⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
LoRAtorio: An intrinsic approach to LoRA Skill Composition
Authors:Niki Foteinopoulou, Ignas Budvytis, Stephan Liwicki
Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has become a widely adopted technique in text-to-image diffusion models, enabling the personalisation of visual concepts such as characters, styles, and objects. However, existing approaches struggle to effectively compose multiple LoRA adapters, particularly in open-ended settings where the number and nature of required skills are not known in advance. In this work, we present LoRAtorio, a novel train-free framework for multi-LoRA composition that leverages intrinsic model behaviour. Our method is motivated by two key observations: (1) LoRA adapters trained on narrow domains produce denoised outputs that diverge from the base model, and (2) when operating out-of-distribution, LoRA outputs show behaviour closer to the base model than when conditioned in distribution. The balance between these two observations allows for exceptional performance in the single LoRA scenario, which nevertheless deteriorates when multiple LoRAs are loaded. Our method operates in the latent space by dividing it into spatial patches and computing cosine similarity between each patch’s predicted noise and that of the base model. These similarities are used to construct a spatially-aware weight matrix, which guides a weighted aggregation of LoRA outputs. To address domain drift, we further propose a modification to classifier-free guidance that incorporates the base model’s unconditional score into the composition. We extend this formulation to a dynamic module selection setting, enabling inference-time selection of relevant LoRA adapters from a large pool. LoRAtorio achieves state-of-the-art performance, showing up to a 1.3% improvement in ClipScore and a 72.43% win rate in GPT-4V pairwise evaluations, and generalises effectively to multiple latent diffusion models.
低秩适应(LoRA)已成为文本到图像扩散模型中的一项广泛采用的技术,使字符、风格和对象等视觉概念的个性化成为可能。然而,现有方法难以有效地组合多个LoRA适配器,特别是在开放式环境中,所需技能的数量和性质是未知的。在这项工作中,我们提出了LoRAtorio,这是一个无需训练的多LoRA组合新型框架,它利用模型的内在行为。我们的方法受到两个关键观察结果的启发:(1)在狭窄领域上训练的LoRA适配器会产生去噪输出,这些输出与基础模型有分歧;(2)在分布之外运行时,LoRA输出显示的行为更接近基础模型,而不是在分布中的条件。这两种观察结果之间的平衡允许在单个LoRA场景中表现出卓越性能,然而当加载多个LoRAs时,性能会下降。我们的方法在潜在空间进行操作,将其分为空间块并计算每个块的预测噪声与基础模型的余弦相似性。这些相似性被用来构建一个空间感知权重矩阵,该矩阵引导LoRA输出的加权聚合。为了解决领域漂移问题,我们进一步提出了无分类器指导的修改,将基础模型的无条件分数纳入组合。我们将这种表述扩展到动态模块选择设置,以在推理时从大量池中选择相关的LoRA适配器。LoRAtorio达到了最先进的性能,在ClipScore上实现了高达1.3%的改进,在GPT-4V配对评估中的胜率为72.43%,并能有效地适应多种潜在扩散模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 17 figures
摘要
LoRAtorio是一种无需训练的多LoRA组合新方法,适用于文本到图像扩散模型中的低等级适应(LoRA)技术。该方法基于两个关键观察结果:LoRA适配器在狭窄领域上训练会产生去噪输出,这些输出与基础模型有所偏差;当超出分布操作时,LoRA输出行为与基础模型更接近。LoRAtorio通过分割潜在空间为空间补丁并计算每个补丁预测噪声与基础模型的余弦相似性,来构建空间感知权重矩阵,指导加权聚合LoRA输出。为解决领域漂移问题,我们进一步提出无分类器指导的修改,将基础模型的无条件分数纳入组合中。该方法可扩展至动态模块选择设置,可在推理时从大量池中选择相关LoRA适配器。LoRAtorio实现了一流的性能,在ClipScore上提高了1.3%,在GPT-4V成对评估中的胜率为72.43%,并能有效地推广到多个潜在扩散模型。
关键见解
- LoRAtorio是一种新的无需训练的多LoRA组合框架,适用于文本到图像扩散模型中的个性化视觉概念。
- LoRA适配器在狭窄领域上训练会产生去噪输出,这些输出与基础模型有所偏差。
- 当超出分布操作时,LoRA输出的行为与基础模型更为接近。
- LoRAtorio通过计算预测噪声的余弦相似性来构建空间感知权重矩阵,指导加权聚合LoRA输出。
- 为解决领域漂移问题,结合基础模型的无条件分数进行优化。
- 该方法能够实现动态模块选择,可在推理时根据需求选择相关的LoRA适配器。
- LoRAtorio在性能上实现了一流的成果,能够有效推广至多个潜在扩散模型。
点此查看论文截图

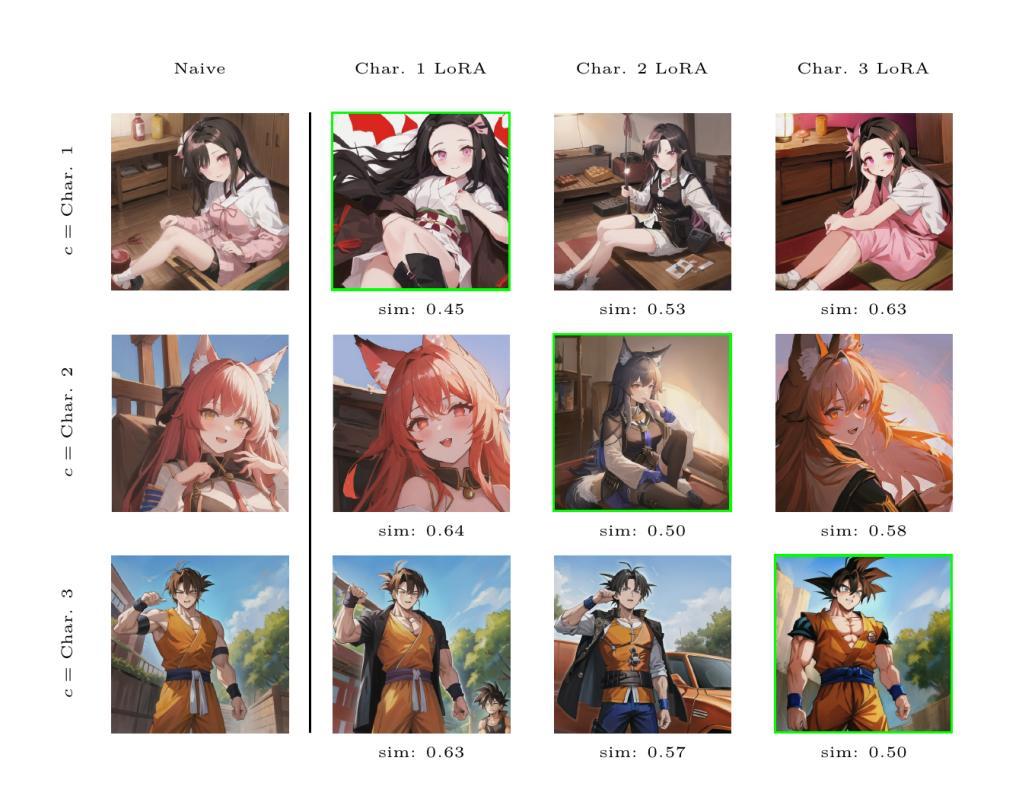
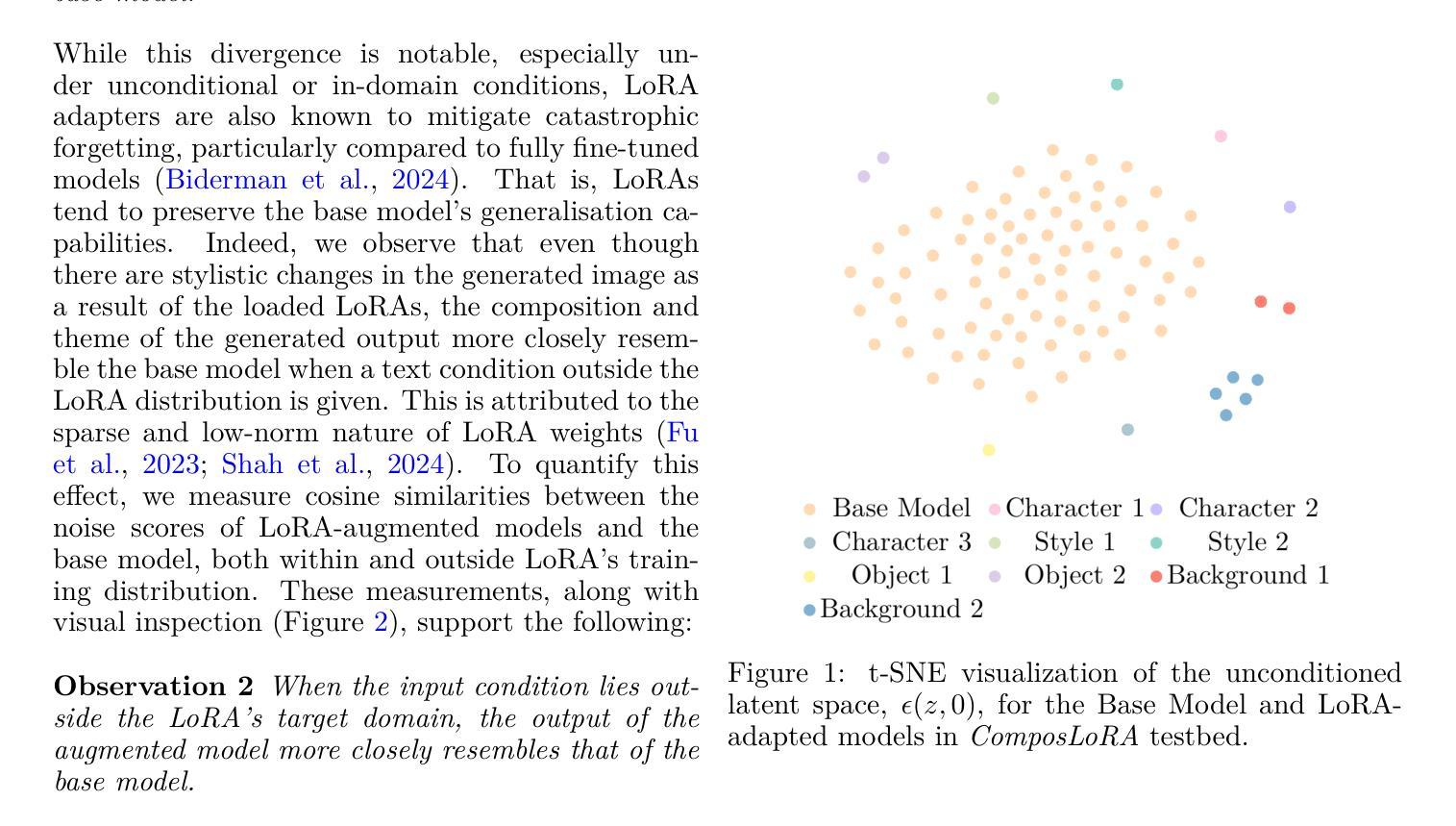
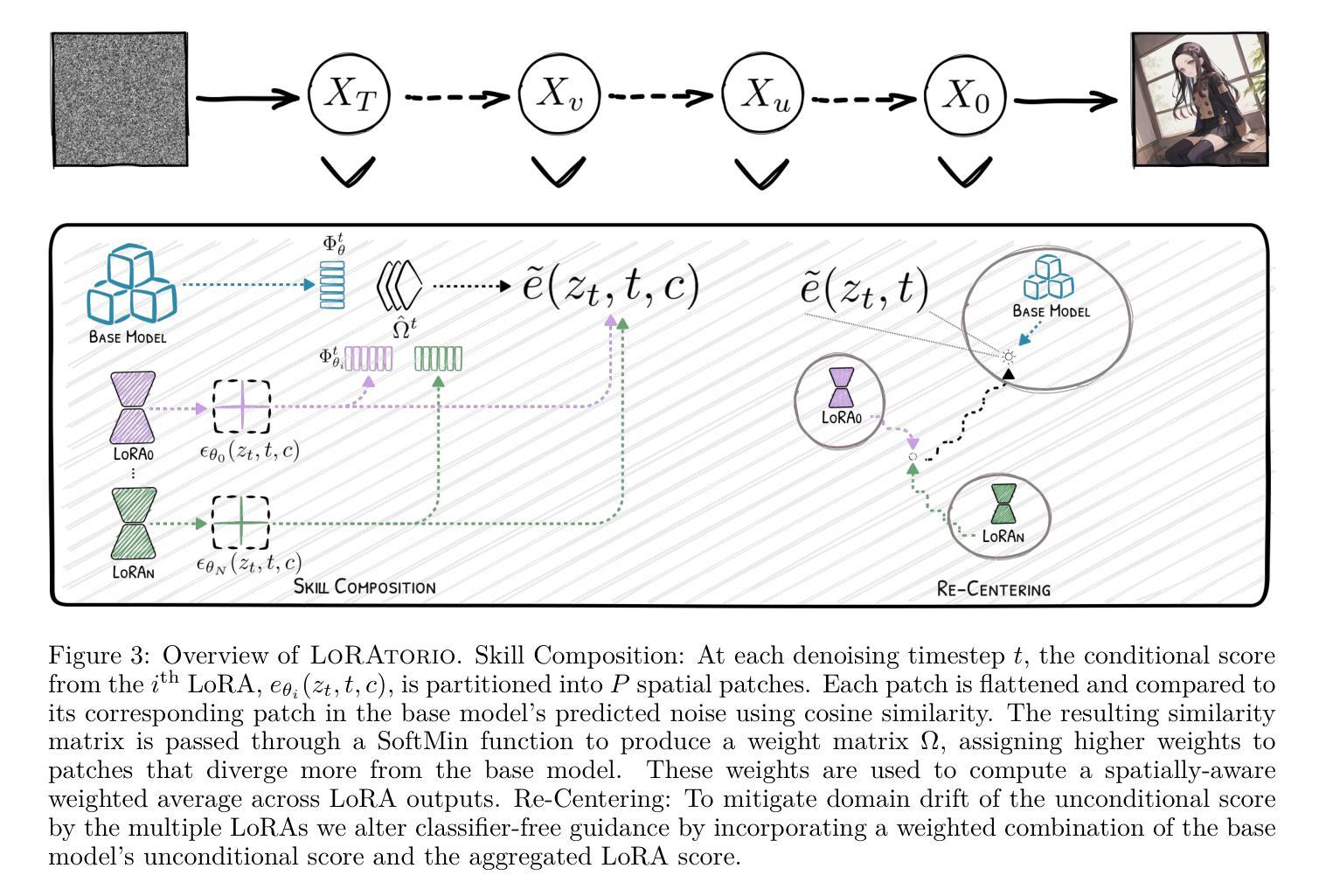
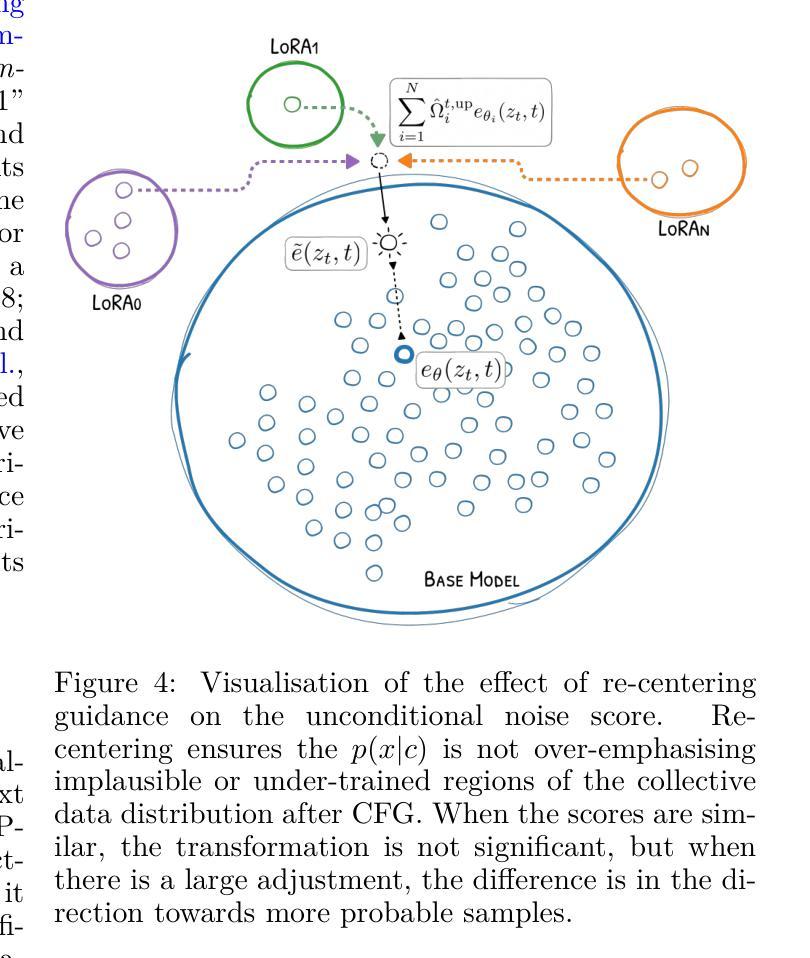
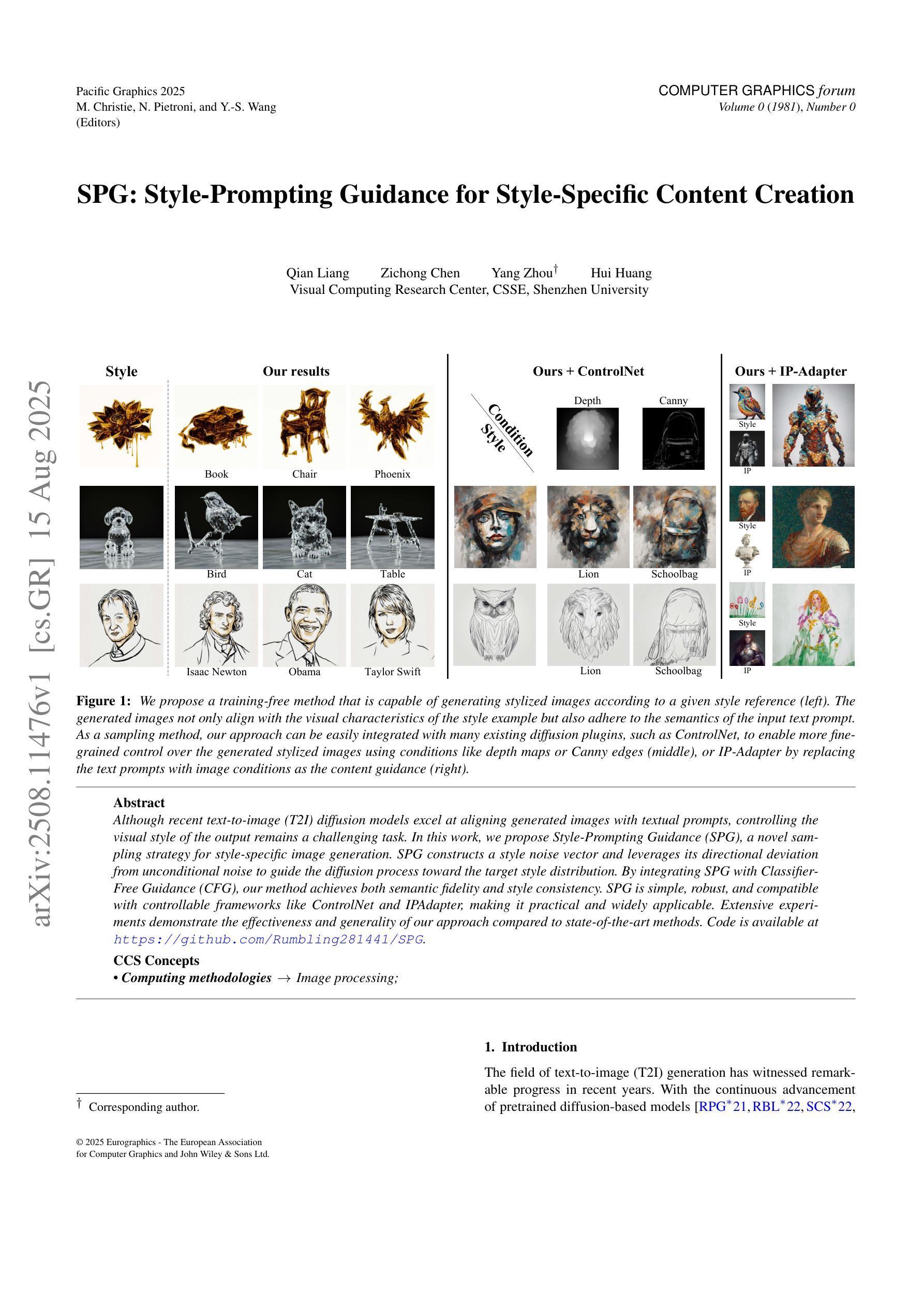
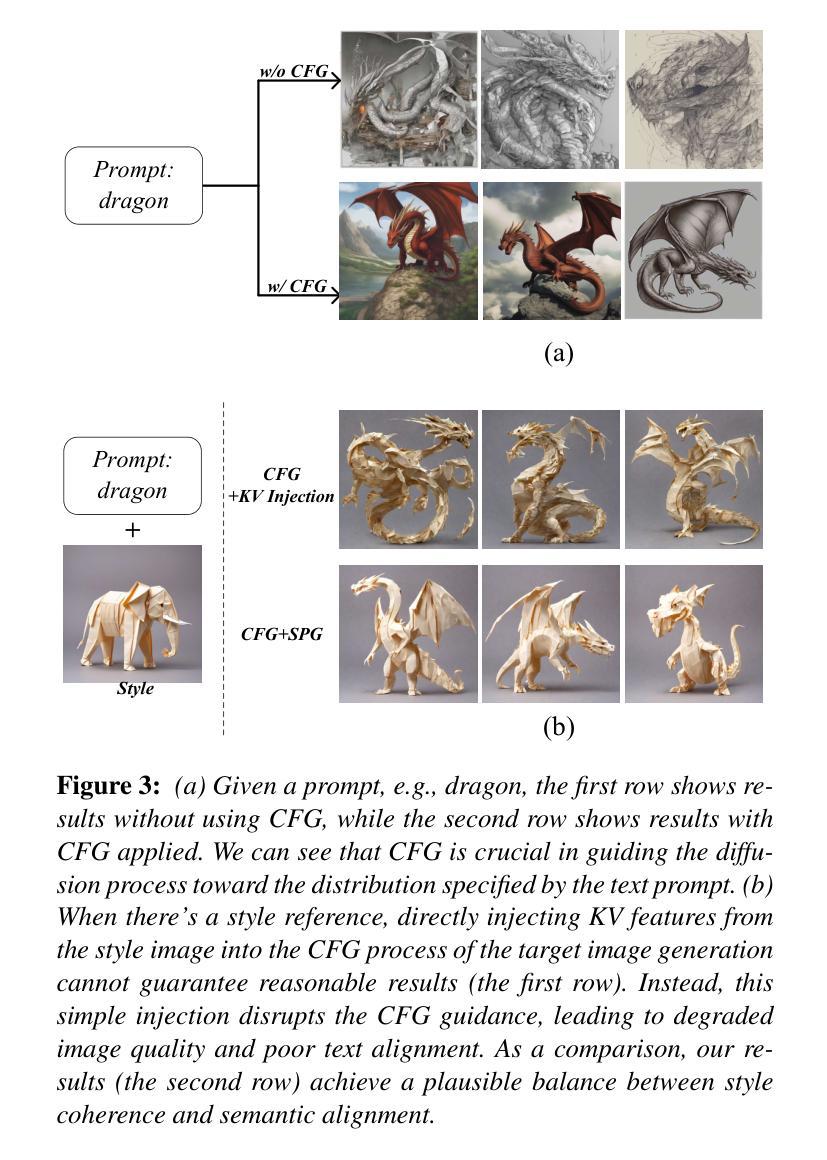
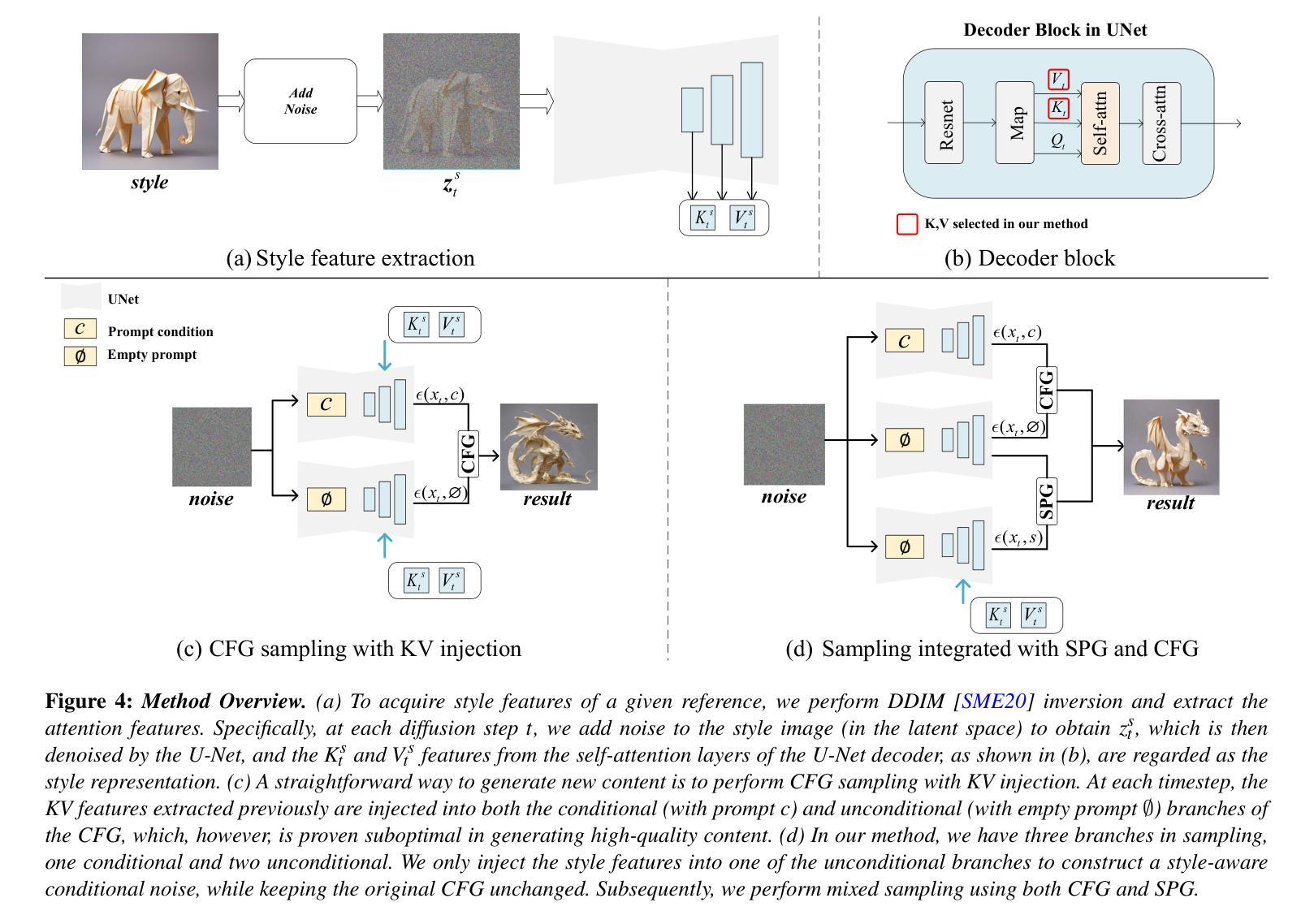
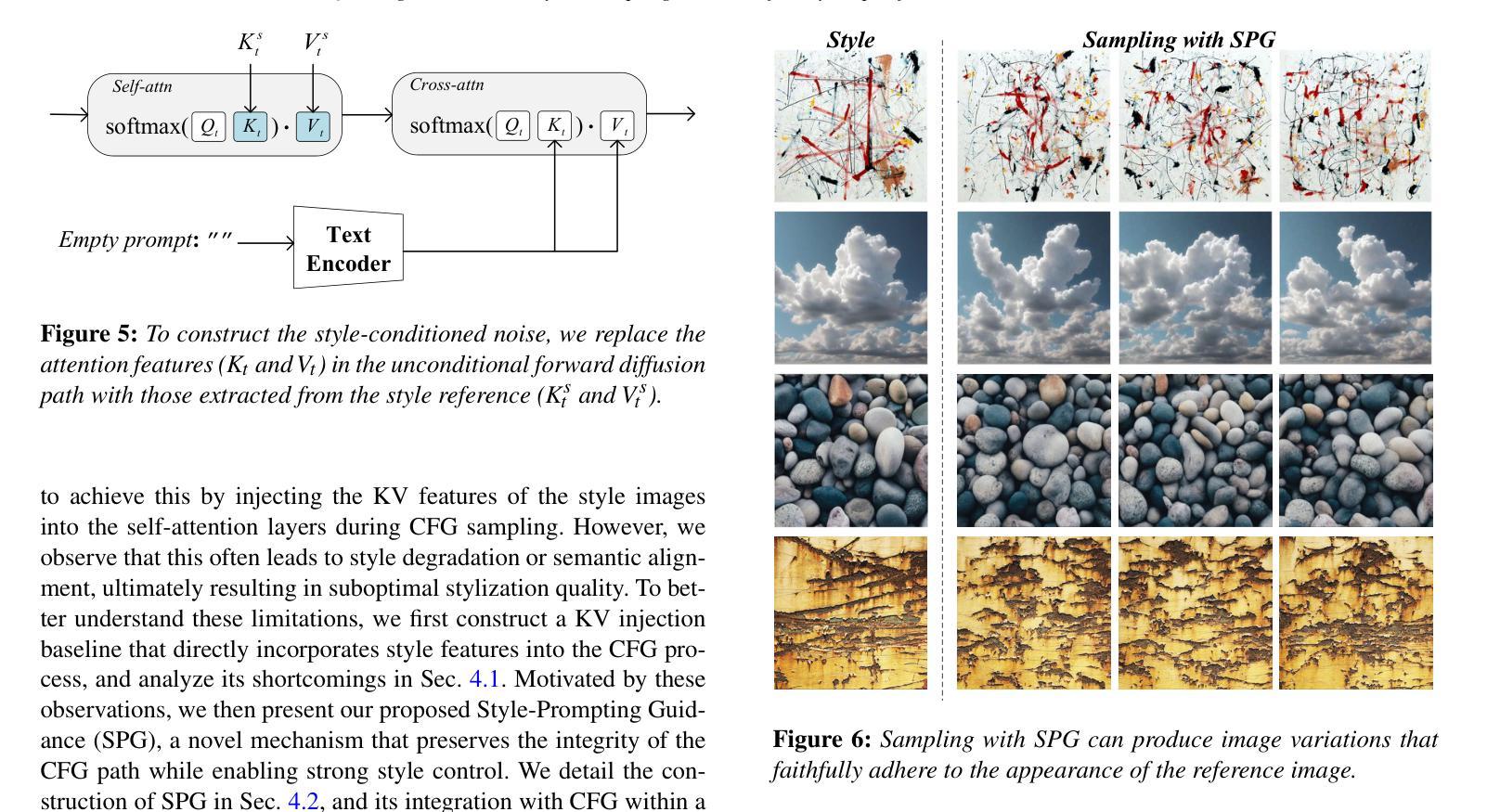
SPG: Style-Prompting Guidance for Style-Specific Content Creation
Authors:Qian Liang, Zichong Chen, Yang Zhou, Hui Huang
Although recent text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models excel at aligning generated images with textual prompts, controlling the visual style of the output remains a challenging task. In this work, we propose Style-Prompting Guidance (SPG), a novel sampling strategy for style-specific image generation. SPG constructs a style noise vector and leverages its directional deviation from unconditional noise to guide the diffusion process toward the target style distribution. By integrating SPG with Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG), our method achieves both semantic fidelity and style consistency. SPG is simple, robust, and compatible with controllable frameworks like ControlNet and IPAdapter, making it practical and widely applicable. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of our approach compared to state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/Rumbling281441/SPG.
尽管最近的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在将生成的图像与文本提示对齐方面表现出色,但控制输出图像的可视风格仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了Style-Prompting Guidance(SPG),这是一种用于特定风格图像生成的新型采样策略。SPG构建了一个风格噪声向量,利用其无条件噪声的方向偏差来引导扩散过程朝向目标风格分布。通过将SPG与无分类器引导(CFG)相结合,我们的方法实现了语义保真和风格一致性。SPG简单、稳健,且与可控框架如ControlNet和IPAdapter兼容,使其具有实用性和广泛适用性。大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们的方法具有有效性和普遍性。代码可在https://github.com/Rumbling281441/SPG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Journal track of Pacific Graphics 2025
Summary
文本描述的扩散模型提出了一个名为Style-Prompting Guidance(SPG)的新采样策略,用于特定风格的图像生成。通过构建风格噪声向量并引导扩散过程朝着目标风格分布进行,该策略实现了语义保真和风格一致性。SPG与Classifier-Free Guidance(CFG)相结合,使方法既简单又稳健,且与可控框架如ControlNet和IPAdapter兼容。实验证明,该方法与现有技术相比具有有效性和普遍性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本描述的扩散模型在生成与文本提示对齐的图像方面表现出色,但控制输出视觉风格仍然具有挑战性。
- 提出了Style-Prompting Guidance(SPG)采样策略,用于特定风格的图像生成。
- SPG通过构建风格噪声向量并引导扩散过程来工作,从而实现目标风格分布。
- SPG与Classifier-Free Guidance(CFG)结合,达到语义保真和风格一致性。
- SPG方法简单、稳健,与可控框架兼容,如ControlNet和IPAdapter。
- 广泛实验证明,与现有技术相比,该方法具有有效性和普遍性。
点此查看论文截图


