⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
A Cross-Modal Rumor Detection Scheme via Contrastive Learning by Exploring Text and Image internal Correlations
Authors:Bin Ma, Yifei Zhang, Yongjin Xian, Qi Li, Linna Zhou, Gongxun Miao
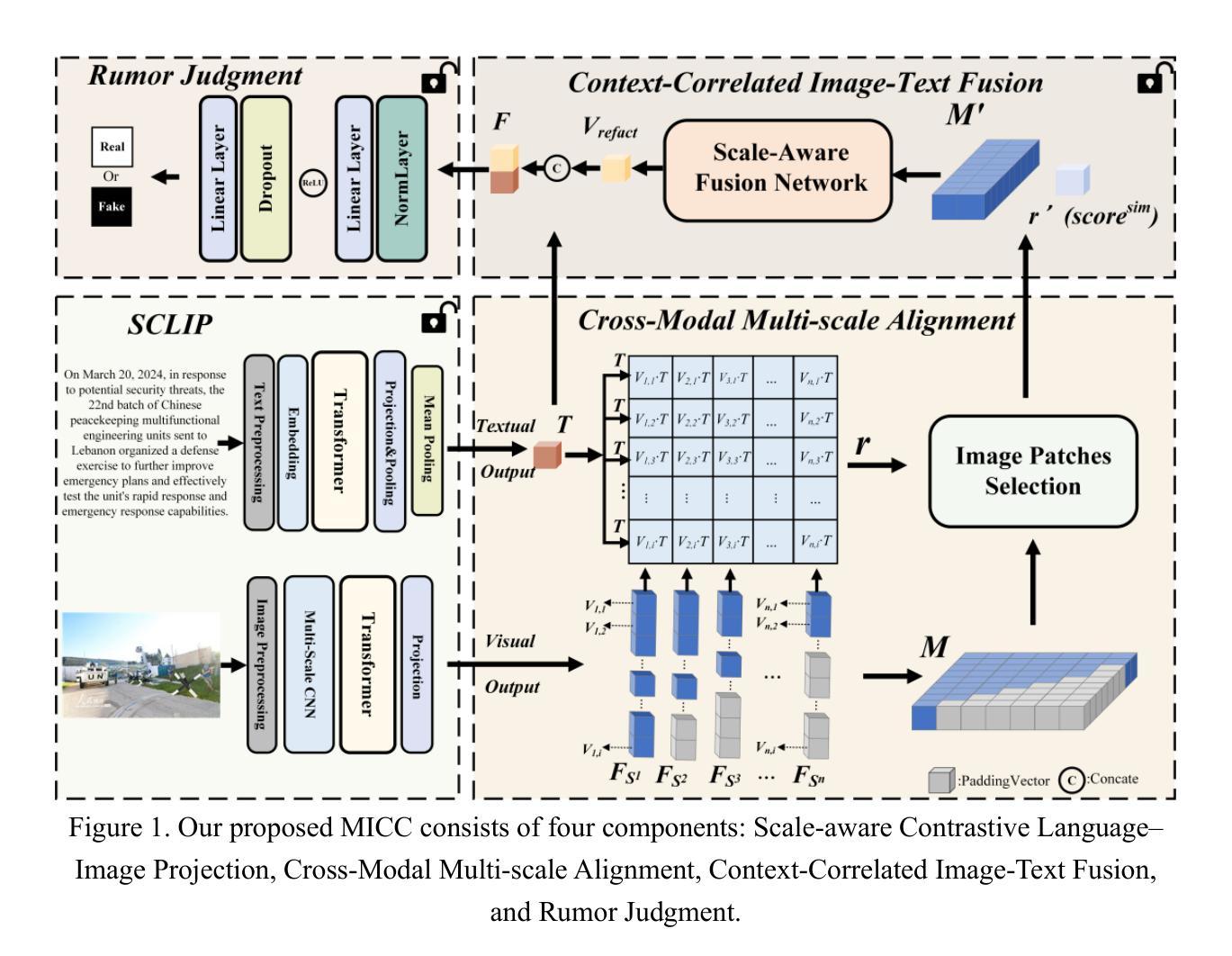
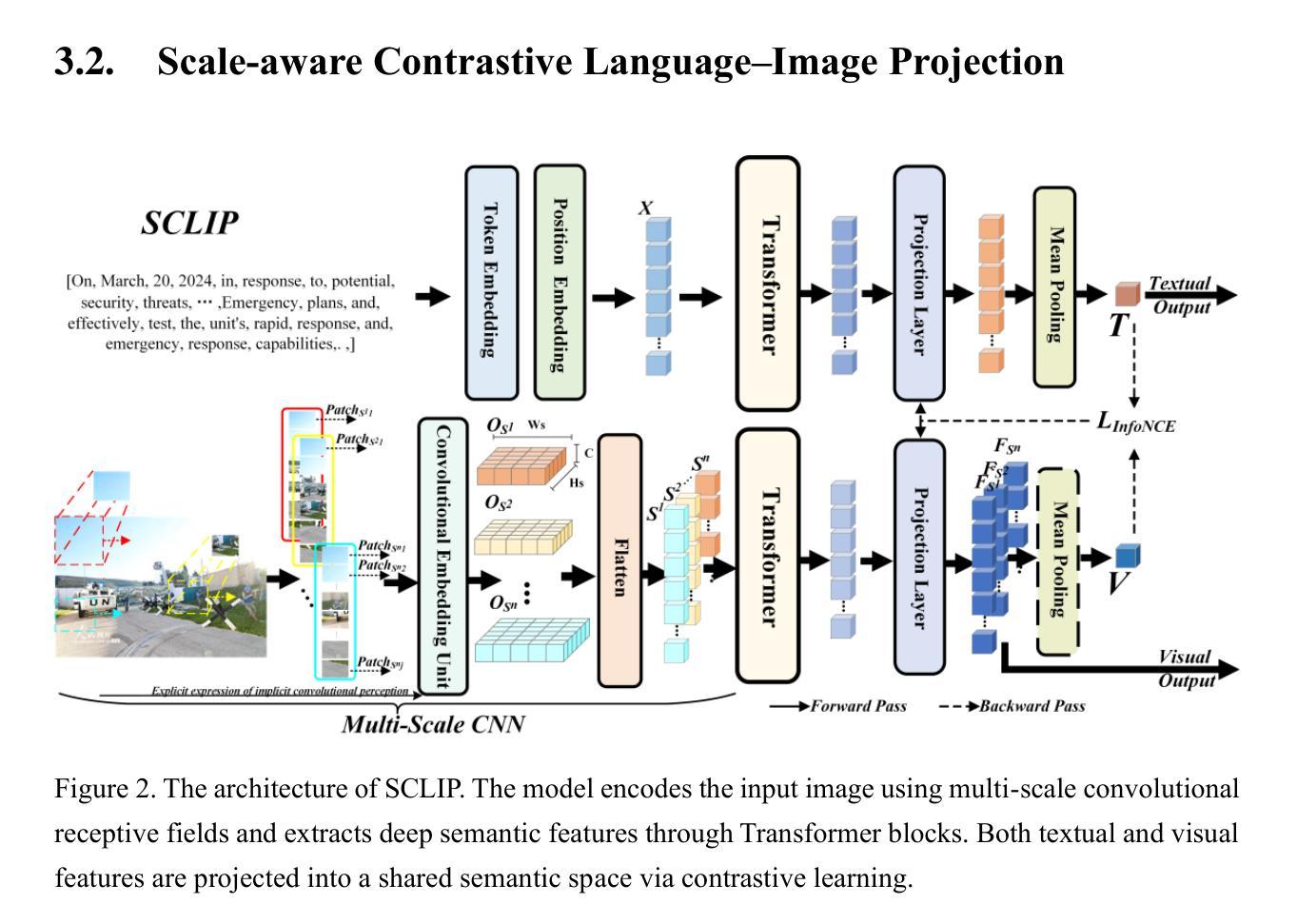
Existing rumor detection methods often neglect the content within images as well as the inherent relationships between contexts and images across different visual scales, thereby resulting in the loss of critical information pertinent to rumor identification. To address these issues, this paper presents a novel cross-modal rumor detection scheme based on contrastive learning, namely the Multi-scale Image and Context Correlation exploration algorithm (MICC). Specifically, we design an SCLIP encoder to generate unified semantic embeddings for text and multi-scale image patches through contrastive pretraining, enabling their relevance to be measured via dot-product similarity. Building upon this, a Cross-Modal Multi-Scale Alignment module is introduced to identify image regions most relevant to the textual semantics, guided by mutual information maximization and the information bottleneck principle, through a Top-K selection strategy based on a cross-modal relevance matrix constructed between the text and multi-scale image patches. Moreover, a scale-aware fusion network is designed to integrate the highly correlated