⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
Thyme: Think Beyond Images
Authors:Yi-Fan Zhang, Xingyu Lu, Shukang Yin, Chaoyou Fu, Wei Chen, Xiao Hu, Bin Wen, Kaiyu Jiang, Changyi Liu, Tianke Zhang, Haonan Fan, Kaibing Chen, Jiankang Chen, Haojie Ding, Kaiyu Tang, Zhang Zhang, Liang Wang, Fan Yang, Tingting Gao, Guorui Zhou
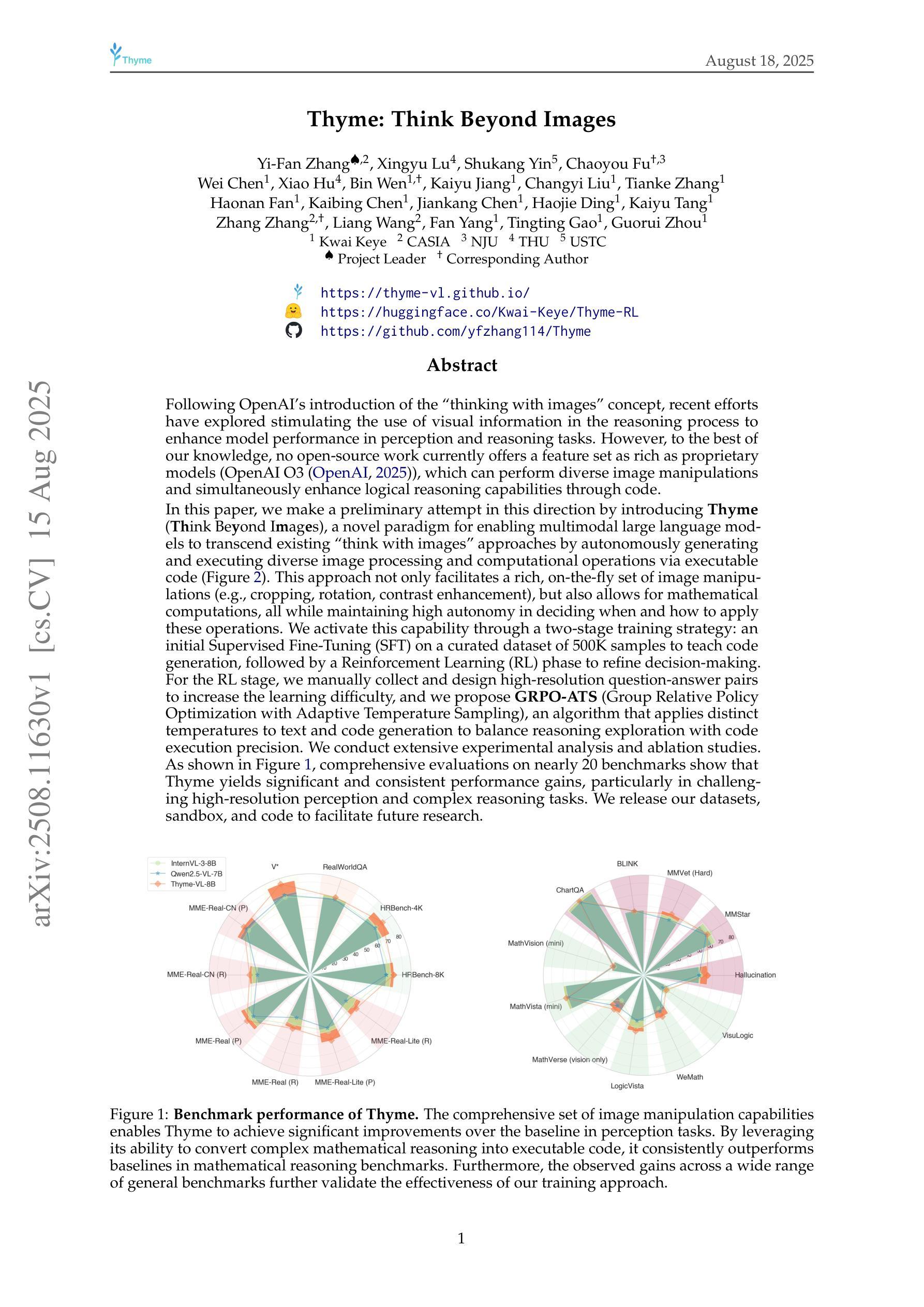
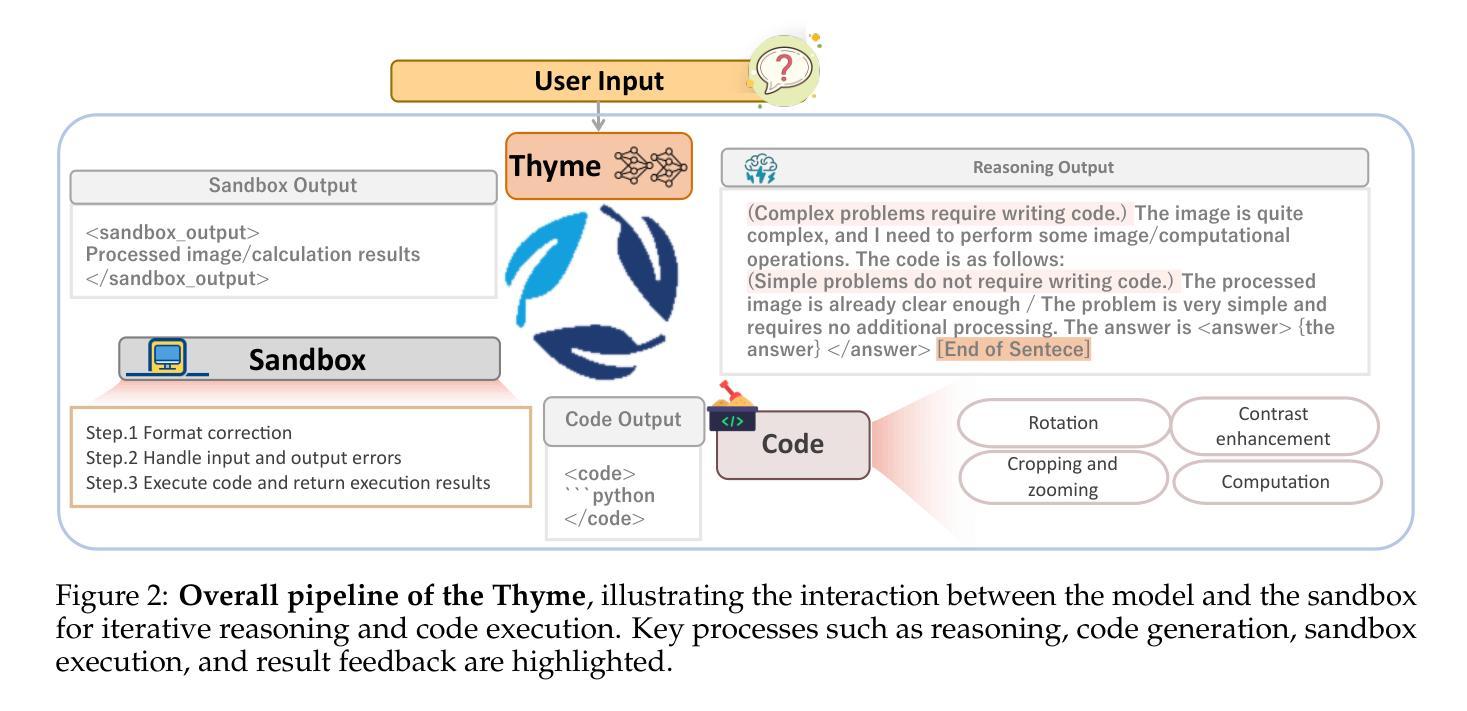
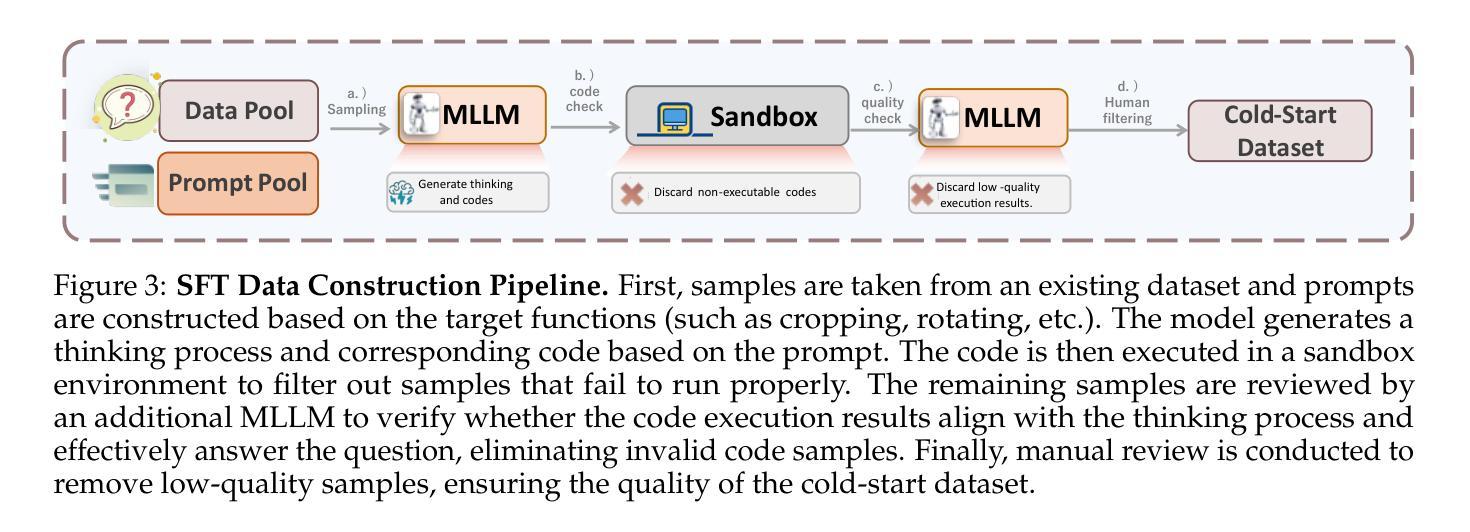
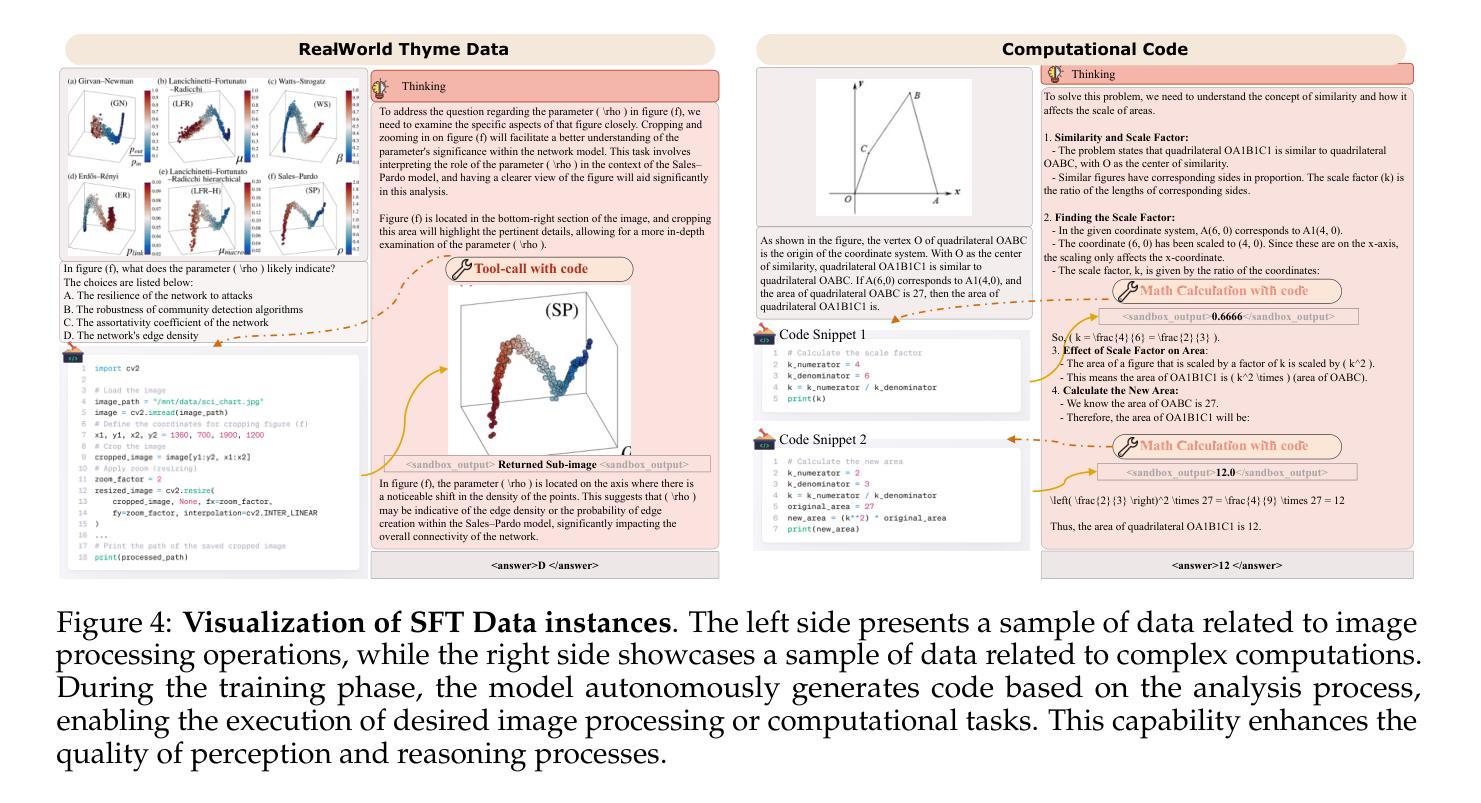
Following OpenAI’s introduction of the thinking with images'' concept, recent efforts have explored stimulating the use of visual information in the reasoning process to enhance model performance in perception and reasoning tasks. However, to the best of our knowledge, no open-source work currently offers a feature set as rich as proprietary models (O3), which can perform diverse image manipulations and simultaneously enhance logical reasoning capabilities through code. In this paper, we make a preliminary attempt in this direction by introducing Thyme (Think Beyond Images), a novel paradigm for enabling MLLMs to transcend existing think with images’’ approaches by autonomously generating and executing diverse image processing and computational operations via executable code. This approach not only facilitates a rich, on-the-fly set of image manipulations (e.g., cropping, rotation, contrast enhancement) but also allows for mathematical computations, all while maintaining high autonomy in deciding when and how to apply these operations. We activate this capability through a two-stage training strategy: an initial SFT on a curated dataset of 500K samples to teach code generation, followed by a RL phase to refine decision-making. For the RL stage, we manually collect and design high-resolution question-answer pairs to increase the learning difficulty, and we propose GRPO-ATS (Group Relative Policy Optimization with Adaptive Temperature Sampling), an algorithm that applies distinct temperatures to text and code generation to balance reasoning exploration with code execution precision. We conduct extensive experimental analysis and ablation studies. Comprehensive evaluations on nearly 20 benchmarks show that Thyme yields significant and consistent performance gains, particularly in challenging high-resolution perception and complex reasoning tasks.
在OpenAI提出“图像思考”概念之后,最近的努力都在探索在推理过程中刺激视觉信息的使用,以提高模型在感知和推理任务中的性能。然而,据我们所知,目前没有任何开源工作能提供与专有模型(O3)一样丰富的功能集,后者可以进行多样化的图像操作,并通过代码同时提高逻辑推理能力。在本文中,我们朝着这个方向进行了初步尝试,引入了Thyme(超越图像思考),这是一种新型范式,使MLLMs能够通过自主生成和执行各种图像处理和计算操作,超越现有的“图像思考”方法,通过可执行代码实现。这种方法不仅便于丰富的即时图像操作(例如裁剪、旋转、对比度增强),还允许数学计算,同时保持高度自主性,以决定何时以及如何应用这些操作。我们通过两阶段训练策略激活此功能:首先在50万个精选样本数据集上进行初始的自监督训练,以教授代码生成,然后强化学习阶段来完善决策制定。对于强化学习阶段,我们手动收集和设计了高分辨率的问题答案对,以增加学习难度,并提出了GRPO-ATS(具有自适应温度采样的群组相对策略优化)算法,该算法对文本和代码生成应用不同的温度,以平衡推理探索与代码执行精度。我们进行了广泛的实验分析和消融研究。近20项基准测试的综合评估表明,Thyme带来了显著且持续的性能提升,特别是在高分辨率感知和复杂推理任务中表现突出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://thyme-vl.github.io/
Summary:随着OpenAI提出的“以图思考”概念的引入,最新努力开始探索在推理过程中利用视觉信息,以提高模型在感知和推理任务中的性能。然而,据我们所知,目前还没有开源工作能提供与专有模型一样丰富的功能集,它们可以进行多种图像操作,并通过代码同时提高逻辑推理能力。本文提出了一种名为Thyme(超越图像思考)的新型范式,使MLLMs能够通过自主生成和执行各种图像处理和计算操作来超越现有的“以图思考”方法。这种方法不仅便于进行丰富的即时图像操作(如裁剪、旋转、对比度增强),还允许进行数学计算,同时保持高度自主决定何时以及如何应用这些操作的能力。我们通过两阶段训练策略激活此功能:首先在精选的50万样本数据集上进行初始SFT(自训练)以教授代码生成,其次是RL(强化学习)阶段以优化决策制定。我们提出了GRPO-ATS算法,将不同的温度应用于文本和代码生成,以平衡推理探索与代码执行精度。经近20项基准测试的综合评估和消融研究,Thyme显示出显著且一致的性能提升,特别是在高分辨率感知和复杂推理任务中。
Key Takeaways:
- Thyme是一种新型范式,使MLLMs能够超越“以图思考”的方法,通过自主生成和执行图像处理和计算操作来提高模型性能。
- Thyme支持丰富的图像操作,如裁剪、旋转、对比度增强等,并允许数学计算。
- Thyme采用两阶段训练策略,初始阶段通过自训练教授代码生成,随后是强化学习阶段优化决策制定。
- GRPO-ATS算法应用于文本和代码生成的不同温度,以平衡推理探索与代码执行精度。
- Thyme在近乎20项基准测试中表现卓越,特别是在高分辨率感知和复杂推理任务中。
- 开源工作目前尚无法提供与Thyme相当的丰富功能集。
点此查看论文截图
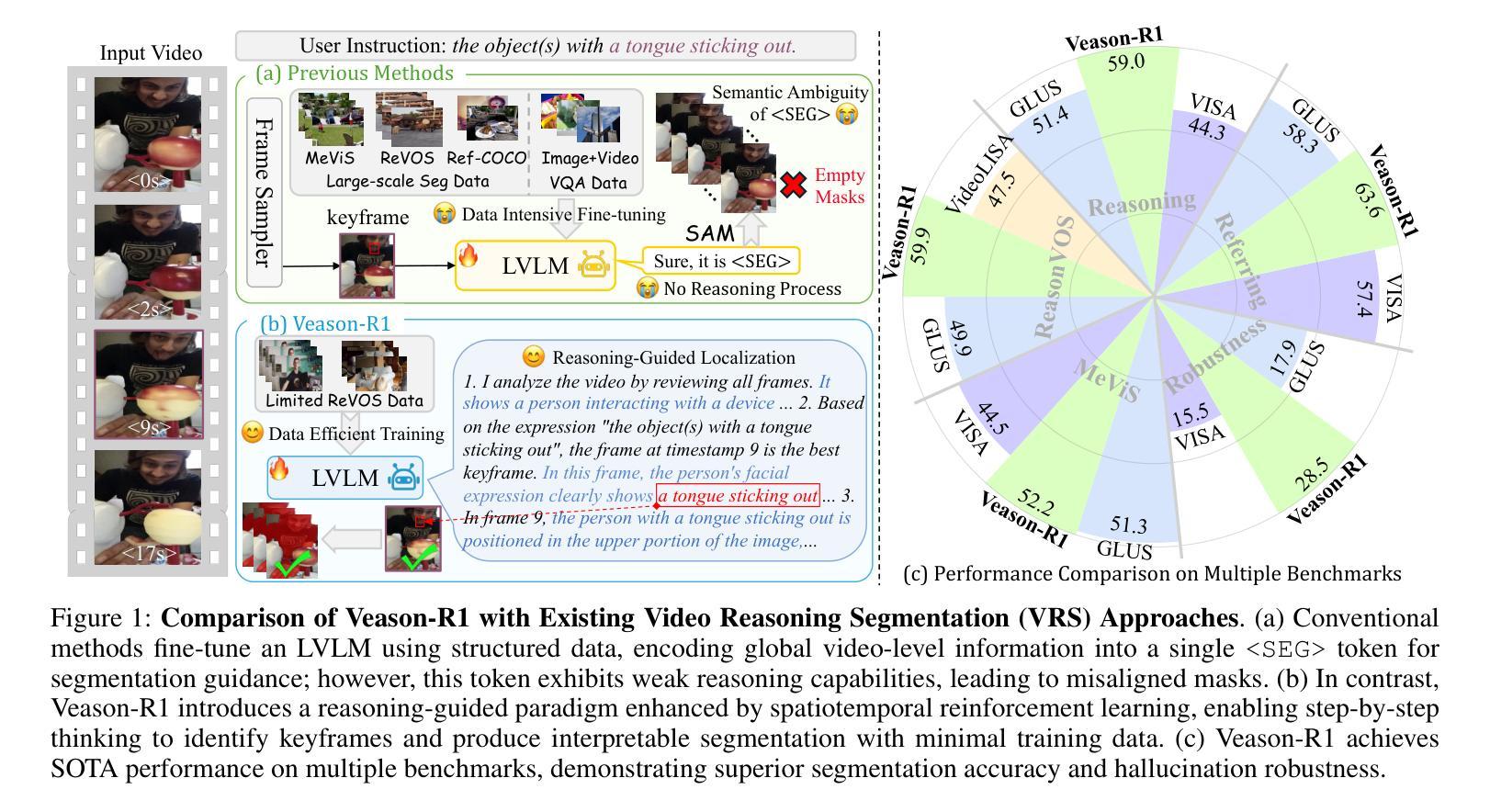
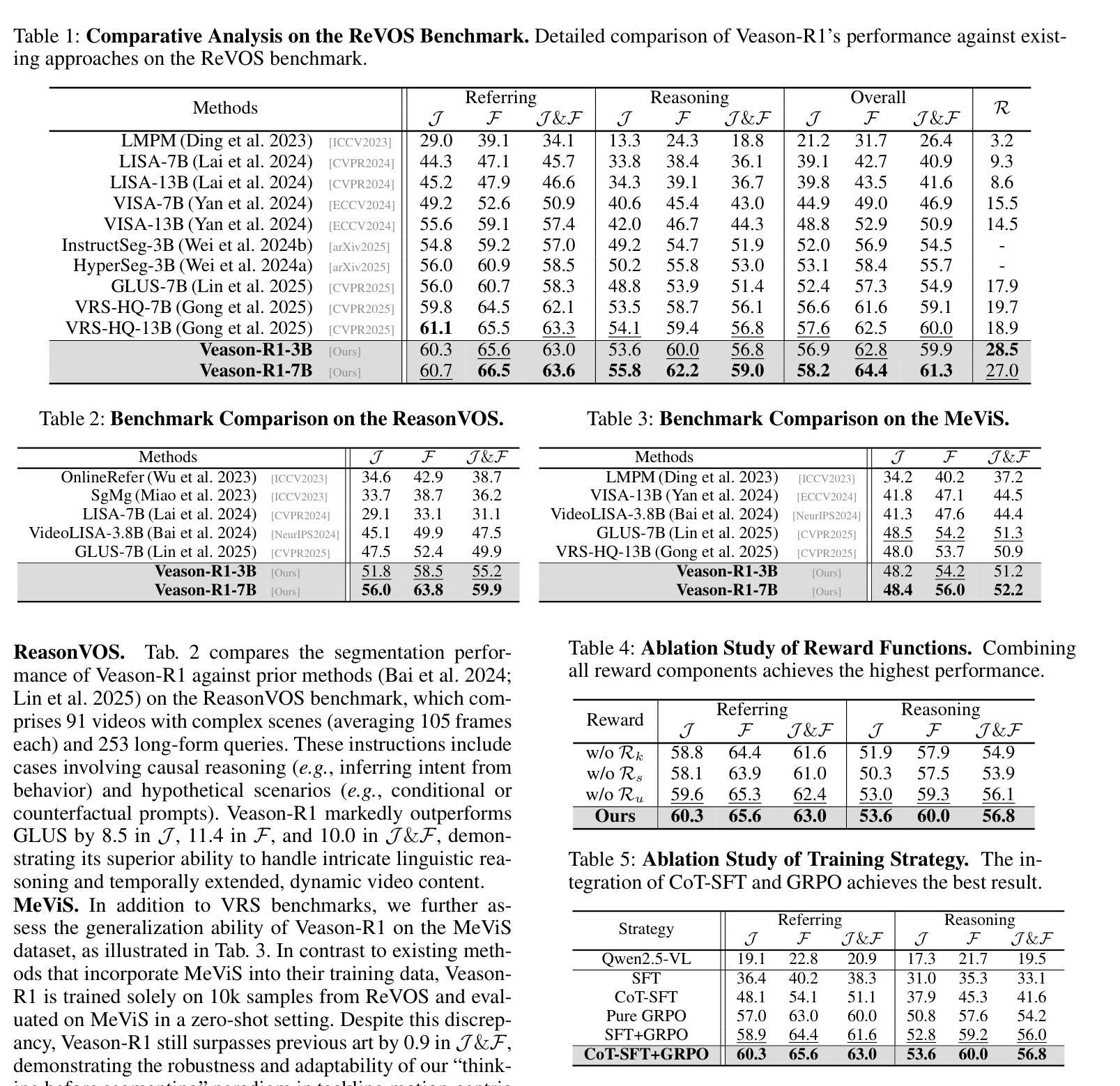
Reinforcing Video Reasoning Segmentation to Think Before It Segments
Authors:Sitong Gong, Lu Zhang, Yunzhi Zhuge, Xu Jia, Pingping Zhang, Huchuan Lu
Video reasoning segmentation (VRS) endeavors to delineate referred objects in videos guided by implicit instructions that encapsulate human intent and temporal logic. Previous approaches leverage large vision language models (LVLMs) to encode object semantics into
视频推理分割(VRS)旨在根据隐含指令(这些指令包含人类意图和时间逻辑)来描绘视频中涉及的对象。之前的方法是利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)将对象语义编码为
标记来进行掩膜预测。然而,由于推理过程中的时空推理不足,这种范式在推理过程中存在可解释性有限和性能不佳的问题。我们从强化学习的开创性突破中汲取灵感,引入了针对VRS的专用LVLM——Veason-R1,它强调分割中的结构化推理。Veason-R1通过Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)和Chain-of-Thought(CoT)初始化进行训练。首先,我们精心整理高质量的CoT训练数据,以培养结构化推理轨迹,从而建立视频级语义和帧级空间定位之间的联系,得到经过监督微调训练的模型Veason-SFT。随后,GRPO微调通过优化推理链来鼓励推理空间的有效探索。为此,我们采用了全面的奖励机制,协同增强空间对齐和时序一致性,提升关键帧定位和精细定位能力。综合实证评估表明,Veason-R1在多个基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,显著超越了先前技术(例如在ReVOS中的J&F增加1.3,在ReasonVOS中的J&F增加10.0),同时对幻觉具有鲁棒性(+8.8 R)。我们的代码和模型权重将在Veason-R1上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
本文介绍了视频推理分割(VRS)领域的一种新方法——Veason-R1。该方法旨在通过大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)实现更结构化、更具解释性的视频对象分割,它通过结合强化学习的技术如Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) 和 Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 初始化来提高模型的推理能力。模型通过在视频级别语义和帧级别空间定位之间建立桥梁,进行结构化推理轨迹的训练,并采用整体奖励机制来优化推理链的空间对齐和时序一致性,从而提高关键帧定位和精细定位的性能。在多个基准测试上,Veason-R1达到了领先水平,显著超越了现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 视频推理分割(VRS)旨在根据隐含指令进行视频中的对象分割,这些指令反映了人类意图和时间逻辑。
- 现有方法主要依赖大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)进行对象语义编码,但存在解释性差和性能不足的问题。
- Veason-R1通过结合强化学习技术,强调结构化推理,旨在解决上述问题。
- Veason-R1采用Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) 和 Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 初始化进行训练。
- 通过高质量的结构化推理轨迹训练数据,Veason-R1在视频级别语义和帧级别空间定位之间建立了桥梁。
- 模型采用整体奖励机制来优化空间对齐和时序一致性,提高了关键帧定位和精细定位的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Remove360: Benchmarking Residuals After Object Removal in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Simona Kocour, Assia Benbihi, Torsten Sattler
Understanding what semantic information persists after object removal is critical for privacy-preserving 3D reconstruction and editable scene representations. In this work, we introduce a novel benchmark and evaluation framework to measure semantic residuals, the unintended semantic traces left behind, after object removal in 3D Gaussian Splatting. We conduct experiments across a diverse set of indoor and outdoor scenes, showing that current methods can preserve semantic information despite the absence of visual geometry. We also release Remove360, a dataset of pre/post-removal RGB images and object-level masks captured in real-world environments. While prior datasets have focused on isolated object instances, Remove360 covers a broader and more complex range of indoor and outdoor scenes, enabling evaluation of object removal in the context of full-scene representations. Given ground truth images of a scene before and after object removal, we assess whether we can truly eliminate semantic presence, and if downstream models can still infer what was removed. Our findings reveal critical limitations in current 3D object removal techniques and underscore the need for more robust solutions capable of handling real-world complexity. The evaluation framework is available at github.com/spatial-intelligence-ai/Remove360.git. Data are available at huggingface.co/datasets/simkoc/Remove360.
理解在移除物体后哪些语义信息得以保留,对于保护隐私的3D重建和可编辑场景表示至关重要。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新的基准测试和评估框架,来测量3D高斯拼贴中物体移除后留下的无意中的语义痕迹。我们在室内和室外场景进行了多样化的实验,结果表明,即使在没有视觉几何的情况下,当前的方法也可以保留语义信息。我们还发布了Remove360数据集,其中包含在现实环境中捕获的预移除和后移除RGB图像以及物体级掩膜。虽然先前的数据集主要集中在孤立的物体实例上,但Remove360涵盖了更广泛和更复杂的室内和室外场景,能够在完整的场景表示中评估物体移除。给定场景移除物体前后的真实图像,我们评估是否真正消除了语义存在性,以及下游模型是否仍然可以推断出被移除的内容。我们的研究结果揭示了当前3D物体移除技术的关键局限性,并强调了需要更稳健的解决方案来处理现实世界的复杂性。评估框架可在github.com/spatial-intelligence-ai/Remove360.git上找到。数据可在huggingface.co/datasets/simkoc/Remove360上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2503.17574
Summary
本文介绍了一个评估框架,用于测量在三维高斯混合技术中移除物体后留下的语义残留信息。研究团队为此开发了一个名为Remove360的数据集,包含室内外场景的前后移除RGB图像和物体级掩膜。研究结果表明,当前的方法能够在没有视觉几何的情况下保留语义信息。然而,现有的三维物体移除技术在真实世界场景中仍存在局限,需要进一步开发更稳健的解决方案来处理真实世界的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义信息在三维重建和可编辑场景表示中的隐私保护至关重要。
- 介绍了一种新的评估框架,用于测量三维高斯混合技术中物体移除后的语义残留。
- 开发了一个名为Remove360的数据集,包含真实环境中室内外场景的前后移除图像和物体级掩膜。
- 当前方法能够在没有视觉几何的情况下保留语义信息。
- 现有的三维物体移除技术在真实世界场景中仍存在局限。
- 需要开发更稳健的解决方案来处理真实世界的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图