Probing the Representational Power of Sparse Autoencoders in Vision Models
Authors:Matthew Lyle Olson, Musashi Hinck, Neale Ratzlaff, Changbai Li, Phillip Howard, Vasudev Lal, Shao-Yen Tseng
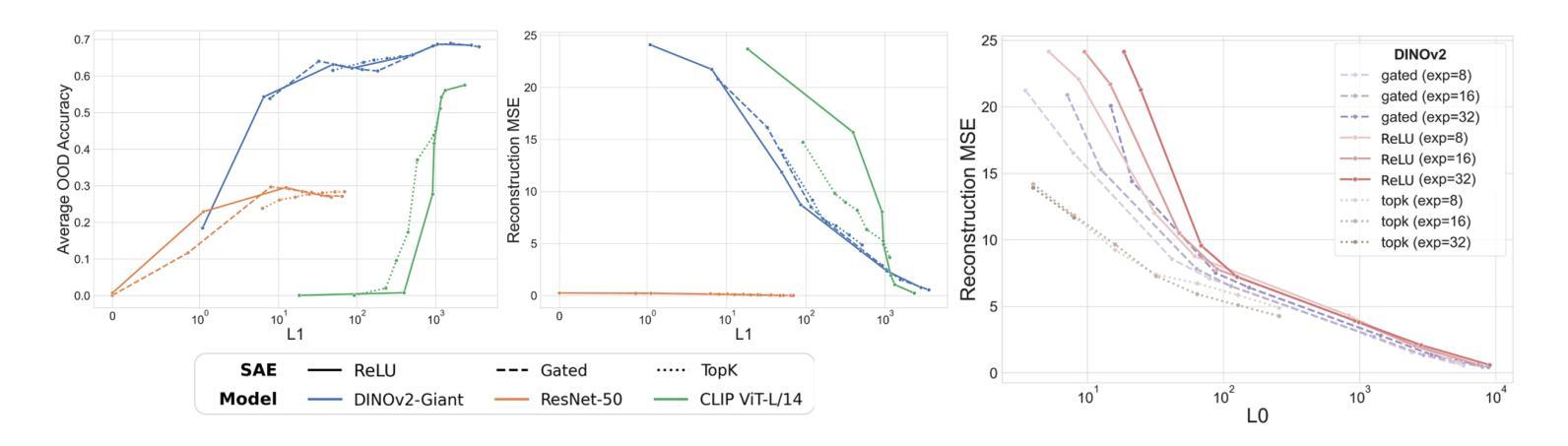
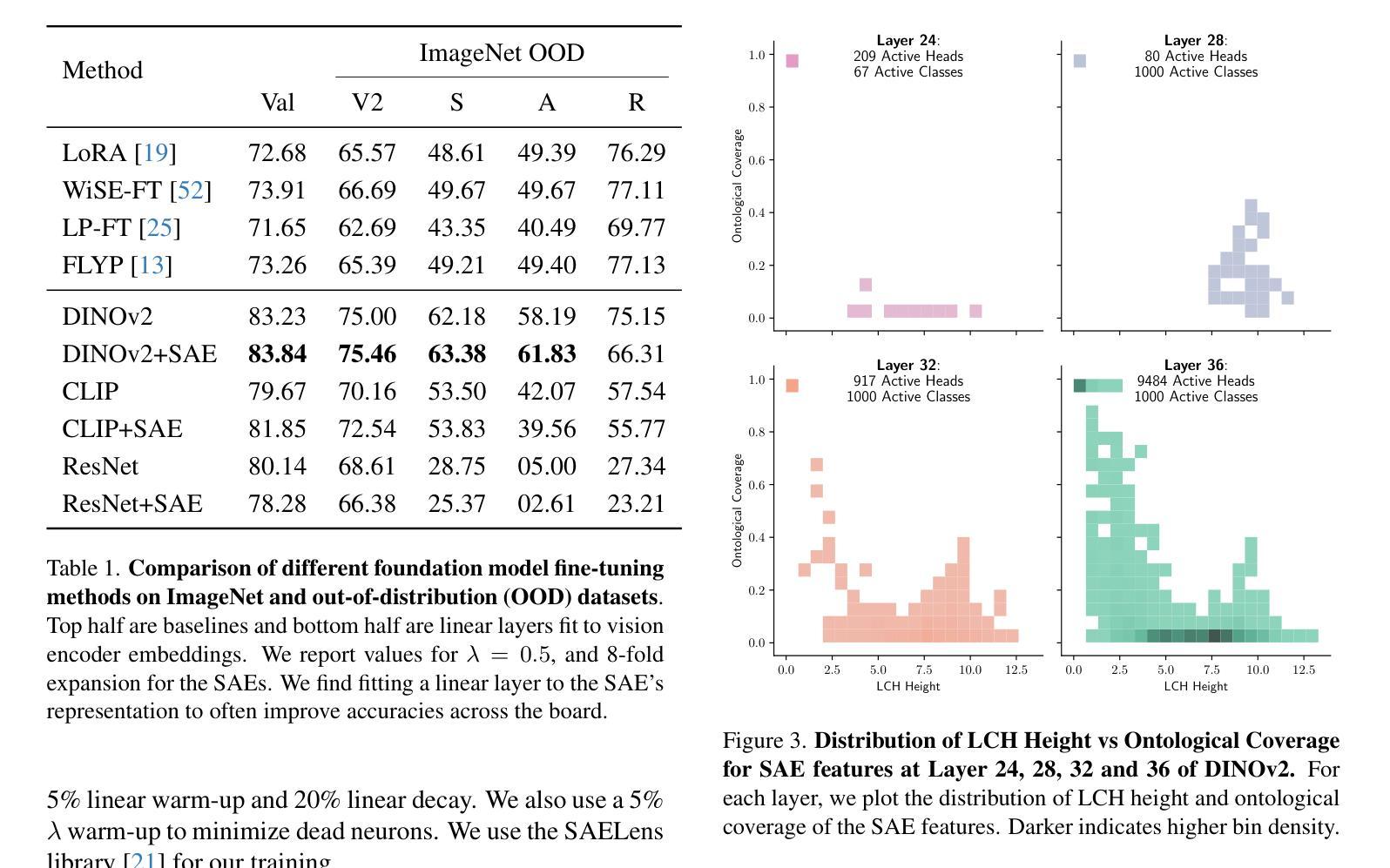
Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a popular tool for interpreting the hidden states of large language models (LLMs). By learning to reconstruct activations from a sparse bottleneck layer, SAEs discover interpretable features from the high-dimensional internal representations of LLMs. Despite their popularity with language models, SAEs remain understudied in the visual domain. In this work, we provide an extensive evaluation the representational power of SAEs for vision models using a broad range of image-based tasks. Our experimental results demonstrate that SAE features are semantically meaningful, improve out-of-distribution generalization, and enable controllable generation across three vision model architectures: vision embedding models, multi-modal LMMs and diffusion models. In vision embedding models, we find that learned SAE features can be used for OOD detection and provide evidence that they recover the ontological structure of the underlying model. For diffusion models, we demonstrate that SAEs enable semantic steering through text encoder manipulation and develop an automated pipeline for discovering human-interpretable attributes. Finally, we conduct exploratory experiments on multi-modal LLMs, finding evidence that SAE features reveal shared representations across vision and language modalities. Our study provides a foundation for SAE evaluation in vision models, highlighting their strong potential improving interpretability, generalization, and steerability in the visual domain.
稀疏自编码器(Sparse Autoencoders, SAEs)作为一种工具,已经被广泛应用于解释大型语言模型(LLMs)的隐藏状态。通过学会从稀疏瓶颈层重建激活,SAE从LLM的高维内部表示中发现可解释的特征。尽管SAE在语言模型中很受欢迎,但在视觉领域它们的研究仍然不足。在这项工作中,我们通过对一系列图像任务进行广泛的评估,全面评估了SAE在视觉模型中的表示能力。我们的实验结果表明,SAE特征是语义上有意义的,能提高超出分布范围的泛化能力,并在三种视觉模型架构中实现了可控生成:视觉嵌入模型、多模态LLM和扩散模型。在视觉嵌入模型中,我们发现学习到的SAE特征可用于OOD检测,并提供证据表明它们恢复了底层模型的本体结构。对于扩散模型,我们证明了SAE通过文本编码器操作实现语义引导,并开发了一个自动化管道来发现人类可解释的属性。最后,我们对多模态LLMs进行了探索性实验,发现证据表明SAE特征揭示了跨视觉和语言模态的共享表示。我们的研究为视觉模型中SAE的评估奠定了基础,突显了它们在提高视觉领域的可解释性、泛化能力和可控性方面的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Findings
Summary
稀疏自编码器(SAE)在解读大型语言模型(LLM)的隐藏状态方面表现出强大的潜力。本研究首次对SAE在视觉模型中的表现进行了全面评估,实验结果显示SAE特征具有语义意义,能提高模型在分布外的泛化能力,并能控制三种视觉模型的生成:视觉嵌入模型、多模态LLM和扩散模型。SAE特征可用于异常检测并揭示底层模型的本体结构。对于扩散模型,SAE能够实现语义控制,并发现人类可解释的属性。在多模态LLM上的实验表明SAE特征揭示了跨视觉和语言模态的共享表示。研究为SAE在视觉模型中的应用奠定了坚实的基础,显示出其在提高可解释性、泛化能力和可控制性方面的强大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏自编码器(SAE)在解读大型语言模型隐藏状态方面具有广泛应用。
- 在视觉模型中,SAE的特征展现出语义意义。
- SAE能提高模型在分布外的泛化能力。
- SAE能控制视觉模型的生成,包括视觉嵌入模型、多模态LLM和扩散模型。
- SAE特征在异常检测方面表现出良好的性能,并能揭示底层模型的本体结构。
- 对于扩散模型,SAE能够实现语义控制并发现人类可解释的属性。
点此查看论文截图


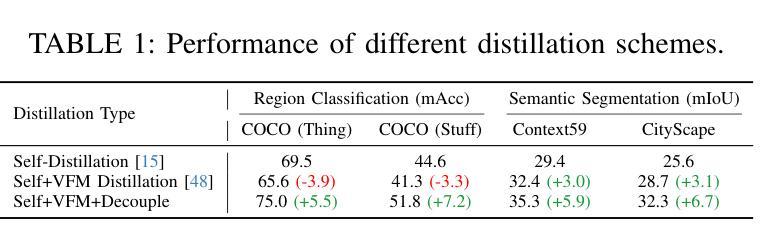
Generalized Decoupled Learning for Enhancing Open-Vocabulary Dense Perception
Authors:Junjie Wang, Keyu Chen, Yulin Li, Bin Chen, Hengshuang Zhao, Xiaojuan Qi, Zhuotao Tian
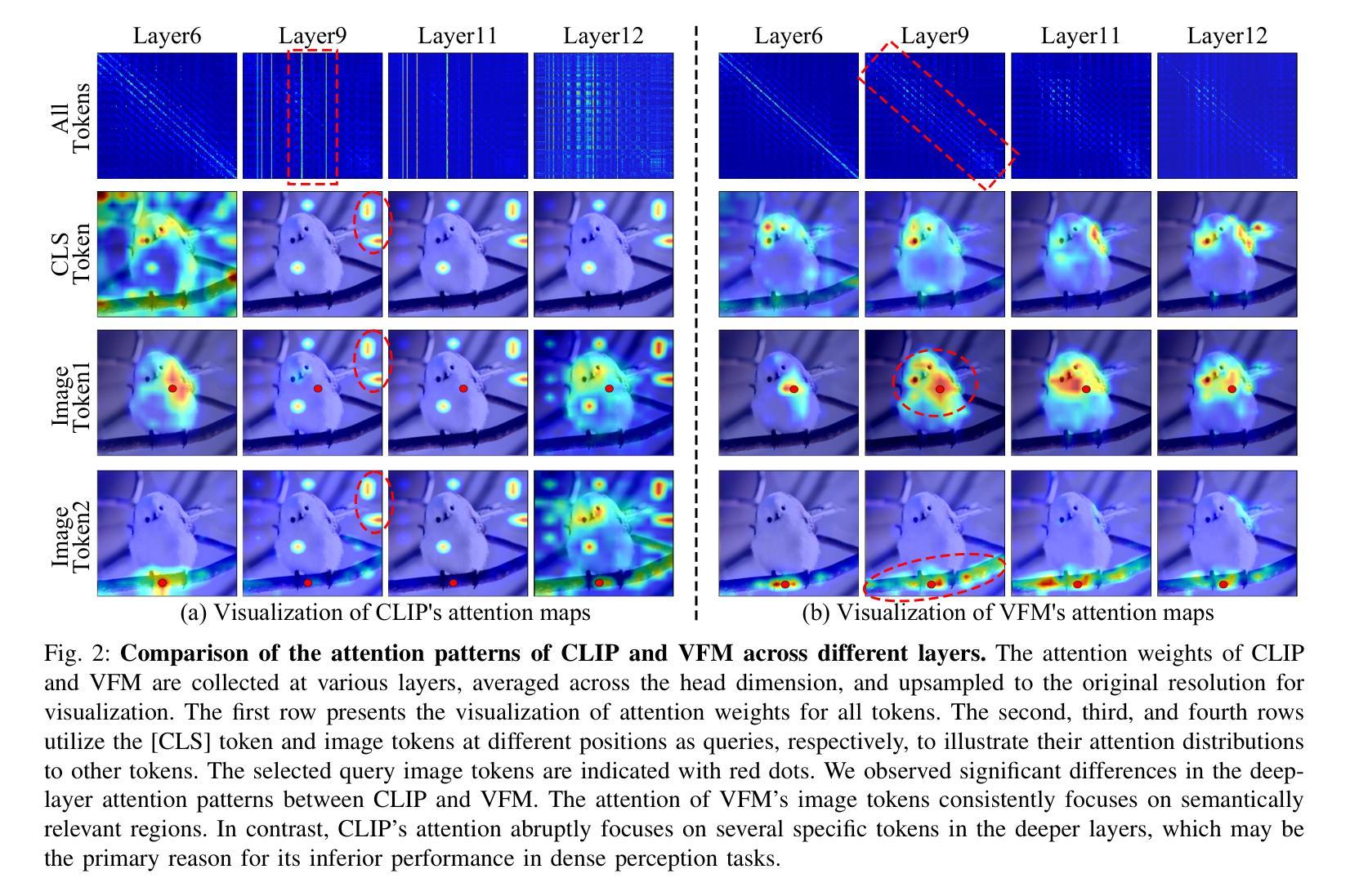
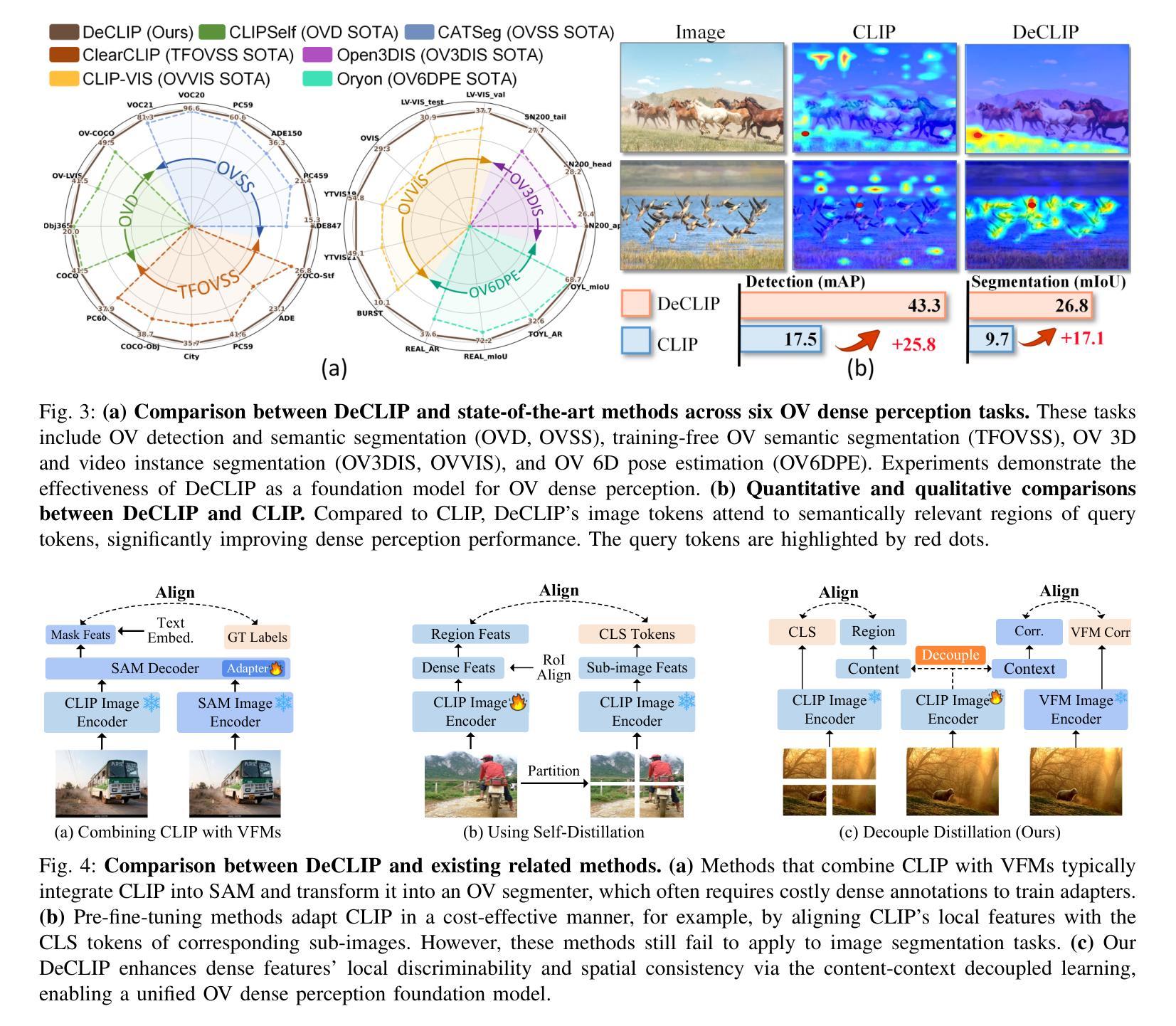
Dense visual perception tasks have been constrained by their reliance on predefined categories, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios where visual concepts are unbounded. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like CLIP have shown promise in open-vocabulary tasks, their direct application to dense perception often leads to suboptimal performance due to limitations in local feature representation. In this work, we present our observation that CLIP’s image tokens struggle to effectively aggregate information from spatially or semantically related regions, resulting in features that lack local discriminability and spatial consistency. To address this issue, we propose DeCLIP, a novel framework that enhances CLIP by decoupling the self-attention module to obtain content'' and context’’ features respectively. \revise{The context features are enhanced by jointly distilling semantic correlations from Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) and object integrity cues from diffusion models, thereby enhancing spatial consistency. In parallel, the content features are aligned with image crop representations and constrained by region correlations from VFMs to improve local discriminability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DeCLIP establishes a solid foundation for open-vocabulary dense perception, consistently achieving state-of-the-art performance across a broad spectrum of tasks, including 2D detection and segmentation, 3D instance segmentation, video instance segmentation, and 6D object pose estimation.} Code is available at https://github.com/xiaomoguhz/DeCLIP
密集视觉感知任务一直受到其依赖于预定义类别的限制,这限制了它们在视觉概念无界的现实场景中的应用。虽然像CLIP这样的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在开放词汇任务中显示出了一定的潜力,但它们直接应用于密集感知往往会导致性能不佳,因为它们在局部特征表示方面存在局限性。在这项工作中,我们观察到CLIP的图像令牌在有效地聚合空间或语义相关区域的信息方面存在困难,导致特征缺乏局部鉴别力和空间一致性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了DeCLIP,这是一种通过解耦自注意力模块来增强CLIP的新型框架,从而分别获得“内容”和“上下文”特征。通过联合蒸馏来自视觉基础模型(VFMs)的语义关联和来自扩散模型的对象完整性线索,增强了上下文特征的表示,从而提高了空间一致性。同时,内容特征与图像裁剪表示进行对齐,并通过VFMs的区域关联进行约束,以提高局部鉴别力。大量实验表明,DeCLIP为开放词汇密集感知建立了坚实的基础,在广泛的任务中实现了最先进的性能,包括二维检测和分割、三维实例分割、视频实例分割和六维对象姿态估计。代码可在https://github.com/xiaomoguhz/DeCLIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2505.04410
Summary
扩散模型在视觉感知任务中的应用取得了显著进展。由于传统的视觉感知任务依赖于预定义的类别,限制了其在真实世界场景中的应用。为解决此问题,本文提出了DeCLIP框架,通过解耦CLIP模型的自注意力模块,增强空间一致性和局部辨别力。实验证明,DeCLIP在开放词汇表密集感知任务上表现卓越,包括二维检测与分割、三维实例分割、视频实例分割和六自由度物体姿态估计等任务。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 传统视觉感知任务受限于预定义类别,难以适应真实世界场景。
- CLIP模型在开放词汇表任务中表现出潜力,但在密集感知任务中表现不佳。
- CLIP的图像标记在聚合空间或语义相关区域的信息时存在困难,导致特征缺乏局部辨别力和空间一致性。
- DeCLIP框架通过解耦CLIP模型的自注意力模块,分别获得“内容”和“上下文”特征,以增强空间一致性和局部辨别力。
- 上下文特征通过联合提炼Vision Foundation Models(VFMs)的语义关联和扩散模型的物体完整性线索,从而提高空间一致性。
- 内容特征通过与图像裁剪表示对齐,并受VFMs的区域关联约束,以提高局部辨别力。
点此查看论文截图

