⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-19 更新
Fine-Grained VLM Fine-tuning via Latent Hierarchical Adapter Learning
Authors:Yumiao Zhao, Bo Jiang, Yuhe Ding, Xiao Wang, Jin Tang, Bin Luo
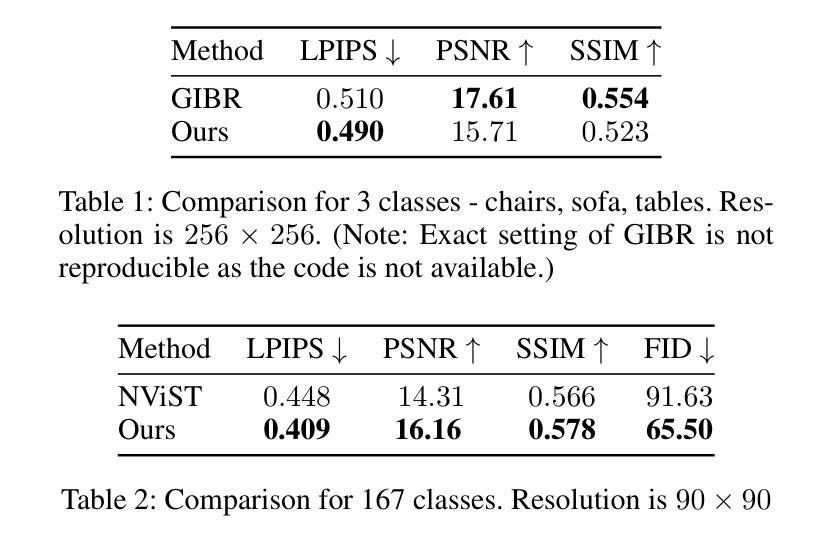
Adapter-based approaches have garnered attention for fine-tuning pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on few-shot classification tasks. These methods strive to develop a lightweight module that better aligns visual and (category) textual representations, thereby enhancing performance on downstream few-shot learning tasks. However, existing adapters generally learn/align (category) textual-visual modalities via explicit spatial proximity in the underlying embedding space, which i) fails to capture the inherent one-to-many associations between categories and image samples and ii) struggles to establish accurate associations between the unknown categories and images. To address these issues, inspired by recent works on hyperbolic learning, we develop a novel Latent Hierarchical Adapter (LatHAdapter) for fine-tuning VLMs on downstream few-shot classification tasks. The core of LatHAdapter is to exploit the latent semantic hierarchy of downstream training data and employ it to provide richer, fine-grained guidance for the adapter learning process. Specifically, LatHAdapter first introduces some learnable `attribute’ prompts as the bridge to align categories and images. Then, it projects the categories, attribute prompts, and images within each batch in a hyperbolic space, and employs hierarchical regularization to learn the latent semantic hierarchy of them, thereby fully modeling the inherent one-to-many associations among categories, learnable attributes, and image samples. Extensive experiments on four challenging few-shot tasks show that the proposed LatHAdapter consistently outperforms many other fine-tuning approaches, particularly in adapting known classes and generalizing to unknown classes.