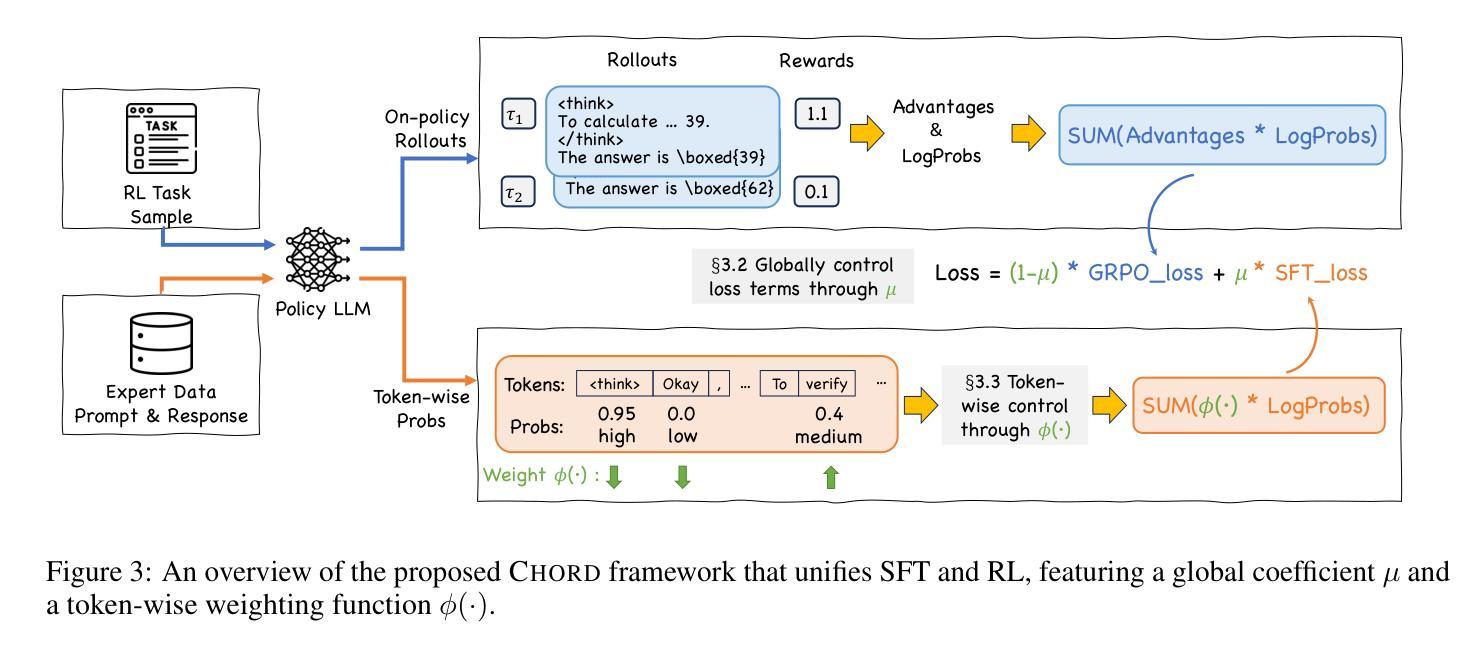
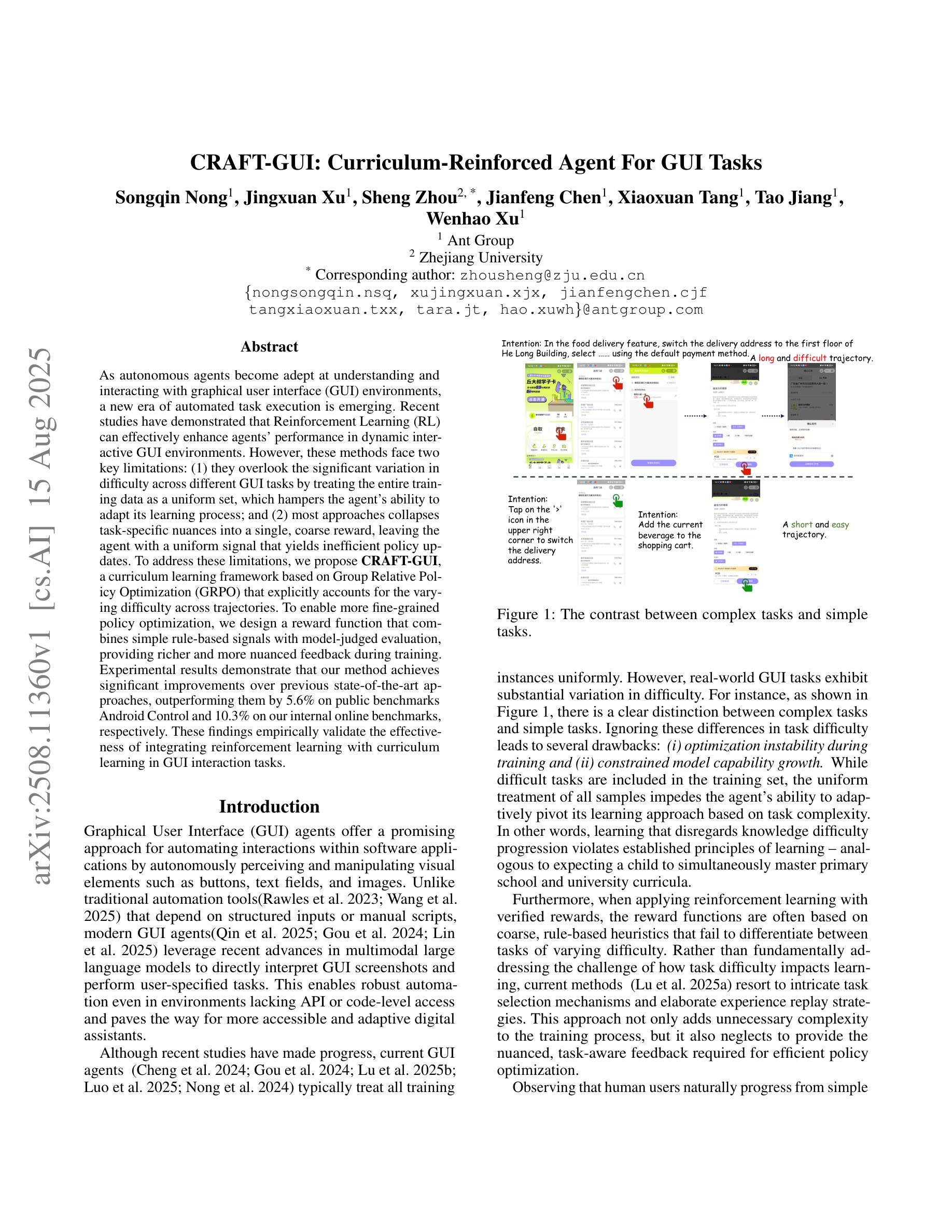
On-Policy RL Meets Off-Policy Experts: Harmonizing Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning via Dynamic Weighting
Authors:Wenhao Zhang, Yuexiang Xie, Yuchang Sun, Yanxi Chen, Guoyin Wang, Yaliang Li, Bolin Ding, Jingren Zhou
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) are two prominent post-training paradigms for refining the capabilities and aligning the behavior of Large Language Models (LLMs). Existing approaches that integrate SFT and RL often face the risk of disrupting established model patterns and inducing overfitting to expert data. To address this, we present a novel investigation into the unified view of SFT and RL through an off-policy versus on-policy lens. We propose CHORD, a framework for the Controllable Harmonization of On- and Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning via Dynamic Weighting, which reframes SFT not as a separate stage but as a dynamically weighted auxiliary objective within the on-policy RL process. Based on an analysis of off-policy expert data’s influence at both holistic and granular levels, we incorporate a dual-control mechanism in CHORD. Specifically, the framework first employs a global coefficient to holistically guide the transition from off-policy imitation to on-policy exploration, and then applies a token-wise weighting function that enables granular learning from expert tokens, which preserves on-policy exploration and mitigates disruption from off-policy data. We conduct extensive experiments on widely used benchmarks, providing empirical evidence that CHORD achieves a stable and efficient learning process. By effectively harmonizing off-policy expert data with on-policy exploration, CHORD demonstrates significant improvements over baselines. We release the implementation at https://github.com/modelscope/Trinity-RFT/tree/main/examples/mix_chord to inspire further research.
监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)是两种用于精炼和提升大型语言模型(LLM)能力并调整其行为的重要后训练范式。现有将SFT和RL结合的方法常常面临破坏已有模型模式和对专家数据过度拟合的风险。为了解决这个问题,我们通过对off-policy和on-policy视角的透镜,对SFT和RL的统一视角进行了新型探究。我们提出了CHORD框架,该框架名为基于动态加权的在线和离线强化学习可控协调框架(Controllable Harmonization of On- and Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning via Dynamic Weighting)。我们认为SFT并非是一个独立阶段,而是作为动态加权辅助目标存在于在线RL过程中。基于对离线专家数据在整体和颗粒化层面影响的全面分析,我们在CHORD框架中融入了一种双重控制机制。具体而言,该框架首先使用一个全局系数来全面指导从离线模仿到在线探索的过渡过程,然后应用一种基于代币的加权函数来利用专家代币进行精细化学习,保持在线探索的同时缓解离线数据的干扰破坏。我们在广泛使用的基准测试上进行了大量实验,提供了实证证据表明CHORD能够实现稳定且高效的学习过程。通过有效地协调离线专家数据和在线探索,CHORD在基准测试上取得了显著改进。我们已将实现发布在https://github.com/modelscope/Trinity-RFT/tree/main/examples/mix_chord上,以激发进一步的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)的结合方式,提出一种名为CHORD的新型框架,用于可控地和谐在线和离线策略强化学习,通过动态加权实现。该框架将SFT视为动态加权辅助目标,融入在线策略RL过程中。通过全局系数和标记级加权函数实现双重控制机制,平衡离线策略专家数据与在线策略探索之间的转换。在广泛使用的基准测试上进行了大量实验,证明了CHORD的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- CHORD框架结合了监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL),旨在和谐在线和离线策略强化学习。
- CHORD将SFT视为动态加权的辅助目标,融入在线策略RL过程中,避免模型模式被打破和过度拟合专家数据的风险。
- 通过全局系数和标记级加权函数实现双重控制机制,平衡离线策略专家数据与在线策略探索之间的转换。
- CHORD框架在广泛使用的基准测试上表现出显著改进。
- 释放了CHORD框架的实现代码,以激发进一步的研究。
点此查看论文截图

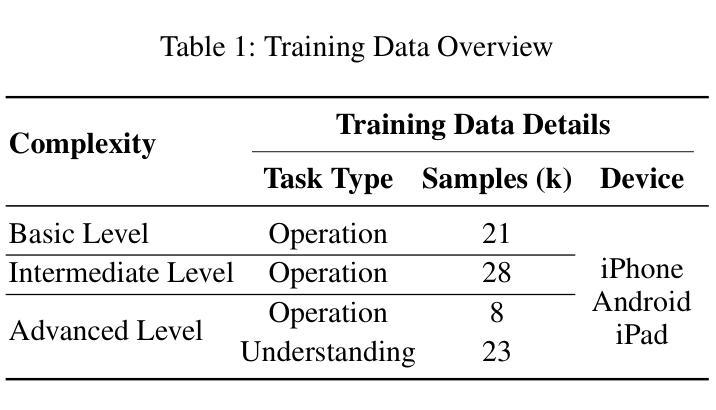
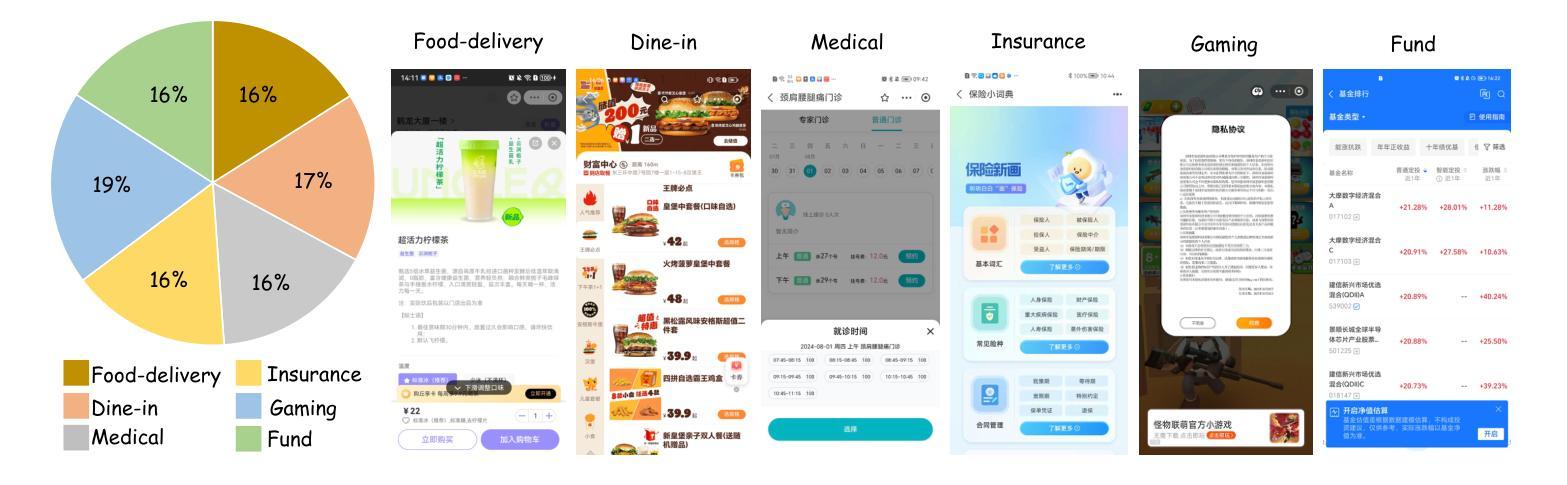
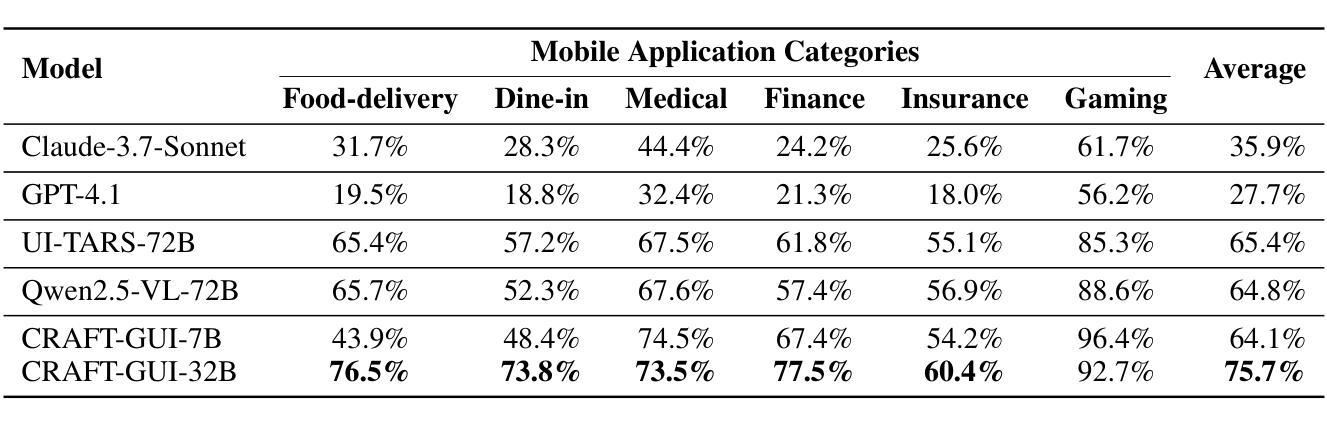
CRAFT-GUI: Curriculum-Reinforced Agent For GUI Tasks
Authors:Songqin Nong, Jingxuan Xu, Sheng Zhou, Jianfeng Chen, Xiaoxuan Tang, Tao Jiang, Wenhao Xu
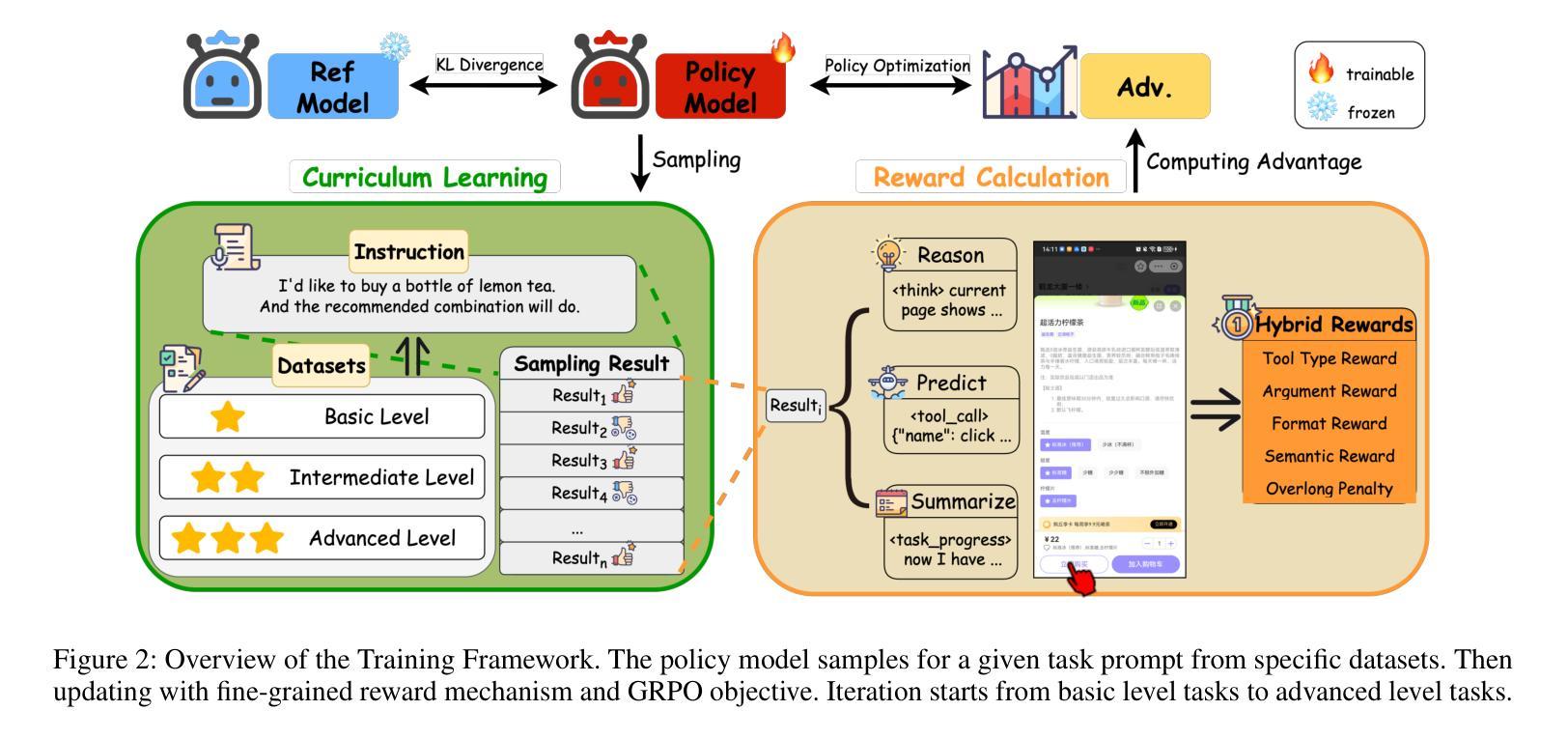
As autonomous agents become adept at understanding and interacting with graphical user interface (GUI) environments, a new era of automated task execution is emerging. Recent studies have demonstrated that Reinforcement Learning (RL) can effectively enhance agents’ performance in dynamic interactive GUI environments. However, these methods face two key limitations: (1) they overlook the significant variation in difficulty across different GUI tasks by treating the entire training data as a uniform set, which hampers the agent’s ability to adapt its learning process; and (2) most approaches collapse task-specific nuances into a single, coarse reward, leaving the agent with a uniform signal that yields inefficient policy updates. To address these limitations, we propose CRAFT-GUI, a curriculum learning framework based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) that explicitly accounts for the varying difficulty across trajectories. To enable more fine-grained policy optimization, we design a reward function that combines simple rule-based signals with model-judged evaluation, providing richer and more nuanced feedback during training. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art approaches, outperforming them by 5.6% on public benchmarks Android Control and 10.3% on our internal online benchmarks, respectively. These findings empirically validate the effectiveness of integrating reinforcement learning with curriculum learning in GUI interaction tasks.
随着自主代理(agents)在理解和图形用户界面(GUI)环境交互方面的能力逐渐增强,一个新的自动化任务执行时代正在兴起。最近的研究表明,强化学习(RL)可以有效地提高代理在动态交互式GUI环境中的性能。然而,这些方法面临两个主要局限性:(1)它们忽略了不同GUI任务之间难度的显著差异,将整个训练数据视为统一集,这阻碍了代理适应其学习过程的能力;(2)大多数方法将任务特定的细微差别归结为单一、粗略的奖励,使代理接收到统一的信号,从而产生低效的策略更新。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的CURAFER-GUI课程学习框架,该框架显式考虑了轨迹间的不同难度。为了实现更精细的策略优化,我们设计了一个奖励函数,它将基于简单规则的信号与模型判断的评价相结合,在训练过程中提供更丰富、更细微的反馈。实验结果表明,我们的方法在公共基准测试Android Control上较之前的最先进方法提高了5.6%,在我们的内部在线基准测试上提高了10.3%。这些发现实证地验证了强化学习与课程学习在GUI交互任务中结合的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着自主代理在图形用户界面(GUI)环境中的理解和交互能力逐渐增强,一个新的自动化任务执行时代正在兴起。然而,强化学习(RL)在处理动态交互式GUI环境时存在两大局限。为解决这些问题,提出了一种基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的课程学习框架CRAFT-GUI,并设计了丰富的奖励函数以提供更精细的策略优化。实验结果表明,该方法在公共基准测试上优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 自主代理在GUI环境中的理解和交互能力增强,开启了新的自动化任务执行时代。
- 强化学习在处理动态交互式GUI环境时面临两大局限:忽视不同GUI任务的难度差异,以及任务特定细节被简化为单一的粗糙奖励。
- CRAFT-GUI课程学习框架基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO),明确考虑轨迹的不同难度。
- CRAFT-GUI设计了结合基于规则的简单信号和模型判断的评估的奖励函数,为训练期间提供更丰富和细微的反馈。
- 实验结果表明,CRAFT-GUI在公共基准测试上较先前的方法有显著改善,分别提高了5.6%和10.3%。
- CRAFT-GUI整合了强化学习与课程学习,在GUI交互任务中展现出有效性。
- CRAFT-GUI能够为不同难度的任务提供适应性的学习策略。
点此查看论文截图
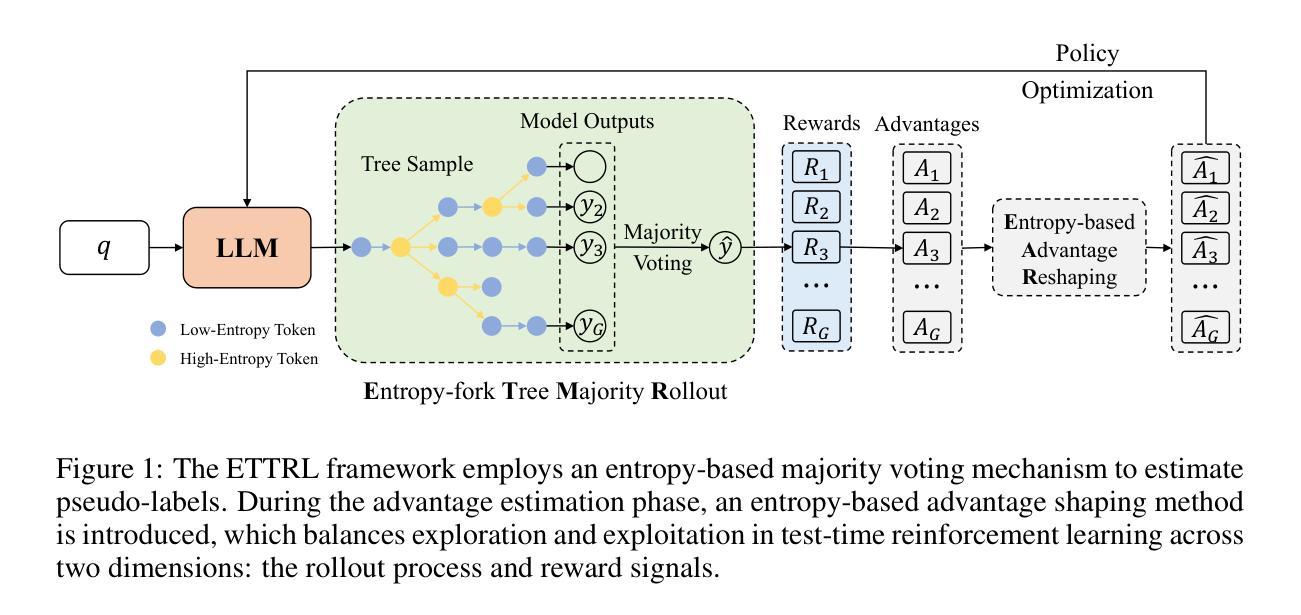
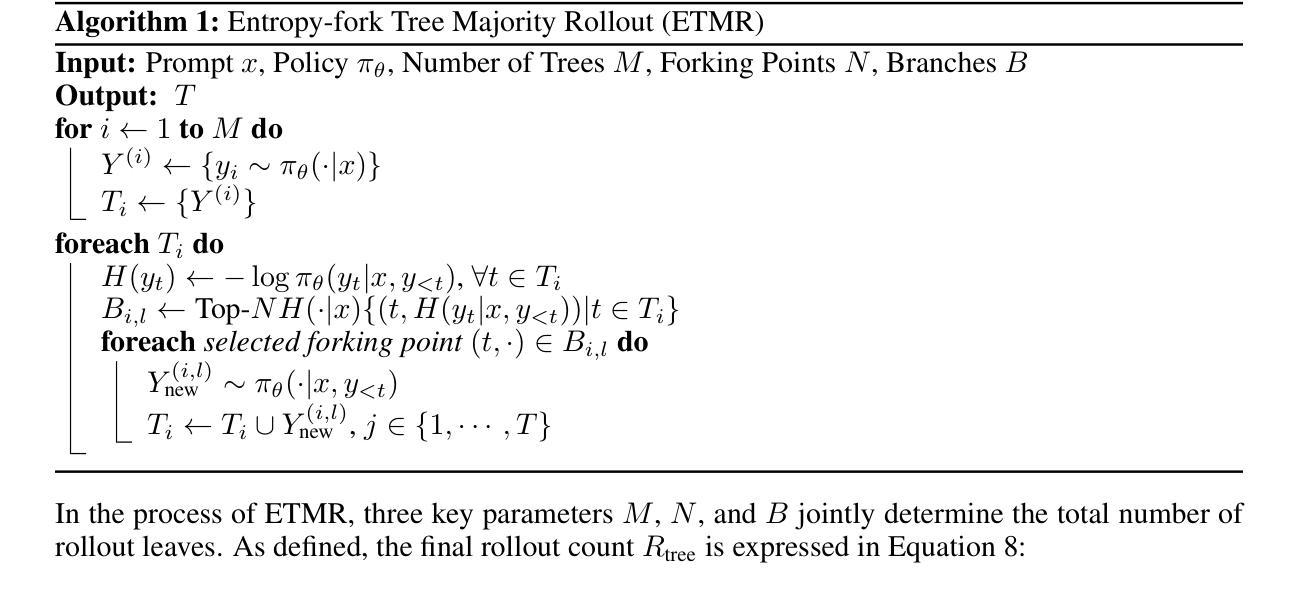
ETTRL: Balancing Exploration and Exploitation in LLM Test-Time Reinforcement Learning Via Entropy Mechanism
Authors:Jia Liu, ChangYi He, YingQiao Lin, MingMin Yang, FeiYang Shen, ShaoGuo Liu, TingTing Gao
Recent advancements in Large Language Models have yielded significant improvements in complex reasoning tasks such as mathematics and programming. However, these models remain heavily dependent on annotated data and exhibit limited adaptability in unsupervised scenarios. To address these limitations, test-time reinforcement learning (TTRL) has been proposed, which enables self-optimization by leveraging model-generated pseudo-labels. Despite its promise, TTRL faces several key challenges, including high inference costs due to parallel rollouts and early-stage estimation bias that fosters overconfidence, reducing output diversity and causing performance plateaus. To address these challenges, we introduce an entropy-based mechanism to enhance the exploration-exploitation balance in test-time reinforcement learning through two strategies: Entropy-fork Tree Majority Rollout (ETMR) and Entropy-based Advantage Reshaping (EAR). Compared with the baseline, our approach enables Llama3.1-8B to achieve a 68 percent relative improvement in Pass at 1 metric on the AIME 2024 benchmark, while consuming only 60 percent of the rollout tokens budget. This highlights our method’s ability to effectively optimize the trade-off between inference efficiency, diversity, and estimation robustness, thereby advancing unsupervised reinforcement learning for open-domain reasoning tasks.
近年来,大型语言模型在复杂的推理任务(如数学和编程)方面取得了显著的进步。然而,这些模型仍然严重依赖于注释数据,并在无监督场景中表现出有限的适应性。为了解决这些局限性,提出了测试时间强化学习(TTRL),它能够通过利用模型生成的伪标签进行自我优化。尽管TTRL具有潜力,但它面临着几个关键挑战,包括由于并行滚动而产生的推理成本高以及早期阶段估计偏差导致的过度自信,这减少了输出多样性并导致性能高原。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种基于熵的机制,通过两种策略——熵叉树多数滚动(ETMR)和基于熵的优势重塑(EAR)——来增强测试时间强化学习中的探索-利用平衡。与基线相比,我们的方法使Llama3.1-8B在AIME 2024基准测试上的Pass at 1指标相对提高了68%,同时只消耗了60%的滚动令牌预算。这凸显了我们的方法在平衡推理效率、多样性和估计稳健性方面的优化能力,从而推动了无监督强化学习在开放域推理任务中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上的进步显著,但仍依赖标注数据,在无人监督的场景下适应性有限。为应对这些挑战,提出了测试时强化学习(TTRL)并利用模型生成的伪标签进行自我优化。然而,TTRL面临高推理成本、早期阶段估计偏差等问题。为此,我们引入基于熵的机制,通过熵叉树多数滚动和基于熵的优势重塑两种策略,提高测试时强化学习的探索与利用平衡。新方法使Llama3.1-8B在AIME 2024基准测试中Pass at 1指标相对提高68%,同时只消耗60%的滚动令牌预算。这表明我们的方法在推理效率、多样性和估计稳健性之间取得了有效平衡,推动了无监督强化学习在开放领域推理任务中的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上取得显著进步,但仍面临依赖标注数据和有限适应无人监督场景的挑战。
- 测试时强化学习(TTRL)通过模型生成的伪标签进行自我优化,但存在高推理成本和早期阶段估计偏差的问题。
- 引入基于熵的机制,以提高测试时强化学习的探索与利用平衡。
- 提出的两种策略:熵叉树多数滚动和基于熵的优势重塑,旨在解决TTRL面临的挑战。
- 新方法使Llama3.1-8B在AIME 2024基准测试中取得相对显著的改进。
- 方法在推理效率、多样性和估计稳健性之间取得了有效平衡。
点此查看论文截图