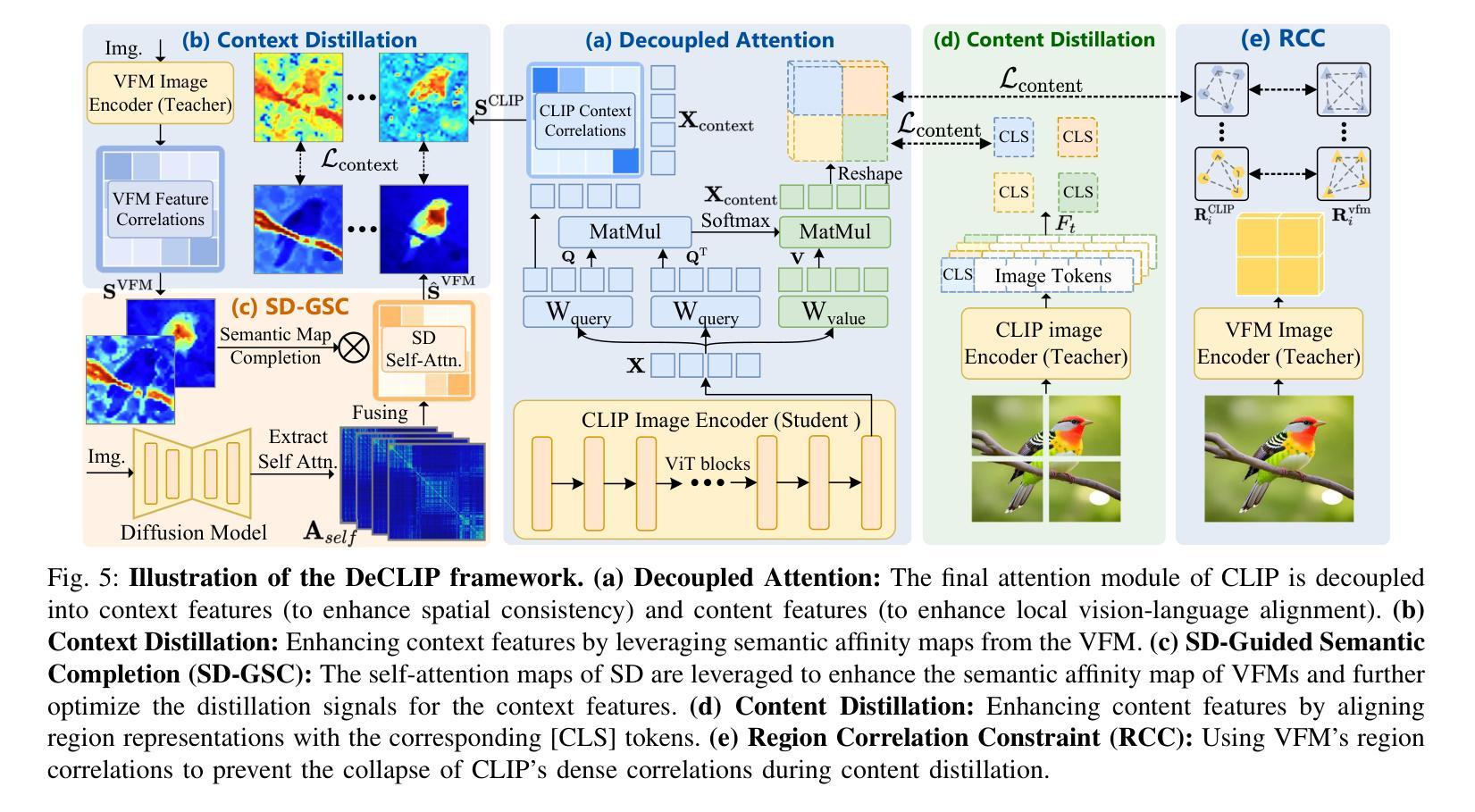
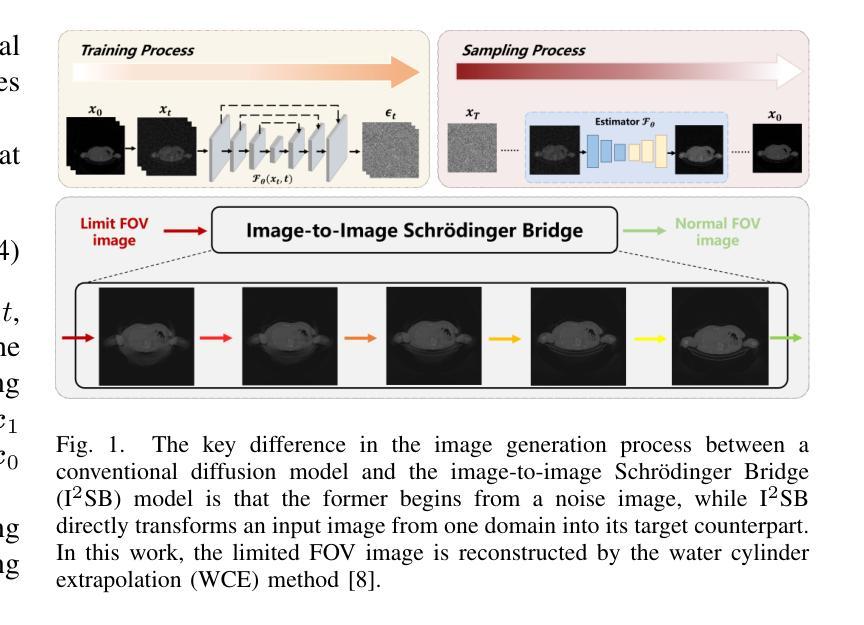
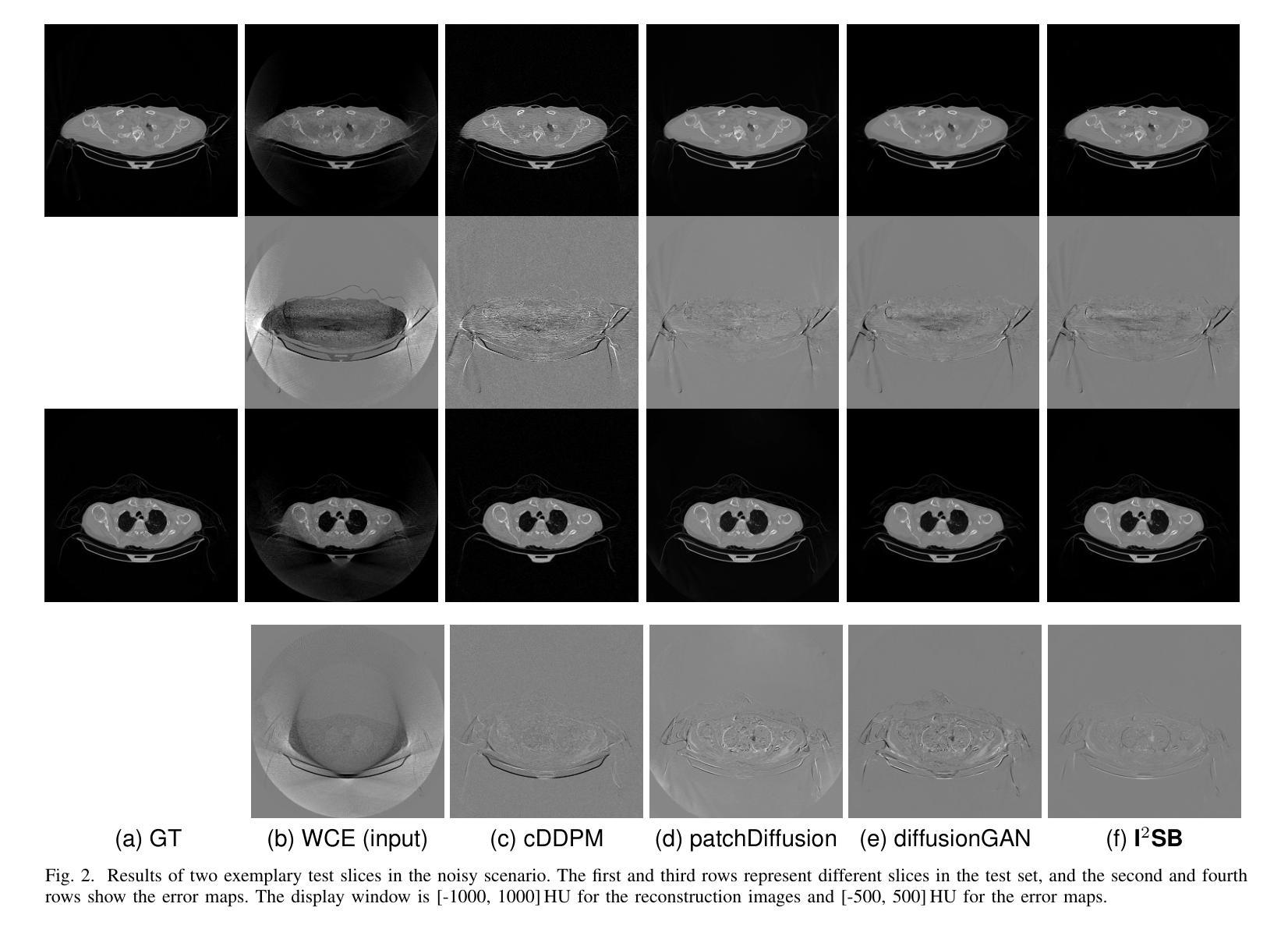
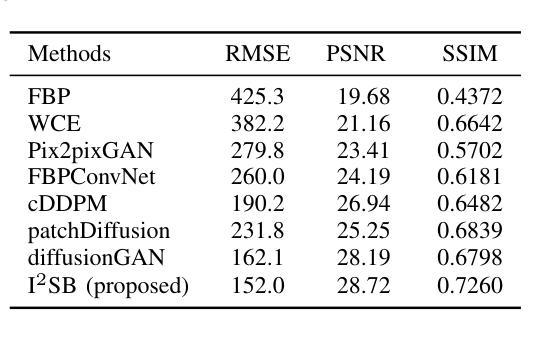
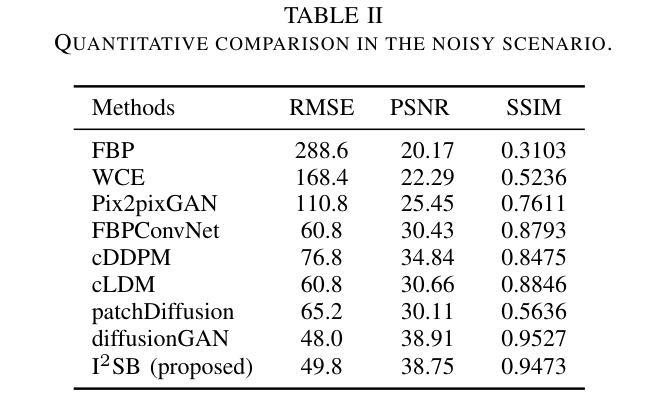
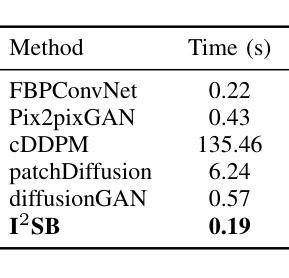
Efficient Image-to-Image Schrödinger Bridge for CT Field of View Extension
Authors:Zhenhao Li, Long Yang, Xiaojie Yin, Haijun Yu, Jiazhou Wang, Hongbin Han, Weigang Hu, Yixing Huang
Computed tomography (CT) is a cornerstone imaging modality for non-invasive, high-resolution visualization of internal anatomical structures. However, when the scanned object exceeds the scanner’s field of view (FOV), projection data are truncated, resulting in incomplete reconstructions and pronounced artifacts near FOV boundaries. Conventional reconstruction algorithms struggle to recover accurate anatomy from such data, limiting clinical reliability. Deep learning approaches have been explored for FOV extension, with diffusion generative models representing the latest advances in image synthesis. Yet, conventional diffusion models are computationally demanding and slow at inference due to their iterative sampling process. To address these limitations, we propose an efficient CT FOV extension framework based on the image-to-image Schr"odinger Bridge (I$^2$SB) diffusion model. Unlike traditional diffusion models that synthesize images from pure Gaussian noise, I$^2$SB learns a direct stochastic mapping between paired limited-FOV and extended-FOV images. This direct correspondence yields a more interpretable and traceable generative process, enhancing anatomical consistency and structural fidelity in reconstructions. I$^2$SB achieves superior quantitative performance, with root-mean-square error (RMSE) values of 49.8,HU on simulated noisy data and 152.0HU on real data, outperforming state-of-the-art diffusion models such as conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models (cDDPM) and patch-based diffusion methods. Moreover, its one-step inference enables reconstruction in just 0.19s per 2D slice, representing over a 700-fold speedup compared to cDDPM (135s) and surpassing diffusionGAN (0.58s), the second fastest. This combination of accuracy and efficiency makes I$^2$SB highly suitable for real-time or clinical deployment.
计算机断层扫描(CT)是对于无创、高分辨率可视化内部解剖结构的重要成像方式。然而,当扫描对象超出扫描仪的视野(FOV)时,投影数据会被截断,导致重建不完整,并且在FOV边界附近出现明显的伪影。传统的重建算法很难从这种数据中恢复准确的解剖结构,从而限制了临床可靠性。深度学习已应用于FOV扩展,扩散生成模型代表图像合成的最新进展。然而,传统的扩散模型计算量大,由于迭代采样过程,推理速度慢。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于图像到图像Schrödinger Bridge(I$^2$SB)扩散模型的CT FOV扩展框架。不同于从纯高斯噪声合成图像的传统扩散模型,I$^2$SB学习配对有限FOV和扩展FOV图像之间的直接随机映射。这种直接对应关系产生了一个更具可解释性和可追溯性的生成过程,提高了重建中的解剖结构一致性和结构保真度。在模拟噪声数据和真实数据上,I$^2$SB取得了优异的定量性能,均方根误差(RMSE)值分别为49.8 HU和152.0 HU,超过了最先进的扩散模型,如条件去噪扩散概率模型(cDDPM)和基于补丁的扩散方法。此外,其一步推理只需0.19秒即可完成每个2D切片的重建,与cDDPM相比实现了超过700倍的加速(135秒),并超越了扩散GAN(0.58秒),成为第二快的模型。I$^2$SB的准确性和高效性相结合,使其成为实时或临床部署的理想选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
摘要
计算机断层扫描(CT)中,当扫描对象超出扫描仪视野(FOV)时,投影数据会被截断,导致重建不完整和在视野边界附近出现明显的伪影。基于图像到图像的Schrödinger Bridge(I$^2$SB)扩散模型的CT FOV扩展框架解决了传统扩散模型计算量大、推理速度慢的问题。I$^2$SB直接从配对的有限视野和扩展视野图像中学习随机映射,提高了重建的解剖一致性和结构保真度。其在模拟噪声数据和真实数据上的均方根误差(RMSE)值分别为49.8 HU和152.0 HU,优于条件去噪扩散概率模型(cDDPM)和基于补丁的扩散方法。其一步推理可在0.19秒内完成每个二维切片的重建,比cDDPM快700倍以上,并超越了第二快的diffusionGAN(0.58秒)。结合精度和效率,I$^2$SB非常适合实时或临床部署。
关键见解
- 当CT扫描对象超出扫描仪视野(FOV)时,会出现数据截断问题,导致重建不准确。
- 传统的扩散模型在计算效率和推理速度方面存在局限性。
- I$^2$SB扩散模型通过直接从配对的有限视野和扩展视野图像中学习随机映射,提高了重建的解剖一致性和结构保真度。
- I$^2$SB在模拟噪声数据和真实数据上的性能优于其他扩散模型,如cDDPM和基于补丁的扩散方法。
- I$^2$SB具有快速的一步推理过程,可在短时间内完成重建,比cDDPM快700倍以上。
- I$^2$SB结合高精度和高效性,非常适合实时或临床部署。
点此查看论文截图

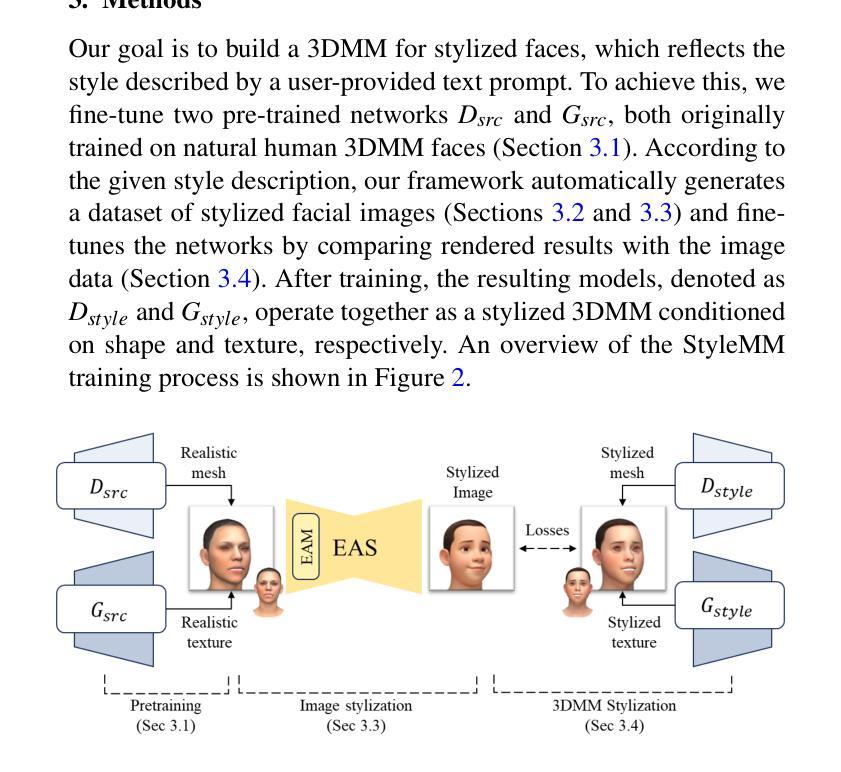
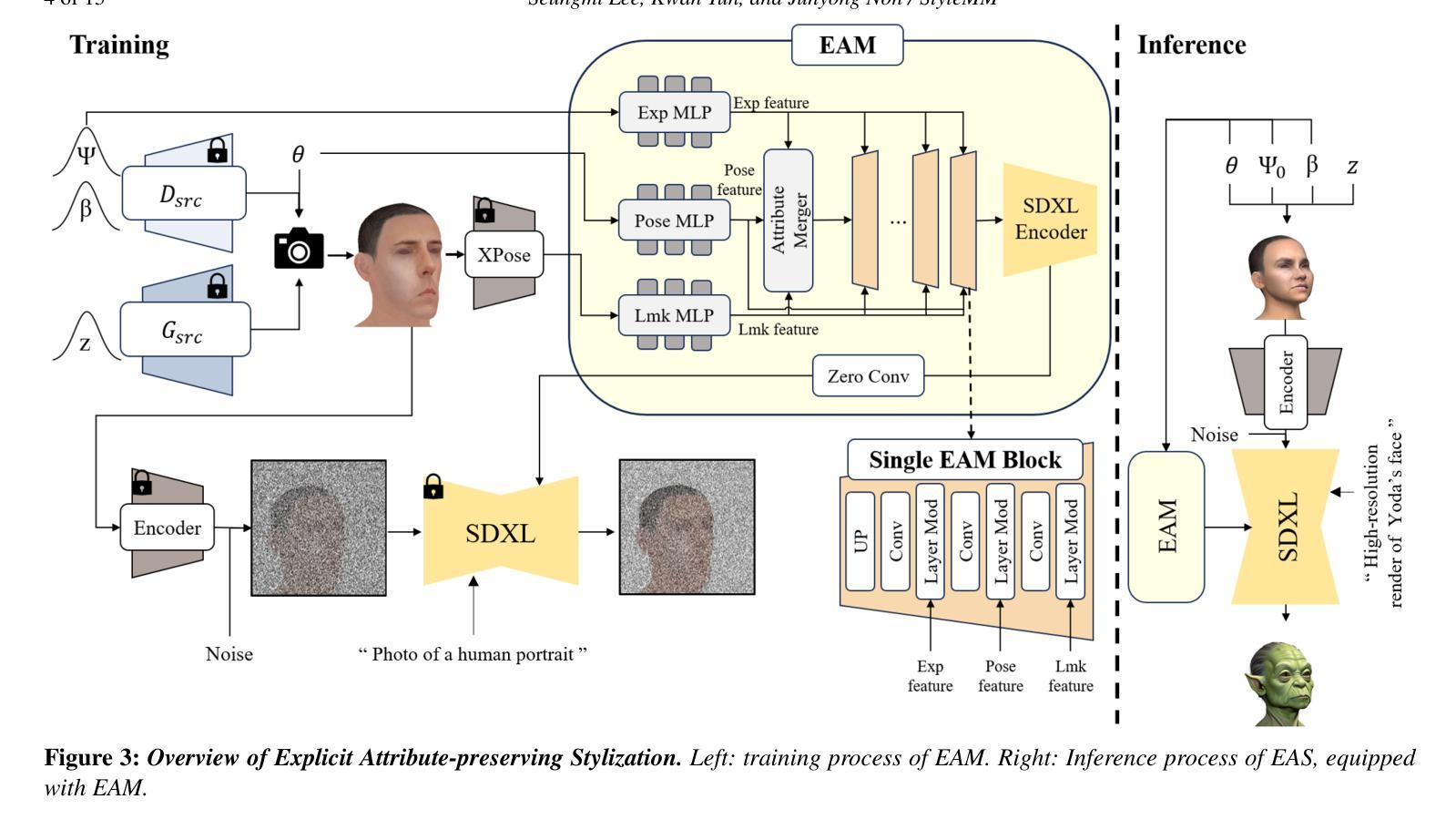
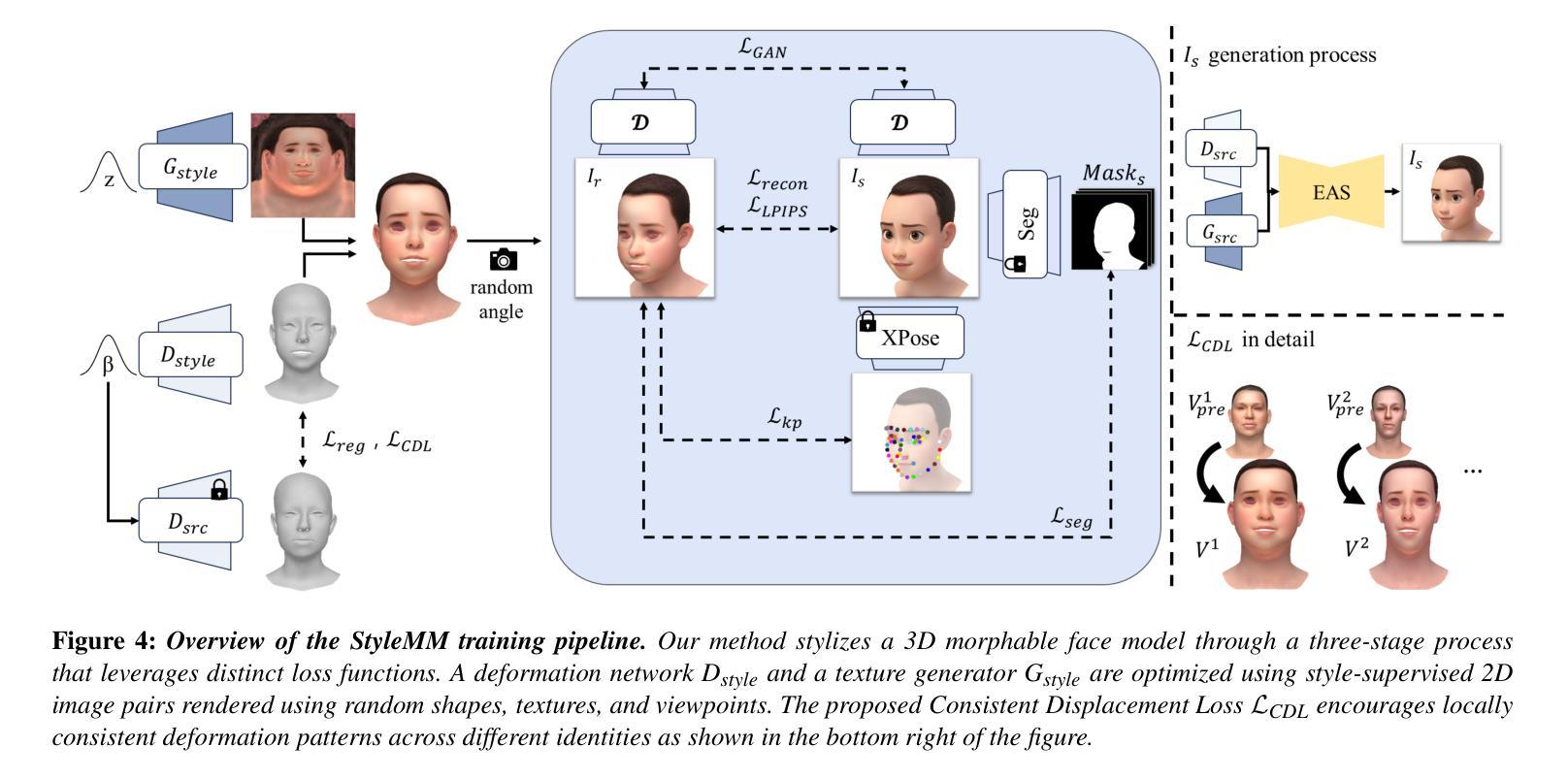
StyleMM: Stylized 3D Morphable Face Model via Text-Driven Aligned Image Translation
Authors:Seungmi Lee, Kwan Yun, Junyong Noh
We introduce StyleMM, a novel framework that can construct a stylized 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) based on user-defined text descriptions specifying a target style. Building upon a pre-trained mesh deformation network and a texture generator for original 3DMM-based realistic human faces, our approach fine-tunes these models using stylized facial images generated via text-guided image-to-image (i2i) translation with a diffusion model, which serve as stylization targets for the rendered mesh. To prevent undesired changes in identity, facial alignment, or expressions during i2i translation, we introduce a stylization method that explicitly preserves the facial attributes of the source image. By maintaining these critical attributes during image stylization, the proposed approach ensures consistent 3D style transfer across the 3DMM parameter space through image-based training. Once trained, StyleMM enables feed-forward generation of stylized face meshes with explicit control over shape, expression, and texture parameters, producing meshes with consistent vertex connectivity and animatability. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of identity-level facial diversity and stylization capability. The code and videos are available at kwanyun.github.io/stylemm_page.
我们介绍了StyleMM,这是一个新型框架,能够根据用户定义的文本描述构建风格化的3D可变形模型(3DMM),这些描述指定了目标风格。我们的方法建立在预训练的网格变形网络和用于原始基于3DMM的逼真人脸的纹理生成器之上。通过利用扩散模型进行文本引导的图像到图像(i2i)翻译生成风格化的面部图像,对这些模型进行微调,这些图像作为渲染网格的风格化目标。为了防止在i2i翻译过程中出现身份、面部对齐或表情等不必要的变化,我们引入了一种显式保留源图像面部特征的风格化方法。通过在图像风格化过程中保持这些关键特征,所提出的方法确保了通过基于图像的训练在整个3DMM参数空间内进行一致的3D风格转换。一旦训练完成,StyleMM就能够以前馈方式生成具有形状、表情和纹理参数明确控制的风格化面部网格,产生具有一致顶点连接和动画能力的网格。定量和定性评估表明,我们的方法在身份级面部多样性和风格化能力方面优于最先进的方法。代码和视频可在kwanyun.github.io/stylemm_page获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pacific graphics 2025, CGF, 15 pages
Summary
基于用户定义文本描述的目标风格,我们引入了StyleMM框架,构建了一个风格化的3D可变形模型(3DMM)。通过预训练的网格变形网络和原始3DMM现实人脸的纹理生成器,我们的方法使用通过文本引导的图像到图像(i2i)翻译与扩散模型生成的风格化面部图像对模型进行微调,这些图像作为风格化的目标网格。为了在进行i2i翻译时防止身份、面部对齐或表情等不需要的更改,我们引入了一种风格化方法,该方法可显式保留源图像的面部属性。通过维持这些关键属性进行图像风格化,所提出的方法确保了通过图像训练在3DMM参数空间中的一致风格转移。训练完成后,StyleMM可以通过前馈生成具有形状、表情和纹理参数明确控制的风格化面部网格,产生具有一致顶点连接和动画能力的网格。
Key Takeaways
- StyleMM是一个可以根据用户定义的文本描述构建风格化3D可变形模型(3DMM)的框架。
- 该方法结合预训练的网格变形网络和纹理生成器,通过文本引导的i2i翻译与扩散模型生成风格化面部图像。
- 为了保持身份一致性,提出了一种保留源图像面部属性的风格化方法。
- StyleMM能在3DMM参数空间内进行一致的风格转移。
- 训练后的StyleMM可以生成具有形状、表达和纹理参数控制的风格化面部网格。
- 这些生成的网格具有一致的顶点连接和动画能力。
- 定量和定性评估表明,该方法在面部多样性和风格化能力方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图


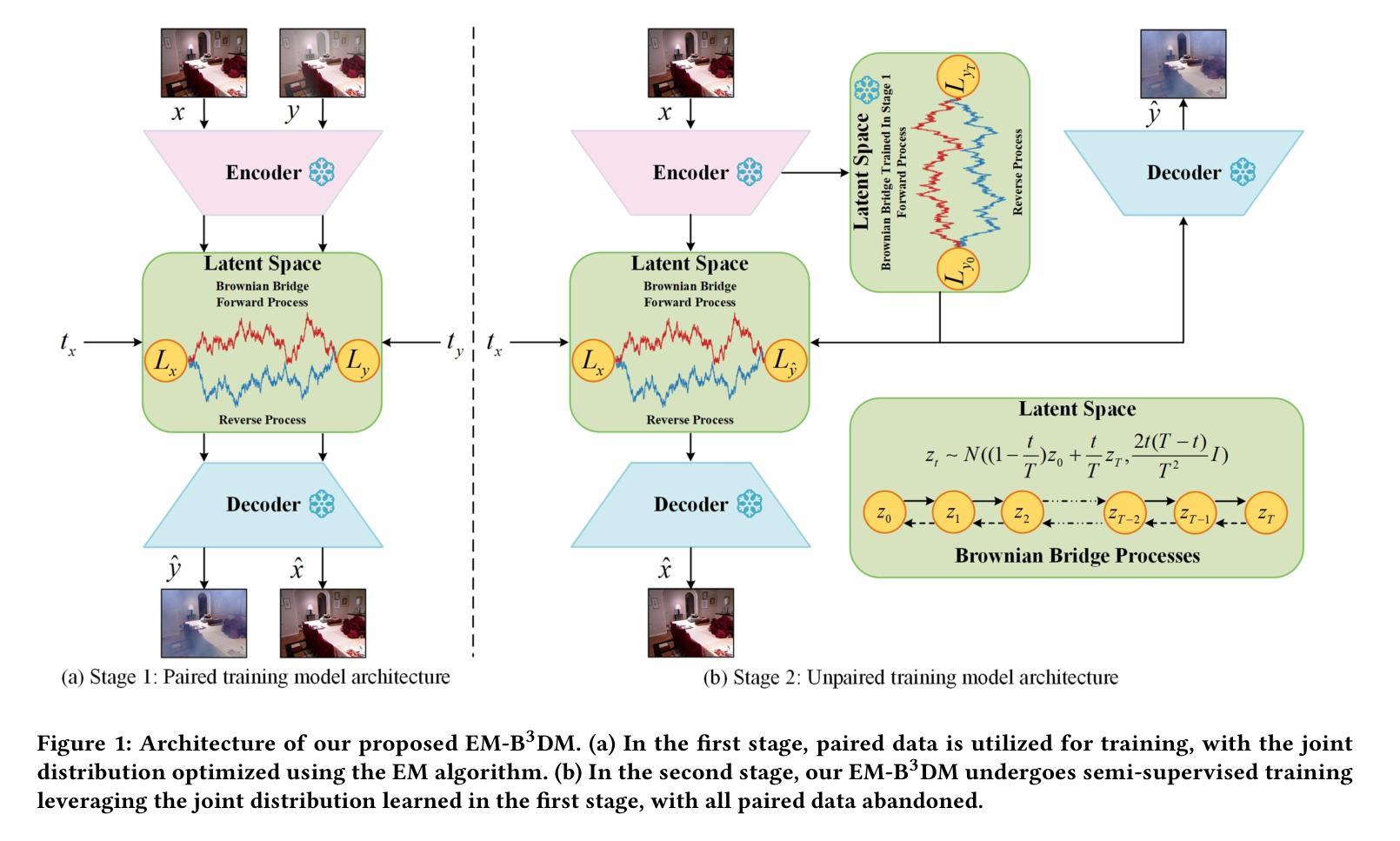
Semi-supervised Image Dehazing via Expectation-Maximization and Bidirectional Brownian Bridge Diffusion Models
Authors:Bing Liu, Le Wang, Mingming Liu, Hao Liu, Rui Yao, Yong Zhou, Peng Liu, Tongqiang Xia
Existing dehazing methods deal with real-world haze images with difficulty, especially scenes with thick haze. One of the main reasons is the lack of real-world paired data and robust priors. To avoid the costly collection of paired hazy and clear images, we propose an efficient semi-supervised image dehazing method via Expectation-Maximization and Bidirectional Brownian Bridge Diffusion Models (EM-B3DM) with a two-stage learning scheme. In the first stage, we employ the EM algorithm to decouple the joint distribution of paired hazy and clear images into two conditional distributions, which are then modeled using a unified Brownian Bridge diffusion model to directly capture the structural and content-related correlations between hazy and clear images. In the second stage, we leverage the pre-trained model and large-scale unpaired hazy and clear images to further improve the performance of image dehazing. Additionally, we introduce a detail-enhanced Residual Difference Convolution block (RDC) to capture gradient-level information, significantly enhancing the model’s representation capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our EM-B3DM achieves superior or at least comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
现有的去雾方法在应对真实世界的雾霾图像时面临困难,特别是在浓厚雾霾的场景中。主要原因之一是缺乏真实的配对数据和稳健的先验知识。为了避免收集配对雾天和晴朗天气的图像的高成本,我们提出了一种高效的半监督图像去雾方法,该方法通过期望最大化与双向布朗桥扩散模型(EM-B3DM)进行两阶段学习方案。在第一阶段,我们使用EM算法将配对雾天和晴朗天气的图像的联合分布解耦为两个条件分布,然后使用统一的布朗桥扩散模型对它们进行建模,以直接捕获雾天和晴朗天气的图像之间的结构和内容相关关联。在第二阶段,我们利用预训练模型和大规模的未配对雾天和晴朗天气的图像进一步提高图像去雾的性能。此外,我们还引入了一个细节增强的残差差分卷积块(RDC),以捕获梯度级别的信息,从而显著增强模型的表示能力。大量实验表明,我们的EM-B3DM在合成和真实世界数据集上的性能均达到或至少与最先进的方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures
摘要
针对现有去雾方法处理真实世界雾图时的困难,特别是场景浓厚雾的情况,提出一种基于期望最大化(EM)和双向布朗桥扩散模型(EM-B3DM)的半监督图像去雾方法。该方法采用两阶段学习策略,利用EM算法将配对雾图和清晰图的联合分布解耦为两个条件分布,并使用统一的布朗桥扩散模型直接捕捉两者之间的结构和内容相关性。借助预训练模型和大规模未配对雾图和清晰图像,进一步提高图像去雾性能。此外,引入细节增强的残差差分卷积块(RDC),以捕捉梯度级信息,显著提高模型的表示能力。实验表明,EM-B3DM在合成和真实世界数据集上的性能均优于或至少与现有先进方法相当。
关键见解
- 现有去雾方法在处理真实世界,特别是场景浓厚雾的情况下存在困难。
- 缺乏真实世界配对数据和稳健先验是主要原因之一。
- 提出一种基于期望最大化(EM)和双向布朗桥扩散模型(EM-B3DM)的半监督图像去雾方法,包含两阶段学习策略。
- 第一阶段使用EM算法解耦配对雾图和清晰图的联合分布。
- 使用统一的布朗桥扩散模型捕捉雾图和清晰图之间的结构和内容相关性。
- 利用预训练模型和大规模未配对图像进一步提高去雾性能。
点此查看论文截图

