⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
DiCriTest: Testing Scenario Generation for Decision-Making Agents Considering Diversity and Criticality
Authors:Qitong Chu, Yufeng Yue, Danya Yao, Huaxin Pei
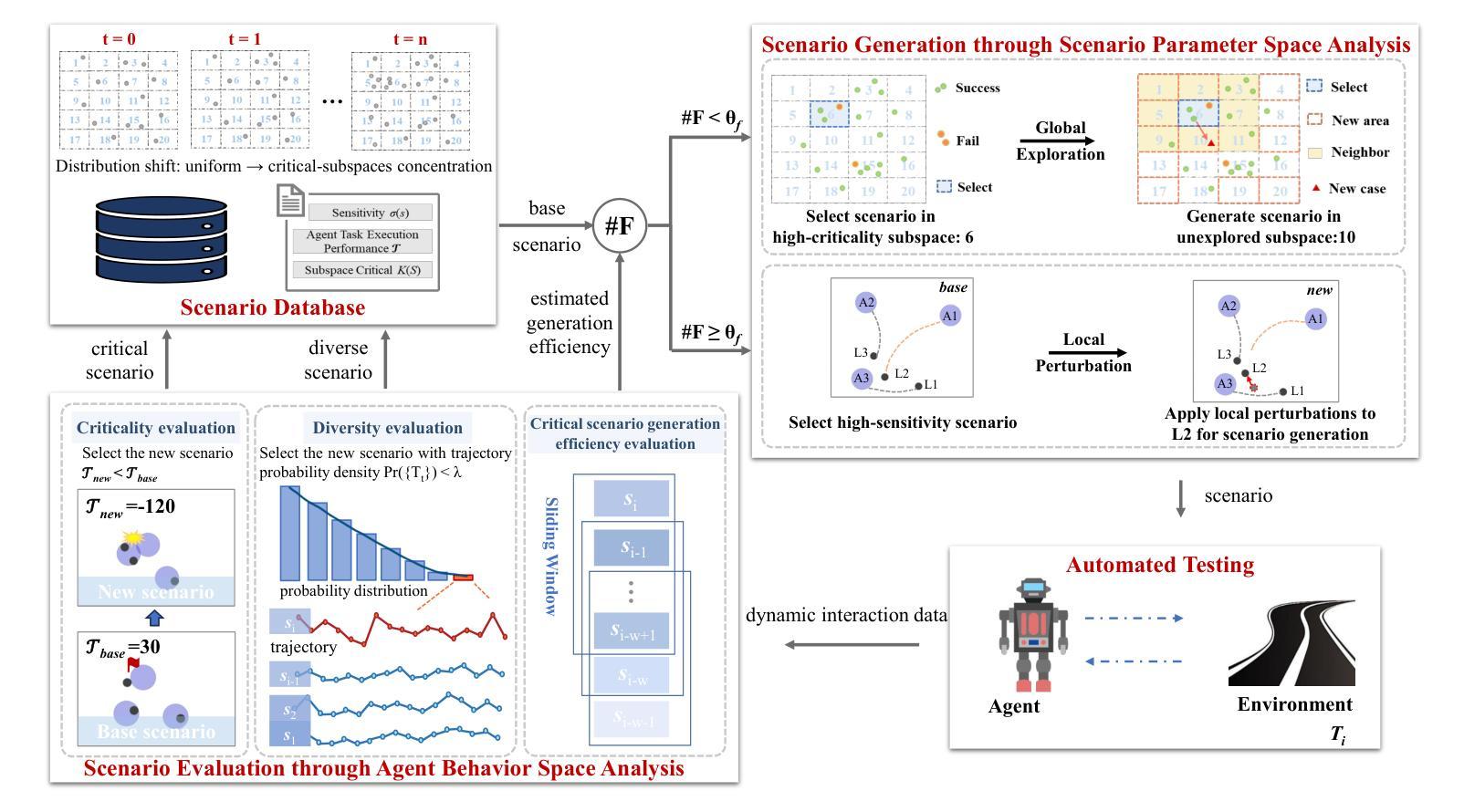
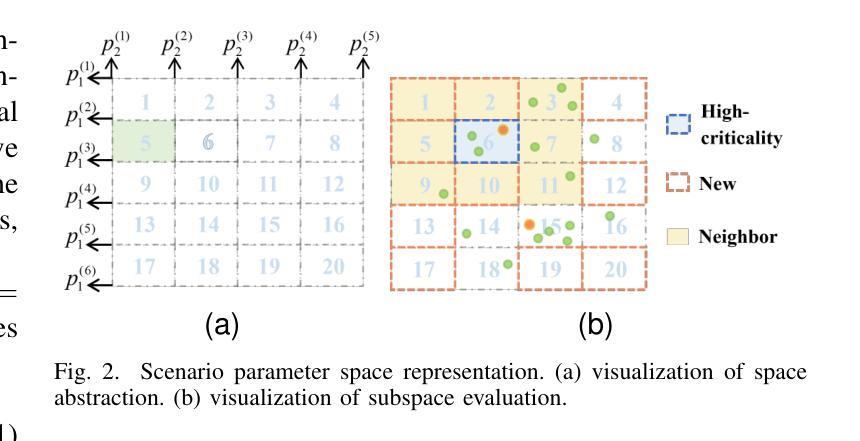
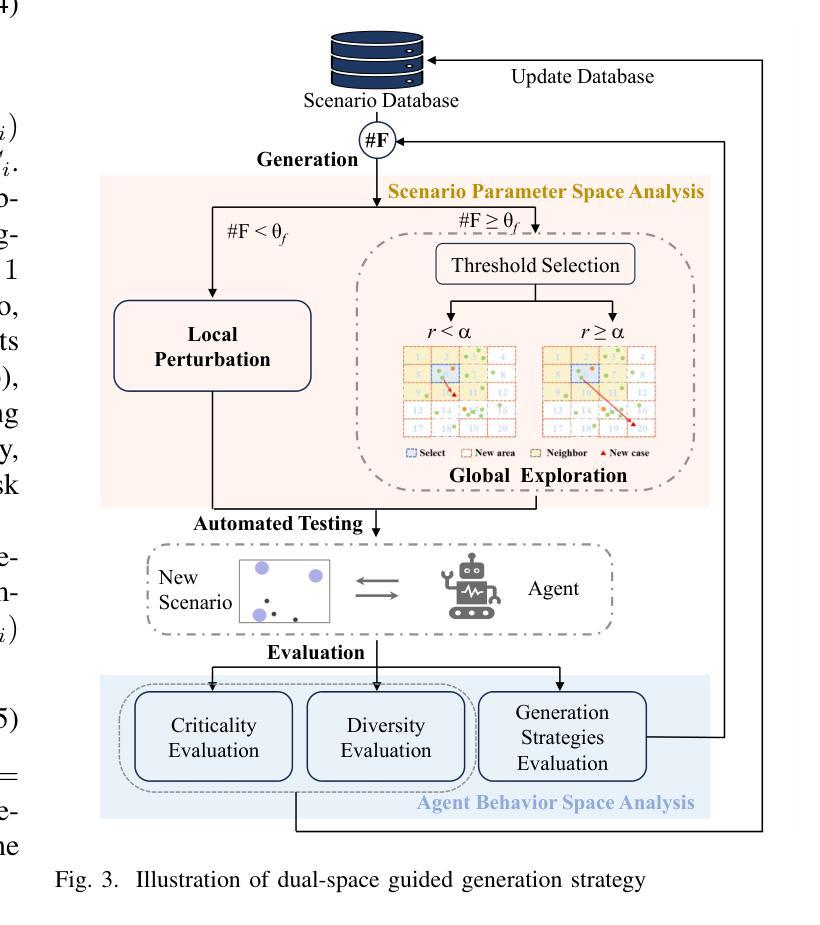
The growing deployment of decision-making agents in dynamic environments increases the demand for safety verification. While critical testing scenario generation has emerged as an appealing verification methodology, effectively balancing diversity and criticality remains a key challenge for existing methods, particularly due to local optima entrapment in high-dimensional scenario spaces. To address this limitation, we propose a dual-space guided testing framework that coordinates scenario parameter space and agent behavior space, aiming to generate testing scenarios considering diversity and criticality. Specifically, in the scenario parameter space, a hierarchical representation framework combines dimensionality reduction and multi-dimensional subspace evaluation to efficiently localize diverse and critical subspaces. This guides dynamic coordination between two generation modes: local perturbation and global exploration, optimizing critical scenario quantity and diversity. Complementarily, in the agent behavior space, agent-environment interaction data are leveraged to quantify behavioral criticality/diversity and adaptively support generation mode switching, forming a closed feedback loop that continuously enhances scenario characterization and exploration within the parameter space. Experiments show our framework improves critical scenario generation by an average of 56.23% and demonstrates greater diversity under novel parameter-behavior co-driven metrics when tested on five decision-making agents, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines.
随着决策代理在动态环境中的部署不断增加,对安全验证的需求也在增长。虽然关键测试场景生成已经成为一种有吸引力的验证方法,但如何在多样性和关键性之间进行有效平衡仍然是现有方法的关键挑战,尤其是在高维度场景空间中的局部最优困境。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种双空间引导测试框架,该框架协调场景参数空间和代理行为空间,旨在生成考虑多样性和关键性的测试场景。具体而言,在场景参数空间中,分层表示框架结合降维和多维子空间评估,以有效地定位多样化和关键的子空间。这指导了两种生成模式之间的动态协调:局部扰动和全局探索,以优化关键场景的数量和多样性。此外,在代理行为空间中,利用代理与环境交互数据来量化行为的关键性和多样性,并自适应地支持生成模式切换,形成一个闭环反馈回路,持续增强场景表征和在参数空间内的探索。实验表明,我们的框架在五个决策代理上测试时,关键场景生成平均提高了56.23%,在新型参数-行为协同驱动指标下表现出更高的多样性,超越了最先进的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
决策代理在动态环境中的部署增长对安全验证提出了更高要求。现有方法在平衡多样性和重要性方面存在挑战,尤其在高维场景空间中容易陷入局部最优解。为此,我们提出了一种双空间引导测试框架,该框架协调场景参数空间和代理行为空间,旨在生成考虑多样性和重要性的测试场景。实验表明,我们的框架在五个决策代理上的关键场景生成平均提高了56.23%,并在新型参数行为协同驱动下展现出更高的多样性,优于现有最新基线技术。
Key Takeaways
- 决策代理在动态环境中的应用对安全验证提出了更高要求。
- 现有方法在生成测试场景时平衡多样性和重要性方面存在挑战。
- 双空间引导测试框架旨在协调场景参数空间和代理行为空间以生成测试场景。
- 该框架使用层次表示框架结合降维和多维子空间评估来定位多样且关键的子空间。
- 该框架优化两种生成模式:局部微调和全局探索,以提高关键场景的多样性和数量。
- 利用代理与环境交互数据来量化行为的重要性和多样性,并支持生成模式切换。
点此查看论文截图

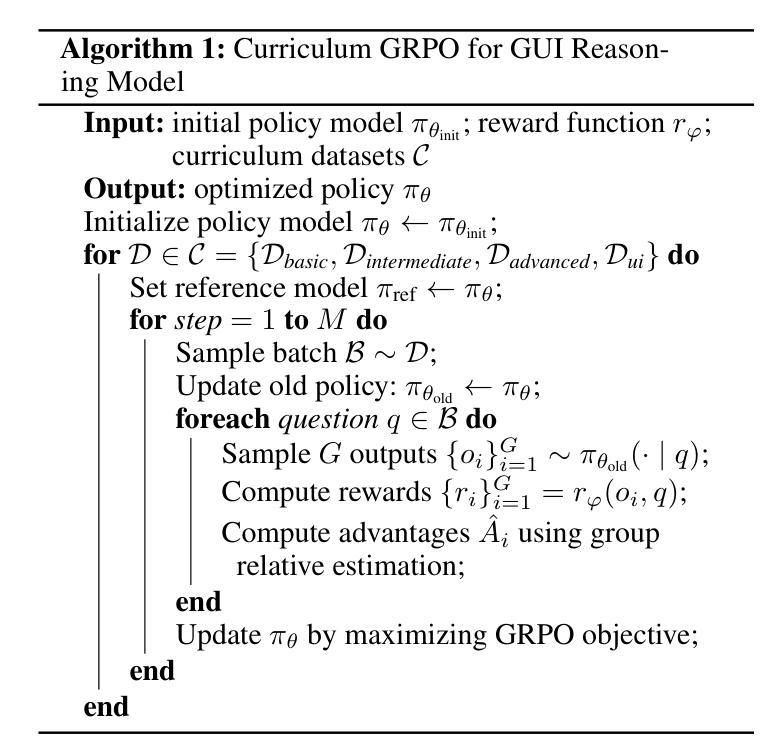
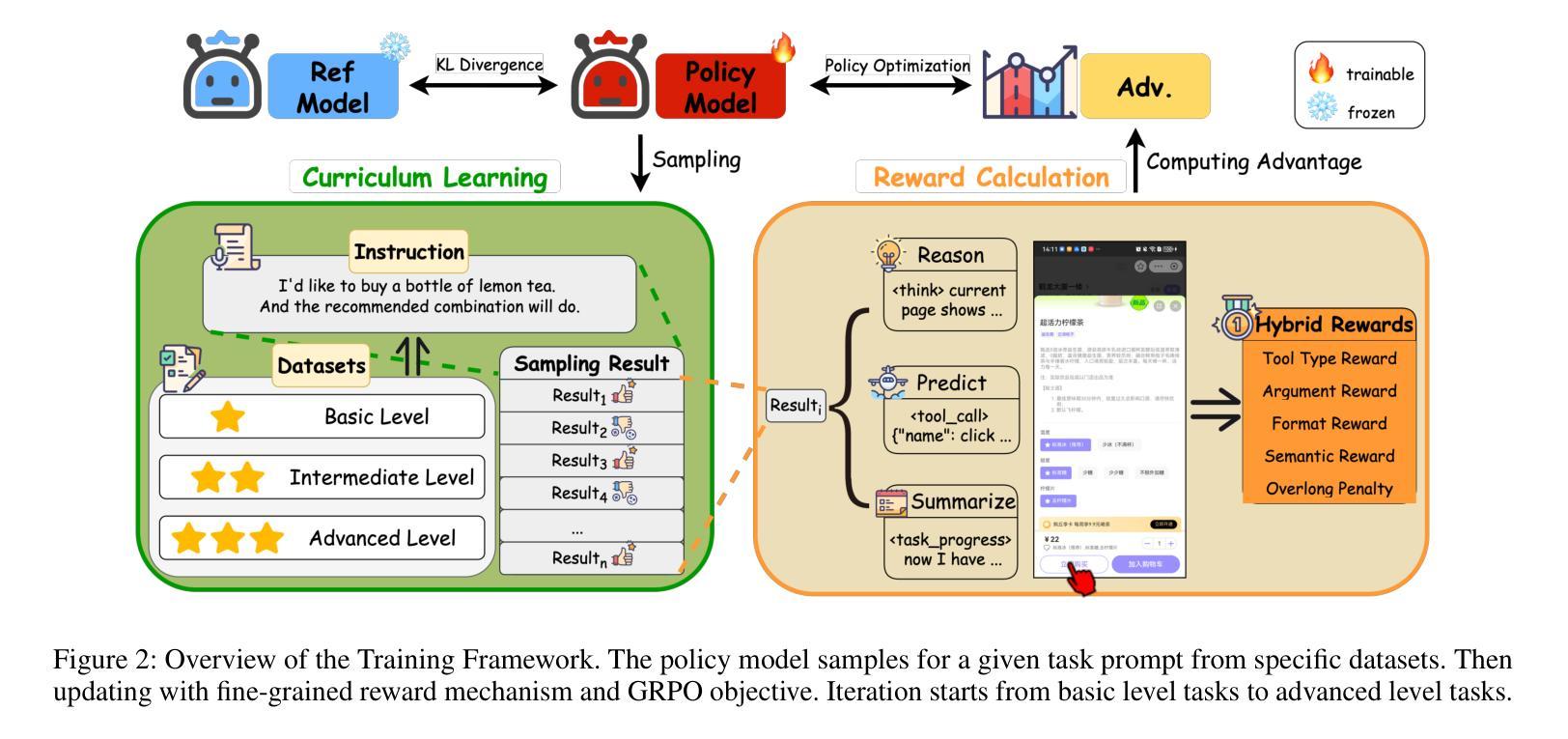
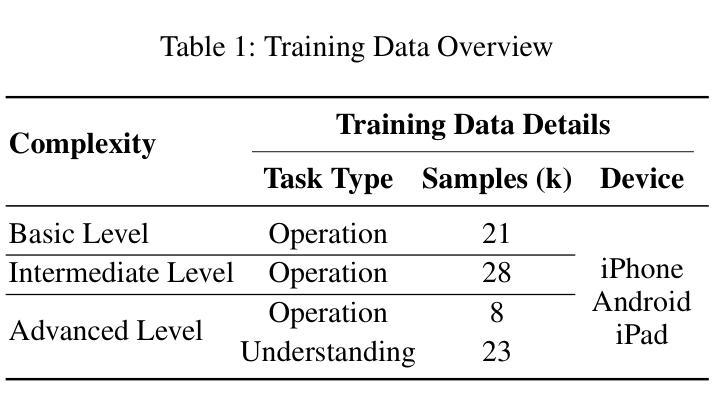
CRAFT-GUI: Curriculum-Reinforced Agent For GUI Tasks
Authors:Songqin Nong, Jingxuan Xu, Sheng Zhou, Jianfeng Chen, Xiaoxuan Tang, Tao Jiang, Wenhao Xu
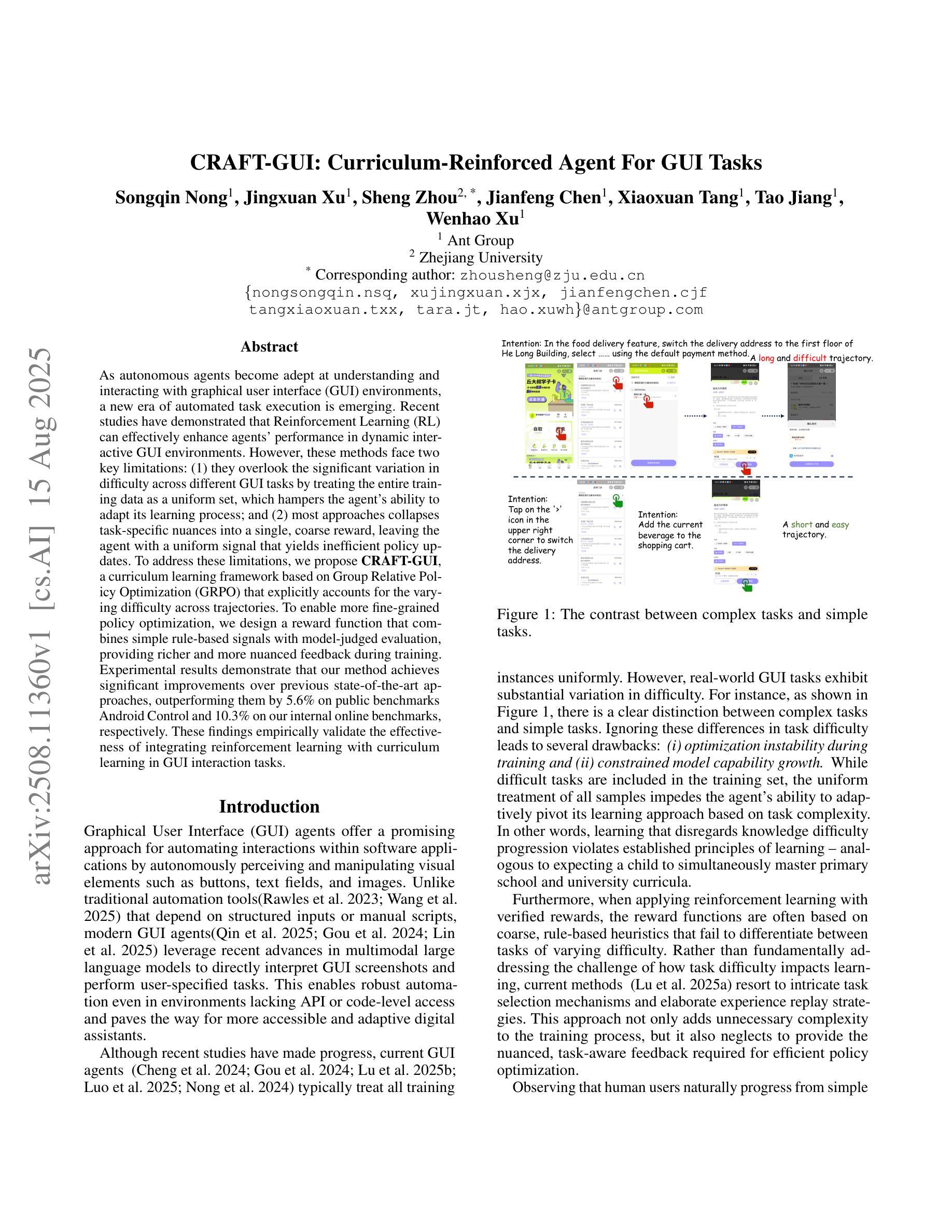
As autonomous agents become adept at understanding and interacting with graphical user interface (GUI) environments, a new era of automated task execution is emerging. Recent studies have demonstrated that Reinforcement Learning (RL) can effectively enhance agents’ performance in dynamic interactive GUI environments. However, these methods face two key limitations: (1) they overlook the significant variation in difficulty across different GUI tasks by treating the entire training data as a uniform set, which hampers the agent’s ability to adapt its learning process; and (2) most approaches collapse task-specific nuances into a single, coarse reward, leaving the agent with a uniform signal that yields inefficient policy updates. To address these limitations, we propose CRAFT-GUI, a curriculum learning framework based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) that explicitly accounts for the varying difficulty across trajectories. To enable more fine-grained policy optimization, we design a reward function that combines simple rule-based signals with model-judged evaluation, providing richer and more nuanced feedback during training. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art approaches, outperforming them by 5.6% on public benchmarks Android Control and 10.3% on our internal online benchmarks, respectively. These findings empirically validate the effectiveness of integrating reinforcement learning with curriculum learning in GUI interaction tasks.