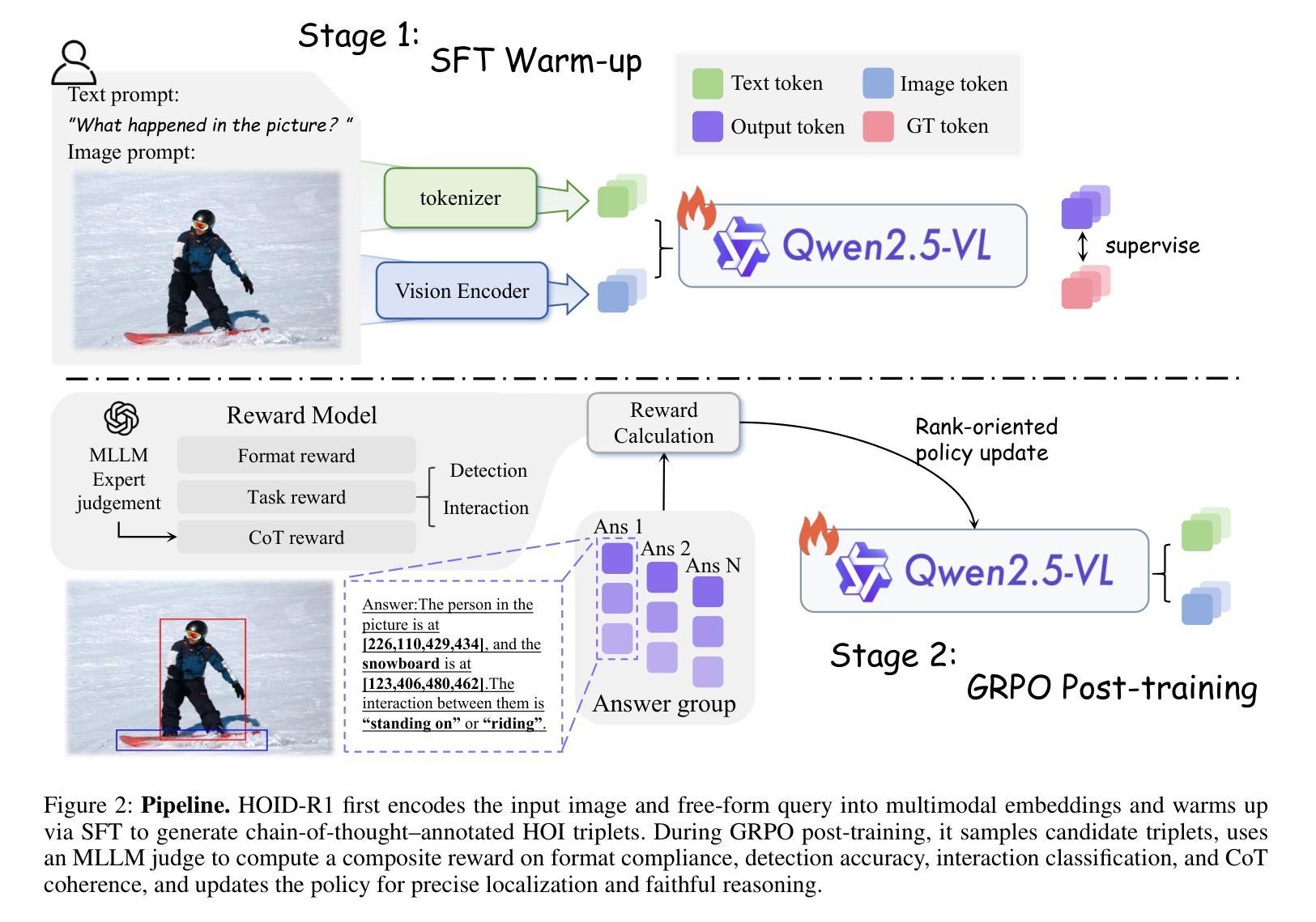
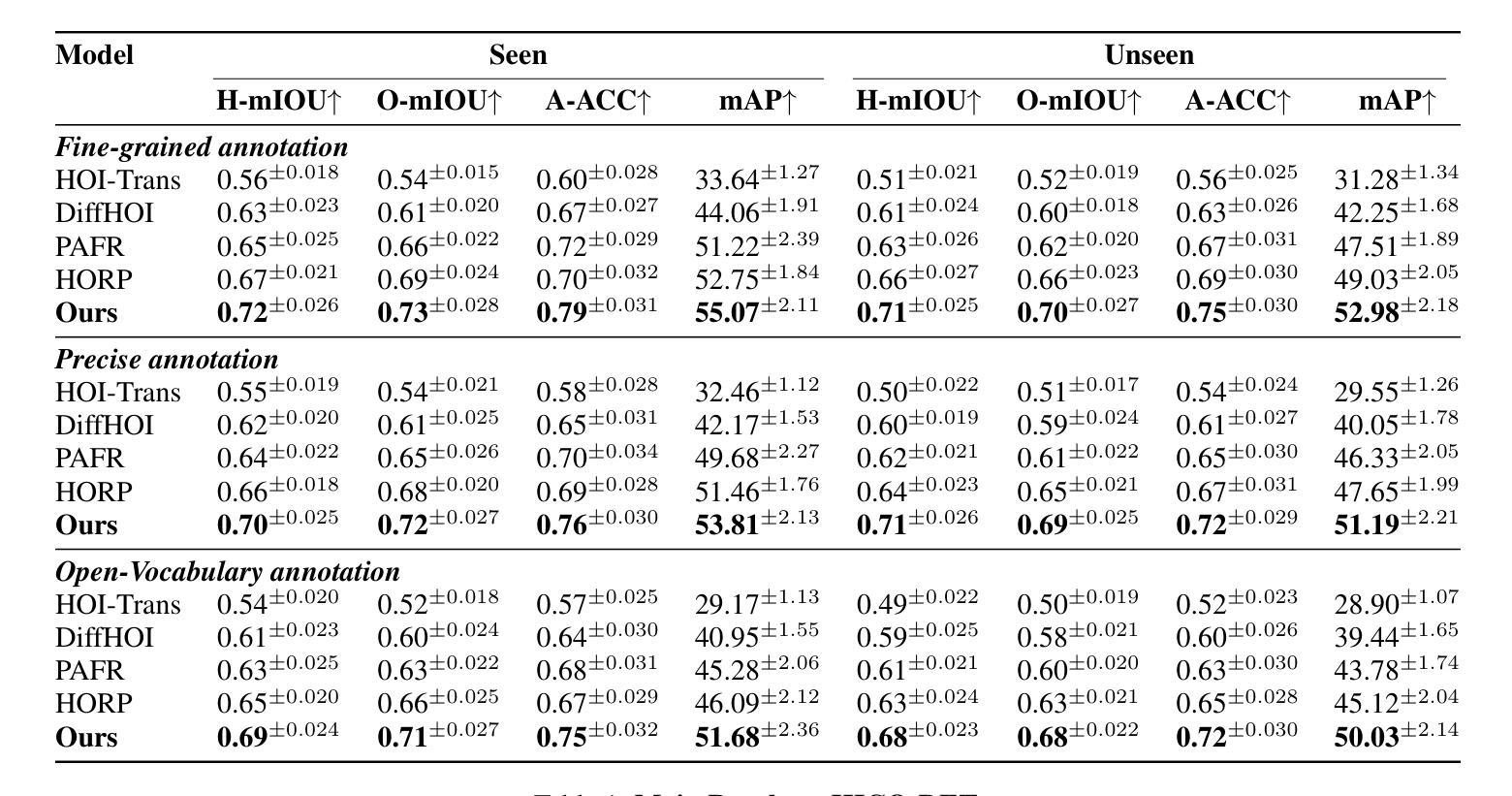
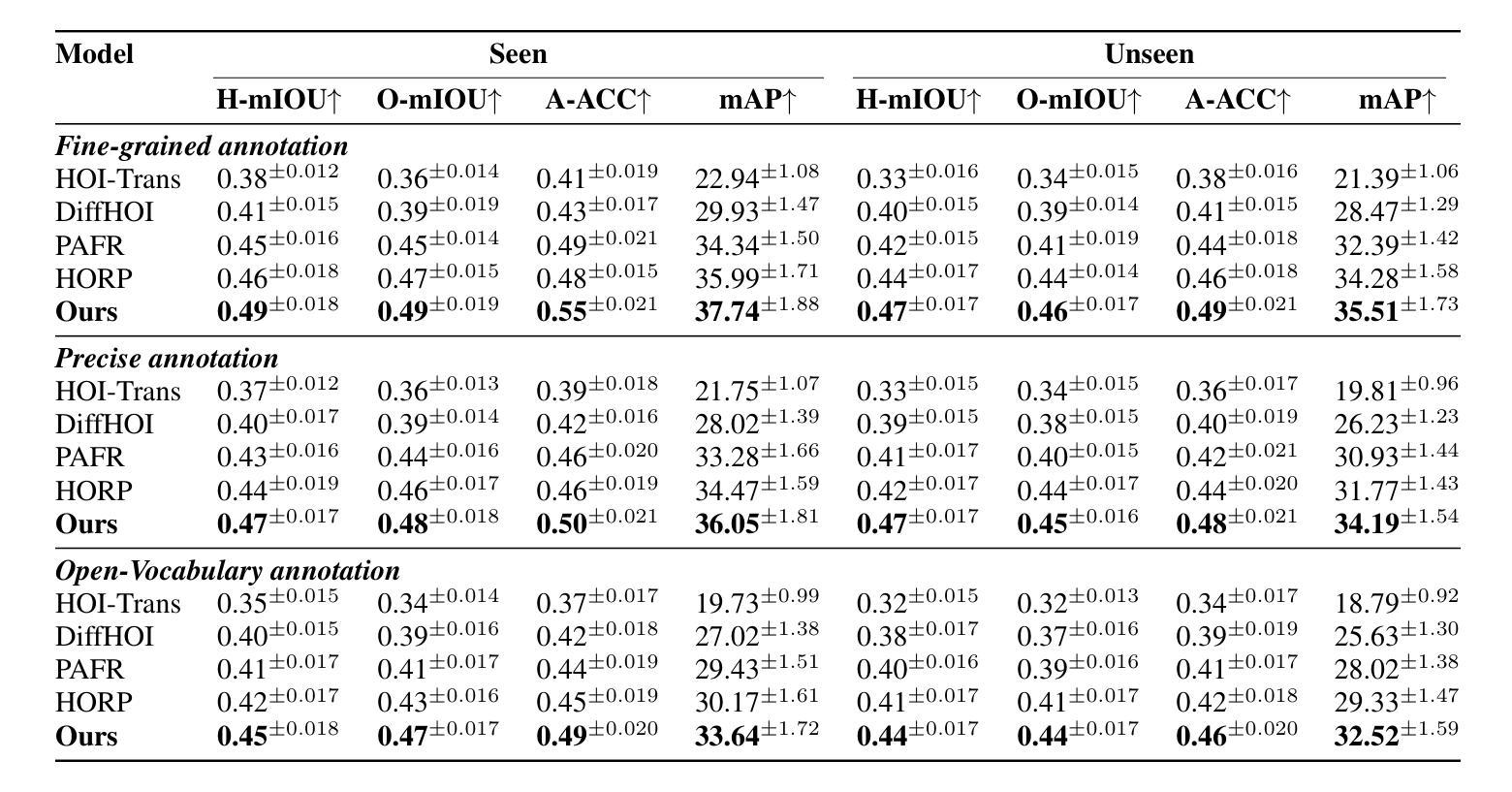
HOID-R1: Reinforcement Learning for Open-World Human-Object Interaction Detection Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Zhenhao Zhang, Hanqing Wang, Xiangyu Zeng, Ziyu Cheng, Jiaxin Liu, Haoyu Yan, Zhirui Liu, Kaiyang Ji, Tianxiang Gui, Ke Hu, Kangyi Chen, Yahao Fan, Mokai Pan
Understanding and recognizing human-object interaction (HOI) is a pivotal application in AR/VR and robotics. Recent open-vocabulary HOI detection approaches depend exclusively on large language models for richer textual prompts, neglecting their inherent 3D spatial understanding capabilities. To address this shortcoming, we introduce HOID-R1, the first HOI detection framework that integrates chain-of-thought (CoT) guided supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with group relative policy optimization (GRPO) within a reinforcement learning (RL) paradigm. Specifically, we initially apply SFT to imbue the model with essential reasoning capabilities, forcing the model to articulate its thought process in the output. Subsequently, we integrate GRPO to leverage multi-reward signals for policy optimization, thereby enhancing alignment across diverse modalities. To mitigate hallucinations in the CoT reasoning, we introduce an “MLLM-as-a-judge” mechanism that supervises the CoT outputs, further improving generalization. Extensive experiments show that HOID-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on HOI detection benchmarks and outperforms existing methods in open-world generalization to novel scenarios.
理解和识别人与物体之间的交互(HOI)是AR/VR和机器人技术中的一项重要应用。最近的开放词汇HOI检测方式完全依赖于大型语言模型来生成更丰富的文本提示,却忽视了其内在的3D空间理解能力。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了HOID-R1,这是首个将思维链引导的监督精细调整(SFT)与强化学习(RL)范式内的群组相对策略优化(GRPO)相结合的HOI检测框架。具体来说,我们最初应用SFT来赋予模型基本的推理能力,迫使模型在输出中阐述其思考过程。随后,我们整合GRPO来利用多奖励信号进行策略优化,从而增强不同模态之间的对齐。为了减轻思维链推理中的幻觉,我们引入了“MLLM作为法官”的机制来监督思维链的输出,进一步提高了模型的泛化能力。大量实验表明,HOID-R1在HOI检测基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,并在开放世界中对新场景进行泛化时超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的人机交互检测框架HOID-R1,该框架结合了链式思维引导的监督微调(SFT)、群体相对策略优化(GRPO)和强化学习(RL)方法。该框架不仅依赖大型语言模型生成丰富文本提示,还融合了模型本身的3D空间理解能力。它实现了优秀性能并改善了通用性。
Key Takeaways
- HOID-R1是首个集成链式思维引导的监督微调(SFT)和群体相对策略优化(GRPO)的人机交互检测框架。
- SFT赋予模型关键推理能力,促使模型在输出时呈现其思考过程。
- GRPO利用多奖励信号进行策略优化,提高了不同模态之间的对齐性。
- “MLLM-as-a-judge”机制用于监督链式思维推理,减少幻觉,进一步提高了模型的泛化能力。
- HOID-R1在人机交互检测基准测试中实现了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


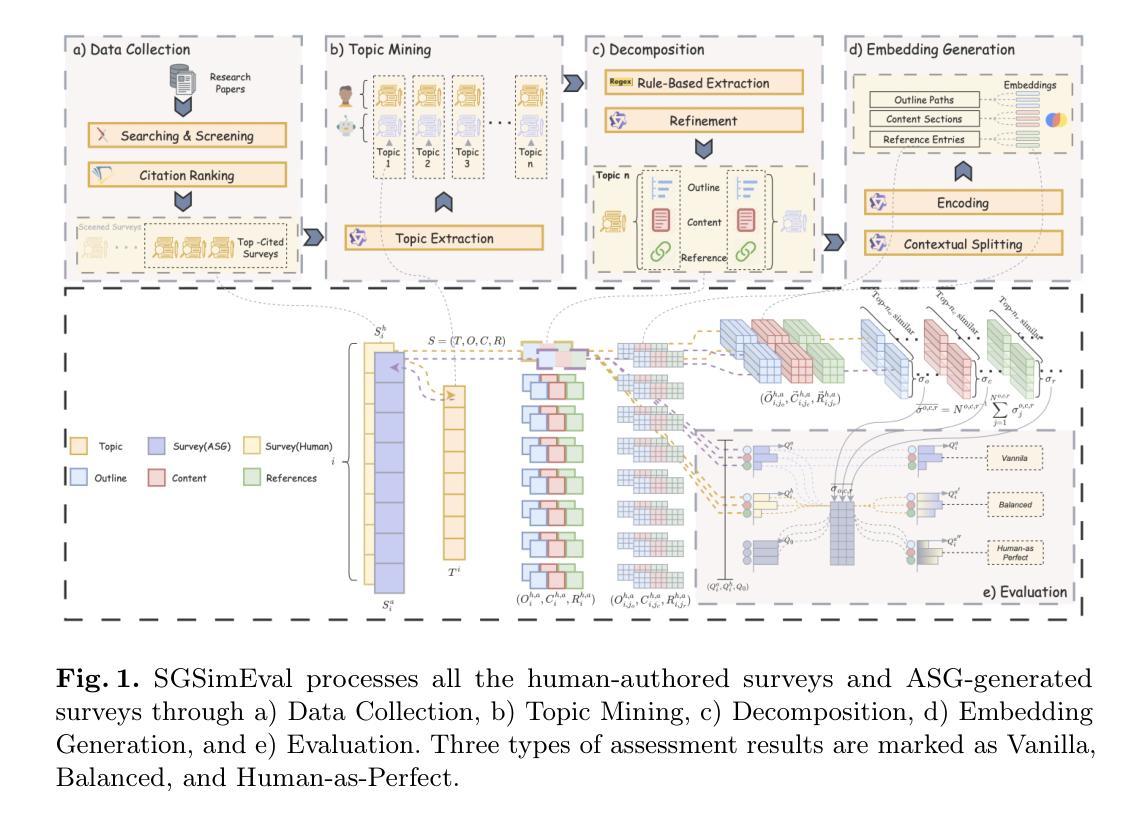
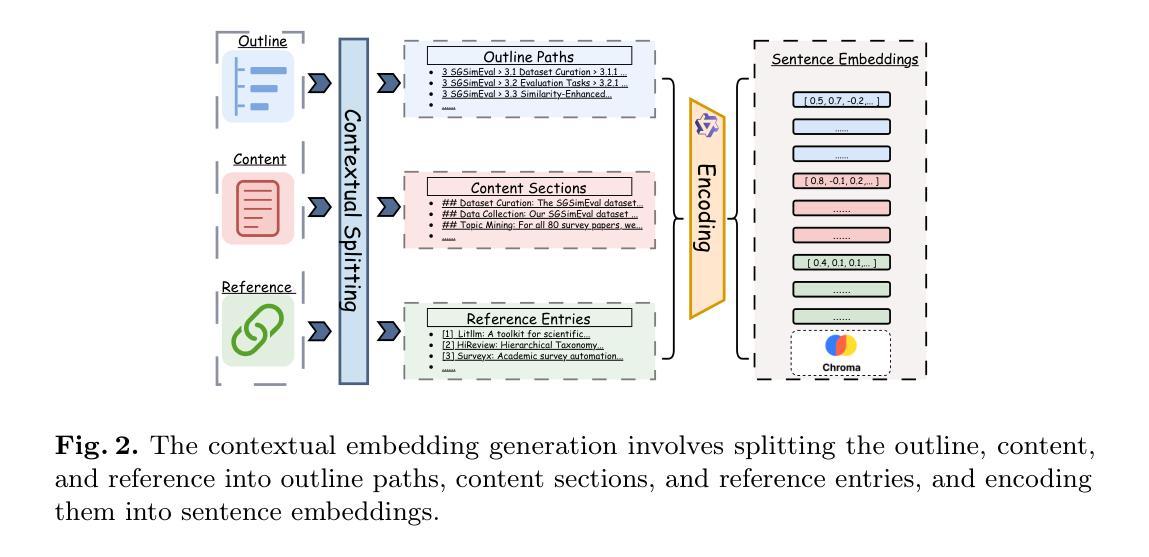
SGSimEval: A Comprehensive Multifaceted and Similarity-Enhanced Benchmark for Automatic Survey Generation Systems
Authors:Beichen Guo, Zhiyuan Wen, Yu Yang, Peng Gao, Ruosong Yang, Jiaxing Shen
The growing interest in automatic survey generation (ASG), a task that traditionally required considerable time and effort, has been spurred by recent advances in large language models (LLMs). With advancements in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and the rising popularity of multi-agent systems (MASs), synthesizing academic surveys using LLMs has become a viable approach, thereby elevating the need for robust evaluation methods in this domain. However, existing evaluation methods suffer from several limitations, including biased metrics, a lack of human preference, and an over-reliance on LLMs-as-judges. To address these challenges, we propose SGSimEval, a comprehensive benchmark for Survey Generation with Similarity-Enhanced Evaluation that evaluates automatic survey generation systems by integrating assessments of the outline, content, and references, and also combines LLM-based scoring with quantitative metrics to provide a multifaceted evaluation framework. In SGSimEval, we also introduce human preference metrics that emphasize both inherent quality and similarity to humans. Extensive experiments reveal that current ASG systems demonstrate human-comparable superiority in outline generation, while showing significant room for improvement in content and reference generation, and our evaluation metrics maintain strong consistency with human assessments.
对于自动生成调查(ASG)这一传统上需要大量时间和精力的任务,日益增长的兴趣得益于大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展。随着检索增强生成(RAG)的兴起和多智能体系统(MAS)的普及,使用LLM合成学术调查已成为一种可行的方法,从而提高了对此领域稳健评估方法的需求。然而,现有的评估方法存在诸多局限性,包括指标偏见、缺乏人类偏好以及过度依赖LLM作为评判标准等。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SGSimEval,这是一个结合了相似性增强评估的综合调查生成基准,它通过评估大纲、内容和参考来评估自动调查生成系统,并将LLM评分与定量指标相结合,提供了一个多方面的评估框架。在SGSimEval中,我们还引入了人类偏好指标,强调内在质量和与人类相似度的重要性。大量实验表明,当前ASG系统在生成大纲方面展现了与人类相当的优势,而在内容和参考生成方面仍大有提升空间,我们的评估指标与人类评估结果保持高度一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to The 21st International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications (ADMA2025)
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的不断发展以及检索增强生成(RAG)技术的兴起和多智能体系统(MASs)的普及,自动摘要生成(ASG)任务逐渐受到关注。然而,当前评估方法存在诸多局限性。为此,我们提出SGSimEval,一个集成了轮廓、内容和参考评估的自动摘要生成综合基准测试。SGSimEval结合LLM评分和定量指标,提供了一个多元化的评估框架,并引入人类偏好指标,强调内在质量和与人类的相似性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的进步推动了自动摘要生成(ASG)的发展。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)和多智能体系统(MASs)的普及使得使用LLMs合成学术摘要成为可能。
- 现有的评估方法存在局限性,如偏置指标、缺乏人类偏好和对LLMs作为判断标准的过度依赖。
- SGSimEval是一个综合基准测试,旨在评估自动摘要生成系统,包括轮廓、内容和参考评估。
- SGSimEval结合了LLM评分和定量指标,提供了一个多元化的评估框架。
- SGSimEval引入的人类偏好指标强调内在质量和与人类的相似性。
点此查看论文截图

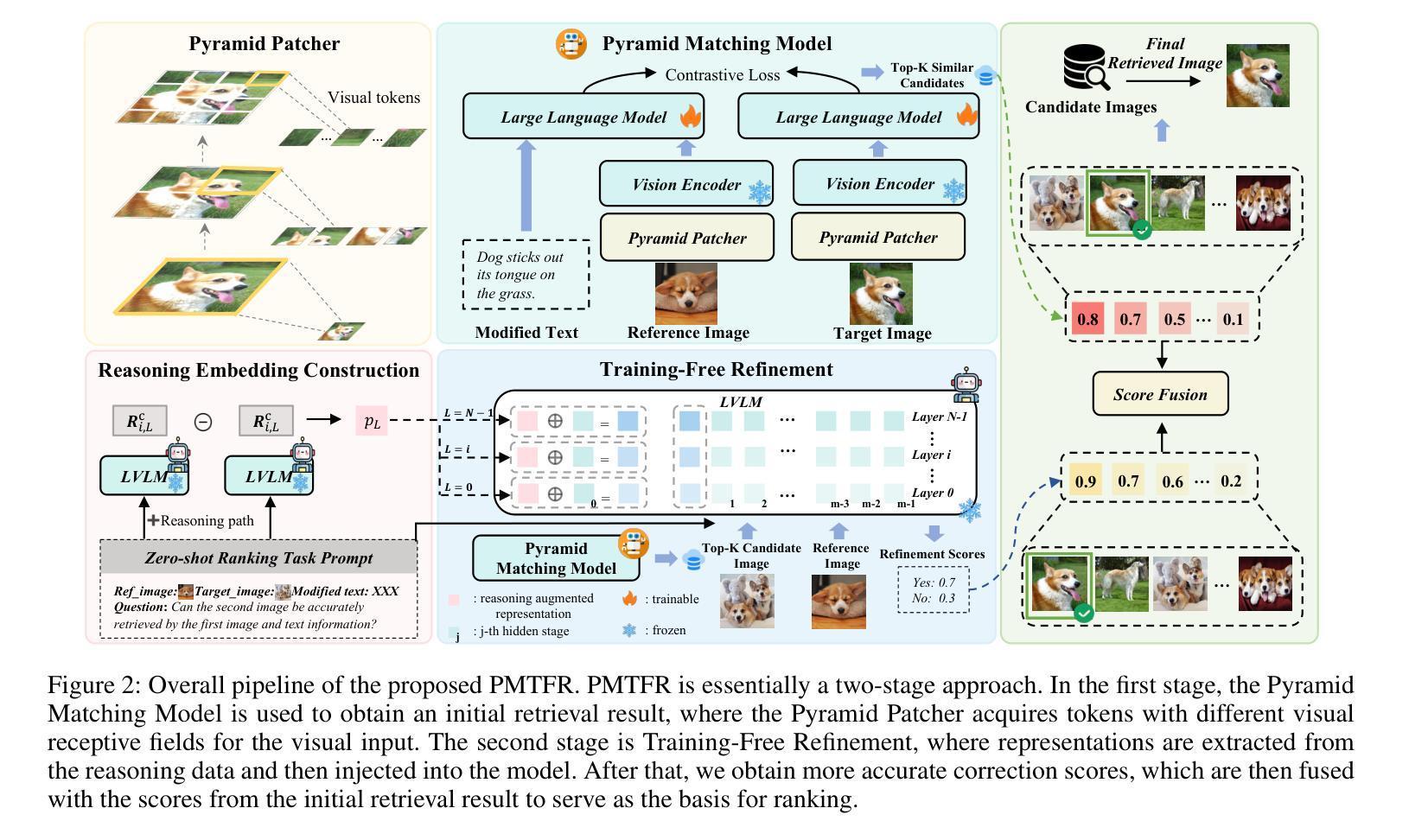
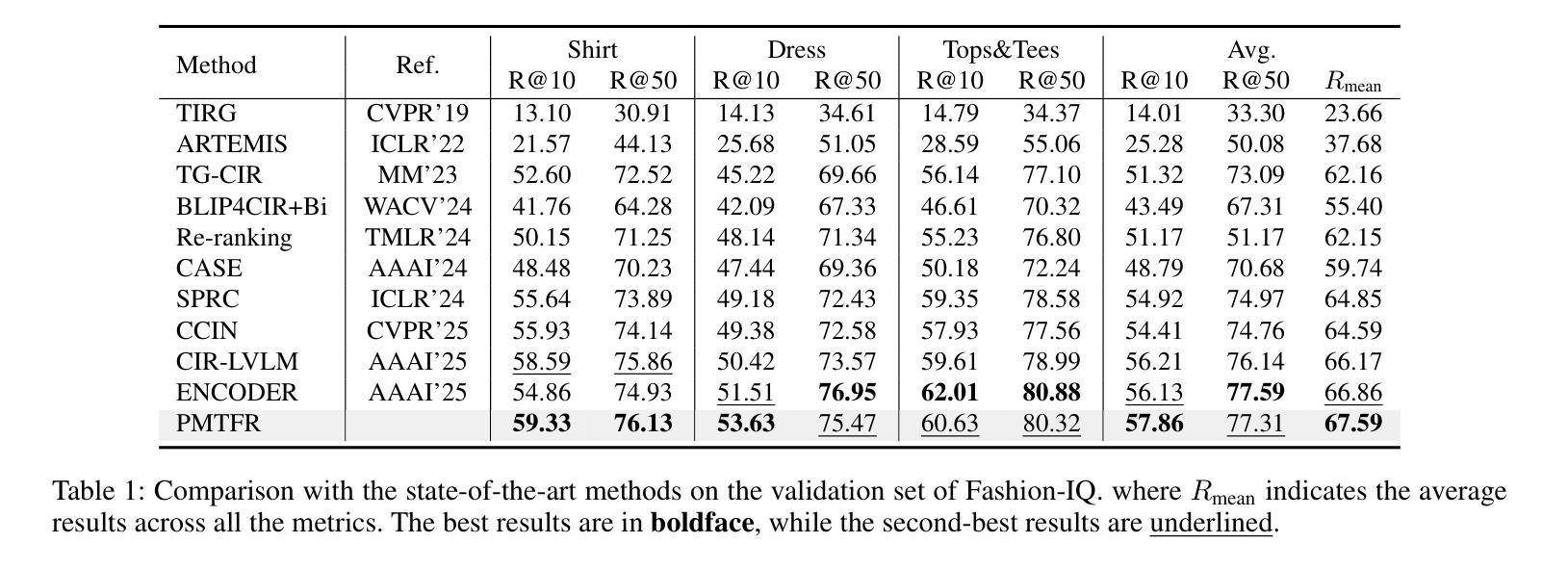
Enhancing Supervised Composed Image Retrieval via Reasoning-Augmented Representation Engineering
Authors:Jun Li, Kai Li, Shaoguo Liu, Tingting Gao
Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) presents a significant challenge as it requires jointly understanding a reference image and a modified textual instruction to find relevant target images. Some existing methods attempt to use a two-stage approach to further refine retrieval results. However, this often requires additional training of a ranking model. Despite the success of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) techniques in reducing training costs for language models, their application in CIR tasks remains limited – compressing visual information into text or relying on elaborate prompt designs. Besides, existing works only utilize it for zero-shot CIR, as it is challenging to achieve satisfactory results in supervised CIR with a well-trained model. In this work, we proposed a framework that includes the Pyramid Matching Model with Training-Free Refinement (PMTFR) to address these challenges. Through a simple but effective module called Pyramid Patcher, we enhanced the Pyramid Matching Model’s understanding of visual information at different granularities. Inspired by representation engineering, we extracted representations from COT data and injected them into the LVLMs. This approach allowed us to obtain refined retrieval scores in the Training-Free Refinement paradigm without relying on explicit textual reasoning, further enhancing performance. Extensive experiments on CIR benchmarks demonstrate that PMTFR surpasses state-of-the-art methods in supervised CIR tasks. The code will be made public.
图像检索(CIR)技术面临着一个重大挑战,因为它需要同时理解参考图像和修改后的文本指令来找到相关的目标图像。一些现有的方法试图采用两阶段方法来进一步改进检索结果。然而,这通常需要额外训练排序模型。尽管链式思维(CoT)技术在降低语言模型训练成本方面取得了成功,但它们在CIR任务中的应用仍然有限——需要压缩视觉信息为文本或依赖于复杂的提示设计。此外,现有工作仅将其用于零样本图像检索(Zero-Shot CIR),因为在有监督的图像检索(Supervised CIR)任务中使用经过良好训练的模型实现满意结果具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个包括金字塔匹配模型与免训练优化(PMTFR)的框架来解决这些挑战。通过一个简单有效的模块——金字塔补丁程序(Pyramid Patcher),我们增强了金字塔匹配模型对不同粒度视觉信息的理解。受表示工程的启发,我们从CoT数据中提取表示并将其注入大型语言模型(LVLMs)。这种方法使我们能够在免训练优化范式中获得精细的检索分数,无需依赖明确的文本推理,从而进一步提高了性能。在CIR基准测试上的大量实验表明,PMTFR在监督图像检索任务中超过了最先进的方法。代码将公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本描述了Composed Image Retrieval(CIR)的挑战性,并介绍了为解决这一挑战而提出的Pyramid Matching Model with Training-Free Refinement(PMTFR)框架。该框架通过Pyramid Patcher模块增强了对不同粒度视觉信息的理解,从Chain-of-Thought(CoT)数据中提取表示并注入到模型中,从而获得更精确的检索分数,且不需要依靠明确的文本推理。该框架在CIR任务上的性能优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- CIR需要同时理解参考图像和修改后的文本指令以找到相关的目标图像,构成一项重大挑战。
- 现有方法尝试使用两阶段方法来进一步改进检索结果,但这通常需要额外训练排名模型。
- Chain-of-Thought(CoT)技术在降低语言模型训练成本方面取得了成功,但在CIR任务中的应用仍然有限。
- PMTFR框架通过Pyramid Patcher模块增强了对不同粒度视觉信息的理解,并从CoT数据中提取表示注入到模型中。
- 该方法允许在没有依靠明确的文本推理的情况下获得更精确的检索分数。
- PMTFR框架在CIR基准测试上的性能优于现有技术,特别是在监督CIR任务中。
点此查看论文截图

