⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-15 更新
SemPT: Semantic Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Xiao Shi, Yangjun Ou, Zhenzhong Chen
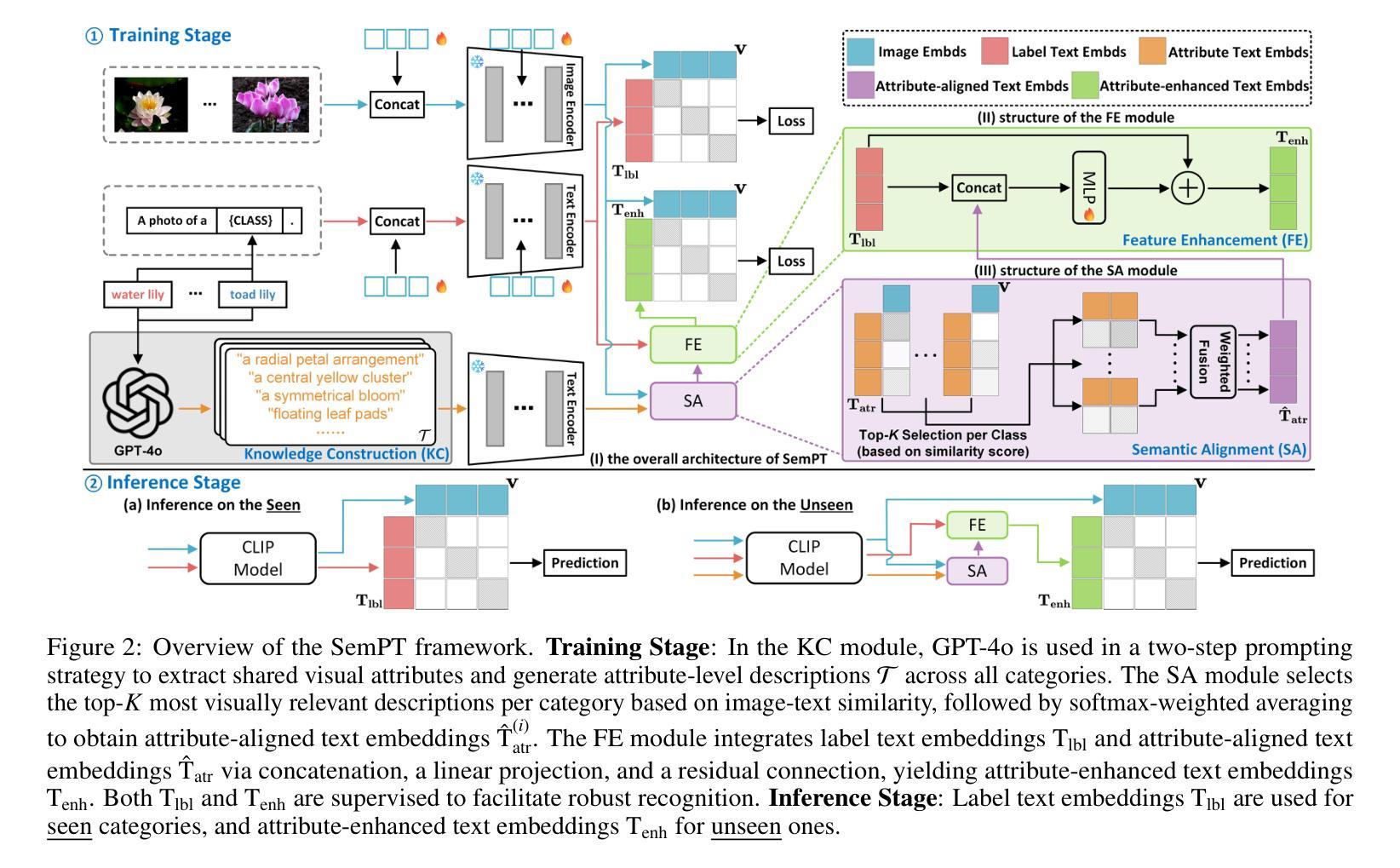
Visual transfer learning for unseen categories presents an active research topic yet a challenging task, due to the inherent conflict between preserving category-specific representations and acquiring transferable knowledge. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) pre-trained on large amounts of image-text pairs offer a promising solution. However, existing prompt tuning methods rely on sparse category labels or disparate LLM-generated descriptions, which fragment knowledge representation and hinder transferability. To address this limitation, we introduce Semantic Prompt Tuning (SemPT), a novel framework that tackles the generalization challenge by leveraging shared attribute-level knowledge across categories. Specifically, SemPT adopts a two-step prompting strategy to guide LLM in extracting shared visual attributes and generating attribute-level descriptions, capturing transferable semantic cues beyond labels while ensuring coherent structure. Then, visually guided weighting is applied to the embeddings of attribute-level descriptions to reduce noise from irrelevant attributes and enhance the text embeddings. Additionally, image embeddings are jointly aligned with both label and attribute-enhanced text embeddings, balancing discrimination for seen categories and transferability to unseen ones. Considering the availability of category exposure, our inference dynamically selects between standard label embeddings for seen categories and attribute-enhanced embeddings for unseen ones to ensure effective adaptation. Extensive experiments on 15 benchmark datasets demonstrate that SemPT achieves state-of-the-art performance across various settings, including base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset transfer, cross-domain transfer, and few-shot learning.
视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个热门的研究课题,同时也是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为保持特定类别的表示和获取可迁移知识之间存在固有的冲突。预训练在大量图像文本对上的视觉语言模型(VLMs)提供了一个有前景的解决方案。然而,现有的提示调整方法依赖于稀疏的类别标签或分散的LLM生成描述,这导致知识表示碎片化并阻碍知识的迁移。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了语义提示调整(SemPT)这一新框架,它通过利用跨类别的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。具体来说,SemPT采用两步提示策略来引导LLM提取共享的视觉属性并生成属性级描述,在确保连贯结构的同时,捕捉超越标签的可迁移语义线索。然后,对属性级描述的嵌入应用视觉引导加权,以减少来自无关属性的噪声并增强文本嵌入。此外,图像嵌入与标签和属性增强文本嵌入共同对齐,平衡对可见类别的区分度和对未见类别的可迁移性。考虑到类别暴露的可用性,我们的推理会动态选择在可见类别时使用标准的标签嵌入,在未见类别时使用属性增强嵌入,以确保有效的适应。在15个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,SemPT在各种设置下均达到了最先进的性能,包括基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集迁移、跨域迁移和少样本学习。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个活跃的研究课题,但也是一个具有挑战性的任务。预训练在大量图像文本对上的视觉语言模型(VLMs)为解决此问题提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,现有的提示调整方法依赖于稀疏的类别标签或分散的LLM生成描述,这破坏了知识表示并阻碍了可转移性。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了语义提示调整(SemPT)这一新框架,它通过利用类别之间的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个挑战,因为需要平衡保持类别特定表示和获取可转移知识之间的矛盾。