基于适配器的方法在微调预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)以执行少量样本分类任务时引起了关注。这些方法致力于开发一个轻量级的模块,以更好地对齐视觉和(类别)文本表示,从而提高在下游的少量样本学习任务上的性能。然而,现有的适配器通常通过潜在嵌入空间中的明确空间邻近关系来学习/对齐(类别)文本视觉模式,这种方式一)无法捕获类别和图像样本之间固有的多对一关联,二)在建立未知类别和图像之间的准确关联方面表现挣扎。为了解决这个问题,我们受到最近超复数学学习工作的启发,开发了一种用于微调下游少量样本分类任务的全新潜在分层适配器(LatHAdapter)。LatHAdapter的核心是利用下游训练数据的潜在语义层次结构,并为其提供更丰富、更精细的引导以进行适配器学习过程。具体来说,LatHAdapter首先引入一些可学习的“属性”提示作为桥梁来对齐类别和图像。然后,它在超复平面上将每批次的类别、属性提示和图像投影出来,并通过分层正则化学习它们的潜在语义层次结构,从而充分建模类别、可学习属性和图像样本之间的固有的一对多关联。在四个具有挑战性的少量样本任务上的广泛实验表明,所提出的LatHAdapter在多个微调方法中表现突出,特别是在适应已知类别和推广到未知类别方面。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注于使用基于适配器的方法对预训练的视觉语言模型进行微调,以应对小样本分类任务。现有适配器主要通过明确的时空邻近性来学习和对齐文本视觉模态,但这种方法存在缺陷。为此,本文受超球面学习的启发,提出了一种新型的潜在层次适配器(LatHAdapter)。它通过利用下游训练数据的潜在语义层次结构,为适配器学习过程提供更丰富的精细指导。LatHAdapter通过引入可学习的属性提示来对齐类别和图像,并在超球面空间中对类别、属性提示和图像进行投影,采用层次正则化来学习它们的潜在语义层次结构。实验表明,LatHAdapter在四个具有挑战性的小样本任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 适配器方法用于微调预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs),以提高小样本分类任务的性能。
- 现有适配器主要通过明确的时空邻近性对齐文本和视觉模态,存在缺陷。
- 本文受超球面学习的启发,提出了一种新型的潜在层次适配器(LatHAdapter)。
- LatHAdapter利用下游训练数据的潜在语义层次结构,为适配器学习过程提供更丰富的精细指导。
- LatHAdapter通过引入属性提示来对齐类别和图像。
- LatHAdapter在超球面空间中对类别、属性提示和图像进行投影,并采用层次正则化。
点此查看论文截图

From Explainable to Explained AI: Ideas for Falsifying and Quantifying Explanations
