⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-15 更新
HM-Talker: Hybrid Motion Modeling for High-Fidelity Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Shiyu Liu, Kui Jiang, Xianming Liu, Hongxun Yao, Xiaocheng Feng
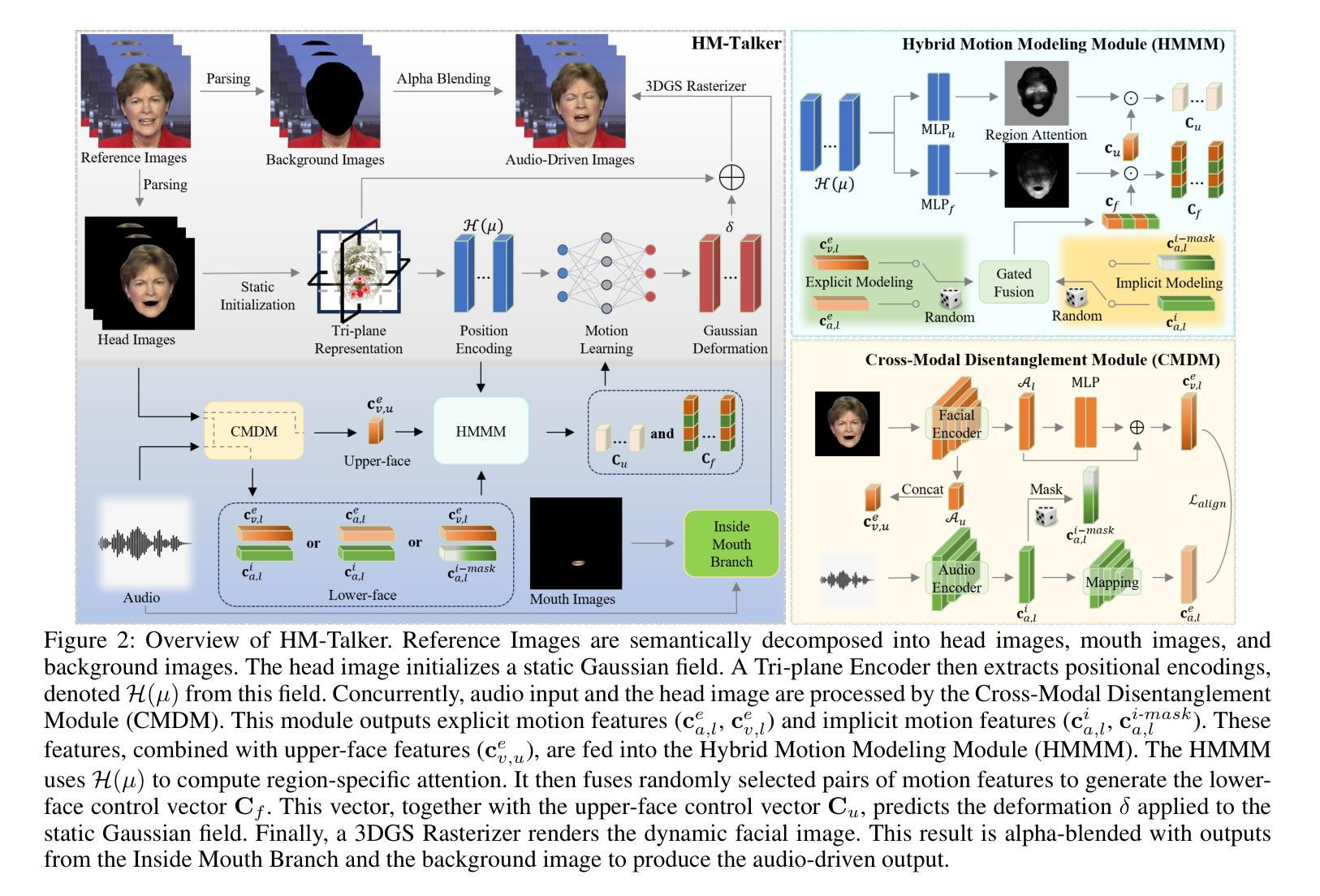
Audio-driven talking head video generation enhances user engagement in human-computer interaction. However, current methods frequently produce videos with motion blur and lip jitter, primarily due to their reliance on implicit modeling of audio-facial motion correlations–an approach lacking explicit articulatory priors (i.e., anatomical guidance for speech-related facial movements). To overcome this limitation, we propose HM-Talker, a novel framework for generating high-fidelity, temporally coherent talking heads. HM-Talker leverages a hybrid motion representation combining both implicit and explicit motion cues. Explicit cues use Action Units (AUs), anatomically defined facial muscle movements, alongside implicit features to minimize phoneme-viseme misalignment. Specifically, our Cross-Modal Disentanglement Module (CMDM) extracts complementary implicit/explicit motion features while predicting AUs directly from audio input aligned to visual cues. To mitigate identity-dependent biases in explicit features and enhance cross-subject generalization, we introduce the Hybrid Motion Modeling Module (HMMM). This module dynamically merges randomly paired implicit/explicit features, enforcing identity-agnostic learning. Together, these components enable robust lip synchronization across diverse identities, advancing personalized talking head synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate HM-Talker’s superiority over state-of-the-art methods in visual quality and lip-sync accuracy.
音频驱动的说话人头视频生成提高了人机交互中的用户参与度。然而,当前的方法经常产生运动模糊和嘴唇抖动的视频,这主要是因为它们依赖于音频面部运动关联的隐式建模——这种方法缺乏明确的发音先验知识(即与语音相关的面部运动的解剖指导)。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了HM-Talker,这是一个生成高保真、时间连贯的说话人头部的全新框架。HM-Talker利用了一种混合运动表示法,结合了隐式和显式运动线索。显式线索使用行为单元(AUs),即面部解剖上定义的肌肉运动,以及隐式特征来最小化音素-表情动作的不对齐。具体来说,我们的跨模态分解模块(CMDM)在预测直接与音频输入对齐的视觉线索的AUs时,提取互补的隐式/显式运动特征。为了减轻显式特征中的身份相关偏见,并增强跨主体泛化,我们引入了混合运动建模模块(HMMM)。该模块动态合并随机配对的隐式/显式特征,强制实施身份无关的学习。这些组件共同作用,实现了跨不同身份的稳健嘴唇同步,推动了个性化说话头部合成的进步。大量实验表明,HM-Talker在视觉质量和嘴唇同步准确性方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为HM-Talker的新型框架,用于生成高保真、时间连贯的说话人头像。该框架结合了隐式和显式运动线索的混合运动表示,使用面部肌肉动作单位(AUs)等显式线索和隐式特征,以最小化音素与表情之间的不匹配。通过跨模态解耦模块(CMDM)提取互补的隐式/显式运动特征,并从音频输入中直接预测与视觉线索对齐的AUs。同时,通过混合运动建模模块(HMMM)动态合并随机配对的隐式/显式特征,实现身份无关的学习,提高了跨主体泛化能力。实验表明,HM-Talker在视觉质量和唇同步准确性方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- HM-Talker框架结合了隐式和显式运动线索,提高了音频驱动的头像生成质量。
- 显式运动线索使用面部肌肉动作单位(AUs),减少了音素与表情之间的不匹配。
- Cross-Modal Disentanglement Module (CMDM)用于提取隐式/显式运动特征的互补信息。
- Hybrid Motion Modeling Module (HMMM)通过动态合并隐式/显式特征实现身份无关的学习,提高了跨主体泛化能力。
- HM-Talker在视觉质量和唇同步准确性方面表现出卓越性能,优于现有技术。
- 该方法能够生成高保真、时间连贯的说话人头像,增强了人机交互中的用户参与度。
点此查看论文截图

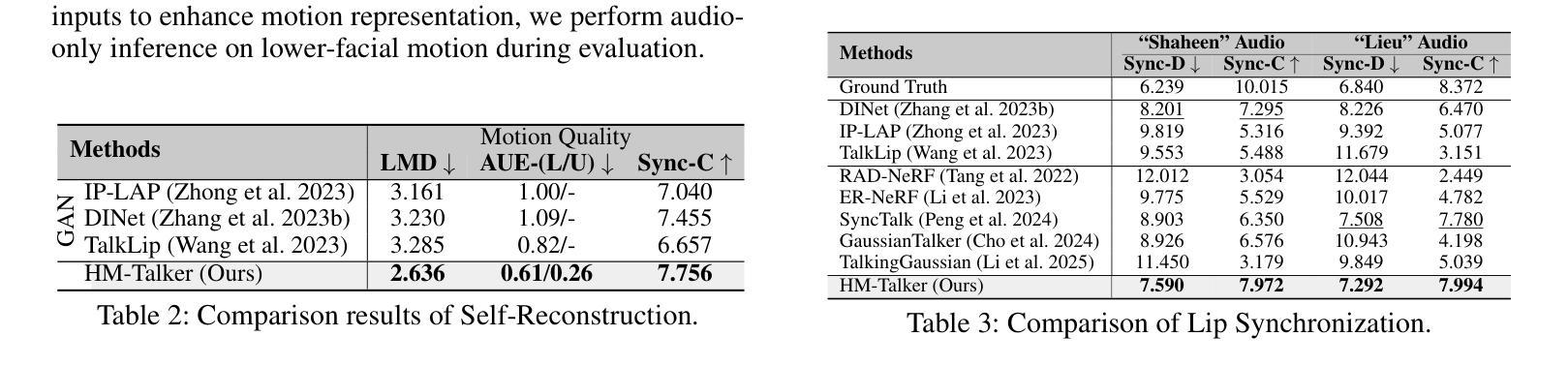
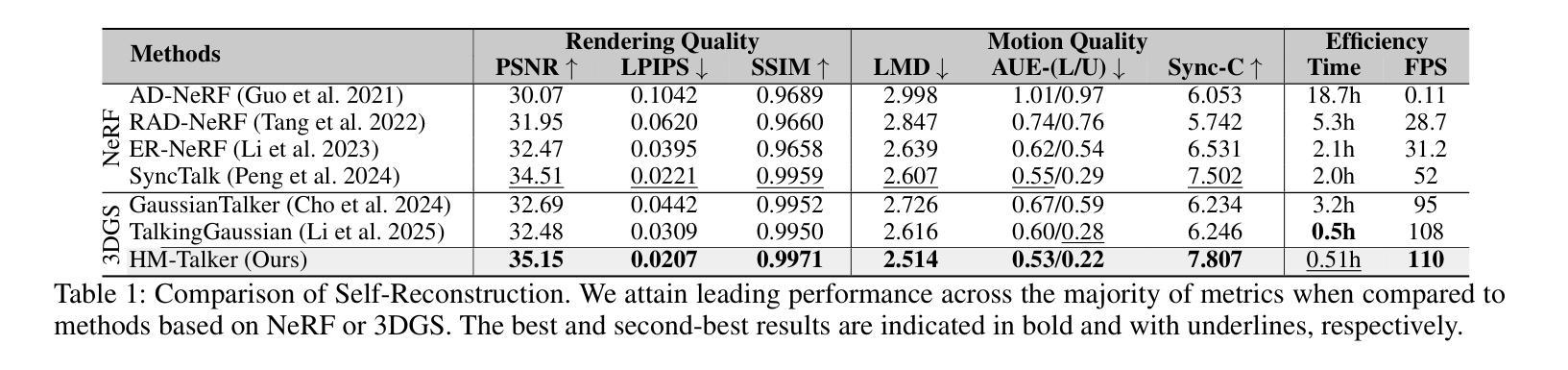
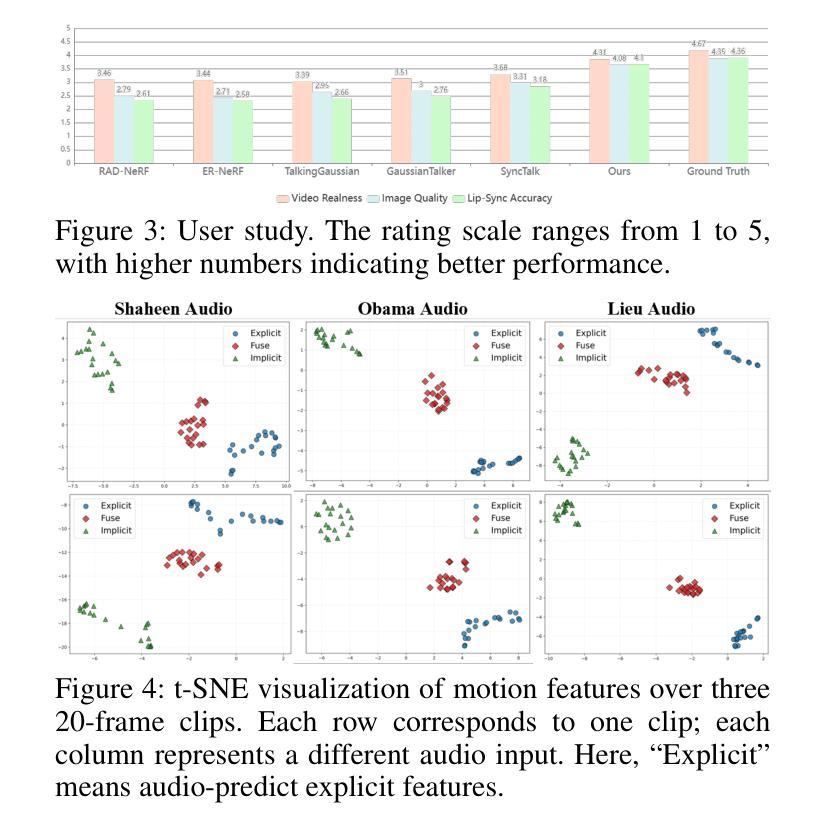
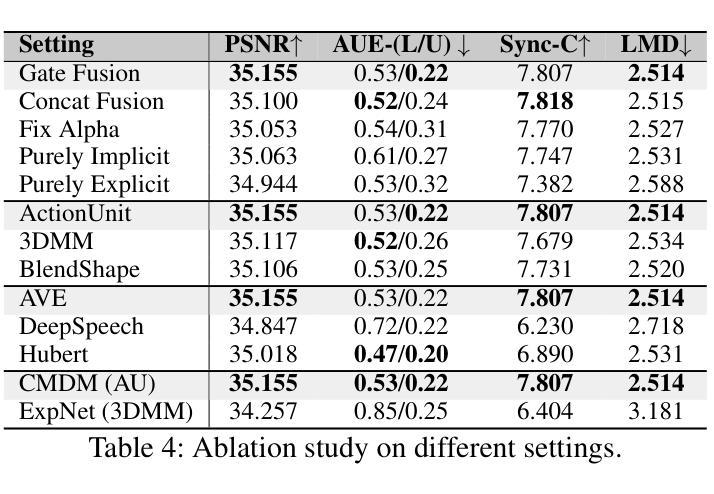
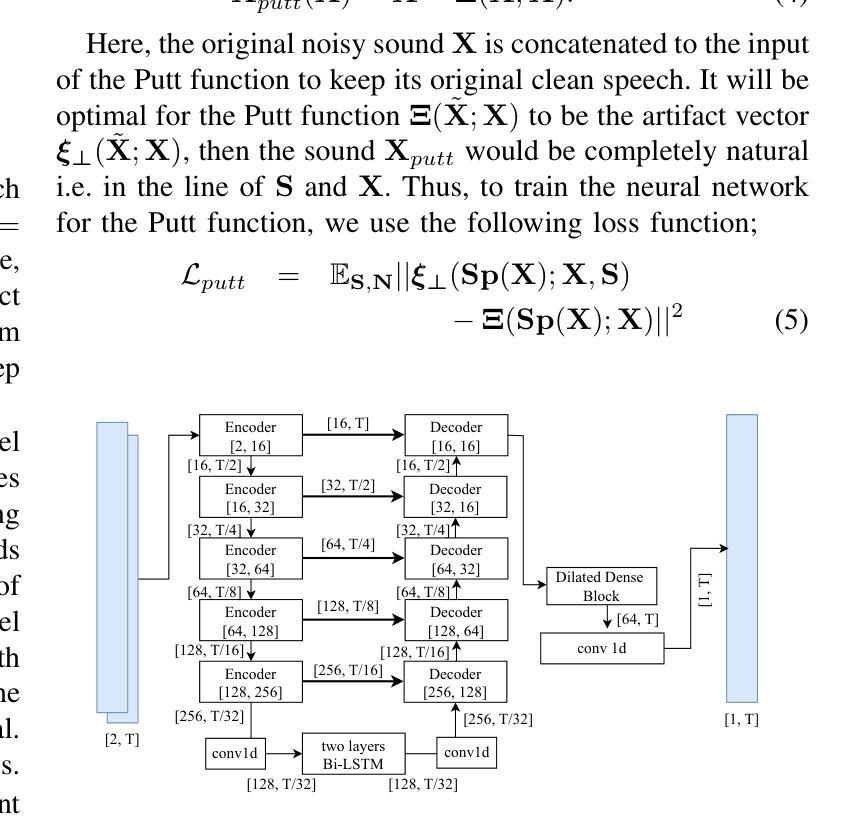
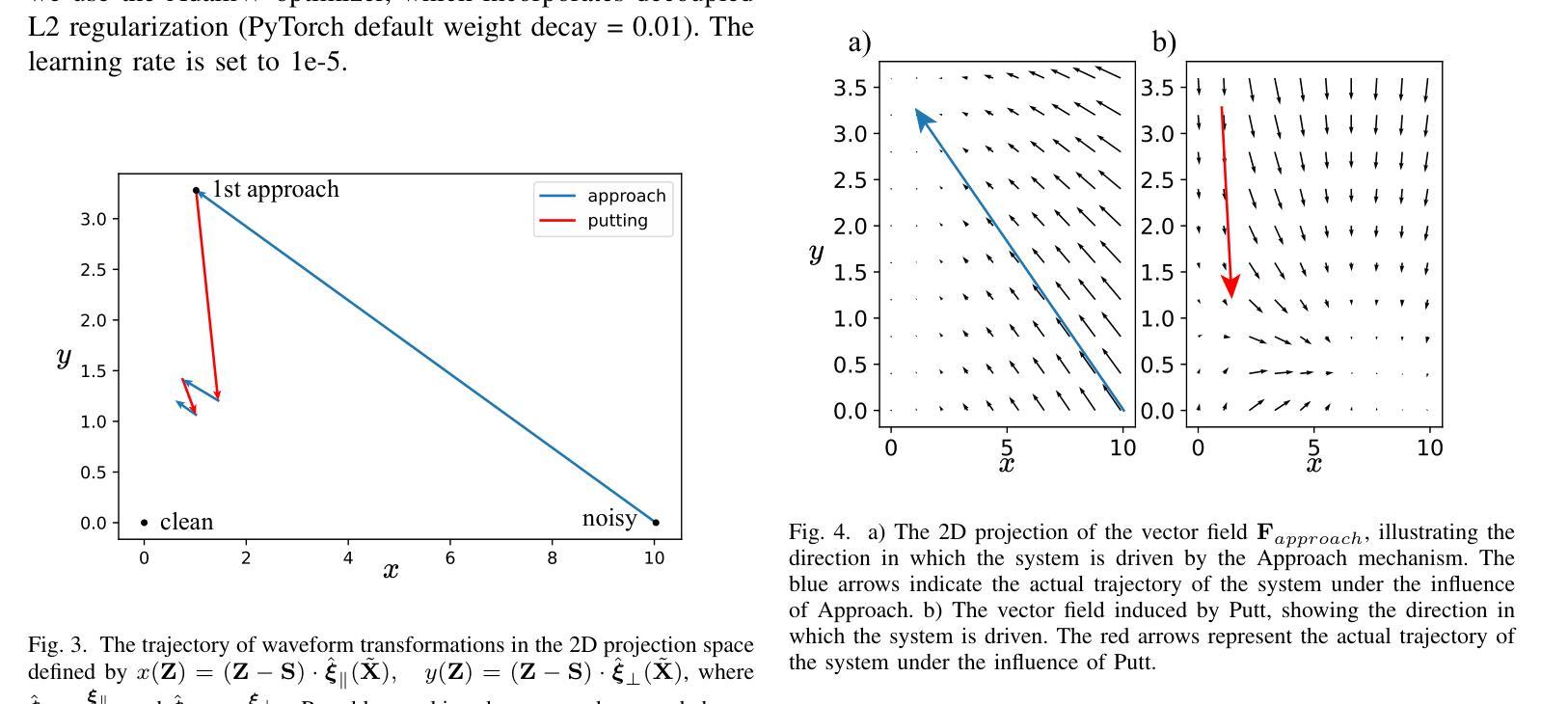
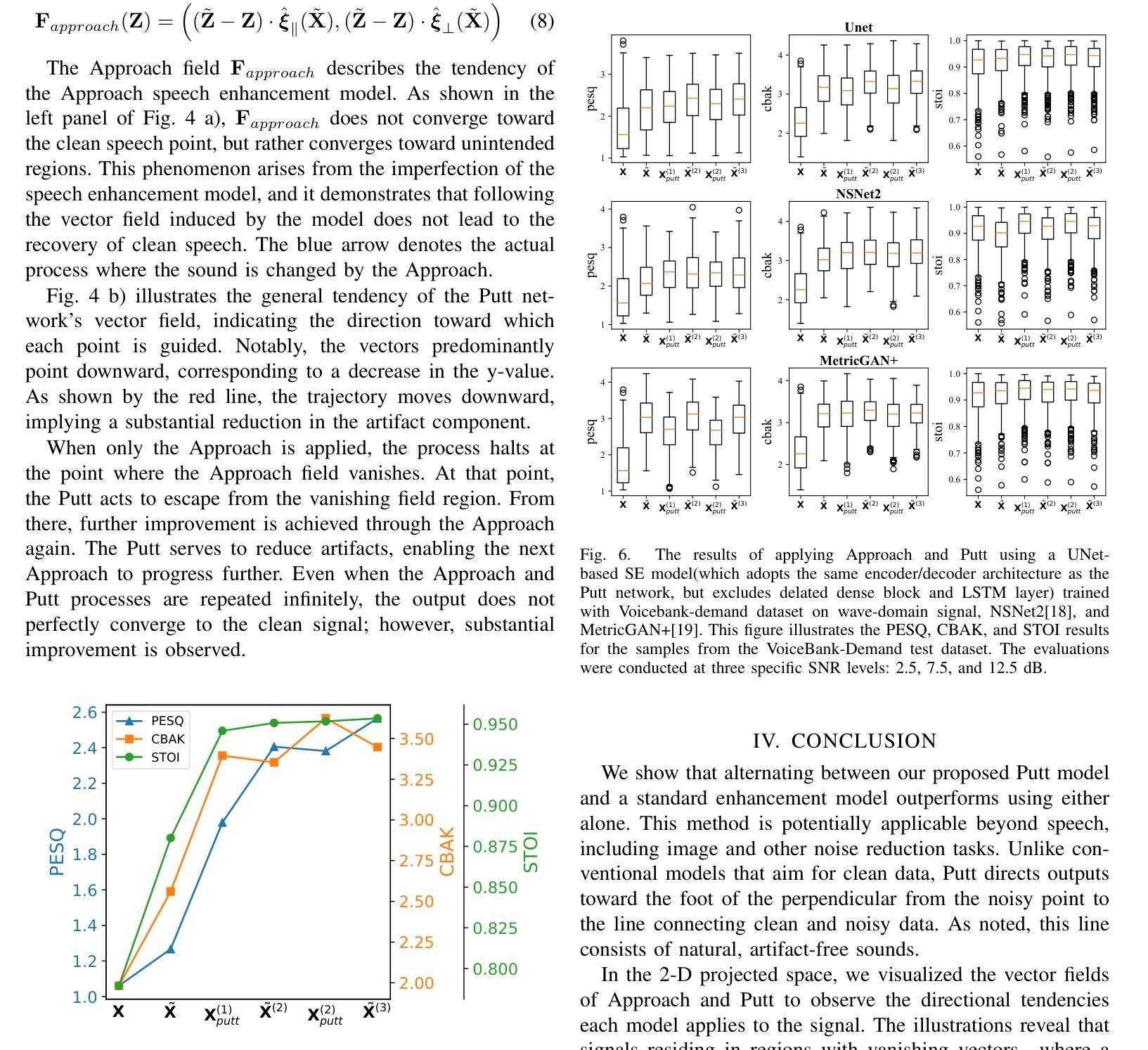
Alternating Approach-Putt Models for Multi-Stage Speech Enhancement