- 预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)是解决此问题的有前途的方法。
- 现有提示调整方法的局限性在于它们依赖于稀疏的类别标签或LLM生成的描述,这阻碍了知识的转移。
- SemPT框架通过利用跨类别的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。
- SemPT采用两步提示策略,引导LLM提取共享视觉属性和生成属性级描述,捕捉可转移语义线索。
- 通过视觉引导的加权方法,减少无关属性的噪声并增强文本嵌入。
- SemPT在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,它在各种设置下实现了最先进的性能,包括从基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集转移、跨域转移和少样本学习。
点此查看论文截图


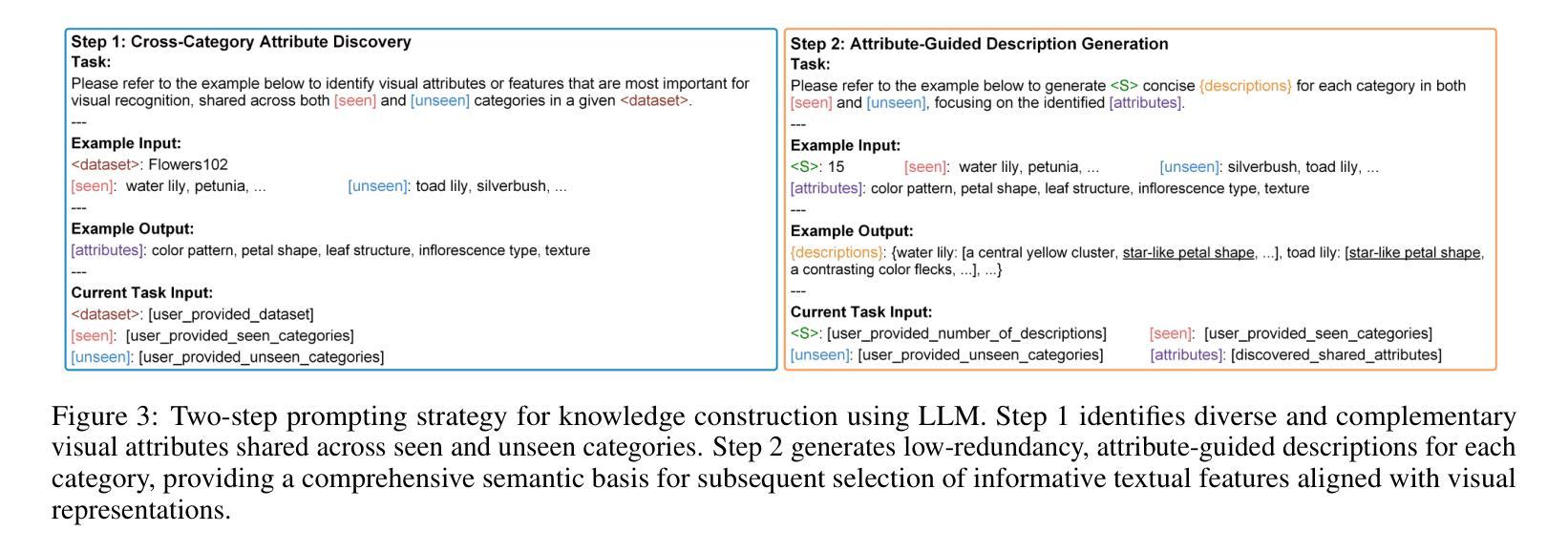
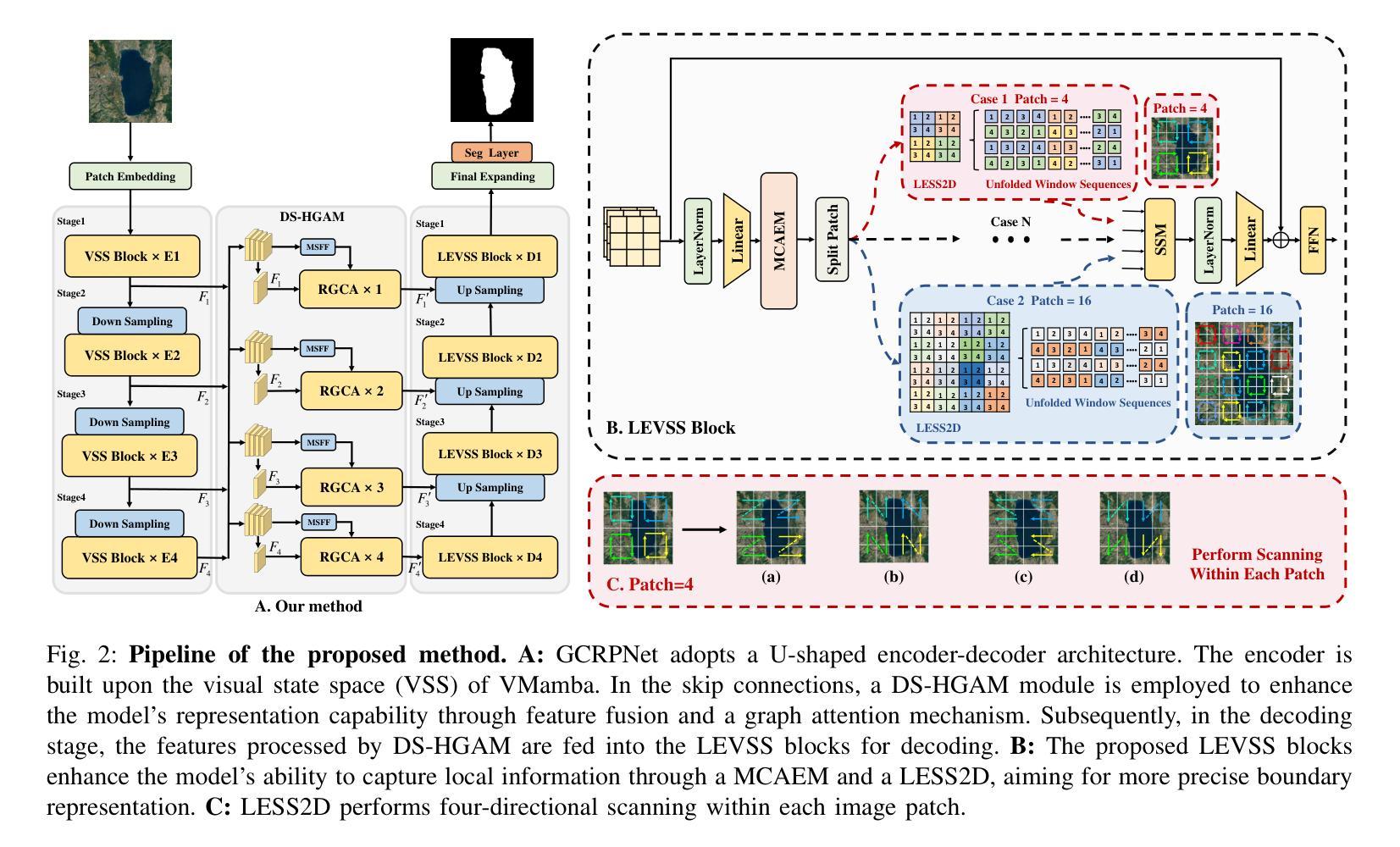
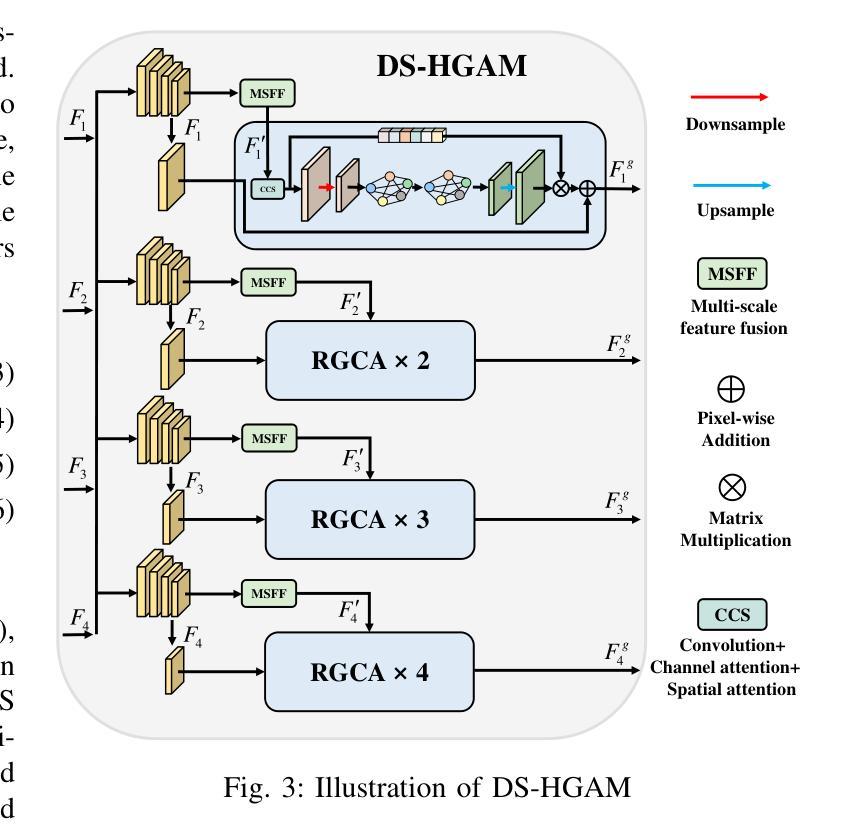
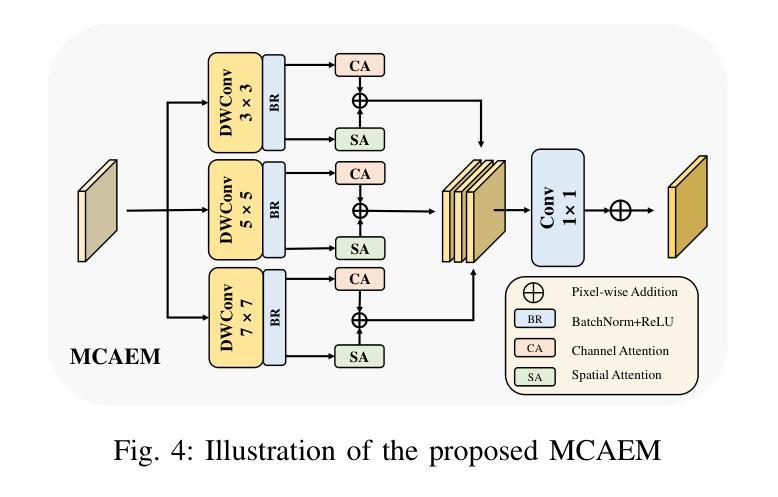
GCRPNet: Graph-Enhanced Contextual and Regional Perception Network For Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Mengyu Ren, Yutong Li, Hua Li, Runmin Cong, Sam Kwong
Salient object detection (SOD) in optical remote sensing images (ORSIs) faces numerous challenges, including significant variations in target scales and low contrast between targets and the background. Existing methods based on vision transformers (ViTs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) architectures aim to leverage both global and local features, but the difficulty in effectively integrating these heterogeneous features limits their overall performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a graph-enhanced contextual and regional perception network (GCRPNet), which builds upon the Mamba architecture to simultaneously capture long-range dependencies and enhance regional feature representation. Specifically, we employ the visual state space (VSS) encoder to extract multi-scale features. To further achieve deep guidance and enhancement of these features, we first design a difference-similarity guided hierarchical graph attention module (DS-HGAM). This module strengthens cross-layer interaction capabilities between features of different scales while enhancing the model’s structural perception,allowing it to distinguish between foreground and background more effectively. Then, we design the LEVSS block as the decoder of GCRPNet. This module integrates our proposed adaptive scanning strategy and multi-granularity collaborative attention enhancement module (MCAEM). It performs adaptive patch scanning on feature maps processed via multi-scale convolutions, thereby capturing rich local region information and enhancing Mamba’s local modeling capability. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating its effectiveness and superiority.