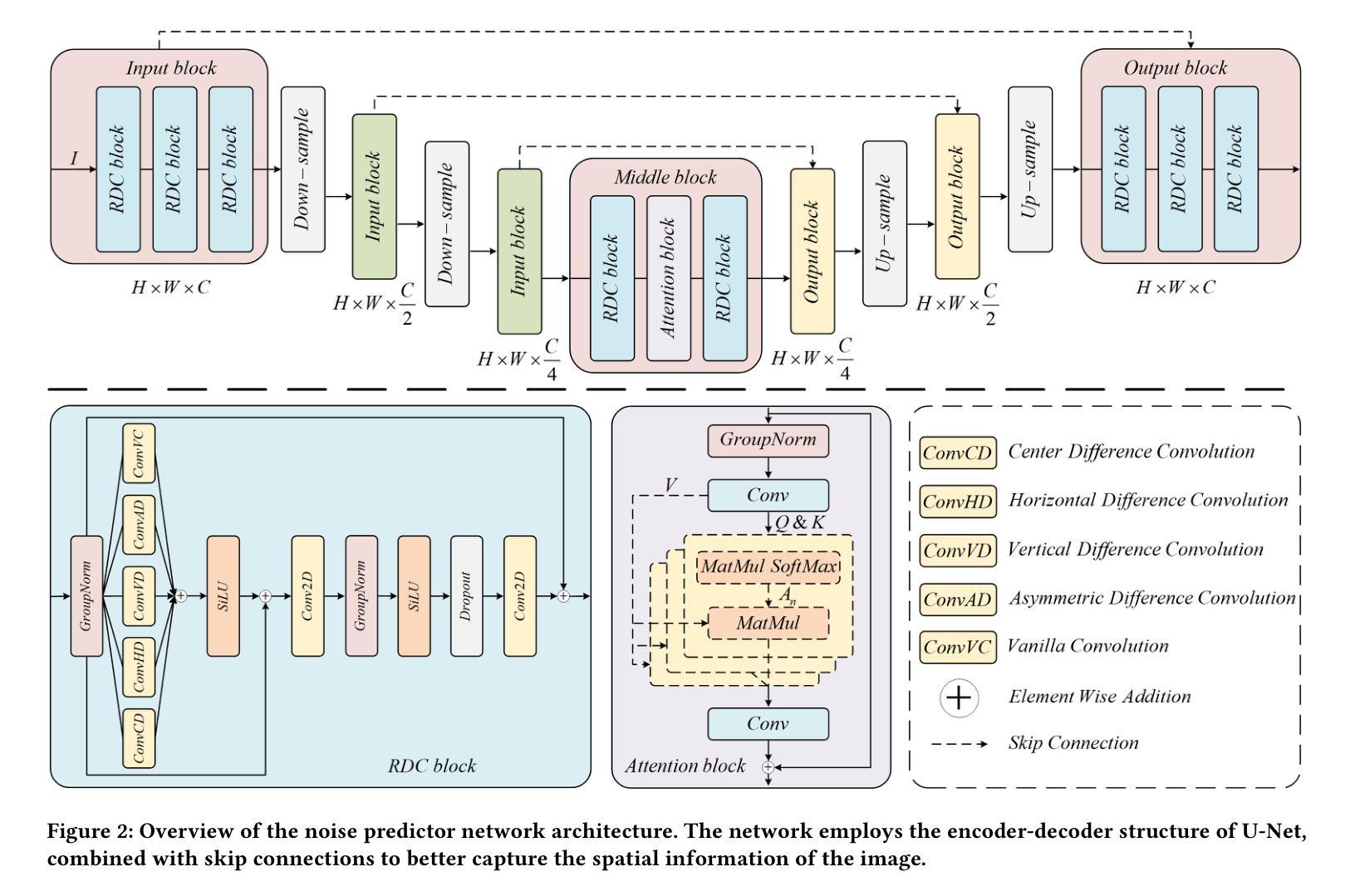
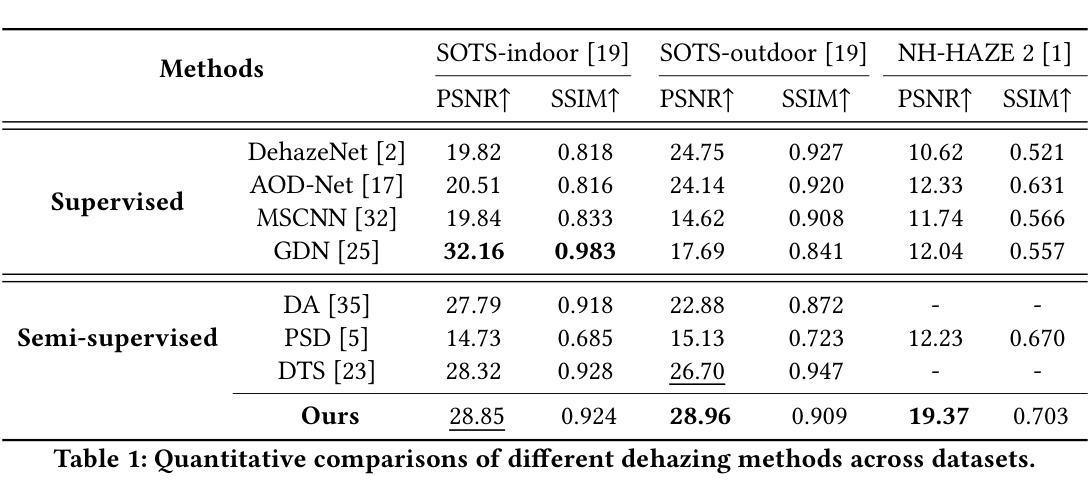

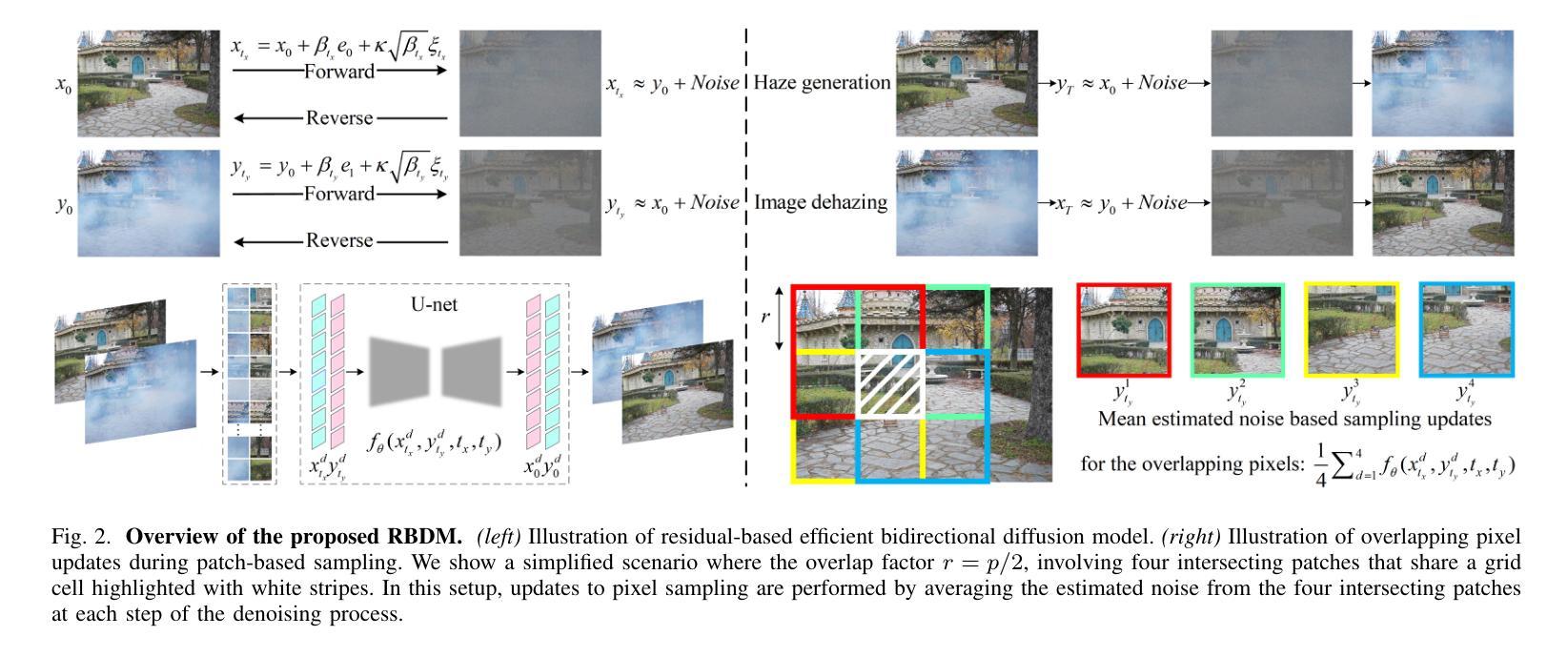
Residual-based Efficient Bidirectional Diffusion Model for Image Dehazing and Haze Generation
Authors:Bing Liu, Le Wang, Hao Liu, Mingming Liu
Current deep dehazing methods only focus on removing haze from hazy images, lacking the capability to translate between hazy and haze-free images. To address this issue, we propose a residual-based efficient bidirectional diffusion model (RBDM) that can model the conditional distributions for both dehazing and haze generation. Firstly, we devise dual Markov chains that can effectively shift the residuals and facilitate bidirectional smooth transitions between them. Secondly, the RBDM perturbs the hazy and haze-free images at individual timesteps and predicts the noise in the perturbed data to simultaneously learn the conditional distributions. Finally, to enhance performance on relatively small datasets and reduce computational costs, our method introduces a unified score function learned on image patches instead of entire images. Our RBDM successfully implements size-agnostic bidirectional transitions between haze-free and hazy images with only 15 sampling steps. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior or at least comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
当前深度去雾方法仅专注于从雾霾图像中去除雾霾,缺乏在雾霾图像和无雾霾图像之间进行翻译的能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于残差的高效双向扩散模型(RBDM),该模型可以对去雾和雾霾生成的条件分布进行建模。首先,我们设计了双马尔可夫链,可以有效地转移残差,促进它们之间的双向平滑过渡。其次,RBDM在单个时间步长内扰动无雾和雾霾图像,并预测受扰数据中的噪声,以同时学习条件分布。最后,为了提高相对较小的数据集的性能并降低计算成本,我们的方法引入了一个在图像块上学习的统一评分函数,而不是在整个图像上。我们的RBDM仅使用15个采样步骤就成功实现了无雾和雾霾图像之间的大小无关双向过渡。大量实验表明,所提出的方法在合成和真实世界数据集上达到了或至少与最先进的方法相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 2025 ICME Accepted
Summary
本文提出了一种基于残差的双向扩散模型(RBDM),该模型能够模拟去雾和生成雾的条件分布。通过构建双马尔可夫链实现残差的转移,并预测扰动数据的噪声以学习条件分布。为提高小数据集性能并降低计算成本,引入统一得分函数对图像块进行学习而非整个图像。RBDM仅需15个采样步骤即可实现去雾与有雾图像之间的双向转换,且在合成和真实数据集上的性能均达到或优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于残差的双向扩散模型(RBDM),能够模拟去雾和生成雾的条件分布。
- 通过双马尔可夫链实现残差的转移,促进双向平滑过渡。
- 通过预测扰动数据的噪声来学习条件分布。
- 引入统一得分函数,对图像块进行学习以提高性能并降低计算成本。
- 实现去雾与有雾图像之间的双向转换只需15个采样步骤。
- 在合成数据集上的性能优越。
点此查看论文截图
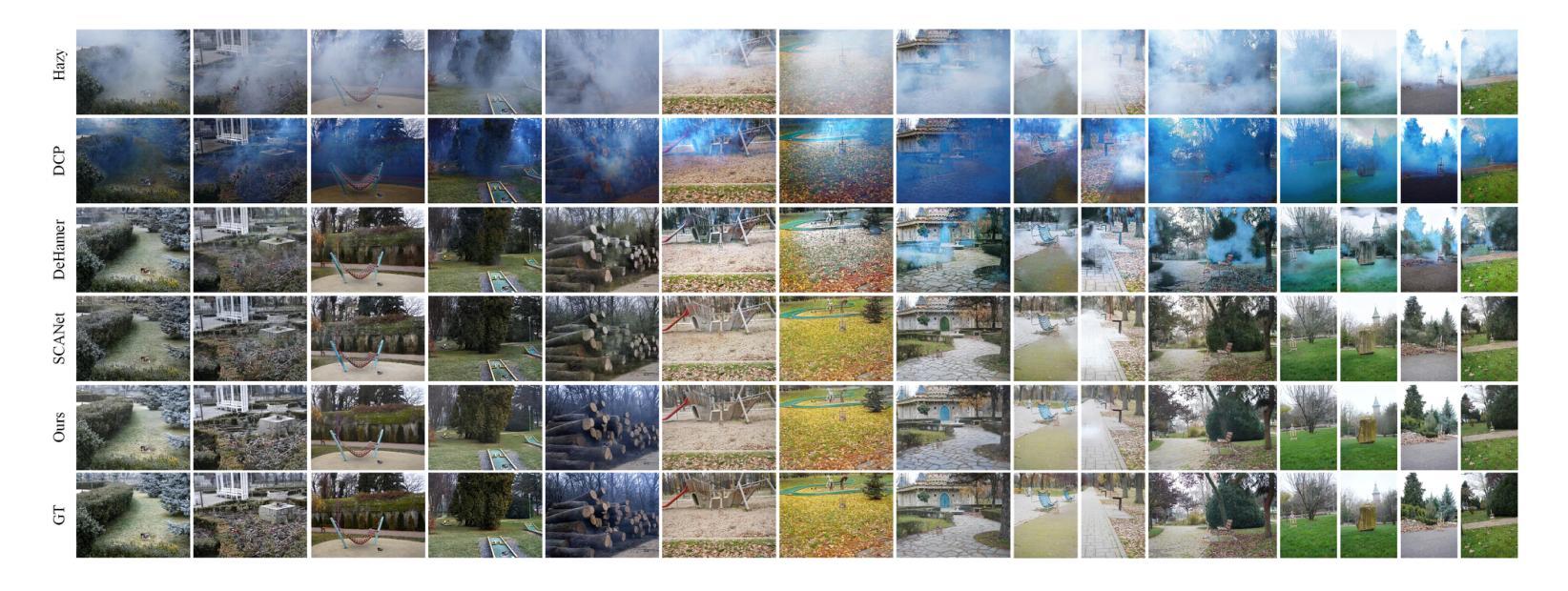


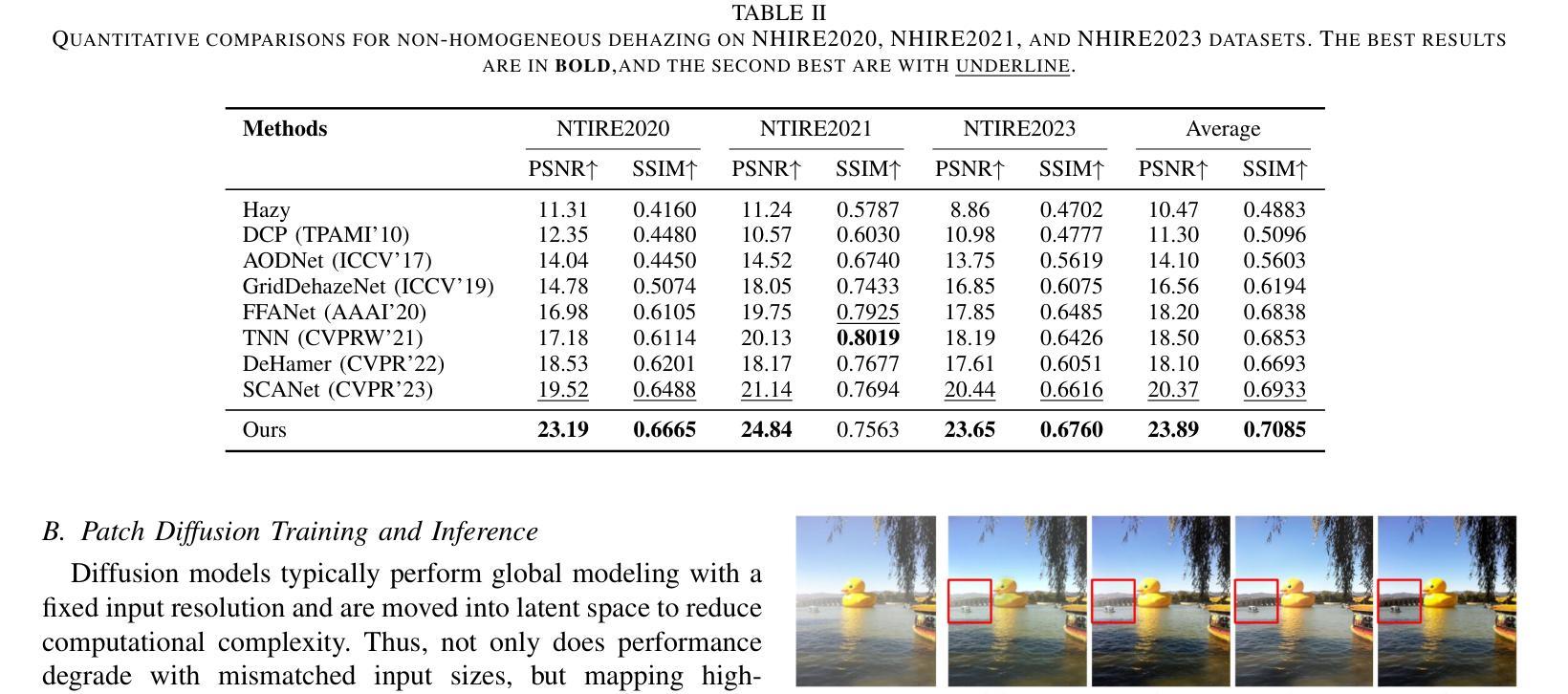
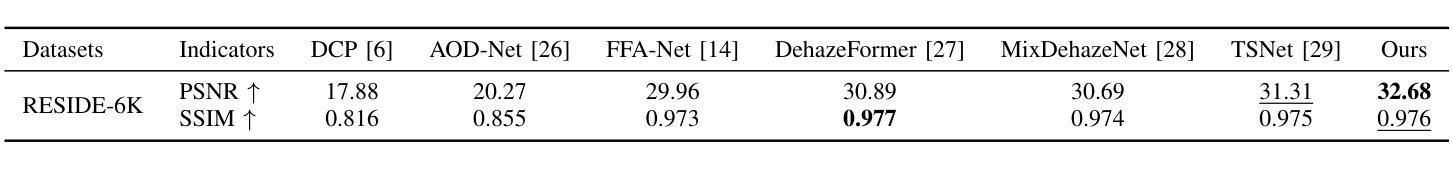

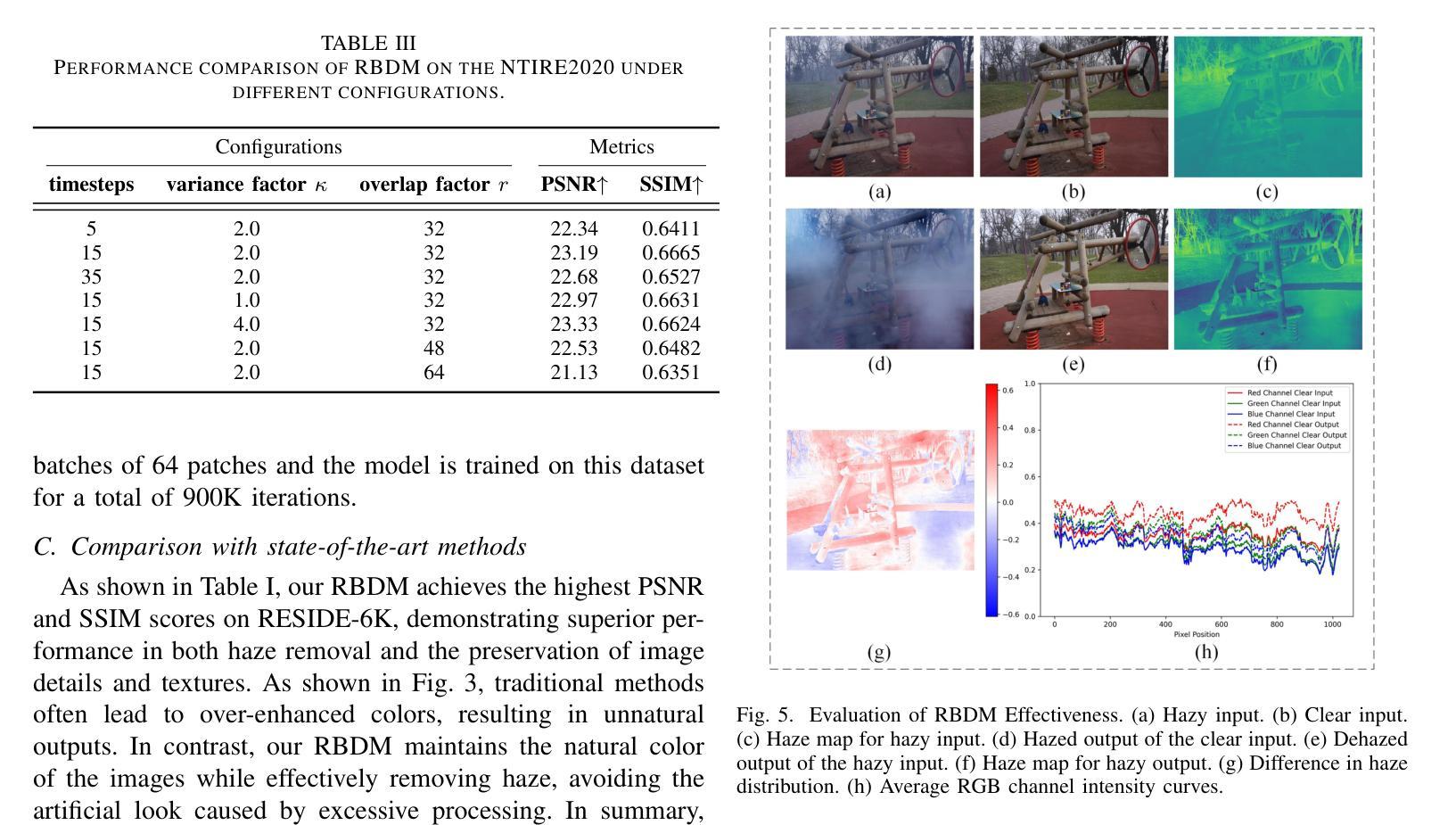
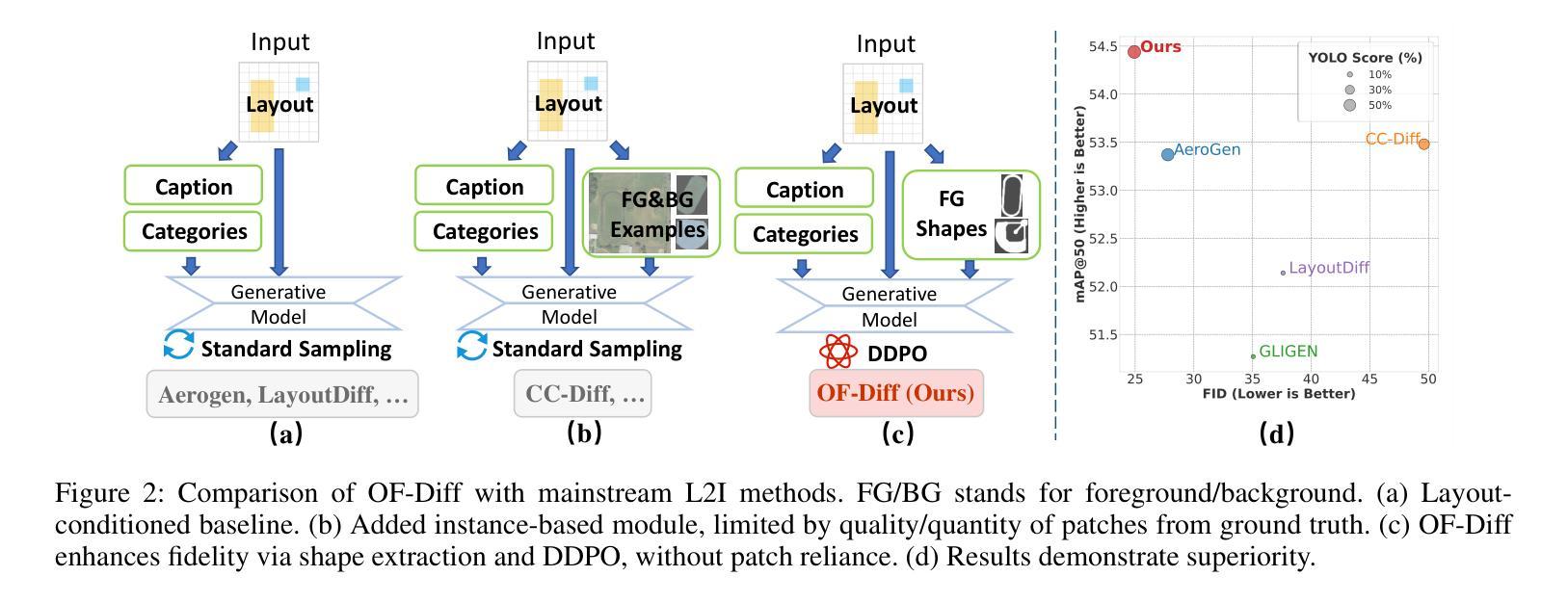
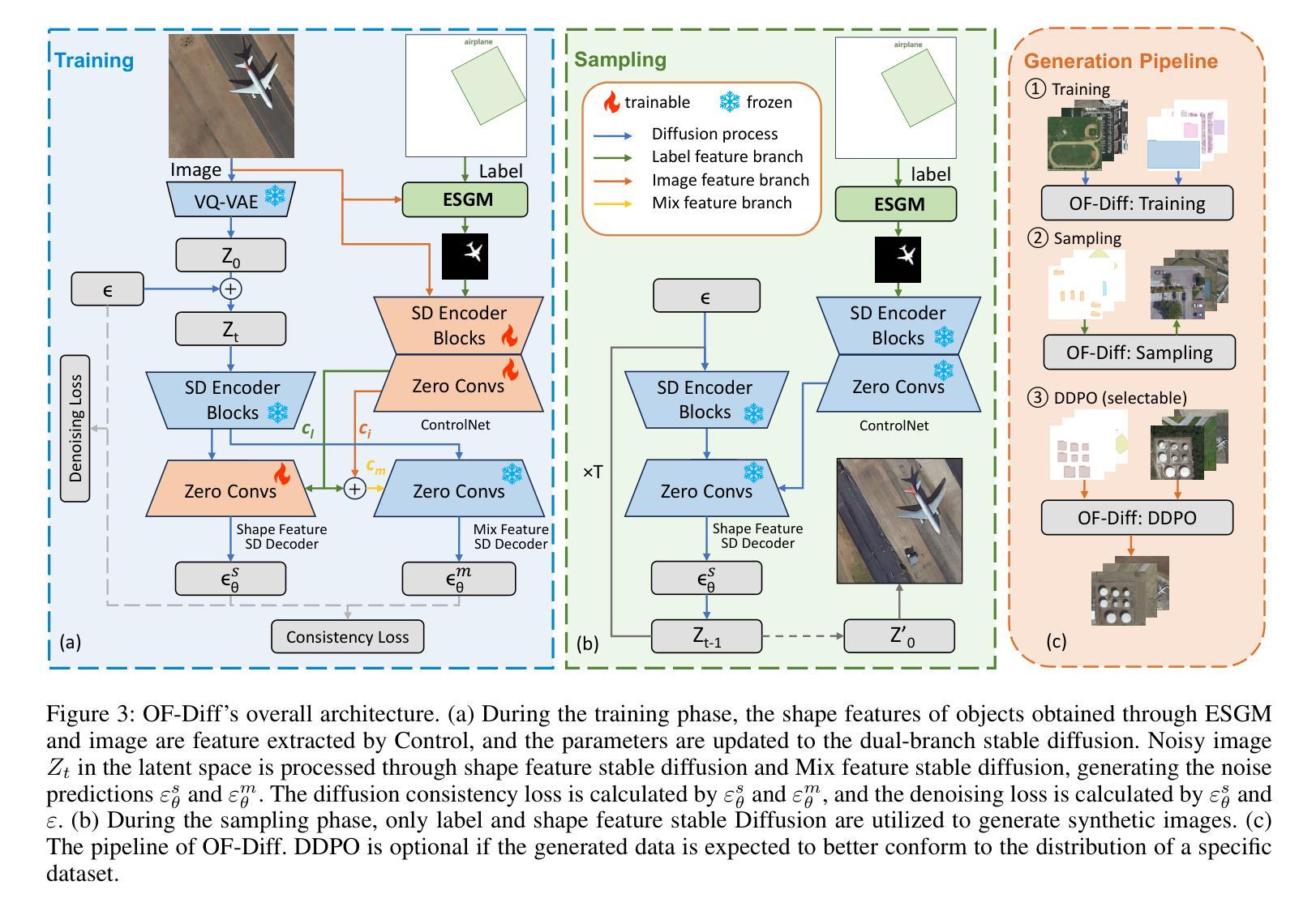
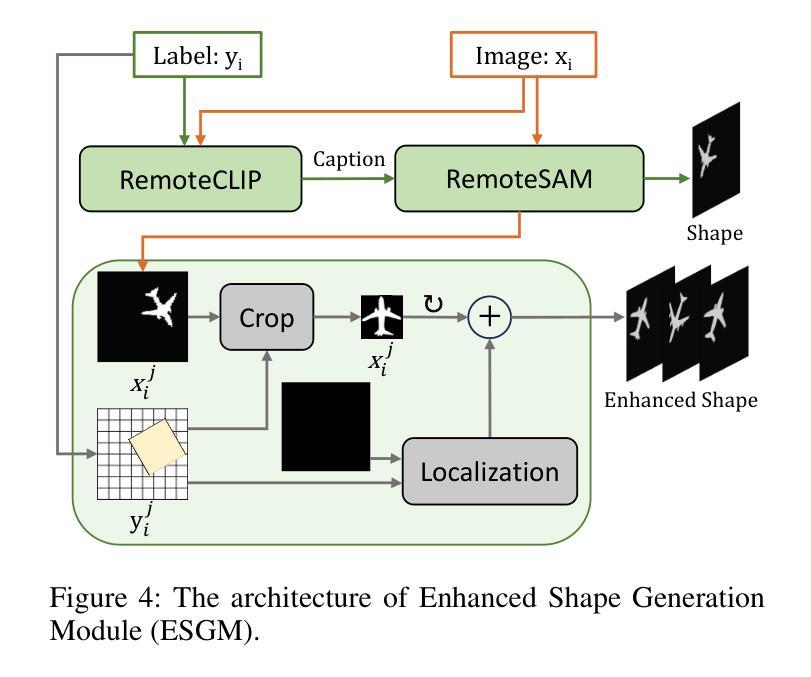
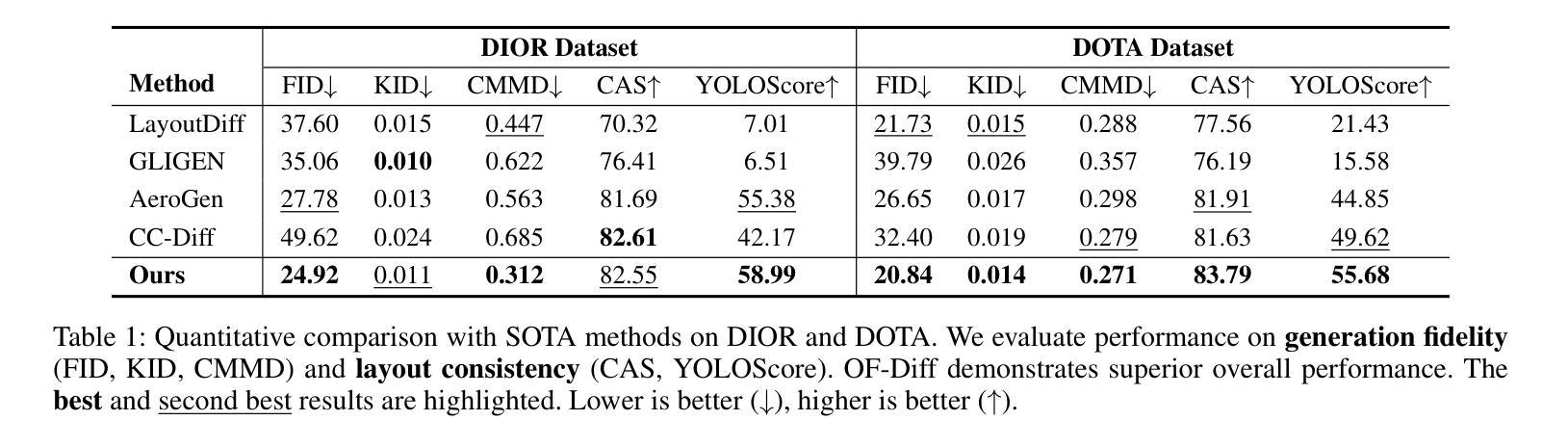
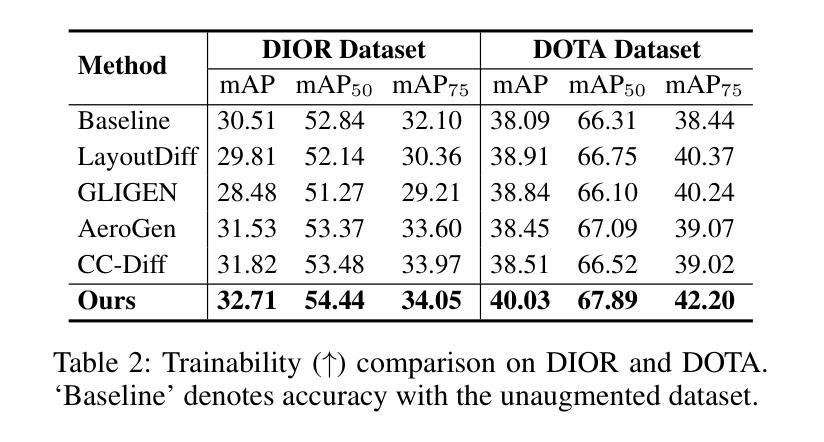
Object Fidelity Diffusion for Remote Sensing Image Generation
Authors:Ziqi Ye, Shuran Ma, Jie Yang, Xiaoyi Yang, Ziyang Gong, Xue Yang, Haipeng Wang
High-precision controllable remote sensing image generation is both meaningful and challenging. Existing diffusion models often produce low-fidelity images due to their inability to adequately capture morphological details, which may affect the robustness and reliability of object detection models. To enhance the accuracy and fidelity of generated objects in remote sensing, this paper proposes Object Fidelity Diffusion (OF-Diff), which effectively improves the fidelity of generated objects. Specifically, we are the first to extract the prior shapes of objects based on the layout for diffusion models in remote sensing. Then, we introduce a dual-branch diffusion model with diffusion consistency loss, which can generate high-fidelity remote sensing images without providing real images during the sampling phase. Furthermore, we introduce DDPO to fine-tune the diffusion process, making the generated remote sensing images more diverse and semantically consistent. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that OF-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art methods in the remote sensing across key quality metrics. Notably, the performance of several polymorphic and small object classes shows significant improvement. For instance, the mAP increases by 8.3%, 7.7%, and 4.0% for airplanes, ships, and vehicles, respectively.
高精度可控遥感图像生成既有意义又具挑战性。现有的扩散模型往往由于无法充分捕捉形态细节,而产生低保真度的图像,这可能会影响到目标检测模型的稳健性和可靠性。为了提高遥感中生成物体的精度和保真度,本文提出了对象保真扩散(OF-Diff),这有效地提高了生成物体的保真度。具体来说,我们首次基于遥感的扩散模型布局提取了物体的先验形状。然后,我们引入了一个具有扩散一致性损失的双分支扩散模型,该模型能够在采样阶段不提供真实图像的情况下生成高保真的遥感图像。此外,我们引入了DDPO来微调扩散过程,使生成的遥感图像更加多样化和语义一致。综合实验表明,OF-Diff在遥感领域的关键质量指标上优于最新技术方法。值得注意的是,多形态和小目标类别的性能表现出显著提升。例如,飞机、船只和车辆的mAP分别提高了8.3%、7.7%和4.0%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Object Fidelity Diffusion(OF-Diff)的方法,旨在提高遥感图像生成对象的精度和保真度。它通过提取对象的先验形状并引入双分支扩散模型和扩散一致性损失,有效改善生成对象的保真度。此外,通过DDPO对扩散过程进行微调,使生成的遥感图像更加多样化和语义一致。实验表明,OF-Diff在遥感领域的关键质量指标上超越了现有方法,特别是在多态和小目标类别上性能提升显著。
Key Takeaways
- OF-Diff方法旨在提高遥感图像生成对象的精度和保真度。
- 通过提取对象的先验形状,基于布局为扩散模型在遥感领域提供新思路。
- 引入双分支扩散模型和扩散一致性损失,有效改善生成遥感图像的质量。
- DDPO用于微调扩散过程,使生成的遥感图像更加多样化和语义一致。
- 实验表明,OF-Diff在遥感关键质量指标上超越现有方法。
- 多态和小目标类别的性能提升显著,如飞机、船只和车辆的mAP分别提升8.3%、7.7%和4.0%。
点此查看论文截图


