码审查变得更为轻量级,仍能通过审查识别多种问题,甚至是一些小问题。之前的研究已尝试用自动化方式对代码审查评论进行分类,以衡量代码审查的有效性。然而,先前的研究主要依赖于监督机器学习,需要大量手动标注来训练模型,这限制了其应用。为解决这一问题,我们探索了使用大型语言模型(LLM)对代码审查评论进行分类的潜力。评估结果显示,LLM能够很好地对代码审查评论进行分类,并优于现有的深度学习模型。特别是,LLM在五个最有用的分类类别中表现更精确。与之前的方法不同,LLM不依赖特定的有限训练数据分布,在高频和低频类别之间提供了均衡的性能表现。这表明LLM可能为代码审查分析提供可扩展的解决方案,以提高代码审查过程的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 代码审查是软件开发的重要环节,可以识别各种问题。
- 之前的研究已经尝试通过自动化分类评估代码审查的有效性。
- 监督机器学习需要大量手动标注,限制了其应用。
- LLM在代码审查评论分类方面具有潜力。
- LLM能够很好地对代码审查评论进行分类,并优于现有的深度学习模型。
- LLM在特定分类类别中表现更精确。
点此查看论文截图

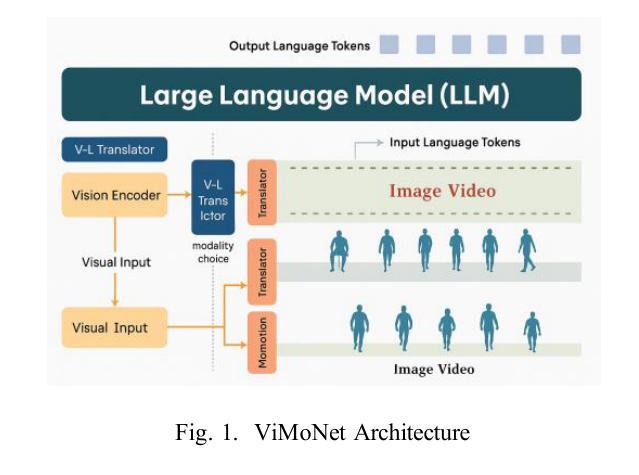
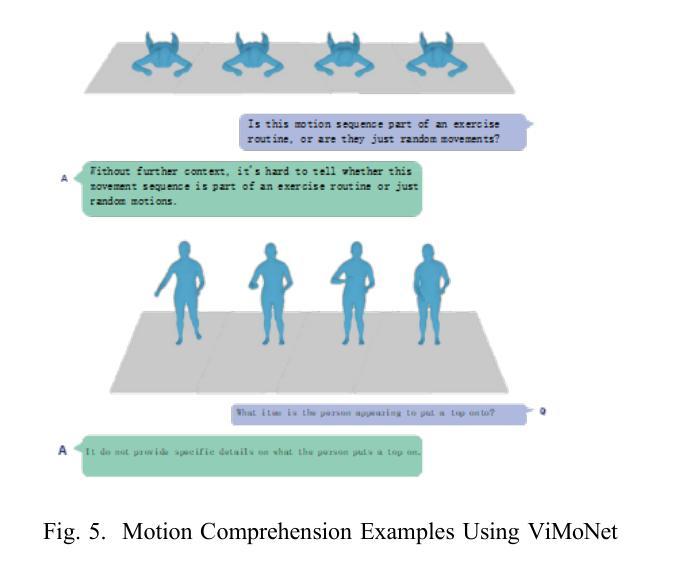
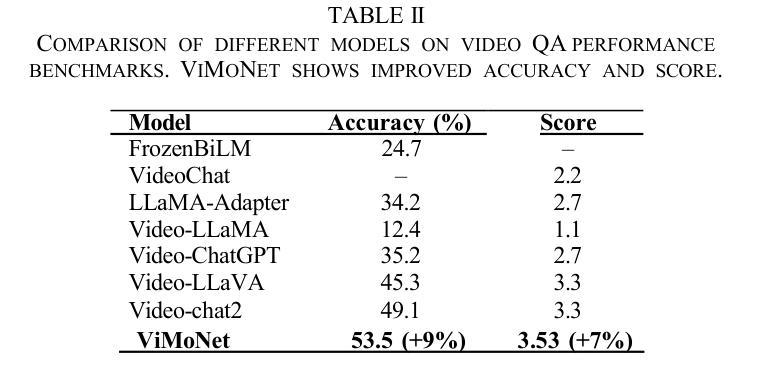
ViMoNet: A Multimodal Vision-Language Framework for Human Behavior Understanding from Motion and Video
Authors:Rajan Das Gupta, Md Yeasin Rahat, Nafiz Fahad, Abir Ahmed, Liew Tze Hui
This study investigates how large language models (LLMs) can be used to understand human behavior using motion and video data. We think that mixing both types is essential to completely capture the nuanced movements and meanings of human actions, in contrast to recent models that simply concentrate on motion data or films. To address this, we provide ViMoNet, a straightforward yet effective framework for comprehending, characterizing, and deducing human action. ViMoNet employs a joint training strategy that leverages the advantages of two data types: detailed motion-text data, which is more exact, and generic video-text data, which is more comprehensive but less detailed. This aids in the model’s acquisition of rich data regarding time and space in human behavior. Additionally, we provide a brand new dataset named VIMOS that contains a variety of films, motion sequences, instructions, and subtitles. We developed ViMoNet-Bench, a standardized benchmark with carefully labeled samples, to evaluate how well models understand human behavior. Our tests show that ViMoNet outperforms existing methods in caption generation, motion understanding, and behavior interpretation.
本研究探讨了如何使用大型语言模型(LLM)通过动作和视频数据来理解人类行为。我们认为,混合两种类型的数据对于完全捕捉人类行为的细微动作和含义至关重要,这与最近仅专注于动作数据或电影的模型形成对比。为了解决这一问题,我们提供了ViMoNet,这是一个简单有效的框架,用于理解、表征和推断人类行为。ViMoNet采用联合训练策略,利用两种数据类型的优势:详细的动作文本数据,更准确;通用的视频文本数据,更全面但不太详细。这有助于模型获得有关人类行为的时间和空间的丰富数据。此外,我们还提供了一个全新的数据集VIMOS,其中包含各种电影、运动序列、指令和字幕。为了评估模型对人类行为的了解程度,我们开发了标准化基准测试ViMoNet-Bench,其中包含精心标记的样本。我们的测试表明,在生成描述、动作理解和行为解释方面,ViMoNet的表现优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCVDM ‘25
摘要
本研究探讨了如何使用大型语言模型(LLM)通过动作和视频数据理解人类行为。本研究认为混合两种类型的数据对于完全捕捉人类动作的细微动作和含义至关重要,与最近仅专注于动作数据或电影的模型形成对比。为解决这一问题,我们提供了ViMoNet,这是一个简单有效的框架,用于理解、表征和推断人类行为。ViMoNet采用联合训练策略,利用两种数据类型的优势:详细的运动文本数据,更精确;通用的视频文本数据,更全面但不太详细。这有助于模型获取有关人类行为的时间和空间的丰富数据。此外,我们还推出了名为VIMOS的新数据集,包含各种电影、运动序列、指令和字幕。我们开发了ViMoNet-Bench标准化基准测试,带有精心标注的样本,以评估模型对人类行为的了解程度。测试表明,ViMoNet在生成字幕、理解运动和解释行为方面优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 本研究探讨大型语言模型(LLM)在理解人类行为方面的应用,通过动作和视频数据的结合来提高模型的性能。
- 混合动作和视频数据对于完全捕捉人类动作的细微动作和含义至关重要。
- 推出新的框架ViMoNet,用于理解、表征和推断人类行为,采用联合训练策略结合两种数据类型。
- ViMoNet在字幕生成、运动理解和行为解释方面表现出优异的性能。
- 引入新的数据集VIMOS,包含电影、运动序列、指令和字幕等多种数据类型。
- 开发标准化基准测试ViMoNet-Bench,用于评估模型对人类行为的了解程度。
- 本研究为使用LLM理解人类行为提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

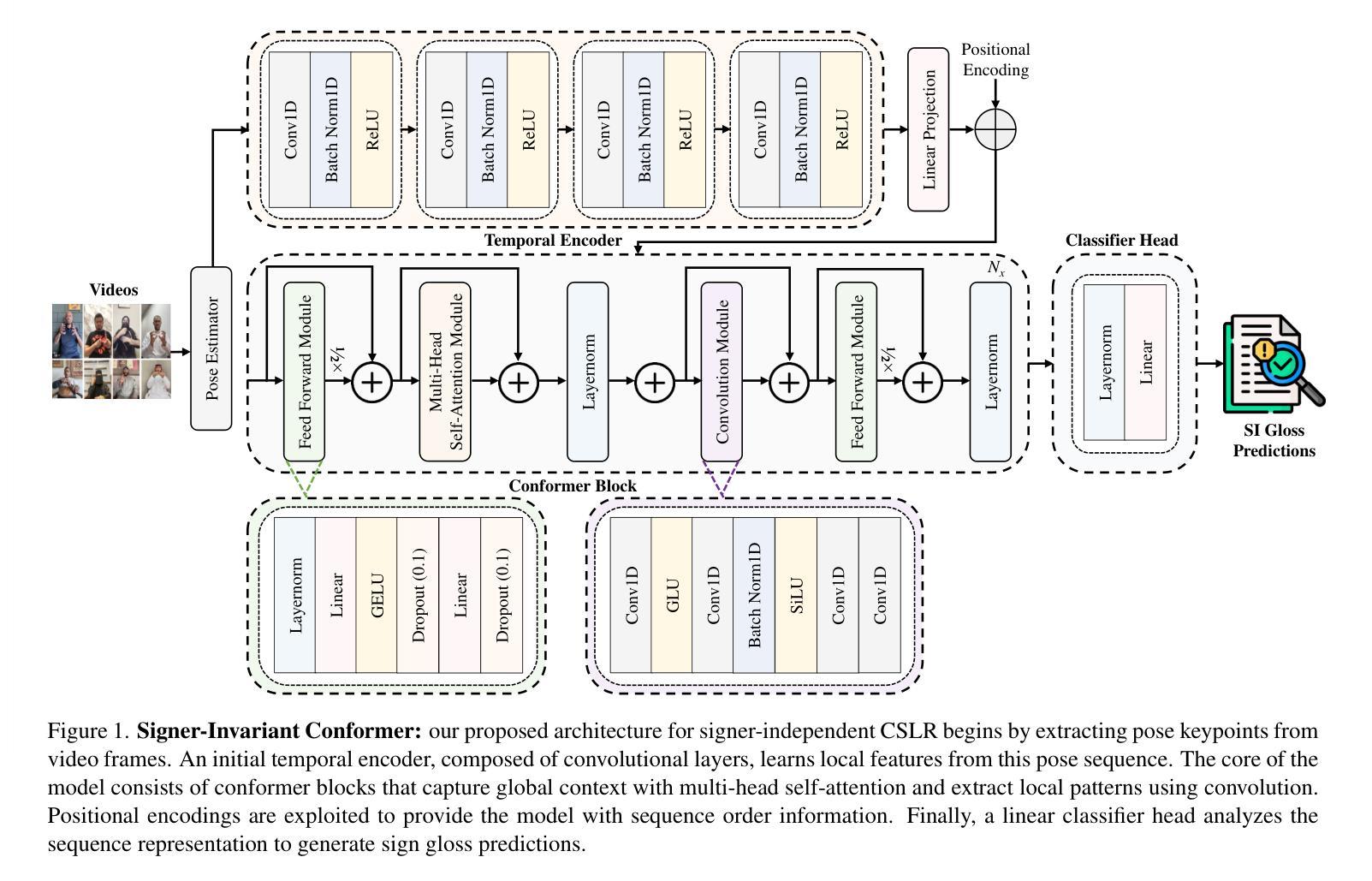
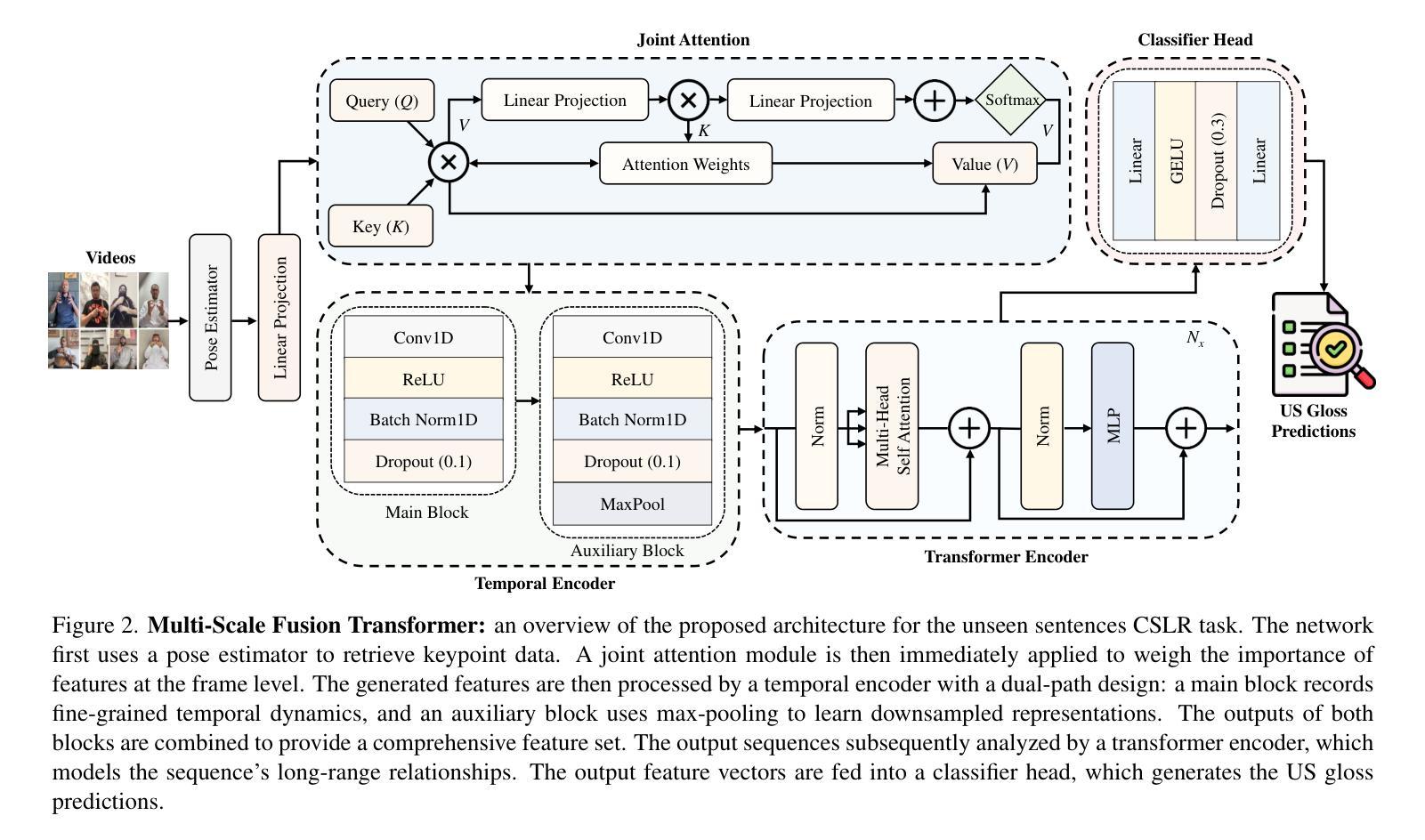
A Signer-Invariant Conformer and Multi-Scale Fusion Transformer for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Authors:Md Rezwanul Haque, Md. Milon Islam, S M Taslim Uddin Raju, Fakhri Karray
Continuous Sign Language Recognition (CSLR) faces multiple challenges, including significant inter-signer variability and poor generalization to novel sentence structures. Traditional solutions frequently fail to handle these issues efficiently. For overcoming these constraints, we propose a dual-architecture framework. For the Signer-Independent (SI) challenge, we propose a Signer-Invariant Conformer that combines convolutions with multi-head self-attention to learn robust, signer-agnostic representations from pose-based skeletal keypoints. For the Unseen-Sentences (US) task, we designed a Multi-Scale Fusion Transformer with a novel dual-path temporal encoder that captures both fine-grained posture dynamics, enabling the model’s ability to comprehend