Authors:Yoni Schirris, Eric Marcus, Jonas Teuwen, Hugo Horlings, Efstratios Gavves
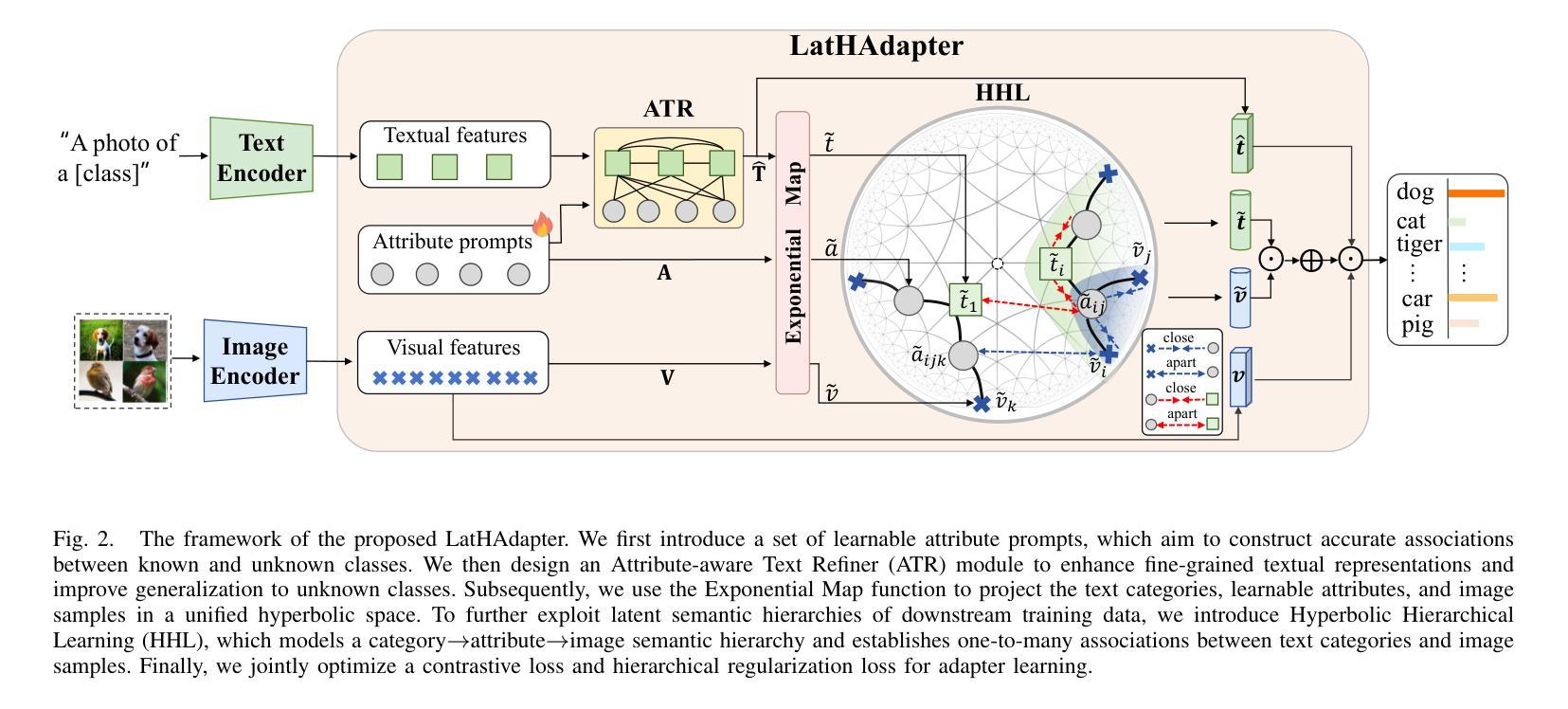
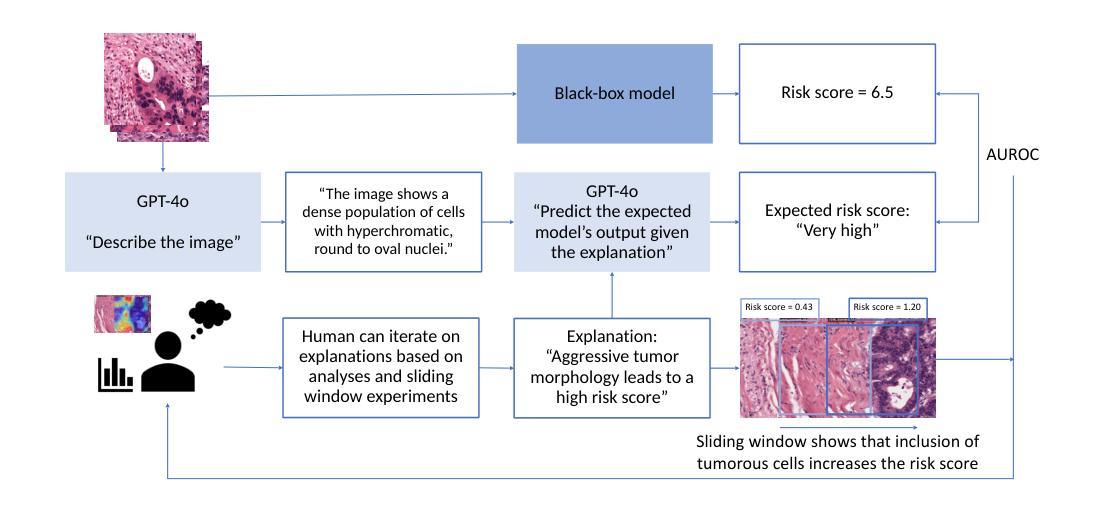
Explaining deep learning models is essential for clinical integration of medical image analysis systems. A good explanation highlights if a model depends on spurious features that undermines generalization and harms a subset of patients or, conversely, may present novel biological insights. Although techniques like GradCAM can identify influential features, they are measurement tools that do not themselves form an explanation. We propose a human-machine-VLM interaction system tailored to explaining classifiers in computational pathology, including multi-instance learning for whole-slide images. Our proof of concept comprises (1) an AI-integrated slide viewer to run sliding-window experiments to test claims of an explanation, and (2) quantification of an explanation’s predictiveness using general-purpose vision-language models. The results demonstrate that this allows us to qualitatively test claims of explanations and can quantifiably distinguish competing explanations. This offers a practical path from explainable AI to explained AI in digital pathology and beyond. Code and prompts are available at https://github.com/nki-ai/x2x.
