⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
Speech Emotion Recognition Using Fine-Tuned DWFormer:A Study on Track 1 of the IERPChallenge 2024
Authors:Honghong Wang, Xupeng Jia, Jing Deng, Rong Zheng
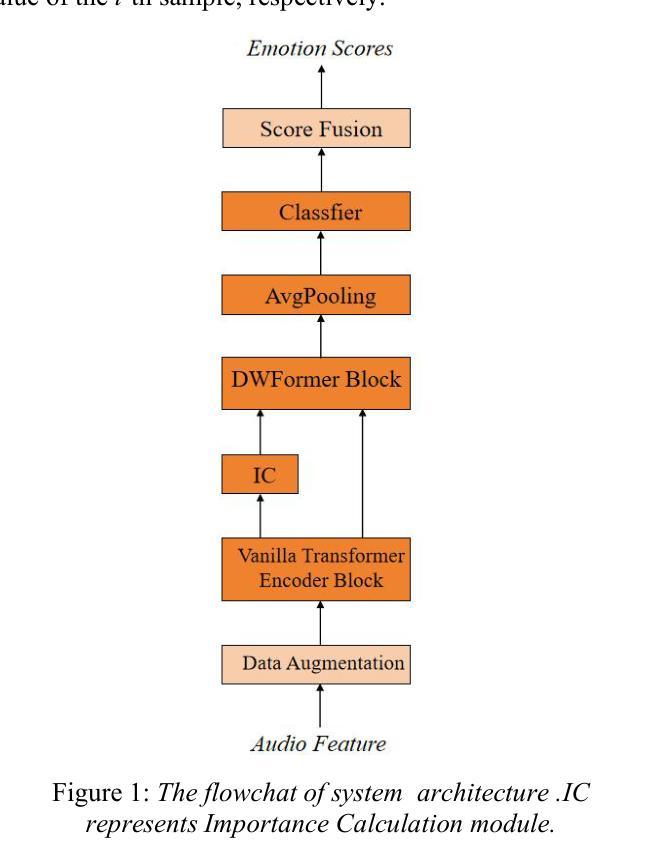
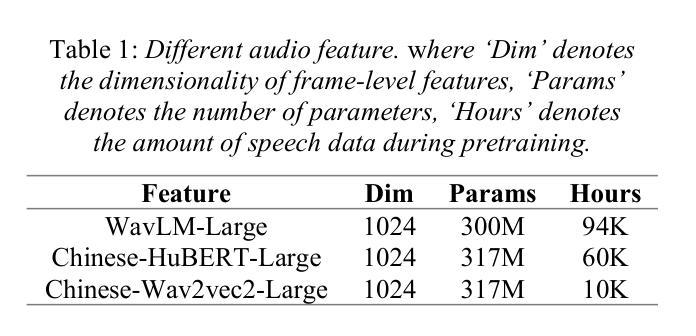
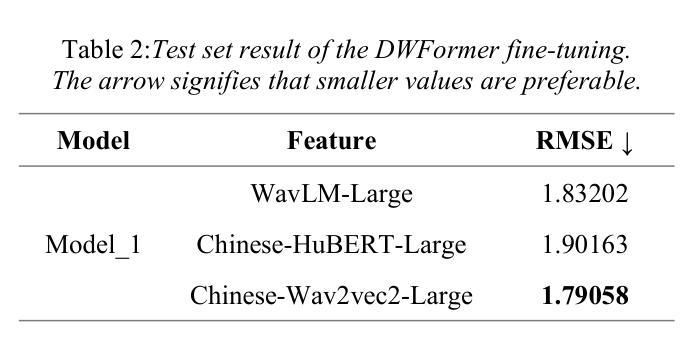
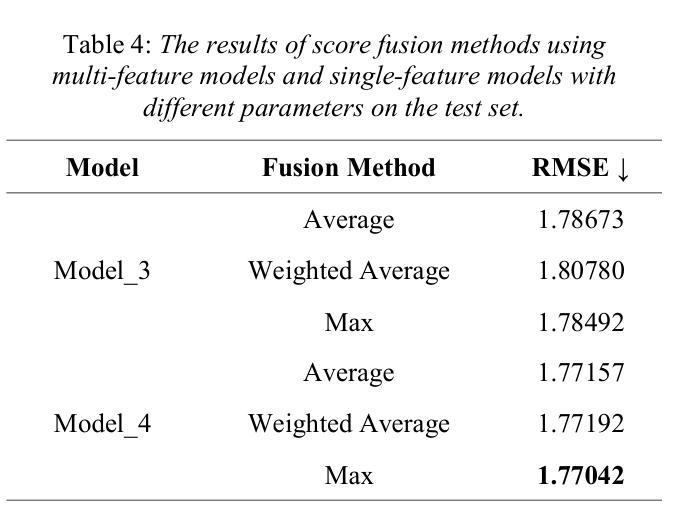
The field of artificial intelligence has a strong interest in the topic of emotion recognition. The majority of extant emotion recognition models are oriented towards enhancing the precision of discrete emotion label prediction. Given the direct relationship between human personality and emotion, as well as the significant inter-individual differences in subjective emotional expression, the IERP Challenge 2024 incorporates personality traits into emotion recognition research. This paper presents the Fosafer submissions to the Track 1 of the IERP Challenge 2024. This task primarily concerns the recognition of emotions in audio, while also providing text and audio features. In Track 1, we utilized exclusively audio-based features and fine-tuned a pre-trained speech emotion recognition model, DWFormer, through the integration of data augmentation and score fusion strategies, thereby achieving the first place among the participating teams.