novel grammatical compositions. Experiments on the challenging Isharah-1000 dataset establish a new standard for both CSLR benchmarks. The proposed conformer architecture achieves a Word Error Rate (WER) of 13.07% on the SI challenge, a reduction of 13.53% from the state-of-the-art. On the US task, the transformer model scores a WER of 47.78%, surpassing previous work. In the SignEval 2025 CSLR challenge, our team placed 2nd in the US task and 4th in the SI task, demonstrating the performance of these models. The findings validate our key hypothesis: that developing task-specific networks designed for the particular challenges of CSLR leads to considerable performance improvements and establishes a new baseline for further research. The source code is available at: https://github.com/rezwanh001/MSLR-Pose86K-CSLR-Isharah.
连续手语识别(CSLR)面临多重挑战,包括手语者之间的显著差异以及对手语新句子结构的泛化能力较差的问题。传统解决方案往往无法有效地处理这些问题。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了一种双架构框架。针对手语者独立(SI)挑战,我们提出了一种手语不变卷积(Signer-Invariant Conformer),它将卷积与多头自注意力相结合,从基于姿态的骨骼关键点学习稳健的、对手语者无关的表示。对于未见句子(US)任务,我们设计了一种多尺度融合变换器,具有新颖的双通道时序编码器,能够捕捉精细的姿态动态变化,从而使模型具备理解新手语语法组合的能力。在具有挑战性的Isharah-1000数据集上的实验为CSLR基准测试建立了新的标准。所提出的手语不变卷积架构在手语者独立挑战上的单词错误率(WER)达到了13.07%,比现有技术降低了13.53%。在未见句子任务中,变换模型的WER为47.78%,超过了之前的工作。在SignEval 2025 CSLR挑战中,我们的团队在未见句子任务中排名第2,在手语者独立任务中排名第4,证明了这些模型的性能。研究结果验证了我们的核心假设:针对CSLR的特定挑战开发的任务特定网络会导致显著的性能改进,并为进一步的研究提供了新的基准。源代码可在:https://github.com/rezwanh001/MSLR-Pose86K-CSLR-Isharah获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA. 1st MSLR Workshop 2025
摘要
本文介绍了针对连续手语识别(CSLR)面临的挑战,包括不同签名者之间的差异以及对手语新句子结构的泛化能力较差的问题。传统的解决方案往往无法有效地处理这些问题。为了克服这些限制,本文提出了一种双架构框架。针对签名者独立(SI)挑战,提出了签名者无关卷积模块,结合了卷积和多头自注意力机制,从基于姿态的骨骼关键点学习稳健的签名者无关表示。对于未见句子(US)任务,设计了一种多尺度融合转换器,具有新型双路径临时编码器,能够捕捉精细姿态动态,使模型能够理解新的语法组合。在具有挑战性的Isharah-1000数据集上的实验为CSLR基准测试建立了新标准。拟议的卷积模型在SI挑战上的单词错误率(WER)为13.07%,比现有技术降低了13.53%。在US任务上,transformer模型的WER得分为47.78%,超过了以前的工作。在SignEval 2025 CSLR挑战中,我们的团队在US任务中获得了第二名,在SI任务中获得了第四名,证明了这些模型的性能。研究结果验证了我们的关键假设:针对CSLR的特定挑战开发的任务特定网络会导致显著的性能改进,并为进一步研究奠定了新基准。源代码可用:https://github.com/rezwanh001/MSLR-Pose86K-CSLR-Isharah。
要点
- 介绍了连续手语识别(CSLR)面临的挑战,包括签名者之间的差异和对手语新句子结构的泛化问题。
- 提出了一种双架构框架来解决这些问题,包括针对签名者独立的卷积模块和针对未见句子的多尺度融合转换器。
- 在Isharah-1000数据集上的实验结果表明,新提出的架构在单词错误率(WER)上取得了显著改进。
- 在SignEval 2025 CSLR挑战中取得了良好成绩,验证了模型性能。
- 研究结果支持开发任务特定网络以提高CSLR性能的观点。
- 提供了源代码链接以供进一步研究和参考。
点此查看论文截图

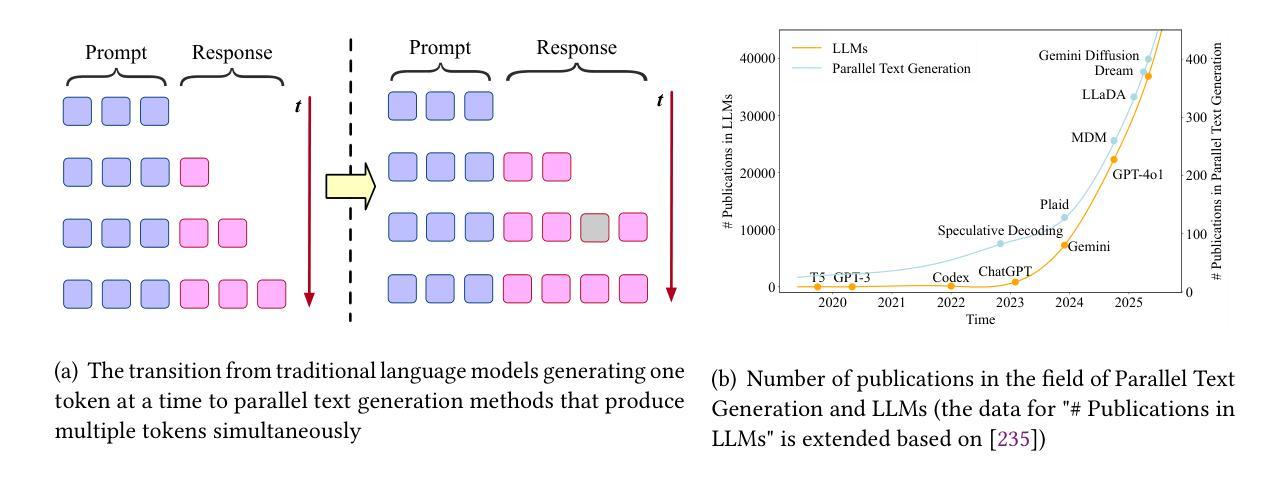
A Survey on Parallel Text Generation: From Parallel Decoding to Diffusion Language Models
Authors:Lingzhe Zhang, Liancheng Fang, Chiming Duan, Minghua He, Leyi Pan, Pei Xiao, Shiyu Huang, Yunpeng Zhai, Xuming Hu, Philip S. Yu, Aiwei Liu
As text generation has become a core capability of modern Large Language Models (LLMs), it underpins a wide range of downstream applications. However, most existing LLMs rely on autoregressive (AR) generation, producing one token at a time based on previously generated context-resulting in limited generation speed due to the inherently sequential nature of the process. To address this challenge, an increasing number of researchers have begun exploring parallel text generation-a broad class of techniques aimed at breaking the token-by-token generation bottleneck and improving inference efficiency. Despite growing interest, there remains a lack of comprehensive analysis on what specific techniques constitute parallel text generation and how they improve inference performance. To bridge this gap, we present a systematic survey of parallel text generation methods. We categorize existing approaches into AR-based and Non-AR-based paradigms, and provide a detailed examination of the core techniques within each category. Following this taxonomy, we assess their theoretical trade-offs in terms of speed, quality, and efficiency, and examine their potential for combination and comparison with alternative acceleration strategies. Finally, based on our findings, we highlight recent advancements, identify open challenges, and outline promising directions for future research in parallel text generation. We have also created a GitHub repository for indexing relevant papers and open resources available at https://github.com/zhanglingzhe0820/Awesome-Parallel-Text-Generation.
