⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
Is ChatGPT-5 Ready for Mammogram VQA?
Authors:Qiang Li, Shansong Wang, Mingzhe Hu, Mojtaba Safari, Zachary Eidex, Xiaofeng Yang
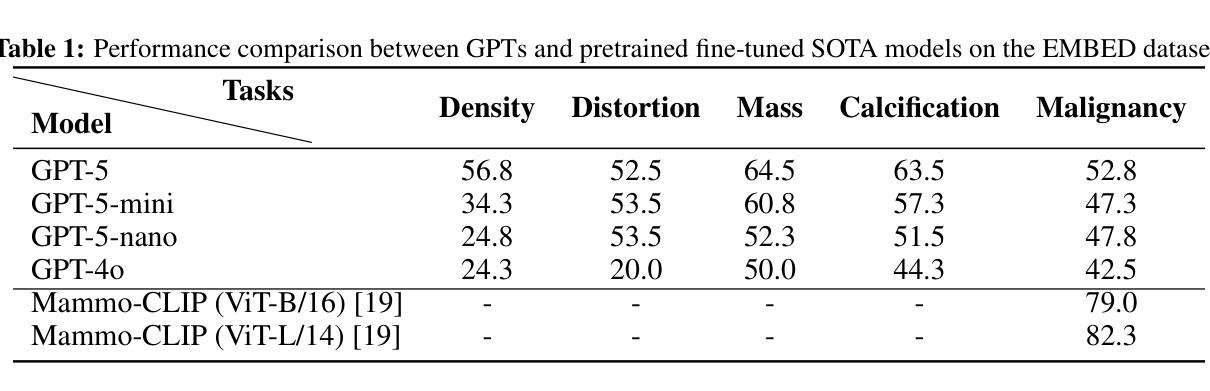
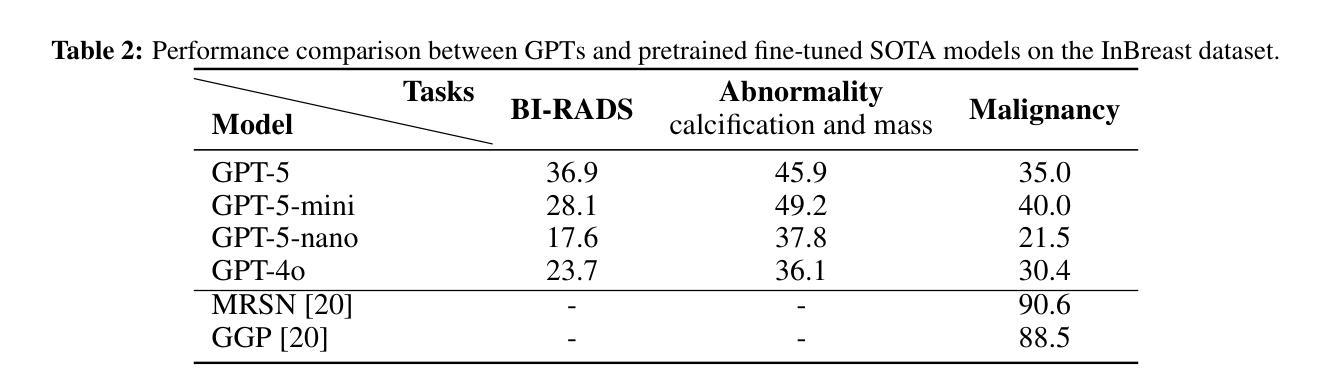
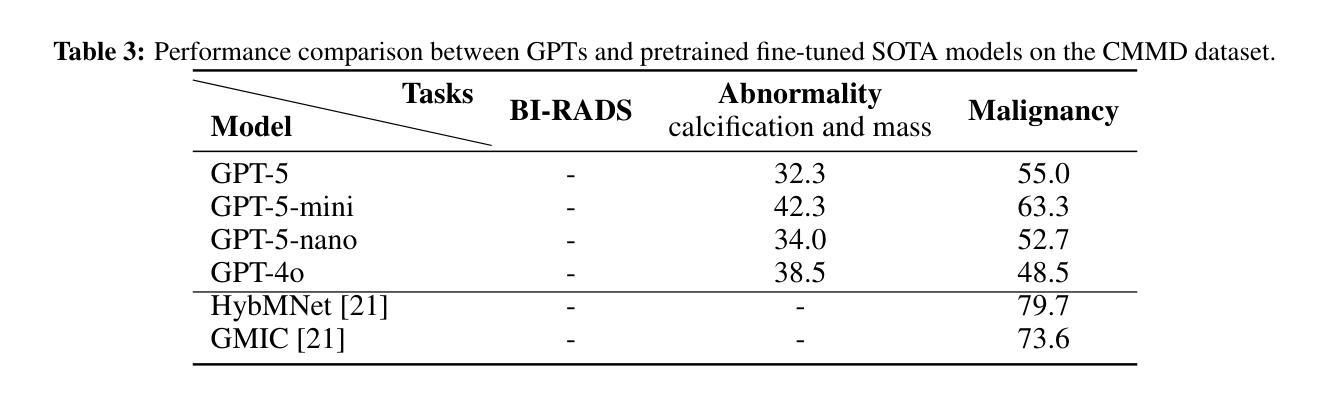
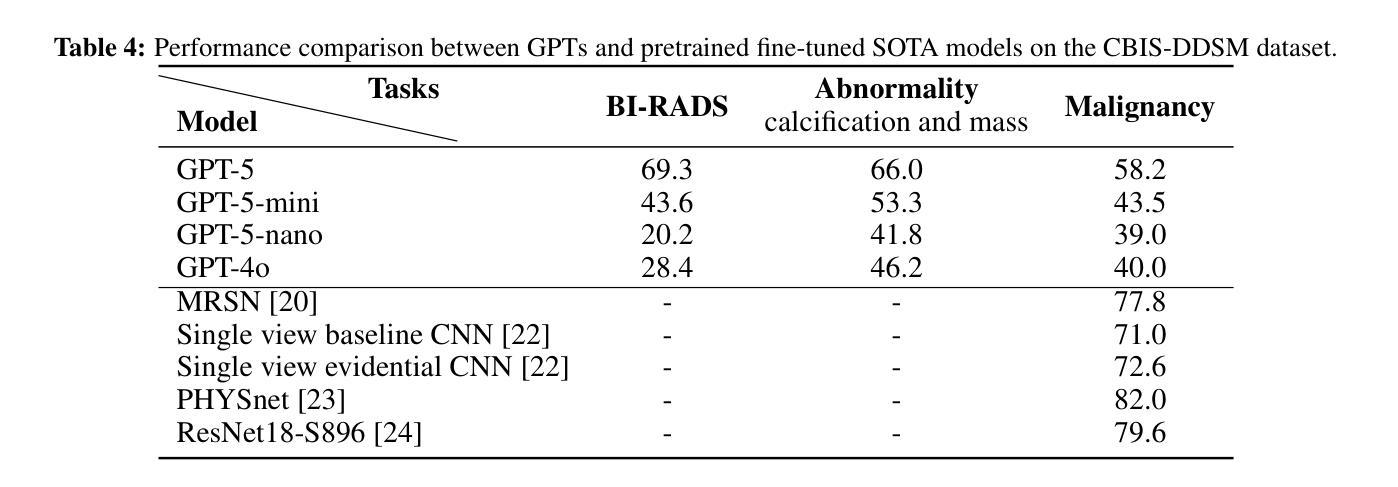
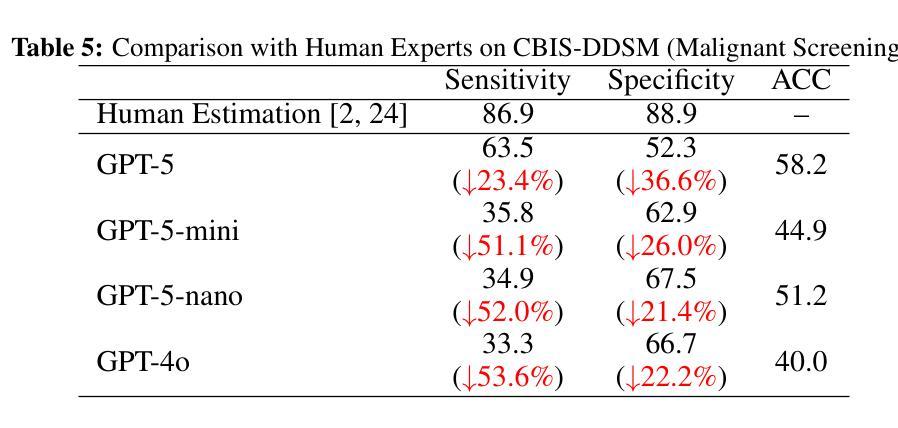
Mammogram visual question answering (VQA) integrates image interpretation with clinical reasoning and has potential to support breast cancer screening. We systematically evaluated the GPT-5 family and GPT-4o model on four public mammography datasets (EMBED, InBreast, CMMD, CBIS-DDSM) for BI-RADS assessment, abnormality detection, and malignancy classification tasks. GPT-5 consistently was the best performing model but lagged behind both human experts and domain-specific fine-tuned models. On EMBED, GPT-5 achieved the highest scores among GPT variants in density (56.8%), distortion (52.5%), mass (64.5%), calcification (63.5%), and malignancy (52.8%) classification. On InBreast, it attained 36.9% BI-RADS accuracy, 45.9% abnormality detection, and 35.0% malignancy classification. On CMMD, GPT-5 reached 32.3% abnormality detection and 55.0% malignancy accuracy. On CBIS-DDSM, it achieved 69.3% BI-RADS accuracy, 66.0% abnormality detection, and 58.2% malignancy accuracy. Compared with human expert estimations, GPT-5 exhibited lower sensitivity (63.5%) and specificity (52.3%). While GPT-5 exhibits promising capabilities for screening tasks, its performance remains insufficient for high-stakes clinical imaging applications without targeted domain adaptation and optimization. However, the tremendous improvements in performance from GPT-4o to GPT-5 show a promising trend in the potential for general large language models (LLMs) to assist with mammography VQA tasks.
乳腺X光摄影视觉问答(VQA)融合了图像解读与临床推理,并支持乳腺癌筛查。我们在四个公共乳腺X光摄影数据集(EMBED、InBreast、CMMD和CBIS-DDSM)上,针对BI-RADS评估、异常检测及恶性分类任务,对GPT-5系列和GPT-4o模型进行了系统评估。GPT-5表现最为出色且持续领先,但在与人类专家和特定领域微调模型的对比中仍有所不足。在EMBED数据集上,GPT-5在密度(56.8%)、扭曲(52.5%)、肿块(64.5%)、钙化(63.5%)和恶性分类(52.8%)方面,在GPT系列中得分最高。在InBreast数据集上,其达到了36.9%的BI-RADS准确率、45.9%的异常检测率和35.0%的恶性分类准确率。在CMMD数据集上,GPT-5达到32.3%的异常检测率和55.0%的恶性准确率。在CBIS-DDSM数据集上,其取得了69.3%的BI-RADS准确率、66.0%的异常检测率和58.2%的恶性分类准确率。与人类专家估算相比,GPT-5的敏感性较低(63.5%),特异性也较低(52.3%)。尽管GPT-5在筛查任务中展现出有前景的能力,但其性能对于高风险的临床成像应用仍然不足,需要进行有针对性的领域适应和优化。然而,从GPT-4o到GPT-5的性能巨大提升显示出大型通用语言模型(LLM)在乳腺X光摄影VQA任务中的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了Mammogram视觉问答(VQA)领域,评价了GPT-5系列模型和GPT-4o模型在四个公共乳腺X光摄影数据集上的表现。GPT-5在BI-RADS评估、异常检测以及恶性分类任务上表现最好,但相较于人类专家和针对特定领域微调过的模型仍有不足。在特定的数据集上,GPT-5的表现在不同任务中有所不同。尽管GPT-5在筛查任务中展现出潜力,但在高风险的临床成像应用中,其性能仍需通过针对性的领域适应和优化来提升。从GPT-4o到GPT-5的改进显示出大型语言模型(LLM)在乳腺X光摄影VQA任务中的潜力。
关键见解
- GPT-5系列模型在乳腺X光摄影数据集上的表现进行了系统评价。
- GPT-5在BI-RADS评估、异常检测和恶性分类任务上展现出最佳性能。
- GPT-5在不同数据集上的表现有所差异,需要进一步的领域适应和优化以提高性能。
- GPT-5在筛查任务中展现出了潜力,但在高风险的临床成像应用中的性能仍不足。
- 与人类专家相比,GPT-5的敏感性和特异性较低。
- 从GPT-4o到GPT-5的改进显示出大型语言模型在乳腺X光摄影VQA任务中的潜力。
- 研究强调了集成图像解读与临床推理的重要性,以支持乳腺癌筛查。
点此查看论文截图

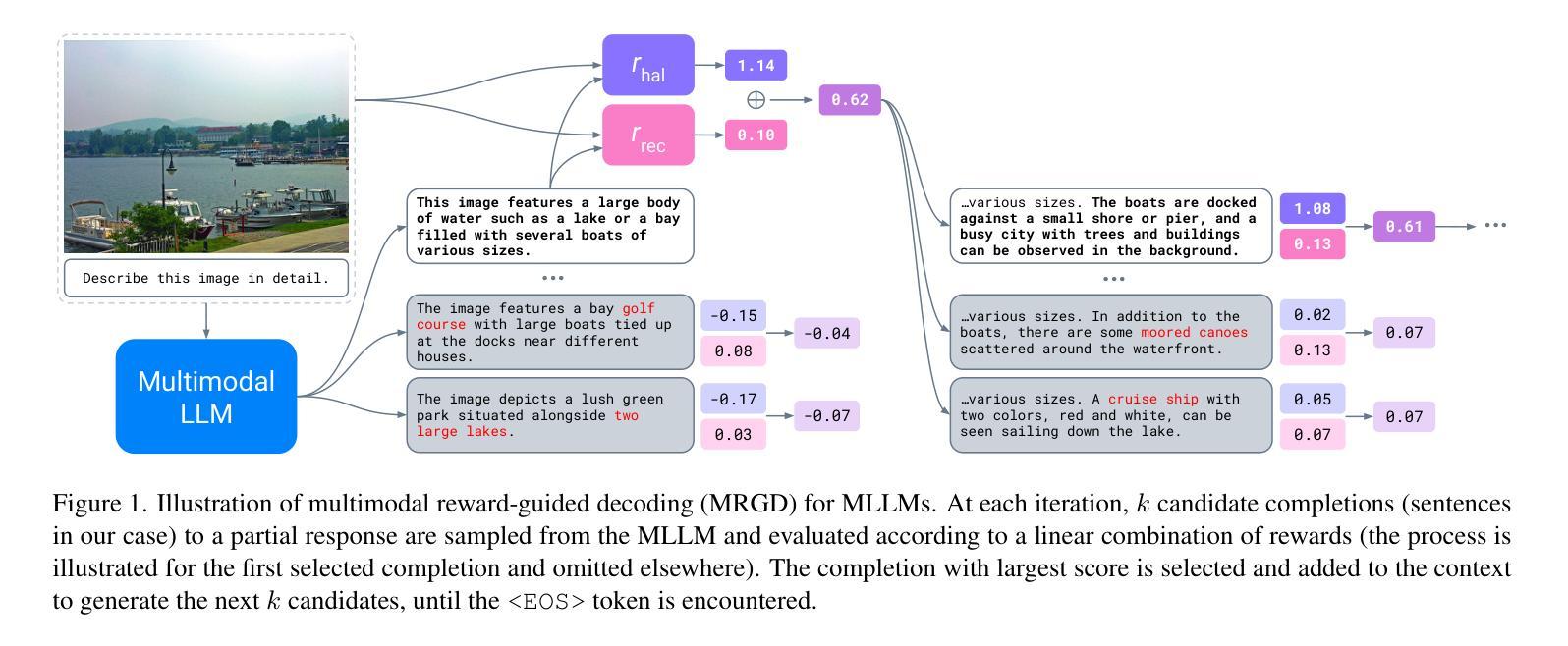
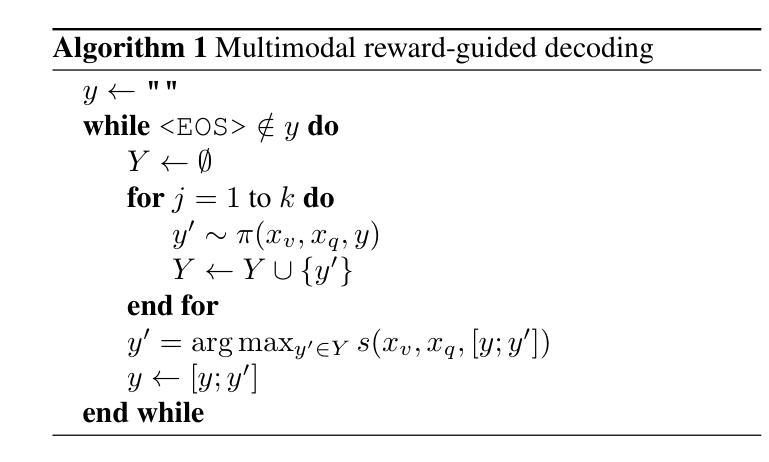
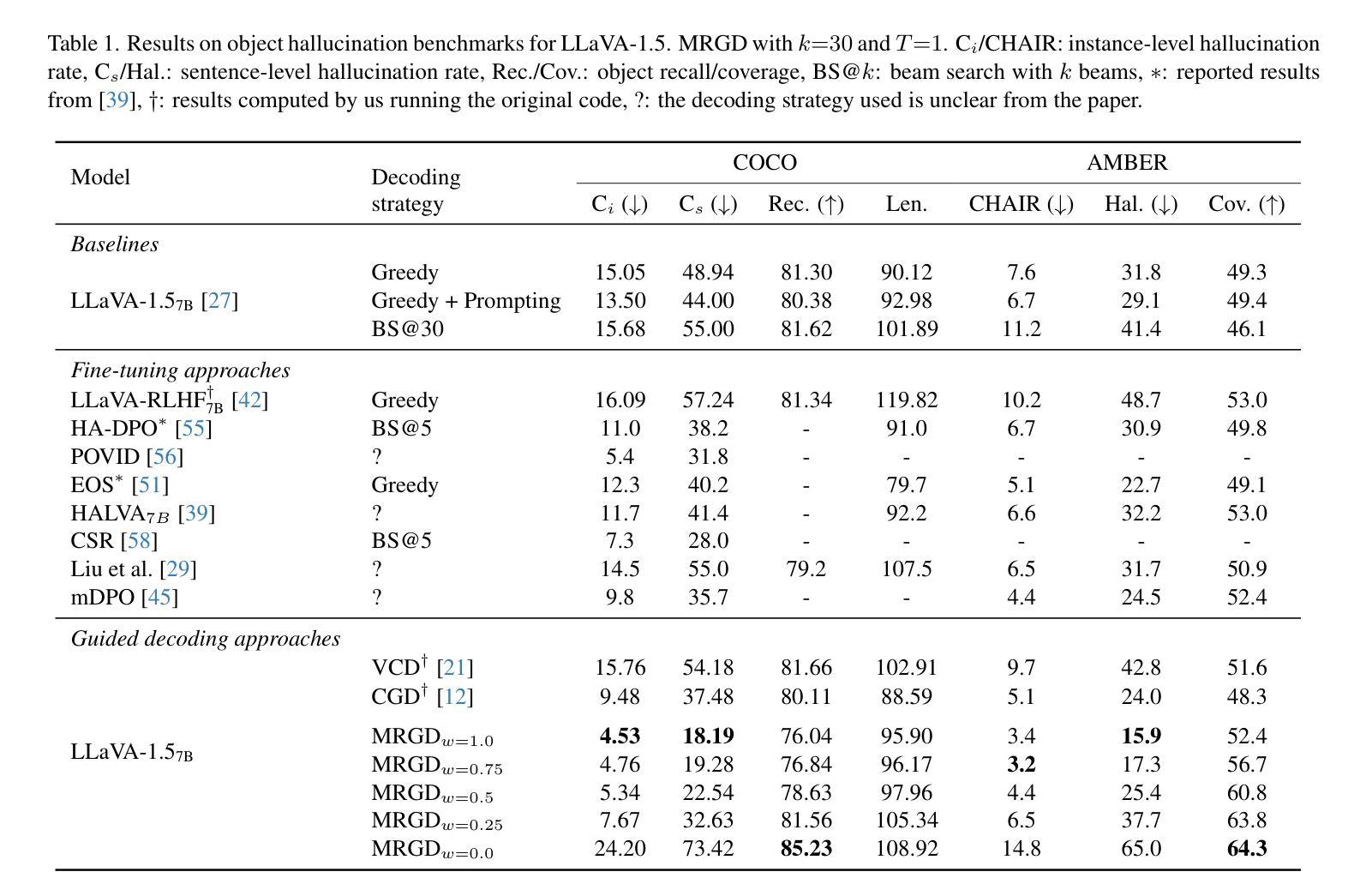
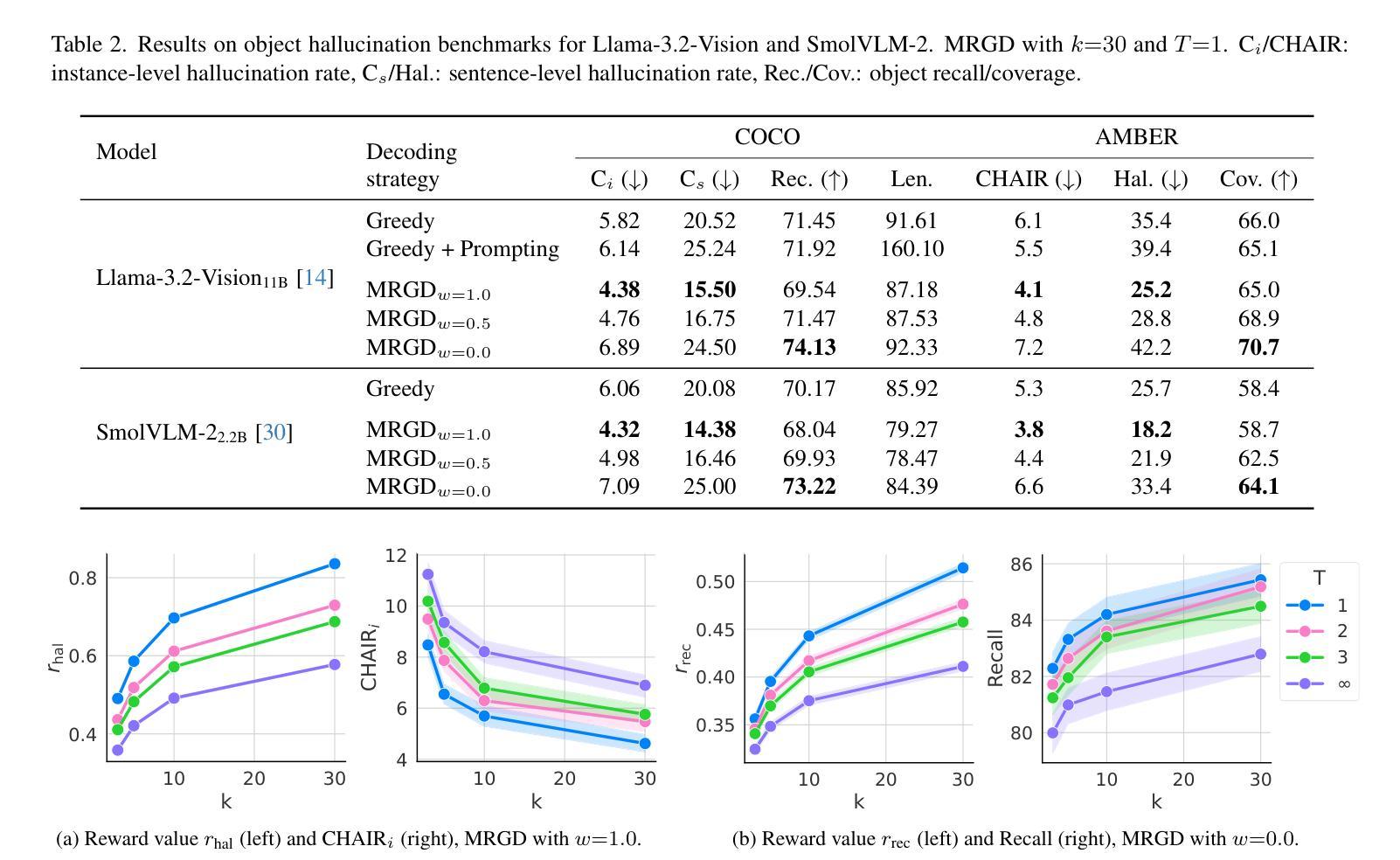
Controlling Multimodal LLMs via Reward-guided Decoding
Authors:Oscar Mañas, Pierluca D’Oro, Koustuv Sinha, Adriana Romero-Soriano, Michal Drozdzal, Aishwarya Agrawal
As Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) gain widespread applicability, it is becoming increasingly desirable to adapt them for diverse user needs. In this paper, we study the adaptation of MLLMs through controlled decoding. To achieve this, we introduce the first method for reward-guided decoding of MLLMs and demonstrate its application in improving their visual grounding. Our method involves building reward models for visual grounding and using them to guide the MLLM’s decoding process. Concretely, we build two separate reward models to independently control the degree of object precision and recall in the model’s output. Our approach enables on-the-fly controllability of an MLLM’s inference process in two ways: first, by giving control over the relative importance of each reward function during decoding, allowing a user to dynamically trade off object precision for recall in image captioning tasks; second, by giving control over the breadth of the search during decoding, allowing the user to control the trade-off between the amount of test-time compute and the degree of visual grounding. We evaluate our method on standard object hallucination benchmarks, showing that it provides significant controllability over MLLM inference, while consistently outperforming existing hallucination mitigation methods.
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的广泛应用,将其适应不同的用户需求变得越来越重要。在本文中,我们研究了通过受控解码适应MLLMs的方法。为此,我们引入了MLLMs的奖励引导解码方法,并展示了它在提高视觉定位方面的应用。我们的方法包括建立视觉定位的奖励模型,并利用它们来引导MLLM的解码过程。具体来说,我们建立了两个独立的奖励模型,分别控制模型输出中目标精度和召回的程度。我们的方法能够以两种方式实时控制MLLM的推理过程:首先,通过控制在解码过程中每个奖励函数的相对重要性,允许用户在图像描述任务中动态权衡目标精度和召回的权衡;其次,通过控制在解码过程中的搜索范围,允许用户控制测试时间计算量与视觉定位程度之间的权衡。我们在标准的目标幻觉评估基准上评估了我们的方法,结果表明它在对MLLM推理的控制方面表现出显著的可控性,同时一致地优于现有的幻觉缓解方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICCV 2025
Summary
本文研究了如何通过控制解码来适应多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)以满足不同用户需求。文章提出了一种奖励引导解码方法,用于改善MLLMs的视觉定位功能。通过构建两个独立的奖励模型,分别控制模型输出中的目标精度和召回率,实现了对MLLM推理过程的实时控制。该方法允许用户在解码过程中动态调整奖励函数的相对重要性,并在图像描述任务中权衡目标精度和召回率;同时,用户还可以控制搜索范围,平衡测试时间计算和视觉定位程度之间的权衡。在标准目标幻觉评估指标上,该方法表现出强大的控制能力,并一致优于现有幻觉缓解方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)需要适应不同用户需求。
- 奖励引导解码方法用于改善MLLMs的视觉定位功能。
- 通过构建两个独立的奖励模型,分别控制模型输出中的目标精度和召回率。
- 用户可以动态调整奖励函数的相对重要性,在图像描述任务中权衡目标精度和召回率。
- 用户可以控制搜索范围,以平衡测试时间计算和视觉定位程度之间的权衡。
- 该方法在标准目标幻觉评估指标上表现出强大的控制能力。
点此查看论文截图

