⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
DashCam Video: A complementary low-cost data stream for on-demand forest-infrastructure system monitoring
Authors:Durga Joshi, Chandi Witharana, Robert Fahey, Thomas Worthley, Zhe Zhu, Diego Cerrai
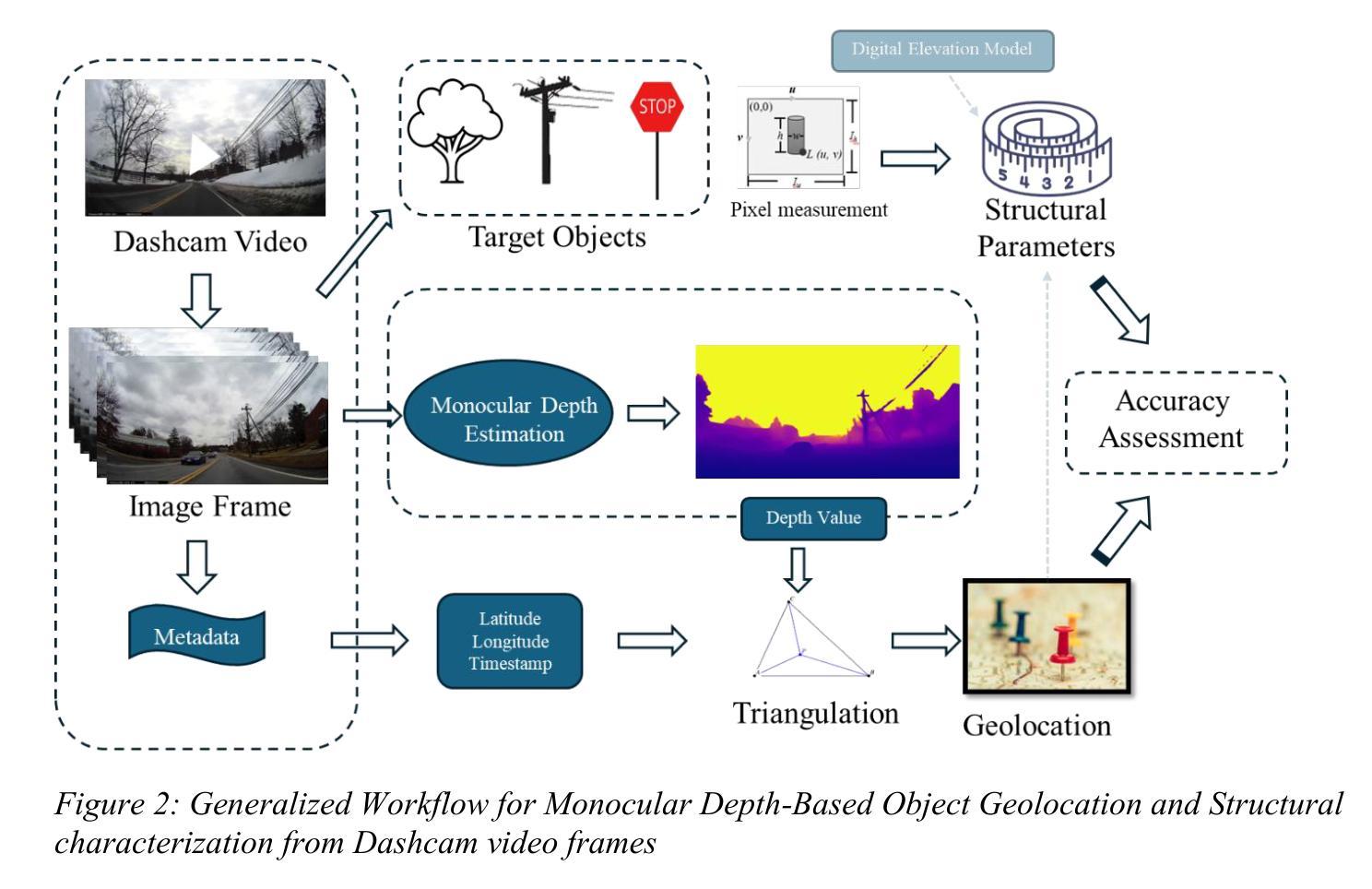
Our study introduces a novel, low-cost, and reproducible framework for real-time, object-level structural assessment and geolocation of roadside vegetation and infrastructure with commonly available but underutilized dashboard camera (dashcam) video data. We developed an end-to-end pipeline that combines monocular depth estimation, depth error correction, and geometric triangulation to generate accurate spatial and structural data from street-level video streams from vehicle-mounted dashcams. Depth maps were first estimated using a state-of-the-art monocular depth model, then refined via a gradient-boosted regression framework to correct underestimations, particularly for distant objects. The depth correction model achieved strong predictive performance (R2 = 0.92, MAE = 0.31 on transformed scale), significantly reducing bias beyond 15 m. Further, object locations were estimated using GPS-based triangulation, while object heights were calculated using pin hole camera geometry. Our method was evaluated under varying conditions of camera placement and vehicle speed. Low-speed vehicle with inside camera gave the highest accuracy, with mean geolocation error of 2.83 m, and mean absolute error (MAE) in height estimation of 2.09 m for trees and 0.88 m for poles. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first framework to combine monocular depth modeling, triangulated GPS-based geolocation, and real-time structural assessment for urban vegetation and infrastructure using consumer-grade video data. Our approach complements conventional RS methods, such as LiDAR and image by offering a fast, real-time, and cost-effective solution for object-level monitoring of vegetation risks and infrastructure exposure, making it especially valuable for utility companies, and urban planners aiming for scalable and frequent assessments in dynamic urban environments.
我们的研究引入了一个新颖、低成本、可复制性的框架,该框架利用常见的但未被充分利用的仪表板摄像头(行车记录仪)视频数据,进行实时、面向对象的植被和结构评估以及地理定位。我们开发了一个端到端的管道,它结合了单目深度估计、深度误差校正和几何三角测量技术,从车载行车记录仪的街头视频流生成准确的空间和结构数据。首先,使用最先进的单目深度模型估计深度图,然后通过梯度增强回归框架对低估进行修正,特别是远处的物体。深度校正模型具有很强的预测性能(转换尺度上的R²= 0.92,MAE = 0.31),显著减少了超过15米以外的偏差。此外,物体位置是使用基于GPS的三角测量技术估计的,而物体高度则是使用针孔相机几何计算的。我们的方法在不同的相机放置位置和车辆速度条件下进行了评估。装有内部相机的低速车辆表现出最高的准确性,树木的地理定位平均误差为2.83米,高度估计的平均绝对误差(MAE)为2.09米,而杆的平均绝对误差为0.88米。据我们所知,这是第一个结合单目深度建模、基于三角测量的GPS地理定位和使用消费者级视频数据进行实时结构评估的框架。我们的方法补充了传统的遥感方法,如激光雷达和图像,提供了一种快速、实时、成本效益高的面向对象的植被风险和结构暴露监测解决方案。这使得它在公用事业公司和城市规划师针对动态城市环境进行可扩展和频繁的评估时具有特别的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 Pages, 15 figures
摘要
本研究提出了一种新颖、低成本、可复制性的框架,该框架可利用常见的但未被充分利用的行车记录仪视频数据,进行实时面向对象的结构评估和路边植被及基础设施的地理位置定位。研究团队建立了一个端到端的管道,结合单目深度估计、深度误差修正和几何三角测量技术,从街道级的视频流中生成准确的空间和结构数据。首先使用先进的单目深度模型估计深度图,然后通过梯度增强回归框架修正深度图的低估问题,特别是对远处物体的低估。深度修正模型预测性能强大(转换尺度上的R²=0.92,MAE=0.31),显著减少了超过15米以外的偏差。此外,还利用基于GPS的三角测量技术估计物体位置,利用针孔相机几何计算物体高度。该研究在不同相机放置位置和车速条件下对方法进行了评估。车内低速行驶、相机朝内的配置提供了最高的准确性,树木的地理定位平均误差为2.83米,高度估计的平均绝对误差为2.09米,而杆状物的平均绝对误差为0.88米。据我们所知,这是首个结合单目深度建模、基于GPS的三角测量地理定位和实时结构评估,利用消费级视频数据对城市植被和基础设施进行分析的框架。该方法补充了传统的遥感方法,如激光雷达和图像数据,提供了一种快速、实时、成本效益高的面向对象的植被风险监测和基础设施暴露监测解决方案,对于电力公司、城市规划师等在动态城市环境中进行可伸缩和频繁评估具有特别的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了结合行车记录仪视频数据的实时面向对象的结构评估和地理定位框架。
- 利用单目深度估计、深度误差修正和几何三角测量技术生成准确的空间和结构数据。
- 深度修正模型表现出强大的预测性能,显著减少了深度估计的偏差。
- 通过GPS-based三角测量技术估计物体位置,并利用针孔相机几何计算物体高度。
- 低速行驶、相机朝内的配置提供了最高的准确性。
- 该研究在动态城市环境中进行植被和基础设施的实时监测具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


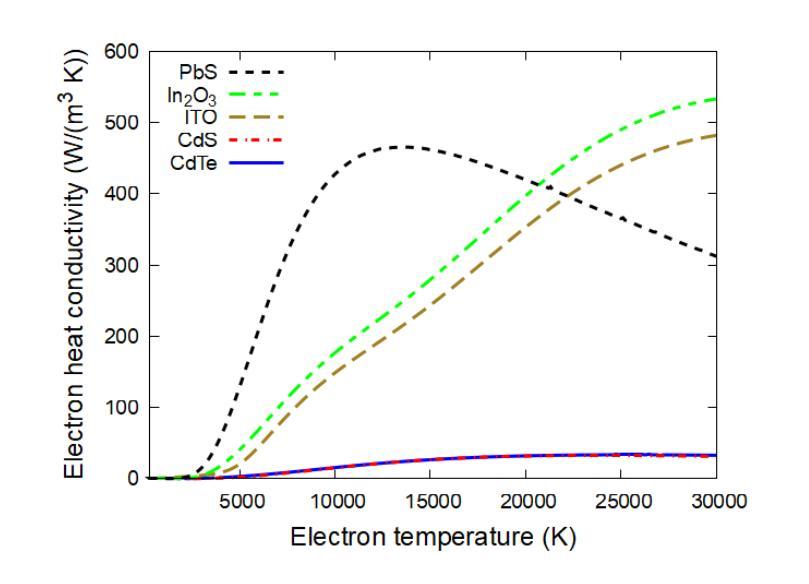
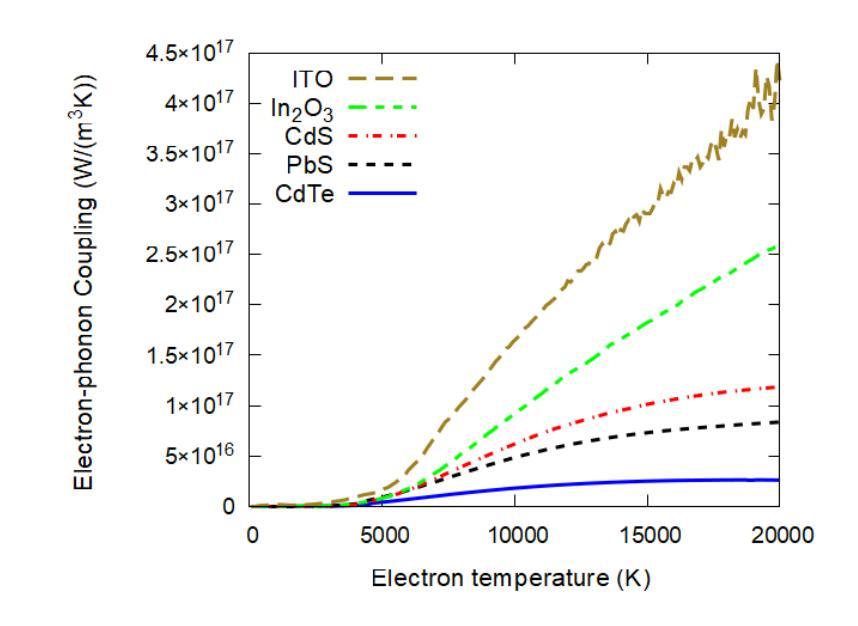
Ultrafast X-ray interaction with photovoltaic materials: Thermal and nonthermal responses
Authors:Aldo Artímez Peña, Nikita Medvedev
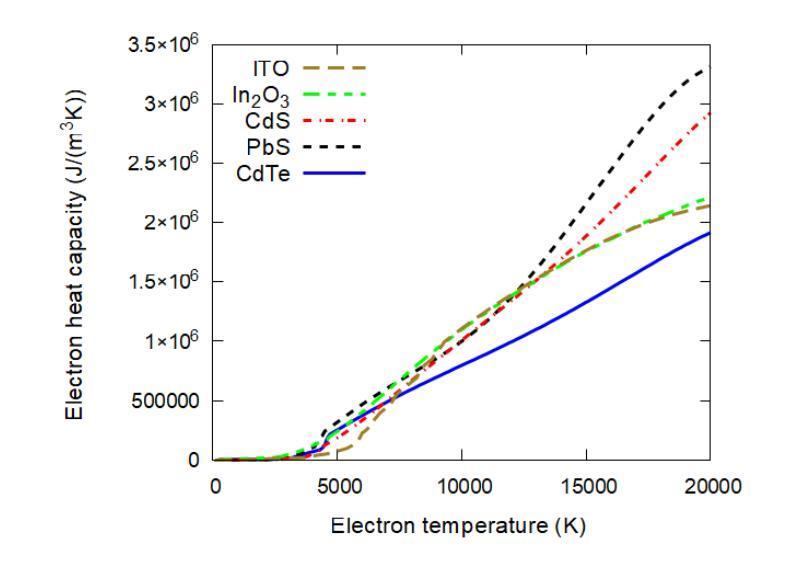
Cadmium telluride (CdTe), lead sulfide (PbS), and indium tin oxide (ITO) are important in various electronic technologies, for which laser irradiation is used to selectively modify and design their unique semiconductor properties. We employ the hybrid multiscale code XTANT-3 to simulate the kinetics of material response to ultrafast X-ray irradiation. The code accounts for nonequilibrium electronic and atomic dynamics, nonadiabatic coupling, nonthermal melting, and bond breaking due to electronic excitation. Among the materials studied, CdTe exhibits the highest radiation resistance, similar to CdS. At the respective threshold doses, the melting is primarily thermal, driven by electron-phonon coupling, which is accompanied by the band gap closure. Additionally, all materials show nonthermal melting at higher doses. Threshold doses increase further if energy sinks and recrystallization are included. In CdTe and PbS, below 1.5 eV/atom, the band gap returns to its original value upon recrystallization. As the dose increases, the cooled state becomes more amorphous, reducing the band gap until it stabilizes. Curiously, in a narrow window of deposited doses, ITO exhibit transient superionic behavior, with the liquid oxygen but solid In and Sn sublattices. At 0.6 eV/atom in CdTe and 0.4 eV/atom in PbS and ITO, material ablation from the surface occurs. The results suggest that femtosecond lasers may be used for tuning the band gap of photovoltaic semiconductors.
镉碲化物(CdTe)、铅硫化物(PbS)和氧化铟锡(ITO)在各种电子技术中扮演着重要角色,激光辐射被用于选择性地修改和设计它们独特的半导体属性。我们采用混合多尺度代码XTANT-3来模拟材料对超快X射线辐射的动力学反应。该代码考虑了非平衡电子和原子动力学、非绝热耦合、非热熔化和因电子激发而导致的键断裂。在所研究的材料中,CdTe表现出最高的抗辐射性,与CdS相似。在各自的阈值剂量下,熔化主要是热驱动,由电子-声子耦合伴随带隙闭合。此外,所有材料在较高剂量下均显示非热熔化。如果包括能量吸收和再结晶,阈值剂量会进一步增加。在CdTe和PbS中,低于1.5 eV/atom的情况下,再结晶后带隙会恢复到其原始值。随着剂量的增加,冷却状态变得更加无定形,减少带隙直至其稳定。奇怪的是,在沉积剂量的狭窄范围内,ITO表现出短暂的超离子行为,具有液态氧但In和Sn子晶格为固态。在CdTe的0.6 eV/atom和PbS及ITO的0.4 eV/atom时,材料会从表面消融。结果表明,飞秒激光可用于调节光伏半导体的带隙。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 22 figures, 2 tables. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2502.05799
摘要
本文研究了Cadmium telluride(CdTe)、lead sulfide(PbS)和indium tin oxide(ITO)在激光照射下材料特性的变化。采用XTANT-3混合多尺度代码模拟了这些材料对超快X射线照射的动力学响应,包括非平衡电子和原子动力学、非绝热耦合、非热熔化和键断裂等过程。CdTe表现出较高的辐射抗性,与CdS相似。在特定阈值剂量下,熔化主要由电子-声子耦合驱动,伴随带隙闭合。更高剂量下则表现出非热熔解。考虑能量沉积和再结晶时,阈值剂量进一步增加。在CdTe和PbS中,低于1.5 eV/atom的情况下,再结晶后带隙可恢复到初始值。剂量增加时,冷却状态变得更无定形,带隙减小直至稳定。在特定的沉积剂量范围内,ITO表现出瞬态超离子行为。研究结果暗示,飞秒激光可用于调节光伏半导体的带隙。
要点总结
- Cadmium telluride (CdTe)、lead sulfide (PbS) 和 indium tin oxide (ITO) 在电子科技中有重要应用。
- 使用XTANT-3代码模拟了这些材料在超快X射线照射下的反应动力学。
- CdTe展现出较高的辐射抗性,类似于CdS。
- 在特定阈值剂量下,材料熔化主要由电子-声子耦合驱动,伴随带隙闭合;更高剂量则表现为非热熔解。
- 考虑能量沉集和再结晶时,阈值剂量会增加。
- ITO在特定沉积剂量范围内展现出瞬态超离子行为。
点此查看论文截图

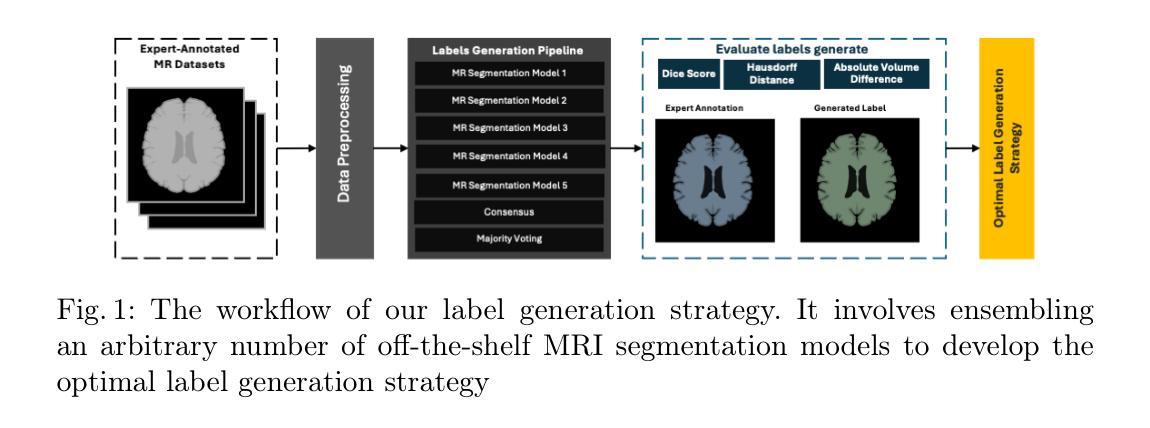
Subcortical Masks Generation in CT Images via Ensemble-Based Cross-Domain Label Transfer
Authors:Augustine X. W. Lee, Pak-Hei Yeung, Jagath C. Rajapakse
Subcortical segmentation in neuroimages plays an important role in understanding brain anatomy and facilitating computer-aided diagnosis of traumatic brain injuries and neurodegenerative disorders. However, training accurate automatic models requires large amounts of labelled data. Despite the availability of publicly available subcortical segmentation datasets for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), a significant gap exists for Computed Tomography (CT). This paper proposes an automatic ensemble framework to generate high-quality subcortical segmentation labels for CT scans by leveraging existing MRI-based models. We introduce a robust ensembling pipeline to integrate them and apply it to unannotated paired MRI-CT data, resulting in a comprehensive CT subcortical segmentation dataset. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed framework. Furthermore, using our generated CT dataset, we train segmentation models that achieve improved performance on related segmentation tasks. To facilitate future research, we make our source code, generated dataset, and trained models publicly available at https://github.com/SCSE-Biomedical-Computing-Group/CT-Subcortical-Segmentation, marking the first open-source release for CT subcortical segmentation to the best of our knowledge.
神经影像中的皮质下分割对于理解大脑结构以及促进计算机辅助的脑外伤和神经退行性疾病的诊断具有重要意义。然而,训练准确的自动模型需要大量的标记数据。尽管存在用于磁共振成像(MRI)的公开皮质下分割数据集,但在计算机断层扫描(CT)方面仍存在较大空白。本文提出一个自动集成框架,通过利用现有的基于MRI的模型,生成高质量的CT扫描皮质下分割标签。我们引入了一个稳健的集成管道来整合这些模型,并将其应用于未配对的MRI-CT数据,从而生成了一个全面的CT皮质下分割数据集。在多个公共数据集上的广泛实验证明了我们提出框架的优越性。此外,使用我们生成的CT数据集,我们训练的分割模型在相关分割任务上实现了性能提升。为了便于未来的研究,我们在https://github.com/SCSE-Biomedical-Computing-Group/CT-Subcortical-Segmentation上公开了我们的源代码、生成的数据集和训练好的模型,据我们所知,这是CT皮质下分割的第一个开源发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于集成学习的框架,利用已有的磁共振成像(MRI)模型生成高质量的计算机断层扫描(CT)子皮层分割标签数据集。该框架通过集成管道整合MRI和CT数据,创建了一个全面的CT子皮层分割数据集。实验证明,该框架在多个公共数据集上的表现优异,能够提高相关分割任务的性能。同时,公开源代码、生成的数据集和训练模型,以促进未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- 子皮层分割在神经图像中扮演着理解大脑结构和促进计算机辅助诊断脑损伤和神经退行性疾病的重要角色。
- 训练准确的自动模型需要大量的标记数据,而CT子皮层分割数据集存在显著缺口。
- 本文提出一种基于集成学习的框架,利用MRI模型生成CT子皮层分割标签。
- 通过集成管道整合MRI和CT数据,创建了一个全面的CT子皮层分割数据集。
- 实验证明该框架在多个公共数据集上表现优异。
- 使用生成的CT数据集训练的分割模型在相关任务上取得了更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

