⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
GANDiff FR: Hybrid GAN Diffusion Synthesis for Causal Bias Attribution in Face Recognition
Authors:Md Asgor Hossain Reaj, Rajan Das Gupta, Md Yeasin Rahat, Nafiz Fahad, Md Jawadul Hasan, Tze Hui Liew
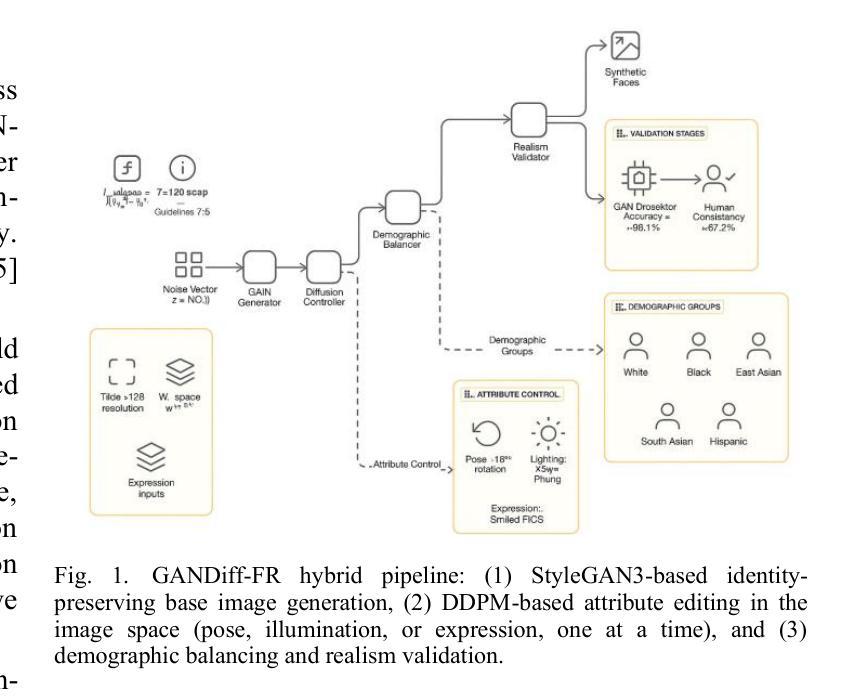
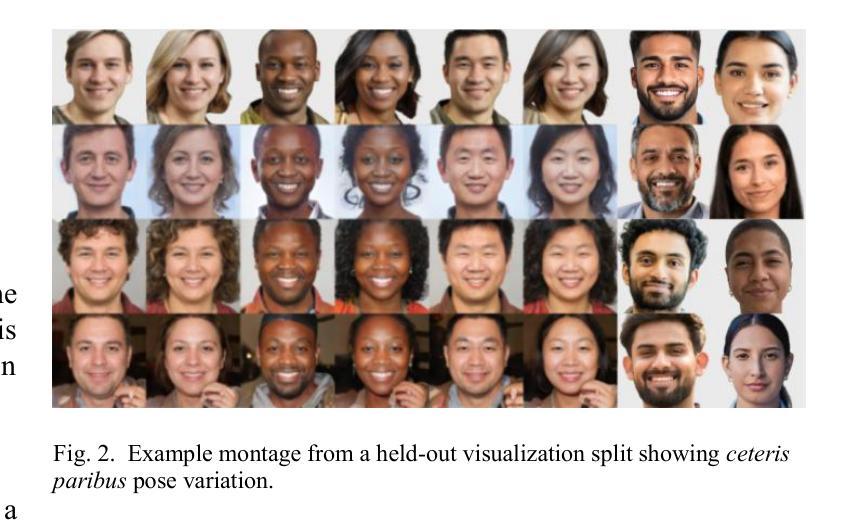
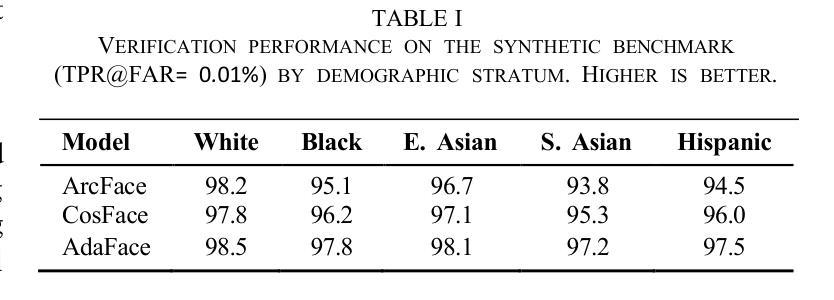
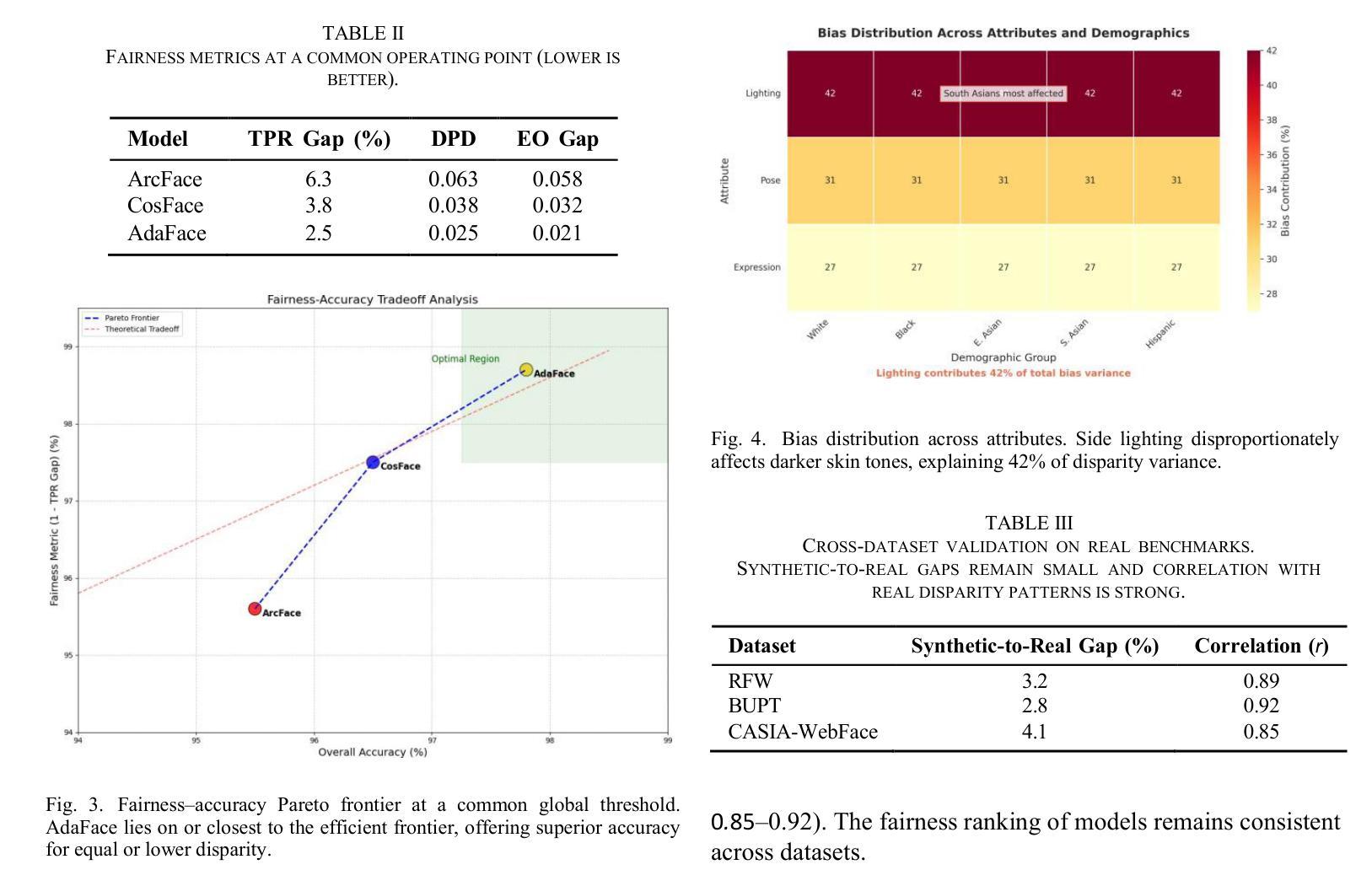
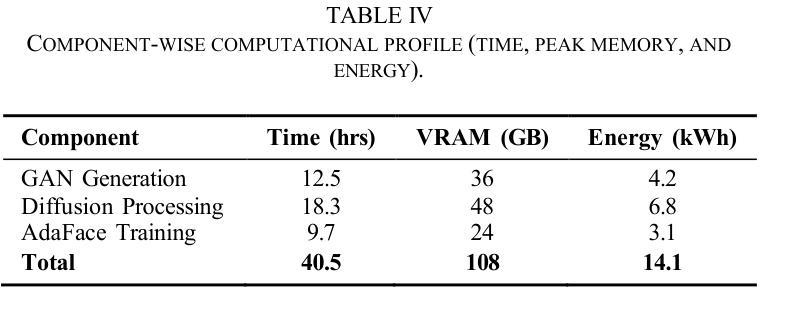
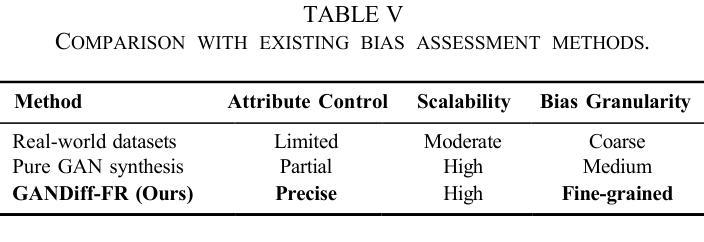
We introduce GANDiff FR, the first synthetic framework that precisely controls demographic and environmental factors to measure, explain, and reduce bias with reproducible rigor. GANDiff FR unifies StyleGAN3-based identity-preserving generation with diffusion-based attribute control, enabling fine-grained manipulation of pose around 30 degrees, illumination (four directions), and expression (five levels) under ceteris paribus conditions. We synthesize 10,000 demographically balanced faces across five cohorts validated for realism via automated detection (98.2%) and human review (89%) to isolate and quantify bias drivers. Benchmarking ArcFace, CosFace, and AdaFace under matched operating points shows AdaFace reduces inter-group TPR disparity by 60% (2.5% vs. 6.3%), with illumination accounting for 42% of residual bias. Cross-dataset evaluation on RFW, BUPT, and CASIA WebFace confirms strong synthetic-to-real transfer (r 0.85). Despite around 20% computational overhead relative to pure GANs, GANDiff FR yields three times more attribute-conditioned variants, establishing a reproducible, regulation-aligned (EU AI Act) standard for fairness auditing. Code and data are released to support transparent, scalable bias evaluation.
我们介绍了GANDiff FR,这是第一个精确控制人口统计和环境因素的合成框架,以衡量、解释和减少偏见,具有可重复的严谨性。GANDiff FR统一了基于StyleGAN3的身份保留生成与基于扩散的属性控制,能够在保持身份不变的情况下,在ceteris paribus条件下实现30度左右的姿态、四个方向的照明和五个级别的表情的精细操控。我们合成了10000张人口统计上平衡的面孔,跨越五个群体,通过自动化检测(98.2%)和人工审查(89%)验证其真实性,以隔离和量化偏见的驱动因素。在匹配的操作点下,对ArcFace、CosFace和AdaFace进行基准测试显示,AdaFace将组间TPR差异减少了60%(2.5%对比6.3%),照明占剩余偏见的42%。在RFW、BUPT和CASIA WebFace数据集上的跨数据集评估证实了从合成到真实的强大迁移能力(r 0.85)。尽管相对于纯GANs约有20%的计算开销,但GANDiff FR生成了三倍多的属性条件变体,建立了一个可重复、符合法规(欧盟人工智能法案)的公平审计标准。我们公开了代码和数据,以支持透明、可扩展的偏见评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCVDM ‘25