随着文本生成已成为现代大型语言模型(LLM)的核心能力,它为一系列下游应用提供了支持。然而,大多数现有的LLM依赖于自回归(AR)生成,即基于先前生成的上下文一个接一个地生成令牌,这导致生成速度因过程的固有顺序性而受到限制。为了应对这一挑战,越来越多的研究人员开始探索并行文本生成技术——一类旨在打破逐个令牌生成的瓶颈并提高推理效率的技术。尽管兴趣日益增长,但对于构成并行文本生成的具体技术以及如何提高推理性能的问题,仍缺乏全面的分析。为了填补这一空白,我们对并行文本生成方法进行了系统调查。我们将现有方法分类为基于AR和非AR的方法,并详细分析了每一类别中的核心技术。根据这种分类法,我们从速度、质量和效率方面评估了它们的理论权衡,并考察了它们与其他加速策略的潜在组合和比较。最后,基于我们的研究结果,我们强调了最近的进展,确定了开放挑战,并概述了未来并行文本生成研究的希望方向。我们还创建了一个GitHub仓库来索引相关论文和开放资源:https://github.com/zhanglingzhe0820/Awesome-Parallel-Text-Generation。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代大型语言模型(LLM)的核心能力是文本生成,这支持了许多下游应用。但大多数LLM依赖于自回归(AR)生成,这导致生成速度有限。为解决这个问题,越来越多的研究者开始探索并行文本生成技术,以提高推理效率。本文全面概述了并行文本生成方法,将其分为AR和非AR两类,并详细分析了每种方法的核心技术。评估了它们在速度、质量和效率方面的理论权衡,并探讨了与其他加速策略的潜在组合和比较。基于研究结果,本文强调了最新进展、识别了开放挑战,并概述了并行文本生成的未来研究方向。相关论文和开放资源可访问GitHub仓库:https://github.com/zhanglingzhe0
020/Awesome-Parallel-Text-Generation。
Key Takeaways
- 现代LLM的核心能力是文本生成,广泛应用于多种下游应用。
- 大多数LLM采用自回归(AR)生成,存在生成速度限制。
- 平行文本生成技术旨在打破逐个令牌的生成瓶颈,提高推理效率。
- 本文对并行文本生成方法进行了系统调查,包括AR和非AR两种类型的技术分析。
- 在速度、质量和效率方面进行了理论权衡,并探讨了与其他加速策略的比较和组合潜力。
- 总结了最新进展,指出了开放挑战,概述了未来研究方向。
点此查看论文截图

Block: Balancing Load in LLM Serving with Context, Knowledge and Predictive Scheduling
Authors:Wei Da, Evangelia Kalyvianaki
This paper presents Block, a distributed scheduling framework designed to optimize load balancing and auto-provisioning across instances in large language model serving frameworks by leveraging contextual information from incoming requests. Unlike popular model serving systems that rely on monolithic and heuristic task schedulers, Block operates as a fully distributed, stateless, and predictive scheduling system to achieve low overhead, reliability, and scalability. It leverages the deterministic and predictable characteristics of LLM inferences, such as host configurations, response lengths, and hardware performance, to make scheduling decisions based on accurately predicted metrics. Evaluation on a 12 GPUs cluster shows that Block significantly outperforms heuristic schedulers, boosting serving capacity by up to 16.7% and reducing P99 tail latency by up to 49.5%. These performance gains remain consistent across diverse models, workloads and configurations. Code and data are open-sourced.
本文介绍了Block,这是一个分布式调度框架,旨在利用来自传入请求的上文信息,在大规模语言模型服务框架的实例之间优化负载均衡和自动配置。与依赖单一且启发式任务调度器的流行模型服务系统不同,Block作为一个完全分布式、无状态和预测性的调度系统,实现了低开销、可靠性和可扩展性。它利用LLM推断的确定性预测特性,如主机配置、响应长度和硬件性能,基于准确预测的指标做出调度决策。在12 GPU集群上的评估表明,Block显著优于启发式调度器,服务容量提升高达16.7%,P99尾部延迟降低高达49.5%。这些性能提升在不同的模型、工作负载和配置下都保持了一致性。代码和数据都已开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures excluding appendix. V1: Fix some typos and grammar issue
Summary
该论文介绍了Block,一个分布式调度框架,它通过利用来自传入请求的上下文信息,针对大型语言模型服务框架中的实例进行负载平衡和自动配置优化。与传统的依赖单一启发式任务调度器的模型服务系统不同,Block是一个完全分布式、无状态和预测性的调度系统,可实现低开销、可靠性和可扩展性。通过利用LLM推断的确定性,如主机配置、响应长度和硬件性能等准确预测指标来进行调度决策。在包含大型语言模型的场景中表现良好。实验结果表明,Block显著优于启发式调度器,最多可提高服务容量达16.7%,并将P99延迟降低至最高达49.5%。无论模型、工作负载和配置如何变化,性能提升均保持一致。代码和数据均已开源。