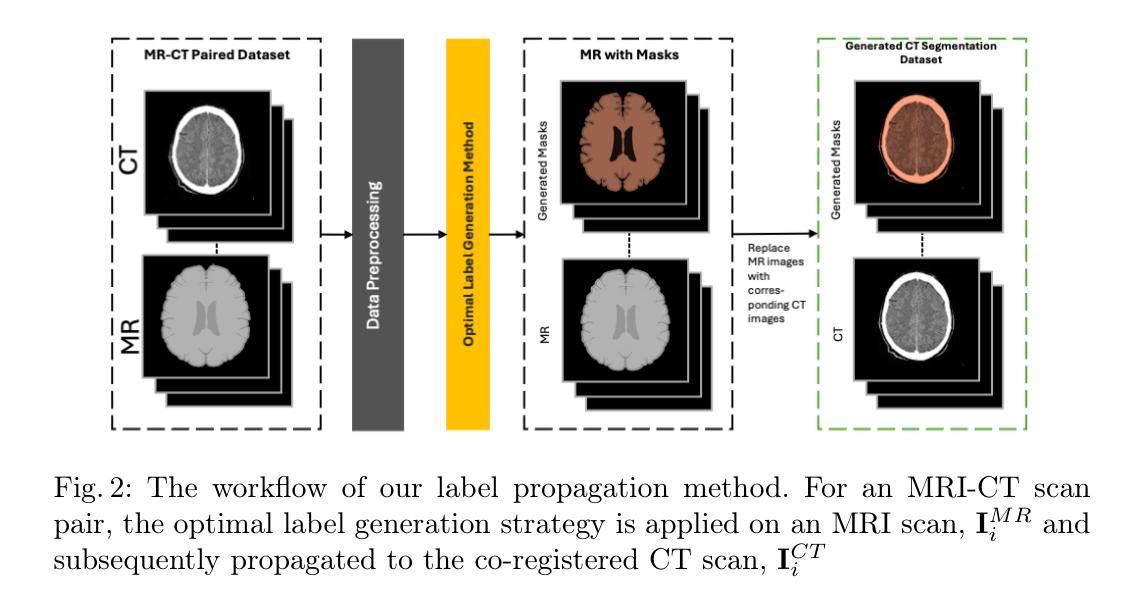
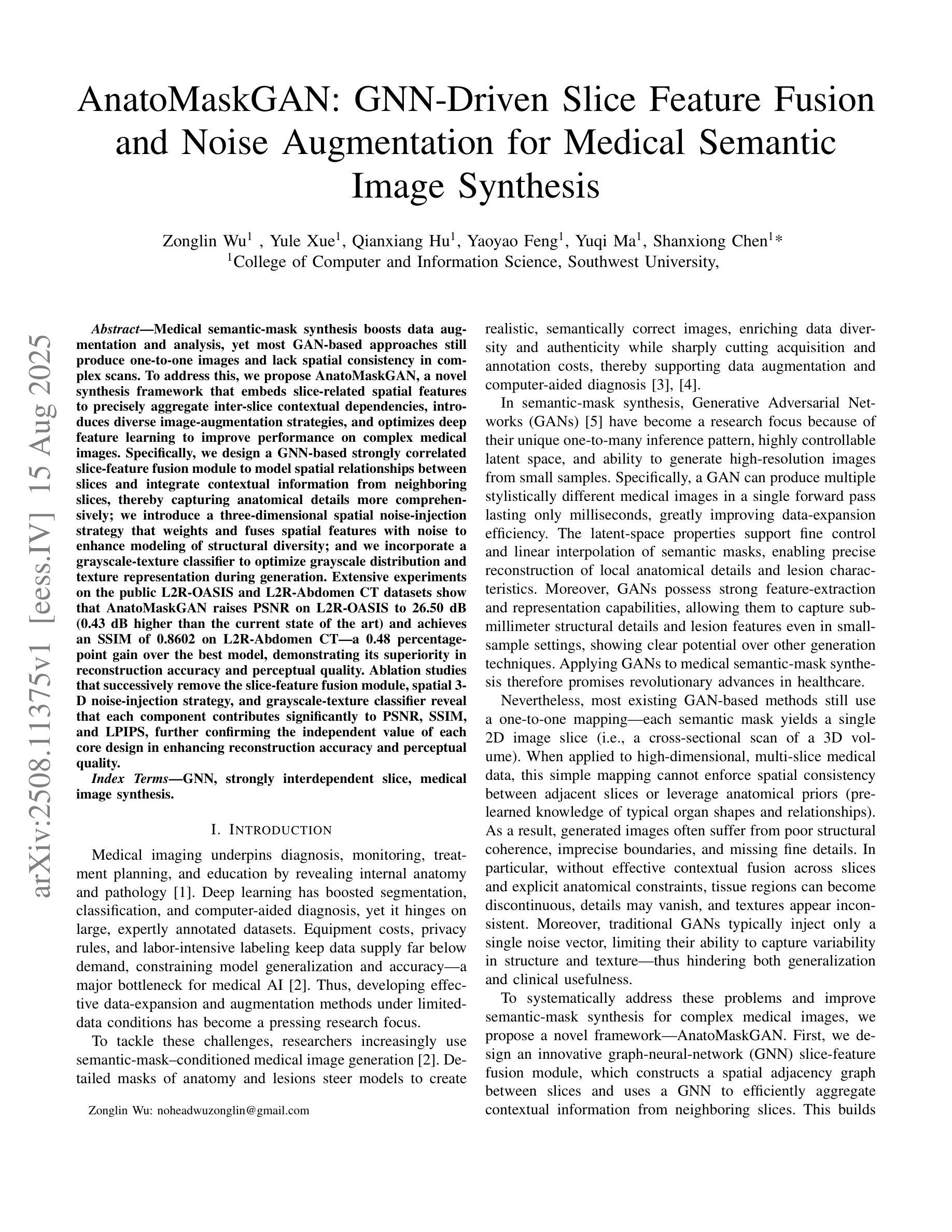
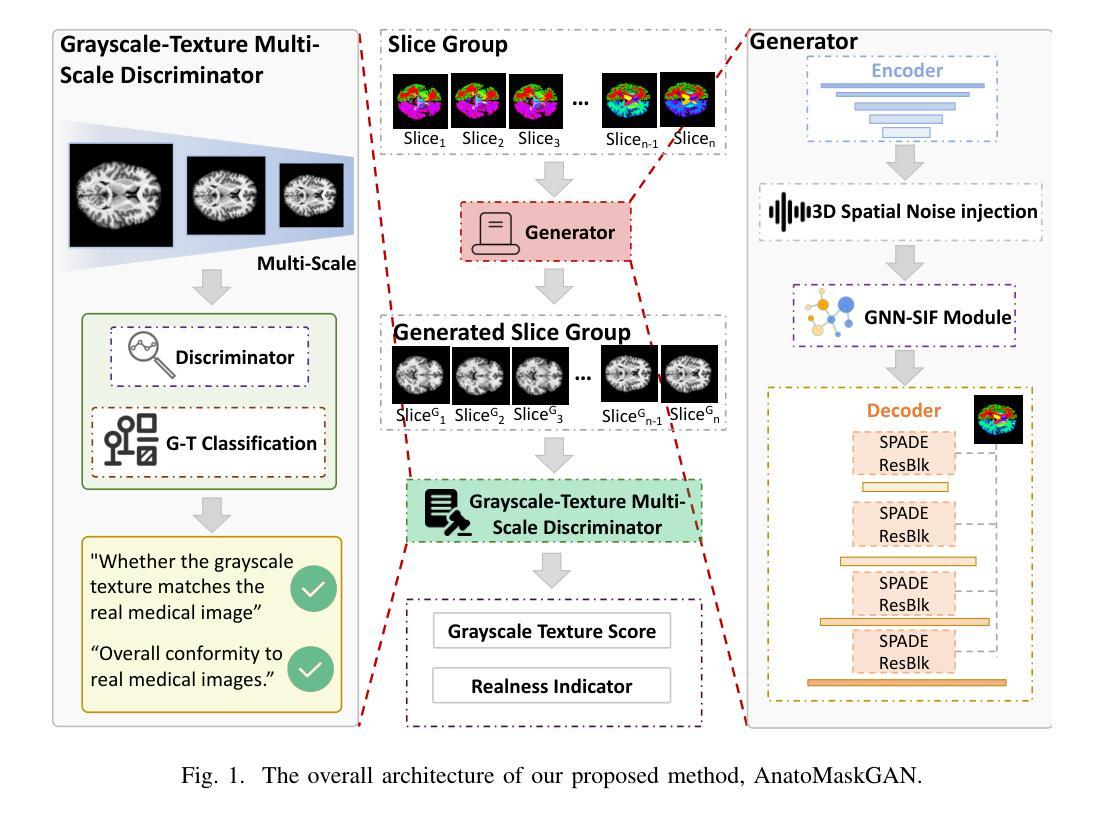
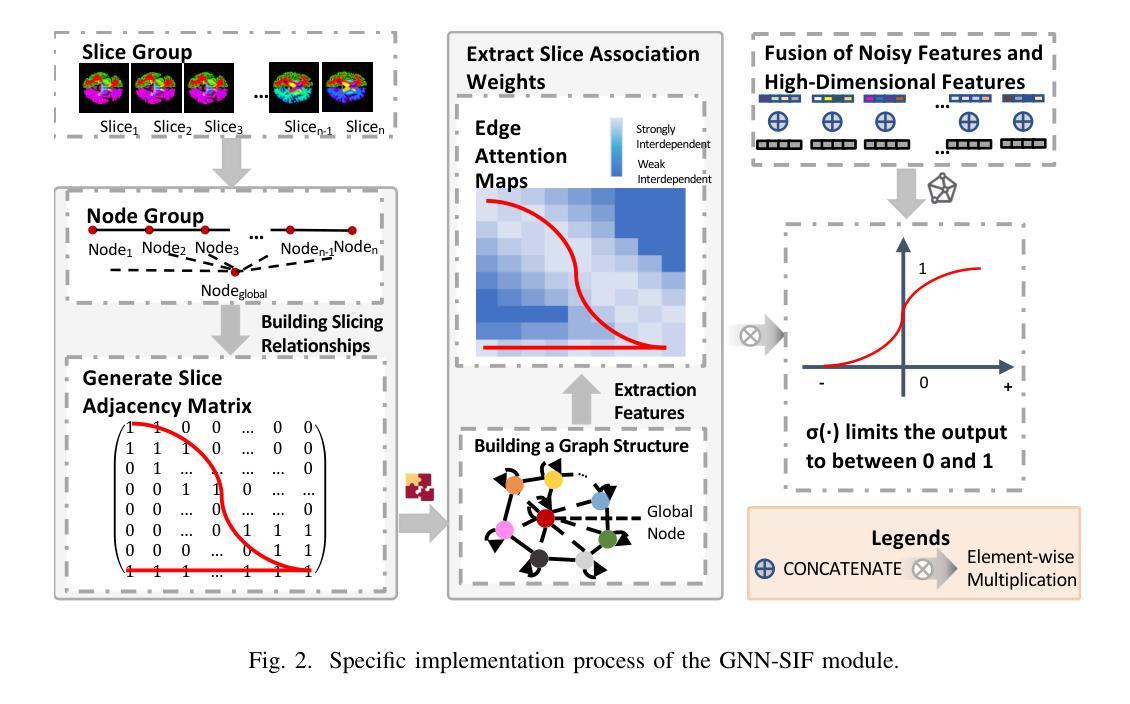
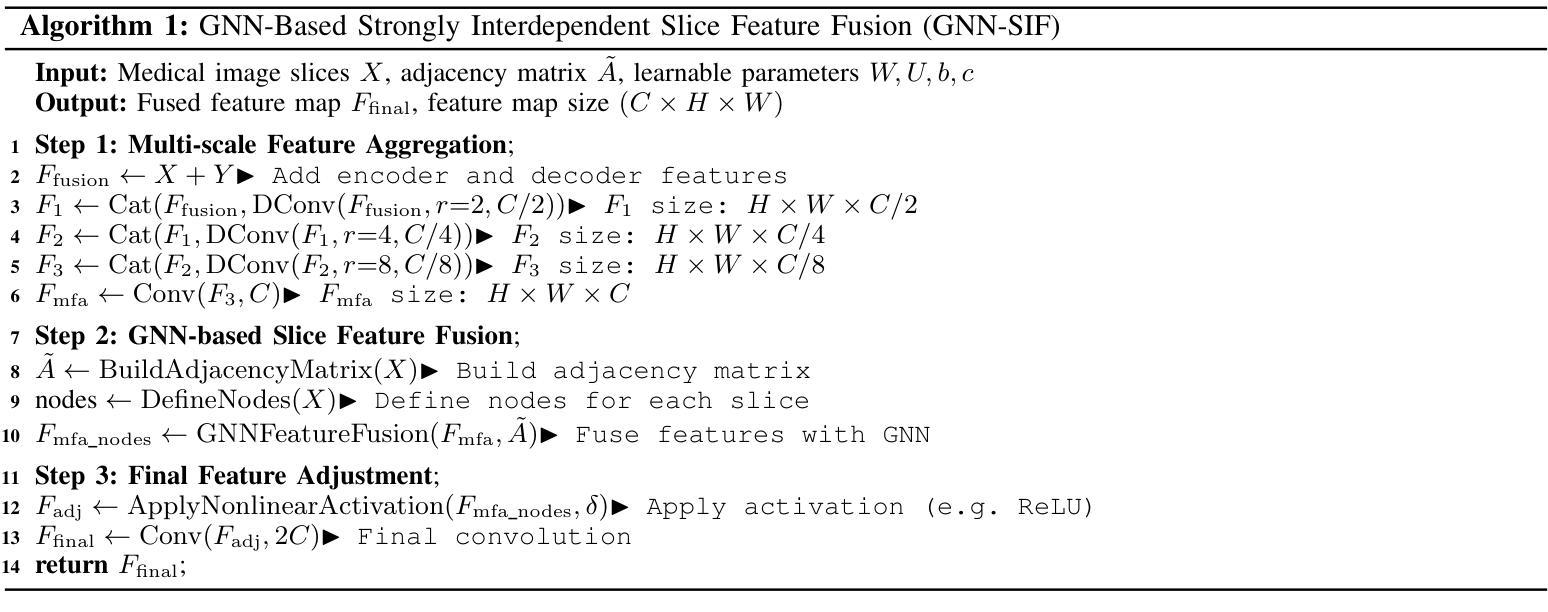
AnatoMaskGAN: GNN-Driven Slice Feature Fusion and Noise Augmentation for Medical Semantic Image Synthesis
Authors:Zonglin Wu, Yule Xue, Qianxiang Hu, Yaoyao Feng, Yuqi Ma, Shanxiong Chen
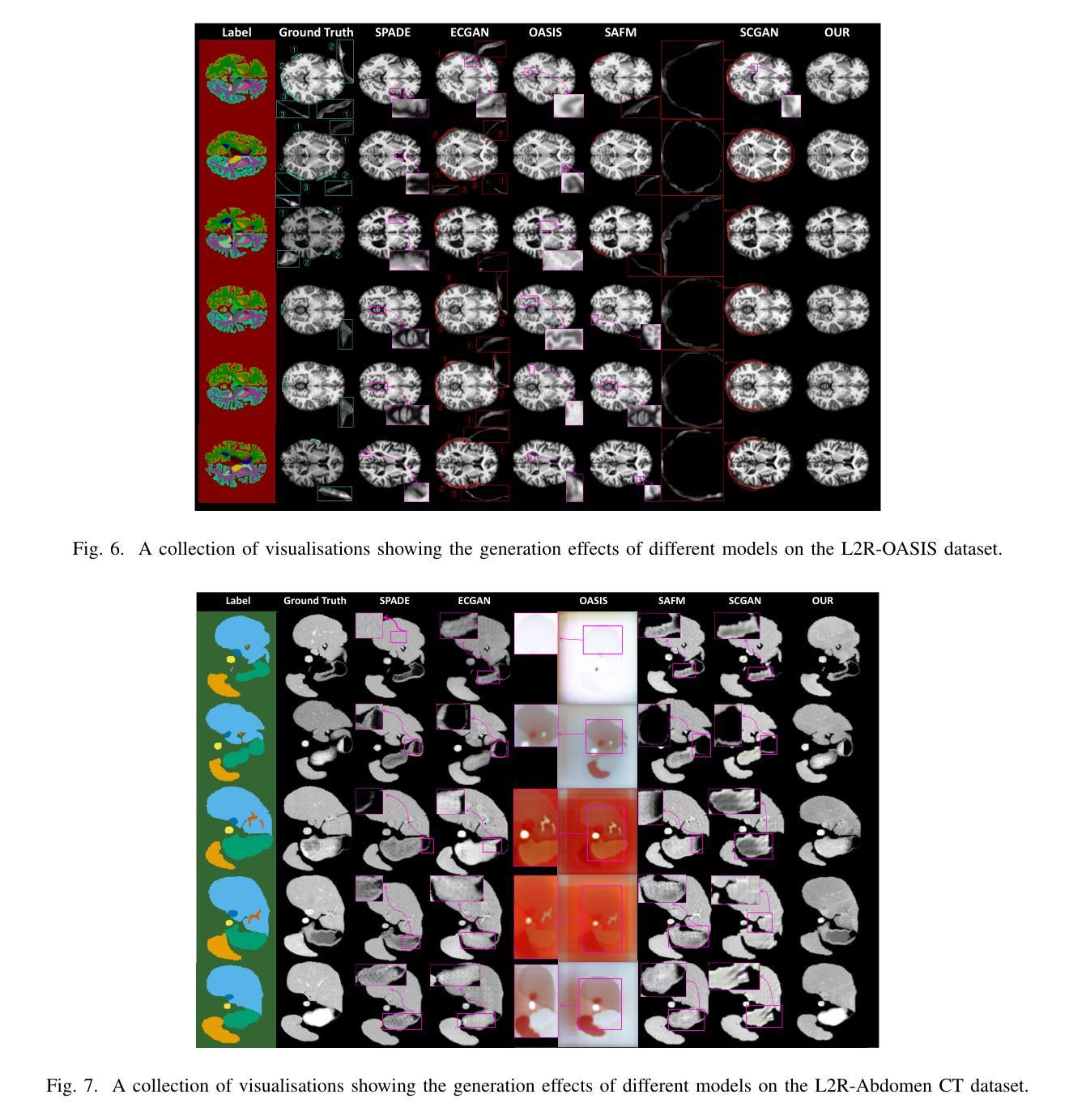
Medical semantic-mask synthesis boosts data augmentation and analysis, yet most GAN-based approaches still produce one-to-one images and lack spatial consistency in complex scans. To address this, we propose AnatoMaskGAN, a novel synthesis framework that embeds slice-related spatial features to precisely aggregate inter-slice contextual dependencies, introduces diverse image-augmentation strategies, and optimizes deep feature learning to improve performance on complex medical images. Specifically, we design a GNN-based strongly correlated slice-feature fusion module to model spatial relationships between slices and integrate contextual information from neighboring slices, thereby capturing anatomical details more comprehensively; we introduce a three-dimensional spatial noise-injection strategy that weights and fuses spatial features with noise to enhance modeling of structural diversity; and we incorporate a grayscale-texture classifier to optimize grayscale distribution and texture representation during generation. Extensive experiments on the public L2R-OASIS and L2R-Abdomen CT datasets show that AnatoMaskGAN raises PSNR on L2R-OASIS to 26.50 dB (0.43 dB higher than the current state of the art) and achieves an SSIM of 0.8602 on L2R-Abdomen CT–a 0.48 percentage-point gain over the best model, demonstrating its superiority in reconstruction accuracy and perceptual quality. Ablation studies that successively remove the slice-feature fusion module, spatial 3D noise-injection strategy, and grayscale-texture classifier reveal that each component contributes significantly to PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, further confirming the independent value of each core design in enhancing reconstruction accuracy and perceptual quality.
医学语义掩膜合成促进了数据增强和分析,但大多数基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法仍然只能生成一对一的图像,在复杂扫描中缺乏空间一致性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了AnatoMaskGAN,这是一种新的合成框架,它嵌入切片相关的空间特征来精确聚合切片间的上下文依赖关系,引入多种图像增强策略,并优化深度特征学习,以提高在复杂医学图像上的性能。具体来说,我们设计了一个基于图神经网络(GNN)的强相关切片特征融合模块,以建模切片之间的空间关系,并整合来自相邻切片的上下文信息,从而更全面地捕捉解剖细节;我们引入了一种三维空间噪声注入策略,该策略通过加权和融合空间特征与噪声,以增强结构多样性的建模;我们还融入了一个灰度纹理分类器,以优化生成过程中的灰度分布和纹理表示。在公共的L2R-OASIS和L2R-Abdomen CT数据集上的大量实验表明,AnatoMaskGAN在L2R-OASIS上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高到26.50 dB(比当前最佳水平高出0.43 dB),在L2R-Abdomen CT上的结构相似性指数(SSIM)达到0.8602(比最佳模型高出0.48个百分点),证明了其在重建精度和感知质量上的优越性。逐步移除切片特征融合模块、空间3D噪声注入策略和灰度纹理分类器的消融研究证实,每个组件对PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS都有显著贡献,进一步证明了每个核心设计在提高重建精度和感知质量方面的独立价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
医学语义遮罩合成提升数据扩充与分析,针对复杂医学图像,AnatoMaskGAN框架嵌入切片相关空间特征,精确聚合切片间上下文依赖关系,引入多样化图像增强策略,优化深度特征学习以提升性能。设计图神经网络(GNN)相关切片特征融合模块,建模切片间空间关系,集成邻近切片上下文信息,全面捕捉解剖细节。引入三维空间噪声注入策略,增强结构多样性建模。结合灰度纹理分类器,优化生成过程中的灰度分布和纹理表示。在公开数据集L2R-OASIS和L2R-Abdomen CT上的实验表明,AnatoMaskGAN在重建精度和感知质量上均优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- AnatoMaskGAN框架通过嵌入切片相关的空间特征,解决了医学图像合成中缺乏空间一致性的问题。
- 切片特征融合模块利用图神经网络(GNN)建模切片间的空间关系,提高了解剖细节的捕捉能力。
- 通过引入三维空间噪声注入策略,增强了结构多样性的建模。
- 结合灰度纹理分类器,优化了生成图像的灰度分布和纹理表示。
- 在公开数据集上的实验表明,AnatoMaskGAN在重建精度和感知质量方面均实现了显著的提升。
- 消融研究证实了框架中的每个组件对性能的提升都起到了重要作用。
点此查看论文截图
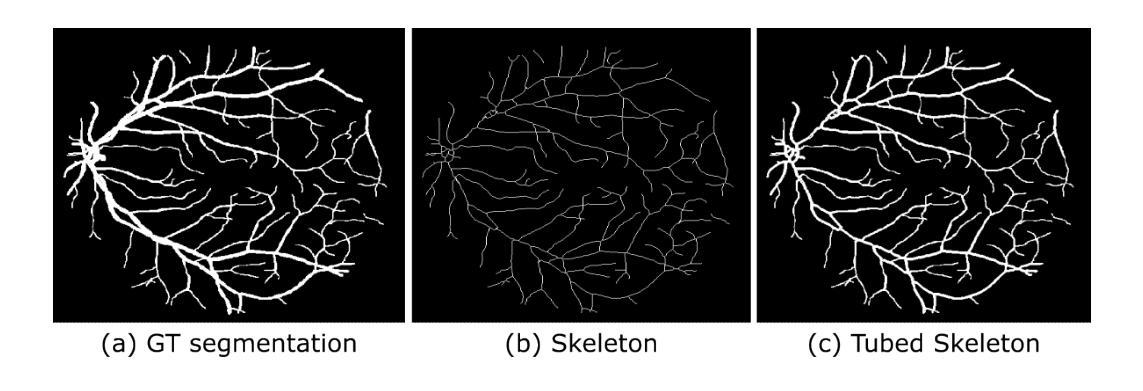
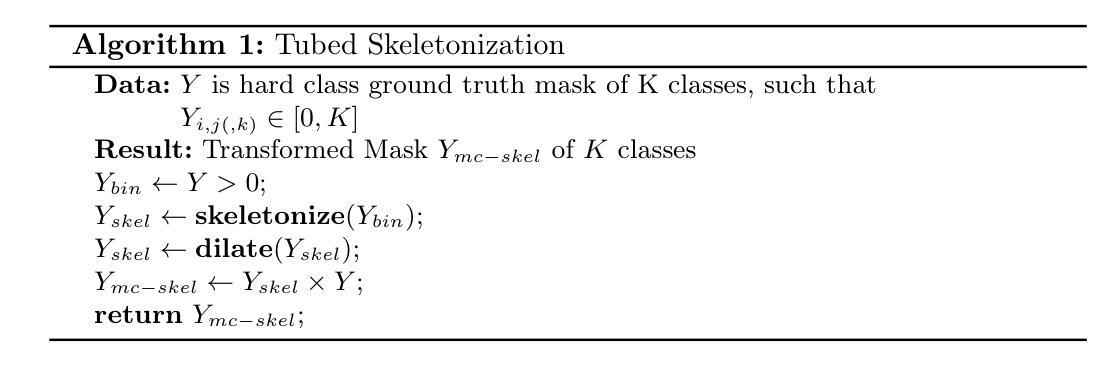
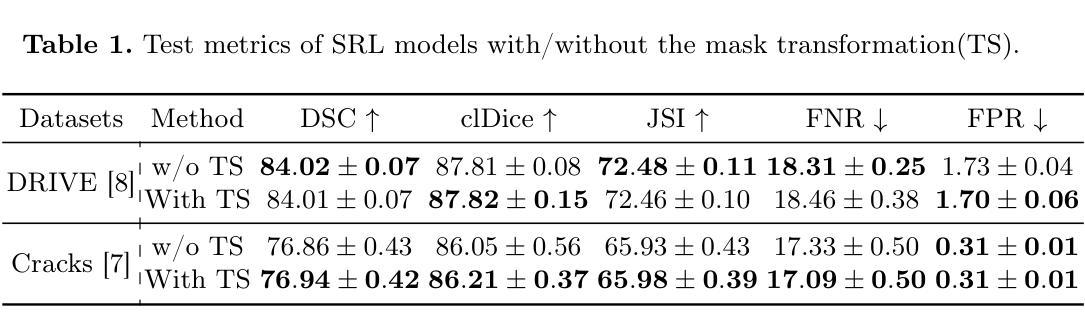
Does the Skeleton-Recall Loss Really Work?
Authors:Devansh Arora, Nitin Kumar, Sukrit Gupta
Image segmentation is an important and widely performed task in computer vision. Accomplishing effective image segmentation in diverse settings often requires custom model architectures and loss functions. A set of models that specialize in segmenting thin tubular structures are topology preservation-based loss functions. These models often utilize a pixel skeletonization process claimed to generate more precise segmentation masks of thin tubes and better capture the structures that other models often miss. One such model, Skeleton Recall Loss (SRL) proposed by Kirchhoff et al.~\cite {kirchhoff2024srl}, was stated to produce state-of-the-art results on benchmark tubular datasets. In this work, we performed a theoretical analysis of the gradients for the SRL loss. Upon comparing the performance of the proposed method on some of the tubular datasets (used in the original work, along with some additional datasets), we found that the performance of SRL-based segmentation models did not exceed traditional baseline models. By providing both a theoretical explanation and empirical evidence, this work critically evaluates the limitations of topology-based loss functions, offering valuable insights for researchers aiming to develop more effective segmentation models for complex tubular structures.
图像分割是计算机视觉中一个重要且广泛执行的任务。在不同的场景下实现有效的图像分割通常需要定制模型架构和损失函数。专门用于分割细长管状结构的模型集是基于拓扑保留的损失函数。这些模型通常利用像素骨架化过程,声称可以生成更精确的细管分割掩膜,并更好地捕捉其他模型常忽略的结构。基尔霍夫等人提出的Skeleton Recall Loss(SRL)就是这样一种模型~\cite {kirchhoff2024srl},据称在基准管状数据集上达到了最先进的结果。在这项工作中,我们对SRL损失的梯度进行了理论分析。在比较所提出方法在部分管状数据集(与原始工作中使用的数据集一起使用的附加数据集)上的性能时,我们发现基于SRL的分割模型的性能并未超过传统基线模型。通过提供理论解释和实证证据,这项工作对基于拓扑的损失函数的局限性进行了批判性评价,为旨在开发针对复杂管状结构更有效分割模型的研究人员提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
骨架回忆损失(SRL)是针对管状结构分割的拓扑保留损失函数之一,但在理论分析和实际数据集上的性能表现并未超过传统基线模型。本研究既提供了理论解释,也给出了实证证据,评估了拓扑基损失函数在复杂管状结构分割模型中的局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割是计算机视觉中的重要任务,尤其在多样化环境中需要定制模型架构和损失函数。
- 拓扑保留损失函数专门用于分割细管状结构,常用像素骨架化过程生成更精确的细管分割掩模。
- 骨架回忆损失(SRL)在管状数据集上的表现被评估,但未超过传统基线模型。
- 研究通过理论分析和实证研究评价了基于拓扑的损失函数在复杂管状结构分割模型中的局限性。
- SRL损失的理论梯度分析也被执行,为损失函数的进一步优化提供了方向。
- 除了原始数据集外,研究还在其他数据集上验证了SRL的性能。
点此查看论文截图

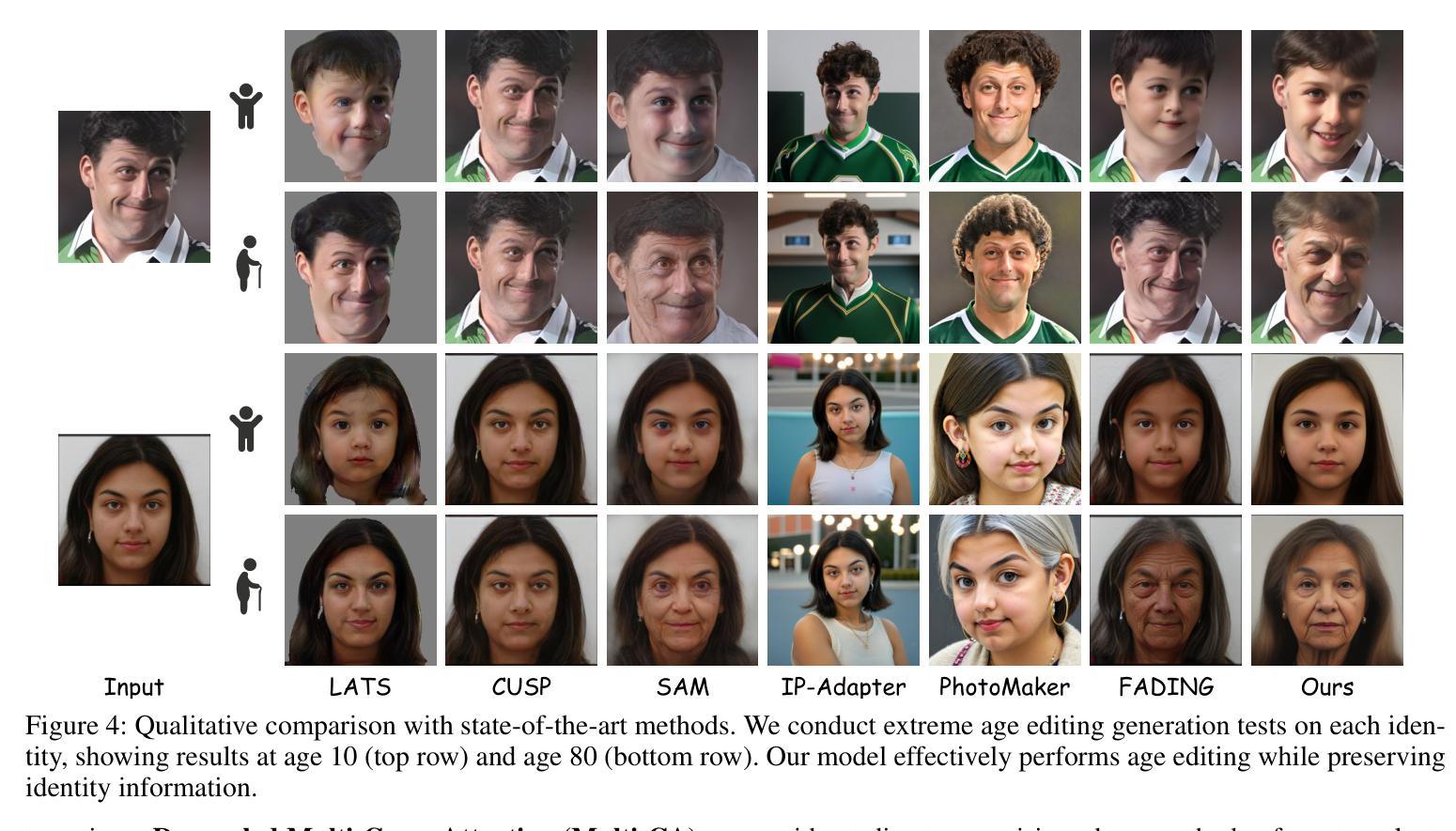
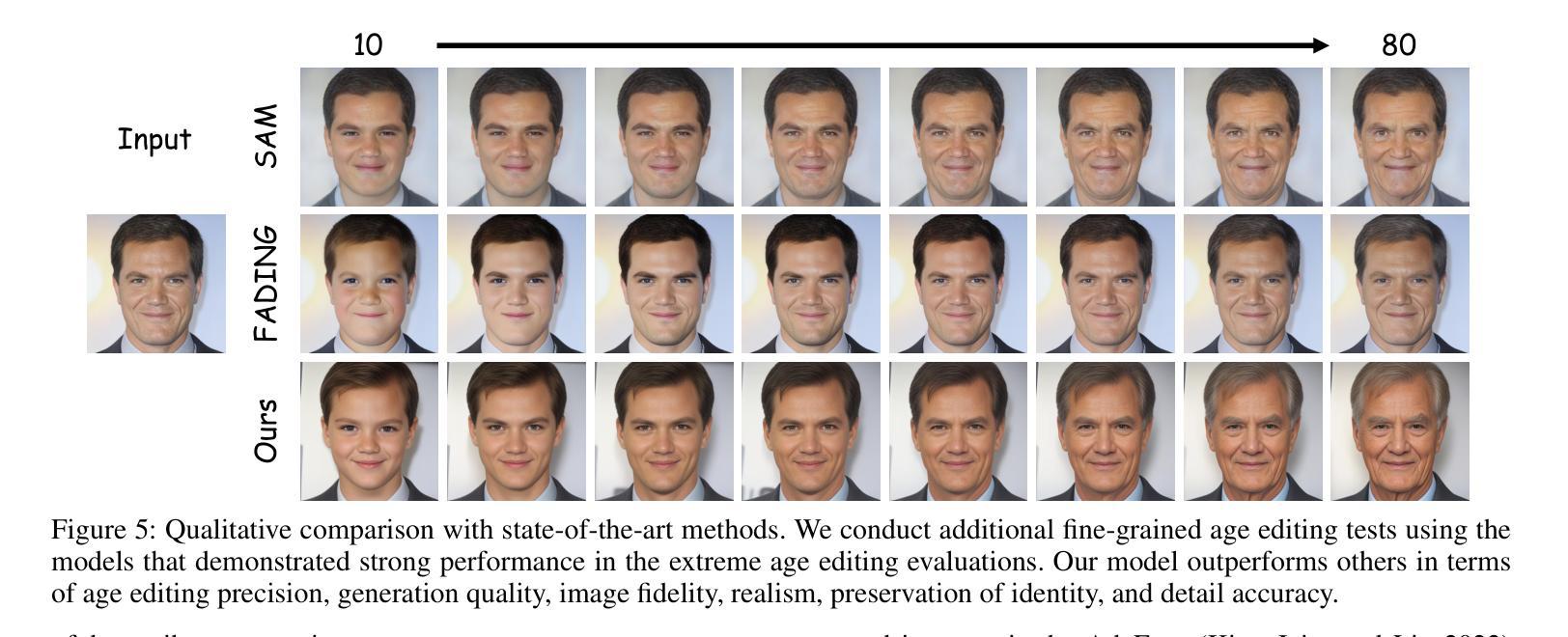
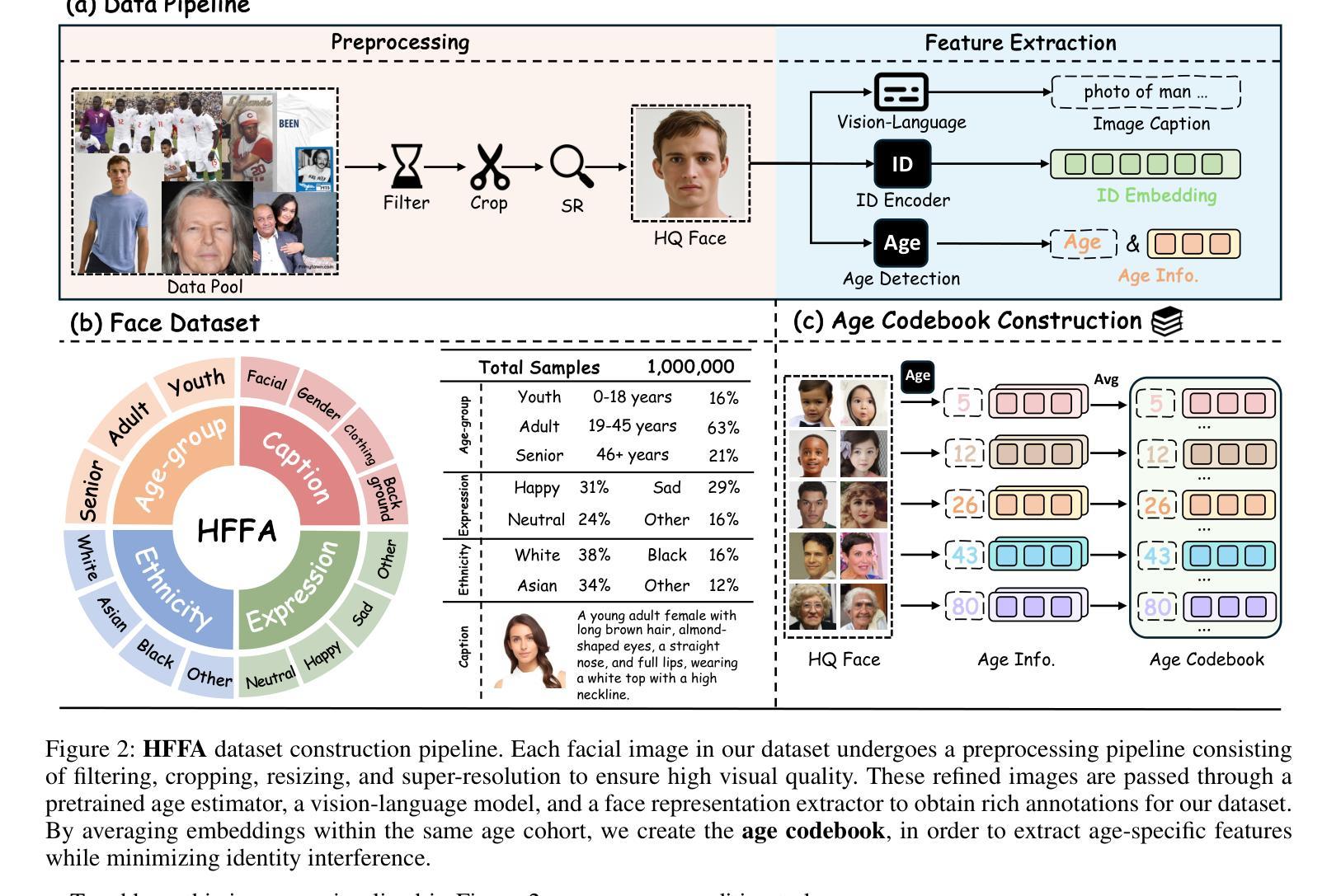
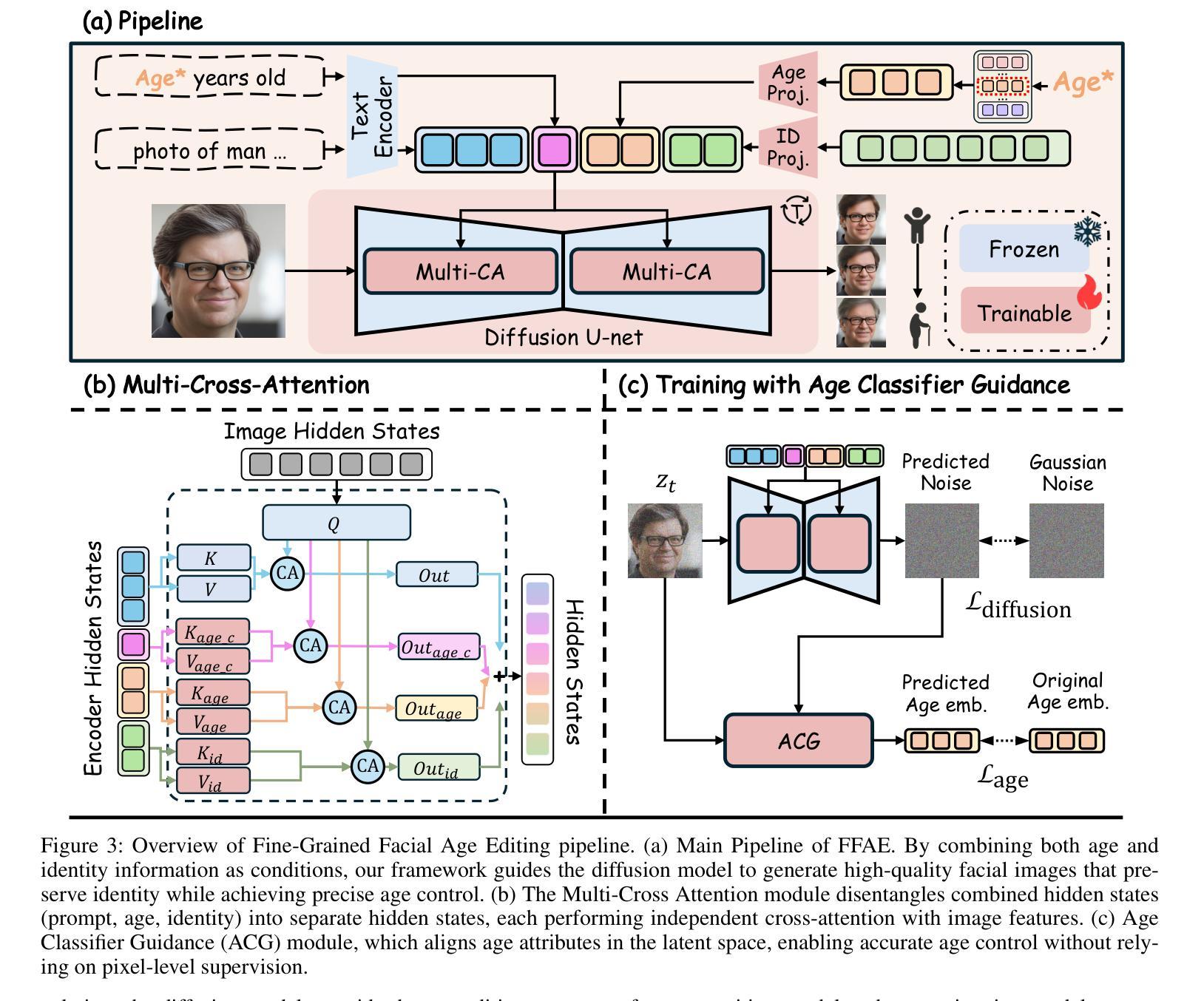
TimeMachine: Fine-Grained Facial Age Editing with Identity Preservation
Authors:Yilin Mi, Qixin Yan, Zheng-Peng Duan, Chunle Guo, Hubery Yin, Hao Liu, Chen Li, Chongyi Li
With the advancement of generative models, facial image editing has made significant progress. However, achieving fine-grained age editing while preserving personal identity remains a challenging task.In this paper, we propose TimeMachine, a novel diffusion-based framework that achieves accurate age editing while keeping identity features unchanged. To enable fine-grained age editing, we inject high-precision age information into the multi-cross attention module, which explicitly separates age-related and identity-related features. This design facilitates more accurate disentanglement of age attributes, thereby allowing precise and controllable manipulation of facial aging.Furthermore, we propose an Age Classifier Guidance (ACG) module that predicts age directly in the latent space, instead of performing denoising image reconstruction during training. By employing a lightweight module to incorporate age constraints, this design enhances age editing accuracy by modest increasing training cost. Additionally, to address the lack of large-scale, high-quality facial age datasets, we construct a HFFA dataset (High-quality Fine-grained Facial-Age dataset) which contains one million high-resolution images labeled with identity and facial attributes. Experimental results demonstrate that TimeMachine achieves state-of-the-art performance in fine-grained age editing while preserving identity consistency.
随着生成模型的发展,面部图像编辑已经取得了重大进展。然而,在保持个人身份的同时实现精细年龄编辑仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们提出了TimeMachine,一种基于扩散的新型框架,能够在保持身份特征不变的情况下实现精确的年龄编辑。为了实现精细年龄编辑,我们将高精度年龄信息注入多交叉注意模块,该模块显式地分离年龄相关和身份相关的特征。这种设计有助于更精确地分离年龄属性,从而允许精确且可控的面部衰老操作。此外,我们提出了年龄分类器指导(ACG)模块,该模块直接在潜在空间中预测年龄,而不是在训练过程中进行去噪图像重建。通过采用轻量级模块来融入年龄约束,这种设计通过适度增加训练成本来提高年龄编辑的准确性。另外,为了解决缺乏大规模高质量面部年龄数据集的问题,我们构建了一个HFFA数据集(高质量精细面部年龄数据集),其中包含一千万张带有身份和面部属性标签的高分辨率图像。实验结果表明,TimeMachine在精细年龄编辑方面达到了最先进的性能,同时保持了身份一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着生成模型的发展,面部图像编辑已取得显著进步,但在保持个人身份的同时实现精细年龄编辑仍具挑战性。本文提出TimeMachine,一种基于扩散的新型框架,可在准确编辑年龄的同时保持身份特征不变。为实现精细年龄编辑,我们在多交叉注意模块中注入高精度年龄信息,明确分离年龄相关和身份相关特征,促进年龄属性的精确分离,从而实现面部衰老的精确可控操作。此外,我们提出年龄分类器指导(ACG)模块,直接在潜在空间中预测年龄,而不是在训练过程中进行去噪图像重建。通过采用轻量级模块来融入年龄约束,这种设计在适度增加训练成本的情况下提高了年龄编辑的准确性。同时,为解决缺乏大规模高质量面部年龄数据集的问题,我们构建了HFFA数据集(高质量精细面部年龄数据集),包含一千万张带有身份和面部属性标签的高分辨率图像。实验结果证明,TimeMachine在精细年龄编辑方面实现了卓越性能,同时保持了身份一致性。
Key Takeaways
- TimeMachine是一个基于扩散的新型面部图像编辑框架,可实现准确年龄编辑同时保持身份特征不变。
- 通过注入高精度年龄信息到多交叉注意模块,实现精细年龄编辑。
- 提出Age Classifier Guidance(ACG)模块,直接在潜在空间预测年龄,提高年龄编辑准确性。
- 采用轻量级模块融入年龄约束,适度增加训练成本。
- 构建HFFA数据集,包含一千万张高质量、精细面部年龄的高分辨率图像。
- TimeMachine在保持身份一致性的同时实现了精细年龄编辑的卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图