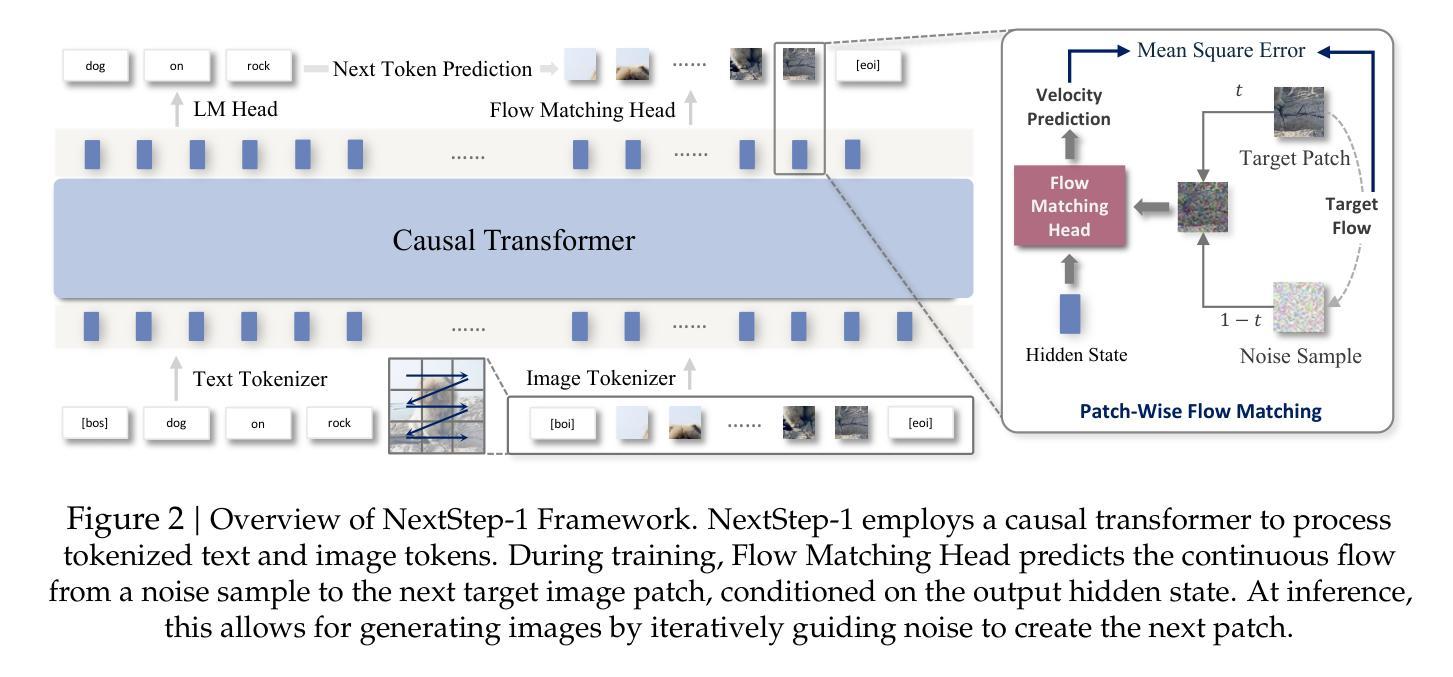
NextStep-1: Toward Autoregressive Image Generation with Continuous Tokens at Scale
Authors: NextStep Team, Chunrui Han, Guopeng Li, Jingwei Wu, Quan Sun, Yan Cai, Yuang Peng, Zheng Ge, Deyu Zhou, Haomiao Tang, Hongyu Zhou, Kenkun Liu, Ailin Huang, Bin Wang, Changxin Miao, Deshan Sun, En Yu, Fukun Yin, Gang Yu, Hao Nie, Haoran Lv, Hanpeng Hu, Jia Wang, Jian Zhou, Jianjian Sun, Kaijun Tan, Kang An, Kangheng Lin, Liang Zhao, Mei Chen, Peng Xing, Rui Wang, Shiyu Liu, Shutao Xia, Tianhao You, Wei Ji, Xianfang Zeng, Xin Han, Xuelin Zhang, Yana Wei, Yanming Xu, Yimin Jiang, Yingming Wang, Yu Zhou, Yucheng Han, Ziyang Meng, Binxing Jiao, Daxin Jiang, Xiangyu Zhang, Yibo Zhu
Prevailing autoregressive (AR) models for text-to-image generation either rely on heavy, computationally-intensive diffusion models to process continuous image tokens, or employ vector quantization (VQ) to obtain discrete tokens with quantization loss. In this paper, we push the autoregressive paradigm forward with NextStep-1, a 14B autoregressive model paired with a 157M flow matching head, training on discrete text tokens and continuous image tokens with next-token prediction objectives. NextStep-1 achieves state-of-the-art performance for autoregressive models in text-to-image generation tasks, exhibiting strong capabilities in high-fidelity image synthesis. Furthermore, our method shows strong performance in image editing, highlighting the power and versatility of our unified approach. To facilitate open research, we will release our code and models to the community.
当前流行的用于文本到图像生成的自回归(AR)模型,要么依赖于重量级、计算密集型的扩散模型来处理连续的图像令牌,要么采用向量量化(VQ)获得离散令牌,但会产生量化损失。在本文中,我们借助NextStep-1推动自回归范式的发展。NextStep-1是一个拥有14B参数的自回归模型,搭配一个规模为1.57亿的流匹配头,通过离散文本令牌和连续图像令牌进行训练,以预测下一个令牌为目标。NextStep-1在文本到图像生成任务中的自回归模型中实现了最先进的性能表现,在高保真图像合成方面表现出强大的能力。此外,我们的方法在图像编辑方面也表现出强大的性能,凸显了我们统一方法的强大和通用性。为了推动开放研究,我们将向社区发布我们的代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/stepfun-ai/NextStep-1
Summary
本文介绍了NextStep-1模型,它是一个结合文本离散令牌和图像连续令牌的14B参数的自回归模型,用于文本到图像生成任务。该模型使用流匹配头进行训练,实现了高保真图像合成的先进性能,并展示了强大的图像编辑能力。本文还强调了统一方法的力量和多功能性,并将代码和模型向社区开放。
Key Takeaways
- NextStep-1模型是一个先进的自回归模型,用于文本到图像生成任务。
- 该模型结合了离散文本令牌和连续图像令牌进行训练。
- NextStep-1实现了高保真图像合成的先进性能。
- 该模型在图像编辑方面也表现出强大的性能。
- 模型具备强大的功能和多功能性,统一了不同的图像生成和编辑任务。
- NextStep-1模型的代码和模型已向社区开放,便于进行开放研究。
点此查看论文截图


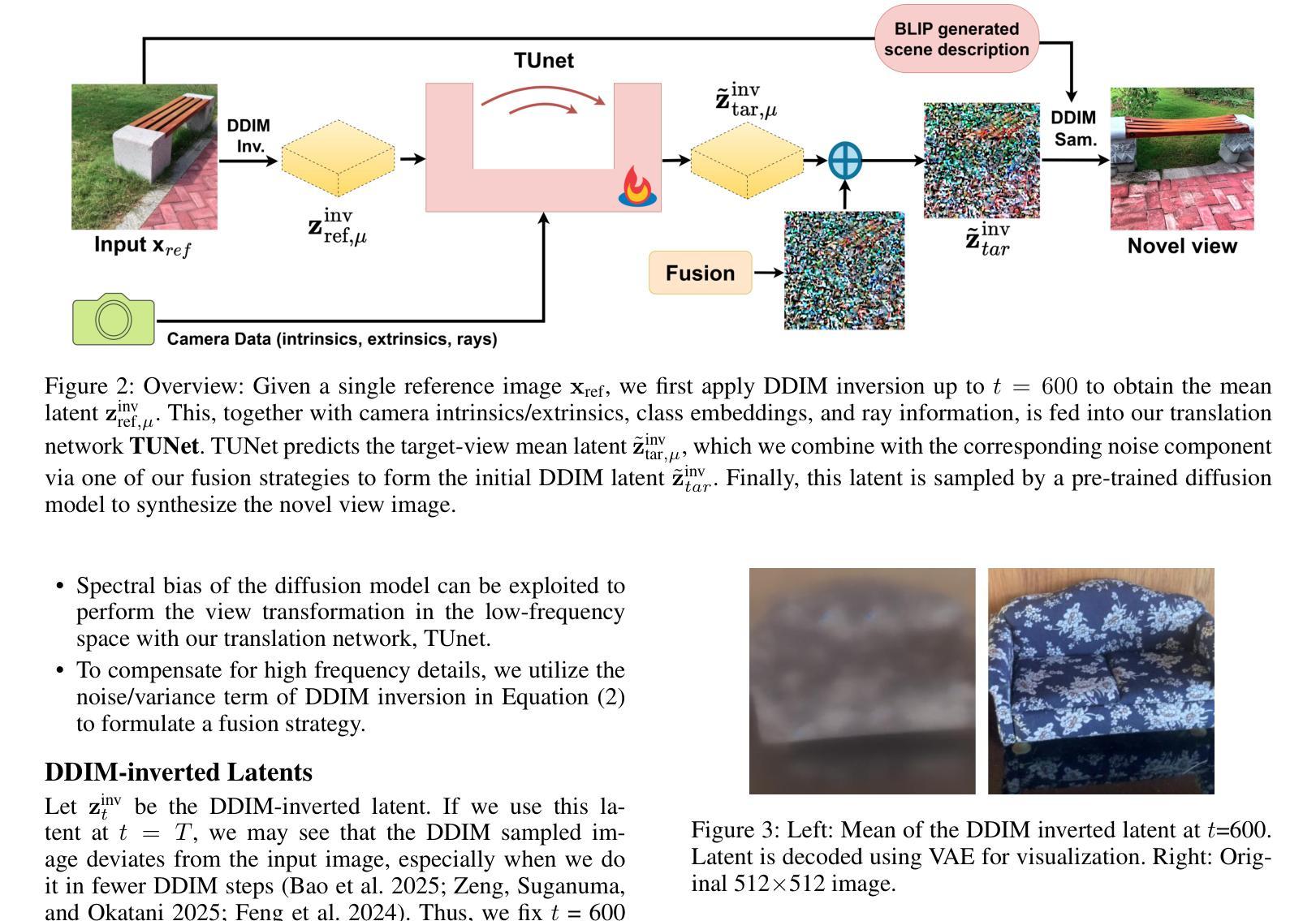
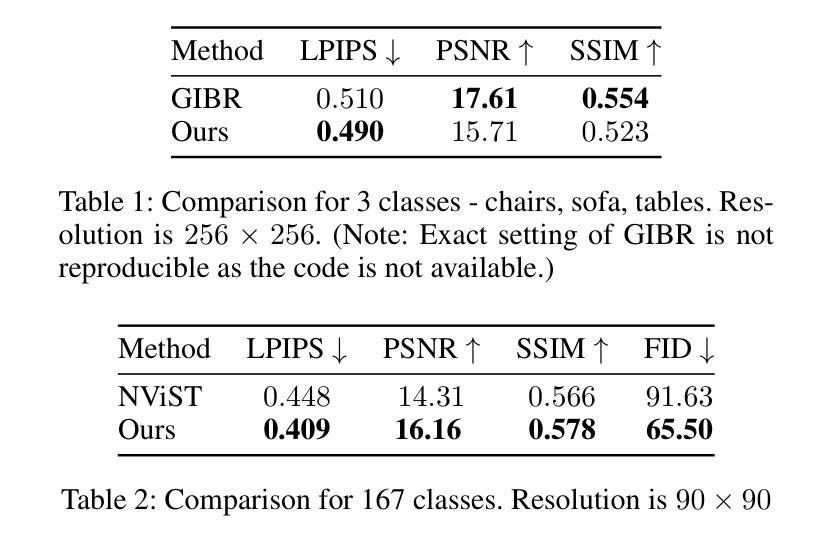
Novel View Synthesis using DDIM Inversion
Authors:Sehajdeep SIngh, A V Subramanyam
Synthesizing novel views from a single input image is a challenging task. It requires extrapolating the 3D structure of a scene while inferring details in occluded regions, and maintaining geometric consistency across viewpoints. Many existing methods must fine-tune large diffusion backbones using multiple views or train a diffusion model from scratch, which is extremely expensive. Additionally, they suffer from blurry reconstruction and poor generalization. This gap presents the opportunity to explore an explicit lightweight view translation framework that can directly utilize the high-fidelity generative capabilities of a pretrained diffusion model while reconstructing a scene from a novel view. Given the DDIM-inverted latent of a single input image, we employ a camera pose-conditioned translation U-Net, TUNet, to predict the inverted latent corresponding to the desired target view. However, the image sampled using the predicted latent may result in a blurry reconstruction. To this end, we propose a novel fusion strategy that exploits the inherent noise correlation structure observed in DDIM inversion. The proposed fusion strategy helps preserve the texture and fine-grained details. To synthesize the novel view, we use the fused latent as the initial condition for DDIM sampling, leveraging the generative prior of the pretrained diffusion model. Extensive experiments on MVImgNet demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods.
从单一输入图像合成新颖视角是一项具有挑战性的任务。它需要在推断遮挡区域的细节时推断场景的3D结构,并在不同观点之间保持几何一致性。许多现有方法必须使用多种视角微调大型扩散主干或从头开始训练扩散模型,这极为昂贵。此外,它们还存在模糊重建和泛化能力差的缺点。这一差距为我们提供了一个机会,即探索一个明确的轻量化视图翻译框架,该框架可以利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力,从新颖视角重建场景。给定单个输入图像的DDIM反向投影潜在特征,我们采用受相机姿态控制的翻译U-Net(TUNet)来预测对应于所需目标视角的反向投影潜在特征。然而,使用预测的潜在特征采样的图像可能会导致重建模糊。为此,我们提出了一种利用DDIM反演中观察到的固有噪声相关结构的新融合策略。该融合策略有助于保留纹理和细节。为了合成新颖视角,我们使用融合后的潜在特征作为DDIM采样的初始条件,利用预训练扩散模型的生成先验。在MVImgNet上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对单一输入图像合成新颖视角的任务挑战性强,需要推断遮挡区域的细节,同时保持不同视角的几何一致性。现有方法需要利用多视角微调大型扩散模型或从头开始训练,成本高昂且模糊重建、泛化能力差。本研究探索了一个显式的轻量级视角转换框架,可直接利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力,从新颖视角重建场景。通过采用单输入图像的DDIM反演潜力和相机姿态调节的翻译U-Net(TUNet),预测目标视角对应的反演潜力。为解决图像采样可能导致的模糊重建问题,提出利用DDIM反演中观察到的固有噪声相关结构的新型融合策略,该策略有助于保持纹理和细节。通过MVImgNet的广泛实验证明,该方法优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 合成新颖视角是一项挑战,需要推断遮挡区域并维持几何一致性。
- 现有方法成本高,且存在模糊重建和泛化问题。
- 研究提出一个轻量级的视角转换框架,利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力。
- 通过DDIM反演潜力和相机姿态调节的翻译U-Net(TUNet)预测目标视角的潜力。
- 提出新型融合策略解决图像采样的模糊重建问题,利用DDIM反演中的噪声相关结构。
- 融合策略有助于保持纹理和细节。
点此查看论文截图


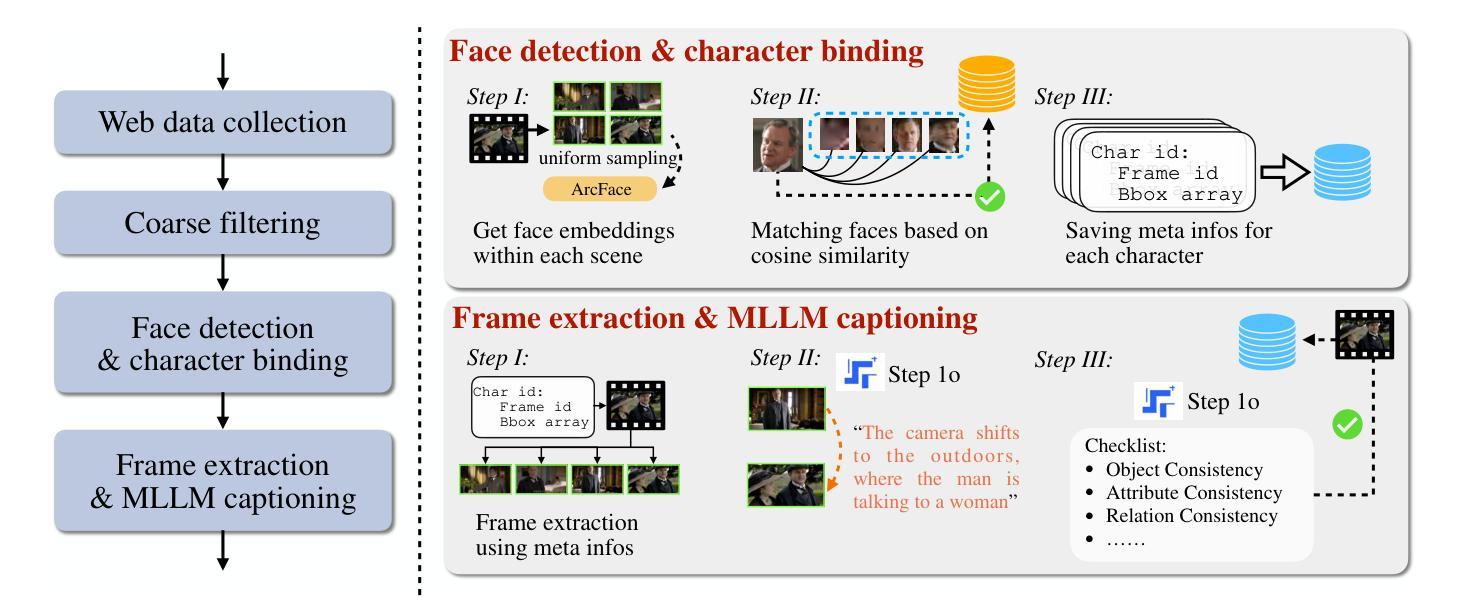
Hybrid Generative Fusion for Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Dataset Generation
Authors:Feiran Li, Qianqian Xu, Shilong Bao, Boyu Han, Zhiyong Yang, Qingming Huang
In this paper, we present our approach to the DataCV ICCV Challenge, which centers on building a high-quality face dataset to train a face recognition model. The constructed dataset must not contain identities overlapping with any existing public face datasets. To handle this challenge, we begin with a thorough cleaning of the baseline HSFace dataset, identifying and removing mislabeled or inconsistent identities through a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) strategy combining face embedding clustering and GPT-4o-assisted verification. We retain the largest consistent identity cluster and apply data augmentation up to a fixed number of images per identity. To further diversify the dataset, we generate synthetic identities using Stable Diffusion with prompt engineering. As diffusion models are computationally intensive, we generate only one reference image per identity and efficiently expand it using Vec2Face, which rapidly produces 49 identity-consistent variants. This hybrid approach fuses GAN-based and diffusion-based samples, enabling efficient construction of a diverse and high-quality dataset. To address the high visual similarity among synthetic identities, we adopt a curriculum learning strategy by placing them early in the training schedule, allowing the model to progress from easier to harder samples. Our final dataset contains 50 images per identity, and all newly generated identities are checked with mainstream face datasets to ensure no identity leakage. Our method achieves \textbf{1st place} in the competition, and experimental results show that our dataset improves model performance across 10K, 20K, and 100K identity scales. Code is available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/datacv_fr.
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了针对DataCV ICCV挑战的解决方案,该方案的重点是构建一个高质量的人脸数据集来训练人脸识别模型。构建的数据集不得与任何现有公共人脸数据集存在身份重叠。为了应对这一挑战,我们首先彻底清理基准HSFace数据集,通过混合专家(MoE)策略结合人脸嵌入聚类和GPT-4o辅助验证来识别和移除错误标记或身份不一致的情况。我们保留最大的连续身份集群,并对每个身份进行最多固定数量的图像数据增强。为了进一步多样化数据集,我们使用Stable Diffusion和提示工程生成合成身份。由于扩散模型计算量大,我们每个身份只生成一个参考图像,并使用Vec2Face有效地进行扩展,迅速生成49个身份一致的变体。这种混合方法融合了基于GAN和基于扩散的样本,能够高效地构建多样且高质量的数据集。针对合成身份之间的高视觉相似性,我们采用了一种课程学习策略,将它们尽早纳入训练计划,允许模型从易到难逐步适应样本。我们的最终数据集每个身份包含50张图像,所有新生成的身份都会与主流人脸数据集进行核对,以确保没有身份泄露。我们的方法在比赛中获得第一名,实验结果表明,我们的数据集在1万、2万和十万身份规模上均提高了模型性能。代码可在https://github.com/Ferry-Li/datacv_fr找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accpeted to ICCV 2025 DataCV Workshop
摘要
该研究为DataCV ICCV挑战赛提出了构建高质量人脸数据集的方法,旨在训练人脸识别模型。通过对基准HSFace数据集的彻底清洗,结合面部嵌入聚类和GPT-4o辅助验证的混合专家策略,去除误标记或身份不一致的数据。保留最大的连续身份集群,并对每个身份进行数据增强。利用Stable Diffusion生成合成身份,并通过Vec2Face快速生成多个一致变体。融合GAN和扩散模型样本,构建多样化、高质量数据集。采用课程学习策略解决合成身份高视觉相似性问题。最终数据集包含50张图像/身份,新生成身份经主流数据集检查无泄露。该方法在竞赛中荣获第一名,实验结果显示数据集在1万、2万、十万身份规模上均提升模型性能。代码已公开。
关键见解
- 该研究为DataCV ICCV挑战赛提出了一种构建高质量人脸数据集的方法,侧重于训练人脸识别模型。
- 采用基于Mixture-of-Experts的策略对基准数据集进行清洗,去除误标记和身份不一致的数据。
- 通过数据增强和合成身份生成技术(Stable Diffusion)丰富数据集多样性。
- 利用Vec2Face快速生成多个一致变体,提高数据效率。
- 融合GAN和扩散模型样本,构建多样化、高质量数据集。
- 采用课程学习策略应对合成身份高视觉相似性的挑战。
点此查看论文截图
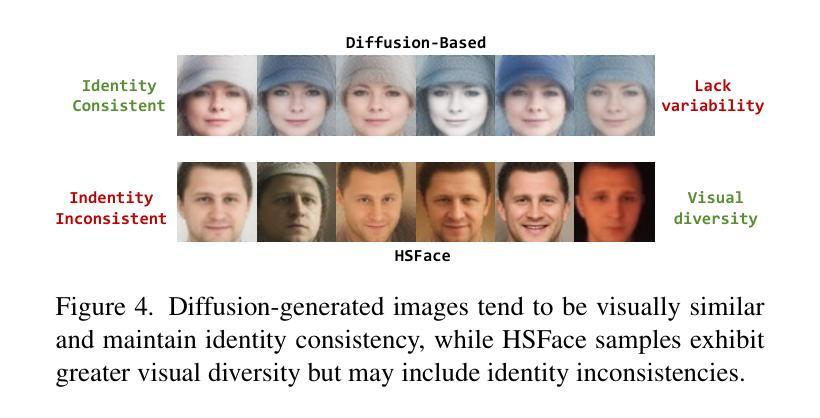



