⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
CoFi: A Fast Coarse-to-Fine Few-Shot Pipeline for Glomerular Basement Membrane Segmentation
Authors:Hongjin Fang, Daniel Reisenbüchler, Kenji Ikemura, Mert R. Sabuncu, Yihe Yang, Ruining Deng
Accurate segmentation of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in electron microscopy (EM) images is fundamental for quantifying membrane thickness and supporting the diagnosis of various kidney diseases. While supervised deep learning approaches achieve high segmentation accuracy, their reliance on extensive pixel-level annotation renders them impractical for clinical workflows. Few-shot learning can reduce this annotation burden but often struggles to capture the fine structural details necessary for GBM analysis. In this study, we introduce CoFi, a fast and efficient coarse-to-fine few-shot segmentation pipeline designed for GBM delineation in EM images. CoFi first trains a lightweight neural network using only three annotated images to produce an initial coarse segmentation mask. This mask is then automatically processed to generate high-quality point prompts with morphology-aware pruning, which are subsequently used to guide SAM in refining the segmentation. The proposed method achieved exceptional GBM segmentation performance, with a Dice coefficient of 74.54% and an inference speed of 1.9 FPS. We demonstrate that CoFi not only alleviates the annotation and computational burdens associated with conventional methods, but also achieves accurate and reliable segmentation results. The pipeline’s speed and annotation efficiency make it well-suited for research and hold strong potential for clinical applications in renal pathology. The pipeline is publicly available at: https://github.com/ddrrnn123/CoFi.
对电子显微镜(EM)图像中的肾小球基底膜(GBM)进行精确分割是量化膜厚度和支持各种肾脏疾病诊断的基础。虽然监督深度学习的方法可以实现高分割精度,但它们对大量像素级注释的依赖使它们不适用于临床工作流程。小样本学习可以减少注释工作量,但往往难以捕获用于GBM分析所需的结构细节。在这项研究中,我们介绍了CoFi,这是一个快速有效的从粗糙到精细的小样本分割管道,旨在用于EM图像中GBM的轮廓描绘。CoFi首先使用仅三个注释的图像训练一个轻量级神经网络,以产生初始的粗略分割掩膜。然后,该掩膜被自动处理以产生高质量的点提示,通过形态感知修剪,随后用于指导SAM进行分割细化。所提出的方法实现了出色的GBM分割性能,Dice系数为74.54%,推理速度为每秒1.9帧。我们证明了CoFi不仅减轻了与传统方法相关的注释和计算负担,而且实现了准确可靠的分割结果。该管道的速度和注释效率使其成为肾脏病理学研究和临床应用的强大潜力工具。管道可在以下网址公开访问:https://github.com/ddrrnn123/CoFi 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为CoFi的快速、高效的粗到细少数镜头分割管道,用于电子显微镜图像中的肾小球基底膜(GBM)分割。该方法使用仅三个标注图像训练轻量级神经网络,生成初始粗略分割掩膜,再通过形态感知修剪生成高质量点提示,引导SAM进行精细分割。该方法实现了GBM分割的高性能,Dice系数为74.54%,推理速度为1.9 FPS。CoFi不仅减轻了传统方法的标注和计算负担,还实现了准确可靠的分割结果,适合在肾病理学中研究和临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- CoFi是一种针对电子显微镜图像中肾小球基底膜(GBM)分割的粗到细少数镜头分割方法。
- 仅需三个标注图像,轻量级神经网络即可生成初始粗略分割掩膜。
- 自动处理初始掩膜以生成高质量点提示,通过形态感知修剪提高分割质量。
- CoFi使用SAM进行精细分割,实现高性能的GBM分割。
- CoFi的Dice系数为74.54%,推理速度为1.9 FPS。
- CoFi减轻了传统GBM分割方法的标注和计算负担。
点此查看论文截图








Group Fairness Meets the Black Box: Enabling Fair Algorithms on Closed LLMs via Post-Processing
Authors:Ruicheng Xian, Yuxuan Wan, Han Zhao
Instruction fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) enable a simple zero-shot or few-shot prompting paradigm, also known as in-context learning, for building prediction models. This convenience, combined with continued advances in LLM capability, has the potential to drive their adoption across a broad range of domains, including high-stakes applications where group fairness – preventing disparate impacts across demographic groups – is essential. The majority of existing approaches to enforcing group fairness on LLM-based classifiers rely on traditional fair algorithms applied via model fine-tuning or head-tuning on final-layer embeddings, but they are no longer applicable to closed-weight LLMs under the in-context learning setting, which include some of the most capable commercial models today, such as GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude. In this paper, we propose a framework for deriving fair classifiers from closed-weight LLMs via prompting: the LLM is treated as a feature extractor, and features are elicited from its probabilistic predictions (e.g., token log probabilities) using prompts strategically designed for the specified fairness criterion to obtain sufficient statistics for fair classification; a fair algorithm is then applied to these features to train a lightweight fair classifier in a post-hoc manner. Experiments on five datasets, including three tabular ones, demonstrate strong accuracy-fairness tradeoffs for the classifiers derived by our framework from both open-weight and closed-weight LLMs; in particular, our framework is data-efficient and outperforms fair classifiers trained on LLM embeddings (i.e., head-tuning) or from scratch on raw tabular features.
指令微调的大型语言模型(LLM)能够实现简单的零样本或少样本提示范式,也称为上下文学习,用于构建预测模型。这种便利结合LLM能力的持续进步,有可能推动其在广泛领域的应用,包括高风险应用,其中群体公平性——防止对不同群体的不同影响——至关重要。现有大多数基于LLM的分类器实施群体公平性的方法都依赖于通过模型微调或头调在最终层嵌入上应用传统的公平算法,但它们不再适用于采用上下文学习设置的固定权重LLM,其中包括目前一些功能最强大的商业模型,如GPT-4、双子座和Claude。在本文中,我们提出了一个通过提示从固定权重LLM派生公平分类器的框架:将LLM视为特征提取器,并使用针对特定公平性标准战略设计的提示来激发其概率预测(例如,令牌对数概率),以获得公平分类的充足统计数据;然后对这些特征应用公平算法,以事后方式训练轻量级公平分类器。在五个数据集上的实验,包括三个表格数据集,证明了我们的框架从公开权重和固定权重LLM派生的分类器在准确性公平性方面的强大权衡;特别是我们的框架数据效率较高,优于在LLM嵌入上训练的公平分类器(即头调)或从原始表格特征开始训练的公平分类器。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在零样本或少量样本提示框架下,大型语言模型(LLM)可以通过上下文学习进行预测模型构建。随着LLM能力的不断提升,其在多个领域的应用潜力日益显现,特别是在高风险的公平性要求严格的领域。然而,现有的基于LLM的分类器实现群体公平的方法主要依赖于传统的公平算法,这些算法不适用于封闭的LLM权重模型。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于提示的公平分类器派生框架,将LLM视为特征提取器,并使用针对特定公平标准设计的提示从概率预测中提取特征,以获得用于公平分类的充足统计数据;然后,在这些特征上应用公平算法以进行事后轻量级公平分类器的训练。实验结果表明,该框架在开放和封闭权重LLM上生成的分类器具有较强的精度公平权衡。特别是在数据效率方面,该框架优于基于LLM嵌入训练的公平分类器或从头开始在原始表格特征上训练的公平分类器。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)能够通过上下文学习实现预测模型构建,这种方法的便捷性有望推动其在多个领域的广泛应用。
- 在高风险且要求公平的领域中,对公平性维护的需求尤为关键。
- 当前在封闭权重的大型语言模型上实现群体公平的方法面临挑战。
- 本文提出了一种基于提示的公平分类器派生框架,适用于封闭权重的大型语言模型。
- 该框架将LLM视为特征提取器,并使用针对特定公平标准设计的提示来提取特征并进行分类。
- 实验结果表明该框架具有良好的精度和公平性权衡。
点此查看论文截图


Fine-Grained VLM Fine-tuning via Latent Hierarchical Adapter Learning
Authors:Yumiao Zhao, Bo Jiang, Yuhe Ding, Xiao Wang, Jin Tang, Bin Luo
Adapter-based approaches have garnered attention for fine-tuning pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on few-shot classification tasks. These methods strive to develop a lightweight module that better aligns visual and (category) textual representations, thereby enhancing performance on downstream few-shot learning tasks. However, existing adapters generally learn/align (category) textual-visual modalities via explicit spatial proximity in the underlying embedding space, which i) fails to capture the inherent one-to-many associations between categories and image samples and ii) struggles to establish accurate associations between the unknown categories and images. To address these issues, inspired by recent works on hyperbolic learning, we develop a novel Latent Hierarchical Adapter (LatHAdapter) for fine-tuning VLMs on downstream few-shot classification tasks. The core of LatHAdapter is to exploit the latent semantic hierarchy of downstream training data and employ it to provide richer, fine-grained guidance for the adapter learning process. Specifically, LatHAdapter first introduces some learnable `attribute’ prompts as the bridge to align categories and images. Then, it projects the categories, attribute prompts, and images within each batch in a hyperbolic space, and employs hierarchical regularization to learn the latent semantic hierarchy of them, thereby fully modeling the inherent one-to-many associations among categories, learnable attributes, and image samples. Extensive experiments on four challenging few-shot tasks show that the proposed LatHAdapter consistently outperforms many other fine-tuning approaches, particularly in adapting known classes and generalizing to unknown classes.
基于适配器的方法已经引起了在少量样本分类任务上微调预训练好的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的关注。这些方法致力于开发一个轻量级的模块,以更好地对齐视觉和(类别)文本表示,从而提高下游少量样本学习任务上的性能。然而,现有的适配器通常通过底层嵌入空间中的明确空间邻近关系来学习/对齐(类别)文本视觉模式,这i)无法捕获类别和图像样本之间固有的多对一关联,并且ii)在建立未知类别和图像之间的准确关联方面表现困难。为了解决这些问题,我们受到最近关于双曲学习的研究的启发,开发了一种用于下游少量样本分类任务上微调VLMs的新型潜在层次适配器(LatHAdapter)。LatHAdapter的核心是利用下游训练数据的潜在语义层次结构,并对其进行利用,为适配器的学习过程提供更丰富、更精细的指导。具体来说,LatHAdapter首先引入一些可学习的“属性”提示作为桥梁来对齐类别和图像。然后,它在双曲空间中投影每个批次中的类别、属性提示和图像,并采用层次正则化来学习它们的潜在语义层次结构,从而充分建模类别、可学习属性和图像样本之间的固有的一对多关联。在四个具有挑战性的少量样本任务上的大量实验表明,所提出的LatHAdapter在许多其他微调方法上表现更优,特别是在适应已知类和泛化到未知类上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注于利用基于适配器的策略对预训练的视觉语言模型进行微调,以解决少量样本分类任务。文中指出现有适配器通过明确的空间邻近在底层嵌入空间对齐文本视觉模式的方法存在局限性。为此,作者受超球面学习的启发,提出了新型的潜在层次适配器(LatHAdapter)。它通过发掘下游训练数据的潜在语义层次,为适配器的学习过程提供更丰富的精细指导。LatHAdapter通过引入可学习的属性提示来对齐类别和图像,并在超球面空间中投影它们,利用层次正则化来学习潜在语义层次结构。实验表明,LatHAdapter在多个具有挑战性的少量样本任务上表现优异,尤其在适应已知类和泛化到未知类上。
Key Takeaways
- 适配器方法被用于微调预训练的视觉语言模型,以应对少量样本分类任务。
- 现有适配器主要通过明确的空间邻近在嵌入空间中对齐文本和视觉模式,但这种方法存在局限性。
- LatHAdapter受超球面学习启发,能发掘下游训练数据的潜在语义层次。
- LatHAdapter通过引入可学习的属性提示,对齐类别和图像。
- 在超球面空间中投影类别、属性提示和图像,并利用层次正则化学习它们的潜在语义结构。
- LatHAdapter能充分建模类别、学习属性和图像样本之间的固有的一对多关联。
点此查看论文截图