Summary
该研究介绍了一个名为GANDiff FR的合成框架,它能精确控制人口统计和环境因素来测量、解释和减少偏见。该框架结合了StyleGAN3的基于身份保留生成和扩散模型,实现了在固定条件下对姿态、照明和表情的精细控制。通过合成具有现实感的面部图像,验证了框架的有效性,并发现AdaFace能显著降低群体间的TPR差异。该框架为公平审计提供了可复制的、符合法规的标准。
Key Takeaways
- GANDiff FR是第一个能够精确控制人口统计和环境因素的合成框架,用于测量、解释和减少偏见。
- 框架结合了StyleGAN3和扩散模型,实现对姿态、照明和表情的精细控制。
- 合成面部图像通过了自动化检测和人类评审验证,能隔离并量化偏见驱动因素。
- AdaFace能有效减少群体间的TPR差异,降低偏见达60%。
- 照明是剩余偏见的主要来源之一,占42%。
- 跨数据集评估表明,GANDiff FR具有良好的从合成到现实的迁移能力。
点此查看论文截图

A Survey on 3D Gaussian Splatting Applications: Segmentation, Editing, and Generation
Authors:Shuting He, Peilin Ji, Yitong Yang, Changshuo Wang, Jiayi Ji, Yinglin Wang, Henghui Ding
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a powerful alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) for 3D scene representation, offering high-fidelity photorealistic rendering with real-time performance. Beyond novel view synthesis, the explicit and compact nature of 3DGS enables a wide range of downstream applications that require geometric and semantic understanding. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of recent progress in 3DGS applications. It first introduces 2D foundation models that support semantic understanding and control in 3DGS applications, followed by a review of NeRF-based methods that inform their 3DGS counterparts. We then categorize 3DGS applications into segmentation, editing, generation, and other functional tasks. For each, we summarize representative methods, supervision strategies, and learning paradigms, highlighting shared design principles and emerging trends. Commonly used datasets and evaluation protocols are also summarized, along with comparative analyses of recent methods across public benchmarks. To support ongoing research and development, a continually updated repository of papers, code, and resources is maintained at https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications.