人工智能领域对情绪识别话题有着浓厚的兴趣。现有大多数情绪识别模型旨在提高离散情绪标签预测的精确度。考虑到人类性格与情绪之间的直接关系,以及主观情绪表达上的个体差异,IEPR Challenge 2024将性格特征纳入情绪识别研究中。本文展示了Fosafer团队参加IEPR Challenge 2024 Track 1的提交内容。这项任务主要涉及音频中的情绪识别,同时提供文本和音频特征。在Track 1中,我们仅使用基于音频的特征,并通过数据增强和评分融合策略的集成,对预训练的语音情绪识别模型DWFormer进行微调,从而在参赛队伍中取得第一名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages,1 figures
Summary
人工智能领域对情绪识别主题具有浓厚兴趣。大多数现有的情绪识别模型旨在提高离散情绪标签预测的精确度。考虑到人类个性与情绪之间的直接关系以及主观情绪表达上的个体差异,IERP Challenge 2024将人格特质融入情绪识别研究中。本文介绍Fosafer团队在IERP Challenge 2024 Track 1中的提交内容。此任务主要涉及音频中的情绪识别,并提供文本和音频特征。在Track 1中,我们仅使用基于音频的特征,并通过数据增强和分数融合策略的集成,微调了预训练的语音情绪识别模型DWFormer,从而在参赛团队中取得第一名。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能领域对情绪识别有浓厚兴趣,多数模型旨在提高情绪标签预测精确度。
- IERP Challenge 2024将人格特质融入情绪识别研究。
- Fosafer团队参加了IERP Challenge 2024的Track 1任务。
- 该任务关注音频中的情绪识别,并提供文本和音频特征。
- Fosafer团队使用基于音频的特征和DWFormer模型进行情绪识别。
- 通过数据增强和分数融合策略,Fosafer团队微调了模型并获得了第一名。
点此查看论文截图

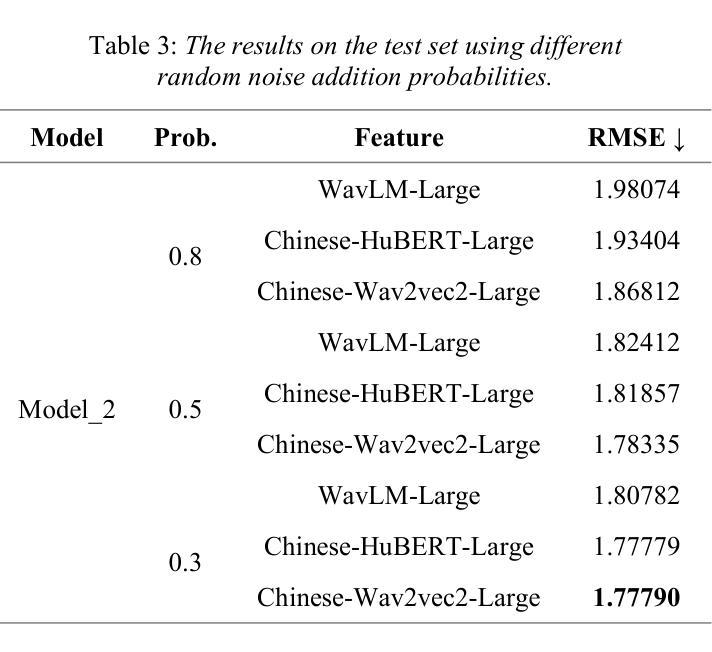
MoE-TTS: Enhancing Out-of-Domain Text Understanding for Description-based TTS via Mixture-of-Experts
Authors:Heyang Xue, Xuchen Song, Yu Tang, Jianyu Chen, Yanru Chen, Yang Li, Yahui Zhou
Description-based text-to-speech (TTS) models exhibit strong performance on in-domain text descriptions, i.e., those encountered during training. However, in real-world applications, the diverse range of user-generated descriptions inevitably introduces numerous out-of-domain inputs that challenge the text understanding capabilities of these systems. To address this issue, we propose MoE-TTS, a description-based TTS model designed to enhance the understanding of out-of-domain text descriptions. MoE-TTS employs a modality-based mixture-of-experts (MoE) approach to augment a pre-trained textual large language model (LLM) with a set of specialized weights adapted