随着自主代理(agents)在理解和图形用户界面(GUI)环境交互方面的能力日益增强,一个新的自动化任务执行时代正在兴起。最近的研究表明,强化学习(RL)可以有效地提高代理在动态交互式GUI环境中的性能。然而,这些方法面临两个主要局限性:(1)它们忽略了不同GUI任务难度的显著差异,将整个训练数据视为统一集,这阻碍了代理适应其学习过程的能力;(2)大多数方法将特定任务的细微差别简化为单一的粗略奖励,使代理只能获得统一的信号,导致策略更新效率低下。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的课程学习框架CRAFT-GUI,它显式地考虑了轨迹间的不同难度。为了实现更精细的策略优化,我们设计了一种奖励函数,将基于简单规则的信号与模型判断的评价相结合,在训练过程中提供更丰富、更细微的反馈。实验结果表明,我们的方法在公共基准测试Android Control上比最新技术高出5.6%,在我们的内部在线基准测试上高出10.3%。这些发现实证了强化学习与课程学习在GUI交互任务中结合的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)在提高自主代理在动态交互式图形用户界面(GUI)环境中的性能方面具有显著效果,但仍存在两个主要局限。为解决这些问题,我们提出了基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的课程学习框架CRAFT-GUI,并设计了一种结合基于规则的简单信号和模型评估的奖励函数,为训练过程提供更丰富、更细微的反馈。实验结果表明,我们的方法在公共基准测试上较之前的最先进方法提高了5.6%,在内部在线基准测试上提高了10.3%。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)已用于提升自主代理在GUI环境中的任务执行能力。
- 当前方法存在两个主要局限:忽视不同GUI任务的难度差异,以及任务特定细节被简化为单一的粗糙奖励。
- CRAFT-GUI是一个基于课程学习的框架,旨在解决以上问题,通过群体相对策略优化(GRPO)显式考虑轨迹的不同难度。
- CRAFT-GUI设计了一种结合规则基础简单信号和模型评估的奖励函数,以提供更丰富和细微的反馈。
- 实验结果表明,CRAFT-GUI在公共和内部基准测试上较现有方法有所改进。
- CRAFT-GUI集成了强化学习与课程学习,在GUI交互任务中展现出有效性。
点此查看论文截图
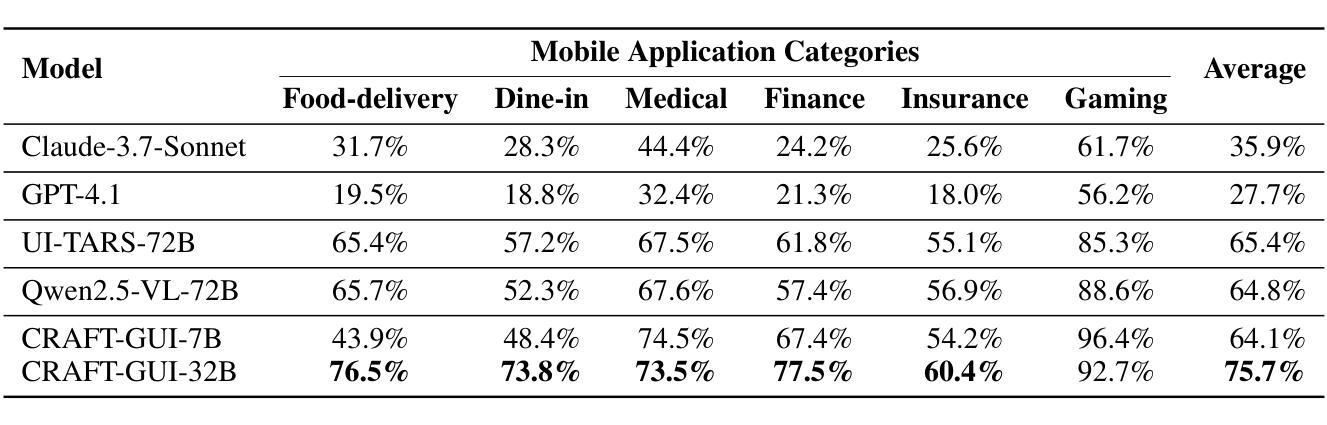
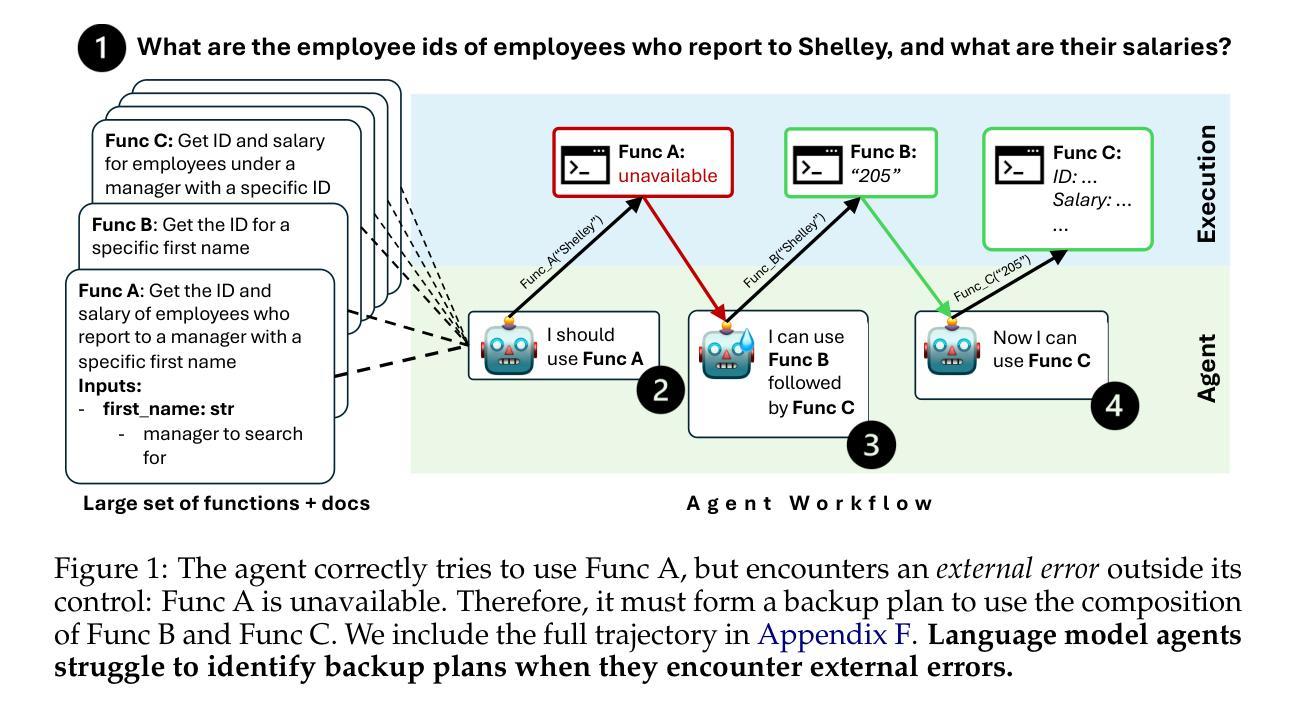
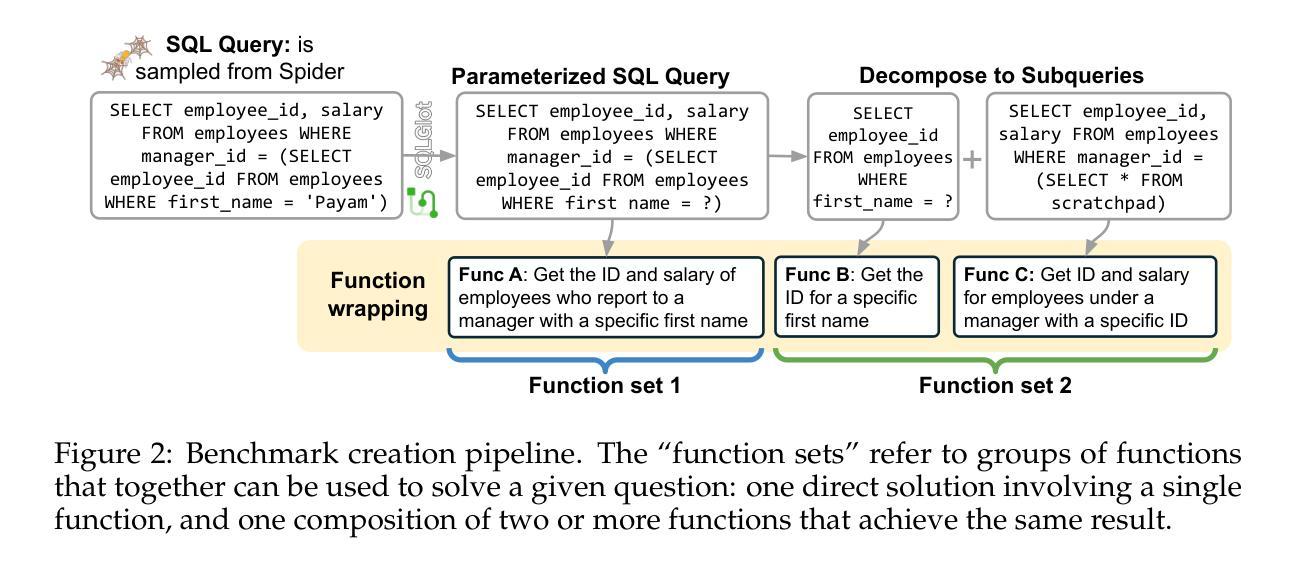
Hell or High Water: Evaluating Agentic Recovery from External Failures
Authors:Andrew Wang, Sophia Hager, Adi Asija, Daniel Khashabi, Nicholas Andrews
As language model agents are applied to real world problems of increasing complexity, they will be expected to formulate plans across large search spaces. If those plans fail for reasons beyond their control, how well do language agents search for alternative ways to achieve their goals? We devise a specialized agentic planning benchmark to study this question. Each planning problem is solved via combinations of function calls. The agent searches for relevant functions from a set of over four thousand possibilities, and observes environmental feedback in the form of function outputs or error messages. Our benchmark confronts the agent with external failures in its workflow, such as functions that suddenly become unavailable. At the same time, even with the introduction of these failures, we guarantee that the task remains solvable. Ideally, an agent’s performance on the planning task should not be affected by the presence of external failures. Overall, we find that language agents struggle to formulate and execute backup plans in response to environment feedback. While state-of-the-art models are often able to identify the correct function to use in the right context, they struggle to adapt to feedback from the environment and often fail to pursue alternate courses of action, even when the search space is artificially restricted. We provide a systematic analysis of the failures of both open-source and commercial models, examining the effects of search space size, as well as the benefits of scaling model size in our setting. Our analysis identifies key challenges for current generative models as well as promising directions for future work.
