⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
StyleMM: Stylized 3D Morphable Face Model via Text-Driven Aligned Image Translation
Authors:Seungmi Lee, Kwan Yun, Junyong Noh
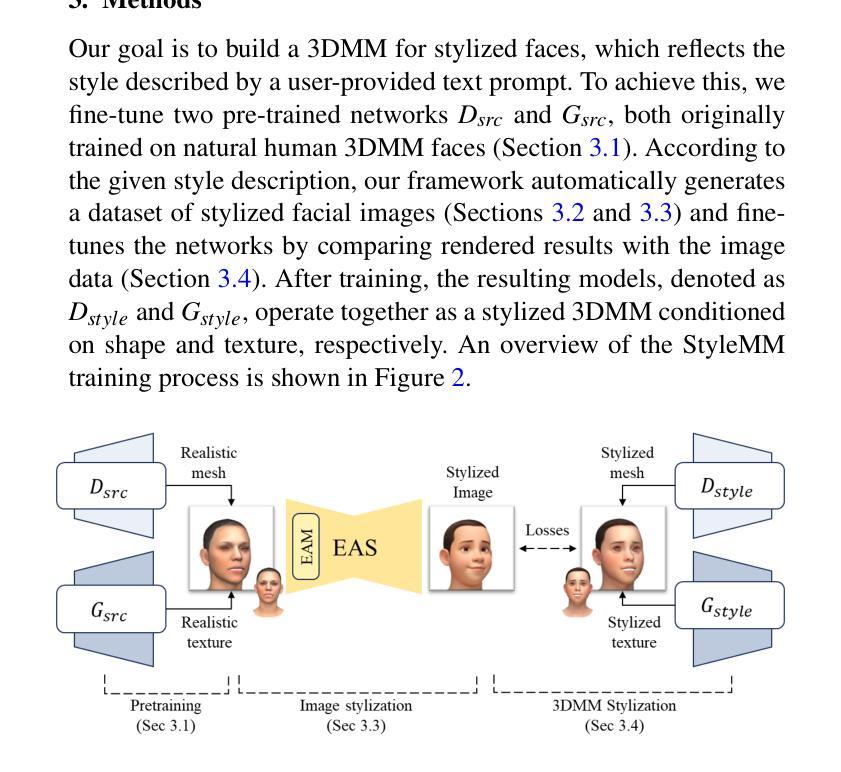
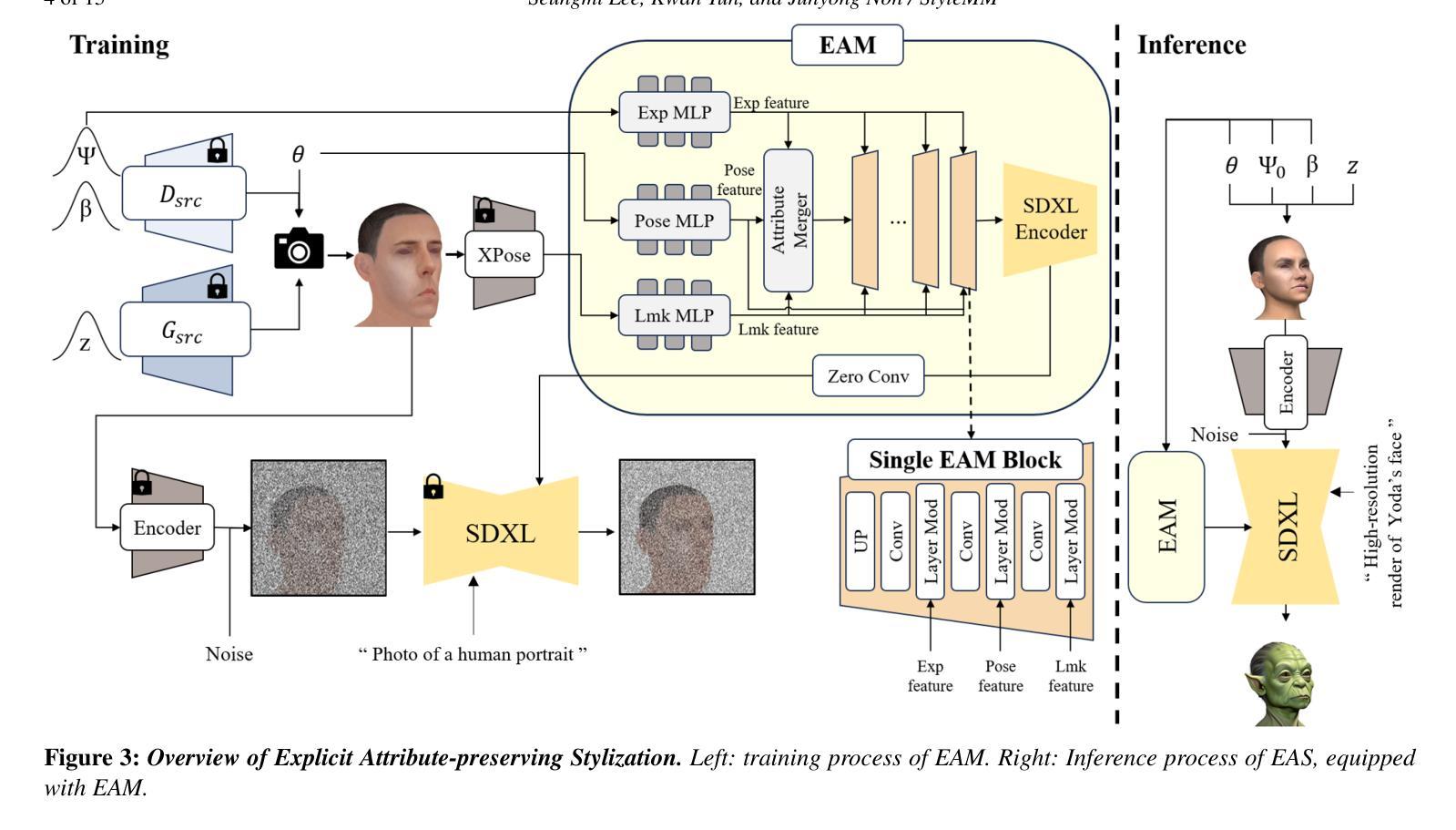
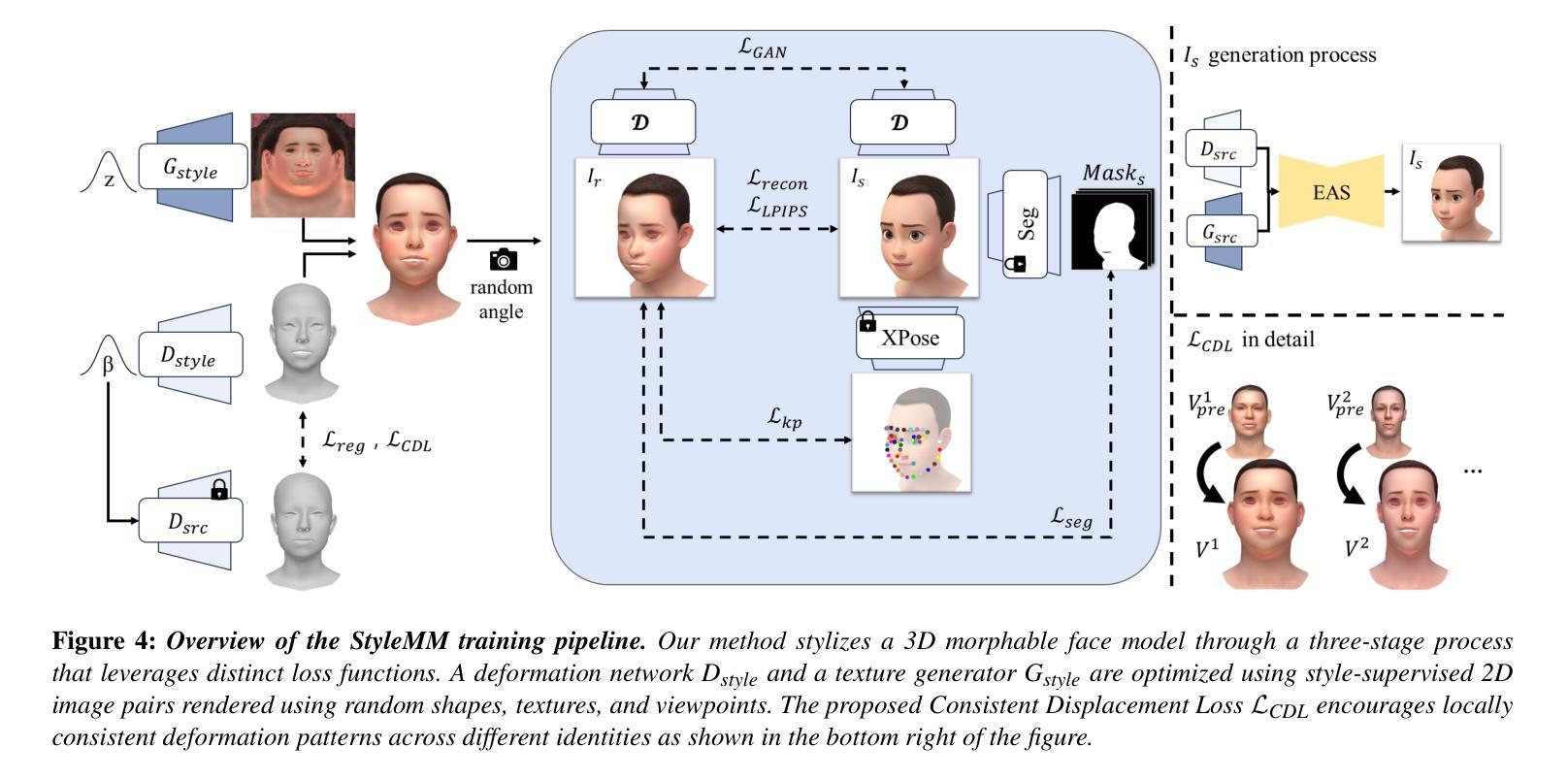
We introduce StyleMM, a novel framework that can construct a stylized 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) based on user-defined text descriptions specifying a target style. Building upon a pre-trained mesh deformation network and a texture generator for original 3DMM-based realistic human faces, our approach fine-tunes these models using stylized facial images generated via text-guided image-to-image (i2i) translation with a diffusion model, which serve as stylization targets for the rendered mesh. To prevent undesired changes in identity, facial alignment, or expressions during i2i translation, we introduce a stylization method that explicitly preserves the facial attributes of the source image. By maintaining these critical attributes during image stylization, the proposed approach ensures consistent 3D style transfer across the 3DMM parameter space through image-based training. Once trained, StyleMM enables feed-forward generation of stylized face meshes with explicit control over shape, expression, and texture parameters, producing meshes with consistent vertex connectivity and animatability. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of identity-level facial diversity and stylization capability. The code and videos are available at kwanyun.github.io/stylemm_page.