在光学遥感图像(ORSIs)中,显著目标检测(SOD)面临诸多挑战,包括目标尺度的显著差异以及目标与背景之间对比度低的问题。现有的基于视觉变压器(ViTs)和卷积神经网络(CNNs)架构的方法旨在利用全局和局部特征,但有效集成这些异质特征的难度限制了它们的整体性能。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了图增强上下文和区域感知网络(GCRPNet),它基于Mamba架构,能够同时捕捉长距离依赖关系并增强区域特征表示。具体来说,我们采用视觉状态空间(VSS)编码器提取多尺度特征。为了进一步实现这些特征的深度引导和增强,我们首先设计了一个差异相似性引导分层图注意力模块(DS-HGAM)。该模块增强了不同尺度特征之间的跨层交互能力,提高了模型的结构感知能力,使其更有效地区分前景和背景。然后,我们设计了LEVSS块作为GCRPNet的解码器。该模块结合了我们的自适应扫描策略和多粒度协同注意力增强模块(MCAEM)。它对通过多尺度卷积处理的特征图执行自适应补丁扫描,从而捕获丰富的局部区域信息并增强Mamba的局部建模能力。大量的实验结果证明了所提出模型达到了最先进的性能,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了在光学遥感图像中进行显著性目标检测的挑战。提出的GCRPNet模型采用图增强上下文与区域感知网络结构,基于Mamba架构实现长距离依赖捕获与区域特征表示增强。利用视觉状态空间编码器提取多尺度特征,并设计差异相似性引导层次图注意力模块强化跨层交互能力,提升模型的结构感知力。此外,设计了LEVSS解码块结合自适应扫描策略和多粒度协作注意力增强模块,增强局部建模能力。实验结果显示该模型性能达到最新水平。
关键见解
- GCRPNet解决了光学遥感图像显著性目标检测中目标尺度变化和背景对比度低的问题。
- 模型结合了全局和局部特征提取技术,并采用图增强上下文与区域感知网络进行优化。
- 通过视觉状态空间编码器实现多尺度特征的提取。
- 差异相似性引导层次图注意力模块强化了不同尺度特征间的跨层交互能力,提升了模型的结构感知能力。
- LEVSS解码块结合了自适应扫描策略和多粒度协作注意力增强模块,能有效捕捉丰富的局部区域信息。
- 实验结果证明了模型的有效性和优越性,达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

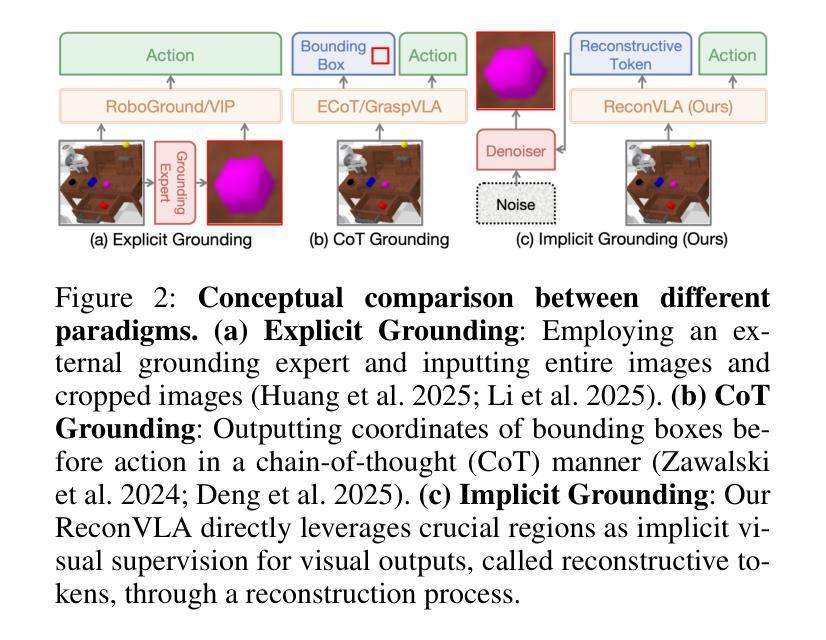
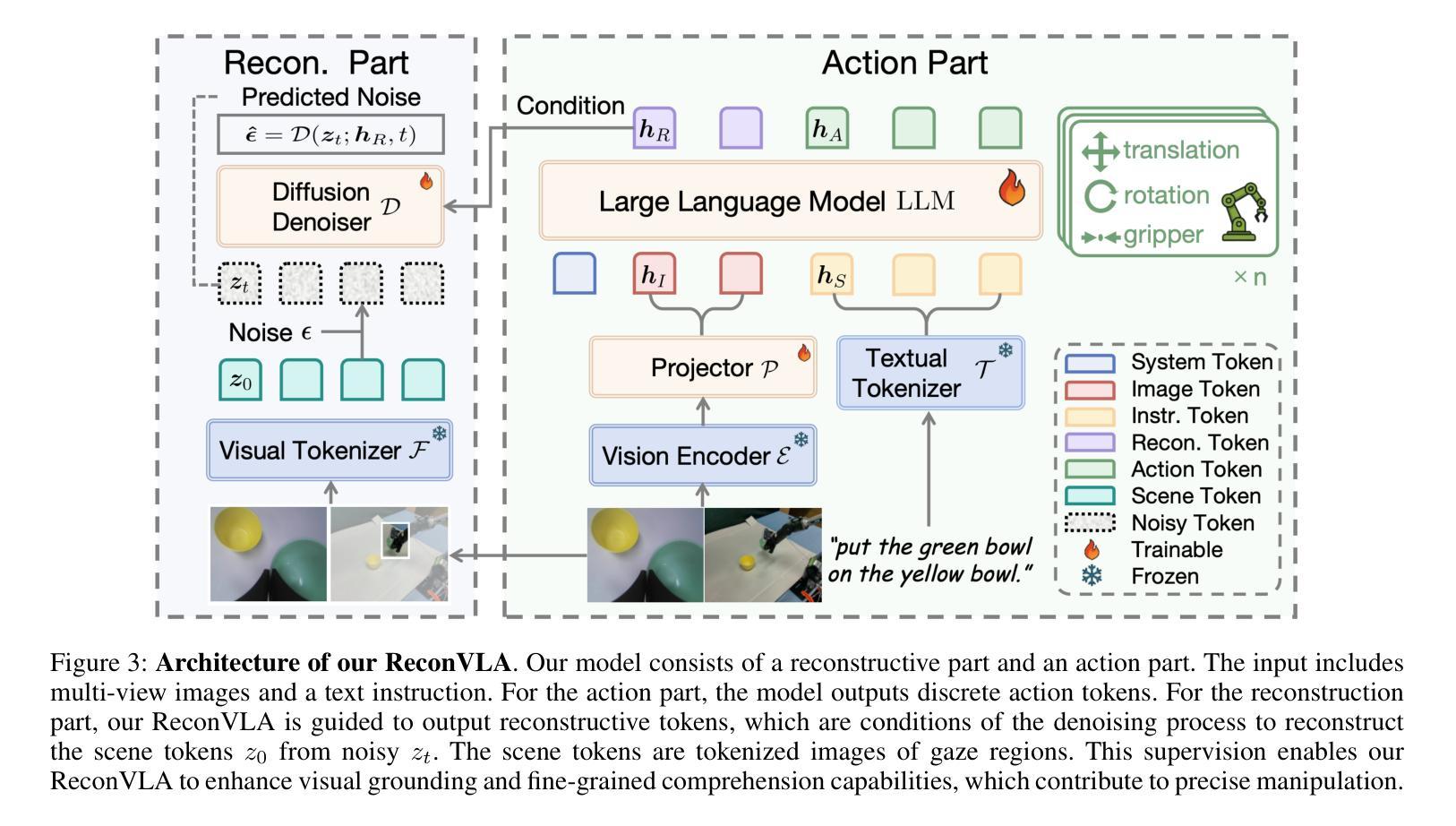
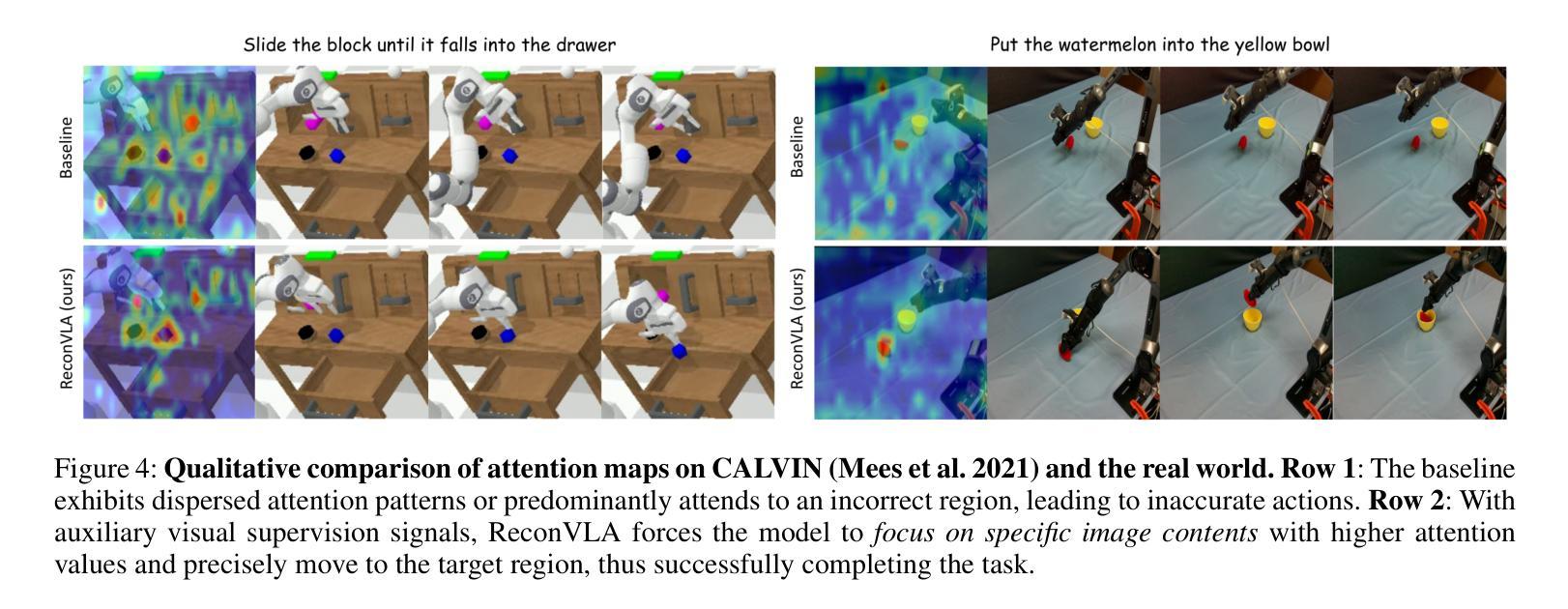
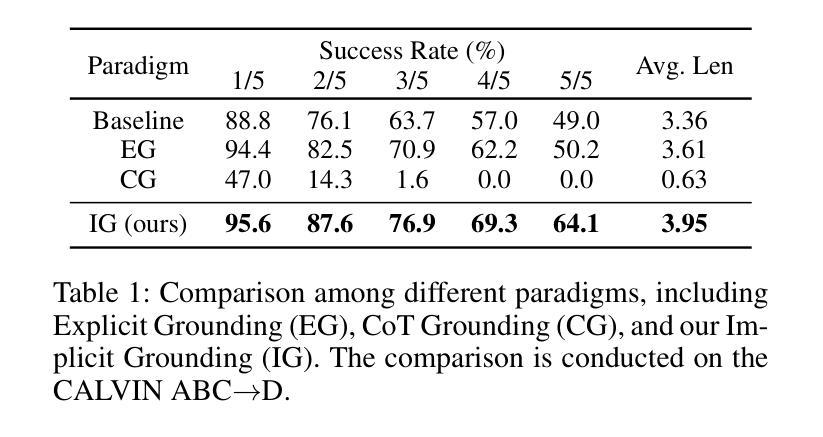
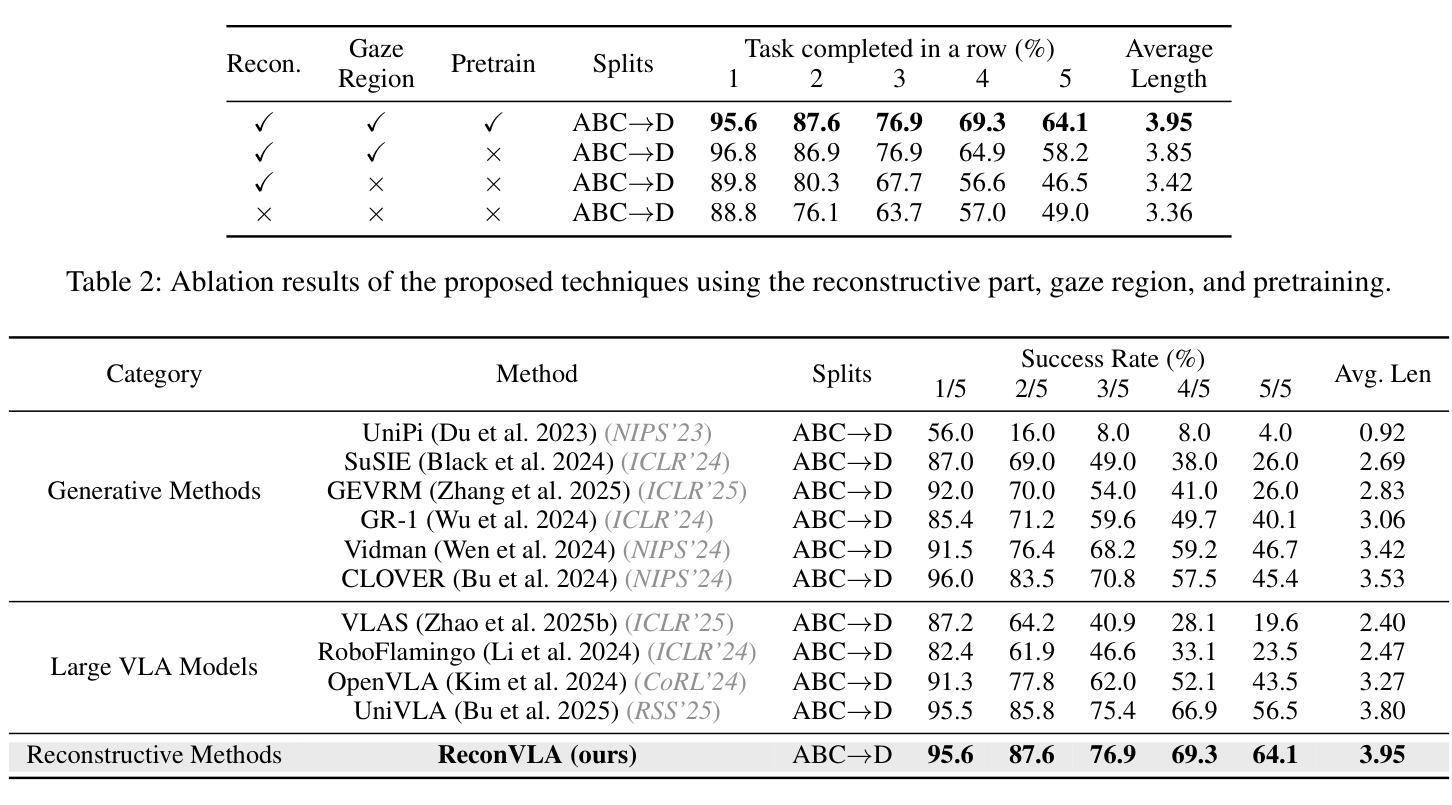
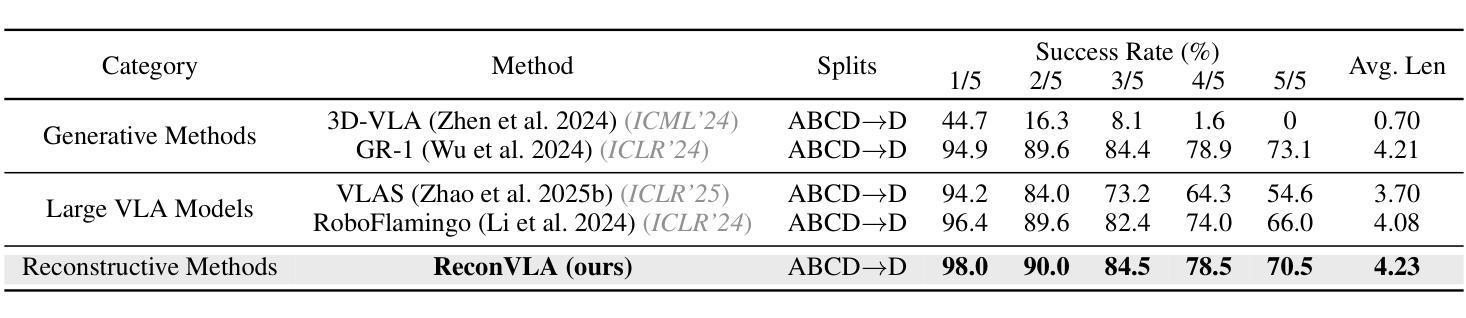
ReconVLA: Reconstructive Vision-Language-Action Model as Effective Robot Perceiver
Authors:Wenxuan Song, Ziyang Zhou, Han Zhao, Jiayi Chen, Pengxiang Ding, Haodong Yan, Yuxin Huang, Feilong Tang, Donglin Wang, Haoang Li
Recent advances in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have enabled robotic agents to integrate multimodal understanding with action execution. However, our empirical analysis reveals that current VLAs struggle to allocate visual attention to target regions. Instead, visual attention is always dispersed. To guide the visual attention grounding on the correct target, we propose ReconVLA, a reconstructive VLA model with an implicit grounding paradigm. Conditioned on the model’s visual outputs, a diffusion transformer aims to reconstruct the gaze region of the image, which corresponds to the target manipulated objects. This process prompts the VLA model to learn fine-grained representations and accurately allocate visual attention, thus effectively leveraging task-specific visual information and conducting precise manipulation. Moreover, we curate a large-scale pretraining dataset comprising over 100k trajectories and 2 million data samples from open-source robotic datasets, further boosting the model’s generalization in visual reconstruction. Extensive experiments in simulation and the real world demonstrate the superiority of our implicit grounding method, showcasing its capabilities of precise manipulation and generalization. Our project page is https://zionchow.github.io/ReconVLA/.
