⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
Remove360: Benchmarking Residuals After Object Removal in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Simona Kocour, Assia Benbihi, Torsten Sattler
Understanding what semantic information persists after object removal is critical for privacy-preserving 3D reconstruction and editable scene representations. In this work, we introduce a novel benchmark and evaluation framework to measure semantic residuals, the unintended semantic traces left behind, after object removal in 3D Gaussian Splatting. We conduct experiments across a diverse set of indoor and outdoor scenes, showing that current methods can preserve semantic information despite the absence of visual geometry. We also release Remove360, a dataset of pre/post-removal RGB images and object-level masks captured in real-world environments. While prior datasets have focused on isolated object instances, Remove360 covers a broader and more complex range of indoor and outdoor scenes, enabling evaluation of object removal in the context of full-scene representations. Given ground truth images of a scene before and after object removal, we assess whether we can truly eliminate semantic presence, and if downstream models can still infer what was removed. Our findings reveal critical limitations in current 3D object removal techniques and underscore the need for more robust solutions capable of handling real-world complexity. The evaluation framework is available at github.com/spatial-intelligence-ai/Remove360.git. Data are available at huggingface.co/datasets/simkoc/Remove360.
理解在移除物体后仍然存在的语义信息对于保护隐私的3D重建和可编辑场景表示至关重要。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的基准测试和评估框架,来测量3D高斯拼贴中物体移除后留下的无意中的语义痕迹。我们在室内和室外场景进行了实验,结果表明,即使在没有视觉几何的情况下,当前的方法也可以保留语义信息。我们还发布了Remove360数据集,其中包含在现实环境中捕获的预/后移除RGB图像和对象级掩膜。虽然先前的数据集主要集中在孤立的物体实例上,但Remove360涵盖了更广泛和更复杂的室内和室外场景,能够在完整的场景表示中评估物体移除。给定物体移除前后的场景地面真实图像,我们评估是否真正消除了语义存在,以及下游模型是否仍然能够推断出已移除的内容。我们的研究结果揭示了当前3D物体移除技术的关键局限性,并强调了需要更稳健的解决方案来处理现实世界的复杂性。评估框架可在github.com/spatial-intelligence-ai/Remove360.git上找到。数据可在huggingface.co/datasets/simkoc/Remove360上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2503.17574
Summary
本文介绍了在隐私保护的三维重建和可编辑场景表示中,理解在物体移除后哪些语义信息会残留下来是非常重要的。为此,研究者们引入了一个新的基准测试与评估框架来衡量三维高斯拼贴中物体移除后所留下的无意中的语义痕迹。实验显示,即便没有视觉几何的存在,当前的方法也能保留语义信息。同时,还发布了Remove360数据集,包含真实环境中预移除和未移除的RGB图像以及物体级别的掩膜。与之前的数据集不同,Remove360涵盖了室内和室外场景的广泛范围,能够在完整的场景表示中评估物体的移除。评估结果揭示了当前三维物体移除技术的关键局限性,并强调了需要更稳健的解决方案来处理真实世界的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 理解物体移除后语义信息的保留对于隐私保护的三维重建和场景表示至关重要。
- 引入了一个新的基准测试与评估框架来衡量三维空间中物体移除后的语义残留。
- 实验表明,当前的方法能够在没有视觉几何的情况下保留语义信息。
- 发布了Remove360数据集,包含真实环境中预移除和未移除的RGB图像和物体级别的掩膜。
- Remove360数据集不同于以往的数据集,涵盖了室内和室外更广泛复杂的场景。
- 评估结果显示当前三维物体移除技术存在关键局限性。
点此查看论文截图
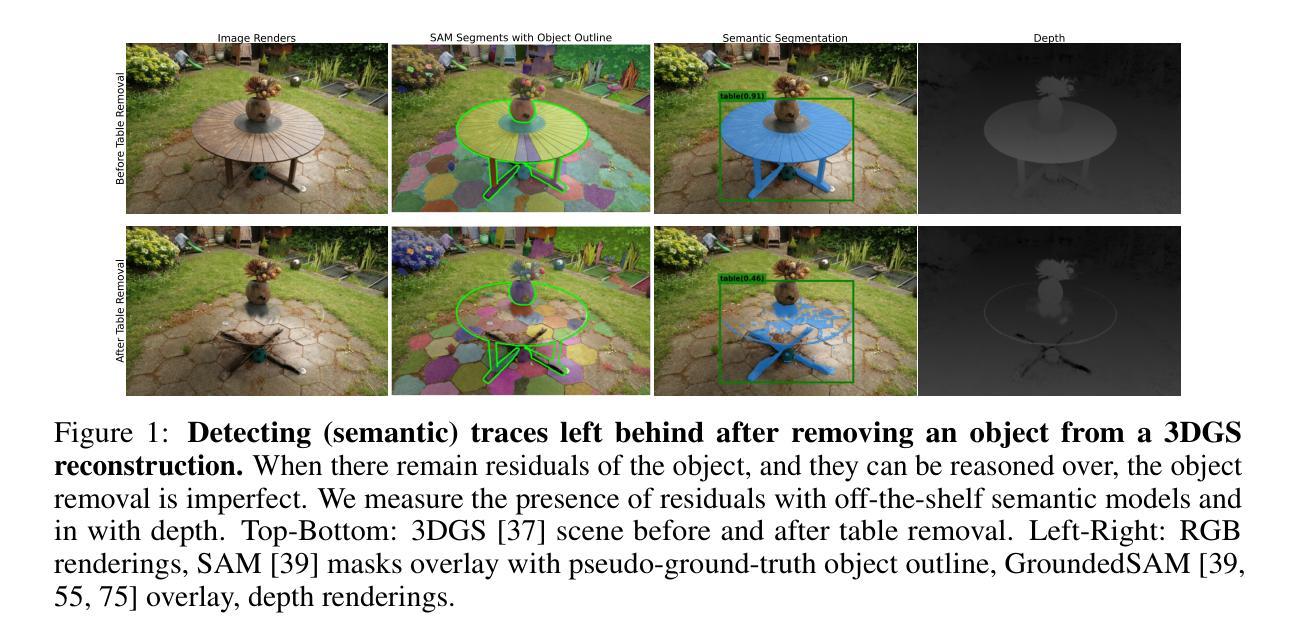




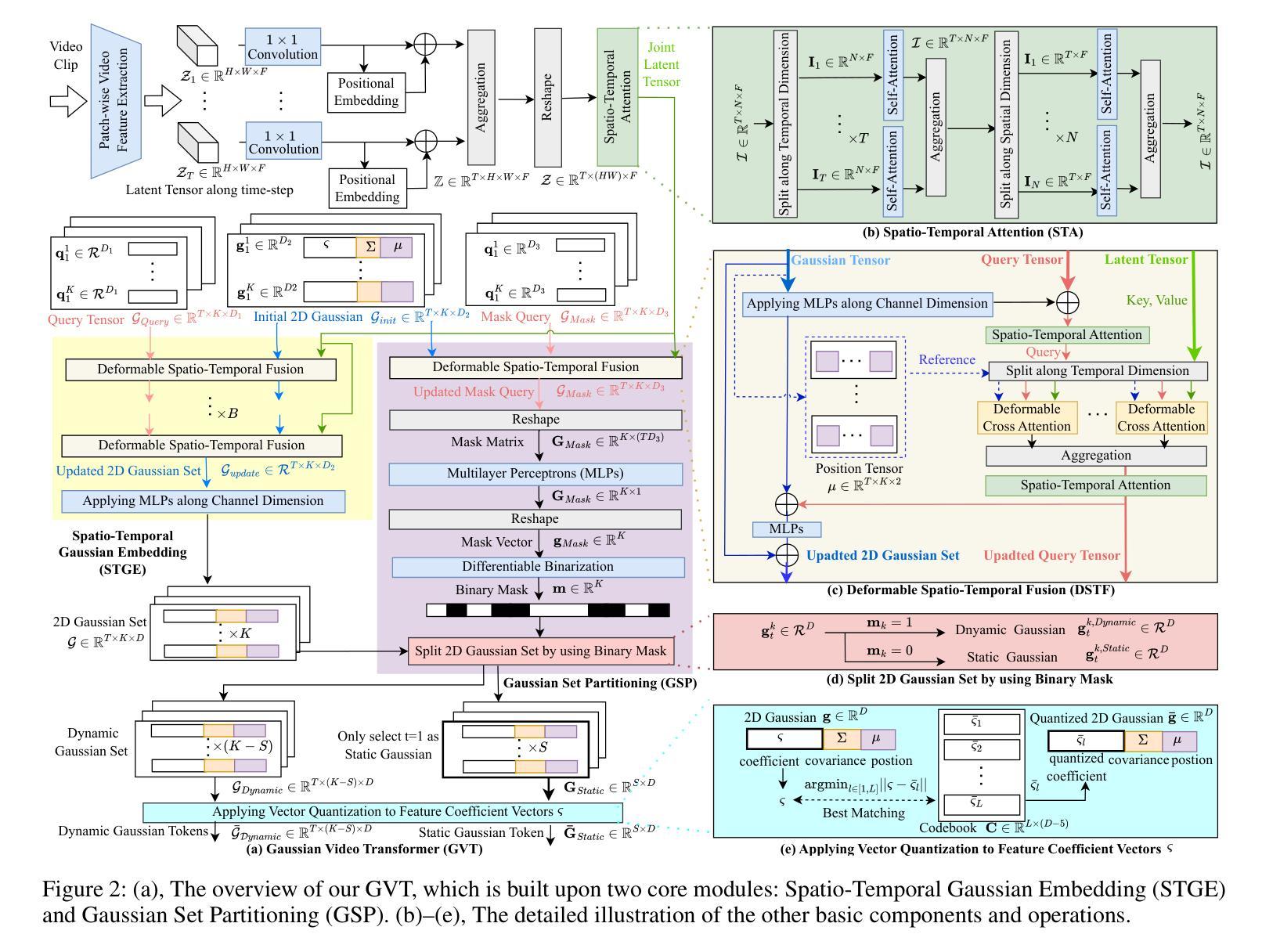
Versatile Video Tokenization with Generative 2D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhenghao Chen, Zicong Chen, Lei Liu, Yiming Wu, Dong Xu
Video tokenization procedure is critical for a wide range of video processing tasks. Most existing approaches directly transform video into fixed-grid and patch-wise tokens, which exhibit limited versatility. Spatially, uniformly allocating a fixed number of tokens often leads to over-encoding in low-information regions. Temporally, reducing redundancy remains challenging without explicitly distinguishing between static and dynamic content. In this work, we propose the Gaussian Video Transformer (GVT), a versatile video tokenizer built upon a generative 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) strategy. We first extract latent rigid features from a video clip and represent them with a set of 2D Gaussians generated by our proposed Spatio-Temporal Gaussian Embedding (STGE) mechanism in a feed-forward manner. Such generative 2D Gaussians not only enhance spatial adaptability by assigning higher (resp., lower) rendering weights to regions with higher (resp., lower) information content during rasterization, but also improve generalization by avoiding per-video optimization.To enhance the temporal versatility, we introduce a Gaussian Set Partitioning (GSP) strategy that separates the 2D Gaussians into static and dynamic sets, which explicitly model static content shared across different time-steps and dynamic content specific to each time-step, enabling a compact representation.We primarily evaluate GVT on the video reconstruction, while also assessing its performance on action recognition and compression using the UCF101, Kinetics, and DAVIS datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GVT achieves a state-of-the-art video reconstruction quality, outperforms the baseline MAGVIT-v2 in action recognition, and delivers comparable compression performance.
视频令牌化程序对于广泛的视频处理任务至关重要。现有的大多数方法直接将视频转换为固定网格和补丁令牌,这表现出有限的灵活性。在空间上,均匀分配固定数量的令牌往往会导致低信息区域的过度编码。在时间上,如何在不显式区分静态和动态内容的情况下减少冗余仍然是一个挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了高斯视频转换器(GVT),这是一种基于生成式二维高斯拼贴(2DGS)策略的通用视频令牌生成器。我们首先从一个视频剪辑中提取潜在刚性特征,并以前馈方式使用我们提出的空间时间高斯嵌入(STGE)机制来生成一组二维高斯分布来表示它们。这种生成式的二维高斯分布不仅通过在光线投射过程中为信息含量较高(较低)的区域分配较高(较低)的渲染权重来增强空间适应性,而且通过避免针对每个视频的优化来提高泛化能力。为了提高时间灵活性,我们引入了高斯集分割(GSP)策略,该策略将二维高斯分布分为静态集和动态集,显式地模拟不同时间步之间共享的静态内容和每个时间步特有的动态内容,从而实现紧凑表示。我们主要使用UCF101、Kinetics和DAVIS数据集评估GVT在视频重建方面的表现,同时评估其在动作识别和压缩方面的性能。大量实验表明,GVT在视频重建方面达到了最先进的水平,在动作识别方面优于MAGVIT-v2基线模型,压缩性能也具有可比性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文本介绍了一种新型的视频令牌化程序,该程序使用生成式二维高斯印模策略构建了通用视频令牌器,针对视频处理任务的广泛需求,实现了高效的视频处理。提出了一种基于二维高斯分布的动态生成视频特征嵌入技术,增强时空自适应能力的同时避免针对视频的单独优化,从而在场景区域生成可调整的、结构化的视频令牌集合。使用高斯集合划分策略分离二维高斯,建模不同时间步长间的静态和动态内容,为视频的重建、动作识别和压缩提供了先进的方法。通过UCF101、Kinetics和DAVIS数据集的实验验证了其在视频重建上的优越性,同时还在动作识别和压缩上展现了竞争力。
关键要点
- 视频令牌化对于各种视频处理任务至关重要。现有方法直接将视频转换为固定网格和补丁令牌,表现出有限的灵活性。
- 提出了一种基于生成式二维高斯印模策略的通用视频令牌器——高斯视频转换器(GVT)。
- 使用时空高斯嵌入(STGE)机制提取视频的潜在刚性特征,并使用生成式二维高斯表示增强时空适应性。
- 高斯集合划分(GSP)策略用于分离静态和动态内容,实现紧凑的视频表示。
点此查看论文截图

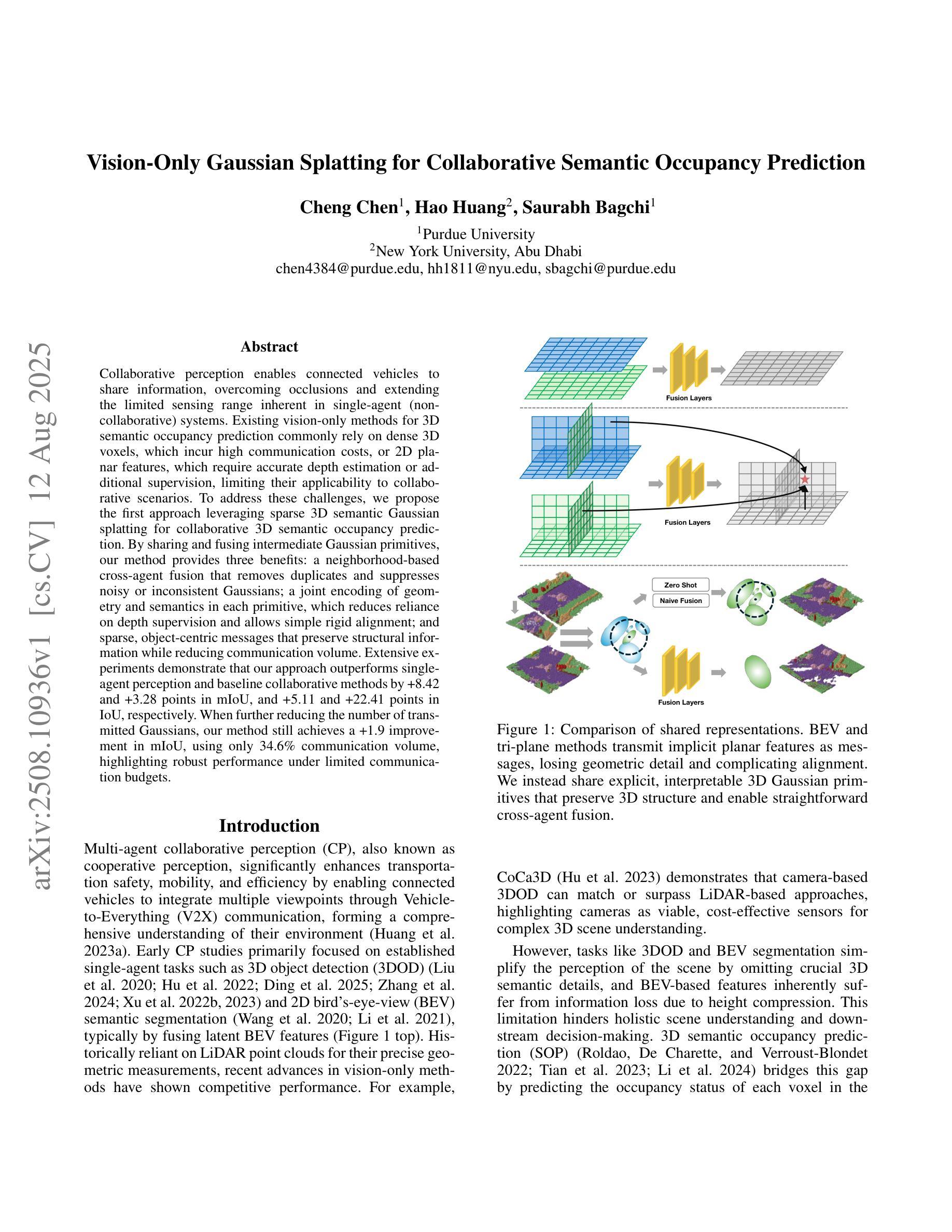
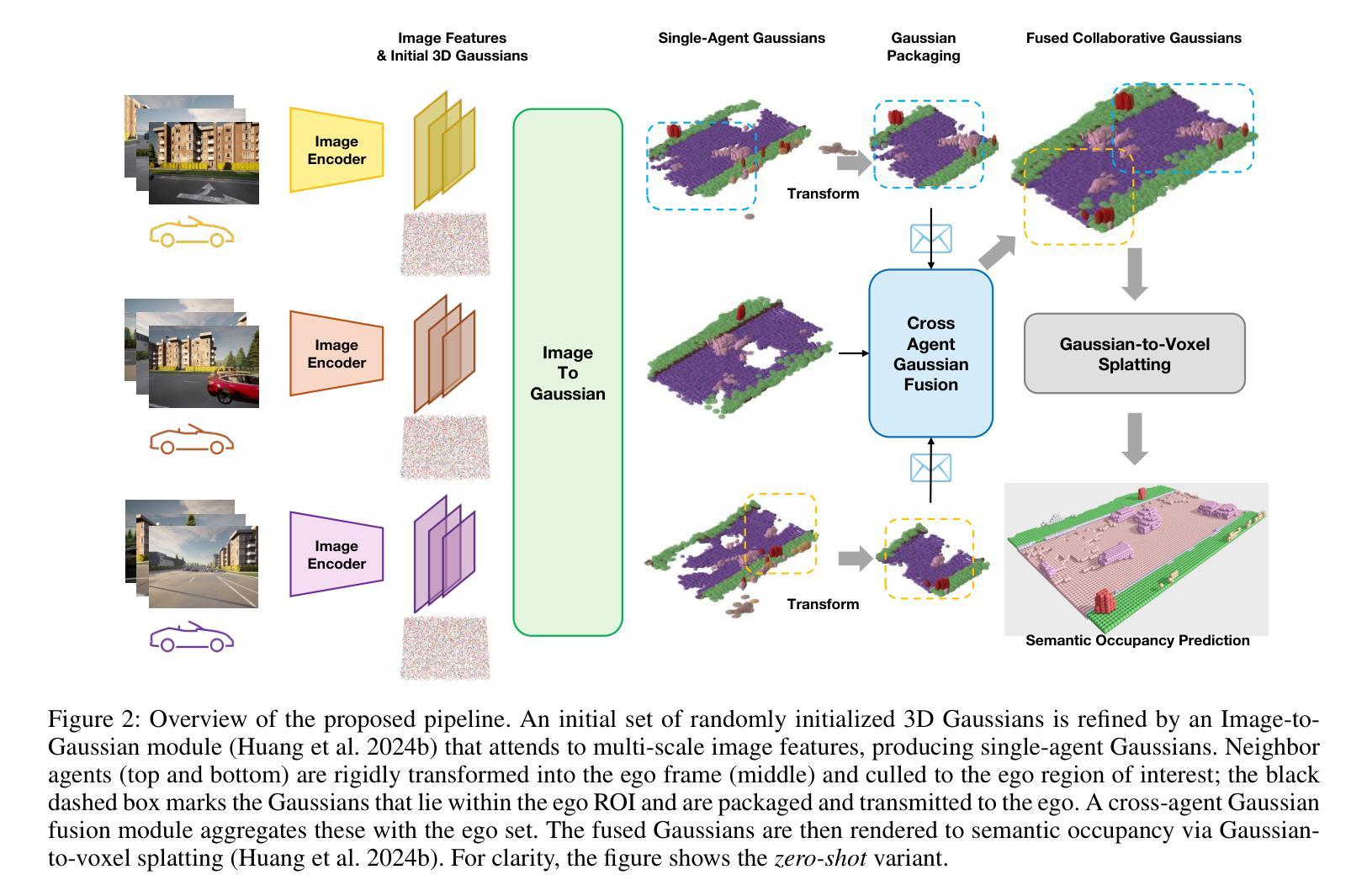
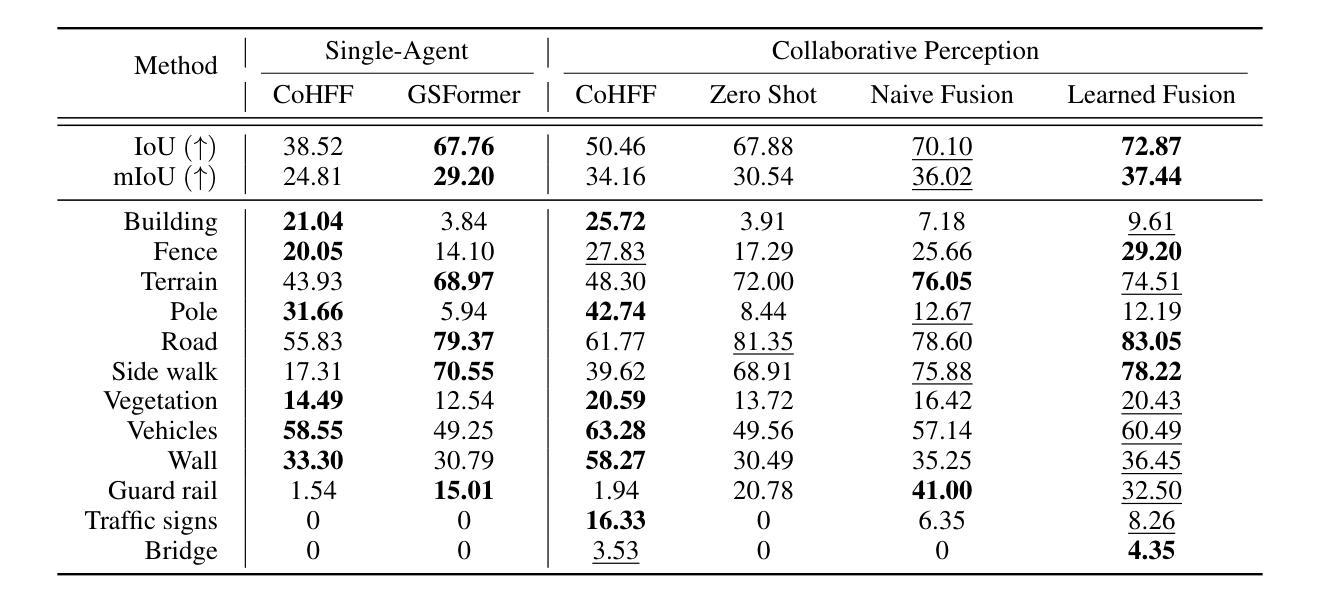
Vision-Only Gaussian Splatting for Collaborative Semantic Occupancy Prediction
Authors:Cheng Chen, Hao Huang, Saurabh Bagchi
Collaborative perception enables connected vehicles to share information, overcoming occlusions and extending the limited sensing range inherent in single-agent (non-collaborative) systems. Existing vision-only methods for 3D semantic occupancy prediction commonly rely on dense 3D voxels, which incur high communication costs, or 2D planar features, which require accurate depth estimation or additional supervision, limiting their applicability to collaborative scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose the first approach leveraging sparse 3D semantic Gaussian splatting for collaborative 3D semantic occupancy prediction. By sharing and fusing intermediate Gaussian primitives, our method provides three benefits: a neighborhood-based cross-agent fusion that removes duplicates and suppresses noisy or inconsistent Gaussians; a joint encoding of geometry and semantics in each primitive, which reduces reliance on depth supervision and allows simple rigid alignment; and sparse, object-centric messages that preserve structural information while reducing communication volume. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms single-agent perception and baseline collaborative methods by +8.42 and +3.28 points in mIoU, and +5.11 and +22.41 points in IoU, respectively. When further reducing the number of transmitted Gaussians, our method still achieves a +1.9 improvement in mIoU, using only 34.6% communication volume, highlighting robust performance under limited communication budgets.
协同感知使连接车辆能够共享信息,克服遮挡问题并扩展单个代理(非协同)系统固有的有限感知范围。现有的仅依赖视觉的3D语义占用预测方法通常依赖于密集的3D体素,这会产生较高的通信成本,或者依赖于2D平面特征,这需要准确的深度估计或额外的监督,从而限制了它们在协同场景中的应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们首次提出了一种利用稀疏3D语义高斯涂抹方法进行协同3D语义占用预测的方法。通过共享和融合中间的Gaussian primitives(高斯原始数据),我们的方法提供了以下三个好处:基于邻域的跨代理融合,可以消除重复并抑制嘈杂或不一致的高斯数据;每个原始数据中的几何和语义联合编码,减少了深度监督的依赖,并允许简单的刚体对齐;以及稀疏的、以对象为中心的消息,保留结构信息的同时减少了通信量。大量实验表明,我们的方法在mIoU和IoU指标上分别比单代理感知和基线协同方法高出+8.42和+3.28点,以及+5.11和+22.41点。在进一步减少传输的高斯数据量时,我们的方法仍能在mIoU上实现+1.9的提升,仅使用34.6%的通信量,凸显了在有限的通信预算下表现稳健。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了利用稀疏三维语义高斯平铺技术实现协作三维语义占用预测的方法。该方法通过共享和融合中间高斯基元,实现邻居间的跨智能体融合,删除重复项并抑制噪声或不一致的高斯分布;同时采用几何和语义的联合编码,减少对深度监督的依赖,允许简单的刚体对齐;此外,稀疏、以对象为中心的消息保留了结构信息,同时减少了通信量。实验表明,该方法在单智能体感知和基准协作方法的基础上,mIoU提高了8.42点和3.28点,IoU提高了5.11点和22.41点。在减少传输的高斯数量的情况下,该方法仍能提高mIoU 1.9点,同时仅使用34.6%的通信量。
Key Takeaways
- 协作感知使连接车辆能够共享信息,克服遮挡并扩展单一智能体系统的有限感知范围。
- 现有仅依赖视觉的3D语义占用预测方法通常依赖于密集的3D体素,这导致了高通信成本,或依赖于2D平面特征,这需要准确的深度估计或额外的监督,限制了它们在协作场景中的应用。
- 本文提出了利用稀疏三维语义高斯平铺的协作三维语义占用预测方法,通过共享和融合中间高斯基元来实现。
- 该方法实现了基于邻居的跨智能体融合,可以删除重复项并抑制噪声或不一致的高斯分布。
- 几何和语义的联合编码减少了深度监督的依赖,允许简单的刚体对齐。
- 该方法采用稀疏、以对象为中心的消息,保留了结构信息并减少了通信量。
点此查看论文截图

