⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
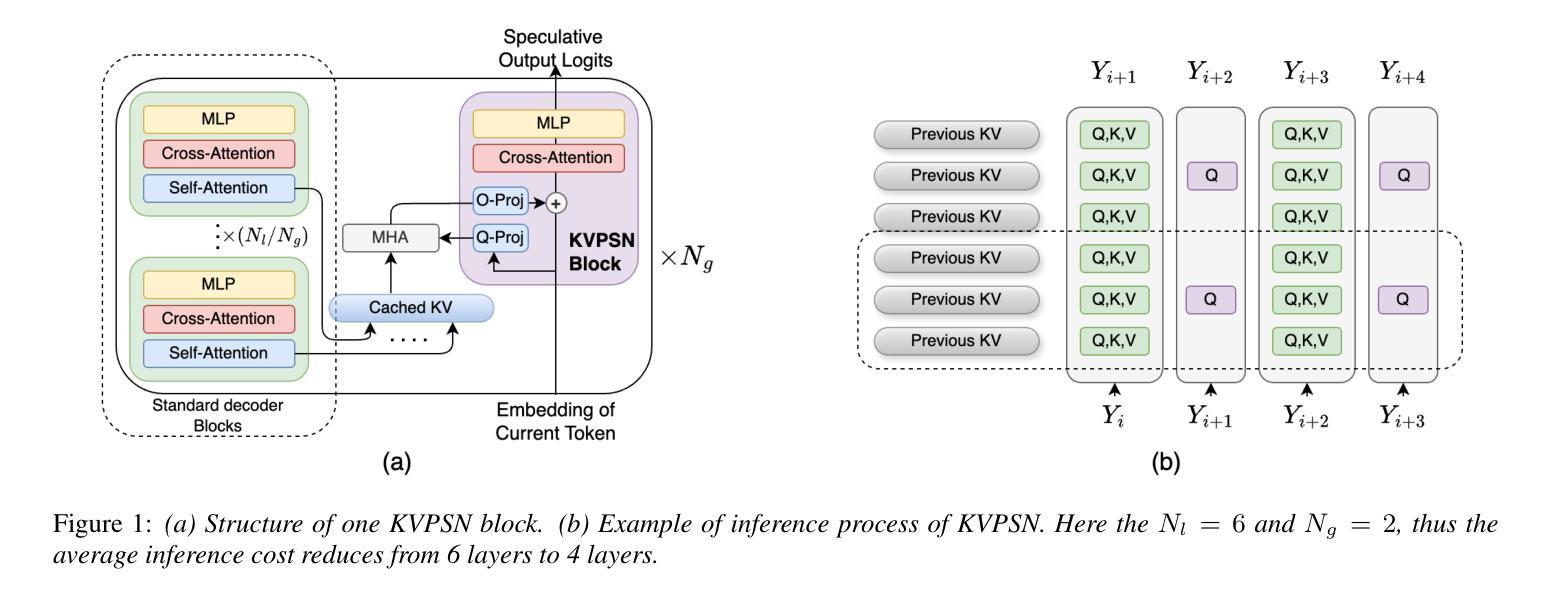
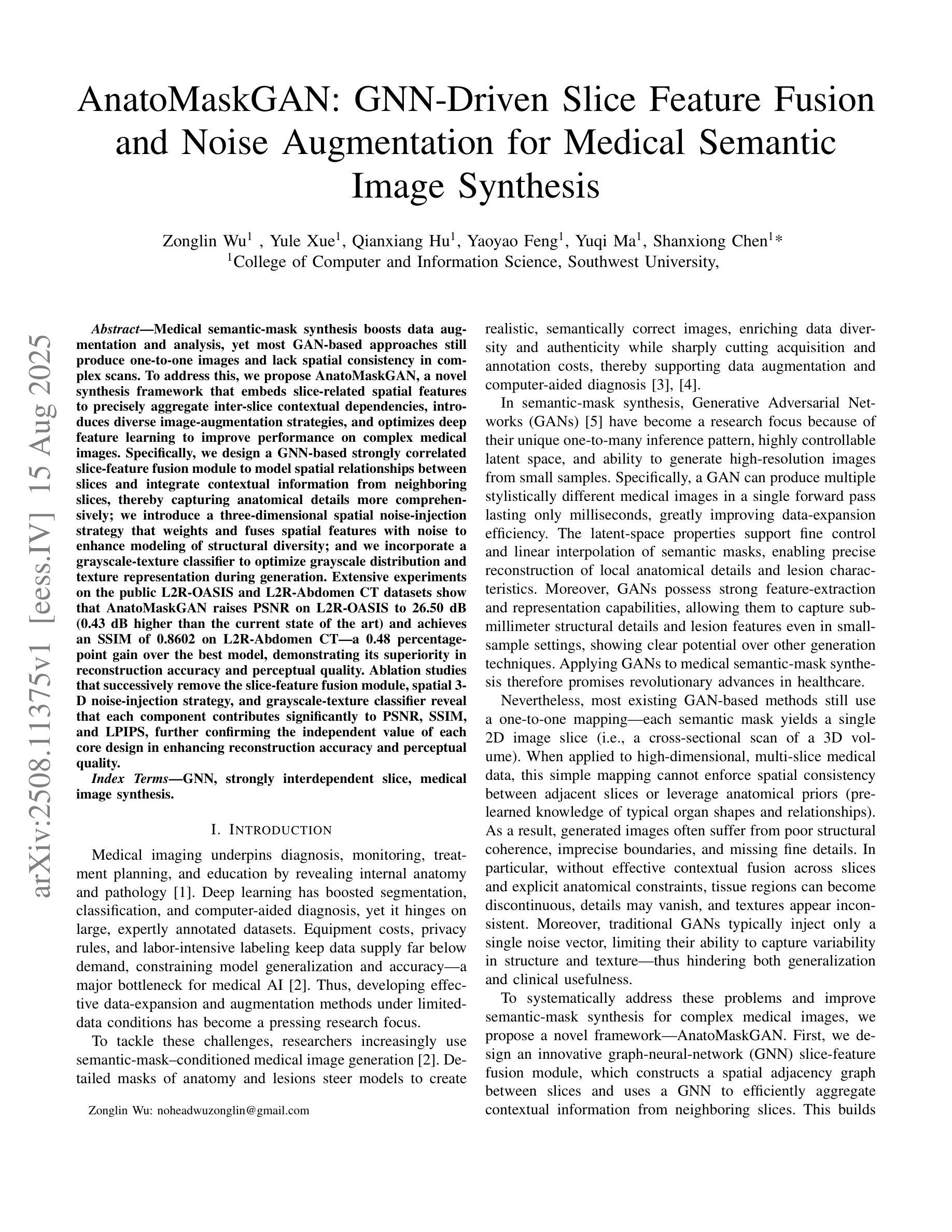
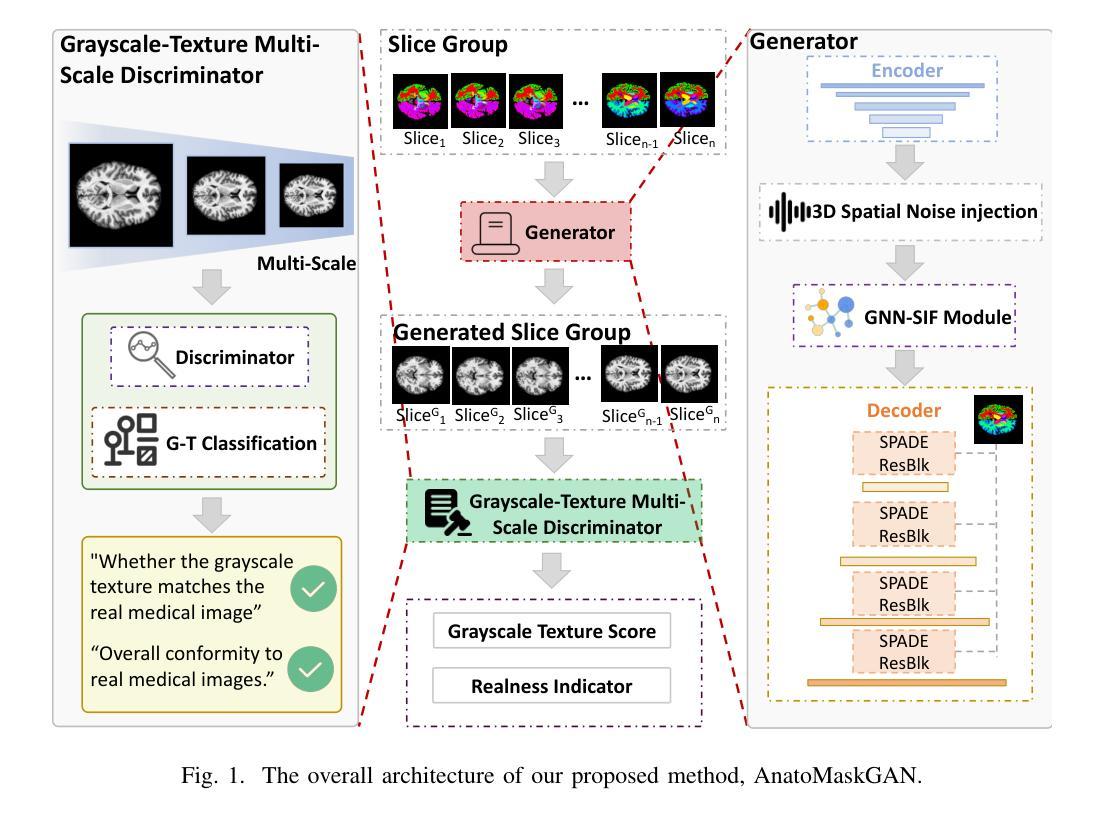
AnatoMaskGAN: GNN-Driven Slice Feature Fusion and Noise Augmentation for Medical Semantic Image Synthesis
Authors:Zonglin Wu, Yule Xue, Qianxiang Hu, Yaoyao Feng, Yuqi Ma, Shanxiong Chen
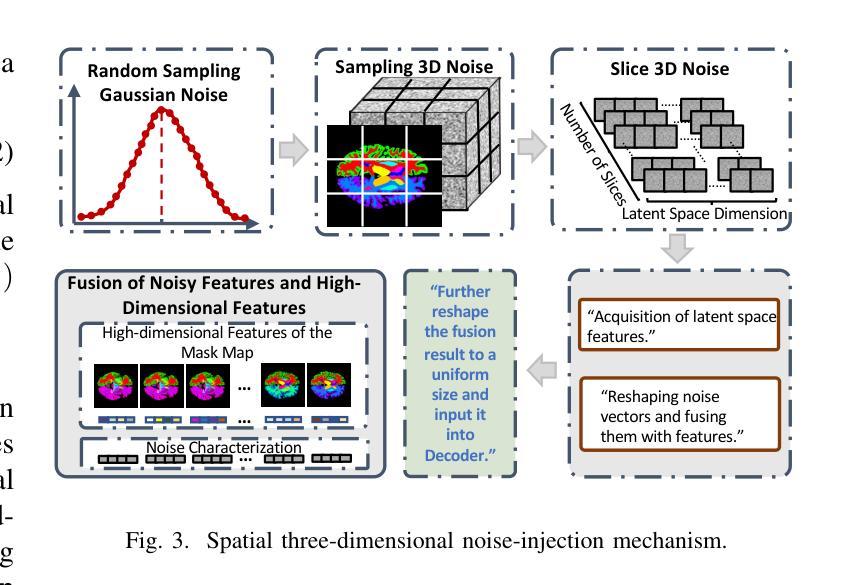
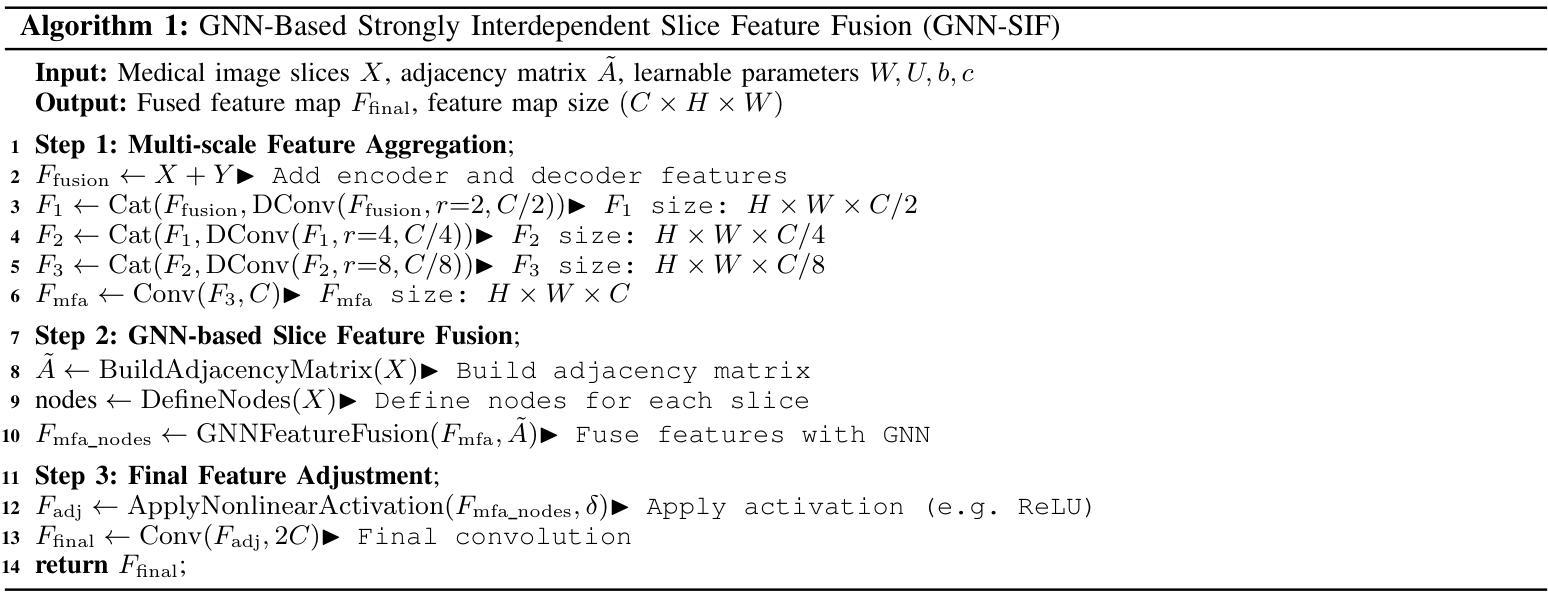
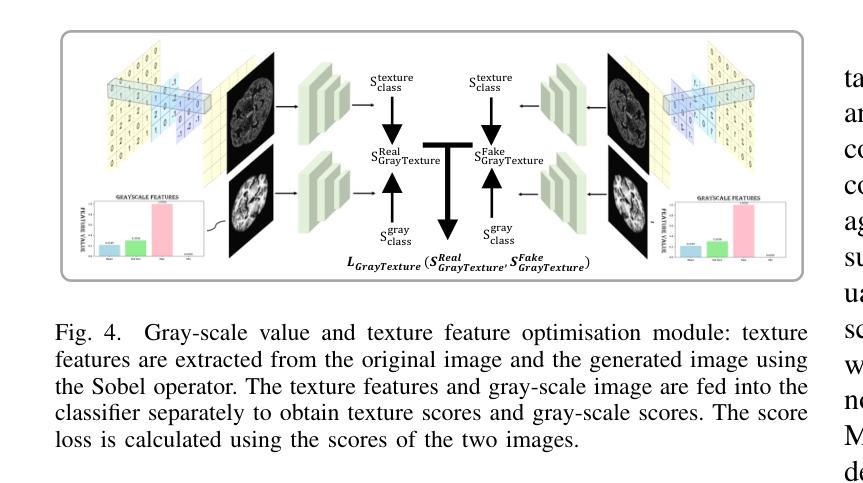
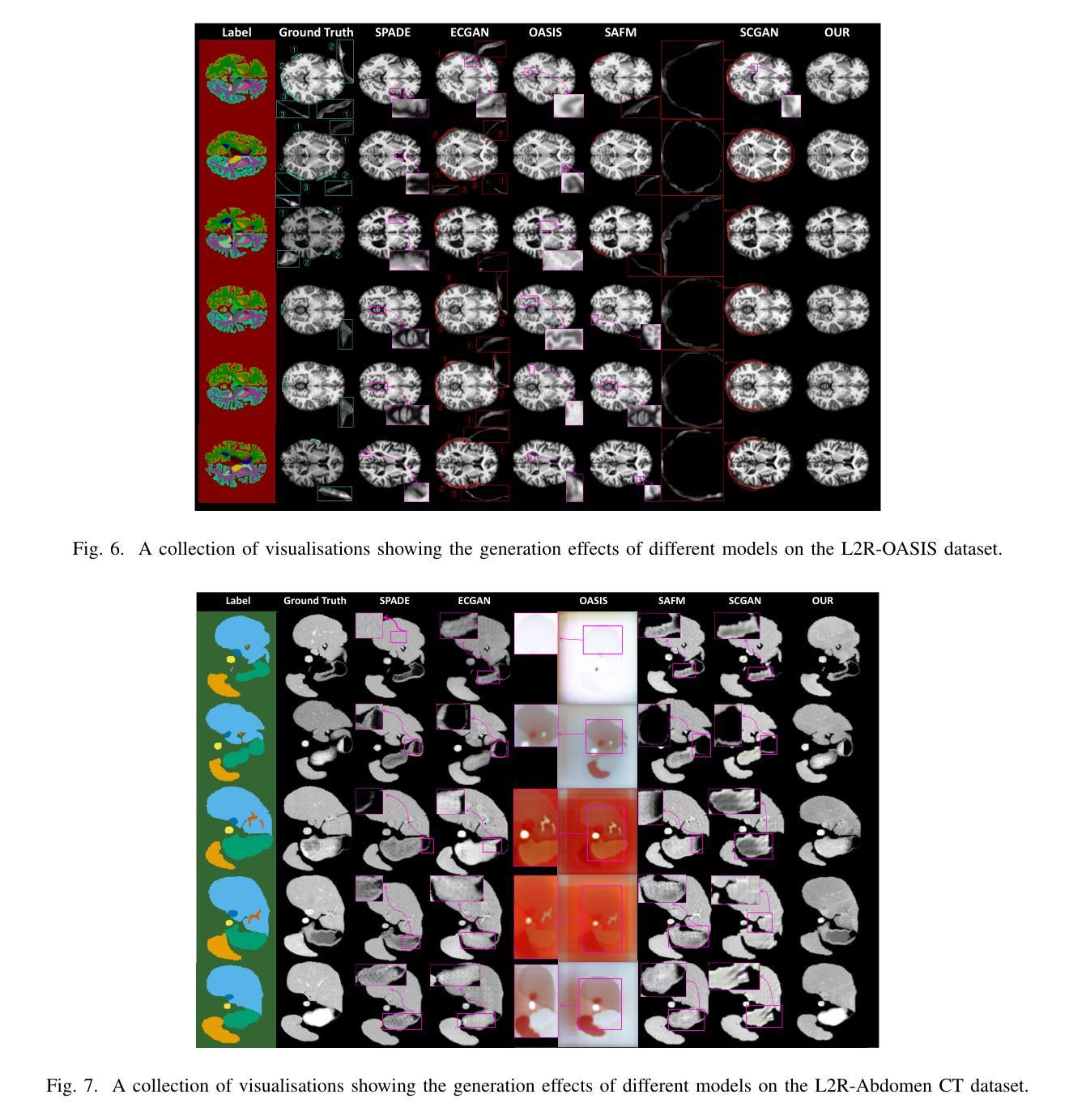
Medical semantic-mask synthesis boosts data augmentation and analysis, yet most GAN-based approaches still produce one-to-one images and lack spatial consistency in complex scans. To address this, we propose AnatoMaskGAN, a novel synthesis framework that embeds slice-related spatial features to precisely aggregate inter-slice contextual dependencies, introduces diverse image-augmentation strategies, and optimizes deep feature learning to improve performance on complex medical images. Specifically, we design a GNN-based strongly correlated slice-feature fusion module to model spatial relationships between slices and integrate contextual information from neighboring slices, thereby capturing anatomical details more comprehensively; we introduce a three-dimensional spatial noise-injection strategy that weights and fuses spatial features with noise to enhance modeling of structural