Are Large Pre-trained Vision Language Models Effective Construction Safety Inspectors?
Authors:Xuezheng Chen, Zhengbo Zou
Construction safety inspections typically involve a human inspector identifying safety concerns on-site. With the rise of powerful Vision Language Models (VLMs), researchers are exploring their use for tasks such as detecting safety rule violations from on-site images. However, there is a lack of open datasets to comprehensively evaluate and further fine-tune VLMs in construction safety inspection. Current applications of VLMs use small, supervised datasets, limiting their applicability in tasks they are not directly trained for. In this paper, we propose the ConstructionSite 10k, featuring 10,000 construction site images with annotations for three inter-connected tasks, including image captioning, safety rule violation visual question answering (VQA), and construction element visual grounding. Our subsequent evaluation of current state-of-the-art large pre-trained VLMs shows notable generalization abilities in zero-shot and few-shot settings, while additional training is needed to make them applicable to actual construction sites. This dataset allows researchers to train and evaluate their own VLMs with new architectures and techniques, providing a valuable benchmark for construction safety inspection.
施工安全检测通常涉及人工检测人员在现场识别安全隐患。随着强大的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的兴起,研究人员正在探索其用于检测现场图像中的安全违规等任务。然而,缺乏开放数据集来全面评估和调整施工安全检查中的VLMs。目前VLMs的应用使用的是小规模、有监督的数据集,限制了其在非直接训练任务中的应用。在本文中,我们提出了“ConstructionSite 10k”数据集,包含1万张施工现场图像,针对三个相互关联的任务进行标注,包括图像描述、安全违规视觉问答(VQA)和施工元素视觉定位。我们对当前最先进的预训练大型VLMs的后续评估显示,它们在零样本和少样本环境中具有显著的泛化能力,但需要额外的训练才能适用于实际施工现场。该数据集允许研究人员使用新的架构和技术训练和评估他们自己的VLMs,为施工安全检测提供了一个有价值的基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于强大的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的崛起,研究人员开始探索其在建筑安全检测领域的应用,如从现场图像中检测安全违规。然而,缺乏开放数据集以全面评估和在建筑安全检测中进一步微调VLMs。本文提出了“ConstructionSite 10k”数据集,包含1万张建筑工地图像,针对三项互联任务进行标注,包括图像描述、安全违规视觉问答(VQA)和建筑元素视觉定位。对当前最先进的预训练VLMs的评估表明,它们在零样本和少样本环境中具有显著的泛化能力,但需要额外的训练才能适用于实际建筑工地。此数据集为研究人员使用新架构和技术训练和评估自己的VLMs提供了宝贵的基准测试,为建筑安全检测领域的发展提供了重要支持。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs正在被探索用于建筑安全检测任务,如从现场图像中检测安全违规。
- 缺乏开放数据集以全面评估和在建筑安全检测中微调VLMs。
- “ConstructionSite 10k”数据集包含1万张建筑工地图像,针对三项任务进行标注。
- 当前先进的预训练VLMs在零样本和少样本环境中具有泛化能力。
- 需要额外的训练才能使VLMs适用于实际建筑工地环境。
- 此数据集为研究人员提供了训练和评估VLMs的基准测试。
点此查看论文截图



Rule2Text: A Framework for Generating and Evaluating Natural Language Explanations of Knowledge Graph Rules
Authors:Nasim Shirvani-Mahdavi, Chengkai Li
Knowledge graphs (KGs) can be enhanced through rule mining; however, the resulting logical rules are often difficult for humans to interpret due to their inherent complexity and the idiosyncratic labeling conventions of individual KGs. This work presents Rule2Text, a comprehensive framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate natural language explanations for mined logical rules, thereby improving KG accessibility and usability. We conduct extensive experiments using multiple datasets, including Freebase variants (FB-CVT-REV, FB+CVT-REV, and FB15k-237) as well as the ogbl-biokg dataset, with rules mined using AMIE 3.5.1. We systematically evaluate several LLMs across a comprehensive range of prompting strategies, including zero-shot, few-shot, variable type incorporation, and Chain-of-Thought reasoning. To systematically assess models’ performance, we conduct a human evaluation of generated explanations on correctness and clarity. To address evaluation scalability, we develop and validate an LLM-as-a-judge framework that demonstrates strong agreement with human evaluators. Leveraging the best-performing model (Gemini 2.0 Flash), LLM judge, and human-in-the-loop feedback, we construct high-quality ground truth datasets, which we use to fine-tune the open-source Zephyr model. Our results demonstrate significant improvements in explanation quality after fine-tuning, with particularly strong gains in the domain-specific dataset. Additionally, we integrate a type inference module to support KGs lacking explicit type information. All code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/idirlab/KGRule2NL.
知识图谱(KG)可以通过规则挖掘进行增强;然而,由于逻辑规则的内在复杂性以及各个知识图谱特有的标签约定,所得的逻辑规则往往难以被人类解读。本研究提出了Rule2Text,这是一个全面的框架,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)来生成对挖掘到的逻辑规则的自然语言解释,从而提高知识图谱的可用性和可访问性。我们使用了多个数据集进行了广泛实验,包括Freebase的各种变体(FB-CVT-REV、FB+CVT-REV和FB15k-237),以及ogbl-biokg数据集,并使用AMIE 3.5.1进行规则挖掘。我们系统地评估了几种LLM,涵盖了多种提示策略,包括零样本、少样本、变量类型融合和链式思维推理。为了系统地评估模型的表现,我们对生成的解释进行了正确性和清晰度的人工评估。为了解决评估的可扩展性问题,我们开发并验证了一个LLM法官框架,该框架与人类评估者之间表现出了强烈的共识。利用表现最佳的模型(Gemini 2.0 Flash)、LLM法官和人类实时反馈,我们构建了高质量的真实数据集,用于微调开源的Zephyr模型。我们的结果表明,在微调后,解释质量得到了显著提高,特别是在特定领域的数据集上获得了显著的收益。此外,我们集成了一个类型推断模块,以支持缺乏显式类型信息的知识图谱。所有代码和数据均可在https://github.com/idirlab/KGRule2NL公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2507.23740
摘要
知识图谱可以通过规则挖掘进行增强,但结果逻辑规则对人类来说难以解读,因为它们的复杂性以及各个知识图谱特有的标签约定。本研究提出Rule2Text框架,利用大型语言模型生成自然语言的解释,为挖掘的逻辑规则提供说明,从而提高知识图谱的可用性和可访问性。我们在多个数据集上进行广泛实验,包括Freebase变体以及ogbl-biokg数据集,并使用AMIE 3.5.1挖掘规则。我们系统地评估了多种语言模型在各种提示策略下的表现,包括零样本、少样本、变量类型融入和链式思维推理。为了系统地评估模型性能,我们对生成的解释进行了正确性评估清晰度的人类评估。为了解决评估的可扩展性问题,我们开发并验证了一个语言模型作为法官的框架,与人类评估者之间达成强一致性。利用表现最佳的模型(Gemini 2.0 Flash)、语言模型法官和人类循环反馈,我们构建了高质量的真实数据集,用于微调开源Zephyr模型。结果显示,在微调后,解释质量显著提高,特别是在特定领域的数据集上取得了显著的进步。此外,我们集成了一个类型推断模块,以支持缺乏显式类型信息的知识图谱。所有代码和数据可在链接找到。
关键见解
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成自然语言的解释,以提高知识图谱(KGs)的易用性和可访问性。
- 在多种数据集上进行广泛实验,包括Freebase变体以及ogbl-biokg数据集。
- 系统地评估了多种语言模型在各种提示策略下的表现。
- 开发了语言模型作为法官的框架,以进行模型性能评估并验证与人类评估者的一致性。
- 利用最佳模型构建高质量真实数据集,用于微调开源Zephyr模型。
- 在微调后显著提高了解释质量,特别是在特定领域的数据集上取得了显著进步。
点此查看论文截图