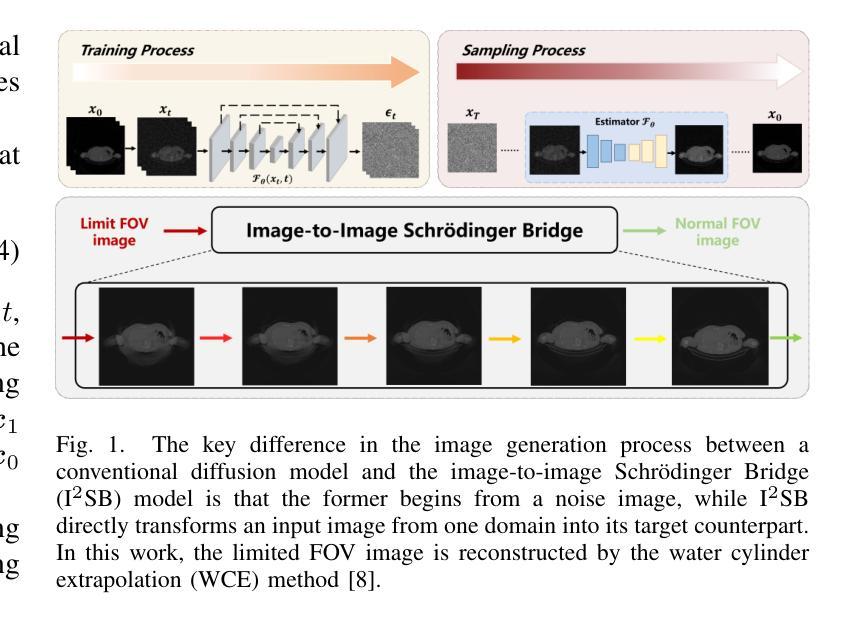
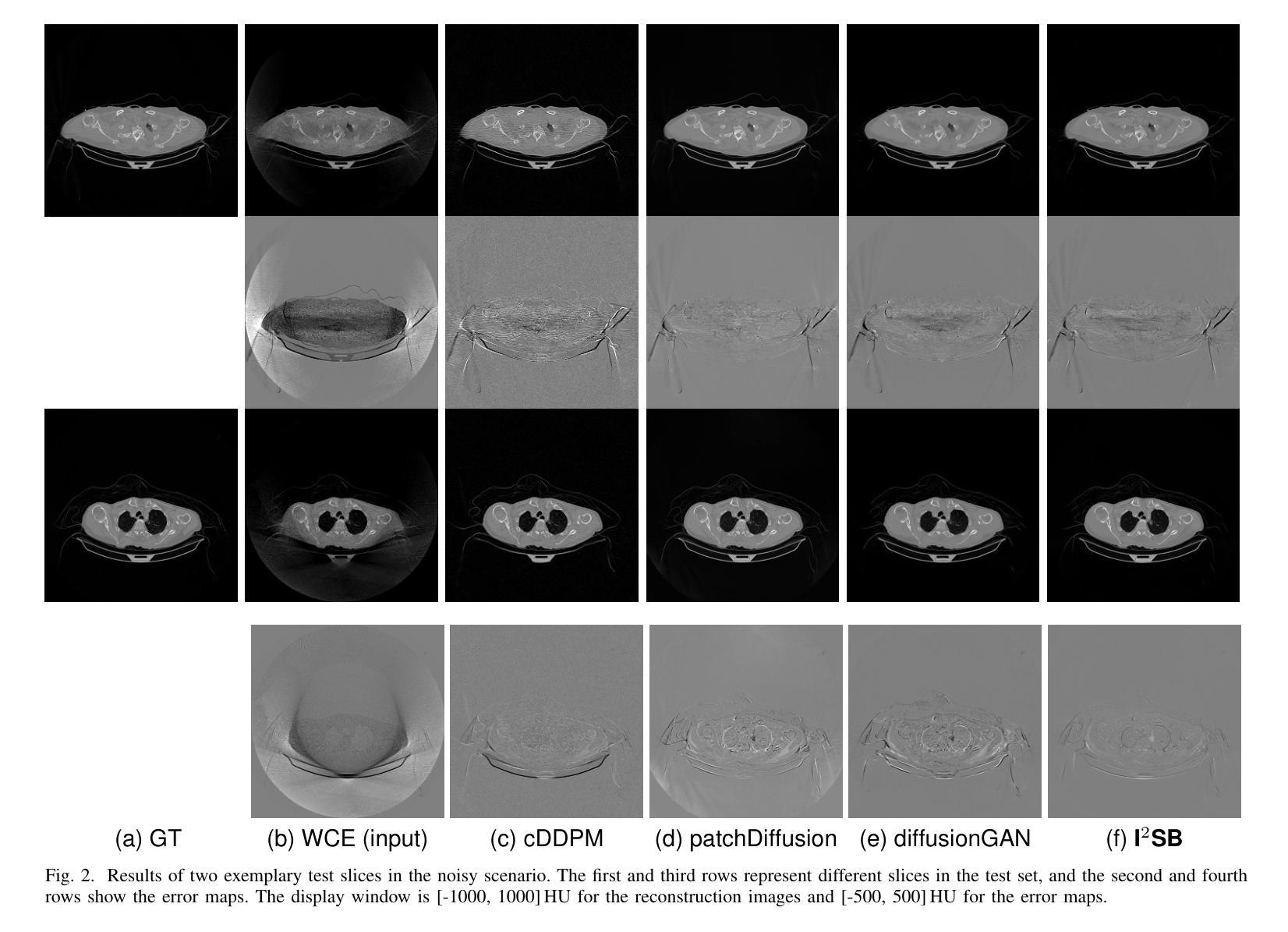
Efficient Image-to-Image Schrödinger Bridge for CT Field of View Extension
Authors:Zhenhao Li, Long Yang, Xiaojie Yin, Haijun Yu, Jiazhou Wang, Hongbin Han, Weigang Hu, Yixing Huang
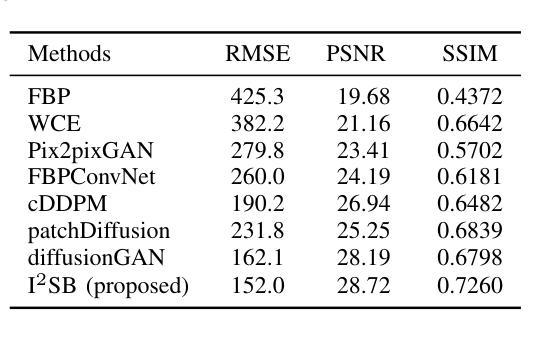
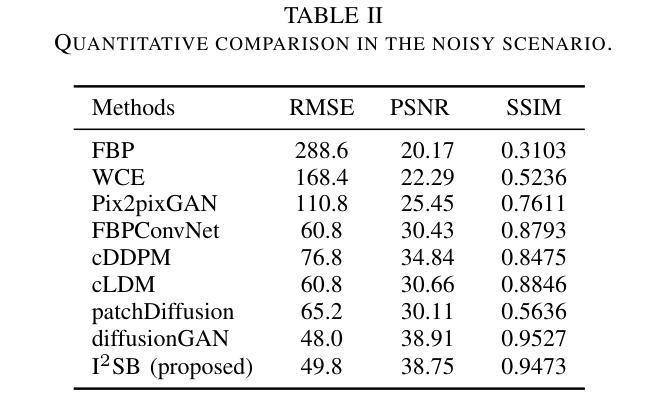
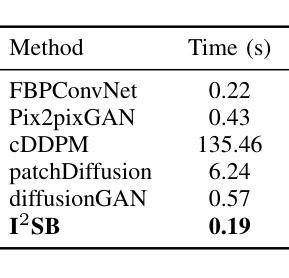
Computed tomography (CT) is a cornerstone imaging modality for non-invasive, high-resolution visualization of internal anatomical structures. However, when the scanned object exceeds the scanner’s field of view (FOV), projection data are truncated, resulting in incomplete reconstructions and pronounced artifacts near FOV boundaries. Conventional reconstruction algorithms struggle to recover accurate anatomy from such data, limiting clinical reliability. Deep learning approaches have been explored for FOV extension, with diffusion generative models representing the latest advances in image synthesis. Yet, conventional diffusion models are computationally demanding and slow at inference due to their iterative sampling process. To address these limitations, we propose an efficient CT FOV extension framework based on the image-to-image Schr"odinger Bridge (I$^2$SB) diffusion model. Unlike traditional diffusion models that synthesize images from pure Gaussian noise, I$^2$SB learns a direct stochastic mapping between paired limited-FOV and extended-FOV images. This direct correspondence yields a more interpretable and traceable generative process, enhancing anatomical consistency and structural fidelity in reconstructions. I$^2$SB achieves superior quantitative performance, with root-mean-square error (RMSE) values of 49.8,HU on simulated noisy data and 152.0HU on real data, outperforming state-of-the-art diffusion models such as conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models (cDDPM) and patch-based diffusion methods. Moreover, its one-step inference enables reconstruction in just 0.19s per 2D slice, representing over a 700-fold speedup compared to cDDPM (135s) and surpassing diffusionGAN (0.58s), the second fastest. This combination of accuracy and efficiency makes I$^2$SB highly suitable for real-time or clinical deployment.
计算机断层扫描(CT)是一种非侵入性的高分辨率成像技术,用于可视化内部解剖结构。然而,当扫描对象超出扫描仪的视野(FOV)时,投影数据会被截断,导致重建不完整,并且在FOV边界附近出现明显的伪影。传统的重建算法难以从这种数据中恢复准确的解剖结构,从而限制了其在临床上的可靠性。深度学习的方法已经被探索用于扩展FOV,其中扩散生成模型代表了图像合成的最新进展。然而,传统的扩散模型计算量大,由于迭代采样过程,推理速度慢。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于图像到图像Schrödinger Bridge(I$^2$SB)扩散模型的CT FOV扩展框架。不同于传统地从纯高斯噪声合成图像的扩散模型,I$^2$SB学习配对有限FOV和扩展FOV图像之间的直接随机映射。这种直接对应关系产生了一个更可解释和可追踪的生成过程,提高了重建中的解剖一致性和结构保真度。I$^2$SB在模拟噪声数据和真实数据上分别达到了49.8 HU和152.0 HU的均方根误差(RMSE)值,超越了最新的扩散模型,如条件去噪扩散概率模型(cDDPM)和基于补丁的扩散方法。此外,其一步推理使得每个2D切片的重建时间仅需0.19秒,与cDDPM相比实现了超过700倍的加速(135秒),并超越了第二快的DiffusionGAN(0.58秒)。这种精度和效率的结合使得I$^2$SB非常适合实时或临床部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
摘要
CT成像中的视场(FOV)扩展问题一直是一个挑战。传统的重建算法无法从截断的数据中恢复准确的解剖结构,而深度学习的方法提供了新的解决方案。本文提出了一种基于图像到图像Schrödinger Bridge(I²SB)扩散模型的CT FOV扩展框架,具有高效、准确的特点。该模型能直接在有限的FOV图像和扩展的FOV图像之间建立随机映射,提高了重建的解剖一致性和结构保真度。实验结果显示,I²SB在模拟和真实数据上的表现均优于其他模型,实现了快速且准确的重建。
关键见解
- CT成像中,当扫描对象超出扫描器视场(FOV)时,会出现数据截断的问题,导致重建不完整和在视场边界附近出现明显的伪影。
- 传统的重建算法难以从这种截断的数据中恢复准确的解剖结构,影响了临床可靠性。
- 深度学习在FOV扩展方面进行了探索,最新的进展是图像合成中的扩散生成模型。
- 然而,传统的扩散模型计算量大,推理速度慢,因为其迭代采样过程。
- 本文提出了一个高效的CT FOV扩展框架,基于图像到图像Schrödinger Bridge(I²SB)扩散模型。
- I²SB模型直接在有限的FOV图像和扩展的FOV图像之间建立直接对应关系,提高了生成的解剖一致性和结构保真度。
点此查看论文截图

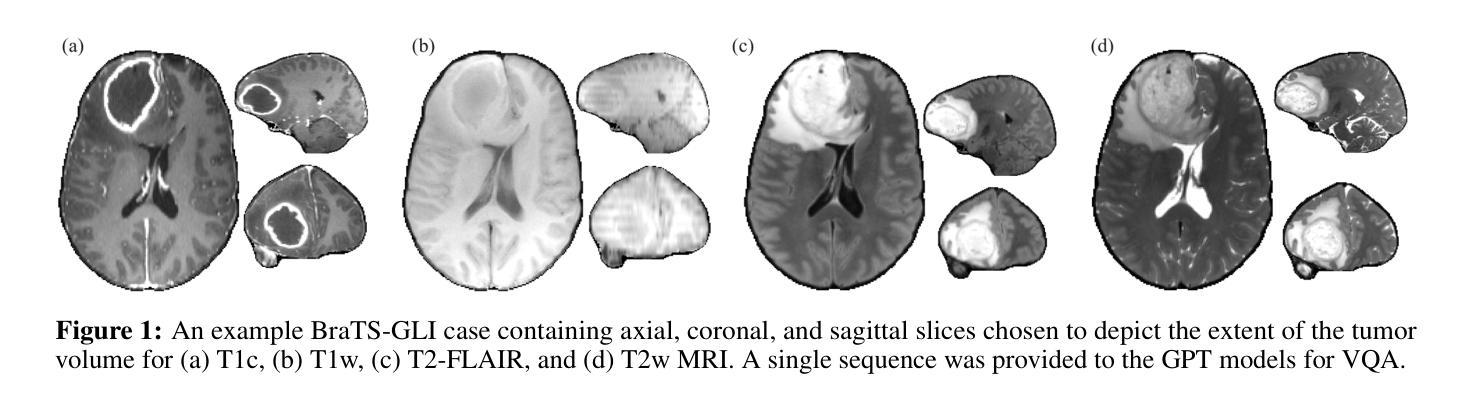
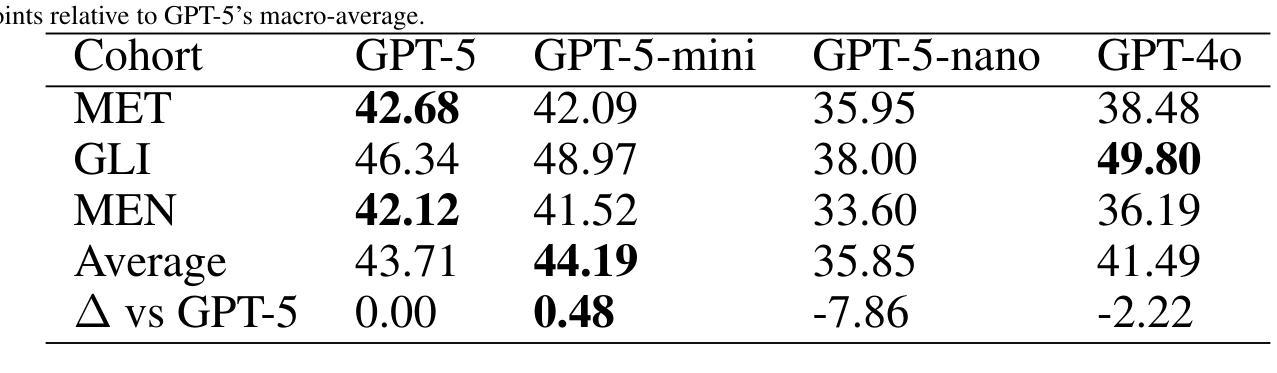
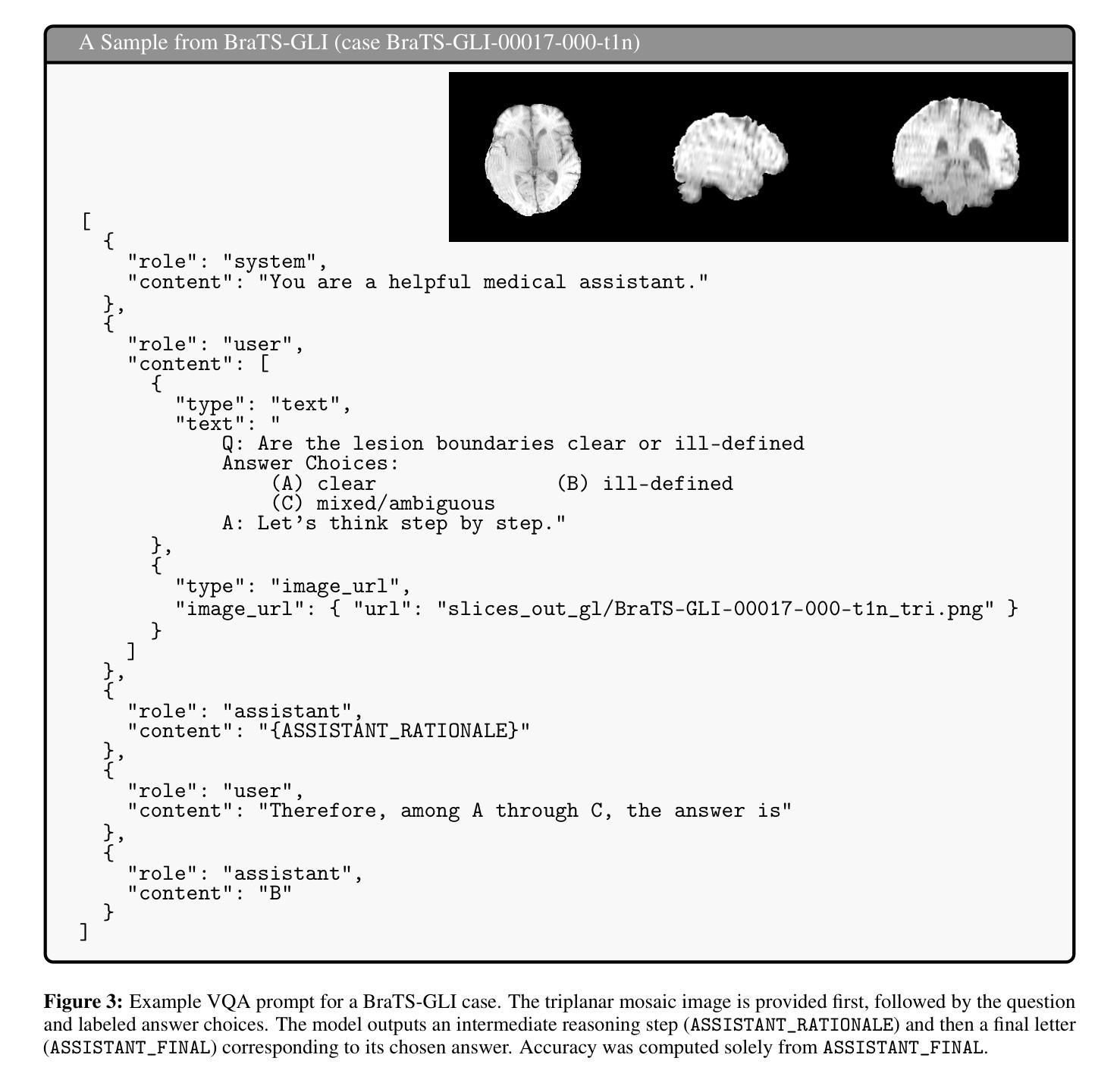
Performance of GPT-5 in Brain Tumor MRI Reasoning
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Shansong Wang, Mingzhe Hu, Zach Eidex, Qiang Li, Xiaofeng Yang
Accurate differentiation of brain tumor types on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical for guiding treatment planning in neuro-oncology. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled visual question answering (VQA) approaches that integrate image interpretation with natural language reasoning. In this study, we evaluated GPT-4o, GPT-5-nano, GPT-5-mini, and GPT-5 on a curated brain tumor VQA benchmark derived from 3 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) datasets - glioblastoma (GLI), meningioma (MEN), and brain metastases (MET). Each case included multi-sequence MRI triplanar mosaics and structured clinical features transformed into standardized VQA items. Models were assessed in a zero-shot chain-of-thought setting for accuracy on both visual and reasoning tasks. Results showed that GPT-5-mini achieved the highest macro-average accuracy (44.19%), followed by GPT-5 (43.71%), GPT-4o (41.49%), and GPT-5-nano (35.85%). Performance varied by tumor subtype, with no single model dominating across all cohorts. These findings suggest that GPT-5 family models can achieve moderate accuracy in structured neuro-oncological VQA tasks, but not at a level acceptable for clinical use.
在神经肿瘤学中,对磁共振成像(MRI)上的脑肿瘤类型进行准确区分对于治疗计划的制定至关重要。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使得视觉问答(VQA)方法得以发展,该方法将图像解读与自然语言推理相结合。在这项研究中,我们评估了GPT-4o、GPT-5-nano、GPT-5-mini和GPT-5在一组经过筛选的脑肿瘤VQA基准测试上的表现,该测试数据集来自三个脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)数据集——胶质母细胞瘤(GLI)、脑膜瘤(MEN)和脑转移瘤(MET)。每个案例都包括多序列MRI三平面镶嵌图和转化为标准化VQA项目的结构化临床特征。模型是在零射击思维链环境中进行评估,对视觉和推理任务的准确性进行评判。结果显示,GPT-5-mini的宏平均准确率最高(44.19%),其次是GPT-5(43.71%)、GPT-4o(41.49%)和GPT-5-nano(35.85%)。不同肿瘤亚型的性能各不相同,没有任何单一模型在所有队列中都占据主导地位。这些结果表明,GPT-5系列模型在结构化的神经肿瘤学VQA任务中可以达到中等准确性,但尚未达到临床使用要求的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究评估了GPT-4o、GPT-5-nano、GPT-5-mini和GPT-5在脑肿瘤VQA鉴别方面的性能,发现GPT-5家族模型在结构化神经肿瘤学VQA任务中能达到中等精度,但尚未达到临床使用要求。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究利用大型语言模型(LLMs)对脑肿瘤进行视觉问答(VQA)评估。
- 使用了包括胶质母细胞瘤(GLI)、脑膜瘤(MEN)和脑转移瘤(MET)在内的三个数据集进行VQA评估。
- 模型在零样本链思维模式下进行评估,GPT-5-mini获得最高宏观平均准确率(44.19%)。
- 不同肿瘤亚型的性能表现存在差异,没有单一模型在所有队列中都占据主导地位。
- GPT-5家族模型在结构化神经肿瘤学VQA任务中表现中等精度。
- 目前尚未达到临床使用要求的水平。
点此查看论文截图