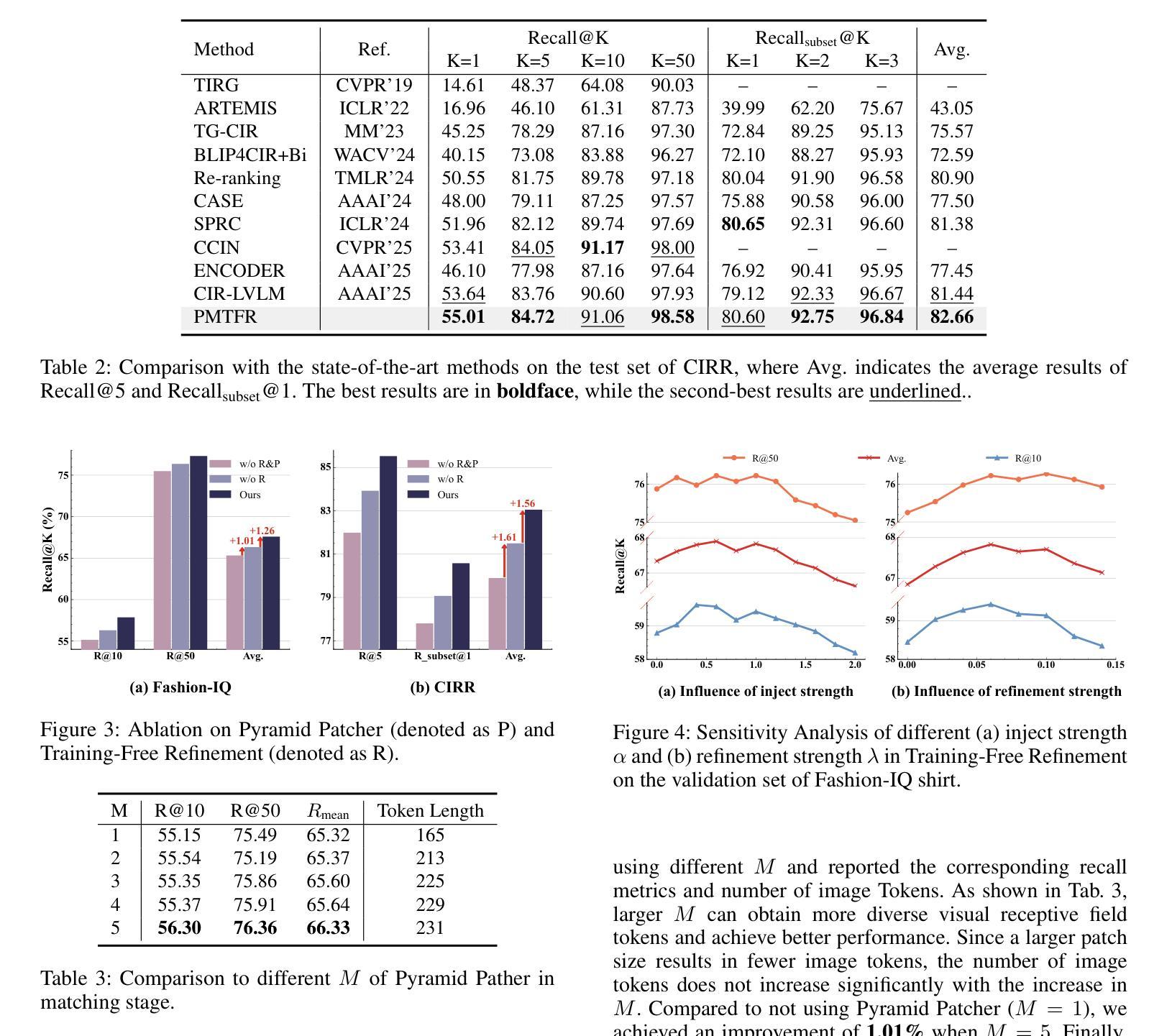
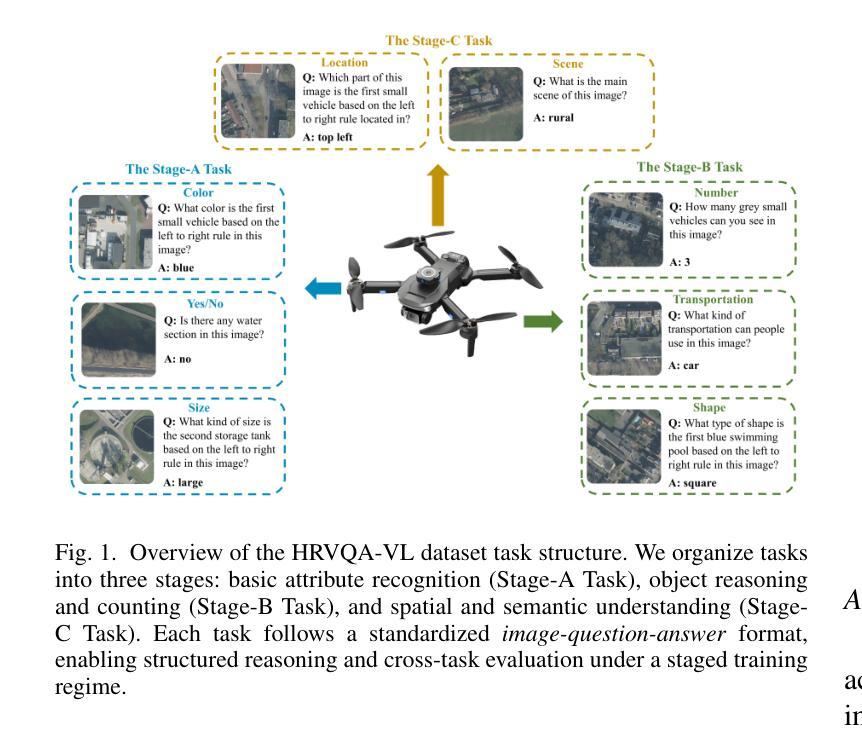
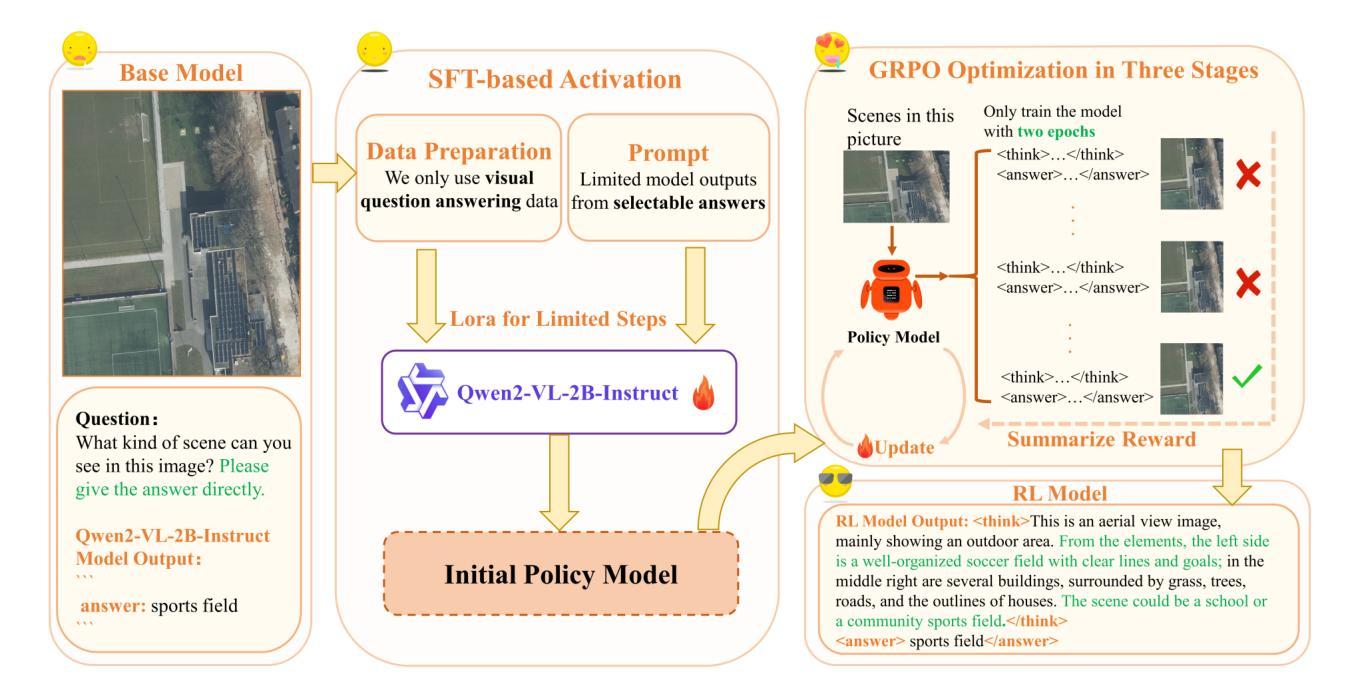
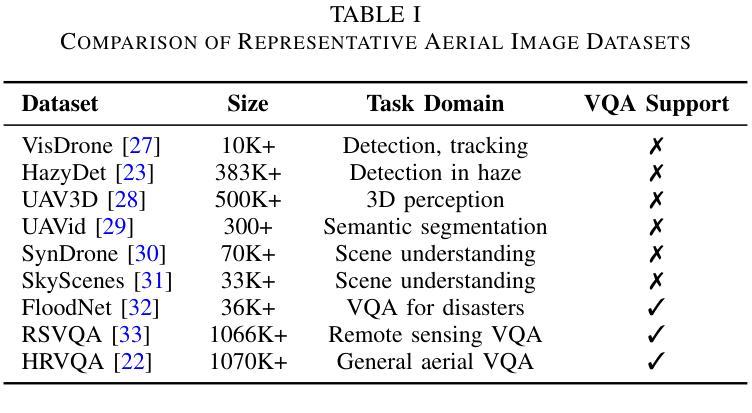
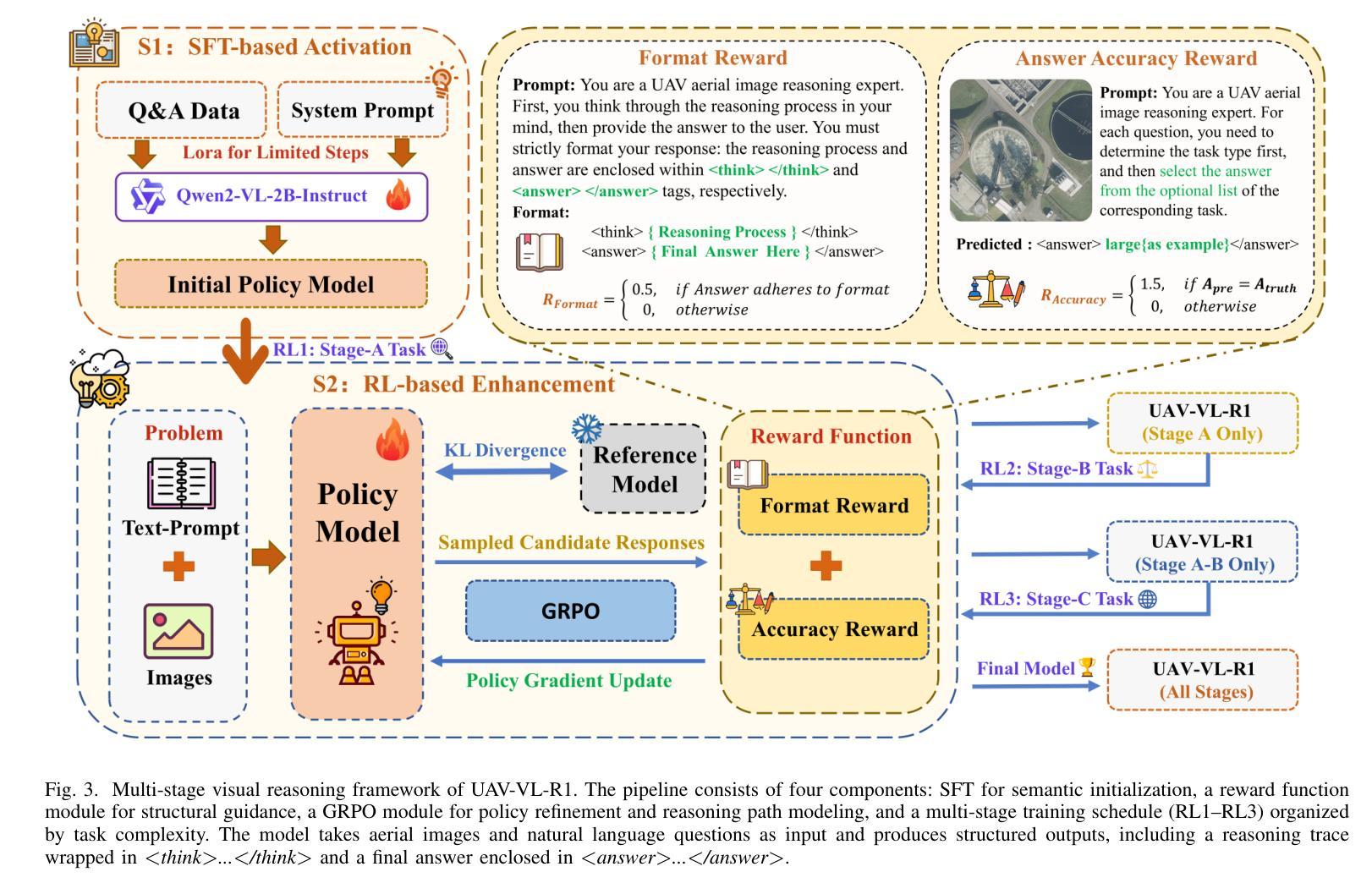
UAV-VL-R1: Generalizing Vision-Language Models via Supervised Fine-Tuning and Multi-Stage GRPO for UAV Visual Reasoning
Authors:Jiajin Guan, Haibo Mei, Bonan Zhang, Dan Liu, Yuanshuang Fu, Yue Zhang
Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated strong generalization in natural image tasks. However, their performance often degrades on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based aerial imagery, which features high resolution, complex spatial semantics, and strict real-time constraints. These challenges limit the applicability of general-purpose VLMs to structured aerial reasoning tasks. To address these challenges, we propose UAV-VL-R1, a lightweight VLM explicitly designed for aerial visual reasoning. It is trained using a hybrid method that combines supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and multi-stage reinforcement learning (RL). We leverage the group relative policy optimization (GRPO) algorithm to promote structured and interpretable reasoning through rule-guided rewards and intra-group policy alignment. To support model training and evaluation, we introduce a high-resolution visual question answering dataset named HRVQA-VL, which consists of 50,019 annotated samples covering eight UAV-relevant reasoning tasks, including object counting, transportation recognition, and spatial scene inference. Experimental results show that UAV-VL-R1 achieves a 48.17% higher zero-shot accuracy than the Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct baseline and even outperforms its 72B-scale variant, which is 36x larger, on multiple tasks. Ablation studies reveal that while SFT improves semantic alignment, it may reduce reasoning diversity in mathematical tasks. GRPO-based RL compensates for this limitation by enhancing logical flexibility and the robustness of inference. Additionally, UAV-VL-R1 requires only 3.9GB of memory under FP16 inference and can be quantized to 2.5GB with INT8, supporting real-time deployment on resource-constrained UAV platforms.
最近,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进步在自然图像任务中显示出强大的泛化能力。然而,它们在基于无人机的航空图像上的性能往往会下降,这些图像具有分辨率高、空间语义复杂和实时约束严格等特点。这些挑战限制了通用VLMs在结构化航空推理任务中的应用。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了UAV-VL-R1,这是一个专为航空视觉推理设计的轻量级VLM。它采用混合方法训练,结合了监督微调(SFT)和多阶段强化学习(RL)。我们利用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法,通过规则引导的奖励和组内策略对齐,促进结构化和可解释性的推理。为了支持模型的训练和评估,我们引入了一个高分辨率视觉问答数据集HRVQA-VL,它包含50,019个注释样本,涵盖八个与无人机相关的推理任务,包括目标计数、交通识别以及空间场景推断等。实验结果表明,UAV-VL-R1的零样本准确率比Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct基线高出48.17%,并且在多个任务上甚至超越了其72B规模的变体。消融研究表明,虽然SFT提高了语义对齐性,但它可能会减少数学任务中的推理多样性。基于GRPO的RL弥补了这一局限性,通过提高逻辑灵活性和推理的稳健性来补偿。此外,UAV-VL-R1在FP16推理下只需3.9GB的内存,可以使用INT8进行量化至2.5GB,支持在资源受限的无人机平台上进行实时部署。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对无人机(UAV)基于空中视觉的任务挑战,提出一种为空中视觉推理设计的轻量级视觉语言模型UAV-VL-R1。该模型结合监督微调(SFT)和多阶段强化学习(RL)进行训练,并利用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法促进结构化、可解释的推理。为支持模型训练与评估,引入了高分辨率视觉问答数据集HRVQA-VL。实验结果显示,UAV-VL-R1在多个任务上的表现优于基准模型,甚至超越了规模更大的模型。强化学习补偿了语义对齐中的推理多样性损失,增强了逻辑灵活性和推理稳健性。此外,UAV-VL-R1在FP16推理下仅需3.9GB内存,可量化至2.5GB的INT8,适合在资源受限的UAV平台上实时部署。
关键见解
- 通用视觉语言模型在处理无人机空中图像时性能下降,因为这些模型难以处理高空图像的复杂空间语义和实时约束。
- 提出了一种针对空中视觉推理任务的轻量级视觉语言模型UAV-VL-R1。
- 结合监督微调(SFT)和多阶段强化学习(RL)进行训练,以提高模型的性能。
- 利用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法促进结构化、可解释的推理过程。
- 引入HRVQA-VL数据集用于模型训练和评估,涵盖多种无人机相关推理任务。
- 实验结果显示UAV-VL-R1在多个任务上表现优异,特别是在零样本准确率上显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

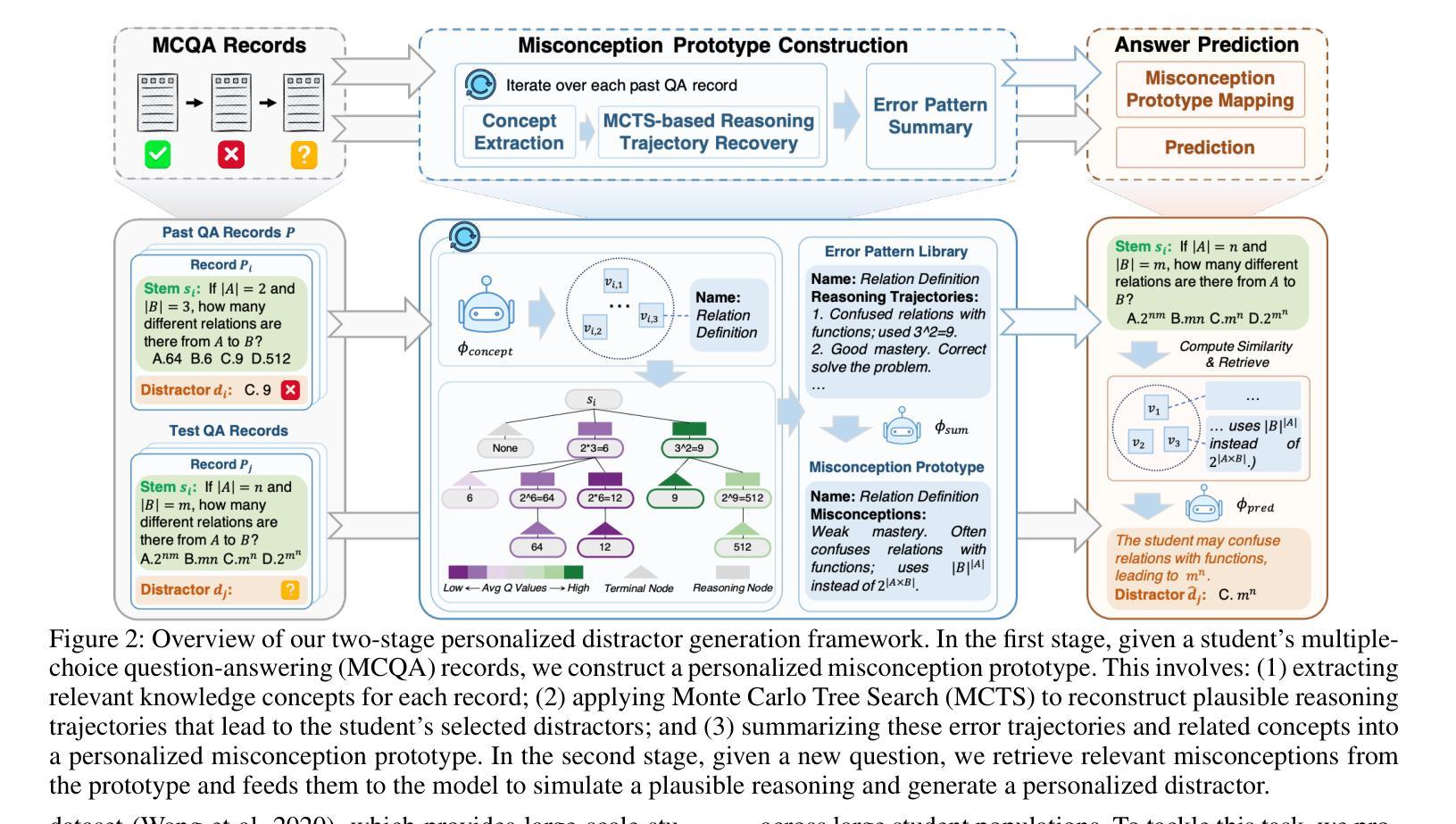
Personalized Distractor Generation via MCTS-Guided Reasoning Reconstruction
Authors:Tao Wu, Jingyuan Chen, Wang Lin, Jian Zhan, Mengze Li, Kun Kuang, Fei Wu
Distractors, incorrect but plausible answer choices in multiple-choice questions (MCQs), play a critical role in educational assessment by diagnosing student misconceptions. Recent work has leveraged large language models (LLMs) to generate shared, group-level distractors by learning common error patterns across large student populations. However, such distractors often fail to capture the diverse reasoning errors of individual students, limiting their diagnostic effectiveness. To address this limitation, we introduce the task of personalized distractor generation, which aims to generate tailored distractors based on individual misconceptions inferred from each student’s past question-answering (QA) records, ensuring every student receives options that effectively exposes their specific reasoning errors. While promising, this task is challenging because each student typically has only a few QA records, which often lack the student’s underlying reasoning processes, making training-based group-level approaches infeasible. To overcome this, we propose a training-free two-stage framework. In the first stage, we construct a student-specific misconception prototype by applying Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to recover the student’s reasoning trajectories from past incorrect answers. In the second stage, this prototype guides the simulation of the student’s reasoning on new questions, enabling the generation of personalized distractors that align with the student’s recurring misconceptions. Experiments show that our approach achieves the best performance in generating plausible, personalized distractors for 140 students, and also effectively generalizes to group-level settings, highlighting its robustness and adaptability.
干扰项在多选题(MCQs)中扮演着诊断学生误解的重要角色,这些选项虽然不正确但具有迷惑性。最近的研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)通过在大规模学生群体中识别常见的错误模式来生成共享的团队级别的干扰项。然而,这种干扰项往往无法捕捉到个体学生的多样化推理错误,从而限制了其诊断的有效性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了个性化干扰项生成任务。该任务旨在根据从每个学生过去的问答记录中推断出的个人误解来生成针对性的干扰项,确保每个学生获得的选项能有效地暴露他们的特定推理错误。尽管前景广阔,但这个任务很有挑战性,因为每个学生通常只有几个问答记录,而且往往缺乏学生潜在的思考过程,使得基于训练的模式群体层面的方法变得不可行。为了克服这一难题,我们提出了一个无需训练的两阶段框架。在第一阶段,我们通过应用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)来恢复学生过去的错误答案中的推理轨迹,从而构建学生特定的误解原型。在第二阶段,这个原型指导学生在新问题上的思考模拟,使个性化干扰项的生成与学生的反复误解保持一致。实验表明,我们的方法在生成针对140名学生的合理个性化干扰项方面取得了最佳性能,并且能够有效地推广到群体级别设置,凸显了其稳健性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了在教育评估中利用个性化干扰项生成技术来诊断学生误解的重要性。针对群体生成的干扰项无法捕捉个体学生多样化推理错误的问题,提出了个性化干扰项生成任务。此任务旨在基于每个学生过去的答题记录中推断出的个人误解来生成定制化的干扰项,以确保每个学生遇到的选项能够有效暴露其特定的推理错误。针对每个学生仅有几份答题记录、缺乏学生底层推理过程的问题,提出了一个无需训练的两阶段框架。第一阶段应用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)从过去的不正确答案中恢复学生的推理轨迹,构建学生特定的误解原型。在第二阶段,该原型模拟学生在新问题上的推理,生成与学生反复出现的误解相符的个性化干扰项。实验表明,该方法在生成针对140名学生的合理个性化干扰项方面表现最佳,并能有效地适应群体级别设置,凸显了其稳健性和适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 干扰项在教育评估中起着诊断学生误解的重要作用。
- 群体生成的干扰项无法捕捉个体学生的多样化推理错误,需要个性化干扰项生成。
- 个性化干扰项生成任务旨在基于学生的个人误解生成定制化的干扰项。
- 学生仅有几份答题记录,缺乏底层推理过程,使得训练基于群体的方法不可行。
- 提出了一个无需训练的两阶段框架来生成个性化干扰项,包括构建学生特定的误解原型和模拟学生在新问题上的推理。
- 实验表明该方法在生成个性化干扰项方面表现最佳,并能够有效适应群体级别设置。
点此查看论文截图