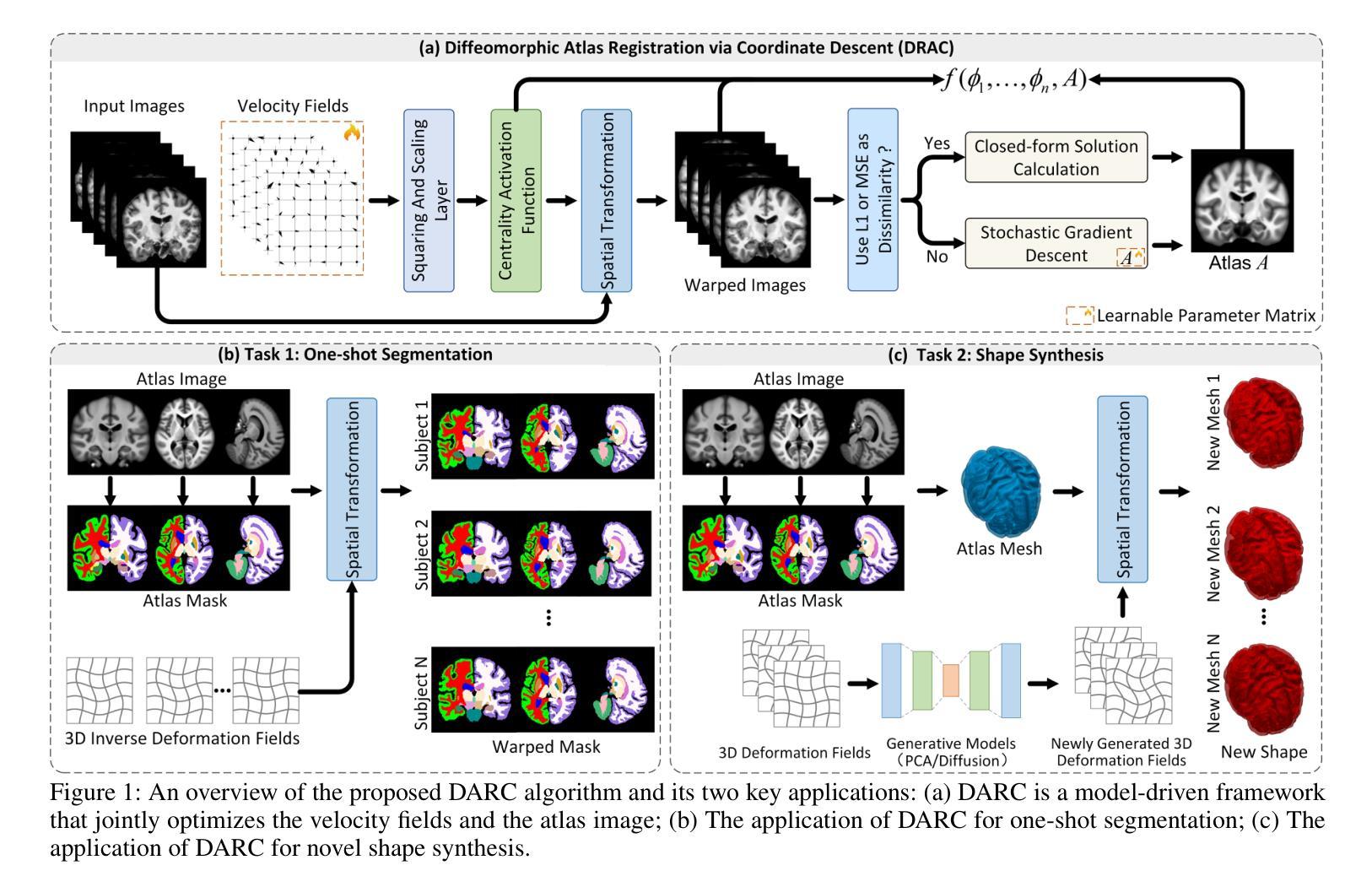
An Efficient Model-Driven Groupwise Approach for Atlas Construction
Authors:Ziwei Zou, Bei Zou, Xiaoyan Kui, Wenqi Lu, Haoran Dou, Arezoo Zakeri, Timothy Cootes, Alejandro F Frangi, Jinming Duan
Atlas construction is fundamental to medical image analysis, offering a standardized spatial reference for tasks such as population-level anatomical modeling. While data-driven registration methods have recently shown promise in pairwise settings, their reliance on large training datasets, limited generalizability, and lack of true inference phases in groupwise contexts hinder their practical use. In contrast, model-driven methods offer training-free, theoretically grounded, and data-efficient alternatives, though they often face scalability and optimization challenges when applied to large 3D datasets. In this work, we introduce DARC (Diffeomorphic Atlas Registration via Coordinate descent), a novel model-driven groupwise registration framework for atlas construction. DARC supports a broad range of image dissimilarity metrics and efficiently handles arbitrary numbers of 3D images without incurring GPU memory issues. Through a coordinate descent strategy and a centrality-enforcing activation function, DARC produces unbiased, diffeomorphic atlases with high anatomical fidelity. Beyond atlas construction, we demonstrate two key applications: (1) One-shot segmentation, where labels annotated only on the atlas are propagated to subjects via inverse deformations, outperforming state-of-the-art few-shot methods; and (2) shape synthesis, where new anatomical variants are generated by warping the atlas mesh using synthesized diffeomorphic deformation fields. Overall, DARC offers a flexible, generalizable, and resource-efficient framework for atlas construction and applications.
医学图像分析中,图谱构建是一项基础工作,它为群体层面的解剖学建模等任务提供了一个标准化的空间参考。虽然数据驱动型的注册方法在近期的配对设置中显示出了一定的潜力,但它们对大型训练数据集的依赖、有限的通用性以及群组环境下的真实推理阶段的缺失,阻碍了它们的实际应用。相比之下,模型驱动的方法提供了免训练、理论扎实和数据高效的选择,但在应用于大型3D数据集时,它们常常面临可扩展性和优化挑战。在这项工作中,我们介绍了DARC(基于坐标下降的微分同胚图谱注册),这是一种用于图谱构建的新型模型驱动群组注册框架。DARC支持广泛的图像不相似度度量,并能高效地处理任意数量的3D图像,而不会引发GPU内存问题。通过坐标下降策略和中心强制激活函数,DARC产生无偏见、微分同胚的图谱,具有高解剖保真度。除了图谱构建之外,我们还展示了两个关键应用:(1)单次分割,其中仅在图谱上标注的标签通过反向变形传播到主体上,超越了最新的少镜头方法;(2)形状合成,通过利用合成的微分同胚变形场对图谱网格进行变形,生成新的解剖变体。总体而言,DARC为图谱构建和应用提供了一个灵活、通用和资源高效的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了DARC(基于坐标下降的微分形态学图谱注册方法),这是一种用于图谱构建的新型模型驱动群组注册框架。DARC支持广泛的图像差异度量,并能有效地处理任意数量的3D图像,而不会导致GPU内存问题。通过坐标下降策略和中心强制激活函数,DARC能够产生具有高精度解剖结构的不偏不倚的微分图谱。此外,DARC还支持图谱构建之外的两个关键应用:一是单张图像分割,即仅通过图谱进行标注标签的传播到目标图像,超越了最先进的少量样本方法;二是形状合成,通过合成微分形态学变形场扭曲图谱网格生成新的解剖变体。总的来说,DARC提供了一个灵活、通用且资源高效的图谱构建与应用框架。
Key Takeaways
- DARC是一种用于图谱构建的模型驱动群组注册框架,适用于任意数量的3D图像。
- DARC支持广泛的图像差异度量,提高了注册的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 通过坐标下降策略和中心强制激活函数,DARC能生成不偏不倚、具有高解剖真实性的微分图谱。
- DARC在图谱构建应用上表现出优秀的性能,包括单张图像分割和形状合成。
- 单张图像分割应用实现了仅通过图谱进行标注标签的传播到目标图像,性能超越现有少量样本方法。
- 形状合成应用通过扭曲图谱网格生成新的解剖变体,展示了DARC的创造性和灵活性。
点此查看论文截图




SemPT: Semantic Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Xiao Shi, Yangjun Ou, Zhenzhong Chen
Visual transfer learning for unseen categories presents an active research topic yet a challenging task, due to the inherent conflict between preserving category-specific representations and acquiring transferable knowledge. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) pre-trained on large amounts of image-text pairs offer a promising solution. However, existing prompt tuning methods rely on sparse category labels or disparate LLM-generated descriptions, which fragment knowledge representation and hinder transferability. To address this limitation, we introduce Semantic Prompt Tuning (SemPT), a novel framework that tackles the generalization challenge by leveraging shared attribute-level knowledge across categories. Specifically, SemPT adopts a two-step prompting strategy to guide LLM in extracting shared visual attributes and generating attribute-level descriptions, capturing transferable semantic cues beyond labels while ensuring coherent structure. Then, visually guided weighting is applied to the embeddings of attribute-level descriptions to reduce noise from irrelevant attributes and enhance the text embeddings. Additionally, image embeddings are jointly aligned with both label and attribute-enhanced text embeddings, balancing discrimination for seen categories and transferability to unseen ones. Considering the availability of category exposure, our inference dynamically selects between standard label embeddings for seen categories and attribute-enhanced embeddings for unseen ones to ensure effective adaptation. Extensive experiments on 15 benchmark datasets demonstrate that SemPT achieves state-of-the-art performance across various settings, including base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset transfer, cross-domain transfer, and few-shot learning.
视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个热门且具挑战性的课题,因为保持特定类别的表示和获取可迁移知识之间存在内在冲突。预训练在大量图像文本对上的视觉语言模型(VLMs)提供了一个有前景的解决方案。然而,现有的提示调整方法依赖于稀疏的类别标签或分散的LLM生成描述,这导致知识表示碎片化并阻碍知识的迁移。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了语义提示调整(SemPT)这一新框架,通过利用类别间的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。具体来说,SemPT采用两步提示策略来指导LLM提取共享的视觉属性并生成属性级描述,捕捉超越标签的可转移语义线索,同时确保连贯的结构。然后,对属性级描述的嵌入应用视觉引导加权,以减少来自无关属性的噪声并增强文本嵌入。此外,图像嵌入与标签和属性增强文本嵌入共同对齐,平衡对可见类别的区分度和对未见类别的可迁移性。考虑到类别的可见性,我们的推理过程会动态选择在可见类别和不可见类别之间使用标准的标签嵌入和属性增强嵌入,以确保有效的适应。在15个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,SemPT在各种设置下均达到了最先进的性能,包括从基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集迁移、跨域迁移和小样本学习。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个活跃的研究课题,但也是一个具有挑战性的任务。由于保持特定类别的表示和获取可迁移知识之间的内在冲突,使得该任务更具挑战性。预训练在大量图像文本对上的视觉语言模型(VLMs)提供了一个有前景的解决方案。然而,现有的提示调整方法依赖于稀疏的类别标签或分散的LLM生成描述,这破坏了知识表示并阻碍了可迁移性。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了语义提示调整(SemPT)这一新框架,通过利用类别之间的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉迁移学习对于未见类别是一个具有挑战性的任务,因为需要平衡保持类别特异性表示和获取可迁移知识。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在解决这一挑战方面提供了有前景的解决方案。
- 现有提示调整方法存在局限性,依赖于稀疏类别标签或LLM生成的描述,这破坏了知识表示并阻碍了可迁移性。
- SemPT框架通过利用类别之间的共享属性级知识来解决泛化挑战。
- SemPT采用两步提示策略,引导LLM提取共享视觉属性和生成属性级描述,捕捉可迁移的语义线索。
- SemPT通过视觉引导加权减少了来自无关属性的噪声,增强了文本嵌入。
点此查看论文截图