Authors:Iksoon Jeong, Kyung-Joong Kim, Kang-Hun Ahn
Speech enhancement using artificial neural networks aims to remove noise from noisy speech signals while preserving the speech content. However, speech enhancement networks often introduce distortions to the speech signal, referred to as artifacts, which can degrade audio quality. In this work, we propose a post-processing neural network designed to mitigate artifacts introduced by speech enhancement models. Inspired by the analogy of making a Putt' after an Approach’ in golf, we name our model PuttNet. We demonstrate that alternating between a speech enhancement model and the proposed Putt model leads to improved speech quality, as measured by perceptual quality scores (PESQ), objective intelligibility (STOI), and background noise intrusiveness (CBAK) scores. Furthermore, we illustrate with graphical analysis why this alternating Approach outperforms repeated application of either model alone.
使用人工神经网络进行语音增强旨在从嘈杂的语音信号中去除噪声,同时保留语音内容。然而,语音增强网络往往会在语音信号中引入失真,称为伪影,这可能会降低音频质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种后处理神经网络,旨在减轻语音增强模型引入的伪影。受高尔夫运动中“推杆”与“挥杆”之间的类比启发,我们将模型命名为PuttNet。我们证明,在语音增强模型和提出的Putt模型之间进行交替,可以提高语音质量,这是通过感知质量得分(PESQ)、客观清晰度(STOI)和背景噪声干扰(CBAK)来衡量的。此外,我们通过图形分析说明了这种交替方法为何优于单独重复应用任一模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
神经网络语音增强技术旨在从含噪语音信号中消除噪声,同时保留语音内容。然而,语音增强网络常常给语音信号引入失真,即所谓的伪影,这会降低音频质量。本研究提出了一种后处理神经网络,旨在减轻语音增强模型引入的伪影。我们借鉴高尔夫运动中开球(Approach)之后的推球(Putt)的类比,将模型命名为PuttNet。我们证明,在语音增强模型和提出的Putt模型之间交替使用,能提高语音质量,这在感知质量得分(PESQ)、客观可懂度(STOI)和背景噪声干扰性(CBAK)得分上都有所体现。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络用于语音增强,目的是从含噪语音中消除噪声,同时保留语音内容。
- 语音增强网络可能引入伪影,即失真,影响音频质量。
- 提出一种后处理神经网络模型PuttNet,旨在减轻语音增强模型引入的伪影。
- PuttNet的命名源于高尔夫运动中的开球(Approach)和推球(Putt)的类比。
- 交替使用语音增强模型和PuttNet模型,能提高语音质量,这在感知质量、客观可懂度和背景噪声干扰性等方面都有体现。
- 图形分析证明了这种交替方法优于单独重复应用任一模型。
- 该研究为改进神经网络在语音增强中的应用提供了新思路。
点此查看论文截图

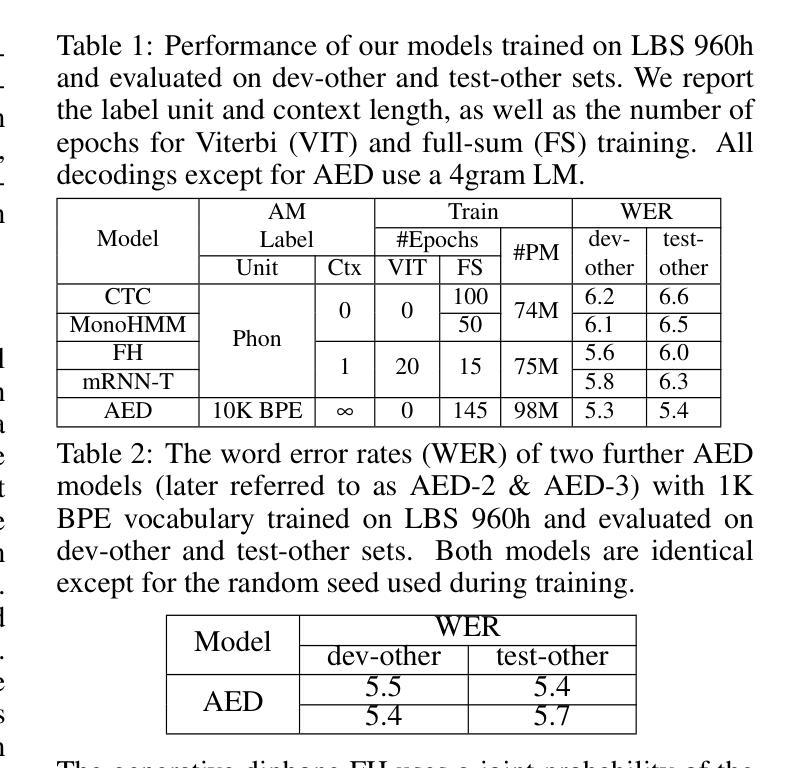
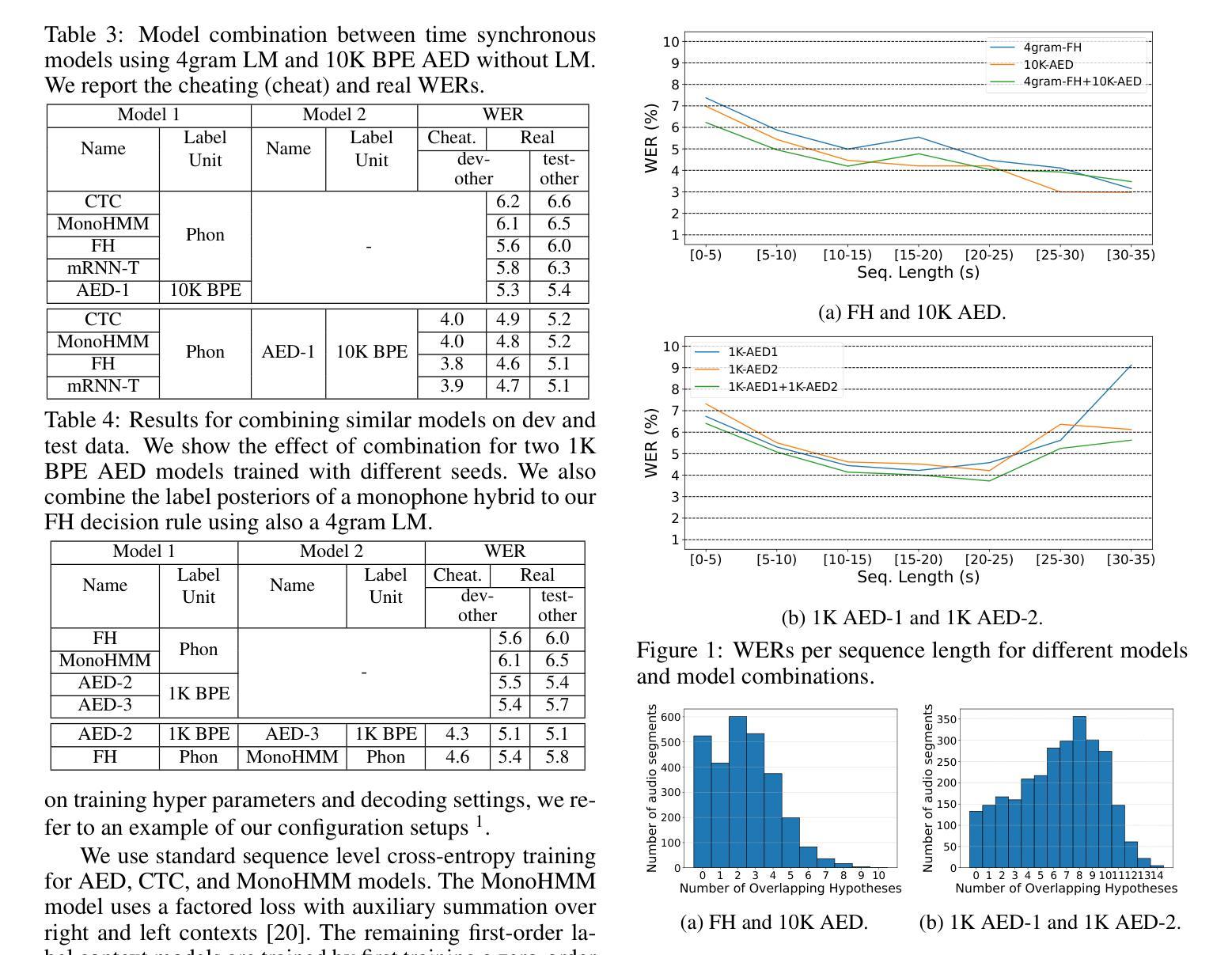
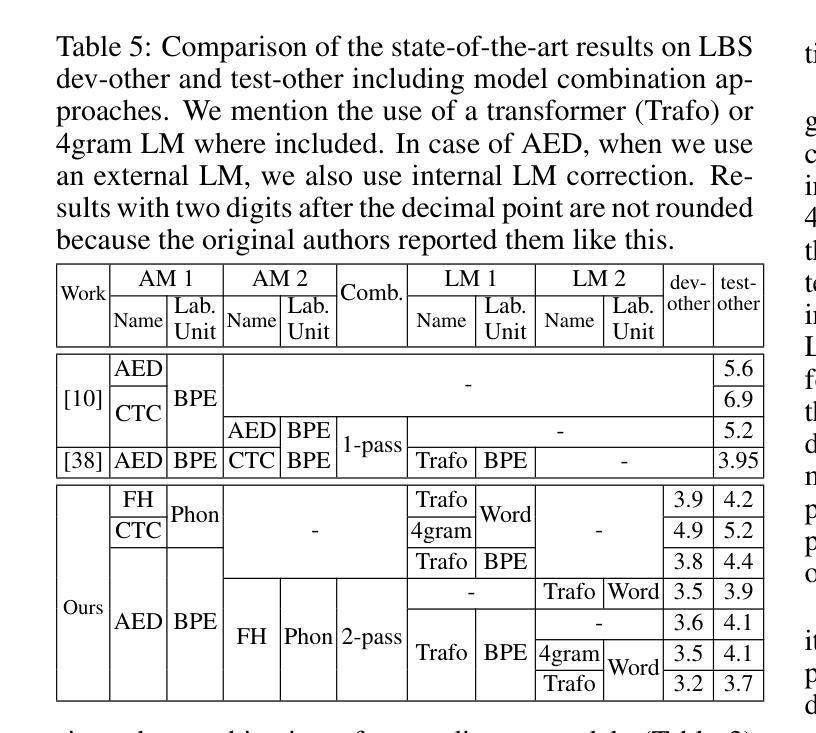
A Comparative Analysis on ASR System Combination for Attention, CTC, Factored Hybrid, and Transducer Models
Authors:Noureldin Bayoumi, Robin Schmitt, Tina Raissi, Albert Zeyer, Ralf Schlüter, Hermann Ney
Combination approaches for speech recognition (ASR) systems cover structured sentence-level or word-based merging techniques as well as combination of model scores during beam search. In this work, we compare model combination across popular ASR architectures. Our method leverages the complementary strengths of different models in exploring diverse portions of the search space. We rescore a joint hypothesis list of two model candidates. We then identify the best hypothesis through log-linear combination of these sequence-level scores. While model combination during first-pass recognition may yield improved performance, it introduces variability due to differing decoding methods, making direct comparison more challenging. Our two-pass method ensures consistent comparisons across all system combination results presented in this study. We evaluate model pair candidates with varying architectures and label topologies and units. Experimental results are provided for the Librispeech 960h task.