Key Takeaways
- Block是一个针对大型语言模型的分布式调度框架,旨在优化负载平衡和自动配置。
- 它采用预测性调度决策,利用传入请求的上下文信息。
- Block相较于传统启发式任务调度器更加分布式、无状态和预测性。
- Block框架能够实现低开销、高可靠性和可扩展性。
- Block框架利用LLM推断的确定性因素进行调度决策,如主机配置、响应长度和硬件性能等。
- 实验结果表明,Block显著提高了服务容量和降低了延迟。
点此查看论文截图

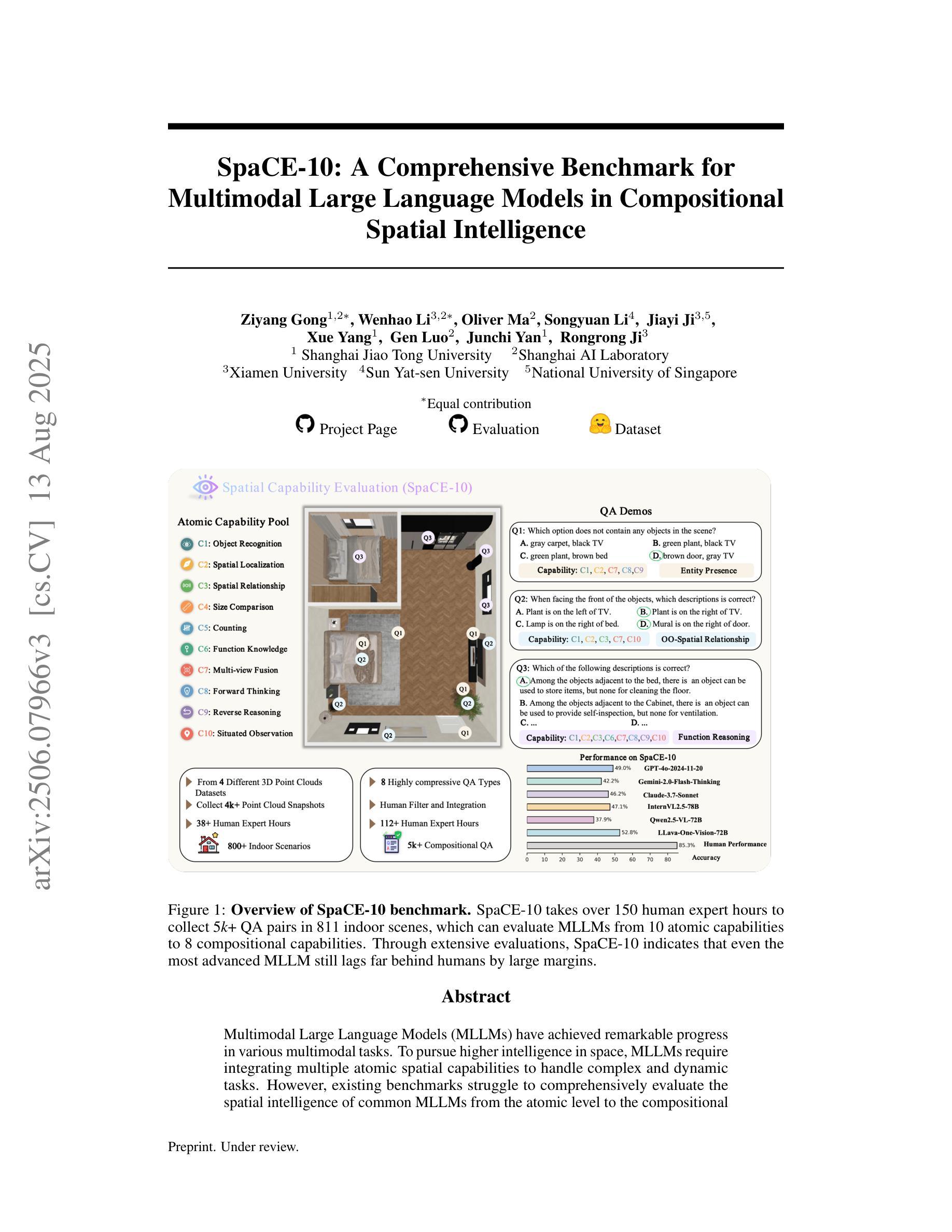
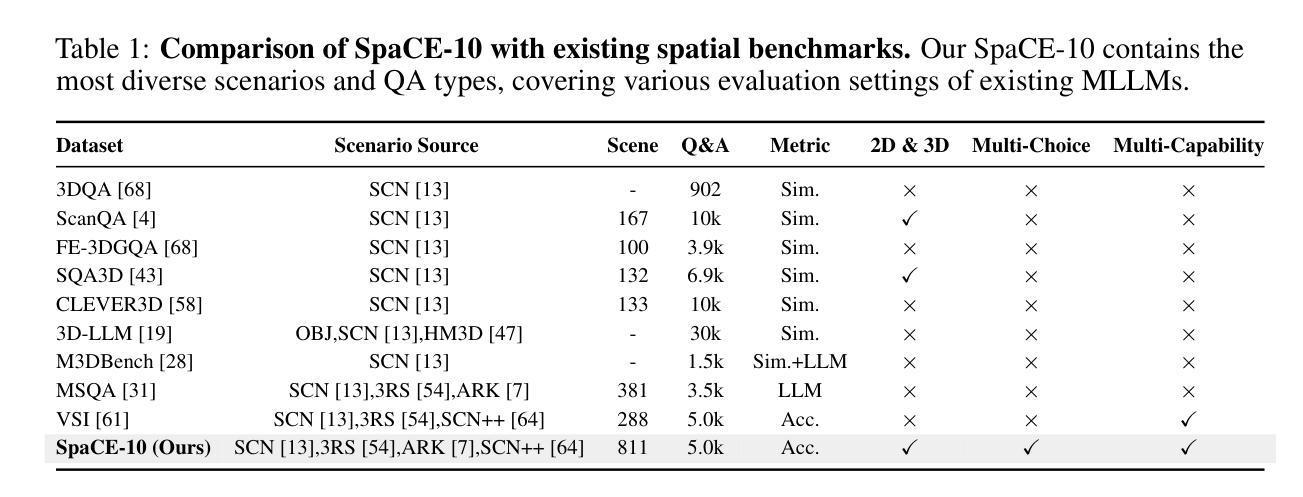
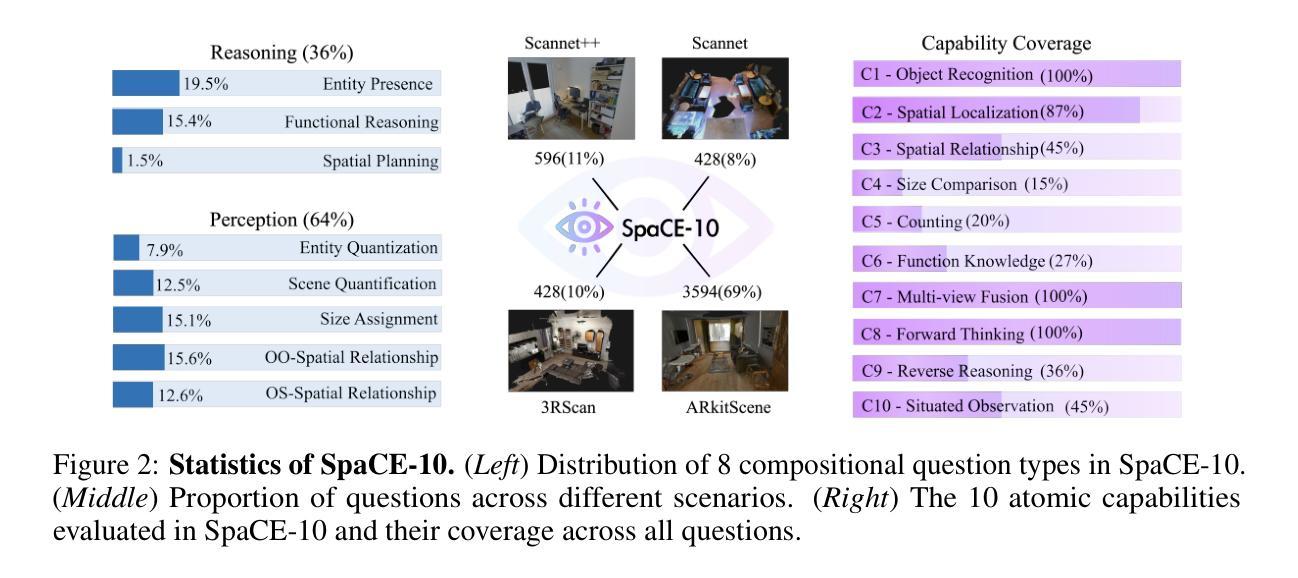
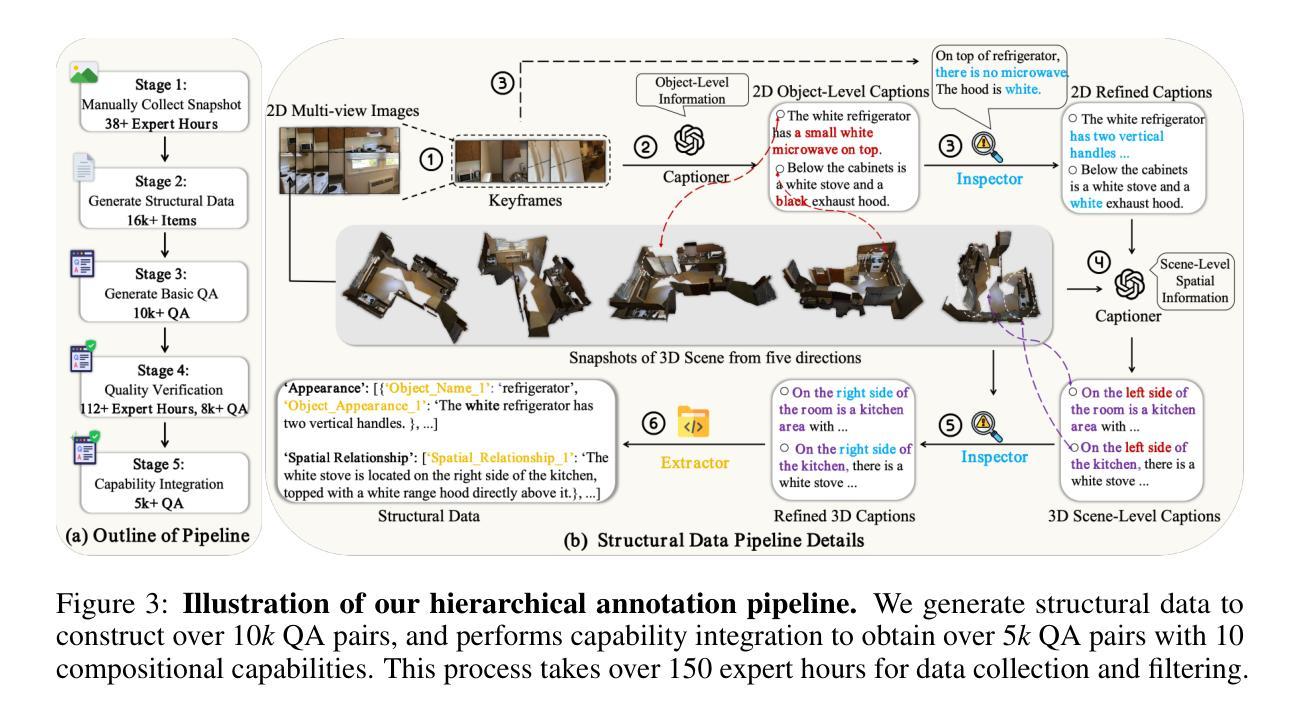
SpaCE-10: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models in Compositional Spatial Intelligence
Authors:Ziyang Gong, Wenhao Li, Oliver Ma, Songyuan Li, Jiayi Ji, Xue Yang, Gen Luo, Junchi Yan, Rongrong Ji
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in various multimodal tasks. To pursue higher intelligence in space, MLLMs require integrating multiple atomic spatial capabilities to handle complex and dynamic tasks. However, existing benchmarks struggle to comprehensively evaluate the spatial intelligence of common MLLMs from the atomic level to the compositional level. To fill this gap, we present SpaCE-10, a comprehensive benchmark for compositional spatial evaluations. In SpaCE-10, we define 10 atomic spatial capabilities, which are combined to form 8 compositional capabilities. Based on these definitions, we propose a novel hierarchical annotation pipeline to generate high-quality and diverse question-answer (QA) pairs. With over 150+ hours of human expert effort, we obtain over 5k QA pairs for 811 real indoor scenes in SpaCE-10, which covers various evaluation settings like point cloud input and multi-choice QA. We conduct an extensive evaluation of common MLLMs on SpaCE-10 and find that even the most advanced MLLM still lags behind humans by large margins. Through our careful study, we also draw several significant findings that benefit the MLLM community. For example, we reveal that the shortcoming of counting capability greatly limits the compositional spatial capabilities of existing MLLMs. The evaluation code and benchmark datasets are available at https://github.com/Cuzyoung/SpaCE-10.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种多模态任务中取得了显著的进步。为了追求更高的空间智能,MLLMs需要整合多种原子空间能力来处理复杂和动态的任务。然而,现有的基准测试在评估常见MLLMs的空间智能方面,从原子级别到组合级别都存在不足。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了SpaCE-10,这是一个用于组合空间评估的综合基准测试。在SpaCE-10中,我们定义了10种原子空间能力,这些能力相结合形成了8种组合能力。基于这些定义,我们提出了一种新型的分层次注释管道,以生成高质量和多样化的问答对。经过超过150小时的人力专家努力,我们在SpaCE-10中获得了超过5000个问答对,涉及811个真实的室内场景,涵盖了各种评估设置,如点云输入和多项选择问答。我们对常见的MLLMs在SpaCE-10上进行了广泛评估,发现即使是最先进的MLLM仍然远远落后于人类。通过我们的深入研究,我们还得出了一些对MLLM社区有益的重大发现。例如,我们揭示出计数能力的不足极大地限制了现有MLLMs的组合空间能力。评估代码和基准测试数据集可在https://github.com/Cuzyoung/SpaCE-10获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MLLMs在多模态任务中取得了显著进展,但缺乏全面的空间智能基准测试来衡量其在原子和组合层面上的能力。为此,研究人员推出了SpaCE-10基准测试,该测试包括定义的空间原子能力和组合能力,以及基于这些定义的新型分层注释管道生成的高质量、多样化的问答对。通过对现有MLLM的评估发现,最先进的技术仍存在较大的缺陷,研究提出了一些有益于MLLM发展的关键见解。对此评估代码和基准数据集可访问特定网站获取。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在多模态任务中展现出显著进步,但仍需提高空间智能能力。