to the speech modality while maintaining the original LLM frozen during training. This approach allows MoE-TTS to effectively leverage the pre-trained knowledge and text understanding abilities of textual LLMs. Our experimental results indicate that: first, even the most advanced closed-source commercial products can be challenged by carefully designed out-of-domain description test sets; second, MoE-TTS achieves superior performance in generating speech that more accurately reflects the descriptions. We encourage readers to listen to the demos at https://welkinyang.github.io/MoE-TTS/.
基于描述的文本到语音(TTS)模型在领域内的文本描述上表现出强大的性能,即那些在训练过程中遇到的描述。然而,在现实世界的应用中,用户生成的各种描述不可避免地引入了大量的域外输入,这挑战了这些系统的文本理解能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了MoE-TTS,这是一种基于描述的TTS模型,旨在增强对域外文本描述的理解。MoE-TTS采用基于模态的混合专家(MoE)方法,用一组适应于语音模态的专用权重来增强预训练的文本大型语言模型(LLM),同时保持原始LLM在训练过程中的冻结。这种方法允许MoE-TTS有效利用预训练的知识和文本理解能力。我们的实验结果表明:首先,甚至最先进的闭源商业产品也会受到精心设计的域外描述测试集的挑战;其次,MoE-TTS在生成更能准确反映描述的语音方面表现出卓越的性能。我们鼓励读者在https://welkinyang.github.io/MoE-TTS/上听取演示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于描述的文本转语音(TTS)模型MoE-TTS,旨在提高对于非域文本描述的理解能力。MoE-TTS采用基于模态的混合专家(MoE)方法,通过添加一系列适应于语音模态的权重来增强预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。这种方法使得MoE-TTS能够充分利用预训练的语言模型和文本理解能力。实验结果表明,即使是最先进的闭源商业产品也会受到精心设计出的非域描述测试集的挑战,而MoE-TTS在生成更准确反映描述的语音方面表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 描述性文本转语音(TTS)模型在非域文本描述上可能面临挑战。
- MoE-TTS模型旨在提高对于非域文本描述的理解能力。
- MoE-TTS使用模态混合专家(MoE)方法来增强预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。
- MoE-TTS方法允许利用预训练的语言模型和文本理解能力。
- 实验表明,最先进的闭源商业产品在非域描述测试集上可能表现不佳。
- MoE-TTS在生成准确反映描述的语音方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


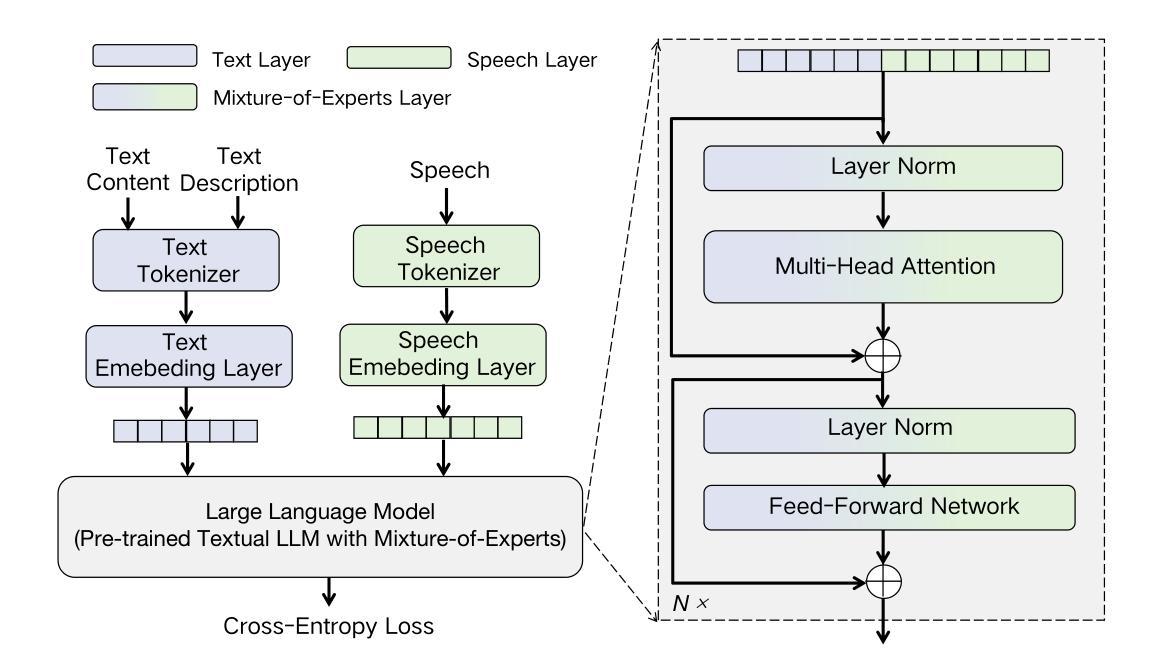

Novel Parasitic Dual-Scale Modeling for Efficient and Accurate Multilingual Speech Translation