随着语言模型代理被应用于日益复杂的实际问题,他们将被期望在大搜索空间内制定计划。如果这些计划因超出其控制的原因而失败,语言模型代理在达成目标的过程中,如何有效地寻找替代方式?我们设计了一个专业的代理规划基准测试来研究这个问题。每个规划问题都是通过函数调用组合来解决的。代理从四千多种可能性中搜索相关函数,并以函数输出或错误消息的形式观察环境反馈。我们的基准测试面对代理工作流程中的外部故障,例如突然无法使用的函数。同时,即使引入了这些故障,我们也能保证任务仍然可以解决。理想情况下,代理在规划任务上的表现不应受到外部故障的影响。总的来说,我们发现语言模型代理在根据环境反馈制定和执行备份计划时遇到了困难。虽然最先进的模型通常能够在正确的上下文中识别出要使用的正确函数,但它们很难适应来自环境的反馈,并且常常无法采取替代的行动,即使搜索空间被人为限制。我们对开源和商业模型的失败进行了系统分析,研究了搜索空间大小的影响,以及在我们环境中扩大模型规模的好处。我们的分析确定了当前生成模型的关键挑战以及未来工作的有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLM 2025
Summary
随着语言模型代理在现实世界中处理日益复杂的问题,它们需要在较大的搜索空间中制定计划。当这些计划因超出控制的原因失败时,语言模型代理在达成目标的过程中如何寻找替代方案?为了研究这一问题,我们设计了一个专门的语言代理规划基准测试。测试中发现,语言模型代理在应对环境反馈时,难以制定并执行替代计划。即使搜索空间被人为限制,它们也很难适应环境反馈并常常无法采取替代行动。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型代理面临日益复杂的现实问题,需要在较大的搜索空间中制定计划。
- 当语言模型代理的计划失败时,它们如何寻找替代方案是一个重要问题。
- 我们设计了一个专门的语言代理规划基准测试来研究这个问题。
- 语言模型代理在应对环境反馈时难以制定替代计划。
- 即使搜索空间被限制,语言模型代理也很难采取替代行动。
- 对开源和商业模型的失败进行了系统分析,发现搜索空间大小和模型规模的影响。
点此查看论文截图

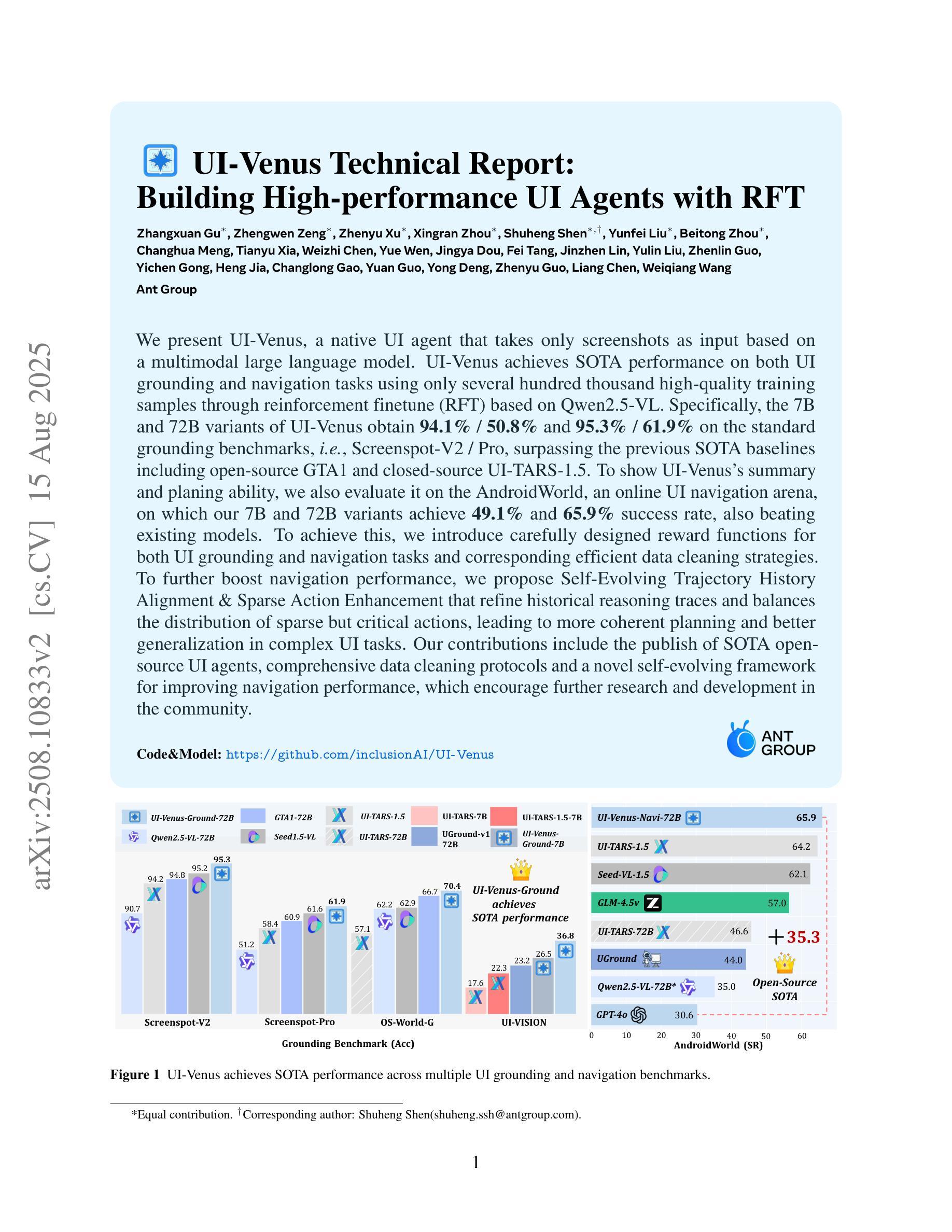
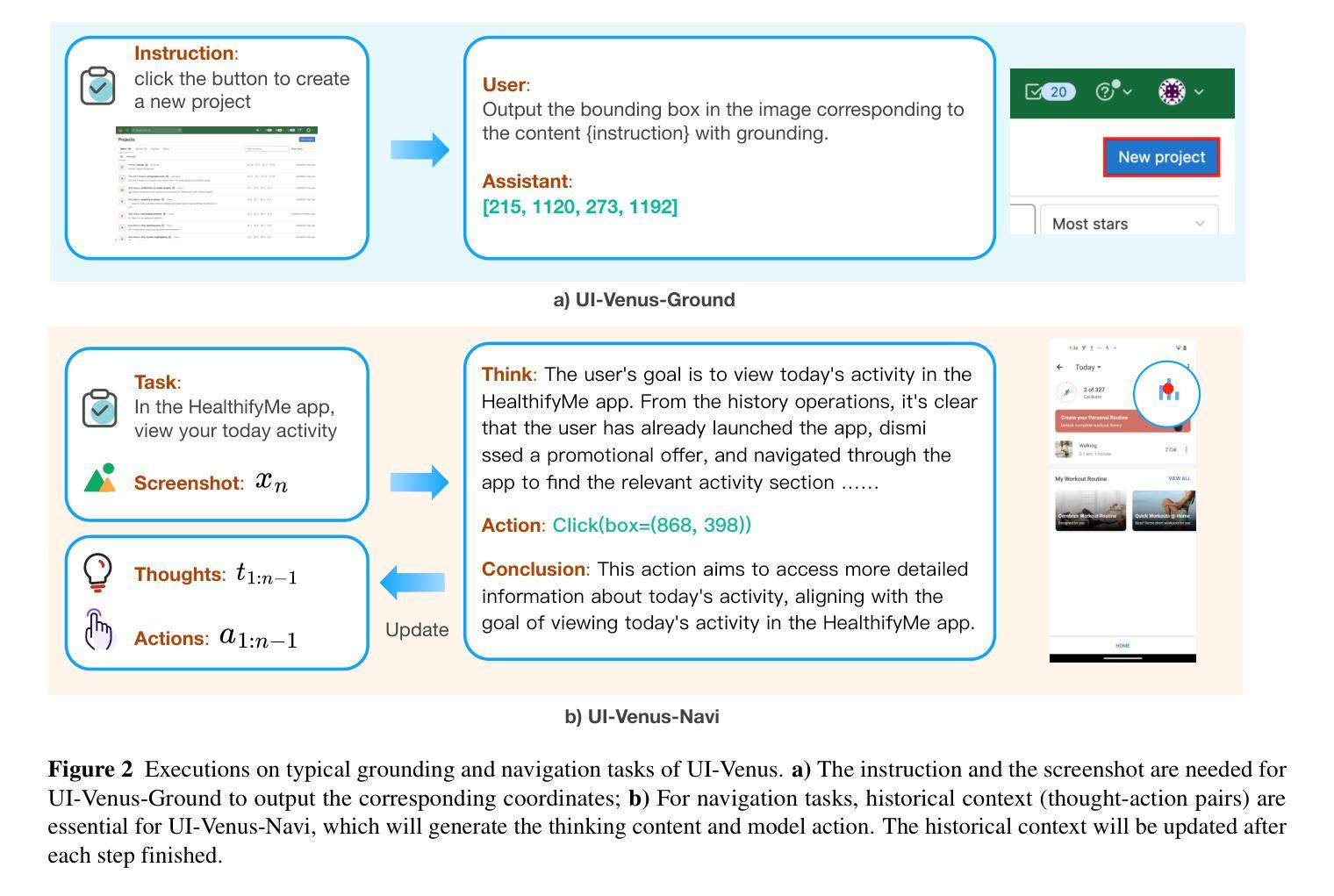
UI-Venus Technical Report: Building High-performance UI Agents with RFT
Authors:Zhangxuan Gu, Zhengwen Zeng, Zhenyu Xu, Xingran Zhou, Shuheng Shen, Yunfei Liu, Beitong Zhou, Changhua Meng, Tianyu Xia, Weizhi Chen, Yue Wen, Jingya Dou, Fei Tang, Jinzhen Lin, Yulin Liu, Zhenlin Guo, Yichen Gong, Heng Jia, Changlong Gao, Yuan Guo, Yong Deng, Zhenyu Guo, Liang Chen, Weiqiang Wang
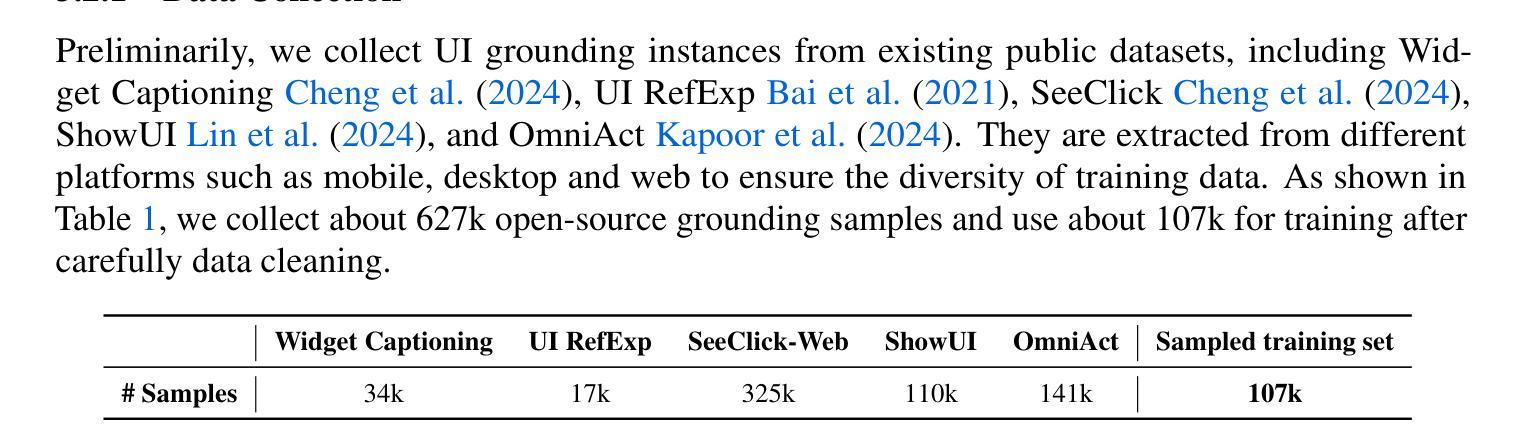
We present UI-Venus, a native UI agent that takes only screenshots as input based on a multimodal large language model. UI-Venus achieves SOTA performance on both UI grounding and navigation tasks using only several hundred thousand high-quality training samples through reinforcement finetune (RFT) based on Qwen2.5-VL. Specifically, the 7B and 72B variants of UI-Venus obtain 94.1% / 50.8% and 95.3% / 61.9% on the standard grounding benchmarks, i.e., Screenspot-V2 / Pro, surpassing the previous SOTA baselines including open-source GTA1 and closed-source UI-TARS-1.5. To show UI-Venus’s summary and planing ability, we also evaluate it on the AndroidWorld, an online UI navigation arena, on which our 7B and 72B variants achieve 49.1% and 65.9% success rate, also beating existing models. To achieve this, we introduce carefully designed reward functions for both UI grounding and navigation tasks and corresponding efficient data cleaning strategies. To further boost navigation performance, we propose Self-Evolving Trajectory History Alignment & Sparse Action Enhancement that refine historical reasoning traces and balances the distribution of sparse but critical actions, leading to more coherent planning and better generalization in complex UI tasks. Our contributions include the publish of SOTA open-source UI agents, comprehensive data cleaning protocols and a novel self-evolving framework for improving navigation performance, which encourage further research and development in the community. Code is available at https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus.
我们介绍了UI-Venus,这是一个基于多模态大型语言模型的原生用户界面代理,它仅使用截图作为输入。UI-Venus通过使用基于Qwen2.5-VL的强化微调(RFT)和仅数百万高质量训练样本,在UI定位和导航任务上实现了最新性能。具体来说,UI-Venus的7B和72B变体在标准的定位基准测试(即Screenspot-V2/Pro)上分别达到了94.1%/50.8%和95.3%/61.9%的性能,超过了包括开源GTA1和闭源UI-TARS-1.5在内的之前最新基线。为了展示UI-Venus的摘要和规划能力,我们还对其在在线UI导航竞技场AndroidWorld上进行了评估,我们的7B和72B变体在该任务上的成功率达到了49.1%和65.9%,也击败了现有模型。为了实现这一目标,我们为UI定位和导航任务精心设计了奖励功能以及相应的有效数据清理策略。为了进一步提高导航性能,我们提出了自演化轨迹历史对齐与稀疏动作增强方法,该方法可以细化历史推理轨迹并平衡稀疏但关键动作的分布,从而导致更连贯的规划以及在复杂UI任务中更好的泛化能力。我们的贡献包括发布最新的开源UI代理、全面的数据清理协议以及一种提高导航性能的自演化框架,这鼓励了社区内的进一步研究和开发。代码可在https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
我们推出了基于多模态大型语言模型的原生UI代理UI-Venus,它仅通过截图作为输入。UI-Venus通过强化微调(RFT)在UI定位和导航任务上实现了卓越性能,其7B和72B变种在标准定位基准测试Screenspot-V2 / Pro上分别达到了94.1% / 50.8%和95.3% / 61.9%,超越了包括开源GTA1和闭源UI-TARS-1.5在内的先前最佳基准测试。我们还评估了UI-Venus的总结和规划能力,在在线UI导航平台AndroidWorld上,我们的7B和72B变种成功率达到49.1%和65.9%,也击败了现有模型。为达到这一目的,我们为UI定位和导航任务精心设计了奖励函数和相应的数据清理策略。为进一步提升导航性能,我们提出了自我进化的轨迹历史对齐与稀疏动作增强方法,该方法可以优化历史推理轨迹,平衡稀疏但关键动作的分布,从而实现更连贯的规划和复杂UI任务中更好的泛化能力。我们的贡献包括公开最佳开源UI代理、全面的数据清理协议以及一种提高导航性能的自我进化框架,这鼓励了社区内的进一步研究和开发。代码可在https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus找到。
关键见解
- UI-Venus是基于多模态大型语言模型的原生UI代理,仅通过截图作为输入。
- UI-Venus在UI定位和导航任务上实现了卓越性能,超越了先前最佳基准测试。
- 在标准定位基准测试Screenspot-V2 / Pro上,UI-Venus的7B和72B变种分别达到了高准确率。
- UI-Venus在在线UI导航平台AndroidWorld上的表现优于其他模型。
- 为提升UI-Venus的性能,精心设计了奖励函数和数据清理策略。
- 提出自我进化的轨迹历史对齐与稀疏动作增强方法,优化历史推理轨迹,实现更好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
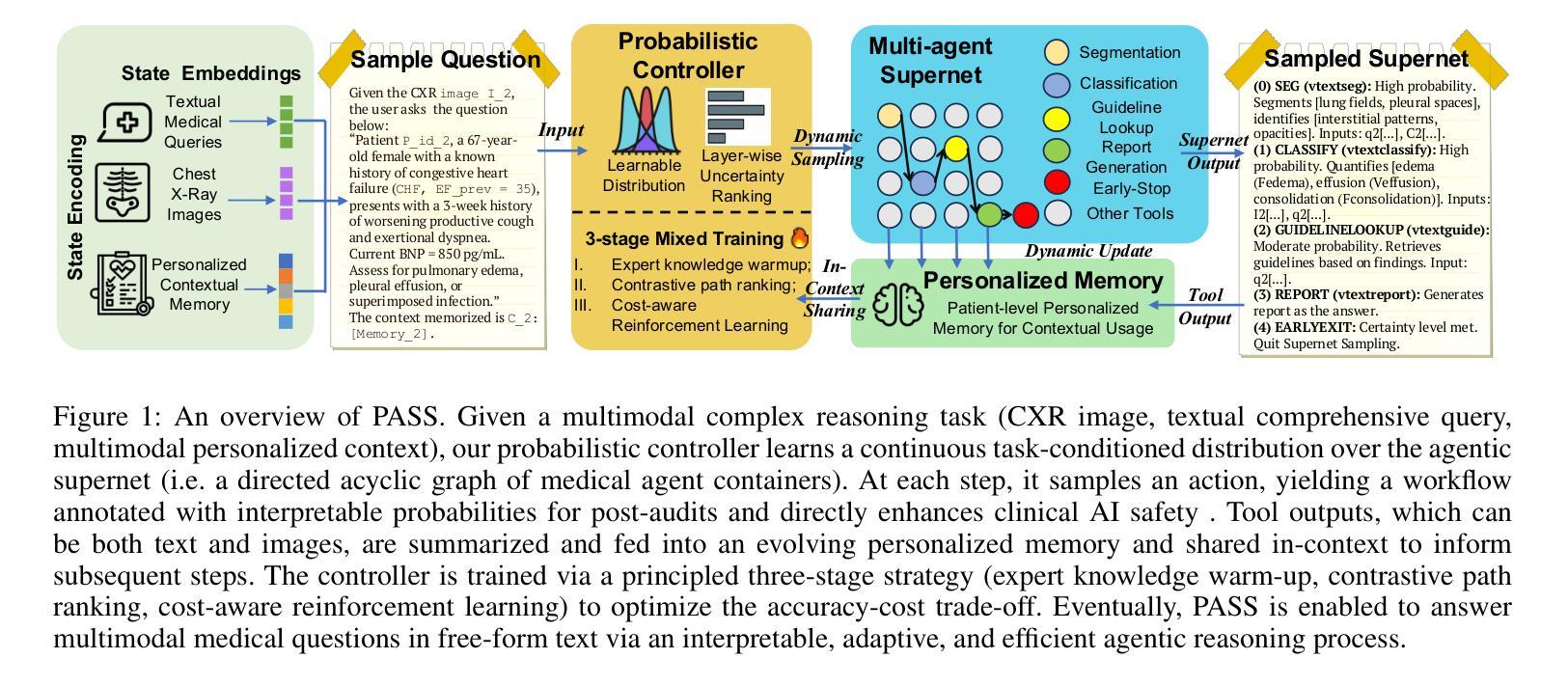
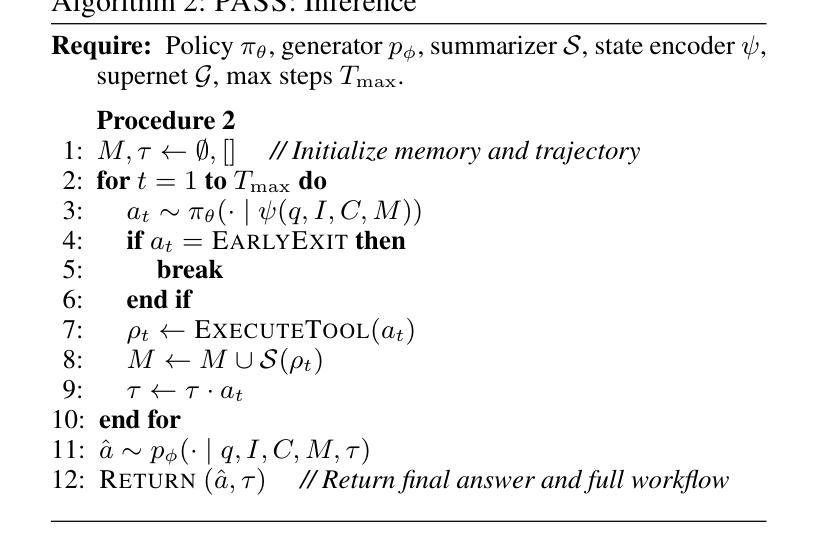
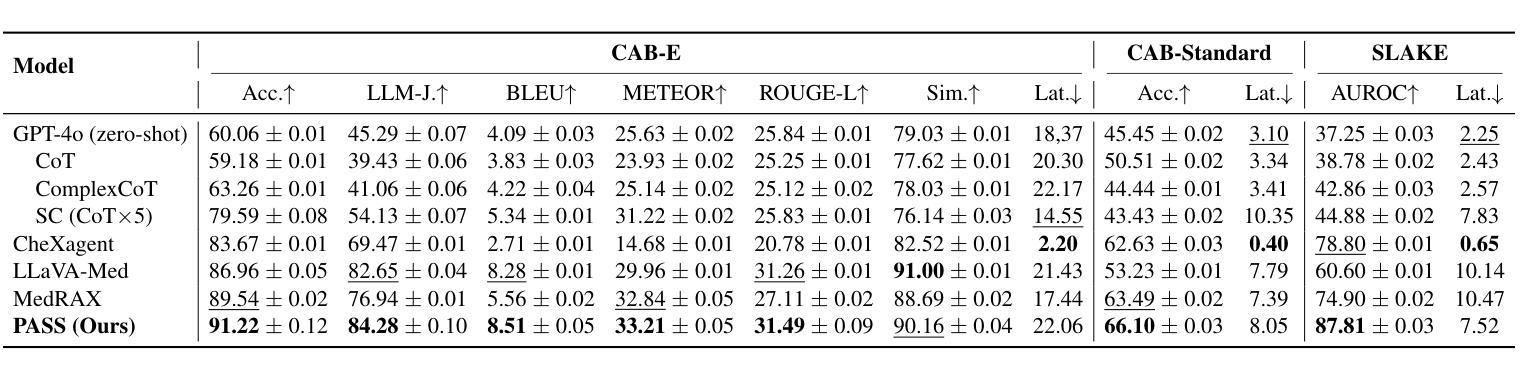
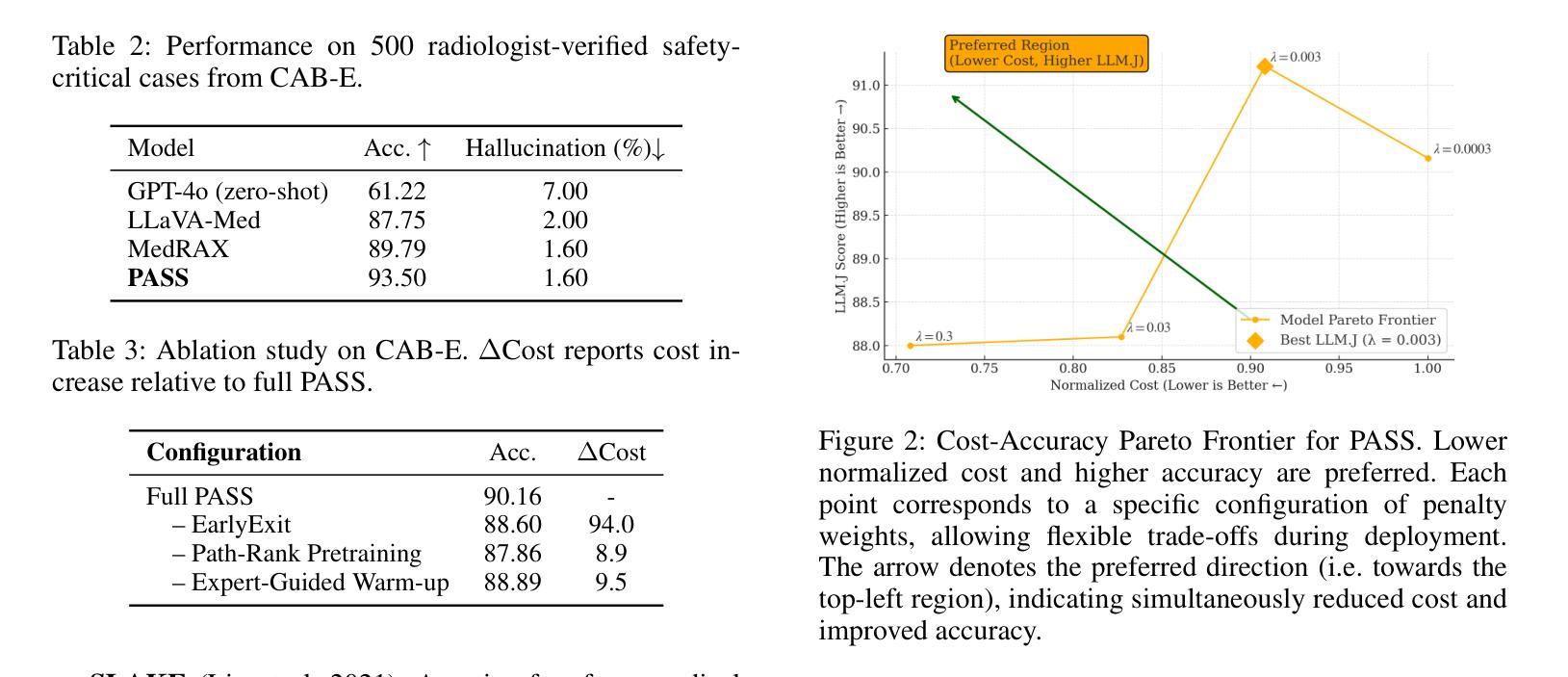
PASS: Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling for Interpretable and Adaptive Chest X-Ray Reasoning
Authors:Yushi Feng, Junye Du, Yingying Hong, Qifan Wang, Lequan Yu
Existing tool-augmented agentic systems are limited in the real world by (i) black-box reasoning steps that undermine trust of decision-making and pose safety risks, (ii) poor multimodal integration, which is inherently critical for healthcare tasks, and (iii) rigid and computationally inefficient agentic pipelines. We introduce PASS (Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling), the first multimodal framework to address these challenges in the context of Chest X-Ray (CXR) reasoning. PASS adaptively samples agentic workflows over a multi-tool graph, yielding decision paths annotated with interpretable probabilities. Given the complex CXR reasoning task with multimodal medical data, PASS leverages its learned task-conditioned distribution over the agentic supernet. Thus, it adaptively selects the most suitable tool at each supernet layer, offering probability-annotated trajectories for post-hoc audits and directly enhancing medical AI safety. PASS also continuously compresses salient findings into an evolving personalized memory, while dynamically deciding whether to deepen its reasoning path or invoke an early exit for efficiency. To optimize a Pareto frontier balancing performance and cost, we design a novel three-stage training procedure, including expert knowledge warm-up, contrastive path-ranking, and cost-aware reinforcement learning. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we introduce CAB-E, a comprehensive benchmark for multi-step, safety-critical, free-form CXR reasoning. Experiments across various benchmarks validate that PASS significantly outperforms strong baselines in multiple metrics (e.g., accuracy, AUC, LLM-J.) while balancing computational costs, pushing a new paradigm shift towards interpretable, adaptive, and multimodal medical agentic systems.