语音识别(ASR)系统的组合方法涵盖了结构化的句子级别或基于单词的合并技术,以及在光束搜索过程中结合模型分数。在这项工作中,我们比较了流行ASR架构中的模型组合。我们的方法利用不同模型在探索搜索空间不同部分的互补优势。我们对两个模型候选者的联合假设列表进行重新评分。然后,我们通过这些序列级分数的对数线性组合来确定最佳假设。虽然在一遍识别过程中使用模型组合可能会提高性能,但它由于不同的解码方法而引入了变化性,使得直接比较更具挑战性。我们的两遍方法确保了本研究中所有系统组合结果的一致比较。我们用不同架构、标签拓扑和单位的模型对候选对象进行了评估。实验结果为Librispeech 960小时任务提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at IEEE Speech Communication; 16th ITG Conference
Summary
本文研究了语音识别(ASR)系统中的组合方法,通过比较不同ASR架构中的模型组合,利用不同模型的互补优势来探索搜索空间的不同部分。通过两阶段方法,首先结合两个模型候选人的假设列表进行重评分,然后通过序列级分数的对数线性组合来确定最佳假设。虽然在第一遍识别过程中使用模型组合可能会提高性能,但由于不同的解码方法会引入变化,使得直接比较更具挑战性。本研究采用的两阶段方法确保了所有系统组合结果的一致比较。
Key Takeaways
- 文章研究了语音识别(ASR)系统中的组合方法,涉及模型组合的多种方式。
- 通过结合不同模型的优点,能够探索搜索空间的不同部分。
- 采用两阶段方法进行模型组合,首先重评分假设列表,然后确定最佳假设。
- 模型组合在第一遍识别中可能提高性能,但直接比较具有挑战性。
- 研究采用的两阶段方法确保了所有系统组合结果的一致比较。
- 文章对具有不同架构和标签拓扑及单元的模型候选进行了评估。
点此查看论文截图

Analysis of Domain Shift across ASR Architectures via TTS-Enabled Separation of Target Domain and Acoustic Conditions
Authors:Tina Raissi, Nick Rossenbach, Ralf Schlüter
We analyze automatic speech recognition (ASR) modeling choices under domain mismatch, comparing classic modular and novel sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) architectures. Across the different ASR architectures, we examine a spectrum of modeling choices, including label units, context length, and topology. To isolate language domain effects from acoustic variation, we synthesize target domain audio using a text-to-speech system trained on LibriSpeech. We incorporate target domain n-gram and neural language models for domain adaptation without retraining the acoustic model. To our knowledge, this is the first controlled comparison of optimized ASR systems across state-of-the-art architectures under domain shift, offering insights into their generalization. The results show that, under domain shift, rather than the decoder architecture choice or the distinction between classic modular and novel seq2seq models, it is specific modeling choices that influence performance.
我们分析了领域不匹配情况下的自动语音识别(ASR)建模选择,对比了经典的模块化架构和新颖的顺序到序列(seq2seq)架构。在不同的ASR架构中,我们研究了包括标签单位、上下文长度和拓扑结构等一系列建模选择。为了将语言领域的影响与声音变化区分开来,我们使用在LibriSpeech上训练的文本到语音系统合成目标领域的音频。我们将目标领域中的n元组和神经网络语言模型融入到无需重新训练声学模型的领域中,实现自适应适配。据我们所知,这是第一次在不同领先架构的ASR系统中进行受控比较,以了解其在领域转移中的表现。结果表明,在领域转移的情况下,影响性能的不是解码器架构的选择或经典模块化与新颖seq2seq模型之间的区别,而是特定的建模选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at IEEE ASRU 2025
Summary
本文分析了领域不匹配情况下自动语音识别(ASR)的建模选择,对比了经典模块化和新型序列到序列(seq2seq)架构。文章通过合成目标域音频,探讨了标签单元、上下文长度和拓扑结构等一系列建模选择的影响。为提高领域适应性,文章引入了目标域n-gram和神经网络语言模型,而无需重新训练声学模型。本文首次对优化后的ASR系统在领域转移情况下的先进架构进行了控制比较,为其泛化能力提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- 本文对比了经典模块化和新型序列到序列(seq2seq)架构在领域不匹配情况下的自动语音识别(ASR)建模选择。
- 通过合成目标域音频,探讨了语言领域效果与声学变化的影响。
- 引入目标域n-gram和神经网络语言模型,提高领域适应性,无需重新训练声学模型。
- 文章重点强调了建模选择,如标签单元、上下文长度和拓扑结构,对ASR性能的影响。
- 在领域转移情况下,解码器架构的选择以及经典模块化和seq2seq模型之间的区别并不是影响性能的主要因素。
- 本文是首次对优化后的ASR系统在领域转移情况下的先进架构进行控制比较。
点此查看论文截图



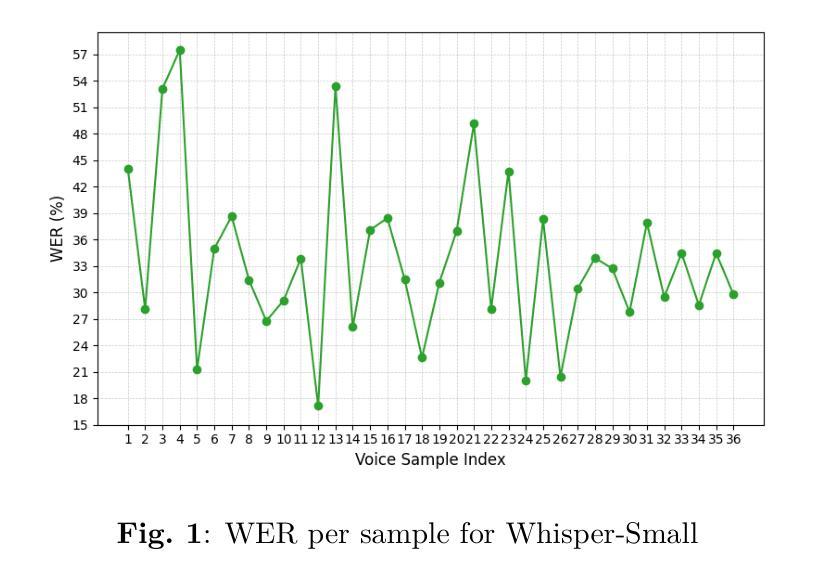
Assessing the Feasibility of Lightweight Whisper Models for Low-Resource Urdu Transcription
Authors:Abdul Rehman Antall, Naveed Akhtar
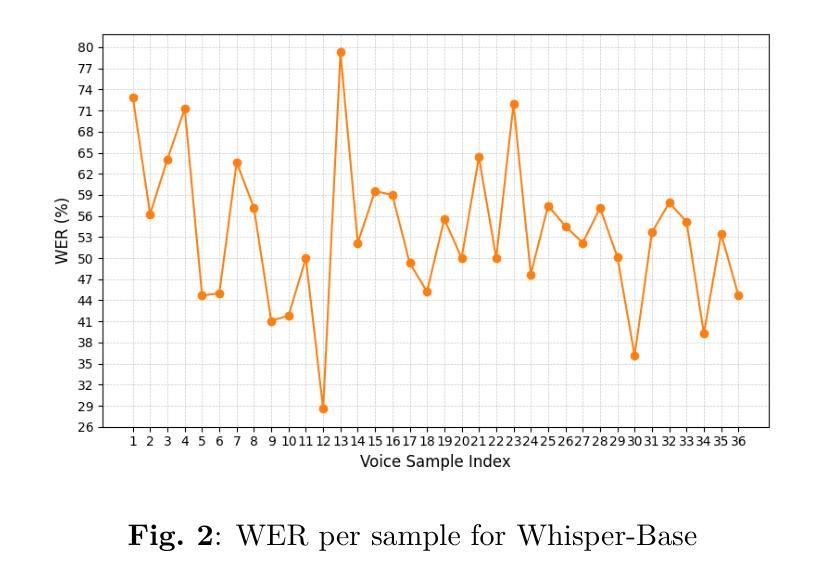
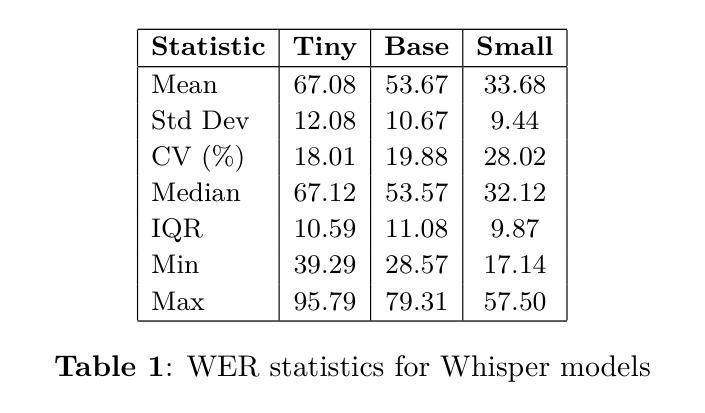
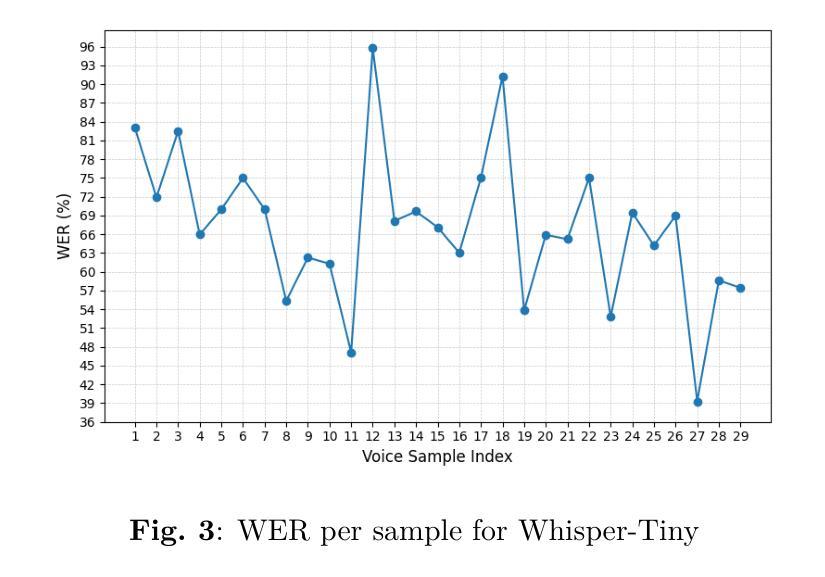
This study evaluates the feasibility of lightweight Whisper models (Tiny, Base, Small) for Urdu speech recognition in low-resource settings. Despite Urdu being the 10th most spoken language globally with over 230 million speakers, its representation in automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems remains limited due to dialectal diversity, code-switching, and sparse training data. We benchmark these models on a curated Urdu dataset using word error rate (WER), without fine-tuning. Results show Whisper-Small achieves the lowest error rates (33.68% WER), outperforming Tiny (67.08% WER) and Base (53.67% WER). Qualitative analysis reveals persistent challenges in phonetic accuracy and lexical coherence, particularly for complex utterances. While Whisper-Small demonstrates promise for deployable Urdu ASR, significant gaps remain. Our findings emphasize lay the groundwork for future research into effective, low-resource ASR systems.