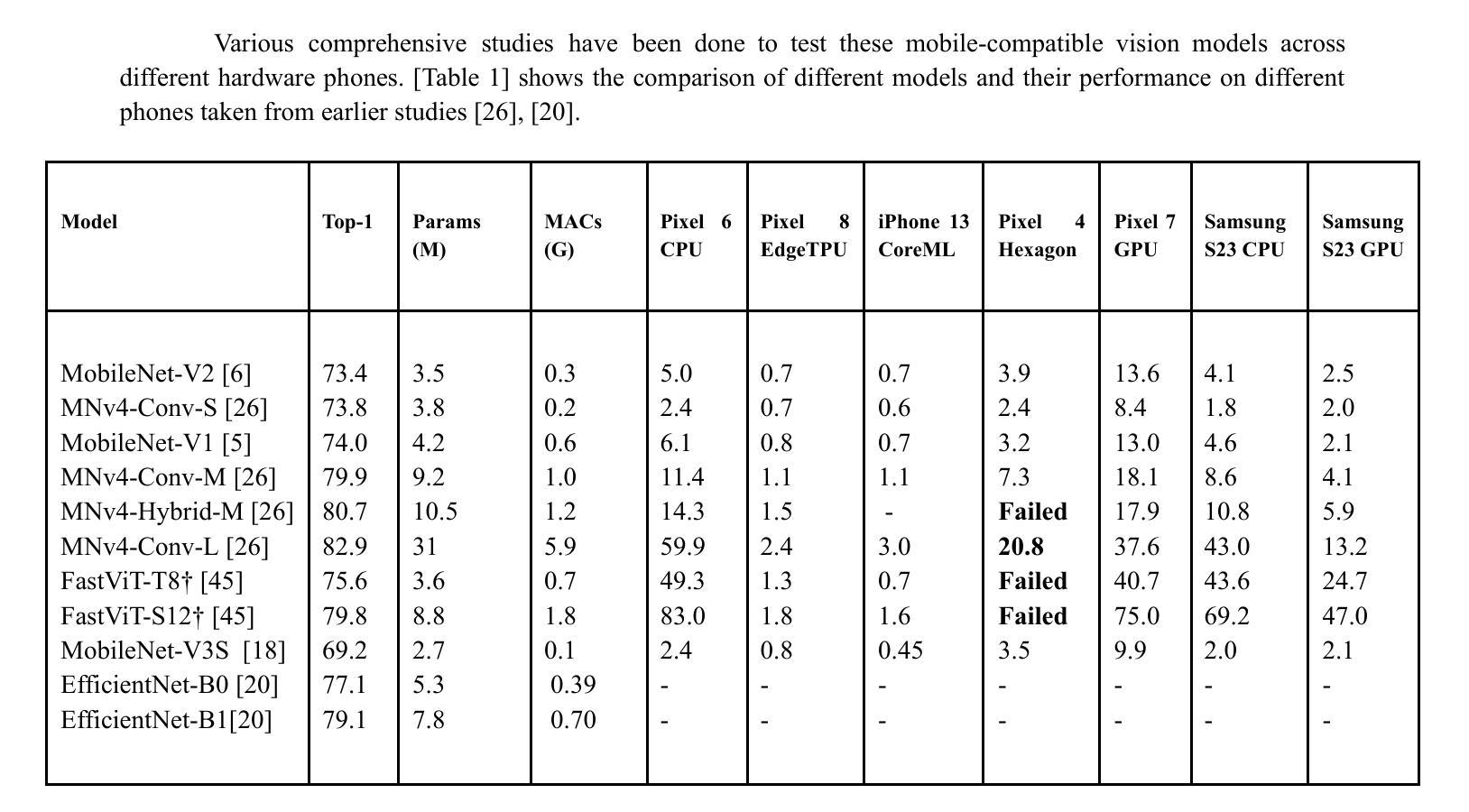
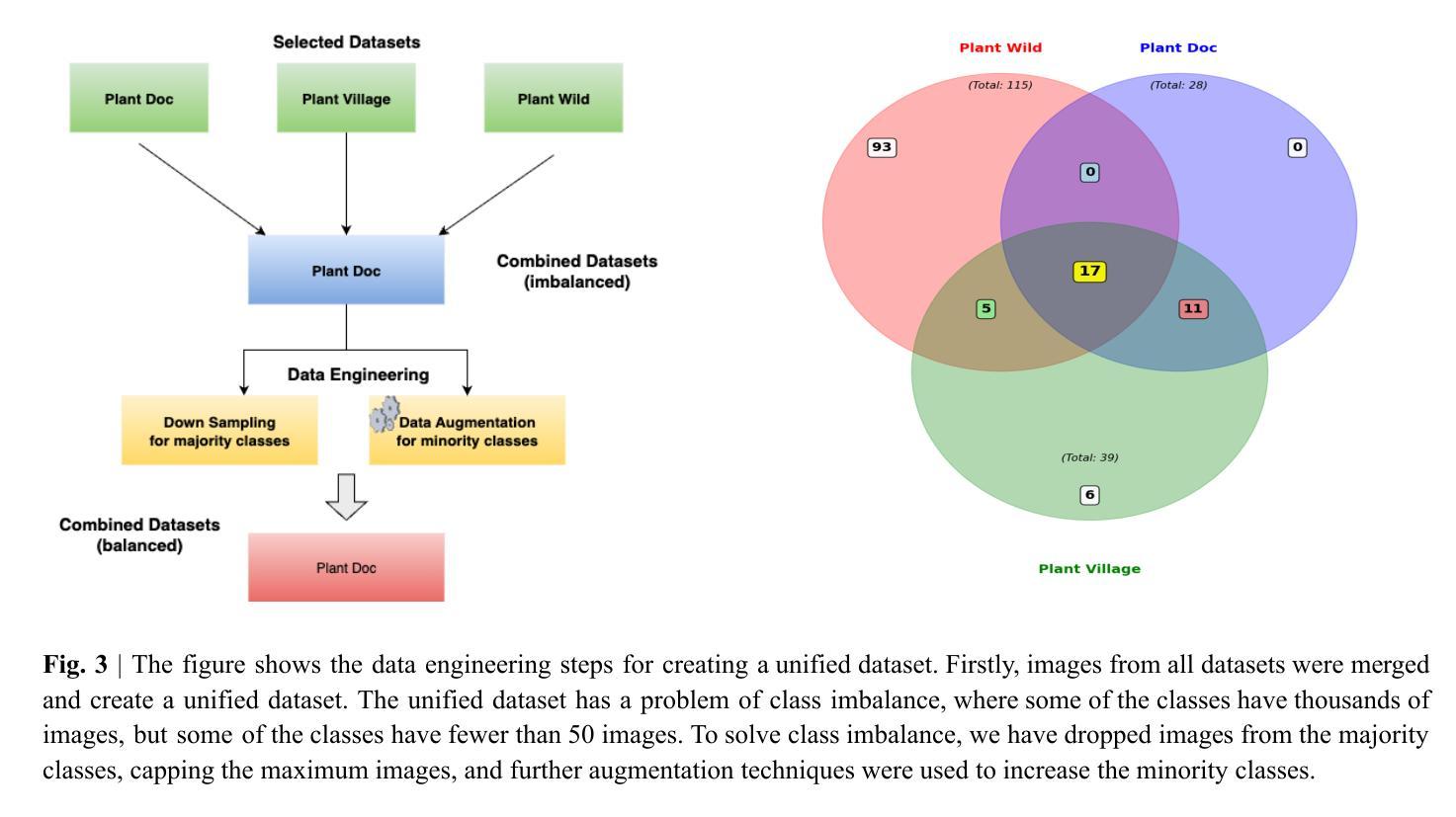
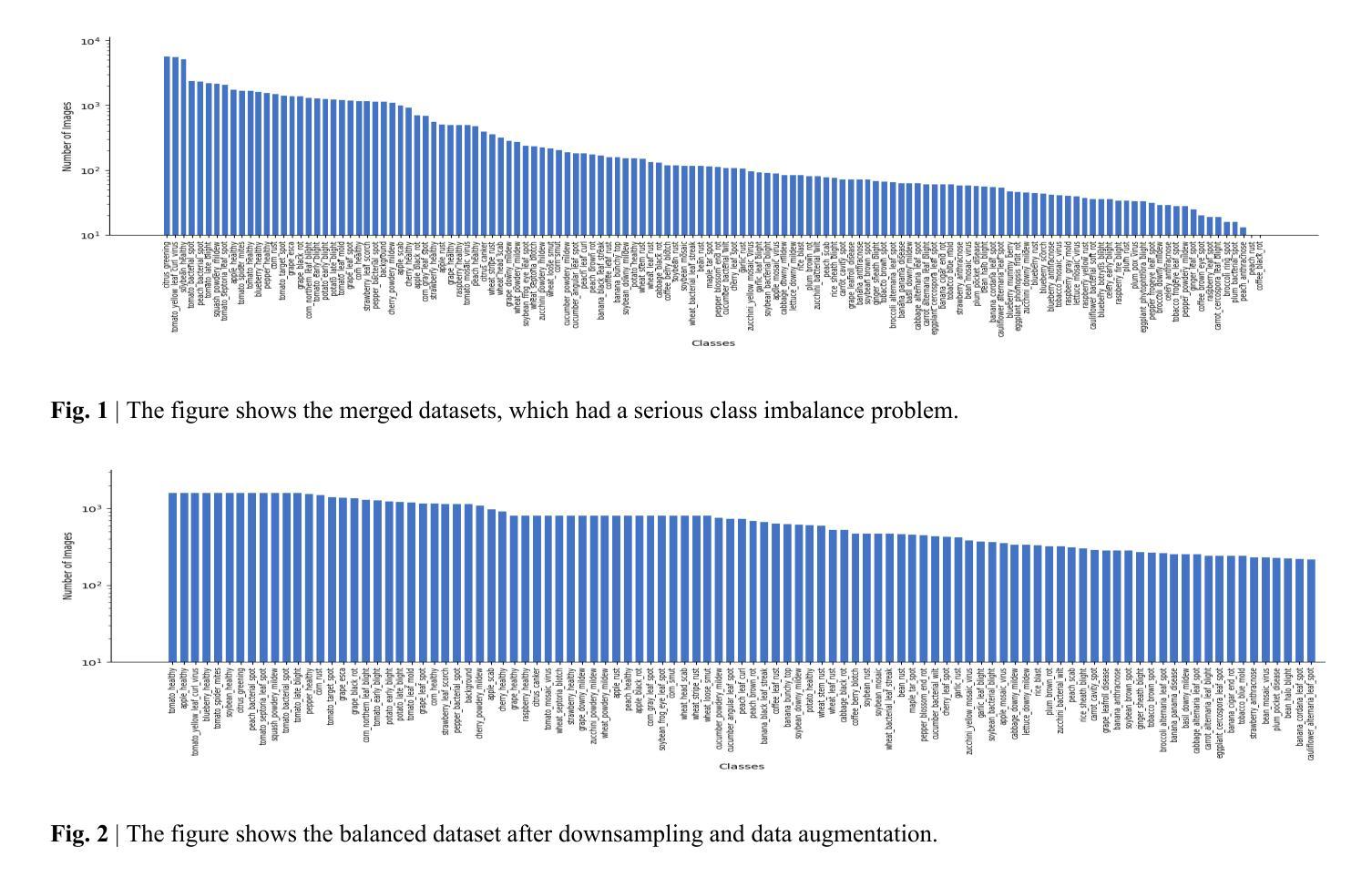
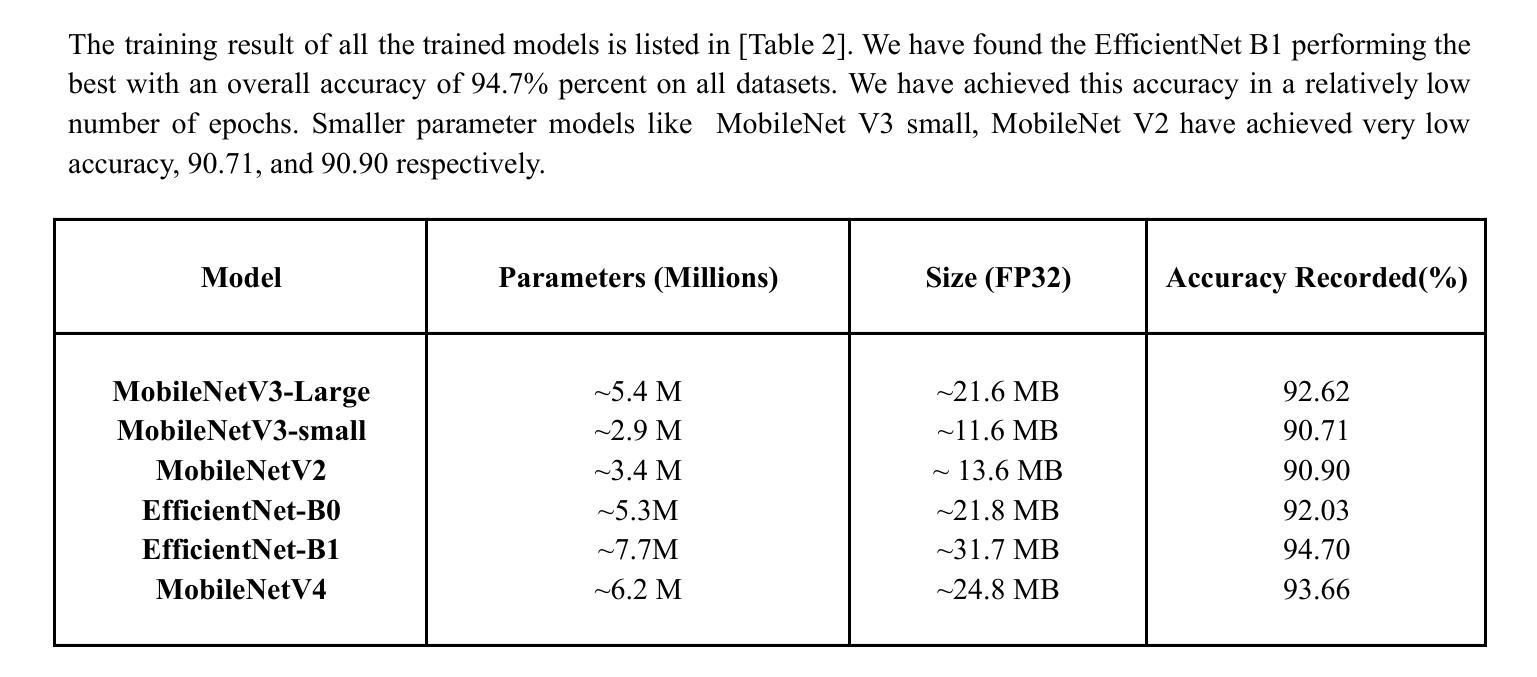
Mobile-Friendly Deep Learning for Plant Disease Detection: A Lightweight CNN Benchmark Across 101 Classes of 33 Crops
Authors:Anand Kumar, Harminder Pal Monga, Tapasi Brahma, Satyam Kalra, Navas Sherif
Plant diseases are a major threat to food security globally. It is important to develop early detection systems which can accurately detect. The advancement in computer vision techniques has the potential to solve this challenge. We have developed a mobile-friendly solution which can accurately classify 101 plant diseases across 33 crops. We built a comprehensive dataset by combining different datasets, Plant Doc, PlantVillage, and PlantWild, all of which are for the same purpose. We evaluated performance across several lightweight architectures - MobileNetV2, MobileNetV3, MobileNetV3-Large, and EfficientNet-B0, B1 - specifically chosen for their efficiency on resource-constrained devices. The results were promising, with EfficientNet-B1 delivering our best performance at 94.7% classification accuracy. This architecture struck an optimal balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, making it well-suited for real-world deployment on mobile devices.
植物疾病对全球食品安全构成重大威胁。因此,开发能够准确检测的早期检测系统非常重要。计算机视觉技术的进步为解决这一挑战提供了潜力。我们开发了一种适用于移动设备的解决方案,可以准确地对33种作物中的101种植物疾病进行分类。我们通过合并不同的数据集建立了综合数据集,包括用于同一目的的Plant Doc、PlantVillage和PlantWild。我们在几个轻量级架构上进行了性能评估,包括专门为了在资源受限的设备上提高效率的MobileNetV2、MobileNetV3、MobileNetV3-Large和EfficientNet-B0、B1。结果令人鼓舞,EfficientNet-B1的表现最佳,分类准确率达到了94.7%。该架构在准确性和计算效率之间达到了最佳平衡,非常适合在移动设备上实现真实世界部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables
Summary
该文本描述了一个移动友好的植物疾病早期检测系统,能够准确识别出跨33种作物的101种植物疾病。通过整合多个数据集并评估不同轻量级架构的性能,发现EfficientNet-B1架构在资源受限设备上实现了94.7%的分类准确率,且在准确性与计算效率之间达到了最佳平衡,适合在移动设备上实际应用。
Key Takeaways
- 植物疾病对全球粮食安全构成重大威胁,需要开发早期检测系统准确识别。
- 计算机视觉技术的进步为解决这一挑战提供了潜力。
- 研究人员开发了一个移动友好的解决方案,能准确识别101种植物疾病,覆盖33种作物。
- 通过整合Plant Doc、PlantVillage和PlantWild等多个数据集,建立了综合数据集。
- 评估了多个轻量级架构的性能,包括MobileNetV2、MobileNetV3、MobileNetV3-Large和EfficientNet-B0、B1。
- EfficientNet-B1架构在准确性与计算效率之间达到最佳平衡,实现了94.7%的分类准确率。
点此查看论文截图

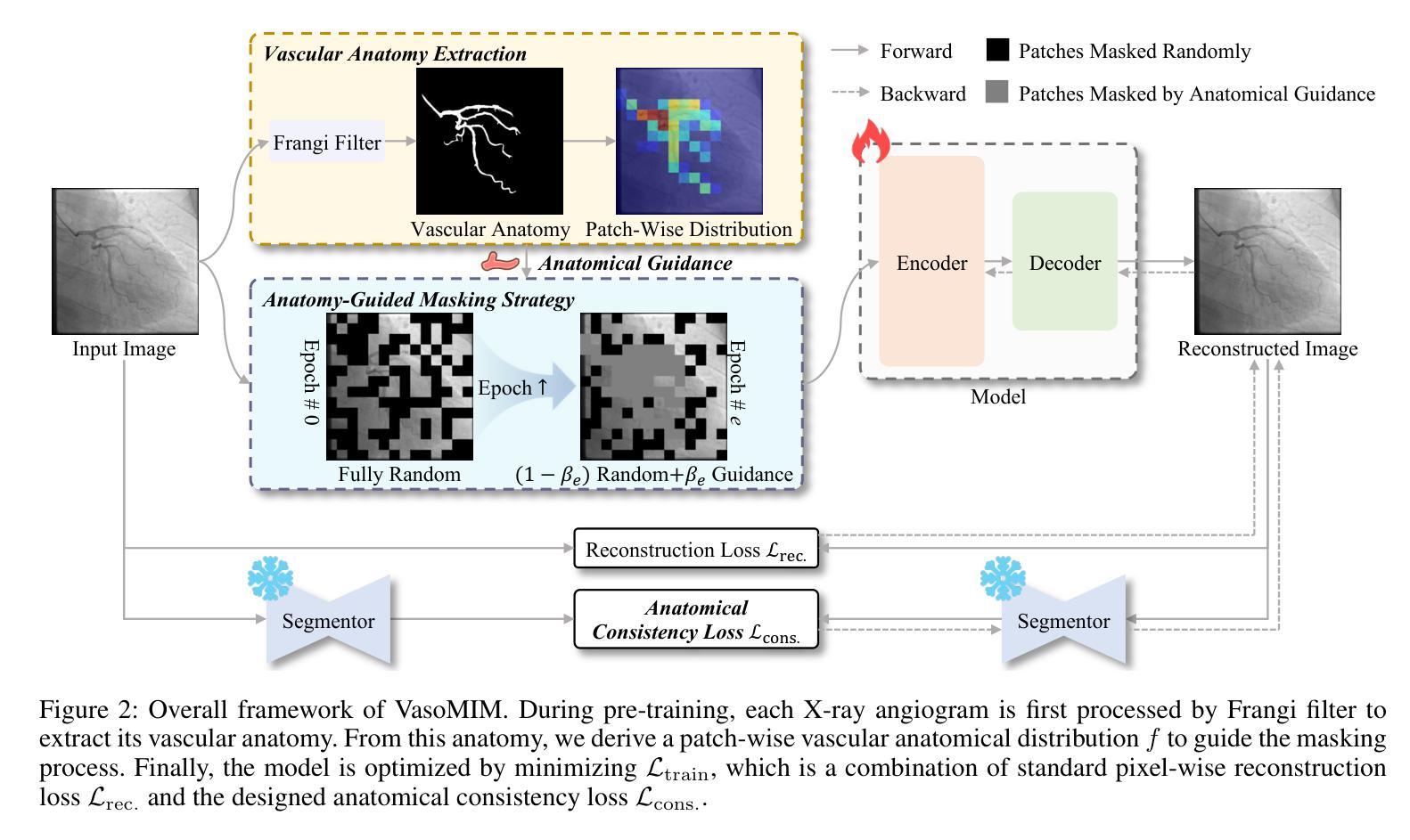
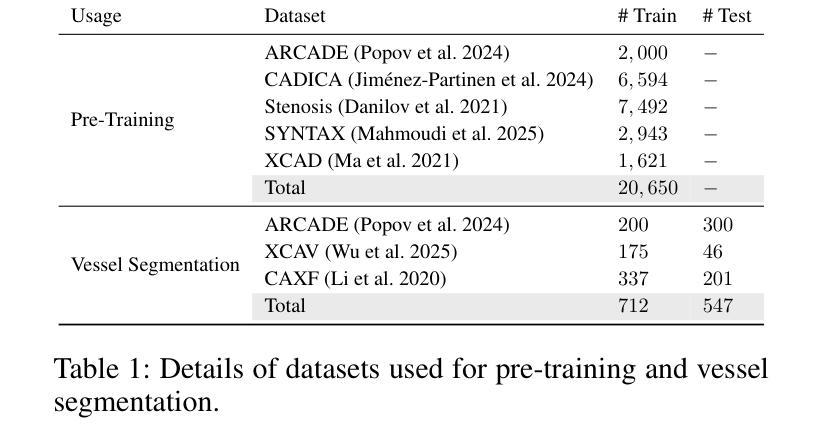
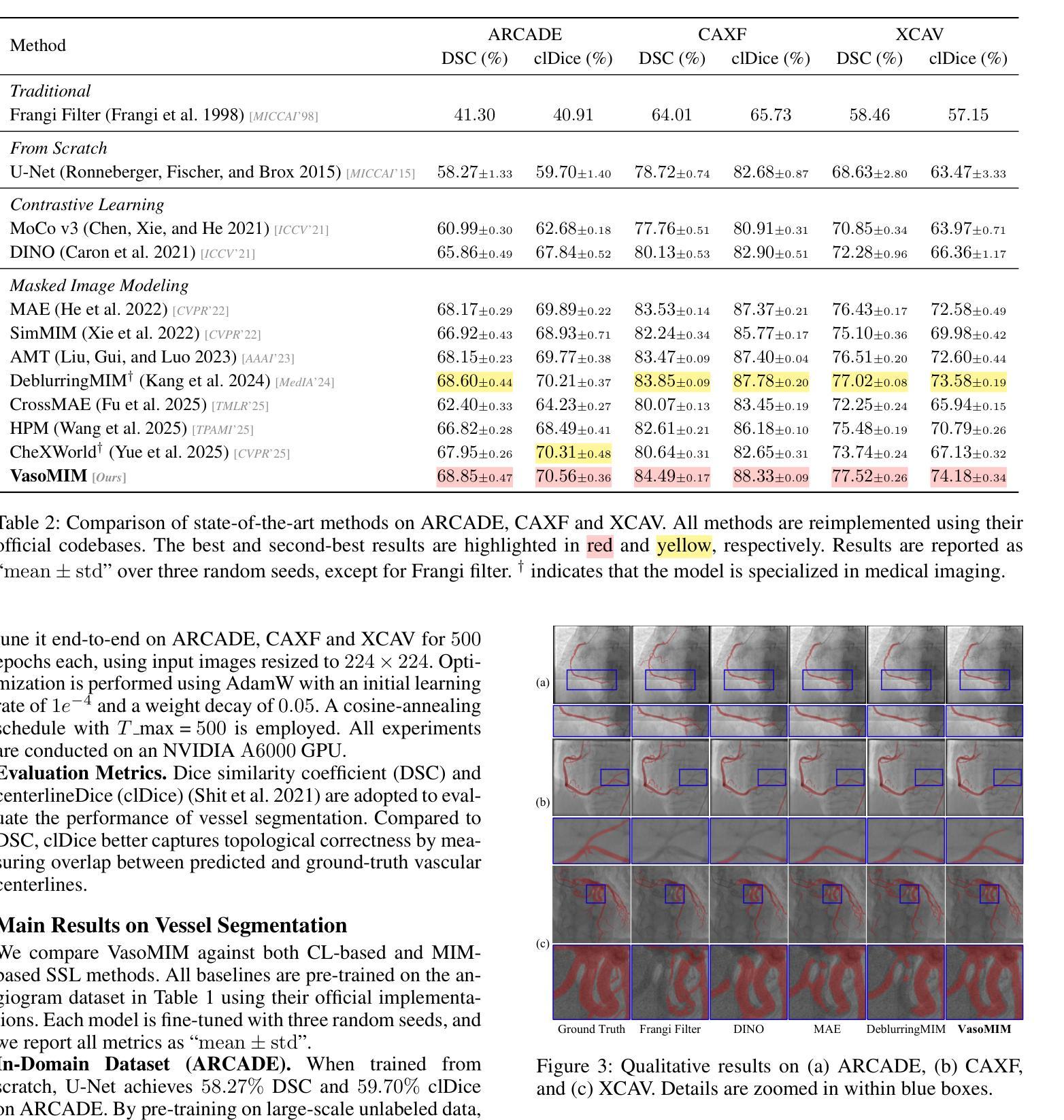
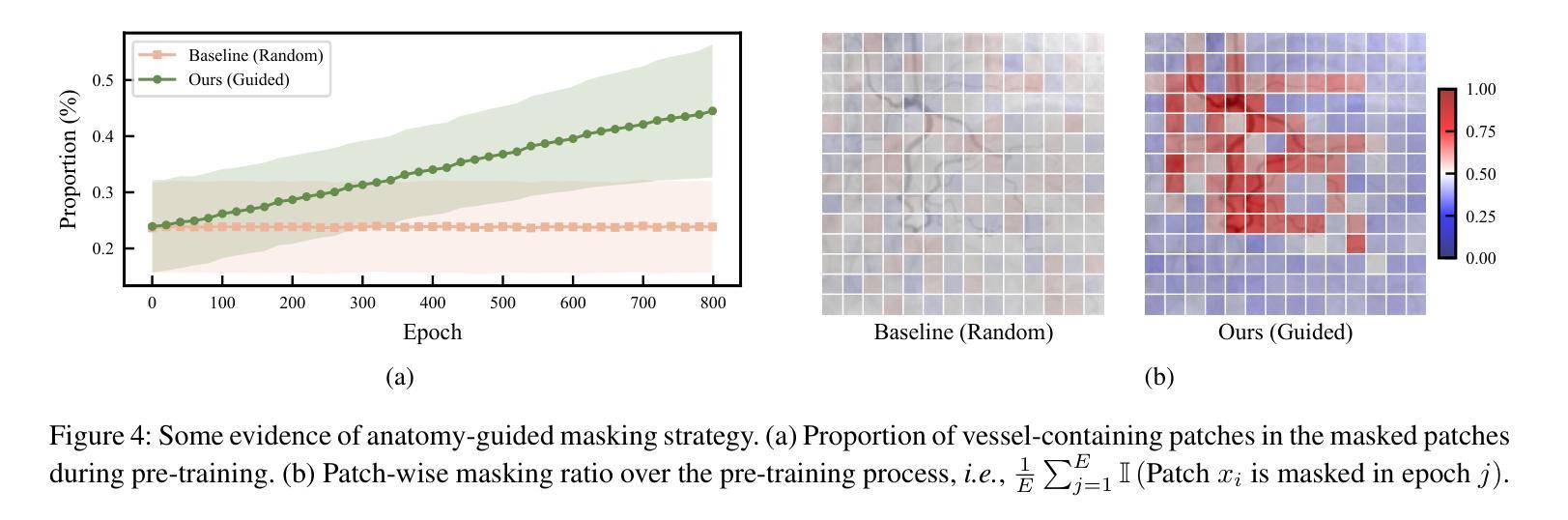
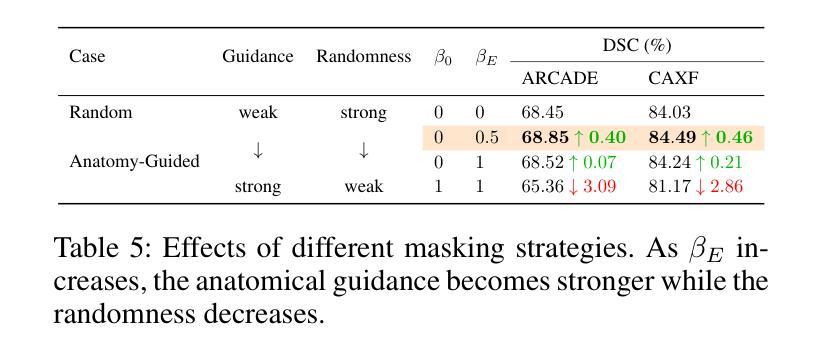
VasoMIM: Vascular Anatomy-Aware Masked Image Modeling for Vessel Segmentation
Authors:De-Xing Huang, Xiao-Hu Zhou, Mei-Jiang Gui, Xiao-Liang Xie, Shi-Qi Liu, Shuang-Yi Wang, Tian-Yu Xiang, Rui-Ze Ma, Nu-Fang Xiao, Zeng-Guang Hou
Accurate vessel segmentation in X-ray angiograms is crucial for numerous clinical applications. However, the scarcity of annotated data presents a significant challenge, which has driven the adoption of self-supervised learning (SSL) methods such as masked image modeling (MIM) to leverage large-scale unlabeled data for learning transferable representations. Unfortunately, conventional MIM often fails to capture vascular anatomy because of the severe class imbalance between vessel and background pixels, leading to weak vascular representations. To address this, we introduce Vascular anatomy-aware Masked Image Modeling (VasoMIM), a novel MIM framework tailored for X-ray angiograms that explicitly integrates anatomical knowledge into the pre-training process. Specifically, it comprises two complementary components: anatomy-guided masking strategy and anatomical consistency loss. The former preferentially masks vessel-containing patches to focus the model on reconstructing vessel-relevant regions. The latter enforces consistency in vascular semantics between the original and reconstructed images, thereby improving the discriminability of vascular representations. Empirically, VasoMIM achieves state-of-the-art performance across three datasets. These findings highlight its potential to facilitate X-ray angiogram analysis.
在X光血管造影中进行精确的血管分割对于许多临床应用至关重要。然而,标注数据的稀缺性是一个巨大的挑战,这促使采用自我监督学习(SSL)方法,如掩膜图像建模(MIM),以利用大规模的无标签数据进行可迁移表示学习。然而,传统的MIM由于血管和背景像素之间的严重类别不平衡,常常无法捕捉到血管结构,导致血管表示较弱。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了血管结构感知掩膜图像建模(VasoMIM),这是一种针对X光血管造影的新型MIM框架,它将解剖知识明确融入预训练过程。具体来说,它包含两个互补的组件:解剖引导掩膜策略和解剖一致性损失。前者优先掩膜含血管的斑块,使模型专注于重建与血管相关的区域。后者强制原始图像和重建图像之间的血管语义一致性,从而提高血管表示的辨别力。经验上,VasoMIM在三个数据集上达到了最先进的性能。这些发现突出了其在X光血管造影分析中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文提出一种针对X光血管造影图像的自我监督学习方法——血管结构感知的掩膜图像建模(VasoMIM)。该方法通过结合解剖学知识和预训练过程,解决了传统掩膜图像建模在血管造影图像中难以捕捉血管结构的问题。VasoMIM包括两个互补的组件:解剖学引导掩膜策略和解剖学一致性损失,旨在提高血管表示的判别力。实验结果显示,VasoMIM在三个数据集上达到最佳性能,有望促进X光血管造影图像的分析。
Key Takeaways
- X光血管造影中的精确血管分割对众多临床应用至关重要。
- 标注数据的稀缺性是血管分割面临的主要挑战之一。
- 自我监督学习方法(如掩膜图像建模)已用于利用大规模无标签数据进行学习。
- 传统掩膜图像建模在血管造影图像中因类别不平衡问题,难以捕捉血管结构。
- 提出的VasoMIM方法通过结合解剖学知识,解决上述问题,实现最佳性能。
- VasoMIM包括解剖学引导掩膜策略和解剖学一致性损失两个关键组件。
点此查看论文截图