现有工具增强型代理系统在现实世界中的应用存在以下局限性:(i)黑箱推理步骤损害决策信任并带来安全风险;(ii)缺乏良好的多模式集成,这对于医疗任务来说至关重要;(iii)代理管道僵化且计算效率低下。我们引入了PASS(概率代理超网采样),这是第一个针对胸部X射线(CXR)推理上下文中的这些挑战的多模式框架。PASS自适应地在多工具图上采样代理工作流程,产生带有可解释概率的决策路径。针对具有多模式医疗数据的复杂CXR推理任务,PASS利用其学习到的任务条件分布来代理超网。因此,它自适应地选择每一超网层上最合适的工具,为事后审计提供概率注释轨迹,并直接增强医疗人工智能的安全性。PASS还不断将重要发现压缩成不断演变的个性化记忆,同时动态决定是深化其推理路径还是提前退出以提高效率。为了优化性能与成本之间的帕累托前沿,我们设计了一种新型的三阶段训练程序,包括专家知识预热、对比路径排名和成本感知强化学习。为了进行严格评估,我们引入了CAB-E,这是一个用于多步骤、安全关键的自由形式CXR推理的综合基准测试。在各种基准测试上的实验验证了PASS在多个指标(例如准确性、AUC、LLM-J)上显著优于强大的基线,同时平衡了计算成本,朝着可解释、自适应和多模式医疗代理系统的新范式转变。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PASS(Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling)这一多模态框架,解决了现有工具增强型代理系统在现实世界面临的挑战,如黑箱推理步骤、多模态整合不足以及代理管道僵化等。PASS在胸部X射线(CXR)推理的上下文中自适应采样代理工作流程,并通过在代理超网上学习的任务条件分布来应对多模态医学数据的复杂任务。这为后验审计提供了可解释的概率轨迹,并直接增强了医疗人工智能的安全性。PASS还能将重要发现不断压缩成不断发展的个性化记忆,同时动态决定是深化其推理路径还是提前退出以提高效率。本文还介绍了为优化性能与成本之间的帕累托前沿而设计的新型三阶段训练程序,以及为严格评估而引入的CAB-E综合基准测试。实验结果表明,PASS在多个指标上显著优于强大的基线,同时平衡了计算成本,推动了向可解释、自适应和多模态医疗代理系统的范式转变。
Key Takeaways
- PASS是解决现有工具增强型代理系统面临挑战的多模态框架,适用于胸部X射线(CXR)推理。
- PASS通过自适应采样代理工作流程和学习的任务条件分布来提高决策的可解释性和安全性。
- PASS能够压缩关键发现到个性化记忆,并根据需要决定推理路径的深度或提前退出,从而提高效率。
- 引入了一种新型三阶段训练程序,旨在平衡性能与成本。
- 通过专家知识预热、对比路径排名和成本感知强化学习来优化训练程序。
- 介绍了CAB-E综合基准测试,以进行严格的评估。
点此查看论文截图



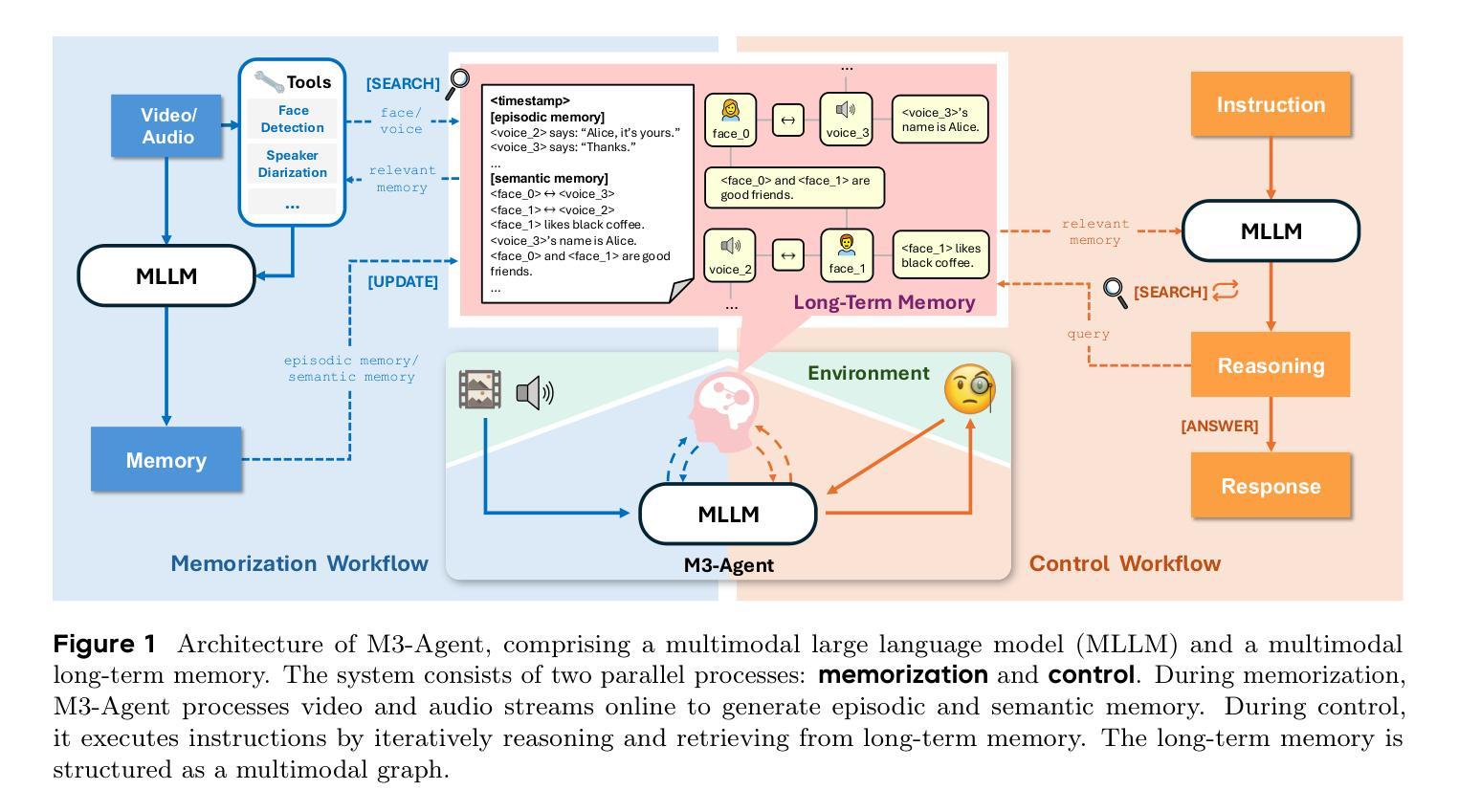
Seeing, Listening, Remembering, and Reasoning: A Multimodal Agent with Long-Term Memory
Authors:Lin Long, Yichen He, Wentao Ye, Yiyuan Pan, Yuan Lin, Hang Li, Junbo Zhao, Wei Li
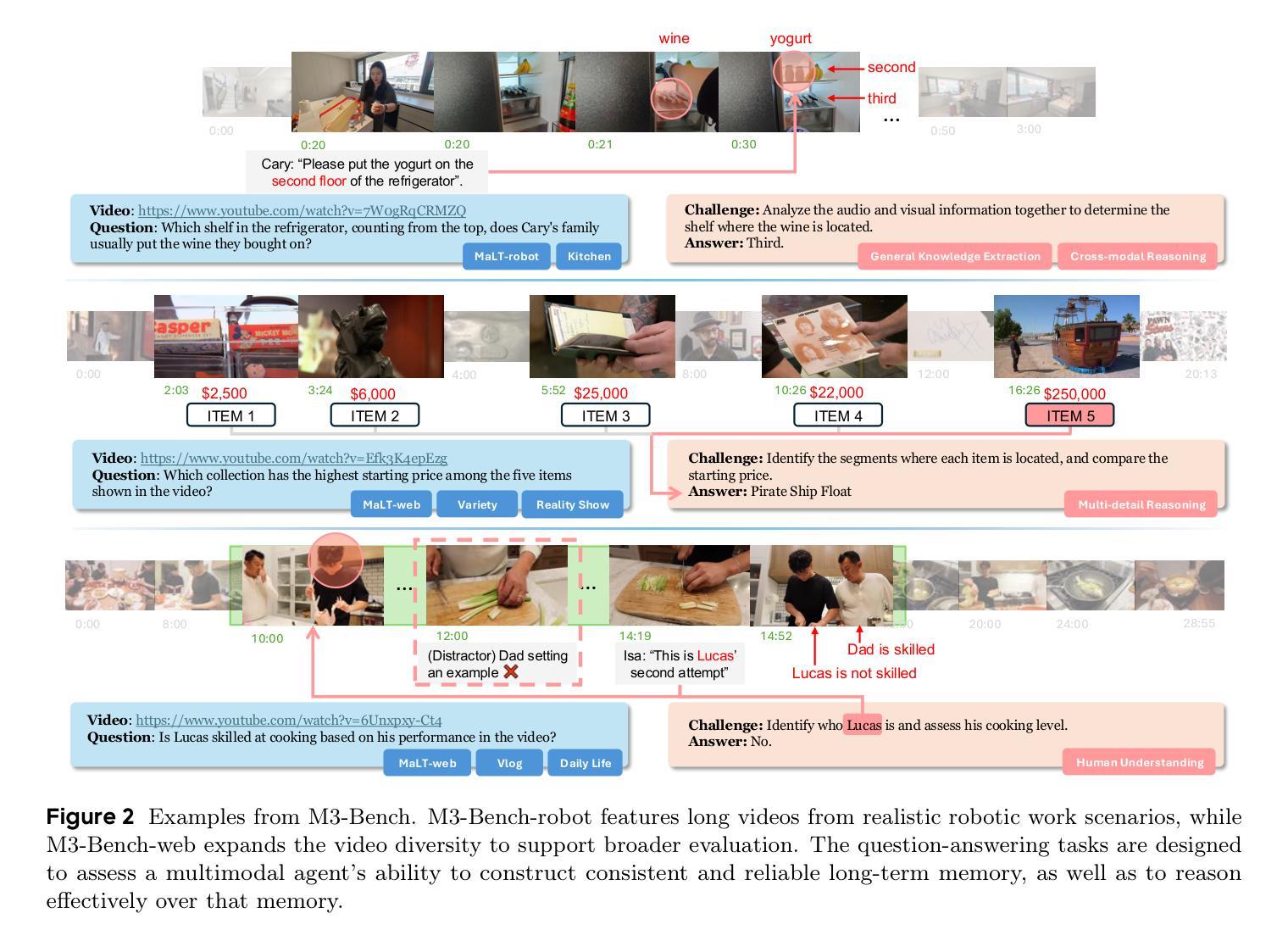
We introduce M3-Agent, a novel multimodal agent framework equipped with long-term memory. Like humans, M3-Agent can process real-time visual and auditory inputs to build and update its long-term memory. Beyond episodic memory, it also develops semantic memory, enabling it to accumulate world knowledge over time. Its memory is organized in an entity-centric, multimodal format, allowing deeper and more consistent understanding of the environment. Given an instruction, M3-Agent autonomously performs multi-turn, iterative reasoning and retrieves relevant information from memory to accomplish the task. To evaluate memory effectiveness and memory-based reasoning in multimodal agents, we develop M3-Bench, a new long-video question answering benchmark. M3-Bench comprises 100 newly recorded real-world videos captured from a robot’s perspective (M3-Bench-robot) and 920 web-sourced videos across diverse scenarios (M3-Bench-web). We annotate question-answer pairs designed to test key capabilities essential for agent applications, such as human understanding, general knowledge extraction, and cross-modal reasoning. Experimental results show that M3-Agent, trained via reinforcement learning, outperforms the strongest baseline, a prompting agent using Gemini-1.5-pro and GPT-4o, achieving 6.7%, 7.7%, and 5.3% higher accuracy on M3-Bench-robot, M3-Bench-web and VideoMME-long, respectively. Our work advances the multimodal agents toward more human-like long-term memory and provides insights into their practical design. Model, code and data are available at https://github.com/bytedance-seed/m3-agent
我们介绍了M3-Agent,这是一种配备长期记忆的新型多模态代理框架。与人类类似,M3-Agent可以处理实时的视觉和听觉输入来构建和更新其长期记忆。除了情景记忆之外,它还发展出语义记忆,使其能够随着时间的推移积累世界知识。它的记忆以实体为中心的多模态格式组织,允许对环境有更深入和一致的理解。接受指令后,M3-Agent可以自主进行多轮迭代推理,从记忆中检索相关信息以完成任务。为了评估多模态代理中的记忆效果和基于记忆推理能力,我们开发了M3-Bench,这是一个新的长视频问答基准测试。M3-Bench包括100个新录制的世界真实视频(从机器人视角捕获)(M3-Bench-robot)和920个来自不同场景的网页视频(M3-Bench-web)。我们注释了问题答案对,旨在测试代理应用程序必需的关键能力,如人类理解、一般知识提取和跨模态推理。实验结果表明,通过强化学习训练的M3-Agent超越了最强基线(使用Gemini-1.5-pro和GPT-4o的提示代理),在M3-Bench-robot、M3-Bench-web和VideoMME-long上的准确率分别提高了6.7%、7.7%和5.3%。我们的工作使多模态代理朝着更像人类的长时记忆方向发展,并为其实践设计提供了见解。模型、代码和数据可在https://github.com/bytedance-seed/m3-agent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
M3-Agent是一种配备长期记忆的多模态代理框架。它能处理实时视觉和听觉输入来构建和更新其长期记忆,并发展语义记忆,能够随时间积累世界知识。其记忆以实体为中心的多模态格式组织,使其对环境有更深入和一致的理解。在接收到指令后,M3-Agent可自主进行多回合迭代推理,从记忆中检索相关信息以完成任务。为评估多模态代理的记忆效果和基于记忆推理能力,我们开发了M3-Bench,新的长视频问答基准测试。M3-Bench包括100个新录制的真实世界机器人视角视频(M3-Bench-robot)和920个网络来源的跨场景视频(M3-Bench-web)。我们标注了问答对,旨在测试代理应用程序必需的关键能力,如人类理解、一般知识提取和跨模态推理。实验结果显示,通过强化学习训练的M3-Agent超越最强基线,使用Gemini-1.5-pro和GPT-4o的提示代理,在M3-Bench-robot、M3-Bench-web和VideoMME-long上分别提高了6.7%、7.7%和5.3%的准确度。我们的工作推动了多模态代理朝更人性化的长期记忆方向发展,并为其实用设计提供了见解。
关键见解
- M3-Agent是一种多模态代理框架,具备处理实时视觉和听觉输入的能力,以构建和更新其长期记忆。
- M3-Agent不仅拥有情景记忆,还发展语义记忆,能够随时间积累知识。
- M3-Agent的记忆以实体为中心的多模态格式组织,提高对环境理解的一致性和深度。
- M3-Agent可自主进行多回合迭代推理,完成复杂任务。
- 为评估多模态代理的记忆和推理能力,推出了新的长视频问答基准测试M3-Bench。
- M3-Bench包含机器人和网络视角的真实世界视频,旨在测试代理的人类理解、知识提取和跨模态推理等关键能力。