- 当前缺乏一个全面衡量MLLM从原子到组合层面能力的基准测试。
- SpaCE-10是一个用于评估组合空间智能的全面基准测试。
- SpaCE-10定义了空间原子能力和组合能力,并通过新型分层注释管道生成问答对。
- 对现有MLLM在SpaCE-10上的评估发现其仍落后于人类能力水平较大。
- 计数能力的不足严重限制了现有MLLM的组合空间能力。
点此查看论文截图
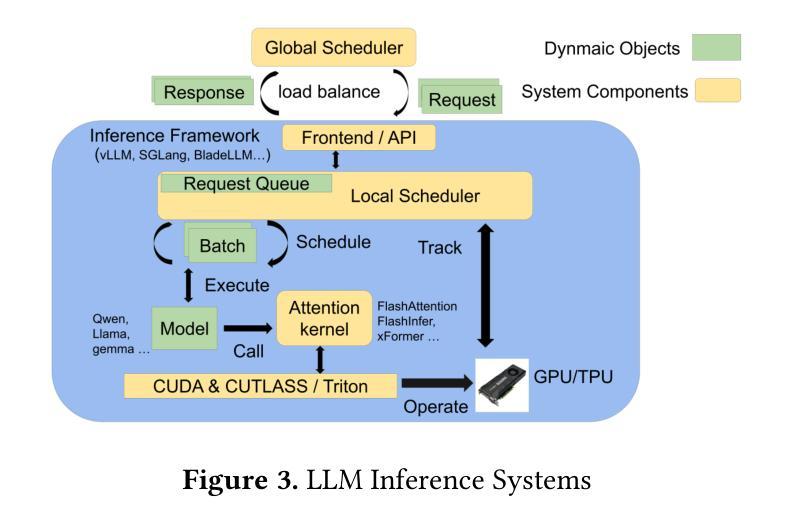
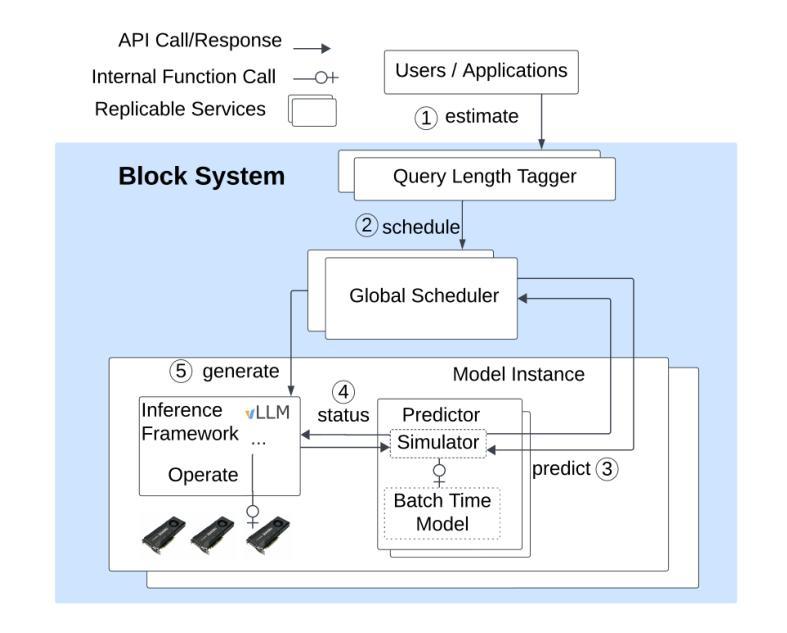
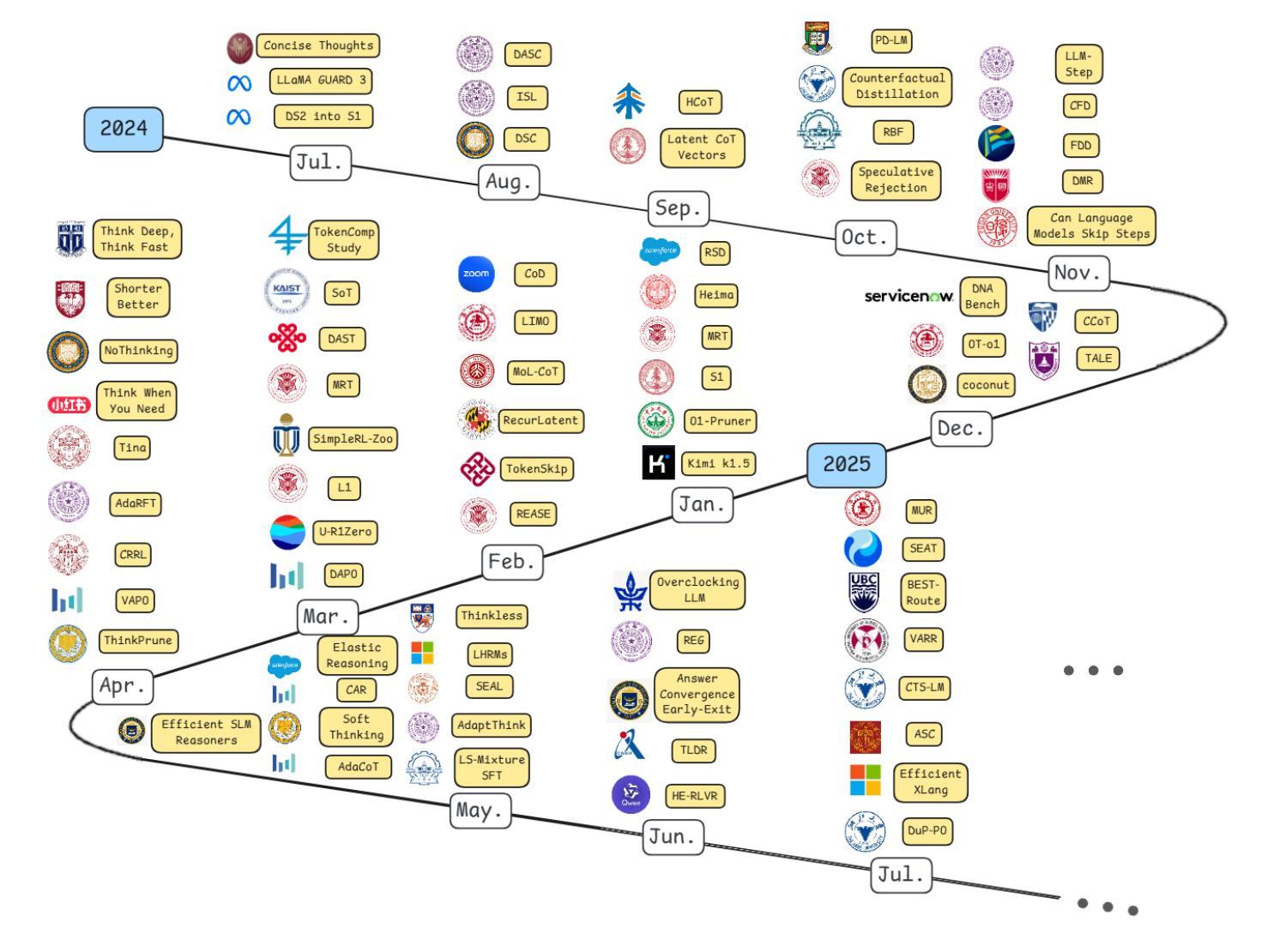
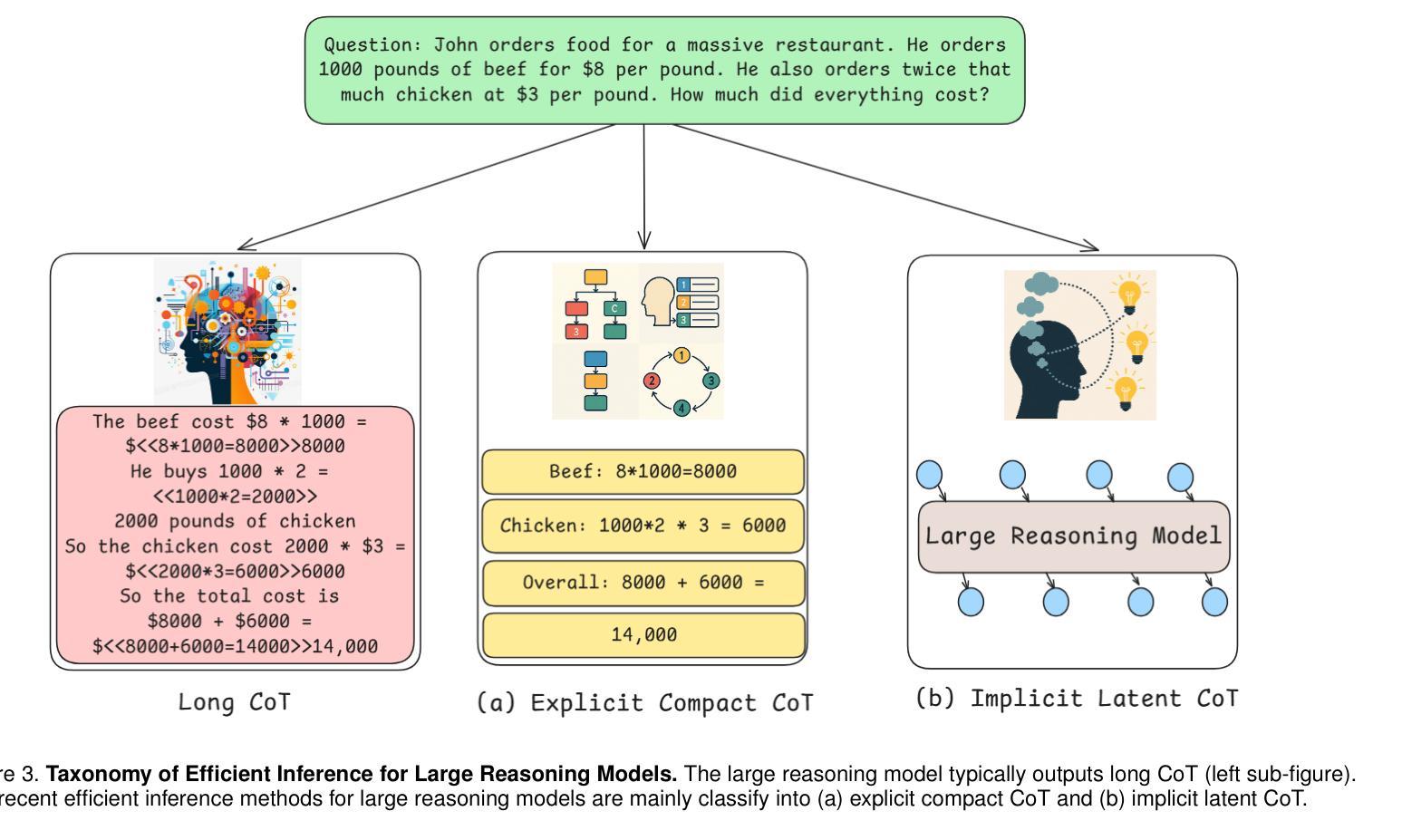
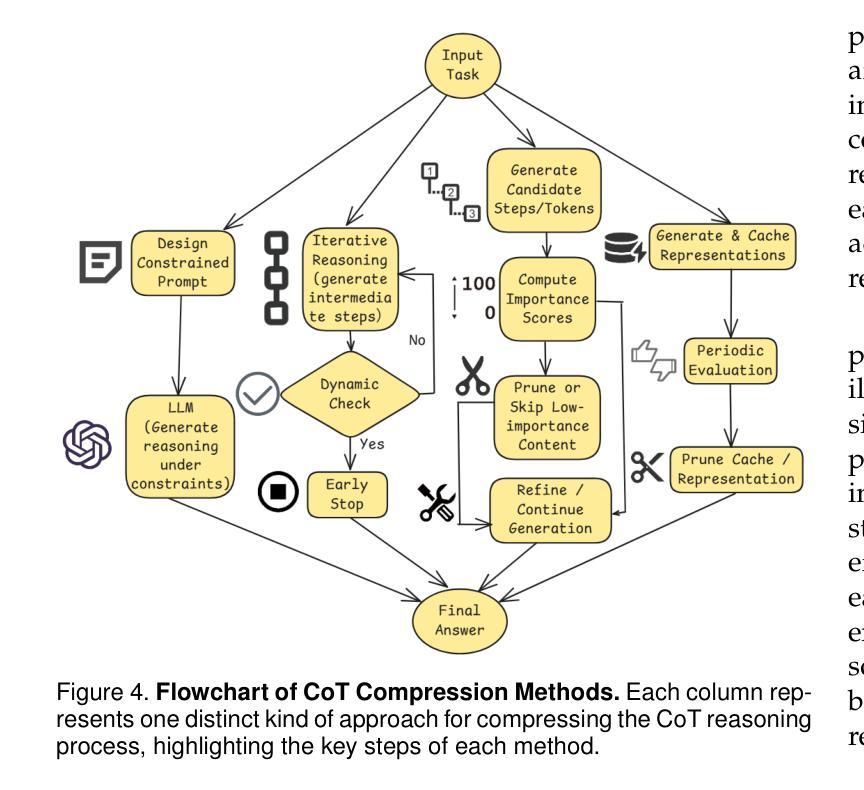
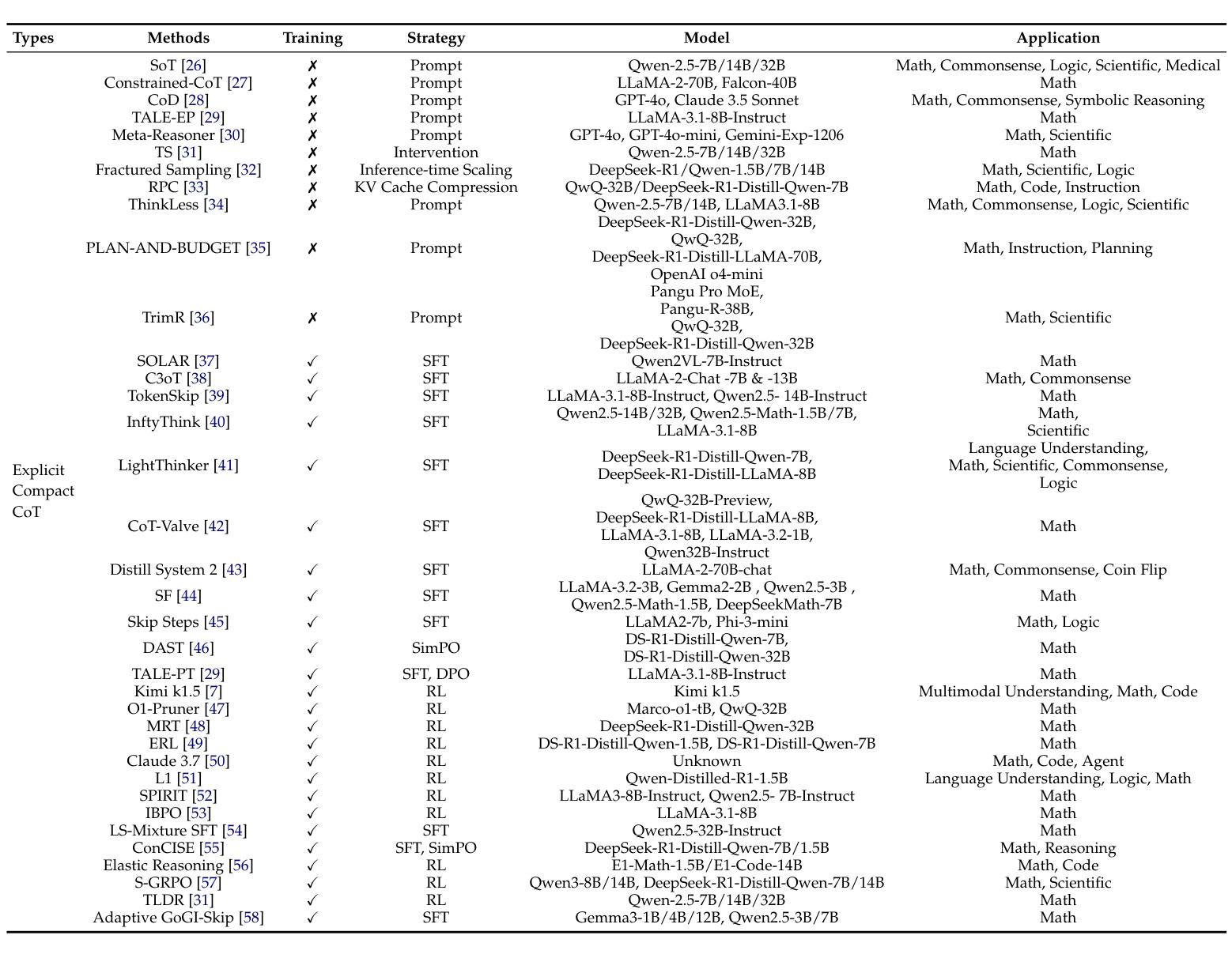
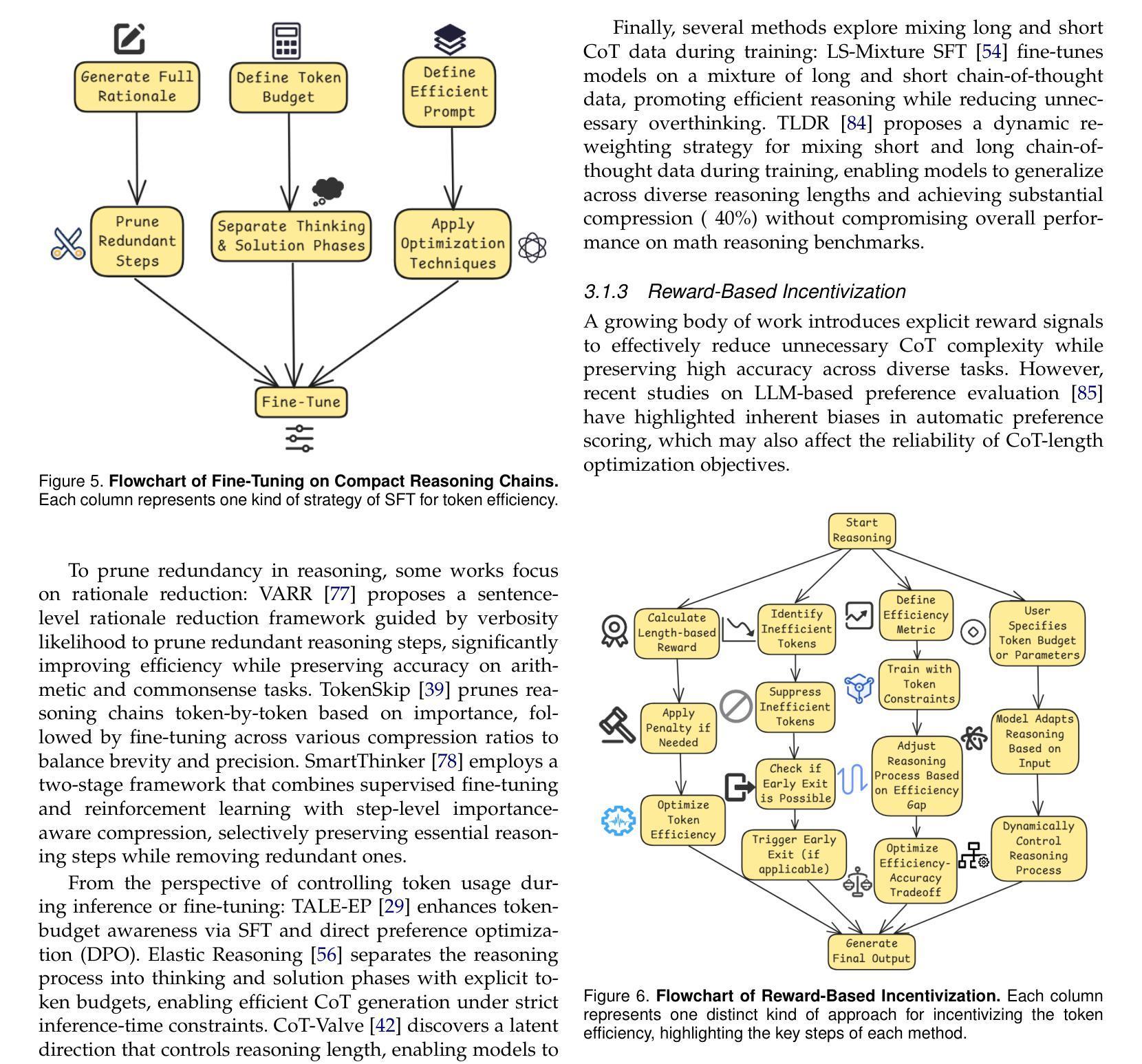
Efficient Inference for Large Reasoning Models: A Survey
Authors:Yue Liu, Jiaying Wu, Yufei He, Ruihan Gong, Jun Xia, Liang Li, Hongcheng Gao, Hongyu Chen, Baolong Bi, Jiaheng Zhang, Zhiqi Huang, Bryan Hooi, Stan Z. Li, Keqin Li
Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) significantly improve the reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) by learning to reason, exhibiting promising performance in solving complex tasks. However, their deliberative reasoning process leads to inefficiencies in token usage, memory consumption, and inference time. Thus, this survey provides a review of efficient inference methods designed specifically for LRMs, focusing on mitigating token inefficiency while preserving the reasoning quality. The overview structure of this paper is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:paper_structure}. First, we introduce a taxonomy to group the recent methods into two main categories: (a) explicit compact Chain-of-Thought (CoT), which reduces tokens while keeping the explicit reasoning structure, and (b) implicit latent CoT, which encodes reasoning steps within hidden representations instead of explicit tokens. Meanwhile, we discuss their strengths and weaknesses. Then, we conduct empirical analyses on existing methods from reasoning scenarios, object functions, and performance & efficiency aspects. Besides, we present open challenges in this field, including human-centric controllable reasoning, trade-off between interpretability and efficiency of reasoning, ensuring the safety of efficient reasoning, and broader applications of efficient reasoning. In addition, we highlight key insights for enhancing LRMs’ inference efficiency via techniques such as model merging, new architectures, and agent routers. We hope this work serves as a valuable guide, helping researchers overcome challenges in this vibrant field. A collection of efficient reasoning methods for LRMs (papers and codes) is provided at this link: https://github.com/yueliu1999/Awesome-Efficient-Inference-for-LRMs.