将深度学习模型的解释对于医学影像分析系统的临床应用集成至关重要。一个好的解释可以突出模型是否依赖于会破坏泛化并伤害患者子集的偶然特征,或者相反,可以呈现新的生物学见解。虽然GradCAM等技术可以识别出有影响力的特征,但它们只是测量工具,本身并不构成解释。我们提出了一种针对计算病理学分类器设计的人机-VLM交互系统,包括用于全幻灯片图像的多实例学习。我们的概念验证包括(1)一个集成AI的幻灯片查看器,用于运行滑动窗口实验来检验解释的主张,以及(2)使用通用视觉语言模型量化解释的预测性。结果表明,这使我们能够定性检验解释的主张,并能够定量区分相互竞争的解释。这为数字病理学及以外的领域从可解释的AI到解释的AI提供了实际路径。代码和提示可在https://github.com/nki-ai/x2x上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables, submitted at MICCAI IMIMIC workshop
Summary
人工智能集成化病理图像观察工具联合多实例学习实现对全视野显微镜图像的AI辅助分类与解释机制验证。此方法能发现用于图像识别的关键特征并验证解释预测能力。具体路径见GitHub链接:[GitHub链接]。此系统可实现人工智能病理图像解释从定性到定量的飞跃。
Key Takeaways
- 在医学图像分析系统中整合深度学习模型解释对于临床使用至关重要。良好的解释能揭示模型依赖的特定特征及其对通用化或特定患者群体的潜在影响。
- 虽然存在如GradCAM等技术可以识别关键特征,但这些技术本身并不提供解释,仅仅是测量工具。
- 提出一种人机结合的互动系统,专门针对计算病理学中的分类器进行解释,包括全视野图像的多实例学习。该系统旨在将AI辅助分类与解释机制验证相结合。
点此查看论文截图

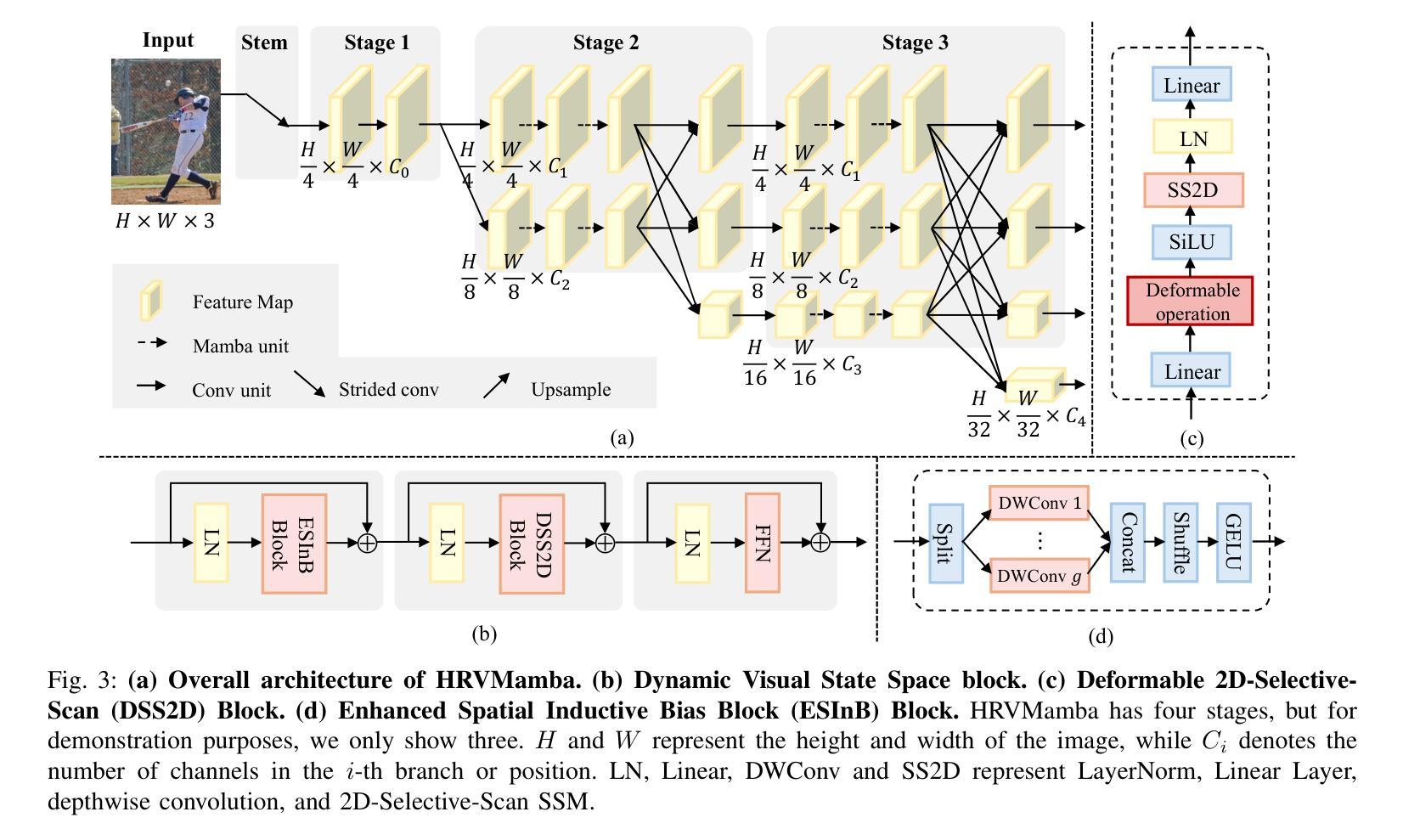
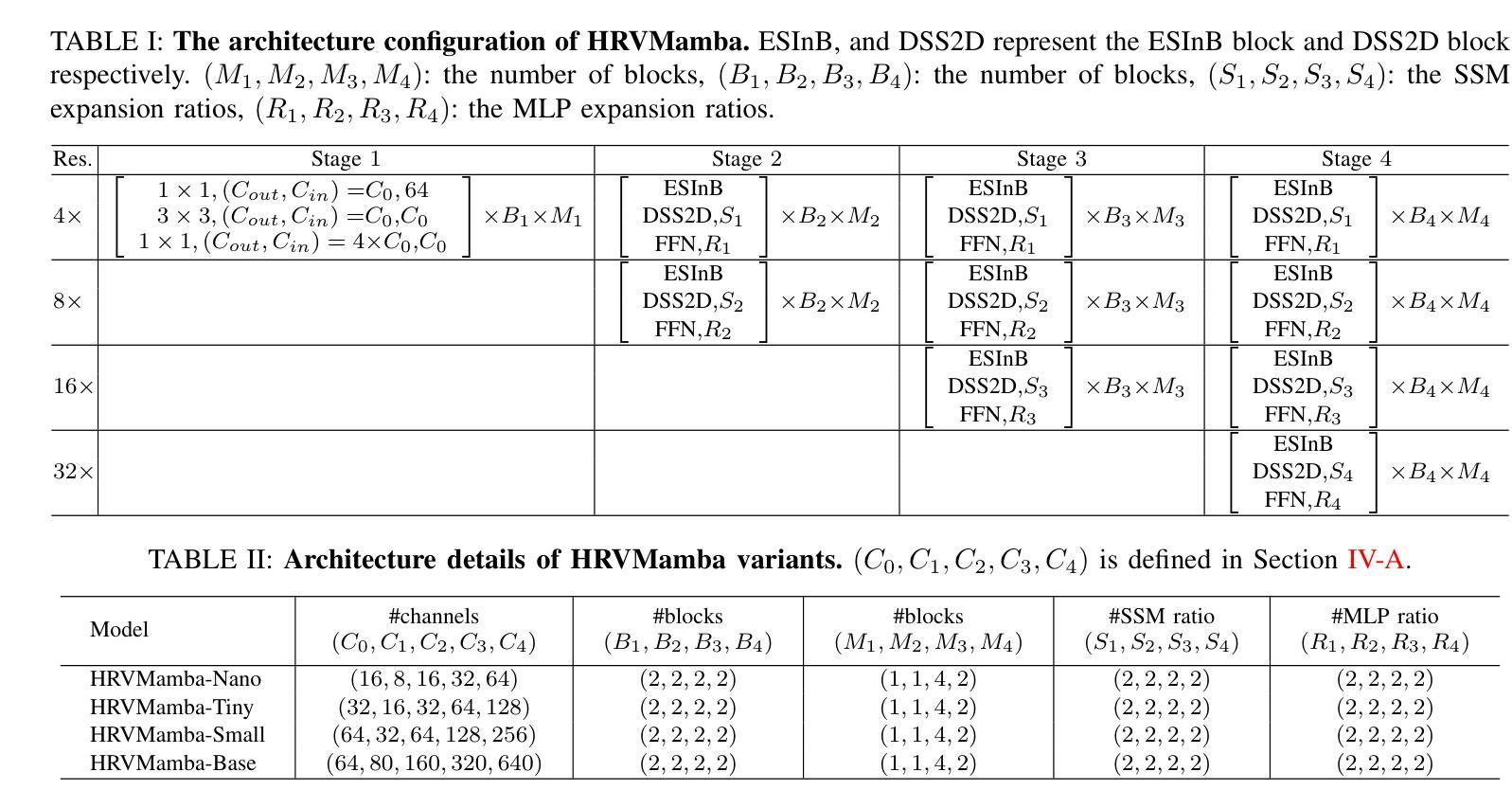
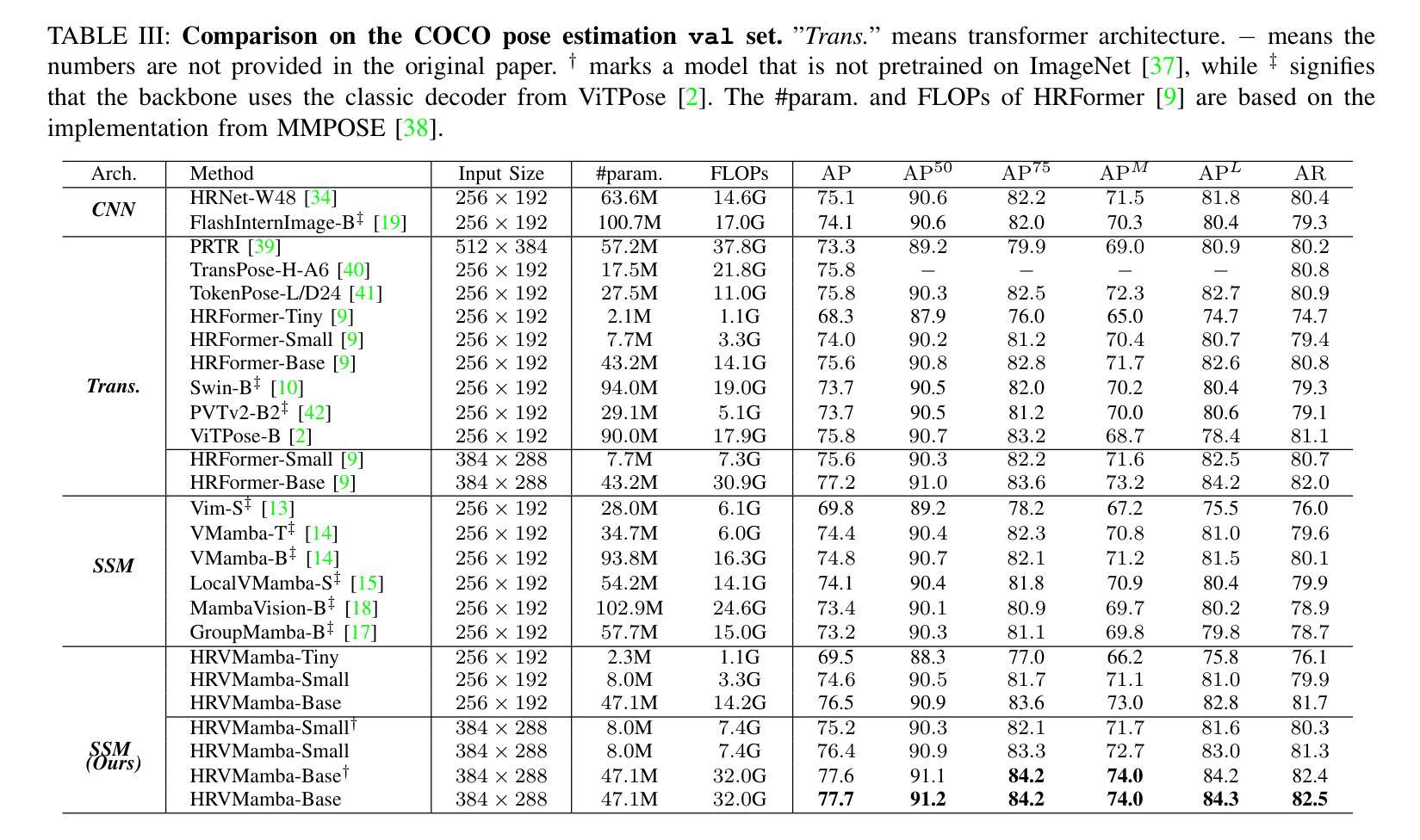
Efficient High-Resolution Visual Representation Learning with State Space Model for Human Pose Estimation