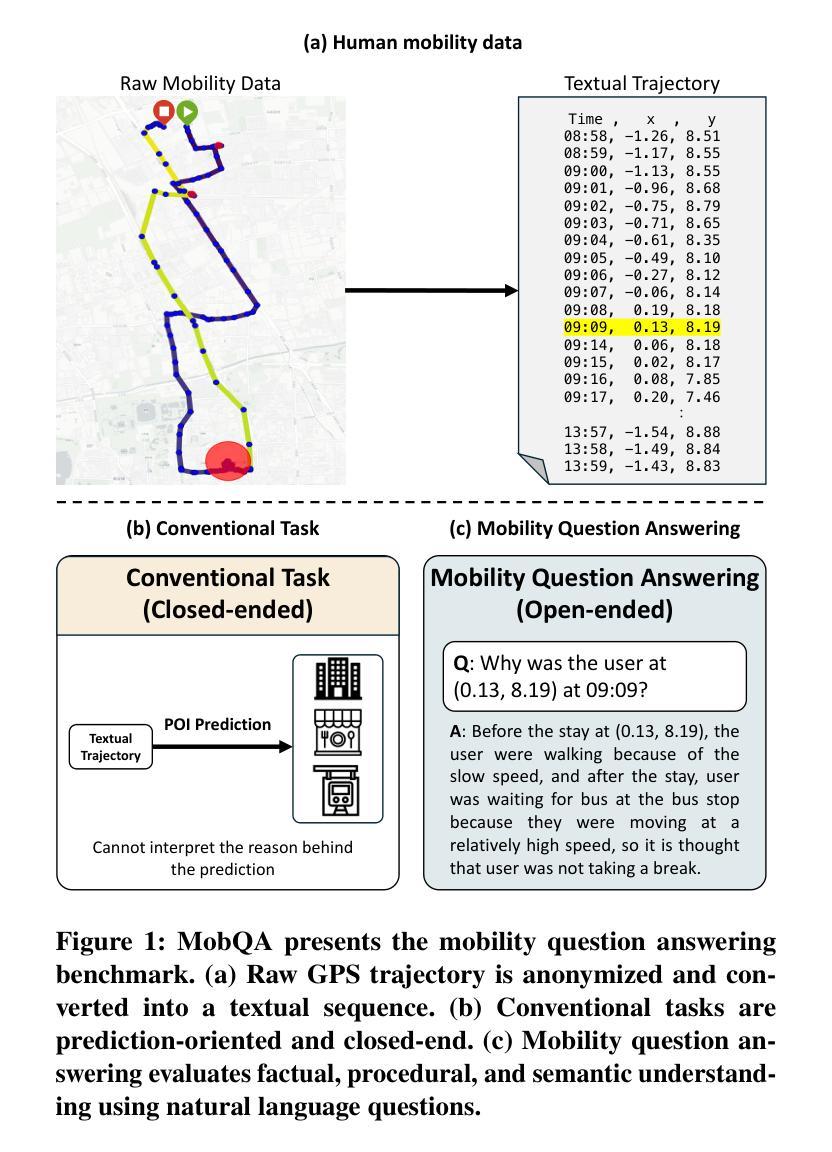
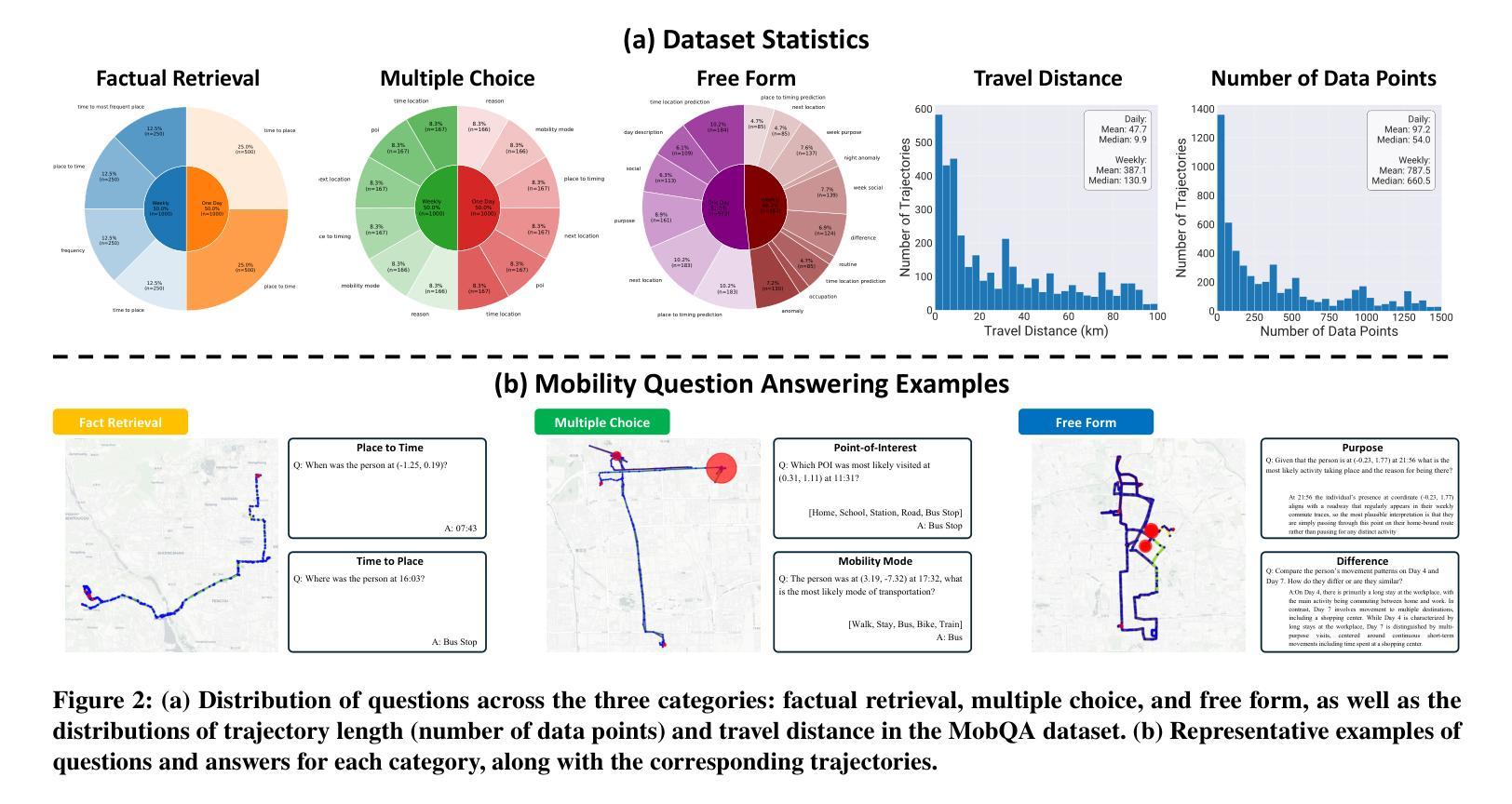
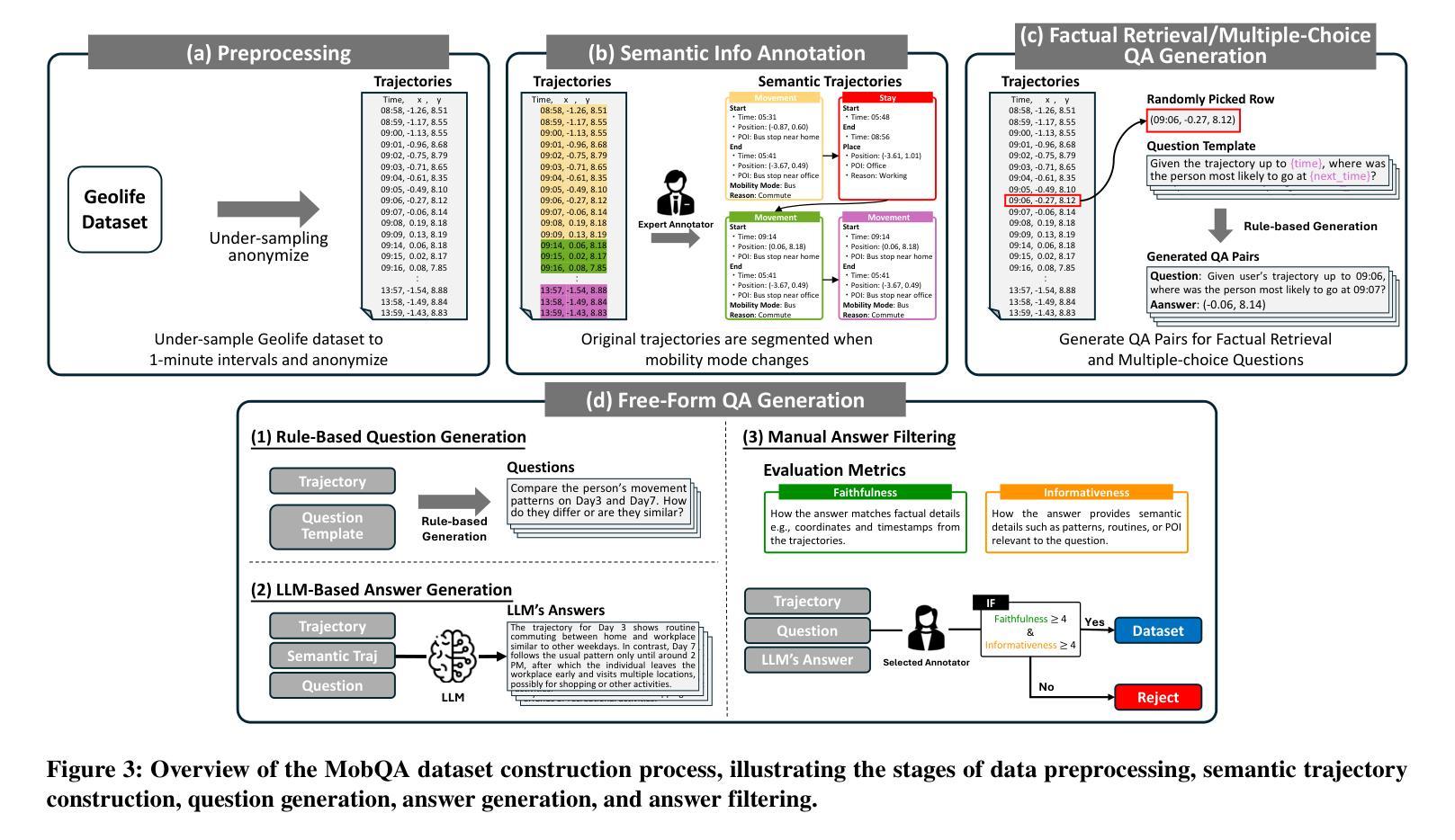
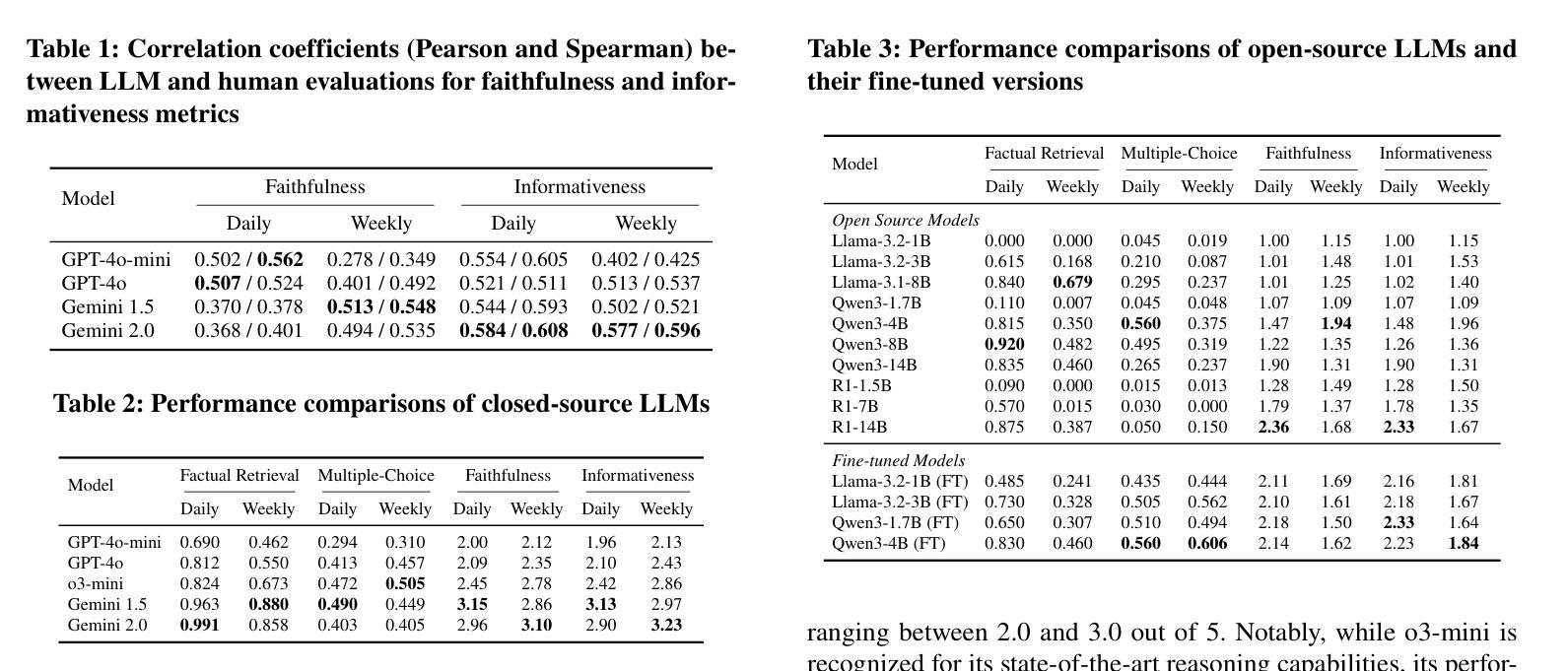
MobQA: A Benchmark Dataset for Semantic Understanding of Human Mobility Data through Question Answering
Authors:Hikaru Asano, Hiroki Ouchi, Akira Kasuga, Ryo Yonetani
This paper presents MobQA, a benchmark dataset designed to evaluate the semantic understanding capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for human mobility data through natural language question answering. While existing models excel at predicting human movement patterns, it remains unobvious how much they can interpret the underlying reasons or semantic meaning of those patterns. MobQA provides a comprehensive evaluation framework for LLMs to answer questions about diverse human GPS trajectories spanning daily to weekly granularities. It comprises 5,800 high-quality question-answer pairs across three complementary question types: factual retrieval (precise data extraction), multiple-choice reasoning (semantic inference), and free-form explanation (interpretive description), which all require spatial, temporal, and semantic reasoning. Our evaluation of major LLMs reveals strong performance on factual retrieval but significant limitations in semantic reasoning and explanation question answering, with trajectory length substantially impacting model effectiveness. These findings demonstrate the achievements and limitations of state-of-the-art LLMs for semantic mobility understanding.\footnote{MobQA dataset is available at https://github.com/CyberAgentAILab/mobqa.}
本文介绍了MobQA,这是一个为了评估大型语言模型(LLM)通过自然语言问答对人类移动数据的语义理解能力而设计的基准数据集。虽然现有模型在预测人类移动模式方面表现出色,但它们能否解释这些模式背后的原因或语义含义仍不明显。MobQA为LLM提供了一个全面的评估框架,用于回答关于日常到每周粒度的不一样的GPS轨迹人类数据问题。它包含三种补充问题类型共计5800个高质量的问题答案对:事实检索(精确数据提取)、多选推理(语义推断)和自由形式解释(解释性描述),所有这些都需要空间、时间和语义推理。我们对主要LLM的评估显示,它们在事实检索方面的表现强劲,但在语义推理和解释问题回答方面存在显著局限性,轨迹长度对模型的有效性有重要影响。这些发现展示了最新LLM在语义移动理解方面的成就和局限性。MobQa数据集可在https://github.com/CyberAgentAILab/mobqa获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文介绍了MobQA数据集,该数据集旨在评估大型语言模型对人类移动性数据的语义理解能力,通过自然语言问答的形式进行。现有模型虽能预测人类移动模式,但对其背后的原因或语义意义的解读能力尚待验证。MobQA为LLMs提供了一个全面的评估框架,回答关于日常到每周粒度的人类GPS轨迹的各种问题。包含5800个高质量的问题答案对,涵盖三种互补性问题类型:事实检索、多项选择推理和自由形式解释,这些都需要空间、时间和语义推理。对主要LLMs的评估显示,它们在事实检索方面表现良好,但在语义推理和解释问题回答方面存在显著局限,轨迹长度对模型效果有实质影响。
Key Takeaways
- MobQA是一个用于评估大型语言模型(LLMs)对人类移动性数据语义理解能力的数据集。
- 数据集通过自然语言问答的形式设计,旨在测试LLMs对GPS轨迹的语义理解能力。
- MobQA包含三种互补性问题类型:事实检索、多项选择推理和自由形式解释。
- 现有模型在预测人类移动模式方面表现出色,但在解读移动背后的语义意义方面存在局限。
- LLMs在事实检索方面表现良好,但在语义推理和解释问题回答方面存在显著局限。
- 轨迹长度对LLMs模型的效果有实质影响。
点此查看论文截图

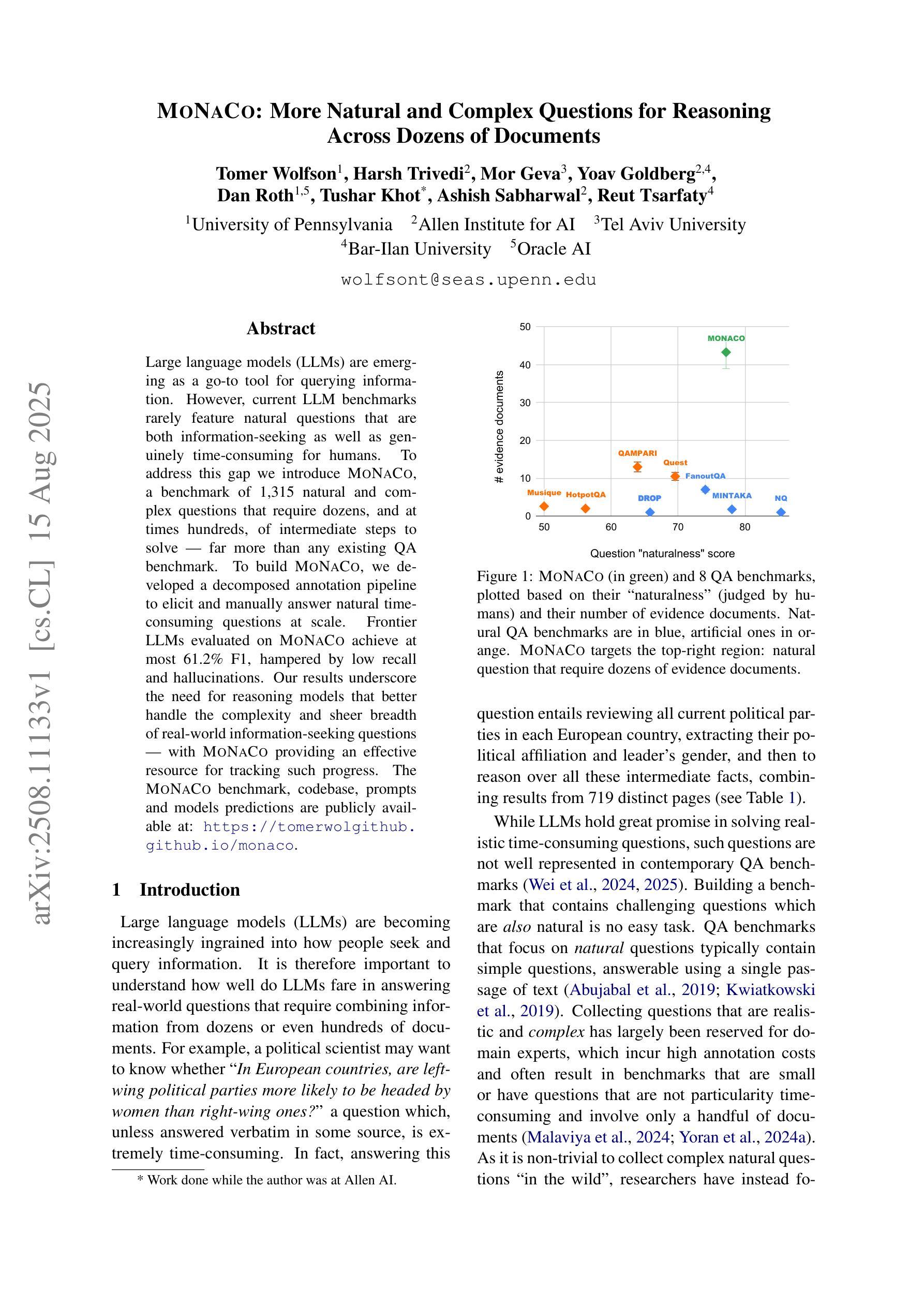
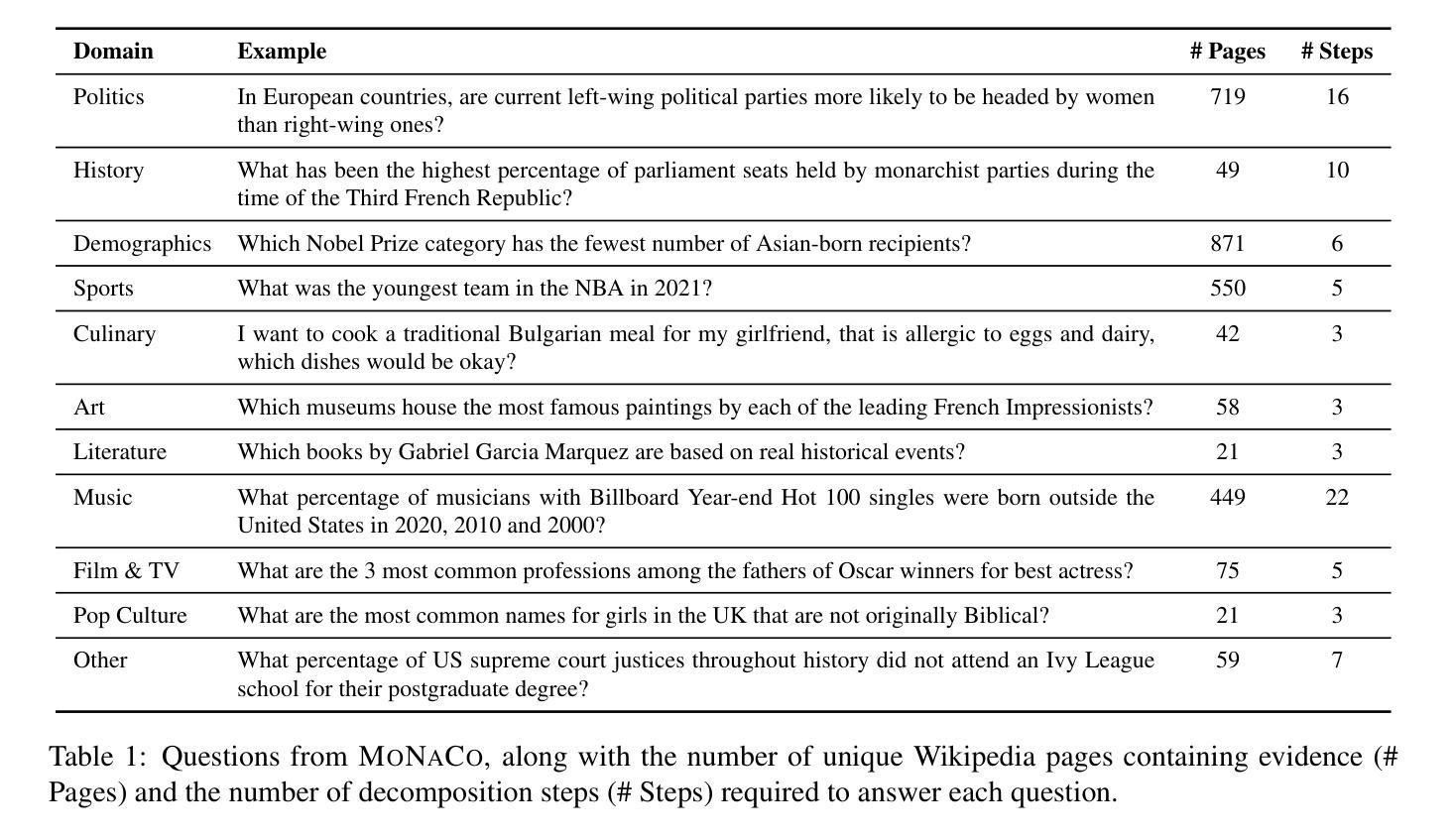
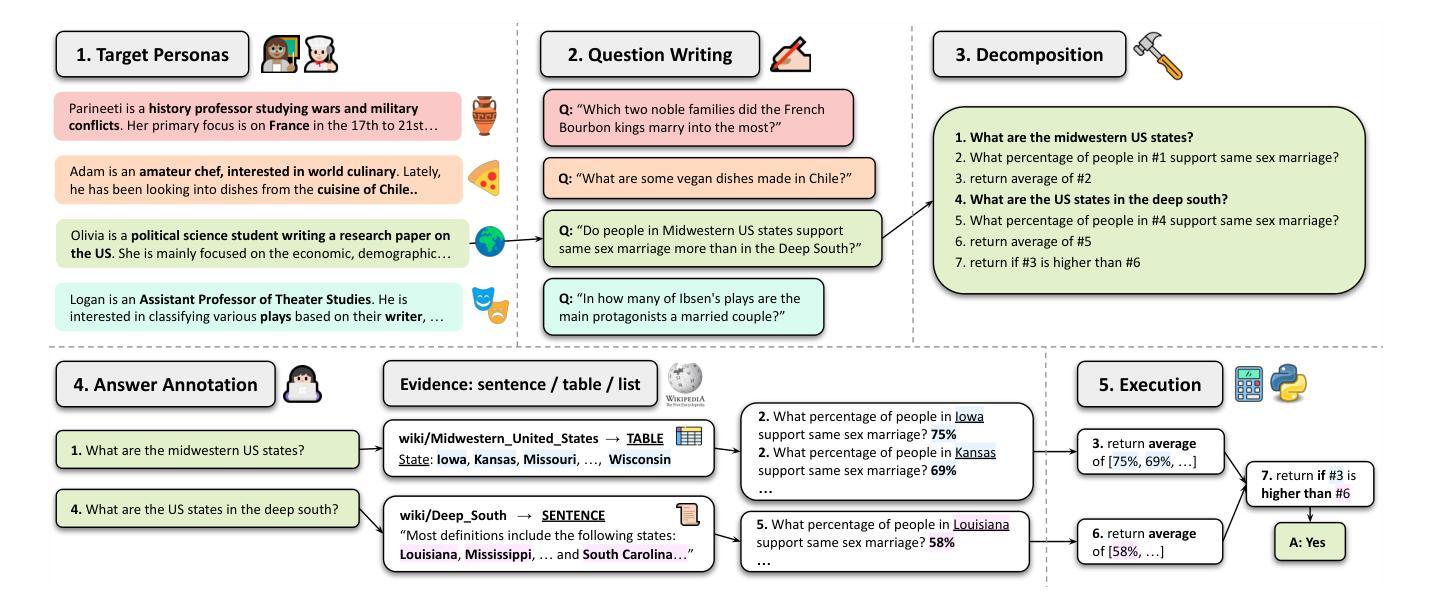
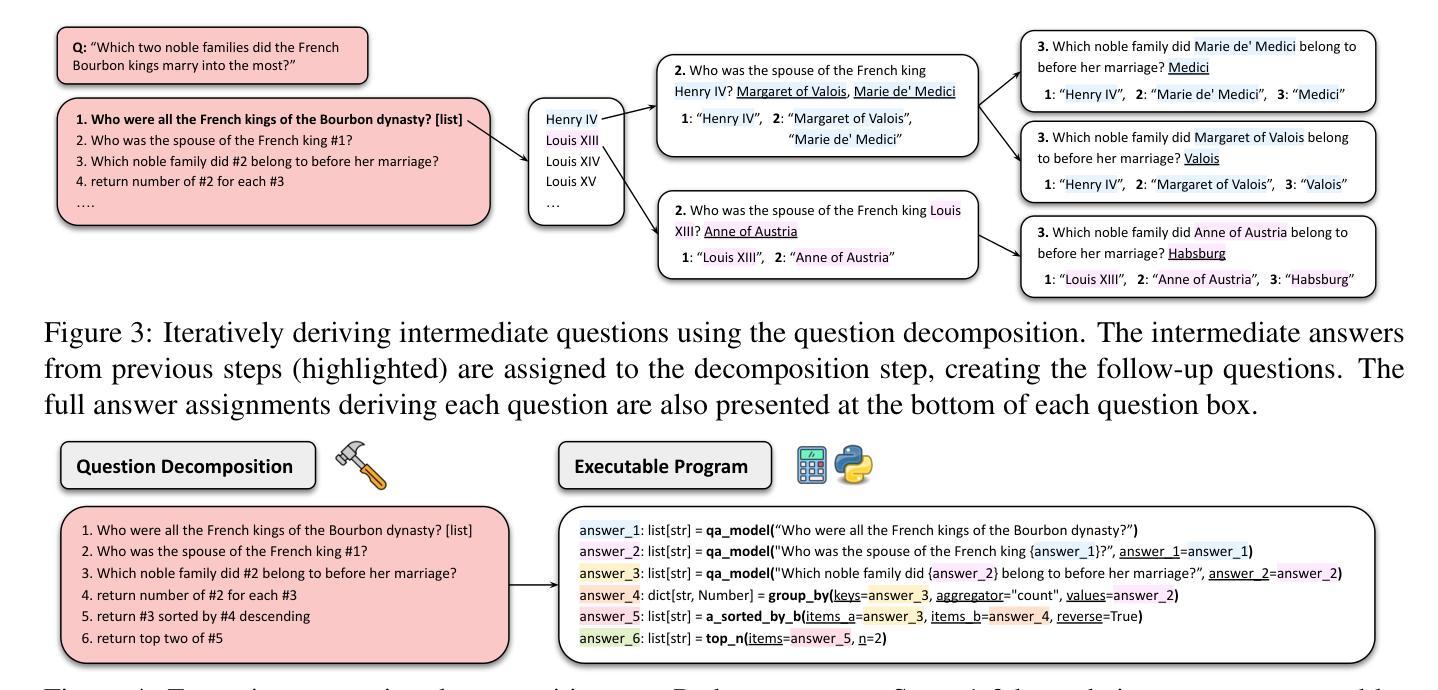
MoNaCo: More Natural and Complex Questions for Reasoning Across Dozens of Documents
Authors:Tomer Wolfson, Harsh Trivedi, Mor Geva, Yoav Goldberg, Dan Roth, Tushar Khot, Ashish Sabharwal, Reut Tsarfaty
Large language models (LLMs) are emerging as a go-to tool for querying information. However, current LLM benchmarks rarely feature natural questions that are both information-seeking as well as genuinely time-consuming for humans. To address this gap we introduce MoNaCo, a benchmark of 1,315 natural and complex questions that require dozens, and at times hundreds, of intermediate steps to solve – far more than any existing QA benchmark. To build MoNaCo, we developed a decomposed annotation pipeline to elicit and manually answer natural time-consuming questions at scale. Frontier LLMs evaluated on MoNaCo achieve at most 61.2% F1, hampered by low recall and hallucinations. Our results underscore the need for reasoning models that better handle the complexity and sheer breadth of real-world information-seeking questions – with MoNaCo providing an effective resource for tracking such progress. The MONACO benchmark, codebase, prompts and models predictions are publicly available at: https://tomerwolgithub.github.io/monaco
大型语言模型(LLM)正逐渐成为查询信息的首选工具。然而,当前的LLM基准测试很少包含既是信息检索所需又对人类来说真正耗时费力的自然问题。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了MoNaCo,这是一个包含1315个自然且复杂的问题的基准测试,这些问题需要数十甚至数百个中间步骤来解决,远远超过现有问答基准测试的范畴。为了构建MoNaCo,我们开发了一个分解注释管道,以激发并大规模手动回答自然耗时的问题。在MoNaCo上评估的前沿LLM最多达到61.2%的F1分数,受到召回率低下和幻觉的阻碍。我们的结果强调了需要更好的处理现实世界信息检索问题的复杂性和广阔性的推理模型,而MoNaCo为跟踪此类进展提供了有效的资源。MONACO基准测试、代码库、提示和模型预测可在以下网址获得:https://tomerwolgithub.github.io/monaco
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics (TACL), 2025. Authors pre-print
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLMs)已成为获取信息的重要工具。为解决现有LLM基准测试缺乏自然且复杂的问题,我们推出了MoNaCo基准测试,包含1315个需要数十甚至数百个中间步骤解决的问题,远超现有问答基准测试的复杂度。我们开发了一种分解注释管道,以大规模地提出并手动回答耗时的问题。在MoNaCo上评估的前沿LLM最多只能达到61.2%的F1分数,存在召回率低和虚构答案的问题。我们的研究结果强调了需要能够更好处理现实世界复杂信息检索问题的推理模型,而MoNaCo则为跟踪此类进展提供了有效资源。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)已成为获取信息的重要工具,现有的基准测试未能充分反映实际复杂问题的需求。
- 推出了MoNaCo基准测试,包含自然且复杂的问题,需要大量的中间步骤来解决。
- MoNaCo问题的复杂性远超现有问答基准测试,旨在更好地模拟人类在实际信息检索中的挑战。
- 我们采用分解注释管道来大规模地提出并手动回答耗时的问题。
- 在MoNaCo上评估的前沿LLM性能受限,存在召回率低和虚构答案的问题。
- 现有的LLM在处理复杂、广泛的现实世界信息检索问题时表现不足。
点此查看论文截图
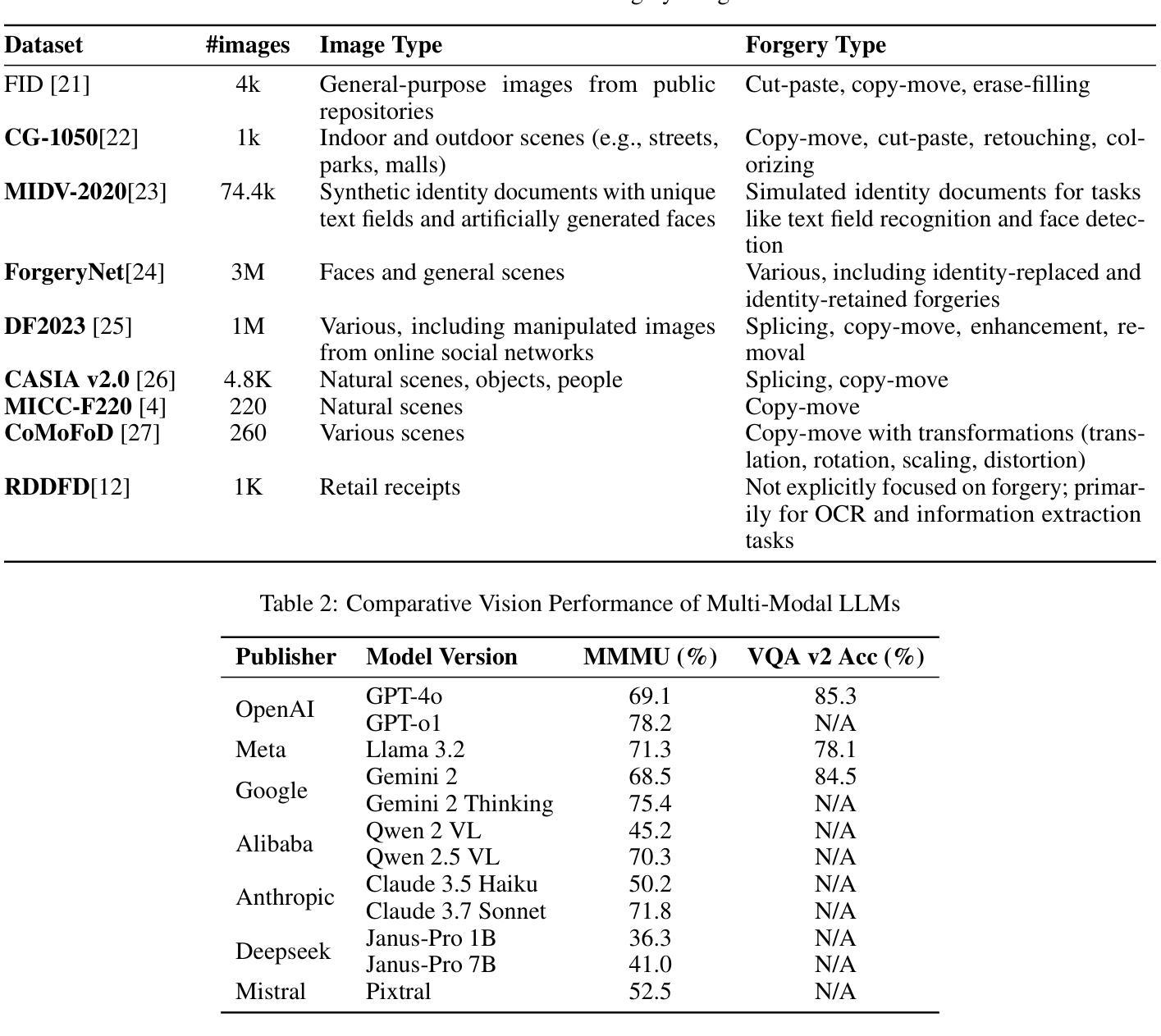
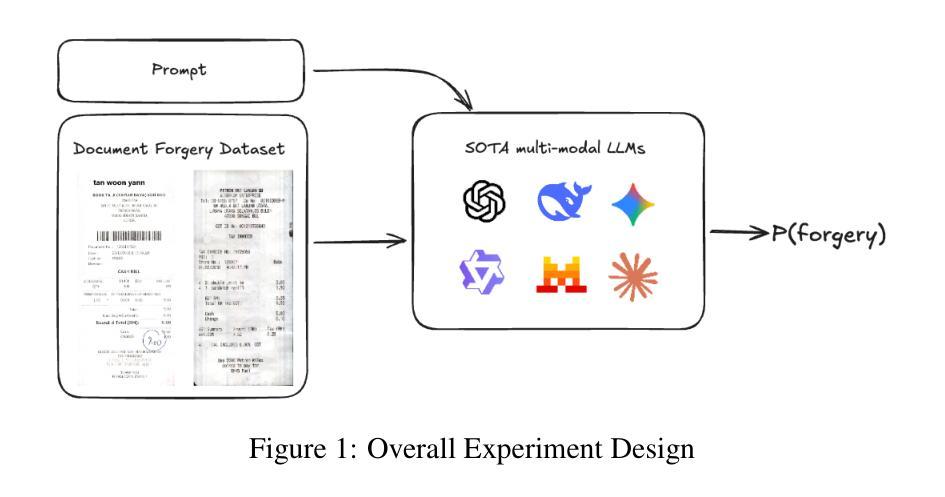
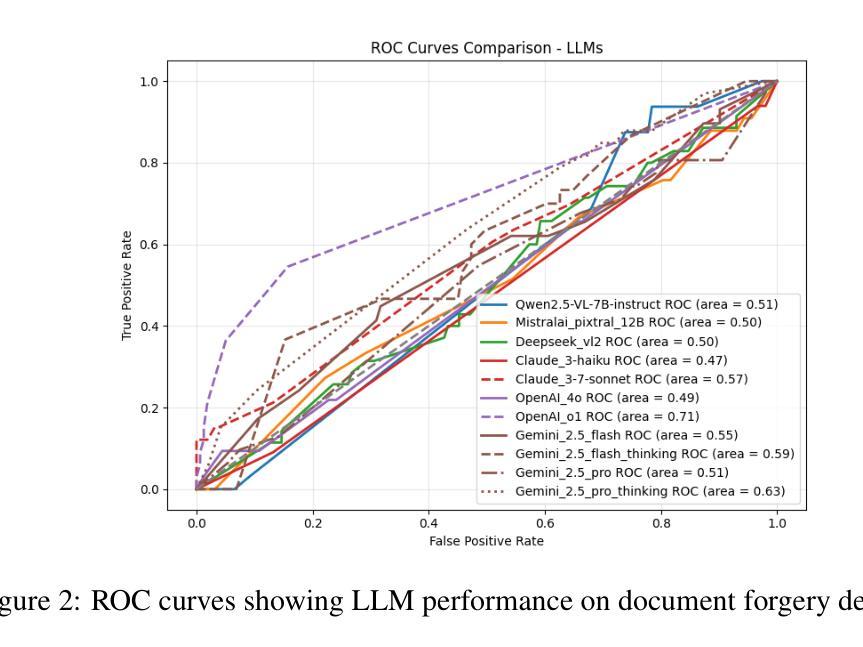
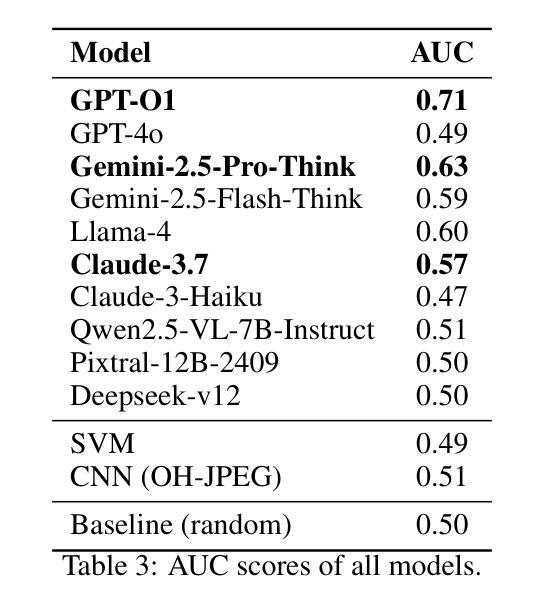
Can Multi-modal (reasoning) LLMs detect document manipulation?
Authors:Zisheng Liang, Kidus Zewde, Rudra Pratap Singh, Disha Patil, Zexi Chen, Jiayu Xue, Yao Yao, Yifei Chen, Qinzhe Liu, Simiao Ren
Document fraud poses a significant threat to industries reliant on secure and verifiable documentation, necessitating robust detection mechanisms. This study investigates the efficacy of state-of-the-art multi-modal large language models (LLMs)-including OpenAI O1, OpenAI 4o, Gemini Flash (thinking), Deepseek Janus, Grok, Llama 3.2 and 4, Qwen 2 and 2.5 VL, Mistral Pixtral, and Claude 3.5 and 3.7 Sonnet-in detecting fraudulent documents. We benchmark these models against each other and prior work on document fraud detection techniques using a standard dataset with real transactional documents. Through prompt optimization and detailed analysis of the models’ reasoning processes, we evaluate their ability to identify subtle indicators of fraud, such as tampered text, misaligned formatting, and inconsistent transactional sums. Our results reveal that top-performing multi-modal LLMs demonstrate superior zero-shot generalization, outperforming conventional methods on out-of-distribution datasets, while several vision LLMs exhibit inconsistent or subpar performance. Notably, model size and advanced reasoning capabilities show limited correlation with detection accuracy, suggesting task-specific fine-tuning is critical. This study underscores the potential of multi-modal LLMs in enhancing document fraud detection systems and provides a foundation for future research into interpretable and scalable fraud mitigation strategies.
文件欺诈对依赖于安全和可验证文件的行业构成重大威胁,需要可靠的检测机制。本研究调查了最先进的跨模态大型语言模型(LLM)在检测欺诈文件方面的有效性,包括OpenAI O1、OpenAI 4o、Gemini Flash(思考)、Deepseek Janus、Grok、Llama 3.2和4、Qwen 2和2.5 VL、Mistral Pixtral以及Claude 3.5和3.7 Sonnet等模型。我们使用包含真实交易文件的标准数据集,对这些模型和之前的文件欺诈检测技术在文档欺诈检测方面的表现进行基准测试。通过对模型的提示优化和详细分析推理过程,我们评估了它们识别欺诈的微妙迹象的能力,如篡改文本、格式不匹配和不一致的交易总和等。我们的结果表明,表现最佳的跨模态LLM显示出卓越的零样本泛化能力,在超出分布的数据集上优于传统方法,而一些视觉LLM则表现出不一致或较差的性能。值得注意的是,模型大小与先进的推理能力与检测精度的相关性有限,这表明针对特定任务的微调至关重要。本研究强调了跨模态LLM在增强文件欺诈检测系统方面的潜力,并为未来的可解释和可扩展的欺诈缓解策略研究提供了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2503.20084
Summary:该研究探讨了多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)在检测欺诈文件方面的有效性。通过对一系列LLMs进行基准测试,并与先前的文档欺诈检测技术进行比对,发现顶级的多模态LLMs在零样本泛化方面具有出色的表现,能够超越传统的检测手段。然而,模型大小和推理能力并不完全与检测精度相关,任务特定的微调至关重要。这为多模态LLMs在增强文档欺诈检测系统中的应用提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)在检测欺诈文件方面展现出有效性。
- 在零样本泛化方面,顶级的多模态LLMs表现出出色的性能。
- 与传统检测手段相比,多模态LLMs在文档欺诈检测方面具有优势。
- 模型大小和推理能力并不完全与检测精度相关。
- 任务特定的微调对于提高检测精度至关重要。
- 多模态LLMs在文档欺诈检测系统中具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