diversity; and we incorporate a grayscale-texture classifier to optimize grayscale distribution and texture representation during generation. Extensive experiments on the public L2R-OASIS and L2R-Abdomen CT datasets show that AnatoMaskGAN raises PSNR on L2R-OASIS to 26.50 dB (0.43 dB higher than the current state of the art) and achieves an SSIM of 0.8602 on L2R-Abdomen CT–a 0.48 percentage-point gain over the best model, demonstrating its superiority in reconstruction accuracy and perceptual quality. Ablation studies that successively remove the slice-feature fusion module, spatial 3D noise-injection strategy, and grayscale-texture classifier reveal that each component contributes significantly to PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, further confirming the independent value of each core design in enhancing reconstruction accuracy and perceptual quality.
医学语义遮罩合成提高了数据扩充和分析能力,然而大多数基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法仍然只产生一对一的图像,在复杂扫描中缺乏空间一致性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了AnatoMaskGAN,这是一种新型合成框架,它嵌入切片相关的空间特征来精确聚合切片间的上下文依赖关系,引入多种图像增强策略,并优化深度特征学习,以提高在复杂医学图像上的性能。具体来说,我们设计了一个基于图神经网络(GNN)的强相关切片特征融合模块,以建模切片之间的空间关系,并整合来自相邻切片的上下文信息,从而更全面地捕捉解剖细节;我们引入了一种三维空间噪声注入策略,该策略通过加权融合空间特征与噪声,以增强结构多样性的建模;我们还融入了一个灰度纹理分类器,以优化生成过程中的灰度分布和纹理表示。在公共的L2R-OASIS和L2R-Abdomen CT数据集上的大量实验表明,AnatoMaskGAN在L2R-OASIS上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高到26.50 dB(比当前最佳水平高出0.43 dB),在L2R-Abdomen CT上的结构相似性(SSIM)达到0.8602(比最佳模型高出0.48个百分点),这证明了其在重建精度和感知质量方面的优越性。