我们介绍了StyleMM,这是一个新型框架,可以根据用户定义的文本描述指定目标风格来构建风格化的3D可变形模型(3DMM)。我们的方法建立在预训练的网格变形网络和原始3DMM现实人脸的纹理生成器之上,使用通过文本引导的图像到图像(i2i)翻译扩散模型生成的风格化面部图像对这些模型进行微调,这些图像作为渲染网格的风格化目标。为了防止在i2i翻译过程中身份、面部对齐或表情发生不必要的变化,我们引入了一种显式保留源图像面部特征的风格化方法。通过保持这些关键特征在图像风格化过程中的一致性,所提出的方法确保了通过基于图像的训练在整个3DMM参数空间进行一致的3D风格转换。一旦训练完成,StyleMM就能够以前馈方式生成具有明确形状、表情和纹理参数控制的风格化面部网格,产生具有一致顶点连接和动画能力的网格。定量和定性评估表明,我们的方法在身份级别的面部多样性和风格化能力方面优于最先进的方法。代码和视频可在kwanyun.github.io/stylemm_page查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pacific graphics 2025, CGF, 15 pages
Summary
基于用户定义文本描述的目标风格,我们引入了StyleMM这一新型框架,构建了一个风格化的3D可变形模型(3DMM)。该框架在预训练的网格变形网络和原始3DMM逼真人脸纹理生成器的基础上,使用文本引导的图像到图像(i2i)翻译扩散模型生成风格化面部图像,作为渲染网格的风格化目标进行微调。为阻止i2i翻译过程中身份、面部对齐或表情的不必要变化,我们引入了一种显式保留源图像面部特征的风格化方法。通过保持这些关键特征在图像风格化过程中的一致性,所提出的方法确保了在整个3DMM参数空间中的3D风格转换通过基于图像的训练实现一致。训练后的StyleMM可以通过前向生成风格化的面部网格,对形状、表情和纹理参数进行显式控制,产生具有一致顶点连接和动画能力的网格。定量和定性评估表明,我们的方法在身份级别的面部多样性和风格化能力方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- StyleMM是一个基于用户定义文本描述构建风格化3D可变形模型(3DMM)的框架。
- 利用预训练模型并结合文本引导的i2i翻译扩散模型生成风格化面部图像。
- 引入风格化方法,显式保留源图像的面部特征,以保持身份、面部对齐和表情的一致性。
- 通过图像基训练实现整个3DMM参数空间中的一致3D风格转换。
- StyleMM可以生成具有一致顶点连接和动画能力的风格化面部网格,具有显式控制形状、表达和纹理参数的能力。
- 与现有技术相比,StyleMM在身份级别的面部多样性和风格化能力方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图


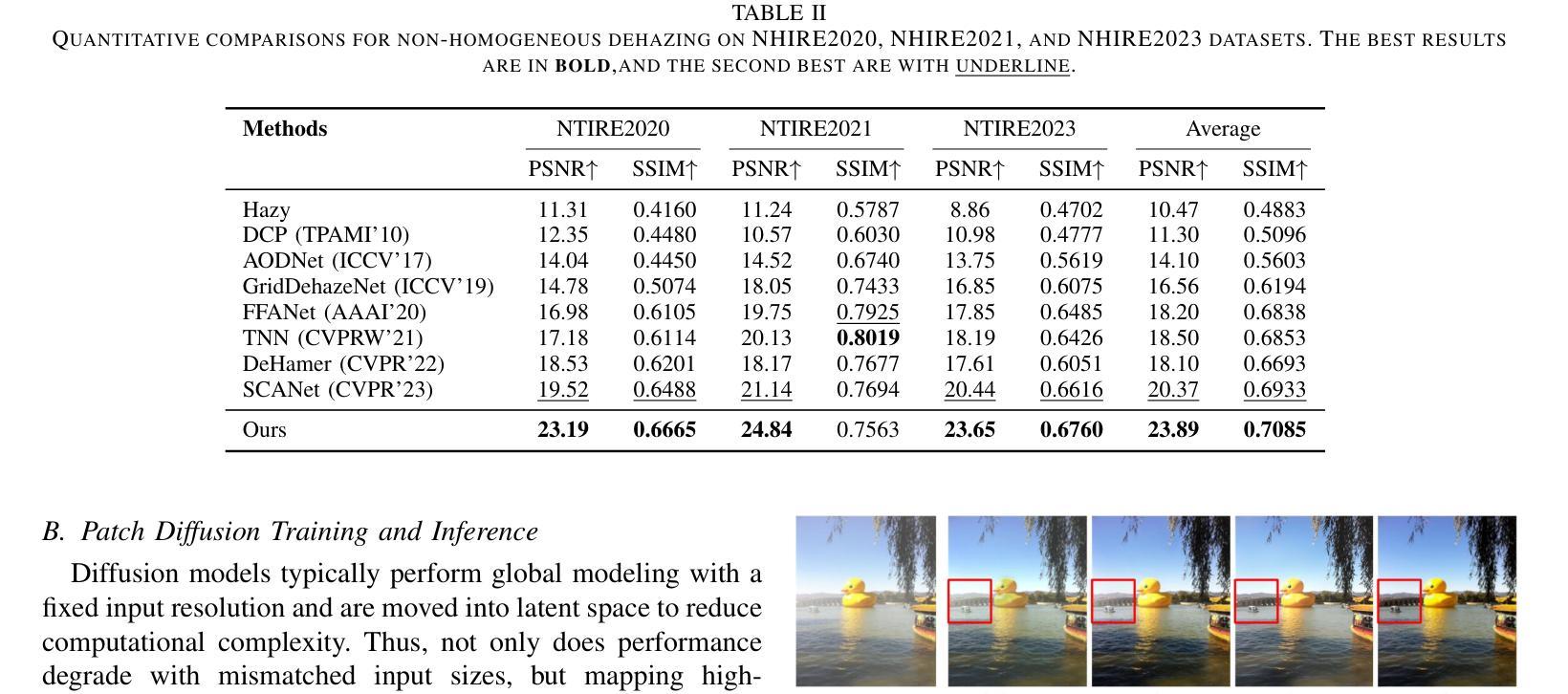
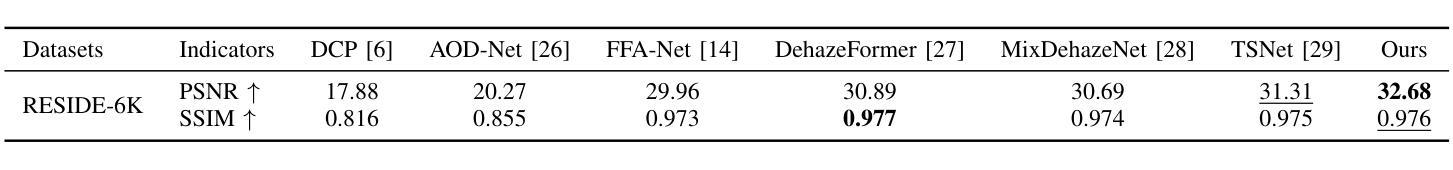
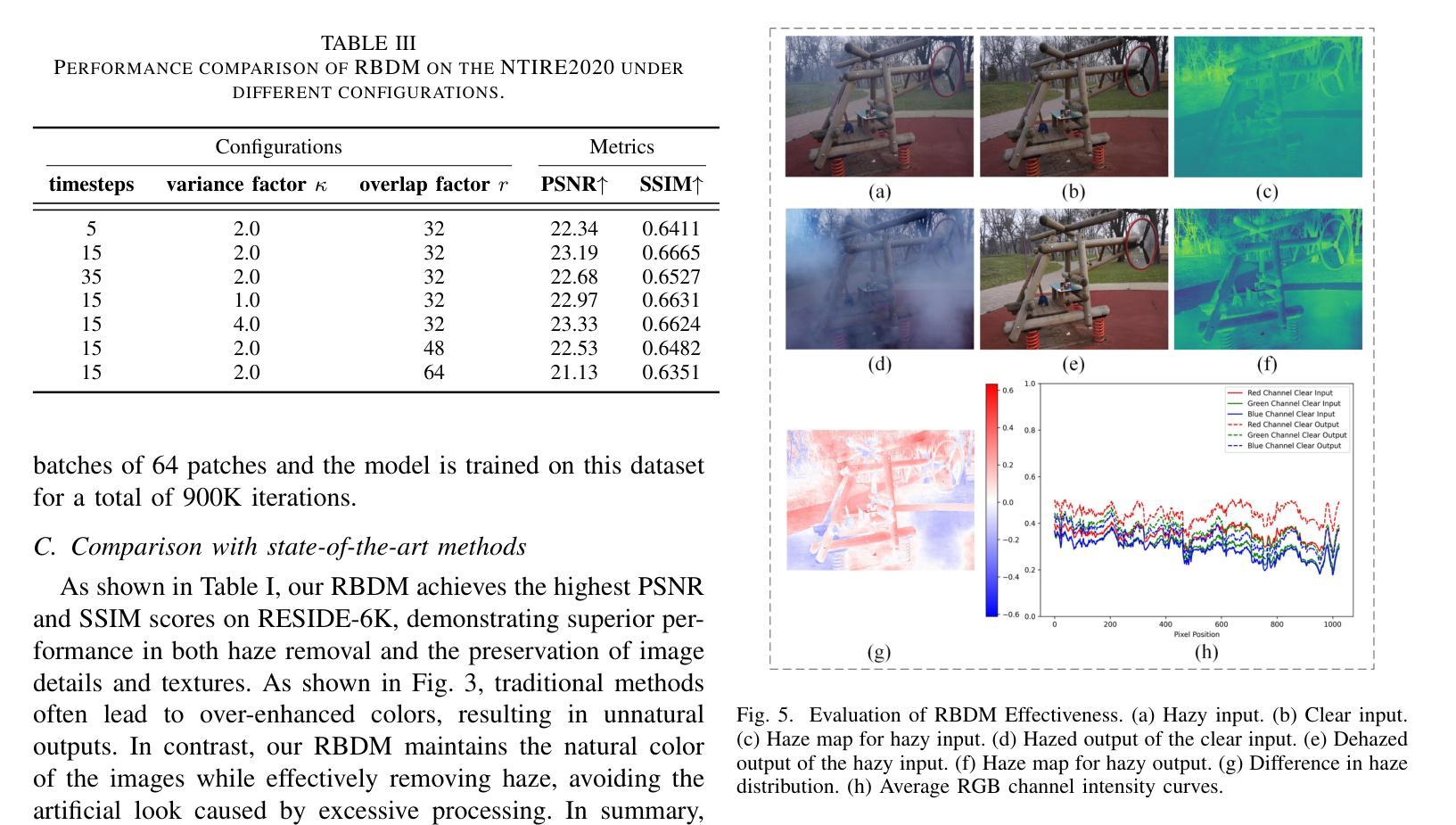
Residual-based Efficient Bidirectional Diffusion Model for Image Dehazing and Haze Generation
Authors:Bing Liu, Le Wang, Hao Liu, Mingming Liu
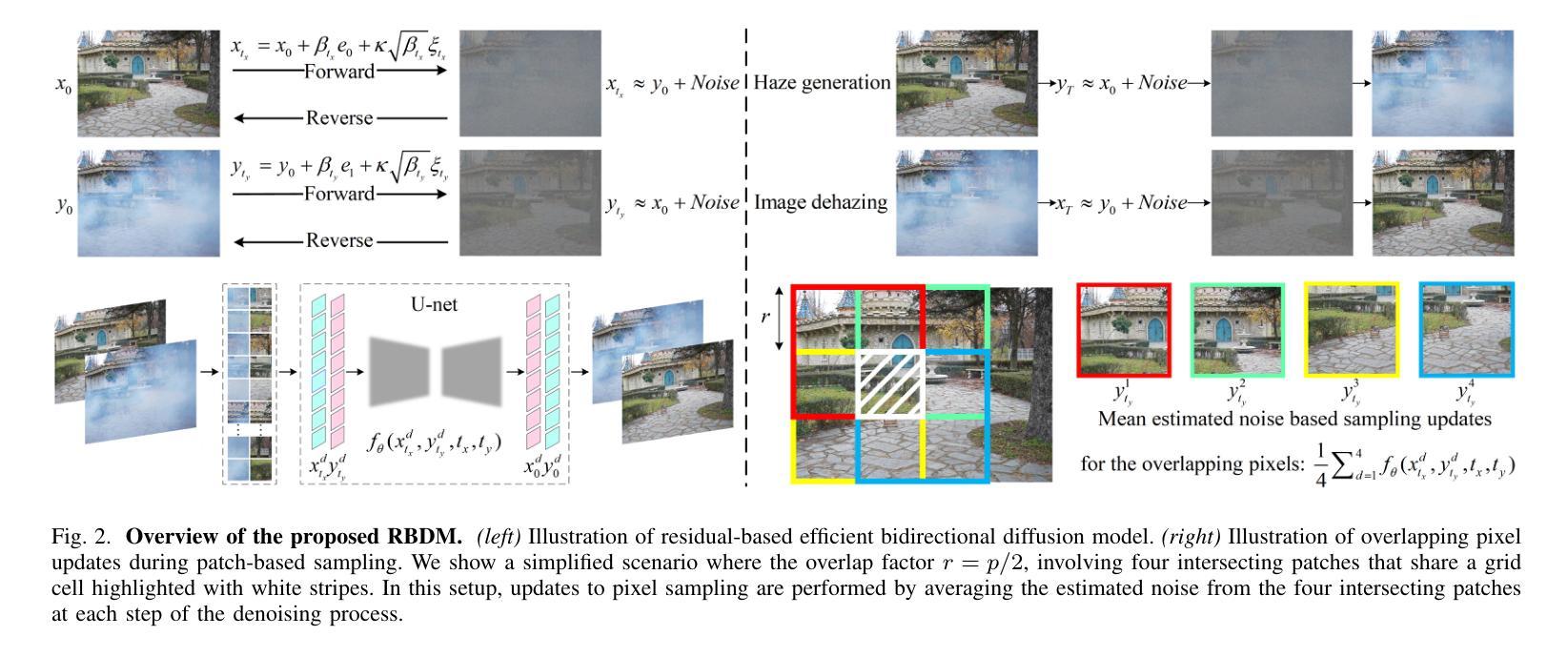
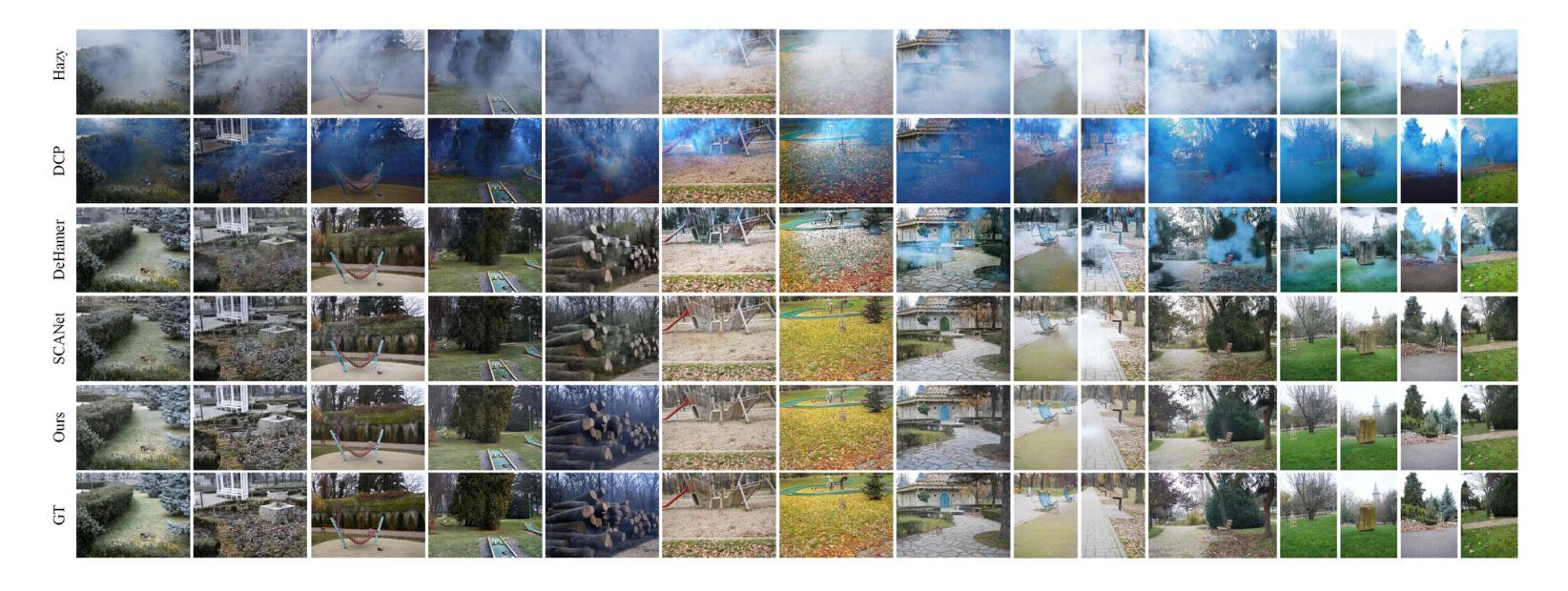
Current deep dehazing methods only focus on removing haze from hazy images, lacking the capability to translate between hazy and haze-free images. To address this issue, we propose a residual-based efficient bidirectional diffusion model (RBDM) that can model the conditional distributions for both dehazing and haze generation. Firstly, we devise dual Markov chains that can effectively shift the residuals and facilitate bidirectional smooth transitions between them. Secondly, the RBDM perturbs the hazy and haze-free images at individual timesteps and predicts the noise in the perturbed data to simultaneously learn the conditional distributions. Finally, to enhance performance on relatively small datasets and reduce computational costs, our method introduces a unified score function learned on image patches instead of entire images. Our RBDM successfully implements size-agnostic bidirectional transitions between haze-free and hazy images with only 15 sampling steps. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior or at least comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