本研究旨在评估轻量化Whisper模型(Tiny、Base、Small)在低资源环境下进行乌尔都语语音识别任务的可行性。尽管乌尔都语是全球第十大语言,拥有超过2.3亿使用者,但由于方言多样性、代码切换和稀疏的训练数据,其在自动语音识别(ASR)系统中的代表性仍然有限。我们在精选的乌尔都语数据集上,未经微调,使用单词错误率(WER)对这些模型进行基准测试。结果表明,Whisper-Small取得了最低的误差率(33.68% WER),优于Tiny(67.08% WER)和Base(53.67% WER)。定性分析表明,在语音准确性和词汇连贯性方面仍然存在持久的挑战,特别是在复杂的话语中。虽然Whisper-Small在可部署的乌尔都语ASR方面显示出潜力,但仍存在重大差距。我们的研究结果强调了未来研究有效低资源ASR系统的基础工作的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 3 figures, 1 table, including references and appendix
摘要
本研究探讨了轻量级Whisper模型(Tiny、Base、Small)在资源有限的环境中用于乌尔都语语音识别技术的可行性。虽然乌尔都语是全球第十大语言并拥有超过两亿三千万的母语者,但由于方言多样性、代码切换以及训练数据稀缺等问题,其在自动语音识别(ASR)系统中的代表性仍然有限。我们在精选的乌尔都语数据集上对这些模型进行了词错误率(WER)的基准测试,且未对其进行微调。结果表明,Whisper-Small取得了最低的错误率(33.68% WER),优于Tiny(67.08% WER)和Base(53.67% WER)。定性分析表明,语音准确度和词汇连贯性方面仍存在持续的挑战,尤其是复杂的陈述。虽然Whisper-Small对于可部署的乌尔都语ASR表现出良好的潜力,但仍存在明显的差距。我们的研究为探索高效、资源有限的ASR系统提供了重要的研究基础。
关键见解
- 研究评估了轻量级Whisper模型在资源有限的场景下对乌尔都语语音识别的适用性。
- 尽管乌尔都语有大量的母语者,其在自动语音识别系统中的代表性仍然受限。
- 主要的挑战来源于方言多样性、代码切换和稀缺的训练数据。
- Whisper-Small模型取得了最低的词错误率(WER),相较于其他模型表现出较好的性能。
- 定性分析揭示了语音准确性和词汇连贯性方面的持续挑战,尤其在处理复杂语句时。
- 虽然Whisper-Small模型在乌尔都语ASR方面显示出潜力,但仍存在显著的改进空间。
点此查看论文截图


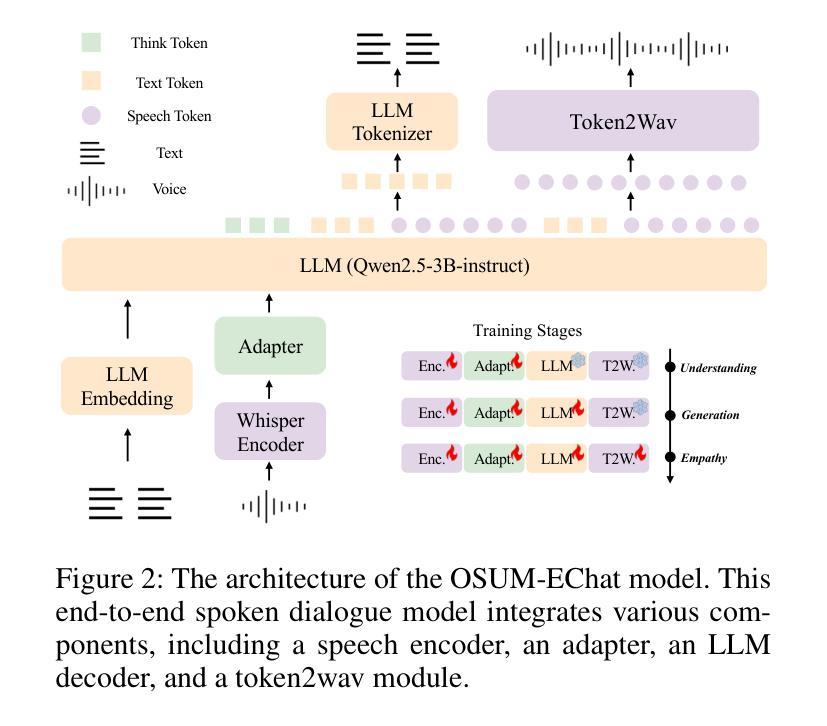
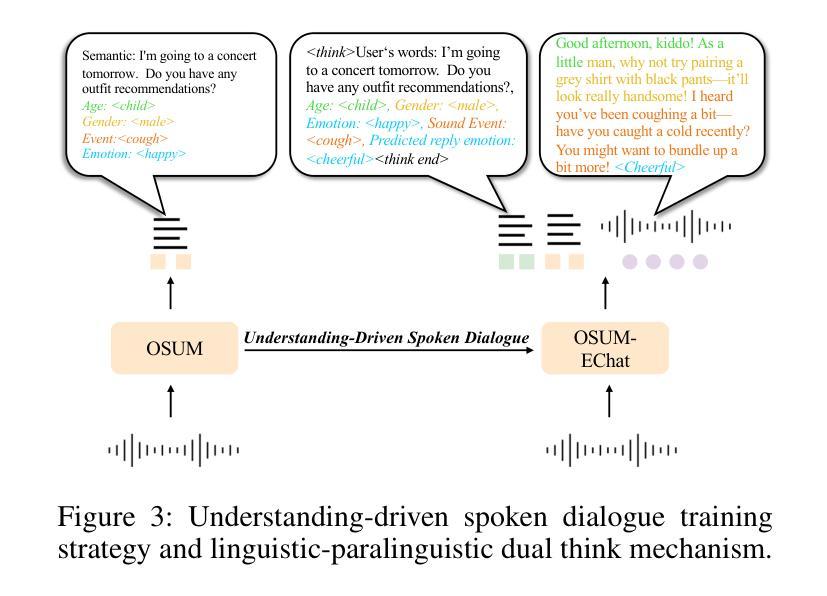
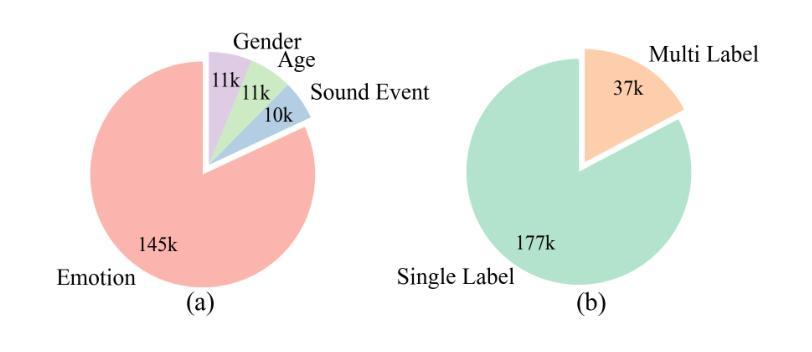
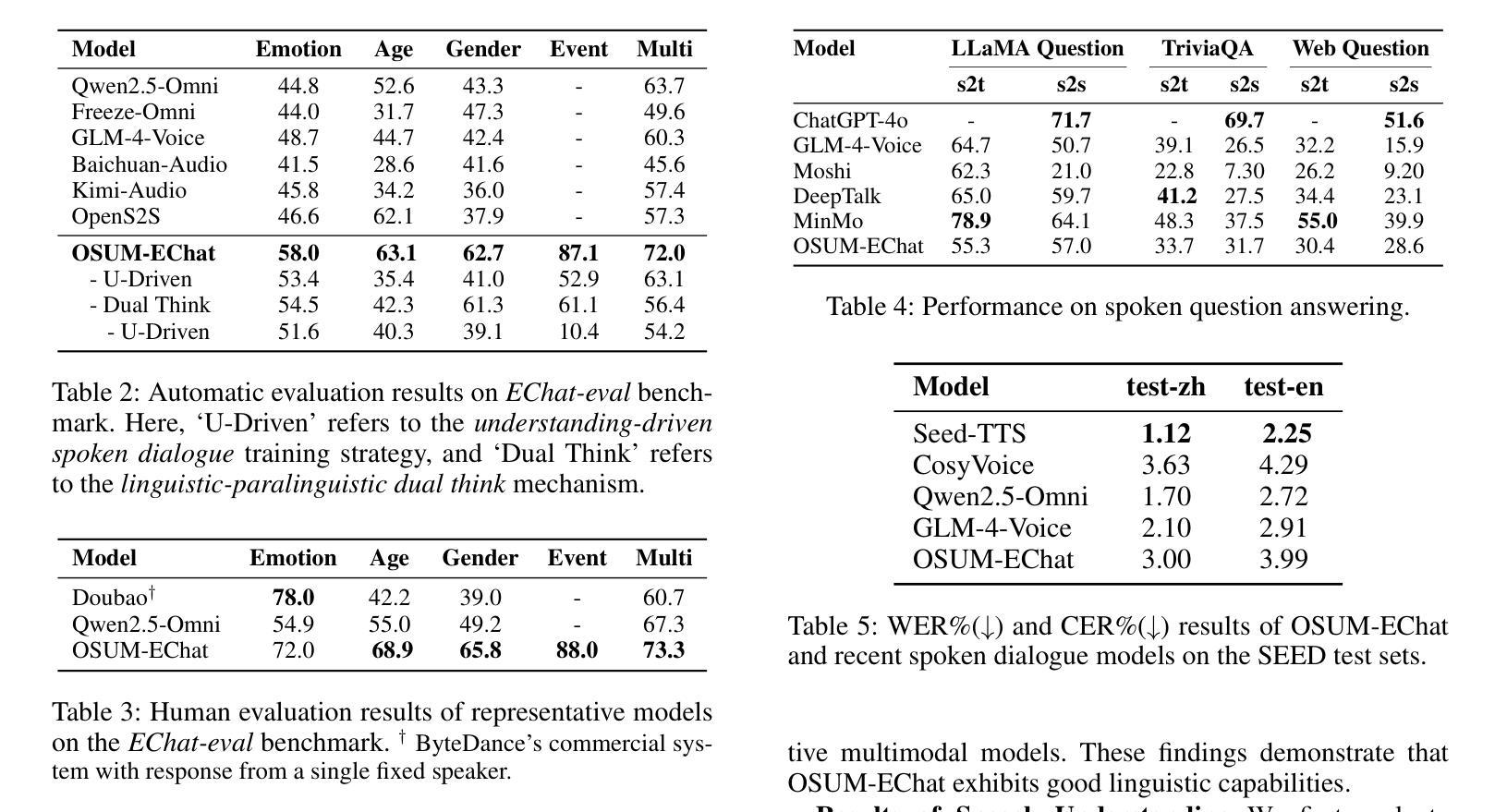
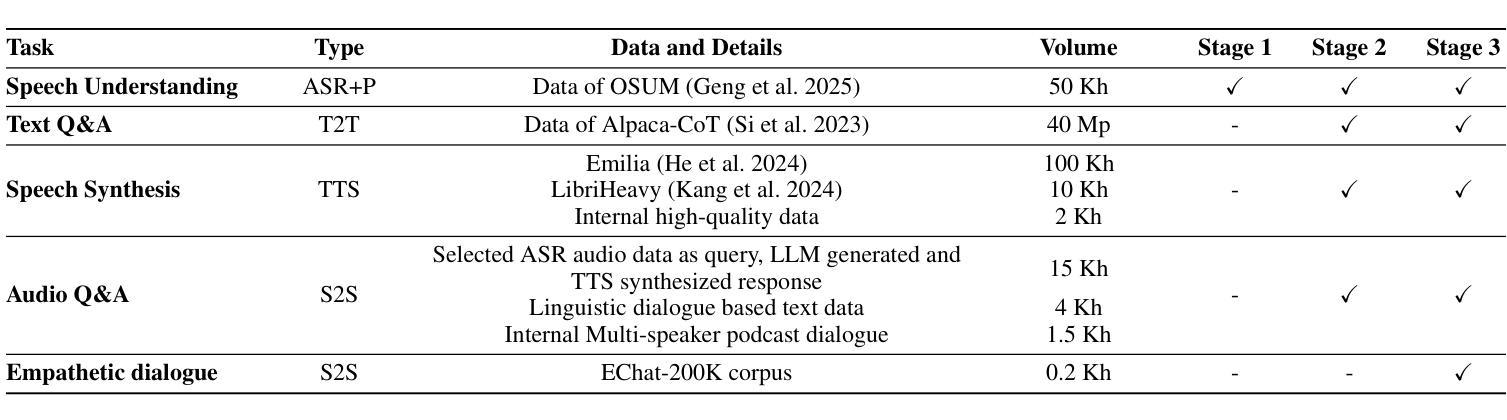
OSUM-EChat: Enhancing End-to-End Empathetic Spoken Chatbot via Understanding-Driven Spoken Dialogue
Authors:Xuelong Geng, Qijie Shao, Hongfei Xue, Shuiyuan Wang, Hanke Xie, Zhao Guo, Yi Zhao, Guojian Li, Wenjie Tian, Chengyou Wang, Zhixian Zhao, Kangxiang Xia, Ziyu Zhang, Zhennan Lin, Tianlun Zuo, Mingchen Shao, Yuang Cao, Guobin Ma, Longhao Li, Yuhang Dai, Dehui Gao, Dake Guo, Lei Xie
Empathy is crucial in enabling natural interactions within spoken dialogue systems, allowing machines to recognize and respond appropriately to paralinguistic cues such as age, gender, and emotion. Recent advancements in end-to-end speech language models, which unify speech understanding and generation, provide promising solutions. However, several challenges persist, including an over-reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets, insufficient extraction of paralinguistic cues vital for conveying empathy, and the lack of empathy-specific datasets and evaluation frameworks. To address these issues, we introduce OSUM-EChat, an open-source, end-to-end spoken dialogue system designed to enhance empathetic interactions, particularly in resource-limited settings. OSUM-EChat introduces two key innovations: (1) a three-stage understanding-driven spoken dialogue training strategy that extends the capabilities of a large speech understanding model to spoken dialogue tasks, and (2) a linguistic-paralinguistic dual thinking mechanism that integrates paralinguistic understanding through a chain of thought with dialogue generation, enabling the system to produce more empathetic responses. This approach reduces reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets while maintaining high-quality empathetic interactions. Additionally, we introduce the EChat-200K dataset, a rich corpus of empathetic speech-to-speech dialogues, and the EChat-eval benchmark, a comprehensive framework for evaluating the empathetic capabilities of dialogue systems. Experimental results demonstrate that OSUM-EChat outperforms end-to-end spoken dialogue models regarding empathetic responsiveness, validating its effectiveness.