逐步移除切片特征融合模块、空间3D噪声注入策略和灰度纹理分类器的消融研究证实,每个组件都对PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS有显著贡献,进一步证明了每个核心设计在提高重建精度和感知质量方面的独立价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
摘要
医学语义掩膜合成促进了数据增强与分析,但基于GAN的方法仍多生成一对一图像,缺乏复杂扫描的空间一致性。为解决此问题,我们提出AnatoMaskGAN,一个嵌入切片相关空间特征的新型合成框架,以精确聚合切片间的上下文依赖关系,引入多样化的图像增强策略,并优化深度特征学习以提升在复杂医学图像上的性能。通过设计基于图神经网络(GNN)的强相关切片特征融合模块,建模切片间的空间关系并整合邻近切片的上下文信息,从而更全面地捕捉解剖细节;引入三维空间噪声注入策略,通过权重和融合空间特征与噪声以增强结构多样性的建模;并融入灰度纹理分类器,以优化生成过程中的灰度分布和纹理表示。在公开数据集L2R-OASIS和L2R-Abdomen CT上的大量实验表明,AnatoMaskGAN在L2R-OASIS上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提升至26.50 dB(较当前最佳水平高出0.43 dB),在L2R-Abdomen CT上的结构相似性指数(SSIM)达到0.8602(较最佳模型高出0.48个百分点),显示出其在重建精度和感知质量上的优越性。通过逐步移除切片特征融合模块、空间三维噪声注入策略和灰度纹理分类器的消融研究证实,每个组件对PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS都有显著贡献,进一步证明了每个核心设计在提高重建精度和感知质量方面的独立价值。
关键见解
- AnatoMaskGAN是一个新的合成框架,用于医学图像数据增强和分析。
- 框架内嵌切片相关空间特征,以捕捉更全面的解剖细节。
- 通过引入多样化的图像增强策略和优化深度特征学习,提升复杂医学图像的生成质量。
- 引入基于图神经网络的切片特征融合模块,有效建模切片间的空间关系。
- 三维空间噪声注入策略增强结构多样性建模。
- 灰度纹理分类器的融入优化了生成图像的灰度分布和纹理表示。
- 在公开数据集上的实验证明了AnatoMaskGAN在重建精度和感知质量上的优越性。
点此查看论文截图
GANDiff FR: Hybrid GAN Diffusion Synthesis for Causal Bias Attribution in Face Recognition
Authors:Md Asgor Hossain Reaj, Rajan Das Gupta, Md Yeasin Rahat, Nafiz Fahad, Md Jawadul Hasan, Tze Hui Liew
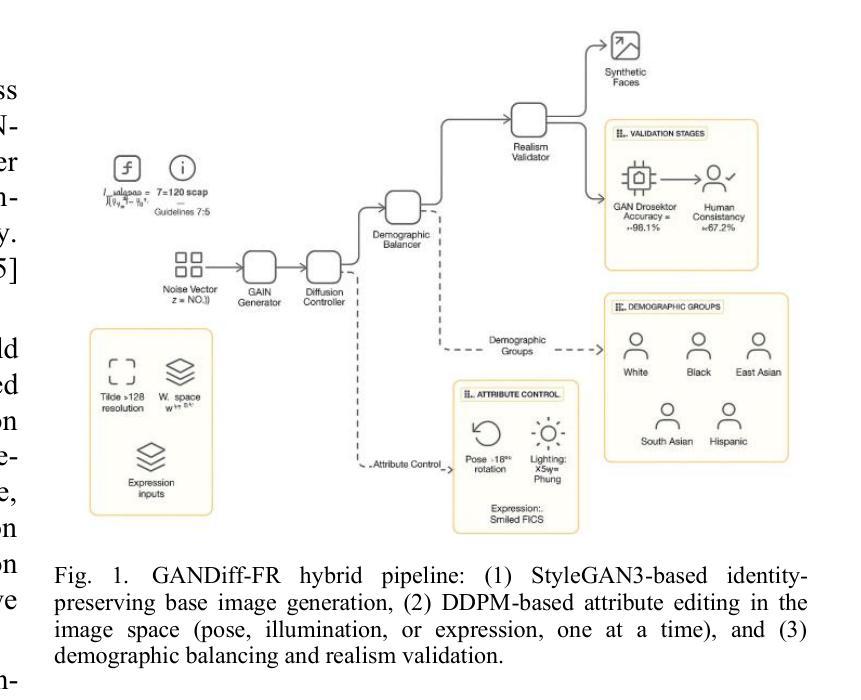