Authors:Chenyang Le, Yinfeng Xia, Huiyan Li, Manhong Wang, Yutao Sun, Xingyang Ma, Yanmin Qian
Recent advancements in speech-to-text translation have led to the development of multilingual models capable of handling multiple language pairs simultaneously. However, these unified models often suffer from large parameter sizes, making it challenging to balance inference efficiency and performance, particularly in local deployment scenarios. We propose an innovative Parasitic Dual-Scale Approach, which combines an enhanced speculative sampling method with model compression and knowledge distillation techniques. Building on the Whisper Medium model, we enhance it for multilingual speech translation into whisperM2M, and integrate our novel KVSPN module, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across six popular languages with improved inference efficiency. KVSPN enables a 40% speedup with no BLEU score degradation. Combined with distillation methods, it represents a 2.6$\times$ speedup over the original Whisper Medium with superior performance.
近期语音到文本的翻译技术进展推动了能够同时处理多种语言对的多语言模型的发展。然而,这些统一模型通常参数规模较大,使得在推理效率和性能之间取得平衡变得具有挑战性,特别是在本地部署场景中。我们提出了一种新颖的寄生双尺度方法,该方法结合了增强的推测采样方法、模型压缩和知识蒸馏技术。我们在Whisper Medium模型的基础上,将其增强为用于多语言语音翻译的自语M2M模型,并集成了我们新颖的知识向量结构化表示模块KVSPN,在六种流行语言上实现了最先进的性能,并提高了推理效率。KVSPN能够实现40%的速度提升且不影响BLEU分数。结合蒸馏方法,其相对于原始Whisper Medium模型实现了2.6倍的速度提升,并且性能更加优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2025
Summary
近期语音转文本翻译技术的新进展推动了多语言模型的开发,能够同时处理多种语言对。然而,这些统一模型通常参数庞大,需要在推理效率和性能之间取得平衡,特别是在本地部署场景中。研究团队提出了一种创新的寄生双尺度方法,结合了改进的投机采样方法、模型压缩和知识蒸馏技术。基于Whisper Medium模型,研究团队增强了其多语言语音翻译能力,推出whisperM2M,并集成了新型KVSPN模块,在六种流行语言上实现最佳性能,同时提高了推理效率。KVSPN实现了40%的加速,且不降低BLEU分数。结合蒸馏方法,其速度比原始Whisper Medium提高了2.6倍,性能更优越。
Key Takeaways
- 语音转文本翻译技术取得新进展,推动多语言模型处理多种语言对的能力。
- 统一模型面临参数庞大、推理效率和性能平衡的挑战。