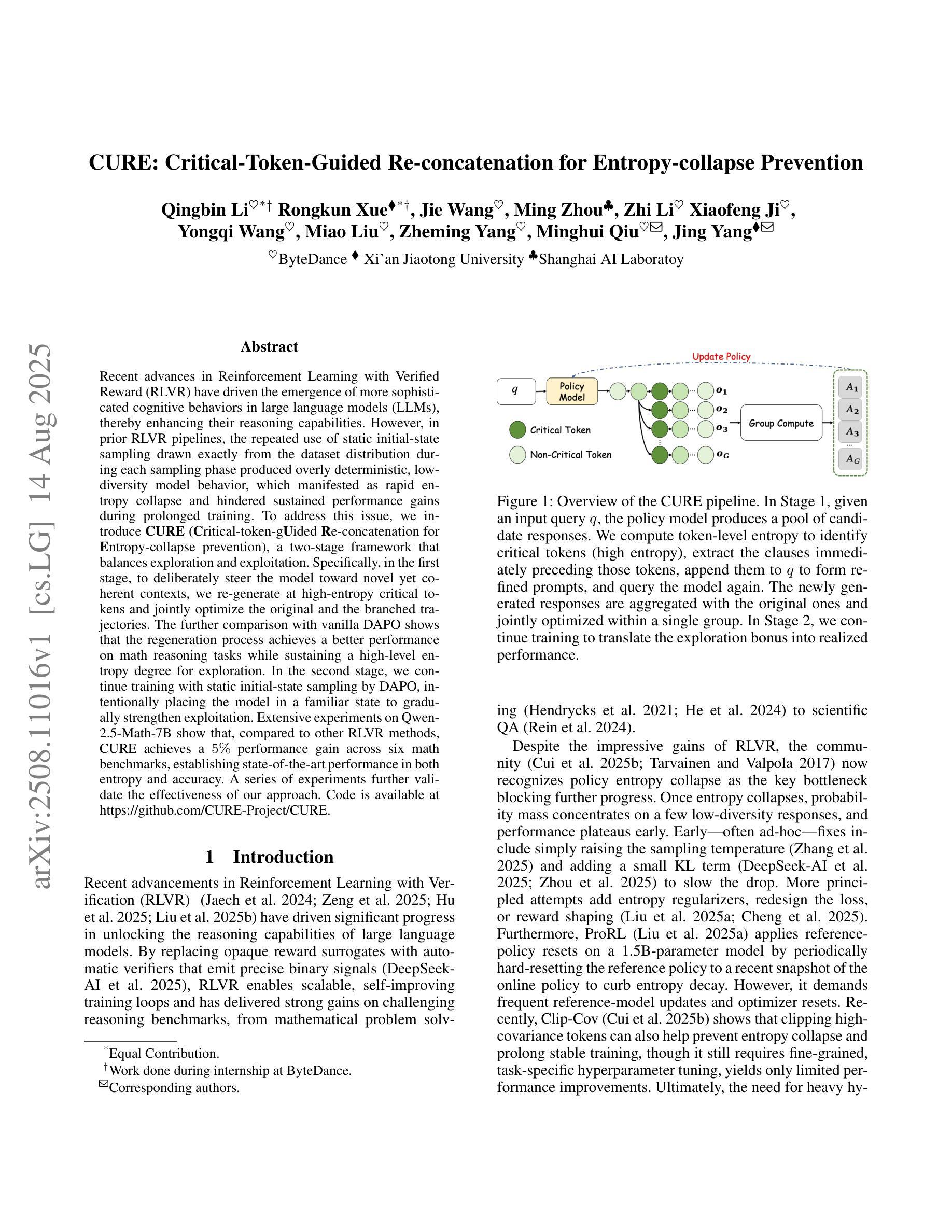
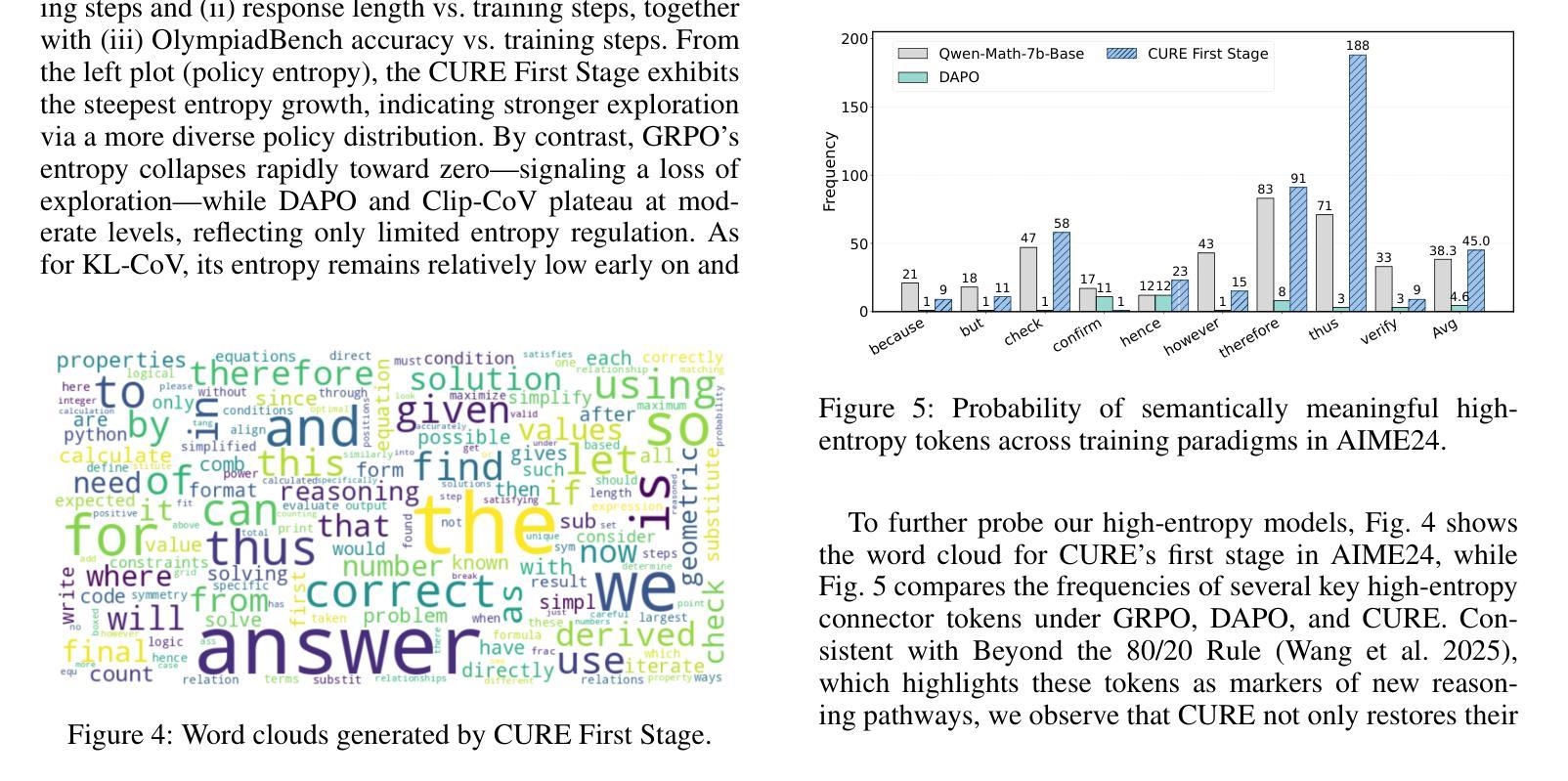
CURE: Critical-Token-Guided Re-concatenation for Entropy-collapse Prevention
Authors:Qingbin Li, Rongkun Xue, Jie Wang, Ming Zhou, Zhi Li, Xiaofeng Ji, Yongqi Wang, Miao Liu, Zheming Yang, Minghui Qiu, Jing Yang
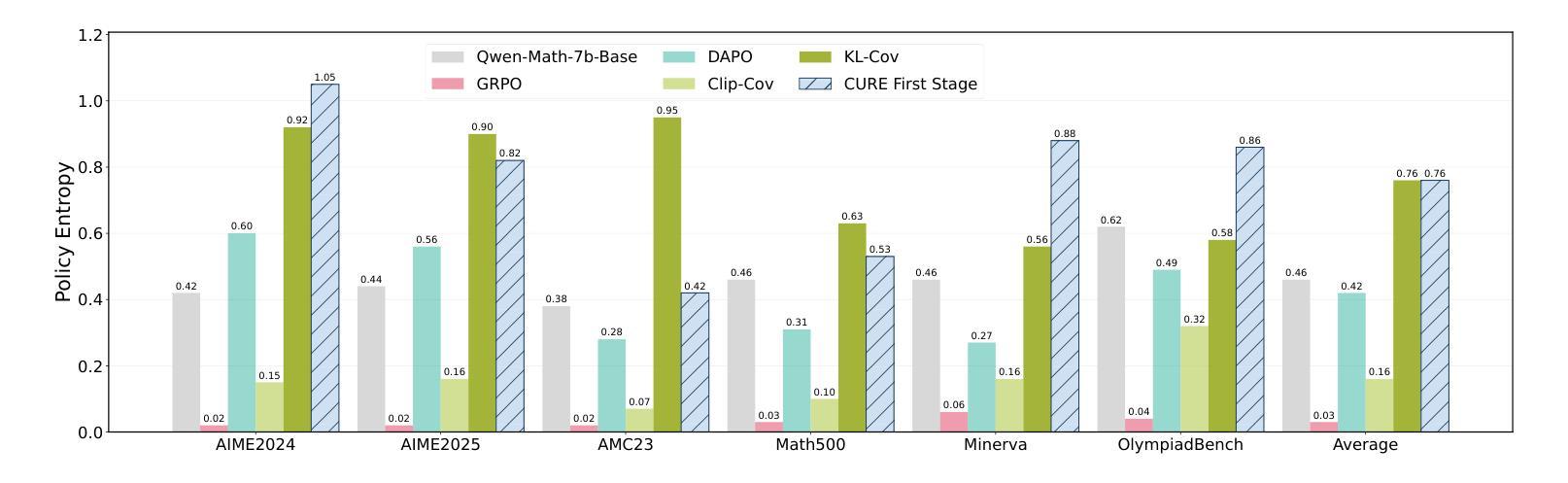
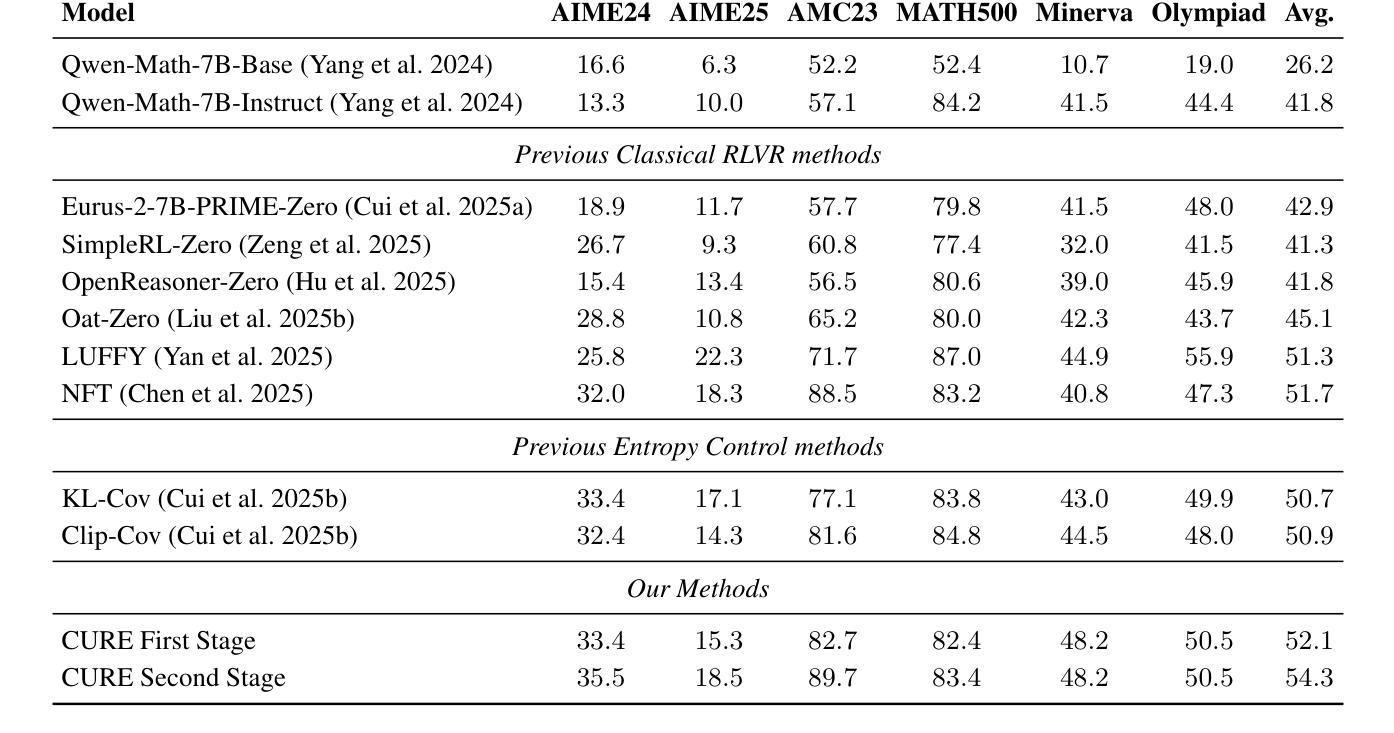
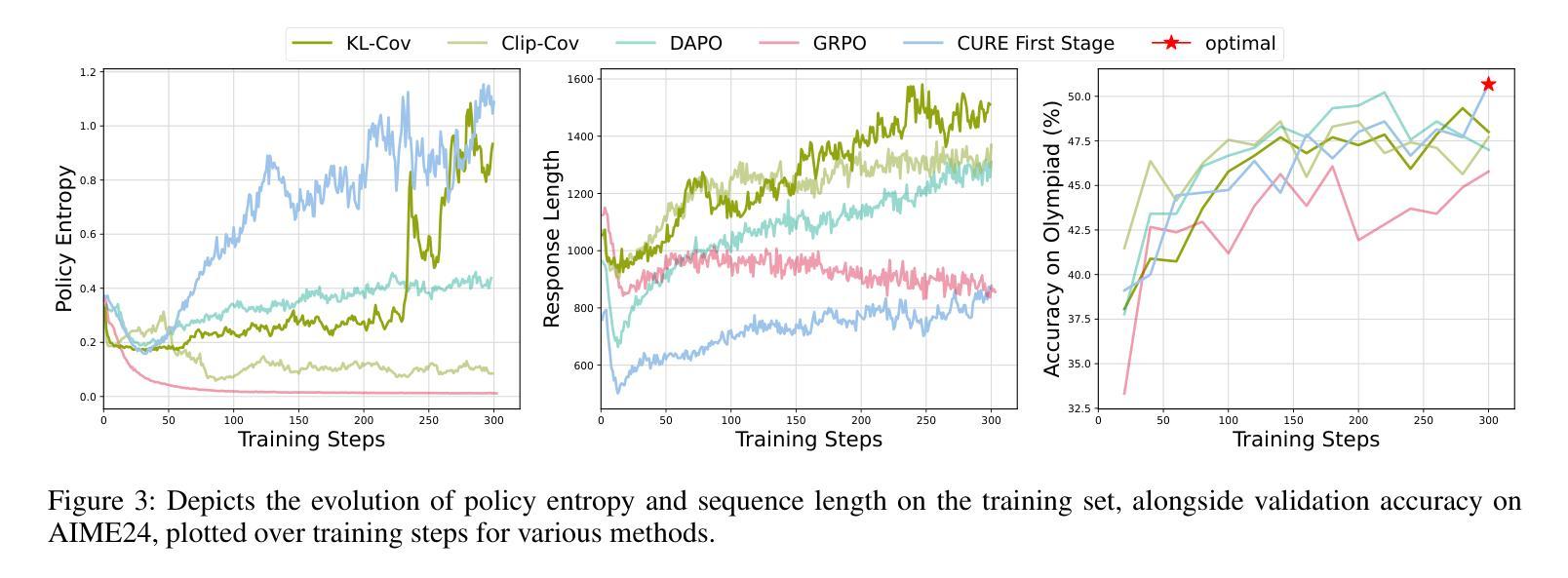
Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning with Verified Reward (RLVR) have driven the emergence of more sophisticated cognitive behaviors in large language models (LLMs), thereby enhancing their reasoning capabilities. However, in prior RLVR pipelines, the repeated use of static initial-state sampling drawn exactly from the dataset distribution during each sampling phase produced overly deterministic, low diversity model behavior, which manifested as rapid entropy collapse and hindered sustained performance gains during prolonged training. To address this issue, we introduce CURE (Critical-token-gUided Re concatenation for Entropy-collapse prevention), a two-stage framework that balances exploration and exploitation. Specifically, in the first stage, to deliberately steer the model toward novel yet coherent contexts, we re-generate at high-entropy critical tokens and jointly optimize the original and the branched trajectories. The further comparison with vanilla DAPO shows that the regeneration process achieves a better performance on math reasoning tasks while sustaining a high-level entropy degree for exploration. In the second stage, we continue training with static initial-state sampling by DAPO, intentionally placing the model in a familiar state to gradually strengthen exploitation. Extensive experiments on Qwen-2.5-Math-7B show that, compared to other RLVR methods, CURE achieves a 5% performance gain across six math benchmarks, establishing state-of-the-art performance in both entropy and accuracy. A series of experiments further validate the effectiveness of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/CURE-Project/CURE.
近期强化学习与验证奖励(RLVR)的进展为大语言模型(LLM)催生出更复杂的认知行为,从而增强了其推理能力。然而,在之前的RLVR管道中,每个采样阶段重复使用直接从数据集分布中抽取的静态初始状态采样,产生了过于确定性的、低多样性的模型行为,表现为熵的快速崩溃,阻碍了在延长训练过程中的持续性能提升。为解决这一问题,我们引入了CURE(用于熵崩溃预防的关键令牌引导重连接),这是一个平衡探索与利用的两阶段框架。具体来说,在第一阶段,为了故意引导模型走向新颖而连贯的上下文,我们重新生成高熵关键令牌,并联合优化原始和分支轨迹。与普通的DAPO相比,再生过程在数学推理任务上实现了更好的性能,同时保持高水平的熵度用于探索。在第二阶段,我们继续采用DAPO的静态初始状态采样,有意将模型置于熟悉的状态,以逐步加强利用。在Qwen-2.5-Math-7B上的大量实验表明,与其他RLVR方法相比,CURE在六个数学基准测试中实现了5%的性能提升,在熵和准确性方面都达到了最新水平。一系列实验进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。相关代码可从https://github.com/CURE-Project/CURE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期强化学习验证奖励(RLVR)技术的进展促使大型语言模型(LLM)展现出更复杂的认知行为,从而提升其推理能力。然而,先前RLVR管道中每次采样阶段重复使用从数据集分布中精确抽取的初始状态采样导致模型行为过于确定性,表现为熵快速崩溃,阻碍了长期训练中的持续性能提升。为解决这一问题,我们提出了CURE(关键令牌引导重组合防熵崩溃两阶段框架),它平衡了探索与利用。第一阶段通过重新生成高熵关键令牌并联合优化原始和分支轨迹,故意引导模型进入新颖而连贯的上下文。与DAPO相比,再生过程在数学推理任务上实现了更好的性能,同时维持高水平的探索熵。第二阶段继续使用静态初始状态采样进行训练,故意将模型置于熟悉的状态以逐步强化利用。在Qwen-2.5-Math-7B上的实验表明,与其他RLVR方法相比,CURE在六个数学基准测试中实现了5%的性能提升,在熵和准确性方面都达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- RLVR技术的最新进展推动了LLM的更复杂认知行为的出现,增强了其推理能力。
- 早期RLVR方法中的模型行为过于确定性,导致熵快速崩溃,影响长期训练性能。
- CURE框架被引入以解决这一问题,通过平衡探索与利用来提升模型性能。
- CURE的第一阶段通过重新生成高熵关键令牌引导模型进入新颖且连贯的上下文。
- 与DAPO相比,CURE在再生过程中实现了更好的数学推理性能。
- CURE在Qwen-2.5-Math-7B实验上与其他RLVR方法相比,实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