当前深度去雾方法仅专注于从雾霾图像中去除雾霾,缺乏在雾霾和无雾图像之间进行翻译的能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于残差的高效双向扩散模型(RBDM),该模型可以对去雾和雾霾生成的条件分布进行建模。首先,我们设计了双马尔可夫链,可以有效地转换残差,促进它们之间的双向平滑过渡。其次,RBDM在单个时间步长内扰动无雾和雾霾图像,并预测受扰动数据中的噪声,以同时学习条件分布。最后,为了提高在相对较小数据集上的性能并降低计算成本,我们的方法引入了一个在图像块上学习的统一评分函数,而不是在整个图像上。我们的RBDM仅使用15个采样步骤就成功实现了无雾和雾霾图像之间大小无关的双向过渡。大量实验表明,所提出的方法在合成和真实世界数据集上均达到了或至少与最先进的方法相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 5 figures, 2025 ICME Accepted
Summary:
提出一种基于残差的双向扩散模型(RBDM),能建模去雾和生成雾的条件分布。通过双马尔可夫链实现残差转移,双向平滑过渡。对去雾和清晰图像进行扰动,预测扰动数据的噪声,学习条件分布。引入统一评分函数,提高小数据集性能,降低计算成本。成功实现去雾和清晰图像之间的尺寸无关双向转换,仅需15个采样步骤。在合成和真实数据集上实现优异性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 引入基于残差的双向扩散模型(RBDM),能处理去雾和雾生成两种情况的图像转换。
- 使用双马尔可夫链实现残差转移,实现图像间的双向平滑过渡。
- 通过扰动图像并预测噪声,学习去雾和清晰图像的条件分布。
- 引入统一评分函数,提高在小数据集上的性能,并降低计算成本。
- 模型能在仅15个采样步骤内实现去雾和清晰图像之间的转换。
- 在合成数据集上的性能优于或至少与现有技术相当。
点此查看论文截图



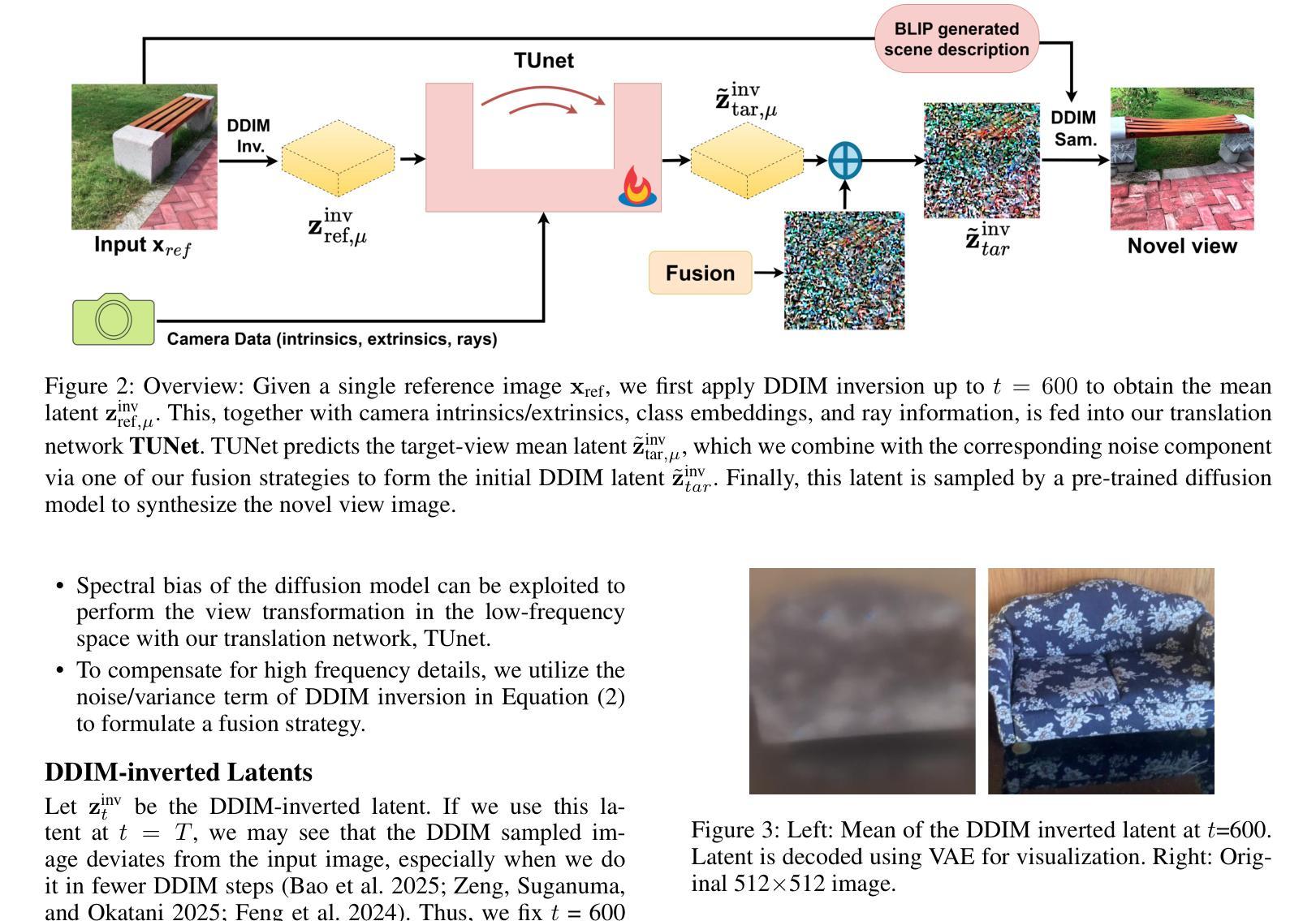
Novel View Synthesis using DDIM Inversion
Authors:Sehajdeep SIngh, A V Subramanyam
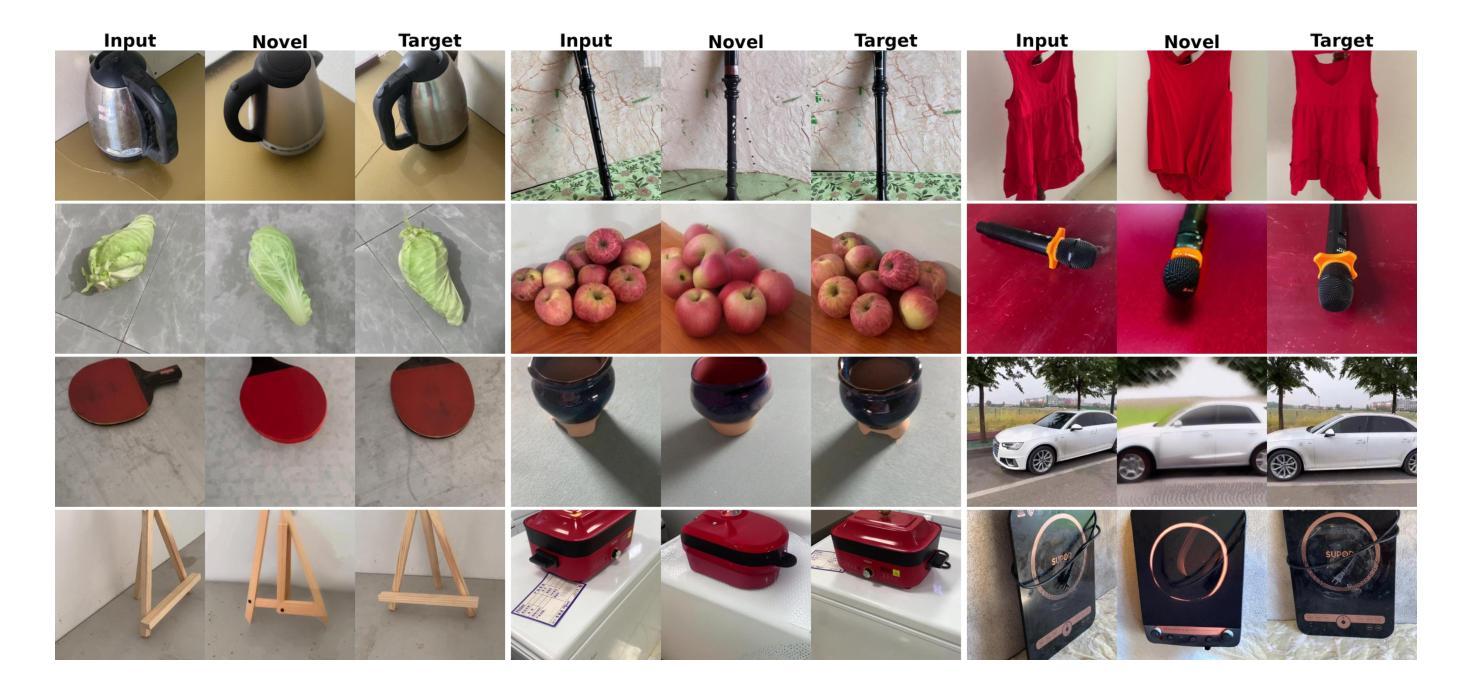
Synthesizing novel views from a single input image is a challenging task. It requires extrapolating the 3D structure of a scene while inferring details in occluded regions, and maintaining geometric consistency across viewpoints. Many existing methods must fine-tune large diffusion backbones using multiple views or train a diffusion model from scratch, which is extremely expensive. Additionally, they suffer from blurry reconstruction and poor generalization. This gap presents the opportunity to explore an explicit lightweight view translation framework that can directly utilize the high-fidelity generative capabilities of a pretrained diffusion model while reconstructing a scene from a novel view. Given the DDIM-inverted latent of a single input image, we employ a camera pose-conditioned translation U-Net, TUNet, to predict the inverted latent corresponding to the desired target view. However, the image sampled using the predicted latent may result in a blurry reconstruction. To this end, we propose a novel fusion strategy that exploits the inherent noise correlation structure observed in DDIM inversion. The proposed fusion strategy helps preserve the texture and fine-grained details. To synthesize the novel view, we use the fused latent as the initial condition for DDIM sampling, leveraging the generative prior of the pretrained diffusion model. Extensive experiments on MVImgNet demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods.