Increasing the Utility of Synthetic Images through Chamfer Guidance
Authors:Nicola Dall’Asen, Xiaofeng Zhang, Reyhane Askari Hemmat, Melissa Hall, Jakob Verbeek, Adriana Romero-Soriano, Michal Drozdzal
Conditional image generative models hold considerable promise to produce infinite amounts of synthetic training data. Yet, recent progress in generation quality has come at the expense of generation diversity, limiting the utility of these models as a source of synthetic training data. Although guidance-based approaches have been introduced to improve the utility of generated data by focusing on quality or diversity, the (implicit or explicit) utility functions oftentimes disregard the potential distribution shift between synthetic and real data. In this work, we introduce Chamfer Guidance: a training-free guidance approach which leverages a handful of real exemplar images to characterize the quality and diversity of synthetic data. We show that by leveraging the proposed Chamfer Guidance, we can boost the diversity of the generations w.r.t. a dataset of real images while maintaining or improving the generation quality on ImageNet-1k and standard geo-diversity benchmarks. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art few-shot performance with as little as 2 exemplar real images, obtaining 96.4% in terms of precision, and 86.4% in terms of distributional coverage, which increase to 97.5% and 92.7%, respectively, when using 32 real images. We showcase the benefits of the Chamfer Guidance generation by training downstream image classifiers on synthetic data, achieving accuracy boost of up to 15% for in-distribution over the baselines, and up to 16% in out-of-distribution. Furthermore, our approach does not require using the unconditional model, and thus obtains a 31% reduction in FLOPs w.r.t. classifier-free-guidance-based approaches at sampling time.
条件图像生成模型具有产生无限合成训练数据的巨大潜力。然而,生成质量方面的最新进展是以牺牲生成多样性为代价的,这限制了这些模型作为合成训练数据来源的实用性。虽然基于引导的方法已经被引入,通过关注质量或多样性来提高生成数据的实用性,但(隐式或显式)效用函数通常忽略了合成数据和真实数据之间潜在分布差异。在这项工作中,我们引入了Chamfer Guidance:一种无需训练的引导方法,它利用少量真实示例图像来表征合成数据的质量和多样性。我们表明,通过利用提出的Chamfer Guidance,我们可以在针对真实图像数据集生成时提高生成的多样性,同时保持在ImageNet-1k和标准地理多样性基准测试集上生成质量的维持或提高。我们的方法使用仅2张真实示例图像即可实现最先进的性能,在精确度方面达到96.4%,在分布覆盖方面达到86.4%,在使用32张真实图像时,这些数字分别提高到97.5%和92.7%。我们通过使用合成数据训练下游图像分类器来展示Chamfer Guidance生成的优势,与基准相比,在内部分布上提高了高达15%的准确率,在外部分布上提高了高达16%的准确率。此外,我们的方法不需要使用无条件模型,因此在采样时间方面与基于无分类器引导的方法相比,实现了31%的FLOPs减少。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Chamfer Guidance的方法,这是一种无需训练的新型指导方法,它通过利用少量真实示例图像来表征合成数据的质量和多样性。该方法能够在提高生成图像多样性的同时,维持或提高生成图像的质量。在ImageNet-1k和地理多样性标准基准测试中,使用仅两个示例真实图像即可实现最先进的性能。此外,本文还展示了Chamfer Guidance在训练下游图像分类器方面的优势,通过合成数据实现了高达15%的准确率提升。此方法无需使用无条件模型,因此在采样时与基于分类器免费的指导方法相比,实现了31%的FLOPs减少。
Key Takeaways
- Chamfer Guidance是一种新型的无训练指导方法,旨在提高合成数据的生成质量和多样性。
- 该方法利用少量真实示例图像来表征合成数据的质量和多样性。
- Chamfer Guidance在ImageNet-1k和地理多样性标准基准测试中实现了先进的性能。
- 通过在下游图像分类器中使用合成数据,Chamfer Guidance实现了显著的准确率提升。
- 与其他方法相比,Chamfer Guidance无需使用无条件模型,因此在采样时效率更高。
- Chamfer Guidance在采样时实现了显著的FLOPs减少,与基于分类器免费的指导方法相比,减少了31%。
- Chamfer Guidance具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在需要高质量合成数据的领域,如图像分类、图像生成等。
点此查看论文截图



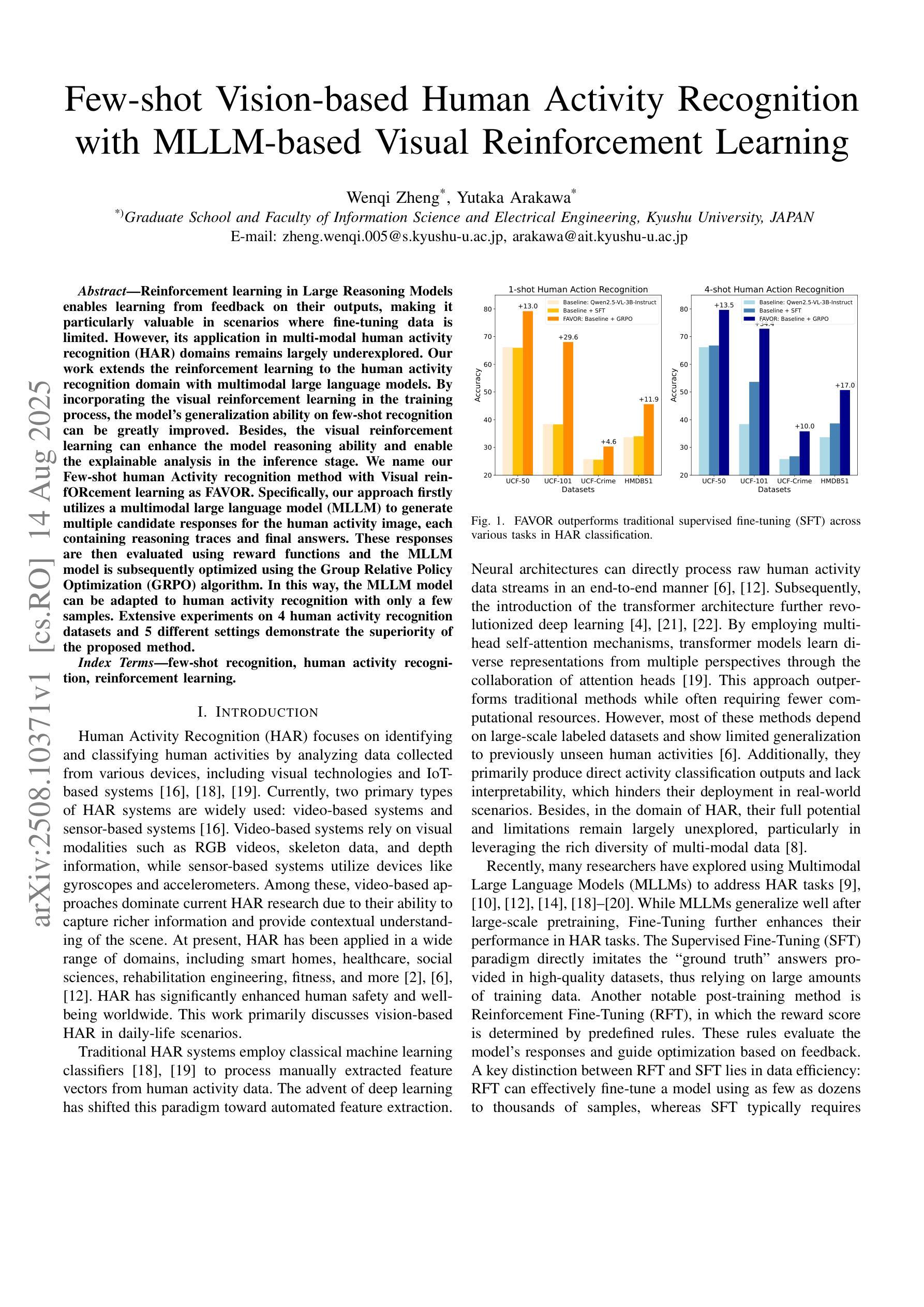
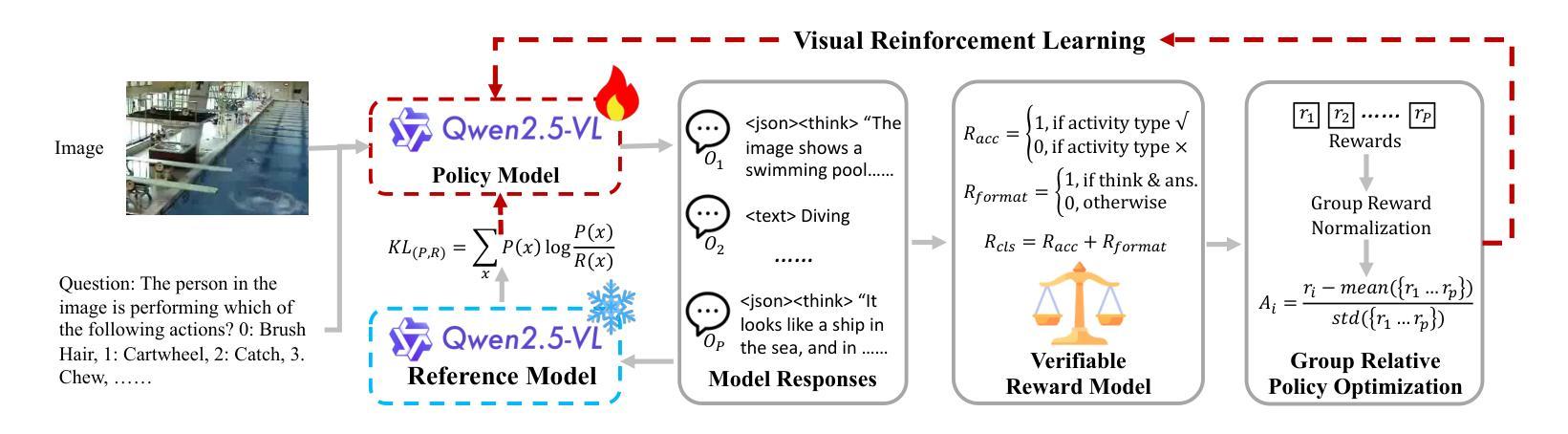
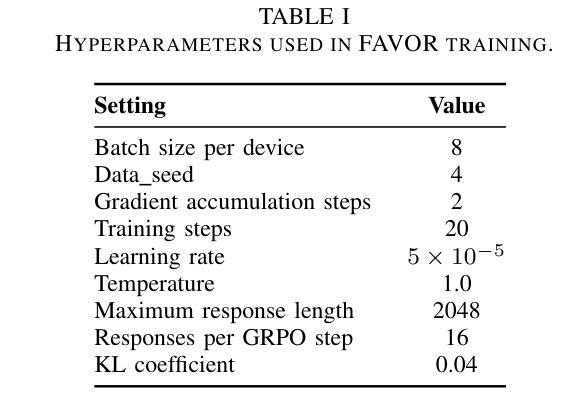
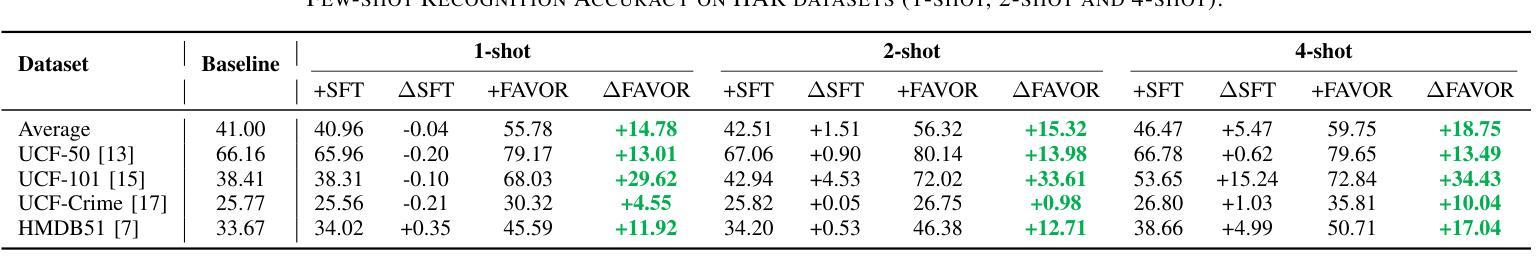
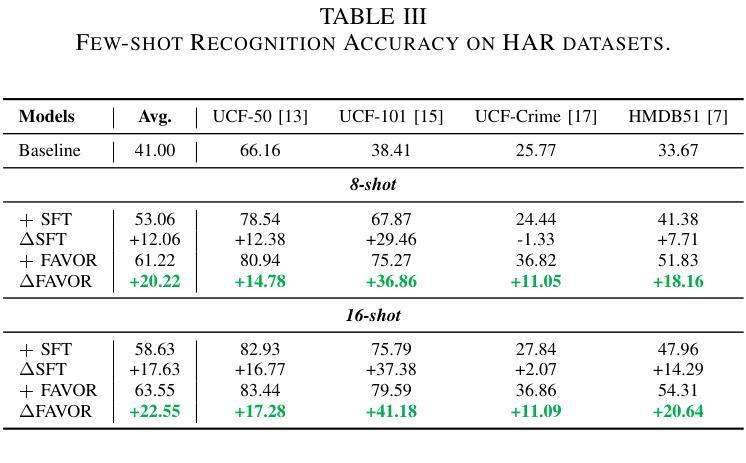
Few-shot Vision-based Human Activity Recognition with MLLM-based Visual Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wenqi Zheng, Yutaka Arakawa
Reinforcement learning in large reasoning models enables learning from feedback on their outputs, making it particularly valuable in scenarios where fine-tuning data is limited. However, its application in multi-modal human activity recognition (HAR) domains remains largely underexplored. Our work extends reinforcement learning to the human activity recognition domain with multimodal large language models. By incorporating visual reinforcement learning in the training process, the model’s generalization ability on few-shot recognition can be greatly improved. Additionally, visual reinforcement learning can enhance the model’s reasoning ability and enable explainable analysis in the inference stage. We name our few-shot human activity recognition method with visual reinforcement learning FAVOR. Specifically, our approach first utilizes a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to generate multiple candidate responses for the human activity image, each containing reasoning traces and final answers. These responses are then evaluated using reward functions, and the MLLM model is subsequently optimized using the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm. In this way, the MLLM model can be adapted to human activity recognition with only a few samples. Extensive experiments on four human activity recognition datasets and five different settings demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
强化学习在大型推理模型中的应用使得模型能够从其输出的反馈中学习,这在精细调整数据有限的场景中尤其有价值。然而,其在多模态人类活动识别(HAR)领域的应用仍被大大忽视。我们的工作将强化学习扩展到人类活动识别领域,采用多模态大型语言模型。通过在训练过程中融入视觉强化学习,可以极大地提高模型在少量样本识别上的泛化能力。此外,视觉强化学习还可以增强模型的推理能力,并在推理阶段实现可解释性分析。我们将带有视觉强化学习的少量人类活动识别方法命名为FAVOR。具体来说,我们的方法首先利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)为人体活动图像生成多个候选响应,每个响应都包含推理轨迹和最终答案。然后使用奖励函数对这些响应进行评估,随后使用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法对MLLM模型进行优化。通过这种方式,MLLM模型可以适应仅使用少量样本的人类活动识别。在四个人类活动识别数据集和五种不同设置上的大量实验证明了所提出方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习可从输出反馈中学习,在数据有限的情况下特别有价值。本文将强化学习扩展到人类活动识别领域,结合多模态大型语言模型,通过视觉强化学习提高模型的泛化能力和推理能力。命名为FAVOR的方法利用多模态大型语言模型生成多个活动图像候选响应,使用奖励函数评估并利用群体相对策略优化算法优化模型。在仅有少量样本的情况下,该模型可适应人类活动识别。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习能够从输出反馈中学习,在数据有限的情况下具有特别价值。
- 本文将强化学习扩展到人类活动识别领域。
- 结合多模态大型语言模型,通过视觉强化学习提高模型的泛化能力。
- 视觉强化学习能够增强模型的推理能力,并在推理阶段实现可解释性分析。
- 本文提出的少样本人类活动识别方法命名为FAVOR。
- FAVOR方法利用多模态大型语言模型生成多个候选响应,并使用奖励函数评估。
点此查看论文截图