- 寄生双尺度方法结合了改进的投机采样、模型压缩和知识蒸馏技术。
- 基于Whisper Medium模型,增强了多语言语音翻译能力,推出whisperM2M。
- KVSPN模块实现40%的加速,且不降低BLEU分数。
- 结合蒸馏方法,KVSPN模块使推理速度比原始模型提高2.6倍。
- whisperM2M在六种流行语言上实现最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

Enabling Differentially Private Federated Learning for Speech Recognition: Benchmarks, Adaptive Optimizers and Gradient Clipping
Authors:Martin Pelikan, Sheikh Shams Azam, Vitaly Feldman, Jan “Honza” Silovsky, Kunal Talwar, Christopher G. Brinton, Tatiana Likhomanenko
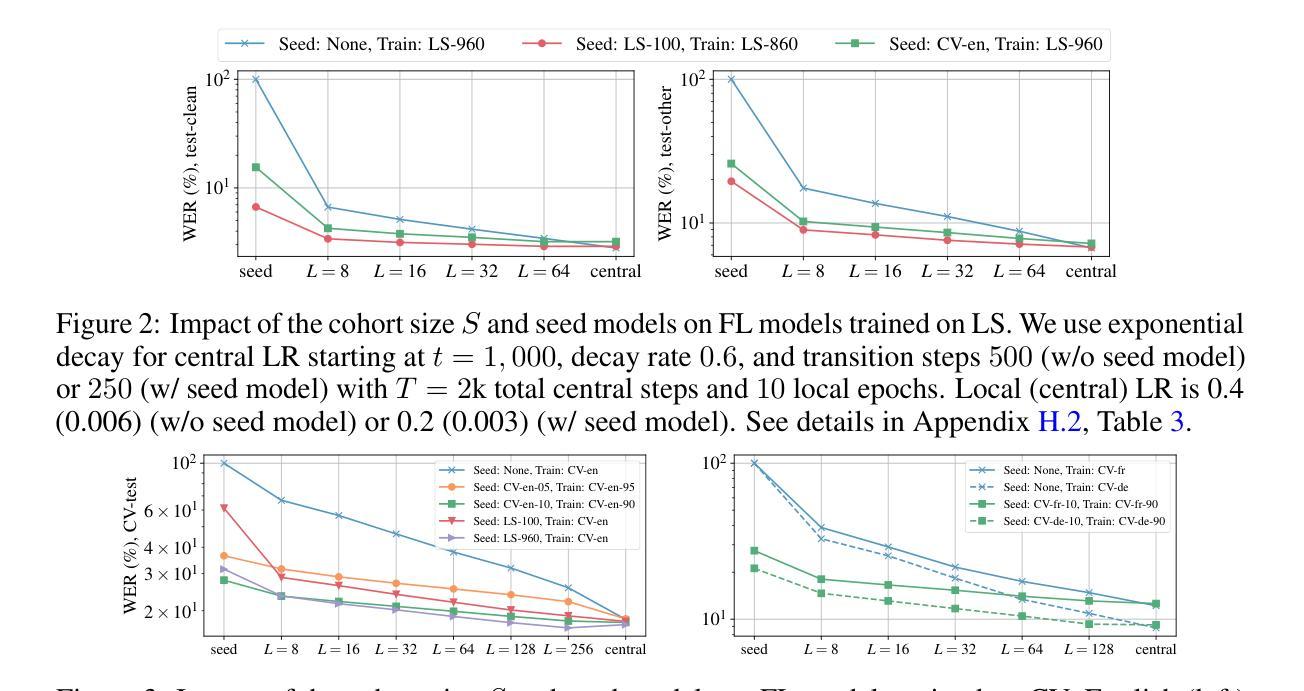
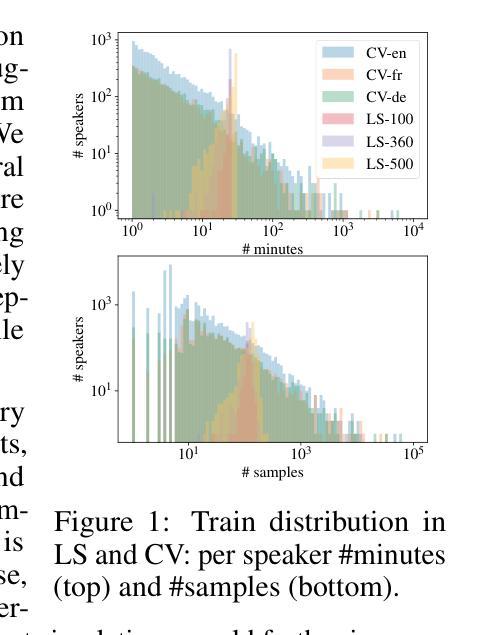
While federated learning (FL) and differential privacy (DP) have been extensively studied, their application to automatic speech recognition (ASR) remains largely unexplored due to the challenges in training large transformer models. Specifically, large models further exacerbate issues in FL as they are particularly susceptible to gradient heterogeneity across layers, unlike the relatively uniform gradient behavior observed in shallow models. As a result, prior works struggle to converge with standard optimization techniques, even in the absence of DP mechanisms. To the best of our knowledge, no existing work establishes a competitive, practical recipe for FL with DP in the context of ASR. To address this gap, we establish \textbf{the first benchmark for FL with DP in end-to-end ASR}. Our approach centers on per-layer clipping and layer-wise gradient normalization: theoretical analysis reveals that these techniques together mitigate clipping bias and gradient heterogeneity across layers in deeper models. Consistent with these theoretical insights, our empirical results show that FL with DP is viable under strong privacy guarantees, provided a population of at least several million users. Specifically, we