- M3-Agent在M3-Bench测试中表现出卓越性能,相较于基线代理有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

Preacher: Paper-to-Video Agentic System
Authors:Jingwei Liu, Ling Yang, Hao Luo, Fan Wang, Hongyan Li, Mengdi Wang
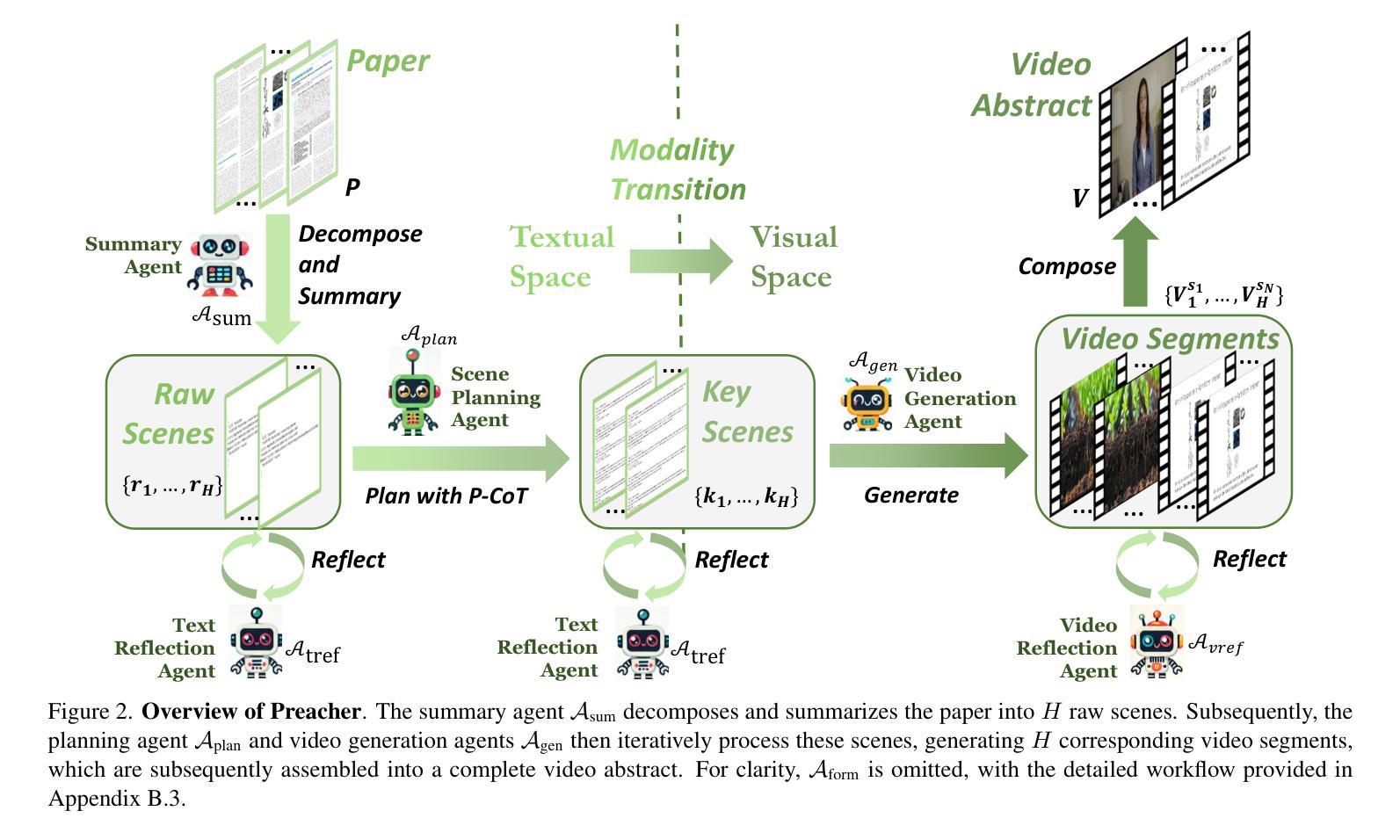
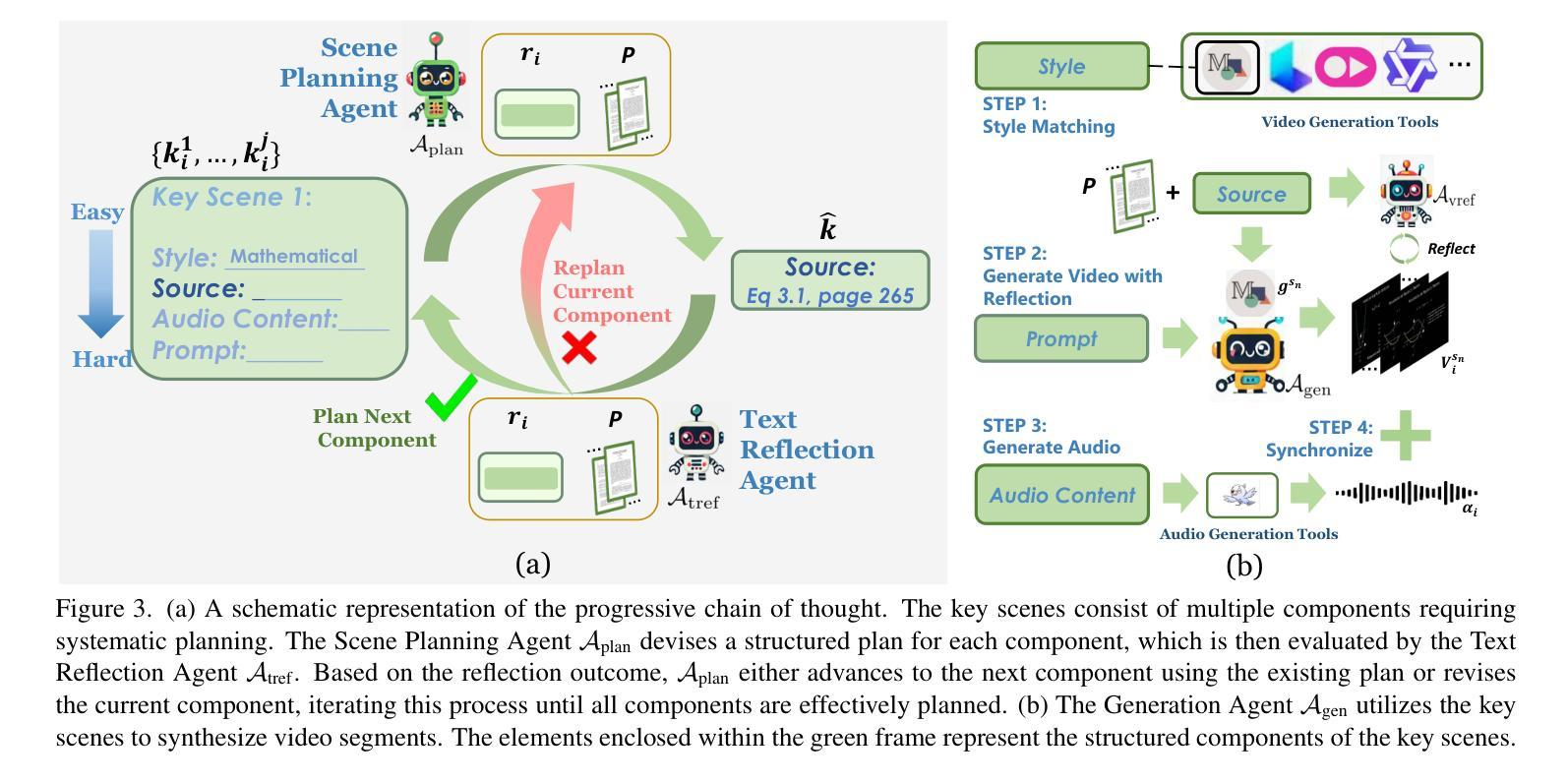
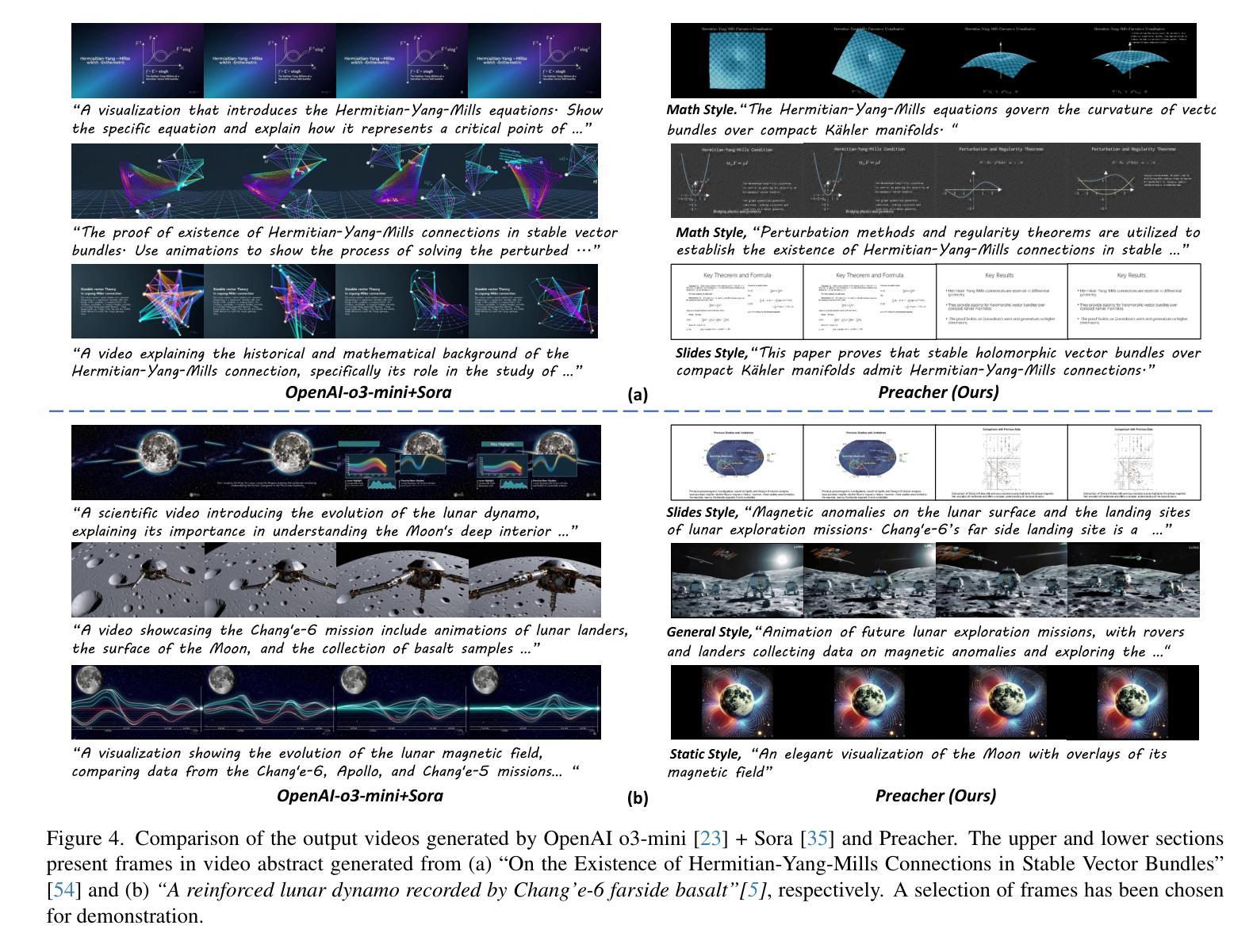
The paper-to-video task converts a research paper into a structured video abstract, distilling key concepts, methods, and conclusions into an accessible, well-organized format. While state-of-the-art video generation models demonstrate potential, they are constrained by limited context windows, rigid video duration constraints, limited stylistic diversity, and an inability to represent domain-specific knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce Preacher, the first paper-to-video agentic system. Preacher employs a topdown approach to decompose, summarize, and reformulate the paper, followed by bottom-up video generation, synthesizing diverse video segments into a coherent abstract. To align cross-modal representations, we define key scenes and introduce a Progressive Chain of Thought (P-CoT) for granular, iterative planning. Preacher successfully generates high-quality video abstracts across five research fields, demonstrating expertise beyond current video generation models. Code will be released at: https://github.com/GenVerse/Paper2Video
该论文到视频的任务是将研究论文转化为结构化的视频摘要,提炼关键概念、方法和结论,使其易于访问和整理。尽管最先进的视频生成模型显示出潜力,但它们受限于有限的上下文窗口、僵化的视频时长约束、有限的风格多样性以及无法表示特定领域知识。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Preacher,首个论文到视频的智能系统。Preacher采用自上而下的方法分解、总结和重构论文,然后进行自下而上的视频生成,将多样化的视频片段综合为连贯的摘要。为了对齐跨模态表示,我们定义了关键场景并引入了渐进思维链(P-CoT)进行精细的迭代规划。Preacher成功地在五个研究领域生成了高质量的视频摘要,展示了超越当前视频生成模型的专业能力。代码将在https://github.com/GenVerse/Paper2Video上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code not ready
Summary
研究论文转化为视频摘要的任务是将关键概念、方法和结论转化为易于理解、组织良好的视频格式。尽管现有视频生成模型具有潜力,但它们受限于上下文窗口、视频时长、风格多样性和无法表达特定领域知识等缺点。为解决这些问题,我们推出Preacher——首个论文转视频的智能系统。Preacher采用自上而下方法分解、总结和重构论文,再通过自下而上的视频生成方式,将不同视频片段合成连贯的摘要。为对齐跨模态表达,我们定义关键场景并引入渐进思维链进行细致、迭代的规划。Preacher成功生成了跨越五个研究领域的优质视频摘要,展现了超越现有视频生成模型的专业能力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究论文转化为视频摘要具有重要性和挑战性。
- 现有视频生成模型存在多种限制,如上下文窗口、视频时长约束等。
- Preacher是首个论文转视频的智能系统,旨在解决现有模型的局限性。
- Preacher采用自上而下和自下而上的双重方法处理论文和视频生成。
- 通过定义关键场景和渐进思维链,Preacher实现跨模态表达的对齐。
- Preacher成功生成了高质量的视频摘要,适用于多个研究领域。
点此查看论文截图

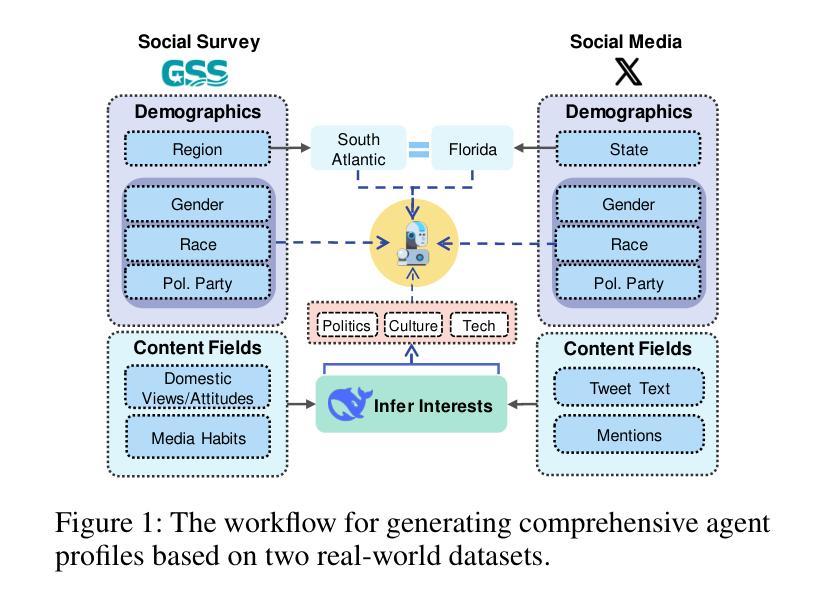
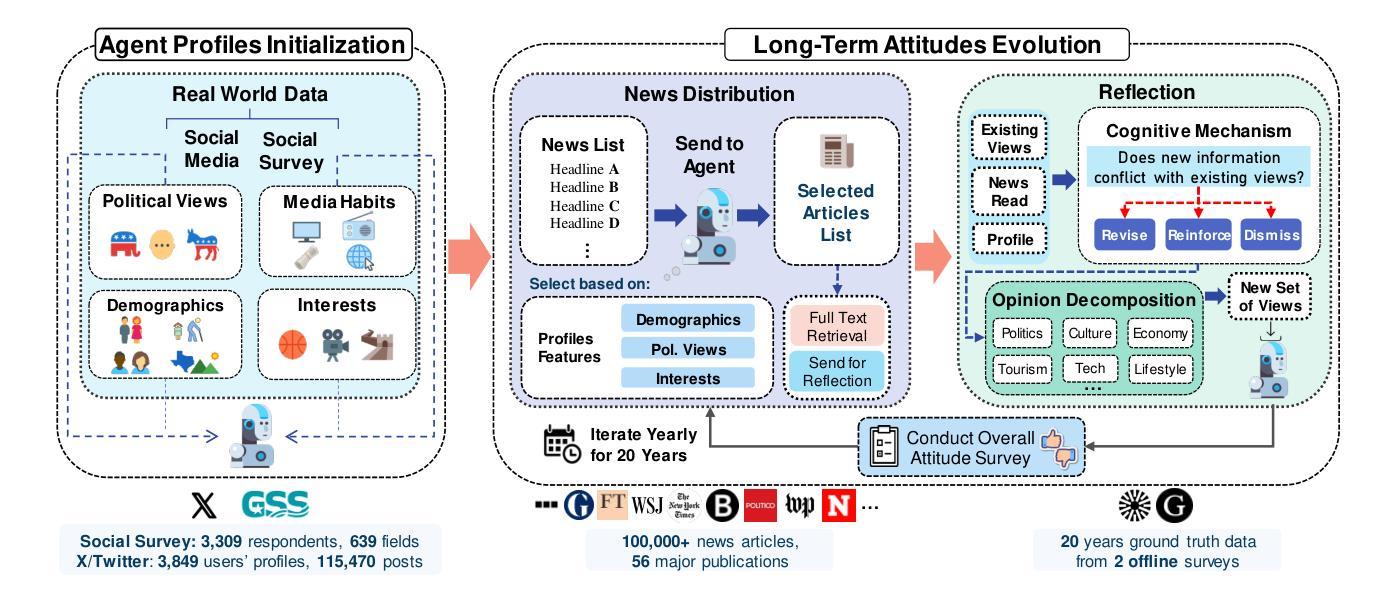
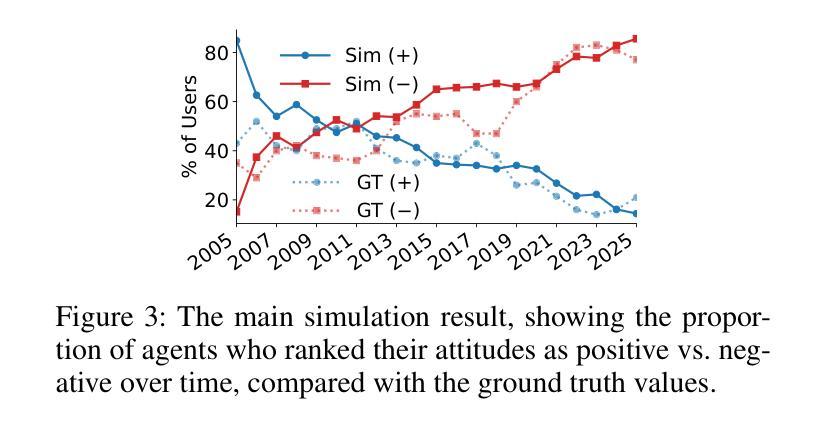
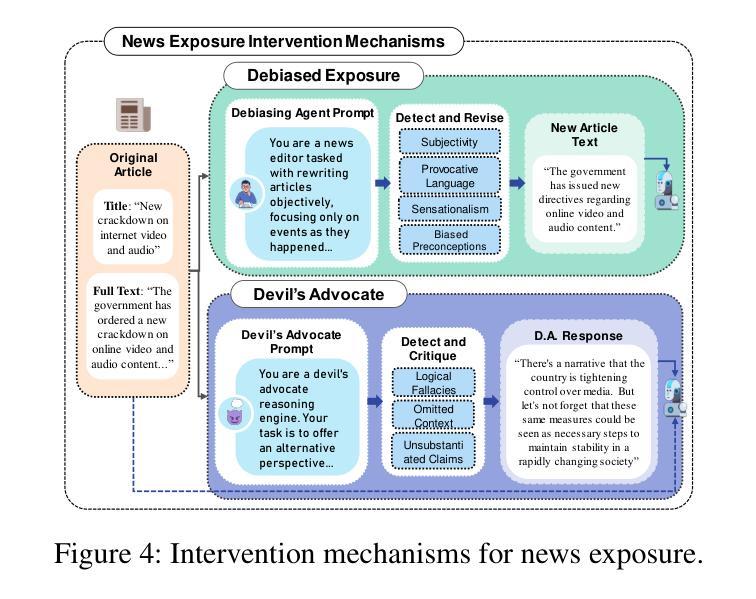
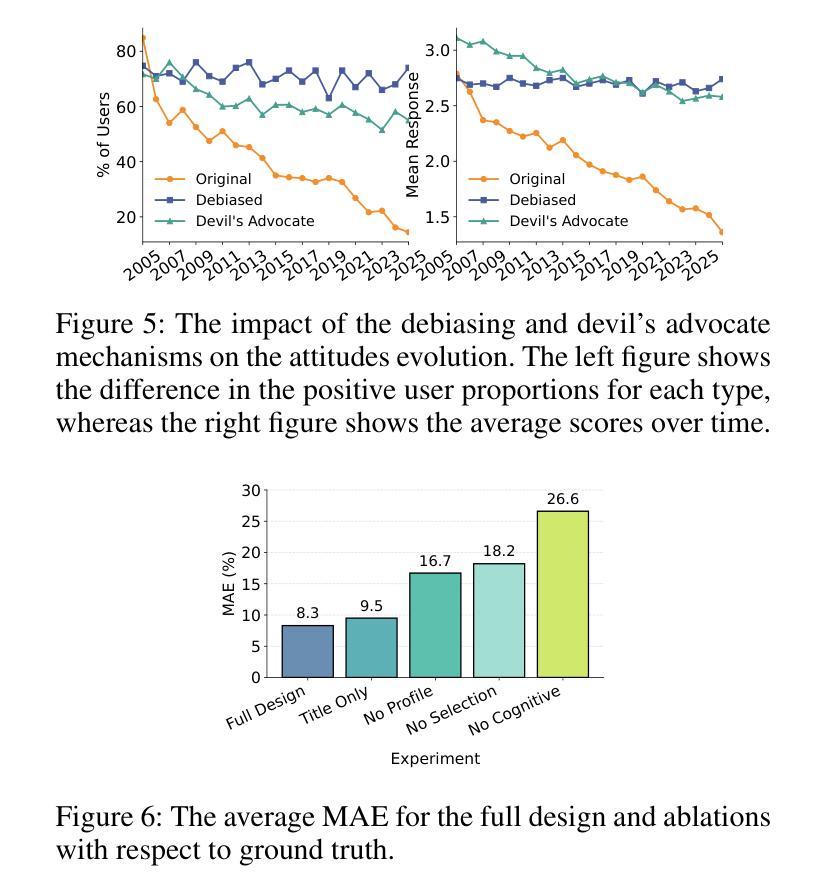
The Roots of International Perceptions: Simulating US Attitude Changes Towards China with LLM Agents
Authors:Nicholas Sukiennik, Yichuan Xu, Yuqing Kan, Jinghua Piao, Yuwei Yan, Chen Gao, Yong Li
The rise of LLMs poses new possibilities in modeling opinion evolution, a long-standing task in simulation, by leveraging advanced reasoning abilities to recreate complex, large-scale human cognitive trends. While most prior works focus on opinion evolution surrounding specific isolated events or the views within a country, ours is the first to model the large-scale attitude evolution of a population representing an entire country towards another – US citizens’ perspectives towards China. To tackle the challenges of this broad scenario, we propose a framework that integrates media data collection, user profile creation, and cognitive architecture for opinion updates to successfully reproduce the real trend of US attitudes towards China over a 20-year period from 2005 to today. We also leverage LLMs’ capabilities to introduce debiased media exposure, extracting neutral events from typically subjective news contents, to uncover the roots of polarized opinion formation, as well as a devils advocate agent to help explain the rare reversal from negative to positive attitudes towards China, corresponding with changes in the way Americans obtain information about the country. The simulation results, beyond validating our framework architecture, also reveal the impact of biased framing and selection bias in shaping attitudes. Overall, our work contributes to a new paradigm for LLM-based modeling of cognitive behaviors in a large-scale, long-term, cross-border social context, providing insights into the formation of international biases and offering valuable implications for media consumers to better understand the factors shaping their perspectives, and ultimately contributing to the larger social need for bias reduction and cross-cultural tolerance.