从单一输入图像合成新颖视角是一项具有挑战性的任务。它要求在推断遮挡区域的细节时推断出场景的3D结构,并在不同视角之间保持几何一致性。许多现有方法必须使用多种视角对大型扩散主干进行微调,或者从头开始训练扩散模型,这成本极高。此外,它们还存在模糊重建和泛化能力差的缺点。这一差距为我们探索一个明确的轻量级视图翻译框架提供了机会,该框架能够利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力,从新颖视角重建场景。给定单个输入图像的DDIM反向传播潜在特征,我们采用受相机姿态控制的翻译U-Net(TUNet)来预测对应目标视角的反向传播潜在特征。然而,使用预测潜在特征所采样的图像可能会导致重建模糊。为此,我们提出了一种利用DDIM反演中观察到的固有噪声相关性结构的新型融合策略。该融合策略有助于保留纹理和细粒度细节。为了合成新颖视角,我们使用融合后的潜在特征作为DDIM采样的初始条件,利用预训练扩散模型的生成先验。在MVImgNet上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对单一输入图像合成新颖视角的任务,现有方法需要微调大型扩散模型或使用多个视角进行训练,成本高昂且存在模糊重建和泛化能力差的问题。为此,我们提出一种显式轻量级视角转换框架,利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力,通过相机姿态调节的翻译U-Net来预测目标视角的倒置潜在对应物。为提高重建图像的清晰度,我们提出了一种利用DDIM反转过程中观察到的固有噪声相关结构的新融合策略。实验证明,该方法在MVImgNet上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 合成新颖视角是一项挑战任务,要求从单一输入图像中推断出场景的3D结构并在隐藏区域进行细节推断,同时保持不同视角的几何一致性。
- 现有方法需要昂贵的微调大型扩散模型或使用多个视角进行训练,存在模糊重建和泛化能力差的问题。
- 提出一种轻量级视角转换框架,利用预训练扩散模型的高保真生成能力。
- 使用相机姿态调节的翻译U-Net(TUNet)预测目标视角的倒置潜在对应物。
- 提出一种新型融合策略,利用DDIM反转过程中的噪声相关结构,帮助保留纹理和细节。
- 使用融合后的潜在条件作为DDIM采样的初始条件,利用预训练扩散模型的生成先验来合成新颖视角。
点此查看论文截图


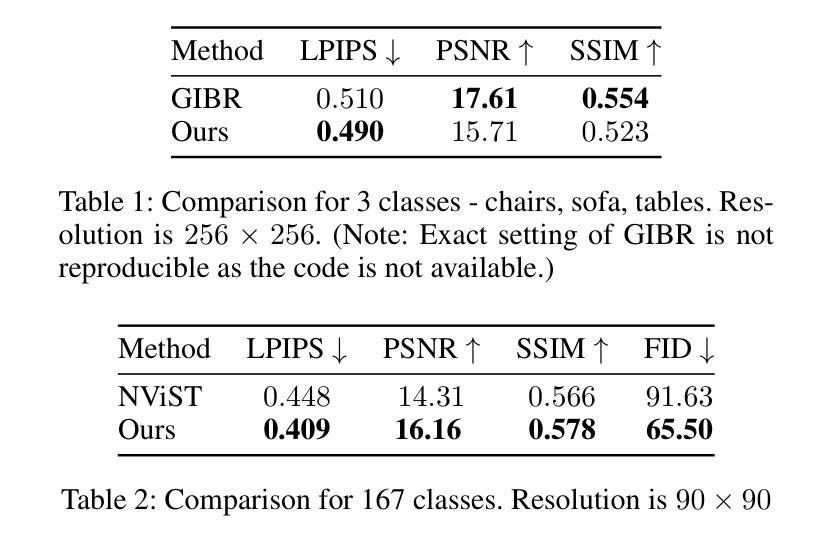
MANGO: Multimodal Attention-based Normalizing Flow Approach to Fusion Learning
Authors:Thanh-Dat Truong, Christophe Bobda, Nitin Agarwal, Khoa Luu
Multimodal learning has gained much success in recent years. However, current multimodal fusion methods adopt the attention mechanism of Transformers to implicitly learn the underlying correlation of multimodal features. As a result, the multimodal model cannot capture the essential features of each modality, making it difficult to comprehend complex structures and correlations of multimodal inputs. This paper introduces a novel Multimodal Attention-based Normalizing Flow (MANGO) approach\footnote{The source code of this work will be publicly available.} to developing explicit, interpretable, and tractable multimodal fusion learning. In particular, we propose a new Invertible Cross-Attention (ICA) layer to develop the Normalizing Flow-based Model for multimodal data. To efficiently capture the complex, underlying correlations in multimodal data in our proposed invertible cross-attention layer, we propose three new cross-attention mechanisms: Modality-to-Modality Cross-Attention (MMCA), Inter-Modality Cross-Attention (IMCA), and Learnable Inter-Modality Cross-Attention (LICA). Finally, we introduce a new Multimodal Attention-based Normalizing Flow to enable the scalability of our proposed method to high-dimensional multimodal data. Our experimental results on three different multimodal learning tasks, i.e., semantic segmentation, image-to-image translation, and movie genre classification, have illustrated the state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance of the proposed approach.