multi-scale image features with global text features by assigning adaptive weights to image regions based on their semantic importance and cross-modal relevance. The proposed methodology has been extensively evaluated on two real-world datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that it achieves a substantial performance improvement over existing state-of-the-art approaches in rumor detection, highlighting its effectiveness and potential for practical applications.
现有的谣言检测方式往往忽略了图像内容以及不同视觉尺度下上下文与图像之间的内在关联,从而导致了与谣言识别相关的关键信息的丢失。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于对比学习的跨模态谣言检测方案,即多尺度图像与上下文关联探索算法(MICC)。具体来说,我们设计了一个SCLIP编码器,通过对比预训练生成文本和多尺度图像补丁的统一语义嵌入,使它们的相关性可以通过点积相似性来衡量。在此基础上,引入了一个跨模态多尺度对齐模块,通过互信息最大化与信息瓶颈原理的指导,通过文本和多尺度图像补丁之间构建的跨模态关联矩阵的Top-K选择策略,来识别与文本语义最相关的图像区域。此外,设计了一个尺度感知融合网络,通过根据图像区域的语义重要性和跨模态相关性分配自适应权重,将高度相关的多尺度图像特征与全局文本特征进行融合。该方法在两个真实数据集上进行了广泛评估。实验结果表明,与现有的最先进的谣言检测方法相比,该方法在谣言检测方面取得了显著的性能提升,凸显了其有效性和实际应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于对比学习,提出一种多尺度图像与文本上下文关联探索算法(MICC),用于跨模态谣言检测。通过设计SCLIP编码器生成文本和多尺度图像的统一语义嵌入,并利用跨模态多尺度对齐模块识别与文本语义最相关的图像区域。同时设计了一个尺度感知融合网络,将高度相关的多尺度图像特征与全局文本特征进行融合。实验结果表明,该方法在谣言检测上取得了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 现有谣言检测方法的局限性在于忽略了图像内容和不同视觉尺度间的上下文关系。
- 提出了一种基于对比学习的跨模态谣言检测方案MICC。
- 设计了SCLIP编码器,用于生成文本和多尺度图像的统一语义嵌入。
- 引入跨模态多尺度对齐模块,通过互信息最大化和信息瓶颈原则识别与文本语义最相关的图像区域。
- 采用Top-K选择策略,构建文本与多尺度图像之间的跨模态相关性矩阵。
- 设计了尺度感知融合网络,通过自适应权重将高度相关的多尺度图像特征与全局文本特征进行融合。
点此查看论文截图