Improving Generative Cross-lingual Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis with Constrained Decoding
Authors:Jakub Šmíd, Pavel Přibáň, Pavel Král
While aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) has made substantial progress, challenges remain for low-resource languages, which are often overlooked in favour of English. Current cross-lingual ABSA approaches focus on limited, less complex tasks and often rely on external translation tools. This paper introduces a novel approach using constrained decoding with sequence-to-sequence models, eliminating the need for unreliable translation tools and improving cross-lingual performance by 5% on average for the most complex task. The proposed method also supports multi-tasking, which enables solving multiple ABSA tasks with a single model, with constrained decoding boosting results by more than 10%. We evaluate our approach across seven languages and six ABSA tasks, surpassing state-of-the-art methods and setting new benchmarks for previously unexplored tasks. Additionally, we assess large language models (LLMs) in zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuning scenarios. While LLMs perform poorly in zero-shot and few-shot settings, fine-tuning achieves competitive results compared to smaller multilingual models, albeit at the cost of longer training and inference times. We provide practical recommendations for real-world applications, enhancing the understanding of cross-lingual ABSA methodologies. This study offers valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of cross-lingual ABSA approaches, advancing the state-of-the-art in this challenging research domain.
基于方面的情感分析(ABSA)虽然取得了重大进展,但对于资源匮乏的语言来说,仍然面临挑战。通常这些语言会被忽略而优先选择英语。当前的跨语言ABSA方法主要集中在有限且不太复杂的任务上,并且经常依赖外部翻译工具。本文介绍了一种使用序列到序列模型的约束解码的新方法,该方法消除了对不可靠翻译工具的依赖,并在最复杂的任务上平均提高了5%的跨语言性能。所提出的方法还支持多任务处理,能够使用一个模型解决多个ABSA任务,约束解码将结果提高了超过10%。我们对七种语言和六个ABSA任务评估了我们的方法,超越了最新方法并设立了以前未探索任务的新基准。此外,我们还在零样本、少样本和微调情况下评估了大型语言模型(LLMs)。虽然LLMs在零样本和少样本设置中的表现不佳,但微调实现了与较小的多语言模型相当的结果,尽管需要更长的训练和推理时间。我们为实际应用提供了实际建议,增强了跨语言ABSA方法的理解。本研究深入探讨了跨语言ABSA方法的优缺点,为该挑战领域的研究提供了先进的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
基于序列到序列模型的约束解码新方法,无需依赖不可靠的翻译工具,提高了跨语言方面的情感分析性能。该方法支持多任务处理,并在七种语言和六个情感分析任务上超越现有方法,设置新的基准。同时评估了大型语言模型在不同场景下的表现,提供实际应用的建议。
Key Takeaways:
- 引入了一种新型约束解码方法,适用于跨语言的方面情感分析(ABSA)。
- 方法无需依赖外部翻译工具,提高了跨语言性能。
- 支持多任务处理,能在多个ABSA任务上取得良好表现。
- 在七个语言和六个ABSA任务上的性能超越现有方法。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本、少样本场景下的表现不佳,但在微调后结果具有竞争力。
- 提供了关于跨语言ABSA方法在实际应用中的建议。
点此查看论文截图


SynBrain: Enhancing Visual-to-fMRI Synthesis via Probabilistic Representation Learning
Authors:Weijian Mai, Jiamin Wu, Yu Zhu, Zhouheng Yao, Dongzhan Zhou, Andrew F. Luo, Qihao Zheng, Wanli Ouyang, Chunfeng Song
Deciphering how visual stimuli are transformed into cortical responses is a fundamental challenge in computational neuroscience. This visual-to-neural mapping is inherently a one-to-many relationship, as identical visual inputs reliably evoke variable hemodynamic responses across trials, contexts, and subjects. However, existing deterministic methods struggle to simultaneously model this biological variability while capturing the underlying functional consistency that encodes stimulus information. To address these limitations, we propose SynBrain, a generative framework that simulates the transformation from visual semantics to neural responses in a probabilistic and biologically interpretable manner. SynBrain introduces two key components: (i) BrainVAE models neural representations as continuous probability distributions via probabilistic learning while maintaining functional consistency through visual semantic constraints; (ii) A Semantic-to-Neural Mapper acts as a semantic transmission pathway, projecting visual semantics into the neural response manifold to facilitate high-fidelity fMRI synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that SynBrain surpasses state-of-the-art methods in subject-specific visual-to-fMRI encoding performance. Furthermore, SynBrain adapts efficiently to new subjects with few-shot data and synthesizes high-quality fMRI signals that are effective in improving data-limited fMRI-to-image decoding performance. Beyond that, SynBrain reveals functional consistency across trials and subjects, with synthesized signals capturing interpretable patterns shaped by biological neural variability. The code will be made publicly available.
解析视觉刺激如何转化为皮层反应是计算神经科学中的一项基本挑战。这种视觉到神经的映射本质上是一种一对应多的关系,因为相同的视觉输入在不同的试验、情境和受试者中可靠地引发了可变的血流动力学反应。然而,现有的确定性方法很难同时模拟这种生物变异性和编码刺激信息的潜在功能一致性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SynBrain,这是一个生成性框架,以概率和生物学上可解释的方式模拟从视觉语义到神经反应的转变。SynBrain有两个关键组成部分:(i)BrainVAE通过概率学习将神经表征建模为连续概率分布,同时通过视觉语义约束保持功能一致性;(ii)语义到神经映射器充当语义传输途径,将视觉语义投射到神经响应流形,以促进高保真度fMRI合成。实验结果表明,SynBrain在特定受试者的视觉到fMRI编码性能方面超越了最新方法。此外,SynBrain能够高效适应新的受试者并处理少量数据,合成高质量的fMRI信号,有效提高数据有限的fMRI到图像解码性能。除此之外,SynBrain揭示了试验和受试者之间的功能一致性,合成的信号捕捉到了由生物神经变异性塑造的可解释模式。代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为SynBrain的生成框架,以概率和可生物解读的方式模拟视觉语义到神经响应的转化。该框架包括BrainVAE和语义到神经映射器两个关键组件,能够在保持功能一致性的同时模拟神经表示的连续概率分布,并投影视觉语义到神经响应流形以合成高保真fMRI信号。实验结果显示,SynBrain在特定的视觉到fMRI编码性能上超越了现有方法,并能有效地适应新的受试者进行少样本数据合成高质量fMRI信号。此外,SynBrain揭示了试验和受试者之间的功能一致性,合成的信号捕捉到了由生物神经变异塑造的可解释模式。
Key Takeaways
- SynBrain是一个生成框架,用于模拟视觉语义到神经响应的转化,以概率和可生物解读的方式呈现这一转化过程。
- 该框架包括BrainVAE和语义到神经映射器两个关键组件,其中BrainVAE能够模拟神经表示的连续概率分布,语义到神经映射器则扮演语义传输通道的角色。
- SynBrain能够在保持功能一致性的同时模拟生物变异。
- 实验证明,SynBrain在视觉到fMRI编码性能上超越现有方法,尤其在新受试者的少样本数据上表现出高效的适应性。
- SynBrain能合成高质量的fMRI信号,并用于提高数据有限时的fMRI到图像解码性能。
- SynBrain揭示了试验和受试者之间的功能一致性,展示其在实际应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图