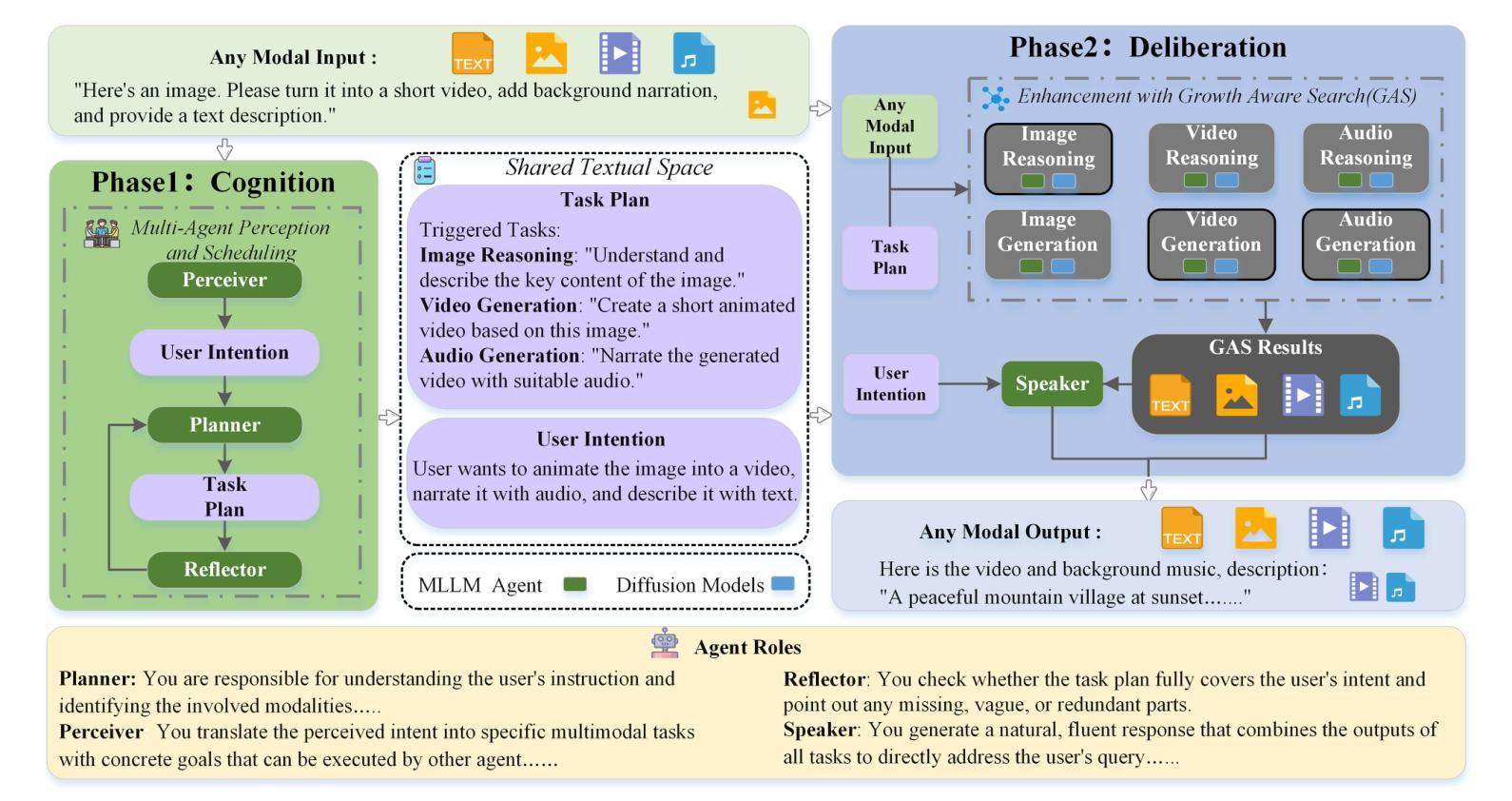
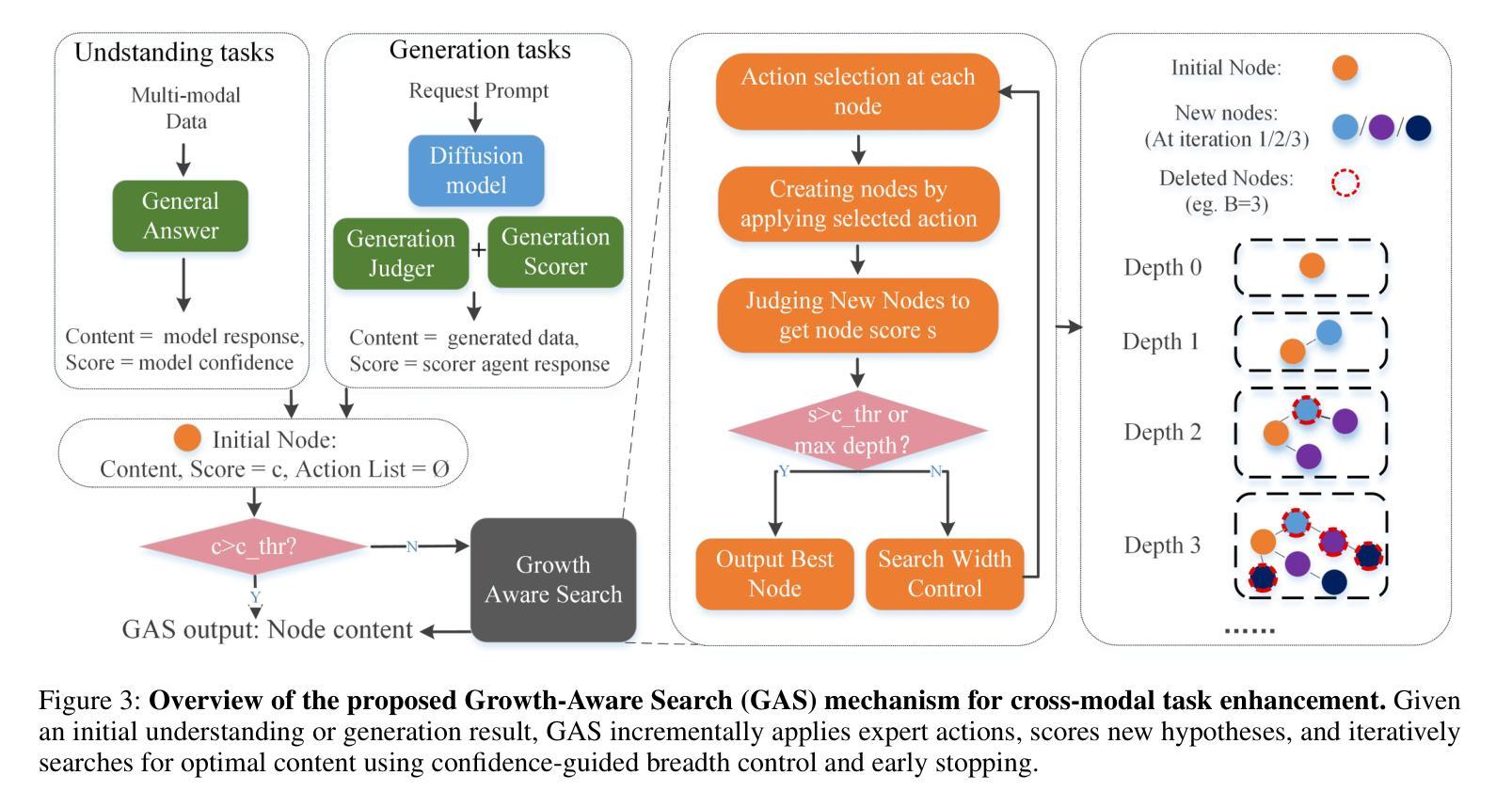
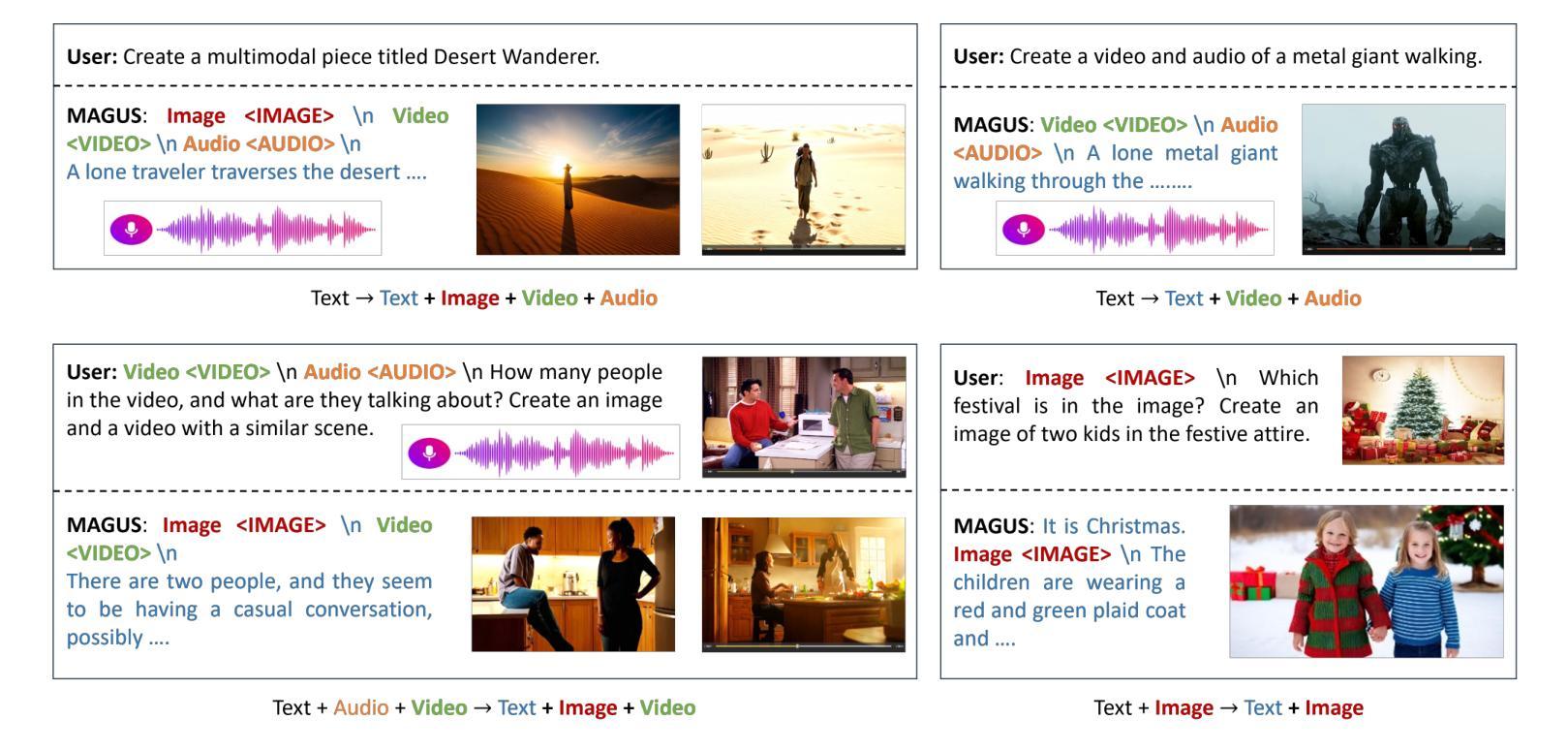
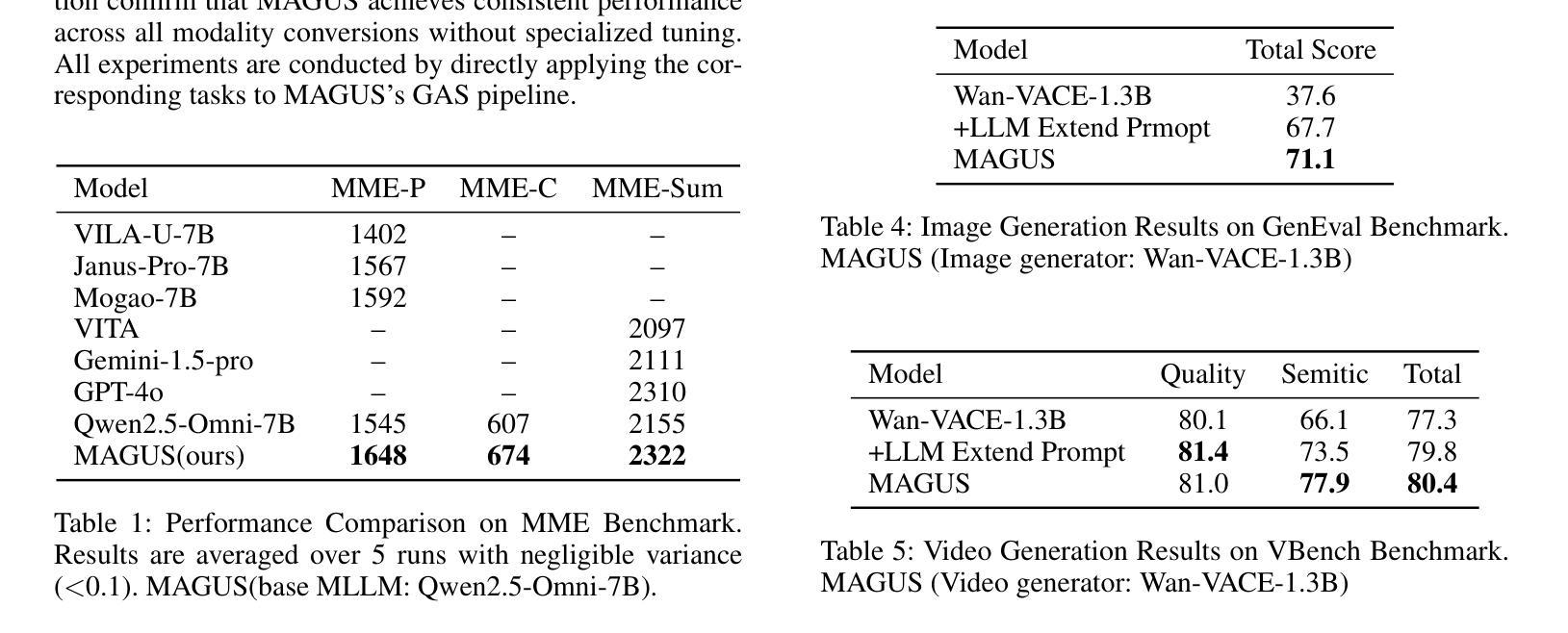
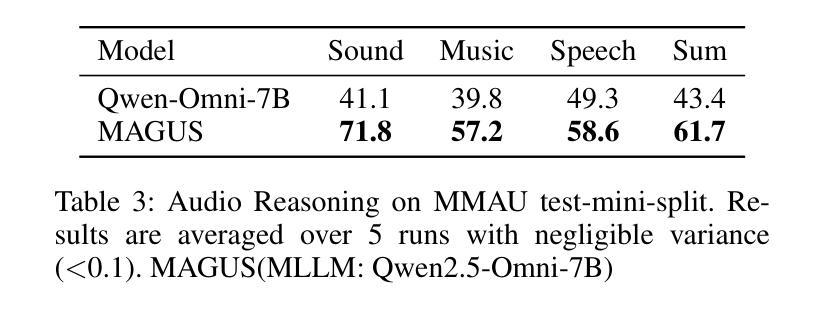
A Unified Multi-Agent Framework for Universal Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Authors:Jiulin Li, Ping Huang, Yexin Li, Shuo Chen, Juewen Hu, Ye Tian
Real-world multimodal applications often require any-to-any capabilities, enabling both understanding and generation across modalities including text, image, audio, and video. However, integrating the strengths of autoregressive language models (LLMs) for reasoning and diffusion models for high-fidelity generation remains challenging. Existing approaches rely on rigid pipelines or tightly coupled architectures, limiting flexibility and scalability. We propose MAGUS (Multi-Agent Guided Unified Multimodal System), a modular framework that unifies multimodal understanding and generation via two decoupled phases: Cognition and Deliberation. MAGUS enables symbolic multi-agent collaboration within a shared textual workspace. In the Cognition phase, three role-conditioned multimodal LLM agents - Perceiver, Planner, and Reflector - engage in collaborative dialogue to perform structured understanding and planning. The Deliberation phase incorporates a Growth-Aware Search mechanism that orchestrates LLM-based reasoning and diffusion-based generation in a mutually reinforcing manner. MAGUS supports plug-and-play extensibility, scalable any-to-any modality conversion, and semantic alignment - all without the need for joint training. Experiments across multiple benchmarks, including image, video, and audio generation, as well as cross-modal instruction following, demonstrate that MAGUS outperforms strong baselines and state-of-the-art systems. Notably, on the MME benchmark, MAGUS surpasses the powerful closed-source model GPT-4o.
现实世界中的多模态应用通常需要任何到任何的能力,能够在文本、图像、音频和视频等多种模态之间进行理解和生成。然而,整合自回归语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力和扩散模型的高保真生成能力仍然是一个挑战。现有方法依赖于僵化的管道或紧密耦合的架构,这限制了灵活性和可扩展性。我们提出了MAGUS(多代理引导统一多模态系统),这是一个模块化框架,通过两个解耦阶段统一多模态理解和生成:认知和思考。MAGUS在共享文本工作空间中实现了符号多代理协作。在认知阶段,三个角色条件的多模态LLM代理——感知者、规划者和反射者——参与协作对话,执行结构化理解和规划。思考阶段采用增长感知搜索机制,以相互加强的方式协调基于LLM的推理和基于扩散的生成。MAGUS支持即插即用的可扩展性,可实现任何到任何的模态转换和语义对齐,而无需联合训练。在图像、视频和音频生成以及跨模态指令遵循等多个基准测试上的实验表明,MAGUS优于强大的基准线和最先进的系统。值得注意的是,在MME基准测试中,MAGUS超越了强大的闭源模型GPT-4o。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于多模态应用的挑战,本文提出了MAGUS(Multi-Agent Guided Unified Multimodal System)框架,实现了跨模态理解和生成的统一。该框架包含认知与决策两个解耦阶段,通过多模态LLM代理的协同工作实现结构化理解和规划。增长感知搜索机制协调LLM推理和扩散生成,支持插件式扩展、可伸缩的任意模态转换和语义对齐。实验证明,MAGUS在多模态任务上表现优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了多模态应用中的挑战和需求,强调集成语言模型与扩散模型的重要性。
- 提出MAGUS框架,包括认知与决策两个解耦阶段,实现跨模态理解和生成的统一。
- 采用多模态LLM代理进行结构化理解和规划,通过符号化的多智能体协作实现文本工作空间共享。
- 增长感知搜索机制用于协调LLM推理和扩散生成,提高模型的协同能力。
- MAGUS支持插件式扩展、可伸缩的任意模态转换和语义对齐,无需联合训练。
- 实验结果表明,MAGUS在多模态任务上表现优于其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图


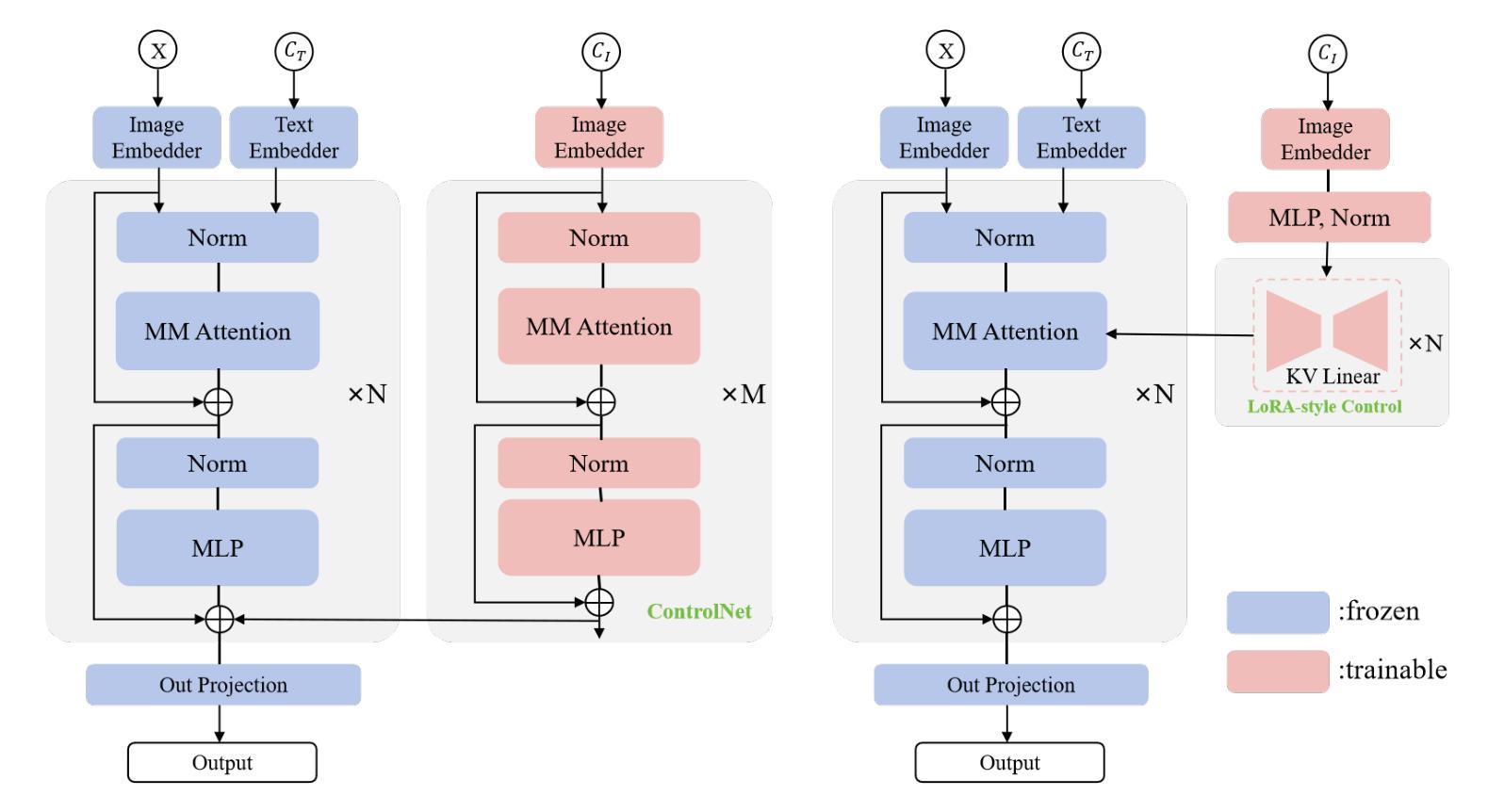
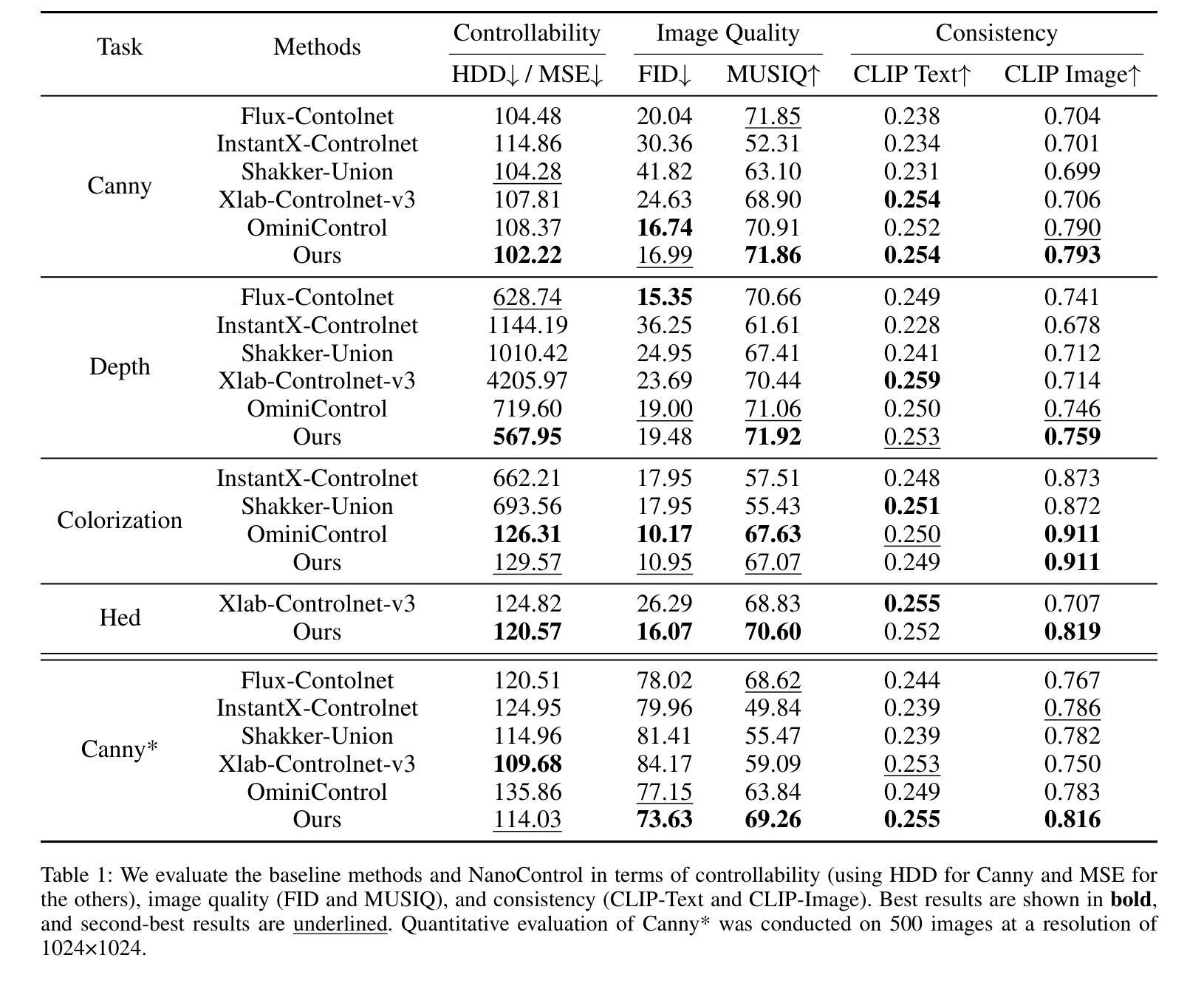
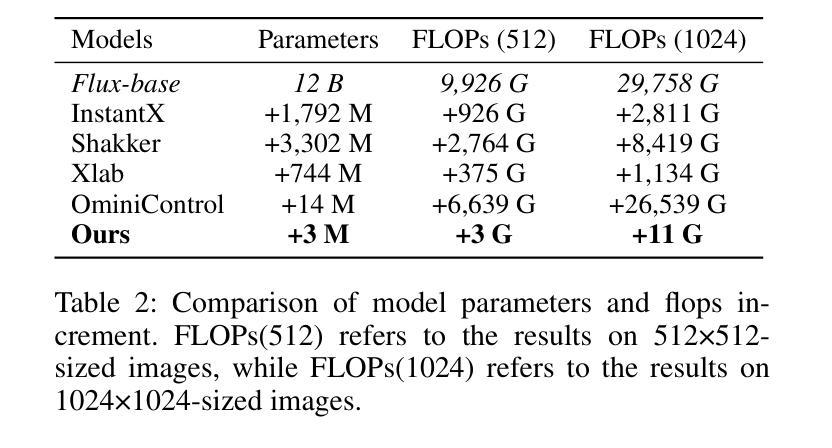
NanoControl: A Lightweight Framework for Precise and Efficient Control in Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Shanyuan Liu, Jian Zhu, Junda Lu, Yue Gong, Liuzhuozheng Li, Bo Cheng, Yuhang Ma, Liebucha Wu, Xiaoyu Wu, Dawei Leng, Yuhui Yin
Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text-to-image synthesis. However, in the domain of controllable text-to-image generation using DiTs, most existing methods still rely on the ControlNet paradigm originally designed for UNet-based diffusion models. This paradigm introduces significant parameter overhead and increased computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose the Nano Control Diffusion Transformer (NanoControl), which employs Flux as the backbone network. Our model achieves state-of-the-art controllable text-to-image generation performance while incurring only a 0.024% increase in parameter count and a 0.029% increase in GFLOPs, thus enabling highly efficient controllable generation. Specifically, rather than duplicating the DiT backbone for control, we design a LoRA-style (low-rank adaptation) control module that directly learns control signals from raw conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce a KV-Context Augmentation mechanism that integrates condition-specific key-value information into the backbone in a simple yet highly effective manner, facilitating deep fusion of conditional features. Extensive benchmark experiments demonstrate that NanoControl significantly reduces computational overhead compared to conventional control approaches, while maintaining superior generation quality and achieving improved controllability.
Diffusion Transformers(DiTs)在文本到图像合成中展现了卓越的能力。然而,在可控文本到图像生成领域,使用DiTs的大多数现有方法仍然依赖于最初为基于UNet的扩散模型设计的ControlNet范式。这种范式引入了显著的参数开销和增加的计算成本。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Nano Control Diffusion Transformer(NanoControl),它采用Flux作为主干网络。我们的模型实现了最先进的可控文本到图像生成性能,同时参数计数仅增加0.024%,GFLOPs增加0.029%,从而实现了高度有效的可控生成。具体来说,我们并没有复制DiT主干来进行控制,而是设计了一个LoRA风格的(低秩适应)控制模块,该模块直接从原始条件输入中学习控制信号。此外,我们引入了一种KV-Context Augmentation机制,以简单而高效的方式将条件特定的键值信息集成到主干中,促进条件特征的深度融合。广泛的基准实验表明,与传统的控制方法相比,NanoControl显著减少了计算开销,同时保持了优越的生成质量和提高了可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本主要介绍了Diffusion Transformers在文本到图像合成方面的卓越能力。针对可控文本到图像生成领域面临的挑战,提出了一种采用Flux作为主干网络的Nano Control Diffusion Transformer(NanoControl)。该模型在保持高效可控生成的同时,实现了最先进的可控文本到图像生成性能,并且只增加了0.024%的参数计数和0.029%的GFLOPs。NanoControl设计了一个LoRA风格的控制模块,直接学习来自原始条件输入的控制信号,并引入了一个KV-Context增强机制,以简单高效的方式将条件特定的键值信息集成到主干中,促进条件特征的深度融合。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) 已成功应用于文本到图像合成。
- 现有大多数可控文本到图像生成方法仍依赖于为UNet设计的ControlNet范式,这增加了参数和计算成本。
- NanoControl模型采用Flux作为主干网络,实现了高效的可控文本到图像生成。
- NanoControl通过设计LoRA风格的控制模块,直接学习原始条件输入的控制信号。
- NanoControl引入了KV-Context Augmentation机制,以集成条件特定的键值信息,促进条件特征的深度融合。
- NanoControl模型在保持高性能生成的同时,显著减少了计算开销。
点此查看论文截图