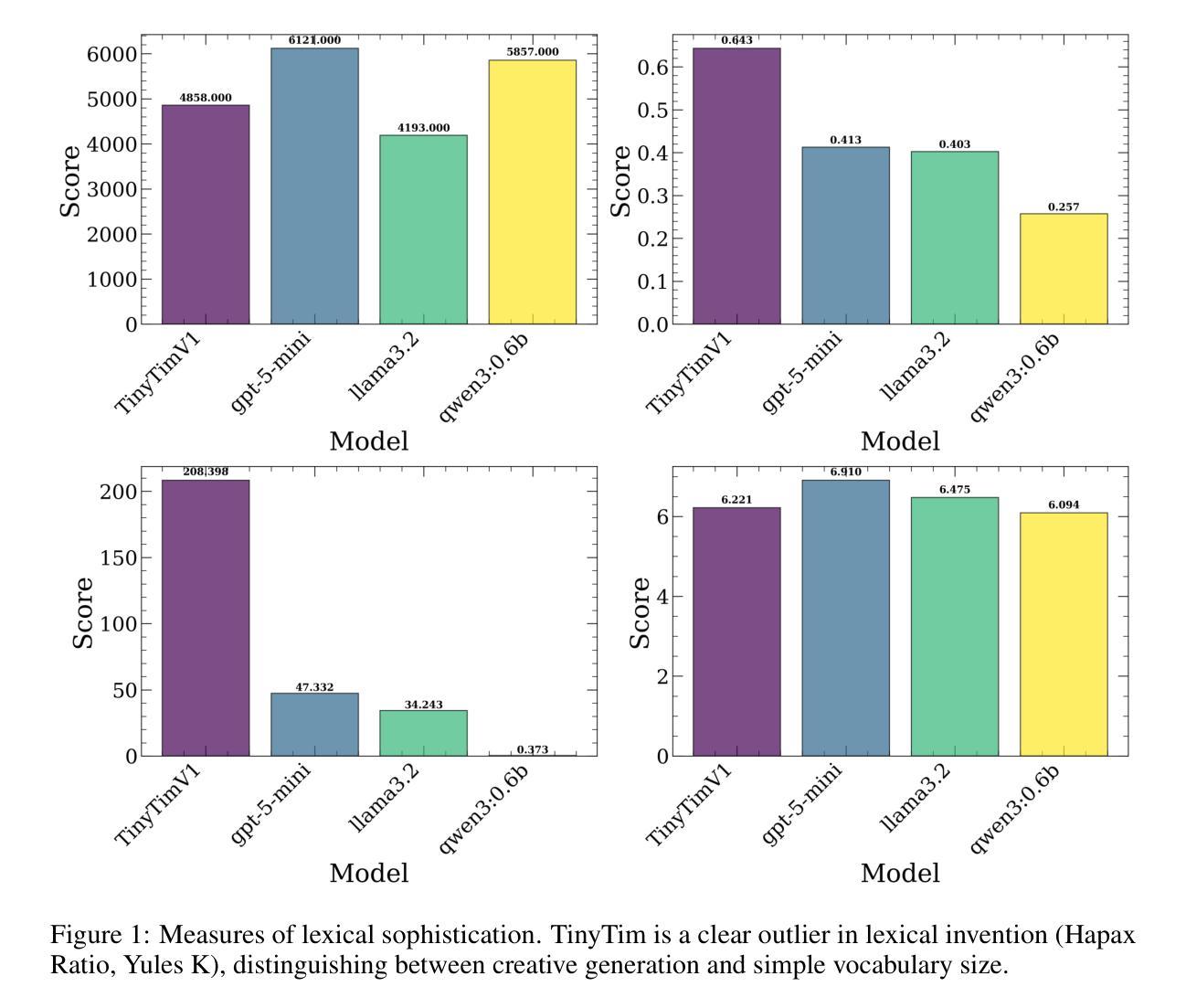
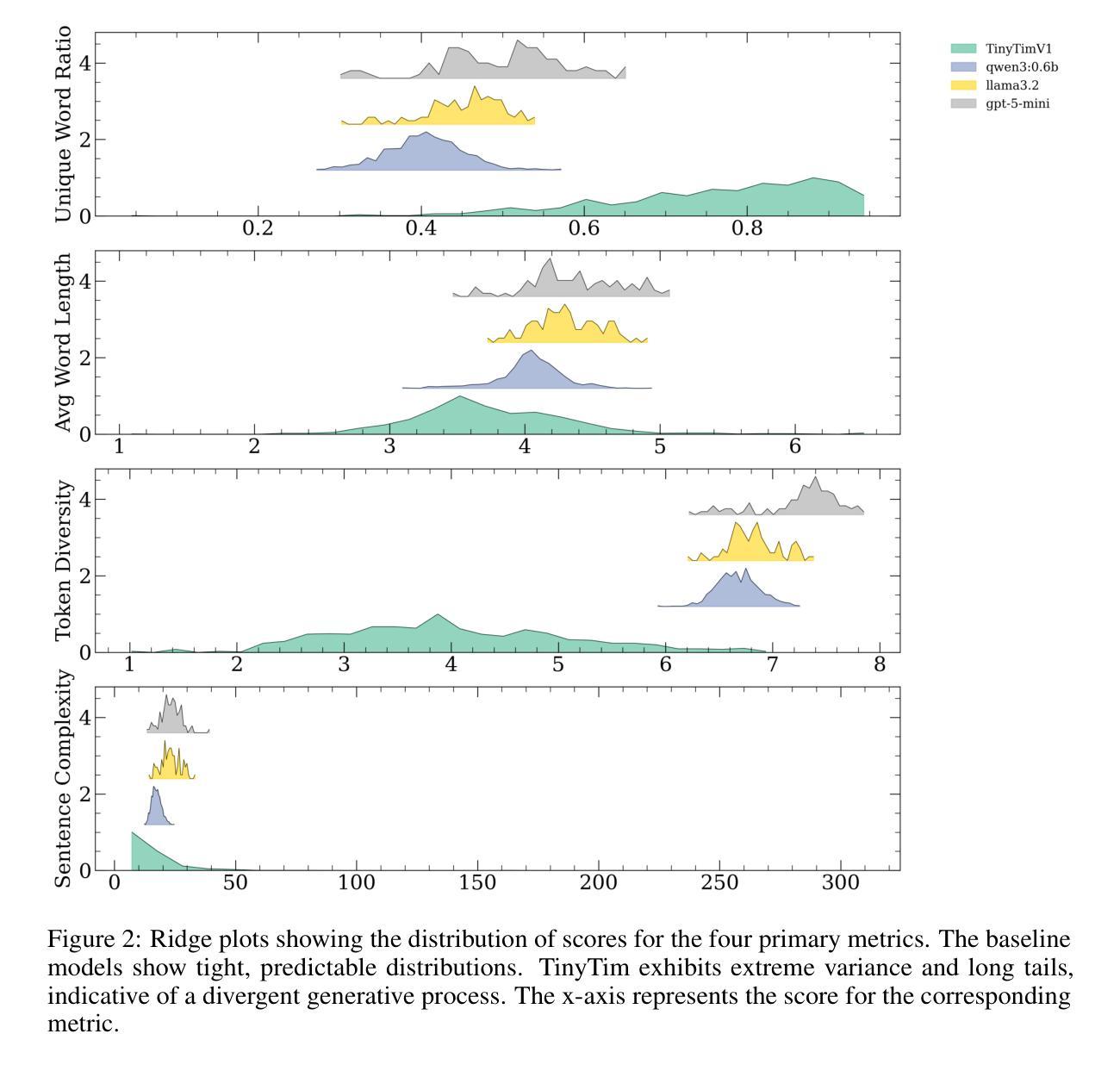
TinyTim: A Family of Language Models for Divergent Generation
Authors:Christopher J. Agostino
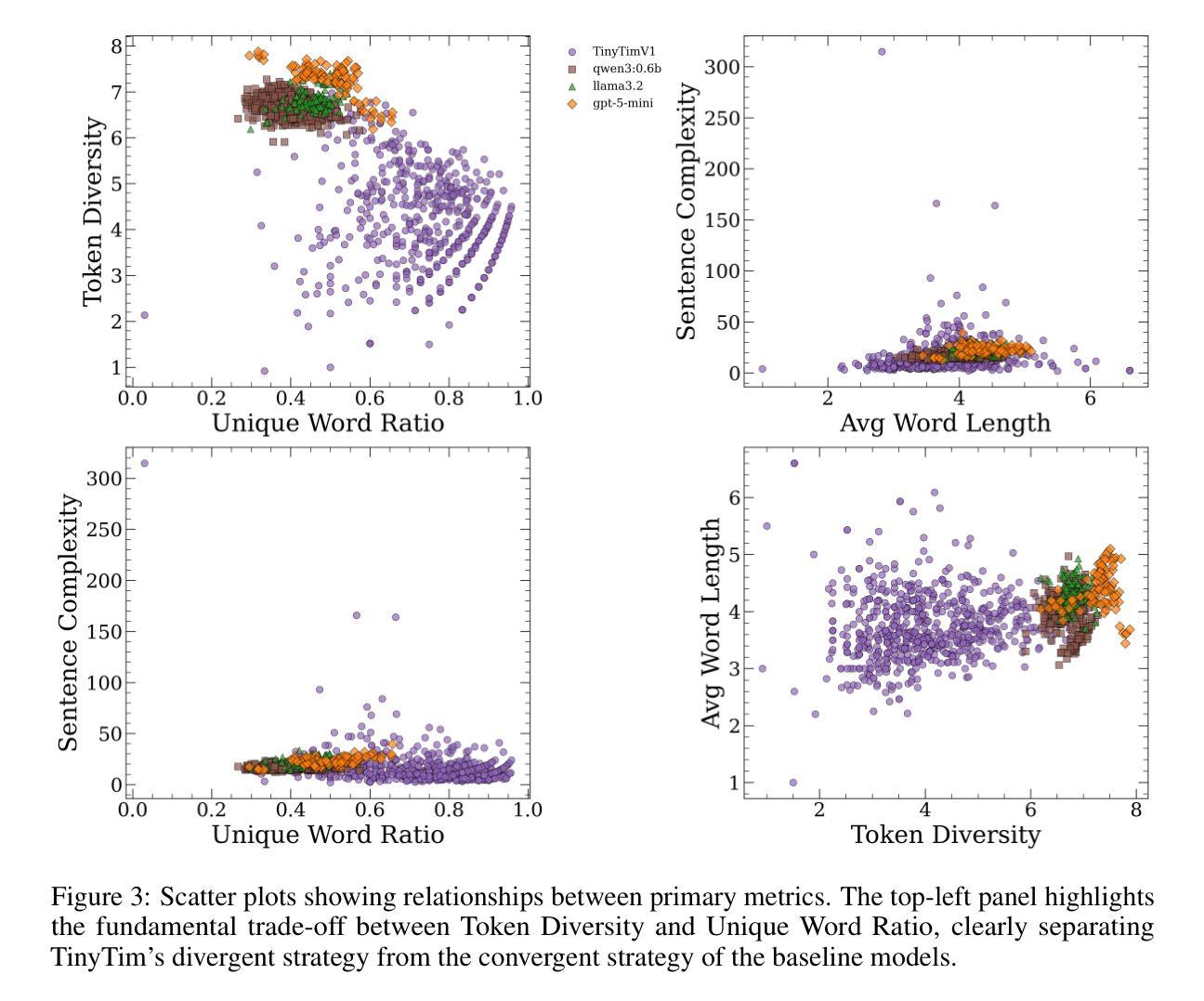
This work introduces TinyTim, a family of large language models fine-tuned on James Joyce’s `Finnegans Wake’. Through quantitative evaluation against baseline models, we demonstrate that TinyTim V1 produces a statistically distinct generative profile characterized by high lexical diversity and low semantic coherence. These findings are interpreted through theories of creativity and complex problem-solving, arguing that such specialized models can function as divergent knowledge sources within more extensive creative architectures, powering automated discovery mechanisms in diverse settings.
本文介绍了TinyTim,这是一系列基于詹姆斯·乔伊斯的《芬尼根守灵夜》调谐的大型语言模型家族。通过对基线模型的定量评估,我们证明TinyTim V1产生了具有高词汇多样性和低语义连贯性的统计独特生成特征。这些发现通过创造力和复杂问题解决的理论进行了解释,认为这种专业模型可以在更广泛的创造性架构中发挥不同的知识源作用,为各种环境中的自动化发现机制提供动力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures, submitted to NeurIPS Creative AI track, code and model available at https://hf.co/npc-worldwide/TinyTimV1
Summary:
本文介绍了TinyTim系列大型语言模型,特别是基于詹姆斯·乔伊斯作品《芬尼根守夜》进行微调后的TinyTim V1模型。通过定量评估,发现该模型生成的内容具有显著的高词汇多样性和低语义连贯性特征。结合创造力和复杂问题解决的理论,论证这种专业模型可以作为广泛创造性架构中的发散知识源,在多种场景中为自动发现机制提供动力。
Key Takeaways:
- TinyTim系列大型语言模型基于詹姆斯·乔伊斯的《芬尼根守夜》进行微调。
- TinyTim V1模型生成的文本具有高词汇多样性和低语义连贯性特征。
- 通过定量评估验证了TinyTim V1模型的生成性能。
- 这种模型可以作为创造性架构中的发散知识源。
- 模型有助于在多种场景中实现自动化发现机制。
- 模型的理论基础结合了创造力和复杂问题解决的理论。
点此查看论文截图

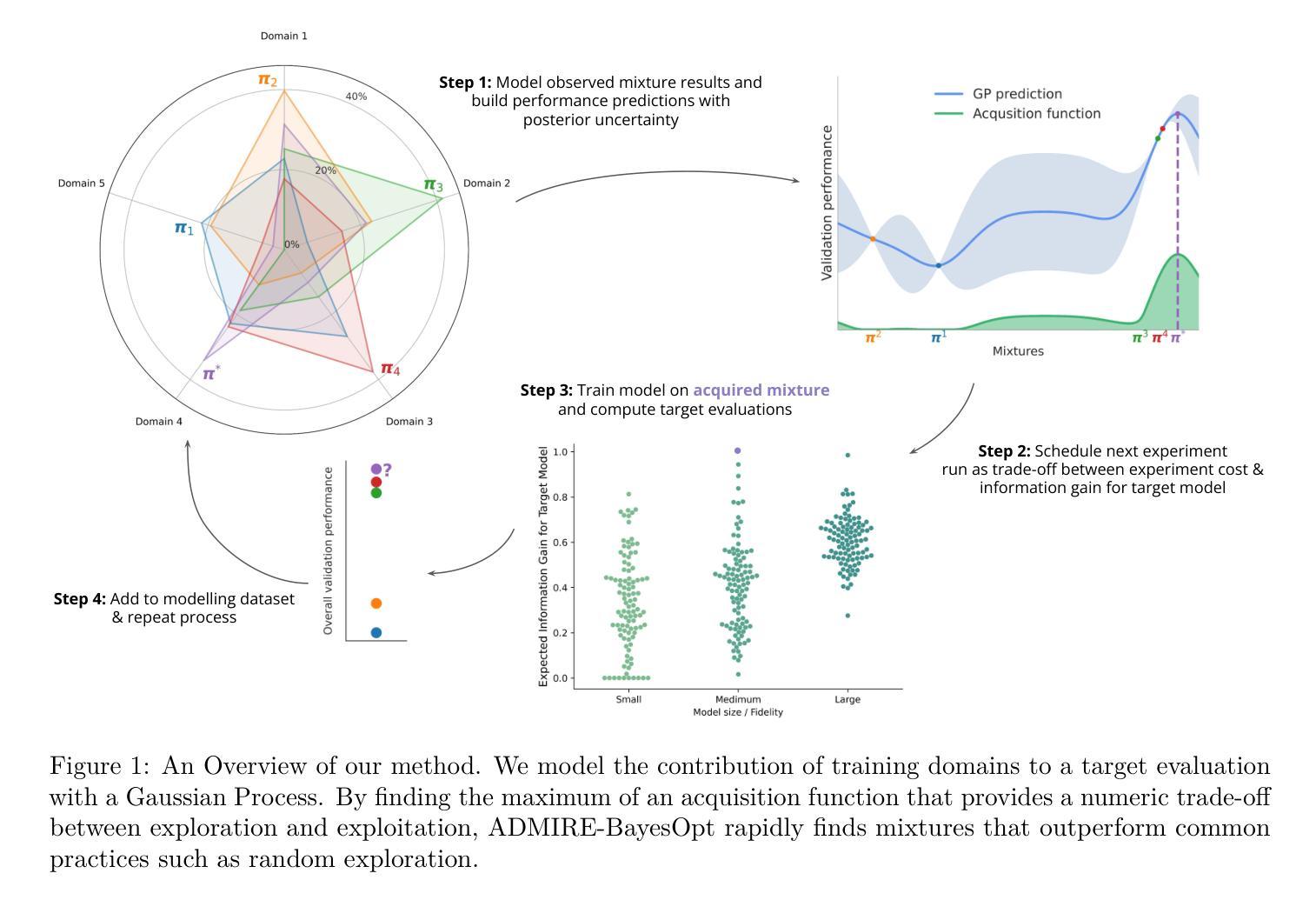
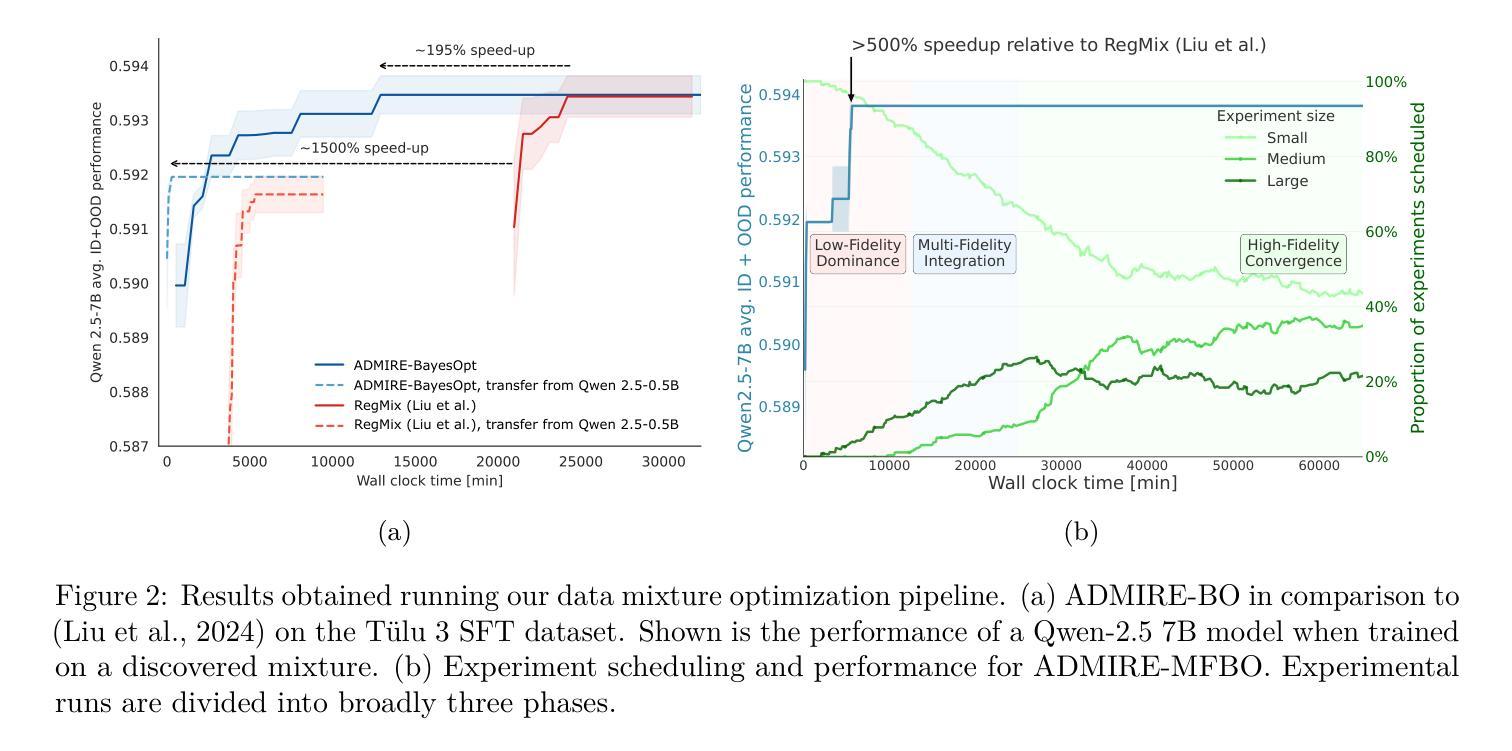
ADMIRE-BayesOpt: Accelerated Data MIxture RE-weighting for Language Models with Bayesian Optimization
Authors:Shengzhuang Chen, Xu Ouyang, Michael Arthur Leopold Pearce, Thomas Hartvigsen, Jonathan Richard Schwarz
Determining the optimal data mixture for large language model training remains a challenging problem with an outsized impact on performance. In practice, language model developers continue to rely on heuristic exploration since no learning-based approach has emerged as a reliable solution. In this work, we propose to view the selection of training data mixtures as a black-box hyperparameter optimization problem, for which Bayesian Optimization is a well-established class of appropriate algorithms. Firstly, we cast data mixture learning as a sequential decision-making problem, in which we aim to find a suitable trade-off between the computational cost of training exploratory (proxy-) models and final mixture performance. Secondly, we systematically explore the properties of transferring mixtures learned at a small scale to larger-scale experiments, providing insights and highlighting opportunities for research at a modest scale. By proposing Multi-fidelity Bayesian Optimization as a suitable method in this common scenario, we introduce a natural framework to balance experiment cost with model fit, avoiding the risks of overfitting to smaller scales while minimizing the number of experiments at high cost. We present results for pre-training and instruction finetuning across models ranging from 1 million to 7 billion parameters, varying from simple architectures to state-of-the-art models and benchmarks spanning dozens of datasets. We demonstrate consistently strong results relative to a wide range of benchmarks, showingspeed-ups of over 500% in determining the best data mixture on our largest experiments relative to recent baselines. In addition, we broaden access to research by sharing ADMIRE IFT Runs, a dataset of 460 full training & evaluation runs across various model sizes worth over 13,000 GPU hours, greatly reducing the cost of conducting research in this area.
确定大型语言模型训练的最优数据混合仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题,它对性能有着重大影响。在实践中,语言模型开发者继续依赖启发式探索,因为没有出现可靠的基于学习的方法。在这项工作中,我们建议将训练数据混合的选择视为一个黑盒超参数优化问题,为此,贝叶斯优化已经建立了一个适当的算法类。首先,我们将数据混合学习转化为一个序列决策问题,旨在找到训练探索性(代理)模型的计算成本与最终混合性能之间的适当权衡。其次,我们系统地探讨了将小规模学习的混合物转移到大规模实验的特性,提供了见解并突出了小规模研究的机会。通过提出多保真贝叶斯优化作为这一常见场景的合适方法,我们引入了一个自然的框架来平衡实验成本与模型拟合,避免了在小规模上过拟合的风险,同时最小化了高成本实验的数量。我们展示了在1百万到7亿参数范围内的模型进行预训练和指令微调的结果,从简单架构到先进模型和基准测试,跨越数十个数据集。与广泛的基准测试相比,我们始终表现出强大的结果,在我们最大的实验中确定最佳数据混合的加速超过500%。此外,我们通过共享ADMIRE IFTRuns(一个包含460次各种模型大小的完整训练与评估运行的数据集,价值超过13000个GPU小时),来扩大研究人员的访问范围,大大降低了该领域的研究成本。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大数据混合训练对于大型语言模型性能的影响至关重要,但确定最佳数据混合仍然是一个挑战性问题。目前语言模型开发者主要依赖启发式探索,尚无可靠的学习型解决方案。本文提出将训练数据混合的选择视为黑盒超参数优化问题,并引入贝叶斯优化作为适用的算法。首先,本文将数据混合学习视为一个序列决策问题,旨在找到训练探索性代理模型的计算成本与最终混合性能之间的平衡。其次,本文系统地探讨了从小规模实验学习到的混合在大规模实验中的迁移特性,提供了一个自然框架来平衡实验成本与模型拟合度。通过提出多保真贝叶斯优化作为这一常见场景的合适方法,本文避免了在小规模上过拟合的风险,同时减少了高成本实验的数量。本文展示了在数百万参数至数十亿参数模型上的预训练和指令微调结果,涉及简单架构和最新模型以及跨越数十个数据集的基准测试。与近期基准测试相比,在确定最佳数据混合方面,我们的最大实验速度提高了超过500%。此外,通过共享ADMIRE IFTRuns数据集,包含超过13,000 GPU小时的460次完整训练与评估运行,本文降低了该领域的研究成本。
关键见解
- 确定最佳数据混合对于大型语言模型训练至关重要,但仍是一个挑战性问题。
- 本文提出将训练数据混合的选择视为黑盒超参数优化问题,并采用贝叶斯优化来解决。
- 介绍了数据混合学习作为序列决策问题的观点,平衡了探索性模型训练的计算成本与最终性能。
- 探讨了从小规模实验到大规模实验的迁移特性。
- 通过多保真贝叶斯优化,避免了在小规模上过拟合的风险,减少了高成本实验。
- 在多种模型和基准测试中展示了强大的性能表现,与近期基准相比有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