近年来,多模态学习取得了巨大的成功。然而,当前的多模态融合方法采用Transformer的注意力机制来隐式地学习多模态特征之间的底层关联。因此,多模态模型无法捕捉每种模态的基本特征,难以理解多模态输入的复杂结构和关联。本文介绍了一种新颖的多模态注意力基础归一化流(MANGO)方法(该工作的源代码将公开发布)来开发明确、可解释和可行的多模态融合学习。特别是,我们提出了一种新的可逆跨注意力(ICA)层来开发基于归一化流的多模态数据模型。为了在我们提出的可逆跨注意力层中有效地捕捉多模态数据中复杂的底层关联,我们提出了三种新的跨注意力机制:模态间跨注意力(MMCA)、跨模态间注意力(IMCA)和学习跨模态间注意力(LICA)。最后,我们引入了一种新的多模态注意力基础归一化流,使所提出的方法能够扩展到高维多模态数据。我们在三种不同的多模态学习任务(即语义分割、图像到图像的翻译和电影类型分类)上的实验结果证明了所提出方法的最新技术性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态学习近年取得了很大进展,但当前的多模态融合方法采用Transformer的注意力机制来隐式学习多模态特征之间的关联。这导致多模态模型无法捕捉每个模态的关键特征,难以理解和分析多模态输入的复杂结构和关联。本文提出一种新颖的多模态注意力基础归一化流(MANGO)方法,开发明确、可解释和可追踪的多模态融合学习。特别是,我们提出了一种新的可逆交叉注意力(ICA)层,用于开发基于归一化流的多模态数据模型。为了在我们的可逆交叉注意力层中有效地捕捉多模态数据的复杂底层关联,我们提出了三种新的交叉注意力机制。最后,我们引入了一种新的多模态注意力基础归一化流,使所提方法能够扩展到高维多模态数据。在三个不同的多模态学习任务上的实验结果证明了所提方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前多模态融合方法存在难以捕捉每个模态关键特征的问题。
- 论文提出一种新的多模态注意力基础归一化流(MANGO)方法,旨在解决上述问题。
- 引入可逆交叉注意力(ICA)层,为开发基于归一化流的多模态数据模型提供基础。
- 提出三种新的交叉注意力机制:模态间交叉注意力(MMCA)、跨模态交叉注意力(IMCA)和可学习跨模态交叉注意力(LICA)。
- 所提方法能够有效捕捉多模态数据的复杂底层关联。
- 论文实验验证了所提方法在三种不同多模态学习任务上的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

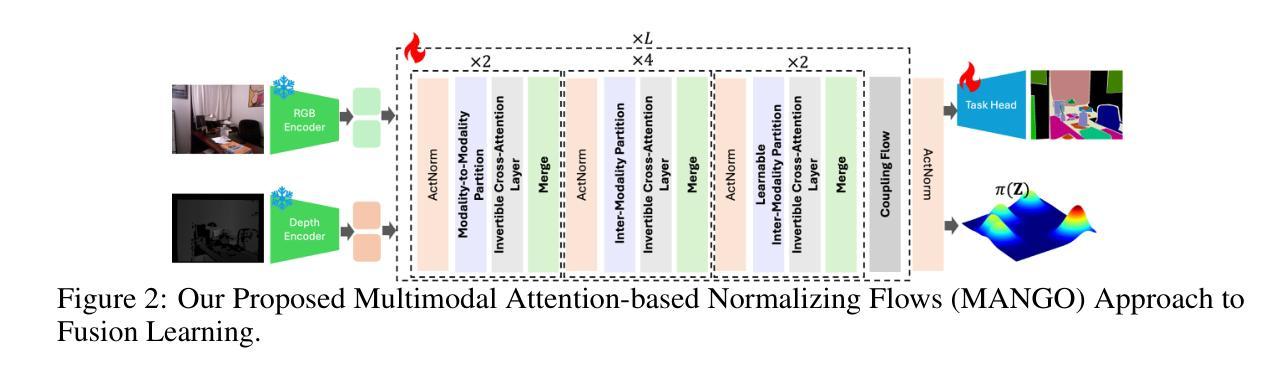
RampNet: A Two-Stage Pipeline for Bootstrapping Curb Ramp Detection in Streetscape Images from Open Government Metadata
Authors:John S. O’Meara, Jared Hwang, Zeyu Wang, Michael Saugstad, Jon E. Froehlich
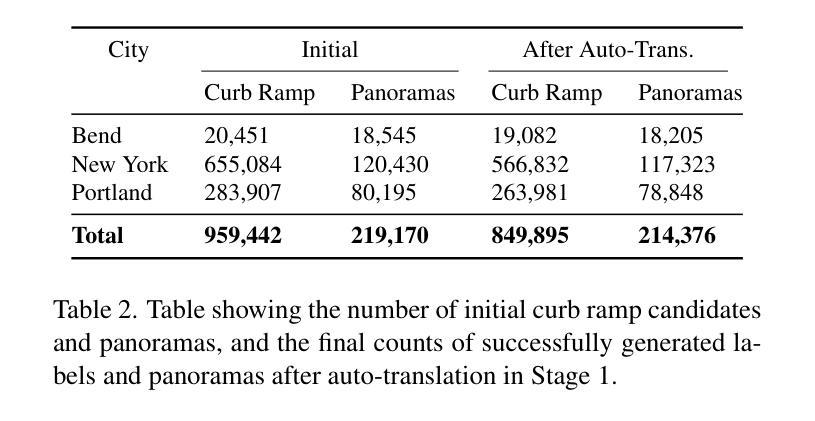
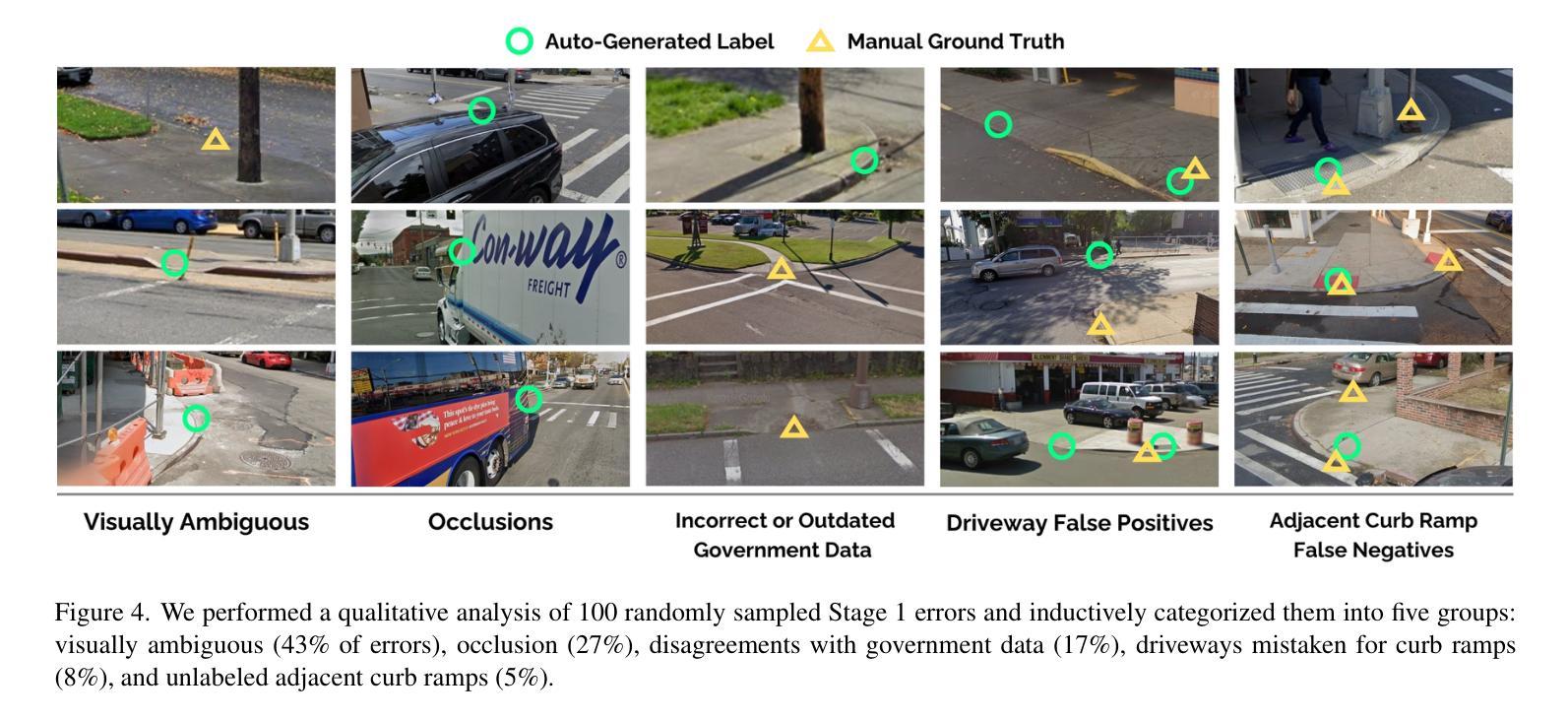
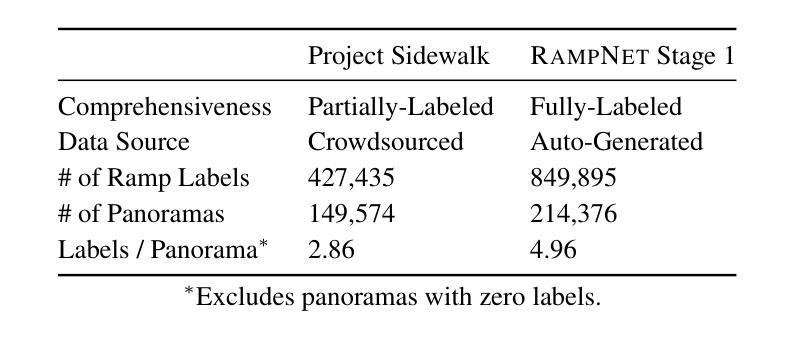
Curb ramps are critical for urban accessibility, but robustly detecting them in images remains an open problem due to the lack of large-scale, high-quality datasets. While prior work has attempted to improve data availability with crowdsourced or manually labeled data, these efforts often fall short in either quality or scale. In this paper, we introduce and evaluate a two-stage pipeline called RampNet to scale curb ramp detection datasets and improve model performance. In Stage 1, we generate a dataset of more than 210,000 annotated Google Street View (GSV) panoramas by auto-translating government-provided curb ramp location data to pixel coordinates in panoramic images. In Stage 2, we train a curb ramp detection model (modified ConvNeXt V2) from the generated dataset, achieving state-of-the-art performance. To evaluate both stages of our pipeline, we compare to manually labeled panoramas. Our generated dataset achieves 94.0% precision and 92.5% recall, and our detection model reaches 0.9236 AP – far exceeding prior work. Our work contributes the first large-scale, high-quality curb ramp detection dataset, benchmark, and model.