Formation and protection of an Eu-Ir surface compound below hexagonal boron nitride
Authors:Alaa Mohammed Idris Bakhit, Khadiza Ali, Frederik Schiller
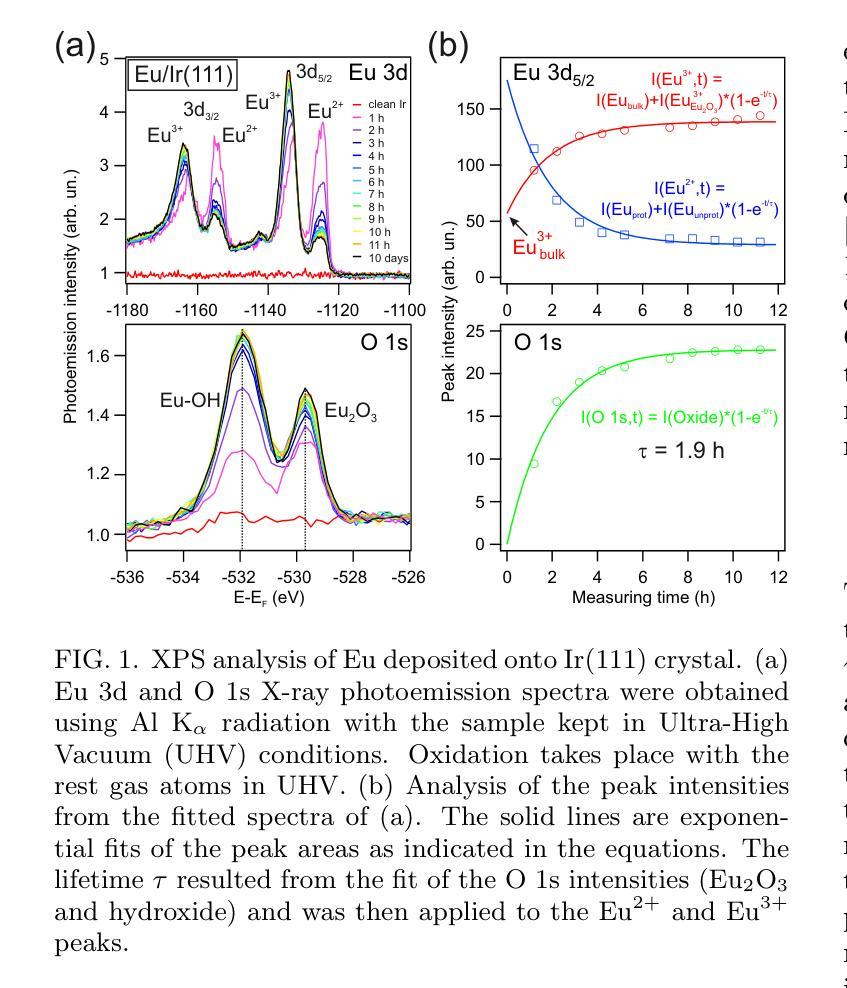
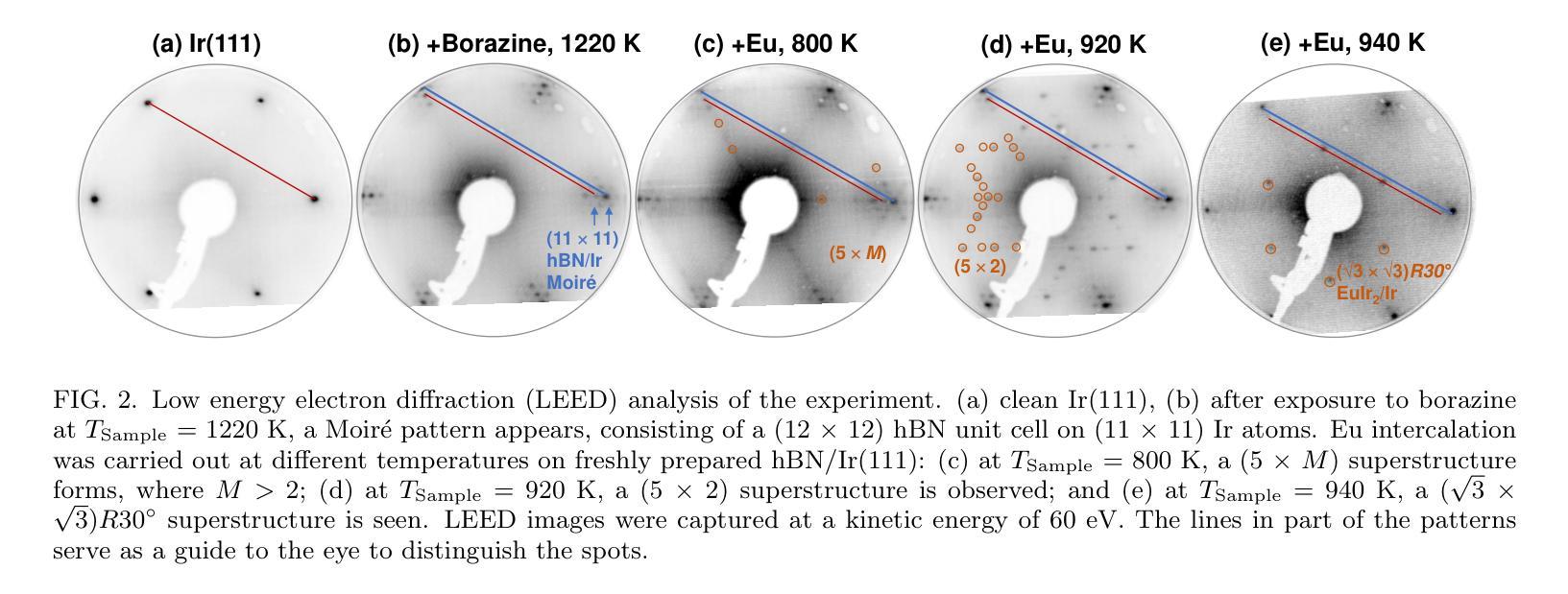
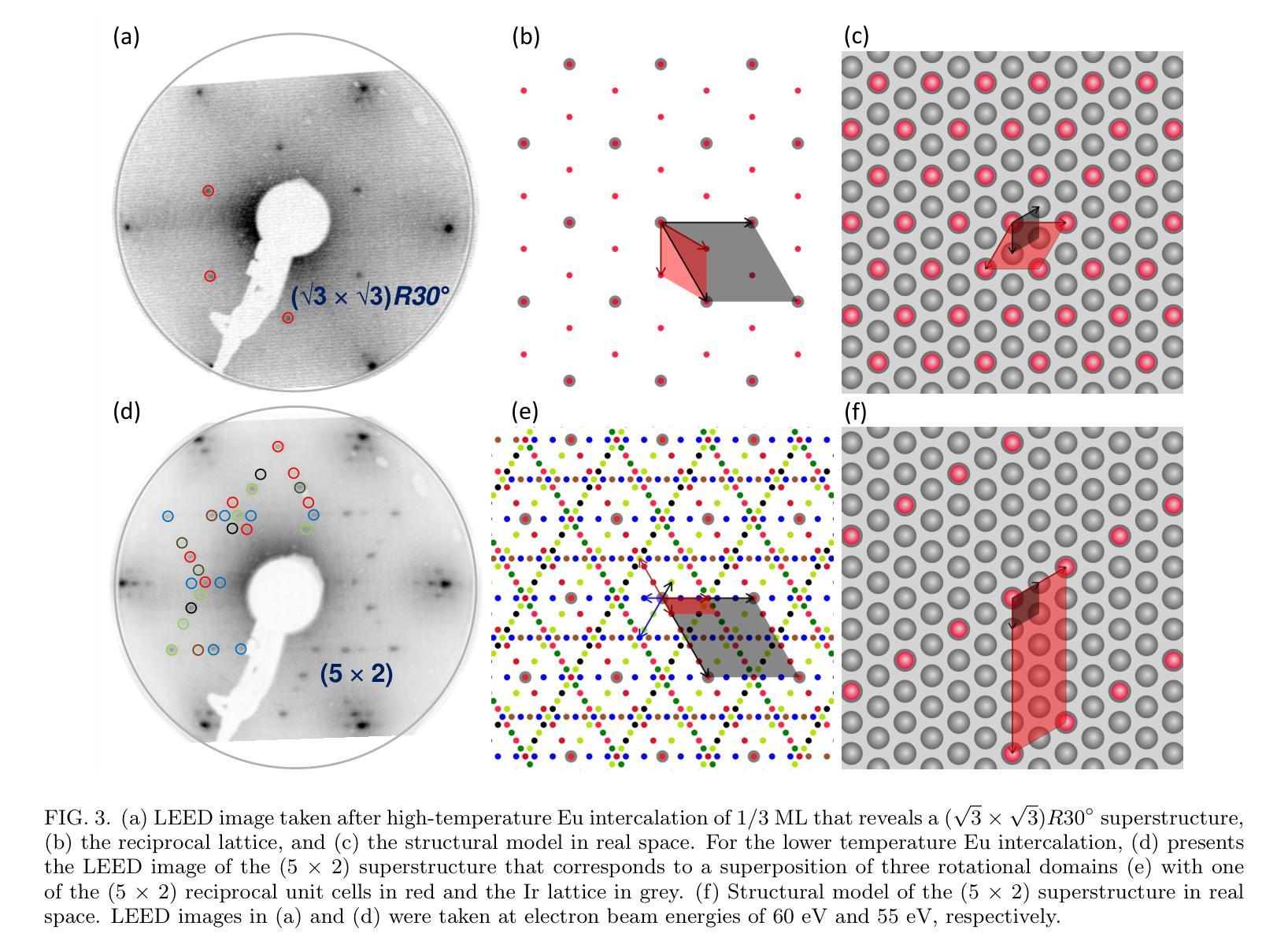
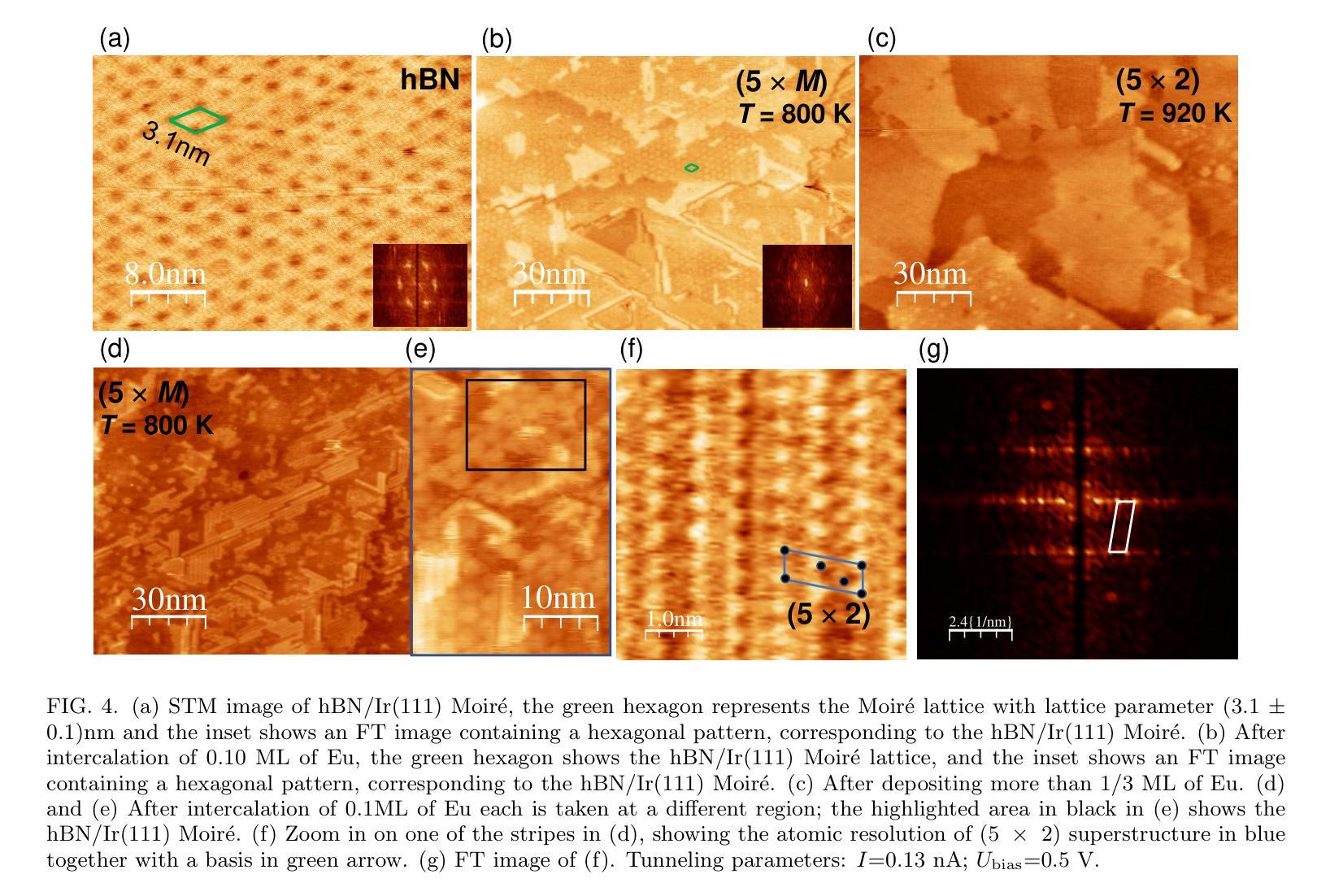
Europium (Eu) intercalation below hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) on an Ir(111) substrate at various Eu coverages is investigated. The structural and electronic properties were examined using low energy electron diffraction (LEED), scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). Depending on the deposition temperature, different superstructures, (5 $\times$ $M$), (5 $\times$ 2), and ($ \sqrt{3}$ $\times$ $\sqrt{3})R30^{\circ}$ with respect to the Ir substrate were identified by LEED. The (5 $\times$ $M$) superstructure ($M$ $>$ 2), at 0.1 monolayer (ML), preserved the hBN/Ir Moir{'e} pattern and exhibited a unidirectional ordering of Eu atoms. At higher coverage of 0.26 ML, a (5 $\times$ 2) superstructure emerged, where excess Eu atoms diffused into the bulk and were analyzed as Eu in a tri-valent state. At the highest preparation temperature with a one-third ML Eu, the formation of a ($\sqrt{3}$ $\times$ $\sqrt{3})R30^{\circ}$ superstructure indicates the presence of a EuIr${2}$ surface alloy beneath the hBN layer, with di-valent Eu atoms suggesting potential ferromagnetic properties. Air exposure was used to evaluate the protection of the hBN layer, and the results indicate that the EuIr${2}$ surface alloy was partially protected. However, the hBN layer remained intact by intercalation and air exposure, as confirmed by ARPES analysis.
在铱(Ir(111))衬底上,对六方氮化硼(hBN)下方不同铕(Eu)覆盖率的铕插层进行了研究。利用低能电子衍射(LEED)、扫描隧道显微镜(STM)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和角分辨光电子能谱(ARPES)对结构和电子特性进行了检查。根据不同的沉积温度,通过LEED识别出与铱衬底相关的不同超结构,如(5倍×M)、(5倍×2)和($\sqrt{3}$ × $\sqrt{3}$)R30°结构。在0.1单层(ML)的(5倍×M)超结构(M>2)中,保留了hBN / Ir的莫尔图案,并表现出铕原子的单向排序。在较高的0.26 ML覆盖下,出现(5倍×2)超结构,过量的铕原子扩散到基体中,被分析为三价铕。在最高制备温度下,三分之一ML铕时形成($\sqrt{3}$ × $\sqrt{3}$)R30°超结构,表明存在铕铱(EuIr₂)表面合金,二价铕原子暗示了潜在的铁磁性质。利用空气暴露评估了hBN层的保护性能,结果表明EuIr₂表面合金得到了部分保护。然而,hBN层通过插层和空气暴露仍然保持完整,如ARPES分析所证实。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
摘要
关于Europium(Eu)在Ir(111)基底上六边形氮化硼(hBN)之间的插层研究,在不同覆盖率的Eu下进行了调查。通过低能电子衍射(LEED)、扫描隧道显微镜(STM)、X光电子能谱(XPS)和角度分辨光电子谱(ARPES)对结构和电子特性进行了研究。根据不同的沉积温度,发现了与Ir基底有关的(5× $M$)、(5× 2)和( $\sqrt{3}$ × $\sqrt{3})R30^{\circ}$的不同超结构。在0.1单层(ML)的(5× $M$)($M$>2)超结构中,保留了hBN / Ir的Moiré图案,并表现出Eu原子的单向排序。在较高的0.26 ML覆盖率下,出现了(5× 2)超结构,过量的Eu原子扩散到主体中,以三价状态分析为Eu。在最高制备温度下,三分之一ML的Eu形成($\sqrt{3}$ × $\sqrt{3})R30^{\circ}$超结构,表明存在EuIr_{2}合金表面,二价Eu原子暗示潜在的铁磁性。通过空气暴露评估hBN层的保护性能,结果表明EuIr_{2}合金表面部分受保护。然而,由于插层和空气暴露,hBN层保持完整,如ARPES分析所证实。
Key Takeaways
- Europium (Eu) 在不同覆盖率下于 Ir(111) 基底上的 hBN 之间的插层行为被研究。
- 通过多种技术如 LEED、STM、XPS 和 ARPES 分析了结构和电子特性。
- 沉积温度影响 Eu 形成的超结构,如 (5× $M$)、(5× 2) 和 ($\sqrt{3}$ × $\sqrt{3})R30^{\circ}$。
- 在较低覆盖率下,Eu 原子有序排列;在较高覆盖率下,形成 EuIr_{2} 表面合金。
- EuIr_{2} 合金可能具有铁磁性性质。
- hBN 层在插层和空气暴露后保持完整。
点此查看论文截图

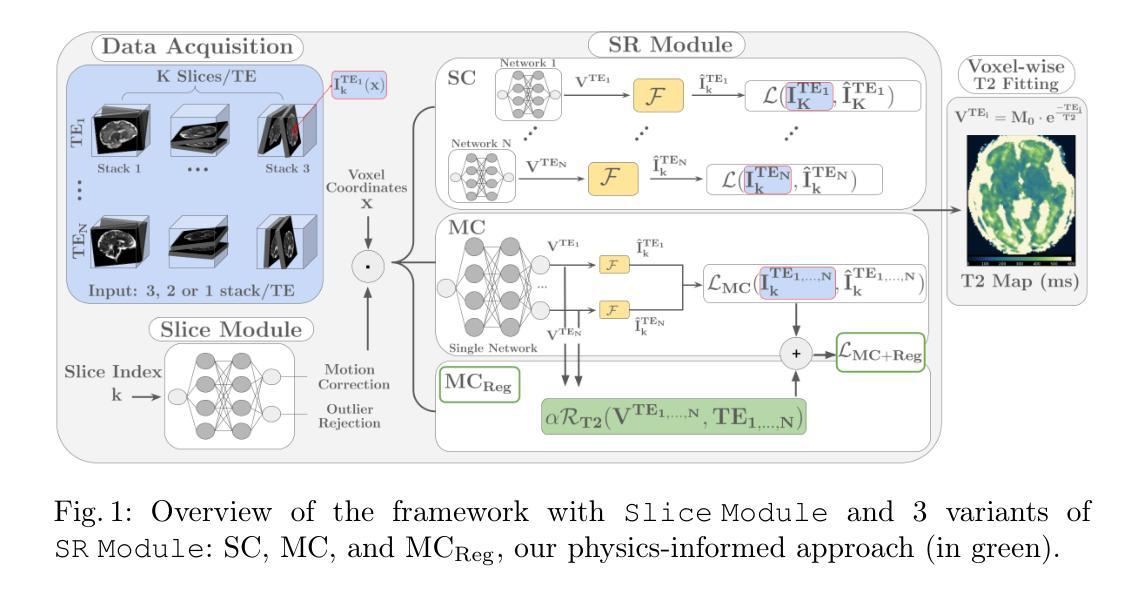
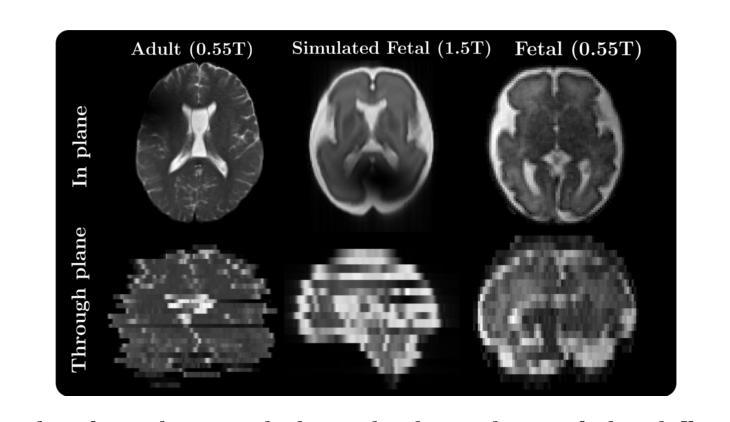
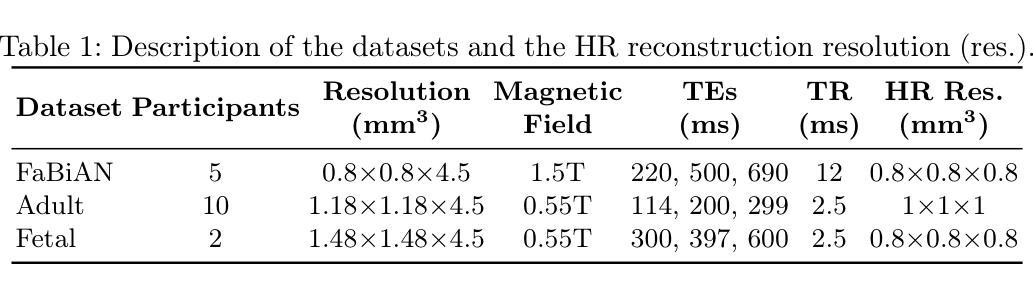
Physics-Informed Joint Multi-TE Super-Resolution with Implicit Neural Representation for Robust Fetal T2 Mapping
Authors:Busra Bulut, Maik Dannecker, Thomas Sanchez, Sara Neves Silva, Vladyslav Zalevskyi, Steven Jia, Jean-Baptiste Ledoux, Guillaume Auzias, François Rousseau, Jana Hutter, Daniel Rueckert, Meritxell Bach Cuadra
T2 mapping in fetal brain MRI has the potential to improve characterization of the developing brain, especially at mid-field (0.55T), where T2 decay is slower. However, this is challenging as fetal MRI acquisition relies on multiple motion-corrupted stacks of thick slices, requiring slice-to-volume reconstruction (SVR) to estimate a high-resolution (HR) 3D volume. Currently, T2 mapping involves repeated acquisitions of these stacks at each echo time (TE), leading to long scan times and high sensitivity to motion. We tackle this challenge with a method that jointly reconstructs data across TEs, addressing severe motion. Our approach combines implicit neural representations with a physics-informed regularization that models T2 decay, enabling information sharing across TEs while preserving anatomical and quantitative T2 fidelity. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on simulated fetal brain and in vivo adult datasets with fetal-like motion. We also present the first in vivo fetal T2 mapping results at 0.55T. Our study shows potential for reducing the number of stacks per TE in T2 mapping by leveraging anatomical redundancy.
胎儿脑部MRI的T2映射具有改善发育中大脑特征描述的潜力,特别是在中场(0.55T),T2衰减较慢。然而,这是一项挑战,因为胎儿MRI采集依赖于多个受运动影响的大厚切片堆叠,需要进行切片到体积重建(SVR)来估计高分辨率(HR)3D体积。目前,T2映射涉及在每个回波时间(TE)进行这些堆栈的重复采集,导致扫描时间长且对运动高度敏感。我们采用一种方法来解决这一挑战,该方法联合重建跨TE的数据,并解决严重的运动问题。我们的方法结合了隐式神经表征和基于物理的正规化,对T2衰减进行建模,实现在TE之间共享信息的同时保持解剖和定量T2保真。我们在模拟的胎儿大脑和具有胎儿样运动的活体验数据集中展示了最新性能。我们还展示了在0.55T下首次实现的在活体验中的胎儿T2映射结果。我们的研究显示了通过利用解剖冗余性减少每个TE的堆栈数量在T2映射中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
T2映射在胎儿脑部MRI中有改善对发育中的大脑特征表征的潜力,特别是在中场(0.55T)中,T2衰减较慢构成挑战。传统的胎儿MRI采集依赖于多次受运动干扰的厚切片堆叠,需要进行切片到体积重建(SVR)以估算高分辨率(HR)的3D体积。当前T2映射涉及在每个回波时间(TE)进行这些堆叠的重复采集,导致扫描时间长且对运动敏感。本研究通过一种联合重建跨越TE数据的方法来解决这一问题,该方法结合了隐式神经表征和模拟T2衰减的物理规律的正则化,实现了信息跨TE共享的同时保持解剖结构和T2值的准确性。在模拟胎儿大脑和具有胎儿样运动的体内成人数据集上取得了卓越的性能表现,并首次展示了在0.55T下的体内胎儿T2映射结果。本研究展示了通过利用解剖冗余性减少每个TE的堆叠数量在T2映射中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- T2映射在胎儿脑部MRI中有重要应用,尤其在0.55T中场环境下,T2衰减较慢构成挑战。
- 传统胎儿MRI采集方法依赖于多次受运动干扰的厚切片堆叠,需通过切片到体积重建(SVR)获取高分辨率3D体积。
- 当前T2映射方法存在扫描时间长、对运动敏感的问题。
- 研究提出一种联合重建跨越TE数据的新方法,结合了隐式神经表征与模拟T2衰减的物理规律正则化。
- 新方法能够实现信息跨TE共享并保持解剖结构和T2值的准确性。
- 在模拟和体内数据集上取得了卓越性能,展示了减少每个TE的堆叠数量在T2映射中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