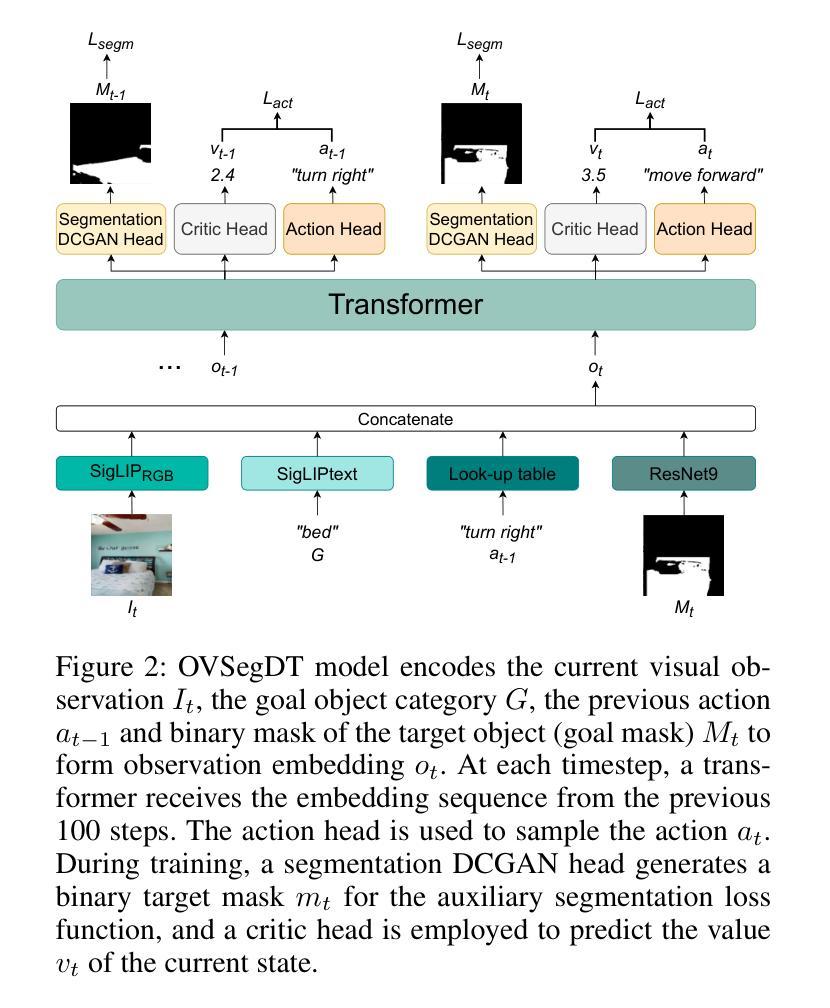
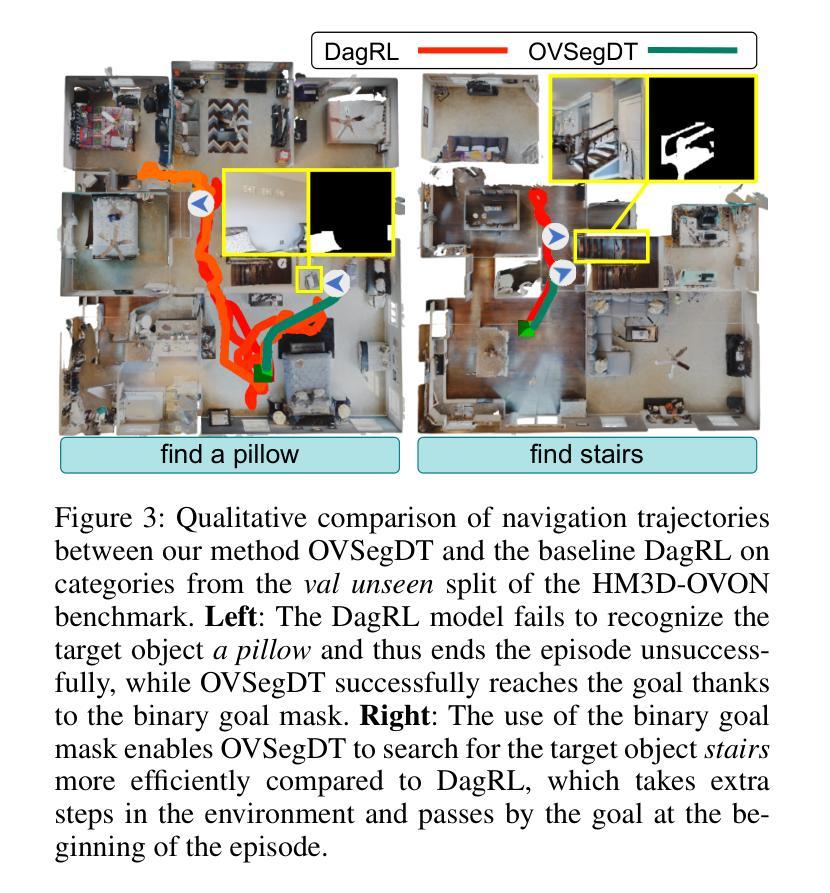
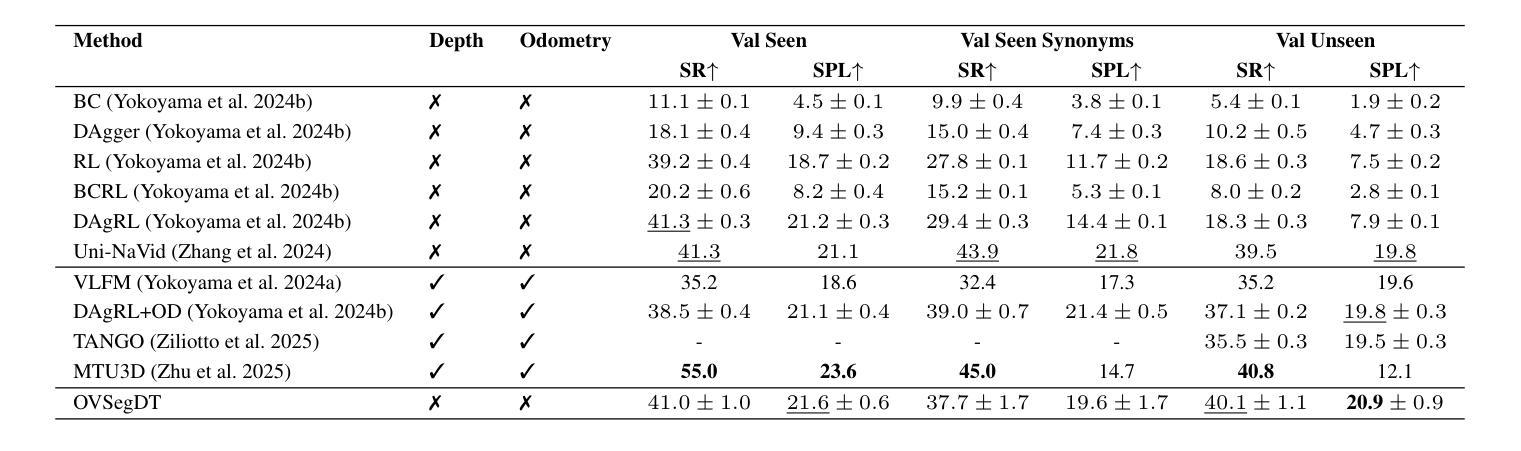
OVSegDT: Segmenting Transformer for Open-Vocabulary Object Goal Navigation
Authors:Tatiana Zemskova, Aleksei Staroverov, Dmitry Yudin, Aleksandr Panov
Open-vocabulary Object Goal Navigation requires an embodied agent to reach objects described by free-form language, including categories never seen during training. Existing end-to-end policies overfit small simulator datasets, achieving high success on training scenes but failing to generalize and exhibiting unsafe behaviour (frequent collisions). We introduce OVSegDT, a lightweight transformer policy that tackles these issues with two synergistic components. The first component is the semantic branch, which includes an encoder for the target binary mask and an auxiliary segmentation loss function, grounding the textual goal and providing precise spatial cues. The second component consists of a proposed Entropy-Adaptive Loss Modulation, a per-sample scheduler that continuously balances imitation and reinforcement signals according to the policy entropy, eliminating brittle manual phase switches. These additions cut the sample complexity of training by 33%, and reduce collision count in two times while keeping inference cost low (130M parameters, RGB-only input). On HM3D-OVON, our model matches the performance on unseen categories to that on seen ones and establishes state-of-the-art results (40.1% SR, 20.9% SPL on val unseen) without depth, odometry, or large vision-language models. Code is available at https://github.com/CognitiveAISystems/OVSegDT.
开放词汇对象目标导航需要实体代理来实现通过自由形式语言描述的对象,包括在训练过程中从未见过的类别。现有的端到端策略过于适应小型模拟器数据集,在训练场景上取得高成功率,但无法推广,并表现出不安全行为(频繁碰撞)。我们引入了OVSegDT,这是一个轻量级的变压器策略,通过两个协同组件来解决这些问题。第一个组件是语义分支,它包括目标二进制掩码的编码器和辅助分割损失函数,它根据文本目标提供精确的空间线索。第二个组件是提出的熵自适应损失调制,这是一个按样本调度的程序,根据策略熵连续平衡模仿和强化信号,消除了脆弱的手动相位开关。这些添加将训练样本的复杂性降低了33%,在保持推理成本低的同时(仅有1300万个参数,仅使用RGB输入)将碰撞计数减少了一半。在HM3D-OVON上,我们的模型在未见过和见过的类别上的性能相匹配,并在没有深度、里程计或大型视觉语言模型的情况下建立了最新的结果(SR为40.1%,val未见SPL为20.9%)。代码可在https://github.com/CognitiveAISystems/OVSegDT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为OVSegDT的轻量级转换器策略,用于解决开放词汇对象目标导航问题。该策略包括两个协同组件:语义分支和熵自适应损失调制。语义分支包括目标二进制掩码的编码器和辅助分割损失函数,用于将文本目标与空间线索相结合。熵自适应损失调制则是一种每样本调度程序,可根据策略熵连续平衡模仿和强化信号,消除了脆弱的手动相位切换。这些改进降低了训练样本的复杂性,减少了碰撞次数,同时保持了较低推理成本。OVSegDT在HM3D-OVON数据集上实现了最新结果,对未见类别和已见类别的性能相匹配,且无需深度、里程计或大型视觉语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- OVSegDT是一种针对开放词汇对象目标导航问题的轻量级转换器策略。
- 策略包含两个协同组件:语义分支和熵自适应损失调制。
- 语义分支结合文本目标和空间线索,通过编码目标二进制掩码和辅助分割损失函数实现。
- 熵自适应损失调制是一种每样本调度程序,能自动平衡模仿和强化信号,消除手动相位切换的需要。
- OVSegDT降低了训练样本复杂性,减少碰撞次数,同时保持较低的推理成本。
- 在HM3D-OVON数据集上,OVSegDT实现了最新结果,未见类别与已见类别的性能相匹配。
点此查看论文截图

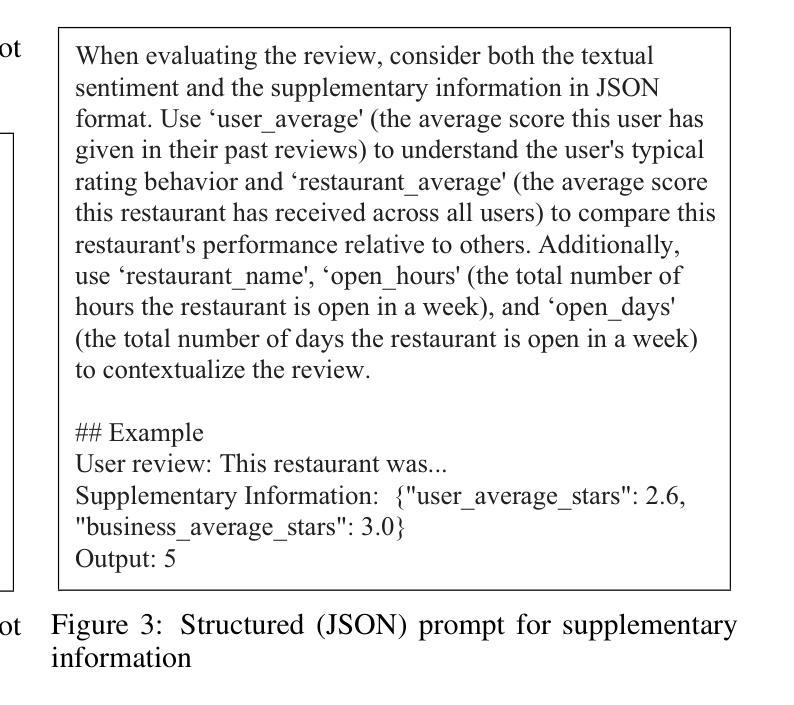
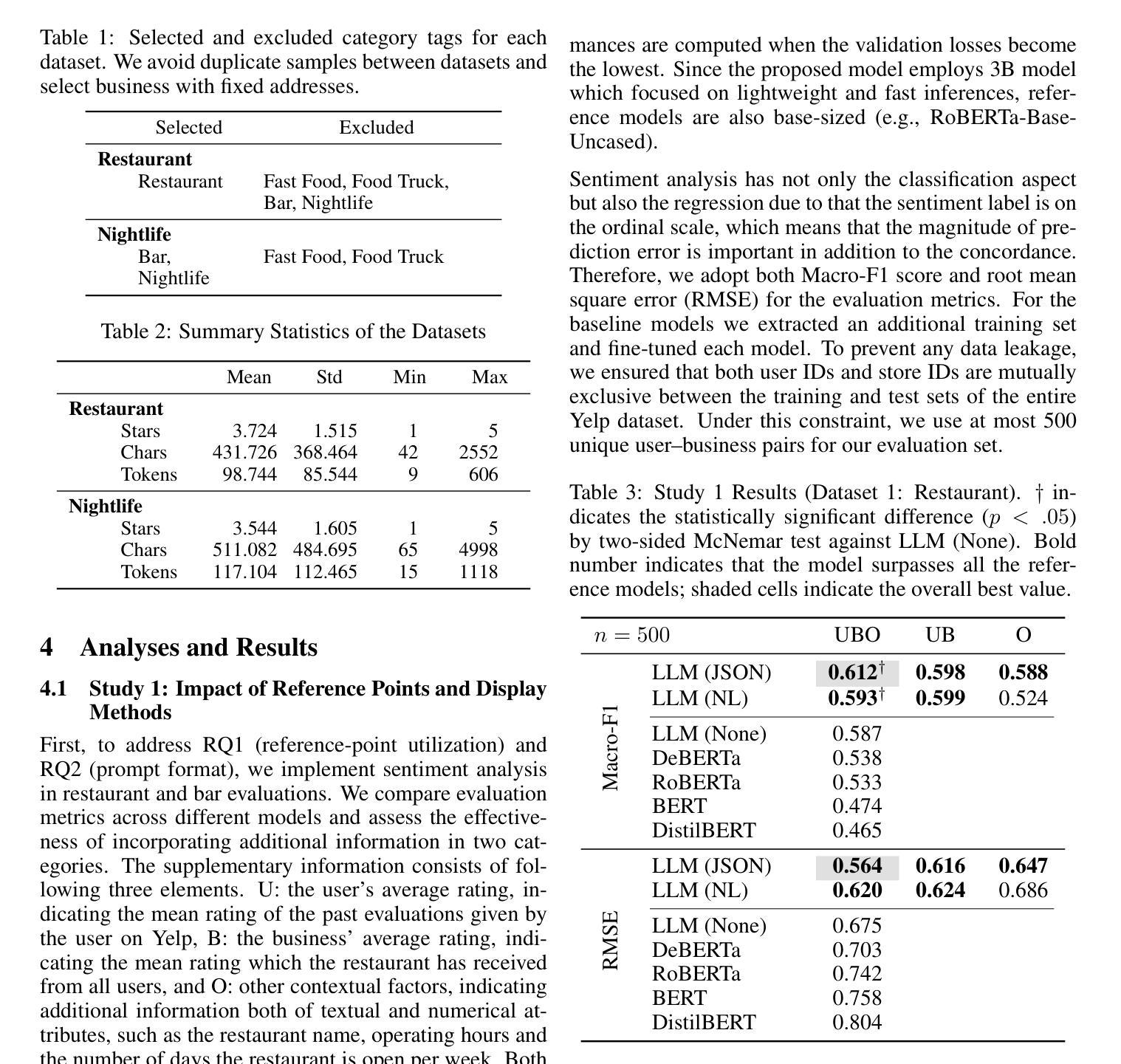
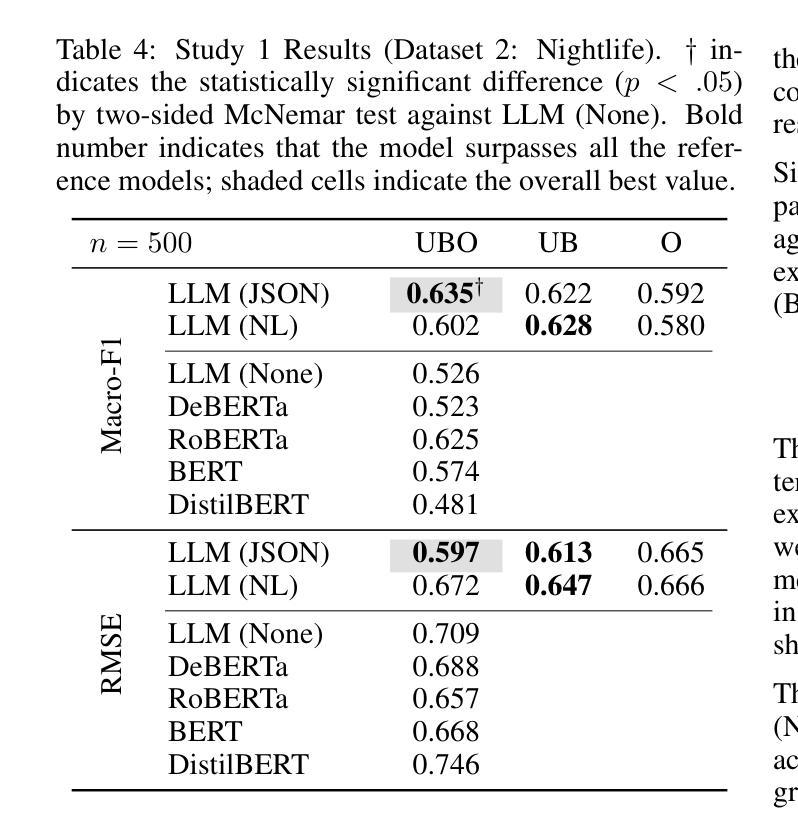
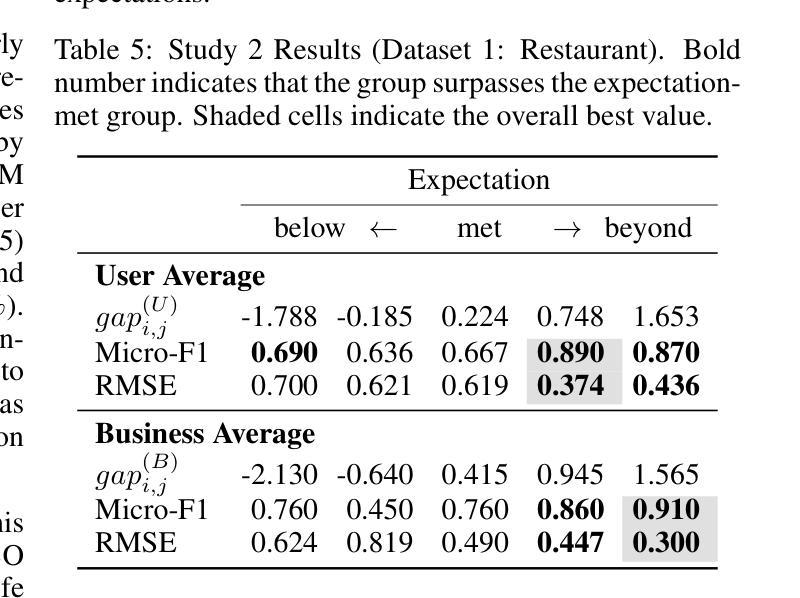
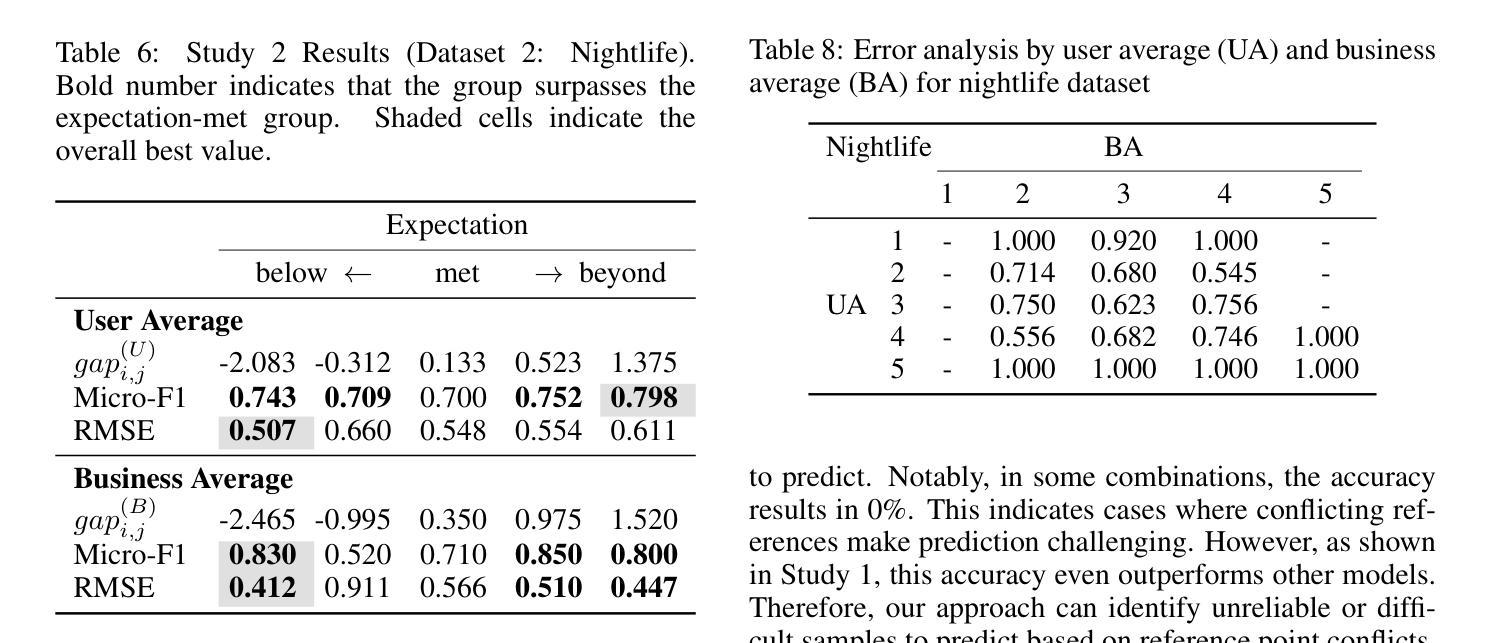
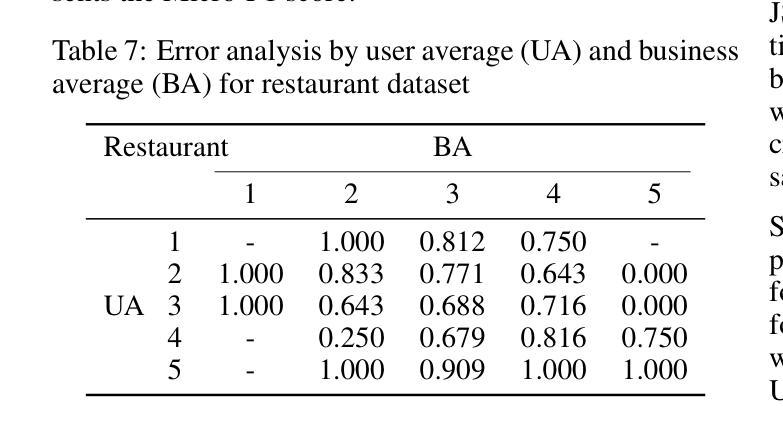
Reference Points in LLM Sentiment Analysis: The Role of Structured Context
Authors:Junichiro Niimi
Large language models (LLMs) are now widely used across many fields, including marketing research. Sentiment analysis, in particular, helps firms understand consumer preferences. While most NLP studies classify sentiment from review text alone, marketing theories, such as prospect theory and expectation–disconfirmation theory, point out that customer evaluations are shaped not only by the actual experience but also by additional reference points. This study therefore investigates how the content and format of such supplementary information affect sentiment analysis using LLMs. We compare natural language (NL) and JSON-formatted prompts using a lightweight 3B parameter model suitable for practical marketing applications. Experiments on two Yelp categories (Restaurant and Nightlife) show that the JSON prompt with additional information outperforms all baselines without fine-tuning: Macro-F1 rises by 1.6% and 4% while RMSE falls by 16% and 9.1%, respectively, making it deployable in resource-constrained edge devices. Furthermore, a follow-up analysis confirms that performance gains stem from genuine contextual reasoning rather than label proxying. This work demonstrates that structured prompting can enable smaller models to achieve competitive performance, offering a practical alternative to large-scale model deployment.
大型语言模型(LLM)现已广泛应用于许多领域,包括市场研究。尤其是情感分析,它有助于企业了解消费者偏好。虽然大多数自然语言处理研究仅从评论文本中分类情感,但市场营销理论,如前景理论和期望-确认理论,指出客户评价不仅受实际体验的影响,还受其他参考点的影响。因此,本研究调查了这种补充信息的内容和格式如何影响使用LLM的情感分析。我们使用适合实际市场营销应用的小型3B参数模型,比较了自然语言(NL)和JSON格式的提示。对Yelp两个类别(餐厅和夜生活)的实验表明,带有附加信息的JSON提示优于所有基线,无需微调:宏观F1分数提高了1.6%和4%,同时RMSE分别下降了16%和9.1%,使其适用于资源受限的边缘设备。此外,后续分析证实,性能提升源于真正的上下文推理,而非标签代理。这项工作表明,结构化提示可以使较小的模型实现有竞争力的性能,为大规模模型部署提供了实用的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在营销研究等领域得到广泛应用,情感分析帮助企业理解消费者偏好。本研究结合营销理论,发现客户评价不仅受实际体验影响,还受其他参考点的影响。因此,本研究探讨了如何使用LLM进行情感分析时,附加信息的内容和格式如何影响结果。通过对比自然语言(NL)和JSON格式的提示,实验结果显示JSON格式的提示表现更佳,无需微调即可超越所有基线。在Yelp的两个类别(餐饮和夜生活)的实验中,Macro-F1分别提高了1.6%和4%,RMSE分别下降了16%和9.1%。此外,后续分析证实性能提升源于真正的上下文推理而非标签代理。这项研究表明,结构化提示可使较小的模型实现具有竞争力的性能,为大规模模型部署提供了实用替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在情感分析领域应用广泛,尤其是营销研究领域。
- 客户评价不仅受实际体验影响,还受其他参考点的影响,这被营销理论所强调。
- 研究对比了自然语言(NL)和JSON格式的提示在情感分析中的效果。
- JSON格式的提示表现优于NL格式,无需微调即可超越所有基线。
- 在Yelp的两个类别实验中,JSON格式提示显著提高了Macro-F1并降低了RMSE。
- 后续分析证实性能提升源于真正的上下文推理。
点此查看论文截图