Authors:Hao Zhang, Yongqiang Ma, Wenqi Shao, Ping Luo, Nanning Zheng, Kaipeng Zhang
Capturing long-range dependencies while preserving high-resolution visual representations is crucial for dense prediction tasks such as human pose estimation. Vision Transformers (ViTs) have advanced global modeling through self-attention but suffer from quadratic computational complexity with respect to token count, limiting their efficiency and scalability to high-resolution inputs, especially on mobile and resource-constrained devices. State Space Models (SSMs), exemplified by Mamba, offer an efficient alternative by combining global receptive fields with linear computational complexity, enabling scalable and resource-friendly sequence modeling. However, when applied to dense prediction tasks, existing visual SSMs face key limitations: weak spatial inductive bias, long-range forgetting from hidden state decay, and low-resolution outputs that hinder fine-grained localization. To address these issues, we propose the Dynamic Visual State Space (DVSS) block, which augments visual state space models with multi-scale convolutional operations to enhance local spatial representations and strengthen spatial inductive biases. Through architectural exploration and theoretical analysis, we incorporate deformable operation into the DVSS block, identifying it as an efficient and effective mechanism to enhance semantic aggregation and mitigate long-range forgetting via input-dependent, adaptive spatial sampling. We embed DVSS into a multi-branch high-resolution architecture to build HRVMamba, a novel model for efficient high-resolution representation learning. Extensive experiments on human pose estimation, image classification, and semantic segmentation show that HRVMamba performs competitively against leading CNN-, ViT-, and SSM-based baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/zhanghao5201/PoseVMamba.