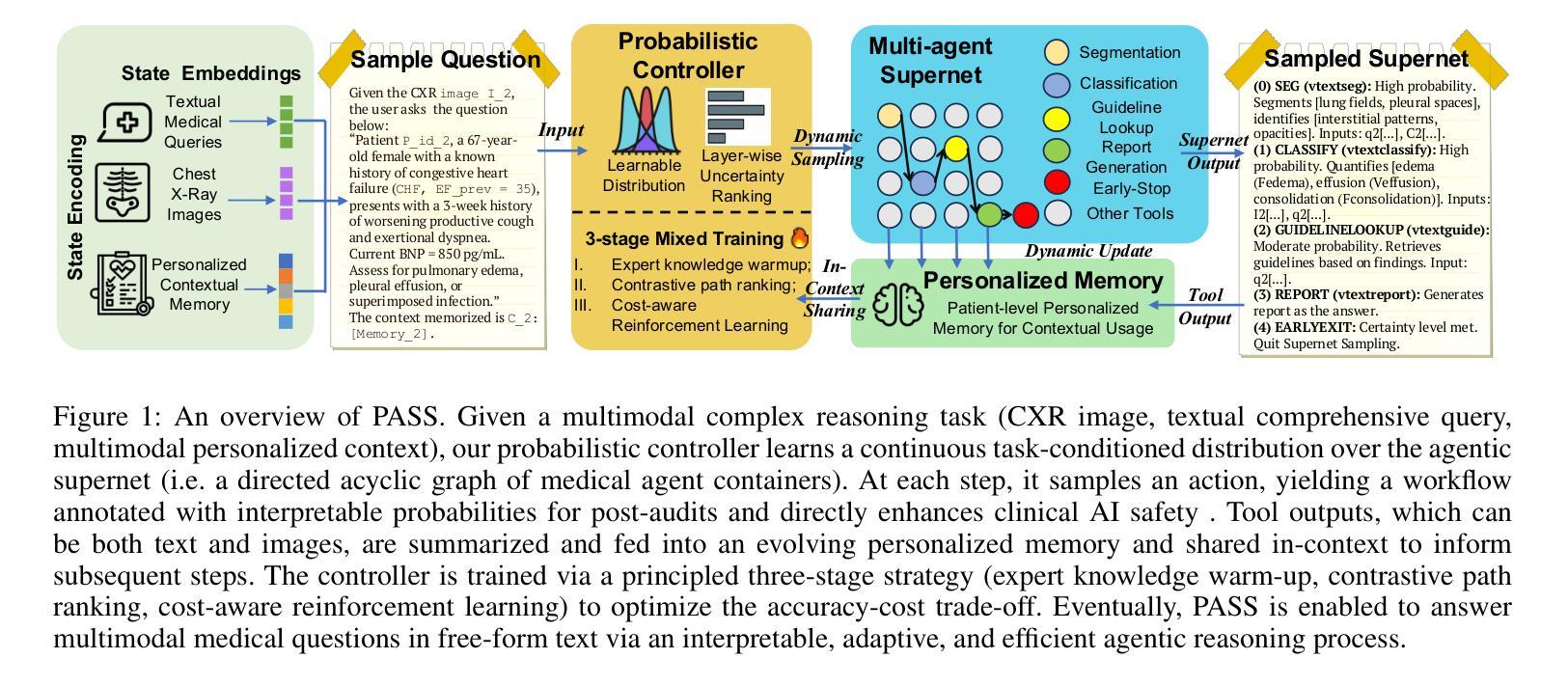
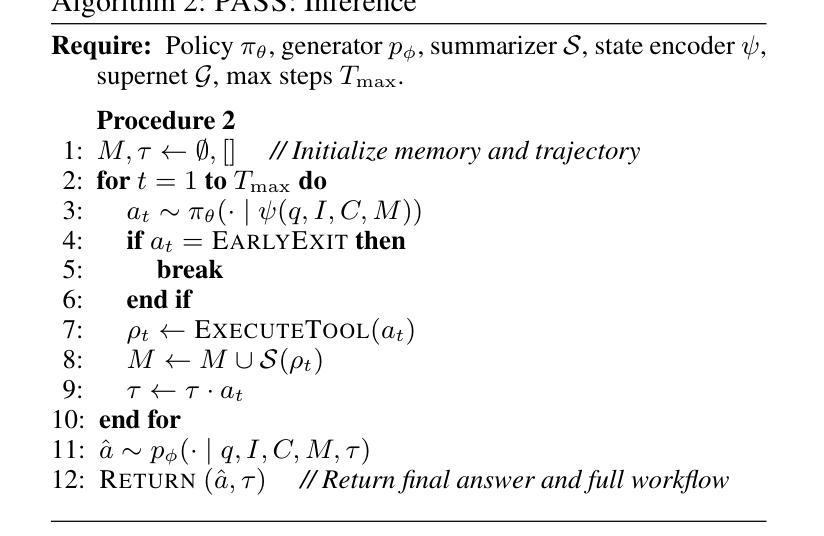
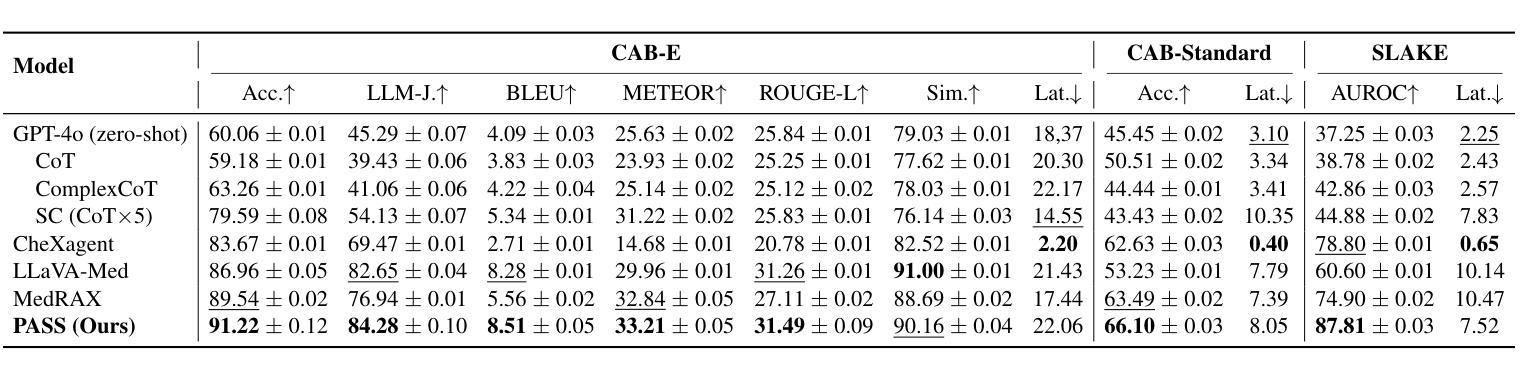
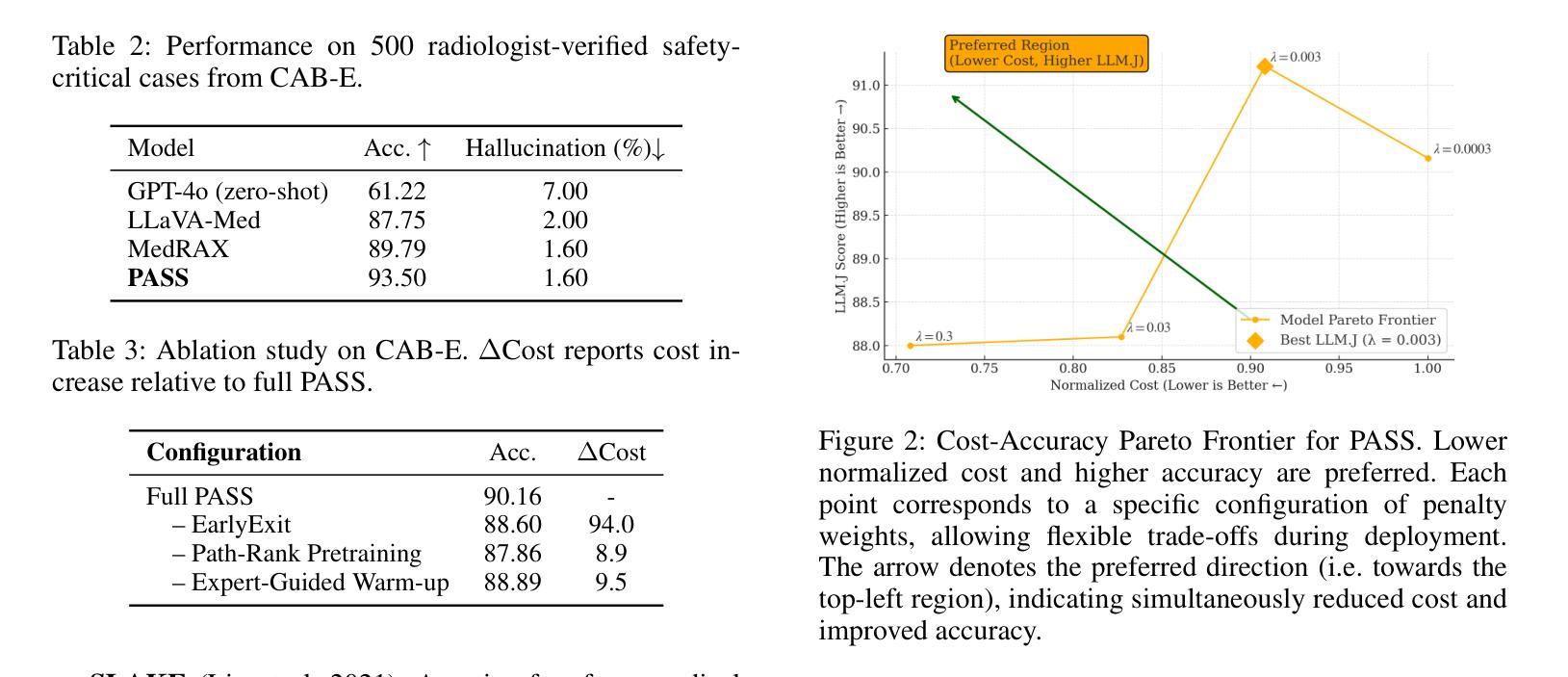
PASS: Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling for Interpretable and Adaptive Chest X-Ray Reasoning
Authors:Yushi Feng, Junye Du, Yingying Hong, Qifan Wang, Lequan Yu
Existing tool-augmented agentic systems are limited in the real world by (i) black-box reasoning steps that undermine trust of decision-making and pose safety risks, (ii) poor multimodal integration, which is inherently critical for healthcare tasks, and (iii) rigid and computationally inefficient agentic pipelines. We introduce PASS (Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling), the first multimodal framework to address these challenges in the context of Chest X-Ray (CXR) reasoning. PASS adaptively samples agentic workflows over a multi-tool graph, yielding decision paths annotated with interpretable probabilities. Given the complex CXR reasoning task with multimodal medical data, PASS leverages its learned task-conditioned distribution over the agentic supernet. Thus, it adaptively selects the most suitable tool at each supernet layer, offering probability-annotated trajectories for post-hoc audits and directly enhancing medical AI safety. PASS also continuously compresses salient findings into an evolving personalized memory, while dynamically deciding whether to deepen its reasoning path or invoke an early exit for efficiency. To optimize a Pareto frontier balancing performance and cost, we design a novel three-stage training procedure, including expert knowledge warm-up, contrastive path-ranking, and cost-aware reinforcement learning. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we introduce CAB-E, a comprehensive benchmark for multi-step, safety-critical, free-form CXR reasoning. Experiments across various benchmarks validate that PASS significantly outperforms strong baselines in multiple metrics (e.g., accuracy, AUC, LLM-J.) while balancing computational costs, pushing a new paradigm shift towards interpretable, adaptive, and multimodal medical agentic systems.
现有工具增强型智能体系统在现实世界中的应用存在以下局限性:(一)黑箱推理步骤损害了决策的可信度并带来安全风险;(二)对医疗任务至关重要的多模式融合能力较差;(三)智能体管道刚性且计算效率低下。我们引入了PASS(概率智能体超网采样),这是第一个用于解决胸部X射线(CXR)推理上下文中这些挑战的多模式框架。PASS自适应地在多工具图上采样智能体工作流程,产生带有可解释概率的决策路径。针对具有多模式医疗数据的复杂CXR推理任务,PASS利用其学习到的任务条件分布的智能体超网。因此,它可以在每个超网层自适应地选择最合适的工具,为事后审计提供带概率注释的轨迹,并直接提高医疗人工智能的安全性。PASS还不断将重要发现压缩成不断发展的个性化记忆,同时动态决定是深化其推理路径还是提前退出以提高效率。为了优化性能与成本之间的帕累托前沿,我们设计了一种新型的三阶段训练程序,包括专家知识预热、对比路径排名和成本感知强化学习。为了进行严格评估,我们引入了CAB-E,这是一个用于多步骤、安全关键的自由形式CXR推理的综合基准测试。在多个基准测试上的实验验证了PASS在多个指标(例如准确性、AUC、LLM-J)上显著优于强大的基线,同时平衡了计算成本,朝着可解释、自适应和多模式医疗智能体系统的新范式转变。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
PASS(Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling)是首个针对胸部X光(CXR)推理的多模式框架,解决了现有工具增强代理系统所面临的信任、安全、多模式集成、计算效率等挑战。PASS通过自适应采样代理工作流程,生成可解释的概率为决策路径注解,利用任务条件分布从多工具图中选择最合适的工具,为事后审计提供概率注解轨迹,提高医疗人工智能的安全性。PASS还通过不断压缩重要发现到一个个性化记忆系统来平衡推理效率和早期退出策略的计算成本。我们引入了一个新颖的第三阶段训练过程来实现性能和成本的平衡,并通过CAB-E基准测试验证了PASS在多个指标上的显著优势。
关键见解
- PASS是首个针对医学图像多模式处理的多模态框架,旨在解决代理系统面临的安全风险和多模式集成问题。
- PASS引入概率解释性标注,通过自适应采样代理工作流程以增强医疗人工智能的透明度和安全性。
- 通过动态选择最合适的工具和早期退出策略,PASS提高了计算效率并优化了性能与成本之间的平衡。
- PASS采用创新的训练过程,包括专家知识预热、对比路径排名和成本感知强化学习,以实现性能优化。
- CAB-E基准测试验证了PASS在多项指标上的显著优势,表明其在医学图像推理方面具有先进性能。
- PASS的持续学习和个性化记忆系统能够适应复杂的医学数据环境并提升长期性能。
点此查看论文截图



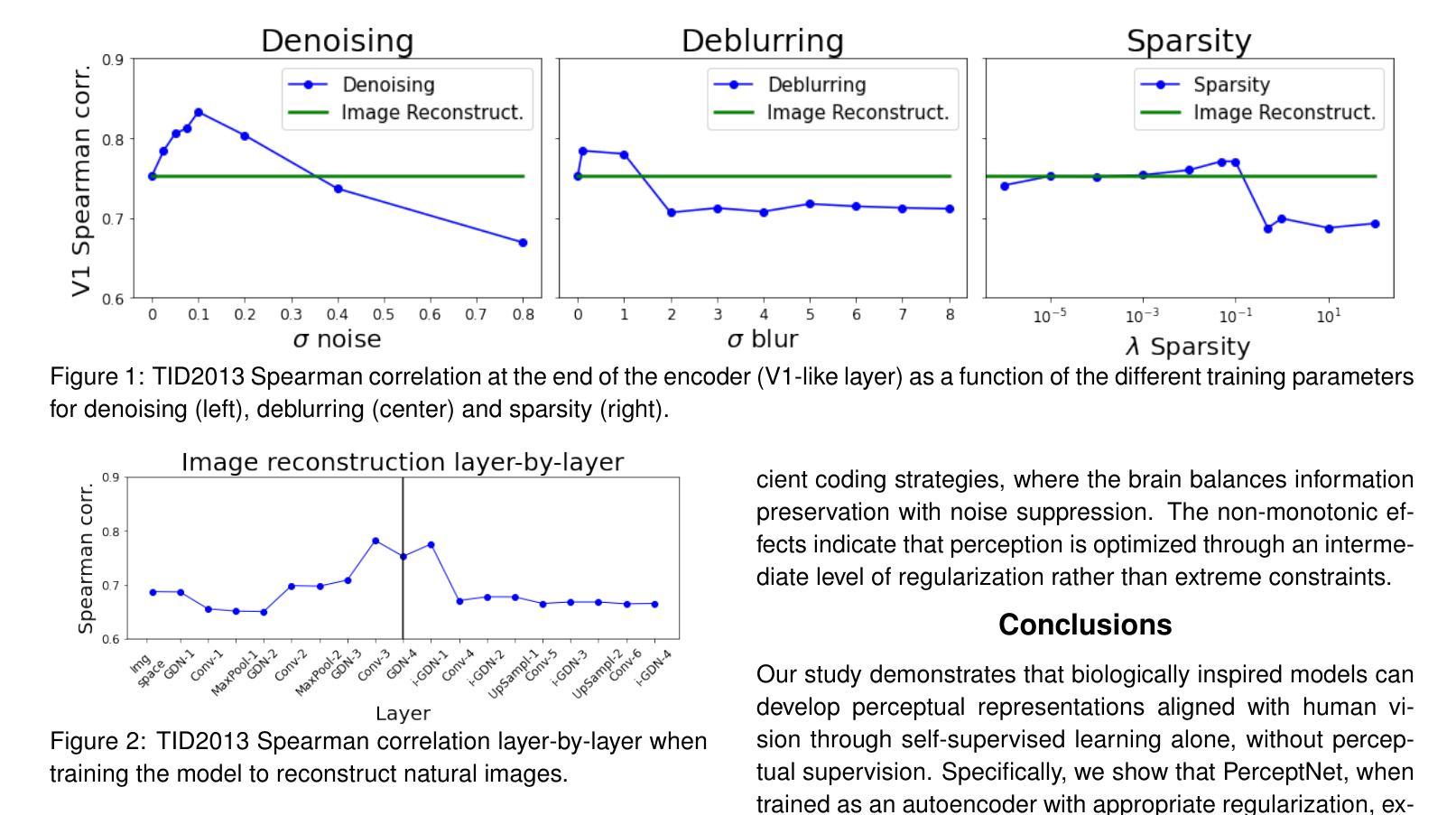
From Images to Perception: Emergence of Perceptual Properties by Reconstructing Images
Authors:Pablo Hernández-Cámara, Jesus Malo, Valero Laparra
A number of scientists suggested that human visual perception may emerge from image statistics, shaping efficient neural representations in early vision. In this work, a bio-inspired architecture that can accommodate several known facts in the retina-V1 cortex, the PerceptNet, has been end-to-end optimized for different tasks related to image reconstruction: autoencoding, denoising, deblurring, and sparsity regularization. Our results show that the encoder stage (V1-like layer) consistently exhibits the highest correlation with human perceptual judgments on image distortion despite not using perceptual information in the initialization or training. This alignment exhibits an optimum for moderate noise, blur and sparsity. These findings suggest that the visual system may be tuned to remove those particular levels of distortion with that level of sparsity and that biologically inspired models can learn perceptual metrics without human supervision.
许多科学家提出,人类视觉感知可能源于图像统计,在早期视觉中形成有效的神经表征。在这项工作中,一种能够容纳视网膜-V1皮层中已知事实的仿生架构——PerceptNet,已经针对与图像重建相关的不同任务进行了端到端的优化:自动编码、去噪、去模糊和稀疏正则化。我们的结果表明,尽管在初始化或训练过程中没有使用感知信息,但编码器阶段(类似V1层)与人类对图像失真的感知判断之间的相关性一直最高。这种对齐在中等程度的噪声、模糊和稀疏性方面表现出最佳效果。这些结果表明,视觉系统可能被调整为消除特定程度的失真与稀疏性相对应的程度,并且生物启发模型可以在无需人类监督的情况下学习感知度量指标。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种生物启发架构PerceptNet,能融合视网膜至V1皮层的多项已知事实,针对图像重建的不同任务进行端到端的优化,包括自动编码、去噪、去模糊和稀疏正则化。研究结果显示,即便在初始化和训练过程中未使用感知信息,编码器阶段(类似V1层)与人类对图像失真的感知判断仍具有最高相关性,特别是在中等噪声、模糊和稀疏性优化方面。这暗示视觉系统可能经过调整以去除特定程度的失真和相应程度的稀疏性,同时生物启发模型可在无需人类监督的情况下学习感知度量。
Key Takeaways
- 人类视觉感知可能源于图像统计,形成早期视觉中的高效神经表征。
- PerceptNet架构融合视网膜至V1皮层的多个已知事实。
- PerceptNet经过端到端的优化,涉及图像重建的多种任务。
- 编码器阶段与人类的感知判断高度相关,特别是在图像失真方面。
- 研究发现,视觉系统可能经过调整以处理特定程度的失真和稀疏性。
- 生物启发模型可在无需人类监督的情况下学习感知度量。
点此查看论文截图

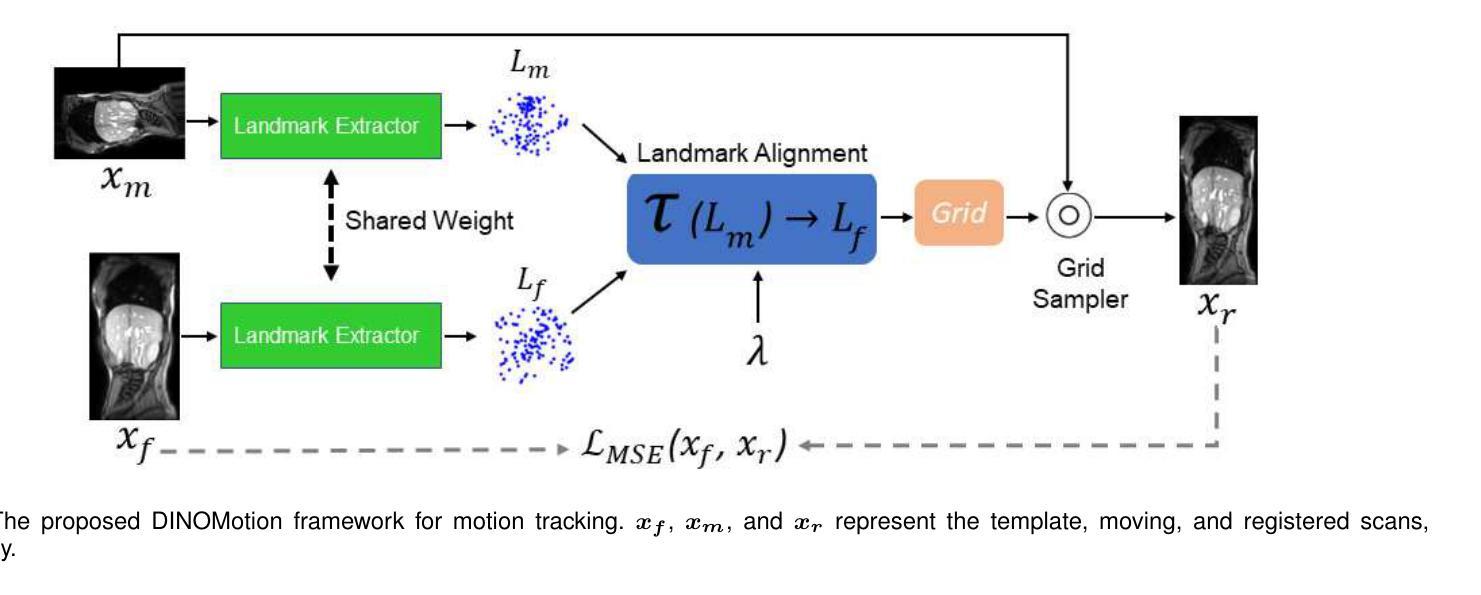
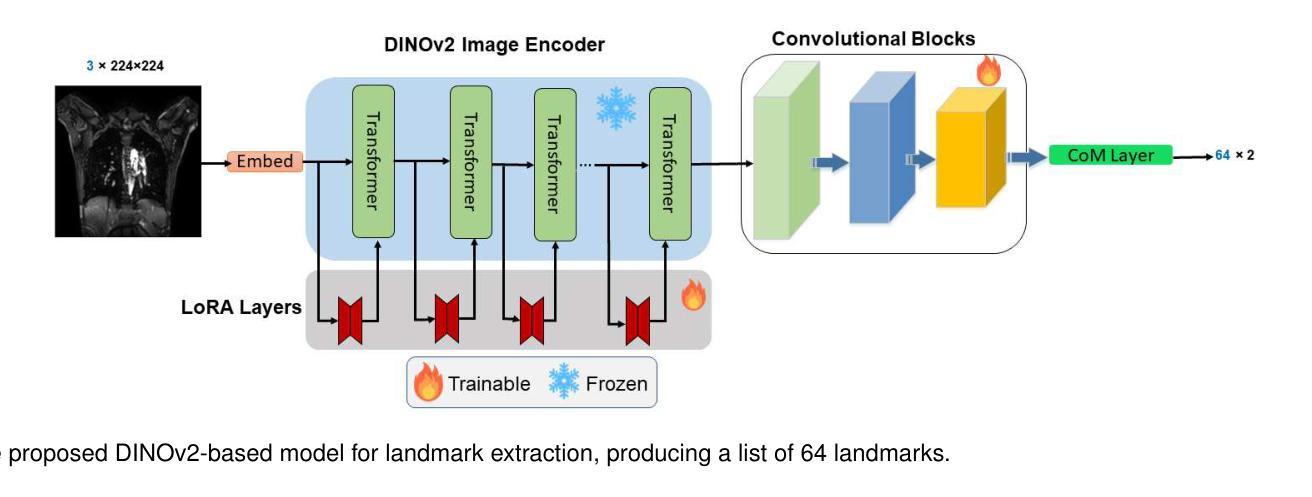
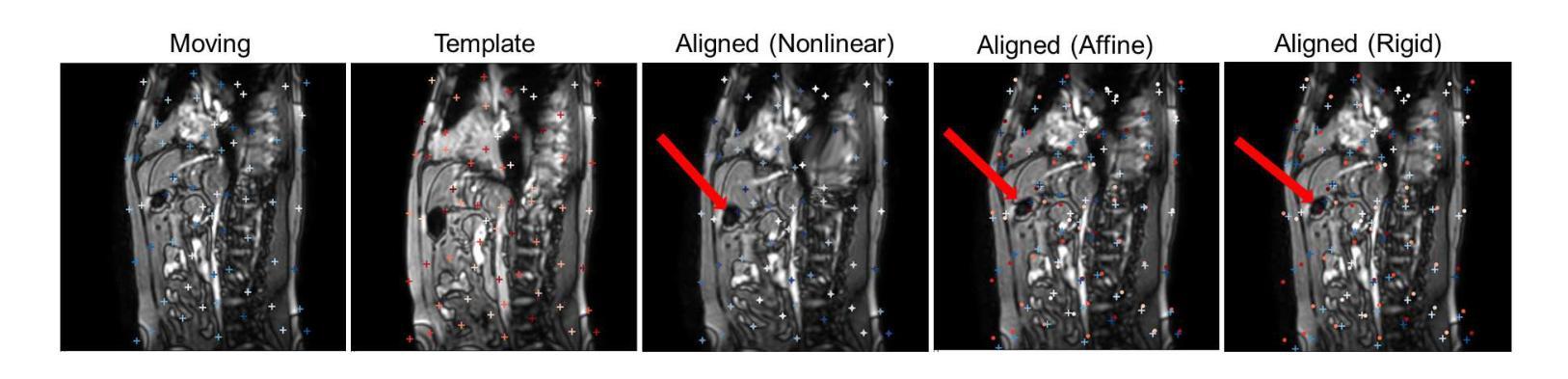
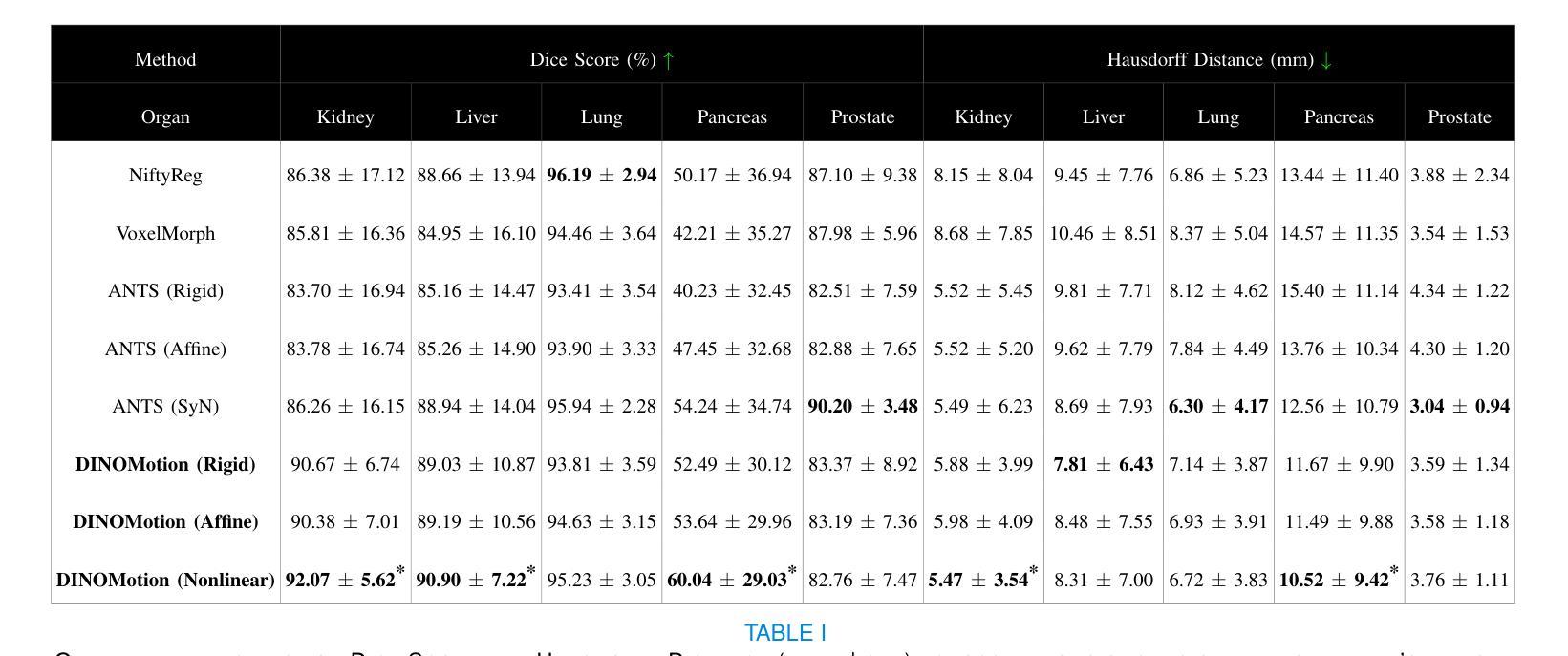
DINOMotion: advanced robust tissue motion tracking with DINOv2 in 2D-Cine MRI-guided radiotherapy
Authors:Soorena Salari, Catherine Spino, Laurie-Anne Pharand, Fabienne Lathuiliere, Hassan Rivaz, Silvain Beriault, Yiming Xiao
Accurate tissue motion tracking is critical to ensure treatment outcome and safety in 2D-Cine MRI-guided radiotherapy. This is typically achieved by registration of sequential images, but existing methods often face challenges with large misalignments and lack of interpretability. In this paper, we introduce DINOMotion, a novel deep learning framework based on DINOv2 with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) layers for robust, efficient, and interpretable motion tracking. DINOMotion automatically detects corresponding landmarks to derive optimal image registration, enhancing interpretability by providing explicit visual correspondences between sequential images. The integration of LoRA layers reduces trainable parameters, improving training efficiency, while DINOv2’s powerful feature representations offer robustness against large misalignments. Unlike iterative optimization-based methods, DINOMotion directly computes image registration at test time. Our experiments on volunteer and patient datasets demonstrate its effectiveness in estimating both linear and nonlinear transformations, achieving Dice scores of 92.07% for the kidney, 90.90% for the liver, and 95.23% for the lung, with corresponding Hausdorff distances of 5.47 mm, 8.31 mm, and 6.72 mm, respectively. DINOMotion processes each scan in approximately 30ms and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in handling large misalignments. These results highlight its potential as a robust and interpretable solution for real-time motion tracking in 2D-Cine MRI-guided radiotherapy.
在二维电影MRI引导的放射治疗过程中,精确的组织运动跟踪对于确保治疗效果和安全至关重要。这通常通过连续图像的注册来实现,但现有方法经常面临大错位和缺乏解释性的挑战。本文介绍了DINOMotion,这是一种基于DINOv2和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)层的新型深度学习框架,可实现稳健、高效、可解释的运动跟踪。DINOMotion自动检测相应的地标以得出最佳图像注册,通过提供连续图像之间的明确视觉对应关系来提高解释性。LoRA层的集成减少了可训练参数,提高了训练效率,而DINOv2的强大特征表示能力则提供了对大错位的稳健性。与基于迭代优化的方法不同,DINOMotion在测试时直接计算图像注册。我们在志愿者和患者数据集上的实验表明,它在估计线性和非线性转换方面的有效性,肾脏、肝脏和肺的Dice得分分别为92.07%、90.90%和95.23%,相应的Hausdorff距离分别为5.47毫米、8.31毫米和6.72毫米。DINOMotion处理每次扫描大约需要30毫秒,并且始终优于最先进的方法,特别是在处理大错位方面。这些结果凸显了其在二维电影MRI引导的放射治疗中进行实时运动跟踪的强大和可解释的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering (TMBE), 14 pages
摘要
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的运动追踪框架DINOMotion,用于在二维电影MRI引导下实现精确的组织运动追踪,从而提高放射治疗的疗效和安全性。DINOMotion采用DINOv2算法结合低秩自适应(LoRA)层,实现稳健、高效、可解释的运动追踪。该方法可自动检测对应地标以实现最佳图像配准,通过提供序列图像之间的明确视觉对应关系增强可解释性。实验结果表明,DINOMotion在处理志愿者及患者数据集时,对线性及非线性转换的估计均表现优异,肾脏、肝脏及肺部的Dice得分分别为92.07%、90.90%及95.23%,对应的Hausdorff距离分别为5.47毫米、8.31毫米及6.72毫米。DINOMotion每个扫描处理时间约为30毫秒,并能持续超越现有的顶尖方法,特别是在处理大错位方面表现出众。因此,DINOMotion可能成为二维电影MRI引导放疗中实现实时运动追踪的稳健、可解方案。
关键见解
- DINOMotion是一个基于深度学习的运动追踪框架,用于确保二维电影MRI引导放射治疗的疗效和安全性。
- DINOMotion结合DINOv2算法和低秩自适应(LoRA)层,实现稳健、高效、可解释的运动追踪。
- 通过自动检测对应地标进行图像配准,增强可解释性并提供明确的视觉对应关系。
- 实验结果表明DINOMotion在处理多种数据集时表现优异,特别是在处理大错位方面。
- DINOMotion处理每个扫描的时间短,约30毫秒,可实现实时运动追踪。
- DINOMotion持续超越现有顶尖方法,具有成为行业标准的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