路缘石坡道对于城市可达性至关重要,但由于缺乏大规模高质量数据集,在图像中稳健地检测它们仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。尽管之前的研究试图通过众包或手动标记的数据来提高数据可用性,但这些努力在质量或规模上往往有所欠缺。在本文中,我们介绍并评估了一个名为RampNet的两阶段流程,以扩大路缘石坡道检测数据集并提高模型性能。在第一阶段,我们通过自动翻译政府提供的路缘石坡道位置数据,生成了超过21万个标注的Google街景(GSV)全景图像数据集。在第二阶段,我们根据生成的数据集训练了路缘石坡道检测模型(修改后的ConvNeXt V2),取得了最先进的性能。为了评估我们流程的两个阶段,我们将结果与手动标记的全景图像进行了比较。我们生成的数据集达到了94.0%的精确度和92.5%的召回率,我们的检测模型达到了0.9236的平均准确率——远远超过以前的工作。我们的工作贡献了一个大规模、高质量的路缘石坡道检测数据集、基准测试和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICCV’25 Workshop on Vision Foundation Models and Generative AI for Accessibility: Challenges and Opportunities
Summary
本文介绍了利用RampNet两阶段管道实现城市坡道检测数据集的规模化以及模型性能的提升。第一阶段通过自动翻译政府提供的坡道位置数据生成超过21万张标注的Google街景全景图像数据集。第二阶段使用修改后的ConvNeXt V2模型进行坡道检测,达到业界领先水平。评估结果显示,生成的数据集精确度和召回率分别达到94.0%和92.5%,检测模型的平均精度达到0.9236,远超先前工作。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏大规模高质量数据集是城市坡道检测面临的主要问题。
- RampNet两阶段管道解决了坡道检测数据集的规模化问题。
- 第一阶段通过自动翻译政府数据生成大规模坡道位置数据集。
- 第二阶段使用修改后的ConvNeXt V2模型进行坡道检测,性能卓越。
- 生成的数据集精确度和召回率均超过92%。
- 检测模型的平均精度达到业界最高水平。
点此查看论文截图

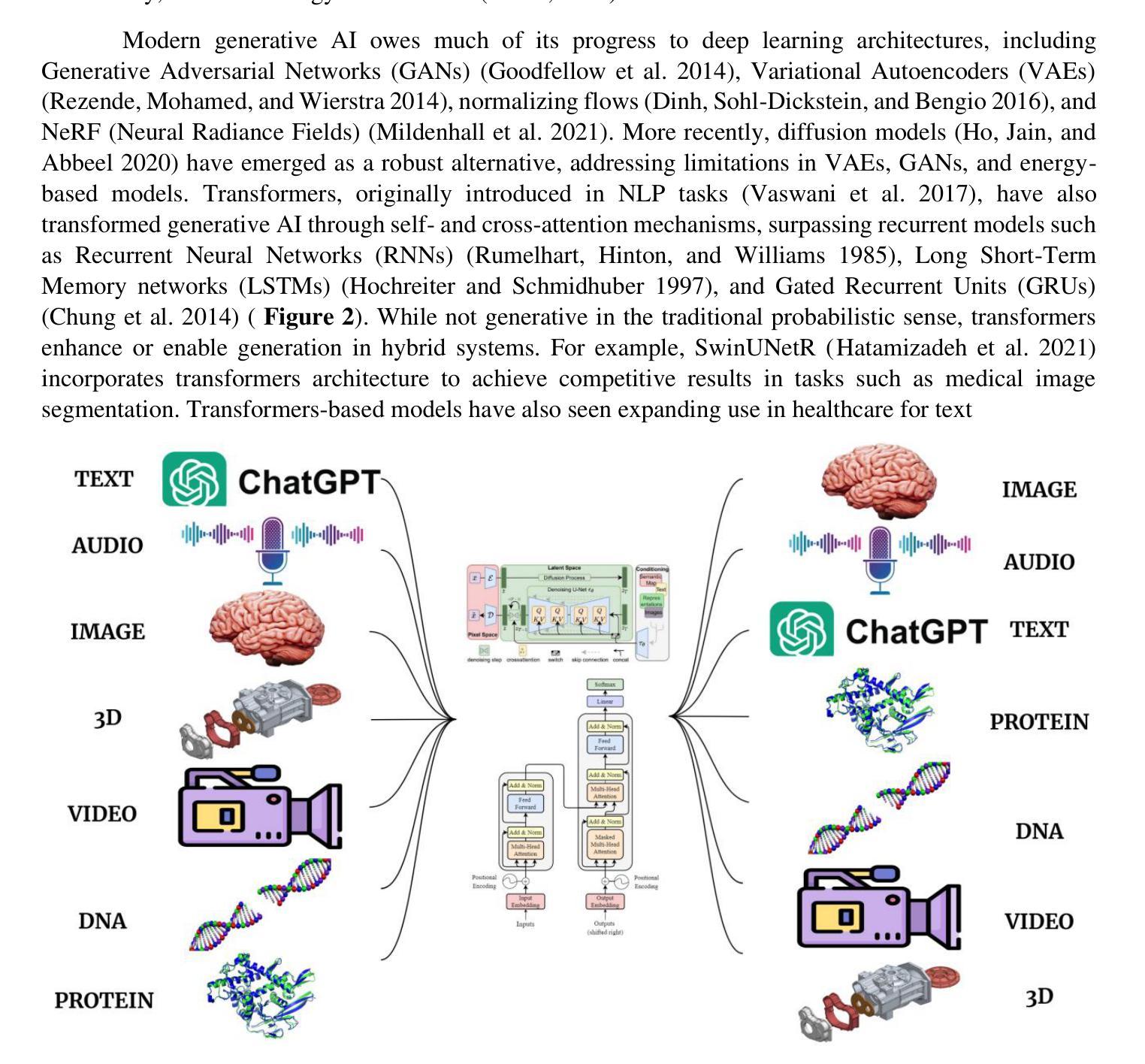
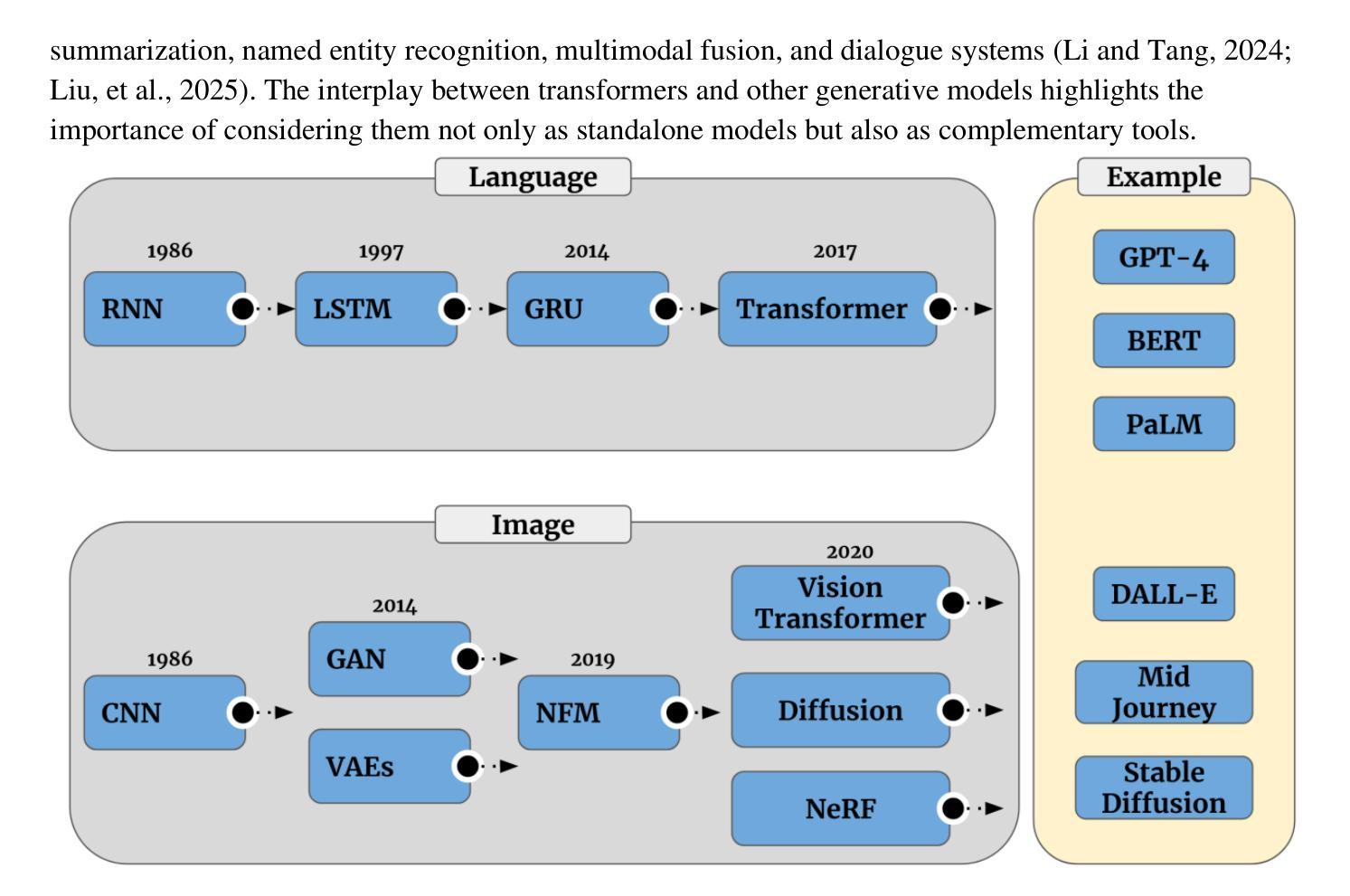
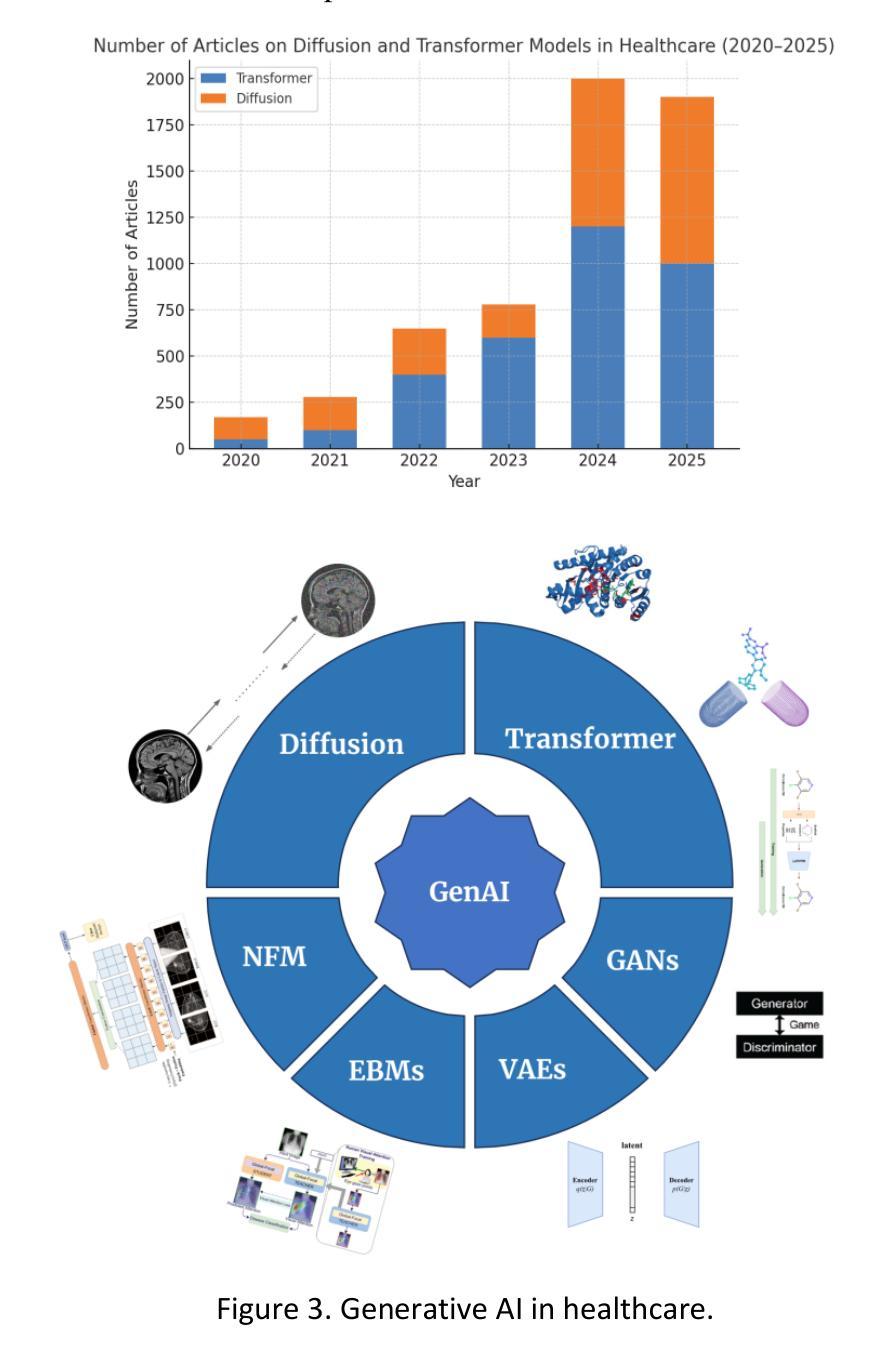
Recent Advances in Generative AI for Healthcare Applications
Authors:Yasin Shokrollahi, Jose Colmenarez, Wenxi Liu, Sahar Yarmohammadtoosky, Matthew M. Nikahd, Pengfei Dong, Xianqi Li, Linxia Gu
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has catalyzed revolutionary changes across various sectors, notably in healthcare. In particular, generative AI-led by diffusion models and transformer architectures-has enabled significant breakthroughs in medical imaging (including image reconstruction, image-to-image translation, generation, and classification), protein structure prediction, clinical documentation, diagnostic assistance, radiology interpretation, clinical decision support, medical coding, and billing, as well as drug design and molecular representation. These innovations have enhanced clinical diagnosis, data reconstruction, and drug synthesis. This review paper aims to offer a comprehensive synthesis of recent advances in healthcare applications of generative AI, with an emphasis on diffusion and transformer models. Moreover, we discuss current capabilities, highlight existing limitations, and outline promising research directions to address emerging challenges. Serving as both a reference for researchers and a guide for practitioners, this work offers an integrated view of the state of the art, its impact on healthcare, and its future potential.