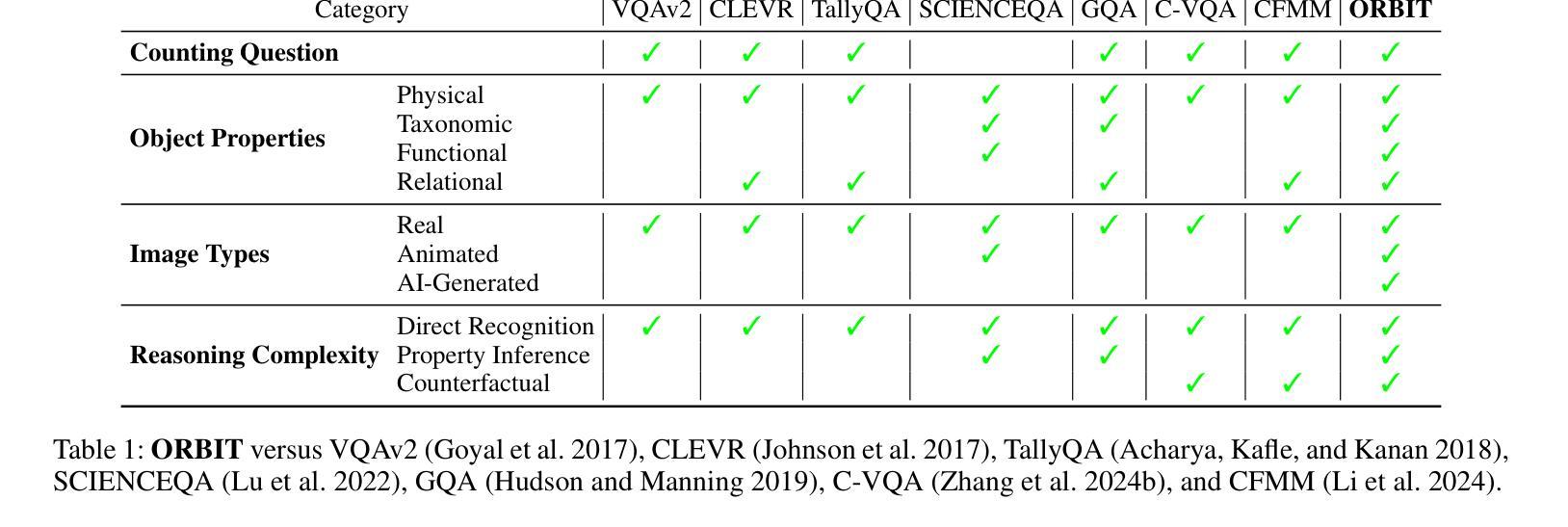
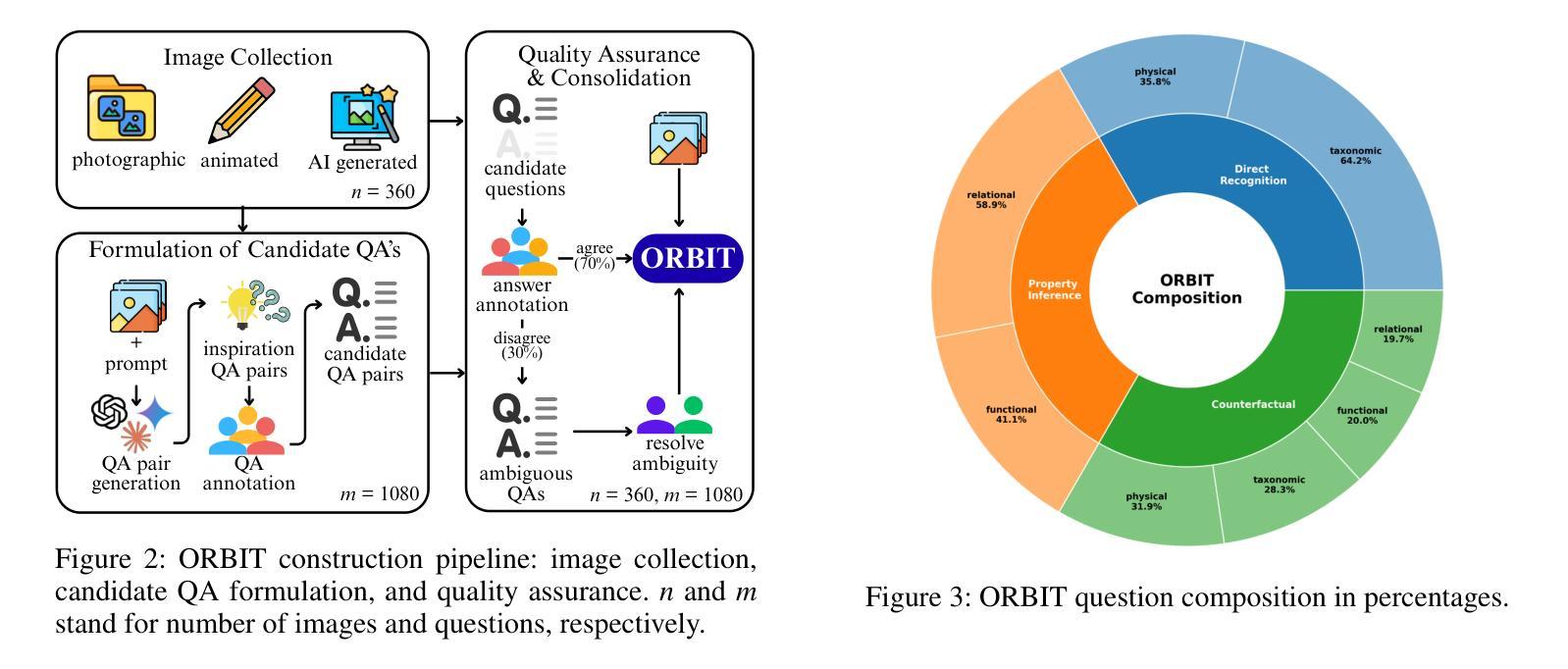
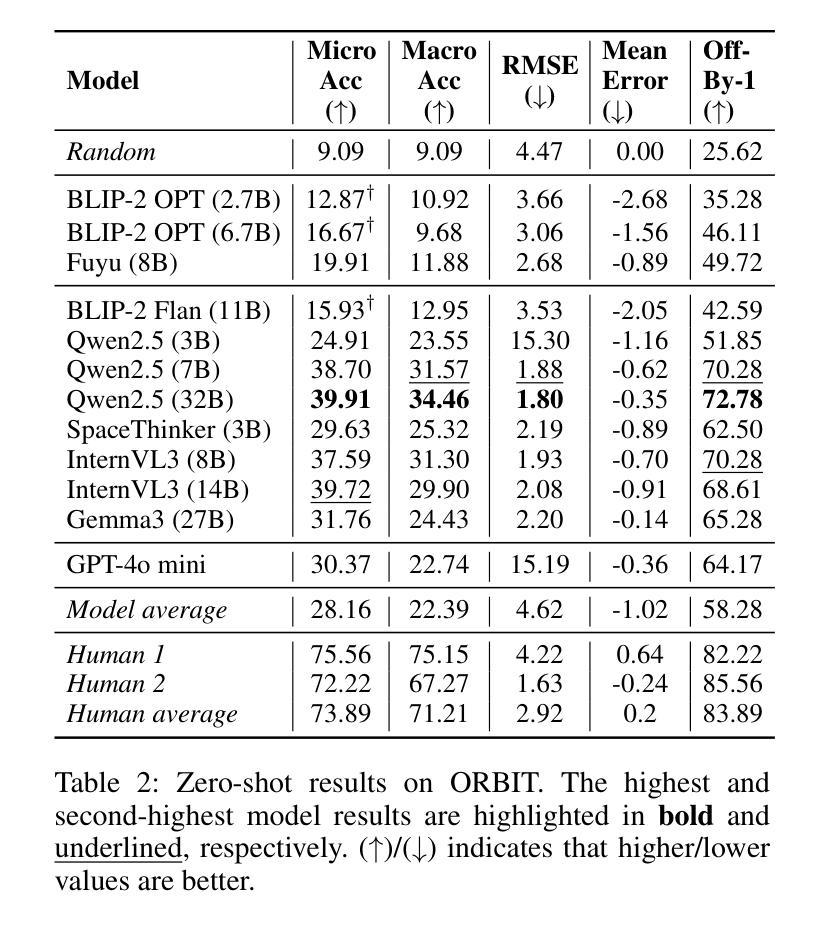
ORBIT: An Object Property Reasoning Benchmark for Visual Inference Tasks
Authors:Abhishek Kolari, Mohammadhossein Khojasteh, Yifan Jiang, Floris den Hengst, Filip Ilievski
While vision-language models (VLMs) have made remarkable progress on many popular visual question answering (VQA) benchmarks, it remains unclear whether they abstract and reason over depicted objects. Inspired by human object categorisation, object property reasoning involves identifying and recognising low-level details and higher-level abstractions. While current VQA benchmarks consider a limited set of object property attributes like size, they typically blend perception and reasoning, and lack representativeness in terms of reasoning and image categories. To this end, we introduce a systematic evaluation framework with images of three representative types, three reasoning levels of increasing complexity, and four object property dimensions driven by prior work on commonsense reasoning. We develop a procedure to instantiate this benchmark into ORBIT, a multi-level reasoning VQA benchmark for object properties comprising 360 images paired with a total of 1,080 count-based questions. Experiments with 12 state-of-the-art VLMs in zero-shot settings reveal significant limitations compared to humans, with the best-performing model only reaching 40% accuracy. VLMs struggle particularly with realistic (photographic) images, counterfactual reasoning about physical and functional properties, and higher counts. ORBIT points to the need to develop methods for scalable benchmarking, generalize annotation guidelines, and explore additional reasoning VLMs. We make the ORBIT benchmark and the experimental code available to support such endeavors.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在许多流行的视觉问答(VQA)基准测试中取得了显著的进步,但它们是否能够抽象和推理描述对象仍然不明确。受人类物体分类的启发,物体属性推理涉及识别和识别低级别细节和高级别抽象。虽然当前的VQA基准测试只考虑有限的对象属性属性,如大小,但它们通常将感知和推理混合在一起,并且在推理和图像类别方面的代表性不足。为此,我们引入了一个系统的评估框架,包含三种有代表性的图像类型、三个逐渐增加复杂度的推理层次,以及由常识推理的先前工作驱动的四个对象属性维度。我们开发了一种方法,将这一基准测试实例化为ORBIT,这是一个多层次推理的VQA基准测试,用于对象属性,包含360张图像和总计的1080个基于计数的问答。在零样本设置下与最新的视觉问答模型的实验显示与人类相比存在显著的局限性,性能最佳的模型只有40%的准确性。模型对于现实照片图像的图像表现最为吃力的是对于物理属性和功能属性的反事实推理和更高的计数问题。ORBIT指出需要开发可扩展的基准测试方法、通用注释指南和探索额外的推理视觉语言模型。我们公开提供ORBIT基准测试和实验代码以支持此类研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对视觉问答模型(VLMs)在物体属性推理方面的系统性评估框架。通过构建包含不同类型图像、不同难度级别的推理问题以及基于常识推理的四个物体属性维度的基准测试,揭示出当前最先进的视觉问答模型在物体属性推理方面的局限性。ORBIT基准测试展示了在真实图像、物理和功能属性上的反事实推理以及高计数方面的挑战。为了提升VLM的性能,需要进一步开发可规模化的基准测试方法,改进标注指南,并探索更多具备推理能力的视觉问答模型。提供的代码和资源可支持此类研究。
Key Takeaways
- 文章重点讨论了视觉问答模型(VLMs)在物体属性推理上的性能表现和挑战。
- 引入了一种新的评估框架ORBIT,涵盖不同类型图像、不同级别的推理难度和四个物体属性维度。
- 当前最先进的VLM在物体属性推理方面存在显著局限性,特别是在真实图像、物理和功能属性的反事实推理以及高计数方面。
点此查看论文截图

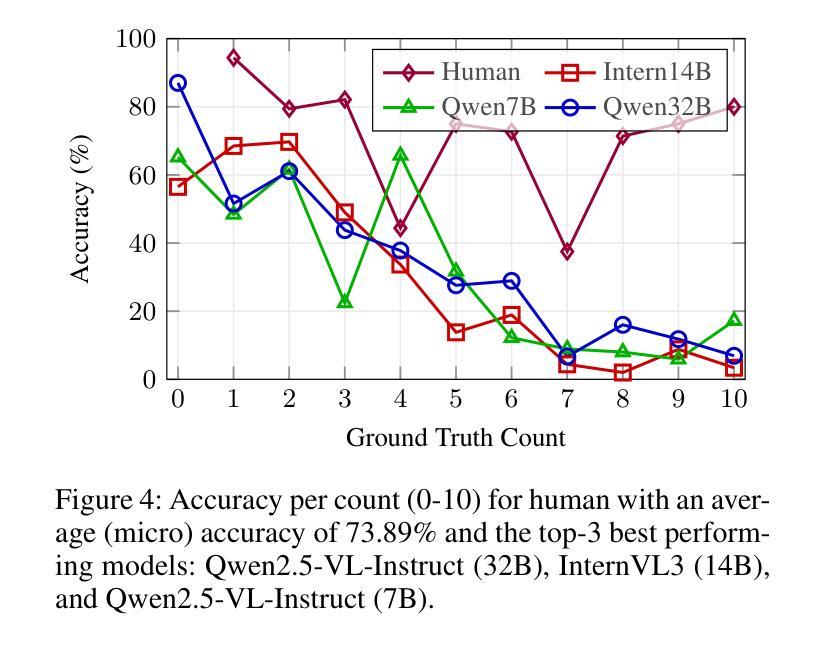
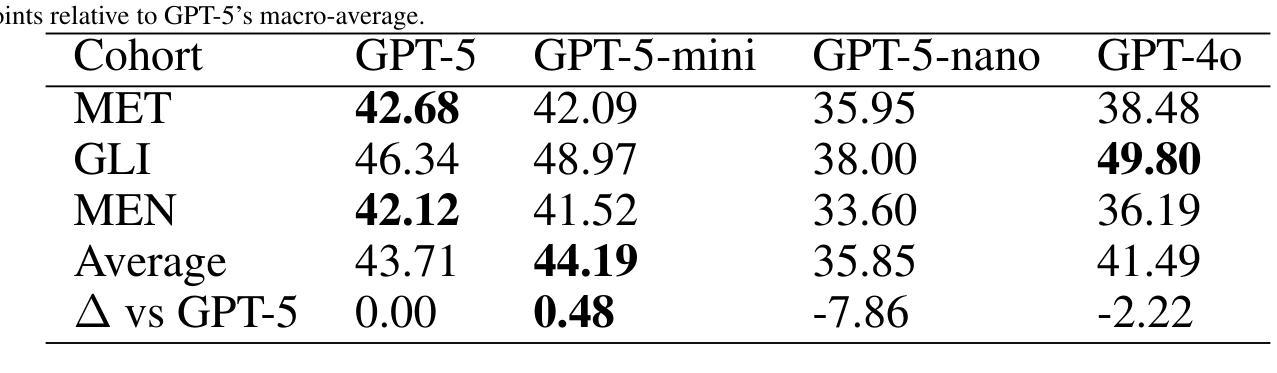
Performance of GPT-5 in Brain Tumor MRI Reasoning
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Shansong Wang, Mingzhe Hu, Zach Eidex, Qiang Li, Xiaofeng Yang
Accurate differentiation of brain tumor types on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical for guiding treatment planning in neuro-oncology. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled visual question answering (VQA) approaches that integrate image interpretation with natural language reasoning. In this study, we evaluated GPT-4o, GPT-5-nano, GPT-5-mini, and GPT-5 on a curated brain tumor VQA benchmark derived from 3 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) datasets - glioblastoma (GLI), meningioma (MEN), and brain metastases (MET). Each case included multi-sequence MRI triplanar mosaics and structured clinical features transformed into standardized VQA items. Models were assessed in a zero-shot chain-of-thought setting for accuracy on both visual and reasoning tasks. Results showed that GPT-5-mini achieved the highest macro-average accuracy (44.19%), followed by GPT-5 (43.71%), GPT-4o (41.49%), and GPT-5-nano (35.85%). Performance varied by tumor subtype, with no single model dominating across all cohorts. These findings suggest that GPT-5 family models can achieve moderate accuracy in structured neuro-oncological VQA tasks, but not at a level acceptable for clinical use.
在神经肿瘤学中,通过磁共振成像(MRI)准确区分脑肿瘤类型对治疗计划至关重要。自然语言模型(LLM)的最新进展已经实现了视觉问答(VQA)方法,该方法结合了图像解读和自然语言推理。在这项研究中,我们评估了GPT-4o、GPT-5-nano、GPT-5-mini和GPT-5在一组经过筛选的脑肿瘤VQA基准测试上的表现,该测试数据来自三个脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)数据集——胶质母细胞瘤(GLI)、脑膜瘤(MEN)和脑转移瘤(MET)。每个病例均包括多序列MRI三平面马赛克图像和转化为标准化VQA项目的结构化临床特征。模型在零射击思维链环境中对视觉和推理任务的准确性进行了评估。结果显示,GPT-5-mini的宏平均准确率最高(44.19%),其次是GPT-5(43.71%)、GPT-4o(41.49%)和GPT-5-nano(35.85%)。不同肿瘤亚型的性能表现有所不同,没有任何单一模型在所有群体中占据主导地位。这些发现表明GPT-5系列模型可以在结构化的神经肿瘤学VQA任务中实现中等准确率,但尚未达到临床使用所要求的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了大型语言模型在神经肿瘤学中对脑肿瘤类型进行磁共振成像(MRI)区分的应用效果。实验评估了GPT-4o、GPT-5-nano、GPT-5-mini和GPT-5在包含胶质母细胞瘤(GLI)、脑膜瘤(MEN)和脑转移瘤(MET)三种脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)数据集的视觉问答(VQA)基准测试上的表现。结果显示GPT-5-mini的宏观平均准确率最高(44.19%),但所有模型的性能均未达到临床接受水平。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在神经肿瘤学的结构化神经肿瘤视觉问答任务中能够达到中等准确率。
- GPT-5家族模型在评估中的表现有所不同,GPT-5-mini的宏观平均准确率最高。
- 不同肿瘤亚型的性能表现存在差异,没有单一模型能在所有队列中占据主导地位。
- 研究结果表明,当前大型语言模型在神经肿瘤学领域的VQA任务中的性能尚未达到临床使用水平。
- 此研究利用多序列MRI三平面镶嵌图像和标准化VQA项目进行评估,展示了VQA在医学图像解读中的潜力。
- 模型是在零样本思维链环境中进行评估,这一环境对模型的视觉和推理任务准确性进行了测试。
点此查看论文截图

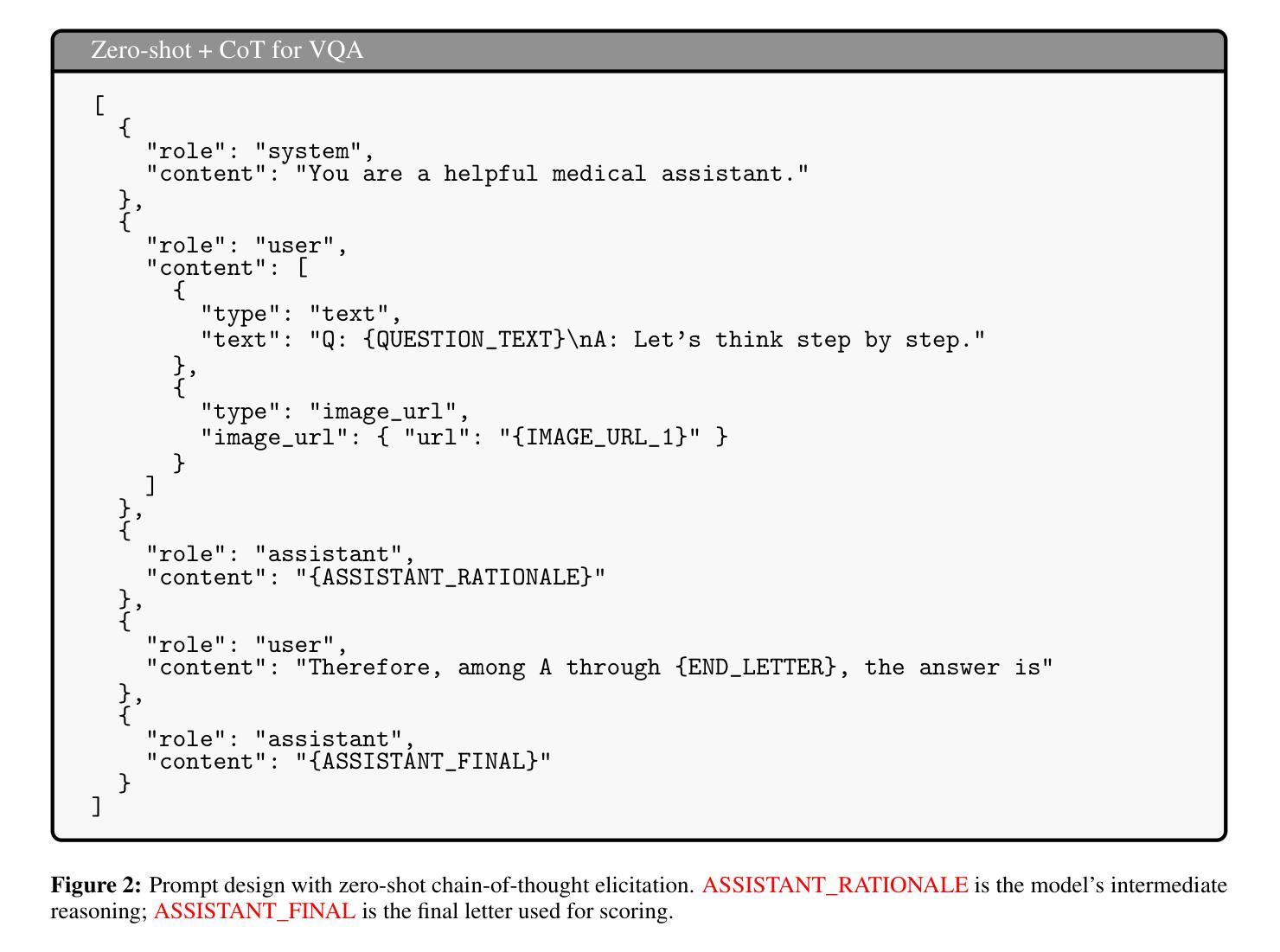
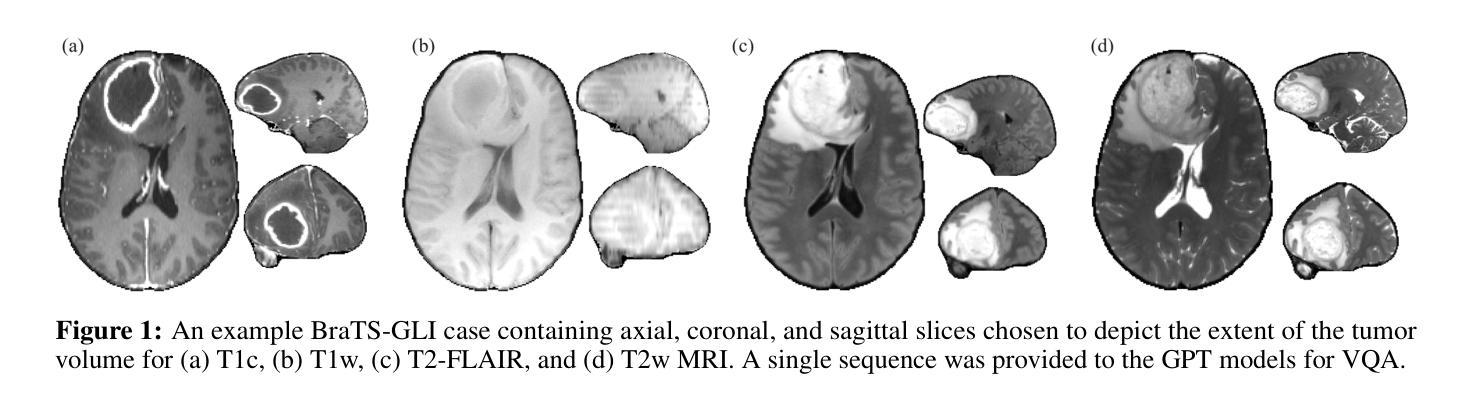
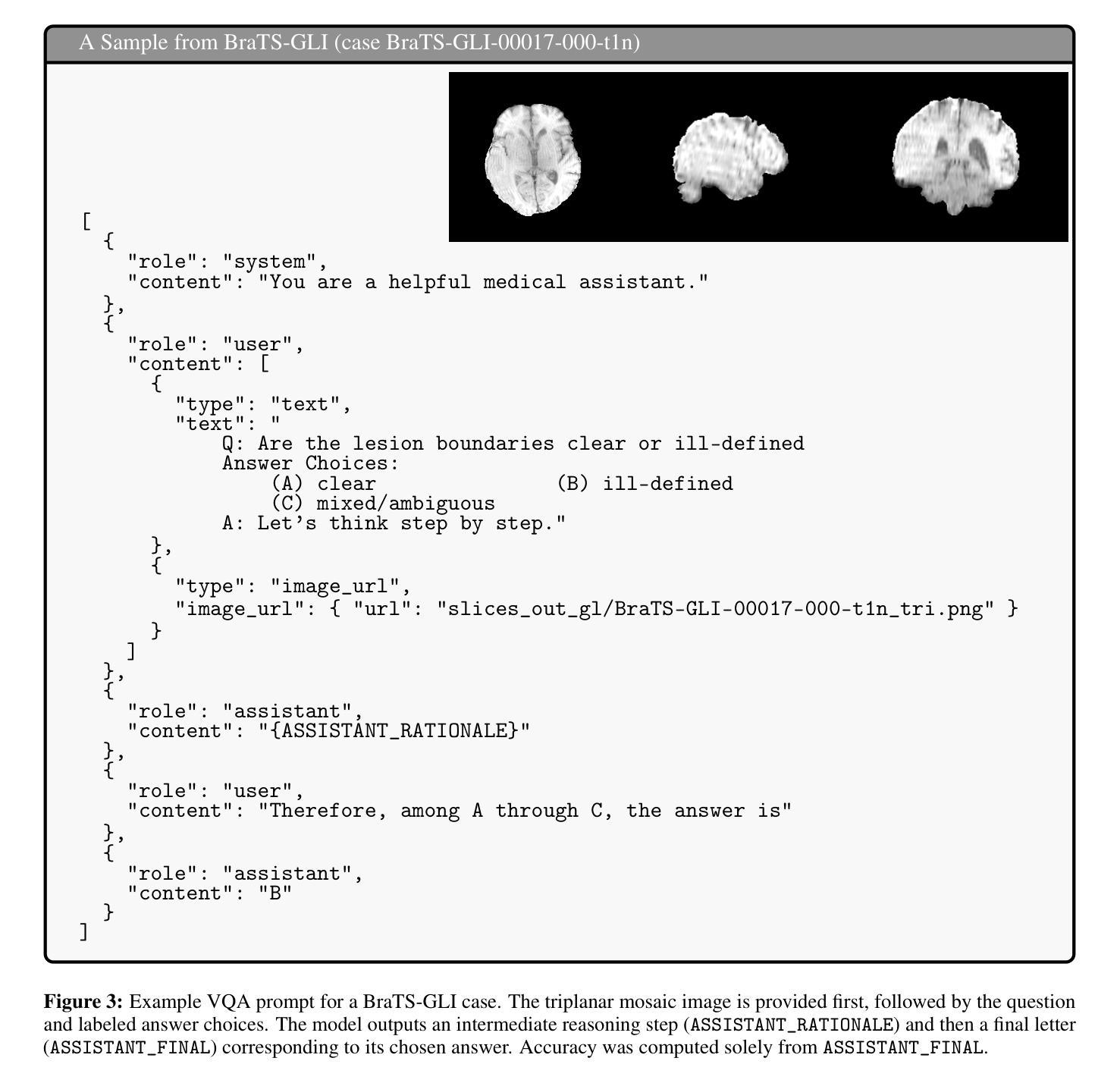
Reinforced Language Models for Sequential Decision Making
Authors:Jim Dilkes, Vahid Yazdanpanah, Sebastian Stein
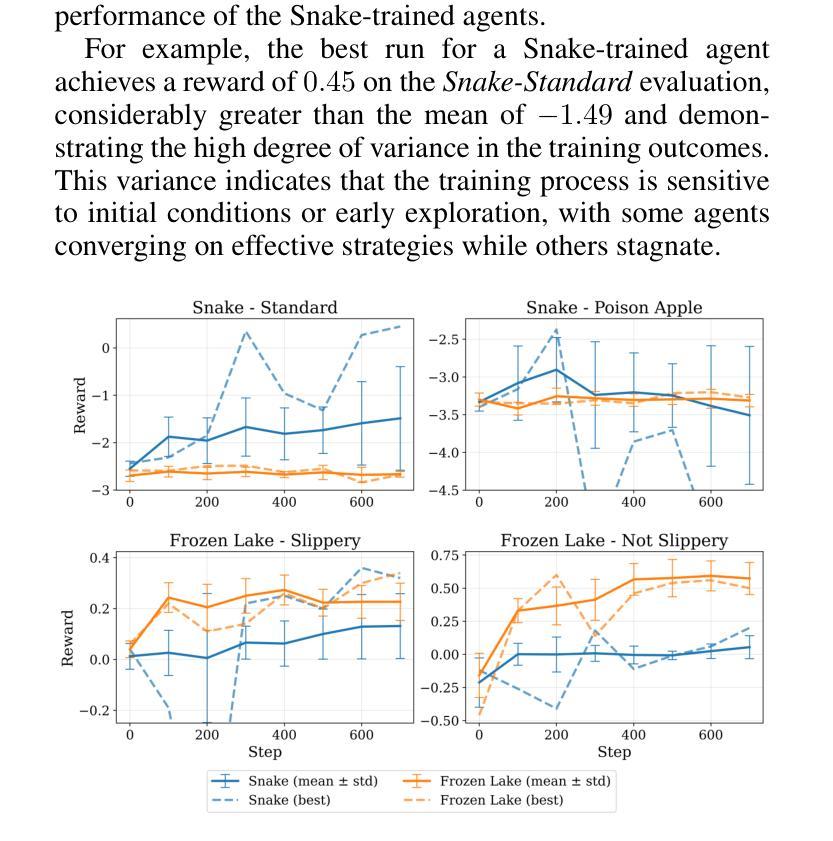
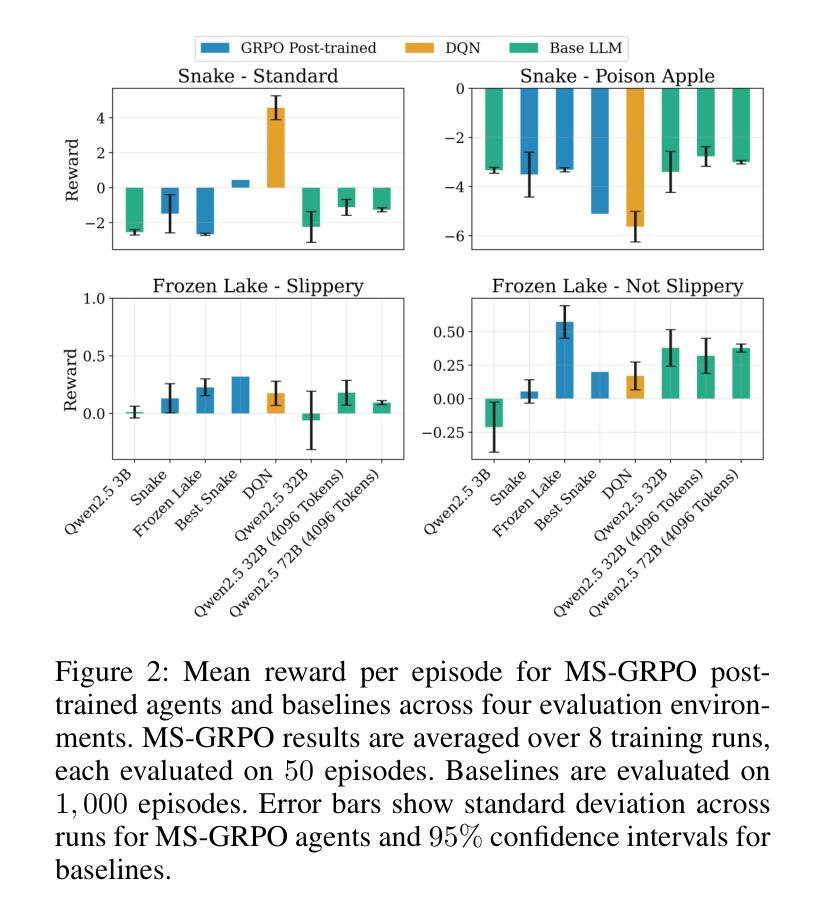
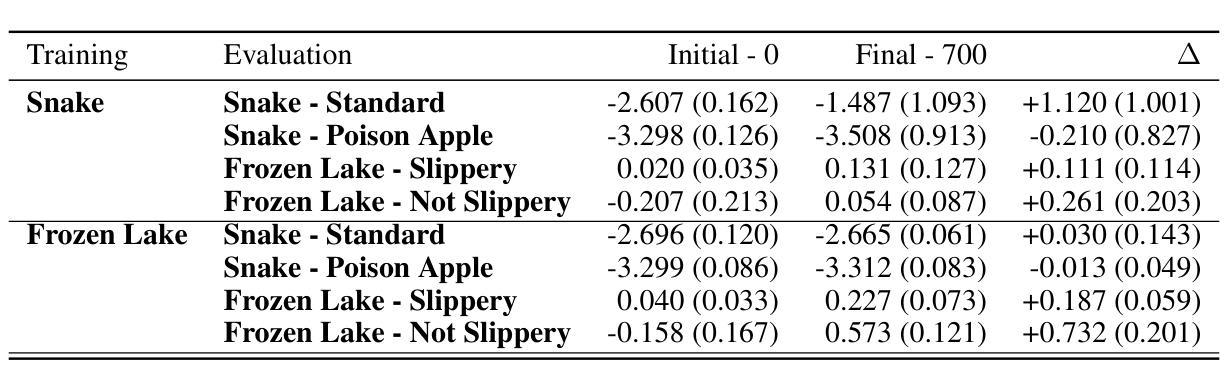
Large Language Models (LLMs) show potential as sequential decision-making agents, but their application is often limited due to a reliance on large, computationally expensive models. This creates a need to improve smaller models, yet existing post-training methods are designed for single-turn interactions and cannot handle credit assignment in multi-step agentic tasks. To address this, we introduce Multi-Step Group-Relative Policy Optimization (MS-GRPO), a new algorithm for post-training LLM agents, grounded in formal Text-Mediated Stochastic Game (TSMG) and Language-Agent Policy (LAP) frameworks. For credit assignment, MS-GRPO attributes the entire cumulative episode reward to each individual episode step. We supplement this algorithm with a novel absolute-advantage-weighted episode sampling strategy that we show improves training performance. We evaluate our approach by post-training a 3-billion parameter model on Snake and Frozen Lake. Our experiments demonstrate that the method is effective in improving decision-making performance: our post-trained 3B parameter model outperforms a 72B parameter baseline by 50% on the Frozen Lake task. This work demonstrates that targeted post-training is a practical and efficient alternative to relying on model scale for creating sequential decision-making agents using LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)作为序贯决策代理的潜力已经显现,但由于它们依赖于计算成本高昂的大型模型,其应用往往受到限制。这产生了改进小型模型的需求,然而现有的后训练方法是针对单轮交互设计的,无法处理多步代理任务中的信用分配问题。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了基于正式文本介导随机游戏(TSMG)和语言代理策略(LAP)框架的多步组相对策略优化(MS-GRPO)这一新型LLM代理后训练算法。在信用分配方面,MS-GRPO将整个累积片段奖励分配给每个单独片段的步骤。我们对该算法进行了补充,提出了一种新型绝对优势加权片段采样策略,我们证明这种策略能提高训练性能。我们通过使用蛇和冰冻湖任务对规模为3亿参数的后训练模型进行了评估。实验表明,该方法在提升决策性能方面是有效的:我们的后训练规模为3亿的参数模型在冰冻湖任务上的表现优于规模为72亿的基准模型,提高了50%。这项工作表明,有针对性的后训练是一种实用且高效的替代方案,不再依赖模型规模来创建使用LLM的序贯决策代理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在作为序列决策代理方面显示出潜力,但其应用受限于大规模计算模型。因此,需要改进小型模型。现有的后训练方法设计用于单回合交互,无法处理多步骤代理任务中的信用分配问题。为解决这一问题,我们提出了基于正式文本介导随机游戏和语言代理策略框架的多步骤组相对策略优化(MS-GRPO)新算法。通过累积集回报将每个个体步骤归功于信用分配。我们补充了一种新型绝对优势加权集采样策略,以提高训练性能。在Snake和Frozen Lake上进行的实验证明该方法可有效提高决策性能:我们后训练的3亿参数模型在Frozen Lake任务上的表现优于72亿参数基线模型,高出50%。这项工作表明,有针对性的后训练是创建使用LLM的序列决策代理的一种实用且高效的选择,不一定依赖模型规模。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在序列决策方面展现出潜力,但存在计算资源限制问题。
- 当前的后训练方法主要针对单回合交互设计,难以处理多步骤任务中的信用分配问题。
- 提出了一种新的后训练算法——多步骤组相对策略优化(MS-GRPO),用于处理LLM代理的多步骤决策问题。
- MS-GRPO基于文本介导随机游戏和语言代理策略框架,可将累积集回报分配给每个个体步骤。
- 引入了一种新型采样策略——绝对优势加权集采样策略,用于提高训练性能。
- 在Snake和Frozen Lake实验上的结果表明,改进后的模型在任务性能上显著优于基线模型。
点此查看论文截图