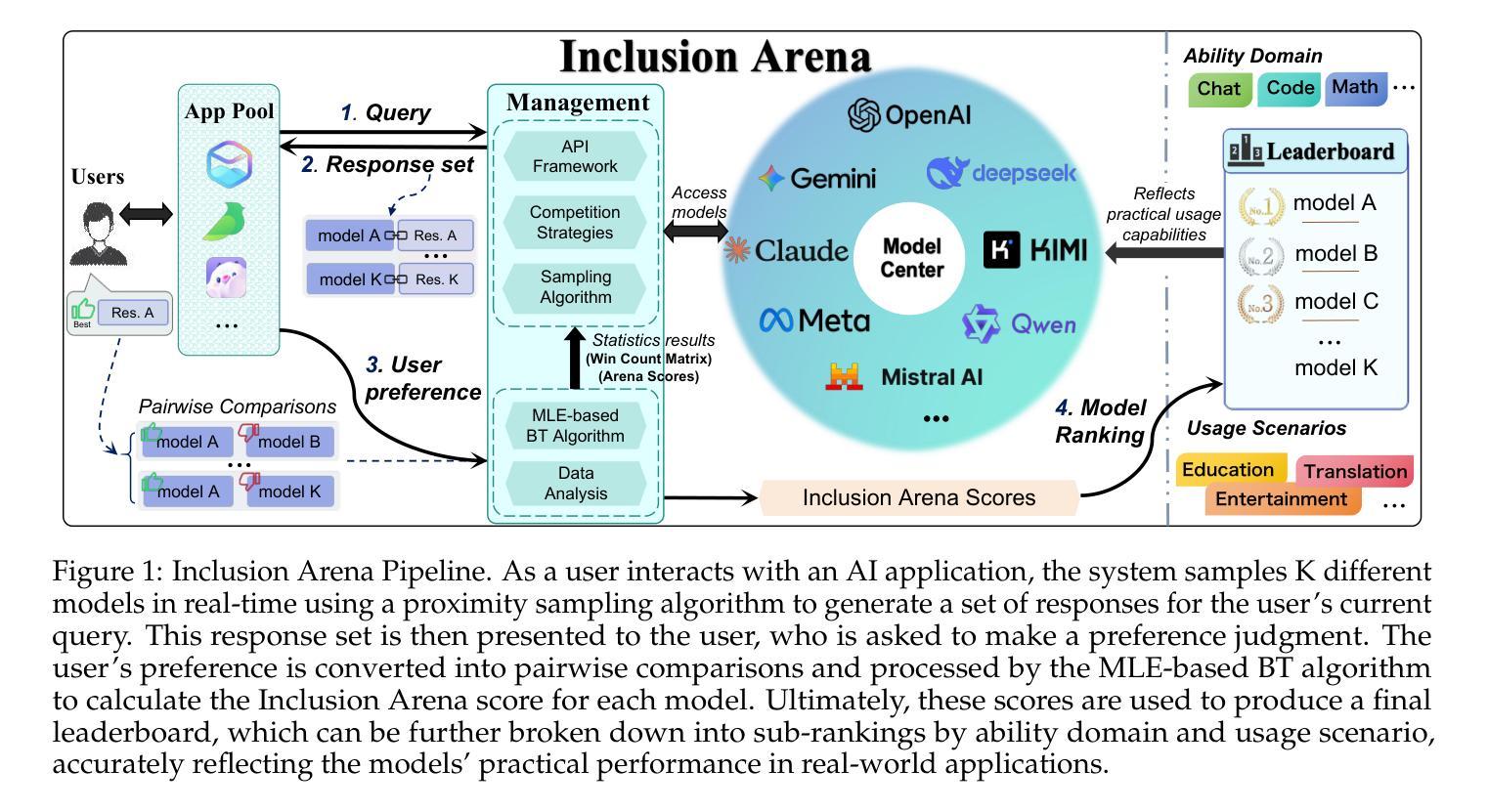
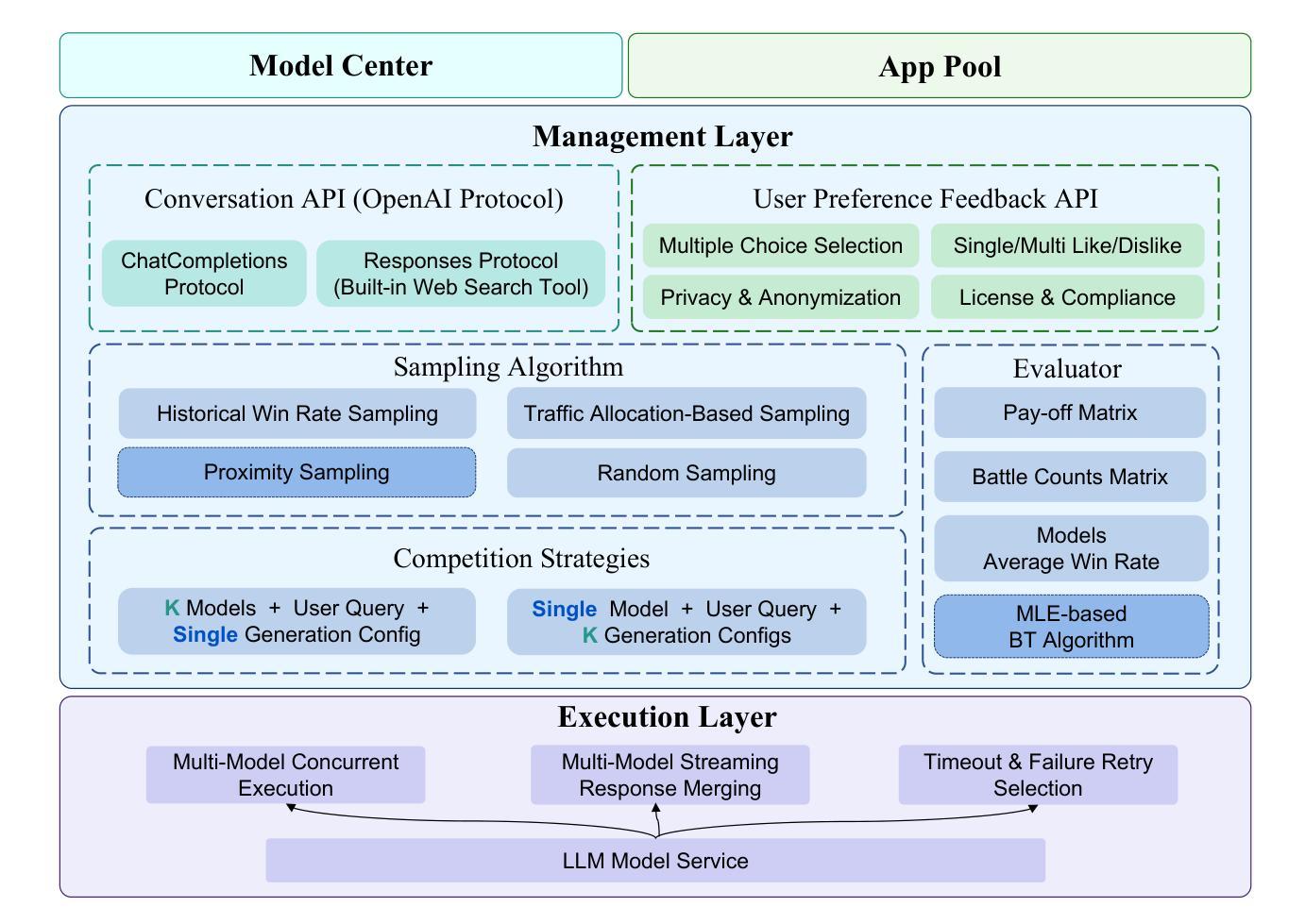
Inclusion Arena: An Open Platform for Evaluating Large Foundation Models with Real-World Apps
Authors:Kangyu Wang, Hongliang He, Lin Liu, Ruiqi Liang, Zhenzhong Lan, Jianguo Li
Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have ushered in a new era of AI capabilities, demonstrating near-human-level performance across diverse scenarios. While numerous benchmarks (e.g., MMLU) and leaderboards (e.g., Chatbot Arena) have been proposed to help evolve the development of LLMs and MLLMs, most rely on static datasets or crowdsourced general-domain prompts, often falling short of reflecting performance in real-world applications. To bridge this critical gap, we present Inclusion Arena, a live leaderboard that ranks models based on human feedback collected directly from AI-powered applications. Our platform integrates pairwise model comparisons into natural user interactions, ensuring evaluations reflect practical usage scenarios. For robust model ranking, we employ the Bradley-Terry model augmented with two key innovations: (1) Placement Matches, a cold-start mechanism to quickly estimate initial ratings for newly integrated models, and (2) Proximity Sampling, an intelligent comparison strategy that prioritizes battles between models of similar capabilities to maximize information gain and enhance rating stability. Extensive empirical analyses and simulations demonstrate that Inclusion Arena yields reliable and stable rankings, exhibits higher data transitivity compared to general crowdsourced datasets, and significantly mitigates the risk of malicious manipulation. By fostering an open alliance between foundation models and real-world applications, Inclusion Arena aims to accelerate the development of LLMs and MLLMs truly optimized for practical, user-centric deployments. The platform is publicly accessible at https://doraemon.alipay.com/model-ranking.
大型语言模型(LLM)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的兴起开启了人工智能能力的新时代,在各种场景中表现出了接近人类的性能。尽管已经提出了许多基准测试(例如MMLU)和排行榜(例如Chatbot Arena)来帮助推动LLM和MLLM的发展,但大多数都依赖于静态数据集或众包通用领域提示,往往无法反映其在现实世界应用中的性能。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了Inclusion Arena,这是一个实时排行榜,根据从AI应用程序中直接收集的人类反馈对模型进行排名。我们的平台将成对模型比较集成到自然用户交互中,确保评估反映实际使用场景。为了对模型进行稳健排名,我们采用Bradley-Terry模型,并辅以两项关键创新:一是位置匹配,这是一种冷启动机制,可以快速估计新集成模型的初始评分;二是邻近采样,这是一种智能比较策略,优先安排能力相似的模型之间的比赛,以最大化信息获取并增强评分稳定性。大量的实证分析和模拟表明,Inclusion Arena产生的排名可靠且稳定,与一般的众包数据集相比,显示出更高的数据传递性,并能显著减少恶意操作的风险。通过促进基础模型与实际应用之间的开放联盟,Inclusion Arena旨在加速针对实际、以用户为中心的部署真正优化的LLM和MLLM的发展。该平台可在https://doraemon.alipay.com/model-ranking公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our platform is publicly accessible at https://doraemon.alipay.com/model-ranking
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)开启了人工智能能力的新时代,在各种场景下展现出接近人类水平的性能。尽管有许多基准测试(如MMLU)和排行榜(如Chatbot Arena),它们大多依赖于静态数据集或众包通用领域提示,往往无法反映实际应用中的性能。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了Inclusion Arena,这是一个基于人类反馈的实时排行榜,直接收集来自人工智能应用程序的反馈来对模型进行排名。我们的平台将成对模型比较集成到自然用户交互中,确保评估反映实际使用场景。为了稳健的模型排名,我们采用Bradley-Terry模型,并辅以两项关键创新:一是位置匹配,这是一种冷启动机制,可以快速估计新集成模型的初始评分;二是邻近采样,这是一种智能对比策略,优先比较能力相近的模型,以最大化信息增益并增强评分稳定性。经过广泛的实证分析和模拟,证明Inclusion Arena的排名可靠稳定,与高层次的众包数据集相比具有更高的数据可转换性,并能有效减少恶意操作的风险。Inclusion Arena旨在促进基础模型与实际应用之间的开放联盟,以加速针对实用、用户为中心的部署真正优化的LLM和MLLM的发展。平台可公开访问:https://doraemon.alipay.com/model-ranking。
关键见解
- LLM和MLLM的发展开启了AI能力的新时代,展现了在各种场景下的近人类表现。
- 当前基准测试和排行榜存在一个问题,即它们往往无法反映模型在实际应用中的性能。
- Inclusion Arena平台通过基于人类反馈的实时排名来解决这个问题,直接收集来自AI应用程序的反馈。
4.该平台集成了成对模型比较到自然用户交互中,确保评估反映实际使用场景。 - 采用Bradley-Terry模型和两项关键创新(位置匹配和邻近采样)来稳健地排名模型。
- 实证分析证明了Inclusion Arena的有效性和可靠性,包括其数据可转换性和对恶意操作的抵御能力。
点此查看论文截图

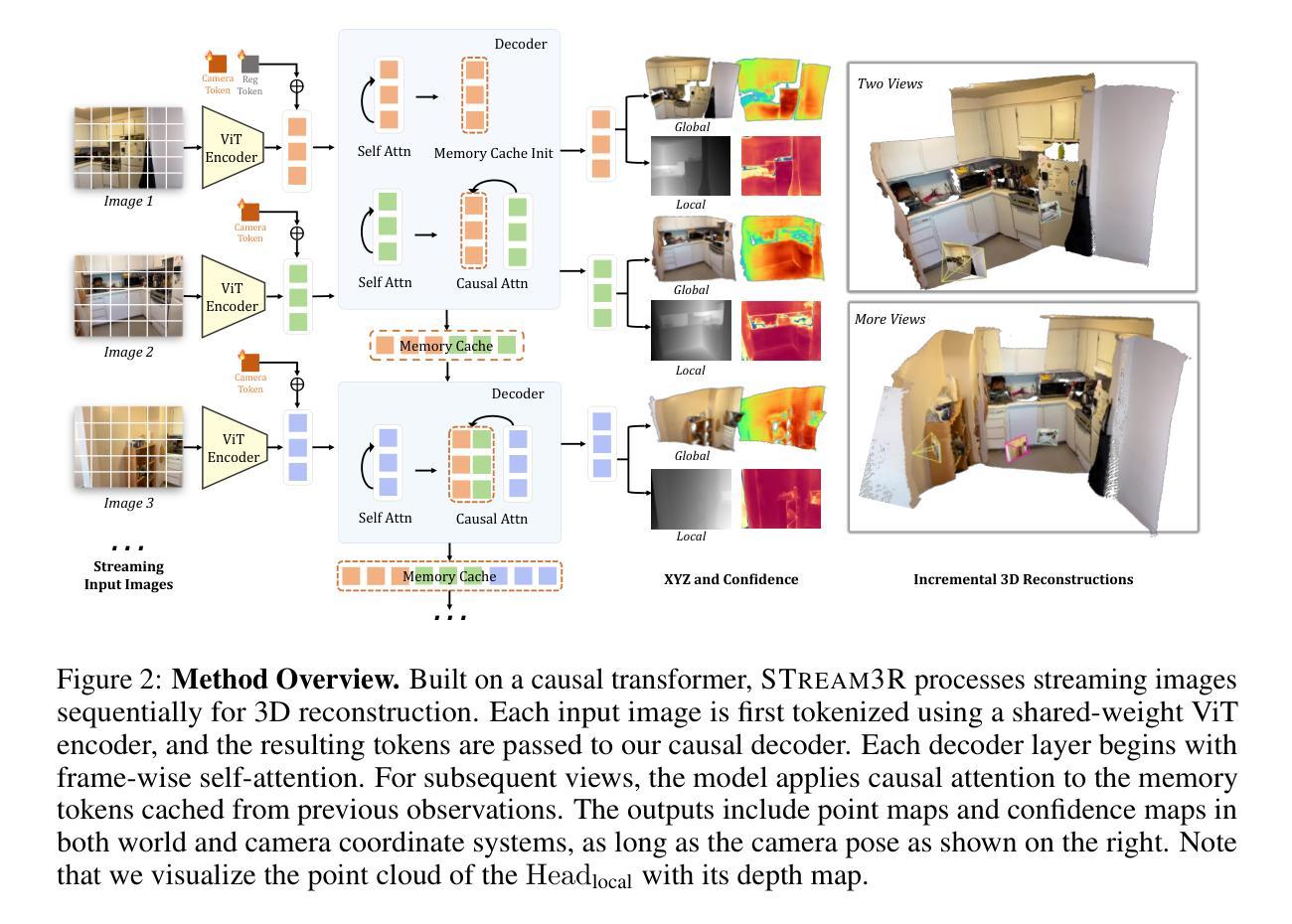
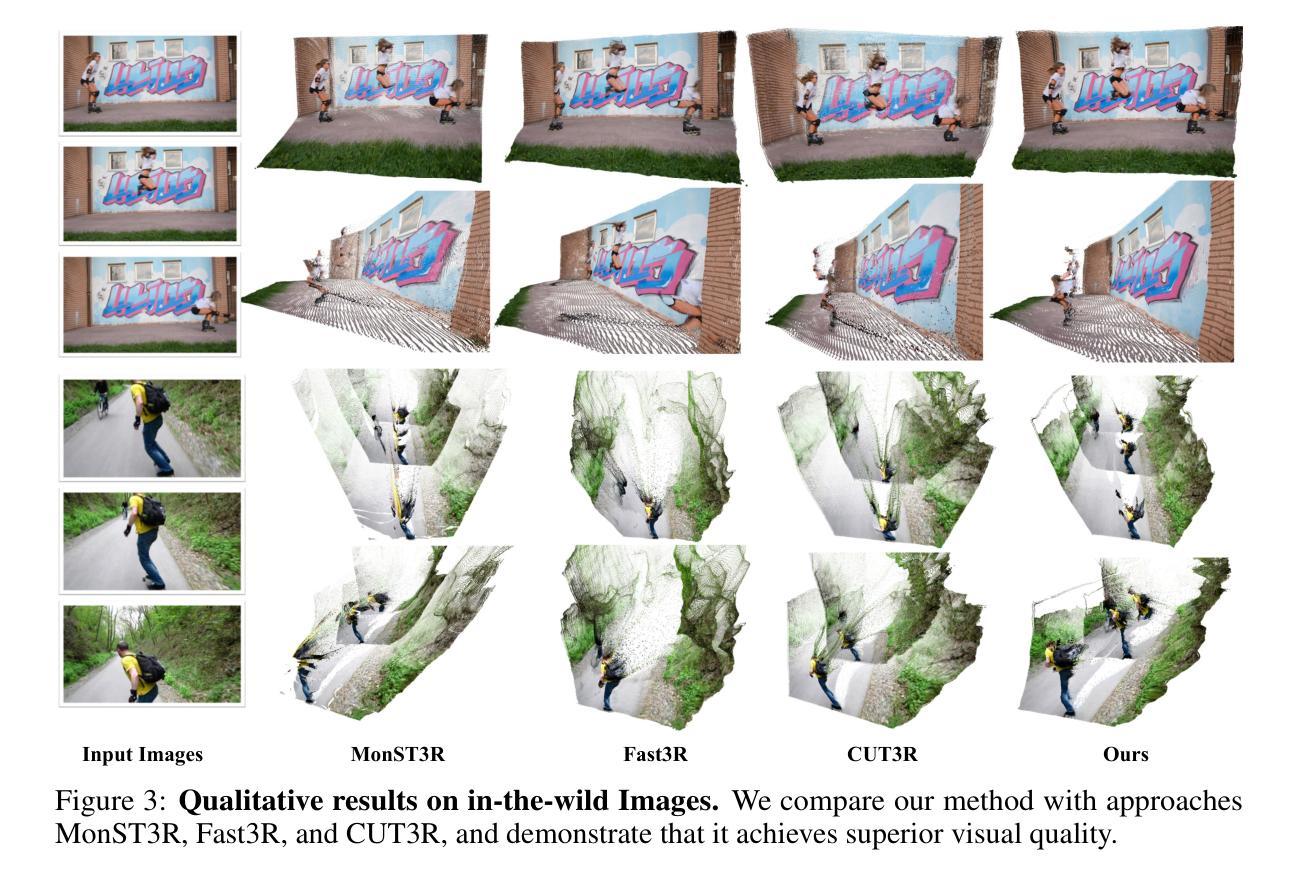
STream3R: Scalable Sequential 3D Reconstruction with Causal Transformer
Authors:Yushi Lan, Yihang Luo, Fangzhou Hong, Shangchen Zhou, Honghua Chen, Zhaoyang Lyu, Shuai Yang, Bo Dai, Chen Change Loy, Xingang Pan
We present STream3R, a novel approach to 3D reconstruction that reformulates pointmap prediction as a decoder-only Transformer problem. Existing state-of-the-art methods for multi-view reconstruction either depend on expensive global optimization or rely on simplistic memory mechanisms that scale poorly with sequence length. In contrast, STream3R introduces an streaming framework that processes image sequences efficiently using causal attention, inspired by advances in modern language modeling. By learning geometric priors from large-scale 3D datasets, STream3R generalizes well to diverse and challenging scenarios, including dynamic scenes where traditional methods often fail. Extensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms prior work across both static and dynamic scene benchmarks. Moreover, STream3R is inherently compatible with LLM-style training infrastructure, enabling efficient large-scale pretraining and fine-tuning for various downstream 3D tasks. Our results underscore the potential of causal Transformer models for online 3D perception, paving the way for real-time 3D understanding in streaming environments. More details can be found in our project page: https://nirvanalan.github.io/projects/stream3r.
我们提出了STream3R,这是一种新型的3D重建方法,它将点云预测重新表述为一个仅解码器的Transformer问题。现有的最先进的多元视图重建方法要么依赖于昂贵的全局优化,要么依赖于简单的记忆机制,这些机制随着序列长度的增加而表现不佳。相比之下,STream3R引入了一个流式框架,该框架利用现代语言建模的进展,通过因果注意力有效地处理图像序列。通过从大规模3D数据集中学习几何先验知识,STream3R在多样化和具有挑战性的场景中具有良好的泛化能力,包括传统方法常常失效的动态场景。大量实验表明,我们的方法在静态和动态场景基准测试上的表现始终优于先前的工作。而且,STream3R与LLM风格的训练基础设施本质上兼容,能够高效地支持大规模预训练和针对各种下游3D任务的微调。我们的结果强调了因果Transformer模型在在线3D感知方面的潜力,为流式环境中实时3D理解铺平了道路。更多细节请参见我们的项目页面:https://nirvanalan.github.io/projects/stream3r。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TL;DR: Streaming 4D reconstruction using causal transformer. Project page: https://nirvanalan.github.io/projects/stream3r
Summary
STream3R是一种新型的三维重建方法,它将点云预测转化为仅解码器参与的Transformer问题。与传统多视角重建方法相比,STream3R采用流式框架,利用因果注意力高效处理图像序列,并从大规模三维数据集中学习几何先验,能够适应多种复杂场景,包括传统方法常失效的动态场景。实验证明,STream3R在静态和动态场景基准测试中均表现优异,且与大型语言模型训练基础设施兼容,可为各种下游三维任务提供高效的大型预训练和微调。
Key Takeaways
- STream3R是一种新的三维重建方法,将点云预测转化为仅解码器Transformer问题。
- 与传统方法不同,STream3R利用流式框架和因果注意力处理图像序列。
- STream3R从大规模三维数据集中学习几何先验,适应多种复杂场景。
- 实验证明STream3R在静态和动态场景基准测试中表现优异。
- STream3R与大型语言模型训练基础设施兼容,便于各种下游三维任务的预训练和微调。
- STream3R为实时三维理解在流式环境中铺平了道路。
- 更多细节可查阅项目网页。
点此查看论文截图