近期,视觉-语言-动作(VLA)模型的进步使得机器人能够整合多模式理解与动作执行。然而,我们的实证分析显示,当前的VLA在分配视觉注意力到目标区域时面临困难。相反,视觉注意力总是分散的。为了引导视觉注意力正确地定位到目标上,我们提出了ReconVLA,这是一种具有隐性定位范式的重建型VLA模型。基于模型的视觉输出,扩散变压器旨在重建图像中的注视区域,该区域对应于被操纵的目标对象。这一过程促使VLA模型学习精细的表征并准确地分配视觉注意力,从而有效地利用任务特定的视觉信息并进行精确操作。此外,我们创建了一个大规模预训练数据集,包含超过10万个轨迹和来自开源机器人数据集的200万个数据样本,进一步提升了模型在视觉重建中的泛化能力。仿真和现实世界的大量实验证明了我们隐性定位方法的优越性,展示了其精确操作和泛化的能力。我们的项目页面是https://zionchow.github.io/ReconVLA/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在机器人视觉领域的一项新研究——ReconVLA模型,该模型解决了机器人对于目标区域的视觉注意力分配问题。研究发现当前VLA模型存在视觉注意力分散的问题,因此提出使用扩散变压器重建图像中的注视区域,引导模型学习精细的表征并准确分配视觉注意力。此外,该研究还构建了一个大规模预训练数据集,并通过仿真和真实世界的实验验证了其精确操控和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型在机器人领域面临视觉注意力分配问题。
- ReconVLA模型通过重建图像中的注视区域来解决这一问题。
- 扩散变压器在模型中的作用是依据模型的视觉输出来重建注视区域。
- 该方法使模型能够学习精细的表征并准确分配视觉注意力。
- 研究构建了一个大规模的预训练数据集,用于提升模型的泛化能力。
- 仿真和真实世界的实验验证了ReconVLA模型的精确操控能力。
点此查看论文截图

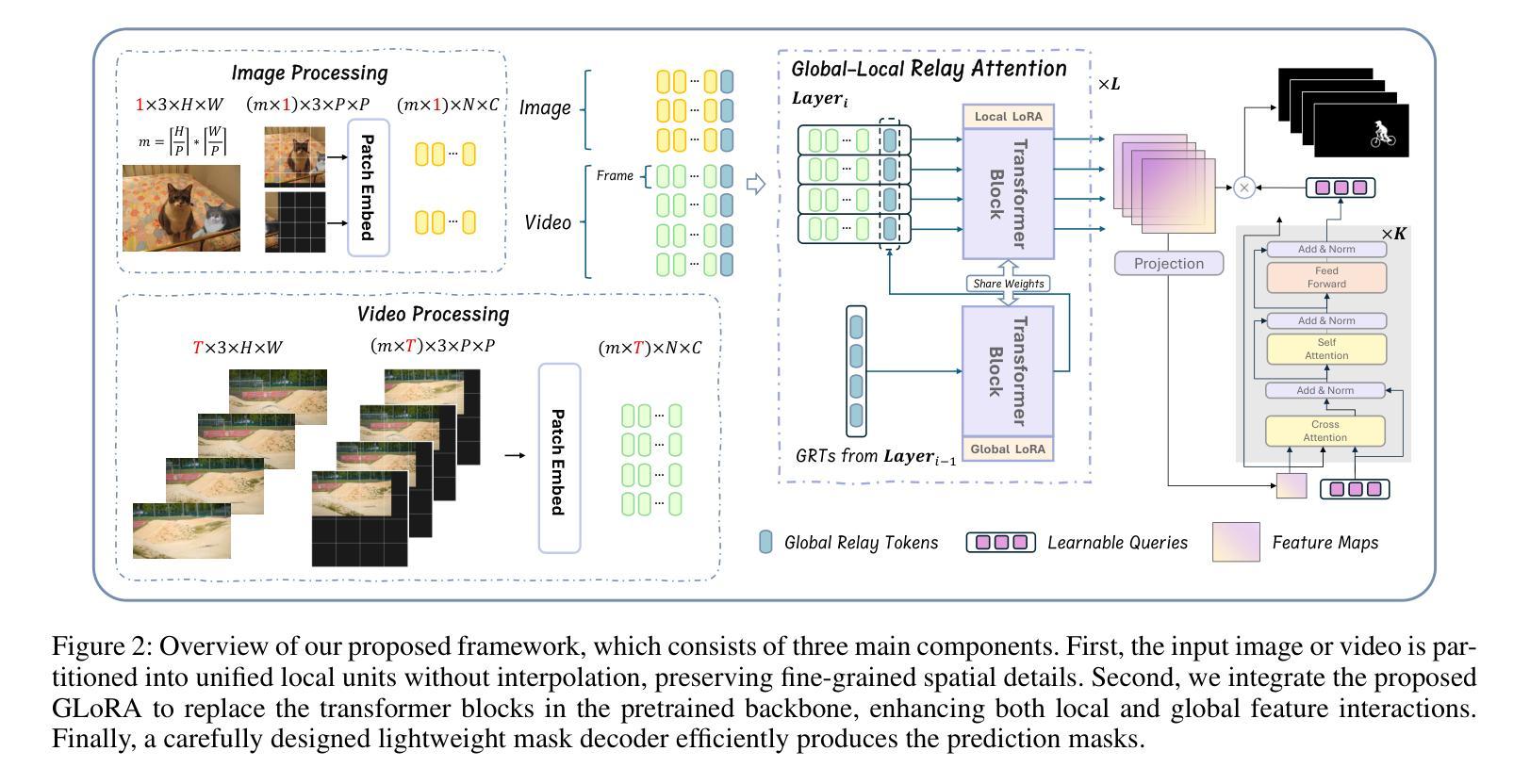
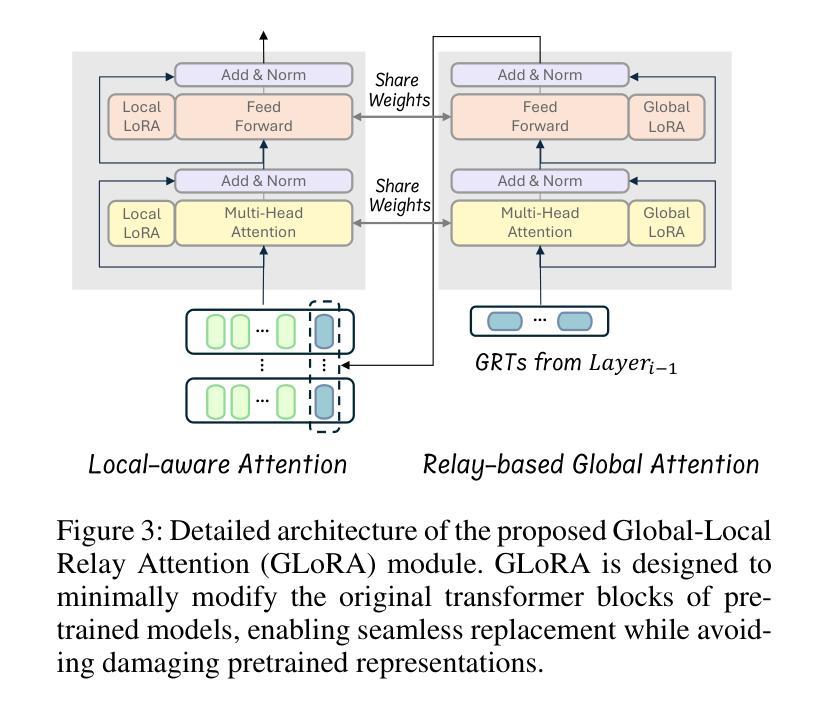
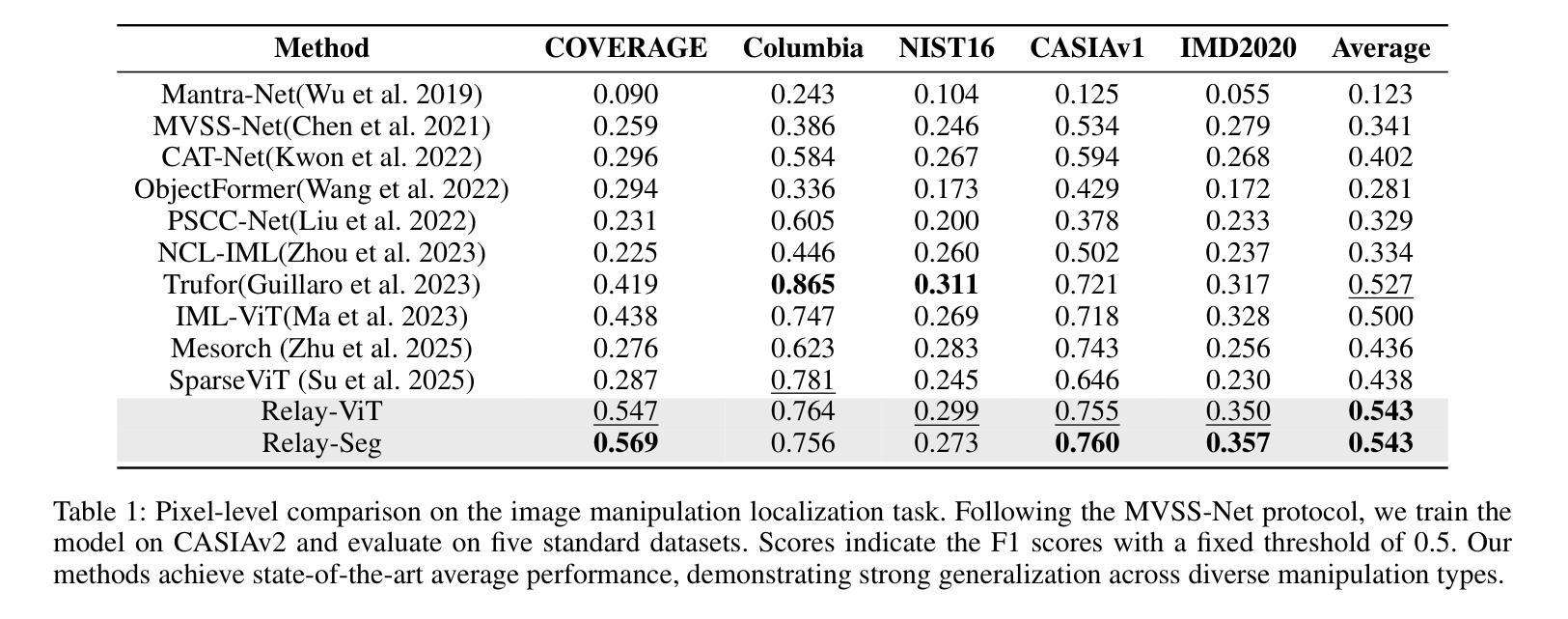
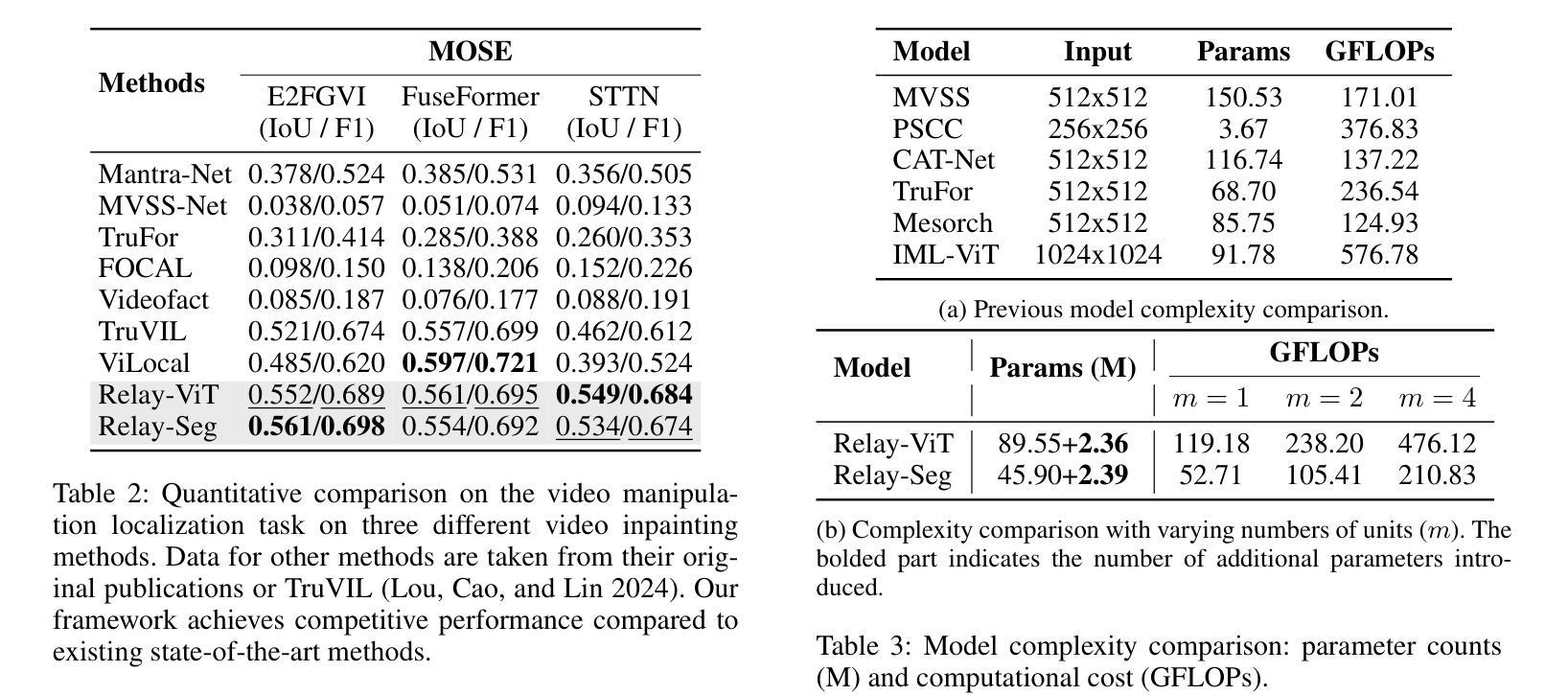
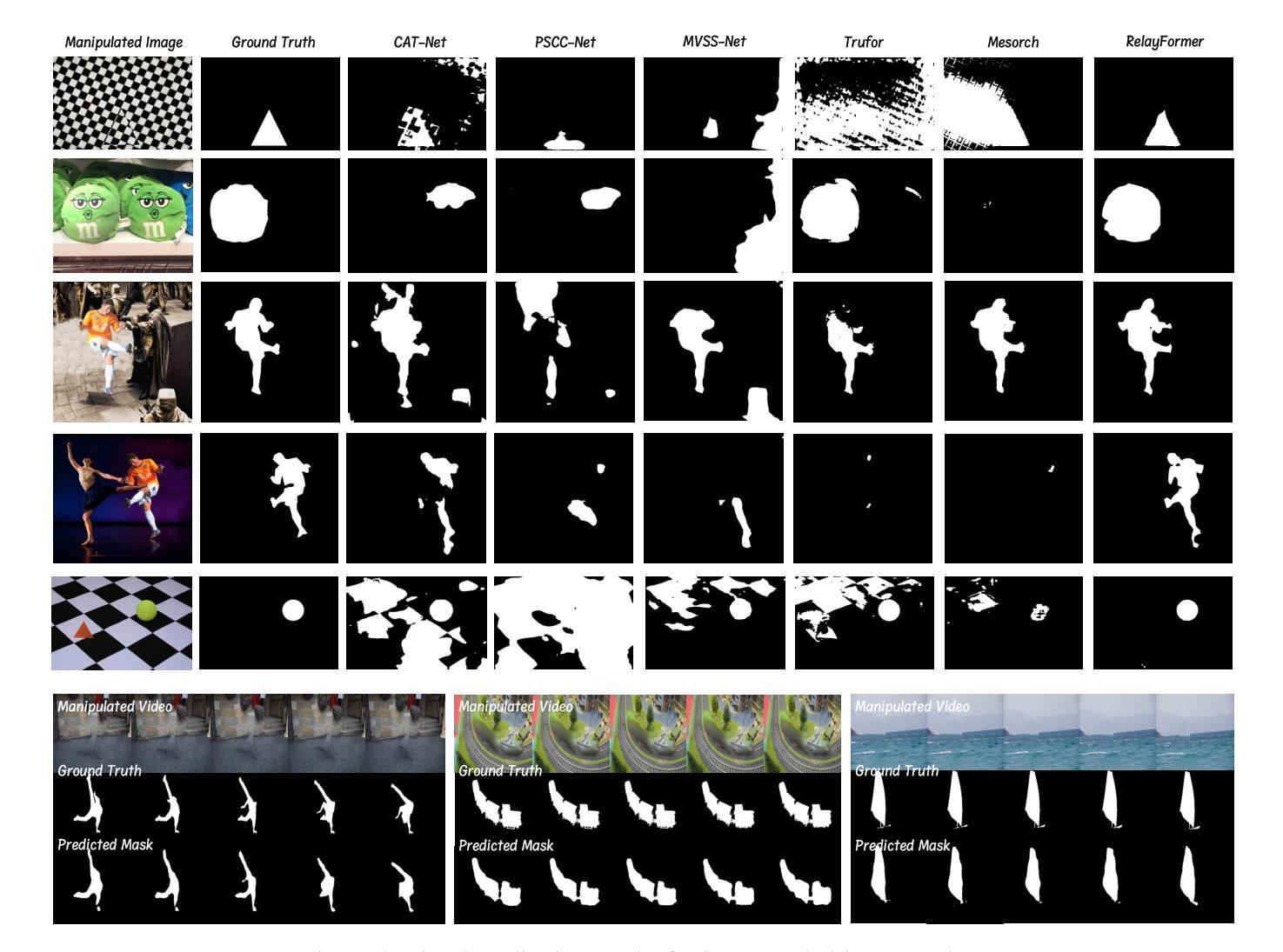
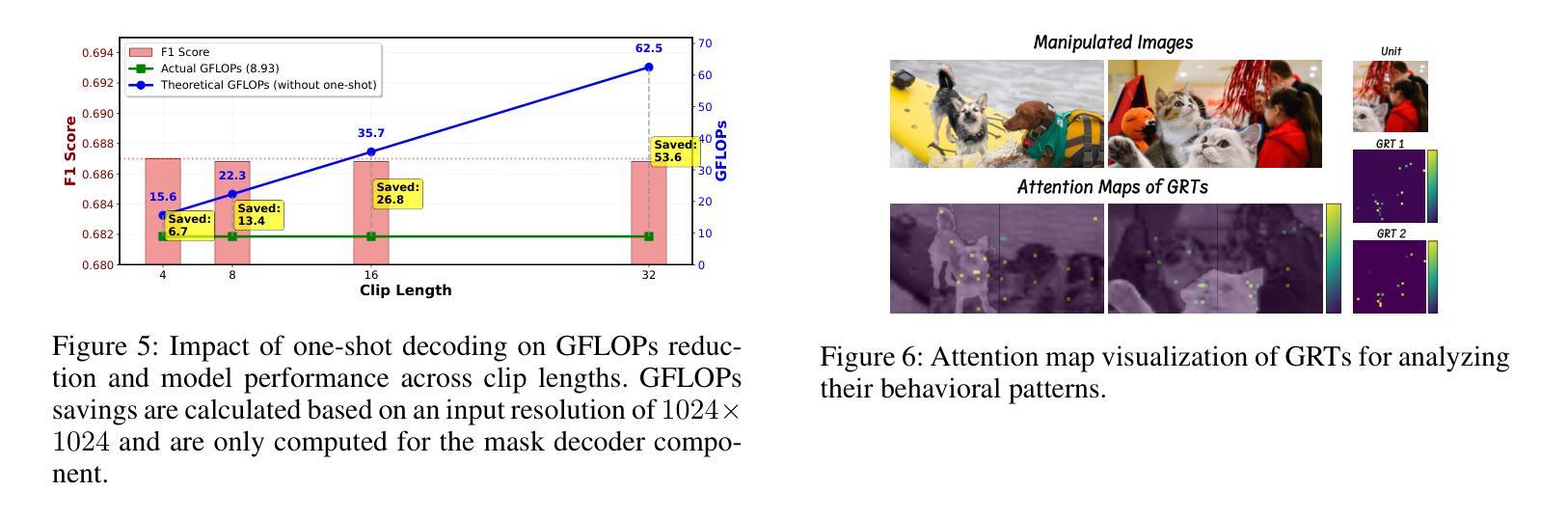
RelayFormer: A Unified Local-Global Attention Framework for Scalable Image and Video Manipulation Localization
Authors:Wen Huang, Jiarui Yang, Tao Dai, Jiawei Li, Shaoxiong Zhan, Bin Wang, Shu-Tao Xia
Visual manipulation localization (VML) – across both images and videos – is a crucial task in digital forensics that involves identifying tampered regions in visual content. However, existing methods often lack cross-modal generalization and struggle to handle high-resolution or long-duration inputs efficiently. We propose RelayFormer, a unified and modular architecture for visual manipulation localization across images and videos. By leveraging flexible local units and a Global-Local Relay Attention (GLoRA) mechanism, it enables scalable, resolution-agnostic processing with strong generalization. Our framework integrates seamlessly with existing Transformer-based backbones, such as ViT and SegFormer, via lightweight adaptation modules that require only minimal architectural changes, ensuring compatibility without disrupting pretrained representations. Furthermore, we design a lightweight, query-based mask decoder that supports one-shot inference across video sequences with linear complexity. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art localization performance, setting a new baseline for scalable and modality-agnostic VML. Code is available at: https://github.com/WenOOI/RelayFormer.