Deep Learning for Crack Detection: A Review of Learning Paradigms, Generalizability, and Datasets
Authors:Xinan Zhang, Haolin Wang, Yung-An Hsieh, Zhongyu Yang, Anthony Yezzi, Yi-Chang Tsai
Crack detection plays a crucial role in civil infrastructures, including inspection of pavements, buildings, etc., and deep learning has significantly advanced this field in recent years. While numerous technical and review papers exist in this domain, emerging trends are reshaping the landscape. These shifts include transitions in learning paradigms (from fully supervised learning to semi-supervised, weakly-supervised, unsupervised, few-shot, domain adaptation and fine-tuning foundation models), improvements in generalizability (from single-dataset performance to cross-dataset evaluation), and diversification in dataset reacquisition (from RGB images to specialized sensor-based data). In this review, we systematically analyze these trends and highlight representative works. Additionally, we introduce a new dataset collected with 3D laser scans, 3DCrack, to support future research and conduct extensive benchmarking experiments to establish baselines for commonly used deep learning methodologies, including recent foundation models. Our findings provide insights into the evolving methodologies and future directions in deep learning-based crack detection. Project page: https://github.com/nantonzhang/Awesome-Crack-Detection
裂缝检测在民事基础设施中发挥着至关重要的作用,包括路面、建筑等的检测,并且近年来深度学习已在此领域取得了重大进展。尽管该领域存在大量的技术和综述性论文,但新兴趋势正在改变这一领域的格局。这些变化包括学习范式(从全监督学习转变到半监督、弱监督、无监督、小样本、域适应和微调基础模型)、通用性的提高(从单一数据集性能到跨数据集评估),以及数据集重新采集的多样化(从RGB图像到基于专业传感器的数据)。在这篇综述中,我们系统地分析了这些趋势,并重点介绍了具有代表性的作品。此外,我们还介绍了使用3D激光扫描收集的新数据集“3DCrack”,以支持未来的研究,并对常用的深度学习方法进行广泛的基准测试,包括最近的基础模型。我们的研究结果提供了对不断发展的方法和未来深度学习裂缝检测方向的新见解。项目页面:https://github.com/nantonzhang/Awesome-Crack-Detection。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
深度学习方法在裂缝检测领域已发挥重要作用,近期出现众多趋势变化,包括学习范式转变、泛化性能提升和多样化数据集采集等。本文系统性分析这些趋势并介绍代表性工作,同时推出新数据集支持未来研究,并开展基准实验评估常用深度学习方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度学习方法在裂缝检测领域具有关键作用,涉及道路、建筑等基础设施检测。
- 学习范式转变,包括从全监督学习到多种衍生形式。
- 泛化性能提升,不仅局限于单一数据集表现。
- 数据集采集方式趋向多样化,引入特殊传感器数据。
- 推出基于三维激光扫描的新数据集3DCrack,支持未来研究。
- 基准实验评估常见深度学习方法。
点此查看论文截图






Stochastic-based Patch Filtering for Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Javier Rodenas, Eduardo Aguilar, Petia Radeva
Food images present unique challenges for few-shot learning models due to their visual complexity and variability. For instance, a pasta dish might appear with various garnishes on different plates and in diverse lighting conditions and camera perspectives. This problem leads to losing focus on the most important elements when comparing the query with support images, resulting in misclassification. To address this issue, we propose Stochastic-based Patch Filtering for Few-Shot Learning (SPFF) to attend to the patch embeddings that show greater correlation with the class representation. The key concept of SPFF involves the stochastic filtering of patch embeddings, where patches less similar to the class-aware embedding are more likely to be discarded. With patch embedding filtered according to the probability of appearance, we use a similarity matrix that quantifies the relationship between the query image and its respective support images. Through a qualitative analysis, we demonstrate that SPFF effectively focuses on patches where class-specific food features are most prominent while successfully filtering out non-relevant patches. We validate our approach through extensive experiments on few-shot classification benchmarks: Food-101, VireoFood-172 and UECFood-256, outperforming the existing SoA methods.
食品图像为小样学习模型带来了独特的挑战,因为它们的视觉复杂性和可变性。例如,一道意大利面可能会出现在不同的盘子上,有着不同的配料,并且在不同的照明条件和相机视角下呈现。这个问题导致在查询与支持图像进行比较时失去对最重要元素的关注,从而导致误分类。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于随机性的小样学习补丁过滤(SPFF)方法,以关注与类别表示相关性更大的补丁嵌入。SPFF的关键概念涉及补丁嵌入的随机过滤,其中与类别感知嵌入不太相似的补丁更有可能被丢弃。根据出现概率过滤补丁嵌入后,我们使用相似度矩阵来量化查询图像与其相应的支持图像之间的关系。通过定性分析,我们证明SPFF可以有效地关注食品特征最突出的补丁,同时成功过滤掉不相关的补丁。我们通过大量实验在少量样本分类基准上验证了我们的方法:Food-101、VireoFood-172和UECFood-256,性能优于现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR Workshop MetaFood 2025
Summary
该文本指出食品图像对少样本学习模型构成独特挑战,因图像视觉复杂多变。如面食料理在不同盘子上展示各种配菜,照明条件与相机视角各异,导致在查询与样本图像比较时容易失去对重点元素的关注,从而产生误判。为解决此问题,本文提出基于随机性的少样本学习(SPFF)方法,重点关注与类别表征更相关的补丁嵌入。SPFF的关键概念在于随机过滤补丁嵌入,对于与类别感知嵌入差异较大的补丁更容易被舍弃。经过出现的概率筛选的补丁嵌入数据,利用相似性矩阵量化查询图像与对应样本图像之间的关系。定性分析表明,SPFF能够有效聚焦于类特定食品特征最突出的补丁,同时成功过滤掉非相关补丁。通过广泛的实验验证,在少样本分类基准数据集Food-101、VireoFood-172和UECFood-256上的表现优于现有最先进的模型。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的关键见解要点:
- 食品图像对少样本学习模型提出了独特挑战,因其视觉上的复杂性和变化多样性。
- 不同的面食料理在不同盘子上呈现多种配菜,照明和相机视角的变化导致识别困难。
- 为解决误判问题,提出了基于随机性的少样本学习(SPFF)方法。
- SPFF通过随机过滤补丁嵌入数据来关注与类别表征更相关的部分。
- SPFF通过相似性矩阵量化查询图像与样本图像之间的关系。
- 定性分析证明了SPFF能够有效识别食品的关键特征并过滤掉非相关元素。
点此查看论文截图




MOC: Meta-Optimized Classifier for Few-Shot Whole Slide Image Classification
Authors:Tianqi Xiang, Yi Li, Qixiang Zhang, Xiaomeng Li
Recent advances in histopathology vision-language foundation models (VLFMs) have shown promise in addressing data scarcity for whole slide image (WSI) classification via zero-shot adaptation. However, these methods remain outperformed by conventional multiple instance learning (MIL) approaches trained on large datasets, motivating recent efforts to enhance VLFM-based WSI classification through fewshot learning paradigms. While existing few-shot methods improve diagnostic accuracy with limited annotations, their reliance on conventional classifier designs introduces critical vulnerabilities to data scarcity. To address this problem, we propose a Meta-Optimized Classifier (MOC) comprising two core components: (1) a meta-learner that automatically optimizes a classifier configuration from a mixture of candidate classifiers and (2) a classifier bank housing diverse candidate classifiers to enable a holistic pathological interpretation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MOC outperforms prior arts in multiple few-shot benchmarks. Notably, on the TCGA-NSCLC benchmark, MOC improves AUC by 10.4% over the state-of-the-art few-shot VLFM-based methods, with gains up to 26.25% under 1-shot conditions, offering a critical advancement for clinical deployments where diagnostic training data is severely limited. Code is available at https://github.com/xmed-lab/MOC.
近期,组织病理学视觉语言基础模型(VLFMs)的进步在通过零样本适应解决全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的数据稀缺问题上表现出了前景。然而,这些方法仍被在大型数据集上训练的常规多实例学习(MIL)方法所超越,这促使最近的努力通过小样学习模式增强基于VLFM的WSI分类。虽然现有的小样方法可以在有限的注释下提高诊断准确性,但它们对常规分类器设计的依赖引发了数据稀缺的关键漏洞。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种由两个核心组件组成的元优化分类器(MOC):(1)元学习者会自动优化来自混合候选分类器的分类器配置;(2)一个包含多种候选分类器的分类器库,以实现全面的病理解释。大量实验表明,MOC在多个小样基准测试中优于以前的技术。值得注意的是,在TCGA-NSCLC基准测试中,MOC比最新的基于小样的VLFM方法提高了10.4%的AUC,在单样本条件下提高幅度高达26.25%,这对于诊断训练数据严重受限的临床部署而言是一个重要的进步。代码可在https://github.com/xmed-lab/MOC找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in MICCAI 2025
Summary
针对组织病理学图像分类任务中数据稀缺的问题,最近的基于视觉语言基础模型的零样本适应策略虽然展现出了潜力,但仍无法匹敌传统的多任务实例学习(MIL)方法。为了改进基于视觉语言基础模型的WSI分类,研究者提出了通过小样本学习模式来增强性能的策略。现有的小样本方法虽然能在有限标注的情况下提高诊断准确性,但它们依赖于传统分类器的设计,在数据稀缺的情况下存在重大漏洞。为了解决这个问题,提出了包含两个核心组件的元优化分类器(MOC):(1)一个元学习者,可以从候选分类器的组合中自动优化分类器配置;(2)一个分类器库,包含各种候选分类器以实现全面的病理解释。实验表明,MOC在多个小样本测试中超过了先前的技术。在TCGA-NSCLC测试中,MOC相较于最新的基于小样本视觉语言基础模型的方法提高了AUC值10.4%,在单样本条件下提升甚至高达26.25%,这对于诊断训练数据严重受限的临床部署环境来说是一个重大进步。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言基础模型在处理组织病理学图像分类时面临数据稀缺的挑战。
- 元优化分类器(MOC)由两个核心组件组成:元学习器和分类器库。
- 元学习者能够自动从候选分类器的组合中优化分类器配置。
- 分类器库包含多种候选分类器,以实现全面的病理解释。
- MOC在多个小样本测试中表现优异,相较于现有技术有显著的提升。
- 在TCGA-NSCLC测试中,MOC相较于基于小样本视觉语言基础模型的方法提高了诊断准确性。
点此查看论文截图