3D高斯贴片(3DGS)作为一种强大的技术,最近作为神经辐射场(NeRF)的替代方案在三维场景表示中崭露头角,它以实时性能提供高保真度照片级渲染。除了新颖视图合成,3DGS的明确和紧凑性质使得它在需要几何和语义理解的一系列下游应用中表现出巨大的潜力。这篇综述全面回顾了近期在3DGS应用方面的进展。首先介绍了支持在3DGS应用中语义理解和控制的二维基础模型,然后回顾了基于NeRF的方法,以启发其对应的3DGS方法。我们将3DGS应用分类为分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务。对于每一项任务,我们总结了代表性方法、监督策略和学习范式,突出共同的设计原则和新兴趋势。此外还总结了常用的数据集和评估协议,以及在公共基准测试中最近方法的比较分析。为了支持持续的研究和开发,相关论文、代码和资源会不断更新维护在 https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications 上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF GitHub Repo: https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications
Summary
在本文中,对名为3D高斯混编(3DGS)的先进技术在最新进展中的多维度应用进行了全面概述。文章首先介绍了支持三维空间语义理解的二维基础模型,随后回顾了NeRF的方法以供参考其对应的三维模型应用。然后,将重点放在各种基于三维高斯混编的应用上,包括分割、编辑、生成以及其他功能性任务。对每一项应用进行简化方法论介绍的同时,本文也详细描述了相应的监督策略和学习模式。为了支撑持续的研究与开发工作,本文还提供了论文、代码和资源的持续更新仓库链接。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的关键要点:
- 介绍了新的三维场景表示技术——三维高斯混编(3DGS),它以其强大的表现力和实时性能引起了人们的关注。这种技术可以实现高保真度的逼真渲染效果。
- 介绍了二维基础模型在三维空间语义理解中的应用,这些模型为三维高斯混编的应用提供了支持。
- 通过回顾NeRF方法,为理解三维高斯混编提供了参考。这些技术间的比较有助于更好地理解它们的优缺点和适用场景。
- 详细描述了三维高斯混编在多种应用领域的进展,包括分割、编辑、生成以及其他功能性任务等。这些应用展示了三维高斯混编的多样性和灵活性。文中详细列举了代表性方法和监督策略等。文中也详细介绍了每个应用的监督策略和学习模式。
点此查看论文截图

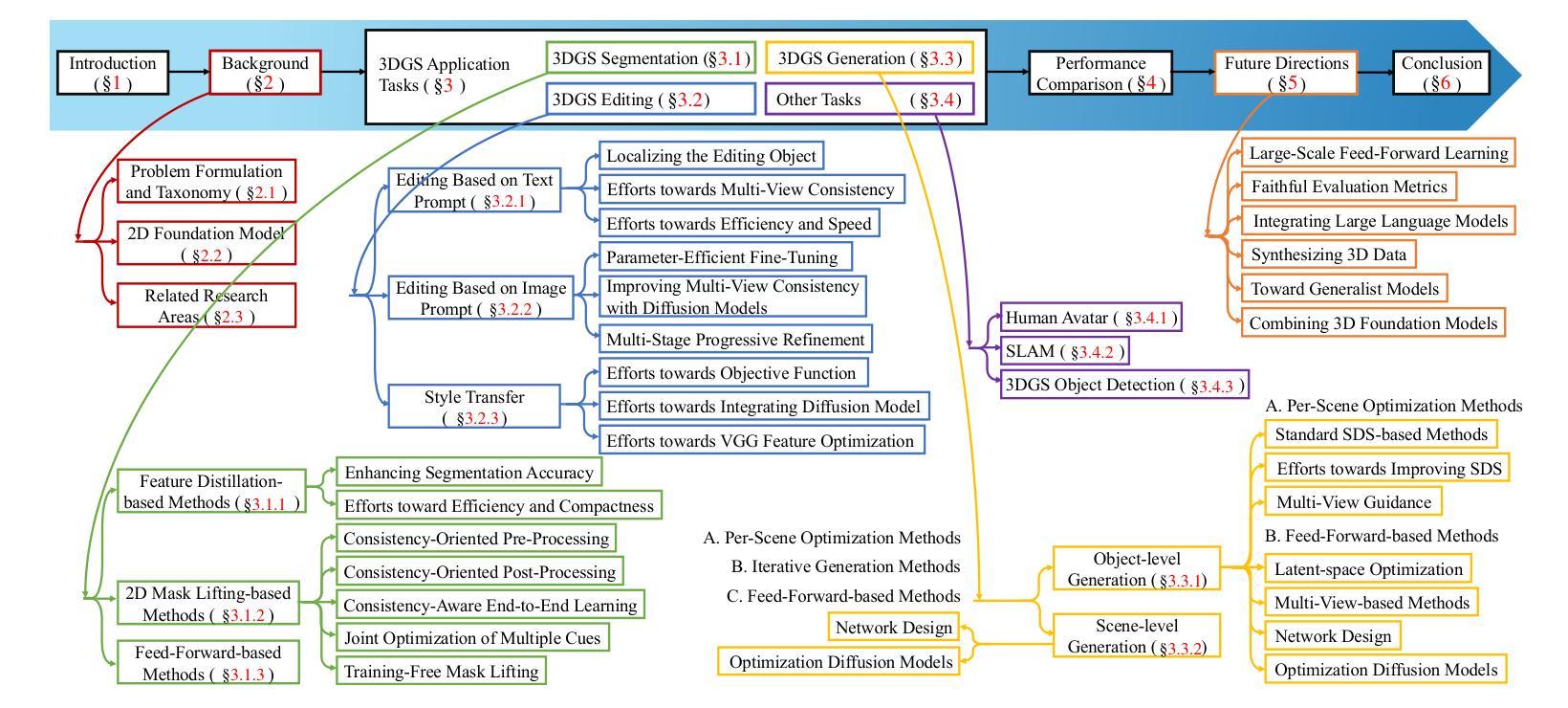
Surg-InvNeRF: Invertible NeRF for 3D tracking and reconstruction in surgical vision
Authors:Gerardo Loza, Junlei Hu, Dominic Jones, Sharib Ali, Pietro Valdastri
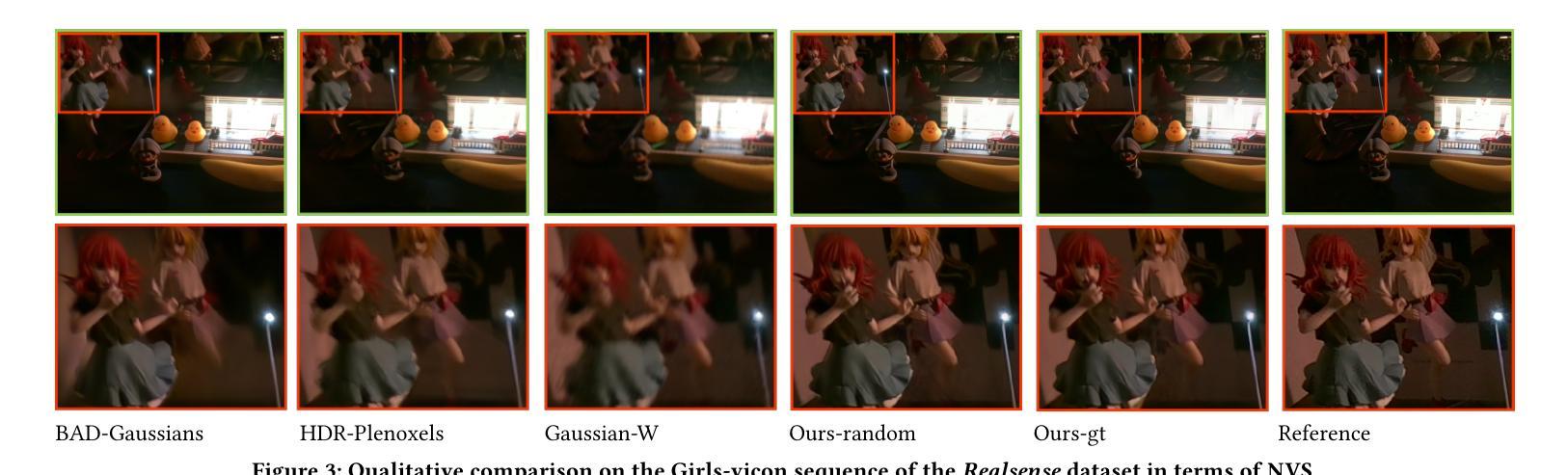
We proposed a novel test-time optimisation (TTO) approach framed by a NeRF-based architecture for long-term 3D point tracking. Most current methods in point tracking struggle to obtain consistent motion or are limited to 2D motion. TTO approaches frame the solution for long-term tracking as optimising a function that aggregates correspondences from other specialised state-of-the-art methods. Unlike the state-of-the-art on TTO, we propose parametrising such a function with our new invertible Neural Radiance Field (InvNeRF) architecture to perform both 2D and 3D tracking in surgical scenarios. Our approach allows us to exploit the advantages of a rendering-based approach by supervising the reprojection of pixel correspondences. It adapts strategies from recent rendering-based methods to obtain a bidirectional deformable-canonical mapping, to efficiently handle a defined workspace, and to guide the rays’ density. It also presents our multi-scale HexPlanes for fast inference and a new algorithm for efficient pixel sampling and convergence criteria. We present results in the STIR and SCARE datasets, for evaluating point tracking and testing the integration of kinematic data in our pipeline, respectively. In 2D point tracking, our approach surpasses the precision and accuracy of the TTO state-of-the-art methods by nearly 50% on average precision, while competing with other approaches. In 3D point tracking, this is the first TTO approach, surpassing feed-forward methods while incorporating the benefits of a deformable NeRF-based reconstruction.