视觉操控定位(VML)——无论是图片还是视频——是数字取证中的一项重要任务,涉及识别视觉内容中被篡改的区域。然而,现有方法往往缺乏跨模态泛化能力,难以高效处理高分辨率或长时间输入的图像。我们提出了RelayFormer,这是一种用于图片和视频视觉操控定位的统一模块化架构。它通过利用灵活的局部单元和全局-局部中继注意力(GLoRA)机制,实现了可伸缩的、与分辨率无关的处理,并具有较强的泛化能力。我们的框架通过轻量级适配模块无缝集成现有的基于Transformer的主干网络,如ViT和SegFormer,只需进行最小的架构更改,确保与预训练表示兼容而不会造成干扰。此外,我们设计了一个轻量级的、基于查询的掩膜解码器,支持在视频序列上进行一次推断,具有线性复杂度。在多个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的定位性能,为可扩展和模态无关的VML设定了新的基准。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/WenOOI/RelayFormer 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RelayFormer是一种用于图像和视频篡改区域定位的统一模块化架构。它通过灵活的局部单元和全局-局部中继注意力(GLoRA)机制,实现了可伸缩的、分辨率无关的处理,并具有较强的泛化能力。该框架通过轻量级适配模块与现有的Transformer基础架构(如ViT和SegFormer)无缝集成,只需进行最小的架构更改,确保了与预训练表示的兼容性。此外,设计了一个轻量级的基于查询的掩膜解码器,支持在视频序列上进行一次推理,具有线性复杂度。在多基准的大量实验表明,该方法达到了最新的定位性能,为可伸缩和模态无关的篡改区域定位设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- RelayFormer是一个用于视觉篡改定位的统一模块化架构,适用于图像和视频。
- 利用灵活的局部单元和全局-局部中继注意力(GLoRA)机制,实现分辨率无关的处理。
- RelayFormer具有强大的泛化能力,能处理各种模态的视觉内容。
- 该框架通过轻量级适配模块与现有Transformer架构兼容。
- 设计了一个轻量级的掩膜解码器,支持一次处理整个视频序列。
- RelayFormer达到了最新的定位性能基准。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

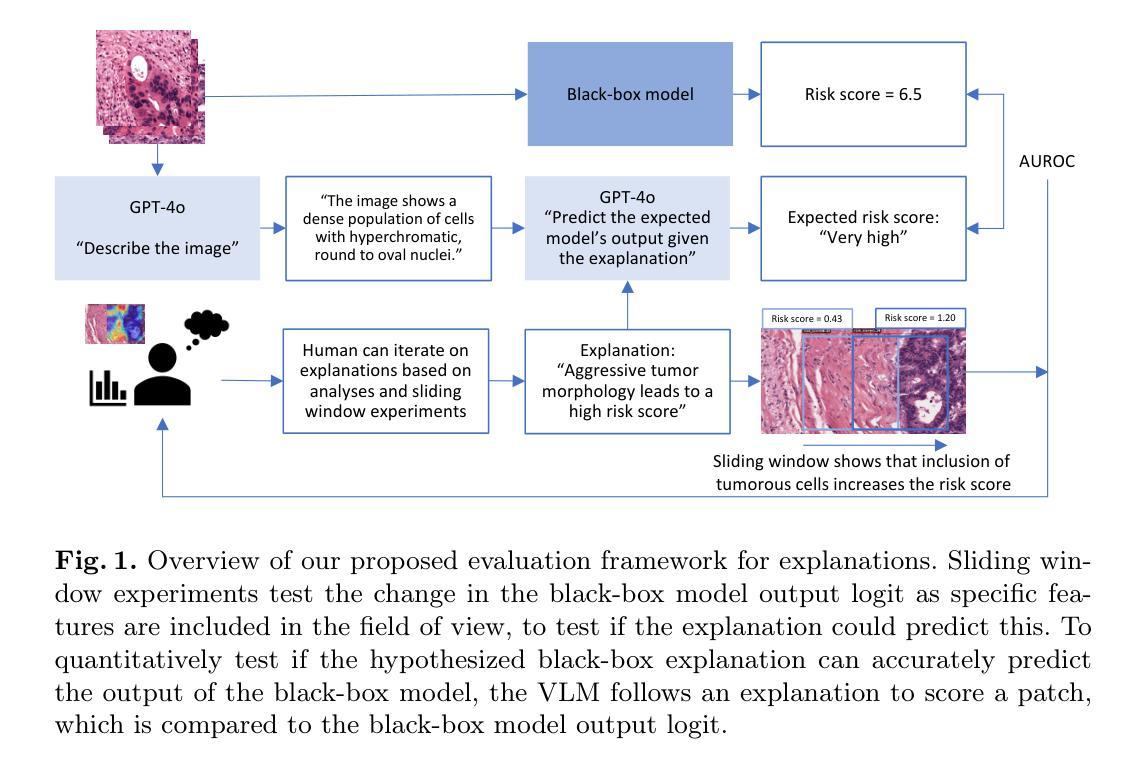
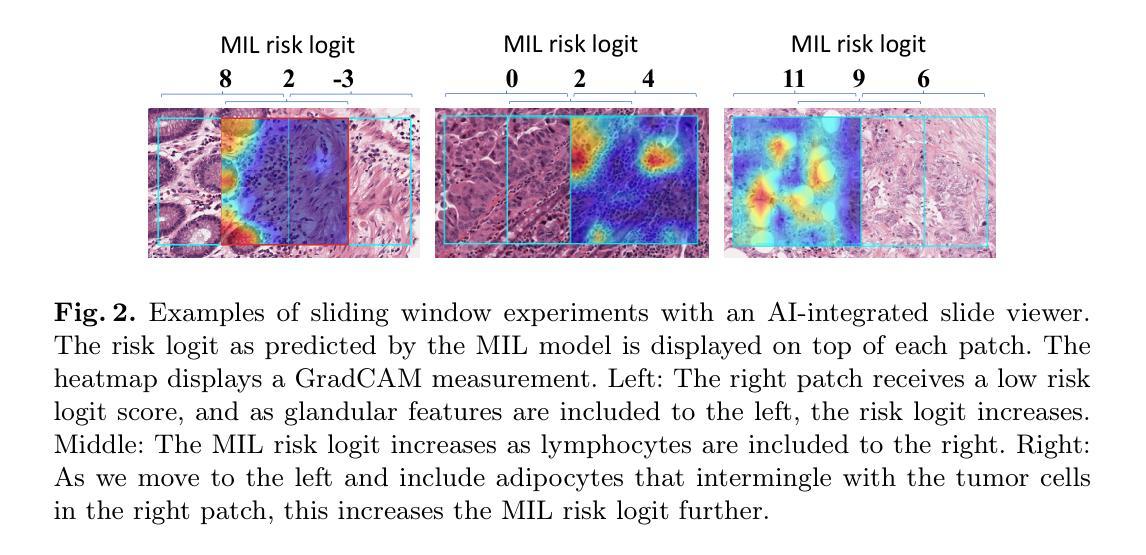
From Explainable to Explained AI: Ideas for Falsifying and Quantifying Explanations
Authors:Yoni Schirris, Eric Marcus, Jonas Teuwen, Hugo Horlings, Efstratios Gavves
Explaining deep learning models is essential for clinical integration of medical image analysis systems. A good explanation highlights if a model depends on spurious features that undermines generalization and harms a subset of patients or, conversely, may present novel biological insights. Although techniques like GradCAM can identify influential features, they are measurement tools that do not themselves form an explanation. We propose a human-machine-VLM interaction system tailored to explaining classifiers in computational pathology, including multi-instance learning for whole-slide images. Our proof of concept comprises (1) an AI-integrated slide viewer to run sliding-window experiments to test claims of an explanation, and (2) quantification of an explanation’s predictiveness using general-purpose vision-language models. The results demonstrate that this allows us to qualitatively test claims of explanations and can quantifiably distinguish competing explanations. This offers a practical path from explainable AI to explained AI in digital pathology and beyond. Code and prompts are available at https://github.com/nki-ai/x2x.