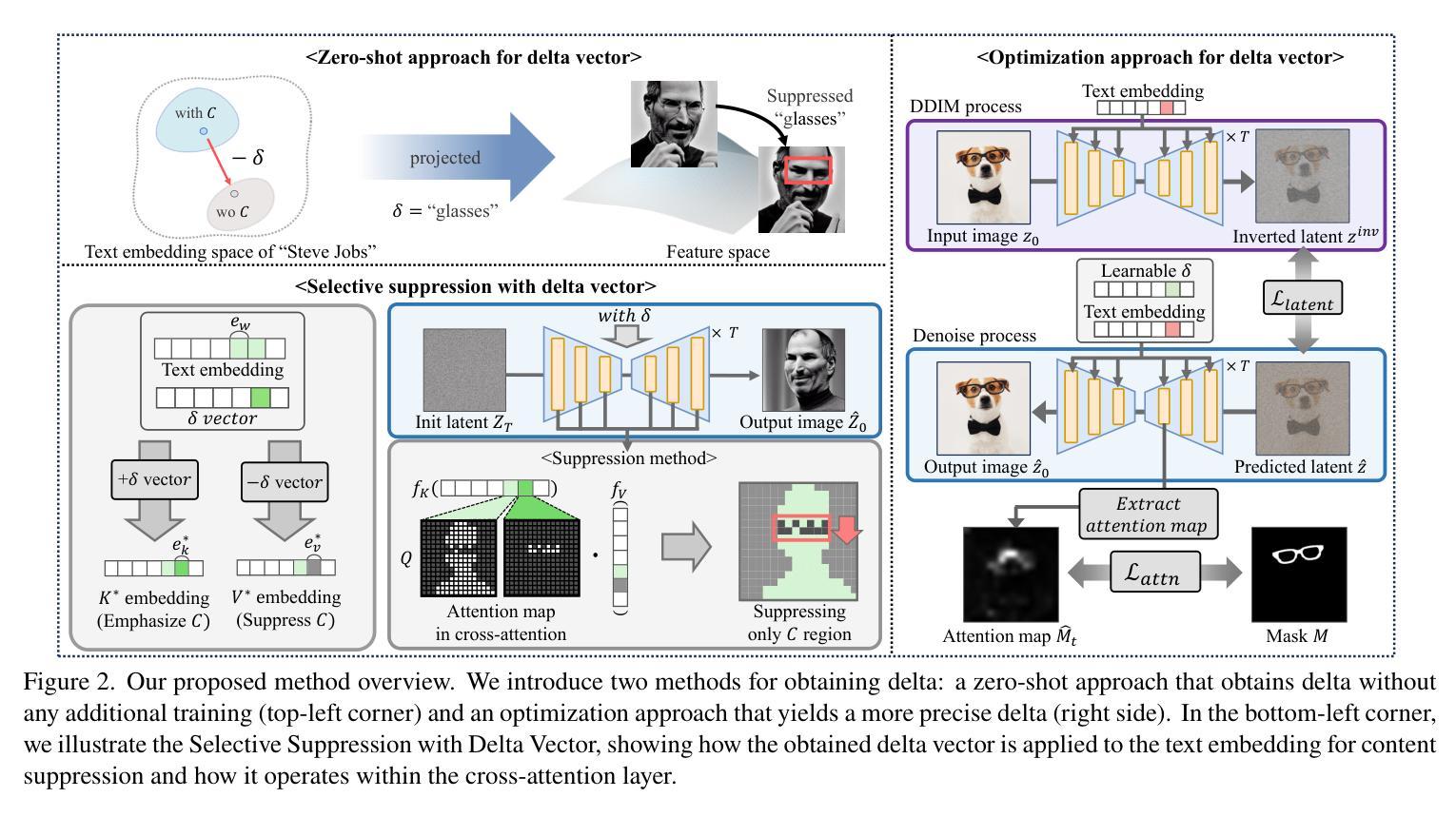
Translation of Text Embedding via Delta Vector to Suppress Strongly Entangled Content in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Eunseo Koh, Seunghoo Hong, Tae-Young Kim, Simon S. Woo, Jae-Pil Heo
Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have made significant progress in generating diverse high-quality images from textual prompts. However, these models still face challenges in suppressing content that is strongly entangled with specific words. For example, when generating an image of Charlie Chaplin", a mustache” consistently appears even if explicitly instructed not to include it, as the concept of mustache" is strongly entangled with Charlie Chaplin”. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach to directly suppress such entangled content within the text embedding space of diffusion models. Our method introduces a delta vector that modifies the text embedding to weaken the influence of undesired content in the generated image, and we further demonstrate that this delta vector can be easily obtained through a zero-shot approach. Furthermore, we propose a Selective Suppression with Delta Vector (SSDV) method to adapt delta vector into the cross-attention mechanism, enabling more effective suppression of unwanted content in regions where it would otherwise be generated. Additionally, we enabled more precise suppression in personalized T2I models by optimizing delta vector, which previous baselines were unable to achieve. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods, both in terms of quantitative and qualitative metrics.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在根据文本提示生成多样化高质量图像方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些模型在抑制与特定单词强烈纠缠的内容方面仍面临挑战。例如,在生成“查理·卓别林”的图像时,即使明确指示不要包含“胡子”,但“胡子”仍然会出现,因为“胡子”的概念与“查理·卓别林”紧密相连。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种在扩散模型的文本嵌入空间中直接抑制这种纠缠内容的新方法。我们的方法引入了一个delta向量,该向量修改文本嵌入以减弱生成图像中不需要内容的影响,我们进一步证明可以通过零样本方法轻松获得这个delta向量。此外,我们提出了一种带有Delta向量的选择性抑制(SSDV)方法,将delta向量适应到交叉注意机制中,从而更有效地抑制了原本会生成的区域的不想要的内容。通过优化delta向量,我们还实现了个性化T2I模型的更精确抑制,这是以前的基础线无法达到的。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在定量和定性指标上都显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型已在根据文本提示生成多样且高质量图像方面取得显著进展。然而,这些模型在抑制与特定单词强烈纠缠的内容方面仍面临挑战。例如,在生成“查理·卓别林”的图像时,即使明确指示不包括“胡子”,但“胡子”仍然会出现,因为“胡子”的概念与“查理·卓别林”紧密相连。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种在扩散模型的文本嵌入空间中直接抑制这种纠缠内容的新方法。我们的方法引入了一个delta向量,该向量修改文本嵌入以减弱生成图像中不需要内容的影响,并且我们进一步证明可以通过零样本方法轻松获得这个delta向量。此外,我们提出了一种带有Delta向量的选择性抑制(SSDV)方法,将delta向量适应到交叉注意机制中,以在可能生成不需要内容的区域更有效地抑制它。另外,通过优化delta向量,我们在个性化T2I模型中实现了更精确的抑制,这是以前的方法无法实现的。大量实验结果表明,我们的方法显著优于现有方法,无论在定量还是定性指标上都是如此。
关键见解
- T2I扩散模型在生成与文本提示相符的高质量图像方面已取得进展,但仍面临抑制特定纠缠内容的挑战。
- 引入delta向量以修改文本嵌入,从而减弱生成图像中不需要内容的影响。
- 通过零样本方法轻松获得delta向量,并应用于交叉注意机制中,以更有效地抑制不需要的内容。
- 提出SSDV方法,将delta向量适应到个性化T2I模型中,实现更精确的抑制。
- 优化的delta向量使模型能够在特定区域更有效地抑制不需要的内容。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在定量和定性指标上均优于现有方法。
- 该方法为提高T2I扩散模型的性能提供了新的思路和技术手段。
点此查看论文截图

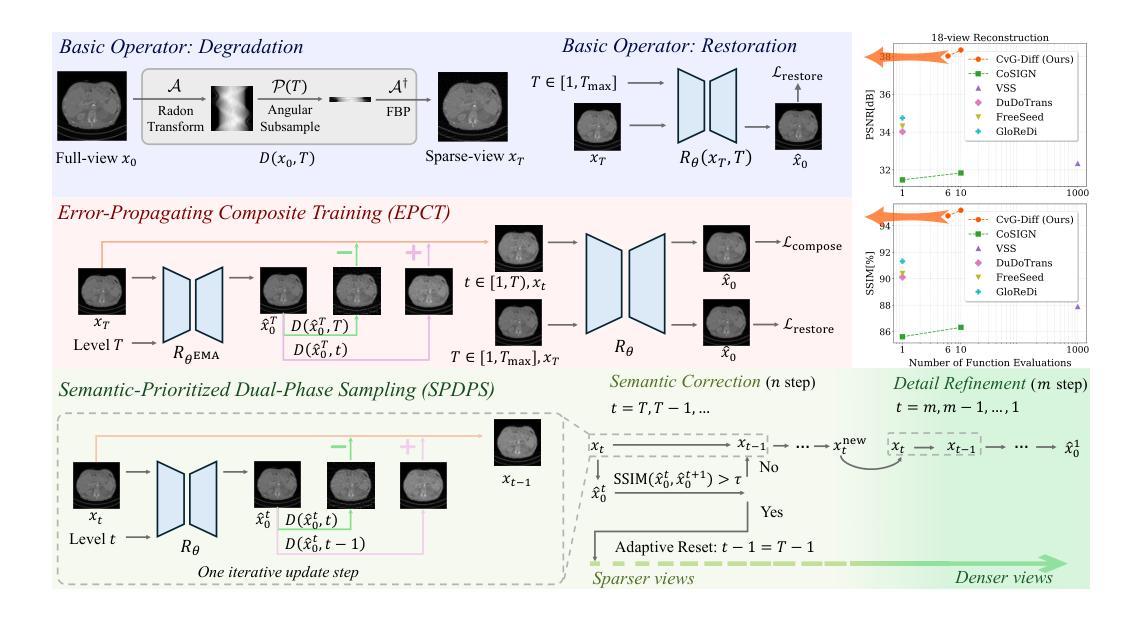
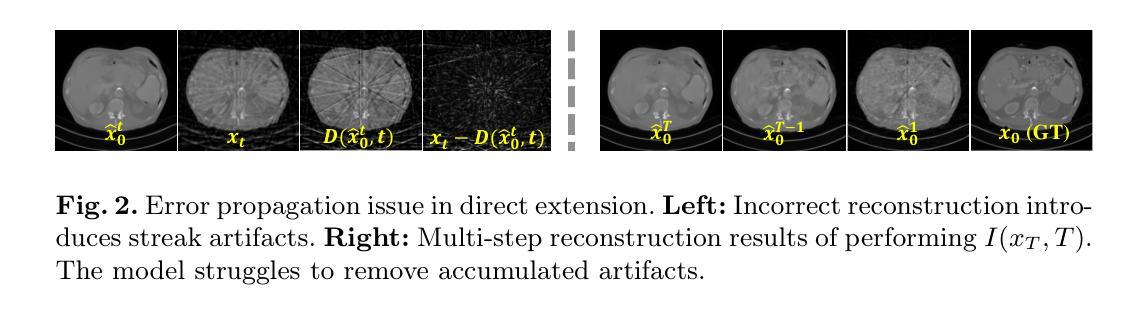
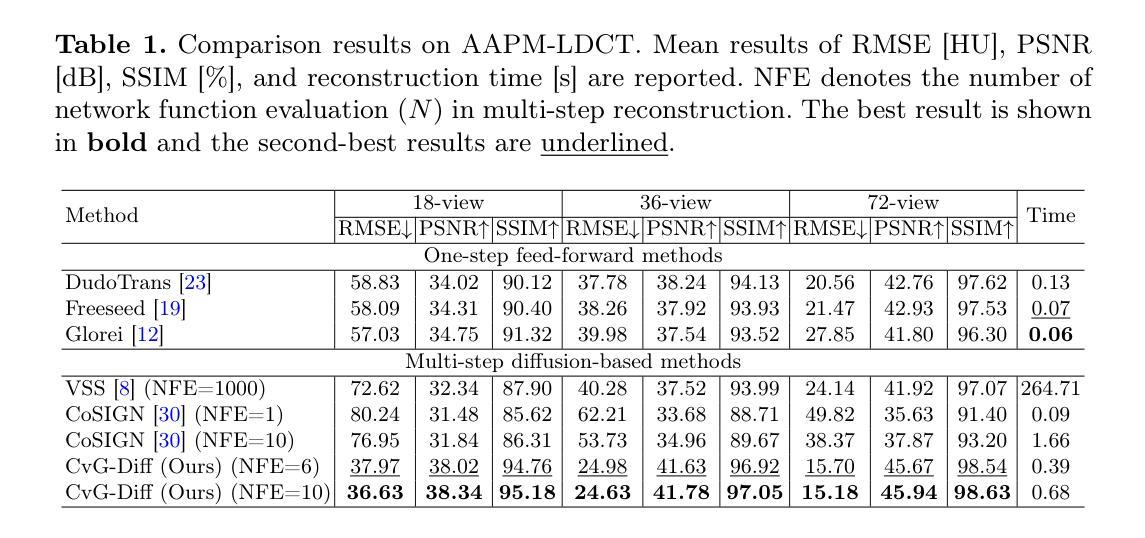
Cross-view Generalized Diffusion Model for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction
Authors:Jixiang Chen, Yiqun Lin, Yi Qin, Hualiang Wang, Xiaomeng Li
Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) reduces radiation exposure by subsampling projection views, but conventional reconstruction methods produce severe streak artifacts with undersampled data. While deep-learning-based methods enable single-step artifact suppression, they often produce over-smoothed results under significant sparsity. Though diffusion models improve reconstruction via iterative refinement and generative priors, they require hundreds of sampling steps and struggle with stability in highly sparse regimes. To tackle these concerns, we present the Cross-view Generalized Diffusion Model (CvG-Diff), which reformulates sparse-view CT reconstruction as a generalized diffusion process. Unlike existing diffusion approaches that rely on stochastic Gaussian degradation, CvG-Diff explicitly models image-domain artifacts caused by angular subsampling as a deterministic degradation operator, leveraging correlations across sparse-view CT at different sample rates. To address the inherent artifact propagation and inefficiency of sequential sampling in generalized diffusion model, we introduce two innovations: Error-Propagating Composite Training (EPCT), which facilitates identifying error-prone regions and suppresses propagated artifacts, and Semantic-Prioritized Dual-Phase Sampling (SPDPS), an adaptive strategy that prioritizes semantic correctness before detail refinement. Together, these innovations enable CvG-Diff to achieve high-quality reconstructions with minimal iterations, achieving 38.34 dB PSNR and 0.9518 SSIM for 18-view CT using only \textbf{10} steps on AAPM-LDCT dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of CvG-Diff over state-of-the-art sparse-view CT reconstruction methods. The code is available at https://github.com/xmed-lab/CvG-Diff.
稀疏视图计算层析成像(CT)通过子采样投影视图减少了辐射暴露,但传统重建方法在处理欠采样数据时会产生严重的条纹伪影。虽然基于深度学习的方法能够实现一步伪影抑制,但它们往往在显著稀疏的情况下产生过于平滑的结果。尽管扩散模型通过迭代优化和生成先验信息改善了重建效果,但它们需要数百个采样步骤,并且在高度稀疏的情况下稳定性较差。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了跨视图广义扩散模型(CvG-Diff),它将稀疏视图CT重建重新表述为广义扩散过程。与现有的依赖随机高斯退化的扩散方法不同,CvG-Diff显式地将角度子采样引起的图像域伪影建模为确定性退化算子,并利用不同采样率的稀疏视图CT之间的相关性。为了解决广义扩散模型中固有的伪影传播和顺序采样的低效问题,我们引入了两项创新:错误传播复合训练(EPCT),它有助于识别错误易发区域并抑制传播的伪影;语义优先双相采样(SPDPS),这是一种自适应策略,在细节优化之前优先关注语义正确性。这些创新的结合使CvG-Diff能够在最少的迭代次数内实现高质量的重建,在AAPM-LDCT数据集上使用仅有10个步骤的18视图CT,获得38.34 dB的PSNR和0.9518的SSIM。大量实验表明,CvG-Diff在稀疏视图CT重建方法中表现卓越。代码可在https://github.com/xmed-lab/CvG-Diff获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Spotlight
摘要
稀疏视图计算机断层扫描(CT)通过子采样投影视图减少辐射暴露,但传统重建方法会产生严重的条纹伪影。基于深度学习的方法能够一步抑制伪影,但在显著稀疏的情况下会产生过于平滑的结果。虽然扩散模型通过迭代优化和生成先验改进重建,但需要数百个采样步骤,并且在高度稀疏的情况下稳定性较差。为解决这些问题,我们提出了跨视图广义扩散模型(CvG-Diff),将稀疏视图CT重建重新表述为广义扩散过程。不同于现有扩散方法依赖于随机高斯退化,CvG-Diff显式地建模由角度子采样引起的图像域伪影作为确定性退化算子,并利用不同采样率的稀疏视图CT之间的相关性。为解决广义扩散模型中固有的伪影传播和顺序采样的低效问题,我们引入了两项创新:错误传播复合训练(EPCT),有助于识别错误区域并抑制传播的伪影;语义优先双相采样(SPDPS),一种自适应策略,在细节优化之前优先语义正确性。这些创新使CvG-Diff能够在少量迭代后实现高质量重建,在AAPM-LDCT数据集上仅使用10个步骤就达到38.34 dB的PSNR和0.9518的SSIM。大量实验表明,CvG-Diff在稀疏视图CT重建方法中表现卓越。代码可在链接中找到。
关键见解
- CvG-Diff将稀疏视图CT重建重新表述为广义扩散过程,以改进现有方法的不足。
- 引入确定性退化算子来显式建模由角度子采样引起的图像域伪影。
- 提出错误传播复合训练(EPCT)以识别错误区域并抑制伪影传播。
- 语义优先双相采样(SPDPS)策略能自适应地优先语义正确性,再进行细节优化。
- CvG-Diff实现了高质量重建,仅使用少量迭代步骤,且在AAPM-LDCT数据集上的表现优于其他先进方法。
- 该模型的代码已在指定链接中公开,供公众查阅和使用。
点此查看论文截图

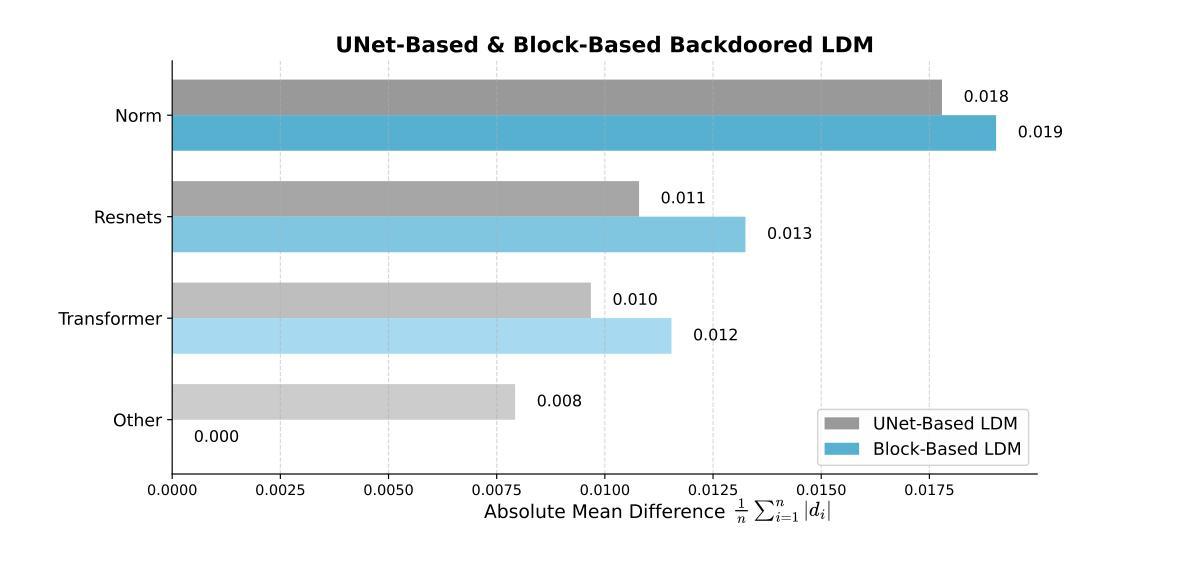
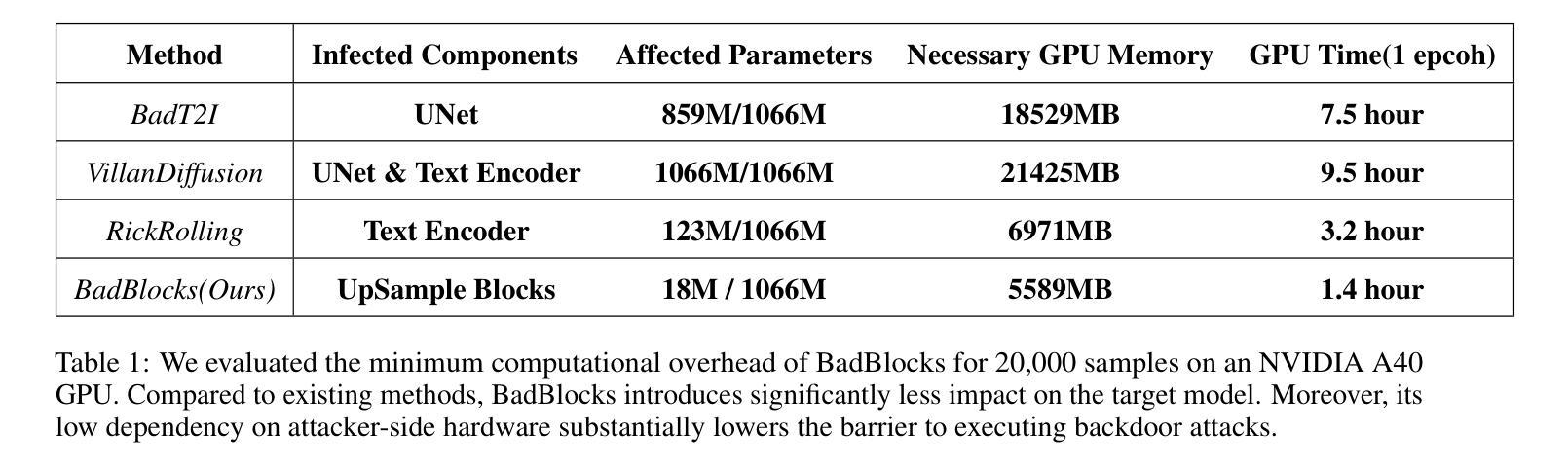
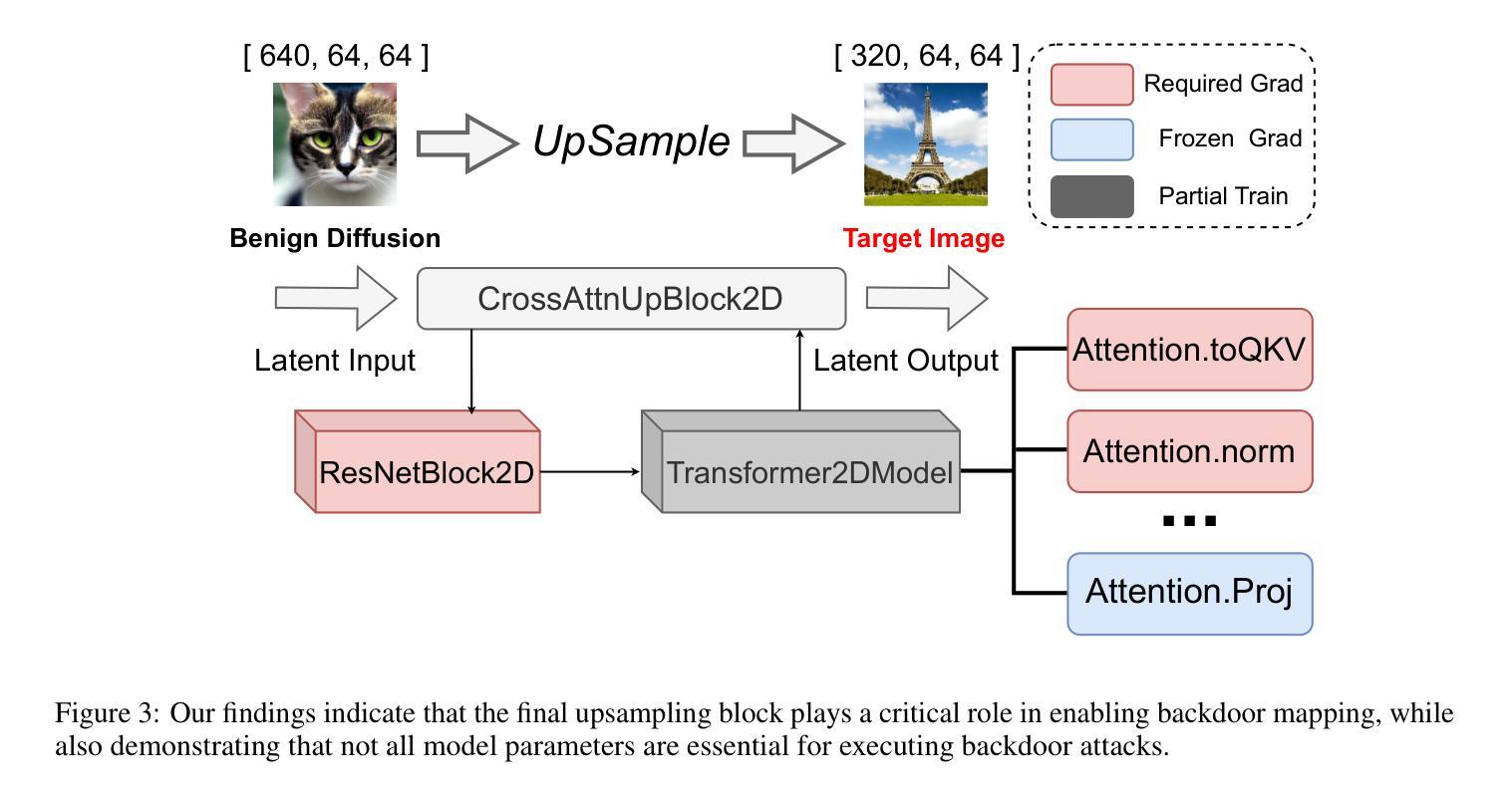
BadBlocks: Low-Cost and Stealthy Backdoor Attacks Tailored for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Jiahao Chen, Lin Wang, Bingrong Dai, Yi Du
In recent years, Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in the field of image generation. However, recent studies have shown that diffusion models are susceptible to backdoor attacks, in which attackers can manipulate the output by injecting covert triggers such as specific visual patterns or textual phrases into the training dataset. Fortunately, with the continuous advancement of defense techniques, defenders have become increasingly capable of identifying and mitigating most backdoor attacks using visual inspection and neural network-based detection methods. However, in this paper, we identify a novel type of backdoor threat that is more lightweight and covert than existing approaches, which we name BadBlocks, requires only about 30 of the computational resources and 20 GPU time typically needed by previous backdoor attacks, yet it successfully injects backdoors and evades the most advanced defense frameworks. BadBlocks enables attackers to selectively contaminate specific blocks within the UNet architecture of diffusion models while maintaining normal functionality in the remaining components. Experimental results demonstrate that BadBlocks achieves a high attack success rate and low perceptual quality loss , even under extremely constrained computational resources and GPU time. Moreover, BadBlocks is able to bypass existing defense frameworks, especially the attention-based backdoor detection method, highlighting it as a novel and noteworthy threat. Ablation studies further demonstrate that effective backdoor injection does not require fine-tuning the entire network and highlight the pivotal role of certain neural network layers in backdoor mapping. Overall, BadBlocks significantly reduces the barrier to conducting backdoor attacks in all aspects. It enables attackers to inject backdoors into large-scale diffusion models even using consumer-grade GPUs.
近年来,扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著的进步。然而,研究表明,扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过向训练数据集中注入隐蔽的触发器(例如特定的视觉模式或文本短语)来操纵输出。幸运的是,随着防御技术的不断进步,防御者越来越能够使用视觉检查和基于神经网络的检测方法来识别和缓解大多数后门攻击。然而,在本文中,我们识别了一种比现有方法更轻量级、更隐蔽的新型后门威胁,我们称之为BadBlocks。BadBlocks仅需要大约30的计算资源和20的GPU时间,而以前的后门攻击通常需要这些资源,然而它却能够成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks使攻击者能够选择性地污染扩散模型UNet架构中的特定块,同时保持其余组件的正常功能。实验结果表明,即使在极其有限的计算资源和GPU时间下,BadBlocks也能实现较高的攻击成功率和较低的可感知质量损失。而且,BadBlocks能够绕过现有的防御框架,尤其是基于注意力的后门检测方法,凸显出它是一种新型且值得关注的威胁。消融研究进一步表明,有效的后门注入并不需要微调整个网络,并突出了某些神经网络层在后门映射中的关键作用。总体而言,BadBlocks在各个方面都大大降低了进行后门攻击的障碍。它使攻击者即使使用消费级GPU也能将后门注入大规模扩散模型。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型在图生成领域取得了显著进展,但近期研究指出其易受后门攻击影响。攻击者通过注入特定视觉模式或文本短语等隐蔽触发因素,操纵输出。尽管防御技术不断发展,大多数后门攻击仍可通过视觉检查和神经网络检测方法进行识别与缓解。然而,本文揭示了一种新型后门威胁——BadBlocks。BadBlocks较现有方法更为轻便、隐蔽,仅需约30的计算资源和20的GPU时间,便能成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks能选择性地污染扩散模型UNet架构内的特定区块,同时保持其余组件的正常功能。实验结果显示,BadBlocks在极低的计算资源和GPU时间下,仍能实现高攻击成功率与低感知质量损失。此外,BadBlocks能绕过现有的防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法,展现其作为新型且值得关注的威胁。综合研究进一步证明,有效的后门注入无需微调整个网络,并突出了某些神经网络层在后门映射中的关键作用。总体而言,BadBlocks显著降低了进行后门攻击的所有方面门槛,使攻击者即使使用消费级GPU,也能将后门注入大规模扩散模型中。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在图生成领域取得显著进展,但易受后门攻击影响。
- BadBlocks是一种新型后门威胁,较现有方法更轻便、隐蔽。
- BadBlocks能在有限的计算资源和GPU时间下成功注入后门。
- BadBlocks能选择性地污染扩散模型的特定区块,同时保持其他部分正常运作。
- BadBlocks实现了高攻击成功率与低感知质量损失。
- BadBlocks能绕过现有防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法。
点此查看论文截图

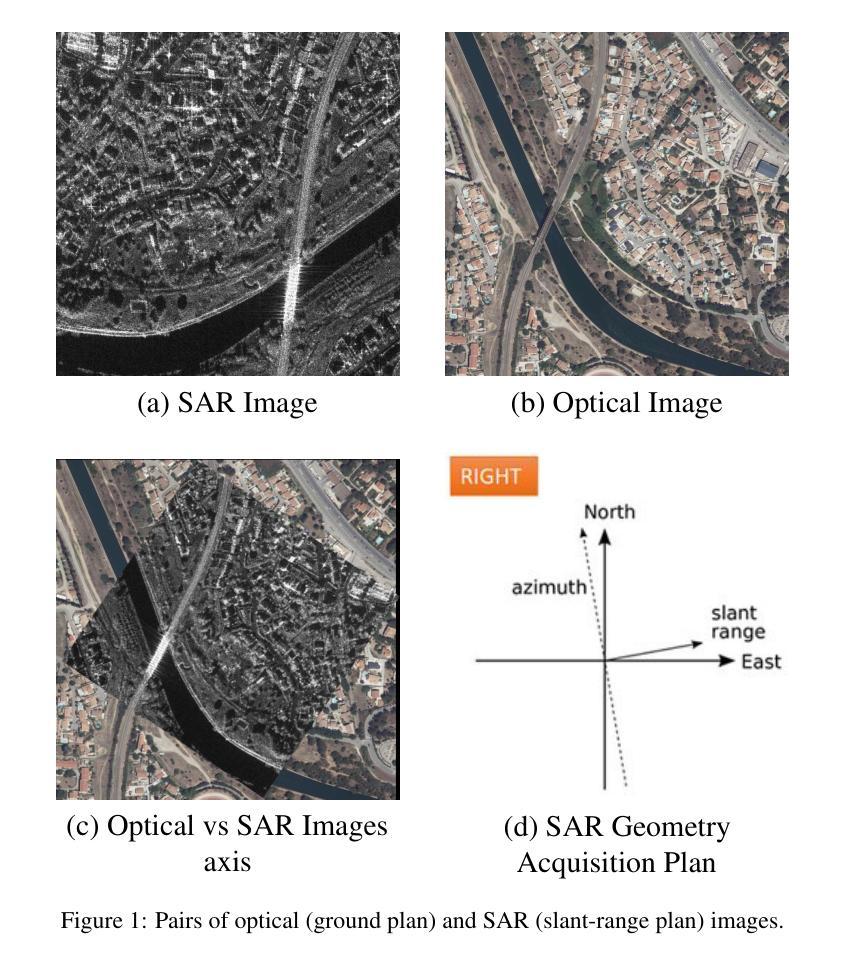
Quantitative Comparison of Fine-Tuning Techniques for Pretrained Latent Diffusion Models in the Generation of Unseen SAR Images
Authors:Solène Debuysère, Nicolas Trouvé, Nathan Letheule, Olivier Lévêque, Elise Colin
We present a framework for adapting a large pretrained latent diffusion model to high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image generation. The approach enables controllable synthesis and the creation of rare or out-of-distribution scenes beyond the training set. Rather than training a task-specific small model from scratch, we adapt an open-source text-to-image foundation model to the SAR modality, using its semantic prior to align prompts with SAR imaging physics (side-looking geometry, slant-range projection, and coherent speckle with heavy-tailed statistics). Using a 100k-image SAR dataset, we compare full fine-tuning and parameter-efficient Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) across the UNet diffusion backbone, the Variational Autoencoder (VAE), and the text encoders. Evaluation combines (i) statistical distances to real SAR amplitude distributions, (ii) textural similarity via Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) descriptors, and (iii) semantic alignment using a SAR-specialized CLIP model. Our results show that a hybrid strategy-full UNet tuning with LoRA on the text encoders and a learned token embedding-best preserves SAR geometry and texture while maintaining prompt fidelity. The framework supports text-based control and multimodal conditioning (e.g., segmentation maps, TerraSAR-X, or optical guidance), opening new paths for large-scale SAR scene data augmentation and unseen scenario simulation in Earth observation.
我们提出了一种适应大型预训练潜在扩散模型用于高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像生成的框架。该方法可实现可控合成,并创建超出训练集范围的稀有或异常场景。我们并不是从头开始训练一个特定任务的小型模型,而是将开源的文本到图像基础模型适应到SAR模式,利用其语义先验来使提示与SAR成像物理(侧视几何、斜距投影和具有重尾统计的相干斑点)对齐。我们使用一个包含10万张图像的SAR数据集,全面微调了UNet扩散主干、变分自编码器(VAE)和文本编码器,并进行了参数高效的低秩适配(LoRA)比较。评估结合了(i)与真实SAR振幅分布的统计距离,(ii)通过灰度共生矩阵(GLCM)描述符的纹理相似性,以及(iii)使用SAR专用CLIP模型的语义对齐。我们的结果表明,混合策略——全面调整UNet,并在文本编码器和学习的令牌嵌入上使用LoRA——最能保持SAR的几何和纹理,同时保持提示保真度。该框架支持基于文本的控制和多模式条件(例如,分割图、TerraSAR-X或光学指导),为地球观测中的大规模SAR场景数据增强和未见场景模拟开辟了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种适应高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像生成的潜扩散模型框架。该方法可实现可控合成,并创建超出训练集的稀有或非常见场景。研究采用开源文本到图像基础模型适应SAR模式,利用语义先验对齐SAR成像物理(斜视几何、斜距投影和具有重尾统计特性的相干斑点)。在10万张SAR图像数据集上,比较了完全微调与低秩自适应(LoRA)技术在UNet扩散主干、变分自编码器(VAE)和文本编码器中的表现。评估包括(i)与真实SAR振幅分布之间的统计距离,(ii)通过灰度共生矩阵(GLCM)描述符的纹理相似性,(iii)使用SAR专用CLIP模型的语义对齐。研究结果表明,混合策略——完全调整UNet结构,同时对文本编码器和标记嵌入使用LoRA技术——最能保留SAR的几何和纹理特征,同时保持提示保真度。该框架支持基于文本的控制和多模式条件(如分割图、TerraSAR-X或光学指导),为大规模SAR场景数据增强和未见场景模拟在地球观测中开辟新途径。
要点掌握
- 介绍了使用潜在扩散模型框架来适应高分辨率SAR图像生成的方法。
- 研究强调通过语义先验将文本提示与SAR成像物理学对齐的重要性。
- 通过实验对比了微调整个UNet扩散模型和仅使用LoRA技术调整部分组件的效果。
- 评估指标涵盖了统计距离、纹理相似性和语义对齐,以确保生成的SAR图像真实且具有意义。
- 研究结果显示混合策略在保留SAR特性与保持提示保真度方面表现最佳。
- 框架支持基于文本的控制和多模式条件,为未来大规模SAR场景数据增强和模拟开辟新途径。
点此查看论文截图