共情在口语对话系统中实现自然交互至关重要,它使机器能够识别和适当回应诸如年龄、性别和情绪等副语言线索。端到端语音识别模型的最新进展,这些模型统一了语音理解和生成,提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,仍然存在一些挑战,包括过度依赖大规模的对话数据集、对传达共情至关重要的副语言线索提取不足,以及缺乏针对共情的特定数据集和评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们推出了OSUM-EChat,这是一个开源的端到端口语对话系统,旨在增强共情互动,特别是在资源有限的环境中。OSUM-EChat引入了两个关键的创新点:(1)一个三阶段的理解驱动口语对话训练策略,它扩展了大型语音识别模型在口语对话任务上的能力;(2)一种语言副语言双重思考机制,它将副语言理解与思维链相结合,推动对话生成,使系统能够产生更具共情的回应。这种方法减少了大规模对话数据集的依赖,同时保持了高质量的共情互动。此外,我们还推出了EChat-200K数据集,这是一份丰富的共情语音对话语料库,以及EChat-eval基准测试,这是一个全面评估对话系统共情能力的框架。实验结果表明,OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于端到端的口语对话模型,验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调了在口语对话系统中实现自然交互时,共情的重要性。文章介绍了共情在口语对话系统中的作用,包括识别和理解非语言线索如年龄、性别和情感的能力。同时提到了端到端的自然语言模型在该领域的最新进展和面临的挑战。为解决这些问题,本文提出了OSUM-EChat系统,它通过引入理解驱动的三阶段口语对话训练策略和结合语言与非语言认知的双重思考机制来增强共感情境下的交互。此外,本文还介绍了为评估共情能力对话系统性能而引入的EChat-200K数据集和EChat-eval基准测试。实验结果显示OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于传统的口语对话模型。
Key Takeaways
以下是本论文的七个关键要点:
- 共情在口语对话系统中是实现自然交互的关键要素。
- 机器需要理解和响应非语言线索如年龄、性别和情感。
- 端到端的自然语言模型为口语对话提供了新的解决方案。
- OSUM-EChat系统通过训练策略和创新机制增强了共感情境下的交互。
- OSUM-EChat引入的理解驱动的三阶段口语对话训练策略提高了模型的性能。
- 语言与非语言认知的双重思考机制使系统能够产生更具共情的响应。
点此查看论文截图

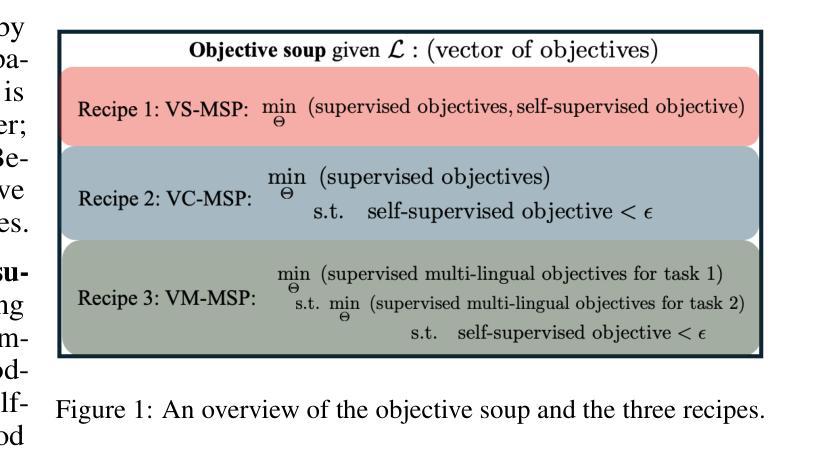
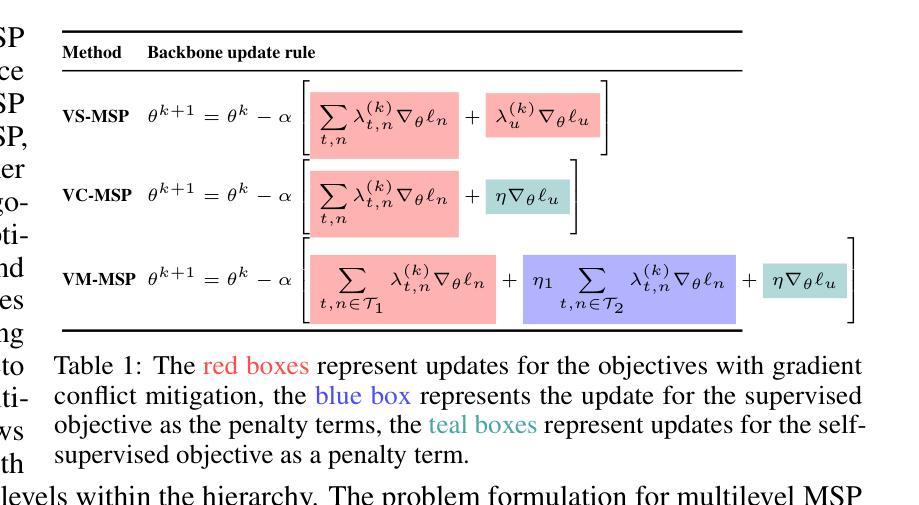
Objective Soups: Multilingual Multi-Task Modeling for Speech Processing
Authors:A F M Saif, Lisha Chen, Xiaodong Cui, Songtao Lu, Brian Kingsbury, Tianyi Chen
Training a single model for multilingual, multi-task speech processing (MSP) is severely hampered by conflicting objectives between tasks like speech recognition and translation. While multi-objective optimization (MOO) aims to align gradient updates, its effectiveness diminishes as the number of tasks grows, making it difficult to find a common descent direction. This raises a fundamental question: should highly conflicting objectives be optimized jointly or separated into a hierarchical structure? To address this question, this paper investigates three multi-objective MSP formulations, which we refer to as \textbf{objective soup recipes}. These formulations apply multi-objective optimization at different optimization levels to mitigate potential conflicts among all objectives. To ensure efficiency, we introduce a lightweight layer-selection mechanism that computes the conflict-avoiding gradient using only the most problematic layers, minimizing computational and memory overhead. Extensive experiments on CoVoST v2, LibriSpeech, and AISHELL-1 reveal that a bi-level recipe separating recognition and translation tasks consistently outperforms standard flat optimization. Our work demonstrates that hierarchical MOO is a more effective and scalable approach for building state-of-the-art MSP models. Our code has been released at https://github.com/afmsaif/Objective_Soups.
对多种语言多任务语音处理(MSP)进行单一模型训练,因任务如语音识别和翻译之间存在目标冲突而受到严重阻碍。虽然多目标优化(MOO)旨在对齐梯度更新,但随着任务数量的增长,其有效性降低,难以找到共同的下降方向。这就提出了一个基本问题:高度冲突的目标应该联合优化还是分层优化?为了回答这个问题,本文研究了三种多目标MSP公式,我们称之为“目标汤配方”。这些公式在不同的优化层次上应用多目标优化,以减轻所有目标之间的潜在冲突。为了保证效率,我们引入了一种轻量级的层选择机制,仅使用最困难的层来计算避免冲突的梯度,以最小化计算和内存开销。在CoVoST v2、LibriSpeech和AISHELL-1上的大量实验表明,将识别和翻译任务分离的二级配方始终优于标准平面优化。我们的工作证明,分层MOO是一种更有效且可扩展的方法,适用于构建最先进的MSP模型。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/afmsaif/Objective_Soups上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了单一模型在多语言多任务语音处理(MSP)中的挑战,尤其是任务目标之间的冲突问题。文章提出了三种多目标语音处理方案,被称为“目标汤配方”,在不同优化层次上应用多目标优化来缓解各目标之间的潜在冲突。同时,引入了一种轻量级的层选择机制,仅使用最具有问题的层来计算避免冲突的梯度,以提高效率。实验表明,采用双层配方分离识别和翻译任务的方法优于标准的平面优化方法。文章证明分层多目标优化是构建先进MSP模型更有效、更可扩展的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多语言多任务语音处理(MSP)在单一模型中面临任务目标冲突的挑战。
- 多目标优化(MOO)旨在对齐梯度更新,但随着任务数量的增加,其有效性会降低,难以找到共同的下降方向。
- 提出了三种“目标汤配方”的多目标MSP方案,以缓解不同优化目标之间的潜在冲突。
- 引入了一种轻量级的层选择机制,以提高计算效率和避免内存开销。
- 双层配方分离识别和翻译任务的方法在实验上表现最好,优于标准的平面优化方法。
- 分层多目标优化是构建先进MSP模型更有效、更可扩展的方法。
点此查看论文截图

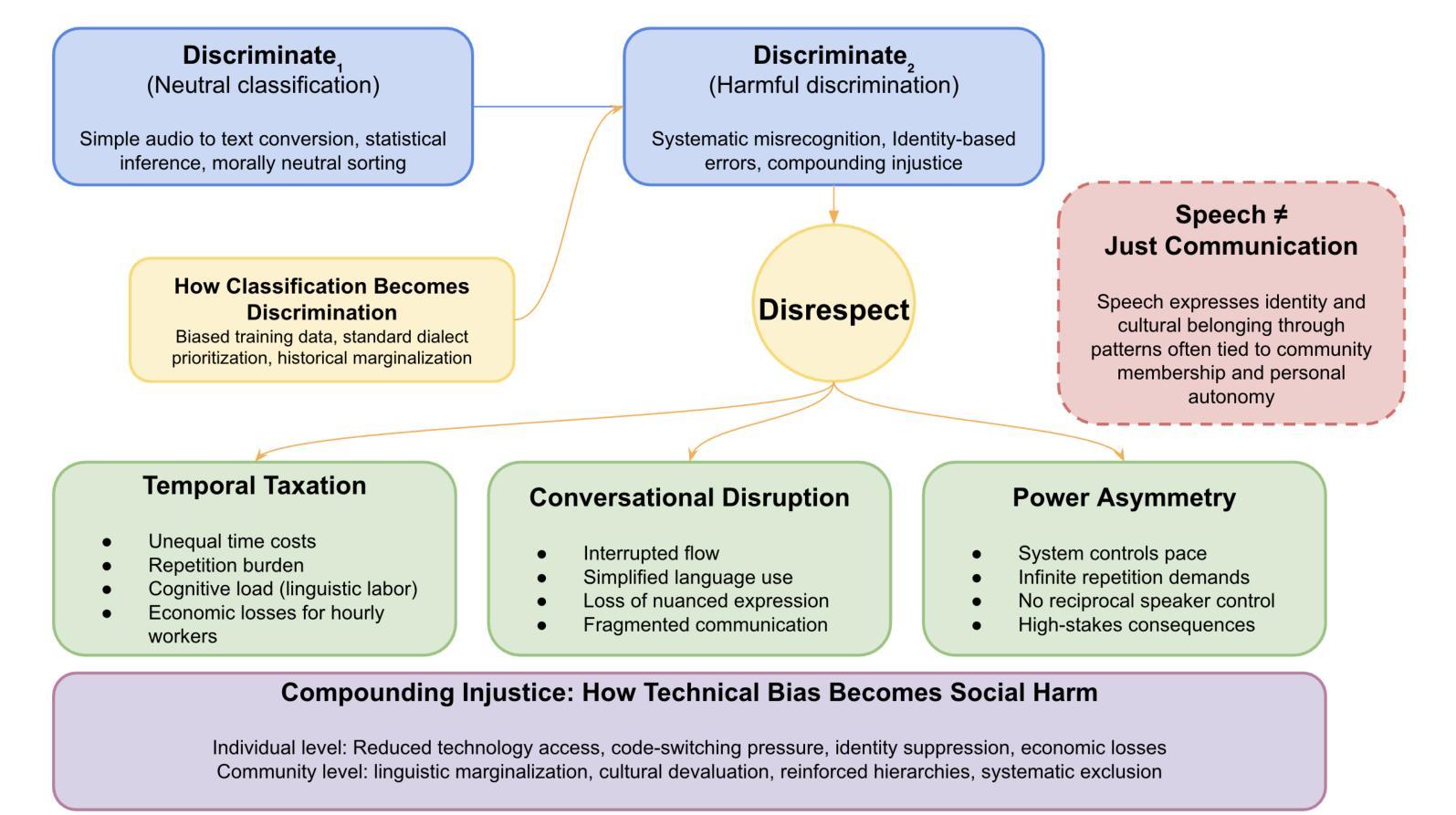
Fairness of Automatic Speech Recognition: Looking Through a Philosophical Lens
Authors:Anna Seo Gyeong Choi, Hoon Choi