大型语言模型(LLMs)的兴起为模拟长期存在的模拟任务——意见演变带来了新的可能性。通过利用先进的推理能力,我们能够重新创建复杂的大规模人类认知趋势。虽然以前的大多数工作都集中在围绕特定孤立事件或国家内的观点的意见演变上,但我们的工作首次对代表整个国家针对另一个国家的人口大规模态度演变进行建模——即美国公民对中国的心态。
为了应对这一广泛场景的挑战,我们提出了一个框架,该框架集成了媒体数据采集、用户角色创建和认知架构以更新意见,从而成功地在从2005年至今的20年期间内复制了美国对中国态度的真实趋势。我们还利用大型语言模型的能力来引入无偏见的媒体曝光,从通常主观的新闻内容中提取中性事件,以揭示偏激意见形成的根源,以及使用魔鬼代言人的角色来帮助解释从负面到正面的态度转变,这种转变与美国人了解该国的方式的变化相对应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AAAI Social Impact 2026
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,为我们提供了一个全新的视角来模拟长期存在的观点演化任务。通过利用先进的推理能力,我们能够重新创建复杂的大规模人类认知趋势。本研究首次关注代表整个国家对另一个国家态度的演化过程,特别是美国公民对中国的态度。我们提出了一个整合媒体数据采集、用户画像创建和认知架构更新意见框架,成功再现了美国对中国态度在长达二十年内的真实趋势。同时,利用LLM的能力引入无偏媒体曝光,提取通常主观新闻内容中的中性事件,揭示意见两极分化的根源。此外,我们的模拟结果还揭示了框架架构验证过程中的偏见框架和选择偏见对态度形成的影响。本研究为在大规模、长期、跨国社会背景下利用LLM进行认知行为建模提供了新的范例,对了解国际偏见形成因素有重要启示,并为媒体消费者提供了理解其观点形成因素的角度。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs为模拟观点演化提供了新的可能性,能够利用先进的推理能力重现大规模人类认知趋势。
- 本研究首次关注代表整个国家对另一个国家态度的演化过程,特别是美国公民对中国的态度。
- 通过整合媒体数据、用户画像和认知架构,成功再现美国对中国态度二十年来的真实趋势。
- LLMs被用来引入无偏媒体曝光,揭示意见两极分化的根源。
- 模拟结果验证了框架架构的有效性,并揭示了偏见框架和选择偏见对态度形成的影响。
- 本研究提供了一个在大规模、长期、跨国社会背景下利用LLM进行认知行为建模的新范例。
点此查看论文截图

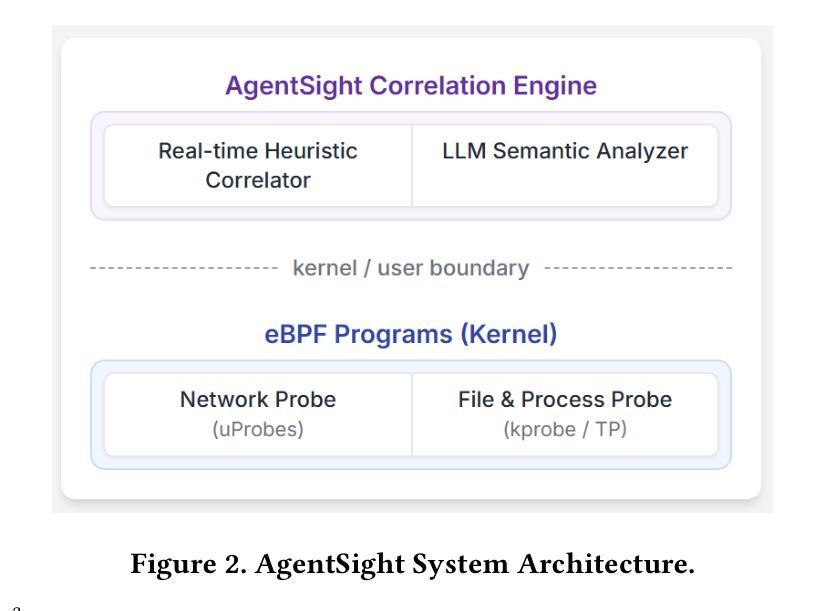
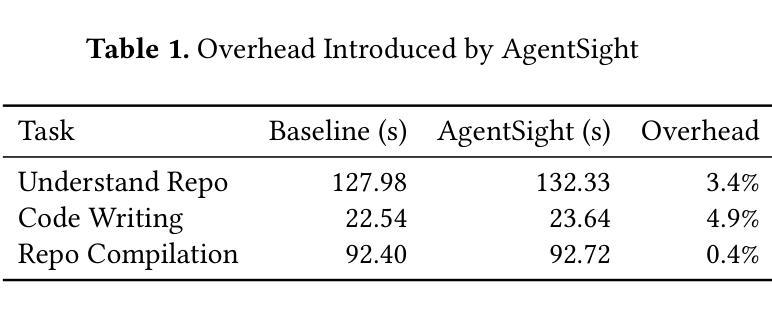
AgentSight: System-Level Observability for AI Agents Using eBPF
Authors:Yusheng Zheng, Yanpeng Hu, Tong Yu, Andi Quinn
Modern software infrastructure increasingly relies on LLM agents for development and maintenance, such as Claude Code and Gemini-cli. However, these AI agents differ fundamentally from traditional deterministic software, posing a significant challenge to conventional monitoring and debugging. This creates a critical semantic gap: existing tools observe either an agent’s high-level intent (via LLM prompts) or its low-level actions (e.g., system calls), but cannot correlate these two views. This blindness makes it difficult to distinguish between benign operations, malicious attacks, and costly failures. We introduce AgentSight, an AgentOps observability framework that bridges this semantic gap using a hybrid approach. Our approach, boundary tracing, monitors agents from outside their application code at stable system interfaces using eBPF. AgentSight intercepts TLS-encrypted LLM traffic to extract semantic intent, monitors kernel events to observe system-wide effects, and causally correlates these two streams across process boundaries using a real-time engine and secondary LLM analysis. This instrumentation-free technique is framework-agnostic, resilient to rapid API changes, and incurs less than 3% performance overhead. Our evaluation shows AgentSight detects prompt injection attacks, identifies resource-wasting reasoning loops, and reveals hidden coordination bottlenecks in multi-agent systems. AgentSight is released as an open-source project at https://github.com/agent-sight/agentsight.
现代软件基础设施越来越依赖LLM代理进行开发和维护,如Claude Code和Gemini-cli。然而,这些AI代理从根本上不同于传统的确定性软件,给传统监控和调试带来了重大挑战。这产生了一个关键语义鸿沟:现有工具只能观察到代理的高级意图(通过LLM提示)或低级操作(例如系统调用),但无法关联这两种视图。这种盲目性使得难以区分良性操作、恶意攻击和成本高昂的故障。我们引入了AgentSight,这是一个AgentOps可观性框架,它使用混合方法来弥合这一语义鸿沟。我们的方法,边界跟踪,从应用程序代码外部在稳定的系统接口上使用eBPF监控代理。AgentSight拦截TLS加密的LLM流量以提取语义意图,监控内核事件以观察系统范围的影响,并使用实时引擎和次要LLM分析跨进程边界因果关联这两股流。这种无需仪器的方法具有框架无关性,对快速API更改具有弹性,并且性能开销小于3%。我们的评估表明,AgentSight可以检测提示注入攻击,识别资源浪费的推理循环,并揭示多代理系统中的隐藏协调瓶颈。AgentSight已在https://github.com/agent-sight/agentsight上作为开源项目发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着现代软件基础设施越来越依赖LLM代理进行开发和维护,如Claude Code和Gemini-cli等AI代理与传统的确定性软件存在根本差异,给传统的监控和调试带来了重大挑战。这造成了一个关键的语义鸿沟:现有工具只能观察到代理的高级意图(通过LLM提示)或低级操作(例如系统调用),无法将这两者结合起来。为解决这一问题,提出了AgentSight,一个AgentOps可观性框架,通过混合方法填补这一语义鸿沟。其采用边界追踪的方法,在稳定的系统接口处从应用程序代码外部监视代理,使用eBPF进行监测。AgentSight能够拦截TLS加密的LLM流量以提取语义意图,监视内核事件以观察系统范围内的效果,并使用实时引擎和二次LLM分析在进程边界处因果关联这两个流。这种无需仪器的方法具有框架无关、对快速API更改具有弹性以及性能开销小于3%的特点。评估表明,AgentSight可以检测提示注入攻击、识别资源浪费的推理循环以及揭示多代理系统中的隐藏协调瓶颈。
Key Takeaways:
- 现代软件基础设施依赖LLM代理进行开发和维护,对传统监控和调试工具带来挑战。
- 现有工具难以同时观察代理的高级意图和低级操作,形成语义鸿沟。
- AgentSight是一个填补语义鸿沟的AgentOps可观性框架,通过边界追踪和eBPF技术监视代理。
- AgentSight能拦截加密LLM流量提取语义意图,同时监视内核事件观察系统范围效果。
- AgentSight能将高级意图和低级操作进行因果关联,具有无需仪器、框架无关、适应快速API变化以及低性能开销的特点。
- AgentSight能检测提示注入攻击和资源浪费推理循环等问题。
点此查看论文截图


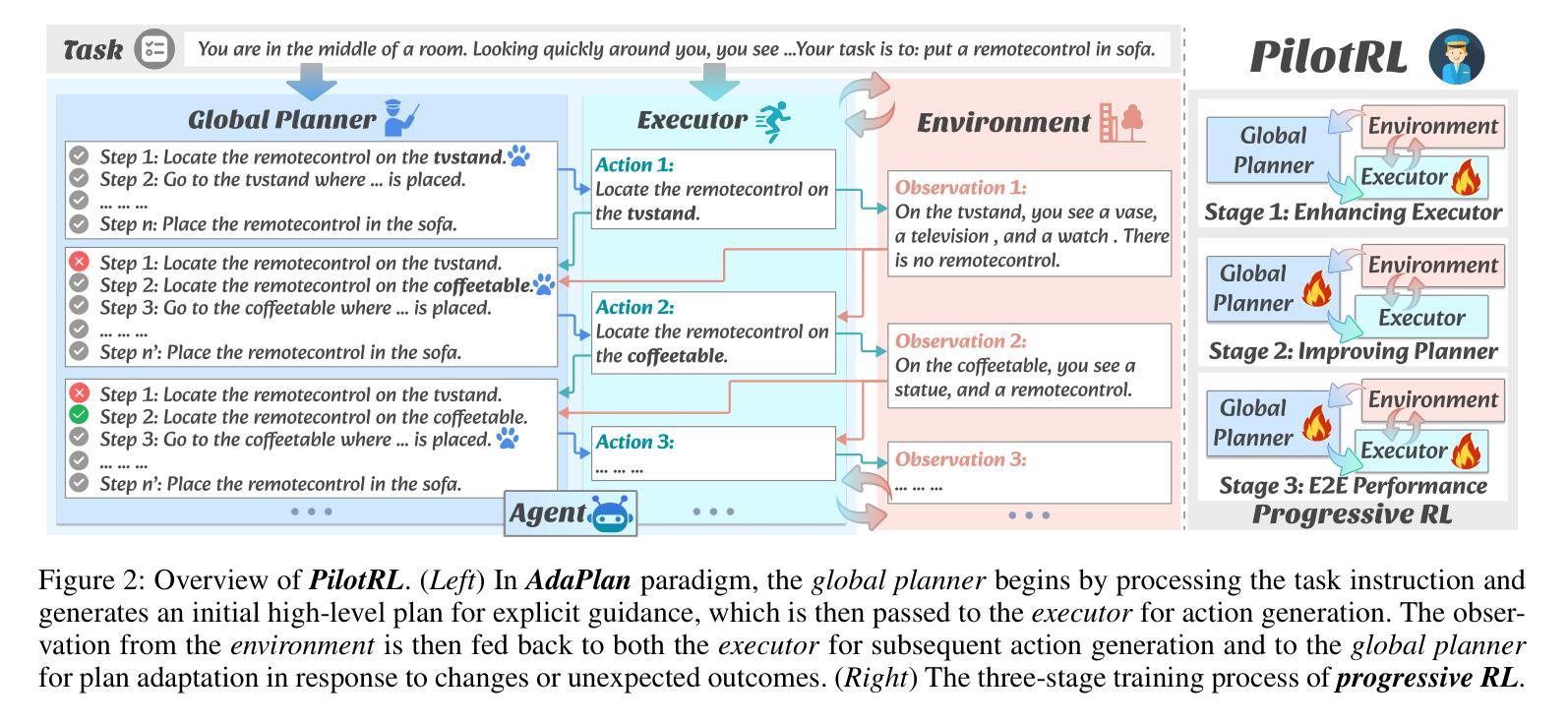
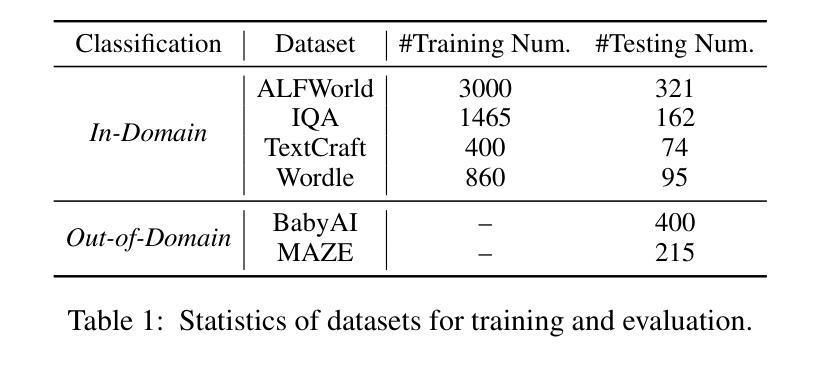
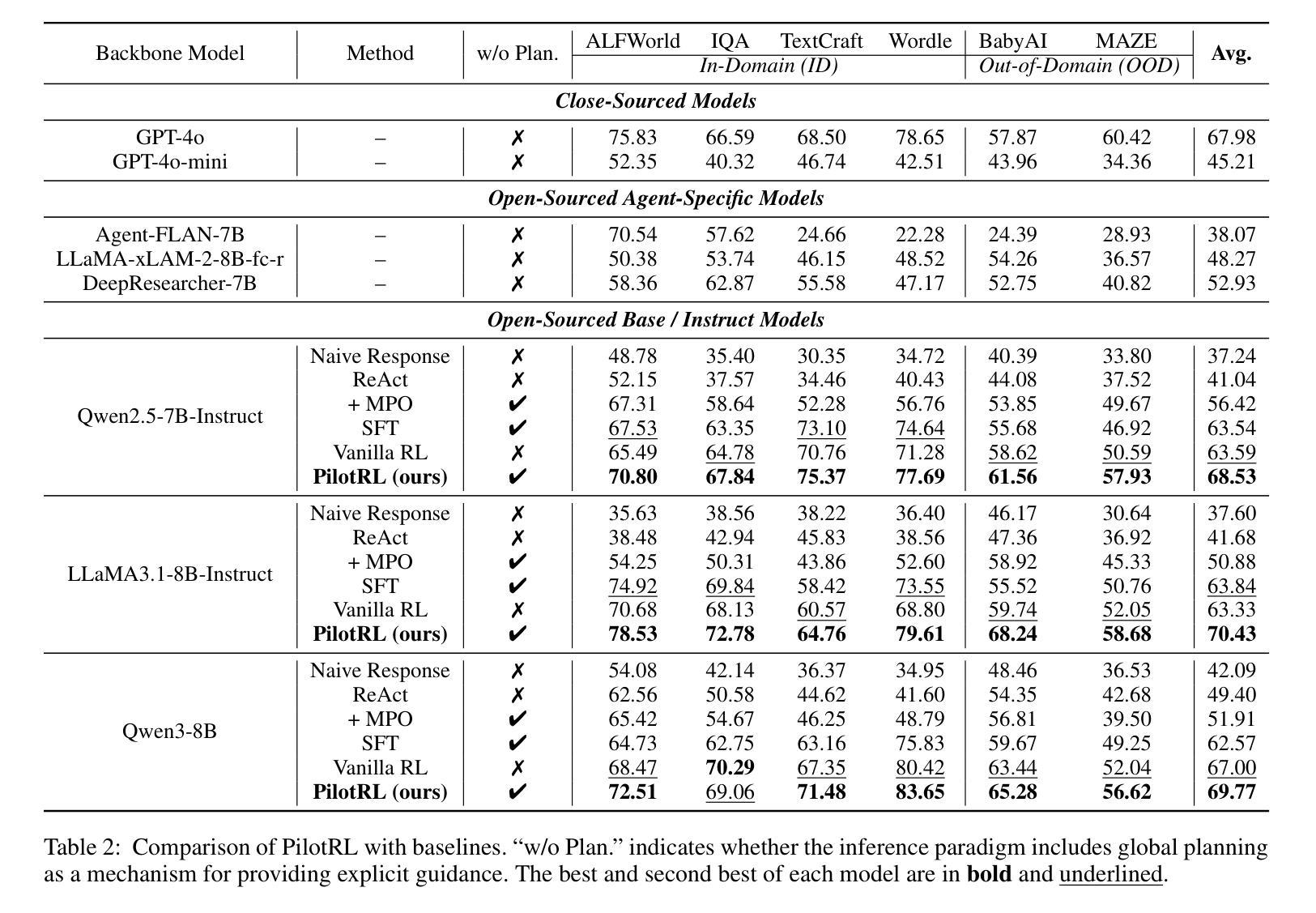
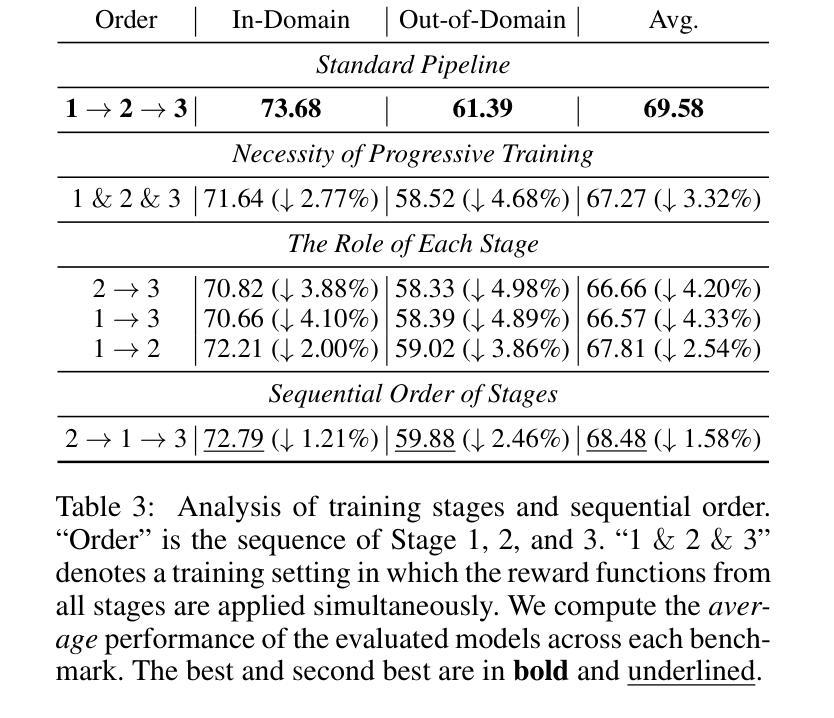