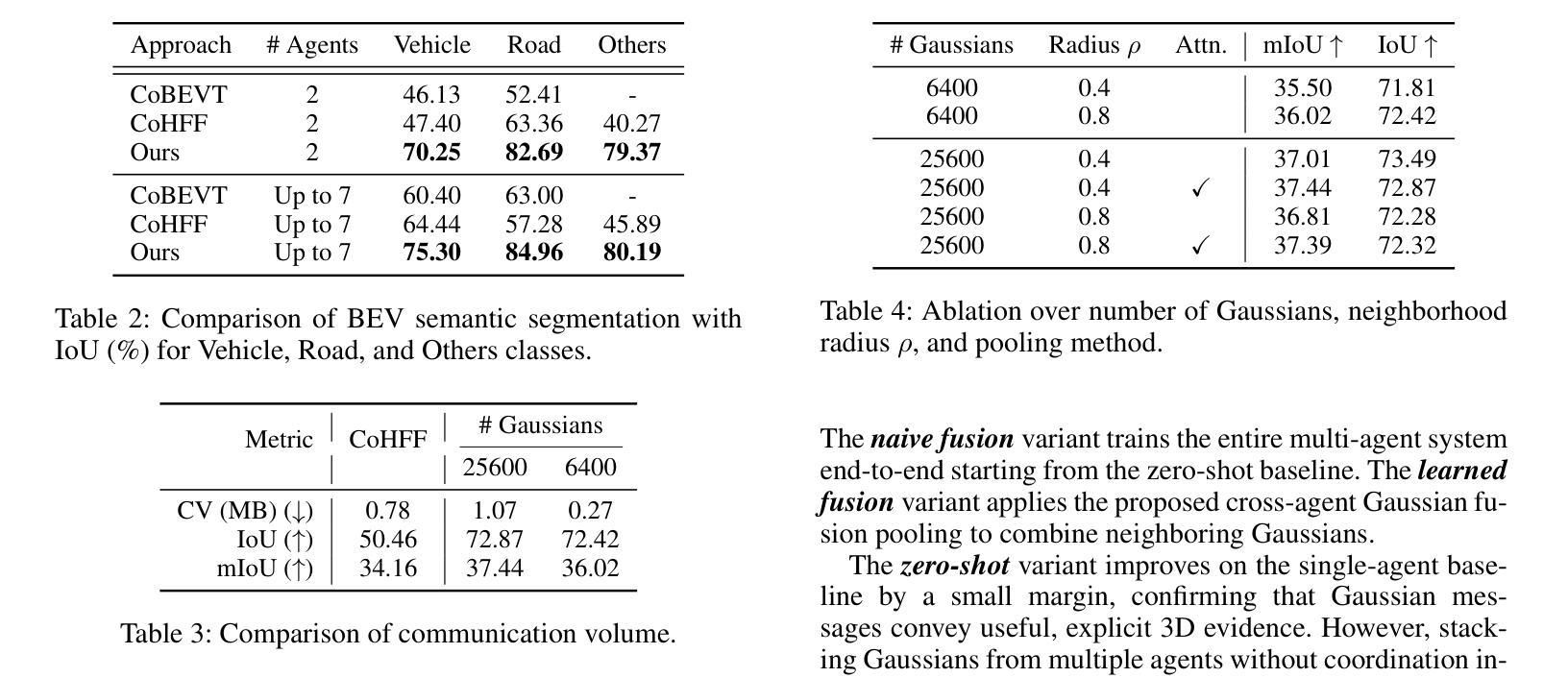
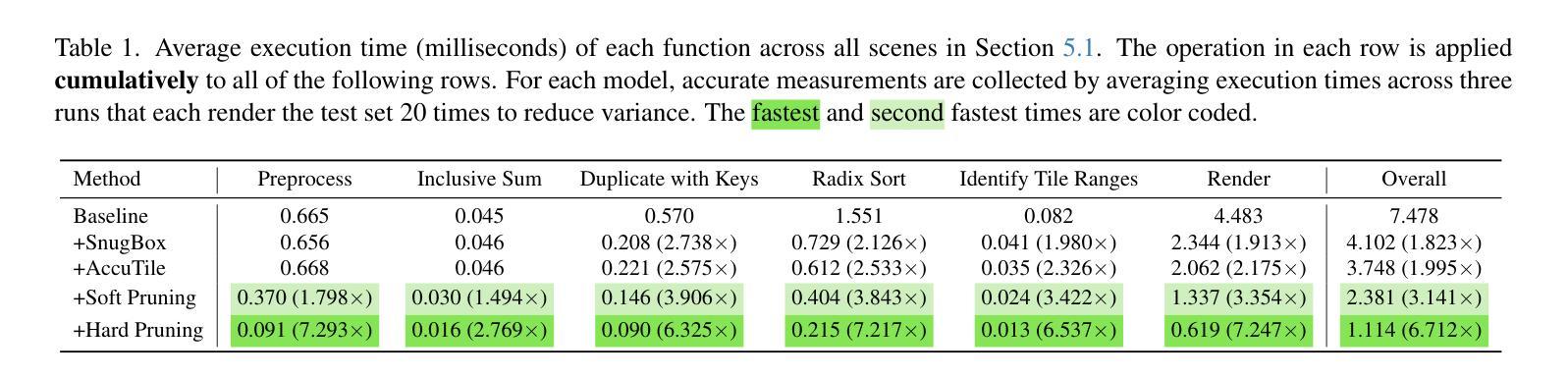
Multi-Sample Anti-Aliasing and Constrained Optimization for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zheng Zhou, Jia-Chen Zhang, Yu-Jie Xiong, Chun-Ming Xia
Recent advances in 3D Gaussian splatting have significantly improved real-time novel view synthesis, yet insufficient geometric constraints during scene optimization often result in blurred reconstructions of fine-grained details, particularly in regions with high-frequency textures and sharp discontinuities. To address this, we propose a comprehensive optimization framework integrating multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) with dual geometric constraints. Our system computes pixel colors through adaptive blending of quadruple subsamples, effectively reducing aliasing artifacts in high-frequency components. The framework introduces two constraints: (a) an adaptive weighting strategy that prioritizes under-reconstructed regions through dynamic gradient analysis, and (b) gradient differential constraints enforcing geometric regularization at object boundaries. This targeted optimization enables the model to allocate computational resources preferentially to critical regions requiring refinement while maintaining global consistency. Extensive experimental evaluations across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in detail preservation, particularly in preserving high-frequency textures and sharp discontinuities, while maintaining real-time rendering efficiency. Quantitative metrics and perceptual studies confirm statistically significant improvements over baseline approaches in both structural similarity (SSIM) and perceptual quality (LPIPS).
在3D高斯贴图技术方面,最近的进展极大地提高了实时新型视图合成的质量。然而,在场景优化过程中几何约束不足常常导致精细细节的模糊重建,特别是在高频纹理和尖锐不连续区域。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种综合优化框架,将多重采样抗锯齿(MSAA)与双重几何约束相结合。我们的系统通过自适应混合四个子样本来计算像素颜色,有效地减少了高频组件中的锯齿状伪影。该框架引入了两个约束:(a)一种自适应加权策略,通过动态梯度分析优先处理重建不足的区域;(b)梯度差分约束,在物体边界处实施几何正则化。这种有针对性的优化使模型能够优先分配计算资源到需要精细化的关键区域,同时保持全局一致性。在多个基准测试上的广泛实验评估表明,我们的方法在细节保留方面达到了最先进的技术性能,特别是在保留高频纹理和尖锐不连续性方面,同时保持了实时渲染的效率。定量指标和感知研究证实,与基准方法相比,我们的方法在结构相似性(SSIM)和感知质量(LPIPS)方面都有统计上的显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,三维高斯绘制技术的新进展极大地推动了实时新型视图合成的发展。但场景优化时几何约束不足常常导致精细细节重建模糊,特别是在高频纹理和清晰边界区域。为此,我们提出了一种综合优化框架,将多重采样抗锯齿技术与双重几何约束相结合。我们的系统通过自适应混合四个子样本来计算像素颜色,有效减少高频成分的锯齿状伪影。该框架引入了两项约束:一是自适应加权策略,通过动态梯度分析优先处理重建不足的区域;二是梯度差异约束,在物体边界处实施几何正则化。这种有针对性的优化使模型能够优先分配计算资源到需要精细化的关键区域,同时保持全局一致性。跨多个基准的广泛实验评估表明,我们的方法在细节保留方面达到了最新技术水平,特别是在保持高频纹理和清晰边界方面,同时保持了实时渲染效率。
Key Takeaways
- 近期三维高斯绘制技术的新进展提升了实时新型视图合成的质量。
- 场景优化时几何约束不足会导致精细细节重建模糊。
- 提出了一种综合优化框架,结合多重采样抗锯齿与双重几何约束。
- 通过自适应混合四个子样本来计算像素颜色,减少高频成分的锯齿状伪影。
- 框架包含两项重要约束:自适应加权策略和梯度差异约束。
- 方法在细节保留方面表现优异,特别是在高频纹理和清晰边界的保留上。
点此查看论文截图
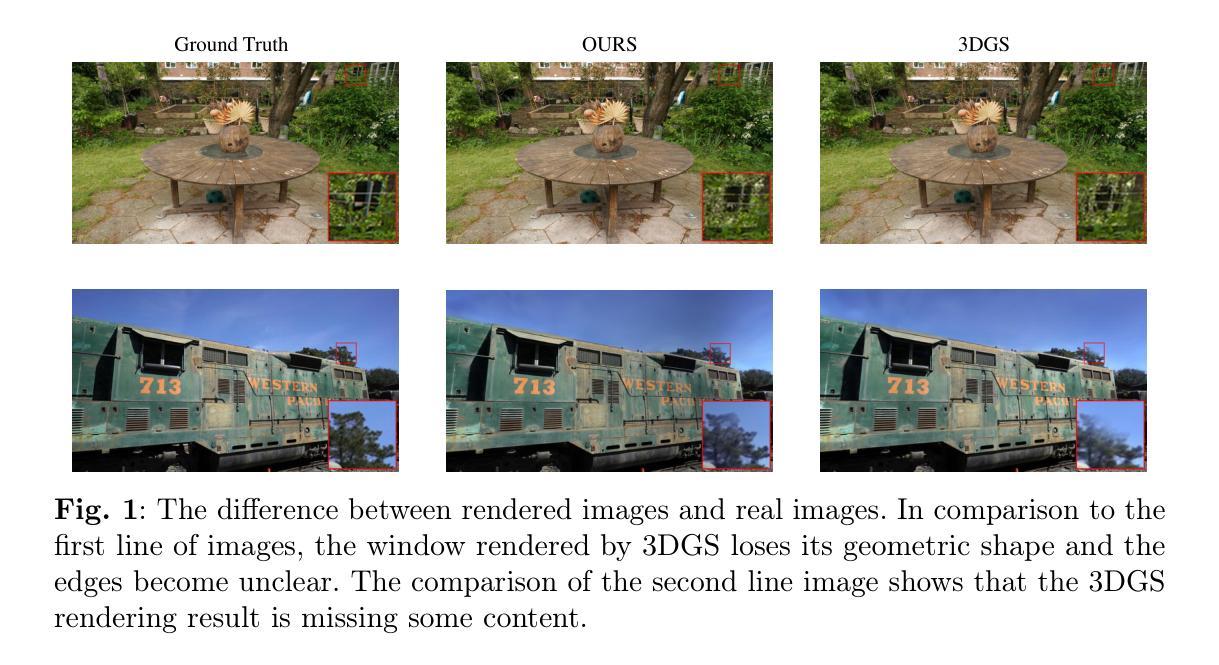


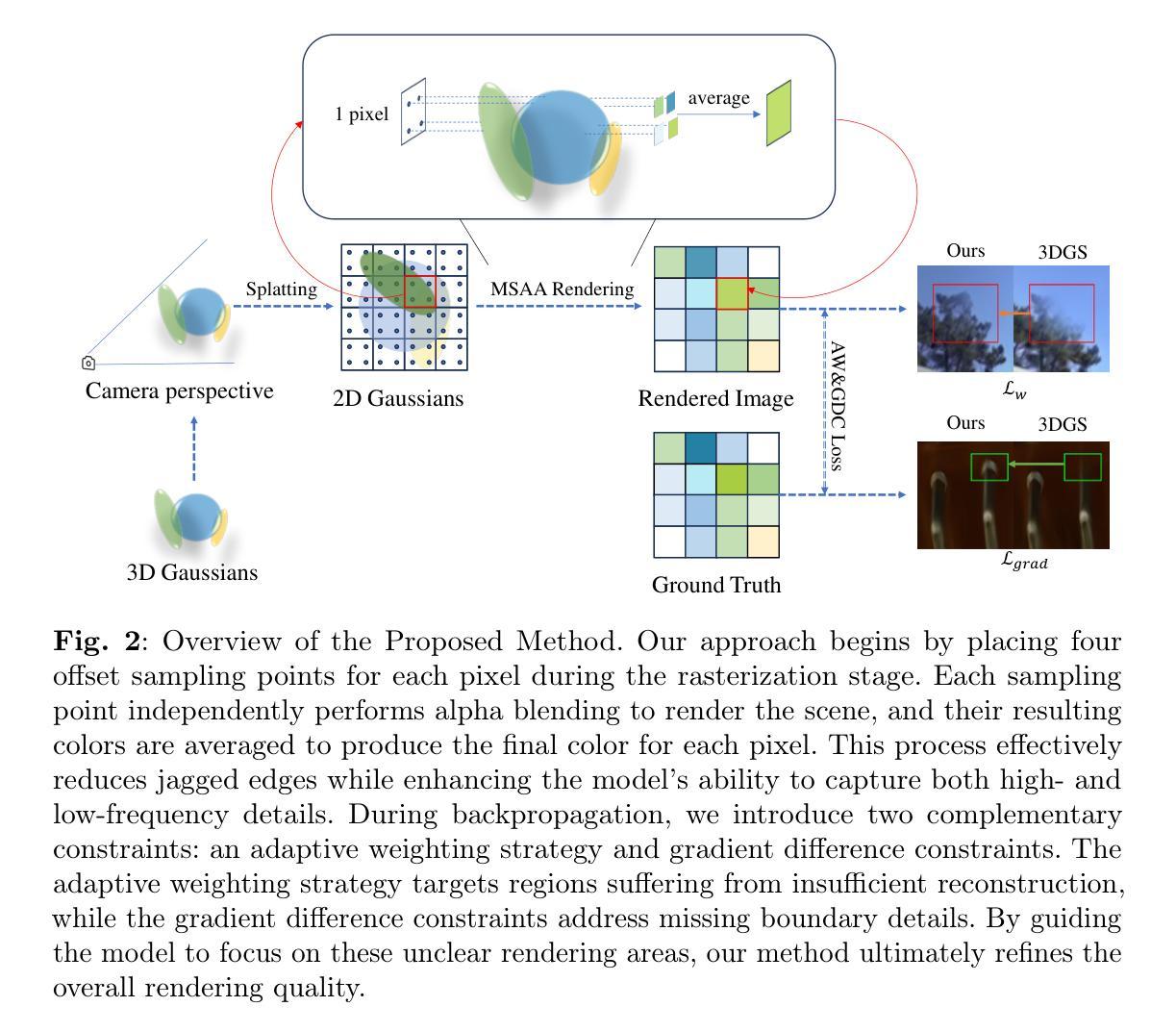
A Survey on 3D Gaussian Splatting Applications: Segmentation, Editing, and Generation
Authors:Shuting He, Peilin Ji, Yitong Yang, Changshuo Wang, Jiayi Ji, Yinglin Wang, Henghui Ding
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a powerful alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) for 3D scene representation, offering high-fidelity photorealistic rendering with real-time performance. Beyond novel view synthesis, the explicit and compact nature of 3DGS enables a wide range of downstream applications that require geometric and semantic understanding. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of recent progress in 3DGS applications. It first introduces 2D foundation models that support semantic understanding and control in 3DGS applications, followed by a review of NeRF-based methods that inform their 3DGS counterparts. We then categorize 3DGS applications into segmentation, editing, generation, and other functional tasks. For each, we summarize representative methods, supervision strategies, and learning paradigms, highlighting shared design principles and emerging trends. Commonly used datasets and evaluation protocols are also summarized, along with comparative analyses of recent methods across public benchmarks. To support ongoing research and development, a continually updated repository of papers, code, and resources is maintained at https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications.
3D高斯贴图(3DGS)作为一种强大的技术,最近作为神经辐射场(NeRF)的替代方案在三维场景表示中崭露头角,它以实时性能提供高保真照片级渲染。除了新颖视图合成,3DGS的明确和紧凑性质使得它在需要大量几何和语义理解的下游应用方面具有广泛的可能性。这篇综述全面概述了3DGS应用的最新进展。它首先介绍了支持3DGS应用中语义理解和控制的二维基础模型,然后回顾了为3DGS同行提供信息的基于NeRF的方法。我们将3DGS应用分类为分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务。对于每一项任务,我们总结了代表性的方法、监督策略和学习范式,并强调了共享设计原则和新兴趋势。本文还总结了常用的数据集和评估协议,以及近期方法在公开基准测试上的比较分析。为了支持持续的研究和开发,我们在https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications上维护了一个持续更新的论文、代码和资源仓库。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF GitHub Repo: https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications
Summary
3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)作为神经辐射场(NeRF)的替代方案,以其明确、紧凑的特性,在三维场景表示中展现出强大的能力,支持高质量的光照真实渲染和实时性能。除了新视角合成,3DGS还广泛应用于需要几何和语义理解的各种下游应用。本文全面概述了3DGS应用的最新进展,介绍了支持3DGS应用的语义理解和控制的二维基础模型,分类介绍了3DGS在分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务中的应用,并总结了常用数据集和评估协议。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 是一种强大的3D场景表示方法,可替代神经辐射场(NeRF)。
- 3DGS 提供了高质量的光照真实渲染和实时性能。
- 3DGS 具有广泛的应用范围,包括分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务。
- 文中介绍了支持3DGS应用的语义理解和控制的二维基础模型。
- 文章对NeRF-based方法进行了回顾,这些方法对3DGS有启示作用。
- 文章总结了常用数据集和评估协议,并对近期方法在公共基准测试上进行了比较分析。
点此查看论文截图

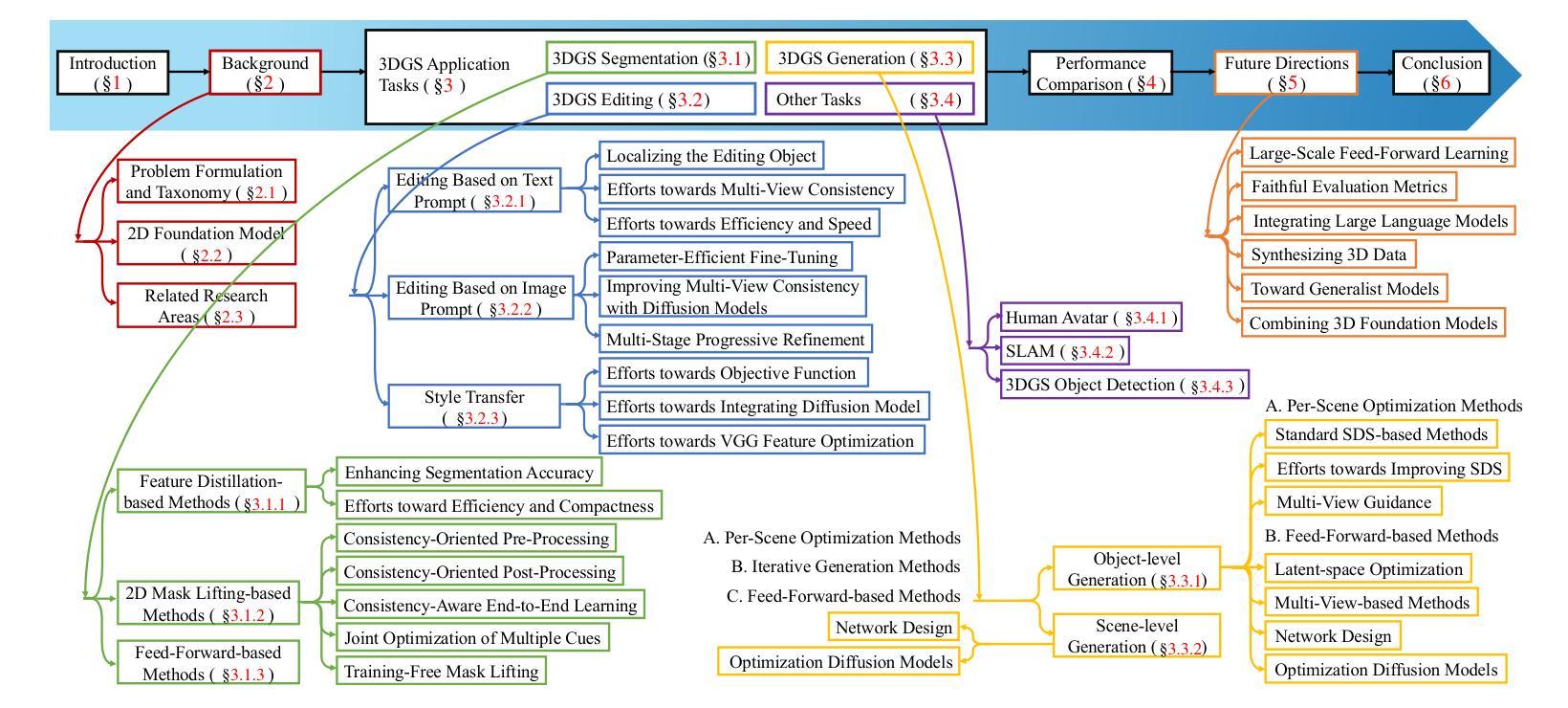
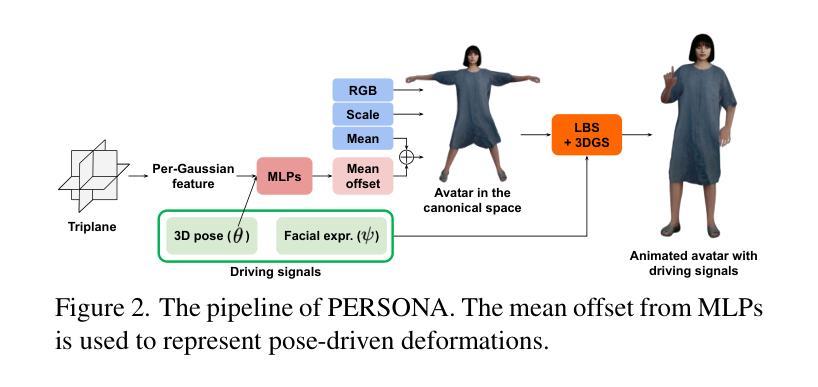
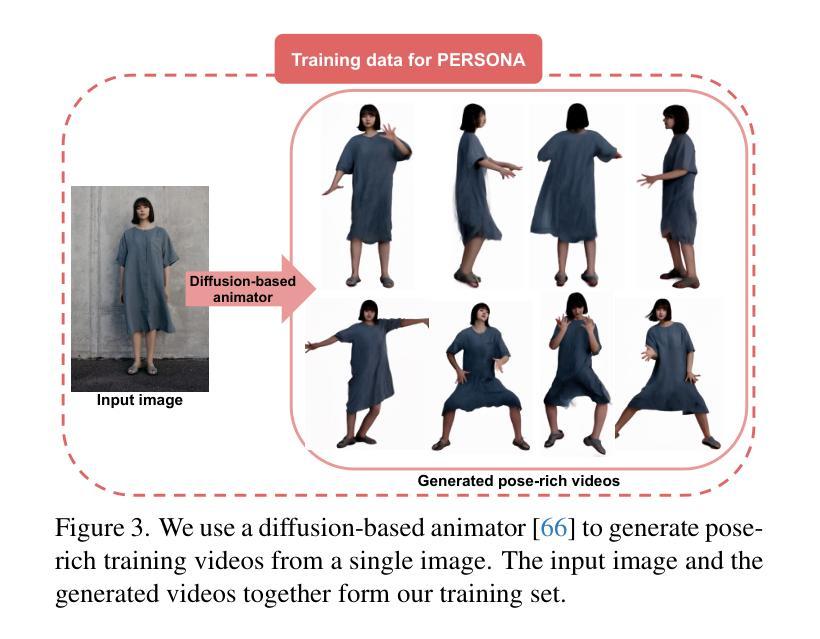
PERSONA: Personalized Whole-Body 3D Avatar with Pose-Driven Deformations from a Single Image
Authors:Geonhee Sim, Gyeongsik Moon
Two major approaches exist for creating animatable human avatars. The first, a 3D-based approach, optimizes a NeRF- or 3DGS-based avatar from videos of a single person, achieving personalization through a disentangled identity representation. However, modeling pose-driven deformations, such as non-rigid cloth deformations, requires numerous pose-rich videos, which are costly and impractical to capture in daily life. The second, a diffusion-based approach, learns pose-driven deformations from large-scale in-the-wild videos but struggles with identity preservation and pose-dependent identity entanglement. We present PERSONA, a framework that combines the strengths of both approaches to obtain a personalized 3D human avatar with pose-driven deformations from a single image. PERSONA leverages a diffusion-based approach to generate pose-rich videos from the input image and optimizes a 3D avatar based on them. To ensure high authenticity and sharp renderings across diverse poses, we introduce balanced sampling and geometry-weighted optimization. Balanced sampling oversamples the input image to mitigate identity shifts in diffusion-generated training videos. Geometry-weighted optimization prioritizes geometry constraints over image loss, preserving rendering quality in diverse poses.
创建可动画人类虚拟形象主要有两种方法。第一种是基于三维的方法,它通过单个人的视频优化基于神经辐射场(NeRF)或三维几何表面(3DGS)的虚拟形象,通过分离的身份表示实现个性化。然而,对姿势驱动的变形进行建模,如非刚性的布料变形,需要大量的丰富姿势的视频,这在日常生活中捕捉起来成本高昂且不切实际。第二种是基于扩散的方法,它从大量的野外视频中学习姿势驱动的变形,但在身份保持和姿势相关的身份纠缠方面存在困难。我们提出了PERSONA,一个结合两种方法优点的框架,可以从单张图像中获得具有姿势驱动变形的个性化三维人类虚拟形象。PERSONA利用基于扩散的方法从输入图像生成姿势丰富的视频,并基于这些视频优化三维虚拟形象。为了确保不同姿势的高真实性和清晰渲染,我们引入了平衡采样和几何加权优化。平衡采样对输入图像进行过采样,以减轻扩散生成训练视频中身份的变化。几何加权优化在几何约束和图像损失之间取得平衡,从而在多种姿势下保持渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025. https://mks0601.github.io/PERSONA/
Summary
该文本介绍了创建动画化人类角色(avatar)的两种主要方法,并结合两种方法优点提出了一个名为PERSONA的框架,能够从单张图片生成个性化的带有动作驱动变形的3D人类角色。通过采用基于扩散的方法生成姿态丰富的视频,并根据这些视频优化3D角色。为了确保在不同姿态下的高真实性和清晰渲染,引入了平衡采样和几何加权优化技术。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了创建动画化人类角色的两种主要方法:基于3D的方法和基于扩散的方法。
- 基于3D的方法通过优化NeRF或3DGS的个性化角色从单一视频实现个性化,但建模动作驱动变形需要大量姿态丰富的视频,成本高昂且日常生活中难以实现。
- 基于扩散的方法能从大规模野外视频中学习动作驱动变形,但面临身份保留和姿态相关的身份纠缠问题。
- 提出了PERSONA框架,结合上述两种方法的优点,从单张图片生成个性化的带有动作驱动变形的3D人类角色。
- PERSONA利用基于扩散的方法生成姿态丰富的视频,并根据这些视频优化3D角色。
- 为确保不同姿态下的高真实性和清晰渲染,引入了平衡采样技术来减轻扩散生成训练视频中身份变化的问题,以及几何加权优化技术来优先处理几何约束,保证图像损失最小化。
点此查看论文截图