解释深度学习模型对于医疗图像分析系统的临床整合至关重要。一个好的解释可以突出显示模型是否依赖于会破坏泛化并伤害部分患者的偶然特征,或者相反,可以呈现新的生物学见解。虽然GradCAM等技术可以识别出有影响力的特征,但它们只是测量工具,本身并不构成解释。我们提出了一种针对计算病理学中分类器解释的人类-机器-视觉语言模型(VLM)交互系统,包括用于全幻灯图像的多实例学习。我们的概念验证包括(1)一个集成了人工智能的幻灯片查看器,用于运行滑动窗口实验来验证解释的主张,以及(2)使用通用视觉语言模型量化解释的预测性。结果表明,这使我们能够定性验证解释的主张,并能够定量区分竞争性的解释。这为数字病理学等领域从可解释的AI到解释的AI提供了一条实用路径。代码和提示可在https://github.com/nki-ai/x2x上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables, submitted at MICCAI IMIMIC workshop
Summary
在医疗图像分析系统的临床整合中,解释深度学习模型至关重要。解释有助于揭示模型是否依赖于影响泛化和损害患者群体的特征,或揭示新的生物学见解。虽然技术如GradCAM可以识别重要特征,但它们只是测量工具而非解释工具。本文提出一种针对计算病理学分类器的解释的人机交互系统,包括用于全幻灯片图像的多实例学习。我们的概念验证包括:(1)AI集成幻灯片查看器运行滑动窗口实验来测试解释主张,(2)使用通用视觉语言模型量化解释的预测性。结果表明,该方法可以定性测试解释主张并可以定量区分不同解释。这为数字病理学等领域实现从可解释的AI到解释的AI的实用路径。Key Takeaways
- 解释深度学习模型对于医疗图像分析系统的临床整合至关重要。
- 良好的模型解释能揭示模型是否依赖影响泛化和患者群体的特征。
- 虽然存在如GradCAM的技术可以识别重要特征,但它们主要是测量工具而非解释工具。
- 提出一种针对计算病理学分类器解释的人机交互系统,包括多实例学习用于全幻灯片图像。
- 该系统通过AI集成幻灯片查看器进行滑动窗口实验来测试解释主张。
- 使用通用视觉语言模型量化解释的预测性,以区分不同的解释。
点此查看论文截图

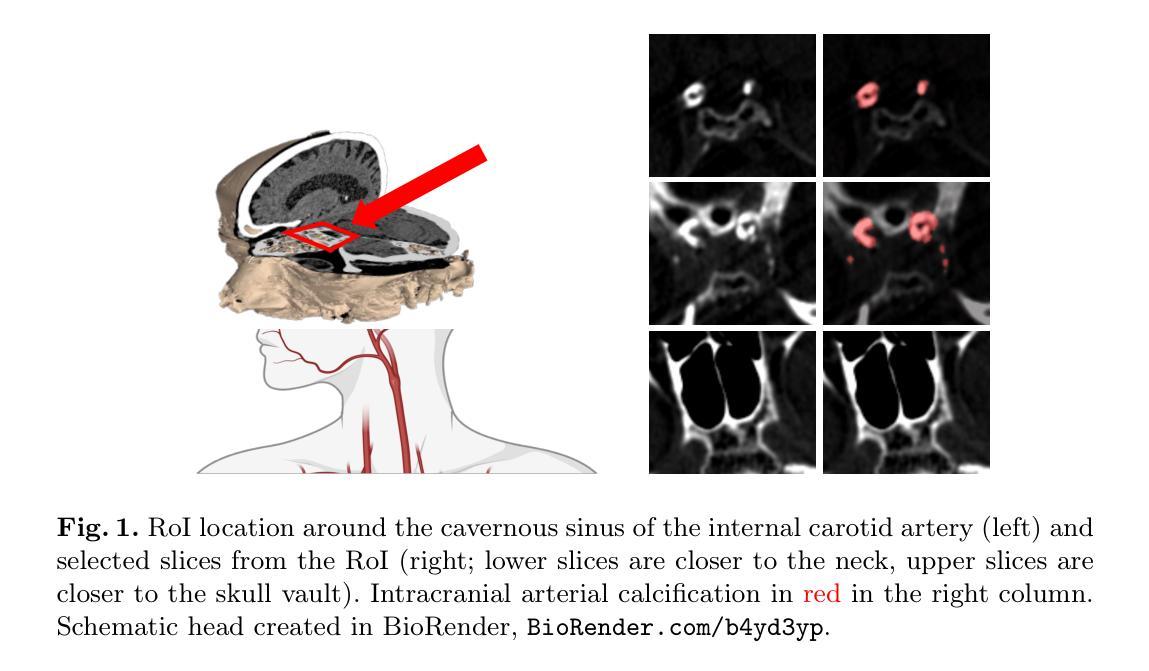
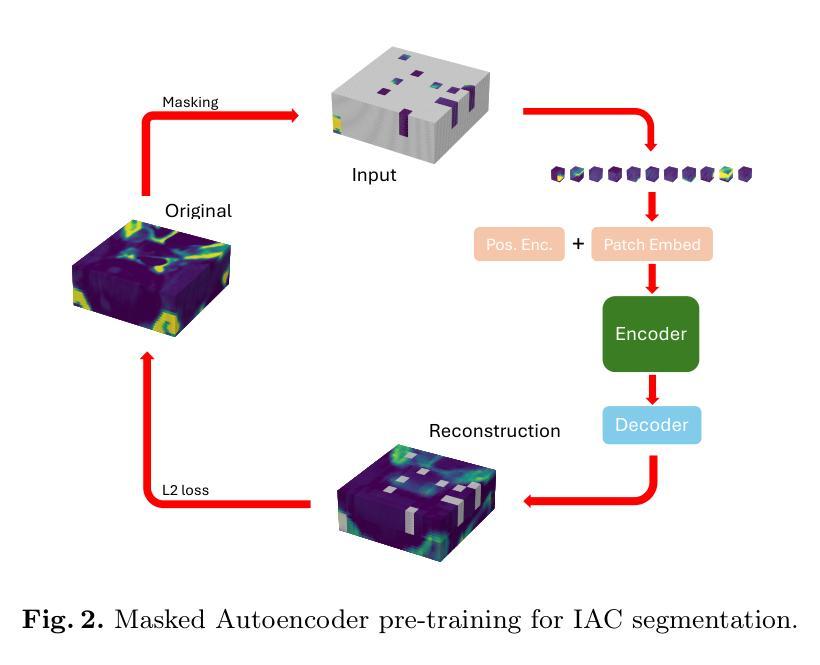
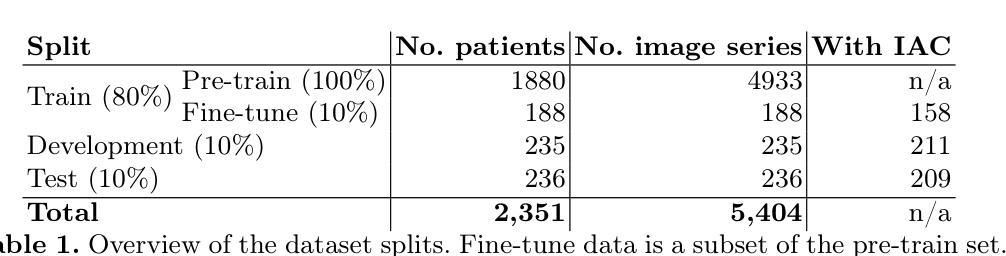
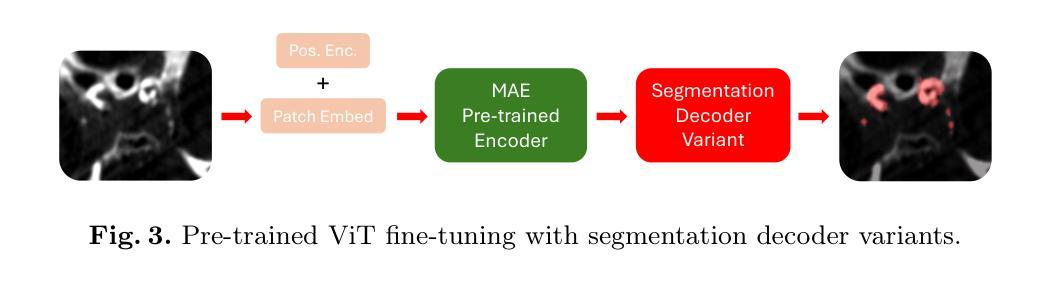
Calibrated Self-supervised Vision Transformers Improve Intracranial Arterial Calcification Segmentation from Clinical CT Head Scans
Authors:Benjamin Jin, Grant Mair, Joanna M. Wardlaw, Maria del C. Valdés Hernández
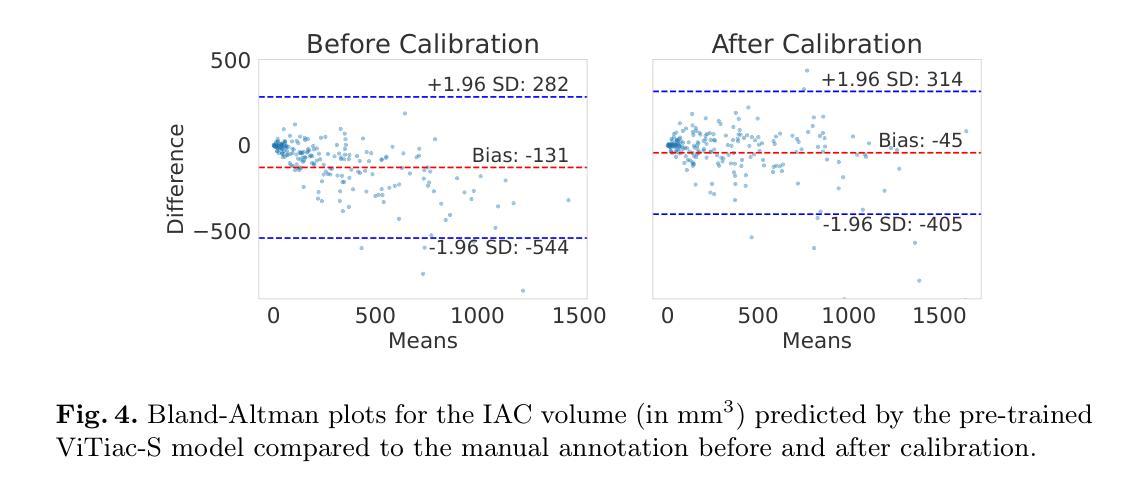
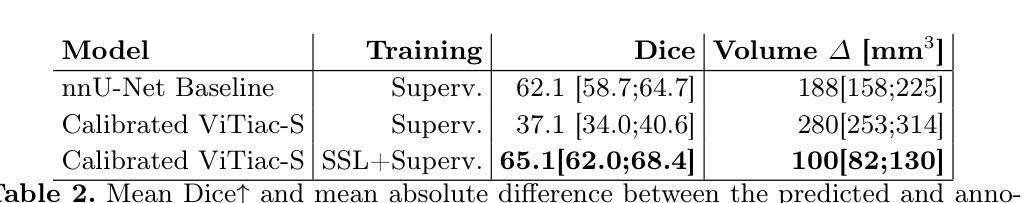
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have gained significant popularity in the natural image domain but have been less successful in 3D medical image segmentation. Nevertheless, 3D ViTs are particularly interesting for large medical imaging volumes due to their efficient self-supervised training within the masked autoencoder (MAE) framework, which enables the use of imaging data without the need for expensive manual annotations. Intracranial arterial calcification (IAC) is an imaging biomarker visible on routinely acquired CT scans linked to neurovascular diseases such as stroke and dementia, and automated IAC quantification could enable their large-scale risk assessment. We pre-train ViTs with MAE and fine-tune them for IAC segmentation for the first time. To develop our models, we use highly heterogeneous data from a large clinical trial, the third International Stroke Trial (IST-3). We evaluate key aspects of MAE pre-trained ViTs in IAC segmentation, and analyse the clinical implications. We show: 1) our calibrated self-supervised ViT beats a strong supervised nnU-Net baseline by 3.2 Dice points, 2) low patch sizes are crucial for ViTs for IAC segmentation and interpolation upsampling with regular convolutions is preferable to transposed convolutions for ViT-based models, and 3) our ViTs increase robustness to higher slice thicknesses and improve risk group classification in a clinical scenario by 46%. Our code is available online.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)在自然图像领域已经大受欢迎,但在3D医学图像分割方面的表现却不尽如人意。然而,对于大型医学图像体积而言,3D ViTs特别有趣,因为它们能在掩码自动编码器(MAE)框架内进行高效的自监督训练,从而能够使用图像数据而无需昂贵的手动注释。颅内动脉钙化(IAC)是常规CT扫描上可见的神经血管疾病(如中风和痴呆症)的成像生物标志物,自动的IAC定量评估可实现大规模风险评估。我们首次使用MAE对ViTs进行预训练,并对其进行微调以进行IAC分割。为了开发我们的模型,我们使用了来自大型临床试验的具有高度异质性的数据——第三次国际中风试验(IST-3)。我们评估了MAE预训练的ViTs在IAC分割方面的关键方面,并分析了其临床意义。我们的研究结果表明:1)我们的校准自监督ViT比受监督的nnU-Net基准测试高出3.2 Dice点;2)对于IAC分割的ViTs而言,较小的补丁尺寸至关重要,并且对于基于ViT的模型而言,使用常规卷积进行插值上采样比转置卷积更可取;3)我们的ViTs提高了对更高切片厚度的鲁棒性,并在临床场景中提高了风险组分类的准确性达46%。我们的代码可在网上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 3rd Data Engineering in Medical Imaging workshop @ MICCAI 2025
Summary
視覺變換器(ViTs)在自然圖像领域廣受欢迎,但在3D医学影像分割上效果較差。然而,由於其内在自监督训练的MAE框架可有效利用影像数据,即使不需昂贵的手动标注,也能在大規模医学影像中實現高功效。本文首次預訓練ViTs於MAE框架上,并微调用于颅内動脉钙化(IAC)分割模型。我们运用來自大规模訓練数据的、具有显著差异的数据進行了訓練和评估,並分析了其临床影响。本文的研究結果包括:我們的校準自监督ViT比强大的监督型nnU-Net基准高出3.2 Dice点;低塊大小對ViT進行IAC分割非常關鍵;插值上采樣使用常規卷積優于轉置卷積對基於ViT的模型;我们的ViT能提高風險群組分期的健碁性達到提高近一半的預測能力。我们提供相關代码。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) are effectively applied to 3D medical image segmentation, particularly for large medical imaging volumes.