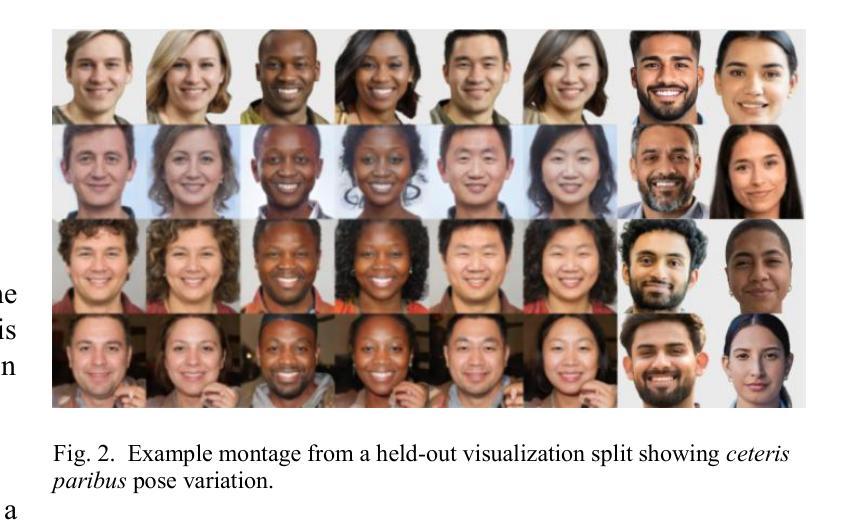
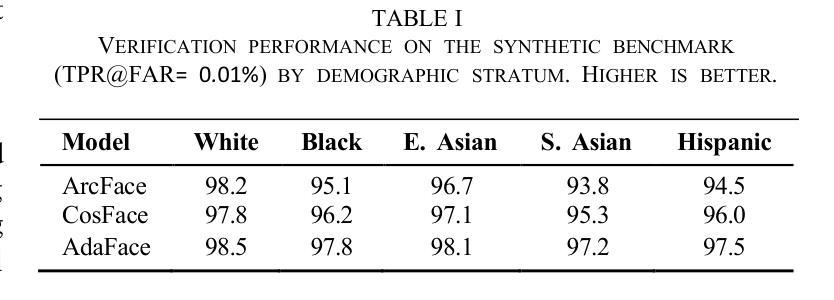
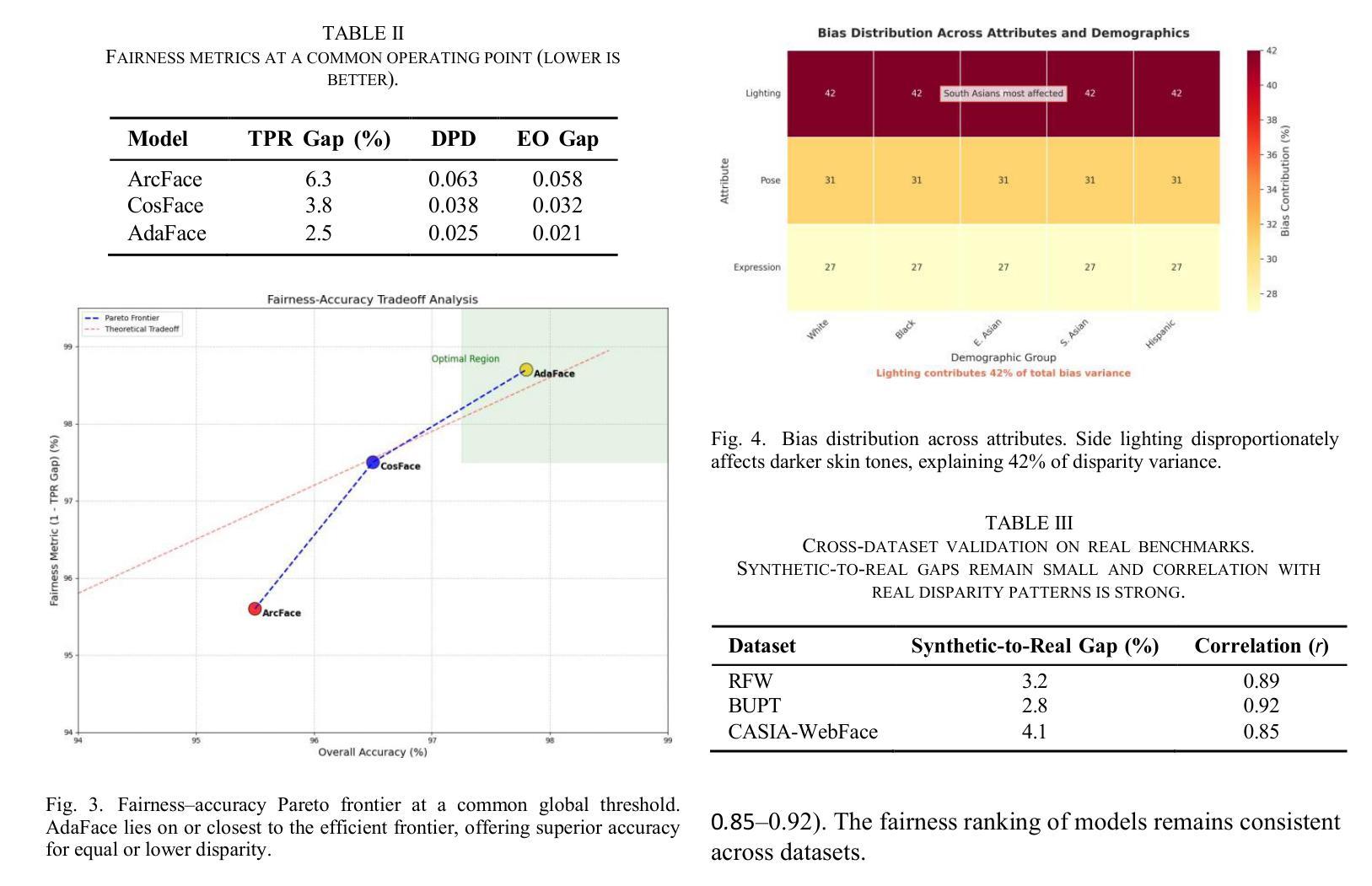
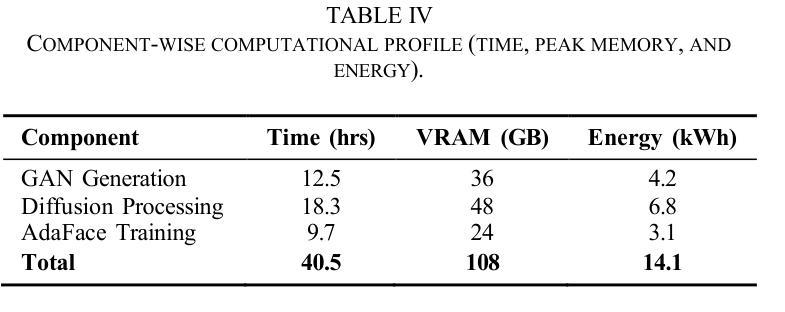
We introduce GANDiff FR, the first synthetic framework that precisely controls demographic and environmental factors to measure, explain, and reduce bias with reproducible rigor. GANDiff FR unifies StyleGAN3-based identity-preserving generation with diffusion-based attribute control, enabling fine-grained manipulation of pose around 30 degrees, illumination (four directions), and expression (five levels) under ceteris paribus conditions. We synthesize 10,000 demographically balanced faces across five cohorts validated for realism via automated detection (98.2%) and human review (89%) to isolate and quantify bias drivers. Benchmarking ArcFace, CosFace, and AdaFace under matched operating points shows AdaFace reduces inter-group TPR disparity by 60% (2.5% vs. 6.3%), with illumination accounting for 42% of residual bias. Cross-dataset evaluation on RFW, BUPT, and CASIA WebFace confirms strong synthetic-to-real transfer (r 0.85). Despite around 20% computational overhead relative to pure GANs, GANDiff FR yields three times more attribute-conditioned variants, establishing a reproducible, regulation-aligned (EU AI Act) standard for fairness auditing. Code and data are released to support transparent, scalable bias evaluation.