人工智能(AI)的快速发展催生了各个领域的革命性变化,特别是在医疗领域。特别是以扩散模型和转换器架构为驱动的生成式人工智能,在医学成像(包括图像重建、图像到图像的翻译、生成和分类)、蛋白质结构预测、临床文档、诊断辅助、放射学解读、临床决策支持、医疗编码和计费以及药物设计和分子表示等方面实现了重大突破。这些创新提高了临床诊断、数据重建和药物合成的能力。这篇综述文章旨在提供关于生成式人工智能在医疗领域应用的最新进展的综合分析,重点介绍扩散模型和转换器模型。此外,我们还讨论了当前的能力,强调了现有的局限性,并概述了解决新兴挑战的有希望的研究方向。这项工作既为研究者提供了参考,也为从业者提供了指南,全面展示了最新技术、其对医疗领域的影响及其未来潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 51 pages, 16 figures, 1table
Summary
人工智能(AI)的快速发展催生了各领域革命性的变革,尤其在医疗领域。生成式AI引领的扩散模型和转换器架构在医疗成像、蛋白质结构预测、临床文档、诊断辅助、放射学解读、临床决策支持等方面取得了重大突破。本文旨在全面综述生成式AI在医疗领域的最新进展,重点介绍扩散模型和转换器模型的应用。同时,本文讨论当前的能力,强调现有的局限性,并概述有前景的研究方向以应对新兴挑战。它为研究人员提供了参考,为从业者提供了指南,展现了最新的技术态势及其对医疗领域的影响和未来潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI在医疗领域引发重大突破,涵盖医疗成像、蛋白质结构预测、临床文档等方面。
- 扩散模型和转换器架构是生成式AI的主要技术驱动力。
- 这些技术增强了临床诊断、数据重建和药物合成的能力。
- 当前生成式AI在医疗领域的应用已产生显著影响。
- 尽管有重大进展,但生成式AI在医疗领域仍存在局限性。
- 有必要进行更多研究以解决新兴挑战,并推动生成式AI在医疗领域的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

Ear-Keeper: A Cross-Platform AI System for Rapid and Accurate Ear Disease Diagnosis
Authors:Feiyan Lu, Yubiao Yue, Zhenzhang Li, Meiping Zhang, Wen Luo, Fan Zhang, Tong Liu, Jingyong Shi, Guang Wang, Xinyu Zeng
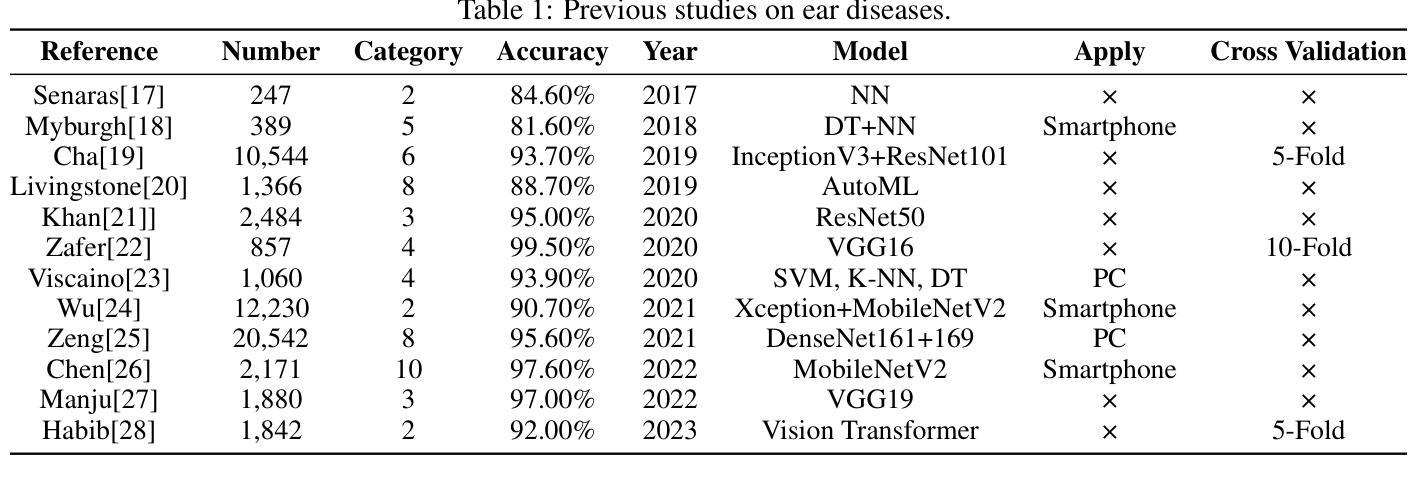
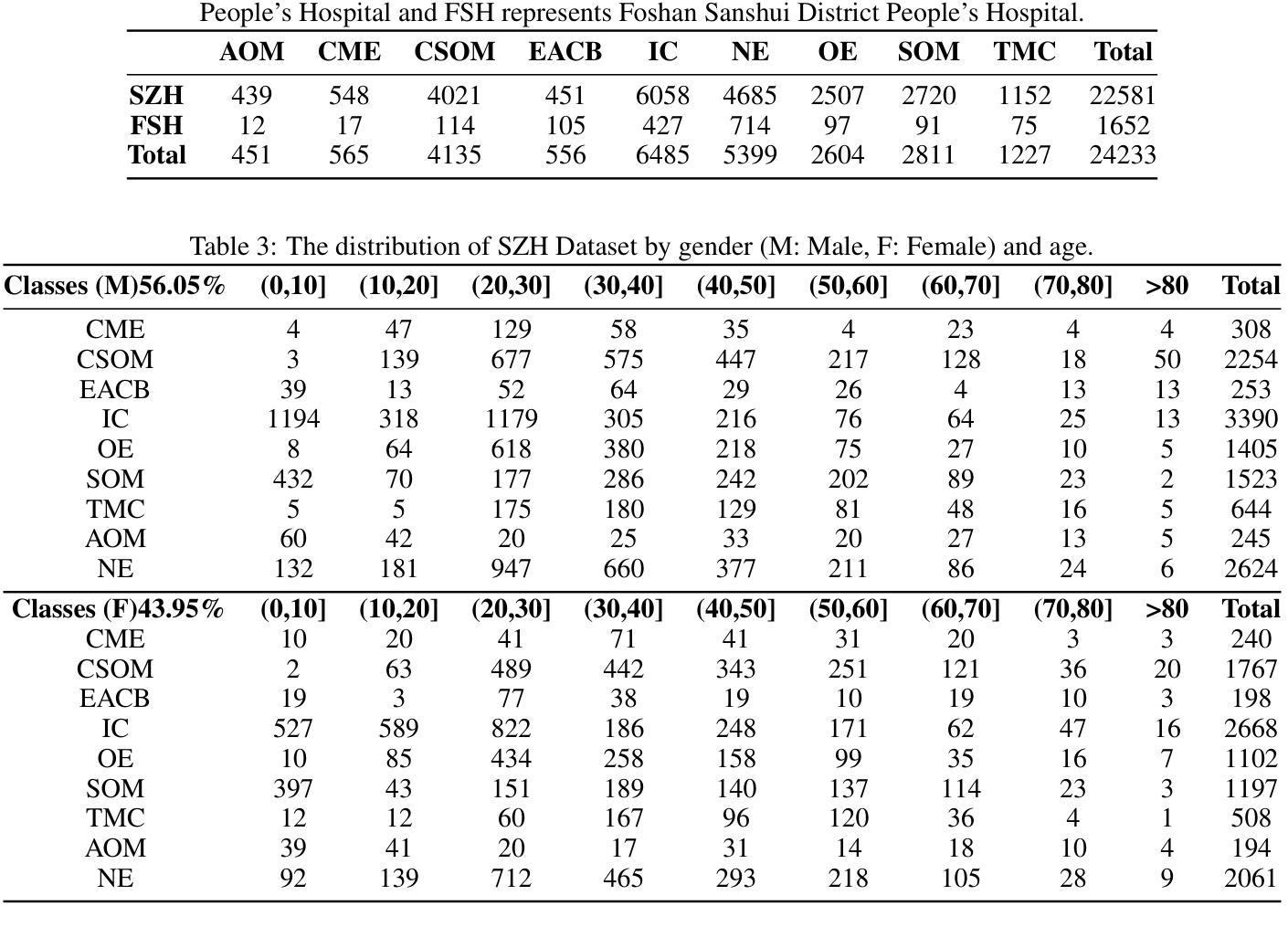
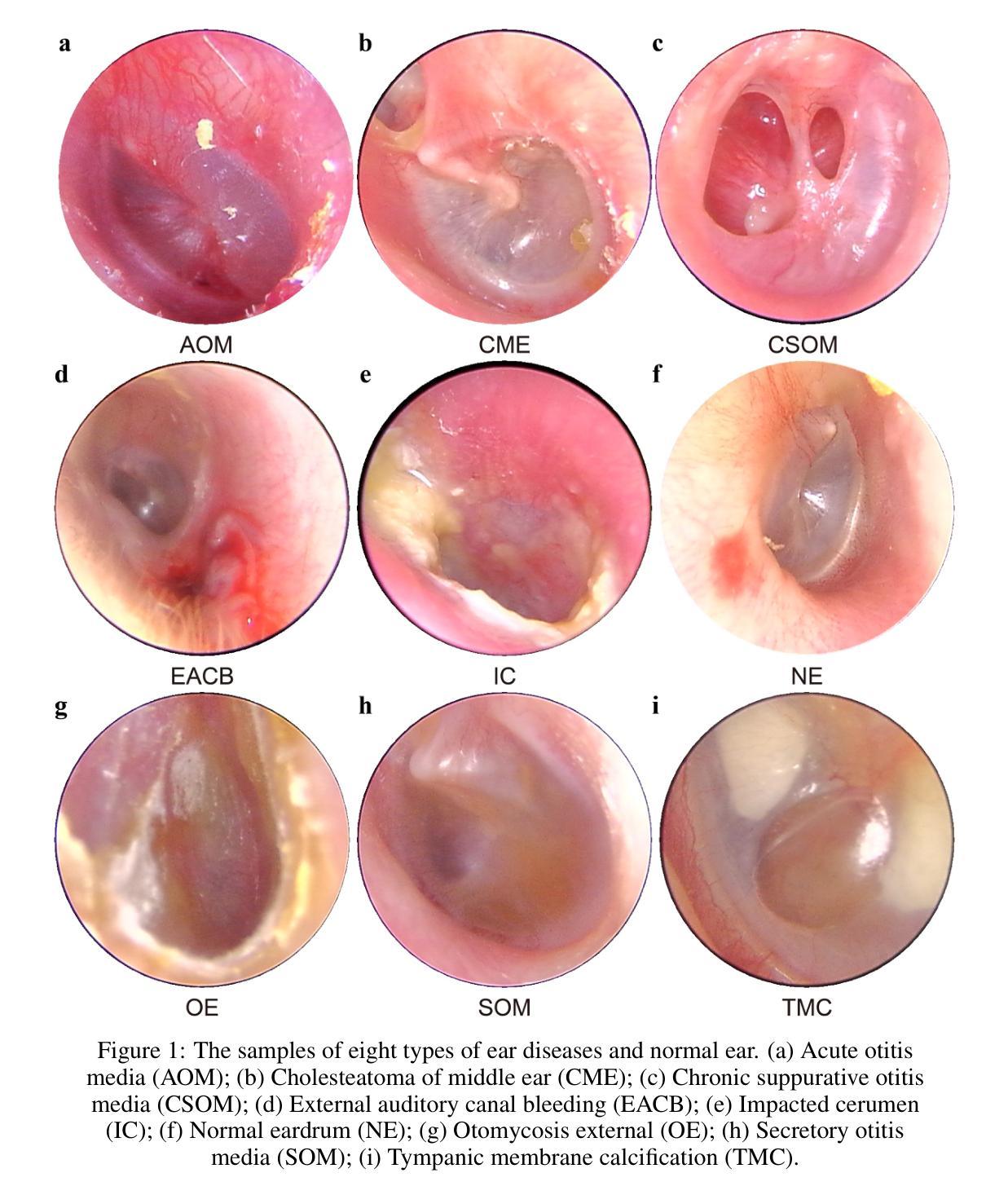
Early and accurate detection systems for ear diseases, powered by deep learning, are essential for preventing hearing impairment and improving population health. However, the limited diversity of existing otoendoscopy datasets and the poor balance between diagnostic accuracy, computational efficiency, and model size have hindered the translation of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms into healthcare applications. In this study, we constructed a large-scale, multi-center otoendoscopy dataset covering eight common ear diseases and healthy cases. Building upon this resource, we developed Best-EarNet, an ultrafast and lightweight deep learning architecture integrating a novel Local-Global Spatial Feature Fusion Module with a multi-scale supervision strategy, enabling real-time and accurate classification of ear conditions. Leveraging