achieve user-level (7.2, $10^{-9}$)-DP (resp. (4.5, $10^{-9}$)-DP) with only a 1.3% (resp. 4.6%) absolute drop in word error rate when extrapolating to high (resp. low) population scales for FL with DP in ASR. Although our experiments focus on ASR, the underlying principles we uncover - particularly those concerning gradient heterogeneity and layer-wise gradient normalization - offer broader guidance for designing scalable, privacy-preserving FL algorithms for large models across domains. Code of all experiments and benchmarks is available at https://github.com/apple/ml-pfl4asr.
虽然联邦学习(FL)和差分隐私(DP)已经得到了广泛的研究,但它们应用于自动语音识别(ASR)仍然在很大程度上未被探索,这是由于训练大型变压器模型带来的挑战。特别是,大型模型会进一步加剧联邦学习的问题,因为它们特别容易受到各层梯度异质性的影响,这与浅层模型中观察到的相对统一的梯度行为形成对比。因此,即便在没有差分隐私机制的情况下,先前的研究工作也很难用标准优化技术实现收敛。据我们所知,目前尚无工作在自动语音识别背景下建立具有竞争力的、实用的联邦学习与差分隐私结合的方法。为了弥补这一空白,我们首次建立了端对端ASR的联邦学习与差分隐私结合的基准测试。我们的方法以每层裁剪和逐层梯度归一化为中心:理论分析表明,这些技术相结合减轻了深层模型中裁剪偏差和跨层梯度异质性的问题。与这些理论洞察相一致,我们的实证结果表明,在至少数百万用户的支持下,带有差分隐私的联邦学习是可行的。具体来说,我们在用户层面实现了(7.2, 10^-9)-差分隐私(对于联邦学习与自动语音识别中的DP应用),在高用户规模情况下绝对字词错误率仅增加了1.3%;在低用户规模情况下,(4.5, 10^-9)-差分隐私的绝对字词错误率增加了4.6%。尽管我们的实验重点在自动语音识别上,但我们揭示的基本原理——特别是关于梯度异质性和逐层梯度归一化的原理——为设计跨领域的大规模、隐私保护的联邦学习算法提供了更广泛的指导。所有实验和基准测试的代码可在https://github.com/apple/ml-pfl4asr找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
摘要
本文探讨了联邦学习与差分隐私在自动语音识别中的应用,针对大模型在联邦学习中的梯度异质性挑战,提出了基于层裁剪和层梯度归一化的解决方案。建立了首个针对此领域的基准测试,并在隐私保护下实现了联邦学习的可行性。理论分析和实证结果表明,该技术能有效缓解深层模型中的裁剪偏差和梯度异质性。在保障用户级别隐私的同时,实现了语音识别的词错误率仅绝对下降1.3%至4.6%。此外,该研究揭示的梯度异质性和层间梯度归一化等原理,为设计跨领域的大规模隐私保护联邦学习算法提供了指导。相关实验代码已公开。
关键见解
- 联邦学习与差分隐私在自动语音识别中的应用仍处于探索阶段。
- 大模型在联邦学习中面临梯度异质性的挑战。
- 层裁剪和层梯度归一化技术能有效缓解深层模型中的裁剪偏差和梯度异质性。
- 在隐私保护下实现了联邦学习的可行性,用户级别的隐私保护可使词错误率仅绝对下降1.3%至4.6%。
- 研究揭示的梯度异质性和层间梯度归一化原理为跨领域的大规模隐私保护联邦学习算法设计提供了指导。
- 相关实验代码已公开,便于后续研究参考与拓展。
- 此研究为联邦学习和差分隐私在自动语音识别领域的发展树立了新的基准。
点此查看论文截图