我们提出了一种新型的基于NeRF架构的测试时优化(TTO)方法,用于长期3D点跟踪。目前大多数点跟踪方法很难获得一致的运动,或者仅限于2D运动。TTO方法将长期跟踪的解决方案定位为优化一个函数,该函数汇聚了来自其他最新专业方法的对应关系。与现有的TTO技术不同,我们提出使用新的可逆神经辐射场(InvNeRF)架构来参数化这样的函数,以在手术场景中进行2D和3D跟踪。我们的方法允许我们利用基于渲染的方法的优势,通过监督像素对应关系的重新投影来实现。它采用最近的基于渲染的方法的策略,获得双向可变形规范映射,以有效处理定义的工作空间并引导射线的密度。它还介绍了我们的用于快速推断的多尺度HexPlanes以及用于高效像素采样和收敛标准的新算法。我们分别在STIR和SCARE数据集上展示了结果,用于评估点跟踪并测试我们管道中运动学数据的集成。在2D点跟踪方面,我们的方法平均精度提高了近50%,超越了TTO最新方法的精度和准确性,同时与其他方法相竞争。在3D点跟踪方面,这是第一个TTO方法,它超越了前馈方法,同时结合了基于可变形NeRF重建的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种基于NeRF架构的新型测试时间优化(TTO)方法,用于长期3D点跟踪。相较于其他跟踪方法,本文方法能在手术场景中实现2D和3D跟踪,通过参数化函数优化对应点的长期跟踪问题,并借助可逆神经辐射场(InvNeRF)架构实现。该方法利用渲染技术实现像素对应点的监督重投影,并借鉴了最近提出的渲染技术中的策略来获得双向可变形规范映射、高效处理定义的工作空间以及指导射线密度。此外,还引入了多尺度HexPlanes用于快速推理和新的像素采样及收敛标准算法。实验结果表明,本文方法在STIR和SCARE数据集上的2D和3D点跟踪性能均表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于NeRF架构的新型测试时间优化(TTO)方法,用于长期3D点跟踪。
- 利用可逆神经辐射场(InvNeRF)架构实现参数化函数优化,支持2D和3D跟踪在手术场景中的应用。
- 采用渲染技术实现像素对应点的监督重投影,借鉴渲染技术中的策略获得双向可变形规范映射。
- 能高效处理定义的工作空间并指导射线密度,引入多尺度HexPlanes用于快速推理。
- 提出了新的像素采样及收敛标准算法。
- 在STIR数据集上,本文方法在2D点跟踪方面的精度和准确性超越现有TTO方法近50%。
点此查看论文截图

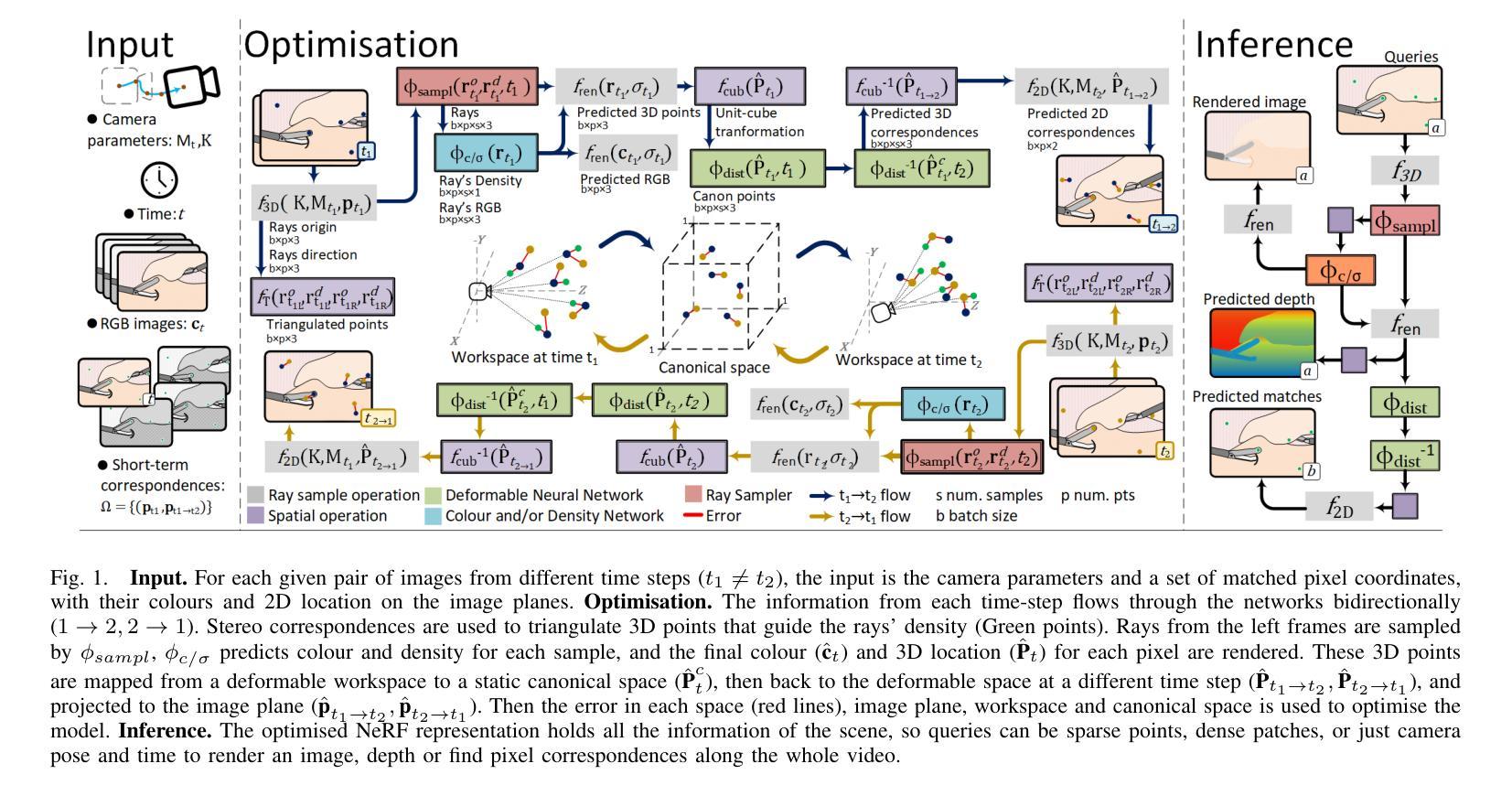
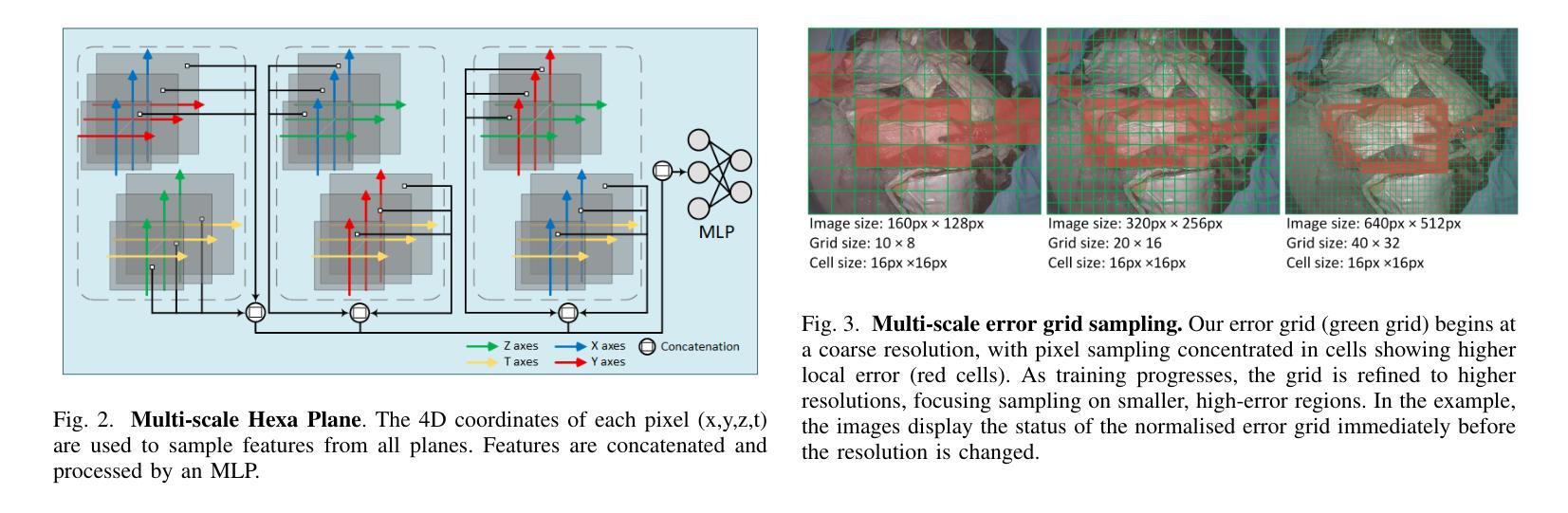

Casual3DHDR: High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos
Authors:Shucheng Gong, Lingzhe Zhao, Wenpu Li, Hong Xie, Yin Zhang, Shiyu Zhao, Peidong Liu
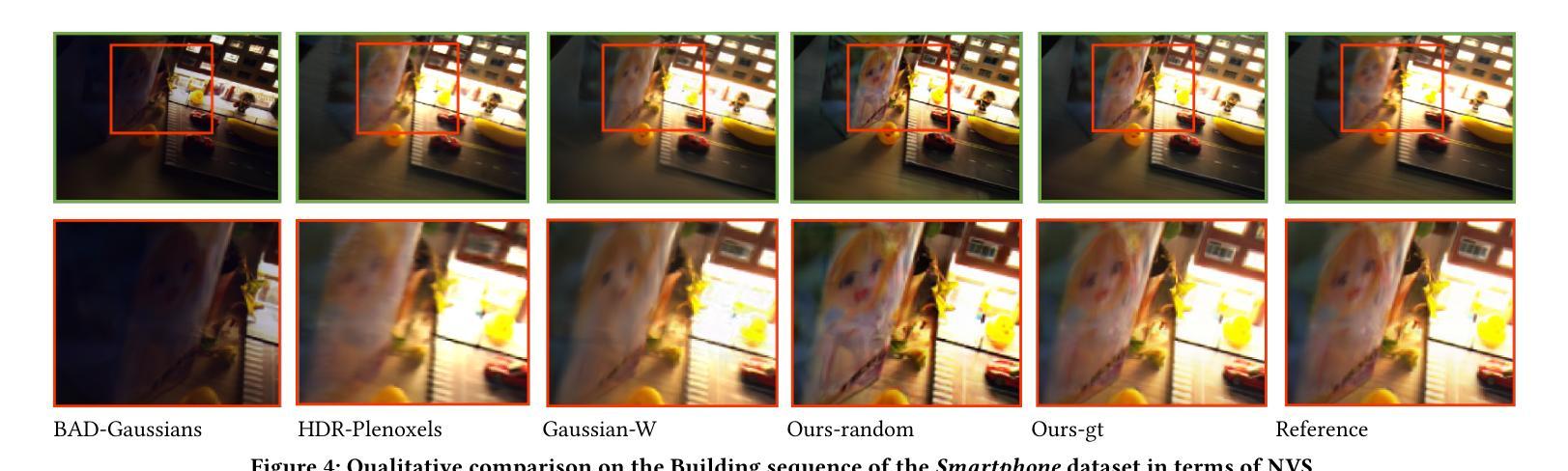
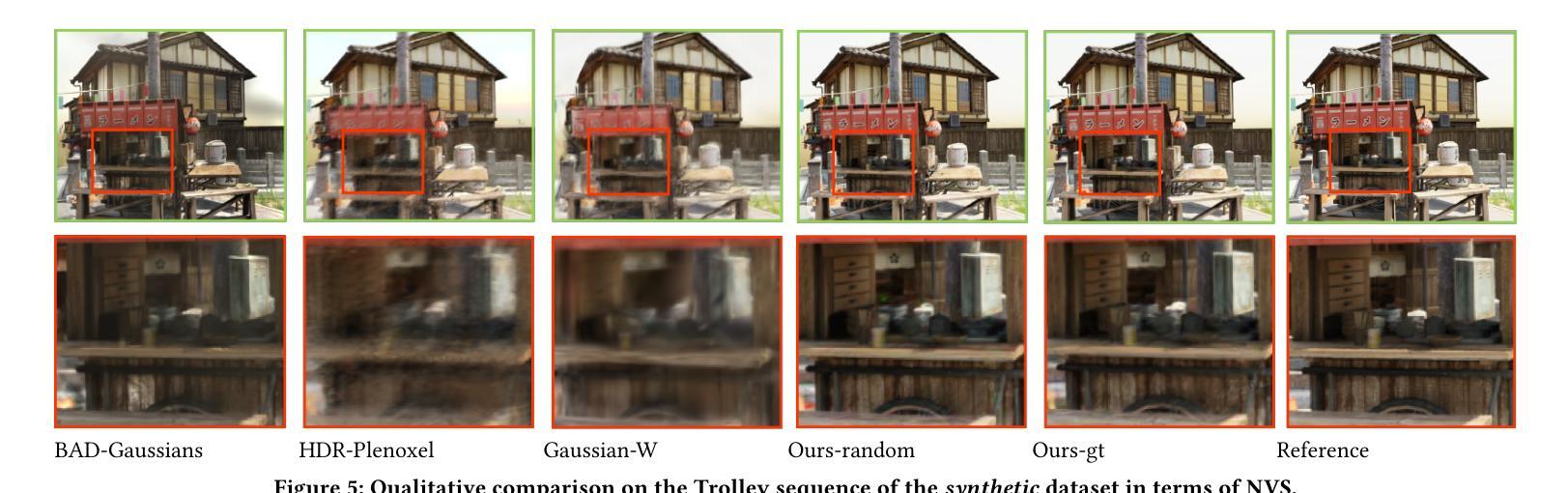
Photo-realistic novel view synthesis from multi-view images, such as neural radiance field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has gained significant attention for its superior performance. However, most existing methods rely on low dynamic range (LDR) images, limiting their ability to capture detailed scenes in high-contrast environments. While some prior works address high dynamic range (HDR) scene reconstruction, they