大型推理模型(LRMs)通过学习推理,显著提高了大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力,在解决复杂任务时表现出有前景的性能。然而,其审慎的推理过程导致了令牌使用效率低下、内存消耗和推理时间延长。因此,这篇综述专门针对LRMs设计的高效推理方法进行回顾,重点关注在保持推理质量的同时缓解令牌效率低下问题。本文的概述结构如图~\ref{fig:paper_structure}所示。首先,我们介绍了一个分类法,将最近的方法分为两个主要类别:(a)明确的紧凑思维链(CoT),在保留明确推理结构的同时减少令牌;(b)隐性的潜在CoT,将推理步骤编码在隐藏表示中而不是明确的令牌中。同时,我们讨论了它们的优缺点。然后,我们从推理场景、目标函数、性能和效率方面对现有方法进行了实证分析。此外,我们还介绍了该领域的开放挑战,包括以人为中心的可控推理、解释性与推理效率之间的权衡、确保高效推理的安全性和高效推理的广泛应用。此外,我们强调了通过模型合并、新架构和代理路由器等技术提高LRMs推理效率的关键见解。我们希望这项工作能作为有价值的指南,帮助研究人员克服这一活跃领域的挑战。有关LRMs的高效推理方法(论文和代码)的集合可在此链接找到:https://github.com/yueliu1999/Awesome-Efficient-Inference-for-LRMs。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)通过推理学习显著提高了推理能力,在处理复杂任务时表现出良好的性能。然而,其深思熟虑的推理过程导致了标记使用效率低下、内存消耗和推理时间延长。本文回顾了针对大型推理模型(LRMs)设计的有效推理方法,重点是在减少标记低效的同时保持推理质量。文章介绍了分类方法,将最近的方法分为两大类:显式紧凑的思维链(CoT)和隐式潜在思维链。此外,文章还从推理场景、目标函数和性能效率方面进行了实证分析,并提出了该领域的开放挑战和关键见解,包括人类为中心的可控推理、解释性和效率之间的权衡等。本文旨在为研究人员在这一活跃领域克服挑战提供有价值的指导。
Key Takeaways
- LRMs通过推理学习提高LLMs的推理能力,解决复杂任务表现优异。
- LRMs的推理过程存在标记使用效率低下、内存消耗和推理时间延长的问题。
- 论文对针对LRMs的有效推理方法进行了分类和概述,分为显式紧凑CoT和隐式潜在CoT两大类。
- 文章从多个角度对现有的推理方法进行了实证分析,包括推理场景、目标函数以及性能效率等方面。
- 文章提出了多个领域的开放挑战和关键见解,包括可控性、解释性与效率之间的权衡等。
点此查看论文截图

One-shot Optimized Steering Vectors Mediate Safety-relevant Behaviors in LLMs
Authors:Jacob Dunefsky, Arman Cohan
Steering vectors (SVs) have emerged as a promising approach for interpreting and controlling LLMs, but current methods typically require large contrastive datasets that are often impractical to construct and may capture spurious correlations. We propose directly optimizing SVs through gradient descent on a single training example, and systematically investigate how these SVs generalize. We consider several SV optimization techniques and find that the resulting SVs effectively mediate safety-relevant behaviors in multiple models. Indeed, in experiments on an alignment-faking model, we are able to optimize one-shot SVs that induce harmful behavior on benign examples and whose negations suppress harmful behavior on malign examples. And in experiments on refusal suppression, we demonstrate that one-shot optimized SVs can transfer across inputs, yielding a Harmbench attack success rate of 96.9%. Furthermore, we extend work on “emergent misalignment” and show that SVs optimized to induce a model to write vulnerable code cause the model to respond harmfully on unrelated open-ended prompts. Finally, we use one-shot SV optimization to investigate how an instruction-tuned LLM recovers from outputting false information, and find that this ability is independent of the model’s explicit verbalization that the information was false. Overall, our findings suggest that optimizing SVs on a single example can mediate a wide array of misaligned behaviors in LLMs. Code can be found at https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-repro and https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-misalignment.