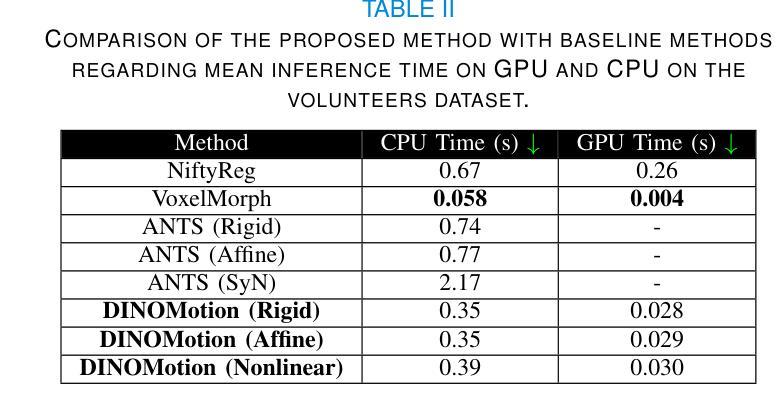
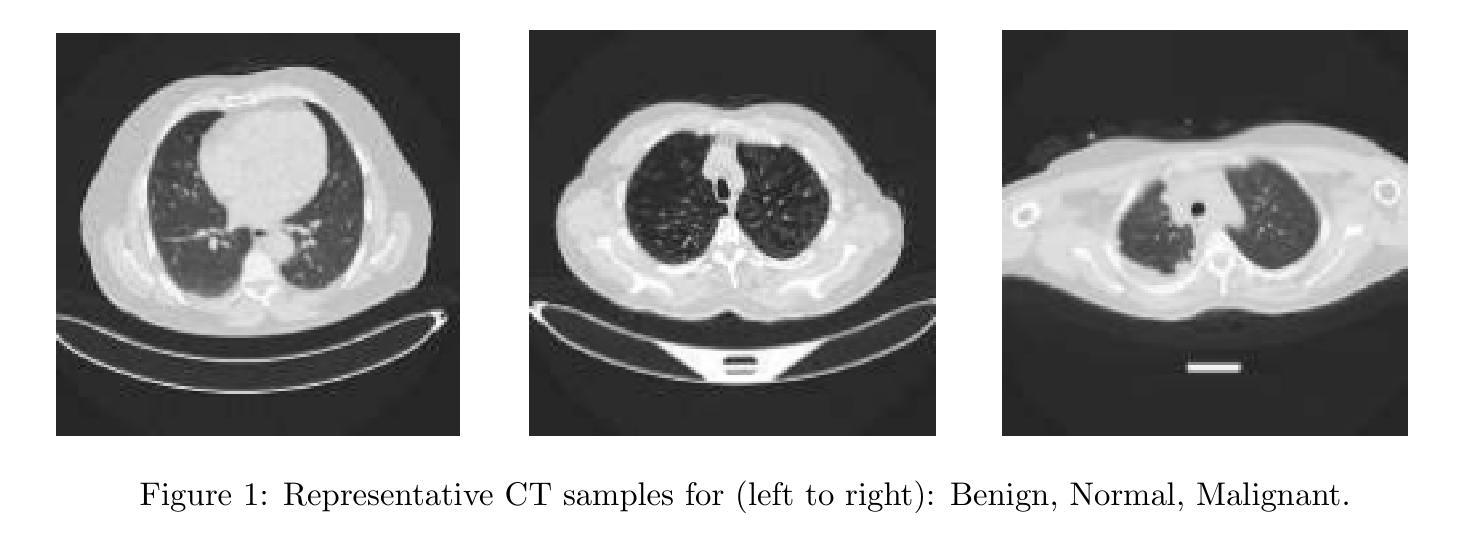
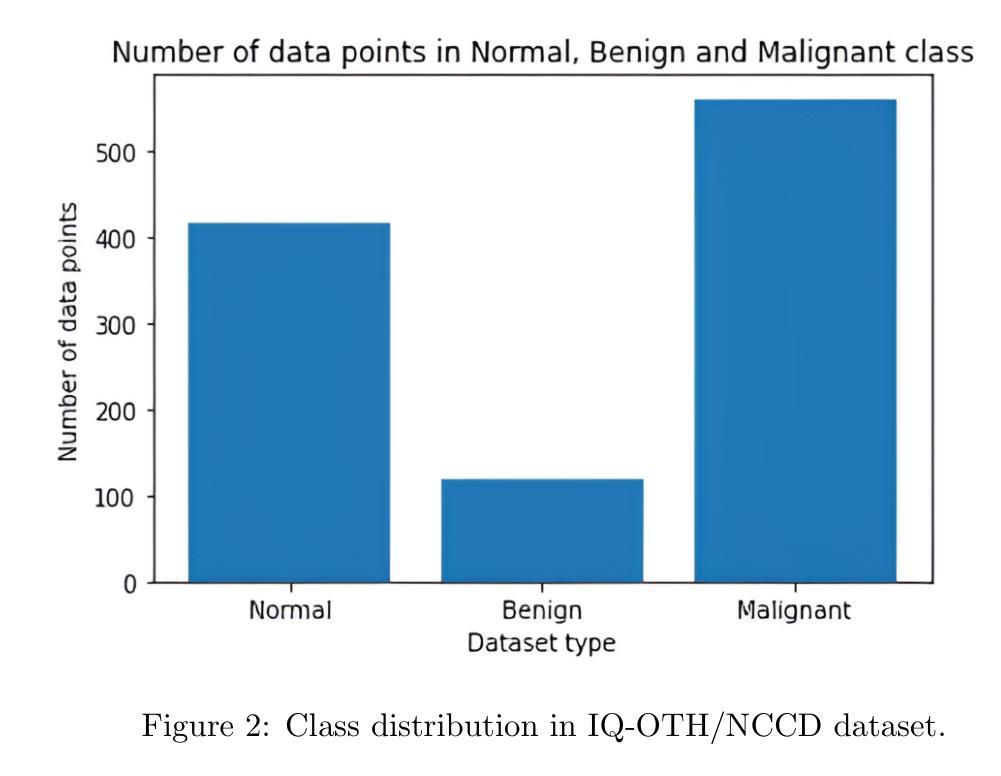
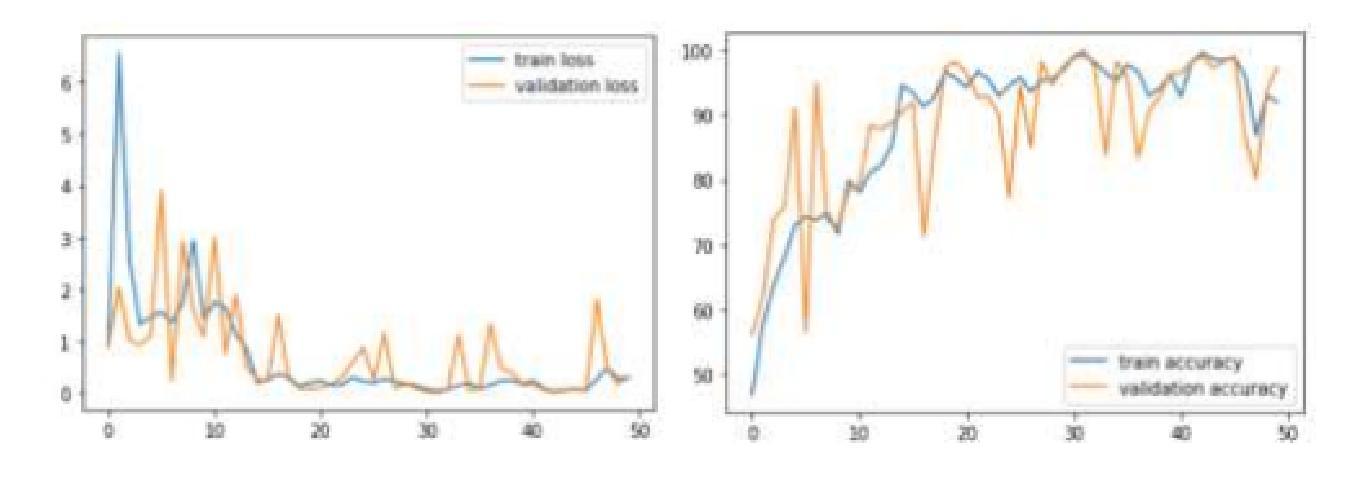
Explainable AI Technique in Lung Cancer Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Authors:Nishan Rai, Sujan Khatri, Devendra Risal
Early detection of lung cancer is critical to improving survival outcomes. We present a deep learning framework for automated lung cancer screening from chest computed tomography (CT) images with integrated explainability. Using the IQ-OTH/NCCD dataset (1,197 scans across Normal, Benign, and Malignant classes), we evaluate a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) and three fine-tuned transfer learning backbones: DenseNet121, ResNet152, and VGG19. Models are trained with cost-sensitive learning to mitigate class imbalance and evaluated via accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC. While ResNet152 achieved the highest accuracy (97.3%), DenseNet121 provided the best overall balance in precision, recall, and F1 (up to 92%, 90%, 91%, respectively). We further apply Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) to visualize evidence contributing to predictions, improving clinical transparency. Results indicate that CNN-based approaches augmented with explainability can provide fast, accurate, and interpretable support for lung cancer screening, particularly in resource-limited settings.
早期发现肺癌对于改善生存结果至关重要。我们提出了一种用于自动肺癌筛查的深度学习框架,该框架基于胸部计算机断层扫描(CT)图像,并集成了可解释性。我们使用IQ-OTH/NCCD数据集(包含正常、良性、恶性三类,共1197张扫描图像)来评估一个自定义的卷积神经网络(CNN)和三个微调过的迁移学习主干网:DenseNet121、ResNet152和VGG19。模型采用成本敏感学习进行训练,以缓解类别不平衡问题,并通过准确率、精确度、召回率、F1分数和ROC-AUC进行评估。虽然ResNet152的准确率最高(97.3%),但DenseNet121在精确度、召回率和F1方面提供了最佳的整体平衡(分别高达92%、90%、91%)。我们进一步应用Shapley Additive Explanations(SHAP)来可视化预测的证据,提高临床透明度。结果表明,具有可解释性的CNN方法可以为肺癌筛查提供快速、准确和可解释的支持,特别是在资源有限的环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 9 figures, 4 tables. Undergraduate research project report
Summary
本研究利用深度学习框架,结合可解释性,实现从胸部计算机断层扫描(CT)图像中自动进行肺癌筛查。研究使用IQ-OTH/NCCD数据集,评估自定义卷积神经网络(CNN)和三种微调后的迁移学习主干网络(DenseNet121、ResNet152和VGG19)的性能。通过成本敏感学习减轻类别不平衡问题,并通过准确度、精确度、召回率、F1分数和ROC-AUC进行评价。ResNet152准确率最高(97.3%),而DenseNet121在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面提供最佳综合平衡。研究还应用Shapley Additive Explanations(SHAP)来可视化预测的贡献证据,提高临床透明度。结果表明,结合解释性的CNN方法可为肺癌筛查提供快速、准确和可解释的支持,特别是在资源有限的环境中。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用深度学习框架进行肺癌筛查,从胸部CT图像中自动检测。
- 研究采用多种神经网络模型进行评估,包括自定义CNN和三种迁移学习主干网络。
- 通过成本敏感学习来减轻类别不平衡问题。
- ResNet152模型在准确率方面表现最佳。
- DenseNet121在精确度、召回率和F1分数方面提供最佳综合表现。
- 研究应用SHAP方法可视化预测的贡献证据,提高临床透明度。
点此查看论文截图



Optimizing Convolution Direction and Template Selection for Difference Image Analysis
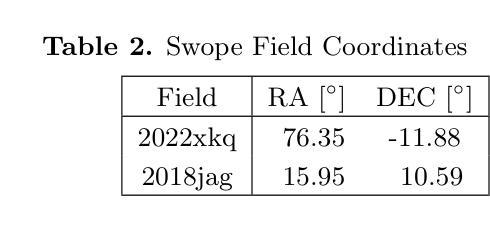
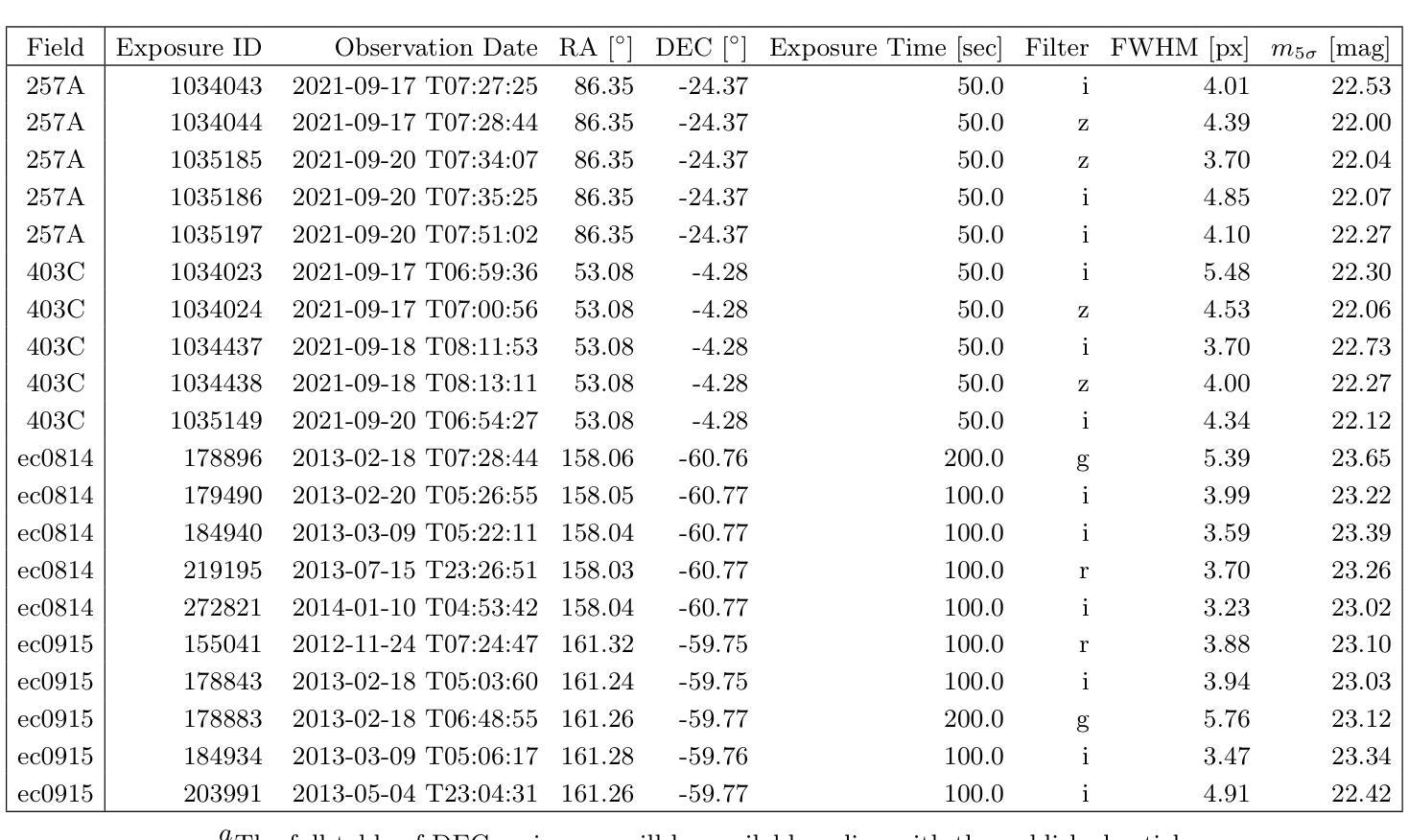
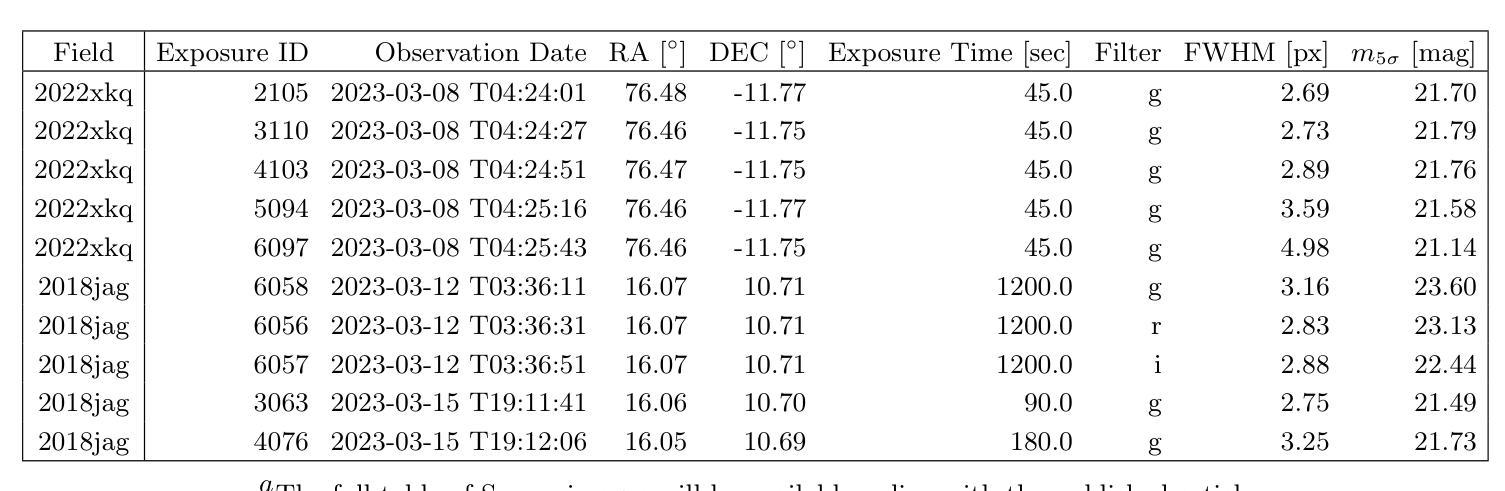
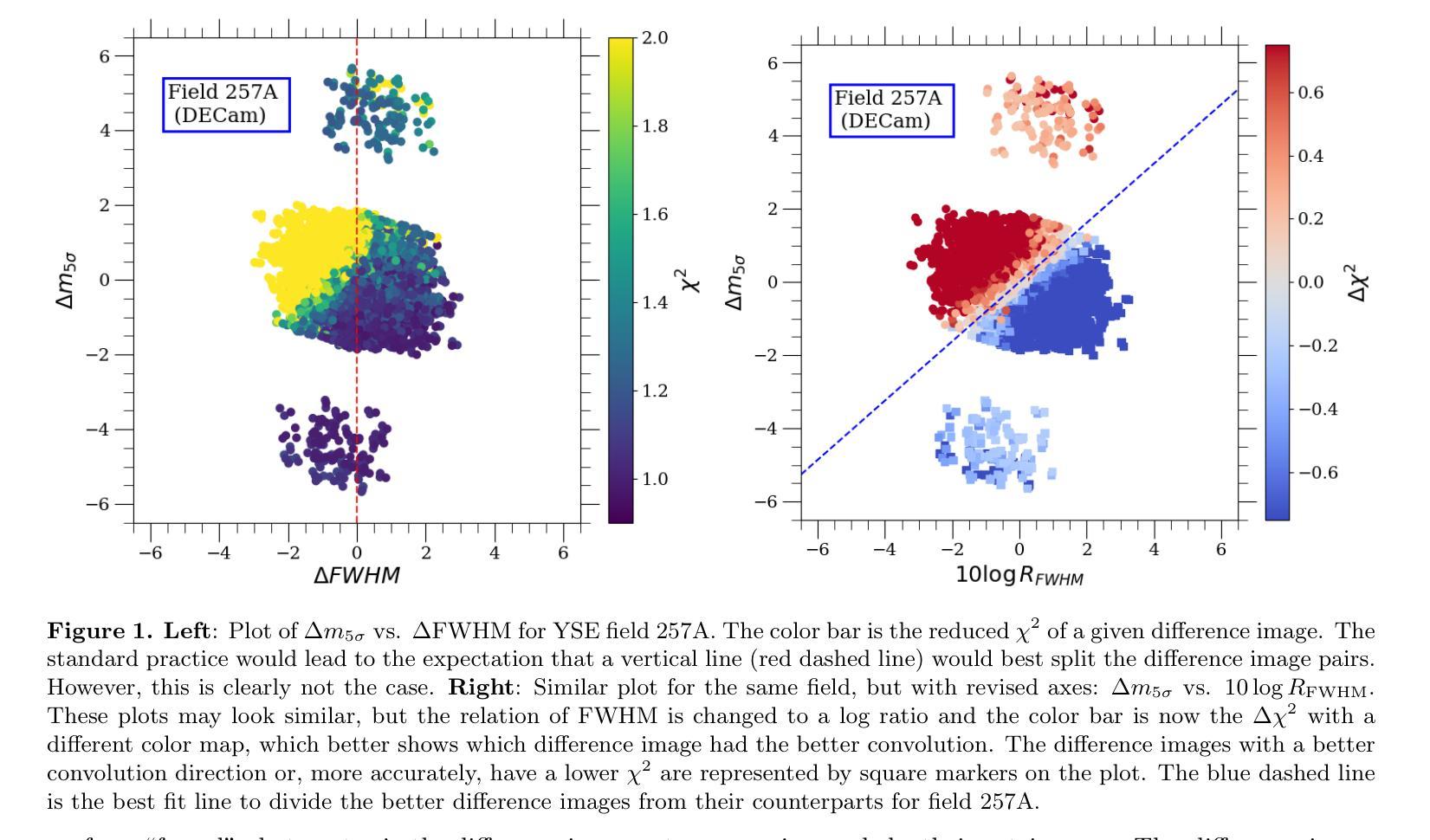
Authors:Rodrigo Angulo, Armin Rest, William P. Blair, Jacob Jencson, David A. Coulter, Qinan Wang, Ryan J. Foley, Charles D. Kilpatrick, Xiaolong Li, Anthony L. Piro
Difference image analysis (DIA) is a powerful tool for studying time-variable phenomena, and has been used by many time-domain surveys. Most DIA algorithms involve matching the spatially-varying PSF shape between science and template images, and then convolving that shape in one image to match the other. The wrong choice of which image to convolve can introduce one of the largest sources of artifacts in the final difference image. We introduce a quantitative metric to determine the optimal convolution direction that depends not only on the sharpness of the images measured by their FWHM, but also on their exposure depths. With this metric, the optimal convolution direction can be determined a priori, depending only on the FWHM and depth of the images. This not only simplifies the process, but also makes it more robust and less prone to creating sub-optimal difference images due to the wrong choice of the convolution direction. As an additional benefit, for a large set of images, we define a Figure-of-Merit based on this metric, which allows us to rank a list of images and determine the ones best suited to be used as templates, thus streamlining and automating the data reduction process.
差异图像分析(DIA)是研究时间变量现象的强大工具,已被许多时域调查所使用。大多数DIA算法涉及匹配科学和模板图像之间空间变化的PSF形状,然后将该形状在一个图像中进行卷积以匹配另一个图像。选择哪个图像进行卷积的错误可能导致最终差异图像中出现最大的伪影来源之一。我们引入了一种定量指标,以确定最佳的卷积方向,这不仅取决于通过它们的FWHM测量的图像清晰度,还取决于它们的曝光深度。使用该指标,可以事先确定最佳的卷积方向,这仅取决于图像的FWHM和深度。这不仅简化了流程,而且使其更加稳健,并且由于选择了错误的卷积方向而不太容易产生次优差异图像。作为附加好处,对于大量图像,我们基于该指标定义了一个品质因数,这使我们能够对图像列表进行排名,并确定最适合用作模板的图像,从而简化和自动化数据缩减过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 11 figures
Summary
差异图像分析(DIA)是研究时变现象的有力工具,已被许多时域调查所使用。大多数DIA算法涉及匹配科学和模板图像之间空间变化的PSF形状,然后将该形状在一个图像中卷积以匹配另一个图像。选择哪个图像进行卷积,可能会对最终差异图像引入最大的伪影来源。我们引入了一种定量指标,以确定最佳卷积方向,该方向不仅取决于通过FWHM测量的图像清晰度,还取决于它们的曝光深度。此指标可预先确定最佳卷积方向,仅取决于图像的FWHM和深度。这不仅简化了流程,而且使其更加稳健,不易因卷积方向选择错误而生成次优差异图像。对于大量图像,我们还基于该指标定义了一个品质因数,可以排名图像列表并确定最适合用作模板的图像,从而简化和自动化数据缩减过程。
Key Takeaways
- DIA是一种研究时间变量现象的有力工具,常用于时域调查。
- DIA算法的核心在于匹配科学和模板图像之间的PSF形状,并卷积以产生匹配。
- 选择卷积的图像方向是关键的,错误的选择可能导致最终差异图像中的重大伪影。
- 引入了一种定量指标来确定最佳卷积方向,该指标考虑图像的FWHM和曝光深度。
- 使用此指标可以预先确定最佳卷积方向,简化流程并增加稳健性。
- 对于大量图像,定义了一个品质因数来排名图像并确定最适合用作模板的图像。
点此查看论文截图