typically require multi-view sharp images with varying exposure times captured at fixed camera positions, which is time-consuming and impractical. To make data acquisition more flexible, we propose \textbf{Casual3DHDR}, a robust one-stage method that reconstructs 3D HDR scenes from casually-captured auto-exposure (AE) videos, even under severe motion blur and unknown, varying exposure times. Our approach integrates a continuous camera trajectory into a unified physical imaging model, jointly optimizing exposure times, camera trajectory, and the camera response function (CRF). Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that \textbf{Casual3DHDR} outperforms existing methods in robustness and rendering quality. Our source code and dataset will be available at https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/
基于多视角图像的写实性新视角合成,如神经网络辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯拼贴(3DGS),因其卓越性能而受到广泛关注。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于低动态范围(LDR)图像,限制了它们在高对比度环境中捕捉精细场景的能力。尽管一些早期作品解决了高动态范围(HDR)场景重建问题,但它们通常需要固定相机位置拍摄的多视角清晰图像,且需要不同的曝光时间,这既耗时又不切实际。为了更灵活地获取数据,我们提出了名为“Casual3DHDR”的稳健一步法,可以从随意捕获的自动曝光(AE)视频中重建出HDR场景,即使在严重运动模糊和未知、多变的曝光时间下也能实现。我们的方法将连续的相机轨迹集成到一个统一的物理成像模型中,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数(CRF)。在合成和真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,“Casual3DHDR”在稳健性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。我们的源代码和数据集将在https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/开放共享。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in ACM Multimedia 2025. Project page: https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/ (Previously titled “CasualHDRSplat: Robust High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos”)
Summary