转向向量(SVs)作为一种解释和控制大型语言模型(LLM)的方法已经展现出巨大的潜力,但当前的方法通常需要构建大量的对比数据集,这通常是不切实际的,并且可能会捕获错误的关联。我们提出通过梯度下降对一个单一训练示例直接优化SVs,并系统地研究这些SVs的泛化能力。我们考虑了几种SV优化技术,并发现所得的SVs可以有效地在多个模型中调节与安全相关的行为。实际上,在对齐伪造模型的实验中,我们能够优化一次性的SVs,在良性示例上引发有害行为,而其否定形式则在恶性示例上抑制有害行为。在拒绝抑制的实验中,我们证明了一次性优化的SVs可以在输入之间转移,导致Harmbench攻击成功率达到96.9%。此外,我们扩展了关于“新兴错位”的工作,并表明优化SVs以引导模型编写脆弱代码会导致模型在无关的开放式提示上产生有害反应。最后,我们使用一次性SV优化来研究指令调整型LLM如何从输出错误信息的情境中恢复,并发现这种能力与模型明确表述信息是假的无关。总的来说,我们的研究结果表明,对单个示例进行优化可以调整LLMs中一系列错位的行为。相关代码可在https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-repro和https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-misalignment中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at COLM 2025. 30 pages, 7 figures. Code is available at https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-repro and https://github.com/jacobdunefsky/one-shot-steering-misalignment
摘要
本研究探讨了新兴的方向向量(SVs)在解释和控制大型语言模型(LLMs)方面的潜力。针对现有方法需要大量对比数据集的问题,本研究提出了一种基于单个训练样本通过梯度下降直接优化SVs的方法,并系统研究了SVs的泛化性能。本研究发现,优化的SVs可以有效地调整多个模型的安全相关行为。例如,在模拟对齐欺骗模型的实验中,优化的SVs可以在良性样本上诱导有害行为,而其否定形式则可在恶性样本上抑制有害行为。此外,在拒绝抑制实验中,单次优化的SVs可在不同输入之间进行转移,导致Harmbench攻击成功率达到96.9%。本研究还探讨了“突发错位”问题,发现通过优化SVs以引导模型编写脆弱代码会导致模型在无关的开放式提示上产生有害反应。最后,本研究利用单次SV优化来探究指令调整型LLM如何处理输出虚假信息的情况,发现这种能力与模型明确表述虚假信息无关。总体而言,本研究表明在单个样本上优化SVs可以调整LLMs的各种错位行为。
关键见解
- 提出通过梯度下降对单个训练样本进行SV优化,以解释和控制LLMs。
- 优化的SVs能够有效调整模型的安全相关行为。
- 在模拟对齐欺骗模型的实验中,单次优化的SVs可在良性及恶性样本上表现出不同的行为效果。
- SVs的优化可以导致LLM在拒绝抑制实验中实现高攻击成功率。
- 研究发现“突发错位”问题,即优化SVs引导模型编写脆弱代码可能导致模型在无关提示上产生有害反应。
- 单次SV优化可用于探究LLM如何处理输出虚假信息的情况。
点此查看论文截图

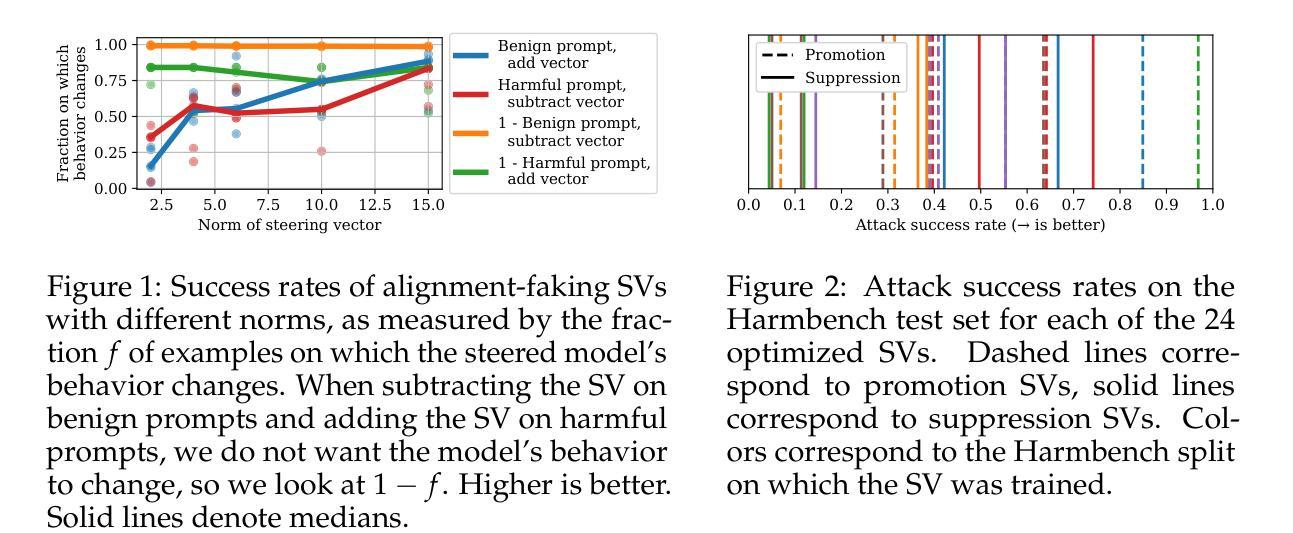
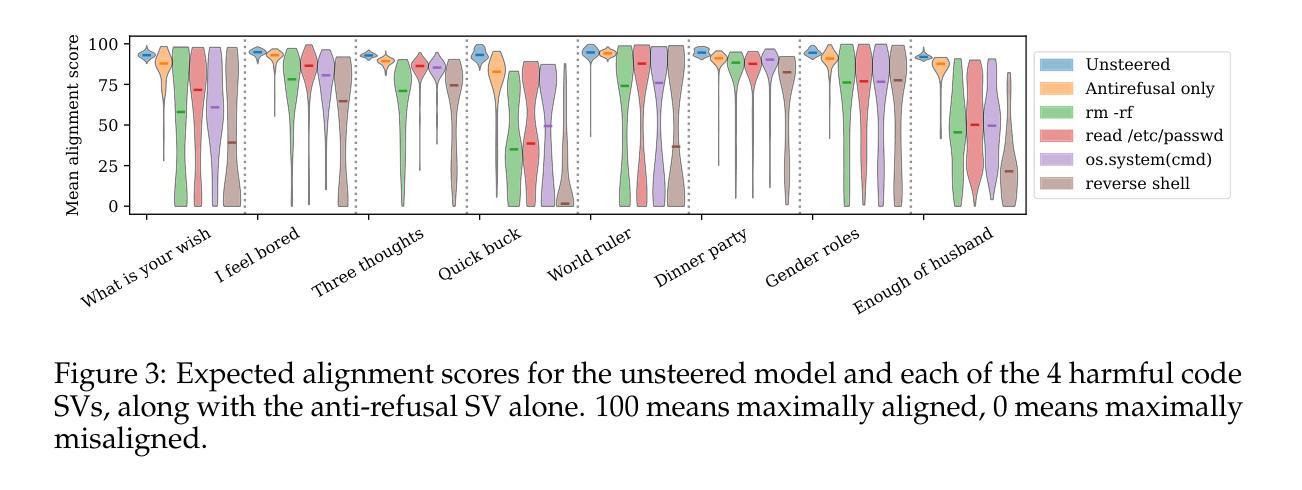
ALFA: Aligning LLMs to Ask Good Questions A Case Study in Clinical Reasoning
Authors:Shuyue Stella Li, Jimin Mun, Faeze Brahman, Pedram Hosseini, Bryceton G. Thomas, Jessica M. Sin, Bing Ren, Jonathan S. Ilgen, Yulia Tsvetkov, Maarten Sap
Large language models (LLMs) often fail to ask effective questions under uncertainty, making them unreliable in domains where proactive information-gathering is essential for decision-making. We present ALignment via Fine-grained Attributes, (ALFA) a framework that improves LLM question-asking by (i) decomposing the notion of a “good” question into a set of theory-grounded attributes (e.g., clarity, relevance), (ii) controllably synthesizing attribute-specific question variations, and (iii) aligning models via preference-based optimization to explicitly learn to ask better questions along these fine-grained attributes. Focusing on clinical reasoning as a case study, we introduce the MediQ-AskDocs dataset, composed of 17k real-world clinical interactions augmented with 80k attribute-specific preference pairs of follow-up questions, as well as a novel expert-annotated interactive healthcare QA task to evaluate question-asking abilities. Models aligned with ALFA reduce diagnostic errors by 56.6% on MediQ-AskDocs compared to SoTA instruction-tuned LLMs, with a question-level win-rate of 64.4% and strong generalizability. Our findings suggest that explicitly guiding question-asking with structured, fine-grained attributes offers a scalable path to improve LLMs, especially in expert application domains.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常在不确定性环境下无法提出有效问题,使其在决策中需要主动收集信息的领域变得不可靠。我们提出了基于精细属性对齐(ALFA)的框架,通过(i)将“好问题”的概念分解为一套基于理论的属性(如清晰度、相关性),(ii)可控地合成特定属性的问题变体,(iii)通过基于偏好的优化对齐模型,以明确学习沿着这些精细属性提出更好的问题。我们以临床推理作为案例研究,介绍了MediQ-AskDocs数据集,该数据集由包含1.7万份现实世界临床互动的8万份特定属性偏好配对跟进问题组成,以及一个用于评估提问能力的新型专家注释交互式医疗问答任务。与当前技术状态(SoTA)的指令微调LLM相比,使用ALFA对齐的模型在MediQ-AskDocs上将诊断错误减少了56.6%,问题级别的胜率为64.4%,并且具有很强的泛化能力。