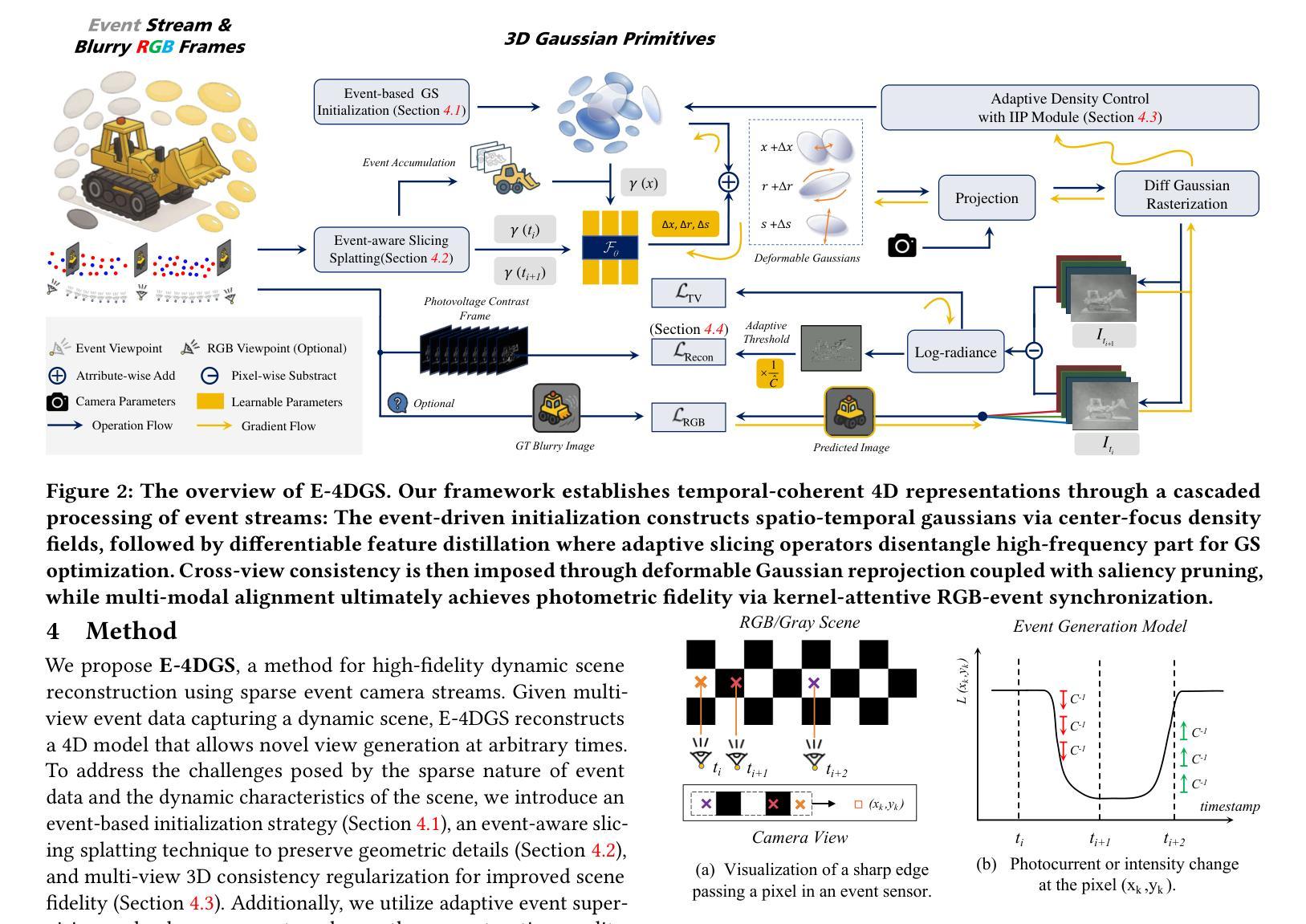
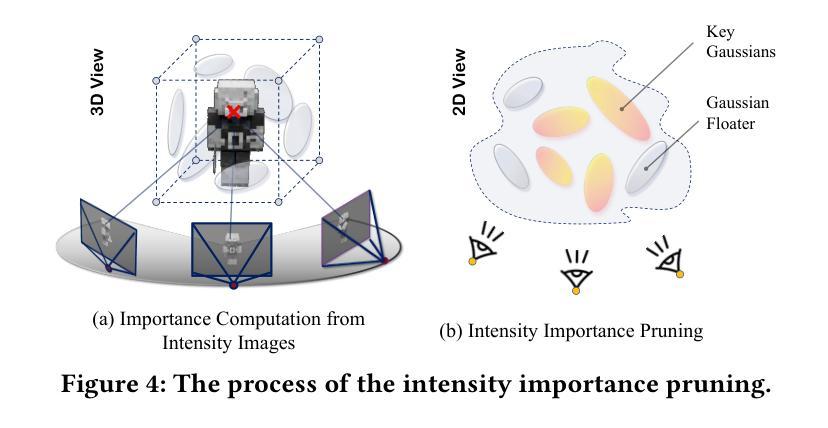
E-4DGS: High-Fidelity Dynamic Reconstruction from the Multi-view Event Cameras
Authors:Chaoran Feng, Zhenyu Tang, Wangbo Yu, Yatian Pang, Yian Zhao, Jianbin Zhao, Li Yuan, Yonghong Tian
Novel view synthesis and 4D reconstruction techniques predominantly rely on RGB cameras, thereby inheriting inherent limitations such as the dependence on adequate lighting, susceptibility to motion blur, and a limited dynamic range. Event cameras, offering advantages of low power, high temporal resolution and high dynamic range, have brought a new perspective to addressing the scene reconstruction challenges in high-speed motion and low-light scenes. To this end, we propose E-4DGS, the first event-driven dynamic Gaussian Splatting approach, for novel view synthesis from multi-view event streams with fast-moving cameras. Specifically, we introduce an event-based initialization scheme to ensure stable training and propose event-adaptive slicing splatting for time-aware reconstruction. Additionally, we employ intensity importance pruning to eliminate floating artifacts and enhance 3D consistency, while incorporating an adaptive contrast threshold for more precise optimization. We design a synthetic multi-view camera setup with six moving event cameras surrounding the object in a 360-degree configuration and provide a benchmark multi-view event stream dataset that captures challenging motion scenarios. Our approach outperforms both event-only and event-RGB fusion baselines and paves the way for the exploration of multi-view event-based reconstruction as a novel approach for rapid scene capture.
新型视图合成和4D重建技术主要依赖于RGB相机,从而继承了如依赖充足光线、易受到运动模糊影响以及动态范围有限的固有局限性。事件相机具有低功耗、高时间分辨率和高动态范围等优点,为高速运动场景和低光场景中的场景重建挑战提供了新的视角。为此,我们提出了E-4DGS,这是第一个基于事件驱动的动态高斯涂抹方法,用于从快速移动的相机多视图事件流中进行新型视图合成。具体来说,我们引入了一种基于事件的初始化方案,以确保稳定的训练,并提出了一种基于事件自适应切片涂抹方法进行时间感知重建。此外,我们采用强度重要性修剪来消除漂浮的伪影,增强3D一致性,同时采用自适应对比度阈值进行更精确的优化。我们设计了一个合成多视角相机设置,包括六个围绕物体以360度配置移动的事件相机,并提供了一个基准多视角事件流数据集,捕捉具有挑战性的运动场景。我们的方法优于仅使用事件和事件-RGB融合基线,为基于多视角事件重建的快速场景捕获新方法的探索铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 10 figures, 5 Tables, accepted by ACMMM 2025
Summary
事件相机具有低功耗、高时间分辨率和高动态范围等优点,为高速运动和低光场景的场景重建带来了新的视角。针对此,提出E-4DGS,首个事件驱动的动态高斯飞溅方法,用于从多视角事件流中进行新颖视图合成。引入事件初始化方案以确保稳定训练,并提出事件自适应切片飞溅进行时间感知重建。采用强度重要性修剪消除浮动伪影并增强3D一致性,同时结合自适应对比度阈值进行更精确的优化。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机在场景重建中具有独特优势,特别是在高速运动和低光场景中。
- E-4DGS是首个事件驱动的动态高斯飞溅方法,用于从多视角事件流进行新颖视图合成。
- 引入事件初始化方案确保稳定训练,并提出事件自适应切片飞溅进行时间感知重建。
- 采用强度重要性修剪技术消除浮动伪影,增强3D一致性。
- 结合自适应对比度阈值进行更精确的优化。
- 设计了一个合成多视角相机装置,采用六个围绕物体360度配置的运动事件相机。
点此查看论文截图

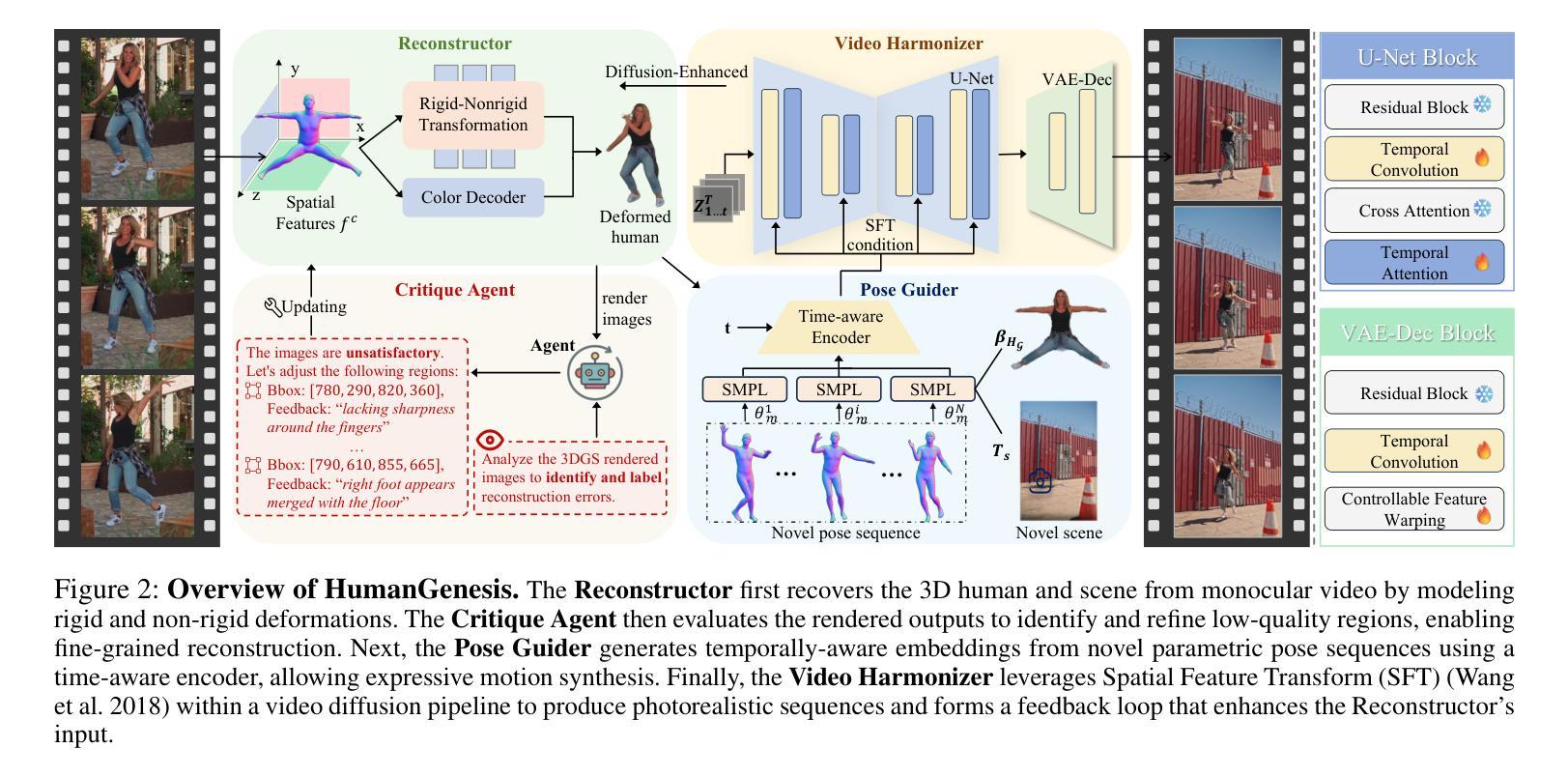
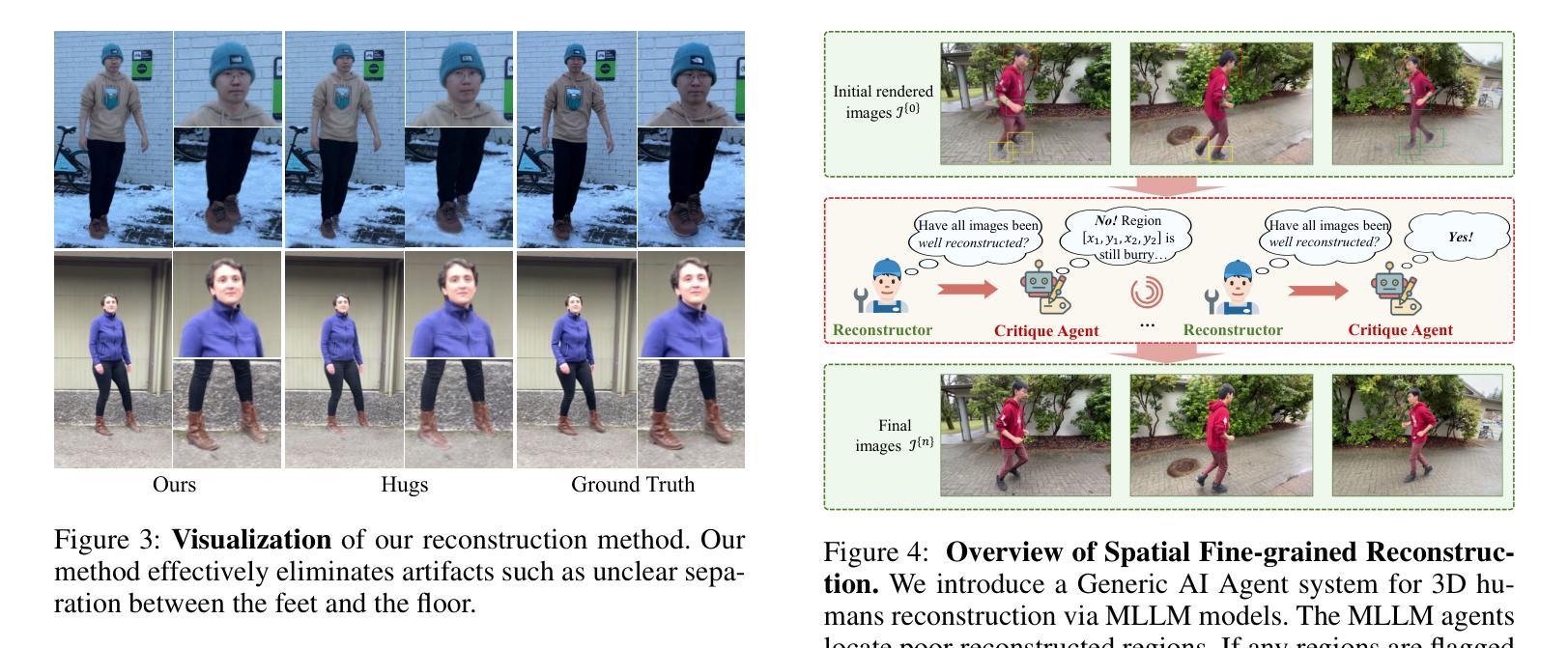
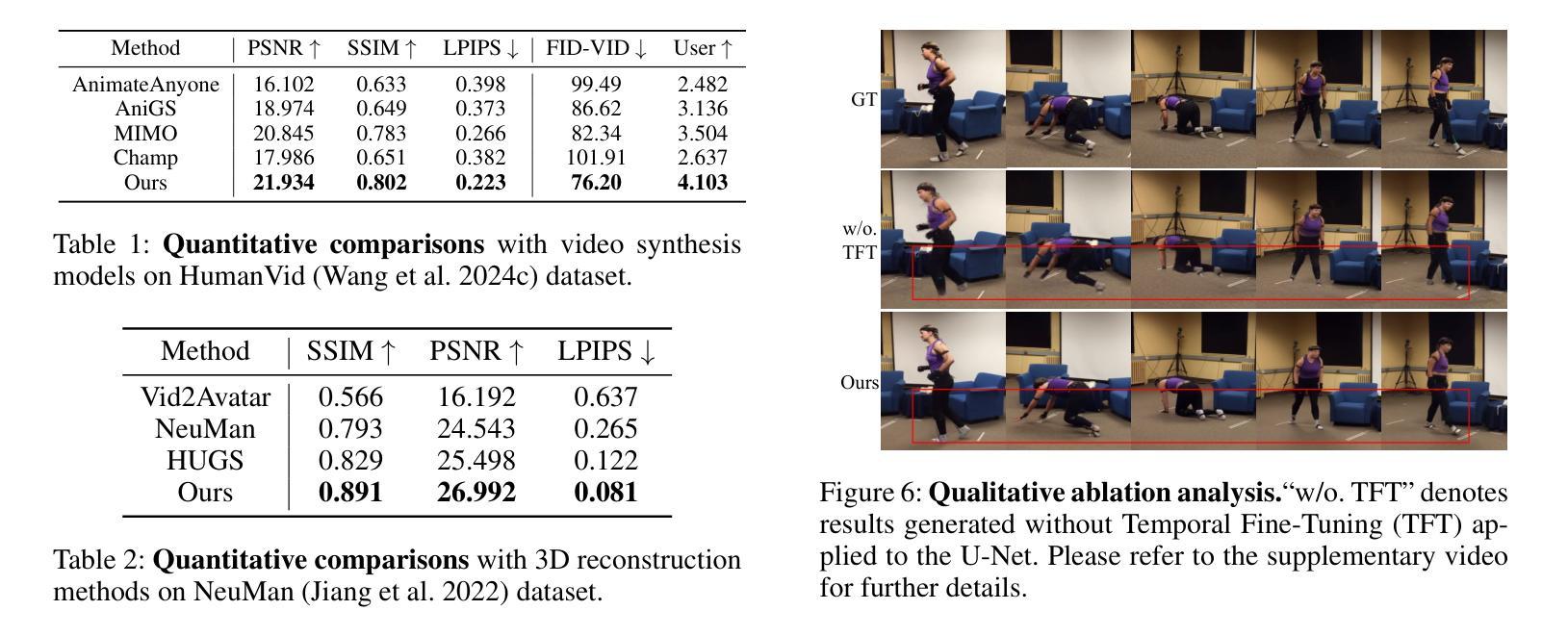
HumanGenesis: Agent-Based Geometric and Generative Modeling for Synthetic Human Dynamics
Authors:Weiqi Li, Zehao Zhang, Liang Lin, Guangrun Wang
\textbf{Synthetic human dynamics} aims to generate photorealistic videos of human subjects performing expressive, intention-driven motions. However, current approaches face two core challenges: (1) \emph{geometric inconsistency} and \emph{coarse reconstruction}, due to limited 3D modeling and detail preservation; and (2) \emph{motion generalization limitations} and \emph{scene inharmonization}, stemming from weak generative capabilities. To address these, we present \textbf{HumanGenesis}, a framework that integrates geometric and generative modeling through four collaborative agents: (1) \textbf{Reconstructor} builds 3D-consistent human-scene representations from monocular video using 3D Gaussian Splatting and deformation decomposition. (2) \textbf{Critique Agent} enhances reconstruction fidelity by identifying and refining poor regions via multi-round MLLM-based reflection. (3) \textbf{Pose Guider} enables motion generalization by generating expressive pose sequences using time-aware parametric encoders. (4) \textbf{Video Harmonizer} synthesizes photorealistic, coherent video via a hybrid rendering pipeline with diffusion, refining the Reconstructor through a Back-to-4D feedback loop. HumanGenesis achieves state-of-the-art performance on tasks including text-guided synthesis, video reenactment, and novel-pose generalization, significantly improving expressiveness, geometric fidelity, and scene integration.
合成人类动力学旨在生成表达强烈、意图驱动动作的人类主体的逼真视频。然而,当前的方法面临两大挑战:(1)由于3D建模和细节保留有限而导致的几何不一致性和粗糙重建;(2)由于生成能力较弱而导致的运动泛化限制和场景不和谐。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了HumanGenesis,这是一个通过四个协作代理整合几何和生成建模的框架:(1)重建器使用3D高斯喷涂和变形分解从单目视频中构建3D一致的人-场景表示。(2)评价代理通过多轮MLLM基于反射来识别和优化不良区域,从而提高重建的保真度。(3)姿势引导者通过使用时间感知参数编码器生成表达性姿势序列,从而实现运动泛化。(4)视频协调器通过混合渲染管道进行扩散,通过Back-to-4D反馈循环优化重建器,合成逼真的、连贯的视频。HumanGenesis在文本引导合成、视频重演和新颖姿势泛化等任务上达到了最新技术水平,在表达性、几何保真性和场景集成方面有了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了合成人类动力学(Synthetic human dynamics)的目标,旨在生成具有表现力、意图驱动动作的光学真实视频。然而,当前的方法面临两个核心挑战:几何不一致性和粗略重建以及运动泛化限制和场景不和谐。为了解决这个问题,提出了HumanGenesis框架,通过四个协作代理整合几何和生成建模,包括重建器、批判代理、姿态引导器和视频和谐器。HumanGenesis在文本引导合成、视频重演和新颖姿态泛化等任务上取得了最先进的性能,显著提高了表现力、几何保真度和场景集成。
Key Takeaways
- 当前合成人类动力学面临的挑战包括几何不一致性和粗略重建,以及运动泛化限制和场景不和谐。
- HumanGenesis框架通过整合几何和生成建模来解决这些问题。
- HumanGenesis包含四个协作代理:重建器、批判代理、姿态引导器和视频和谐器。
- 重建器使用3D高斯拼贴和变形分解技术从单目视频中构建一致的3D人类场景表示。
- 批判代理通过多轮MLLM反馈增强重建的保真度。
- 姿态引导器通过时间感知编码器生成表现力姿势序列,使运动泛化成为可能。
- 视频和谐器通过混合渲染管道和扩散技术,合成光学真实的连贯视频,并通过反馈循环优化重建器。
点此查看论文截图