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems now mediate countless human-technology interactions, yet research on their fairness implications remains surprisingly limited. This paper examines ASR bias through a philosophical lens, arguing that systematic misrecognition of certain speech varieties constitutes more than a technical limitation – it represents a form of disrespect that compounds historical injustices against marginalized linguistic communities. We distinguish between morally neutral classification (discriminate1) and harmful discrimination (discriminate2), demonstrating how ASR systems can inadvertently transform the former into the latter when they consistently misrecognize non-standard dialects. We identify three unique ethical dimensions of speech technologies that differentiate ASR bias from other algorithmic fairness concerns: the temporal burden placed on speakers of non-standard varieties (“temporal taxation”), the disruption of conversational flow when systems misrecognize speech, and the fundamental connection between speech patterns and personal/cultural identity. These factors create asymmetric power relationships that existing technical fairness metrics fail to capture. The paper analyzes the tension between linguistic standardization and pluralism in ASR development, arguing that current approaches often embed and reinforce problematic language ideologies. We conclude that addressing ASR bias requires more than technical interventions; it demands recognition of diverse speech varieties as legitimate forms of expression worthy of technological accommodation. This philosophical reframing offers new pathways for developing ASR systems that respect linguistic diversity and speaker autonomy.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统如今中介了无数的人机交互,然而关于它们对公平性的影响的研究仍然出人意料地有限。本文通过哲学视角研究ASR偏见,认为对某些语音特性的系统性误识别不仅仅是技术局限——它代表了对边缘化语言社群历史不公的一种不尊重。我们区分了道德中立的分类(辨别1)和有害的歧视(辨别2),展示了当ASR系统持续误识别非标准方言时,如何将前者无意中转变为后者。我们确定了语音技术的三个独特的道德维度,这些维度将ASR偏见与其他算法公平性问题区分开来:对非标准方言发言人的时间负担(“时间税负”)、系统误识别语音时对会话流程的破坏,以及语音模式与个人/文化身份之间的根本联系。这些因素造成了不对称的权力关系,而现有的技术公平指标却无法捕捉到这一点。本文分析了ASR发展中语言标准化和多元化的紧张关系,认为当前的方法往往嵌入并强化了有问题的语言理念。我们得出结论,解决ASR偏见不仅需要技术干预;它要求将多样的语音变体视为值得技术适应的合法表达方式。这种哲学重构为开发尊重语言多样性和说话者自主权的ASR系统提供了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AIES 2025
Summary:
语音识别系统对多种语言的公平性影响备受关注,该文探讨了其背后的偏见问题。文章指出,语音识别系统对特定语音种类的系统性误识别不仅是技术局限,更是对边缘语言群体历史不公的加剧。文章区分了道德中立分类和有害歧视,并指出语音识别系统在误识别非标准方言时如何将前者转化为后者。此外,文章还强调了语音识别技术的三个独特伦理维度,包括非标准语音说话者的时间负担、系统误识别导致的对话流畅性的破坏以及语音模式与个人文化身份的紧密联系。现有技术公平指标无法捕捉这些不对称的权力和关系问题。文章呼吁在语音识别发展中平衡语言标准化和多元化的张力,并强调解决语音识别偏见不仅需要技术干预,还需要承认多种语音形式作为值得技术适应的合法表达方式。
Key Takeaways:
- 语音识别系统的偏见问题受到关注,它对特定语音种类的系统性误识别代表了边缘语言群体的历史不公。
- 区分了道德中立分类和有害歧视,并指出了二者在语音识别系统中的应用。
- 语音识别技术的伦理问题包括非标准语音说话者的时间负担、对话流畅性的破坏以及语音模式与个人文化身份的紧密联系。
- 现有技术公平指标无法捕捉这些伦理问题中的不对称权力关系。
- 文章强调平衡语言标准化和多元化的重要性在语音识别发展中。
- 解决语音识别偏见不仅需要技术干预,还需要承认多种语音形式作为合法表达方式。
点此查看论文截图

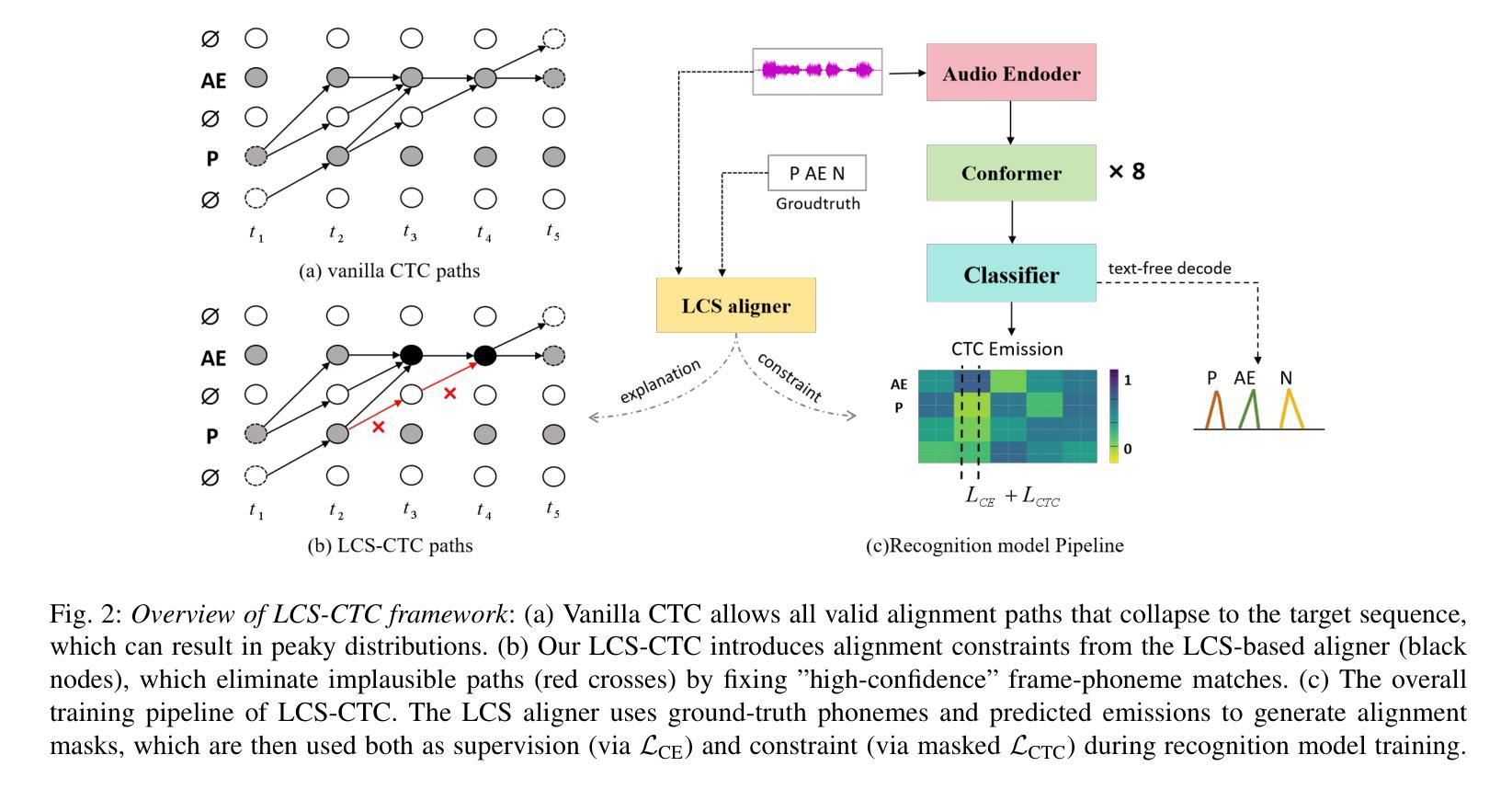
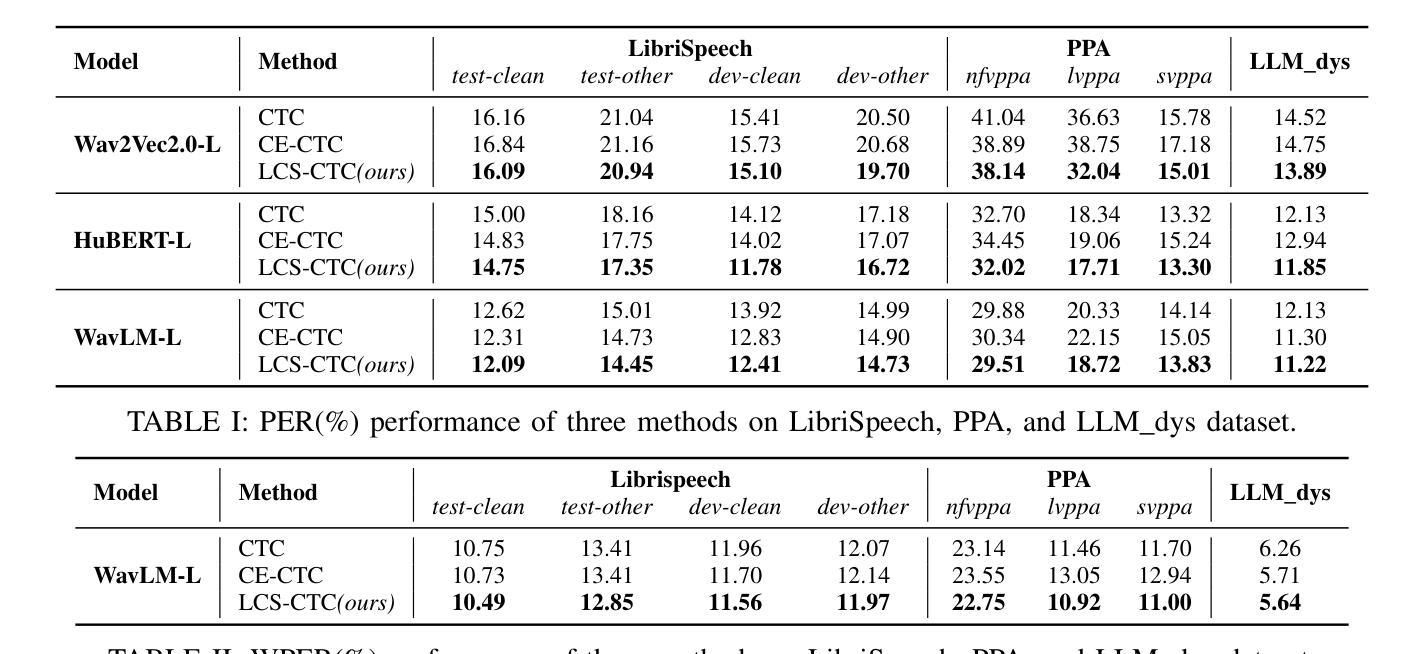
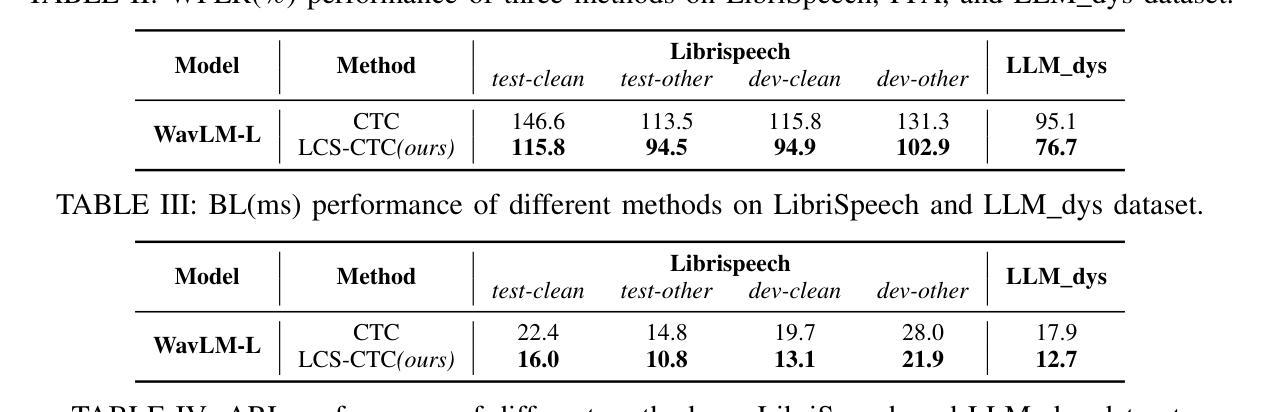
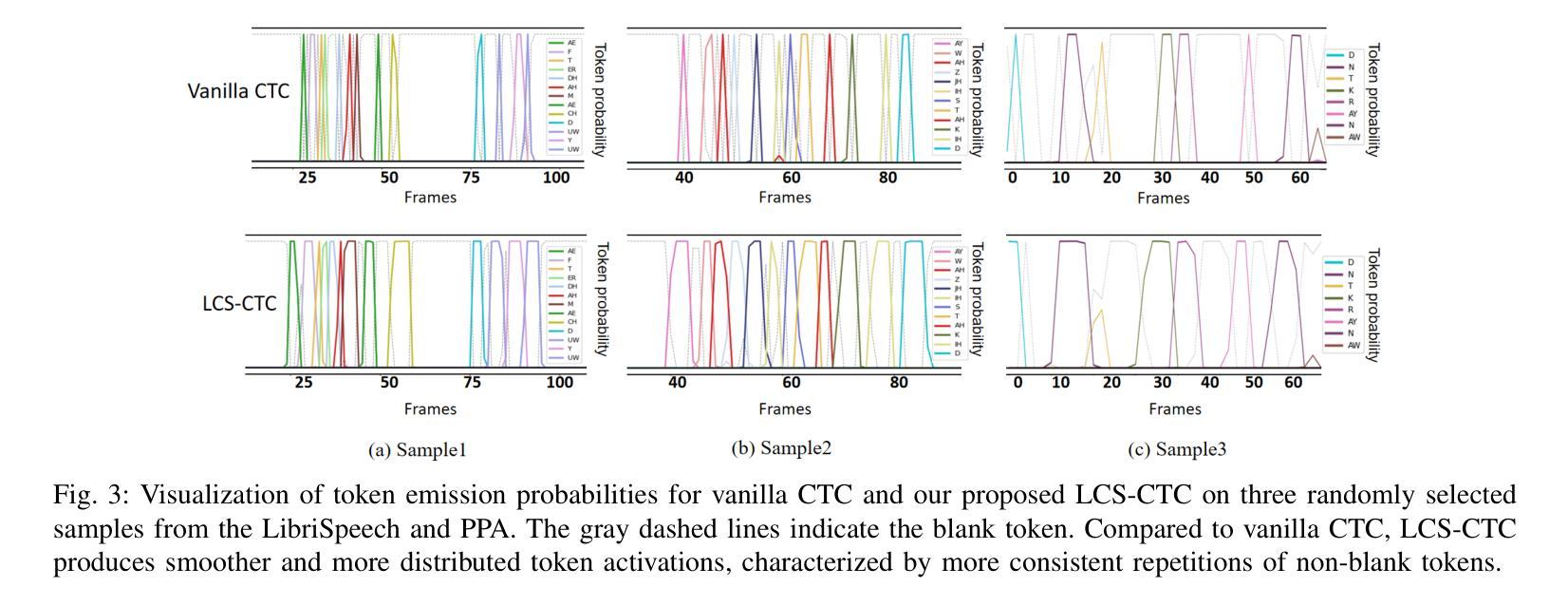
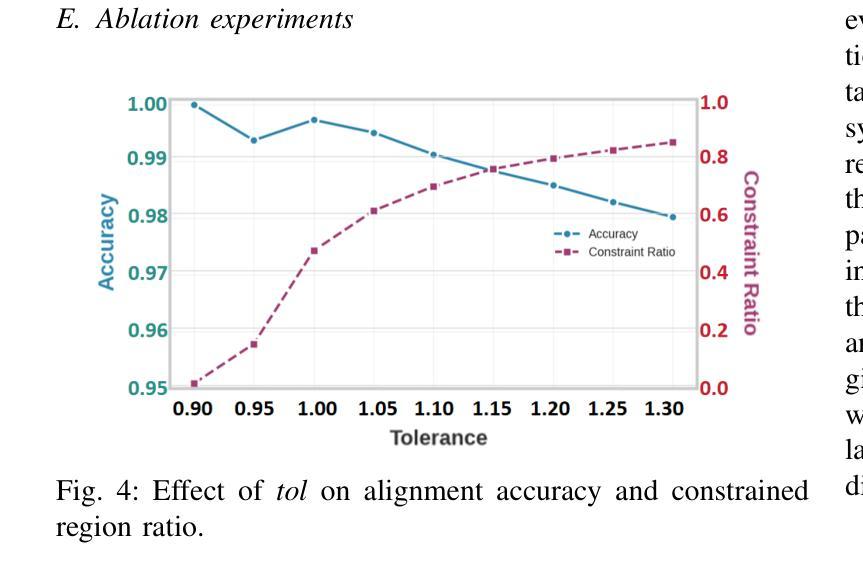
LCS-CTC: Leveraging Soft Alignments to Enhance Phonetic Transcription Robustness
Authors:Zongli Ye, Jiachen Lian, Akshaj Gupta, Xuanru Zhou, Haodong Li, Krish Patel, Hwi Joo Park, Dingkun Zhou, Chenxu Guo, Shuhe Li, Sam Wang, Iris Zhou, Cheol Jun Cho, Zoe Ezzes, Jet M. J. Vonk, Brittany T. Morin, Rian Bogley, Lisa Wauters, Zachary A. Miller, Maria Luisa Gorno-Tempini, Gopala Anumanchipalli
Phonetic speech transcription is crucial for fine-grained linguistic analysis and downstream speech applications. While Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) is a widely used approach for such tasks due to its efficiency, it often falls short in recognition performance, especially under unclear and nonfluent speech. In this work, we propose LCS-CTC, a two-stage framework for phoneme-level speech recognition that combines a similarity-aware local alignment algorithm with a constrained CTC training objective. By predicting fine-grained frame-phoneme cost matrices and applying a modified Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) algorithm, our method identifies high-confidence alignment zones which are used to constrain the CTC decoding path space, thereby reducing overfitting and improving generalization ability, which enables both robust recognition and text-free forced alignment. Experiments on both LibriSpeech and PPA demonstrate that LCS-CTC consistently outperforms vanilla CTC baselines, suggesting its potential to unify phoneme modeling across fluent and non-fluent speech.