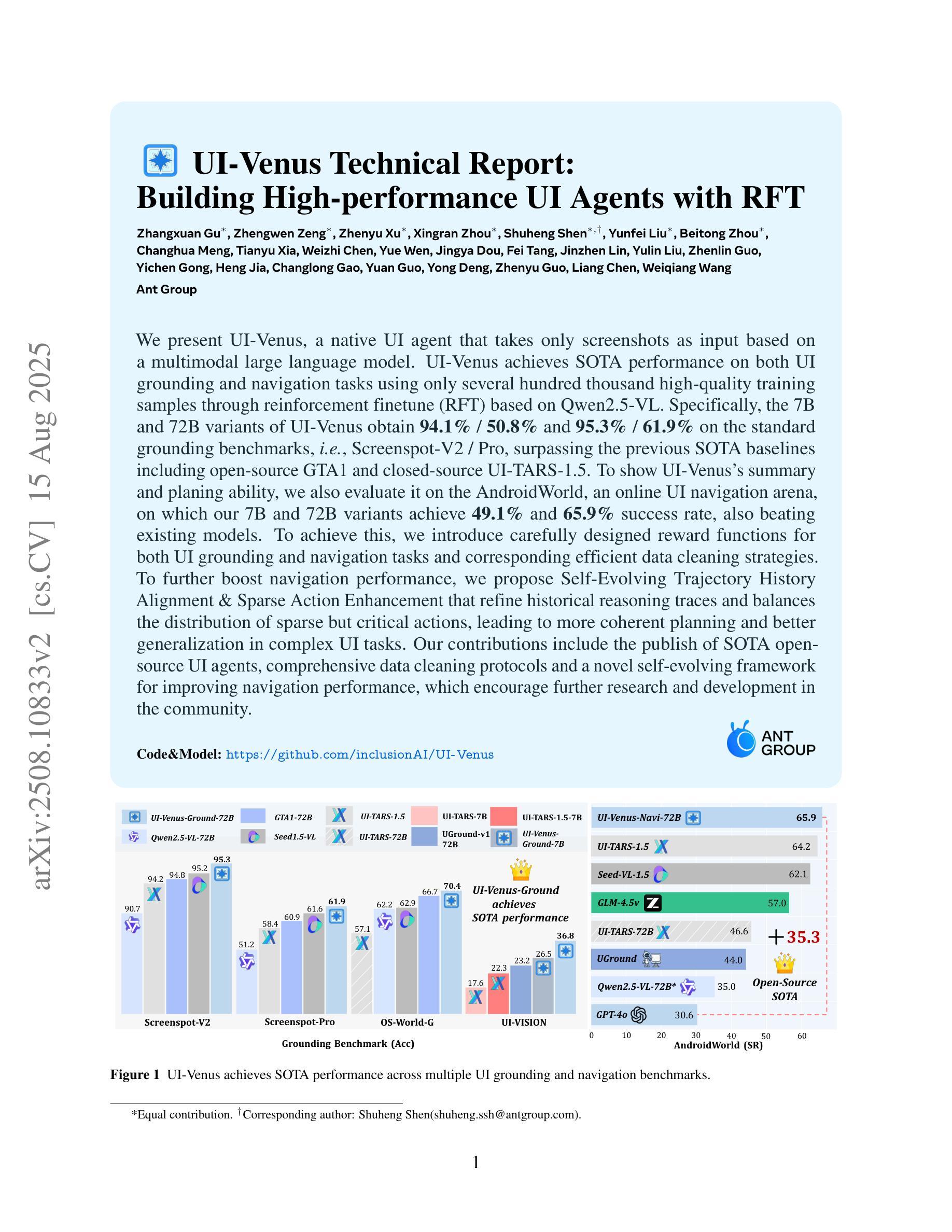
UI-Venus Technical Report: Building High-performance UI Agents with RFT
Authors:Zhangxuan Gu, Zhengwen Zeng, Zhenyu Xu, Xingran Zhou, Shuheng Shen, Yunfei Liu, Beitong Zhou, Changhua Meng, Tianyu Xia, Weizhi Chen, Yue Wen, Jingya Dou, Fei Tang, Jinzhen Lin, Yulin Liu, Zhenlin Guo, Yichen Gong, Heng Jia, Changlong Gao, Yuan Guo, Yong Deng, Zhenyu Guo, Liang Chen, Weiqiang Wang
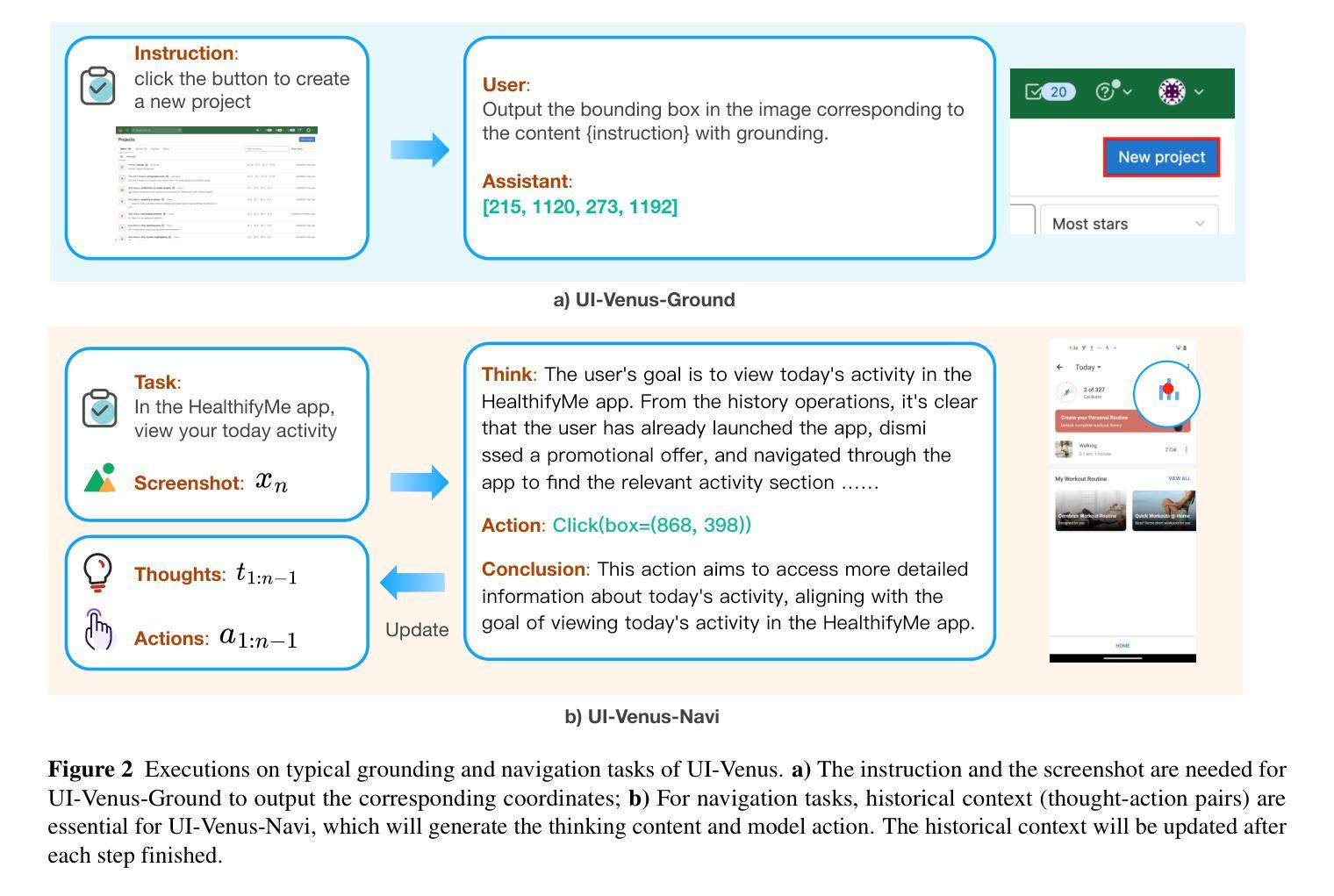
We present UI-Venus, a native UI agent that takes only screenshots as input based on a multimodal large language model. UI-Venus achieves SOTA performance on both UI grounding and navigation tasks using only several hundred thousand high-quality training samples through reinforcement finetune (RFT) based on Qwen2.5-VL. Specifically, the 7B and 72B variants of UI-Venus obtain 94.1% / 50.8% and 95.3% / 61.9% on the standard grounding benchmarks, i.e., Screenspot-V2 / Pro, surpassing the previous SOTA baselines including open-source GTA1 and closed-source UI-TARS-1.5. To show UI-Venus’s summary and planing ability, we also evaluate it on the AndroidWorld, an online UI navigation arena, on which our 7B and 72B variants achieve 49.1% and 65.9% success rate, also beating existing models. To achieve this, we introduce carefully designed reward functions for both UI grounding and navigation tasks and corresponding efficient data cleaning strategies. To further boost navigation performance, we propose Self-Evolving Trajectory History Alignment & Sparse Action Enhancement that refine historical reasoning traces and balances the distribution of sparse but critical actions, leading to more coherent planning and better generalization in complex UI tasks. Our contributions include the publish of SOTA open-source UI agents, comprehensive data cleaning protocols and a novel self-evolving framework for improving navigation performance, which encourage further research and development in the community. Code is available at https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus.
我们介绍了UI-Venus,这是一个基于多模态大型语言模型的原生用户界面代理,它仅通过截屏作为输入。UI-Venus通过使用基于Qwen2.5-VL的强化微调(RFT)和仅数百万的高质量训练样本,在UI定位和导航任务上达到了最新性能。具体来说,UI-Venus的7B和72B变种在标准的定位基准测试(即Screenspot-V2/Pro)上分别达到了94.1%/50.8%和95.3%/61.9%,超越了包括开源GTA1和闭源UI-TARS-1.5在内的先前最新基线。为了展示UI-Venus的总结和规划能力,我们还将其评估了一个在线UI导航平台AndroidWorld,我们的7B和72B变种在该平台上分别达到了49.1%和65.9%的成功率,也击败了现有模型。为了实现这一点,我们为UI定位和导航任务精心设计了奖励函数和相应的有效数据清理策略。为了进一步提高导航性能,我们提出了自我进化的轨迹历史对齐和稀疏动作增强方法,该方法可以优化历史推理轨迹并平衡稀疏但关键动作的分布,从而导致更连贯的规划以及在复杂UI任务中更好的泛化能力。我们的贡献包括发布领先的开源UI代理、全面的数据清理协议以及一种提高导航性能的自我进化框架,这鼓励了社区内的进一步研究和开发。代码可在https://github.com/inclusionAI/UI-Venus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于多模态大型语言模型的原生用户界面代理UI-Venus。该代理仅通过截图作为输入,通过强化微调(RFT)在UI接地和导航任务上取得了最新性能。UI-Venus的7B和72B变体在标准接地基准测试Screenspot-V2 / Pro上分别达到了94.1% / 50.8%和95.3% / 61.9%的性能,超过了包括开源GTA1和闭源UI-TARS-1.5在内的先前最新基线。此外,UI-Venus在在线UI导航区域AndroidWorld上的成功率也超过了现有模型。为实现这些性能,本文引入了针对UI接地和导航任务的精心设计奖励函数和相应的有效数据清理策略。为进一步提高导航性能,提出了自我进化的轨迹历史对齐与稀疏动作增强方法,该方法优化了历史推理轨迹,平衡了稀疏但关键动作的分布,从而实现了更连贯的规划,并在复杂的UI任务中实现了更好的泛化。本文的贡献包括公布最新的开源UI代理、全面的数据清理协议以及一种提高导航性能的自我进化框架,这鼓励了社区进一步的研究和发展。
Key Takeaways
- UI-Venus是一个基于多模态大型语言模型的原生用户界面代理,仅通过截图作为输入。
- UI-Venus在UI接地和导航任务上取得了最新性能,其7B和72B变体在标准基准测试上表现优异。
- UI-Venus在在线UI导航区域AndroidWorld上的成功率超过了现有模型。
- 为提高性能,本文引入了奖励函数、数据清理策略和自我进化的轨迹历史对齐与稀疏动作增强方法。
- 本文公布了开源UI代理、数据清理协议和提高导航性能的自我进化框架。
- UI-Venus的代码已公开,可供进一步研究和使用。
点此查看论文截图
A Transformer-Based Approach for DDoS Attack Detection in IoT Networks
Authors:Sandipan Dey, Payal Santosh Kate, Vatsala Upadhyay, Abhishek Vaish
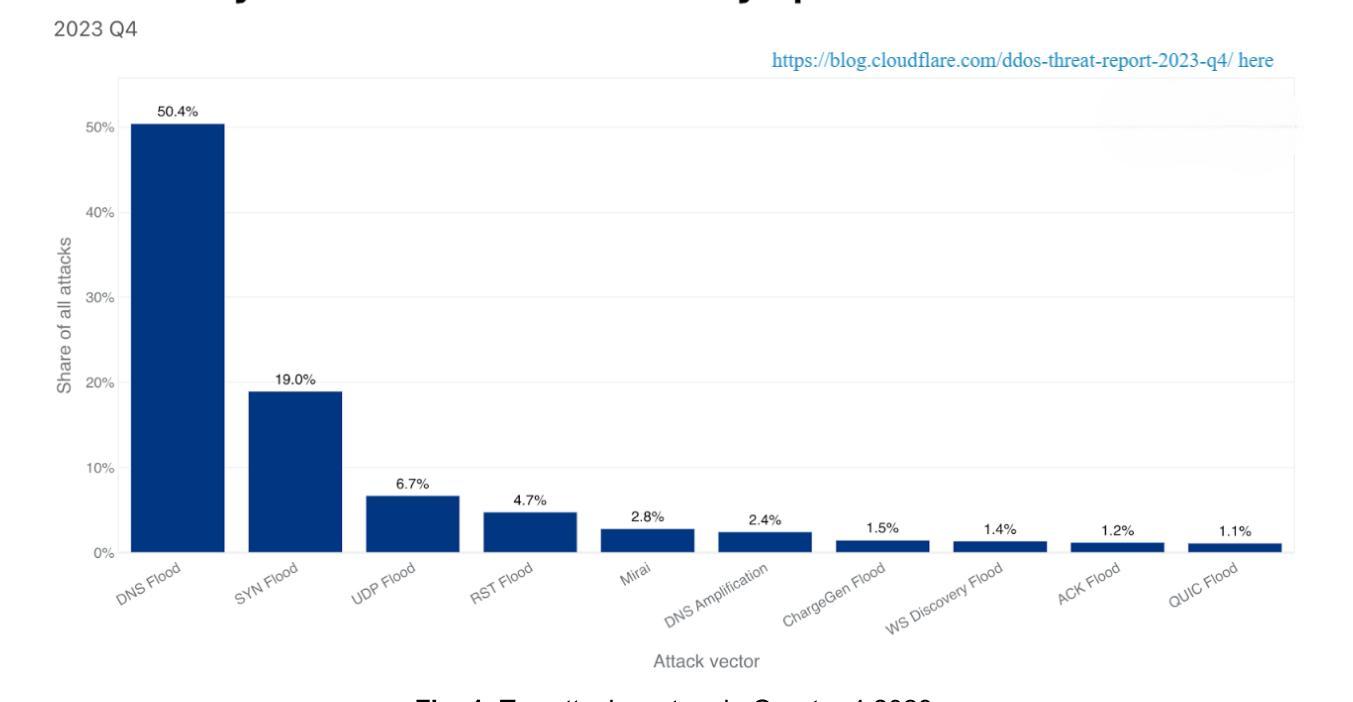
DDoS attacks have become a major threat to the security of IoT devices and can cause severe damage to the network infrastructure. IoT devices suffer from the inherent problem of resource constraints and are therefore susceptible to such resource-exhausting attacks. Traditional methods for detecting DDoS attacks are not efficient enough to cope with the dynamic nature of IoT networks, as well as the scalability of the attacks, diversity of protocols, high volume of traffic, and variability in device behavior, and variability of protocols like MQTT, CoAP, making it hard to implement security across all the protocols. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, i.e., the use of Transformer models, which have shown remarkable performance in natural language processing tasks, for detecting DDoS attacks on IoT devices. The proposed model extracts features from network traffic data and processes them using a self-attention mechanism. Experiments conducted on a real-world dataset demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms traditional machine learning techniques, which can be validated by comparing both approaches’ accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The results of this study show that the Transformer models can be an effective solution for detecting DDoS attacks on IoT devices and have the potential to be deployed in real-world IoT environments.
DDoS攻击已成为物联网设备安全的主要威胁,并可能对网络基础设施造成严重损害。物联网设备存在资源约束的内在问题,因此容易受到此类耗尽资源的攻击。传统的检测DDoS攻击的方法不足以应对物联网网络的动态性,以及攻击的可扩展性、协议的多样性、流量的大量性以及设备行为的可变性,以及MQTT、CoAP等协议的多样性,使得在所有协议上实施安全变得困难。在本文中,我们提出了一种新方法,即使用Transformer模型检测物联网设备上的DDoS攻击。该模型从网络流量数据中提取特征,并使用自注意力机制进行处理。在真实数据集上进行的实验表明,该方法优于传统机器学习方法,可以通过比较两者的准确率、精确率、召回率和F1分数进行验证。本研究的结果表明,Transformer模型是检测物联网设备上DDoS攻击的有效解决方案,并有可能在真实的物联网环境中部署。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对物联网设备的DDoS攻击已成为重大安全威胁,可能导致网络基础设施严重受损。由于物联网设备存在资源约束问题,传统检测DDoS攻击的方法难以应对物联网网络的动态性、攻击的规模化、协议多样性和高流量等挑战。本文提出一种新型方法,即利用在自然语言处理任务中表现出色的Transformer模型检测物联网设备的DDoS攻击。该方法从网络流量数据中提取特征,并使用自注意力机制进行处理。在真实数据集上进行的实验表明,该方法优于传统机器学习技术,可以通过比较两者的准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数进行验证。
Key Takeaways
- DDoS攻击对物联网设备构成重大威胁,可造成网络基础设施严重损害。
- 物联网设备因资源约束问题,面临DDoS攻击时的防护面临挑战。
- 传统方法难以应对物联网网络的动态性、攻击的规模化等挑战。
- 本文提出利用Transformer模型检测物联网设备的DDoS攻击。
- Transformer模型通过提取网络流量数据特征,并使用自注意力机制进行处理。
- 在真实数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于传统机器学习技术。
点此查看论文截图

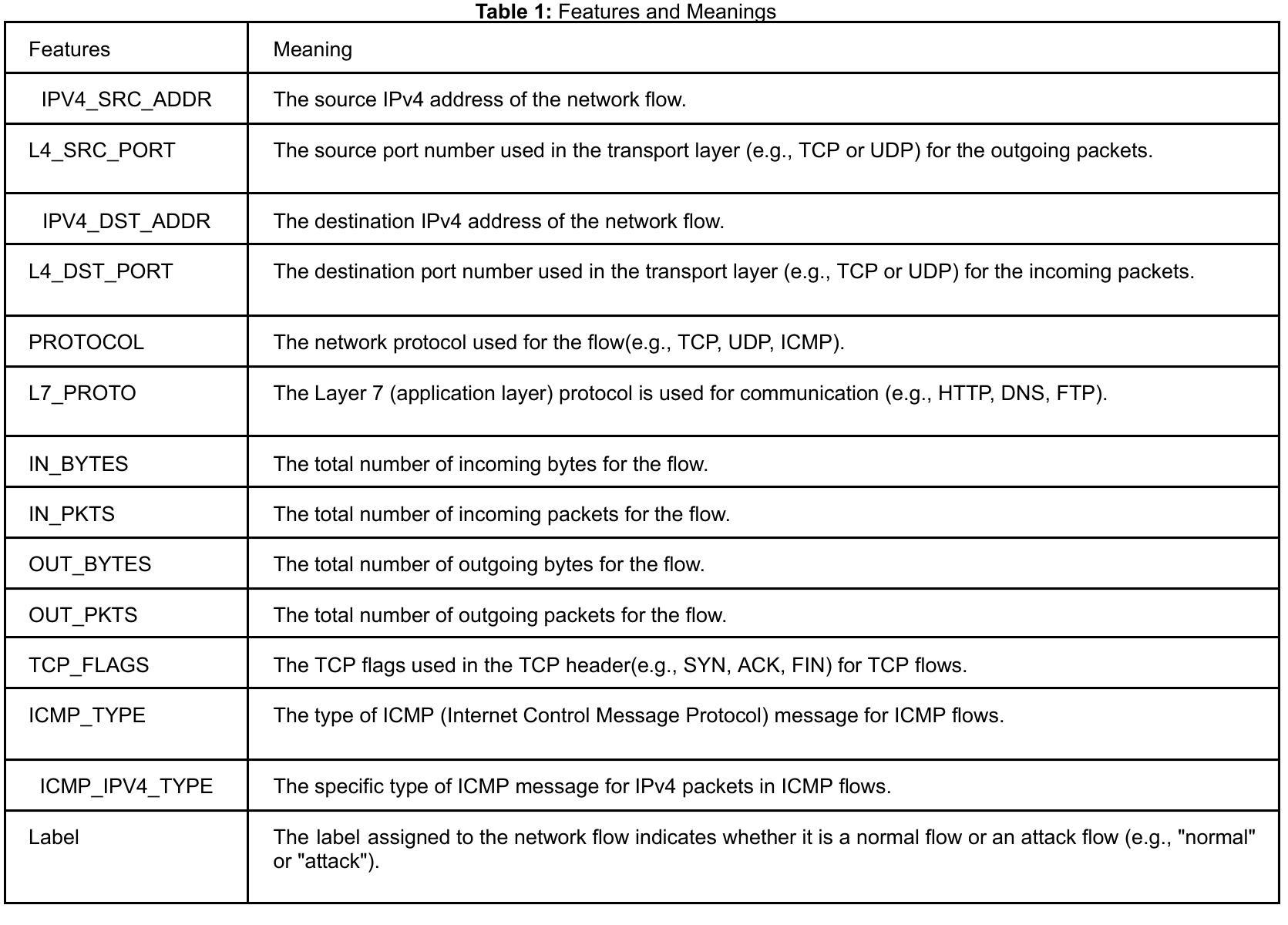
Concepts or Skills? Rethinking Instruction Selection for Multi-modal Models
Authors:Andrew Bai, Justin Cui, Ruochen Wang, Cho-Jui Hsieh
Vision-language instruction tuning achieves two main purposes: learning visual concepts and learning visual skills. In this paper, we found that vision-language benchmarks fall into the dichotomy of mainly benefiting from training on instructions with similar skills or visual concepts. Inspired by the discovery, we designed a simple targeted training data selection method to optimize the performance of a given benchmark. We first extract the concepts/skills from the benchmark, determine whether the benchmark predominantly benefits from similar concepts or skills, and finally select instructions with the most matching concepts/skills. Experiments on 10+ benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our targeted data selection method, showing +0.9% over the best existing baseline averaged over all benchmarks and +1.5% on the skill-focused subset. Our findings underscore the importance of recognizing the inherent trade-off within instruction selection, which requires balancing the acquisition of conceptual knowledge against visual skill.
视觉语言指令调整实现了两个主要目标:学习视觉概念和学习视觉技能。在本文中,我们发现视觉语言基准测试主要受益于具有类似技能或视觉概念的指令训练。受此发现启发,我们设计了一种简单的有针对性的训练数据选择方法,以优化给定基准测试的性能。我们首先从基准测试中提取概念/技能,确定基准测试主要受益于类似的概念还是技能,并最终选择概念/技能最匹配的指令。在10多个基准测试上的实验验证了我们有针对性的数据选择方法的有效性,在所有基准测试上的平均表现优于现有最佳基线+0.9%,在技能导向的子集上+1.5%。我们的研究强调了在选择指令时认识到内在权衡的重要性,这需要平衡概念知识的获取和视觉技能的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure
Summary
本文探讨了视觉语言指令调整的两个主要目标:学习视觉概念和学习视觉技能。研究发现,视觉语言基准测试主要受益于类似技能和视觉概念的指令训练。基于这一发现,设计了一种简单的针对性训练数据选择方法,以优化给定基准测试的性能。通过从基准测试中提取概念/技能,确定主要受益于类似概念或技能,最终选择匹配度最高的指令。在多个基准测试上的实验验证了该定向数据选择方法的有效性,在所有基准测试上的平均表现优于最佳现有基线+0.9%,在侧重技能的子集上+1.5%。研究强调了指令选择中固有权衡的重要性,需要在获取概念知识和视觉技能之间取得平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言指令调整旨在实现学习视觉概念和学习视觉技能两个主要目标。
- 视觉语言基准测试主要受益于类似技能和视觉概念的指令训练。
- 设计了一种简单的针对性训练数据选择方法来优化给定基准测试的性能。
- 通过从基准测试中提取概念/技能来确定主要受益点。
- 实验验证了定向数据选择方法的有效性,表现优于现有基线。
- 研究强调了指令选择中需要在获取概念知识和视觉技能之间取得平衡的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

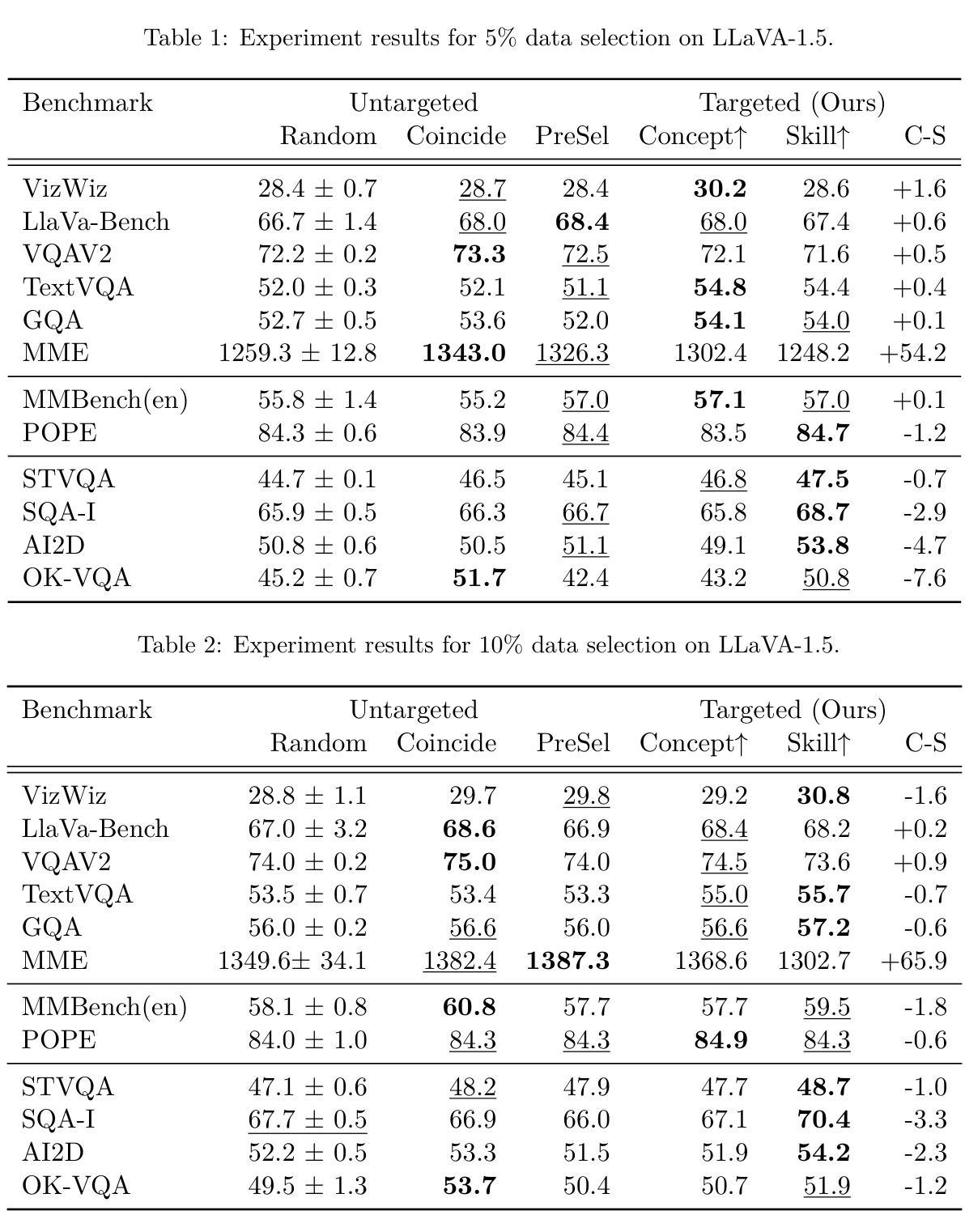
Pruning and Malicious Injection: A Retraining-Free Backdoor Attack on Transformer Models
Authors:Taibiao Zhao, Mingxuan Sun, Hao Wang, Xiaobing Chen, Xiangwei Zhou
Transformer models have demonstrated exceptional performance and have become indispensable in computer vision (CV) and natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, recent studies reveal that transformers are susceptible to backdoor attacks. Prior backdoor attack methods typically rely on retraining with clean data or altering the model architecture, both of which can be resource-intensive and intrusive. In this paper, we propose Head-wise Pruning and Malicious Injection (HPMI), a novel retraining-free backdoor attack on transformers that does not alter the model’s architecture. Our approach requires only a small subset of the original data and basic knowledge of the model architecture, eliminating the need for retraining the target transformer. Technically, HPMI works by pruning the least important head and injecting a pre-trained malicious head to establish the backdoor. We provide a rigorous theoretical justification demonstrating that the implanted backdoor resists detection and removal by state-of-the-art defense techniques, under reasonable assumptions. Experimental evaluations across multiple datasets further validate the effectiveness of HPMI, showing that it 1) incurs negligible clean accuracy loss, 2) achieves at least 99.55% attack success rate, and 3) bypasses four advanced defense mechanisms. Additionally, relative to state-of-the-art retraining-dependent attacks, HPMI achieves greater concealment and robustness against diverse defense strategies, while maintaining minimal impact on clean accuracy.
Transformer模型在计算机视觉(CV)和自然语言处理(NLP)任务中表现出了卓越的性能,并成为了不可或缺的存在。然而,最近的研究表明,Transformer容易受到后门攻击。之前的后门攻击方法通常依赖于使用干净数据的重新训练或改变模型架构,这两种方法都可能是资源密集型的且具侵入性。在本文中,我们提出了Head-wise Pruning and Malicious Injection(HPMI),这是一种新型的、无需重新训练的Transformer后门攻击方法,它不会改变模型架构。我们的方法只需要原始数据的一个小子集和模型架构的基本知识,从而无需对目标Transformer进行重新训练。从技术上讲,HPMI通过删除最不重要的头部并注入一个预训练的恶意头部来建立后门。我们提供了严格的理论证明,证明植入的后门能够在合理的假设下抵抗最先进的防御技术的检测和移除。跨多个数据集的实验评估进一步验证了HPMI的有效性,表明它1)几乎不会造成清洁精度的损失,2)攻击成功率至少达到99.55%,3)绕过了四种先进的防御机制。此外,与最先进的依赖于重新训练的攻击相比,HPMI在多种防御策略面前具有更高的隐蔽性和稳健性,同时几乎不影响清洁精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对Transformer模型的新型后门攻击方法——Head-wise Pruning and Malicious Injection (HPMI)。该方法无需重训模型,且不改变模型架构,仅利用原始数据子集和模型基础架构知识即可实现攻击。HPMI通过删除次要头部并注入预训练的恶意头部来建立后门,具有抵御先进防御技术检测和移除的能力。实验评估显示,HPMI不仅清洁精度损失小,攻击成功率高达至少99.55%,而且能绕过四种先进的防御机制。相较于依赖重训的攻击方法,HPMI更具隐蔽性和对多种防御策略的稳健性,同时保持较低的清洁精度影响。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型在计算机视觉和自然语言处理任务中表现出卓越性能,但易受后门攻击。
- 传统的后门攻击方法通常需要重训模型或改变模型架构,资源消耗大且侵入性强。
- HPMI是一种新型的后门攻击方法,无需重训模型,不改变模型架构。
- HPMI通过删除次要头部并注入预训练的恶意头部来建立后门。
- HPMI具有抵御先进防御技术检测和移除的能力。
- 实验评估显示,HPMI具有高的攻击成功率和低的清洁精度损失。
点此查看论文截图