我们介绍了GANDiff FR,这是第一个精确控制人口统计和环境因素的合成框架,以衡量、解释和减少偏见,并具有可重复的严谨性。GANDiff FR将基于StyleGAN3的身份保留生成与基于扩散的属性控制统一起来,能够在保持其他条件不变的情况下,实现约30度的姿态、四个方向的照明和五个级别的表情的精细操控。我们合成了10,000张人口统计上平衡的面孔,跨越五个经过自动化检测(98.2%)和人类评审(89%)验证的真实性群体,以隔离和量化偏见的驱动因素。在匹配的条件下对ArcFace、CosFace和AdaFace进行基准测试显示,AdaFace将群体间的TPR差异减少了60%(从6.3%降至2.5%),照明占剩余偏见的42%。在RFW、BUPT和CASIA WebFace数据集上的跨数据集评估证实了强大的从合成到现实的迁移能力(r 0.85)。尽管相对于纯GANs约有20%的计算开销,但GANDiff FR生成的属性条件变体增加了三倍,建立了可重复、符合监管(欧盟人工智能法案)的标准,用于公平性审计。我们公开了代码和数据,以支持透明、可扩展的偏见评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCVDM ‘25
Summary
在生成式框架GANDiff FR中,通过精确控制人口统计学和环境因素来测量、解释和减少偏见。该框架结合了StyleGAN3的身份保留生成和基于扩散的属性控制,实现了在相同条件下对姿态、照明和表情的精细操控。通过合成10,000张人口统计学上平衡的面孔图像,并在五个群组中进行验证,该框架被证明能够有效隔离和量化偏见驱动因素。相较于其他面部识别模型,AdaFace在减少跨组TPR差异方面表现出优越性能,照明因素占剩余偏见的42%。该框架符合欧盟人工智能法案的规范,并已成为一个透明的、可扩展的偏见评估标准。此外,相较于纯GANs模型,尽管存在大约20%的计算开销,但GANDiff FR能够生成三倍以上的属性条件变体。
Key Takeaways
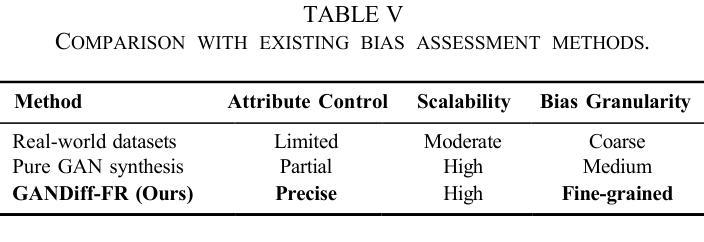
- GANDiff FR是首个能够精确控制人口统计学和环境因素的合成框架,用于测量、解释和减少偏见。
- 该框架结合了StyleGAN3和扩散模型,实现对姿态、照明和表情的精细操控。
- 通过合成面孔图像,有效隔离和量化偏见驱动因素。
- AdaFace模型在减少跨组TPR差异方面表现优越,能有效减少偏见。
- 照明因素在偏见中占有重要比重。
- GANDiff FR符合欧盟人工智能法案的规范,为公平审计提供了标准。
点此查看论文截图

HepatoGEN: Generating Hepatobiliary Phase MRI with Perceptual and Adversarial Models
Authors:Jens Hooge, Gerard Sanroma-Guell, Faidra Stavropoulou, Alexander Ullmann, Gesine Knobloch, Mark Klemens, Carola Schmidt, Sabine Weckbach, Andreas Bolz
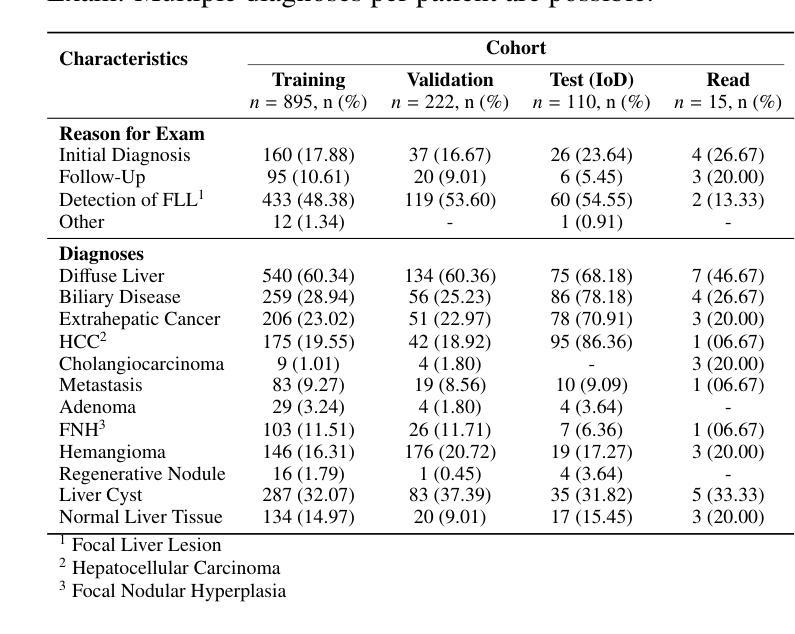
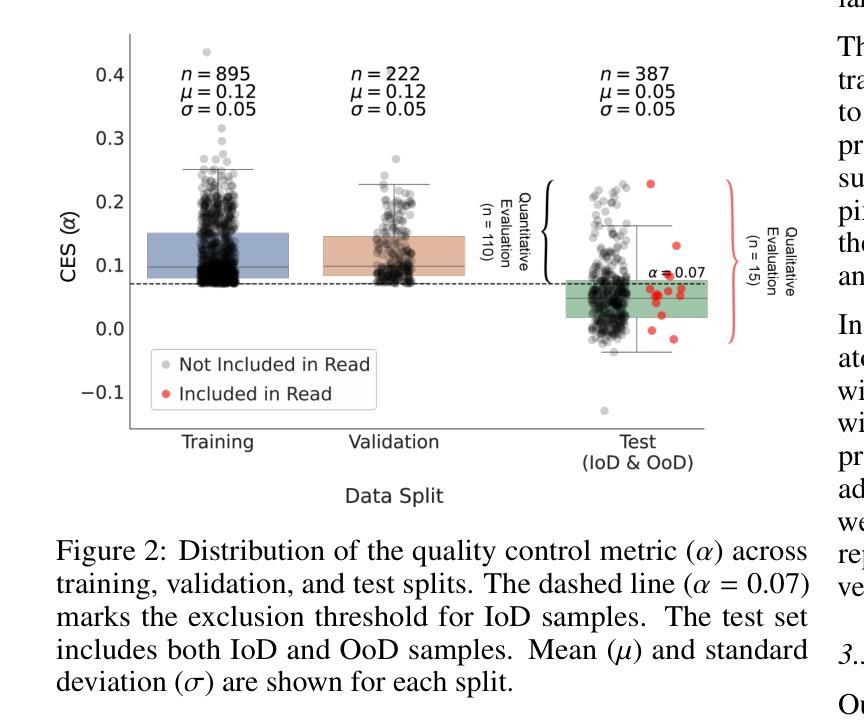
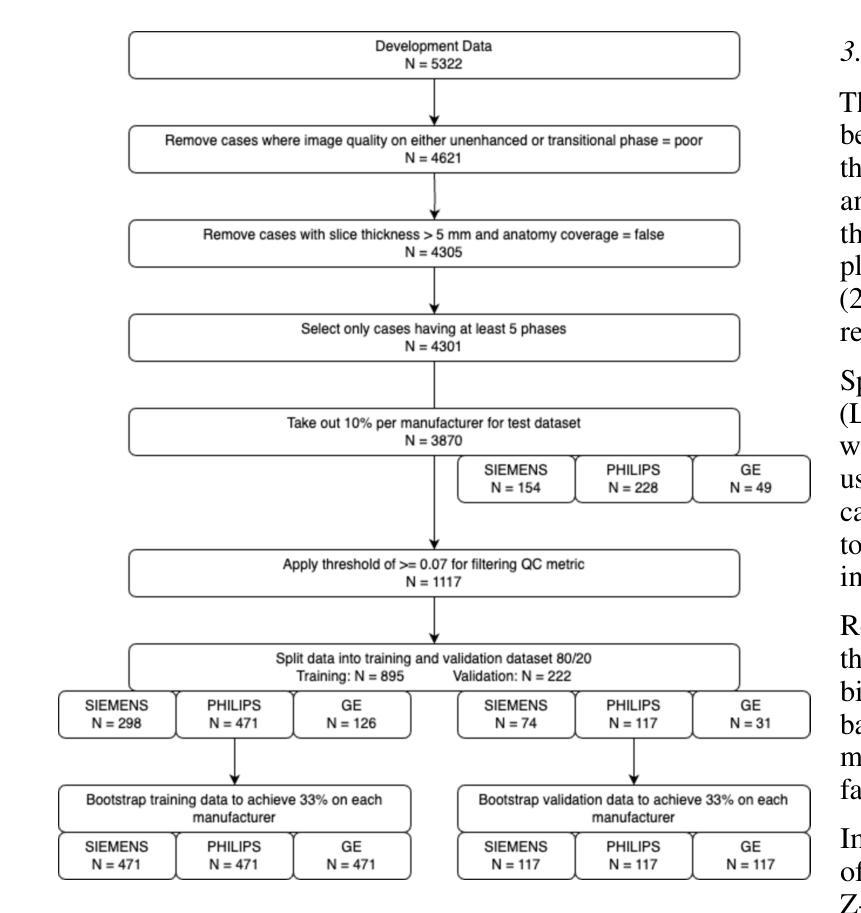
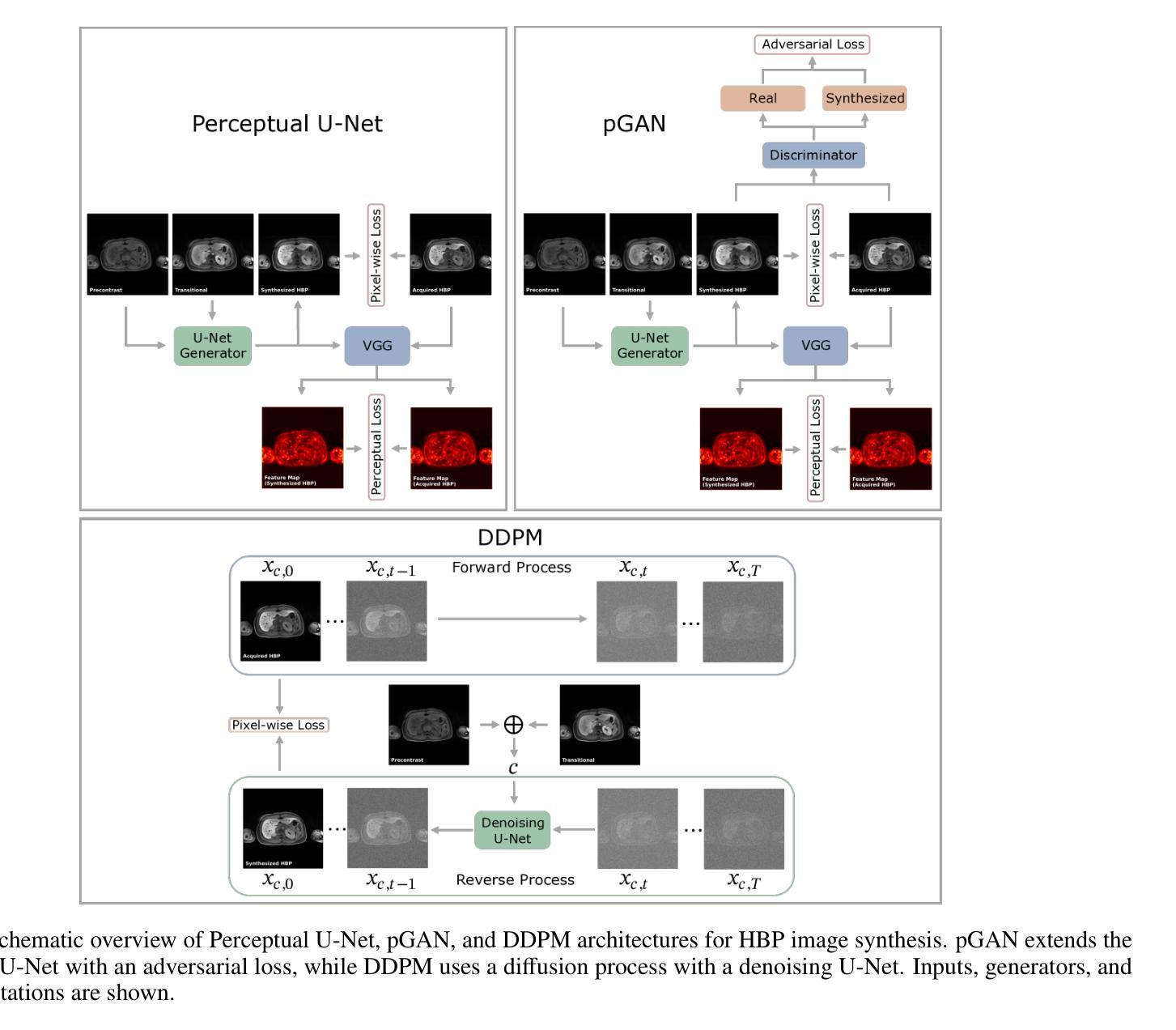
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) plays a crucial role in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions, with the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) providing essential diagnostic information. However, acquiring HBP images requires prolonged scan times, which may compromise patient comfort and scanner throughput. In this study, we propose a deep