DSS-Prompt: Dynamic-Static Synergistic Prompting for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Linpu He, Yanan Li, Bingze Li, Elvis Han Cui, Donghui Wang
Learning from large-scale pre-trained models with strong generalization ability has shown remarkable success in a wide range of downstream tasks recently, but it is still underexplored in the challenging few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) task. It aims to continually learn new concepts from limited training samples without forgetting the old ones at the same time. In this paper, we introduce DSS-Prompt, a simple yet effective approach that transforms the pre-trained Vision Transformer with minimal modifications in the way of prompts into a strong FSCIL classifier. Concretely, we synergistically utilize two complementary types of prompts in each Transformer block: static prompts to bridge the domain gap between the pre-training and downstream datasets, thus enabling better adaption; and dynamic prompts to capture instance-aware semantics, thus enabling easy transfer from base to novel classes. Specially, to generate dynamic prompts, we leverage a pre-trained multi-modal model to extract input-related diverse semantics, thereby generating complementary input-aware prompts, and then adaptively adjust their importance across different layers. In this way, on top of the prompted visual embeddings, a simple prototype classifier can beat state-of-the-arts without further training on the incremental tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on four benchmarks to validate the effectiveness of our DSS-Prompt and show that it consistently achieves better performance than existing approaches on all datasets and can alleviate the catastrophic forgetting issue as well.
从具有强大泛化能力的大规模预训练模型中学习,最近在广泛的下游任务中取得了显著的成功,但在具有挑战性的少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)任务中仍然探索不足。其目标是从有限的训练样本中持续学习新概念,同时不忘记旧知识。在本文中,我们介绍了DSS-Prompt,这是一种简单而有效的方法,它通过最小化的提示方式将预训练的视觉转换器转变为强大的FSCIL分类器。具体来说,我们协同利用Transformer块中的两种互补提示:静态提示,以缩小预训练和下游数据集之间的域差距,从而实现更好的适应;动态提示,以捕获实例感知语义,从而实现从基础类别到新颖类别的轻松迁移。特别是,为了生成动态提示,我们利用预训练的多模态模型来提取与输入相关的多样语义,从而产生互补的输入感知提示,然后自适应地调整它们在不同层中的重要性。通过这种方式,基于提示的视觉嵌入,一个简单的原型分类器可以在无需对增量任务进行进一步训练的情况下超越现有技术。我们在四个基准上进行了大量实验,验证了DSS-Prompt的有效性,并表明它在所有数据集上始终实现了比现有方法更好的性能,并可以缓解灾难性遗忘问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACMMM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在具有挑战性的少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)任务中,利用大型预训练模型进行学习的方法。通过引入DSS-Prompt技术,将预训练的视觉转换器进行微调,转化为强大的FSCIL分类器。该技术利用静态提示和动态提示,缩小了预训练和下游数据集之间的领域差距,并捕捉实例感知语义,从而实现了从基础类别到新颖类别的轻松迁移。通过预训练的多模态模型生成动态提示,并自适应调整其在不同层的重要性。实验证明,DSS-Prompt在四个基准测试上的表现均优于现有方法,并能有效缓解灾难性遗忘问题。
Key Takeaways
- DSS-Prompt技术将预训练的视觉转换器转化为少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)分类器。
- DSS-Prompt结合了静态提示和动态提示来适应FSCIL任务。
- 静态提示缩小了预训练和下游数据集之间的领域差距。
- 动态提示通过捕捉实例感知语义,实现了从基础类别到新颖类别的迁移。
- 利用预训练的多模态模型生成动态提示,增强了模型的适应性。
- DSS-Prompt在多个基准测试上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图







Slot Attention-based Feature Filtering for Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Javier Rodenas, Eduardo Aguilar, Petia Radeva
Irrelevant features can significantly degrade few-shot learn ing performance. This problem is used to match queries and support images based on meaningful similarities despite the limited data. However, in this process, non-relevant fea tures such as background elements can easily lead to confu sion and misclassification. To address this issue, we pro pose Slot Attention-based Feature Filtering for Few-Shot Learning (SAFF) that leverages slot attention mechanisms to discriminate and filter weak features, thereby improving few-shot classification performance. The key innovation of SAFF lies in its integration of slot attention with patch em beddings, unifying class-aware slots into a single attention mechanism to filter irrelevant features effectively. We intro duce a similarity matrix that computes across support and query images to quantify the relevance of filtered embed dings for classification. Through experiments, we demon strate that Slot Attention performs better than other atten tion mechanisms, capturing discriminative features while reducing irrelevant information. We validate our approach through extensive experiments on few-shot learning bench marks: CIFAR-FS, FC100, miniImageNet and tieredIma geNet, outperforming several state-of-the-art methods.
不相关的特征可能会显著影响小样本学习的性能。此问题的解决方案是用于在有限数据的基础上,根据有意义的相似性来匹配查询图像和支持图像。然而,在此过程中,不相关的特征(如背景元素)很容易引起混淆和误分类。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于插槽注意力的小样本学习特征过滤(SAFF),它利用插槽注意力机制来区分和过滤弱特征,从而提高小样本分类性能。SAFF的关键创新之处在于它将插槽注意力与补丁嵌入相结合,将类感知插槽统一到一个单一的注意力机制中,有效地过滤掉不相关的特征。我们引入了一个相似度矩阵,该矩阵跨支持图像和查询图像进行计算,以量化过滤嵌入物在分类中的相关性。通过实验,我们证明了插槽注意力比其他注意力机制表现更好,能够捕捉区分特征同时减少无关信息。我们在小样本学习的基准测试上进行了广泛的实验验证,包括CIFAR-FS、FC100、miniImageNet和tieredImageNet,我们的方法优于几种最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR Workshop LatinX 2025
Summary
本文探讨了少样本学习中的特征选择问题,指出无关特征会严重影响模型性能。为此,提出了基于插槽注意力的特征过滤方法(SAFF),通过结合插槽注意力和补丁嵌入,有效过滤掉不相关特征,提高少样本分类性能。实验证明,SAFF在多个少样本学习基准测试集上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 无关特征对少样本学习性能有重要影响。
- 提出基于插槽注意力的特征过滤方法(SAFF)以改善少样本分类性能。
- SAFF通过结合插槽注意力和补丁嵌入,统一类感知插槽,有效过滤掉不相关特征。
- 引入相似度矩阵来计算支持图像和查询图像之间的相关性,以量化过滤嵌入的分类重要性。
- 插槽注意力机制在捕获判别特征的同时减少了无关信息。
- 在多个少样本学习基准测试集上,SAFF表现优于其他最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图





Leveraging Failed Samples: A Few-Shot and Training-Free Framework for Generalized Deepfake Detection
Authors:Shibo Yao, Renshuai Tao, Xiaolong Zheng, Chao Liang, Chunjie Zhang
Recent deepfake detection studies often treat unseen sample detection as a zero-shot" task, training on images generated by known models but generalizing to unknown ones. A key real-world challenge arises when a model performs poorly on unknown samples, yet these samples remain available for analysis. This highlights that it should be approached as a few-shot” task, where effectively utilizing a small number of samples can lead to significant improvement. Unlike typical few-shot tasks focused on semantic understanding, deepfake detection prioritizes image realism, which closely mirrors real-world distributions. In this work, we propose the Few-shot Training-free Network (FTNet) for real-world few-shot deepfake detection. Simple yet effective, FTNet differs from traditional methods that rely on large-scale known data for training. Instead, FTNet uses only one fake samplefrom an evaluation set, mimicking the scenario where new samples emerge in the real world and can be gathered for use, without any training or parameter updates. During evaluation, each test sample is compared to the known fake and real samples, and it is classified based on the category of the nearest sample. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of AI-generated images from 29 different generative models and achieve a new SoTA performance, with an average improvement of 8.7% compared to existing methods. This work introduces a fresh perspective on real-world deepfake detection: when the model struggles to generalize on a few-shot sample, leveraging the failed samples leads to better performance.
最近关于深度伪造检测的研究通常将未见样本检测视为“零样本”任务,通过在已知模型生成的图像上进行训练,然后推广到未知模型。当模型在未知样本上表现不佳时,现实世界的关键挑战就会出现,但这些样本仍然可用于分析。这强调应该将其视为一个“小样本”任务,有效利用少量样本可以导致显著改进。与关注语义理解的典型小样本任务不同,深度伪造检测更侧重于图像的真实性,这紧密地反映了现实世界的分布。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于现实世界中深度伪造检测的小样本无训练网络(FTNet)。FTNet简单有效,不同于传统方法依赖于大规模已知数据进行训练。相反,FTNet仅使用评估集中的一个伪造样本,模仿现实中新样本的出现并可以收集使用的情况,无需任何训练或参数更新。在评估过程中,每个测试样本都与已知的伪造和真实样本进行比较,并基于最接近的样本类别进行分类。我们对29种不同生成模型生成的AI图像进行了综合分析,达到了最新的技术水平,平均而言,与现有方法相比提高了8.7%。这项工作为现实世界的深度伪造检测提供了新的视角:当模型在少量样本上难以推广时,利用失败的样本会导致更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出将深度伪造检测视为一种“少样本”任务,当模型在未知样本上表现不佳时,可以利用少量样本进行有效改善。针对现实世界的深度伪造检测问题,本文提出了一种无需训练的少样本网络(FTNet),该网络仅需使用评价集中的单个伪造样本即可实现高效的检测。通过对来自29种不同生成模型的AI生成图像进行全面分析,FTNet实现了先进性能,平均比现有方法提高了8.7%。这表明在实际场景中遇到新的挑战时,应灵活运用样本以增强模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 最近深度伪造检测研究倾向于将未见样本检测视为“零样本”任务,但实际应用中面临未知样本性能不佳的问题。
- 当模型在未知样本上表现不佳时,应将其视为“少样本”任务,利用少量样本提升性能。
- FTNet网络被提出用于现实世界的少样本深度伪造检测,无需大规模已知数据进行训练。
- FTNet仅需评价集中的单个伪造样本进行分类比较。它模仿现实中新样本的出现并能即时收集利用的情况,无需任何额外的训练或参数更新。
- FTNet实现了全面分析AI生成图像的性能,并显著提高现有方法的平均性能达8.7%。这表明有效利用失败样本能够提高模型性能。
- 本文提出了一种全新的视角看待现实世界的深度伪造检测问题,强调了在实际场景中遇到新的挑战时灵活使用样本的重要性。
点此查看论文截图