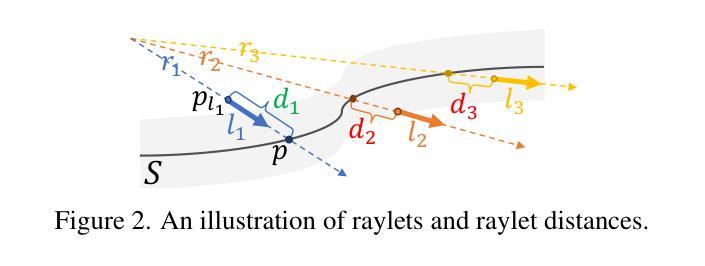
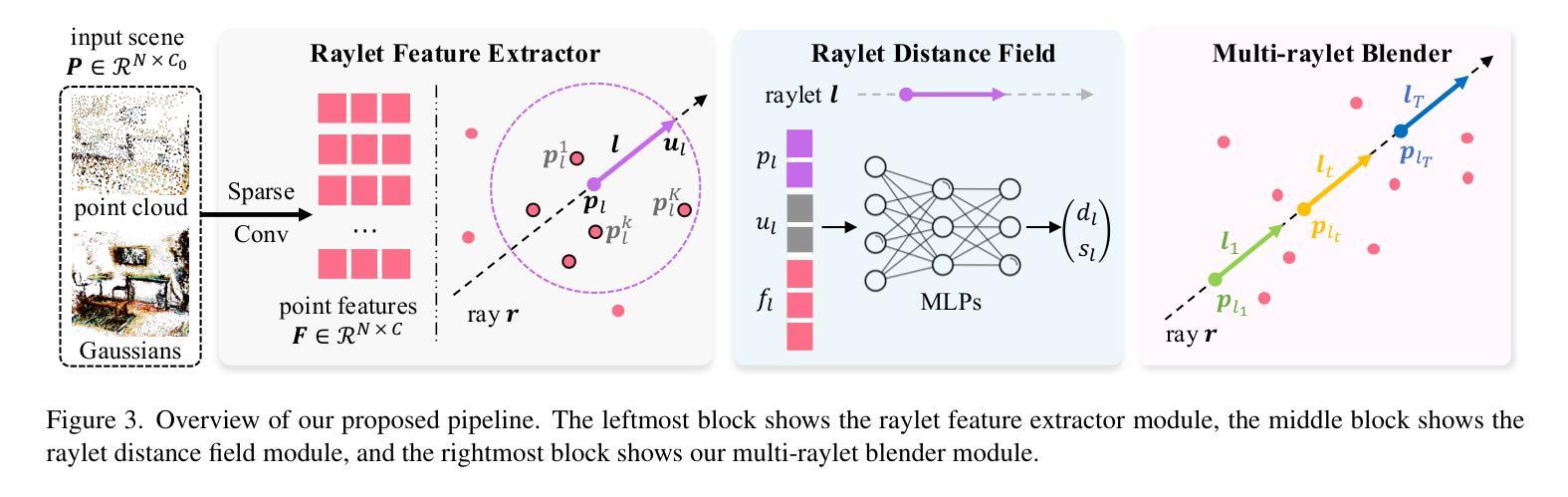
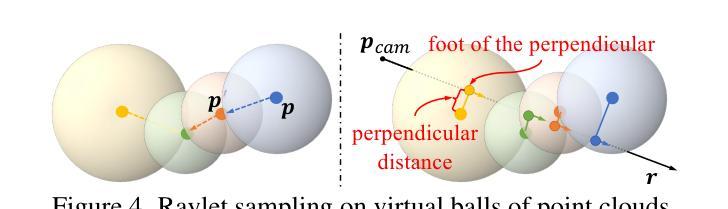
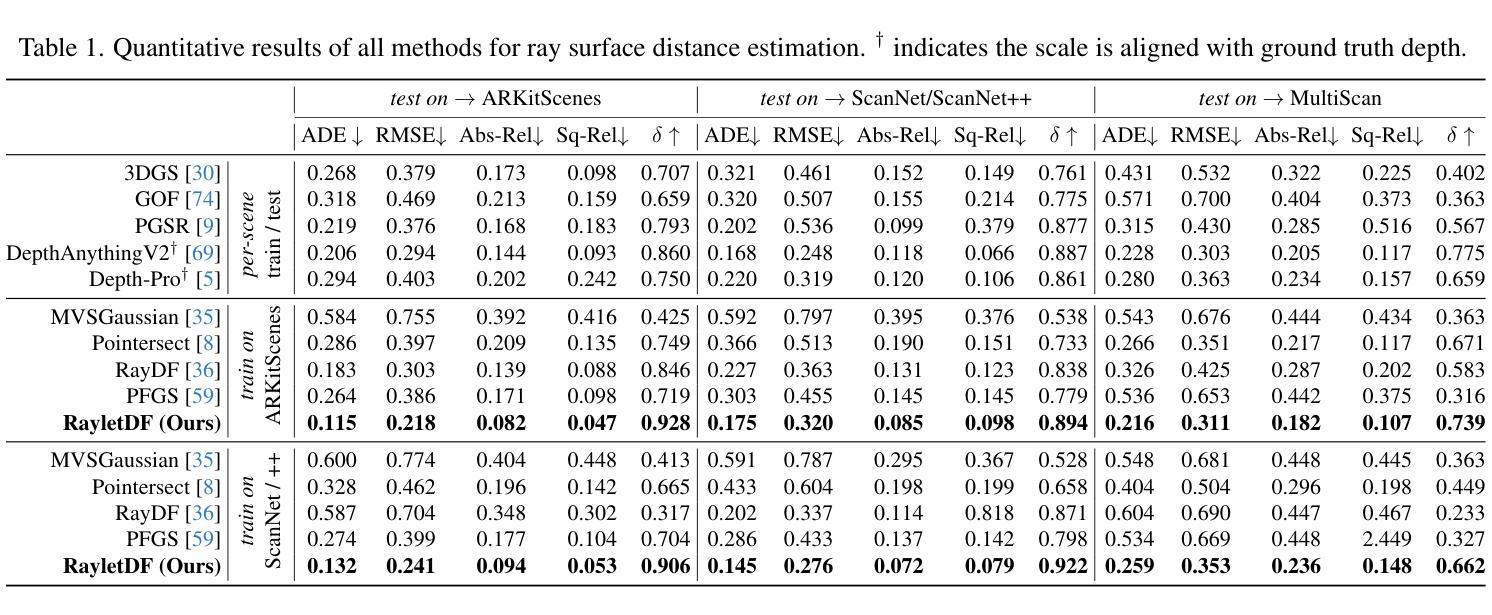
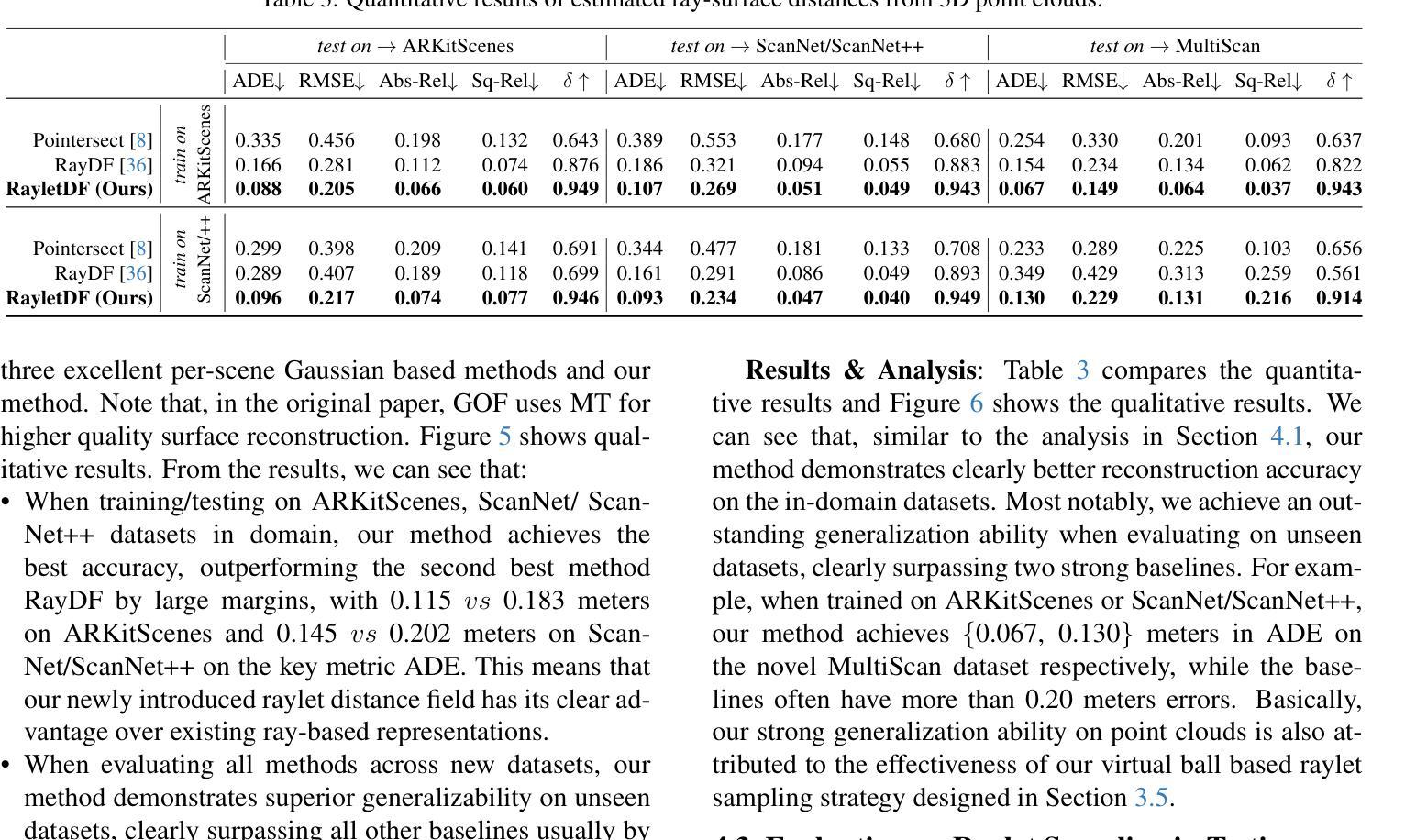
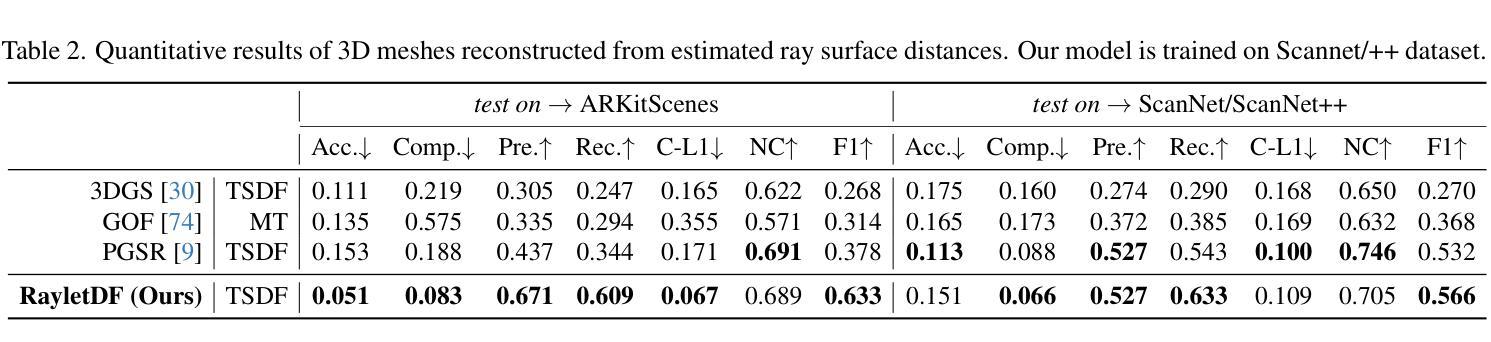
RayletDF: Raylet Distance Fields for Generalizable 3D Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds or Gaussians
Authors:Shenxing Wei, Jinxi Li, Yafei Yang, Siyuan Zhou, Bo Yang
In this paper, we present a generalizable method for 3D surface reconstruction from raw point clouds or pre-estimated 3D Gaussians by 3DGS from RGB images. Unlike existing coordinate-based methods which are often computationally intensive when rendering explicit surfaces, our proposed method, named RayletDF, introduces a new technique called raylet distance field, which aims to directly predict surface points from query rays. Our pipeline consists of three key modules: a raylet feature extractor, a raylet distance field predictor, and a multi-raylet blender. These components work together to extract fine-grained local geometric features, predict raylet distances, and aggregate multiple predictions to reconstruct precise surface points. We extensively evaluate our method on multiple public real-world datasets, demonstrating superior performance in surface reconstruction from point clouds or 3D Gaussians. Most notably, our method achieves exceptional generalization ability, successfully recovering 3D surfaces in a single-forward pass across unseen datasets in testing.
本文提出了一种利用RGB图像进行基于3DGS的原始点云或预估计的3D高斯分布的通用方法进行三维表面重建的方法。不同于现有的坐标回归方法经常需要大量计算进行显性表面的渲染,我们提出的方法称为RayletDF,引入了raylet距离场这一新技术,旨在直接从查询射线预测表面点。我们的管道包括三个关键模块:raylet特征提取器、raylet距离场预测器和多raylet混合器。这些组件协同工作,提取精细的局部几何特征,预测raylet距离,并融合多个预测结果以重建精确的表面点。我们在多个公开的真实世界数据集上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估,展示了从点云或三维高斯分布进行表面重建方面的优越性能。最值得注意的是,我们的方法具有出色的泛化能力,在测试时能在单张未接触过的数据集上一次性成功地重建出三维表面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Highlight. Shenxing and Jinxi are co-first authors. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vLAR-group/RayletDF
Summary
本文提出一种利用RGB图像通过3DGS进行三维表面重建的通用方法,该方法可从原始点云或预先估计的3D高斯数据中重建三维表面。与现有的坐标基础方法不同,我们的方法名为RayletDF,引入了一种名为射线距离场的新技术,旨在直接从查询射线预测表面点。该方法包含三个关键模块:射线特征提取器、射线距离场预测器和多射线混合器。这三个组件协同工作,用于提取精细局部几何特征、预测射线距离并聚合多个预测结果以重建精确的表面点。我们在多个公共真实世界数据集上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估,展示了对点云或三维高斯数据的表面重建的卓越性能。尤其值得一提的是,我们的方法具有出色的泛化能力,能够在测试中的未见数据集上一次性通过恢复三维表面。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种名为RayletDF的新方法,用于从RGB图像通过3DGS进行三维表面重建。
- 引入射线距离场技术,直接预测查询射线上的表面点。
- 方法包含三个关键模块:射线特征提取器、射线距离场预测器和多射线混合器。
- 广泛评估表明在多个公共真实世界数据集上的表面重建性能优越。
- 方法具有出色的泛化能力,能在未见数据集上成功恢复三维表面。
点此查看论文截图

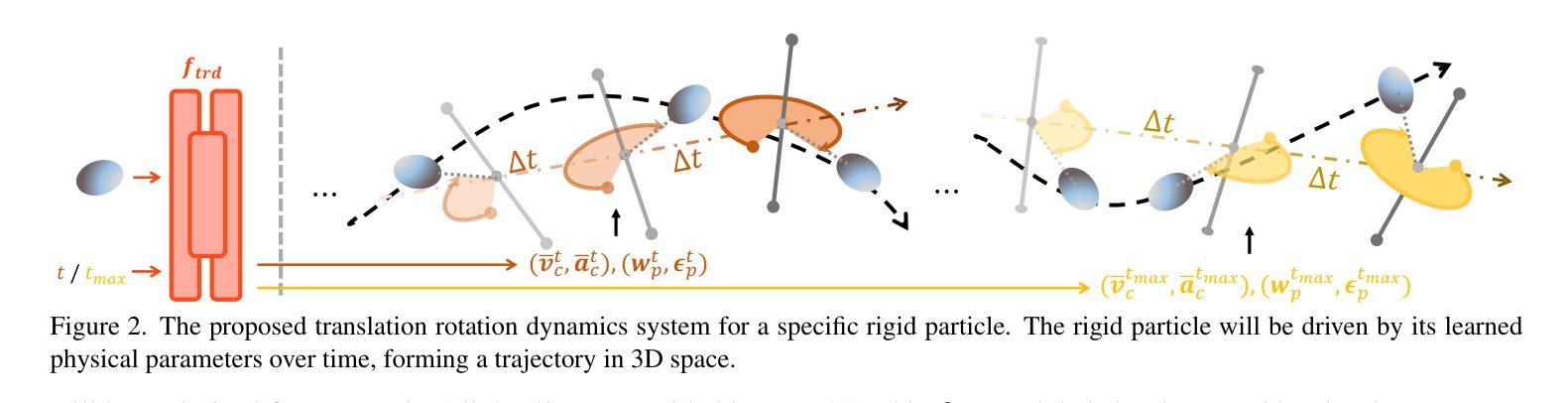
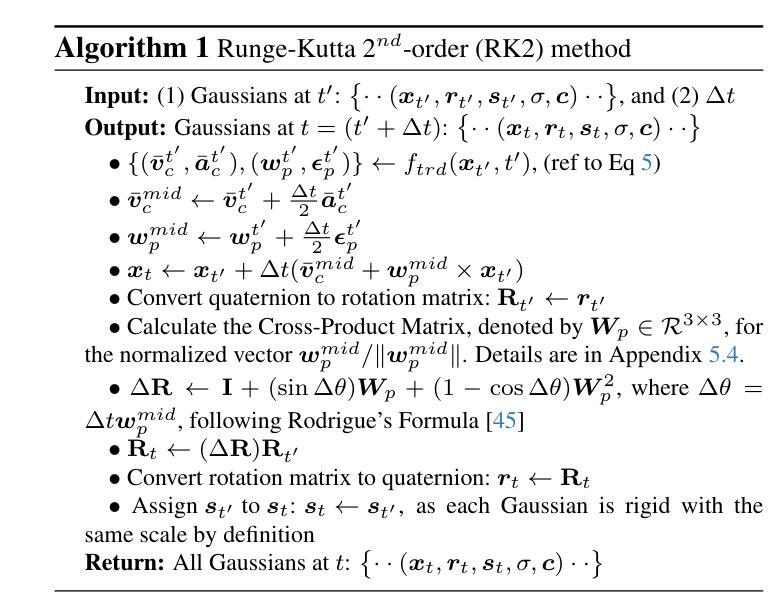
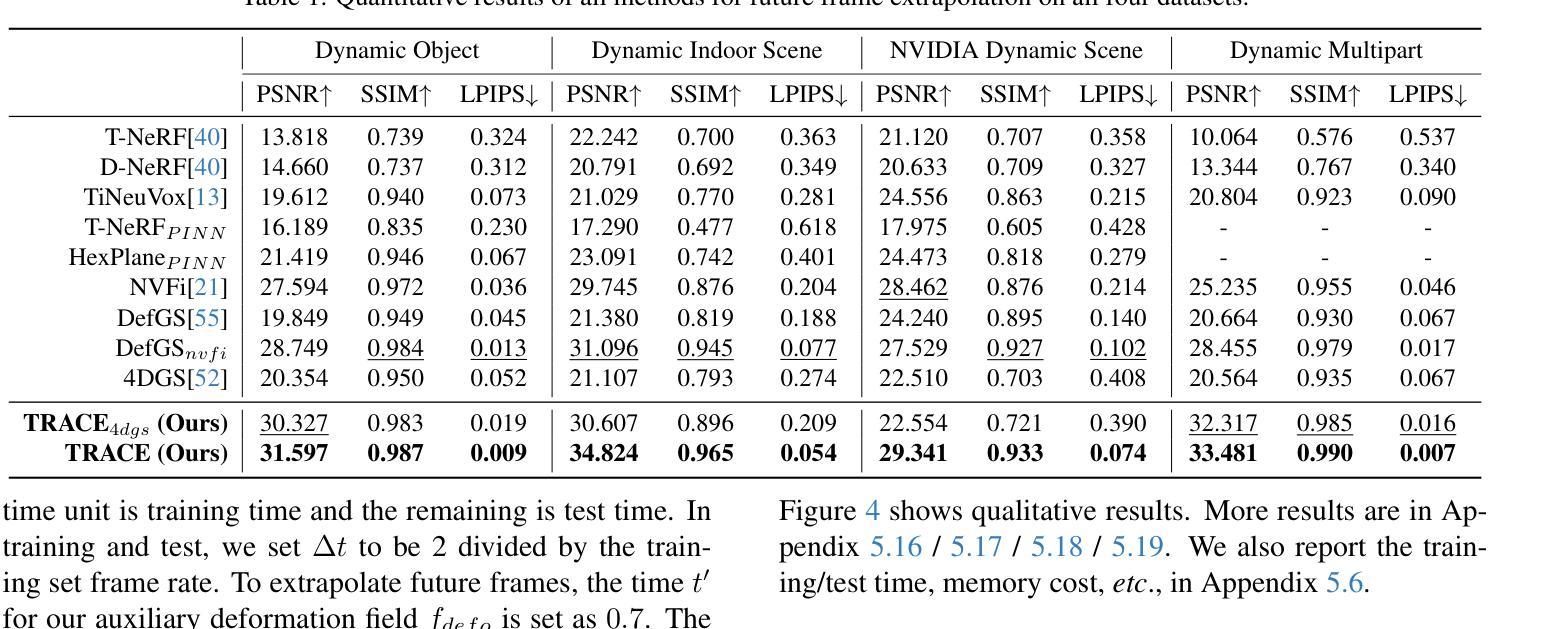
TRACE: Learning 3D Gaussian Physical Dynamics from Multi-view Videos
Authors:Jinxi Li, Ziyang Song, Bo Yang
In this paper, we aim to model 3D scene geometry, appearance, and physical information just from dynamic multi-view videos in the absence of any human labels. By leveraging physics-informed losses as soft constraints or integrating simple physics models into neural nets, existing works often fail to learn complex motion physics, or doing so requires additional labels such as object types or masks. We propose a new framework named TRACE to model the motion physics of complex dynamic 3D scenes. The key novelty of our method is that, by formulating each 3D point as a rigid particle with size and orientation in space, we directly learn a translation rotation dynamics system for each particle, explicitly estimating a complete set of physical parameters to govern the particle’s motion over time. Extensive experiments on three existing dynamic datasets and one newly created challenging synthetic datasets demonstrate the extraordinary performance of our method over baselines in the task of future frame extrapolation. A nice property of our framework is that multiple objects or parts can be easily segmented just by clustering the learned physical parameters.
本文的目标是从无标签的动态多视角视频中,对3D场景进行几何、外观和物理信息的建模。尽管现有的工作通过利用物理信息损失作为软约束或将简单的物理模型集成到神经网络中,但往往无法学习到复杂的运动物理,或者需要进行额外的标签标注,如对象类型或掩码。我们提出了一种新的框架TRACE来模拟复杂动态场景的运动物理。我们的方法的关键新颖之处在于,通过将每个3D点定义为具有大小和空间方向的刚性粒子,我们为每个粒子直接学习一个翻译旋转动力系统,并明确估计一套完整的物理参数来支配粒子随时间变化的运动。在三个现有的动态数据集和一个新创建的有挑战性的合成数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在未来帧外推任务上的表现优于基准线。我们的框架的另一个优点是,可以通过聚类学习的物理参数轻松分割多个对象或部分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vLAR-group/TRACE
Summary
本文旨在从动态多视角视频中建模3D场景几何、外观和物理信息,无需任何人工标签。文章提出了一种名为TRACE的新框架,用于模拟复杂动态3D场景的运动物理。该方法的关键创新之处在于将每个3D点视为具有空间和方向性的刚性粒子,直接学习每个粒子的平移旋转动力系统,并显式估计一组物理参数来管理粒子随时间变化的运动。实验表明,该方法在多个数据集上的未来帧外推任务中表现卓越,并可通过学习到的物理参数轻松实现对多个对象或部分的分割。
Key Takeaways
- 该文章目标是利用动态多视角视频建模3D场景的几何、外观和物理信息,无需人工标签。
- 文章提出了一种名为TRACE的新框架,用以模拟复杂动态场景的运动物理。
- 该方法的关键创新在于将每个3D点视为刚性粒子,并学习其平移旋转动力系统。
- 方法通过显式估计物理参数来管理粒子运动的复杂性。
- 实验证明,该方法在未来帧外推任务上表现卓越。
- 该方法可以轻松通过聚类学习到的物理参数实现对多个对象或部分的分割。
点此查看论文截图