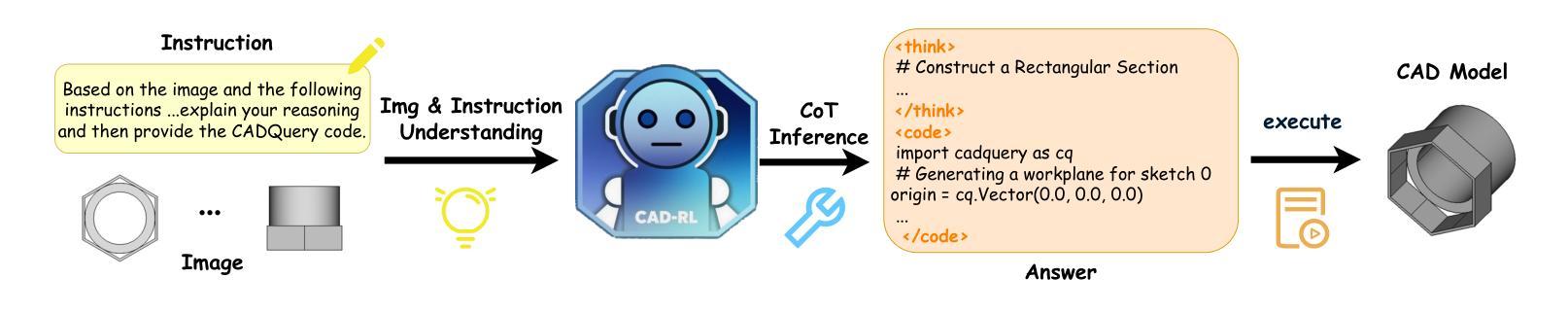
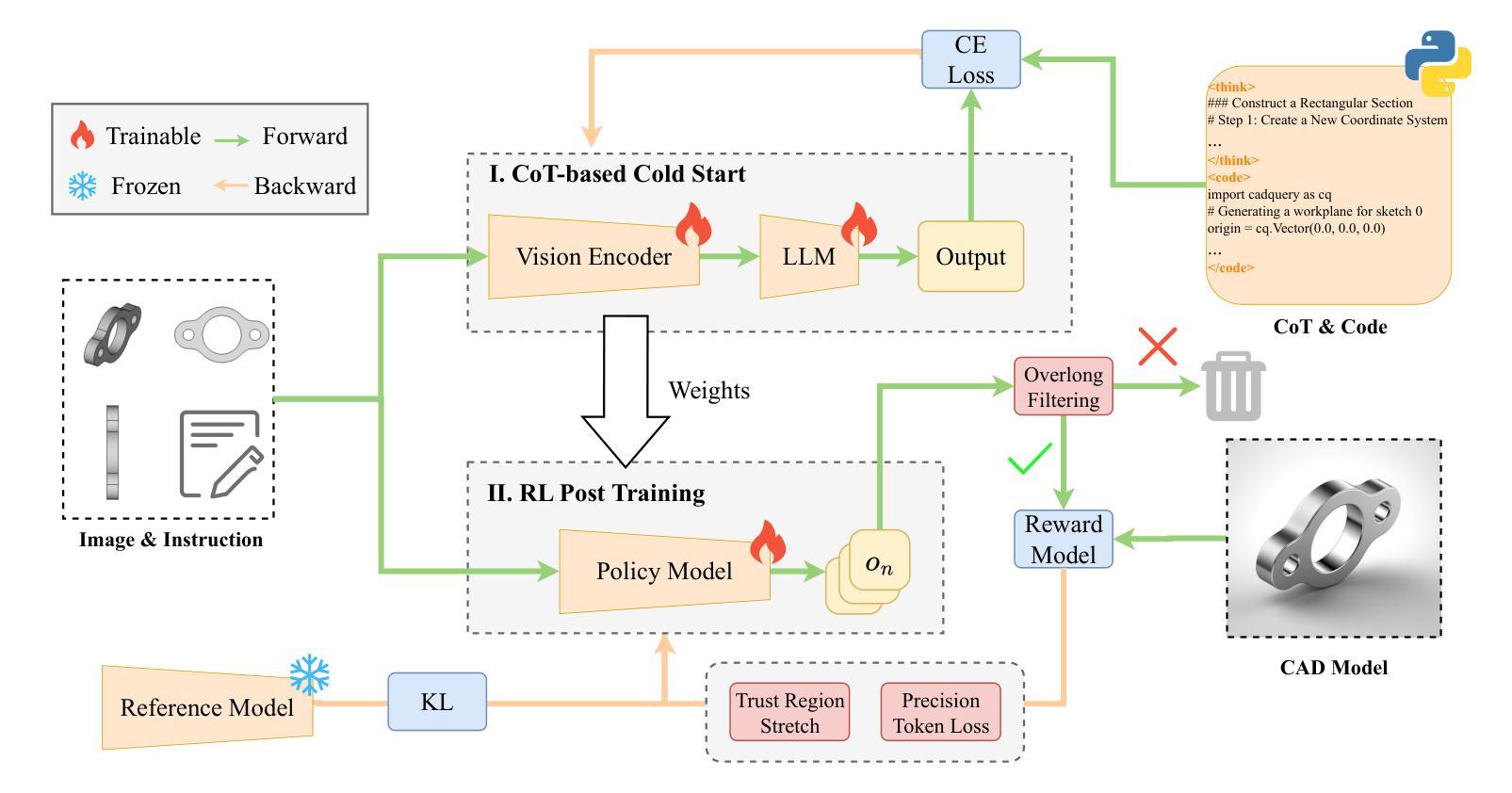
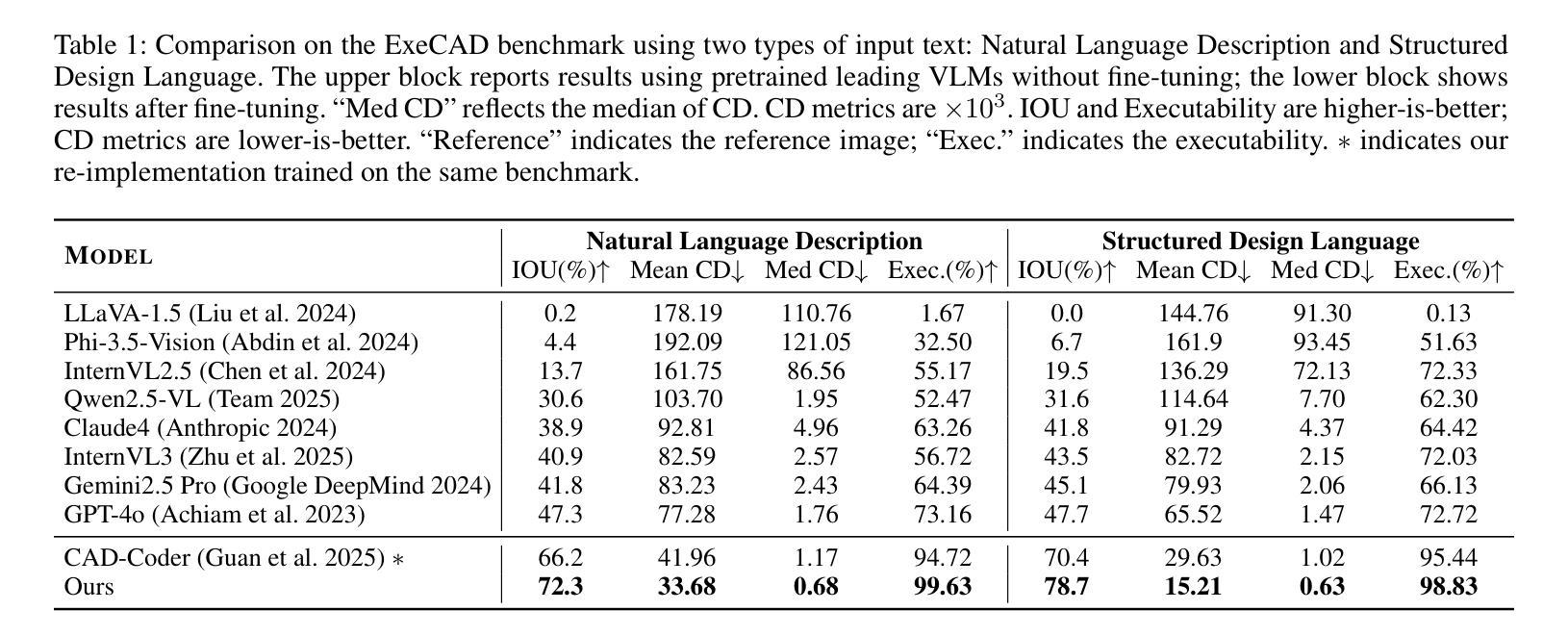
From Intent to Execution: Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reinforcement Learning for Precise CAD Code Generation
Authors:Ke Niu, Haiyang Yu, Zhuofan Chen, Mengyang Zhao, Teng Fu, Bin Li, Xiangyang Xue
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a vital role in engineering and manufacturing, yet current CAD workflows require extensive domain expertise and manual modeling effort. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have made it possible to generate code from natural language, opening new opportunities for automating parametric 3D modeling. However, directly translating human design intent into executable CAD code remains highly challenging, due to the need for logical reasoning, syntactic correctness, and numerical precision. In this work, we propose CAD-RL, a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) guided reinforcement learning post training framework for CAD modeling code generation. Our method combines CoT-based Cold Start with goal-driven reinforcement learning post training using three task-specific rewards: executability reward, geometric accuracy reward, and external evaluation reward. To ensure stable policy learning under sparse and high-variance reward conditions, we introduce three targeted optimization strategies: Trust Region Stretch for improved exploration, Precision Token Loss for enhanced dimensions parameter accuracy, and Overlong Filtering to reduce noisy supervision. To support training and benchmarking, we release ExeCAD, a noval dataset comprising 16,540 real-world CAD examples with paired natural language and structured design language descriptions, executable CADQuery scripts, and rendered 3D models. Experiments demonstrate that CAD-RL achieves significant improvements in reasoning quality, output precision, and code executability over existing VLMs.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造中发挥着至关重要的作用,但当前的CAD工作流程需要丰富的领域专业知识和手动建模工作。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使得从自然语言生成代码成为可能,为自动化参数化3D建模提供了新的机会。然而,直接将人类的设计意图翻译成可执行的CAD代码仍然面临巨大挑战,这需要进行逻辑推理、语法正确和数值精确。在这项工作中,我们提出了CAD-RL,这是一个用于CAD建模代码生成的多模态思维链(CoT)引导强化学习后训练框架。我们的方法结合了基于CoT的冷启动和基于目标驱动强化学习后训练,使用三种特定任务奖励:可执行性奖励、几何精度奖励和外部评估奖励。为了确保在稀疏和高方差奖励条件下的稳定策略学习,我们引入了三种有针对性的优化策略:用于改进探索的信任区域扩展、用于提高维度参数精度的精确令牌损失以及用于减少噪声监督的过长过滤。为了支持训练和基准测试,我们发布了ExeCAD数据集,该数据集包含16540个现实世界中的CAD示例,配有自然语言描述和结构化设计语言描述、可执行的CADQuery脚本和渲染的3D模型。实验表明,在推理质量、输出精度和代码可执行性方面,CAD-RL相较于现有的VLMs取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)引导强化学习的CAD建模代码生成框架CAD-RL。该框架结合了CoT的冷启动技术,并利用目标驱动强化学习进行训练后的优化,通过三种特定任务奖励确保生成的CAD代码可执行、几何精度高并得到外部评价。此外,还引入了三种优化策略来提高策略学习的稳定性。为支持训练和基准测试,发布了ExeCAD数据集,包含配对自然语言描述和结构化设计语言的真实CAD模型实例。实验证明,CAD-RL在推理质量、输出精度和代码可执行性方面均优于现有VLMs。
Key Takeaways
- CAD设计在工程和制造中扮演重要角色,但当前CAD工作流程需要专业知识和手动建模努力。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)能够生成代码,为自动化参数化3D建模带来新机会。
- CAD-RL框架结合了CoT技术并引入三种特定任务奖励和三种优化策略,确保生成CAD代码的质量和稳定性。
- 发布ExeCAD数据集,用于训练和基准测试CAD建模方法。
点此查看论文截图

In silico study on the cytotoxicity against Hela cancer cells of xanthones bioactive compounds from Garcinia cowa: QSAR based on Graph Deep Learning, Network Pharmacology, and Molecular Docking
Authors:Nguyen Manh Son, Pham Huu Vang, Nguyen Thi Dung, Nguyen Manh Ha. Ta Thi Thao, Tran Thi Thu Thuy, Phan Minh Giang
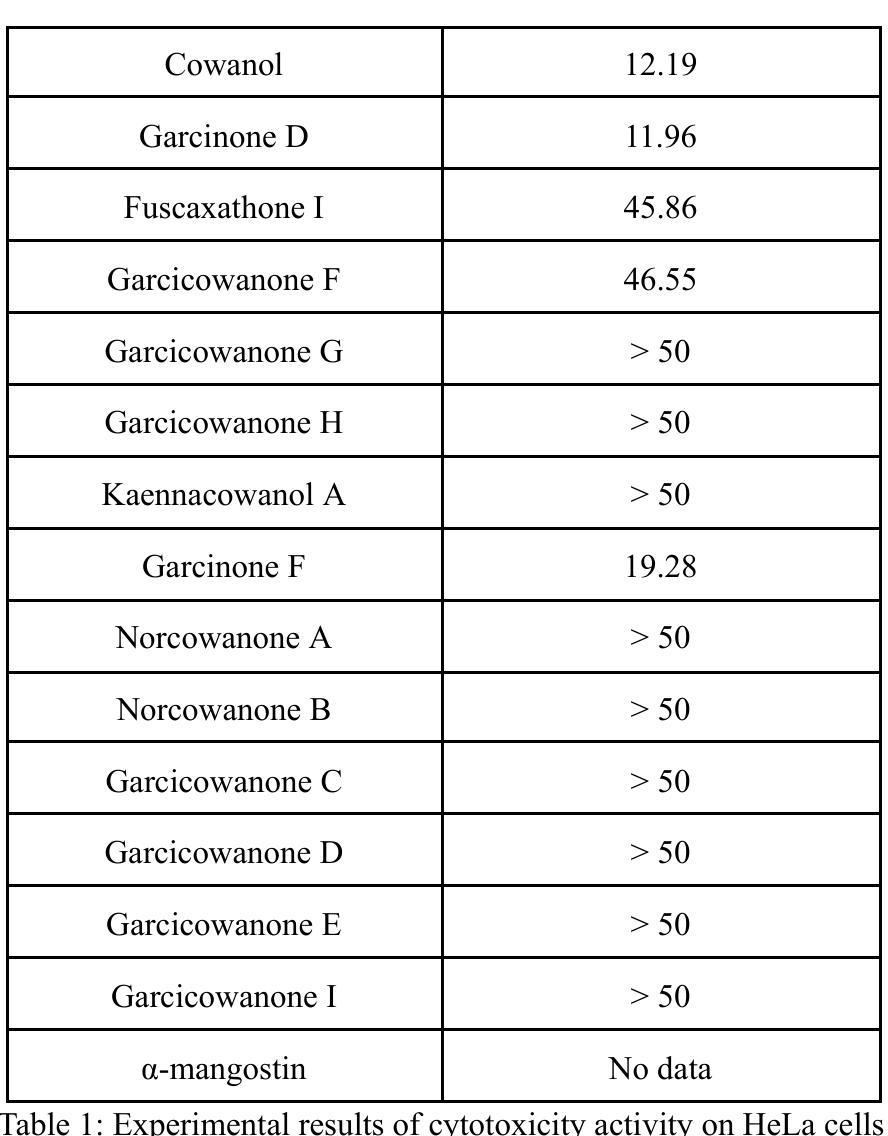
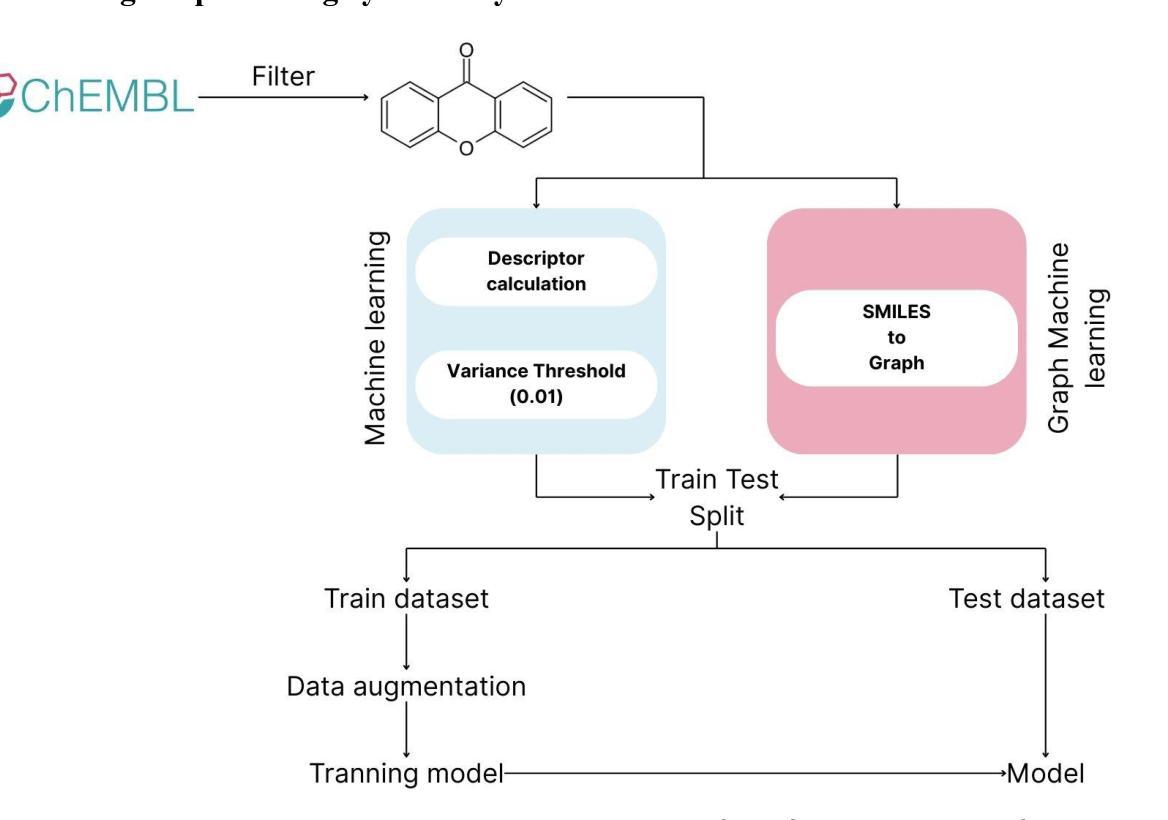
Cancer is recognized as a complex group of diseases, contributing to the highest global mortality rates, with increasing prevalence and a trend toward affecting younger populations. It is characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells, invasion of adjacent tissues, and metastasis to distant organs. Garcinia cowa, a traditional medicinal plant widely used in Southeast Asia, including Vietnam, is employed to treat fever, cough, indigestion, as a laxative, and for parasitic diseases. Numerous xanthone compounds isolated from this species exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities, with some showing promise as anti cancer and antimalarial agents. Network pharmacology analysis successfully identified key bioactive compounds Rubraxanthone, Garcinone D, Norcowanin, Cowanol, and Cowaxanthone alongside their primary protein targets (TNF, CTNNB1, SRC, NFKB1, and MTOR), providing critical insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying their anti-cancer effects. The Graph Attention Network algorithm demonstrated superior predictive performance, achieving an R2 of 0.98 and an RMSE of 0.02 after data augmentation, highlighting its accuracy in predicting pIC50 values for xanthone based compounds. Additionally, molecular docking revealed MTOR as a potential target for inducing cytotoxicity in HeLa cancer cells from Garcinia cowa.
癌症被认定为一组复杂的疾病,具有全球最高的死亡率,且发病率不断上升,且有越来越年轻化的发展趋势。其特点为异常细胞的无限增殖、邻近组织的侵袭和向远处器官的转移。Garcinia cowa是一种在东南亚(包括越南)广泛使用的传统药用植物,用于治疗发热、咳嗽、消化不良、泻药和寄生虫病等。从这种植物中提取出的众多xanthone化合物具有广泛的生物活性,其中一些显示出抗癌和抗疟疾的潜力。网络药理学分析成功确定了关键生物活性化合物,如Rubraxanthone、Garcinone D、Norcowanin、Cowanol和Cowaxanthone及其主要蛋白质靶标(TNF、CTNNB1、SRC、NFKB1和MTOR),为我们深入了解了这些化合物抗癌作用的分子机制提供了重要见解。Graph Attention Network算法在数据增强后表现出优异的预测性能,R2达到0.98,RMSE为0.02,凸显其在预测基于xanthone化合物的pIC50值方面的准确性。此外,分子对接显示MTOR可能是Garcinia cowa诱导HeLa癌细胞毒性的潜在靶点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了癌症作为全球高死亡率疾病的特点和趋势,以及Garcinia cowa这种东南亚传统药用植物在治疗癌症方面的潜力。研究通过网络药理学分析确定了该植物中的关键生物活性化合物及其主要蛋白质靶点,并借助Graph Attention Network算法和分子对接技术,揭示了其在抗癌作用中的分子机制和潜在靶点。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症特点包括细胞异常增生失控、侵犯邻近组织以及向远处器官转移。
- Garcinia cowa是一种广泛用于治疗多种疾病的传统药用植物。
- 该植物中的xanthone化合物具有广泛的生物活性,一些化合物具有抗癌和抗疟疾的潜力。
- 网络药理学分析确定了Garcinia cowa中的关键生物活性化合物及其主要蛋白质靶点。
- Graph Attention Network算法在预测xanthone基化合物的pIC50值方面表现出优异的性能。
- 分子对接研究显示MTOR可能是Garcinia cowa诱导HeLa癌细胞毒性的潜在靶点。
点此查看论文截图

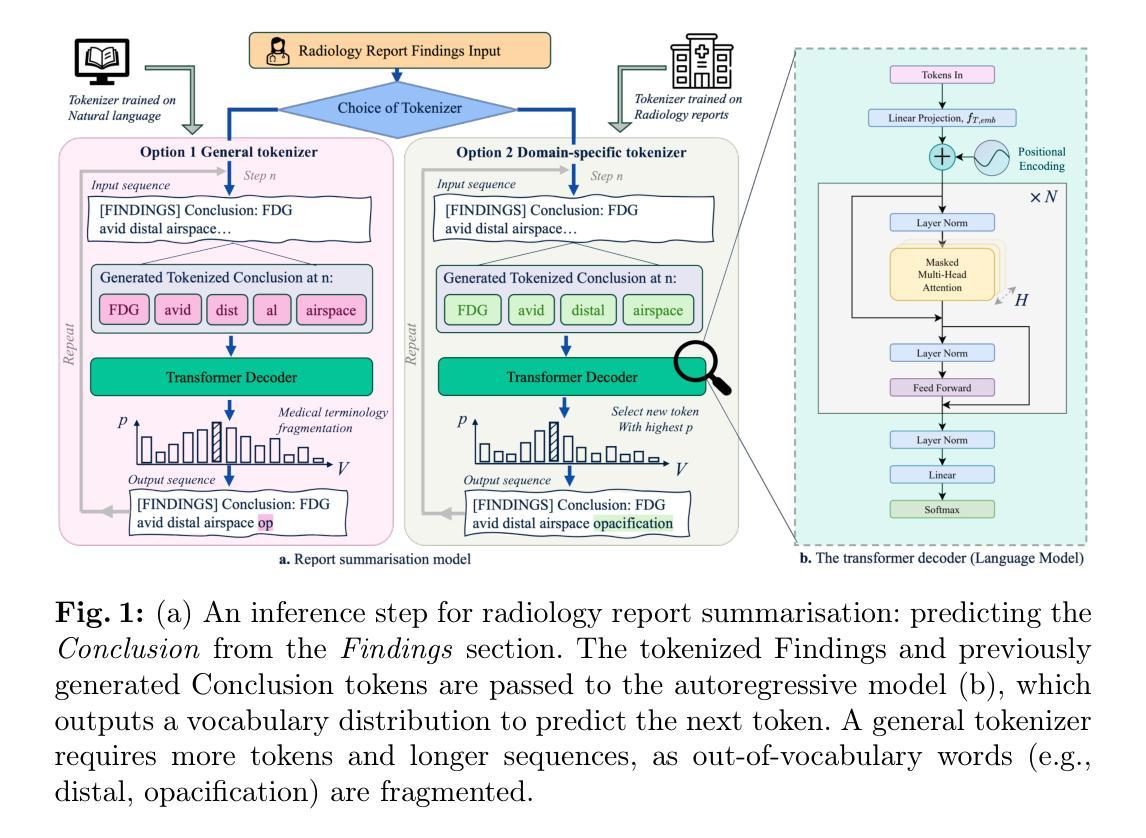
Specialised or Generic? Tokenization Choices for Radiology Language Models
Authors:Hermione Warr, Wentian Xu, Harry Anthony, Yasin Ibrahim, Daniel McGowan, Konstantinos Kamnitsas
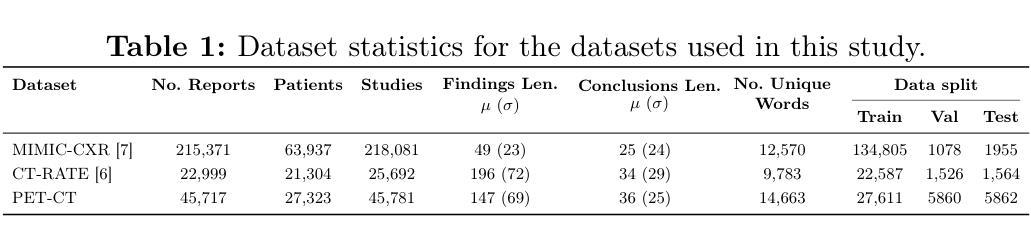
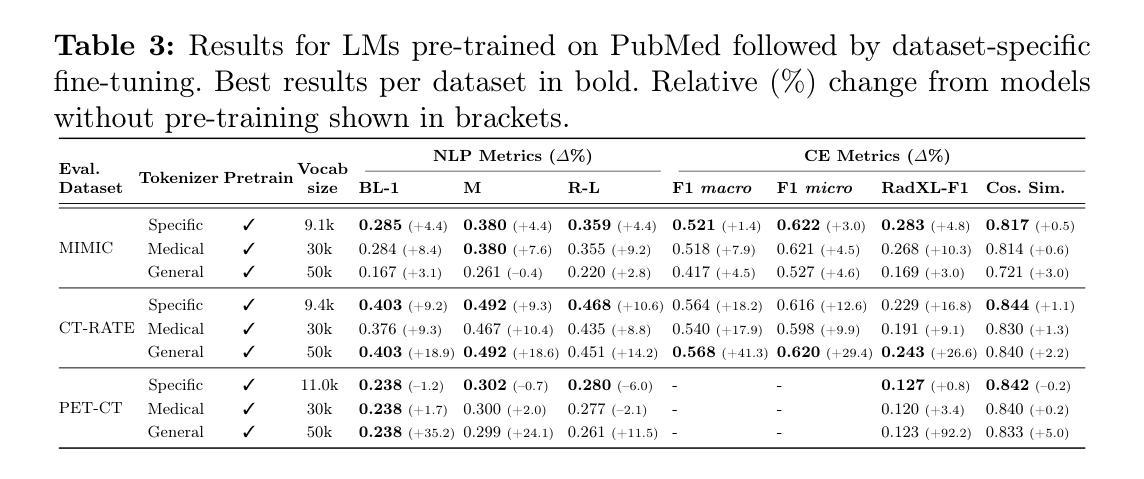
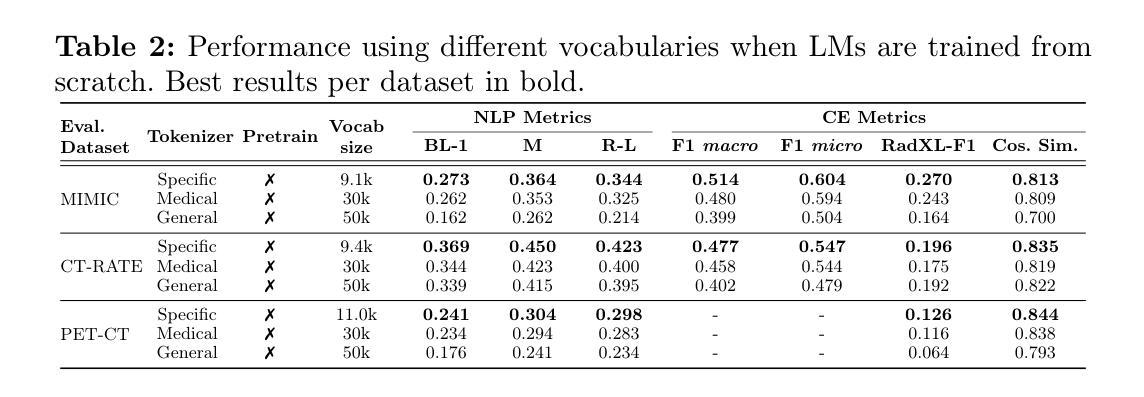
The vocabulary used by language models (LM) - defined by the tokenizer - plays a key role in text generation quality. However, its impact remains under-explored in radiology. In this work, we address this gap by systematically comparing general, medical, and domain-specific tokenizers on the task of radiology report summarisation across three imaging modalities. We also investigate scenarios with and without LM pre-training on PubMed abstracts. Our findings demonstrate that medical and domain-specific vocabularies outperformed widely used natural language alternatives when models are trained from scratch. Pre-training partially mitigates performance differences between tokenizers, whilst the domain-specific tokenizers achieve the most favourable results. Domain-specific tokenizers also reduce memory requirements due to smaller vocabularies and shorter sequences. These results demonstrate that adapting the vocabulary of LMs to the clinical domain provides practical benefits, including improved performance and reduced computational demands, making such models more accessible and effective for both research and real-world healthcare settings.
语言模型(LM)所使用的词汇由分词器定义,这在文本生成质量中起着关键作用。然而,其在放射学领域的影响尚未得到充分研究。在这项工作中,我们通过系统地比较三种成像模态下用于放射学报告摘要任务的通用、医疗和领域特定分词器来填补这一空白。我们还研究了有无在PubMed摘要上进行LM预训练的场景。我们的研究结果表明,当模型从头开始训练时,医疗和领域特定的词汇表现优于广泛使用的自然语言替代方案。预训练在一定程度上减轻了分词器之间的性能差异,而领域特定的分词器取得了最理想的结果。领域特定的分词器由于词汇量较小、序列较短,还减少了内存需求。这些结果表明,将LM的词汇适应临床领域提供了实际好处,包括提高性能和降低计算需求,使得这些模型在研究和现实世界的医疗环境中都更容易访问和更有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ELAMI@MICCAI2025
Summary
本文研究了在自然语言处理中的语言模型(LM)中,不同的分词器(tokenizer)对放射学报告摘要生成质量的影响。通过对通用、医疗和领域特定分词器的系统比较,发现医疗和领域特定的分词器在从头开始训练模型时表现优于广泛使用的自然语言处理分词器。预训练部分缓解了分词器之间的性能差异,而领域特定的分词器取得了最理想的结果。此外,领域特定的分词器由于词汇较小、序列较短,还降低了内存需求。研究结果表明,将语言模型的词汇适应临床领域具有实际效益,包括提高性能和降低计算需求,使得这样的模型在研究和现实医疗环境中更加可用和有效。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型(LM)中使用的分词器(tokenizer)对放射学报告摘要生成的质量有重要影响。
- 医疗和领域特定的分词器在训练模型时表现优于通用分词器。
- 预训练可以部分缓解不同分词器之间的性能差异。
- 领域特定的分词器取得最理想结果。
- 领域特定的分词器能降低内存需求,因为它们的词汇较小,序列较短。
- 适应临床领域的语言模型词汇有助于提高性能和降低计算需求。
点此查看论文截图