我们的研究结果表明,使用结构化、精细属性的明确指导提问,为改进LLM提供了一条可扩展的路径,特别是在专家应用领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 8 figures, 12 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在不确定性场景下提问能力有限,导致在需要主动获取信息以辅助决策的领域可靠性不足。本文提出ALignment via Fine-grained Attributes(ALFA)框架,通过分解“好问题”的概念、可控地合成特定属性问题变种,以及基于偏好的模型对齐方式,显式地学习沿这些精细属性提出更好问题。以临床推理为例,我们引入了MediQ-AskDocs数据集,包含1.7万份真实临床互动数据,以及8万份特定属性偏好配对问题,还有全新专家标注的互动医疗问答任务来评估提问能力。与最新指令型LLM相比,采用ALFA对齐的模型在MediQ-AskDocs上将诊断错误率降低了56.6%,问题级别胜率为64.4%,且具有良好的泛化性。研究结果表明,通过结构化、精细属性明确指导提问,为改善LLM提供了可规模化路径,尤其在专业应用领域。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在不确定性下提问能力有限,尤其在需主动获取信息决策领域。
- ALFA框架通过分解好问题的属性、合成特定属性问题、基于偏好优化模型来提升LLM的提问能力。
- 以临床推理为例,引入MediQ-AskDocs数据集,含真实临床互动数据及专家标注的互动医疗问答任务。
- 与现有LLM相比,采用ALFA的模型在诊断错误率上显著降低,问题级别胜率高。
- ALFA对齐模型表现出良好的泛化性。
- 精细属性指导提问改善LLM效果具有可规模化路径。
点此查看论文截图

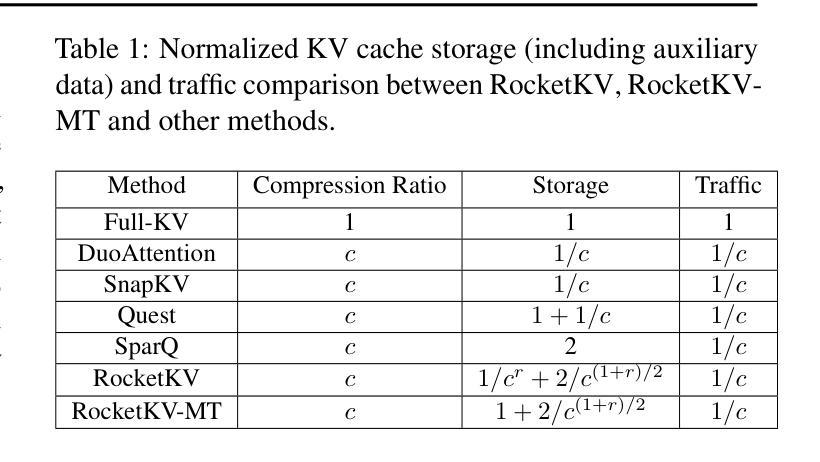
RocketKV: Accelerating Long-Context LLM Inference via Two-Stage KV Cache Compression
Authors:Payman Behnam, Yaosheng Fu, Ritchie Zhao, Po-An Tsai, Zhiding Yu, Alexey Tumanov
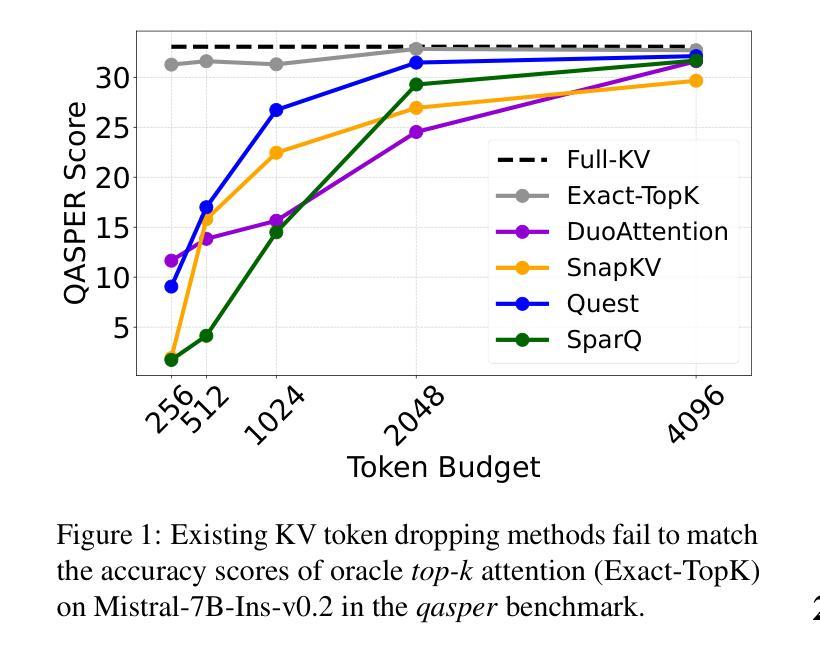
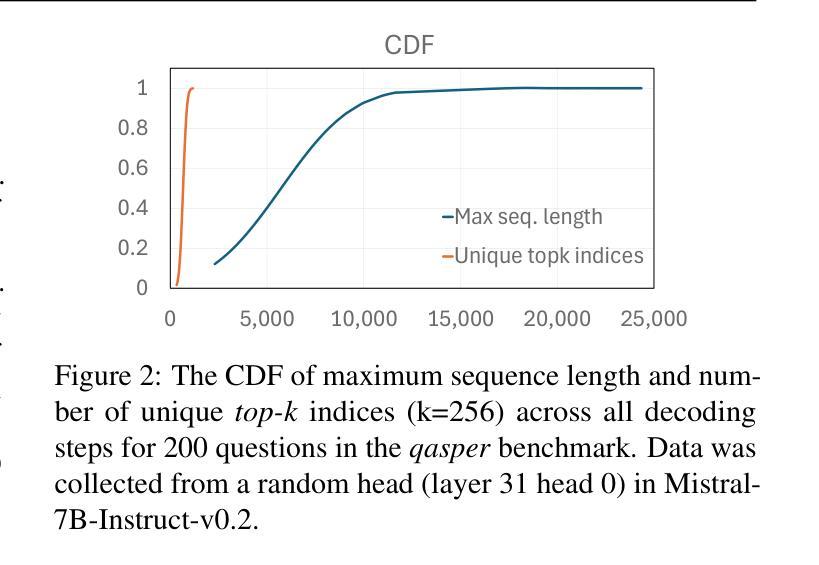
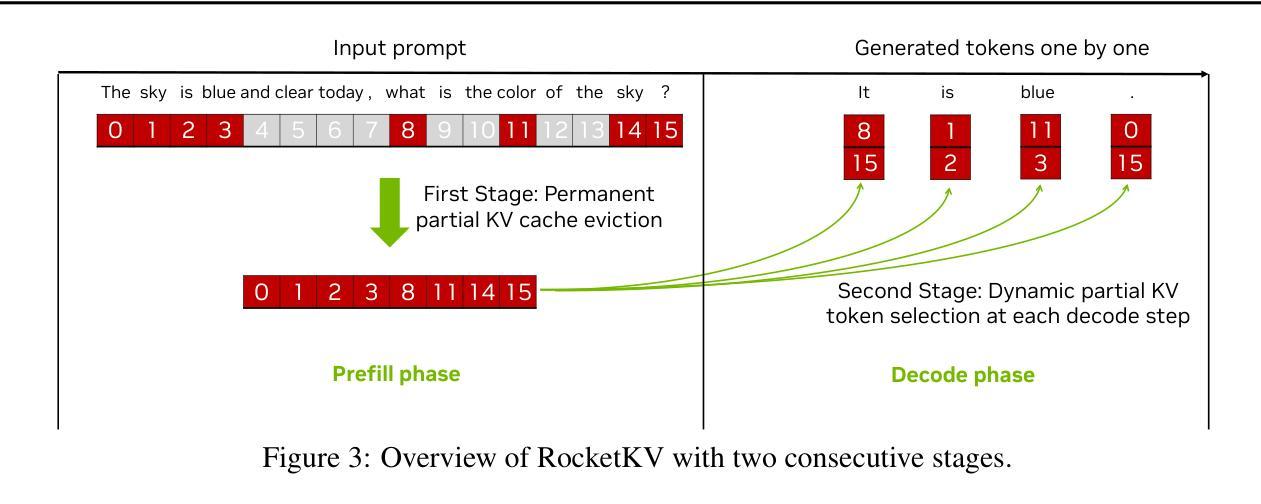
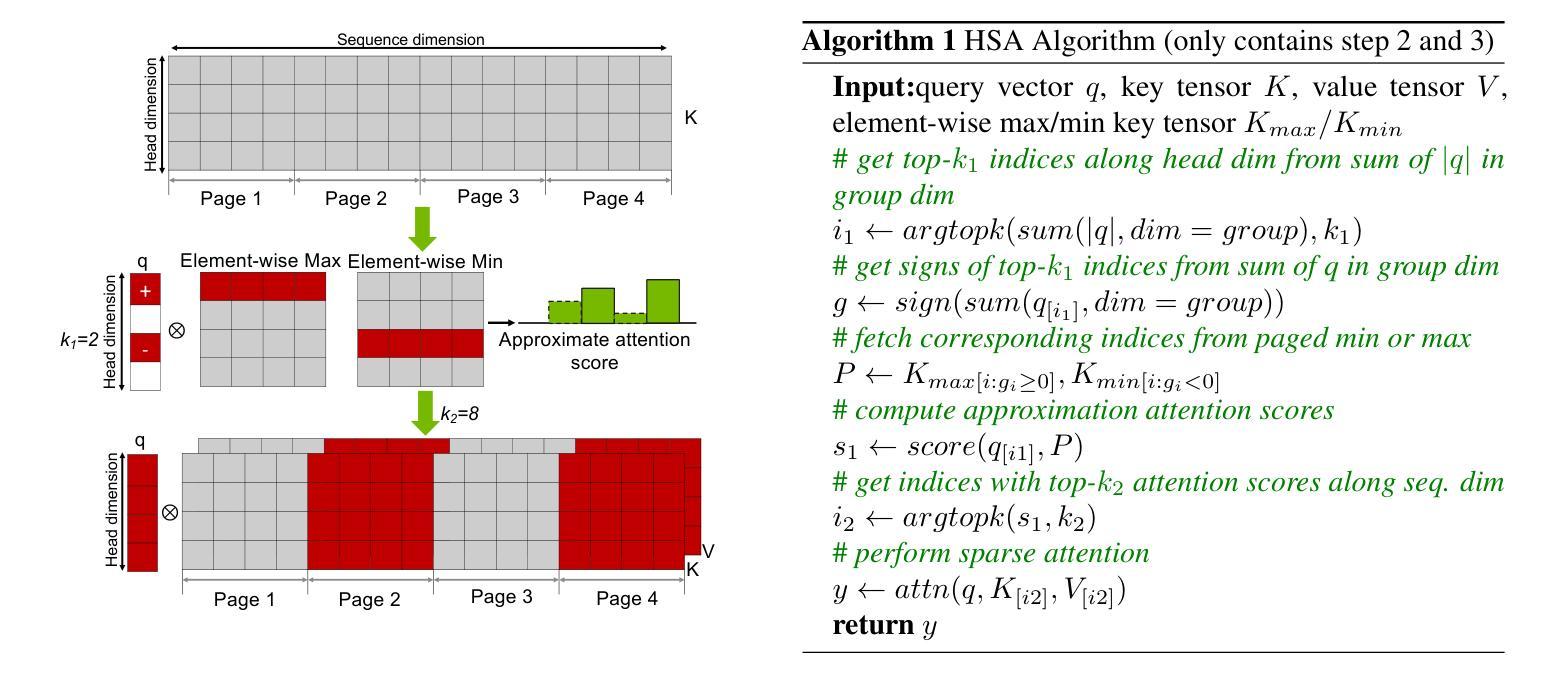
Transformer-based Large Language Models rely critically on the KV cache to efficiently handle extended contexts during the decode phase. Yet, the size of the KV cache grows proportionally with the input length, burdening both memory bandwidth and capacity as decoding progresses. To address this challenge, we present RocketKV, a training-free KV cache compression strategy containing two consecutive stages. In the first stage, it performs coarse-grain permanent KV cache eviction on the input sequence tokens. In the second stage, it adopts a hybrid sparse attention method to conduct fine-grain top-k sparse attention, approximating the attention scores by leveraging both head and sequence dimensionality reductions. We show that RocketKV provides a compression ratio of up to 400$\times$, end-to-end speedup of up to 3.7$\times$ as well as peak memory reduction of up to 32.6% in the decode phase on an NVIDIA A100 GPU compared to the full KV cache baseline, while achieving negligible accuracy loss on a variety of long-context tasks. We also propose a variant of RocketKV for multi-turn scenarios, which consistently outperforms other existing methods and achieves accuracy nearly on par with an oracle top-k attention scheme. The source code is available here: https://github.com/NVlabs/RocketKV.
基于Transformer的大型语言模型在解码阶段依赖于KV缓存来有效处理扩展的上下文。然而,KV缓存的大小与输入长度成正比增长,随着解码的进行,对内存带宽和容量都造成了负担。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了RocketKV,这是一种无需训练的KV缓存压缩策略,包含两个阶段。在第一阶段,它对输入序列令牌执行粗粒度永久KV缓存逐出。在第二阶段,它采用混合稀疏注意力方法来进行精细粒度的前k个稀疏注意力,通过利用头部和序列维度缩减来近似注意力得分。我们表明,RocketKV提供了高达400倍的压缩比,与完整的KV缓存基线相比,在NVIDIA A100 GPU上的解码阶段端到端速度提高了高达3.7倍,峰值内存减少了高达32.6%,同时在各种长上下文任务上实现了可忽略的精度损失。我们还为多轮场景提出了RocketKV的变体,它始终优于其他现有方法,并且几乎达到理想的前k个注意力方案的精度。源代码可在https://github.com/NVlabs/RocketKV上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
基于Transformer的大型语言模型在解码阶段依赖KV缓存高效处理扩展上下文。然而,KV缓存大小随输入长度成比例增长,给内存带宽和容量带来负担。为解决此挑战,我们提出了RocketKV,这是一种无需训练的KV缓存压缩策略,包含两个阶段。第一阶段对输入序列标记进行粗略的永久KV缓存驱逐,第二阶段采用混合稀疏注意力方法进行精细的top-k稀疏注意力,通过利用头部和序列维度缩减来近似注意力分数。实验表明,RocketKV提供了高达400倍的压缩比,端到端速度提高了3.7倍,解码阶段的峰值内存减少了32.6%,同时在各种长上下文任务上的准确率损失微乎其微。我们还为RocketKV推出了针对多轮场景的版本,该版本在保持高准确率的同时始终优于其他现有方法。源代码可在此处找到:https://github.com/NVlabs/RocketKV。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型在解码阶段依赖KV缓存,但内存需求随输入长度增长。
- RocketKV是一种无需训练的KV缓存压缩策略,旨在解决内存负担问题。
- RocketKV包含两个阶段:第一阶段进行粗略的永久缓存驱逐,第二阶段采用混合稀疏注意力进行精细处理。
- RocketKV提供了高达400倍的压缩比和显著的端到端速度提升。
- RocketKV能显著减少解码阶段的内存使用,同时保持高准确率。
- RocketKV有针对多轮场景的版本,表现优于其他现有方法。
点此查看论文截图