语音发音转录对于精细的语言分析和下游语音应用至关重要。尽管连接时序分类(CTC)由于其效率而广泛应用于此类任务,但在识别性能上往往表现不佳,特别是在不清晰和非流利语音的情况下。在这项工作中,我们提出了LCS-CTC,这是一个两阶段的音素级语音识别框架,它将相似感知局部对齐算法与受约束的CTC训练目标相结合。通过预测精细的帧音素成本矩阵并应用修改后的最长公共子序列(LCS)算法,我们的方法能够识别高置信度的对齐区域,这些区域用于约束CTC解码路径空间,从而减少过拟合并提高泛化能力,从而实现稳健的识别和免文本强制对齐。在LibriSpeech和PPA上的实验表明,LCS-CTC始终优于普通CTC基准测试,这表明其在流利和非流利语音的音素建模上具有统一潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 ASRU. Correct Author List
摘要
文本提出了LCS-CTC,这是一个两阶段的音素级语音识别框架,结合了相似度感知的局部对齐算法和约束性CTC训练目标。通过预测精细的帧-音素成本矩阵并应用改进的最长公共子序列算法,LCS-CTC能够识别高置信度的对齐区域,用于约束CTC解码路径空间,从而减少过拟合并提高泛化能力。这使得LCS-CTC既具有稳健的识别能力,又能实现无文本强制对齐。在LibriSpeech和PPA上的实验表明,LCS-CTC持续优于传统的CTC基线,显示出其在流利和非流利语音中的音素建模潜力。
关键见解
- Phonetic speech transcription对于精细的语言分析和下游语音应用至关重要。
- CTC(连接时序分类)因效率而广泛应用于语音任务,但在不清晰和非流利的语音中识别性能较差。
- LCS-CTC是一个两阶段的音素级语音识别框架,通过结合相似度感知的局部对齐算法和约束性CTC训练目标来解决CTC的识别问题。
- LCS-CTC通过预测精细的帧-音素成本矩阵并应用LCS算法,能识别高置信度的对齐区域,约束CTC解码路径。
- LCS-CTC减少了模型过拟合,提高了泛化能力。
- LCS-CTC实现了稳健的语音识别和无文本强制对齐。
- 在LibriSpeech和PPA的实验中,LCS-CTC优于传统的CTC基线,显示出其在语音识别的广泛应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图


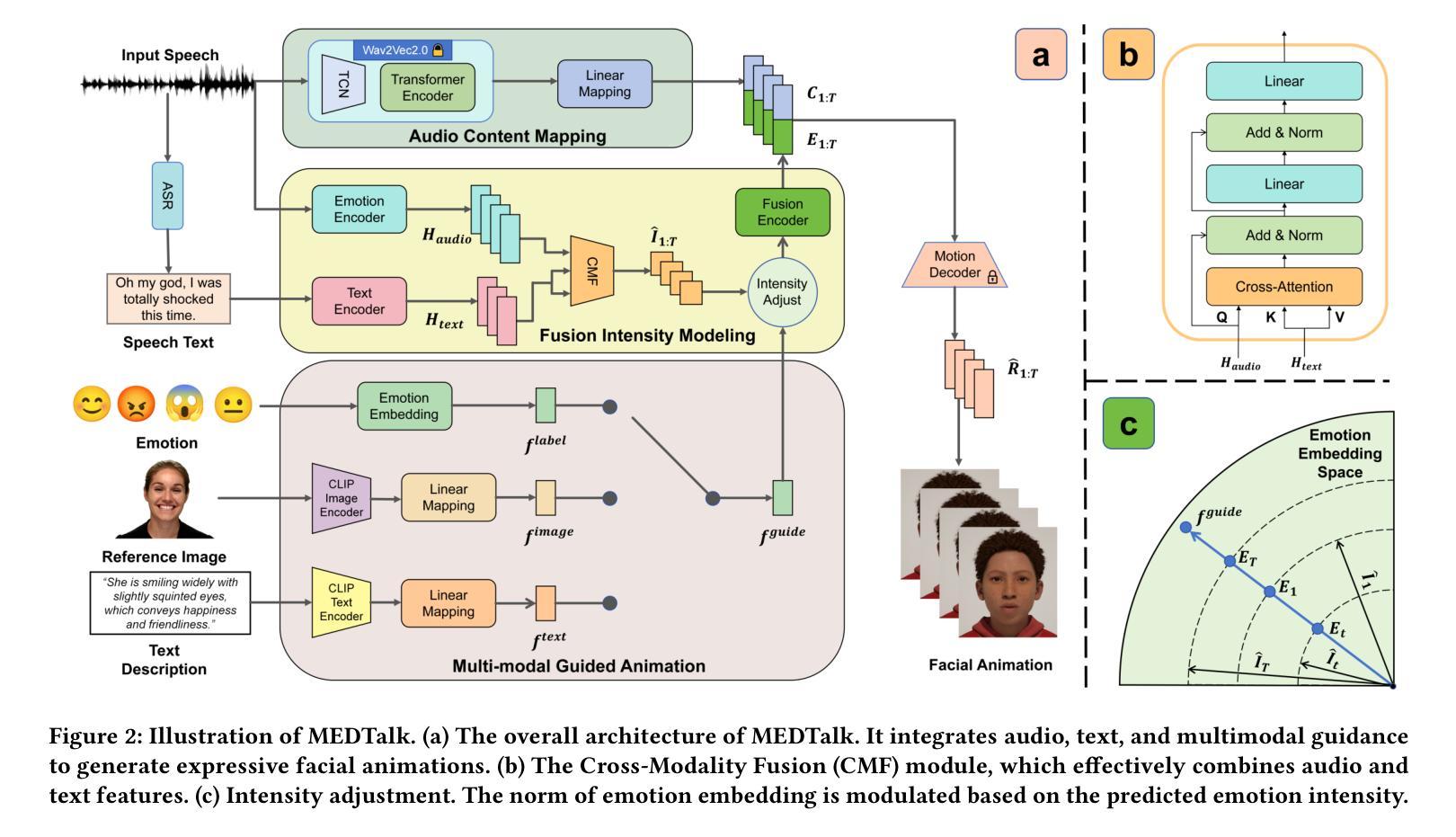
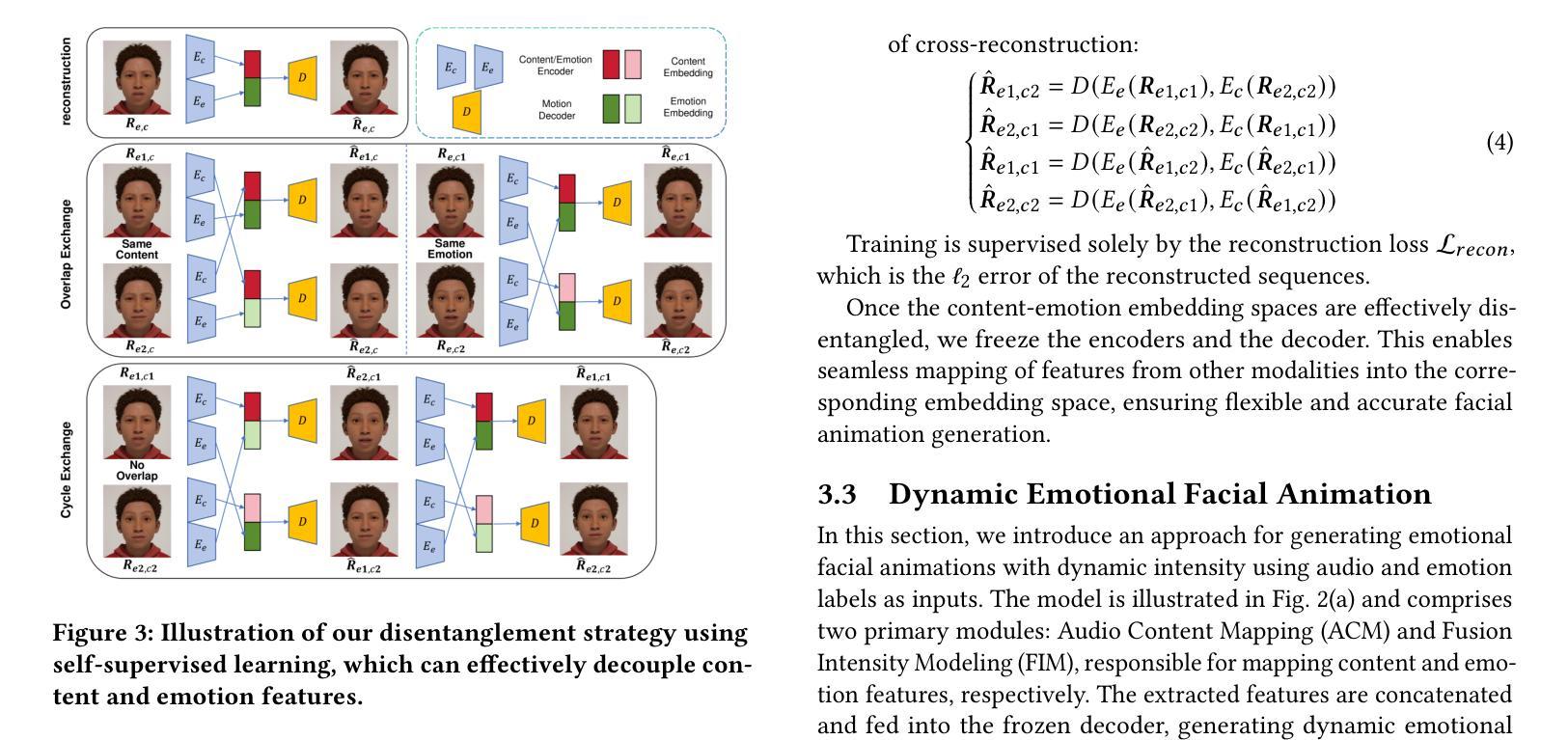
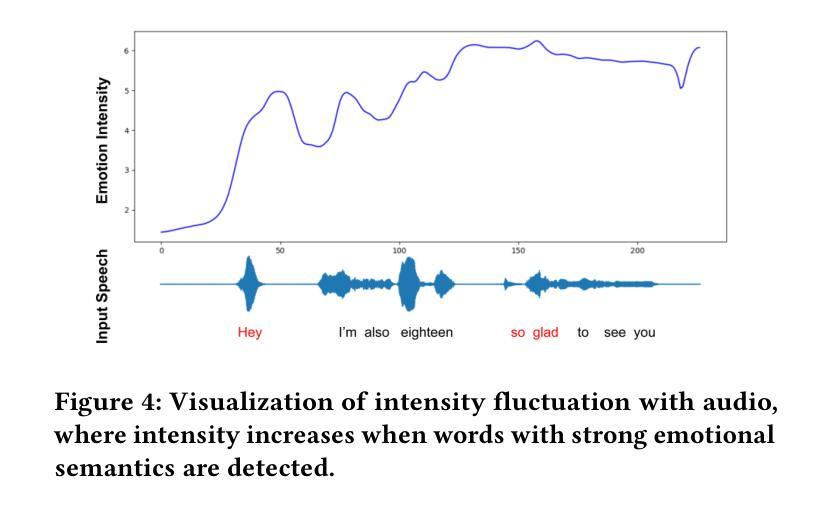
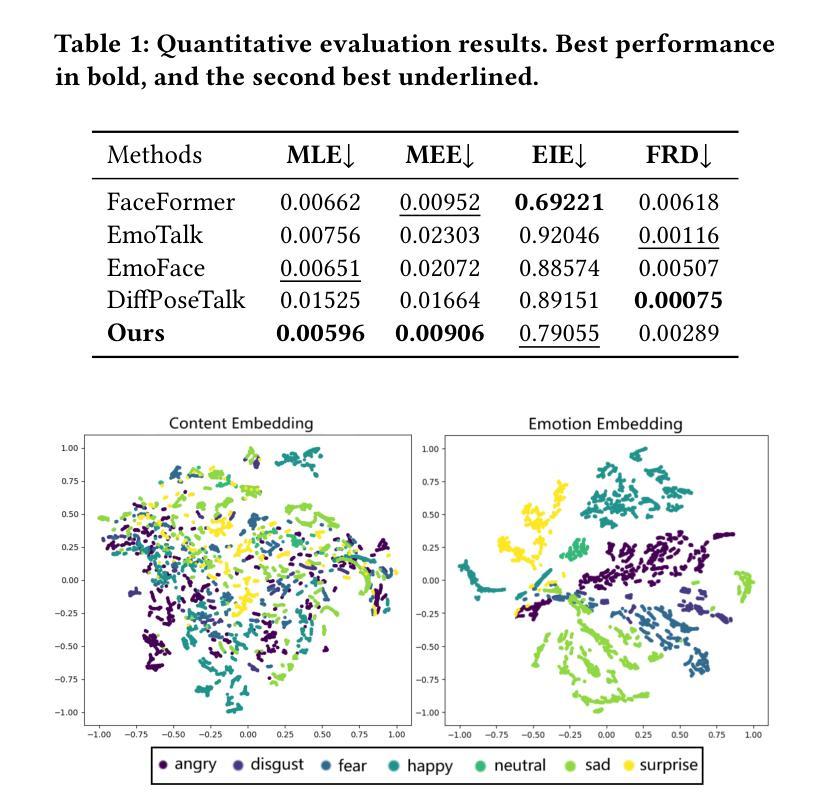
MEDTalk: Multimodal Controlled 3D Facial Animation with Dynamic Emotions by Disentangled Embedding
Authors:Chang Liu, Ye Pan, Chenyang Ding, Susanto Rahardja, Xiaokang Yang
Audio-driven emotional 3D facial animation aims to generate synchronized lip movements and vivid facial expressions. However, most existing approaches focus on static and predefined emotion labels, limiting their diversity and naturalness. To address these challenges, we propose MEDTalk, a novel framework for fine-grained and dynamic emotional talking head generation. Our approach first disentangles content and emotion embedding spaces from motion sequences using a carefully designed cross-reconstruction process, enabling independent control over lip movements and facial expressions. Beyond conventional audio-driven lip synchronization, we integrate audio and speech text, predicting frame-wise intensity variations and dynamically adjusting static emotion features to generate realistic emotional expressions. Furthermore, to enhance control and personalization, we incorporate multimodal inputs-including text descriptions and reference expression images-to guide the generation of user-specified facial expressions. With MetaHuman as the priority, our generated results can be conveniently integrated into the industrial production pipeline. The code is available at: https://github.com/SJTU-Lucy/MEDTalk.
音频驱动的情感3D面部动画旨在生成同步的唇部运动和生动的面部表情。然而,大多数现有方法侧重于静态和预定义的情感标签,这限制了其多样性和自然性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MEDTalk,这是一个用于精细粒度和动态情感说话人头部生成的全新框架。我们的方法首先通过使用精心设计的跨重建过程,从运动序列中分离内容和情感嵌入空间,实现对唇部运动和面部表情的独立控制。除了传统的音频驱动唇同步外,我们还整合了音频和语音文本,预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征,以生成逼真的情感表达。此外,为了增强控制和个性化,我们纳入多模式输入,包括文本描述和参考表情图像,以引导用户指定的面部表情生成。以MetaHuman为优先,我们生成的结果可以方便地集成到工业生产流程中。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/SJTU-Lucy/MEDTalk。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为MEDTalk的新型框架,用于精细粒度和动态情感说话头生成。该框架通过精心设计交叉重建过程,从运动序列中分离内容和情感嵌入空间,实现对唇动和面部表情的独立控制。除传统音频驱动的唇部同步外,还结合了音频和语音文本,预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征,以生成逼真的情感表达。同时,为提高控制和个性化,还纳入了包括文本描述和参考表情图像在内的多模式输入,以指导用户指定的面部表情生成。最终生成的结果可以便捷地融入工业生产流程中,如MetaHuman等。
Key Takeaways
- MEDTalk框架旨在生成精细粒度和动态的情感面部动画。
- 通过交叉重建过程分离内容和情感嵌入空间,实现唇动和面部表情的独立控制。
- 结合音频、语音文本进行唇部同步和面部表情预测。
- 预测帧强度变化并动态调整静态情感特征以生成更真实的情感表达。
- 纳入多模式输入,包括文本描述和参考表情图像,以增强控制和个性化。
- 生成的结果可融入工业生产流程。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

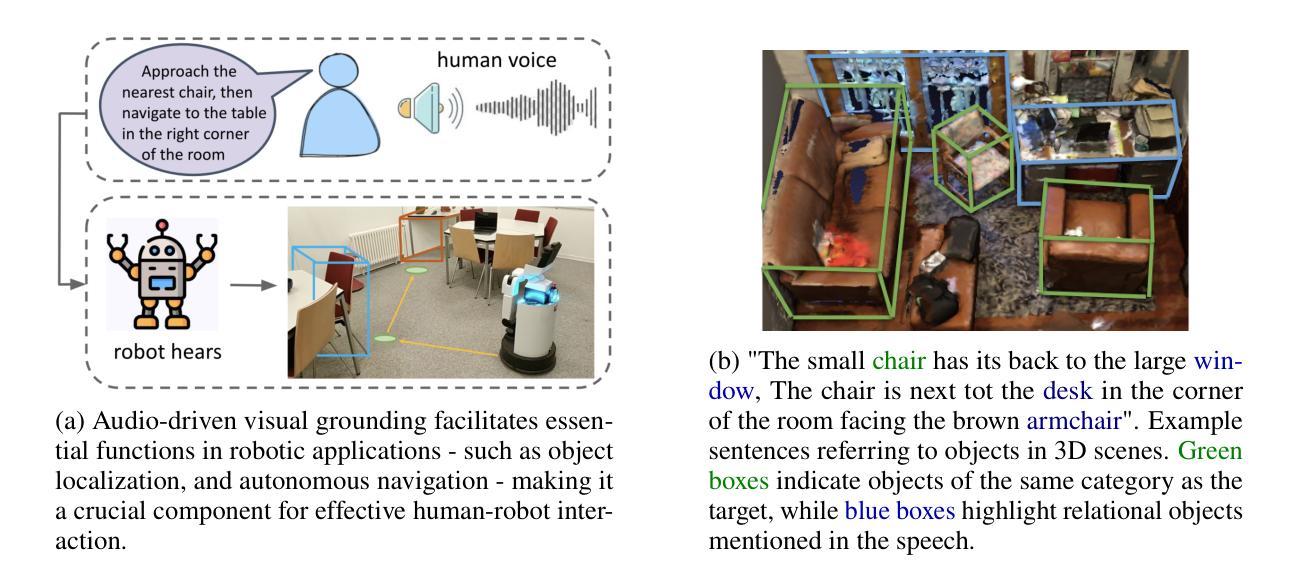
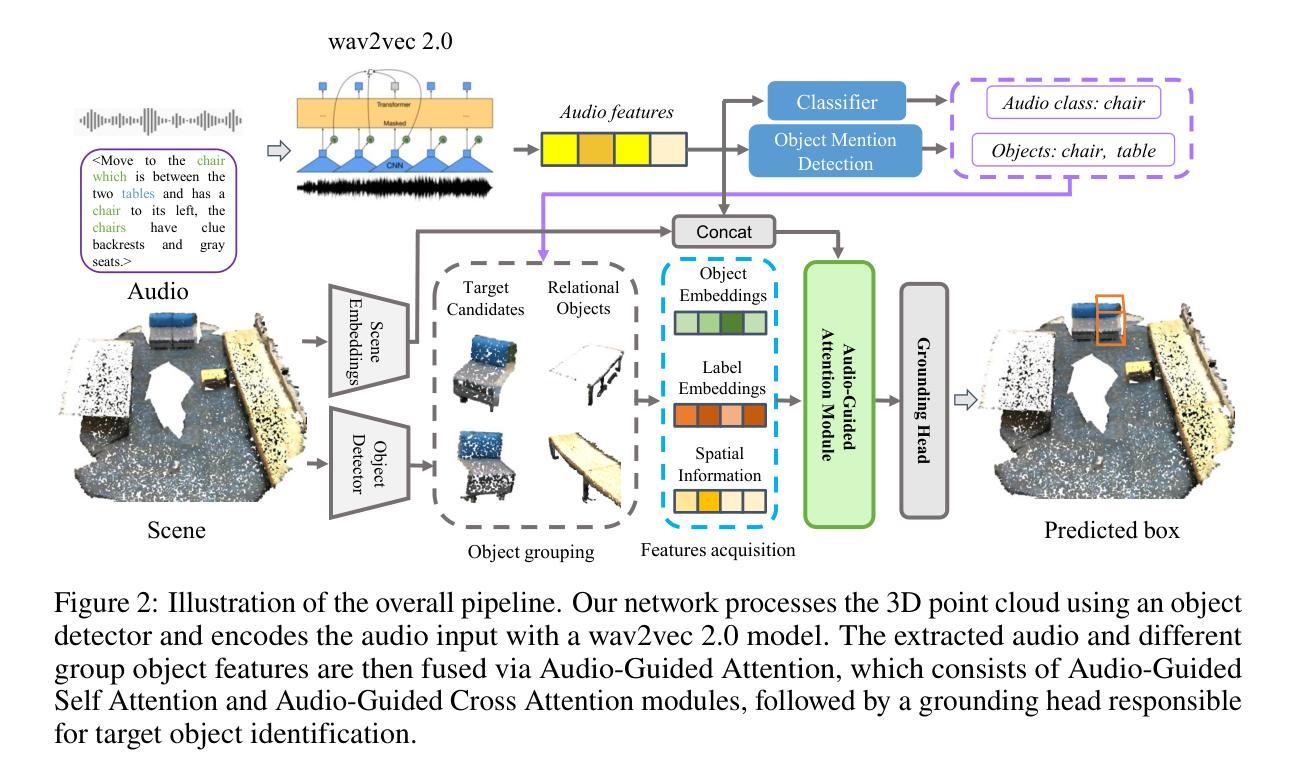
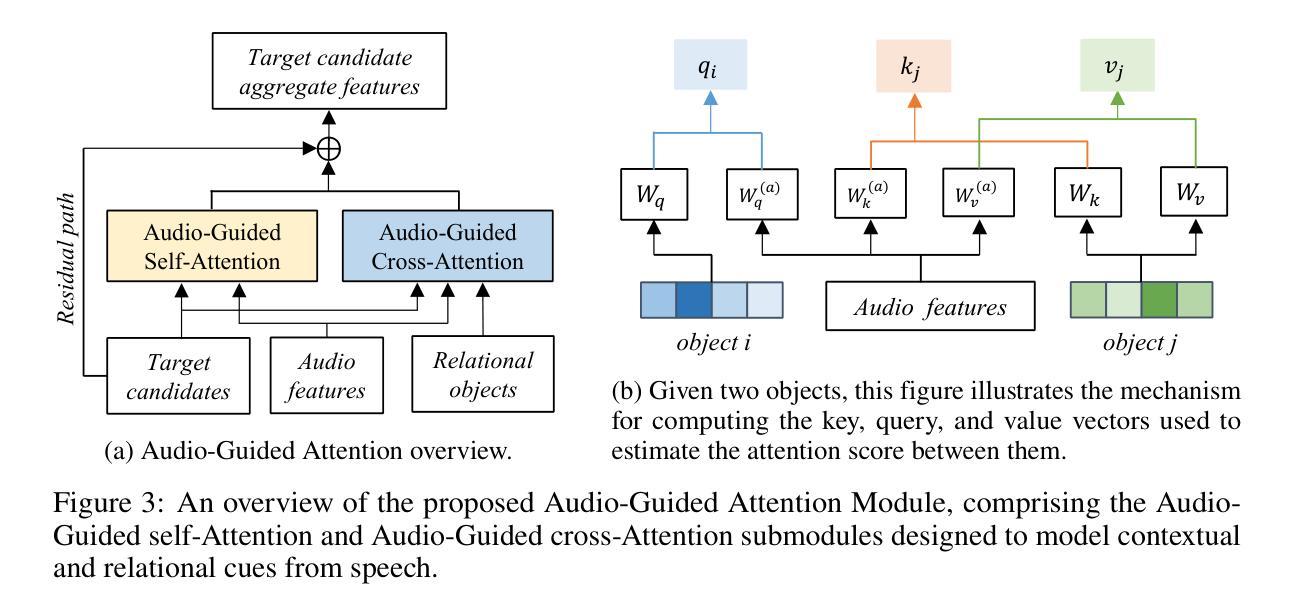
Audio-3DVG: Unified Audio – Point Cloud Fusion for 3D Visual Grounding
Authors:Duc Cao-Dinh, Khai Le-Duc, Anh Dao, Bach Phan Tat, Chris Ngo, Duy M. H. Nguyen, Nguyen X. Khanh, Thanh Nguyen-Tang
3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) involves localizing target objects in 3D point clouds based on natural language. While prior work has made strides using textual descriptions, leveraging spoken language-known as Audio-based 3D Visual Grounding-remains underexplored and challenging. Motivated by advances in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech representation learning, we propose Audio-3DVG, a simple yet effective framework that integrates audio and spatial information for enhanced grounding. Rather than treating speech as a monolithic input, we decompose the task into two complementary components. First, we introduce (i) Object Mention Detection, a multi-label classification task that explicitly identifies which objects are referred to in the audio, enabling more structured audio-scene reasoning. Second, we propose an (ii) Audio-Guided Attention module that models the interactions between target candidates and mentioned objects, enhancing discrimination in cluttered 3D environments. To support benchmarking, we (iii) synthesize audio descriptions for standard 3DVG datasets, including ScanRefer, Sr3D, and Nr3D. Experimental results demonstrate that Audio-3DVG not only achieves new state-of-the-art performance in audio-based grounding, but also competes with text-based methods, highlight the promise of integrating spoken language into 3D vision tasks.