- MAE framework enables self-supervised training of ViTs, facilitating the use of imaging data without manual annotations.
- For the first time, ViTs are pre-trained and fine-tuned for intracranial arterial calcification (IAC) segmentation.
- Low patch sizes are crucial for ViTs in IAC segmentation, and interpolation upsampling with regular convolutions is preferred.
- ViTs improve robustness to higher slice thicknesses and enhance risk group classification in a clinical scenario.
- The study demonstrates a significant performance boost over a strong supervised nnU-Net baseline, with a 3.2 Dice point increase.
- The research has practical implications in large-scale risk assessment for neurovascular diseases like stroke and dementia through automated IAC quantification.
点此查看论文截图

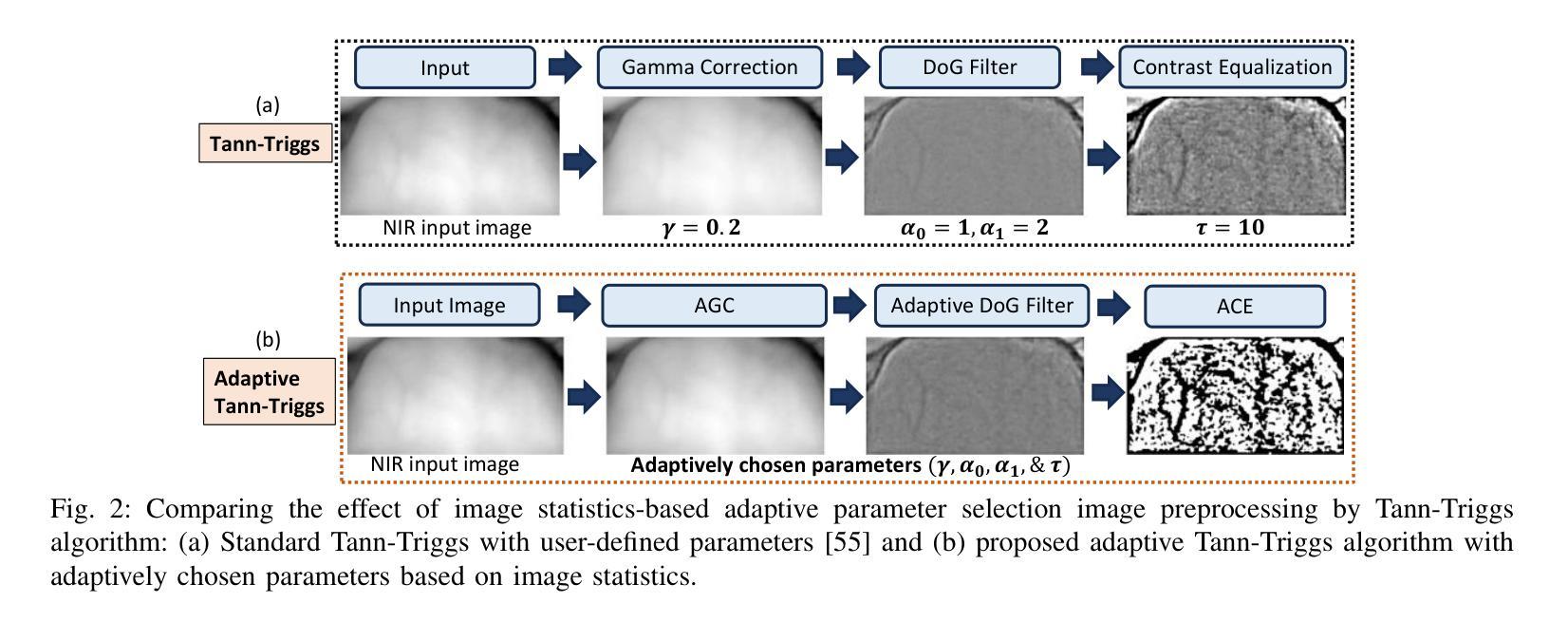
A Lightweight Transformer with Phase-Only Cross-Attention for Illumination-Invariant Biometric Authentication
Authors:Arun K. Sharma, Shubhobrata Bhattacharya, Motahar Reza, Bishakh Bhattacharya
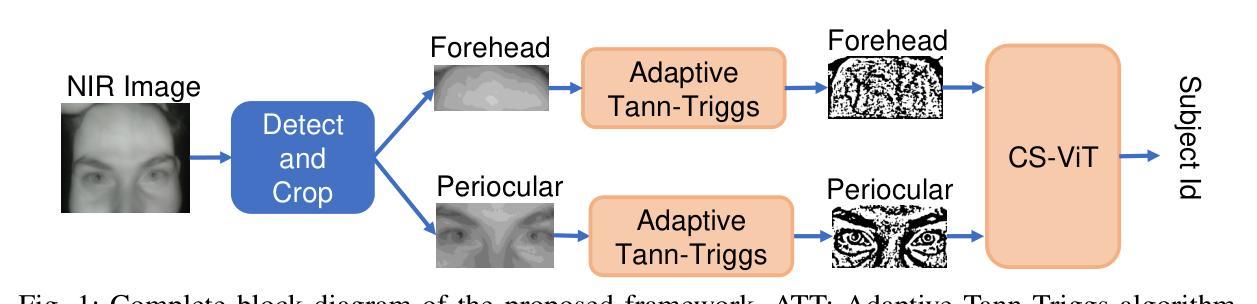
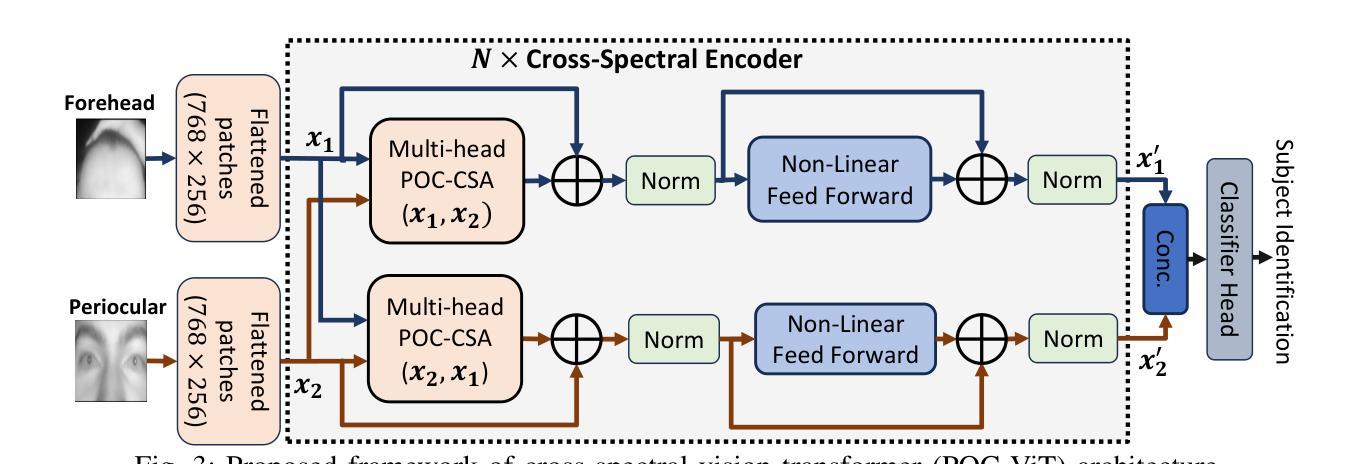
Traditional biometric systems have encountered significant setbacks due to various unavoidable factors, for example, wearing of face masks in face recognition-based biometrics and hygiene concerns in fingerprint-based biometrics. This paper proposes a novel lightweight vision transformer with phase-only cross-attention (POC-ViT) using dual biometric traits of forehead and periocular portions of the face, capable of performing well even with face masks and without any physical touch, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods. The POC-ViT framework is designed to handle two biometric traits and to capture inter-dependencies in terms of relative structural patterns. Each channel consists of a Cross-Attention using phase-only correlation (POC) that captures both their individual and correlated structural patterns. The computation of cross-attention using POC extracts the phase correlation in the spatial features. Therefore, it is robust against variations in resolution and intensity, as well as illumination changes in the input images. The lightweight model is suitable for edge device deployment. The performance of the proposed framework was successfully demonstrated using the Forehead Subcutaneous Vein Pattern and Periocular Biometric Pattern (FSVP-PBP) database, having 350 subjects. The POC-ViT framework outperformed state-of-the-art methods with an outstanding classification accuracy of $98.8%$ with the dual biometric traits.
传统生物识别系统由于各种不可避免的因素而遭遇了重大挫折,例如在基于面部识别的生物识别中佩戴口罩的问题,以及在基于指纹识别的生物识别中的卫生问题。本文提出了一种新型轻量级视觉转换器,即仅相位交叉注意力(POC-ViT),它使用额头和眼部周围的面部双重生物特征,即使佩戴口罩无需任何物理接触也能表现良好,为传统方法提供了有前景的替代方案。POC-ViT框架被设计成处理两种生物特征,并捕获相对结构模式的相互依赖性。每个通道由仅使用相位相关性的交叉注意力(POC)组成,能够捕获它们各自的和相关联的结构模式。使用POC计算交叉注意力提取空间特征的相位相关性。因此,它对分辨率和强度的变化、输入图像中的照明变化具有鲁棒性。这种轻量级模型适合在边缘设备进行部署。使用额头皮下静脉模式和眼部生物特征模式(FSVP-PBP)数据库(包含350个主体)成功展示了所提出框架的性能。POC-ViT框架利用双重生物特征实现了卓越的分类准确率(98.8%),超越了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE
Summary
一种新型轻量级视觉转换器POC-ViT被提出,它利用额头和眼周的双生物特征进行面部识别,能够在佩戴口罩的情况下和无须任何物理接触的情况下表现良好,为传统生物识别方法提供了有前景的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 传统生物识别系统因不可抗因素(如戴口罩、卫生问题)而受阻。
- POC-ViT是一种新型轻量级视觉转换器,使用额头和眼周的双生物特征进行识别。
- POC-ViT设计用于处理两种生物特征,并捕捉其相对结构模式的相互依赖性。
- 跨注意使用POC计算提取空间特征的相位相关性,使其对分辨率和强度变化、输入图像中的照明变化具有鲁棒性。
- 该轻量级模型适合在边缘设备进行部署。
- 在使用额头皮下血管模式和眼周生物特征模式的数据库中进行测试,POC-ViT框架表现出卓越的分类准确性,达到98.8%。
点此查看论文截图