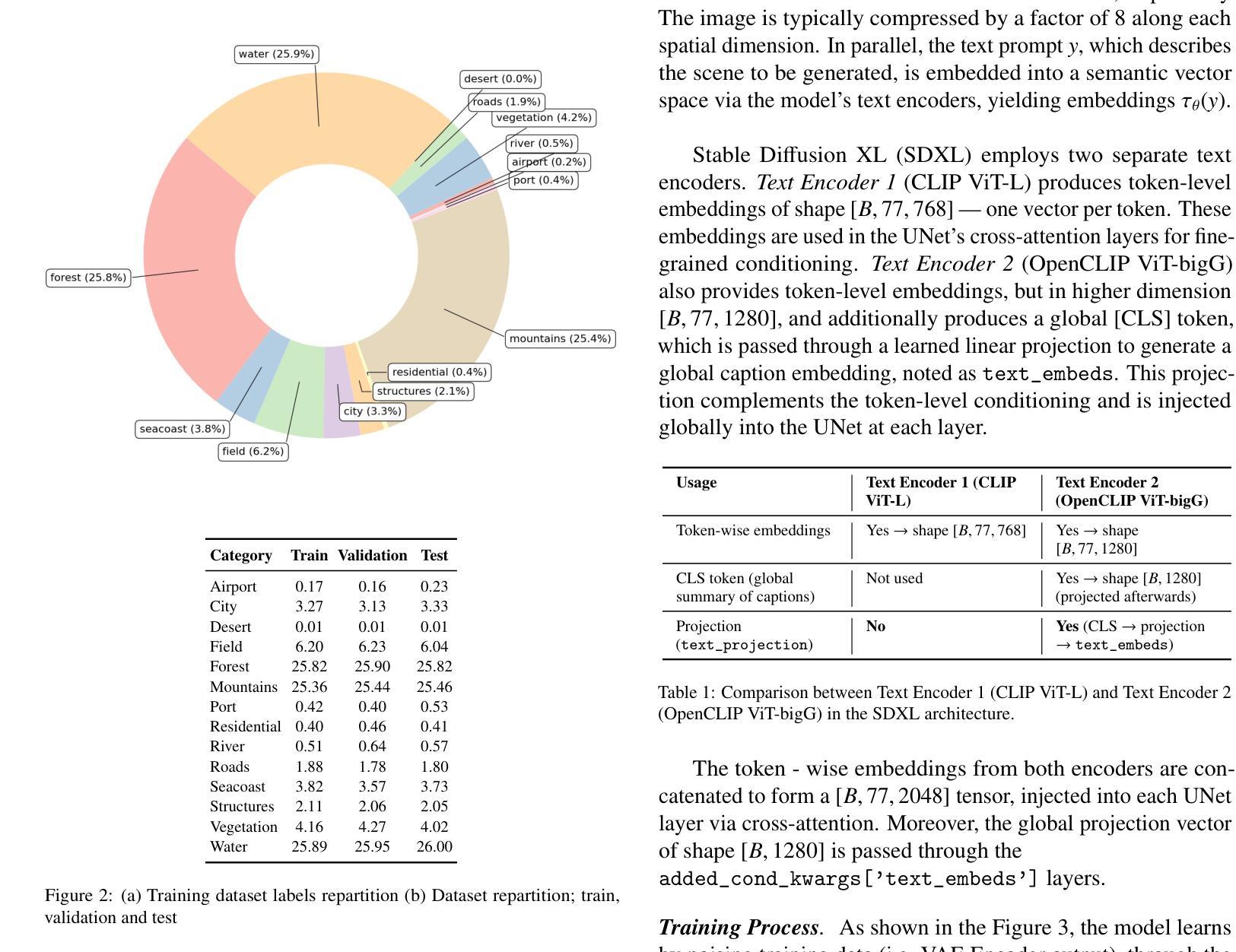
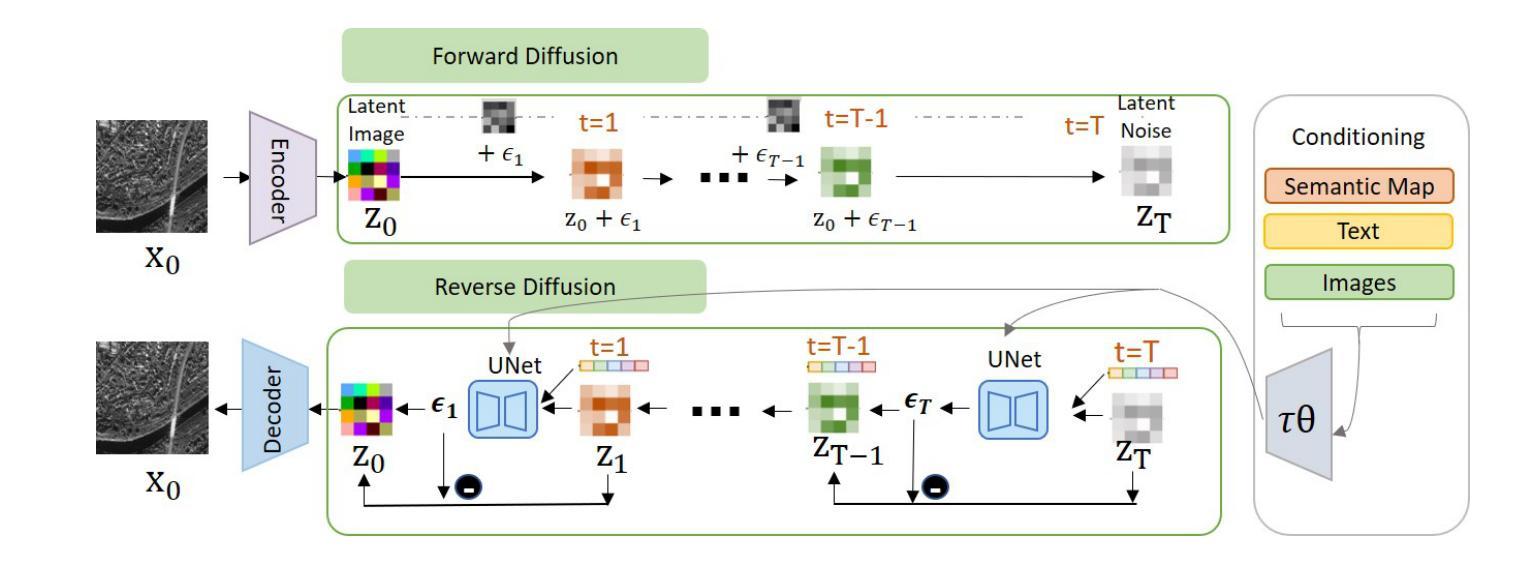
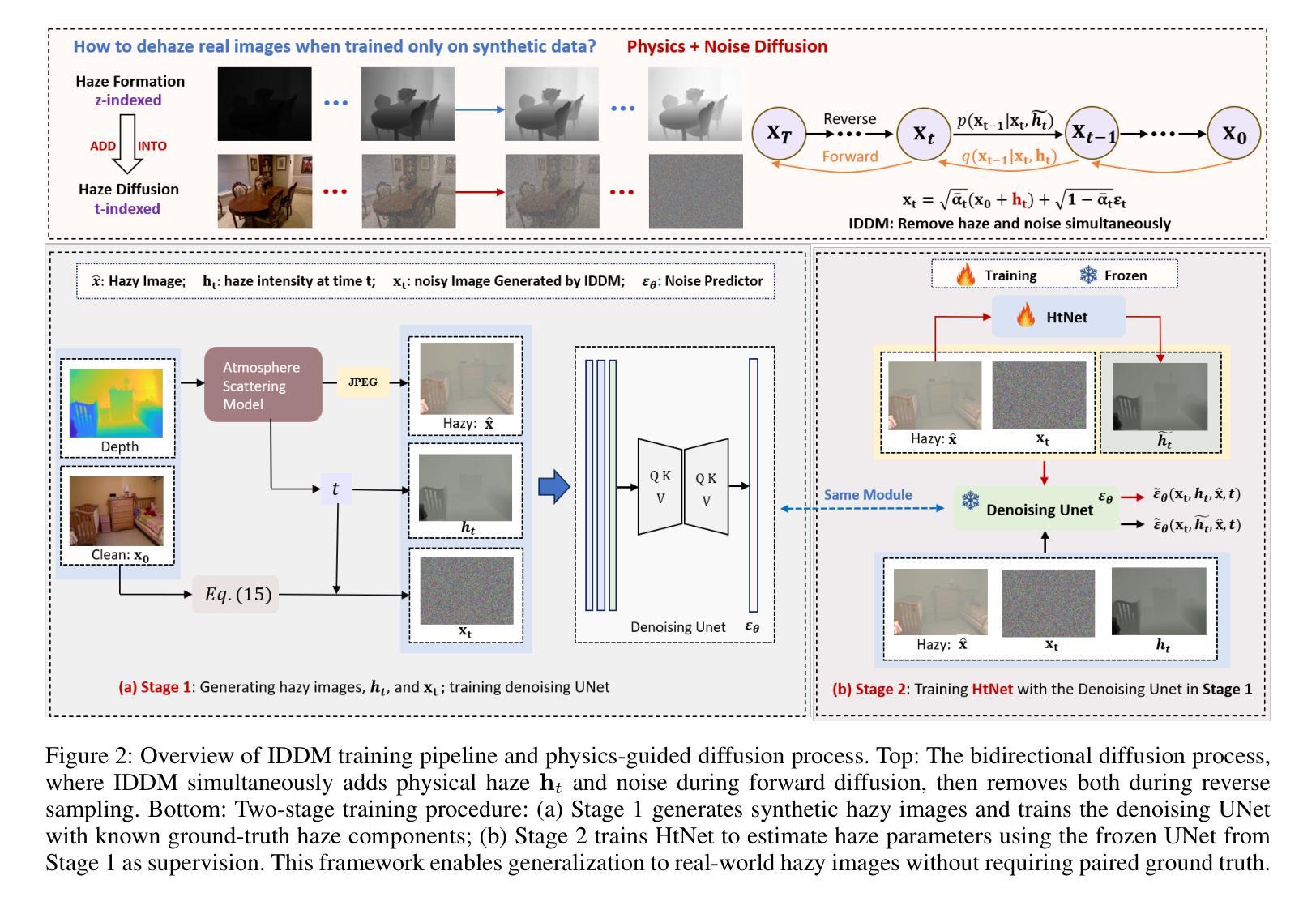
Physics-Guided Image Dehazing Diffusion
Authors:Shijun Zhou, Baojie Fan, Jiandong Tian
Due to the domain gap between real-world and synthetic hazy images, current data-driven dehazing algorithms trained on synthetic datasets perform well on synthetic data but struggle to generalize to real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{I}mage \textbf{D}ehazing \textbf{D}iffusion \textbf{M}odels (IDDM), a novel diffusion process that incorporates the atmospheric scattering model into noise diffusion. IDDM aims to use the gradual haze formation process to help the denoising Unet robustly learn the distribution of clear images from the conditional input hazy images. We design a specialized training strategy centered around IDDM. Diffusion models are leveraged to bridge the domain gap from synthetic to real-world, while the atmospheric scattering model provides physical guidance for haze formation. During the forward process, IDDM simultaneously introduces haze and noise into clear images, and then robustly separates them during the sampling process. By training with physics-guided information, IDDM shows the ability of domain generalization, and effectively restores the real-world hazy images despite being trained on synthetic datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art approaches.
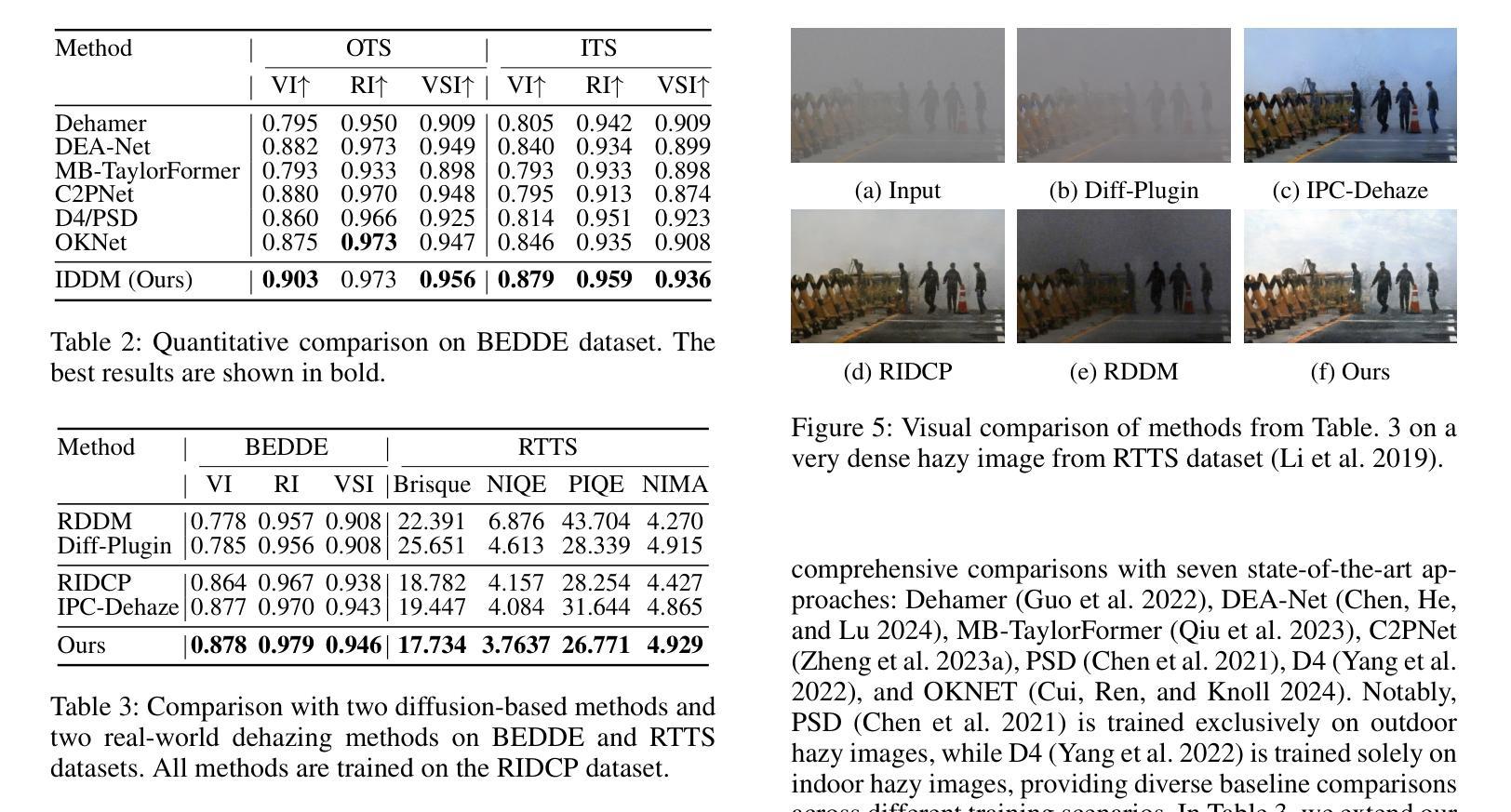
由于真实世界和合成雾图像之间的领域差距,当前基于合成数据集训练的数据驱动去雾算法在合成数据上表现良好,但在真实场景中的泛化能力较差。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了图像去雾扩散模型(IDDM),这是一种新的扩散过程,将大气散射模型融入噪声扩散中。IDDM旨在利用逐步的雾形成过程帮助去噪U-Net从条件输入雾图像中稳健地学习清晰图像分布。我们围绕IDDM设计了一种专门的训练策略。扩散模型被用来缩小合成和真实世界之间的领域差距,而大气散射模型为雾的形成提供了物理指导。在正向过程中,IDDM同时将雾和噪声引入清晰图像,然后在采样过程中稳健地分离它们。通过物理指导信息进行训练,IDDM展示了领域泛化的能力,并有效地恢复了真实世界的雾图像,尽管它是在合成数据集上进行训练的。大量实验表明,我们的方法通过与最新方法的定量和定性比较,证明了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为图像去雾扩散模型(IDDM)的新方法,旨在解决合成数据集训练的现有数据驱动去雾算法在真实场景下的泛化问题。IDDM结合大气散射模型进行噪声扩散,利用逐步的雾形成过程帮助去噪U-Net从条件输入的去雾图像中学习清晰图像分布。通过特定的训练策略,IDDM能够缩小合成与真实世界之间的领域差距,同时大气散射模型为雾的形成提供了物理指导。实验证明,该方法在真实世界去雾任务中表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- IDDM是一种新的图像去雾扩散模型,旨在解决合成数据集训练的算法在真实场景下的泛化问题。
- IDDM结合噪声扩散和大气散射模型,利用逐步雾形成过程帮助学习清晰图像分布。
- IDDM设计了一种以模型为中心的训练策略,能够缩小合成与真实世界之间的领域差距。
- 大气散射模型为雾的形成提供了物理指导,增强了模型的去雾能力。
- IDDM在真实世界去雾任务中表现出优异的性能,通过定量和定性实验验证了其有效性。
- IDDM通过引入雾和噪声到清晰图像,然后在其采样过程中稳健地分离它们,实现了去雾效果。
点此查看论文截图


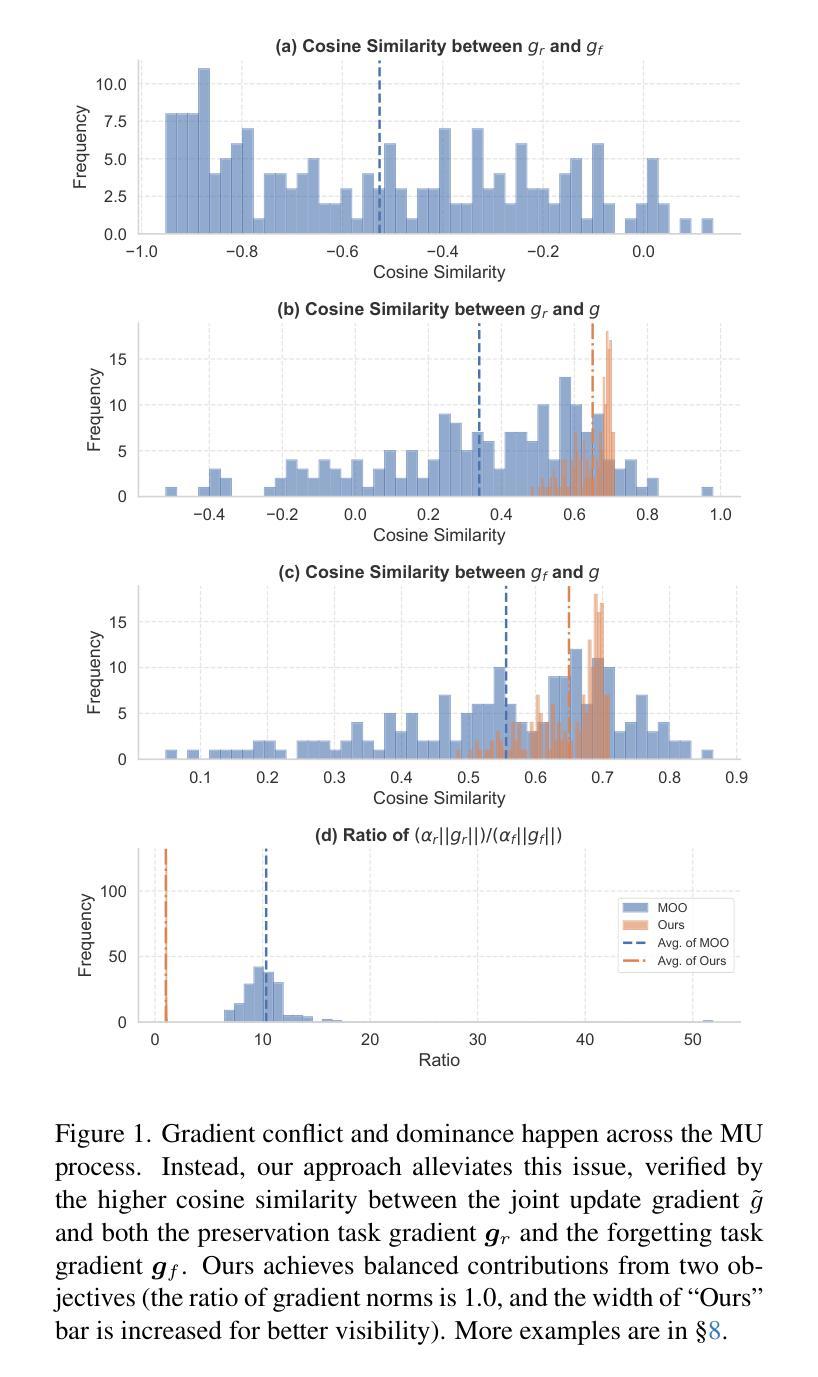
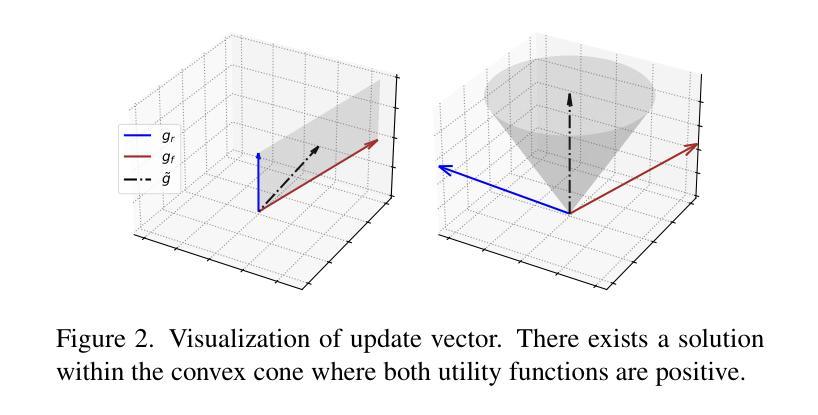
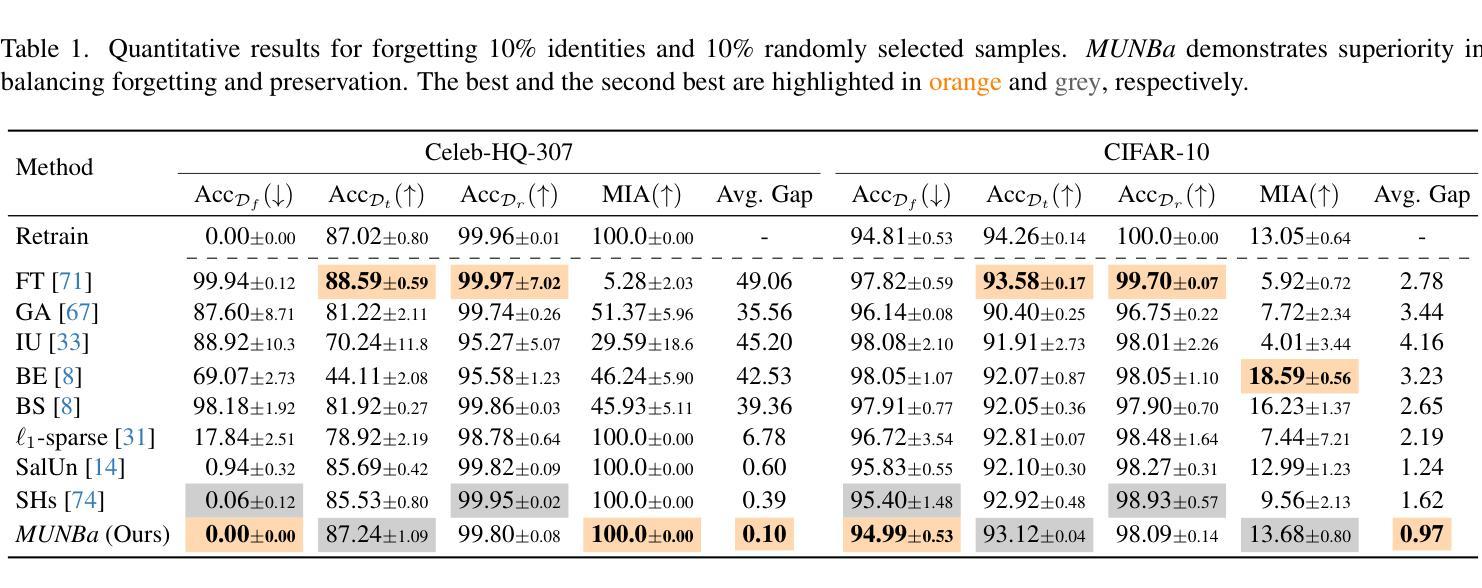
MUNBa: Machine Unlearning via Nash Bargaining
Authors:Jing Wu, Mehrtash Harandi
Machine Unlearning (MU) aims to selectively erase harmful behaviors from models while retaining the overall utility of the model. As a multi-task learning problem, MU involves balancing objectives related to forgetting specific concepts/data and preserving general performance. A naive integration of these forgetting and preserving objectives can lead to gradient conflicts and dominance, impeding MU algorithms from reaching optimal solutions. To address the gradient conflict and dominance issue, we reformulate MU as a two-player cooperative game, where the two players, namely, the forgetting player and the preservation player, contribute via their gradient proposals to maximize their overall gain and balance their contributions. To this end, inspired by the Nash bargaining theory, we derive a closed-form solution to guide the model toward the Pareto stationary point. Our formulation of MU guarantees an equilibrium solution, where any deviation from the final state would lead to a reduction in the overall objectives for both players, ensuring optimality in each objective. We evaluate our algorithm’s effectiveness on a diverse set of tasks across image classification and image generation. Extensive experiments with ResNet, vision-language model CLIP, and text-to-image diffusion models demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art MU algorithms, achieving a better trade-off between forgetting and preserving. Our results also highlight improvements in forgetting precision, preservation of generalization, and robustness against adversarial attacks.
机器学习反遗忘(MU)旨在从模型中剔除有害行为,同时保留模型的整体实用性。作为多任务学习问题,MU涉及平衡与遗忘特定概念/数据相关的目标和保持整体性能的目标。这些遗忘和保留目标的简单集成可能导致梯度冲突和主导,阻碍MU算法达到最优解。为了解决梯度冲突和主导问题,我们将MU重新构建为一个两玩家合作游戏,其中两个玩家分别是遗忘玩家和保留玩家,他们通过各自的梯度提案来最大化整体收益并平衡各自的贡献。为此,受到纳什谈判理论的启发,我们推导出了一个封闭形式的解决方案,以引导模型走向帕累托稳定点。我们对MU的公式化保证了均衡解,即任何偏离最终状态的行为都会导致整体目标减少,从而确保每个目标的优化。我们在图像分类和图像生成等任务上评估了算法的有效性。使用ResNet、视觉语言模型CLIP和文本到图像扩散模型的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的权衡,优于最先进的MU算法。我们的结果还凸显了遗忘精确度、保持泛化能力以及对抗攻击稳健性的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习模型中的机器遗忘(MU)旨在选择性删除模型中的有害行为,同时保留模型的总体效用。作为多任务学习问题,MU需要平衡忘记特定概念和保存整体性能的目标。为了解决梯度冲突和主导问题,我们将MU重新构建为一个双人合作游戏,包括遗忘玩家和保留玩家,他们通过梯度提案来最大化整体收益并平衡各自贡献。受纳什谈判理论的启发,我们推导出了一个封闭形式的解决方案来指导模型走向帕累托稳定点。我们的MU公式保证了均衡解,任何偏离最终状态都会导致双方总体目标减少,从而确保每个目标的优化。在图像分类和图像生成等多个任务上进行的实验证明,我们的算法在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的平衡,优于最新的MU算法。我们的结果还显示了提高遗忘精度、保持泛化能力和增强对对抗攻击的稳健性等优点。
Key Takeaways
- 机器遗忘(MU)旨在从机器学习模型中删除有害行为,同时保持模型的整体效用。
- MU作为多任务学习问题,需要平衡忘记特定概念和保持整体性能的目标。
- 梯度冲突和主导问题是MU面临的主要挑战。
- 将MU重新构建为双人合作游戏,包括遗忘玩家和保留玩家,以平衡各自贡献。
- 受纳什谈判理论启发,推导出了封闭形式的解决方案来指导模型走向帕累托稳定点。
- 实验证明,该算法在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的平衡,优于其他MU算法。
点此查看论文截图