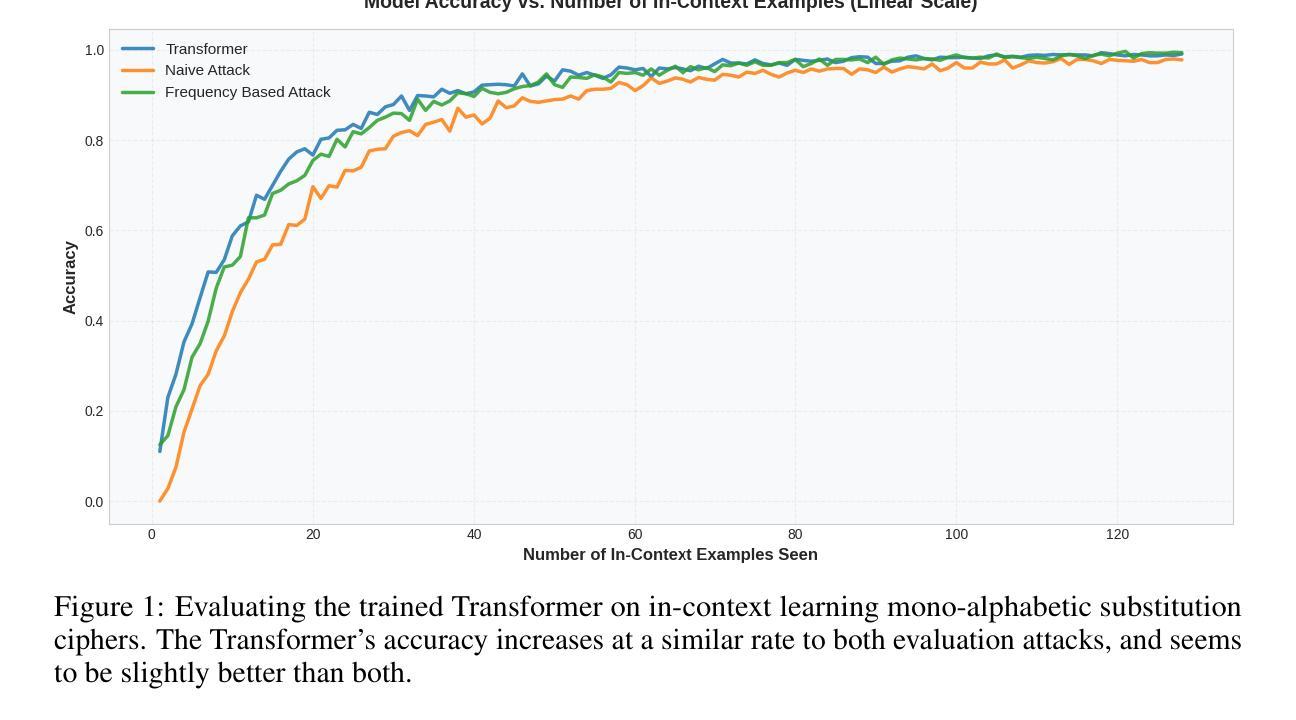
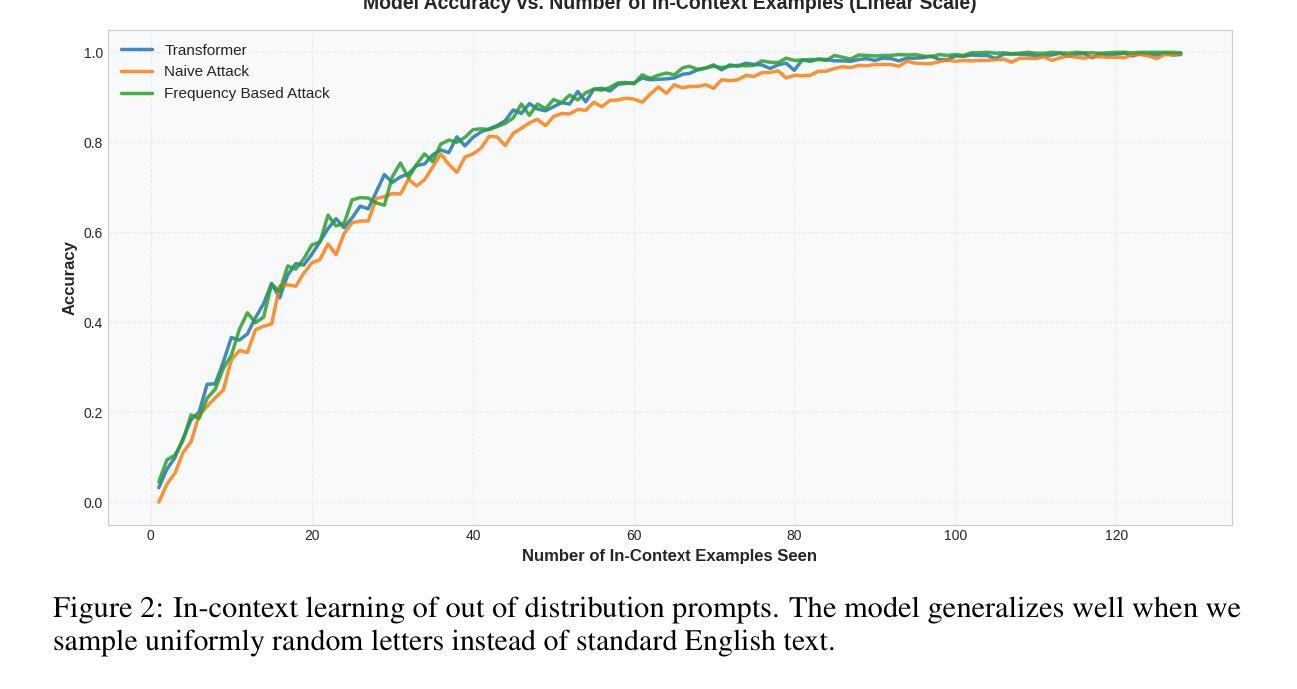
Can Transformers Break Encryption Schemes via In-Context Learning?
Authors:Jathin Korrapati, Patrick Mendoza, Aditya Tomar, Abein Abraham
In-context learning (ICL) has emerged as a powerful capability of transformer-based language models, enabling them to perform tasks by conditioning on a small number of examples presented at inference time, without any parameter updates. Prior work has shown that transformers can generalize over simple function classes like linear functions, decision trees, even neural networks, purely from context, focusing on numerical or symbolic reasoning over underlying well-structured functions. Instead, we propose a novel application of ICL into the domain of cryptographic function learning, specifically focusing on ciphers such as mono-alphabetic substitution and Vigen`ere ciphers, two classes of private-key encryption schemes. These ciphers involve a fixed but hidden bijective mapping between plain text and cipher text characters. Given a small set of (cipher text, plain text) pairs, the goal is for the model to infer the underlying substitution and decode a new cipher text word. This setting poses a structured inference challenge, which is well-suited for evaluating the inductive biases and generalization capabilities of transformers under the ICL paradigm. Code is available at https://github.com/adistomar/CS182-project.
上下文学习(ICL)已经成为基于转换器的语言模型的一种强大功能,使它们能够在推理时间呈现少量示例的情况下执行任务,而无需进行任何参数更新。先前的工作已经表明,转换器可以根据上下文概括简单的函数类别,如线性函数、决策树,甚至是神经网络,专注于对基础结构良好的函数的数值或符号推理。相反,我们提出将ICL的新应用引入到密码函数学习领域,特别是关注单字母替代密码和维吉尼亚密码等密码。这两类密码都属于私钥加密方案,涉及明文和密文字符之间的固定但隐藏的双向映射。给定一组(密文,明文)对,模型的目标是推断出潜在的替代关系并解码新的密文单词。此设置提出了结构化推理挑战,非常适合于评估转换器在ICL范式下的归纳偏见和泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/adistomar/CS182-project找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于转换器的语言模型展现出强大的上下文学习能力(ICL),能够在推理阶段通过少量示例进行任务执行,无需更新任何参数。本研究将ICL应用于密码学函数学习领域,特别是针对单字母替代密码和Vigenère密码等私钥加密算法。给定一组(密文,明文)对,模型的目标是推断出潜在的替代规则并解码出新的密文单词。这为评估转换器的归纳偏见和泛化能力提供了良好的结构化推理挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 转换器语言模型展现出强大的上下文学习能力(ICL)。
- ICL能在推理阶段通过少量示例执行任务,无需更新参数。
- ICL被应用于密码学函数学习领域。
- 针对的是私钥加密算法,如单字母替代密码和Vigenère密码。
- 模型需从给定的(密文,明文)对中推断出潜在替代规则。
- 此领域的应用为评估模型的归纳偏见和泛化能力提供了结构化推理挑战。
点此查看论文截图

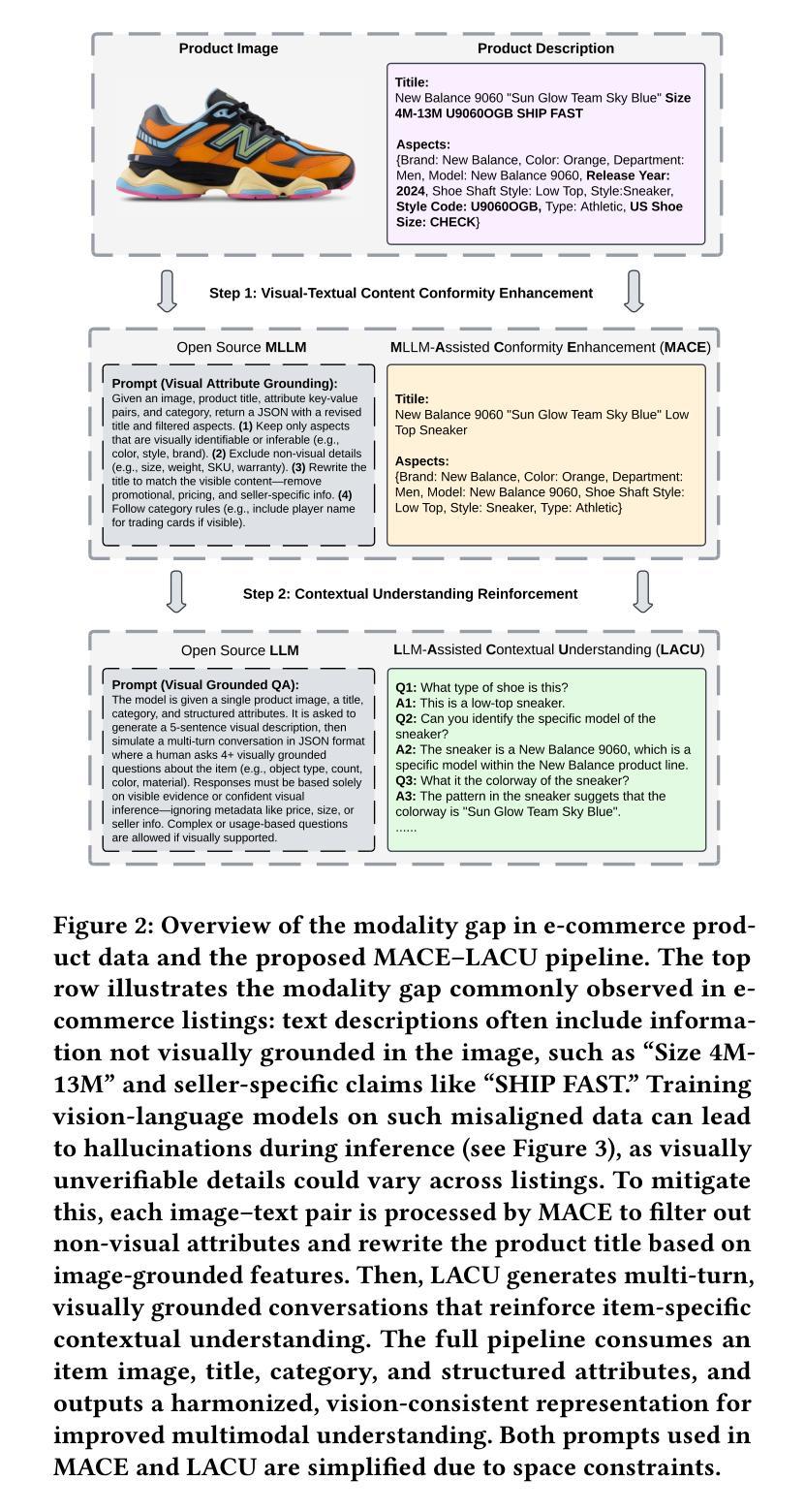
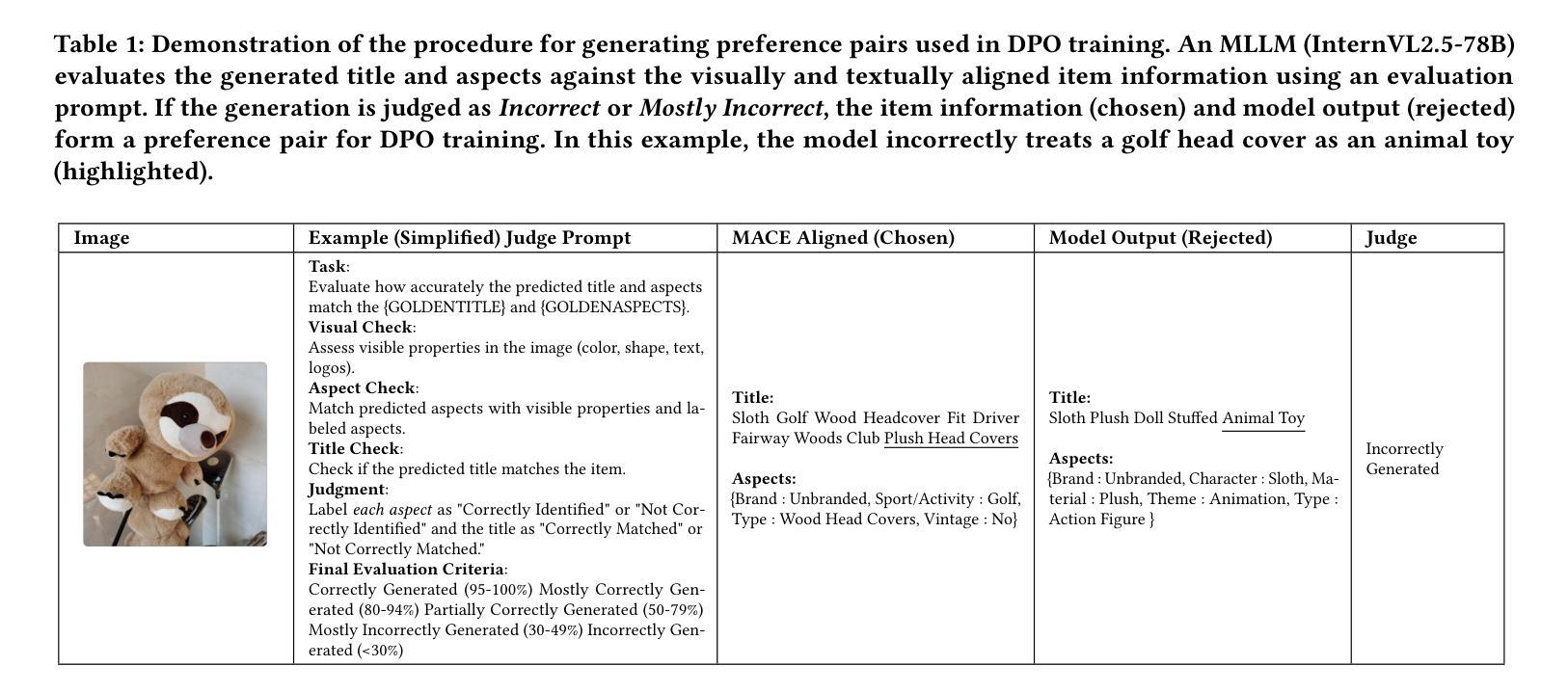
Bridging Modality Gaps in e-Commerce Products via Vision-Language Alignment
Authors:Yipeng Zhang, Hongju Yu, Aritra Mandal, Canran Xu, Qunzhi Zhou, Zhe Wu
Item information, such as titles and attributes, is essential for effective user engagement in e-commerce. However, manual or semi-manual entry of structured item specifics often produces inconsistent quality, errors, and slow turnaround, especially for Customer-to-Customer sellers. Generating accurate descriptions directly from item images offers a promising alternative. Existing retrieval-based solutions address some of these issues but often miss fine-grained visual details and struggle with niche or specialized categories. We propose Optimized Preference-Based AI for Listings (OPAL), a framework for generating schema-compliant, high-quality item descriptions from images using a fine-tuned multimodal large language model (MLLM). OPAL addresses key challenges in multimodal e-commerce applications, including bridging modality gaps and capturing detailed contextual information. It introduces two data refinement methods: MLLM-Assisted Conformity Enhancement, which ensures alignment with structured schema requirements, and LLM-Assisted Contextual Understanding, which improves the capture of nuanced and fine-grained information from visual inputs. OPAL uses visual instruction tuning combined with direct preference optimization to fine-tune the MLLM, reducing hallucinations and improving robustness across different backbone architectures. We evaluate OPAL on real-world e-commerce datasets, showing that it consistently outperforms baseline methods in both description quality and schema completion rates. These results demonstrate that OPAL effectively bridges the gap between visual and textual modalities, delivering richer, more accurate, and more consistent item descriptions. This work advances automated listing optimization and supports scalable, high-quality content generation in e-commerce platforms.
商品信息,如标题和属性,对于电子商务中的有效用户参与至关重要。然而,手动或半手动输入的结构化商品详细信息往往会产生质量不稳定、错误和响应慢的问题,特别是对于客户对客户卖家而言。直接从商品图片生成准确的描述提供了一种有前景的替代方案。现有的基于检索的解决方案解决了其中的一些问题,但往往忽略了细微的视觉细节,并且在小众或专业类别中表现挣扎。我们提出了Optimized Preference-Based AI for Listings (OPAL)框架,该框架使用经过微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)从图像生成符合架构的高质量商品描述。OPAL解决了多模态电子商务应用中的关键挑战,包括弥合模态差距和捕获详细的上下文信息。它引入了两种数据优化方法:MLLM辅助一致性增强,确保与结构化架构要求的一致性;LLM辅助上下文理解,提高了从视觉输入中捕获细微和精细信息的能力。OPAL使用视觉指令调整结合直接偏好优化来微调MLLM,减少了幻觉并提高了不同主干架构的稳健性。我们在真实的电子商务数据集上评估了OPAL的性能,结果表明,它在描述质量和架构完成率方面都始终优于基准方法。这些结果证明了OPAL在弥合视觉和文本模态之间的差距方面的有效性,提供了更丰富、更准确、更一致的商品描述。这项工作推动了自动列表优化支持,并在电子商务平台中实现了可扩展的高质量内容生成。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
商品信息,如标题和属性,对于电子商务中的有效用户参与至关重要。然而,手动或半自动输入结构化商品详情往往产生质量不一、错误较多和响应慢的问题,特别是在客户对客户销售中。直接从商品图片生成准确描述提供了一个有前景的解决方案。我们提出Optimized Preference-Based AI for Listings (OPAL),一个使用微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)从图片生成符合架构要求的高质量商品描述的框架。OPAL解决了多模态电子商务应用的关键挑战,包括弥合模态差距和捕捉详细的上下文信息。它引入两种数据优化方法:MLLM辅助一致性增强,确保与结构化架构要求的对齐;LLM辅助上下文理解,提高从视觉输入中捕捉细微和精细信息的能力。OPAL使用视觉指令调整与直接偏好优化相结合来微调MLLM,减少幻觉并提高不同主干架构的稳健性。我们在真实的电子商务数据集上评估OPAL,显示其在描述质量和架构完成率方面均优于基准方法。这些结果证明OPAL有效地弥合了视觉和文本模态之间的差距,提供更加丰富、准确和一致的商品描述。这项工作推动了自动列表优化,并支持电子商务平台中的可扩展和高品质内容生成。
关键见解
- 商品信息对用户参与度至关重要,但手动或半自动输入存在质量不一、错误和响应慢的问题。
- 直接从商品图片生成描述提供了一个解决方案。
- 提出OPAL框架,使用多模态大型语言模型从图片生成高质量商品描述。
- OPAL通过两种数据优化方法解决多模态应用中的关键挑战。
- OPAL使用视觉指令调整与偏好优化结合来微调模型,减少幻觉并提高稳健性。
- 在真实数据集上的评估显示OPAL在描述质量和架构完成率方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