PilotRL: Training Language Model Agents via Global Planning-Guided Progressive Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Keer Lu, Chong Chen, Bin Cui, Huang Leng, Wentao Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in tackling agent-oriented tasks. Despite their potential, existing work faces challenges when deploying LLMs in agent-based environments. The widely adopted agent paradigm ReAct centers on integrating single-step reasoning with immediate action execution, which limits its effectiveness in complex tasks requiring long-term strategic planning. Furthermore, the coordination between the planner and executor during problem-solving is also a critical factor to consider in agent design. Additionally, current approaches predominantly rely on supervised fine-tuning, which often leads models to memorize established task completion trajectories, thereby restricting their generalization ability when confronted with novel problem contexts. To address these challenges, we introduce an adaptive global plan-based agent paradigm AdaPlan, aiming to synergize high-level explicit guidance with execution to support effective long-horizon decision-making. Based on the proposed paradigm, we further put forward PilotRL, a global planning-guided training framework for LLM agents driven by progressive reinforcement learning. We first develop the model’s ability to follow explicit guidance from global plans when addressing agent tasks. Subsequently, based on this foundation, we focus on optimizing the quality of generated plans. Finally, we conduct joint optimization of the model’s planning and execution coordination. Experiments indicate that PilotRL could achieve state-of-the-art performances, with LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL surpassing closed-sourced GPT-4o by 3.60%, while showing a more substantial gain of 55.78% comparing to GPT-4o-mini at a comparable parameter scale.
面向代理任务的大型语言模型(LLMs)已经取得了显著的进步。尽管它们具有潜力,但在基于代理的环境中部署LLMs时,现有工作仍面临挑战。广泛采用的ReAct代理范式侧重于将单步推理与即时行动执行相结合,这限制了其在需要长期战略规划的复杂任务中的有效性。此外,在解决问题过程中,规划者和执行者之间的协调也是代理设计需要考虑的关键因素。另外,当前的方法主要依赖于监督微调,这往往导致模型记忆已建立的任务完成轨迹,从而在面对新问题上下文时限制其泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了基于自适应全局规划的代理范式AdaPlan,旨在将高级显式指导与执行相结合,以支持有效的长期决策。基于这一范式,我们进一步提出了PilotRL,这是一个由全局规划引导的LLM代理训练框架,由渐进强化学习驱动。我们首先开发模型在解决代理任务时遵循全局计划的显式指导能力。在此基础上,我们专注于优化生成的计划的质量。最后,我们对模型的规划和执行协调进行联合优化。实验表明,PilotRL可以达到最先进的性能,LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL在封闭源码GPT-4o上超越3.60%,而在可比参数规模的GPT-4o-mini上表现出更大的优势,提高了55.78%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理面向任务的代理方面取得了显著进展,但仍面临部署在代理环境中的挑战。现有工作面临的问题是单一步骤推理与即时行动执行的集成限制了在复杂任务中的长期战略规划的有效性。文章提出了自适应全局计划代理范式AdaPlan,旨在结合高级明确指导与执行,以支持有效的长期决策制定。基于该范式,提出了PilotRL,一个由渐进强化学习驱动的全球规划指导的LLM代理训练框架。实验表明,PilotRL可以达到最新性能水平,LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL超越了封闭式GPT-4o 3.60%,在相似参数规模下,相较于GPT-4o-mini有更大的提升幅度。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理面向任务的代理方面展现出显著进展,但仍面临部署挑战。
- 当前代理设计主要依赖单一步骤推理与即时行动执行,限制了长期战略规划的有效性。
- AdaPlan自适应全局计划代理范式旨在结合高级明确指导与执行,以支持长期决策制定。
- PilotRL框架是一个基于全球规划指导的LLM代理训练框架,采用渐进强化学习驱动。
- 模型具备遵循全局计划完成代理任务的能力,并在此基础上优化计划质量。
- 通过联合优化模型的规划与执行协调,实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

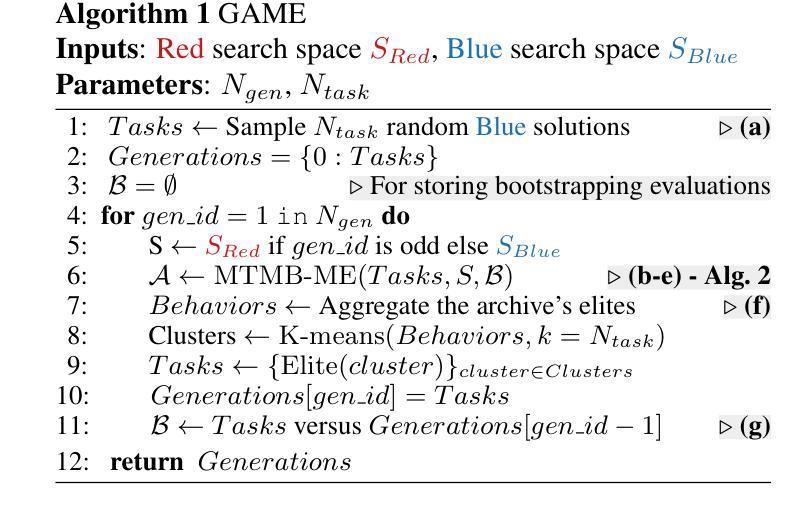
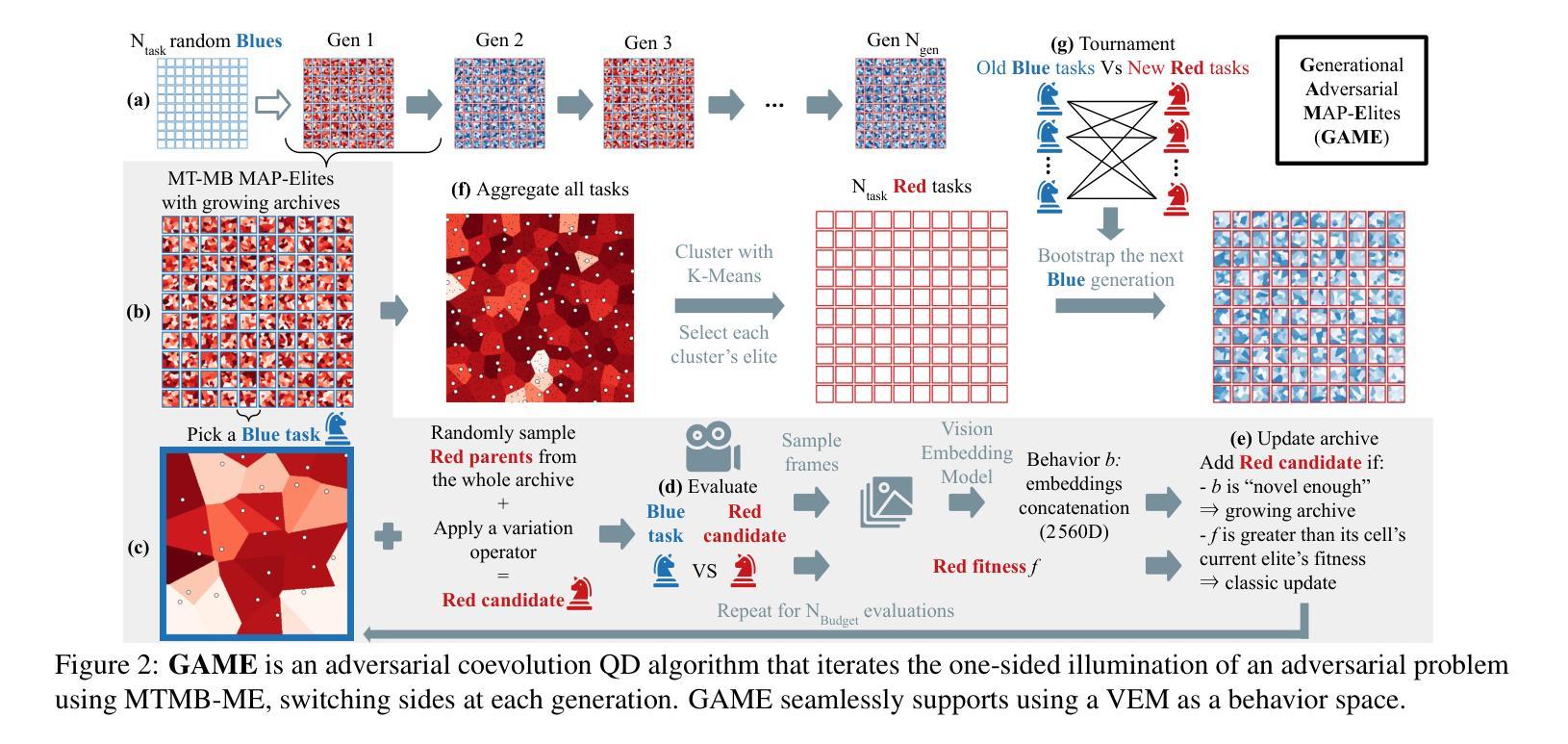
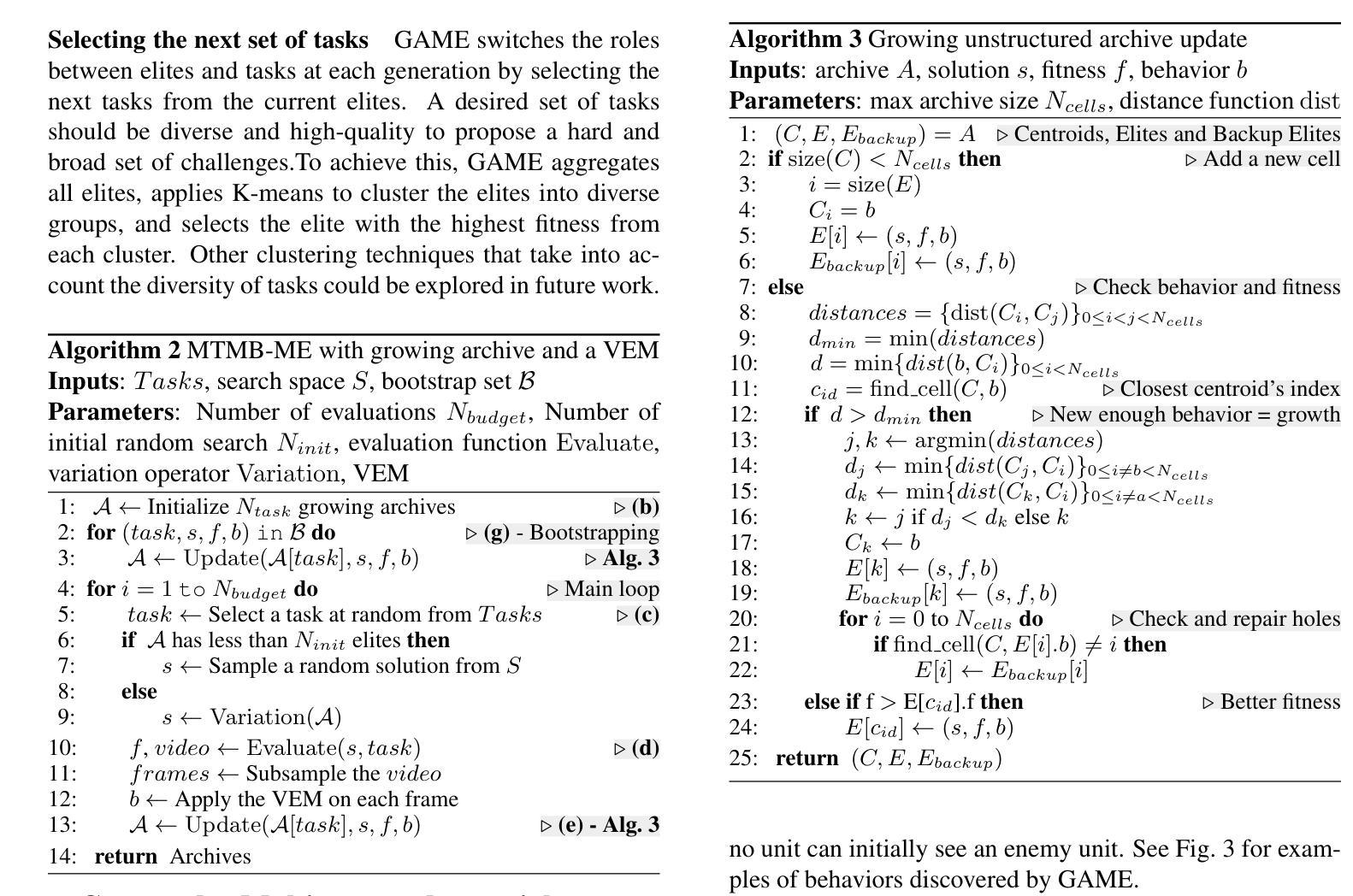
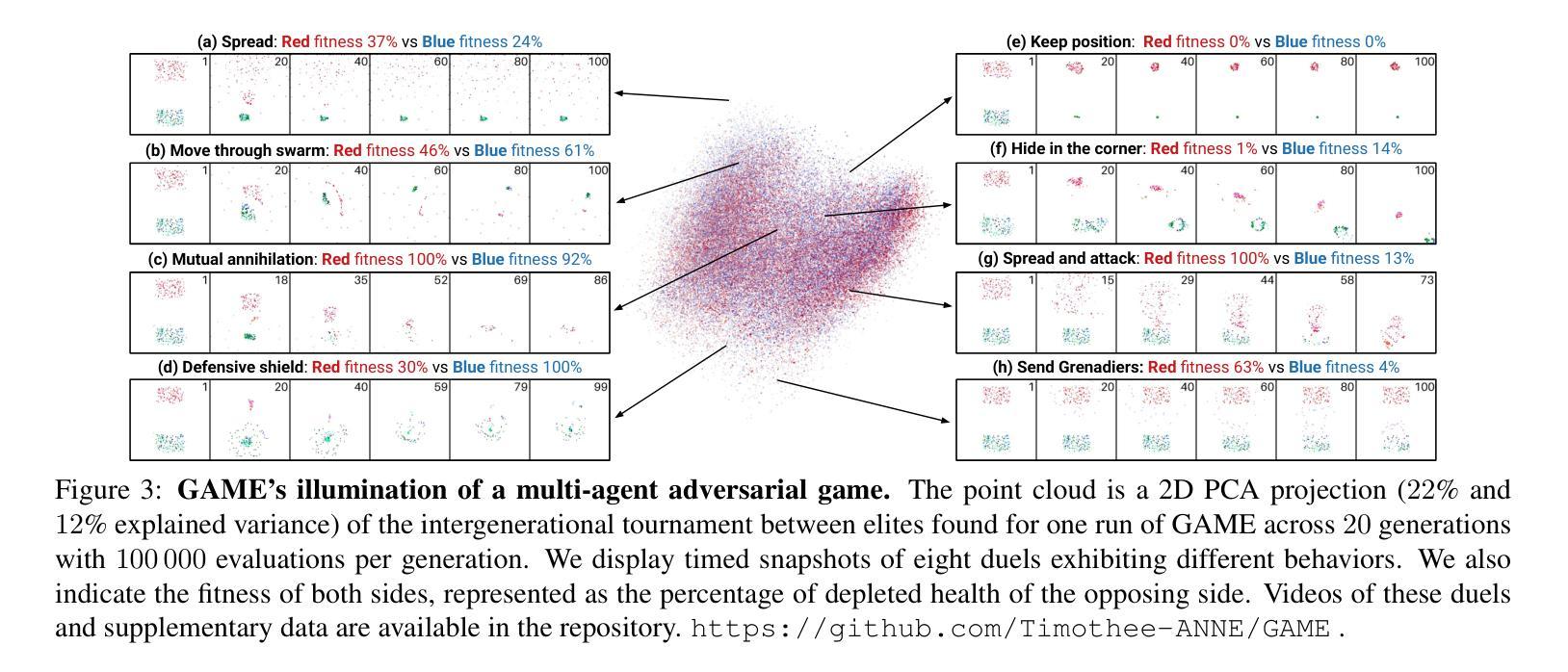
Generational Adversarial MAP-Elites for Multi-Agent Game Illumination
Authors:Timothée Anne, Noah Syrkis, Meriem Elhosni, Florian Turati, Franck Legendre, Alain Jaquier, Sebastian Risi
Unlike traditional optimization algorithms, which focus on finding a single optimal solution, Quality-Diversity (QD) algorithms illuminate a search space by finding high-performing solutions that cover a specified behavior space. However, tackling adversarial problems is more challenging due to the behavioral interdependence between opposing sides. Most applications of QD algorithms to these problems evolve only one side, thus reducing illumination coverage. In this paper, we propose a new QD algorithm, Generational Adversarial MAP-Elites (GAME), which coevolves solutions by alternating sides through a sequence of generations. Combining GAME with vision embedding models enables the algorithm to operate directly on videos of behaviors, rather than relying on handcrafted descriptors. Some key findings are that (1) emerging evolutionary dynamics sometimes resemble an arms race, (2) starting each generation from scratch increases open-endedness, and (3) keeping neutral mutations preserves stepping stones that seem necessary to reach the highest performance. In conclusion, the results demonstrate that GAME can successfully illuminate an adversarial multi-agent game, opening up interesting future directions in understanding the emergence of open-ended coevolution.