该文本介绍了基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯贴图(3DGS)技术的多视角图像合成真实感视图的方法。然而,现有方法主要依赖于低动态范围(LDR)图像,难以在高对比度环境中捕捉详细场景。针对这一问题,提出了一种名为Casual3DHDR的稳健一次性方法,可从随意捕获的自动曝光(AE)视频中重建3D HDR场景,甚至在严重运动模糊和未知、变化曝光时间的情况下也可实现。该方法将连续的相机轨迹集成到一个统一的物理成像模型中,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数(CRF)。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛实验表明,Casual3DHDR在鲁棒性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于NeRF和3DGS的多视角图像合成方法主要依赖LDR图像,难以处理高对比度环境。
- Casual3DHDR方法能够从随意捕获的AE视频中重建3D HDR场景。
- Casual3DHDR方法在严重运动模糊和未知、变化的曝光时间下仍具有稳健性。
- 该方法将连续的相机轨迹集成到物理成像模型中,并联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和CRF。
- 广泛实验证明Casual3DHDR在鲁棒性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。
- 该方法的源代码和数据集将公开可访问。
- Casual3DHDR为数据获取提供了更大的灵活性,尤其是在复杂的拍摄环境下。
点此查看论文截图

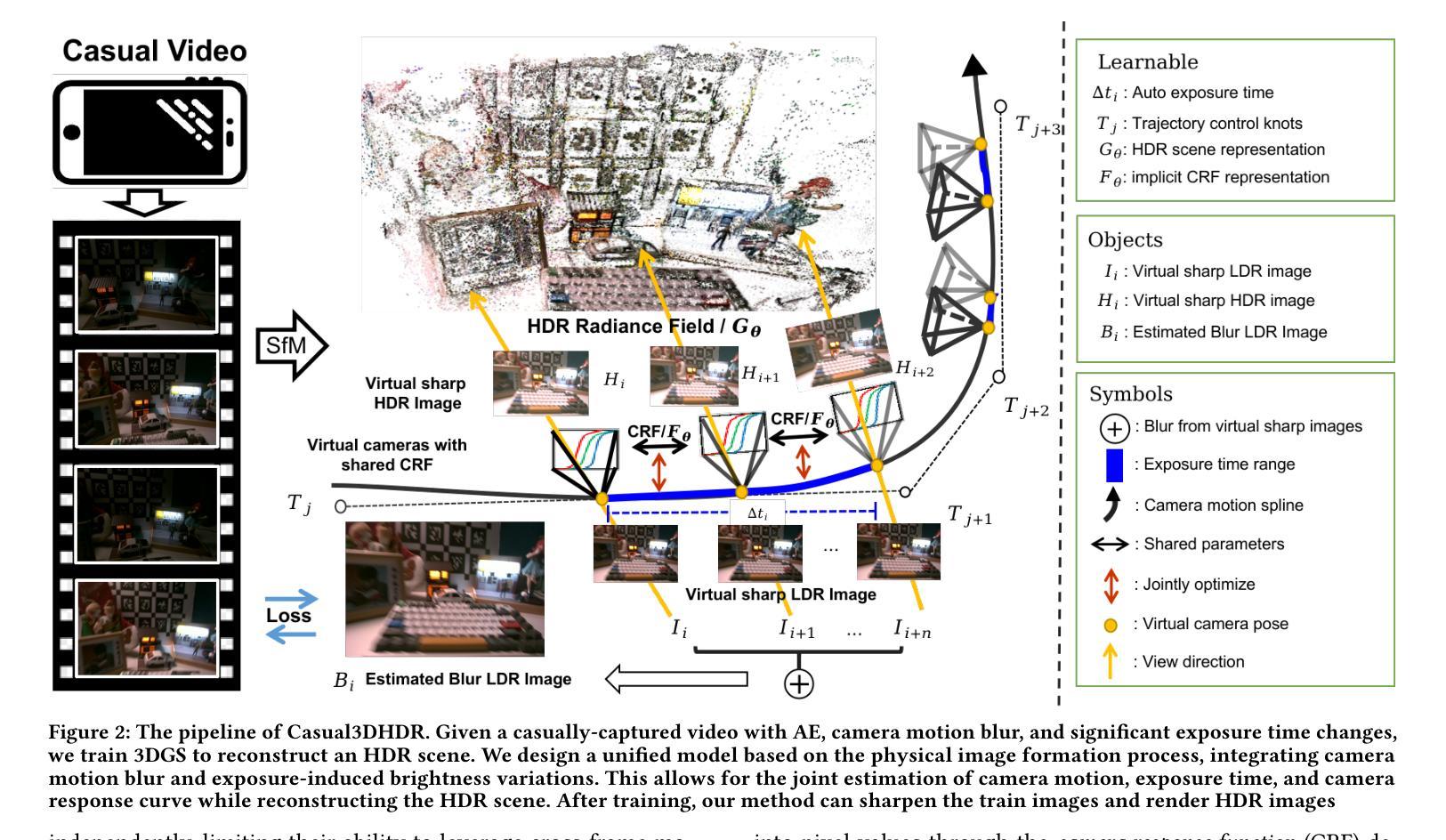




Speedy-Splat: Fast 3D Gaussian Splatting with Sparse Pixels and Sparse Primitives
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Geng Lin, Vasu Singla, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
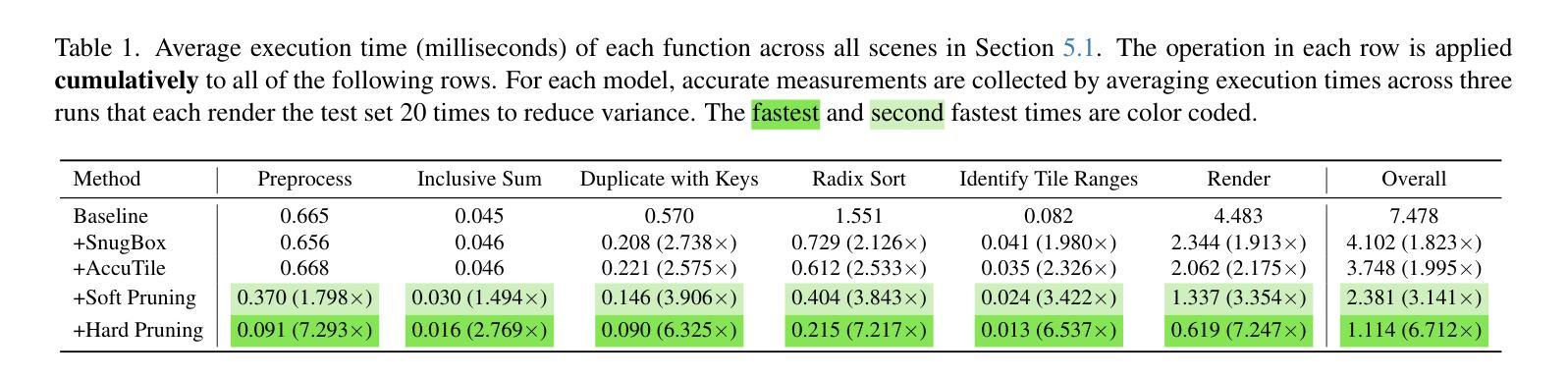
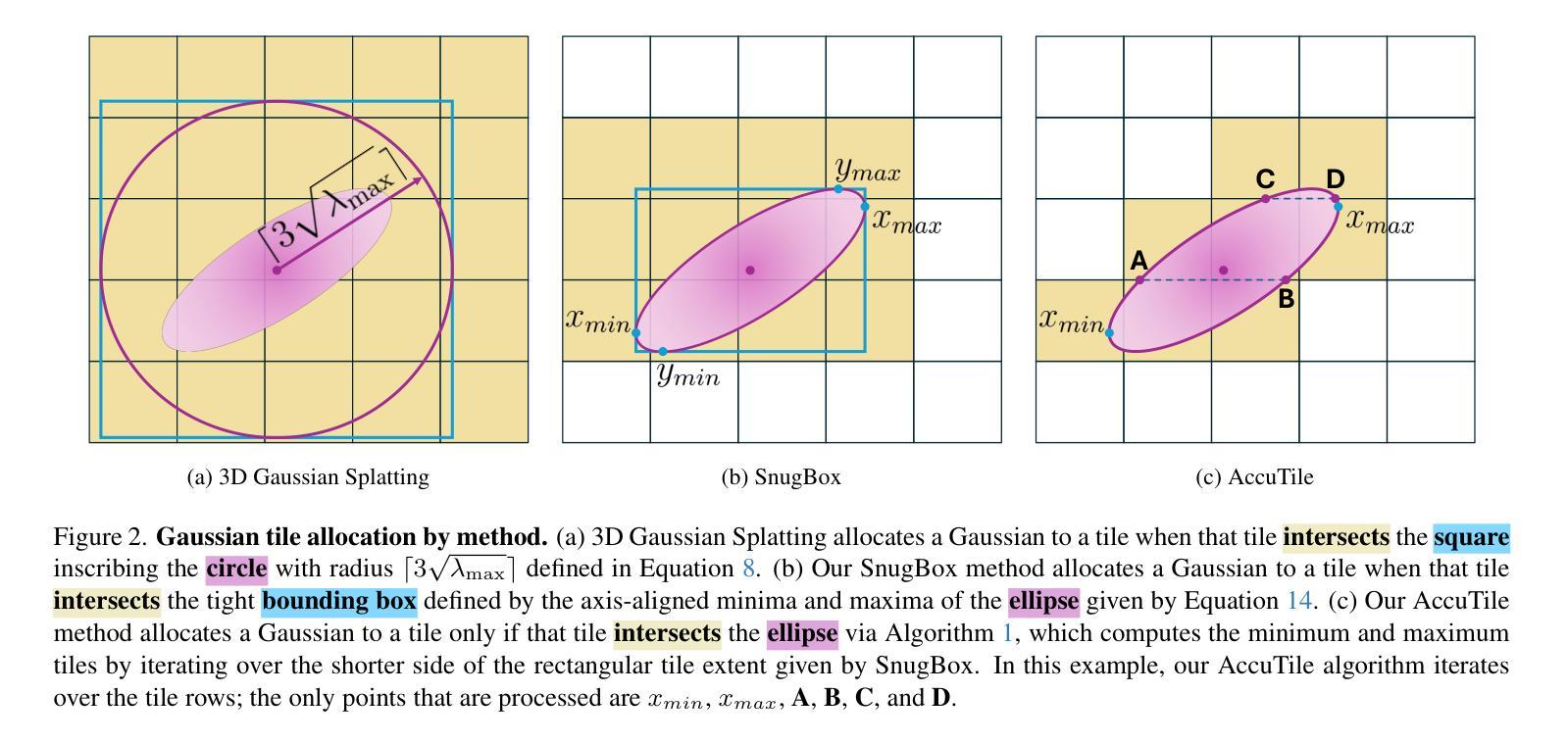
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) is a recent 3D scene reconstruction technique that enables real-time rendering of novel views by modeling scenes as parametric point clouds of differentiable 3D Gaussians. However, its rendering speed and model size still present bottlenecks, especially in resource-constrained settings. In this paper, we identify and address two key inefficiencies in 3D-GS to substantially improve rendering speed. These improvements also yield the ancillary benefits of reduced model size and training time. First, we optimize the rendering pipeline to precisely localize Gaussians in the scene, boosting rendering speed without altering visual fidelity. Second, we introduce a novel pruning technique and integrate it into the training pipeline, significantly reducing model size and training time while further raising rendering speed. Our Speedy-Splat approach combines these techniques to accelerate average rendering speed by a drastic $\mathit{6.71\times}$ across scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