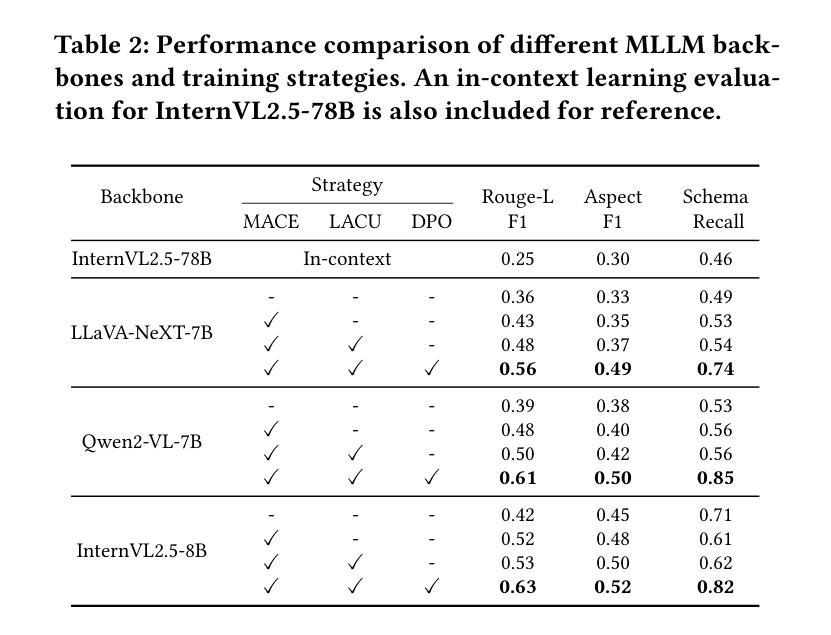
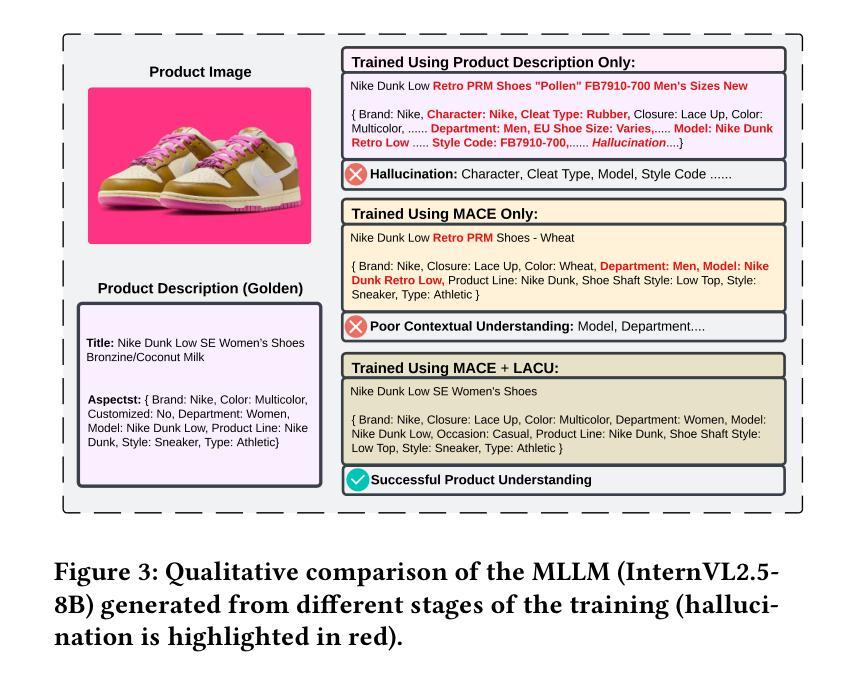
Exploring Superior Function Calls via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Bingguang Hao, Maolin Wang, Zengzhuang Xu, Yicheng Chen, Cunyin Peng, Jinjie GU, Chenyi Zhuang
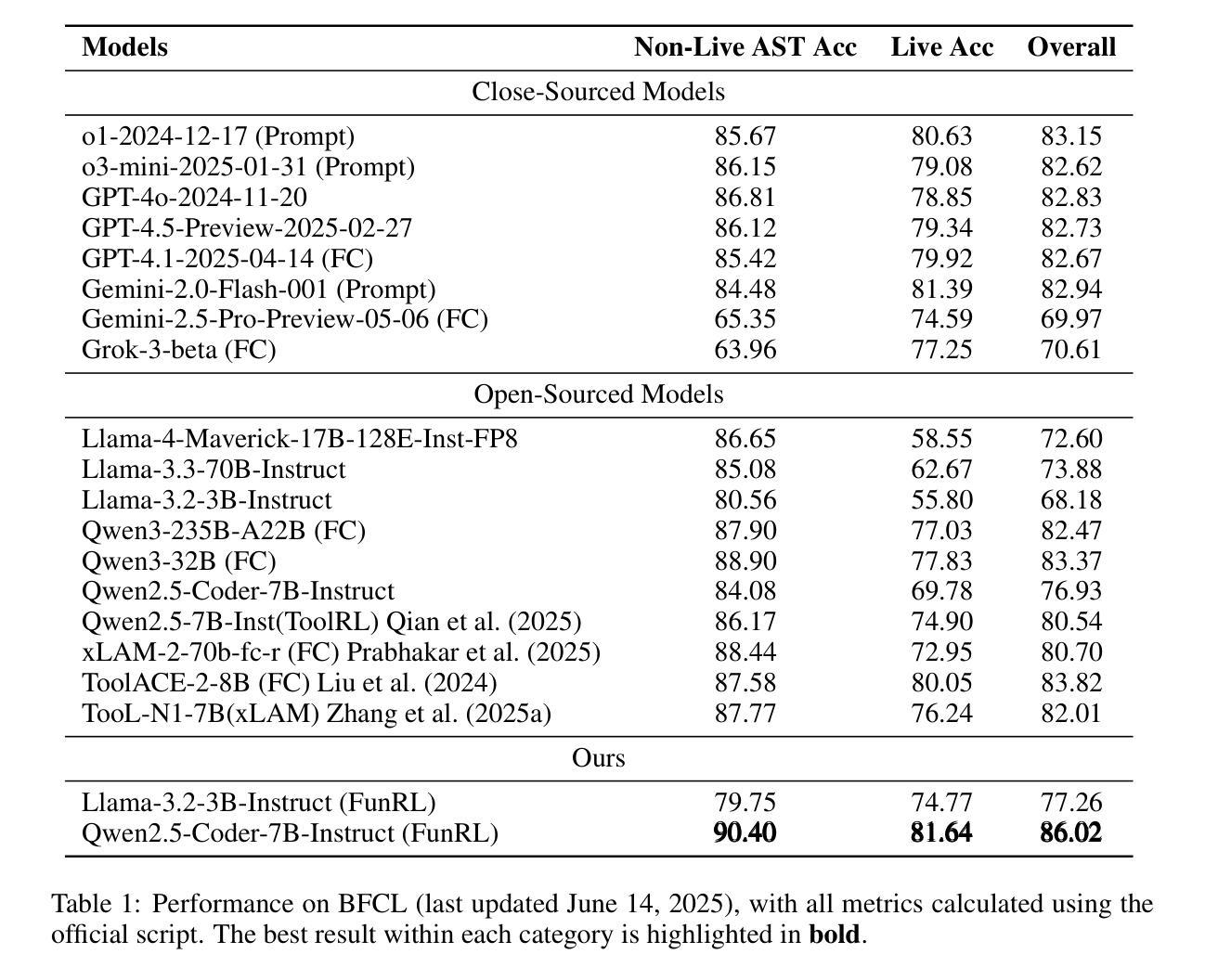
Function calling capabilities are crucial for deploying Large Language Models in real-world applications, yet current training approaches fail to develop robust reasoning strategies. Supervised fine-tuning produces models that rely on superficial pattern matching, while standard reinforcement learning methods struggle with the complex action space of structured function calls. We present a novel reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance group relative policy optimization through strategic entropy based exploration specifically tailored for function calling tasks. Our approach addresses three critical challenges in function calling: insufficient exploration during policy learning, lack of structured reasoning in chain-of-thought generation, and inadequate verification of parameter extraction. Our two-stage data preparation pipeline ensures high-quality training samples through iterative LLM evaluation and abstract syntax tree validation. Extensive experiments on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard demonstrate that this framework achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models with 86.02% overall accuracy, outperforming standard GRPO by up to 6% on complex multi-function scenarios. Notably, our method shows particularly strong improvements on code-pretrained models, suggesting that structured language generation capabilities provide an advantageous starting point for reinforcement learning in function calling tasks. We will release all the code, models and dataset to benefit the community.
函数调用能力对于将大型语言模型部署在真实世界应用中至关重要,然而当前的训练方法未能发展出稳健的推理策略。监督微调产生的模型依赖于肤浅的模式匹配,而标准强化学习方法在复杂的结构化函数调用动作空间中挣扎。我们提出了一种新型的强化学习框架,旨在通过基于策略熵的探索增强群体相对策略优化,该框架专门针对函数调用任务设计。我们的方法解决了函数调用中的三个关键挑战:策略学习过程中的探索不足,思维链生成中结构化推理的缺乏,以及参数提取的验证不足。我们的两阶段数据准备管道通过迭代的大型语言模型评估和抽象语法树验证,确保高质量的训练样本。在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上的大量实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现了最先进的性能,总体准确率为86.02%,在复杂的多功能场景下,比标准GRPO高出6%。值得注意的是,我们的方法在代码预训练模型上显示出特别强大的改进,这表明结构化语言生成能力为强化学习在函数调用任务中提供了一个有利的起点。我们将发布所有的代码、模型和数据集以造福社区。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文探讨了在大规模语言模型(LLM)中部署现实世界应用时的函数调用能力的重要性。当前训练方式无法发展出稳健的推理策略,监督微调产生的模型依赖于表面模式匹配,而传统的强化学习方法在复杂的函数调用动作空间中表现不佳。文章提出了一种新的强化学习框架,旨在通过基于战略熵的探索增强群体相对策略优化,特别是针对函数调用任务。该方法解决了函数调用中的三个关键挑战:策略学习过程中的探索不足、思维链生成中结构化推理的缺乏以及参数提取验证的不足。通过两阶段数据准备管道确保高质量的训练样本,通过迭代LLM评估和抽象语法树验证。在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上的大量实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现了最先进的性能,总体准确度达到86.02%,在复杂的多功能场景下将标准GRPO的准确率提高了高达6%。特别是在代码预训练模型上的改进尤为显著,表明结构化语言生成能力为函数调用的强化学习提供了一个有利的起点。我们将发布所有代码、模型和数据集以造福社区。
关键见解
- 当前训练方式在开发LLM的稳健推理策略方面存在缺陷。
- 监督微调产生的模型依赖于表面模式匹配。
- 传统强化学习方法在复杂的函数调用动作空间中面临挑战。
- 新强化学习框架通过战略熵探索增强群体相对策略优化,专门用于函数调用任务。
- 该方法解决了函数调用中的关键挑战,包括探索不足、结构化推理缺乏和参数验证不足。
- 在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上取得了最先进的性能,总体准确度达到86.02%,复杂场景下表现尤其出色。
点此查看论文截图

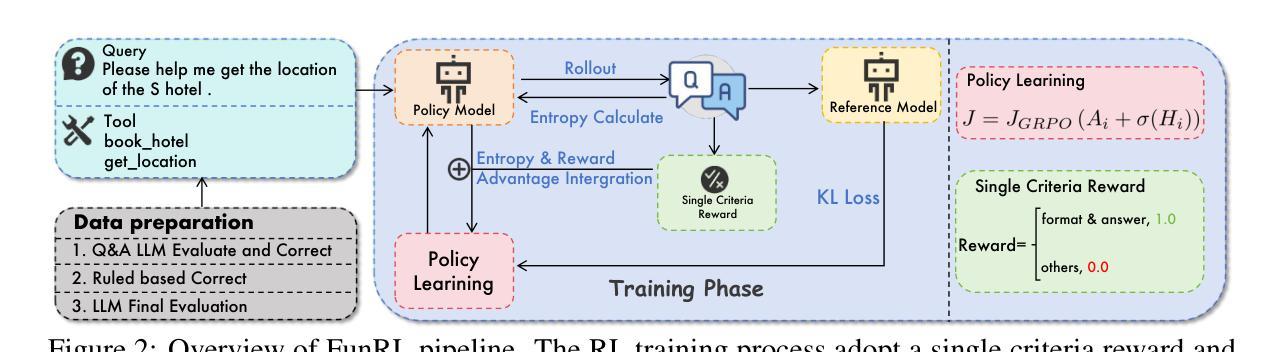
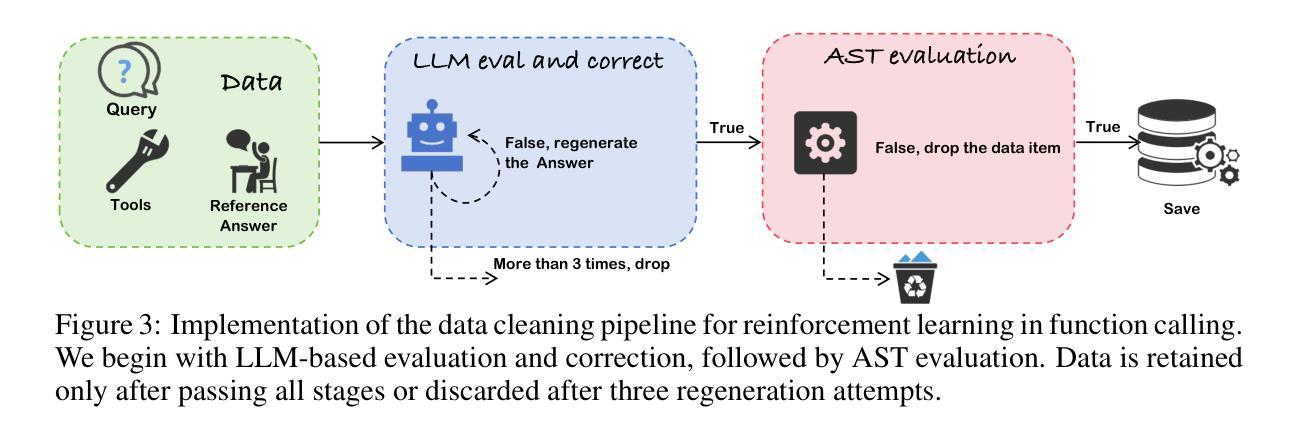
Diffusion Beats Autoregressive in Data-Constrained Settings
Authors:Mihir Prabhudesai, Mengning Wu, Amir Zadeh, Katerina Fragkiadaki, Deepak Pathak
Autoregressive (AR) models have long dominated the landscape of large language models, driving progress across a wide range of tasks. Recently, diffusion-based language models have emerged as a promising alternative, though their advantages over AR models remain underexplored. In this paper, we systematically study masked diffusion models in data-constrained settings-where training involves repeated passes over limited data and find that they significantly outperform AR models when compute is abundant but data is scarce. Diffusion models make better use of repeated data, achieving lower validation loss and superior downstream performance. We find new scaling laws for diffusion models and derive a closed-form expression for the critical compute threshold at which diffusion begins to outperform AR. Finally, we explain why diffusion models excel in this regime: their randomized masking objective implicitly trains over a rich distribution of token orderings, acting as an implicit data augmentation that AR’s fixed left-to-right factorization lacks. Our results suggest that when data, not compute, is the bottleneck, diffusion models offer a compelling alternative to the standard AR paradigm. Our code is available at: https://diffusion-scaling.github.io.
自回归(AR)模型长期以来一直在大型语言模型领域占据主导地位,在广泛的任务中推动进展。最近,基于扩散的语言模型作为一种有前途的替代方法而出现,尽管它们相对于AR模型的优势仍未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们系统地研究了数据受限环境中掩蔽扩散模型的训练过程,该过程涉及在有限数据上多次迭代。我们发现,在算力充足但数据稀缺的情况下,它们显著优于自回归模型。扩散模型能更好地利用重复数据,达到更低的验证损失和更高的下游性能。我们发现了扩散模型的新扩展定律,并推导出临界计算阈值的闭式表达式,在该阈值下,扩散开始优于AR。最后,我们解释了为什么在这种环境中扩散模型表现卓越:它们的随机掩蔽目标隐式地在丰富的标记顺序分布上进行训练,充当了一种隐式数据增强方法,而AR的固定从左到右的分解则缺乏这一特点。我们的结果表明,当数据成为瓶颈而不是算力时,扩散模型是标准AR范式的有吸引力的替代方案。我们的代码可以在:https://diffusion-scaling.github.io 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Webpage: https://diffusion-scaling.github.io
Summary
本文探讨了数据受限环境下掩码扩散模型相较于自回归模型的性能表现。研究发现,在算力充足但数据稀缺的情况下,扩散模型显著优于自回归模型,能够更好地利用重复数据,实现更低的验证损失和更优的下游任务性能。文章还揭示了扩散模型的性能随着计算量的变化遵循特定的规律,并给出了计算阈值的表达式。此外,扩散模型之所以能在这方面表现优秀,是因为其随机掩码目标能够隐式地训练各种丰富的单词顺序分布,而这是自回归模型缺乏的左至右固定分解所无法比拟的。研究指出,当数据成为瓶颈而非算力时,扩散模型提供了一个引人注目的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在数据受限环境下表现出显著优势。
- 在算力充足但数据稀缺的情况下,扩散模型优于自回归模型。
- 扩散模型能更好地利用重复数据,实现更低的验证损失和更优的下游任务性能。
- 扩散模型的性能随计算量的变化遵循特定规律,存在计算阈值。
- 扩散模型的随机掩码目标隐式地训练各种单词顺序分布,这是自回归模型所缺乏的。
- 数据成为瓶颈时,扩散模型成为了一个有吸引力的替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

Omni-DPO: A Dual-Perspective Paradigm for Dynamic Preference Learning of LLMs
Authors:Shangpin Peng, Weinong Wang, Zhuotao Tian, Senqiao Yang, Xing Wu, Haotian Xu, Chengquan Zhang, Takashi Isobe, Baotian Hu, Min Zhang
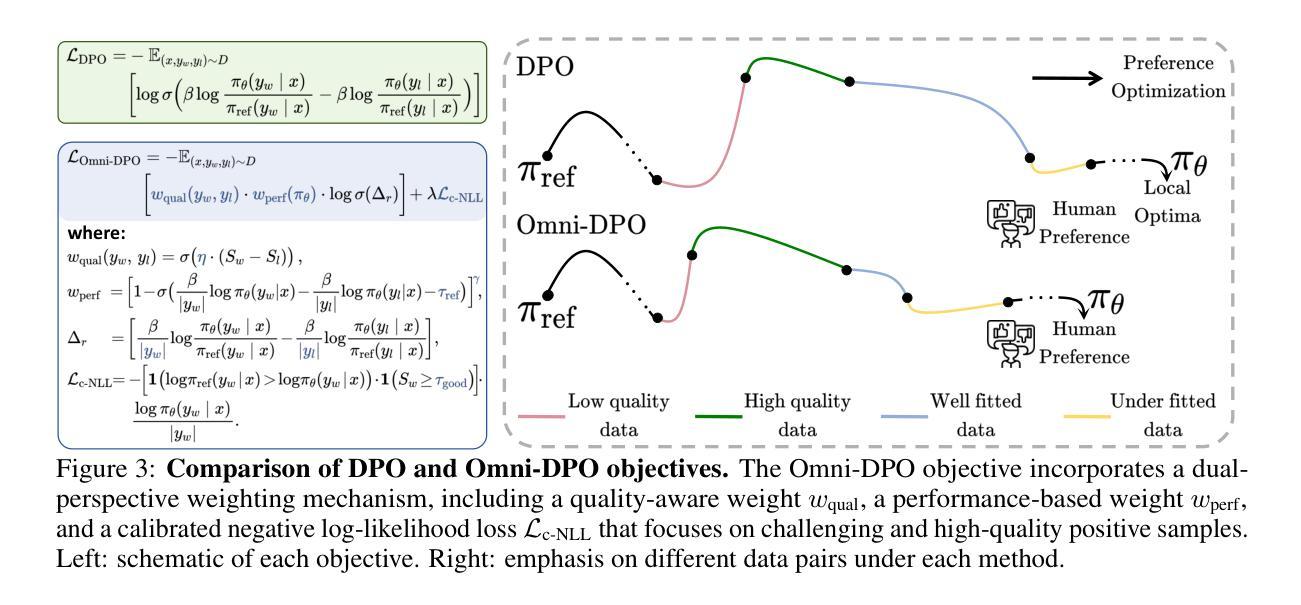
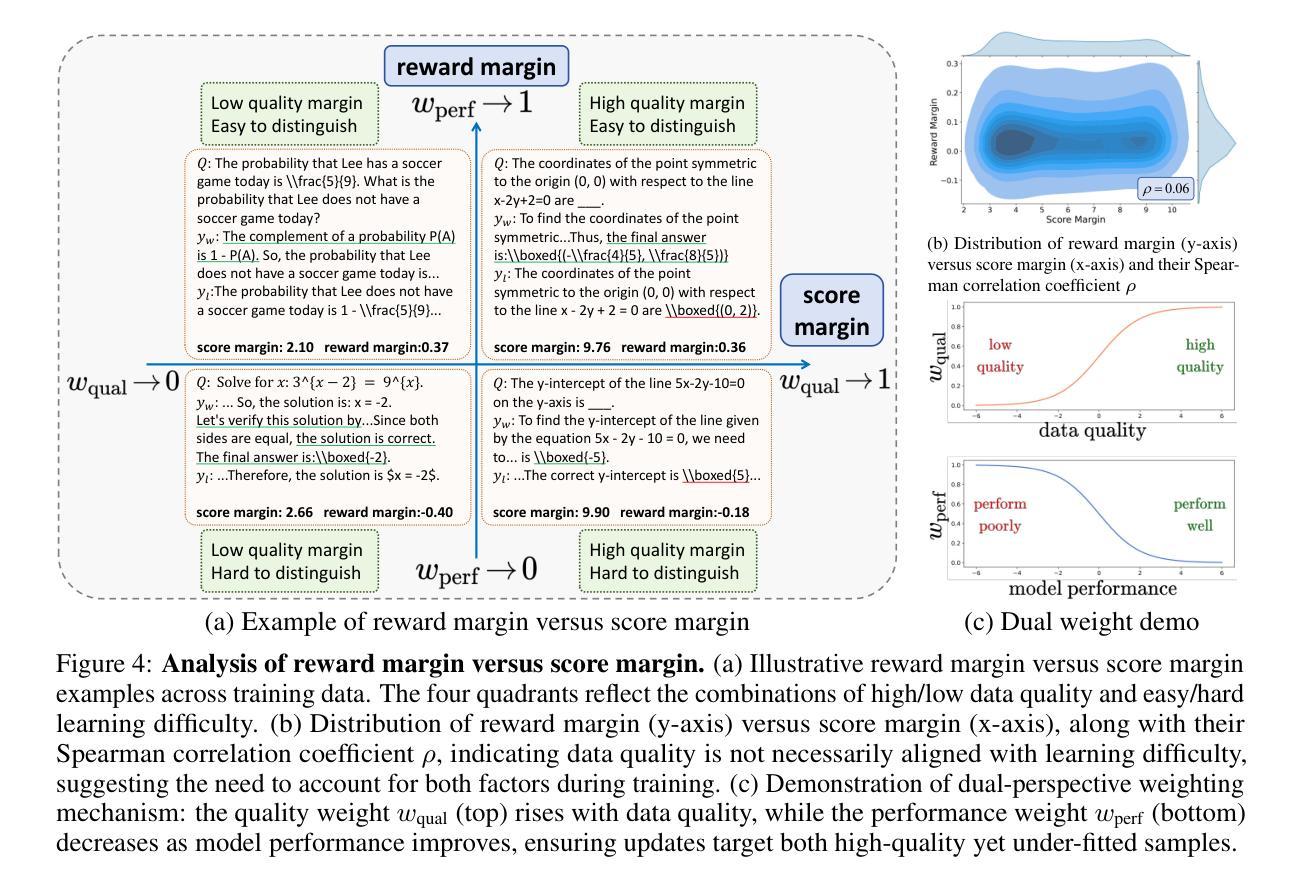
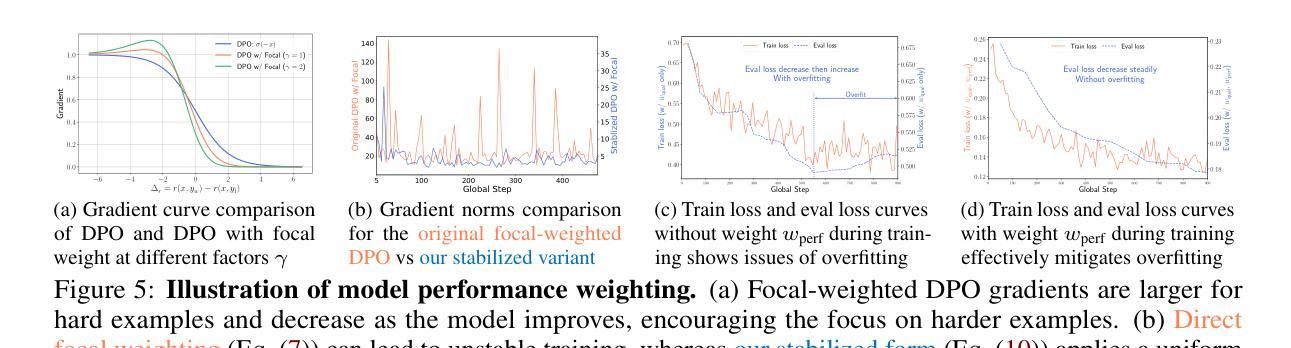
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has become a cornerstone of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) due to its simplicity and efficiency. However, existing DPO-based approaches typically treat all preference pairs uniformly, ignoring critical variations in their inherent quality and learning utility, leading to suboptimal data utilization and performance. To address this challenge, we propose Omni-DPO, a dual-perspective optimization framework that jointly accounts for (1) the inherent quality of each preference pair and (2) the model’s evolving performance on those pairs. By adaptively weighting samples according to both data quality and the model’s learning dynamics during training, Omni-DPO enables more effective training data utilization and achieves better performance. Experimental results on various models and benchmarks demonstrate the superiority and generalization capabilities of Omni-DPO. On textual understanding tasks, Gemma-2-9b-it finetuned with Omni-DPO beats the leading LLM, Claude 3 Opus, by a significant margin of 6.7 points on the Arena-Hard benchmark. On mathematical reasoning tasks, Omni-DPO consistently outperforms the baseline methods across all benchmarks, providing strong empirical evidence for the effectiveness and robustness of our approach. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/pspdada/Omni-DPO.
直接偏好优化(DPO)因其简单性和高效性已成为人类反馈强化学习(RLHF)的核心。然而,现有的基于DPO的方法通常对所有偏好对一视同仁,忽略了它们内在质量和学习效用中的关键差异,导致数据利用和性能不佳。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了Omni-DPO,这是一个双视角优化框架,同时考虑(1)每个偏好对的内在质量和(2)模型在这些对上的不断变化的性能。Omni-DPO通过根据数据质量和模型在训练过程中的学习动态来自适应地加权样本,从而实现了更有效的训练数据利用和更好的性能。在各种模型和基准测试上的实验结果表明了Omni-DPO的优越性和通用性。在文本理解任务上,使用Omni-DPO微调过的Gemma-2-9b-it在Arena-Hard基准测试上大幅领先领先LLM Claude 3 Opus,领先了6.7分。在数学推理任务上,Omni-DPO在所有基准测试上均优于基准方法,为我们方法的有效性和稳健性提供了有力的实证证据。代码和模型将在https://github.com/pspdada/Omni-DPO上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
优化直接偏好优化(DPO)在强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)中的核心地位,因为它简单高效。然而,现有DPO方法忽略偏好对本身的质量和学习的实用性差异,导致数据利用不佳和性能下降。为应对此挑战,我们提出Omni-DPO,一个双视角优化框架,同时考虑偏好对的内在质量和模型在这些偏好对上的性能变化。通过根据数据质量和模型学习动态在训练中自适应地加权样本,Omni-DPO更有效地利用训练数据并实现更好的性能。实验证明Omni-DPO的优越性和泛化能力。在文本理解任务上,使用Omni-DPO微调后的Gemma-2-9b-it在Arena-Hard基准测试中大幅超越领先的LLM Claude 3 Opus。在数学推理任务上,Omni-DPO在所有基准测试中均优于基准方法,为我们的方法和稳健性提供了强有力的实证证据。
Key Takeaways
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)是强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)中的核心方法,但现有方法忽略偏好对的质量和学习的实用性差异。
- Omni-DPO是一个双视角优化框架,考虑偏好对的内在质量和模型性能变化。
- Omni-DPO通过自适应加权样本实现更有效的训练数据利用。
- 实验证明Omni-DPO在文本理解任务上超越领先的LLM。
- Omni-DPO在数学推理任务上优于所有基准测试中的基准方法。
- Omni-DPO方法具有优越性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