3D视觉定位(3DVG)涉及在自然语言的基础上在3D点云中定位目标对象。虽然先前的工作在使用文本描述方面取得了进展,但利用口语的基于音频的3D视觉定位仍然被低估且具有挑战性。受自动语音识别(ASR)和语音表示学习的进步的推动,我们提出了Audio-3DVG,这是一个简单有效的框架,它集成了音频和空间信息以增强定位。我们并不将语音视为单一输入,而是将任务分解为两个互补的组成部分。首先,我们引入了(i)对象提及检测,这是一个多标签分类任务,它明确地识别了音频中提到的哪些对象,从而实现了更结构化的音频场景推理。其次,我们提出了(ii)音频引导注意力模块,该模块对目标候选物和提及的对象之间的交互进行建模,提高了在杂乱的3D环境中的辨别能力。(iii)为了支持基准测试,我们对包括ScanRefer、Sr3D和Nr3D在内的标准3DVG数据集进行了音频描述合成。实验结果表明,Audio-3DVG不仅在基于音频的定位方面取得了最新的最先进的性能,而且在与基于文本的方法竞争时也有优势,这突显了将口语融入3D视觉任务的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 51 pages
Summary
本文介绍了3D视觉定位(3DVG)在三维点云中定位目标物体的自然语言处理技术。针对音频为基础的3D视觉定位(Audio-based 3DVG)这一尚未充分探索且具有挑战性的领域,提出了Audio-3DVG框架。该框架结合了音频和空间信息,将语音分解为对象提及检测和音频引导注意力两个互补的任务。同时,为支持基准测试,对标准3DVG数据集进行了音频描述合成。实验结果证明,Audio-3DVG不仅在音频定位方面取得了最新技术成果,而且在与基于文本的3D视觉任务方法相比也有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 3D视觉定位(3DVG)涉及在三维点云中根据自然语言定位目标物体。
- 音频为基础的3D视觉定位(Audio-based 3DVG)是一个具有挑战性和尚未充分探索的领域。
- 提出的Audio-3DVG框架结合了音频和空间信息,用于增强定位。
- 语音被分解为对象提及检测和音频引导注意力两个互补的任务。
- 对象提及检测是一个多标签分类任务,明确识别音频中提到的物体,使音频场景推理更加结构化。
- 音频引导注意力模块旨在建模目标候选物和提及物体之间的交互,提高在杂乱的三维环境中的辨别力。
点此查看论文截图

EmoVoice: LLM-based Emotional Text-To-Speech Model with Freestyle Text Prompting
Authors:Guanrou Yang, Chen Yang, Qian Chen, Ziyang Ma, Wenxi Chen, Wen Wang, Tianrui Wang, Yifan Yang, Zhikang Niu, Wenrui Liu, Fan Yu, Zhihao Du, Zhifu Gao, ShiLiang Zhang, Xie Chen
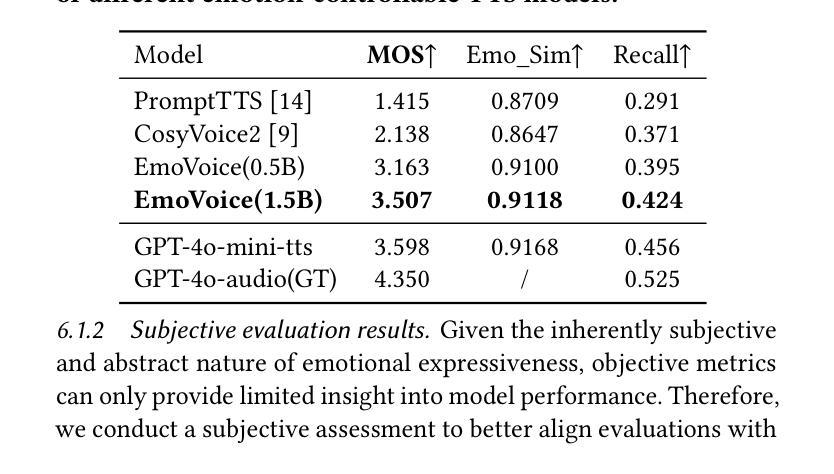
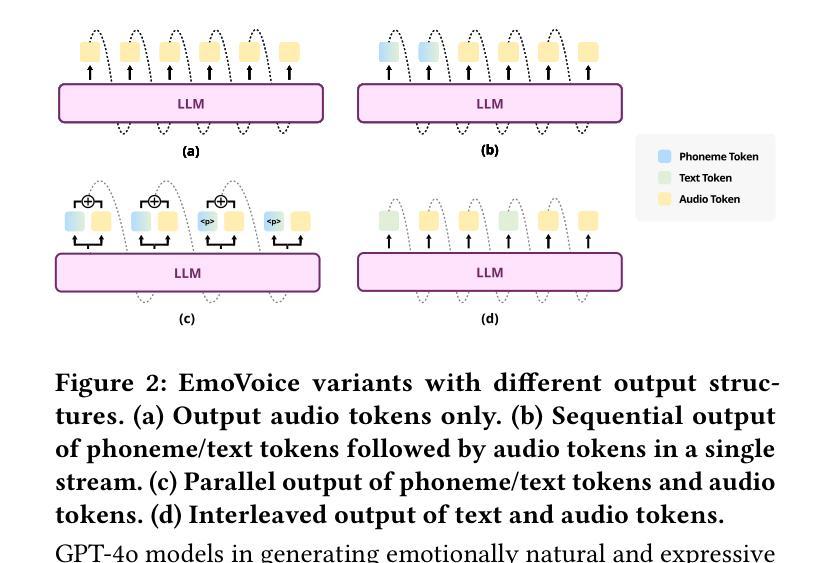
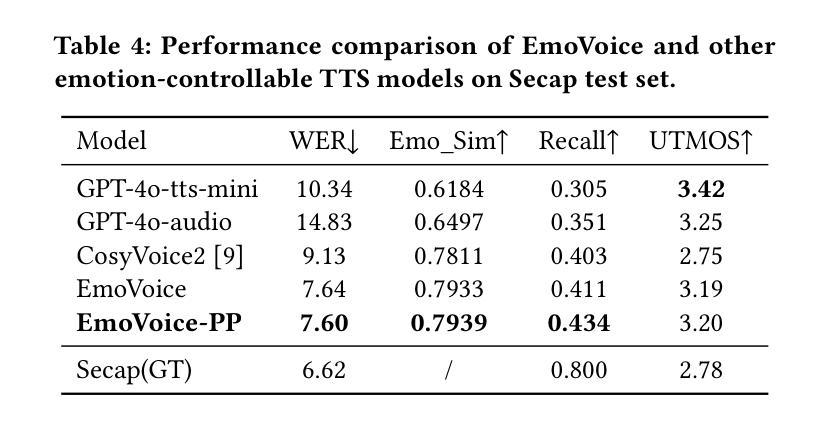
Human speech goes beyond the mere transfer of information; it is a profound exchange of emotions and a connection between individuals. While Text-to-Speech (TTS) models have made huge progress, they still face challenges in controlling the emotional expression in the generated speech. In this work, we propose EmoVoice, a novel emotion-controllable TTS model that exploits large language models (LLMs) to enable fine-grained freestyle natural language emotion control, and a phoneme boost variant design that makes the model output phoneme tokens and audio tokens in parallel to enhance content consistency, inspired by chain-of-thought (CoT) and chain-of-modality (CoM) techniques. Besides, we introduce EmoVoice-DB, a high-quality 40-hour English emotion dataset featuring expressive speech and fine-grained emotion labels with natural language descriptions. EmoVoice achieves state-of-the-art performance on the English EmoVoice-DB test set using only synthetic training data, and on the Chinese Secap test set using our in-house data. We further investigate the reliability of existing emotion evaluation metrics and their alignment with human perceptual preferences, and explore using SOTA multimodal LLMs GPT-4o-audio and Gemini to assess emotional speech. Dataset, code, checkpoints, and demo samples are available at https://github.com/yanghaha0908/EmoVoice.
人类言语不仅仅是为了传递信息,更是一种情感上的深刻交流和个人之间的连接。尽管文本转语音(TTS)模型已经取得了巨大的进步,但在控制生成语音的情感表达方面仍然面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了EmoVoice,这是一种新型的情感可控TTS模型,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)来实现精细的自由形式自然语言情感控制,以及一种并行输出音素标记和音频标记的变体设计,以增强内容一致性,这受到了思维链(CoT)和模态链(CoM)技术的启发。此外,我们介绍了EmoVoice-DB,这是一个高质量的40小时英语情感数据集,包含表达性语音和具有自然语言描述的精细情感标签。EmoVoice仅使用合成训练数据,在英语EmoVoice-DB测试集上实现了最先进的性能,在使用我们内部数据的中文Secap测试集上也取得了良好表现。我们还进一步研究了现有情感评估指标的可靠性及其与人类感知偏好的一致性,并探讨了使用最先进的多模态LLMs GPT-4o-audio和Gemini来评估情感语音。数据集、代码、检查点和演示样本可在https://github.com/yanghaha0908/EmoVoice找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACMMM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了EmoVoice,一种新型情感可控的文本转语音模型。该模型利用大型语言模型实现精细的自然语言情感控制,并通过并行输出音素标记和音频标记来提高内容一致性。此外,还推出了EmoVoice-DB,一个高质量的情感数据集,包含表达性语音和精细情感标签的自然语言描述。EmoVoice在英文数据集和中文数据集上均达到领先水平。同时,本文还探讨了现有情感评估指标的可靠性及其与人类感知偏好的一致性,并探索了使用最先进的多模态LLM对情感语音进行评估的方法。
Key Takeaways
- EmoVoice是一个新型的情感可控文本转语音模型,能够实现精细的自然语言情感控制。
- EmoVoice利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行建模,提高了情感表达的准确性。
- EmoVoice通过并行输出音素标记和音频标记,增强了内容一致性。
- 推出了高质量的情感数据集EmoVoice-DB,包含表达性语音和精细情感标签的自然语言描述。
- EmoVoice在英文和中文数据集上均达到了领先水平。
- 研究人员探讨了现有情感评估指标的可靠性及其与人类感知偏好的一致性。
点此查看论文截图