3D高斯涂抹(3D-GS)是一种最新的3D场景重建技术,它通过将以可微分的高斯形式进行参数化点云建模的场景进行实时渲染,生成新颖的视图。然而,其渲染速度和模型大小仍然存在瓶颈,特别是在资源受限的环境中。在本文中,我们确定了3D-GS中的两个关键低效问题并解决了它们,从而大大提高了渲染速度。这些改进还带来了模型大小和训练时间减少的额外好处。首先,我们优化了渲染流程,精确地将高斯定位在场景中,提高了渲染速度而不影响视觉保真度。其次,我们引入了一种新的修剪技术并将其集成到训练流程中,这大大减少了模型大小和训练时间,并进一步提高了渲染速度。我们的Speedy-Splat方法结合了这些技术,使Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集场景的平均渲染速度提高了惊人的6.71倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://speedysplat.github.io/
Summary
这篇论文针对三维高斯模型(3D-GS)的两个关键瓶颈进行了改进,提升了渲染速度并优化了模型大小和训练时间。通过优化渲染管道并引入新的剪枝技术,论文提出了一种名为Speedy-Splat的方法,显著提高了渲染速度,平均提高了$\mathit{6.71\times}$。这一改进对于资源受限的环境尤为重要。
Key Takeaways
- 论文针对现有技术中的两个关键瓶颈进行了改进,旨在提升渲染速度并优化模型大小和训练时间。
- 通过优化渲染管道,提高了渲染速度同时保持视觉质量不变。
- 引入了新的剪枝技术并集成到训练流程中,进一步提高了渲染速度并减少了模型大小和训练时间。
- Speedy-Splat方法结合了上述技术,显著提高了渲染速度。
- 实验结果显示Speedy-Splat方法在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks & Temples和Deep Blending数据集上的平均渲染速度提高了$\mathit{6.71\times}$。
- 这些改进对于资源受限的环境特别重要。
点此查看论文截图


Reconstructing Satellites in 3D from Amateur Telescope Images
Authors:Zhiming Chang, Boyang Liu, Yifei Xia, Youming Guo, Boxin Shi, He Sun
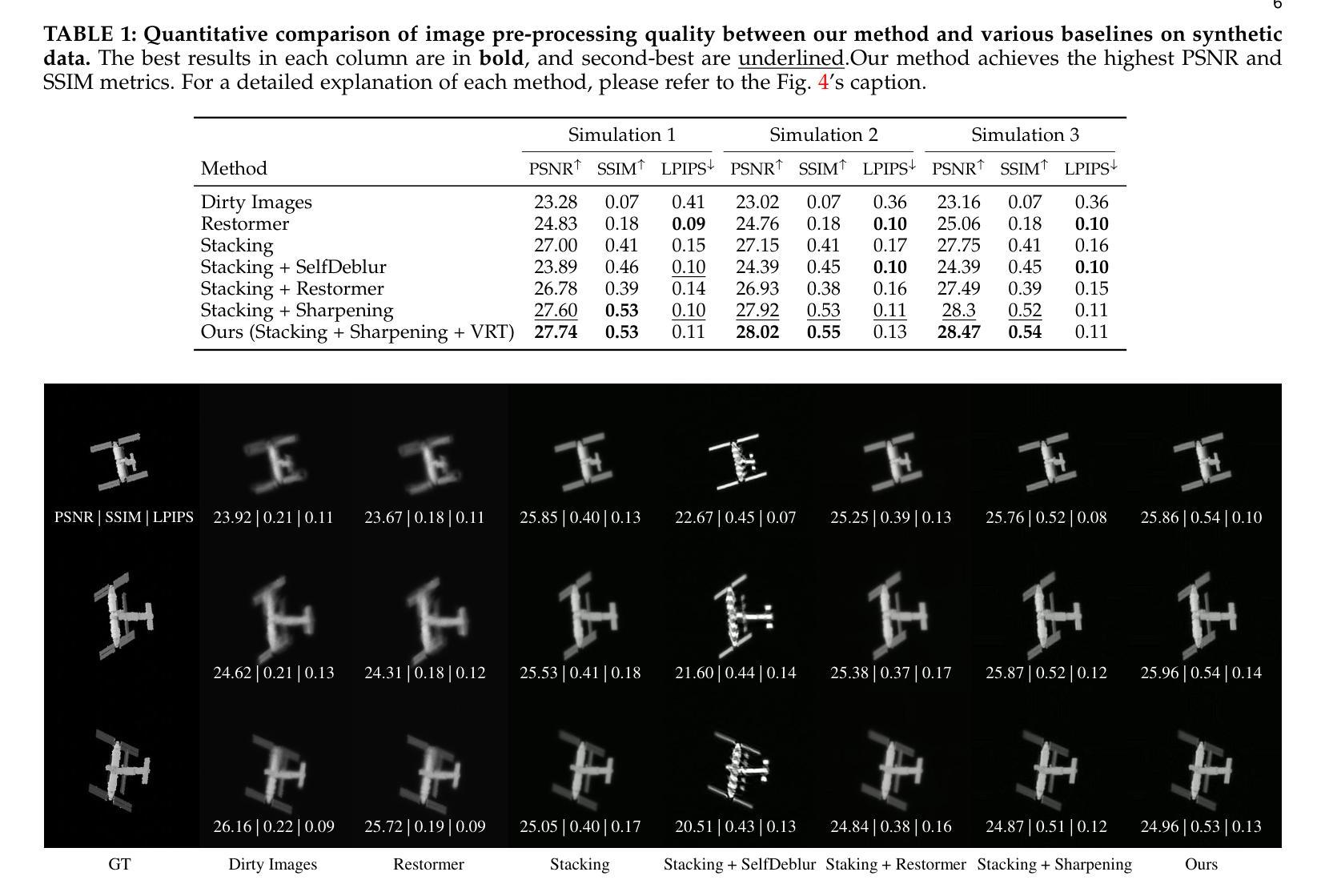
Monitoring space objects is crucial for space situational awareness, yet reconstructing 3D satellite models from ground-based telescope images is challenging due to atmospheric turbulence, long observation distances, limited viewpoints, and low signal-to-noise ratios. In this paper, we propose a novel computational imaging framework that overcomes these obstacles by integrating a hybrid image pre-processing pipeline with a joint pose estimation and 3D reconstruction module based on controlled