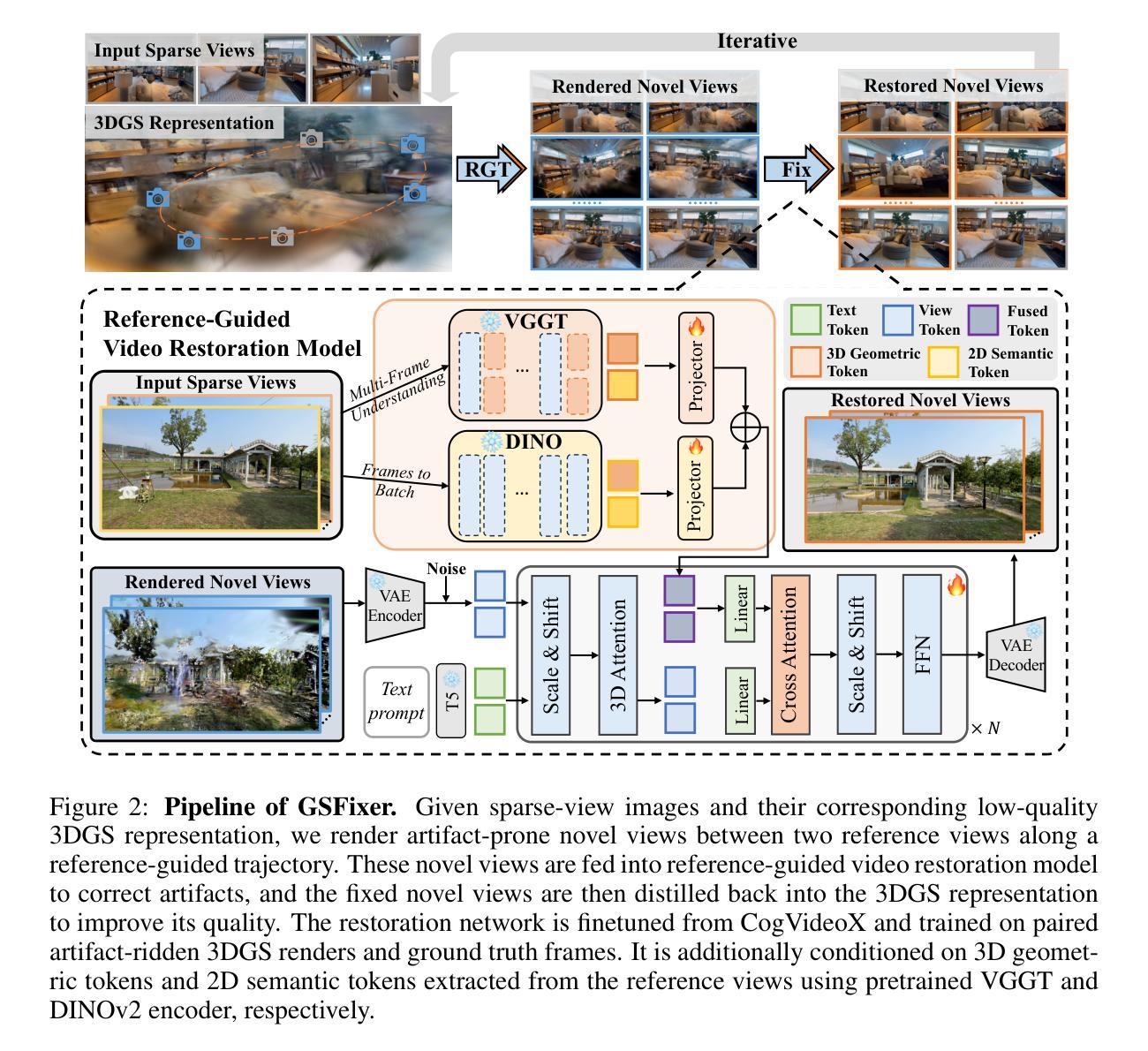
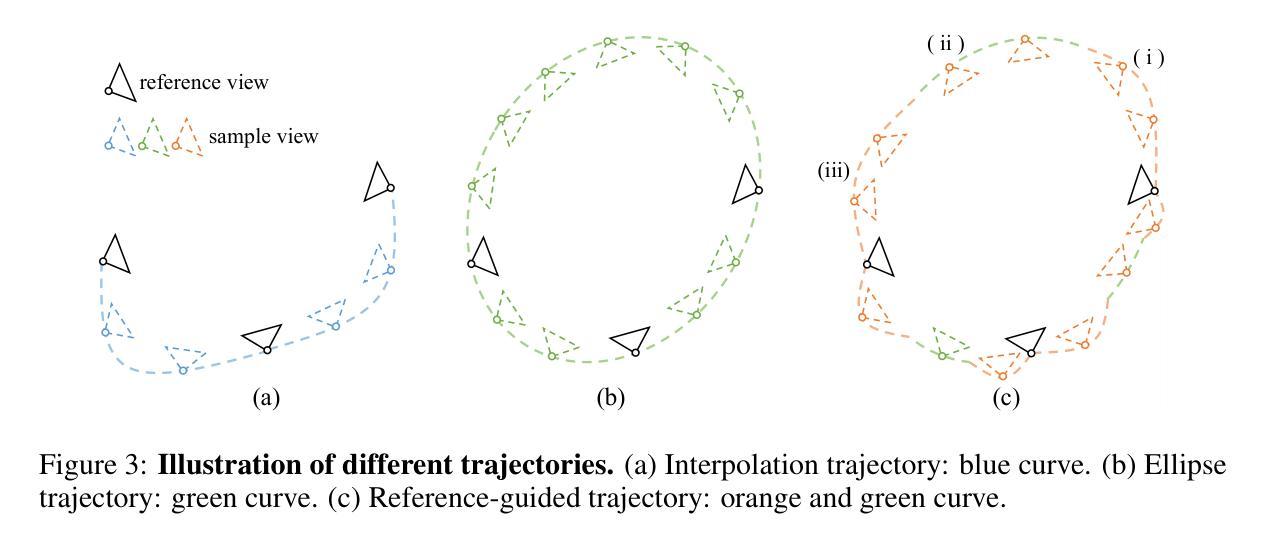
GSFixer: Improving 3D Gaussian Splatting with Reference-Guided Video Diffusion Priors
Authors:Xingyilang Yin, Qi Zhang, Jiahao Chang, Ying Feng, Qingnan Fan, Xi Yang, Chi-Man Pun, Huaqi Zhang, Xiaodong Cun
Reconstructing 3D scenes using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) from sparse views is an ill-posed problem due to insufficient information, often resulting in noticeable artifacts. While recent approaches have sought to leverage generative priors to complete information for under-constrained regions, they struggle to generate content that remains consistent with input observations. To address this challenge, we propose GSFixer, a novel framework designed to improve the quality of 3DGS representations reconstructed from sparse inputs. The core of our approach is the reference-guided video restoration model, built upon a DiT-based video diffusion model trained on paired artifact 3DGS renders and clean frames with additional reference-based conditions. Considering the input sparse views as references, our model integrates both 2D semantic features and 3D geometric features of reference views extracted from the visual geometry foundation model, enhancing the semantic coherence and 3D consistency when fixing artifact novel views. Furthermore, considering the lack of suitable benchmarks for 3DGS artifact restoration evaluation, we present DL3DV-Res which contains artifact frames rendered using low-quality 3DGS. Extensive experiments demonstrate our GSFixer outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in 3DGS artifact restoration and sparse-view 3D reconstruction. Project page: https://github.com/GVCLab/GSFixer.
使用基于稀疏视角的3D高斯分裂(3DGS)重建三维场景是一个病态问题,由于信息不足,常常会产生明显的伪影。尽管近期的方法试图利用生成先验来填补约束不足的区域的完整性信息,但它们仍然难以生成与输入观测一致的像素级别的三维几何结构和内容保持连贯性的内容。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了GSFixer框架,旨在提高从稀疏输入重建的3DGS表示的质量。我们的方法的核心是参考引导的视频恢复模型,该模型基于在配对的伪影渲染的3DGS帧和干净的帧上训练的基于扩散模型的视频扩散模型,并附加了基于参考的条件。我们的模型将参考视角的二维语义特征和三维几何特征融入其中,通过从视觉几何基础模型中提取这些信息,在修复伪影的新视角时增强语义连贯性和三维一致性。此外,考虑到缺乏适合用于评估3DGS伪影恢复的基准数据集,我们推出了DL3DV-Res数据集,其中包含使用低质量3DGS渲染的伪影帧。大量的实验表明,我们的GSFixer在解决基于伪影的评估和稀疏视角三维重建方面具有优于当前最新技术的性能。项目页面:https://github.com/GVCLab/GSFixer。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于稀疏视图的3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)重建是一个不适定的问题,可能导致显著的伪影。为了解决此问题,提出了GSFixer框架,通过参考引导的视频修复模型提高重建质量。该模型结合二维语义特征和三维几何特征,增强了语义连贯性和三维一致性。此外,还推出了针对缺乏适当基准的问题而设计的新数据集DL3DV-Res用于评估修复效果。实验证明,GSFixer在解决伪影和稀疏视图重建方面表现优于现有技术。有关详细信息,请访问项目页面:https://github.com/GVCLab/GSFixer。
Key Takeaways
- 重建基于稀疏视图的3D场景是一个挑战性问题,因为信息不足可能导致显著的伪影。
- GSFixer框架旨在解决这一问题,采用参考引导的视频修复模型来提高重建质量。
- GSFixer结合了二维语义特征和三维几何特征,增强语义连贯性和三维一致性。为此引入了新的数据集DL3DV-Res用于评估伪影修复效果。
点此查看论文截图

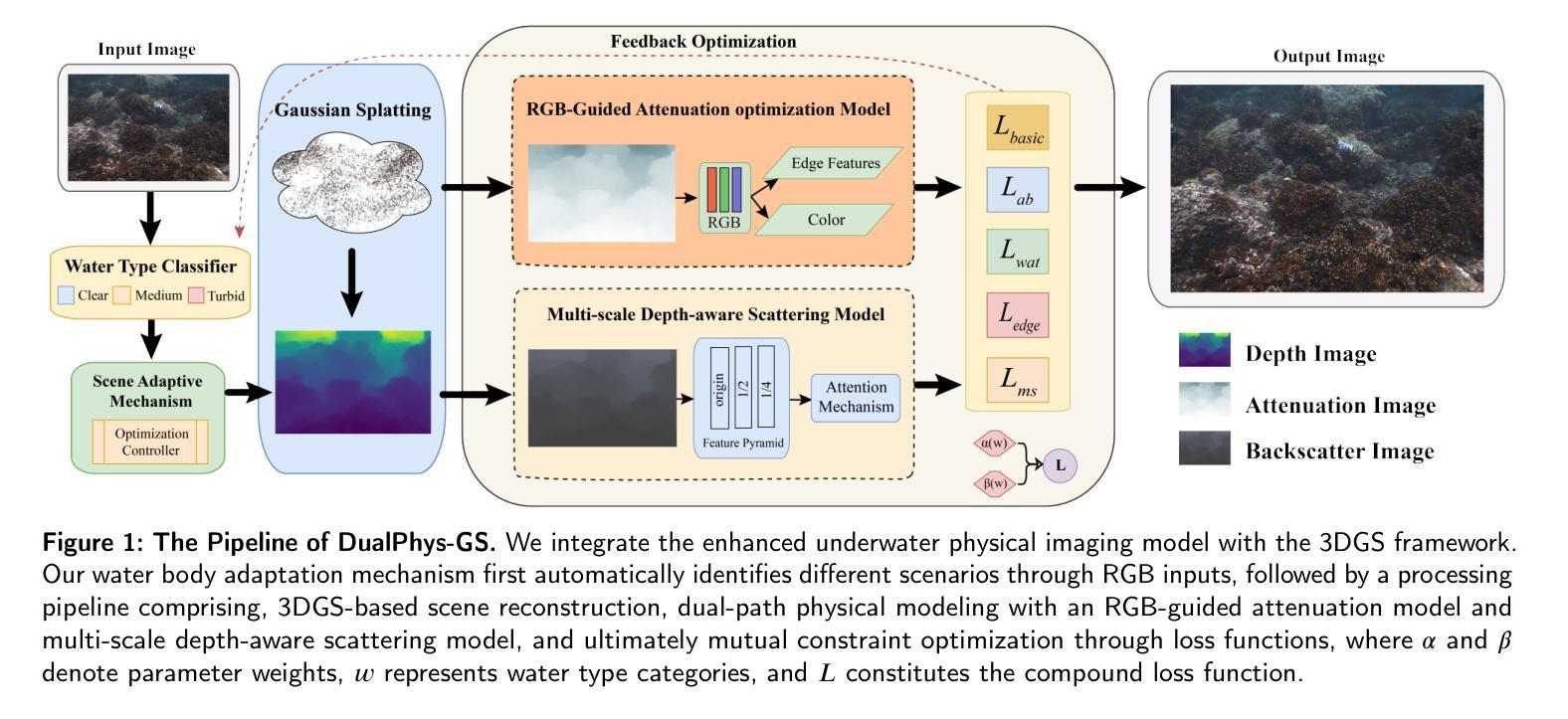
DualPhys-GS: Dual Physically-Guided 3D Gaussian Splatting for Underwater Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Jiachen Li, Guangzhi Han, Jin Wan, Yuan Gao, Delong Han
In 3D reconstruction of underwater scenes, traditional methods based on atmospheric optical models cannot effectively deal with the selective attenuation of light wavelengths and the effect of suspended particle scattering, which are unique to the water medium, and lead to color distortion, geometric artifacts, and collapsing phenomena at long distances. We propose the DualPhys-GS framework to achieve high-quality underwater reconstruction through a dual-path optimization mechanism. Our approach further develops a dual feature-guided attenuation-scattering modeling mechanism, the RGB-guided attenuation optimization model combines RGB features and depth information and can handle edge and structural details. In contrast, the multi-scale depth-aware scattering model captures scattering effects at different scales using a feature pyramid network and an attention mechanism. Meanwhile, we design several special loss functions. The attenuation scattering consistency loss ensures physical consistency. The water body type adaptive loss dynamically adjusts the weighting coefficients. The edge-aware scattering loss is used to maintain the sharpness of structural edges. The multi-scale feature loss helps to capture global and local structural information. In addition, we design a scene adaptive mechanism that can automatically identify the water-body-type characteristics (e.g., clear coral reef waters or turbid coastal waters) and dynamically adjust the scattering and attenuation parameters and optimization strategies. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing methods in several metrics, especially in suspended matter-dense regions and long-distance scenes, and the reconstruction quality is significantly improved.
在水下场景的3D重建中,基于大气光学模型的传统方法无法有效处理光波长的选择性衰减和悬浮粒子散射等水体独有的效应,这会导致颜色失真、几何伪影以及远距离处的崩溃现象。我们提出了DualPhys-GS框架,通过双路径优化机制实现高质量的水下重建。我们的方法进一步开发了一种双特征引导衰减-散射建模机制。RGB-引导衰减优化模型结合了RGB特征和深度信息,能够处理边缘和结构细节。相比之下,多尺度深度感知散射模型使用特征金字塔网络和注意力机制在不同尺度上捕捉散射效应。同时,我们设计了多种特殊损失函数。衰减散射一致性损失确保物理一致性。水体类型自适应损失动态调整权重系数。边缘感知散射损失用于保持结构边缘的清晰度。多尺度特征损失有助于捕获全局和局部结构信息。此外,我们设计了一种场景自适应机制,可以自动识别水体特征(例如清澈的珊瑚礁水域或浑浊的沿海水域),并动态调整散射和衰减参数以及优化策略。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个指标上优于现有方法,尤其在悬浮物密集区域和远距离场景上,重建质量得到显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了在水下场景三维重建中,传统方法存在的问题以及提出的DualPhys-GS框架的优势。该框架通过双路径优化机制实现高质量的水下重建,并建立了双特征引导衰减散射建模机制。同时,设计多种特殊损失函数和场景自适应机制,能够自动识别水体特征并调整参数和优化策略。实验结果表明,该方法在多个指标上优于现有方法,尤其在悬浮物密集区域和远距离场景上重建质量显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 传统方法在水下场景三维重建中面临选择性光波长衰减和悬浮颗粒散射问题的挑战。
- DualPhys-GS框架通过双路径优化机制实现高质量水下重建。
- 建立双特征引导衰减散射建模机制,包括RGB特征引导的衰减优化模型和跨尺度深度感知散射模型。
- 设计多种特殊损失函数,确保物理一致性、自适应调整权重系数、保持边缘清晰度并捕捉全局和局部结构信息。
- 场景自适应机制可自动识别水体特征并动态调整散射和衰减参数及优化策略。
点此查看论文截图

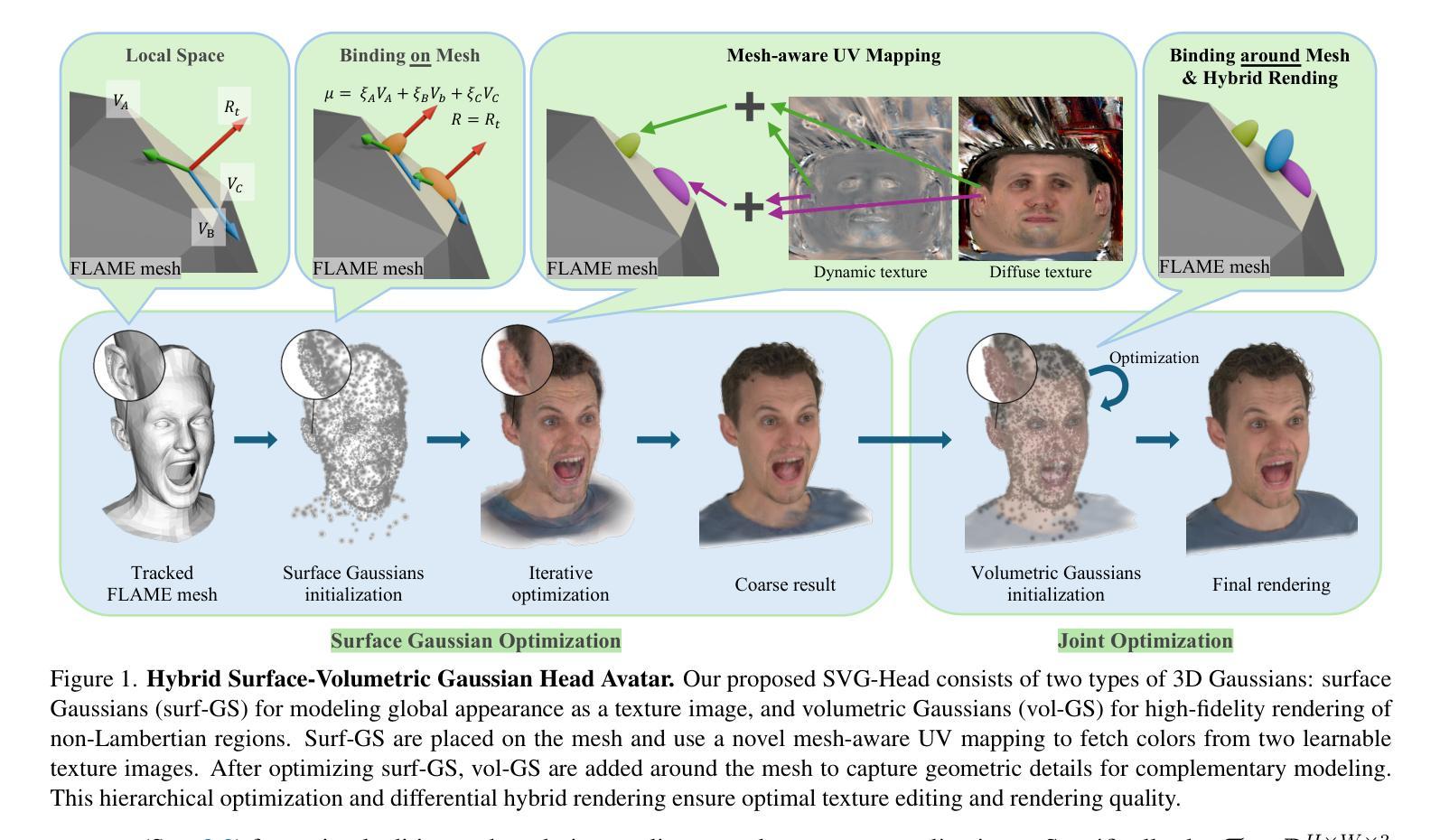
SVG-Head: Hybrid Surface-Volumetric Gaussians for High-Fidelity Head Reconstruction and Real-Time Editing
Authors:Heyi Sun, Cong Wang, Tian-Xing Xu, Jingwei Huang, Di Kang, Chunchao Guo, Song-Hai Zhang
Creating high-fidelity and editable head avatars is a pivotal challenge in computer vision and graphics, boosting many AR/VR applications. While recent advancements have achieved photorealistic renderings and plausible animation, head editing, especially real-time appearance editing, remains challenging due to the implicit representation and entangled modeling of the geometry and global appearance. To address this, we propose Surface-Volumetric Gaussian Head Avatar (SVG-Head), a novel hybrid representation that explicitly models the geometry with 3D Gaussians bound on a FLAME mesh and leverages disentangled texture images to capture the global appearance. Technically, it contains two types of Gaussians, in which surface Gaussians explicitly model the appearance of head avatars using learnable texture images, facilitating real-time texture editing, while volumetric Gaussians enhance the reconstruction quality of non-Lambertian regions (e.g., lips and hair). To model the correspondence between 3D world and texture space, we provide a mesh-aware Gaussian UV mapping method, which leverages UV coordinates given by the FLAME mesh to obtain sharp texture images and real-time rendering speed. A hierarchical optimization strategy is further designed to pursue the optimal performance in both reconstruction quality and editing flexibility. Experiments on the NeRSemble dataset show that SVG-Head not only generates high-fidelity rendering results, but also is the first method to obtain explicit texture images for Gaussian head avatars and support real-time appearance editing.
创建高保真和可编辑的头部化身是计算机视觉和图形学中的一项关键挑战,推动了许多AR/VR应用程序的发展。尽管最近的进步已经实现了逼真的渲染和逼真的动画,但头部编辑,尤其是实时外观编辑,仍然是一个挑战,因为几何形状和全局外观的隐式表示和纠缠建模。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Surface-Volumetric Gaussian Head Avatar(SVG-Head)这一新型混合表示方法。它通过绑定在FLAME网格上的三维高斯分布显式地建模几何形状,并利用解耦纹理图像捕捉全局外观。从技术上讲,它包含两种高斯分布,其中表面高斯分布使用可学习的纹理图像显式地模拟头部化身的外观,从而实现实时纹理编辑,而体积高斯分布则提高了非朗伯地区(例如嘴唇和头发)的重建质量。为了建立三维世界和纹理空间之间的对应关系,我们提供了一种网格感知的高斯UV映射方法,该方法利用FLAME网格提供的UV坐标来获得清晰的纹理图像和实时渲染速度。为了进一步追求在重建质量和编辑灵活性方面的最佳性能,我们还设计了一种分层优化策略。在NeRSemble数据集上的实验表明,SVG-Head不仅生成了高保真度的渲染结果,而且是第一种获得高斯头部化身显式纹理图像并支持实时外观编辑的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025. Project page: https://heyy-sun.github.io/SVG-Head/
Summary
本文提出了Surface-Volumetric Gaussian Head Avatar(SVG-Head)方法,采用混合表示方式,用3D高斯模型显式建模几何形状,并结合纹理图像捕捉全局外观。该方法能够生成高保真度的头像,并支持实时编辑。
Key Takeaways
- SVG-Head是一种新型的头像素描方法,采用混合表示方式,结合了三维高斯模型和纹理图像。
- SVG-Head能够生成高保真度的头像,并提升AR/VR应用体验。
- SVG-Head通过表面高斯模型显式建模头像的外观,并使用可学习的纹理图像进行建模,从而实现实时纹理编辑。
- 体积高斯模型增强了非Lambertian区域(如嘴唇和头发)的重建质量。
- SVG-Head提供了网格感知的Gaussian UV映射方法,实现了从三维世界到纹理空间的对应。
- 层次优化策略用于追求重建质量和编辑灵活性的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