Explainable Sentiment Analysis with DeepSeek-R1: Performance, Efficiency, and Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Donghao Huang, Zhaoxia Wang
Large language models (LLMs) have transformed sentiment analysis, yet balancing accuracy, efficiency, and explainability remains a critical challenge. This study presents the first comprehensive evaluation of DeepSeek-R1–an open-source reasoning model–against OpenAI’s GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini. We test the full 671B model and its distilled variants, systematically documenting few-shot learning curves. Our experiments show DeepSeek-R1 achieves a 91.39% F1 score on 5-class sentiment and 99.31% accuracy on binary tasks with just 5 shots, an eightfold improvement in few-shot efficiency over GPT-4o. Architecture-specific distillation effects emerge, where a 32B Qwen2.5-based model outperforms the 70B Llama-based variant by 6.69 percentage points. While its reasoning process reduces throughput, DeepSeek-R1 offers superior explainability via transparent, step-by-step traces, establishing it as a powerful, interpretable open-source alternative.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经改变了情感分析领域,但在平衡准确性、效率和可解释性方面仍然是一个关键挑战。本研究首次对DeepSeek-R1这一开源推理模型进行全面评估,并与OpenAI的GPT-4o和GPT-4o-mini进行对比。我们测试了完整的671B模型及其蒸馏变体,系统地记录了小样本学习曲线。实验表明,DeepSeek-R1在5类情感分析上达到91.39%的F1分数,在二元任务上达到99.31%的准确率,仅需要5个样本,相比于GPT-4o,其在小样本效率上提高了八倍。出现特定架构的蒸馏效应,其中基于32B Qwen2.5的模型优于基于70B Llama的变体,高出6.69个百分点。虽然其推理过程降低了吞吐量,但DeepSeek-R1通过透明、分步的跟踪提供了卓越的可解释性,使其成为强大、可解释的开源替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables, revised and re-submitted to an IEEE journal
Summary
DeepSeek-R1模型在情感分析领域表现卓越,与OpenAI的GPT-4o系列模型相比,其在少量样本学习方面展现出显著优势。本研究全面评估了DeepSeek-R1的性能,发现其在5类情感分析的F1分数上达到91.39%,在二元任务上的准确率高达99.31%,且仅需少量样本。此外,DeepSeek-R1具有优越的可解释性,且作为开源模型,具有强大的竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- DeepSeek-R1在情感分析领域表现出卓越性能,特别是在少量样本学习方面。
- 与GPT-4o系列模型相比,DeepSeek-R1在F1分数和准确率方面表现出显著优势。
- DeepSeek-R1的可解释性强大,通过透明的步骤追踪,使用户能够理解其推理过程。
- 架构特定的蒸馏效果在DeepSeek-R1中显现,其中基于Qwen2.5的模型性能优于基于Llama的模型。
- 尽管推理过程可能会降低吞吐量,但DeepSeek-R1仍具有高效的性能。
- DeepSeek-R1是一个强大的开源模型,提供了可替代大型语言模型的另一种选择。
点此查看论文截图





Leveraging Audio and Text Modalities in Mental Health: A Study of LLMs Performance
Authors:Abdelrahman A. Ali, Aya E. Fouda, Radwa J. Hanafy, Mohammed E. Fouda
Mental health disorders are increasingly prevalent worldwide, creating an urgent need for innovative tools to support early diagnosis and intervention. This study explores the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in multimodal mental health diagnostics, specifically for detecting depression and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder through text and audio modalities. Using the E-DAIC dataset, we compare text and audio modalities to investigate whether LLMs can perform equally well or better with audio inputs. We further examine the integration of both modalities to determine if this can enhance diagnostic accuracy, which generally results in improved performance metrics. Our analysis specifically utilizes custom-formulated metrics; Modal Superiority Score and Disagreement Resolvement Score to evaluate how combined modalities influence model performance. The Gemini 1.5 Pro model achieves the highest scores in binary depression classification when using the combined modality, with an F1 score of 0.67 and a Balanced Accuracy (BA) of 77.4%, assessed across the full dataset. These results represent an increase of 3.1% over its performance with the text modality and 2.7% over the audio modality, highlighting the effectiveness of integrating modalities to enhance diagnostic accuracy. Notably, all results are obtained in zero-shot inferring, highlighting the robustness of the models without requiring task-specific fine-tuning. To explore the impact of different configurations on model performance, we conduct binary, severity, and multiclass tasks using both zero-shot and few-shot prompts, examining the effects of prompt variations on performance. The results reveal that models such as Gemini 1.5 Pro in text and audio modalities, and GPT-4o mini in the text modality, often surpass other models in balanced accuracy and F1 scores across multiple tasks.
精神健康障碍在全球范围内越来越普遍,这迫切需要创新工具来支持早期诊断和治疗。本研究探讨大型语言模型(LLM)在多模式精神健康诊断中的潜力,特别是通过文本和音频模式检测抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍。我们使用E-DAIC数据集,比较文本和音频模式,以研究LLM是否可以通过音频输入实现同等或更好的性能。我们进一步探讨了两种模式的融合,以确定这是否能提高诊断的准确性,从而提高性能指标。我们的分析特别利用定制的指标,即模态优势评分和分歧解决评分,来评估组合模式如何影响模型性能。在二元抑郁症分类中,使用组合模式的Gemini 1.5 Pro模型得分最高,F1分数为0.67,平衡精度(BA)为77.4%,在全数据集上进行了评估。与仅使用文本模式或音频模式相比,这些结果分别提高了3.1%和提高了2.7%,这突显了融合模式以提高诊断准确性的有效性。值得注意的是,所有结果均是在零样本推断中获得的,这表明模型在不需要特定任务微调的情况下具有很强的稳健性。为了探讨不同配置对模型性能的影响,我们使用零样本和少量样本提示进行二元、严重性和多类别任务,并研究提示变化对性能的影响。结果显示,在各种任务中,如文本和音频模式中的Gemini 1.5 Pro以及文本模式中的GPT-4o mini等模型经常在平衡精度和F1分数方面超越其他模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了大型语言模型(LLMs)在多模态心理健康诊断中的潜力,研究通过文本和音频模态检测抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍。研究使用E-DAIC数据集比较文本和音频模态,发现LLMs在音频输入方面表现优异。同时,研究也考察了两种模态的整合是否能提高诊断准确性,结果显示整合后的性能有所提升。其中,Gemini 1.5 Pro模型在二元抑郁症分类中表现最佳,结合模态的F1分数为0.67,平衡准确率为77.4%。值得注意的是,所有结果均为零样本推断,突显了模型的稳健性,无需特定任务微调。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多模态心理健康诊断中具有潜力。
- 通过文本和音频模态检测抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍的研究得到开展。
- LLMs在音频输入方面的表现优异。
- 整合文本和音频模态能提高诊断准确性。
- Gemini 1.5 Pro模型在二元抑郁症分类中表现最佳。
- 模型表现稳健,可在零样本推断下取得良好结果。
- 不同配置和提示方式对模型性能有影响。
点此查看论文截图



Multi-Step Reasoning with Large Language Models, a Survey
Authors:Aske Plaat, Annie Wong, Suzan Verberne, Joost Broekens, Niki van Stein, Thomas Back
Language models with billions of parameters exhibit in-context learning abilities, enabling few-shot learning on tasks that the model was not specifically trained for. Traditional models achieve breakthrough performance on language tasks, but do not perform well on basic reasoning benchmarks. However, a new in-context learning approach, Chain-of-thought, has demonstrated strong multi-step reasoning abilities on these benchmarks. The research on LLM reasoning abilities started with the question whether LLMs can solve grade school math word problems, and has expanded to other tasks in the past few years. This paper reviews the field of multi-step reasoning with LLMs. We propose a taxonomy that identifies different ways to generate, evaluate, and control multi-step reasoning. We provide an in-depth coverage of core approaches and open problems, and we propose a research agenda for the near future. We find that multi-step reasoning approaches have progressed beyond math word problems, and can now successfully solve challenges in logic, combinatorial games, and robotics, sometimes by first generating code that is then executed by external tools. Many studies in multi-step methods are using reinforcement learning for finetuning, external optimization loops, in context reinforcement learning, and self-reflection.
具有数十亿参数的语言模型展现出上下文学习能力,能够在未专门训练的任务上实现少量学习。传统模型在语言任务上取得了突破性进展,但在基本推理基准测试上的表现并不出色。然而,一种新的上下文学习方法——思维链(Chain-of-thought)在这些基准测试中表现出了强大的多步推理能力。关于大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的研究始于大型语言模型是否能解决小学数学文字题的问题,并在过去几年中扩展到了其他任务。本文综述了大型语言模型的多步推理领域。我们提出了一种分类法,确定了生成、评估和控制多步推理的不同方法。我们对核心方法和开放问题进行了深入探讨,并提出了今后的研究议程。我们发现,多步推理方法已经超越了数学文字题的范围,现在能够成功解决逻辑、组合游戏和机器人技术等方面的挑战,有时是先生成代码,然后交由外部工具执行。多步方法的研究正在使用强化学习进行微调、外部优化循环、上下文强化学习和自我反思等方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF revised version
Summary
语言模型拥有数十亿参数,展现出上下文学习能力,可在未专门训练的任务中实现少量学习。传统模型在语言任务上表现卓越,但在基本推理基准测试上表现不佳。一种新型的上下文学习法——Chain-of-thought展现出强大的多步骤推理能力。本文回顾了大型语言模型的多步骤推理领域,提出了识别生成、评估和控制多步骤推理的不同方式的新分类法,深入探讨了核心方法和开放问题,并为近期未来提出了研究议程。研究发现,多步骤推理方法已不仅限于解决数学文字问题,还能成功应对逻辑、组合游戏和机器人技术中的挑战,有时通过生成代码并由外部工具执行来完成。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型具备在无需专门训练的情况下处理新任务的能力,这被称为上下文学习或少量学习。
- 传统语言模型在基本推理测试上的表现不佳。
- Chain-of-thought是一种新型上下文学习方法,具有强大的多步骤推理能力。
- 多步骤推理方法不仅可以解决数学文字问题,还能成功应对逻辑、组合游戏和机器人技术中的挑战。
- 多步骤推理方法有时会生成代码并由外部工具执行来完成任务。
- 目前的研究领域涵盖了多种方法,包括使用强化学习进行微调、外部优化循环、上下文强化学习和自我反思。
点此查看论文截图