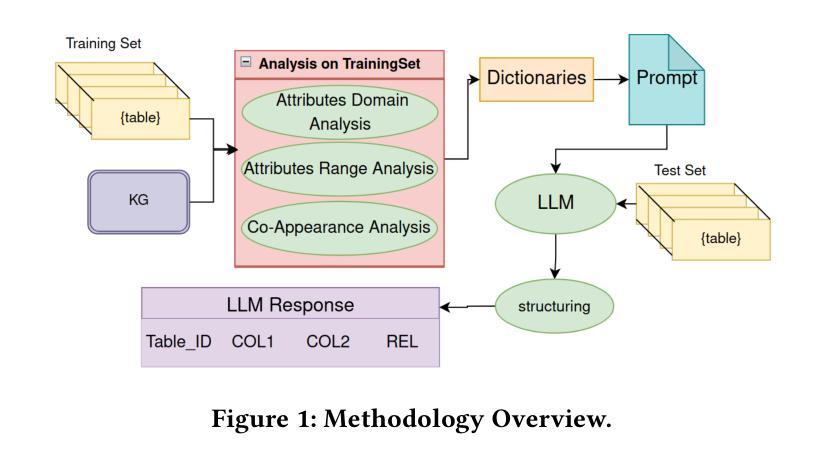
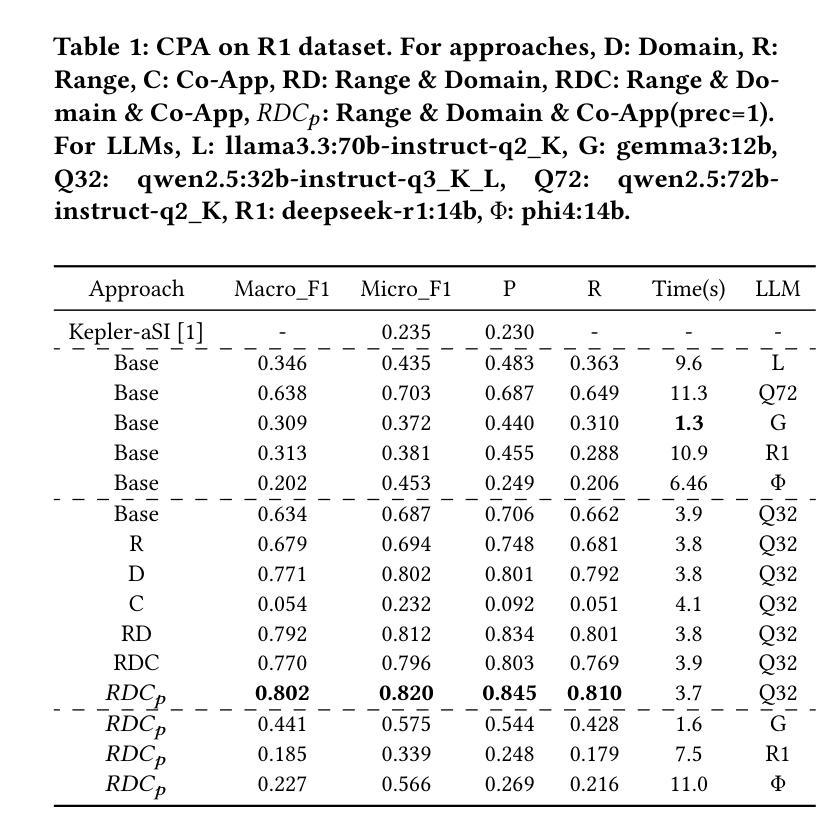
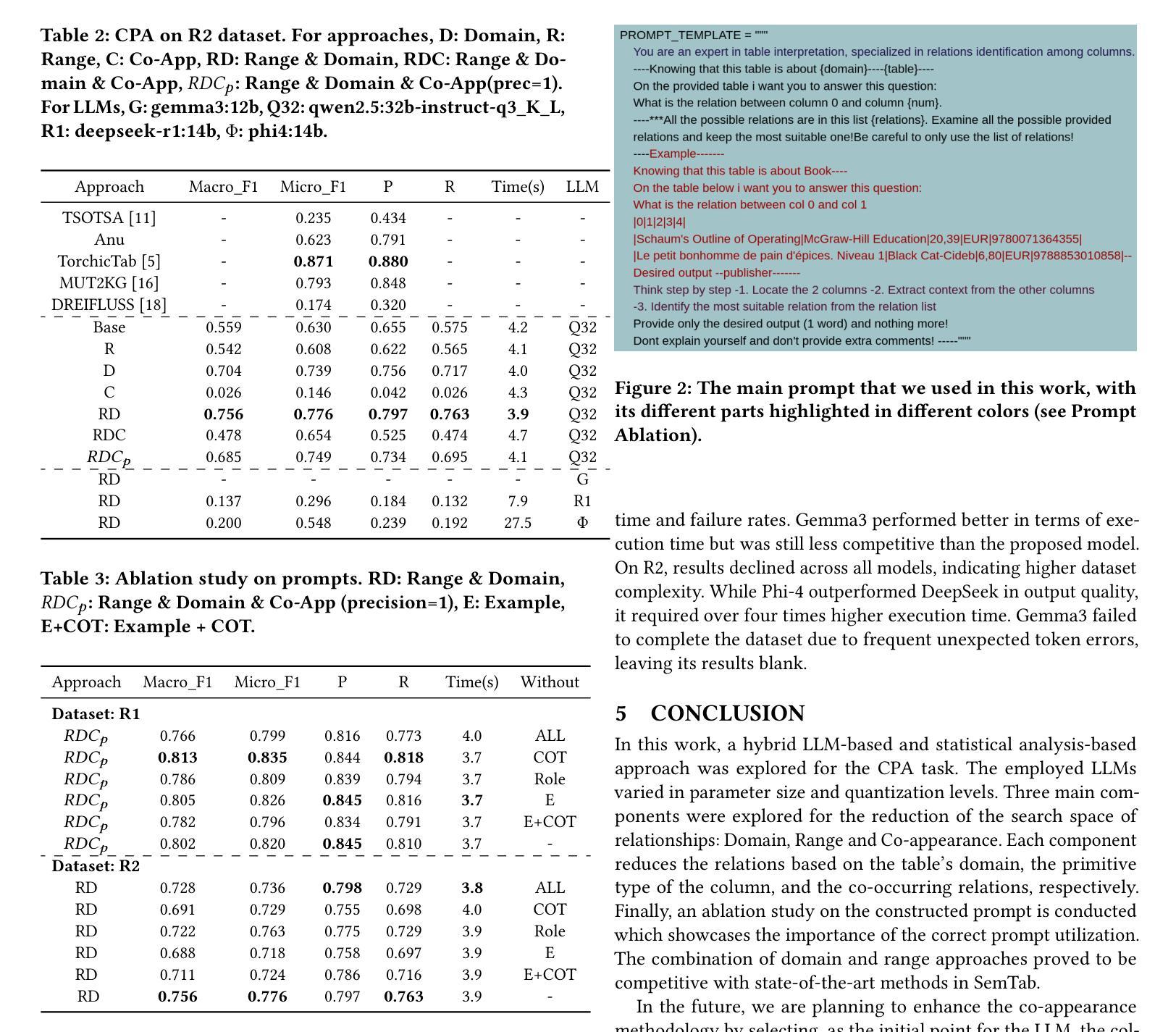
Relationship Detection on Tabular Data Using Statistical Analysis and Large Language Models
Authors:Panagiotis Koletsis, Christos Panagiotopoulos, Georgios Th. Papadopoulos, Vasilis Efthymiou
Over the past few years, table interpretation tasks have made significant progress due to their importance and the introduction of new technologies and benchmarks in the field. This work experiments with a hybrid approach for detecting relationships among columns of unlabeled tabular data, using a Knowledge Graph (KG) as a reference point, a task known as CPA. This approach leverages large language models (LLMs) while employing statistical analysis to reduce the search space of potential KG relations. The main modules of this approach for reducing the search space are domain and range constraints detection, as well as relation co-appearance analysis. The experimental evaluation on two benchmark datasets provided by the SemTab challenge assesses the influence of each module and the effectiveness of different state-of-the-art LLMs at various levels of quantization. The experiments were performed, as well as at different prompting techniques. The proposed methodology, which is publicly available on github, proved to be competitive with state-of-the-art approaches on these datasets.
过去几年,由于表格解读任务的重要性以及该领域新技术的引入和基准测试的发展,其取得了显著进展。本工作尝试使用混合方法检测无标签表格数据列之间的关系,以知识图谱(KG)为参考点,这项任务被称为CPA。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLM),同时采用统计分析来减少知识图谱潜在关系的搜索空间。该方法减少搜索空间的主要模块是域和范围约束检测,以及关系共现分析。在SemTab挑战提供的两个基准数据集上进行的实验评估了每个模块的影响以及在各级量化下不同最先进LLMs的有效性。实验还采用了不同的提示技术。所提出的方法在GitHub上公开可用,在这些数据集上被证明与最先进的方法具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
过去几年,由于表格解读任务的重要性以及新技和基准测试的出现,该领域取得了显著进展。本文尝试利用知识图谱(KG)作为参照点,采用一种混合方法检测无标签表格数据列之间的关系,这被称为CPA任务。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLM)并采用统计分析来缩小潜在KG关系的搜索范围。缩小搜索范围的主要模块包括域和范围约束检测以及关系共现分析。在SemTab挑战提供的两个基准数据集上进行的实验评估了每个模块的影响以及不同先进LLM在不同量化水平上的有效性,以及不同的提示技术。所提出的方法在公共GitHub上证明其在这些数据集上具有竞争力。
要点分析
- 表格解读任务因重要性和新技术的引入在过去几年取得了显著进展。
- 本文尝试利用知识图谱作为参照点,采用混合方法检测无标签表格数据列之间的关系,被称为CPA任务。
- 方法结合了大型语言模型和统计分析,旨在缩小潜在关系的搜索范围。
- 域和范围约束检测以及关系共现分析是该方法的主要模块,用于缩小搜索范围。
- 在SemTab挑战提供的两个基准数据集上进行的实验评估表明,该方法在多个量化水平上表现出竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

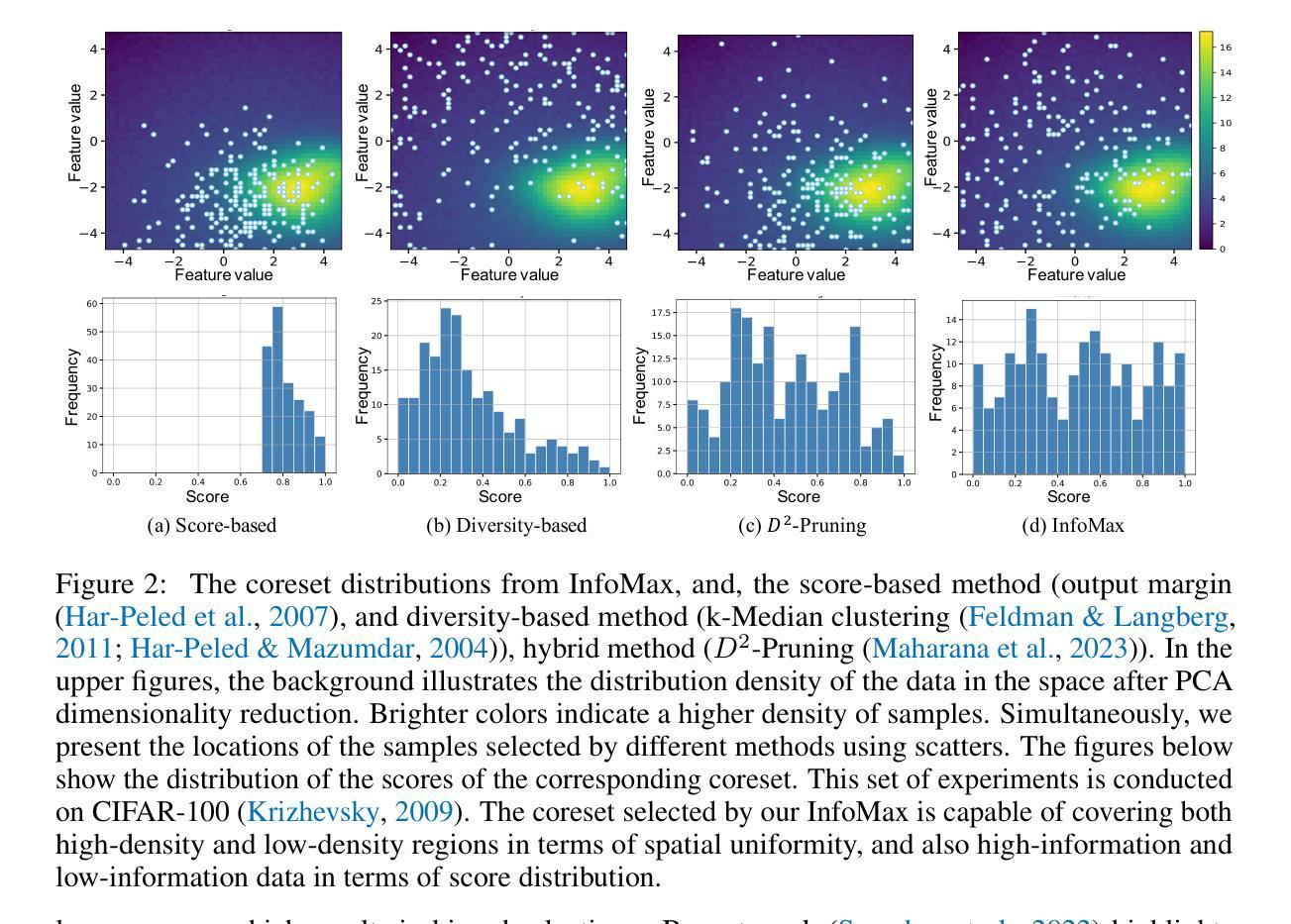
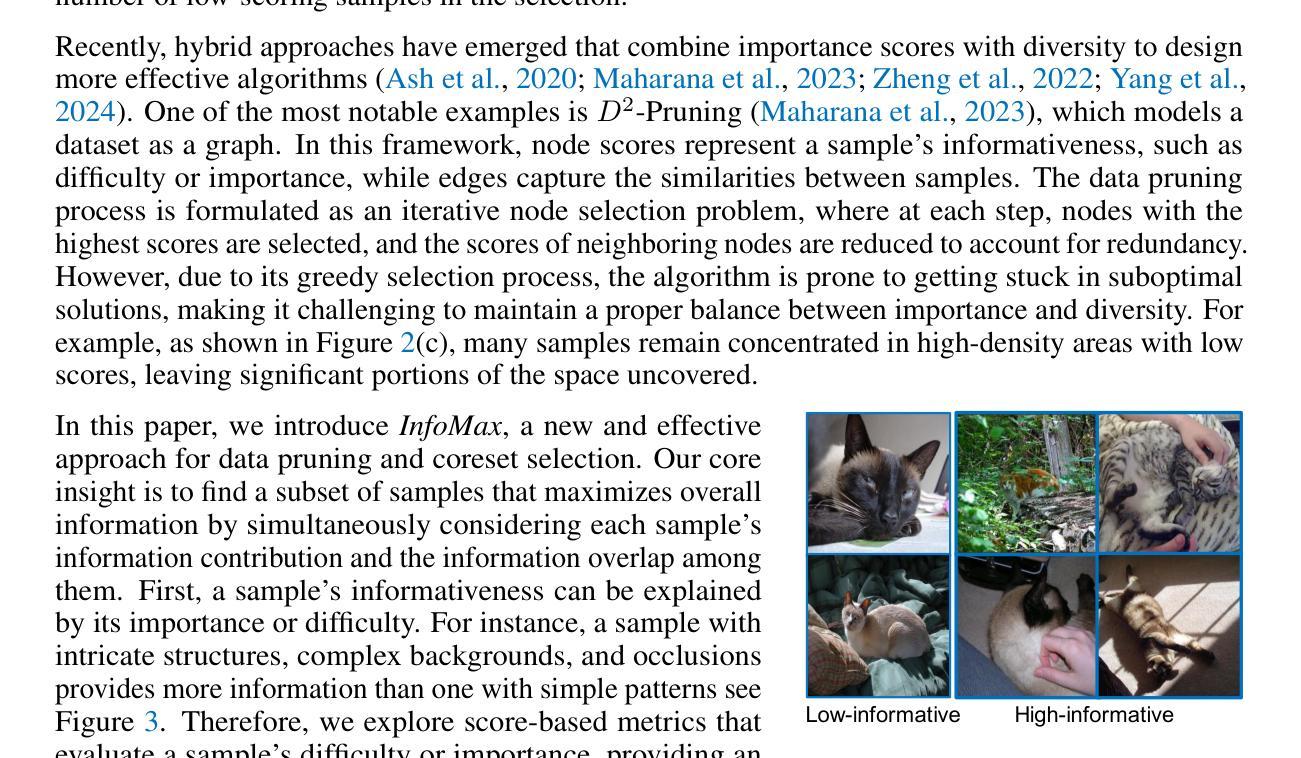
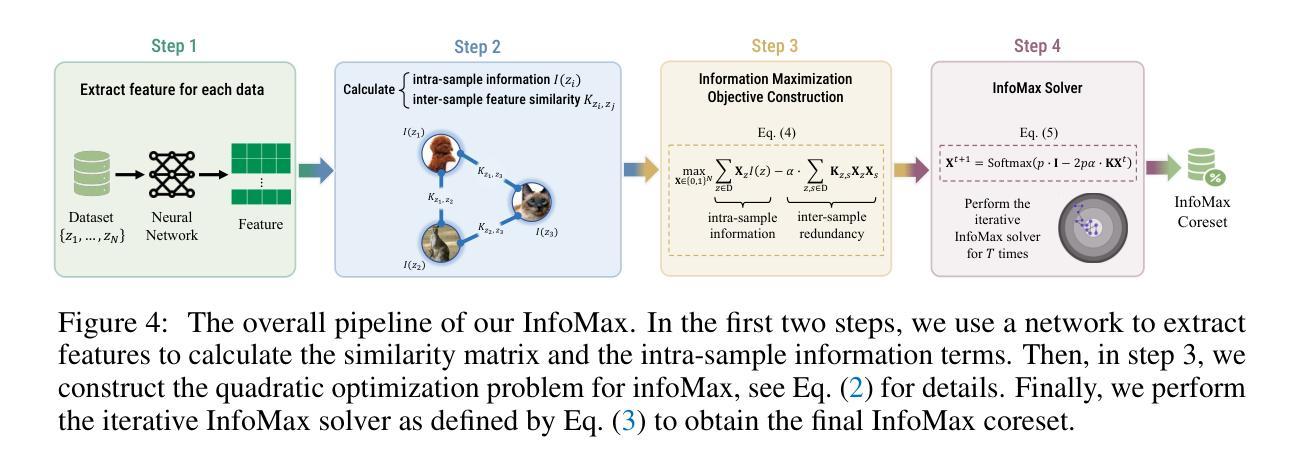
Data Pruning by Information Maximization
Authors:Haoru Tan, Sitong Wu, Wei Huang, Shizhen Zhao, Xiaojuan Qi
In this paper, we present InfoMax, a novel data pruning method, also known as coreset selection, designed to maximize the information content of selected samples while minimizing redundancy. By doing so, InfoMax enhances the overall informativeness of the coreset. The information of individual samples is measured by importance scores, which capture their influence or difficulty in model learning. To quantify redundancy, we use pairwise sample similarities, based on the premise that similar samples contribute similarly to the learning process. We formalize the coreset selection problem as a discrete quadratic programming (DQP) task, with the objective of maximizing the total information content, represented as the sum of individual sample contributions minus the redundancies introduced by similar samples within the coreset. To ensure practical scalability, we introduce an efficient gradient-based solver, complemented by sparsification techniques applied to the similarity matrix and dataset partitioning strategies. This enables InfoMax to seamlessly scale to datasets with millions of samples. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of InfoMax in various data pruning tasks, including image classification, vision-language pre-training, and instruction tuning for large language models. Code is available at https://github.com/hrtan/InfoMax.
本文介绍了一种新型数据修剪方法InfoMax,也称为核心集选择。该方法旨在最大化所选样本的信息内容的同时最小化冗余。通过这种方式,InfoMax提高了核心集的整体信息性。我们通过重要性分数来衡量单个样本的信息,重要性分数反映了样本在模型学习中的影响力或难度。为了量化冗余,我们基于相似样本对学习过程产生相似贡献的假设,使用成对的样本相似性。我们将核心集选择问题形式化为离散二次规划(DQP)任务,目标是最大化总信息内容,表示为单个样本贡献的总和减去核心集中相似样本引起的冗余。为了确保实际的可扩展性,我们引入了一种高效的基于梯度的求解器,并结合相似性矩阵的稀疏化技术和数据集分区策略。这使得InfoMax能够无缝地扩展到具有数百万样本的数据集。大量实验表明,InfoMax在各种数据修剪任务中的性能卓越,包括图像分类、视觉语言预训练和大型语言模型的指令调整。代码可通过https://github.com/hrtan/InfoMax获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at \url{https://github.com/hrtan/InfoMax}
Summary
本文介绍了InfoMax,一种新型数据裁剪方法(也称为核心集选择)。该方法旨在最大化选定样本的信息内容,同时最小化冗余,从而提高核心集的整体信息量。通过重要性分数来衡量单个样本的信息量,这些分数反映了模型学习中样本的影响或难度。为了量化冗余,文章使用基于样本相似性的成对样本相似性。核心集选择问题被形式化为离散二次规划(DQP)任务,目标是最大化总信息内容,表示为单个样本贡献的总和减去核心集中相似样本引入的冗余。为确保实际的可扩展性,文章引入了一种高效的基于梯度的求解器,并结合相似性矩阵的稀疏化技术和数据集分区策略。这使得InfoMax能够无缝地扩展到数百万样本的数据集。实验表明,InfoMax在各种数据裁剪任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括图像分类、视觉语言预训练和大型语言模型的指令调整。
Key Takeaways
- InfoMax是一种数据裁剪方法,旨在最大化选定样本的信息内容并最小化冗余。
- 通过重要性分数衡量单个样本的信息量,反映模型学习中的影响或难度。
- 使用基于样本相似性的成对样本相似性来量化冗余。
- 核心集选择问题被形式化为离散二次规划(DQP)任务。
- InfoMax采用高效的基于梯度的求解器,可扩展到数百万样本的数据集。
- 实验中,InfoMax在图像分类、视觉语言预训练和大型语言模型的指令调整等任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

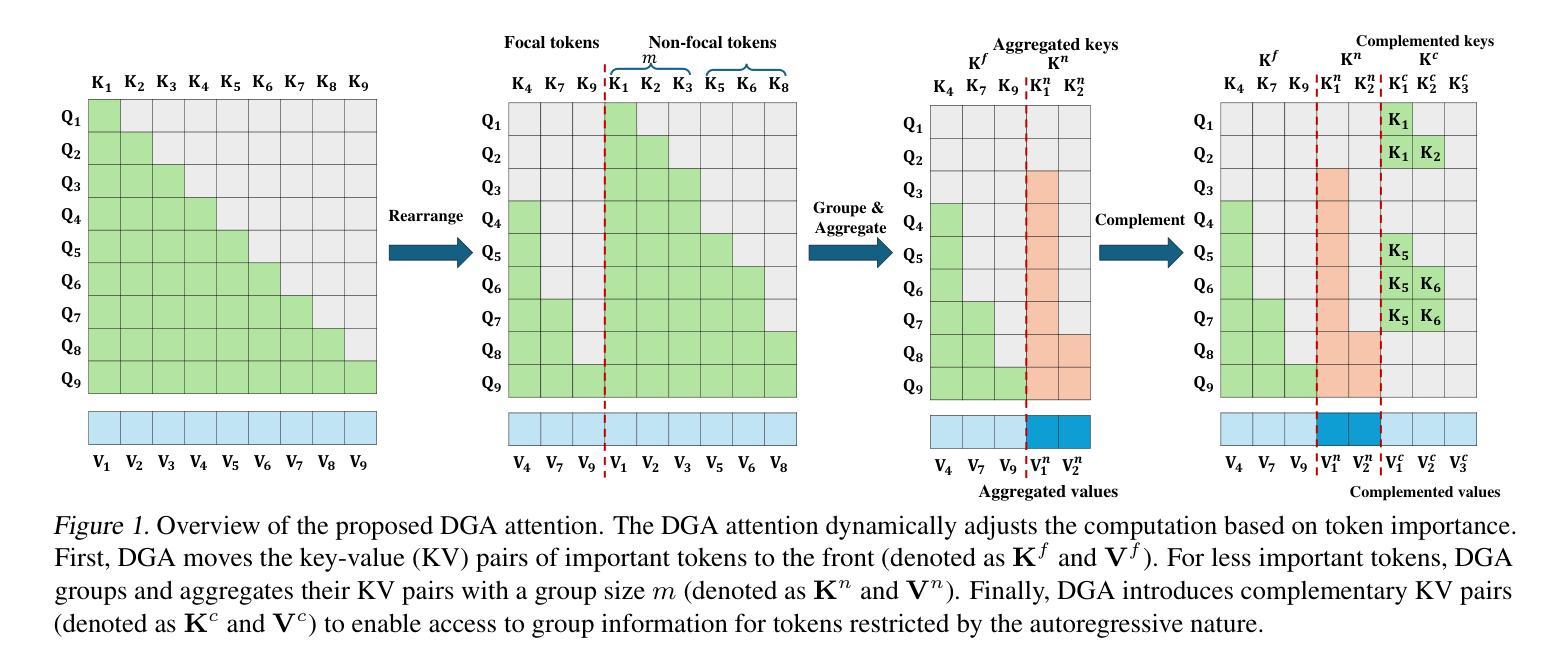
Curse of High Dimensionality Issue in Transformer for Long-context Modeling
Authors:Shuhai Zhang, Zeng You, Yaofo Chen, Zhiquan Wen, Qianyue Wang, Zhijie Qiu, Yuanqing Li, Mingkui Tan
Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) excel in natural language processing tasks by capturing long-range dependencies through self-attention mechanisms. However, long-context modeling faces significant computational inefficiencies due to \textit{redundant} attention computations: while attention weights are often \textit{sparse}, all tokens consume \textit{equal} computational resources. In this paper, we reformulate traditional probabilistic sequence modeling as a \textit{supervised learning task}, enabling the separation of relevant and irrelevant tokens and providing a clearer understanding of redundancy. Based on this reformulation, we theoretically analyze attention sparsity, revealing that only a few tokens significantly contribute to predictions. Building on this, we formulate attention optimization as a linear coding problem and propose a \textit{group coding strategy}, theoretically showing its ability to improve robustness against random noise and enhance learning efficiency. Motivated by this, we propose \textit{Dynamic Group Attention} (DGA), which leverages the group coding to explicitly reduce redundancy by aggregating less important tokens during attention computation. Empirical results show that our DGA significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining competitive performance.Code is available at https://github.com/bolixinyu/DynamicGroupAttention.
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)通过自注意力机制捕捉长距离依赖关系,在自然语言处理任务上表现出色。然而,由于冗余的注意力计算,长上下文建模面临重大的计算效率低下问题:虽然注意力权重通常是稀疏的,但所有令牌都消耗着平等的计算资源。在本文中,我们将传统的概率序列建模重新定义为“监督学习任务”,这能够分离相关和不相关的令牌,并提供对冗余性的更清晰理解。基于这种重新表述,我们从理论上分析了注意力稀疏性,揭示只有少数令牌对预测做出了重大贡献。在此基础上,我们将注意力优化表述为线性编码问题,并提出“分组编码策略”,从理论上证明了其提高对抗随机噪声的稳健性和提高学习效率的能力。受此启发,我们提出了“动态组注意力”(DGA),它利用分组编码来通过聚合不太重要的令牌来明确减少冗余的注意力计算。经验结果表明,我们的DGA在保持竞争力的同时显著降低了计算成本。代码可在https://github.com/bolixinyu/DynamicGroupAttention找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)通过自注意力机制进行自然语言处理任务表现出色。然而,由于冗余的注意力计算,长上下文建模面临重大的计算效率问题。本文重新定义了概率序列建模为监督学习任务,区分了相关和不相关的令牌,明确了冗余的概念。基于理论分析,我们发现只有少数令牌对预测有显著贡献。因此,我们将注意力优化表述为线性编码问题,并提出分组编码策略,该策略理论上可以提高对随机噪声的鲁棒性和学习效率。受这些研究的启发,我们提出了动态分组注意力(DGA),它通过分组编码来明确减少冗余,在计算注意力时聚合不太重要的令牌。实证结果表明,DGA在保持竞争力的同时显著降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer-based LLMs 通过自注意力机制擅长自然语言处理任务,但长上下文建模存在计算效率问题。
- 冗余的注意力计算是计算效率问题的主要原因。
- 本文重新定义概率序列建模为监督学习任务,以区分相关和不相关的令牌,明确冗余概念。
- 只有少数令牌对预测有显著贡献。
- 提出动态分组注意力(DGA)方法,通过分组编码策略减少冗余计算。
- DGA显著提高了计算效率且保持竞争力。
点此查看论文截图