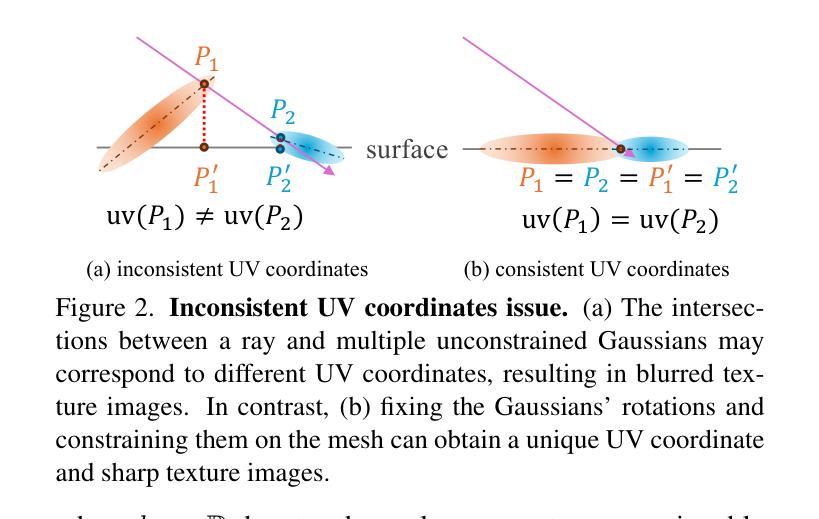

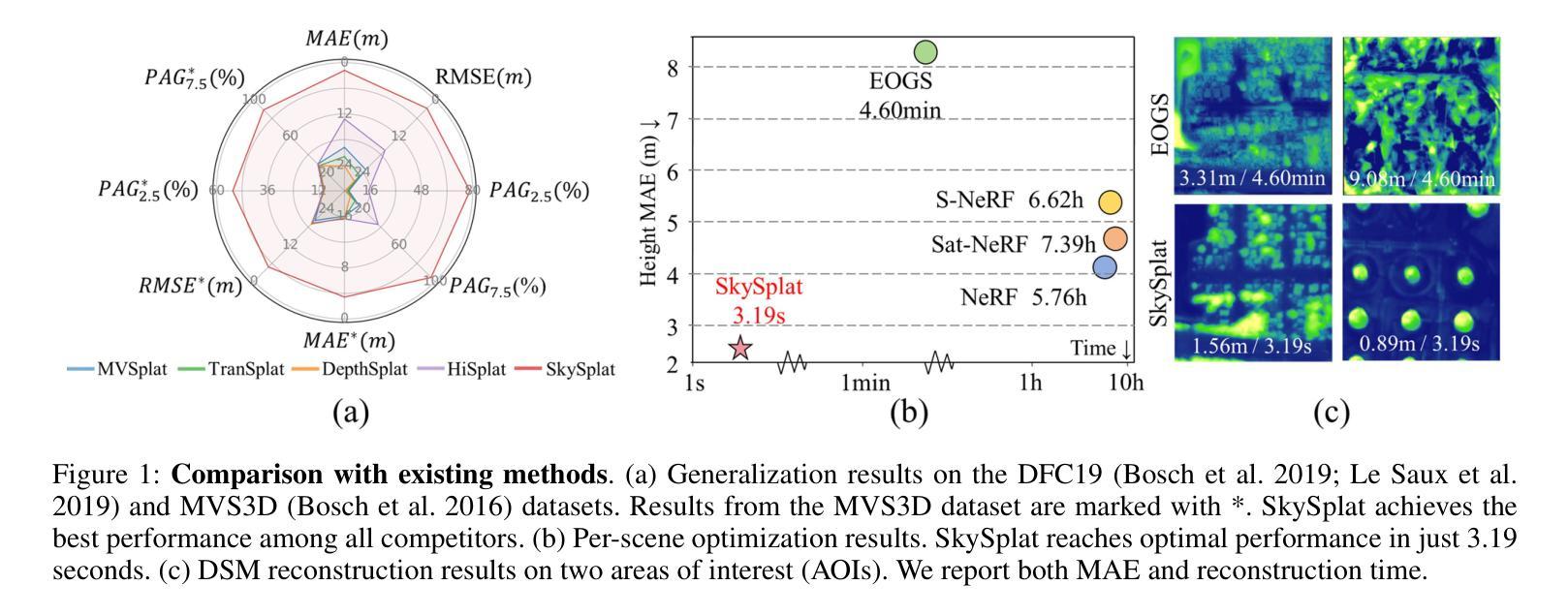
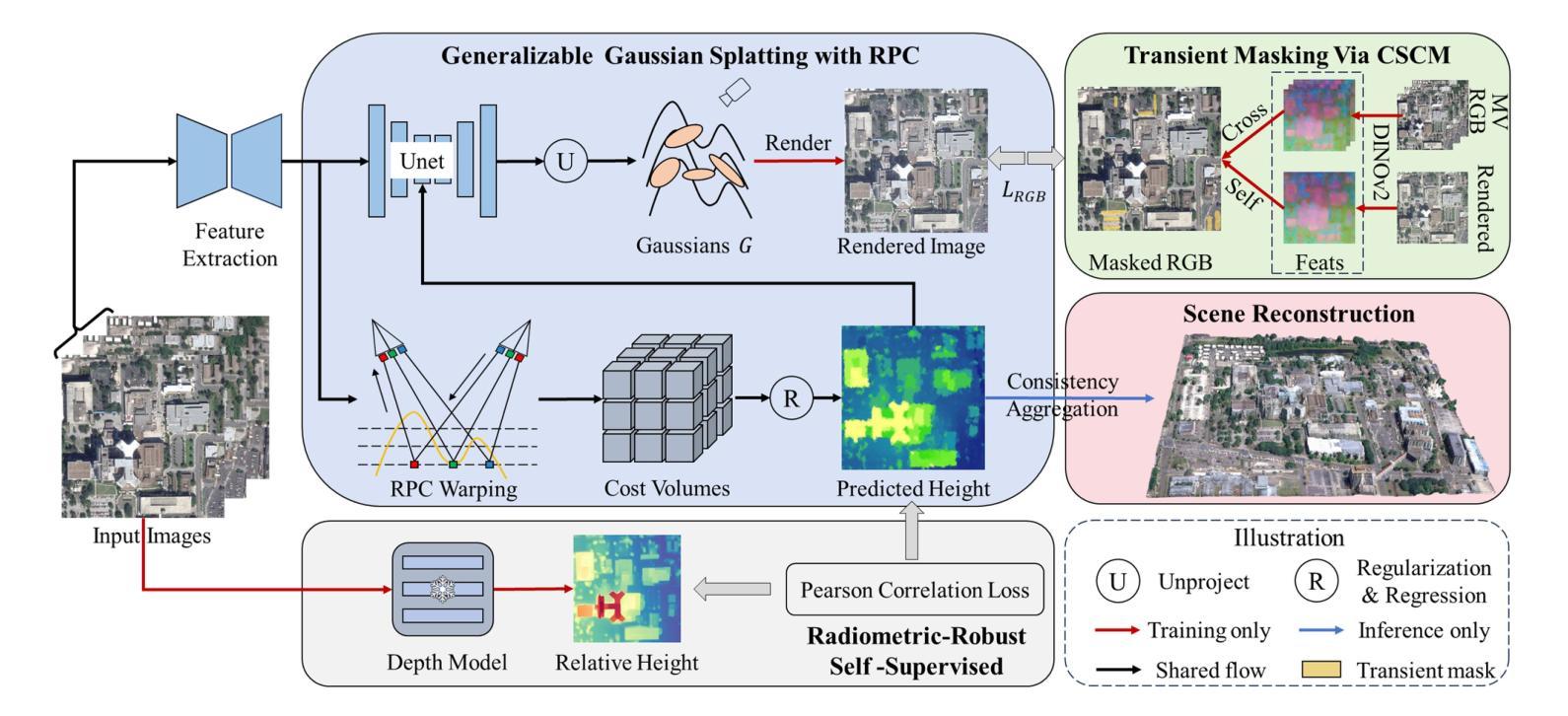
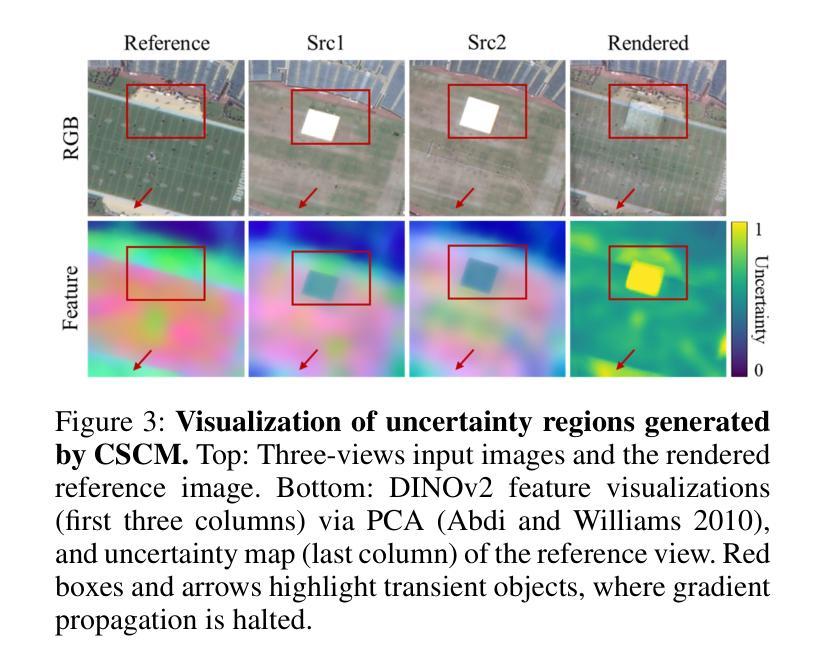
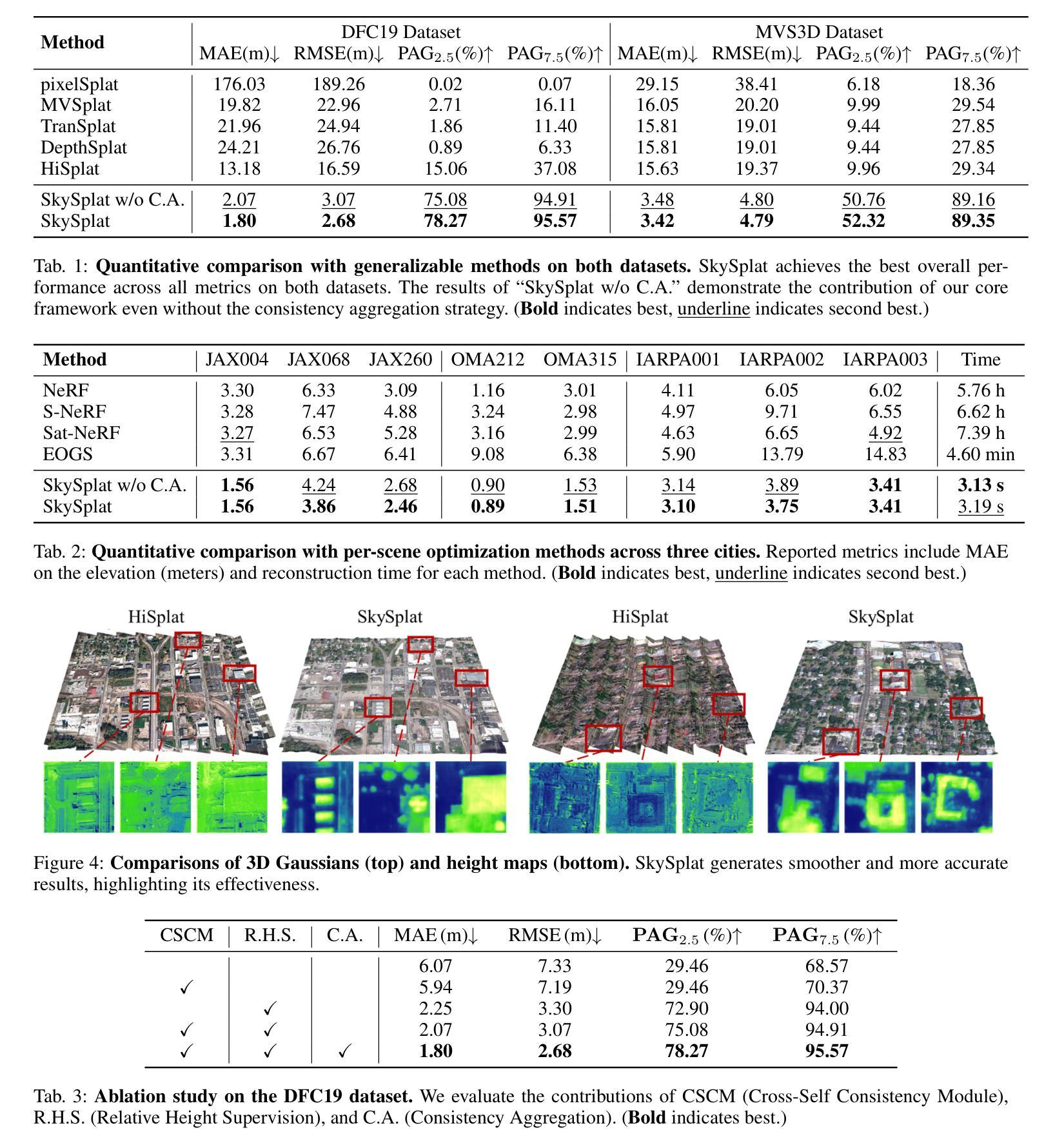
SkySplat: Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting from Multi-Temporal Sparse Satellite Images
Authors:Xuejun Huang, Xinyi Liu, Yi Wan, Zhi Zheng, Bin Zhang, Mingtao Xiong, Yingying Pei, Yongjun Zhang
Three-dimensional scene reconstruction from sparse-view satellite images is a long-standing and challenging task. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and its variants have recently attracted attention for its high efficiency, existing methods remain unsuitable for satellite images due to incompatibility with rational polynomial coefficient (RPC) models and limited generalization capability. Recent advances in generalizable 3DGS approaches show potential, but they perform poorly on multi-temporal sparse satellite images due to limited geometric constraints, transient objects, and radiometric inconsistencies. To address these limitations, we propose SkySplat, a novel self-supervised framework that integrates the RPC model into the generalizable 3DGS pipeline, enabling more effective use of sparse geometric cues for improved reconstruction. SkySplat relies only on RGB images and radiometric-robust relative height supervision, thereby eliminating the need for ground-truth height maps. Key components include a Cross-Self Consistency Module (CSCM), which mitigates transient object interference via consistency-based masking, and a multi-view consistency aggregation strategy that refines reconstruction results. Compared to per-scene optimization methods, SkySplat achieves an 86 times speedup over EOGS with higher accuracy. It also outperforms generalizable 3DGS baselines, reducing MAE from 13.18 m to 1.80 m on the DFC19 dataset significantly, and demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization on the MVS3D benchmark.
从稀疏视角卫星图像进行三维场景重建是一项长期且富有挑战性的任务。尽管3D高斯贴图(3DGS)及其变体因其高效率而近期备受关注,但现有方法由于与有理多项式系数(RPC)模型不兼容以及泛化能力有限,仍不适用于卫星图像。可泛化的3DGS方法的最新进展显示出潜力,但它们由于几何约束有限、瞬时物体和辐射不一致性,在多时间稀疏卫星图像上的表现不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了SkySplat,这是一种新型自监督框架,它将RPC模型集成到可泛化的3DGS管道中,从而更有效地利用稀疏几何线索来改善重建。SkySplat仅依赖于RGB图像和辐射稳健的相对高度监督,从而消除了对真实高度地图的需求。关键组件包括跨自一致性模块(CSCM),它通过基于一致性的掩码来缓解瞬时物体干扰,以及多视角一致性聚合策略,用于优化重建结果。与逐场景优化方法相比,SkySplat实现了相对于EOGS的86倍加速和高精度。它在DFC19数据集上将MAE从13.18米显著减少到1.80米,并在MVS3D基准测试上展示了强大的跨数据集泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于稀疏视角卫星图像的三维场景重建是一项具有挑战的任务。尽管三维高斯喷溅(3DGS)及其变体因其高效率而备受关注,但现有方法因无法适应有理多项式系数(RPC)模型以及泛化能力有限,在卫星图像上效果不佳。为解决这些问题,本文提出SkySplat,一种新型自监督框架,将RPC模型融入可泛化的三维高斯喷溅管道中,更有效地利用稀疏几何线索进行改进重建。SkySplat仅依赖RGB图像和鲁棒的相对高度监督,从而无需真实高度图。其关键组件包括跨自我一致性模块(CSCM),通过一致性掩码缓解瞬时物体干扰,以及多视角一致性聚合策略,优化重建结果。相较于针对场景的优化方法,SkySplat实现了对EOGS的86倍加速并提高了准确性。此外,它在DFC19数据集上将MAE从13.18米降至1.80米,并在MVS3D基准测试中展现出强大的跨数据集泛化能力。
关键见解
- SkySplat是一种自监督框架,整合RPC模型到可泛化的三维高斯喷溅管道中,提升稀疏几何线索的有效使用。
- SkySplat仅依赖RGB图像和鲁棒的相对高度监督,无需真实高度图。
- 跨自我一致性模块(CSCM)通过一致性掩码减少瞬时物体的干扰。
- 多视角一致性聚合策略优化重建结果。
- SkySplat实现了对场景优化方法的速度提升,并保持了高准确性。
- 在DFC19数据集上,SkySplat显著降低了MAE(平均绝对误差)。
- SkySplat展现出强大的跨数据集泛化能力,在MVS3D基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

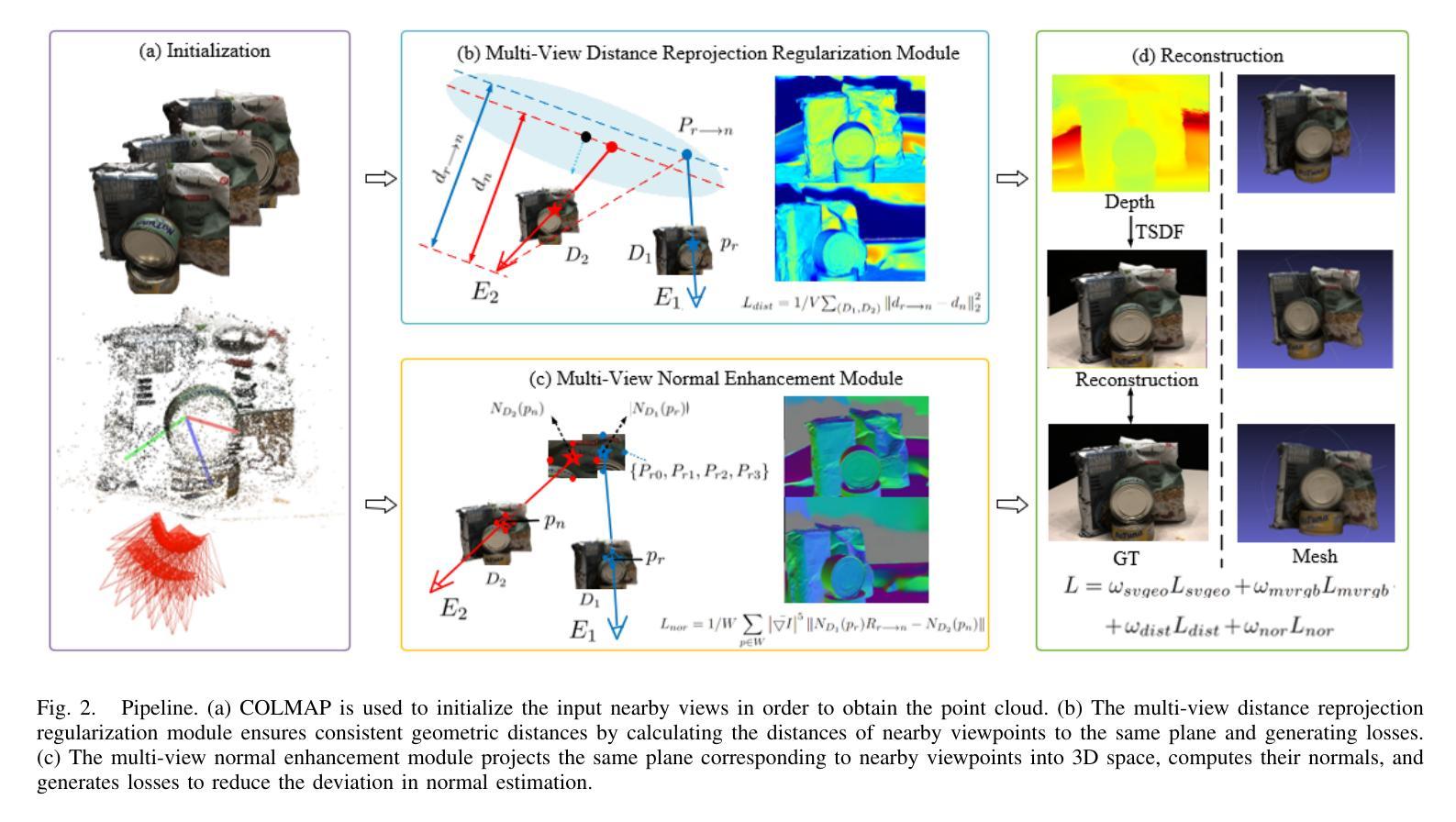
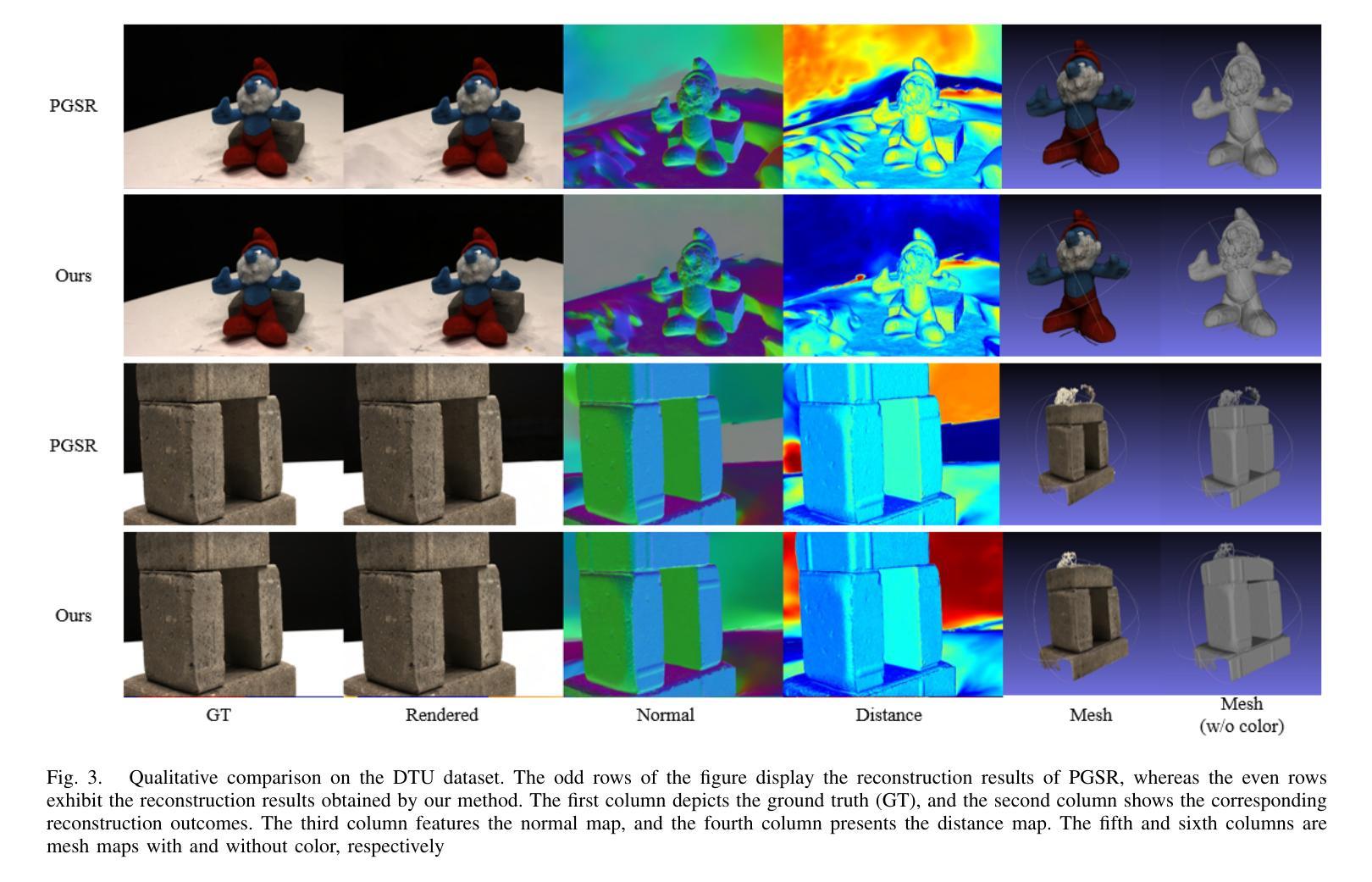
Multi-view Normal and Distance Guidance Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Bo Jia, Yanan Guo, Ying Chang, Benkui Zhang, Ying Xie, Kangning Du, Lin Cao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieves remarkable results in the field of surface reconstruction. However, when Gaussian normal vectors are aligned within the single-view projection plane, while the geometry appears reasonable in the current view, biases may emerge upon switching to nearby views. To address the distance and global matching challenges in multi-view scenes, we design multi-view normal and distance-guided Gaussian splatting. This method achieves geometric depth unification and high-accuracy reconstruction by constraining nearby depth maps and aligning 3D normals. Specifically, for the reconstruction of small indoor and outdoor scenes, we propose a multi-view distance reprojection regularization module that achieves multi-view Gaussian alignment by computing the distance loss between two nearby views and the same Gaussian surface. Additionally, we develop a multi-view normal enhancement module, which ensures consistency across views by matching the normals of pixel points in nearby views and calculating the loss. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the baseline in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, significantly enhancing the surface reconstruction capability of 3DGS. Our code will be made publicly available at (https://github.com/Bistu3DV/MND-GS/).
3D高斯贴合技术(3DGS)在表面重建领域取得了显著成果。然而,当高斯法线向量在单视投影平面内对齐时,虽然在当前视角下几何形态看起来是合理的,但在切换到邻近视角时可能会出现偏差。为了解决多视角场景中的距离和全局匹配挑战,我们设计了多视角法线和距离引导的高斯贴合方法。该方法通过约束邻近深度图和对齐3D法线,实现了几何深度统一和高精度重建。具体来说,对于室内外小场景的重建,我们提出了多视角距离重投影正则化模块,通过计算两个邻近视角和同一高斯表面之间的距离损失来实现多视角高斯对齐。此外,我们还开发了一个多视角法线增强模块,通过匹配邻近视角中像素点的法线并计算损失,确保不同视角之间的一致性。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在定量和定性评估上都超越了基线方法,显著提高了3DGS的表面重建能力。我们的代码将在[https://github.com/Bistu3DV/MND-GS/]上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IROS 2025. Code: https://github.com/Bistu3DV/MND-GS/
Summary
本文介绍了基于多视角距离引导的高斯平滑法,解决单一视角投影平面内高斯矢量对齐在多个视角之间存在的偏差问题。此方法通过约束邻近深度图和对齐三维法线实现几何深度统一和高精度重建。对于室内外小场景的重建,提出多视角距离重投影正则化模块和多视角法线增强模块,有效提升了多视角高斯对齐效果,实现了优异的表面重建能力。相关代码将在网站上公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于多视角距离引导的高斯平滑法在表面重建领域的优势。
- 提出一种针对高斯矢量的多视角方法和策略来处理在不同视角下的高斯偏差问题。
- 通过约束邻近深度图和对齐三维法线实现几何深度统一和高精度重建,提高重建质量。
- 针对室内外小场景的重建需求,设计特定的多视角距离重投影正则化模块和多视角法线增强模块。
- 通过实验验证,该方法在定量和定性评估上均优于基线方法,显著提升了表面重建能力。
- 该方法适用于多视角场景下的表面重建问题。
点此查看论文截图
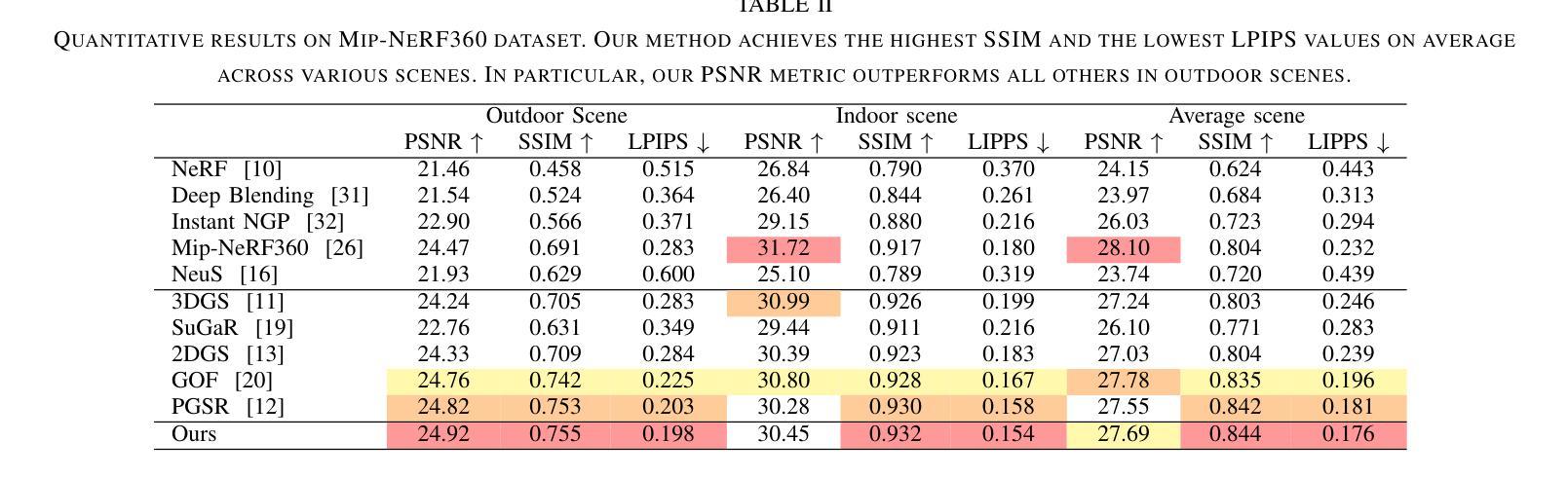
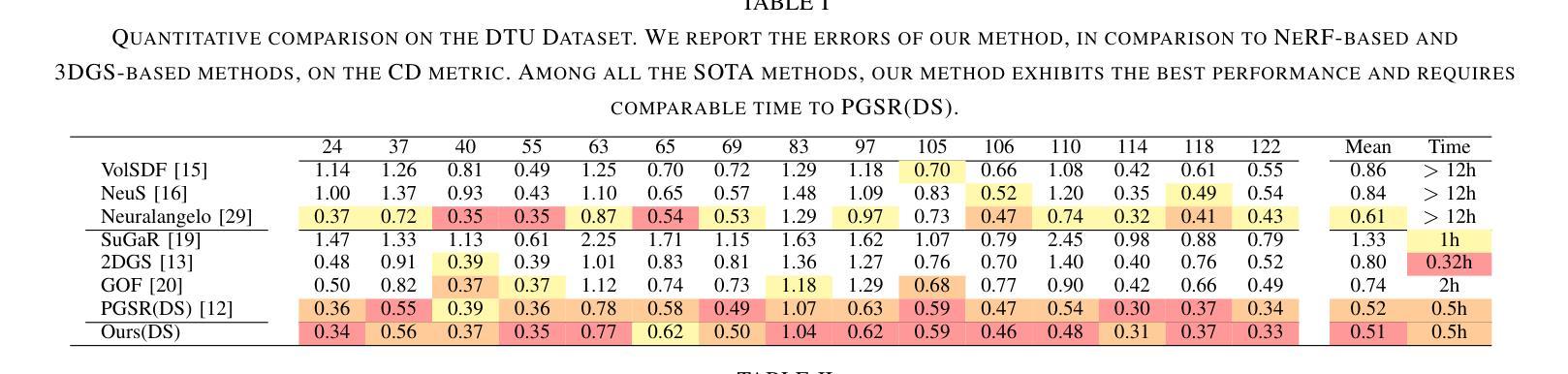
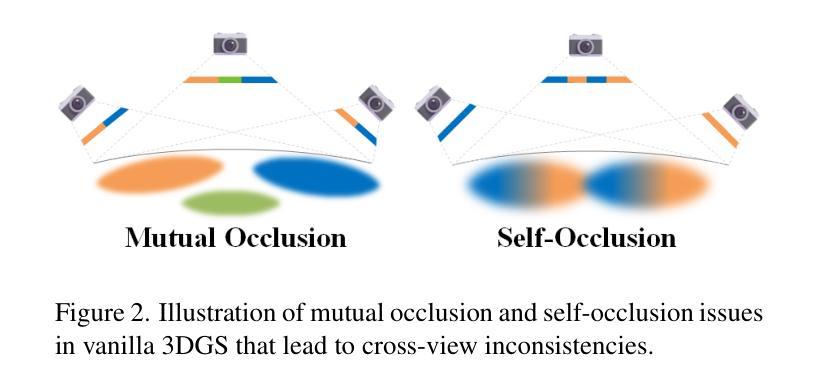
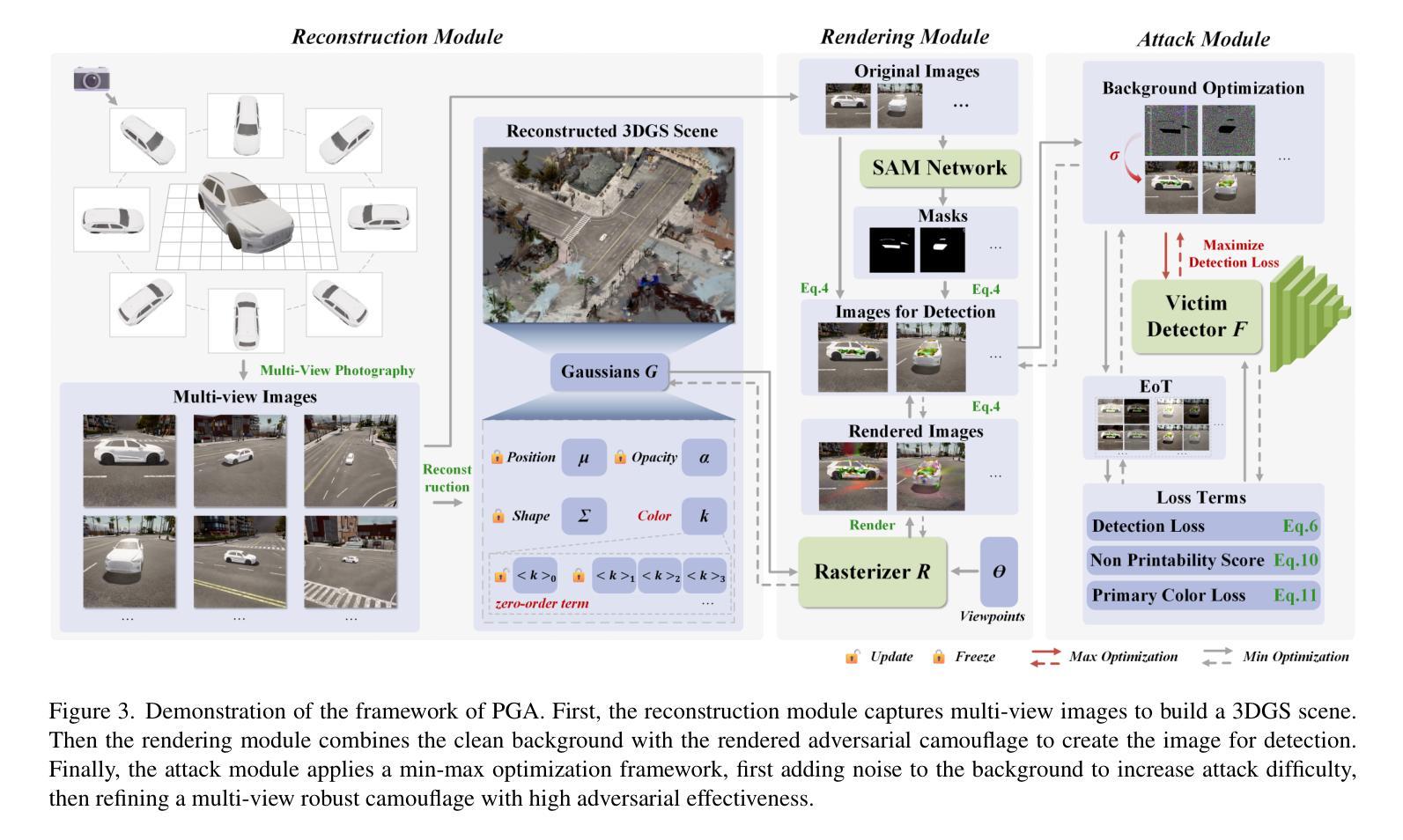
3D Gaussian Splatting Driven Multi-View Robust Physical Adversarial Camouflage Generation
Authors:Tianrui Lou, Xiaojun Jia, Siyuan Liang, Jiawei Liang, Ming Zhang, Yanjun Xiao, Xiaochun Cao
Physical adversarial attack methods expose the vulnerabilities of deep neural networks and pose a significant threat to safety-critical scenarios such as autonomous driving. Camouflage-based physical attack is a more promising approach compared to the patch-based attack, offering stronger adversarial effectiveness in complex physical environments. However, most prior work relies on mesh priors of the target object and virtual environments constructed by simulators, which are time-consuming to obtain and inevitably differ from the real world. Moreover, due to the limitations of the backgrounds in training images, previous methods often fail to produce multi-view robust adversarial camouflage and tend to fall into sub-optimal solutions. Due to these reasons, prior work lacks adversarial effectiveness and robustness across diverse viewpoints and physical environments. We propose a physical attack framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), named PGA, which provides rapid and precise reconstruction with few images, along with photo-realistic rendering capabilities. Our framework further enhances cross-view robustness and adversarial effectiveness by preventing mutual and self-occlusion among Gaussians and employing a min-max optimization approach that adjusts the imaging background of each viewpoint, helping the algorithm filter out non-robust adversarial features. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and superiority of PGA. Our code is available at:https://github.com/TRLou/PGA.
物理对抗攻击方法揭示了深度神经网络的脆弱性,并对自动驾驶等安全关键场景构成了重大威胁。与基于补丁的攻击相比,基于伪装攻击的解决方案是一种更有前途的方法,它在复杂的物理环境中具有更强的对抗效果。然而,大多数早期的工作依赖于目标物体的网格先验和由模拟器构建的虚拟环境,这些都需要花费大量时间且不可避免地与真实世界存在差异。此外,由于训练图像背景的限制,先前的方法往往无法生成多视角稳健的对抗伪装,并容易陷入次优解决方案。由于这些原因,早期工作的对抗效果和在不同视角和物理环境中的稳健性都相对不足。我们提出了一种基于三维高斯展布(3DGS)的物理攻击框架,名为PGA。该框架具有快速精确的重建能力和逼真的渲染能力,仅使用少量图像即可实现。我们的框架通过防止高斯之间的相互和自遮挡并采用一种最小最大优化方法调整每个视角的成像背景,进一步增强了跨视图稳健性和对抗效果,有助于算法过滤掉非稳健的对抗特征。大量实验验证了PGA的有效性和优越性。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/TRLou/PGA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了物理对抗攻击方法揭示深度神经网络脆弱性,并在自动驾驶等安全关键场景中构成重大威胁。相比基于补丁的攻击,伪装攻击是一种更有前途的方法,在复杂的物理环境中具有更强的对抗效果。然而,大多数先前的工作依赖于目标物体的网格先验和模拟器构建的虚拟环境,这些环境的获取耗时且不可避免地与真实世界存在差异。此外,由于训练图像背景的限制,先前的方法往往无法产生多视角稳健的对抗伪装,并倾向于陷入次优解决方案。因此,先前的工作在跨越不同视角和物理环境的对抗性和稳健性方面存在不足。为此,我们提出了一种基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的物理攻击框架,名为PGA,该框架具有快速精确重建和逼真的渲染能力。我们的框架通过防止高斯之间的相互和自遮挡,并采用调整每个视点成像背景的minmax优化方法,提高了跨视图稳健性和对抗性效果,过滤掉非稳健的对抗特征。实验验证了PGA的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 物理对抗攻击威胁深度神经网络在自动驾驶等安全关键场景的应用。
- 伪装攻击相比补丁攻击在复杂物理环境中具有更强对抗效果。
- 大多数先前工作依赖虚拟环境构建和模拟器训练存在与现实差异的问题。
- 训练图像背景限制导致难以产生多视角稳健的对抗伪装。
- PGA框架基于3DGS技术实现快速精确重建和逼真渲染。
- PGA框架提高了跨视图稳健性和对抗性效果通过防止高斯遮挡和优化成像背景方法。
点此查看论文截图