learning based approach for synthesizing HBP images from earlier contrast phases (precontrast and transitional) and compare three generative models: a perceptual U-Net, a perceptual GAN (pGAN), and a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). We curated a multi-site DCE-MRI dataset from diverse clinical settings and introduced a contrast evolution score (CES) to assess training data quality, enhancing model performance. Quantitative evaluation using pixel-wise and perceptual metrics, combined with qualitative assessment through blinded radiologist reviews, showed that pGAN achieved the best quantitative performance but introduced heterogeneous contrast in out-of-distribution cases. In contrast, the U-Net produced consistent liver enhancement with fewer artifacts, while DDPM underperformed due to limited preservation of fine structural details. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of synthetic HBP image generation as a means to reduce scan time without compromising diagnostic utility, highlighting the clinical potential of deep learning for dynamic contrast enhancement in liver MRI. A project demo is available at: https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在检测和鉴别局部肝脏病变中起着至关重要的作用,其中肝胆相(HBP)提供了关键的诊断信息。然而,获取HBP图像需要较长的扫描时间,这可能会影响到患者的舒适度和扫描器的通过率。本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的方法,通过合成早期对比相(预对比和过渡相)的HBP图像,并比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知GAN(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。我们从多种临床环境中整理了一个多站点DCE-MRI数据集,并引入对比演化评分(CES)来评估训练数据质量,以提高模型性能。通过像素级和感知指标的定量评估,以及通过盲态放射科医生审查的定性评估表明,pGAN在定量性能方面表现最佳,但在非分布案例中引入了异质对比。相比之下,U-Net产生的肝脏增强效果一致且伪影较少,而DDPM由于精细结构细节的保护有限而表现不佳。这些发现证明了合成HBP图像生成的可行性,作为一种减少扫描时间而不损害诊断效用的手段,突出了深度学习在肝脏MRI动态对比增强中的临床潜力。项目演示可在:[https://jhooge.github.io/hepatogen] 访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Author disagreement