Gaussian Splatting (GS) and Branch-and-Bound (BnB) search. We validate our approach on both synthetic satellite datasets and on-sky observations of China’s Tiangong Space Station and the International Space Station, achieving robust 3D reconstructions of low-Earth orbit satellites from ground-based data. Quantitative evaluations using SSIM, PSNR, LPIPS, and Chamfer Distance demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based approaches, and ablation studies confirm the critical role of each component. Our framework enables high-fidelity 3D satellite monitoring from Earth, offering a cost-effective alternative for space situational awareness. Project page: https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
对空间目标进行监测对于了解空间态势至关重要,然而从地面望远镜图像重建卫星的三维模型面临许多挑战,如大气湍流、观察距离长、视点有限以及信噪比低等问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的计算机成像框架,通过结合混合图像预处理管道与基于受控高斯点扩展(GS)和分治(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和三维重建模块,克服了这些障碍。我们在合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站及国际空间站的实时观测数据上验证了我们的方法,实现了从地面数据对低地球轨道卫星的稳健三维重建。使用结构相似性度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)和Chamfer距离进行的定量评估表明,我们的方法优于最新的基于NeRF的方法,消融研究证实了每个组件的关键作用。我们的框架能够实现从地球的高保真三维卫星监测,为态势感知提供了经济实惠的替代方案。项目页面:https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,该框架通过混合图像预处理管道与基于受控高斯溅射(GS)和分支定界(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和3D重建模块,克服了从地面望远镜图像重建卫星模型的困难。该框架在合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站及国际空间站的实时观测上进行了验证,实现了从地面数据对低地球轨道卫星的稳健3D重建。定量评估表明,该方法优于最新的NeRF技术,并证实了每个组件的关键作用。此框架为从地球进行的高保真3D卫星监测提供了成本效益高的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新的计算成像框架,旨在从地面望远镜图像重建卫星模型。
- 该框架集成了混合图像预处理管道和基于受控高斯溅射(GS)与分支定界(BnB)搜索的3D重建模块。
- 框架在合成卫星数据集和真实卫星观测上进行了验证,展示了对低地球轨道卫星的稳健3D重建能力。
- 定量评估表明,该框架在性能上超越了现有的NeRF技术。
- 框架的每个组成部分都经过了严格的测试,证明了其关键作用。
- 此框架为空间态势感知提供了一种成本效益高的方法,实现了高保真3D卫星监测。
点此查看论文截图