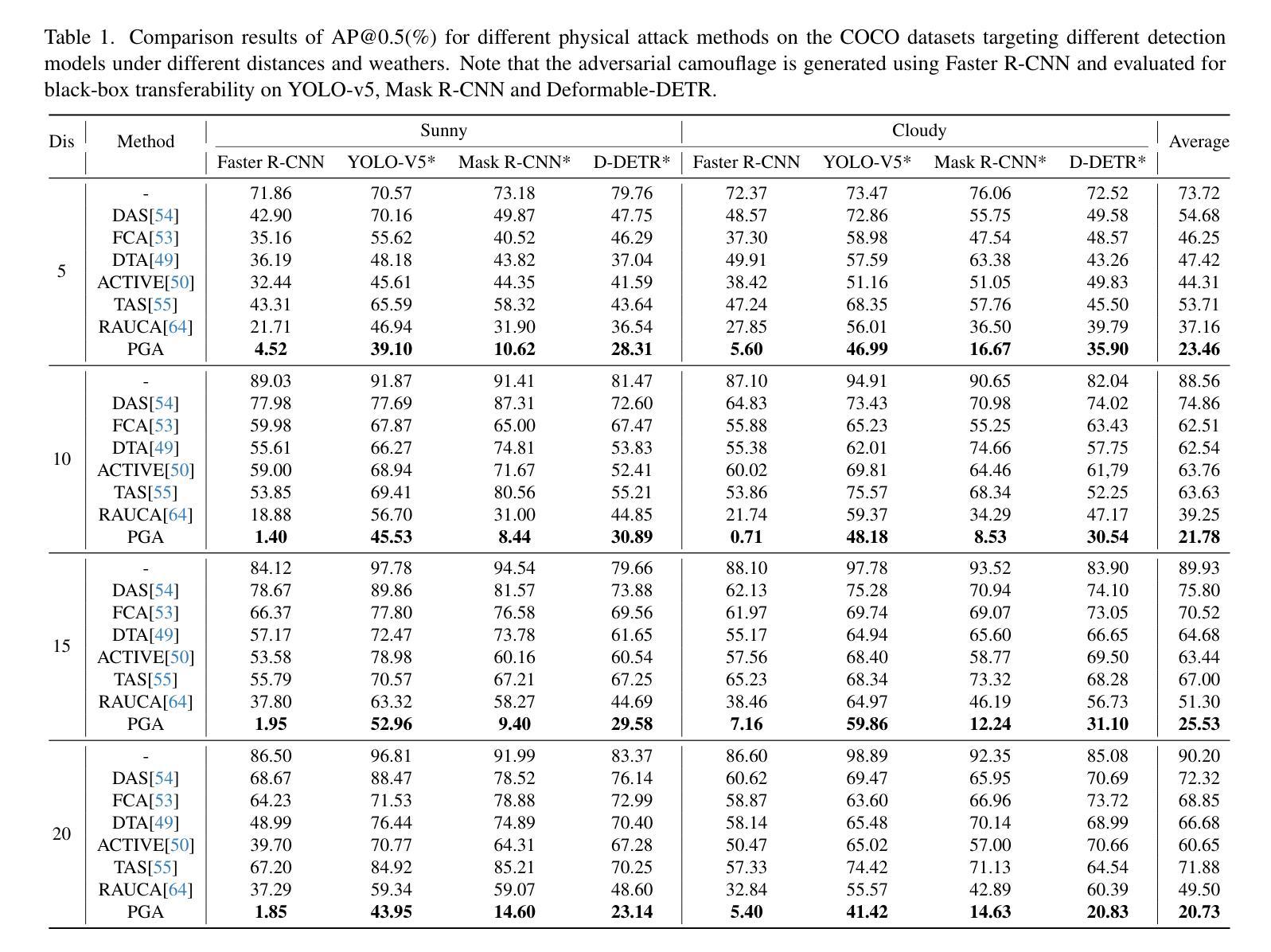
CCL-LGS: Contrastive Codebook Learning for 3D Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lei Tian, Xiaomin Li, Liqian Ma, Hao Yin, Zirui Zheng, Hefei Huang, Taiqing Li, Huchuan Lu, Xu Jia
Recent advances in 3D reconstruction techniques and vision-language models have fueled significant progress in 3D semantic understanding, a capability critical to robotics, autonomous driving, and virtual/augmented reality. However, methods that rely on 2D priors are prone to a critical challenge: cross-view semantic inconsistencies induced by occlusion, image blur, and view-dependent variations. These inconsistencies, when propagated via projection supervision, deteriorate the quality of 3D Gaussian semantic fields and introduce artifacts in the rendered outputs. To mitigate this limitation, we propose CCL-LGS, a novel framework that enforces view-consistent semantic supervision by integrating multi-view semantic cues. Specifically, our approach first employs a zero-shot tracker to align a set of SAM-generated 2D masks and reliably identify their corresponding categories. Next, we utilize CLIP to extract robust semantic encodings across views. Finally, our Contrastive Codebook Learning (CCL) module distills discriminative semantic features by enforcing intra-class compactness and inter-class distinctiveness. In contrast to previous methods that directly apply CLIP to imperfect masks, our framework explicitly resolves semantic conflicts while preserving category discriminability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCL-LGS outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. Our project page is available at https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/.
近期三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的进步极大地推动了三维语义理解的发展,这一能力对于机器人技术、自动驾驶和虚拟现实/增强现实至关重要。然而,依赖二维先验的方法面临着一项重大挑战:由遮挡、图像模糊和视角变化引起的跨视图语义不一致性。这些不一致性通过投影监督进行传播,会恶化三维高斯语义场的品质,并在渲染输出中引入伪影。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了CCL-LGS这一新型框架,它通过整合多视图语义线索来实施视图一致的语义监督。具体来说,我们的方法首先采用零样本追踪器来对齐一组由SAM生成的二维蒙版,并可靠地识别出它们对应的类别。然后,我们利用CLIP在不同视角下提取稳健的语义编码。最后,我们的对比代码本学习(CCL)模块通过强制类内紧凑性和类间差异性来提炼出鉴别性语义特征。与之前直接应用于不完美蒙版的CLIP方法不同,我们的框架能够显式解决语义冲突,同时保留类别鉴别能力。大量实验表明,CCL-LGS超越了先前最先进的方法。我们的项目页面可在https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了3D重建技术和视觉语言模型的新进展对3D语义理解的重要性及其在机器人、自动驾驶和虚拟现实等领域的应用。然而,依赖二维先验的方法面临一个关键挑战:由于遮挡、图像模糊和视角变化导致的跨视图语义不一致性。为解决此问题,本文提出了CCL-LGS框架,通过整合多视图语义线索来实施视图一致语义监督。该框架采用零样本跟踪器对齐一组SAM生成的2D掩膜并可靠识别其对应的类别,然后使用CLIP提取跨视图的稳健语义编码。最后,对比代码本学习(CCL)模块通过实现类内紧凑性和类间区分性来提炼判别语义特征。实验证明,CCL-LGS框架优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建技术和视觉语言模型的新进展推动了3D语义理解领域的显著进步。
- 依赖二维先验的方法面临跨视图语义不一致性的挑战,这会影响3D高斯语义场的质量和渲染输出。
- CCL-LGS框架通过整合多视图语义线索来实施视图一致语义监督,解决了这个问题。
- CCL-LGS采用零样本跟踪器对齐SAM生成的2D掩膜,并使用CLIP提取稳健的跨视图语义编码。
- 对比代码本学习(CCL)模块提高了语义特征的判别力。
- 实验证明,CCL-LGS框架在性能上超越了先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图

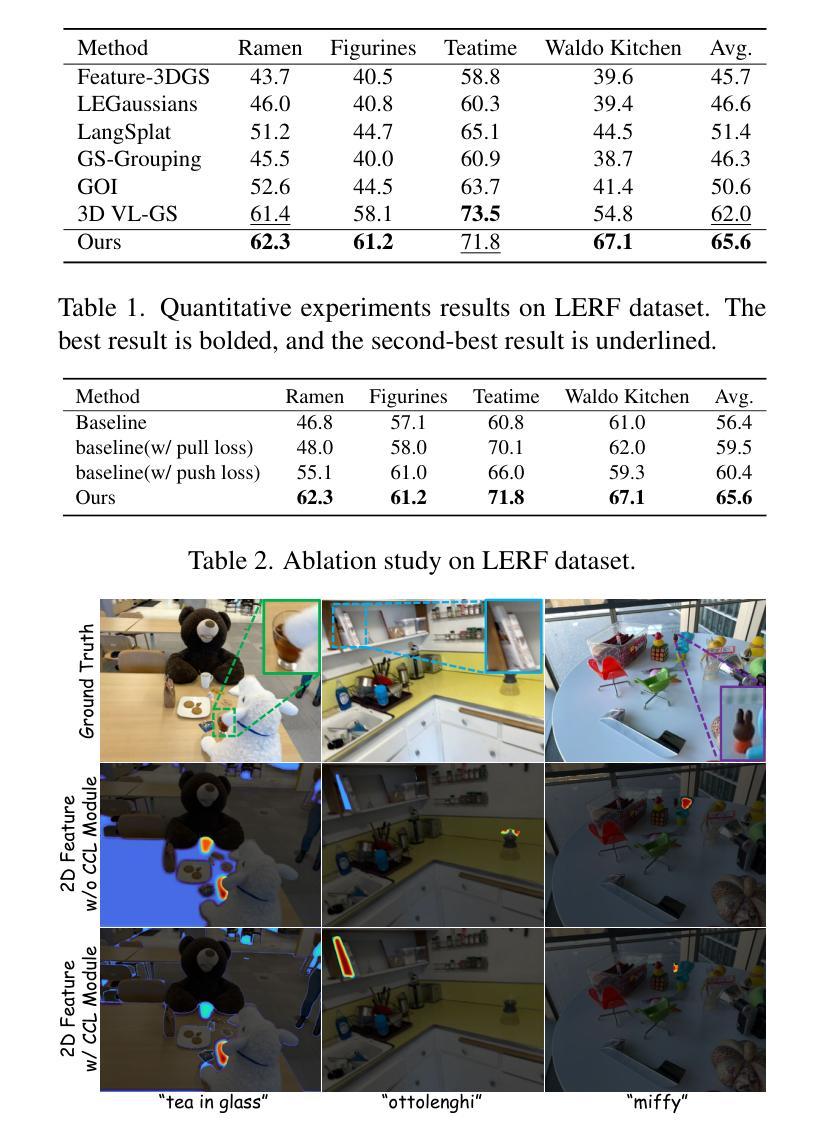
Casual3DHDR: High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos
Authors:Shucheng Gong, Lingzhe Zhao, Wenpu Li, Hong Xie, Yin Zhang, Shiyu Zhao, Peidong Liu
Photo-realistic novel view synthesis from multi-view images, such as neural radiance field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has gained significant attention for its superior performance. However, most existing methods rely on low dynamic range (LDR) images, limiting their ability to capture detailed scenes in high-contrast environments. While some prior works address high dynamic range (HDR) scene reconstruction, they typically require multi-view sharp images with varying exposure times captured at fixed camera positions, which is time-consuming and impractical. To make data acquisition more flexible, we propose \textbf{Casual3DHDR}, a robust one-stage method that reconstructs 3D HDR scenes from casually-captured auto-exposure (AE) videos, even under severe motion blur and unknown, varying exposure times. Our approach integrates a continuous camera trajectory into a unified physical imaging model, jointly optimizing exposure times, camera trajectory, and the camera response function (CRF). Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that \textbf{Casual3DHDR} outperforms existing methods in robustness and rendering quality. Our source code and dataset will be available at https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/
基于多视角图像的光照真实感新型视图合成,例如神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),因其卓越性能而受到广泛关注。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于低动态范围(LDR)图像,这限制了它们在高对比度环境中捕捉详细场景的能力。虽然一些早期的工作解决了高动态范围(HDR)场景重建问题,但它们通常需要固定相机位置拍摄的多视角清晰图像,这些图像具有不同的曝光时间,既耗时又不实用。为了使数据采集更加灵活,我们提出了Casual3DHDR,这是一种稳健的一阶段方法,可以从随意拍摄的自适应曝光(AE)视频中重建3D HDR场景,即使在严重运动模糊和未知、变化的曝光时间下也可以。我们的方法将连续的相机轨迹集成到一个统一的物理成像模型中,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数(CRF)。在合成和真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,Casual3DHDR在稳健性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。我们的源代码和数据集将在https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in ACM Multimedia 2025. Project page: https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/ (Previously titled “CasualHDRSplat: Robust High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos”)
Summary
该文本介绍了基于神经辐射场和3D高斯溅射等技术的新型视图合成方法,在真实感渲染方面受到广泛关注。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于低动态范围图像,无法捕捉高对比度环境下的精细场景。针对这一问题,文本提出了一种名为Casual3DHDR的稳健单阶段方法,能够从非专业拍摄的自动曝光视频中重建3D HDR场景,即使在严重运动模糊和未知、不同曝光时间下也能实现。该方法将连续的相机轨迹整合到统一的物理成像模型中,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数。实验证明,Casual3DHDR在鲁棒性和渲染质量上均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 新型视图合成技术如神经辐射场和3D高斯溅射在真实感渲染方面表现优异。
- 现有方法大多依赖于低动态范围图像,难以捕捉高对比度环境下的精细场景。
- Casual3DHDR是一种新的HDR场景重建方法,能够从非专业拍摄的自动曝光视频中重建场景。
- Casual3DHDR能够在严重运动模糊和未知、不同的曝光时间下实现重建。
- 该方法将连续的相机轨迹整合到物理成像模型中,并联合优化多个参数。
- 实验证明Casual3DHDR在鲁棒性和渲染质量上超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
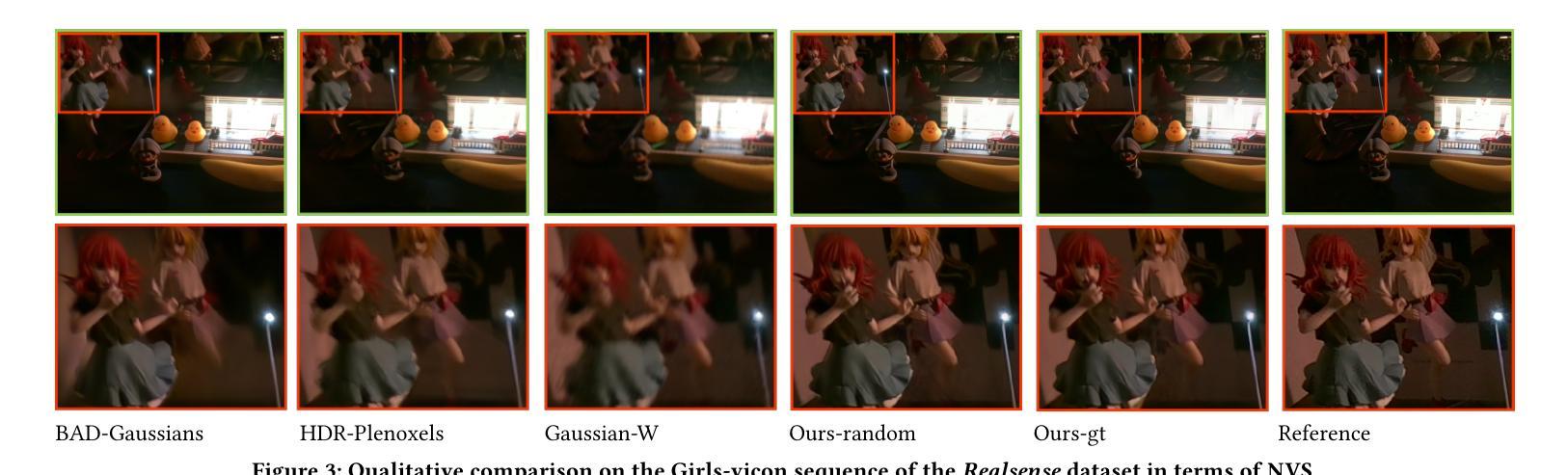
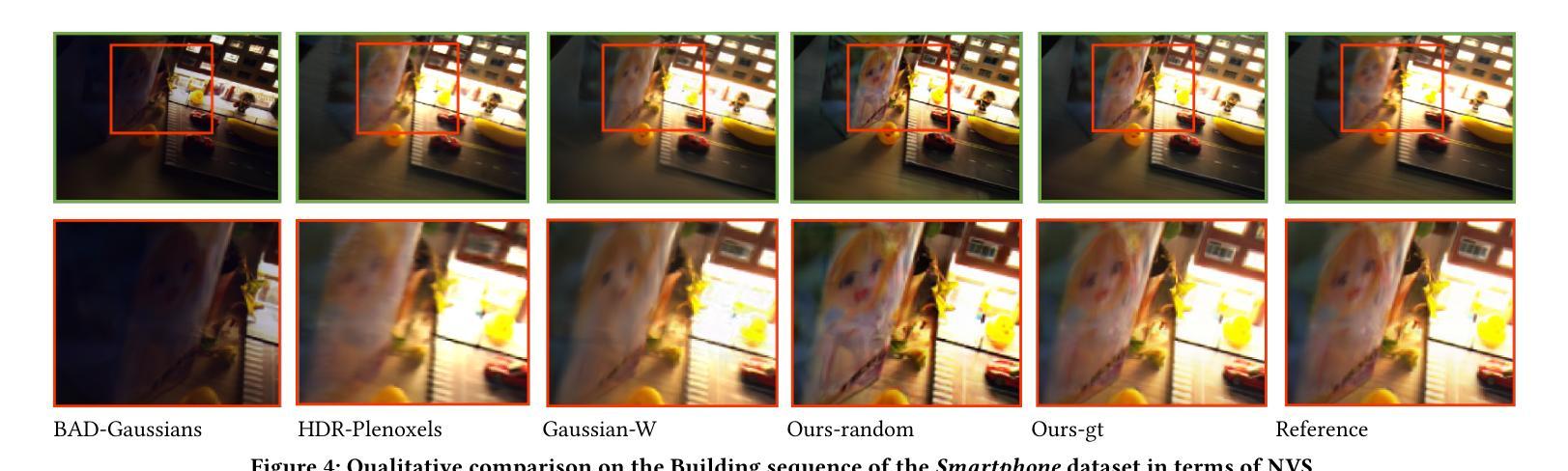
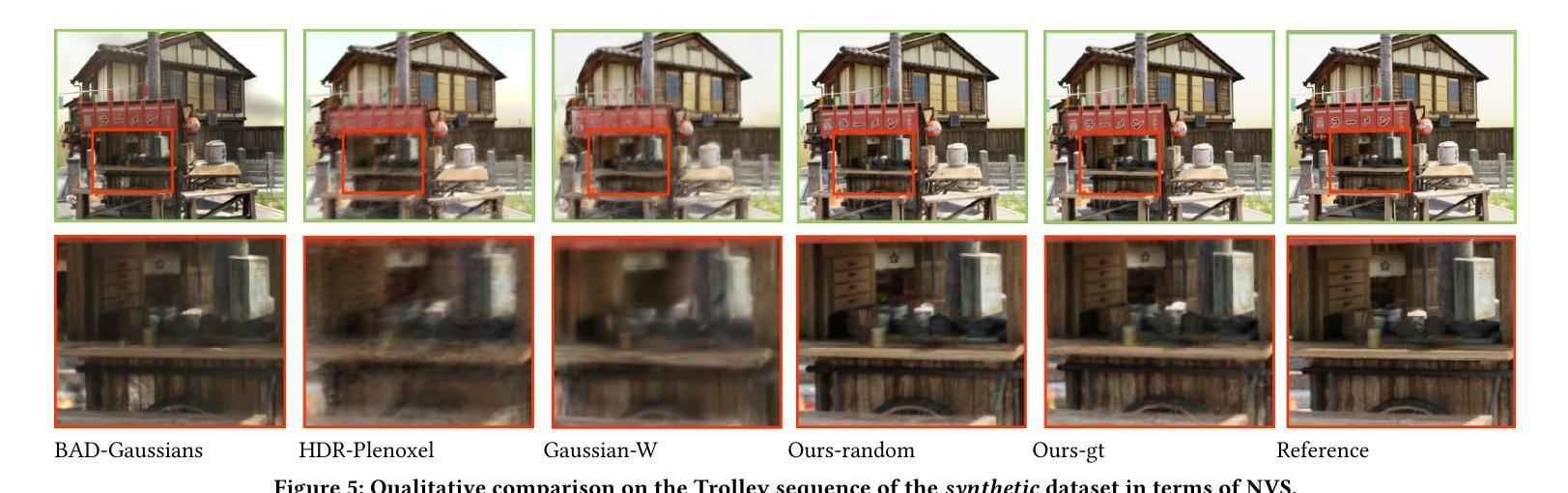