不同于传统的优化算法只专注于寻找单一的最优解,质量多样性(QD)算法通过寻找覆盖指定行为空间的高性能解来照亮搜索空间。然而,由于对立双方之间的行为相互依赖性,解决对抗性问题更具挑战性。大多数QD算法在处理这些问题时只进化一侧,从而降低了照明覆盖率。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的QD算法——世代对抗MAP精英(GAME),它通过一系列世代交替进化解决方案。将GAME与视觉嵌入模型相结合,使算法能够直接在行为视频上运行,而不是依赖于手工设计的描述符。一些关键发现是:(1)出现的进化动态有时类似于军备竞赛;(2)从头开始每一代增加了开放性;(3)保持中性突变保留了似乎达到最高性能所必需的垫脚石。总之,结果表明,GAME能够成功照亮对抗性多智能体游戏,为研究开放式协同进化的出现提供了有趣的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ALIFE 2025
Summary
QD算法与传统优化算法不同,它不仅寻找单一最优解,还致力于找到覆盖指定行为空间的高性能解。处理对抗性问题时面临挑战,因对抗双方的行为相互依赖。大部分QD算法的应用仅针对单一侧演化,降低了照明覆盖率。本文提出新的QD算法——世代对抗MAP精英(GAME),通过交替世代共同演化解决方案。结合视觉嵌入模型,算法可直接处理行为视频,而非依赖手工描述。研究结果显示,游戏内的进化动态有时类似于军备竞赛,从零开始每一代增加了开放性,保持中性突变可保留通往最高性能的必经之路。总的来说,游戏成功照亮了对抗性多智能体游戏,为理解开放协同进化的出现打开了有趣的方向。
Key Takeaways
- QD算法旨在覆盖行为空间的高性能解,而非仅寻找单一最优解。
- 对抗性问题中,由于双方行为的相互依赖,解决起来具有挑战性。
- 大部分QD算法在处理对抗性问题时仅针对单一侧演化,降低了照明覆盖率。
- 提出的世代对抗MAP精英(GAME)算法通过交替世代共同演化解决方案。
- 结合视觉嵌入模型,可直接处理行为视频。
- 研究发现,在某些情况下,游戏内的进化动态类似于军备竞赛。
点此查看论文截图

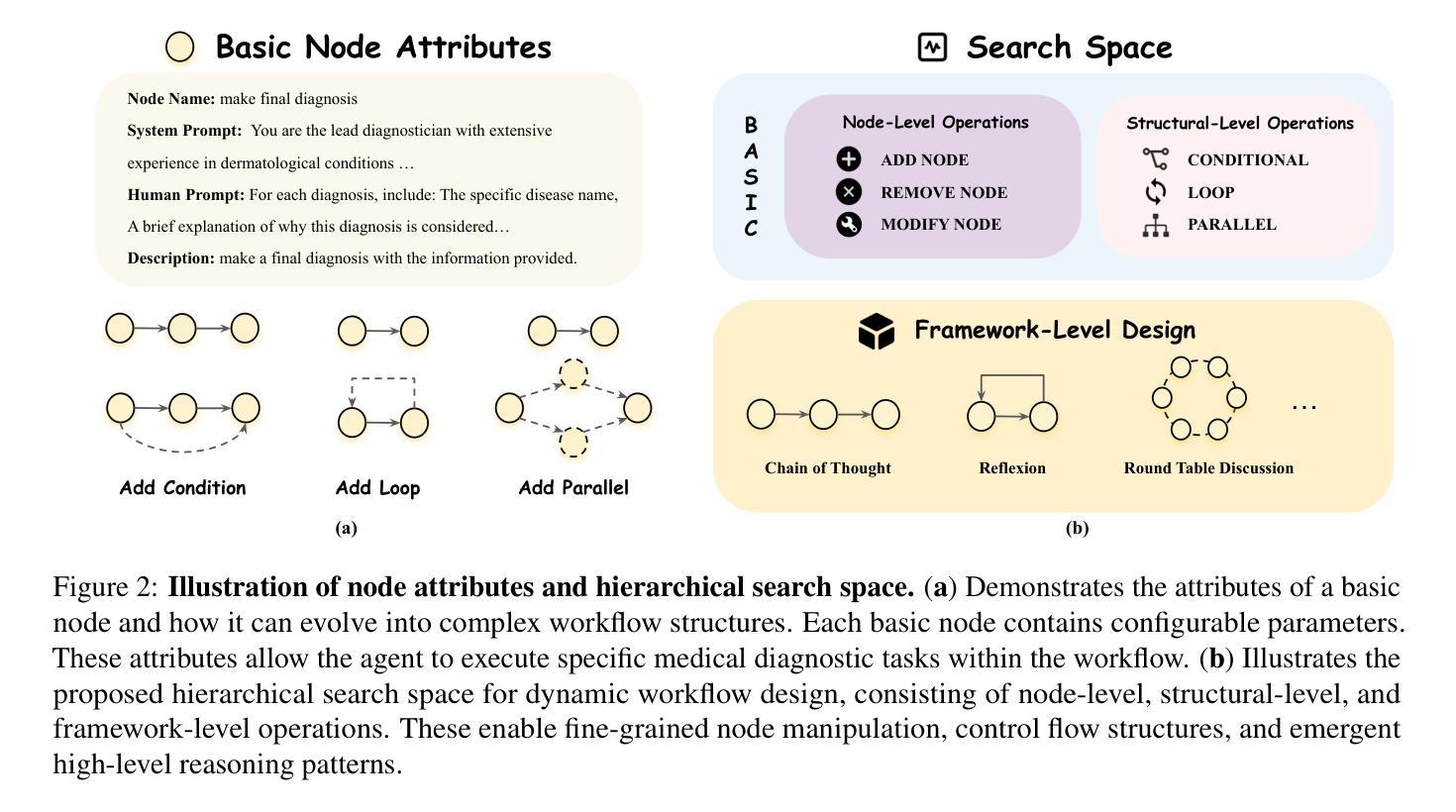
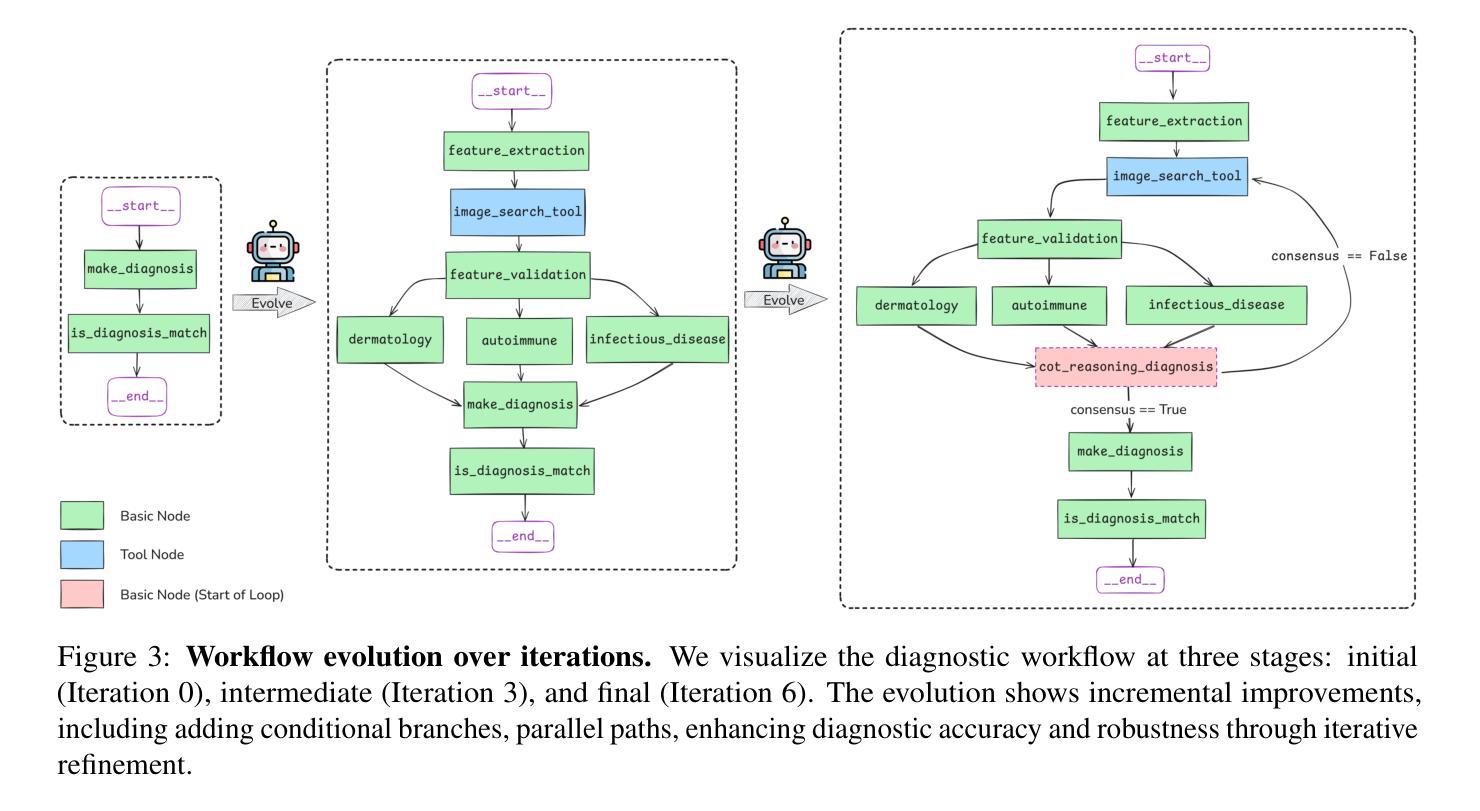
Learning to Be A Doctor: Searching for Effective Medical Agent Architectures
Authors:Yangyang Zhuang, Wenjia Jiang, Jiayu Zhang, Ze Yang, Joey Tianyi Zhou, Chi Zhang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have demonstrated strong capabilities across a wide range of tasks, and their application in the medical domain holds particular promise due to the demand for high generalizability and reliance on interdisciplinary knowledge. However, existing medical agent systems often rely on static, manually crafted workflows that lack the flexibility to accommodate diverse diagnostic requirements and adapt to emerging clinical scenarios. Motivated by the success of automated machine learning (AutoML), this paper introduces a novel framework for the automated design of medical agent architectures. Specifically, we define a hierarchical and expressive agent search space that enables dynamic workflow adaptation through structured modifications at the node, structural, and framework levels. Our framework conceptualizes medical agents as graph-based architectures composed of diverse, functional node types and supports iterative self-improvement guided by diagnostic feedback. Experimental results on skin disease diagnosis tasks demonstrate that the proposed method effectively evolves workflow structures and significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy over time. This work represents the first fully automated framework for medical agent architecture design and offers a scalable, adaptable foundation for deploying intelligent agents in real-world clinical environments.
基于大规模语言模型(LLM)的代理人在各种任务中表现出强大的能力,它们在医疗领域的应用由于需要高度泛化能力和依赖跨学科知识而具有特殊前景。然而,现有的医疗代理系统通常依赖于静态、手动设计的工作流程,缺乏适应不同诊断要求和适应新兴临床场景的灵活性。受自动机器学习(AutoML)成功的启发,本文介绍了一种用于自动设计医疗代理架构的新型框架。具体来说,我们定义了一个分层且表达性强的代理搜索空间,通过节点、结构和框架层面的结构化修改,实现动态工作流程的适应。我们的框架将医疗代理人概念化为基于图形的架构,由多种功能节点类型组成,并支持通过诊断反馈指导的迭代自我改进。在皮肤病诊断任务上的实验结果表明,所提出的方法有效地进化了工作流程结构,并随着时间的推移显著提高了诊断准确性。这项工作代表了医疗代理架构设计的第一个完全自动化的框架,为在现实世界临床环境中部署智能代理人提供了可扩展和可适应的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACM MM 2025
总结
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在多种任务上展现出强大的能力,其在医疗领域的应用因需求高泛化能力和跨学科知识而具有特别前景。然而,现有的医疗代理系统通常依赖于静态、手动构建的工作流程,缺乏适应多样诊断需求和新兴临床情境的灵活性。受自动化机器学习(AutoML)成功的启发,本文介绍了一种用于医疗代理架构自动化设计的新型框架。该框架定义了层次化和表达性的代理搜索空间,通过节点、结构和框架级别的结构化修改,实现动态工作流程适应。该框架将医疗代理概念化为基于图形的架构,由各种功能节点类型组成,并可通过诊断反馈进行迭代自我改进。在皮肤疾病诊断任务上的实验结果证明,该方法有效地进化了工作流程结构,并随时间显著提高了诊断准确性。这项工作代表了医疗代理架构设计的首个完全自动化框架,为在真实临床环境中部署智能代理提供了可扩展和可适应的基础。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在医疗领域具有广泛应用前景,因其高泛化能力和跨学科知识需求。
- 现有医疗代理系统缺乏灵活性,不能适应多样诊断需求和新兴临床情境。
- 自动化机器学习在医疗代理设计中的应用有助于提高代理的灵活性和效率。
- 提出的框架实现了医疗代理架构的自动化设计,通过层次化和表达性的搜索空间实现动态工作流程适应。
- 框架将医疗代理概念化为基于图形的架构,由功能节点组成,支持迭代自我改进。
- 在皮肤疾病诊断任务上,该框架有效提高诊断准确性。
- 该工作为在真实临床环境中部署智能代理提供了可扩展和可适应的基础。
点此查看论文截图