transfer learning, Best-EarNet, with a model size of only 2.94 MB, achieved diagnostic accuracies of 95.23% on an internal test set (22,581 images) and 92.14% on an external test set (1,652 images), while requiring only 0.0125 seconds (80 frames per second) to process a single image on a standard CPU. Further subgroup analysis by gender and age showed consistently excellent performance of Best-EarNet across all demographic groups. To enhance clinical interpretability and user trust, we incorporated Grad-CAM-based visualization, highlighting the specific abnormal ear regions contributing to AI predictions. Most importantly, we developed Ear-Keeper, a cross-platform intelligent diagnosis system built upon Best-EarNet, deployable on smartphones, tablets, and personal computers. Ear-Keeper enables public users and healthcare providers to perform comprehensive real-time video-based ear canal screening, supporting early detection and timely intervention of ear diseases.
由深度学习驱动的早期且精确的疾病检测系统对于预防听力受损并改善公众健康至关重要。然而,现有的耳内窥镜数据集多样性有限,诊断准确性、计算效率和模型大小之间的平衡不佳,这些都阻碍了人工智能算法在医疗保健应用中的转化。在这项研究中,我们构建了一个大规模、多中心的耳内窥镜数据集,涵盖了八种常见的耳部疾病和健康状况。基于这一资源,我们开发了Best-EarNet,这是一种超快速且轻量级的深度学习架构,它结合了新颖的全局局部空间特征融合模块和多尺度监督策略,能够实现耳部状况的实时和准确分类。通过迁移学习,仅2.94MB的Best-EarNet在内部测试集(22,581张图像)上实现了95.23%的诊断准确率,在外部测试集(1,652张图像)上实现了92.14%的准确率,同时在标准CPU上处理单张图像仅需0.0125秒(每秒80帧)。按性别和年龄的进一步亚组分析显示,Best-EarNet在所有年龄段的表现均非常出色。为了提高临床解释性和用户信任度,我们结合了基于Grad-CAM的可视化,突出显示对人工智能预测起特定作用的异常耳部区域。最重要的是,我们开发了Ear-Keeper,这是一款基于Best-EarNet的跨平台智能诊断系统,可在智能手机、平板电脑和个人电脑上部署。Ear-Keeper使公众用户和医疗服务提供者能够进行全面实时的基于视频的耳道筛查,支持耳部疾病的早期检测和及时干预。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages,8 figures
Summary
基于深度学习技术的早期准确耳病检测系统对于预防听力受损、提升全民健康水平至关重要。本研究构建了一个大规模、多中心耳内镜数据集,覆盖八种常见耳病及健康案例。在此基础上,研究团队开发出Best-EarNet模型,融合了局部全局空间特征融合模块和多尺度监督策略,实现了耳部状况的实时准确分类。该模型利用迁移学习,仅2.94MB的模型大小便在内部测试集上实现了95.23%的诊断准确率,在外部测试集上达到了92.14%,处理单张图片仅需0.0125秒(每秒处理80帧)。研究还通过性别和年龄分组分析证明了Best-EarNet在所有人群中的卓越表现。为提升临床解释性和用户信任度,研究团队引入了基于Grad-CAM的可视化技术,突出显示导致AI预测异常的特定耳部区域。最重要的是,研究团队开发了跨平台的智能诊断系统Ear-Keeper,可部署于智能手机、平板电脑和个人电脑,支持公众和医疗工作者进行实时视频耳道筛查,实现早期检测和及时干预。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习驱动的耳病早期检测系统对预防听力受损和提高人口健康水平至关重要。
- 研究构建了一个大规模、多中心的耳内镜数据集,覆盖多种常见耳病。
- Best-EarNet模型实现耳部状况的实时准确分类,具备出色的诊断准确率。
- Best-EarNet模型具备超快处理速度和轻量级特点,便于实际应用。
- 模型在多种人口分组中表现优秀,具备广泛的适用性。
- 引入Grad-CAM可视化技术,提升模型临床解释性和用户信任度。
点此查看论文截图