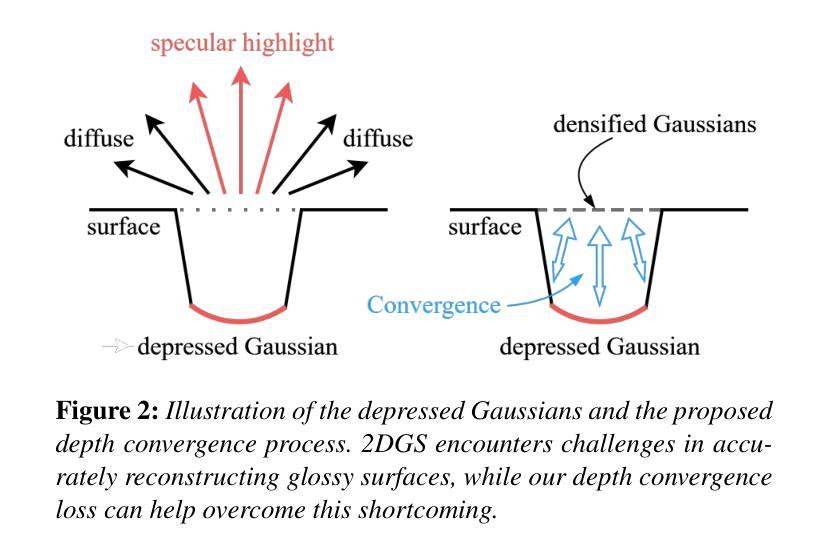
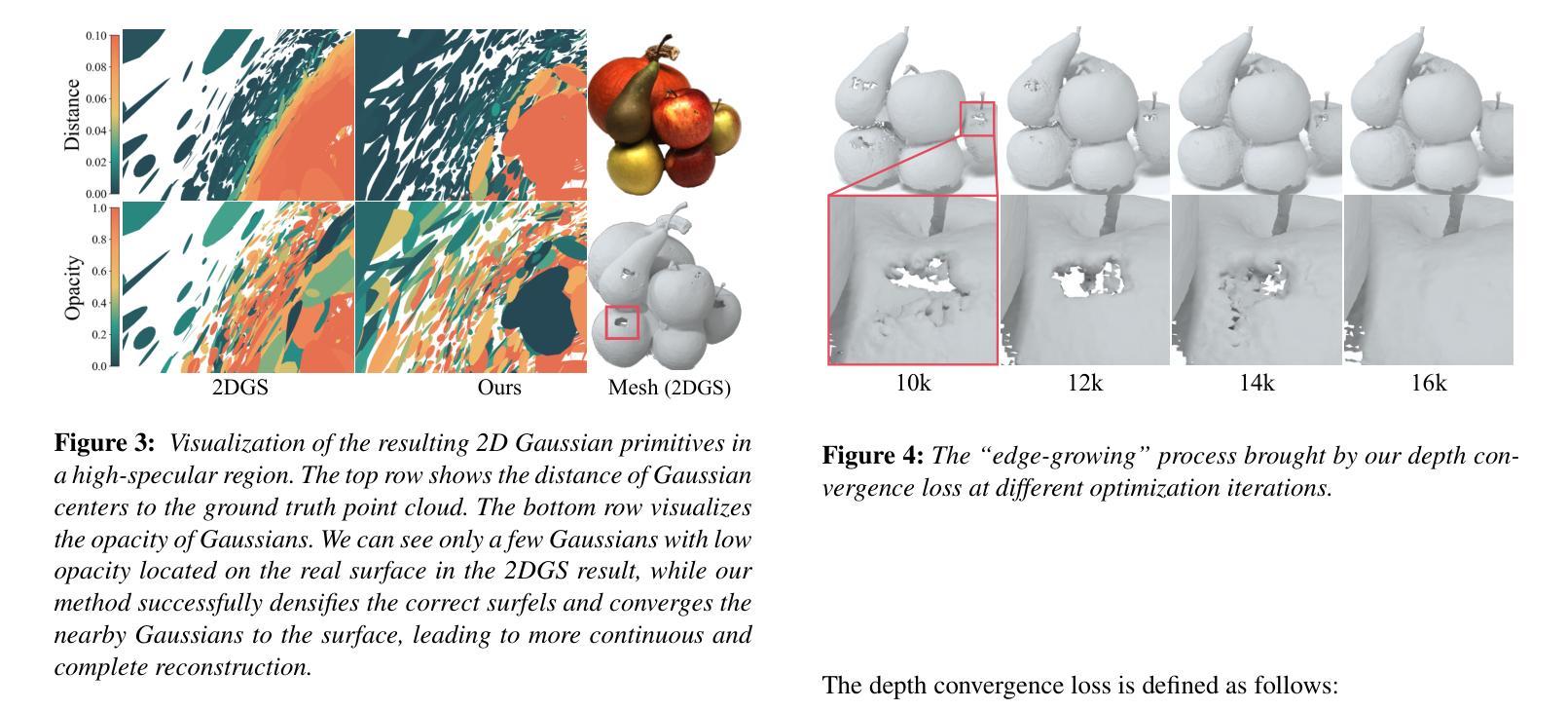
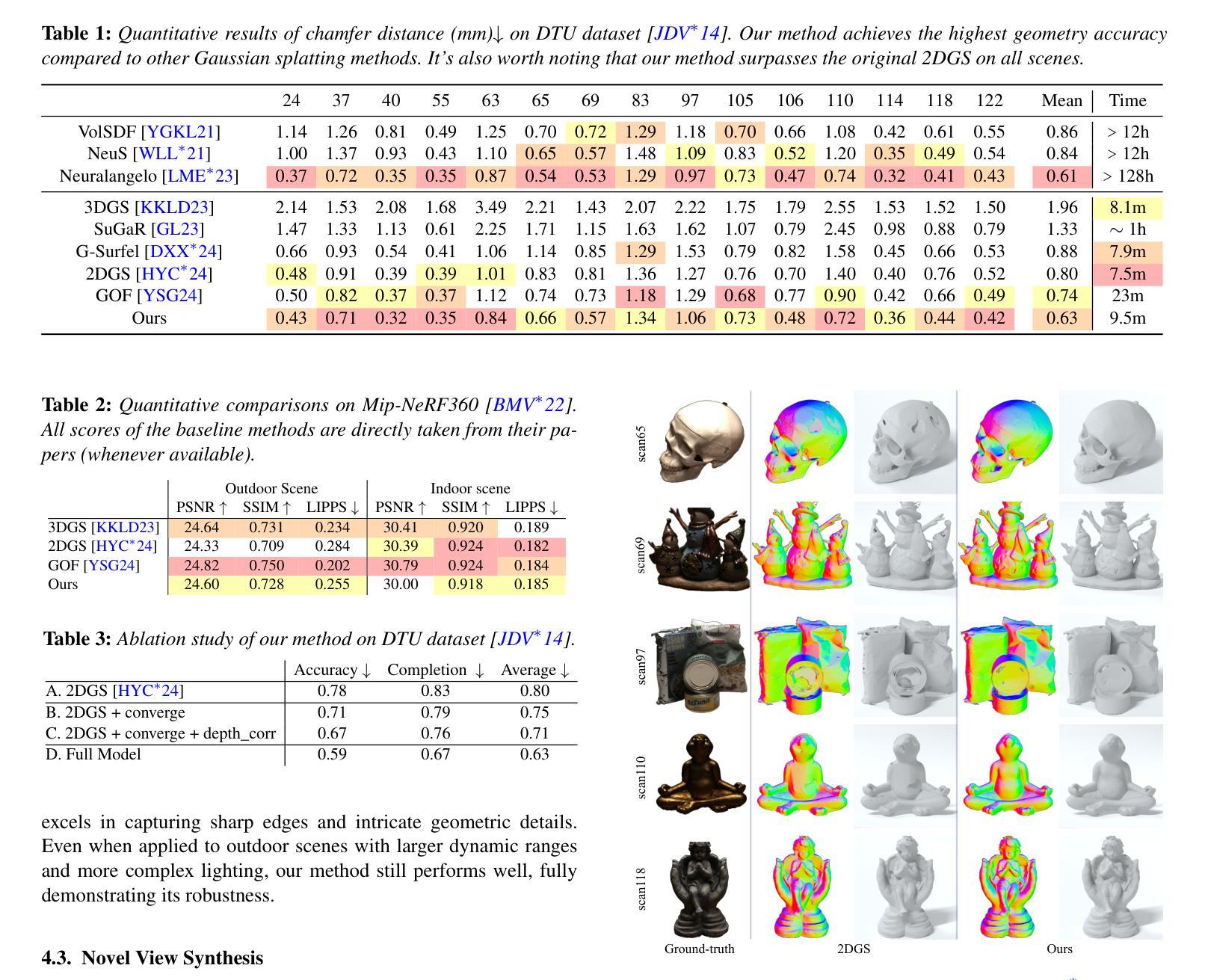
Introducing Unbiased Depth into 2D Gaussian Splatting for High-accuracy Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Yixin Yang, Yang Zhou, Hui Huang
Recently, 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) has demonstrated superior geometry reconstruction quality than the popular 3DGS by using 2D surfels to approximate thin surfaces. However, it falls short when dealing with glossy surfaces, resulting in visible holes in these areas. We find that the reflection discontinuity causes the issue. To fit the jump from diffuse to specular reflection at different viewing angles, depth bias is introduced in the optimized Gaussian primitives. To address that, we first replace the depth distortion loss in 2DGS with a novel depth convergence loss, which imposes a strong constraint on depth continuity. Then, we rectify the depth criterion in determining the actual surface, which fully accounts for all the intersecting Gaussians along the ray. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations across various datasets reveal that our method significantly improves reconstruction quality, with more complete and accurate surfaces than 2DGS. Code is available at https://github.com/XiaoXinyyx/Unbiased_Surfel.
近期,二维高斯点云(2DGS)通过使用二维面元来近似薄表面,展现出了比流行的三维高斯点云(3DGS)更优越的几何重建质量。然而,在处理光滑表面时,它还存在缺陷,导致这些区域出现明显的空洞。我们发现反射不连续是造成这个问题的原因。为了拟合不同视角下的漫反射到镜面反射的跳跃,在优化的高斯基元中引入了深度偏差。为了解决这个问题,我们首先用新型深度收敛损失替换了二维高斯点云中的深度失真损失,对深度连续性施加了严格的约束。然后,我们修正了确定实际表面时的深度标准,充分考虑沿光线方向的所有相交高斯。跨多个数据集的质量和数量评估表明,我们的方法显著提高了重建质量,与二维高斯点云相比,表面更加完整和准确。代码可在https://github.com/XiaoXinyyx/Unbiased_Surfel找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Journal track of Pacific Graphics 2025
Summary
二维高斯贴片(2DGS)在几何重建上具有高质量的表现,通过二维基本几何元素来近似薄表面,相较于流行的三维高斯贴片(3DGS)有更佳的表现。然而,在处理具有光泽的表面时,存在明显的缺陷,显示为空洞。问题源于反射的不连续性,优化的高斯基本体在适应漫反射到镜面反射的跳跃时产生深度偏差。为解决此问题,我们以深度收敛损失取代深度失真损失,增强深度连续性的约束。此外,我们还修正了用于确定实际表面的深度标准,充分考虑到射线上的所有相交高斯体。经过跨多个数据集的质量和数量评估,我们的方法显著提高了重建质量,表面更加完整和准确。
Key Takeaways
- 2DGS在几何重建上表现出优于3DGS的质量,尤其擅长近似薄表面。
- 处理具有光泽的表面时,2DGS存在空洞问题。
- 空洞问题源于反射的不连续性以及优化高斯基本体时的深度偏差。
- 引入深度收敛损失以替代深度失真损失,增强深度连续性的约束。
- 修正用于确定实际表面的深度标准,综合考虑射线上的所有相交高斯体。
- 新方法显著提高了重建质量,表面更加完整和准确。
点此查看论文截图

GBR: Generative Bundle Refinement for High-fidelity Gaussian Splatting with Enhanced Mesh Reconstruction
Authors:Jianing Zhang, Yuchao Zheng, Ziwei Li, Qionghai Dai, Xiaoyun Yuan
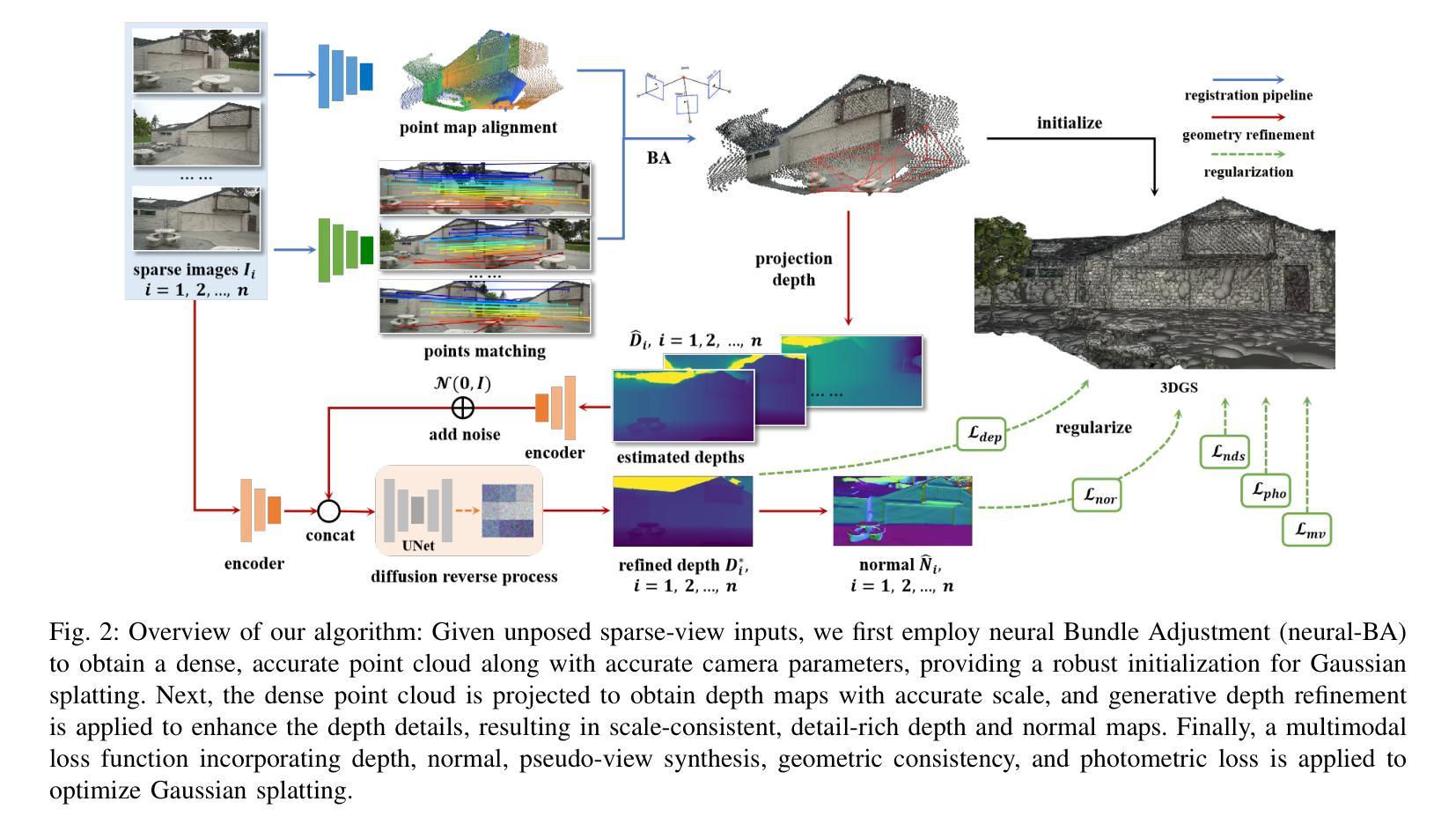
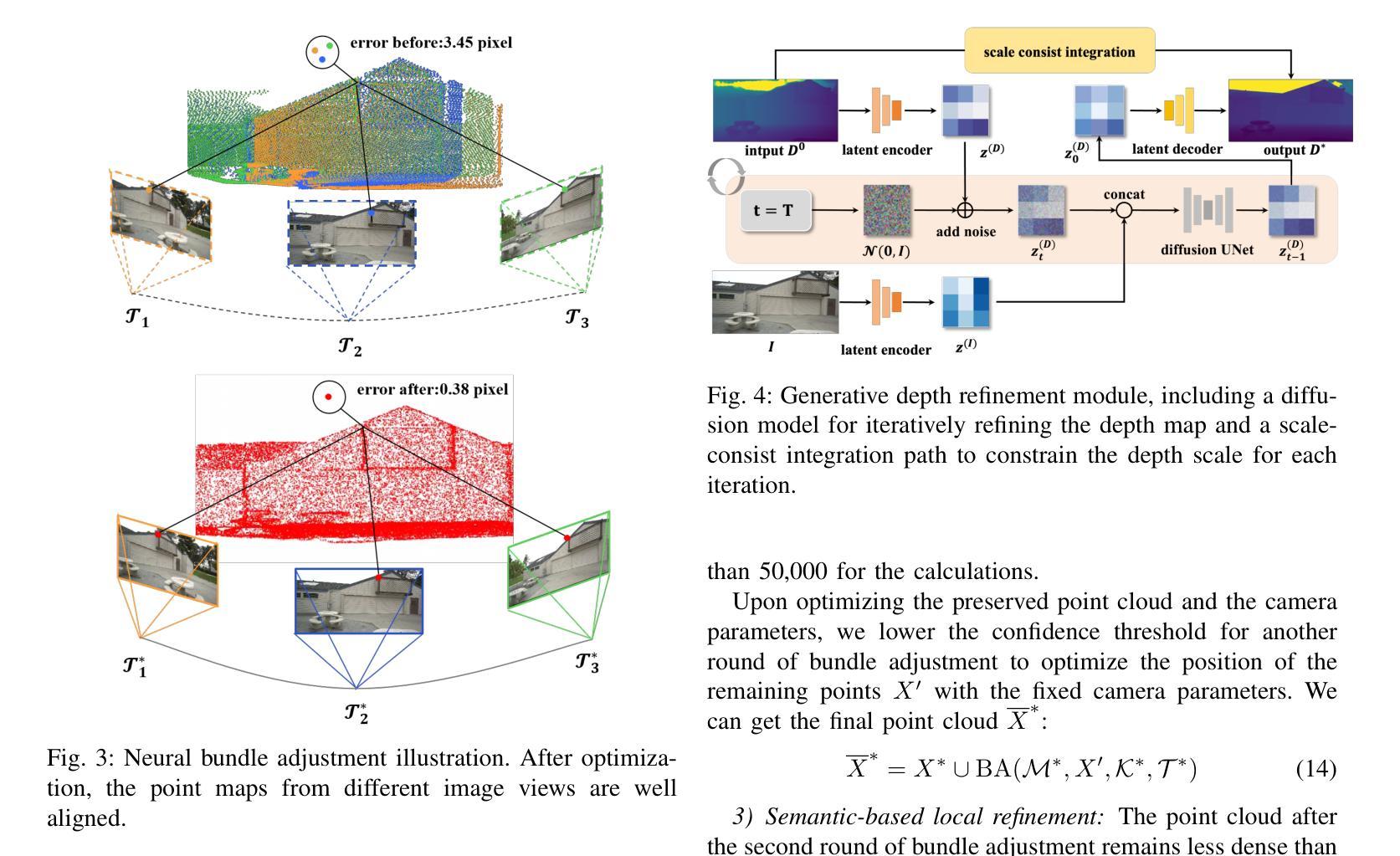
Gaussian splatting has gained attention for its efficient representation and rendering of 3D scenes using continuous Gaussian primitives. However, it struggles with sparse-view inputs due to limited geometric and photometric information, causing ambiguities in depth, shape, and texture. we propose GBR: Generative Bundle Refinement, a method for high-fidelity Gaussian splatting and meshing using only 4-6 input views. GBR integrates a neural bundle adjustment module to enhance geometry accuracy and a generative depth refinement module to improve geometry fidelity. More specifically, the neural bundle adjustment module integrates a foundation network to produce initial 3D point maps and point matches from unposed images, followed by bundle adjustment optimization to improve multiview consistency and point cloud accuracy. The generative depth refinement module employs a diffusion-based strategy to enhance geometric details and fidelity while preserving the scale. Finally, for Gaussian splatting optimization, we propose a multimodal loss function incorporating depth and normal consistency, geometric regularization, and pseudo-view supervision, providing robust guidance under sparse-view conditions. Experiments on widely used datasets show that GBR significantly outperforms existing methods under sparse-view inputs. Additionally, GBR demonstrates the ability to reconstruct and render large-scale real-world scenes, such as the Pavilion of Prince Teng and the Great Wall, with remarkable details using only 6 views.
高斯贴图技术因其使用连续的高斯基本元素来高效表示和渲染3D场景而受到关注。然而,由于几何和光度信息有限,它在稀疏视角输入方面遇到了困难,导致深度、形状和纹理的不确定性。我们提出GBR:生成捆调整优化方法(Generative Bundle Refinement),这是一种仅使用4-6个输入视角进行高保真高斯贴图和网格化的方法。GBR集成了一个神经网络捆调整模块,以提高几何精度,以及一个生成深度优化模块,以提高几何保真度。更具体地说,神经网络捆调整模块首先集成基础网络,从非定位图像生成初始的3D点图和点匹配,然后通过捆调整优化提高多视角的一致性和点云精度。生成深度优化模块采用基于扩散的策略,以提高几何细节和保真度,同时保持尺度不变。最后,针对高斯贴图优化,我们提出了一个多模态损失函数,结合了深度和法线一致性、几何正则化和伪视图监督,在稀疏视角条件下提供稳健的引导。在常用数据集上的实验表明,GBR在稀疏视角输入下显著优于现有方法。此外,GBR展示了仅使用6个视角就能重建和渲染大规模真实场景,如太子亭和大长城,具有令人惊叹的细节。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了基于高斯涂绘(Gaussian splatting)技术的改进方法GBR(Generative Bundle Refinement),用于高效表示和渲染三维场景。针对稀疏视角输入导致的高斯涂绘在深度、形状和纹理上的模糊问题,GBR通过引入神经束调整模块和生成深度细化模块,提高了几何精度和保真度。通过优化神经网络和调整策略,GBR在仅使用4-6个输入视角的情况下实现了高保真度的高斯涂绘和网格化。实验证明,GBR在稀疏视角输入下显著优于现有方法,并可在仅有6个视角的情况下重建和渲染大规模真实场景,如滕王阁和长城等。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯涂绘是一种用于高效表示和渲染三维场景的技术,但在稀疏视角输入时存在深度、形状和纹理的模糊问题。
- GBR通过引入神经束调整模块和生成深度细化模块解决了上述问题,提高了几何精度和保真度。
- GBR使用基础网络生成初始三维点图和点匹配,并通过束调整优化提高多视角一致性和点云精度。
- 生成深度细化模块采用扩散策略,在提高几何细节和保真度的同时保持尺度不变。
- 为优化高斯涂绘,GBR提出多模态损失函数,包括深度与法线一致性、几何正则化和伪视角监督,为稀疏视角条件下的重建提供稳健指导。
- 实验证明,GBR在稀疏视角输入下显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图