Summary:该研究采用深度学习技术合成肝细胞期(HBP)图像,以缩短扫描时间并改善诊断效果。研究比较了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、感知生成对抗网络(pGAN)和去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)。结果显示,pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在异常情况下会出现异质对比。相比之下,U-Net产生一致的肝脏增强和较少的伪影,而DDPM由于细节保护有限而表现不佳。该研究证明了合成HBP图像生成的可行性,可作为减少扫描时间而不影响诊断效用的手段,展示了深度学习在动态对比增强肝脏MRI中的临床潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- DCE-MRI在检测肝脏局部病变中起到关键作用,其中HBP图像提供重要诊断信息。
- 深度学习技术被用于合成HBP图像,以缩短扫描时间并改善诊断效果。
- 对比了三种生成模型:感知U-Net、pGAN和DDPM。
- pGAN在定量性能上表现最佳,但在异常情况下出现异质对比。
- U-Net产生的肝脏增强效果一致且伪影较少。
- DDPM在细节保护方面表现不佳,性能较差。
点此查看论文截图

HealthiVert-GAN: A Novel Framework of Pseudo-Healthy Vertebral Image Synthesis for Interpretable Compression Fracture Grading
Authors:Qi Zhang, Cheng Chuang, Shunan Zhang, Ziqi Zhao, Kun Wang, Jun Xu, Jianqi Sun
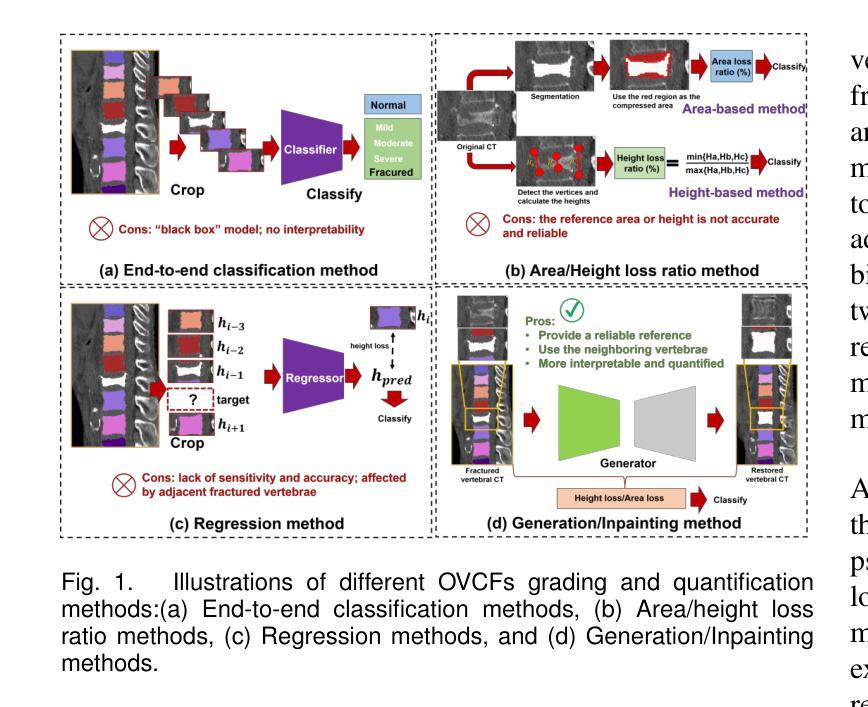
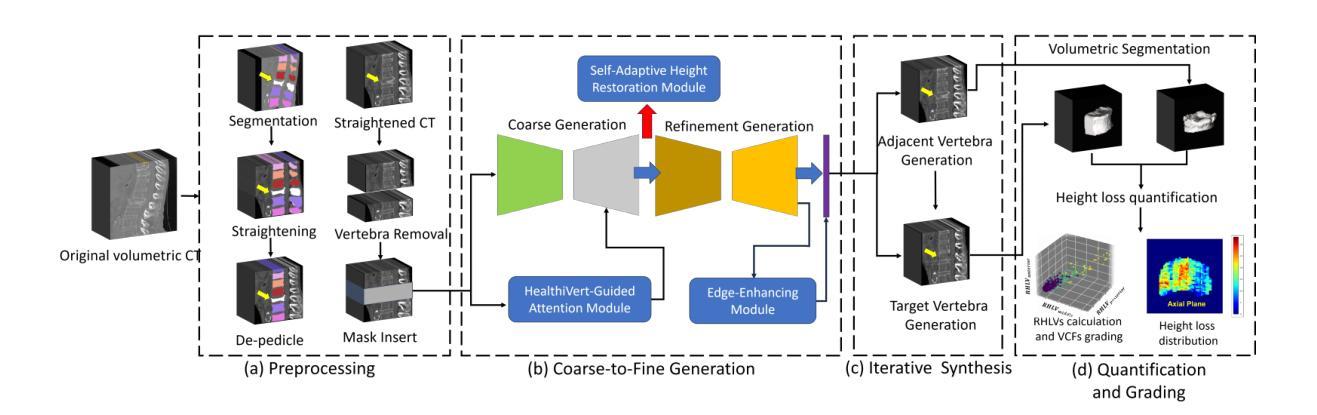
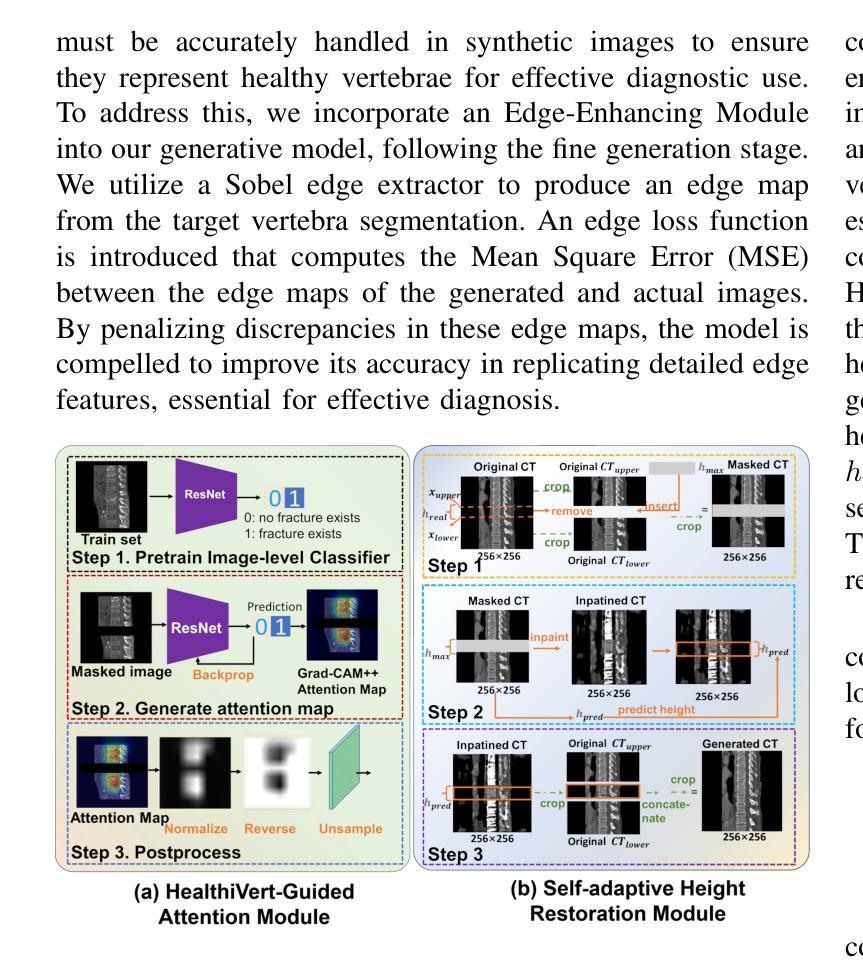
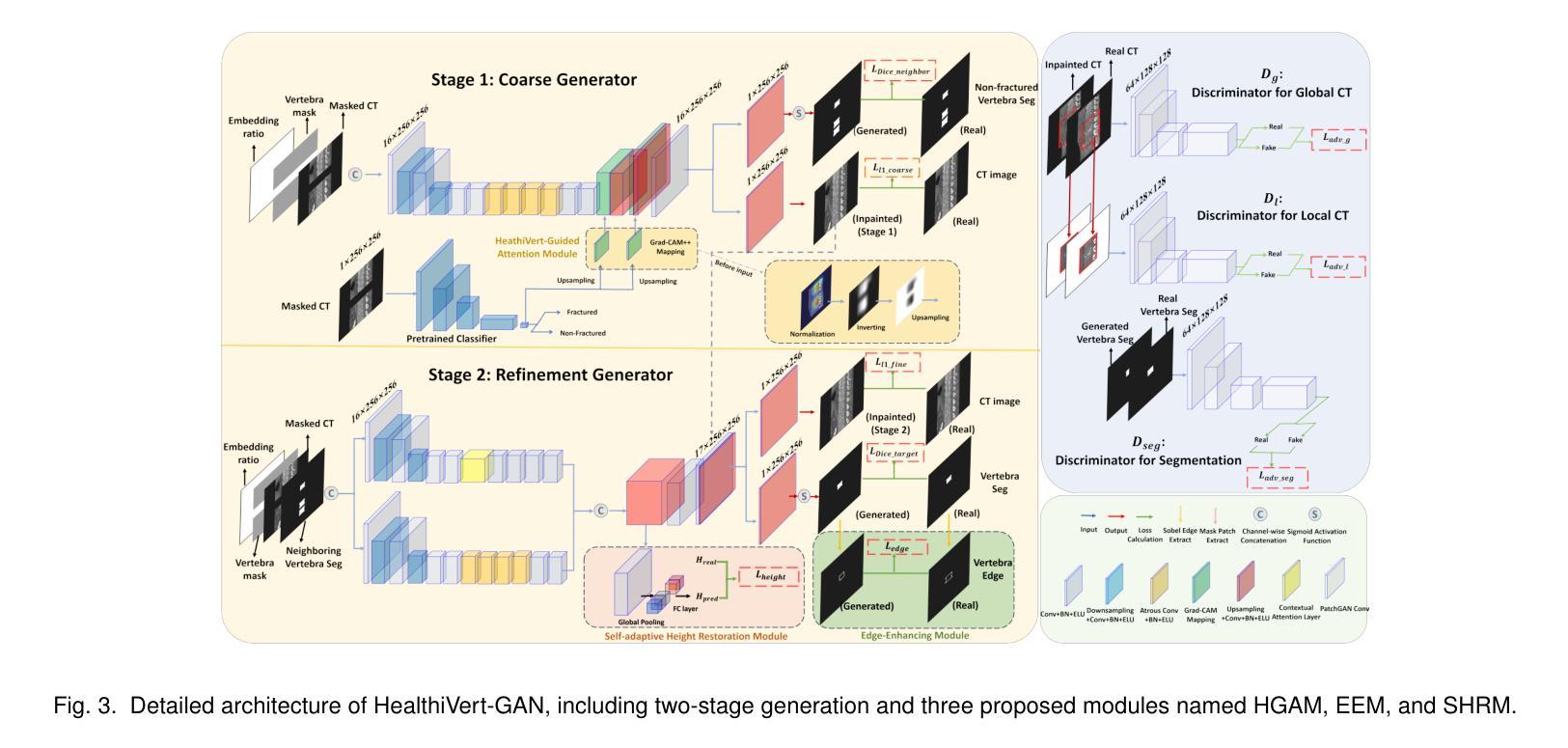
Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) are prevalent in the elderly population, typically assessed on computed tomography (CT) scans by evaluating vertebral height loss. This assessment helps determine the fracture’s impact on spinal stability and the need for surgical intervention. However, the absence of pre-fracture CT scans and standardized vertebral references leads to measurement errors and inter-observer variability, while irregular compression patterns further challenge the precise grading of fracture severity. While deep learning methods have shown promise in aiding OVCFs screening, they often lack interpretability and sufficient sensitivity, limiting their clinical applicability. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel vertebra synthesis-height loss quantification-OVCFs grading framework. Our proposed model, HealthiVert-GAN, utilizes a coarse-to-fine synthesis network designed to generate pseudo-healthy vertebral images that simulate the pre-fracture state of fractured