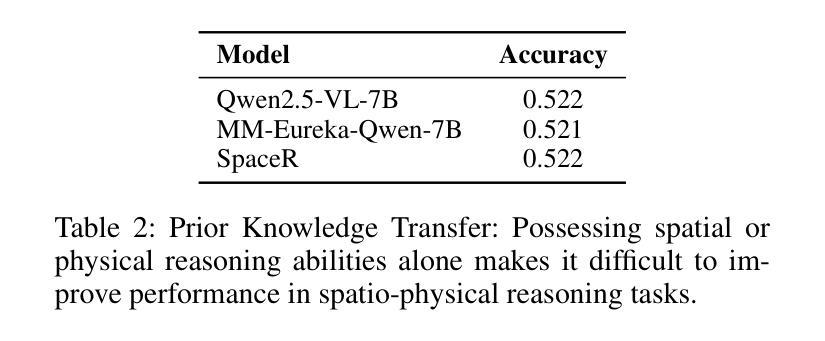
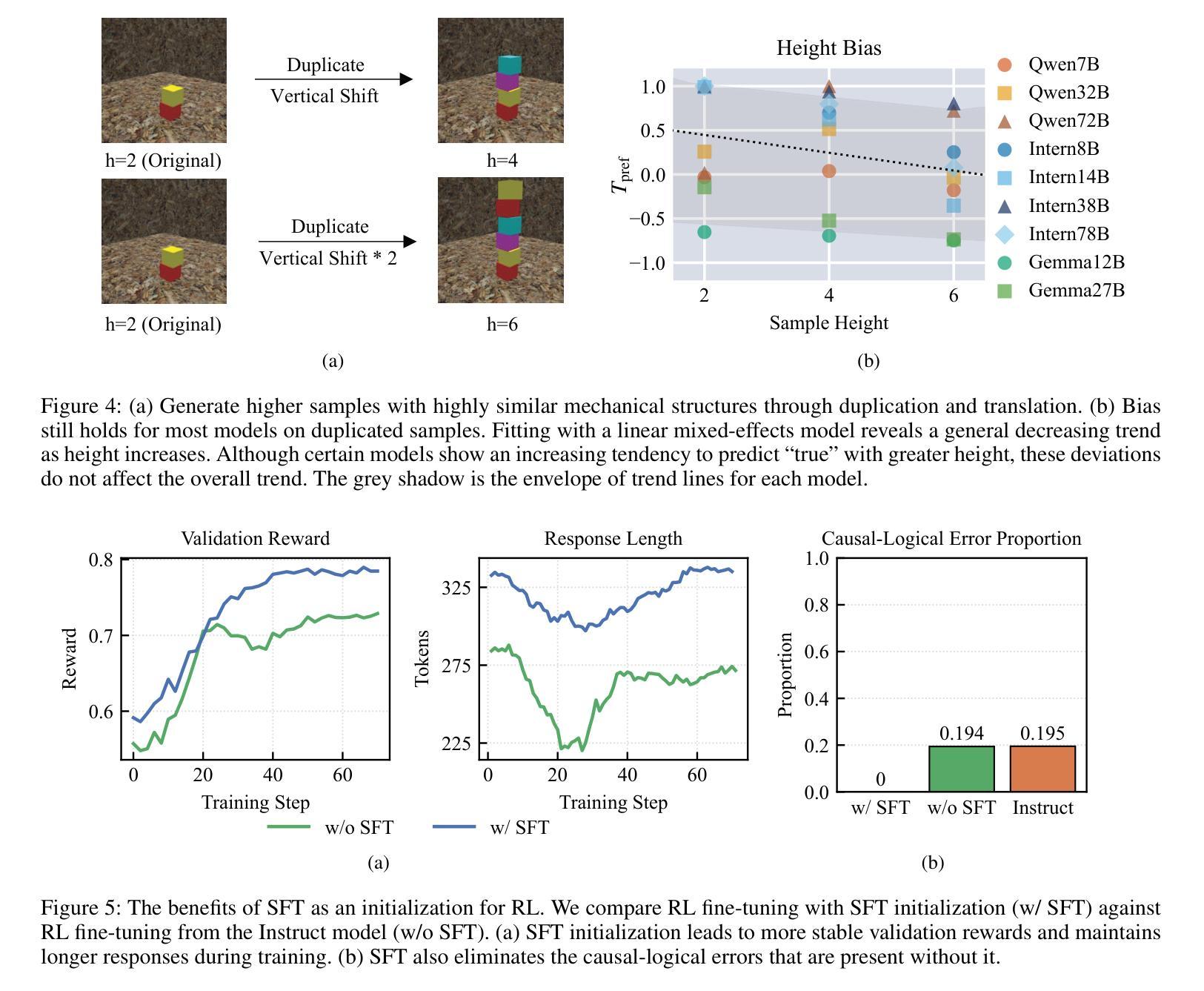
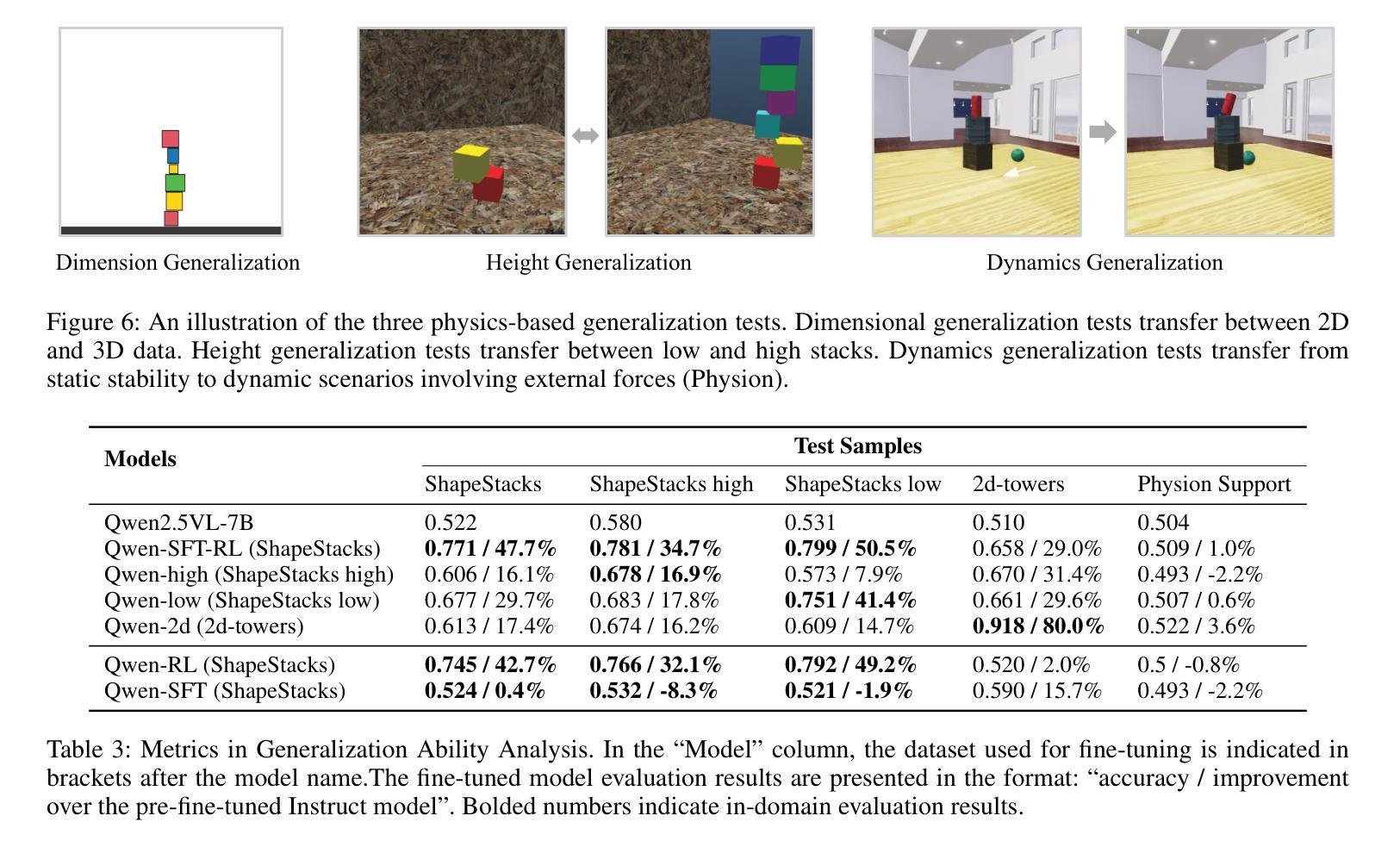
From Diagnosis to Improvement: Probing Spatio-Physical Reasoning in Vision Language Models
Authors:Tiancheng Han, Yunfei Gao, Yong Li, Wuzhou Yu, Qiaosheng Zhang, Wenqi Shao
Spatio-physical reasoning, a foundation capability for understanding the real physics world, is a critical step towards building robust world models. While recent vision language models (VLMs) have shown remarkable progress in specialized domains like multimodal mathematics and pure spatial understanding, their capability for spatio-physical reasoning remains largely unexplored. This paper provides a comprehensive diagnostic analysis of mainstream VLMs, revealing that current models perform inadequately on this crucial task. Further detailed analysis shows that this underperformance is largely attributable to biases caused by human-like prior and a lack of deep reasoning. To address these challenges, we apply supervised fine-tuning followed by rule-based reinforcement learning to Qwen2.5-VL-7B, resulting in significant improvements in spatio-physical reasoning capabilities and surpassing leading proprietary models. Nevertheless, despite this success, the model’s generalization to new physics scenarios remains limited – underscoring the pressing need for new approaches in spatio-physical reasoning.
时空物理推理是理解真实物理世界的基础能力,也是构建稳健世界模型的关键步骤。虽然最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态数学和纯空间理解等特定领域取得了显著进展,但它们在时空物理推理方面的能力仍然很大程度上未被探索。本文对所提出的主流视觉语言模型进行了全面的诊断分析,发现当前模型在这一关键任务上的表现不佳。进一步的详细分析表明,这种表现不佳在很大程度上是由于人为先验导致的偏见和缺乏深度推理所造成的。为了解决这些挑战,我们对Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型应用了基于监督微调后的规则强化学习,这大大提高了其时空物理推理能力并超越了领先的专有模型。然而,尽管取得了成功,该模型在新物理场景下的泛化能力仍然有限,这突显了对时空物理推理新方法迫切的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures
Summary
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在特定领域如多模态数学和纯空间理解方面取得了显著进展,但在空间物理推理这一关键任务上的能力尚未得到充分探索。本文主流VLMs进行了全面的诊断分析,发现当前模型在此任务上的表现不佳,主要原因是人为先验的偏见和缺乏深度推理。为解决这些挑战,对Qwen2.5-VL-7B进行了监督微调,并采用基于规则的强化学习,显著提高了其空间物理推理能力并超越了领先的专有模型。然而,模型在新物理场景下的泛化能力仍然有限,凸显出空间物理推理的新方法迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 空间物理推理是构建稳健世界模型的关键步骤,对于理解真实物理世界至关重要。
- 主流视觉语言模型(VLMs)在空间物理推理任务上的表现不佳。
- 当前模型的不足主要源于人为先验的偏见和缺乏深度推理。
- 通过监督微调及规则强化学习,Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型的空间物理推理能力得到显著提高。
- 尽管有所进步,模型在新物理场景下的泛化能力仍然有限。
- 需要探索新的空间物理推理方法以提高模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

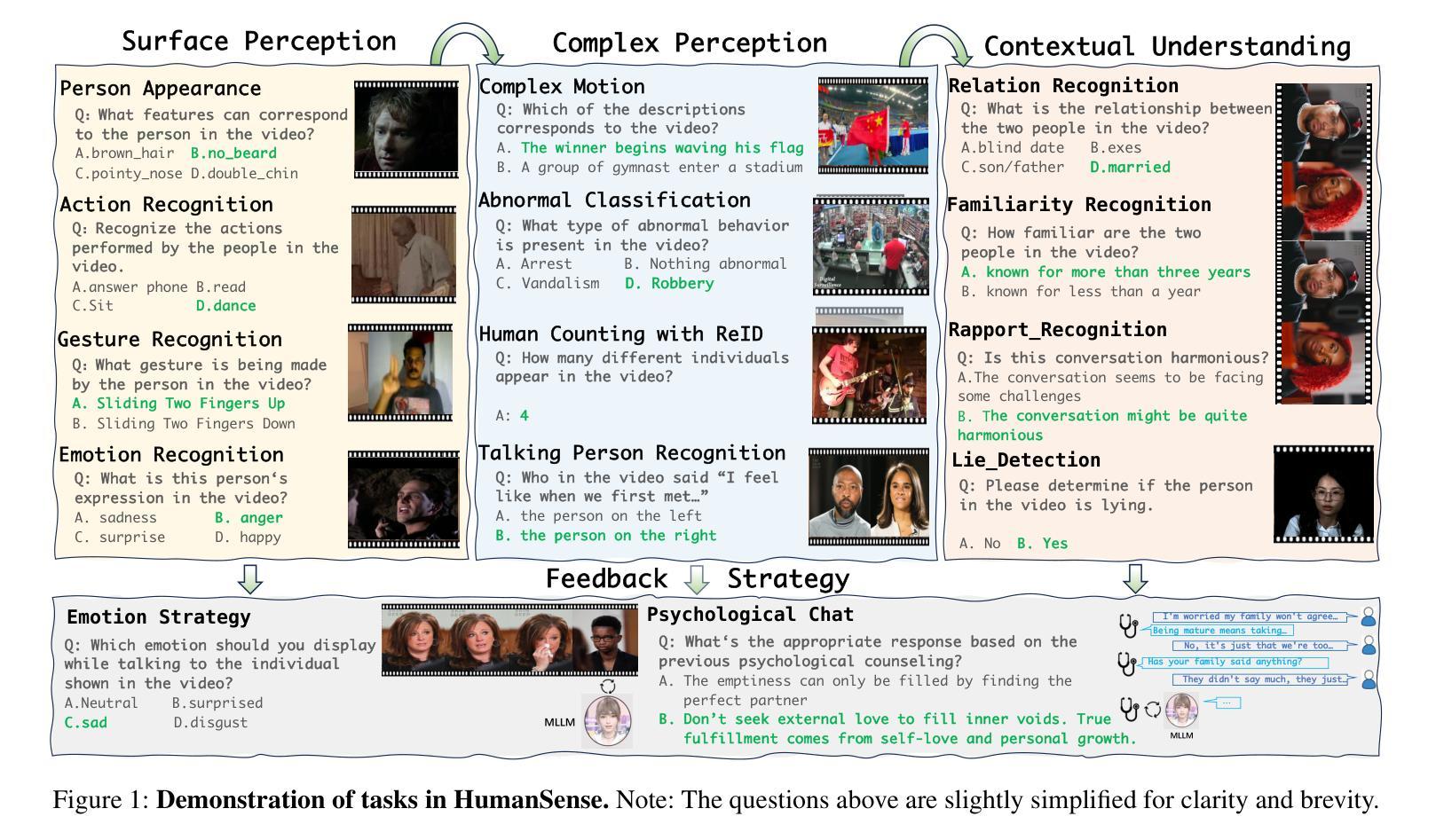
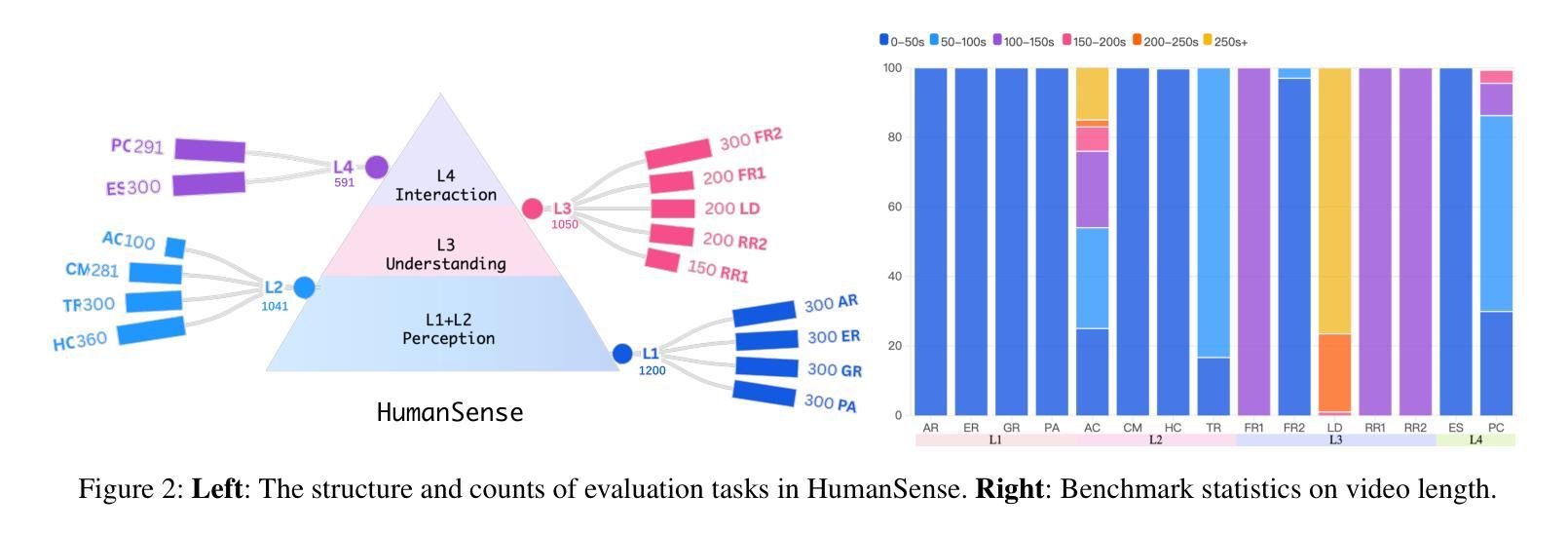
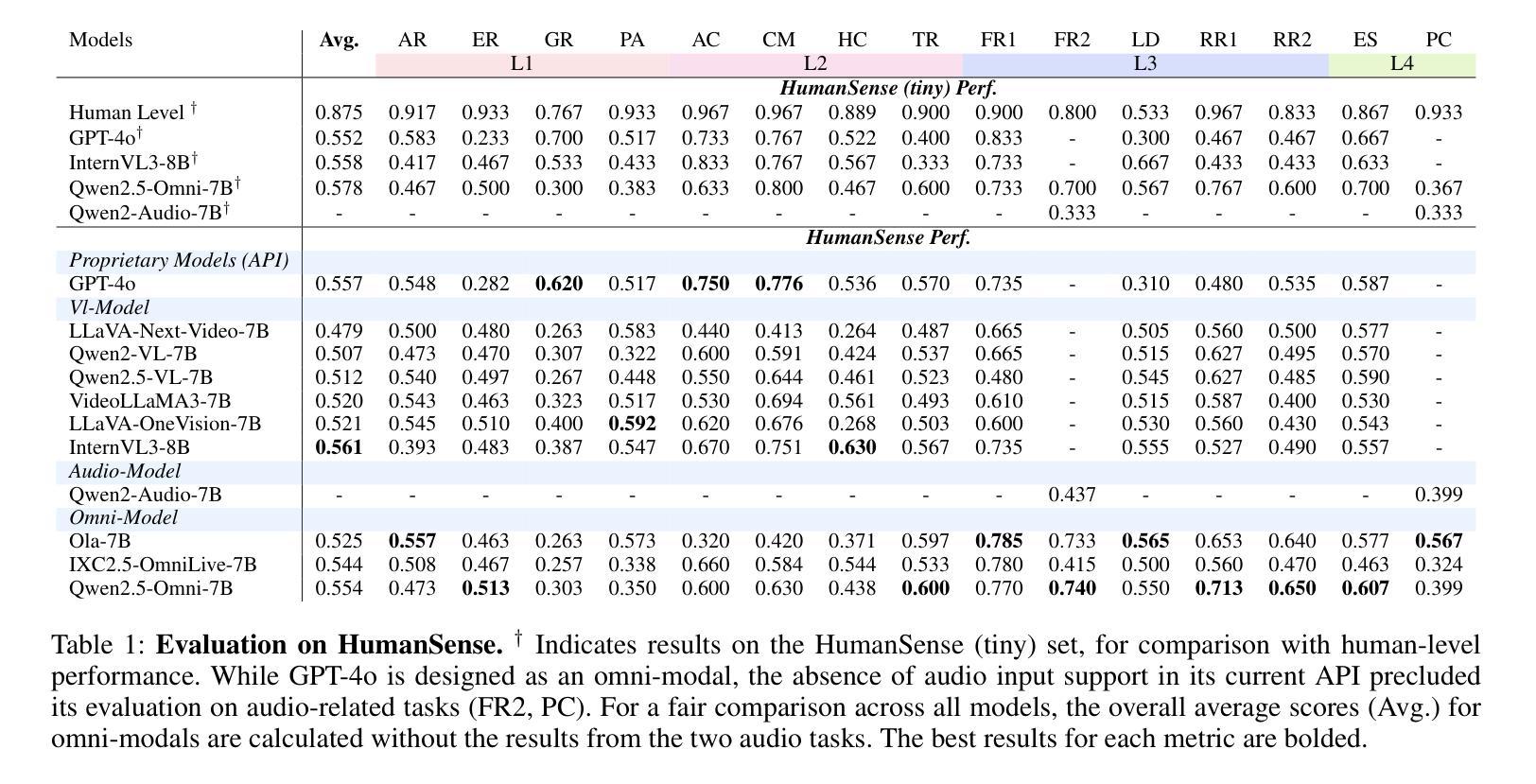
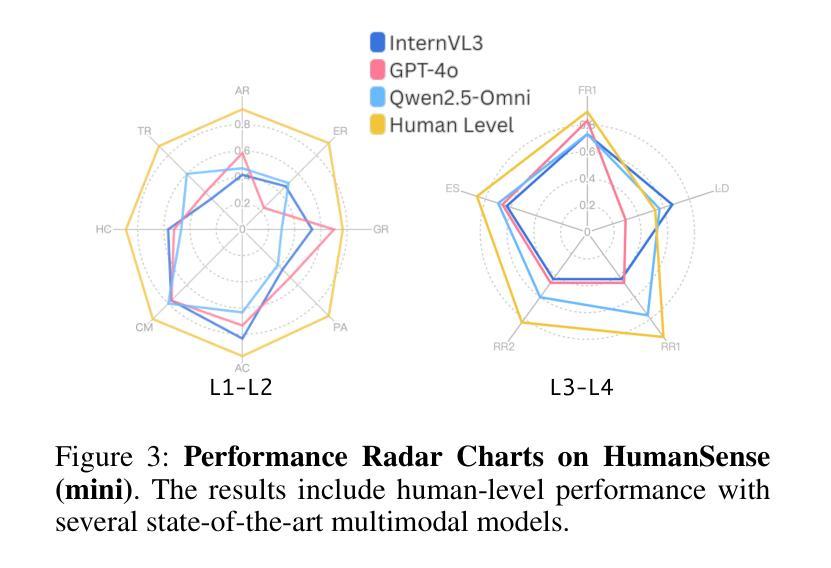
HumanSense: From Multimodal Perception to Empathetic Context-Aware Responses through Reasoning MLLMs
Authors:Zheng Qin, Ruobing Zheng, Yabing Wang, Tianqi Li, Yi Yuan, Jingdong Chen, Le Wang
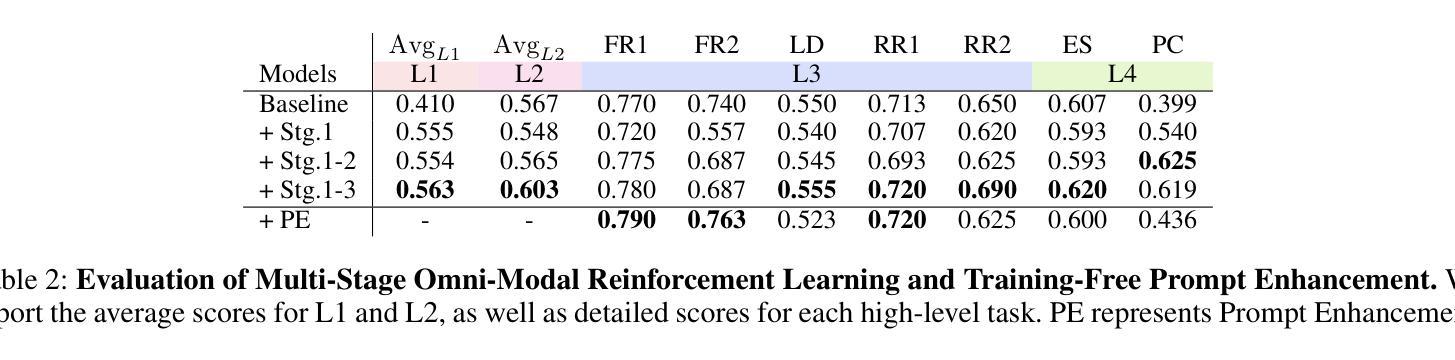
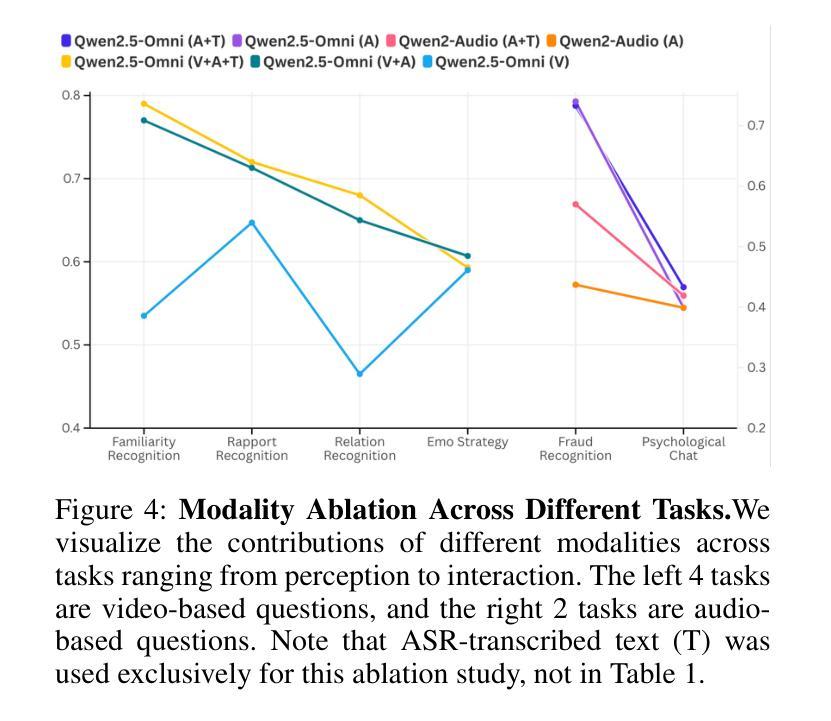
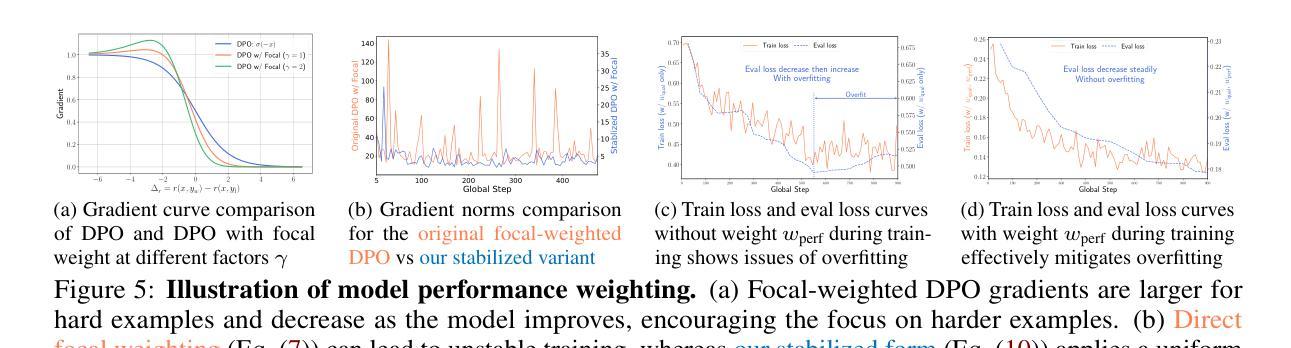
While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show immense promise for achieving truly human-like interactions, progress is hindered by the lack of fine-grained evaluation frameworks for human-centered scenarios, encompassing both the understanding of complex human intentions and the provision of empathetic, context-aware responses. Here we introduce HumanSense, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the human-centered perception and interaction capabilities of MLLMs, with a particular focus on deep understanding of extended multimodal contexts and the formulation of rational feedback. Our evaluation reveals that leading MLLMs still have considerable room for improvement, particularly for advanced interaction-oriented tasks. Supplementing visual input with audio and text information yields substantial improvements, and Omni-modal models show advantages on these tasks. Furthermore, we argue that appropriate feedback stems from a contextual analysis of the interlocutor’s needs and emotions, with reasoning ability serving as the key to unlocking it. Accordingly, we employ a multi-stage, modality-progressive reinforcement learning to enhance the reasoning abilities of an Omni model, achieving substantial gains on evaluation results. Additionally, we observe that successful reasoning processes exhibit highly consistent thought patterns. By designing corresponding prompts, we also enhance the performance of non-reasoning models in a training-free manner. Project page: \textcolor{brightpink}https://digital-avatar.github.io/ai/HumanSense/
虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在实现真正人类般的交互方面显示出巨大的潜力,但进展受到缺乏以人类为中心的情景的精细评估框架的阻碍,这些框架需要包含对复杂人类意图的理解和提供富有同情心和情境意识的响应。在这里,我们介绍了HumanSense,这是一个综合基准测试,旨在评估MLLMs以人类为中心的感知和交互能力,特别侧重于对扩展的多模态上下文的深入理解以及理性反馈的形成。我们的评估表明,领先的大型语言模型仍有很大的改进空间,特别是在面向高级交互的任务方面。通过补充视觉输入与音频和文本信息相结合的方式,产生了实质性的改进,多模态模型在这些任务上显示出优势。此外,我们认为适当的反馈来自于对话者需求和情绪的上下文分析,推理能力是解锁它的关键。因此,我们采用多阶段、模态渐进式强化学习来增强Omni模型的推理能力,在评估结果上取得了重大收获。此外,我们还观察到成功的推理过程展现出高度一致的思考模式。通过设计相应的提示,我们还以无培训的方式增强了非推理模型的性能。项目页面:
链接[待添加实际链接地址]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:介绍了针对多模态大型语言模型的人类中心感知交互能力的基准测试系统HumanSense,用于评估对复杂人类意图的理解和对移情和上下文感知的响应提供的能力。虽然当前的模型在许多任务上还有很大的改进空间,但研究发现将视觉输入与音频和文本信息相结合能带来显著的改进,同时强调推理能力在提供适当反馈中的关键作用。研究还通过采用多阶段、模态渐进的强化学习来增强模型的推理能力,并通过设计相应的提示来增强非推理模型的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 缺乏针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的精细评价框架,无法全面评估其在理解复杂人类意图和提供移情、上下文感知响应方面的能力。
- HumanSense基准测试系统旨在评估MLLMs在人类中心感知交互方面的能力,特别强调对扩展的多模态上下文的理解和提供合理反馈的能力。
- 现有MLLMs在高级交互任务上有较大改进空间,融合多种模态(如视觉、音频和文本)信息有助于提高模型性能。
- 推理能力是提供适当反馈的关键,研究采用多阶段、模态渐进的强化学习提升模型的推理能力。
- 成功推理过程展现出高度一致的思考模式,通过设计相应提示,可以在不增加训练成本的情况下提高非推理模型的性能。
- HumanSense项目提供了一个评估和增强MLLMs人类中心交互能力的平台。
点此查看论文截图