vertebrae. This model integrates three auxiliary modules that leverage the morphology and height information of adjacent healthy vertebrae to ensure anatomical consistency. Additionally, we introduce the Relative Height Loss of Vertebrae (RHLV) as a quantification metric, which divides each vertebra into three sections to measure height loss between pre-fracture and post-fracture states, followed by fracture severity classification using a Support Vector Machine (SVM). Our approach achieves state-of-the-art classification performance on both the Verse2019 dataset and in-house dataset, and it provides cross-sectional distribution maps of vertebral height loss. This practical tool enhances diagnostic accuracy in clinical settings and assisting in surgical decision-making.
骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折(OVCFs)在老年人群中普遍存在,通常通过计算机断层扫描(CT)评估椎体高度损失来检测。这种评估方法有助于确定骨折对脊柱稳定性的影响以及是否需要手术干预。然而,缺乏骨折前的CT扫描和标准化的椎体参考会导致测量误差和观察者之间的差异,而不规则的压缩模式进一步挑战了骨折严重程度的精确分级。虽然深度学习的方法在辅助OVCFs筛查中显示出潜力,但它们往往缺乏解释性和足够的敏感性,限制了其在临床上的适用性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种新颖的椎体合成-高度损失量化-OVCFs分级框架。我们提出的HealthiVert-GAN模型利用从粗糙到精细的合成网络生成模拟骨折椎体预骨折状态的伪健康椎体图像。该模型集成了三个辅助模块,这些模块利用相邻健康椎体的形态和高度信息来保证解剖一致性。此外,我们引入了相对椎体高度损失(RHLV)作为量化指标,将每个椎体分为三部分,测量预骨折和骨折后状态之间的高度损失,然后使用支持向量机(SVM)进行骨折严重程度分类。我们的方法在Verse2019数据集和内部数据集上实现了最先进的分类性能,并提供了椎体高度损失的横截面分布图。这个实用的工具提高了临床环境中的诊断准确性,并有助于手术决策。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:老年人口中的骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折(OVCFs)通常通过计算机断层扫描(CT)评估椎体高度损失来检测。本文提出一种新型的椎体合成-高度损失量化-OVCFs分级框架,引入HealthiVert-GAN模型,利用粗到细的合成网络生成模拟骨折椎体预骨折状态的伪健康椎体图像。并结合辅助模块和相对高度损失量化指标RHLV进行骨折严重程度的分类,达到行业前沿的分类性能,增强临床诊断准确性并辅助手术决策。
Key Takeaways:
- 骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折在老年群体中普遍,通常通过CT扫描评估椎体高度损失。
- 现有的评估方法存在测量误差和观察者间差异的问题。
- HealthiVert-GAN模型利用粗到细的合成网络生成伪健康椎体图像,模拟预骨折状态。
- 引入相对高度损失量化指标RHLV,对椎体高度损失进行精细测量。
- 结合辅助模块确保解剖一致性,提高诊断准确性。
- 该方法在公开数据集和院内数据集上均达到最佳分类性能。
点此查看论文截图