在密集预测任务(如人体姿态估计)中,捕捉长距离依赖关系同时保留高分辨率的视觉表示至关重要。视觉Transformer(ViTs)通过自注意力实现了全局建模,但其在令牌计数方面的二次计算复杂度限制了其效率和处理高分辨率输入的扩展性,特别是在移动和资源受限的设备上。以Mamba为代表的状态空间模型(SSMs)通过结合全局感受野和线性计算复杂度,提供了高效的替代方案,实现了可扩展且资源友好的序列建模。然而,当应用于密集预测任务时,现有的视觉SSM面临关键局限性:空间归纳偏置较弱、隐藏状态衰减导致长距离遗忘以及阻碍精细定位的低分辨率输出。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了动态视觉状态空间(DVSS)块,它通过多尺度卷积操作增强视觉状态空间模型,以改善局部空间表示并加强空间归纳偏置。通过架构探索和理论分析,我们将可变形操作纳入DVSS块,将其识别为一种高效有效的机制,可以通过输入相关的自适应空间采样来增强语义聚合并缓解长距离遗忘。我们将DVSS嵌入多分支高分辨率架构中,构建了HRVMamba,这是一种用于高效高分辨率表示学习的新型模型。在人类姿态估计、图像分类和语义分割方面的广泛实验表明,HRVMamba在与领先的CNN、ViT和SSM基准测试的竞争中表现良好。相关代码可在https://github.com/zhanghao5201/PoseVMamba找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
为捕捉长期依赖并保留高分辨率视觉表征,研究者提出将动态视觉状态空间(DVSS)块与视觉状态空间模型(SSM)相结合,应用于密集预测任务如人体姿态估计。该模型结合了全局感受野与线性计算复杂度,并通过多尺度卷积操作增强局部空间表征,以缓解长期遗忘并提高分辨率输出。HRVMamba模型在人体姿态估计、图像分类和语义分割任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs)面临计算效率问题,特别是在处理高分辨率输入时。
- State Space Models (SSMs)具有全局感受野和线性计算复杂度的优势。
- 应用于密集预测任务时,SSMs存在空间归纳偏见弱、隐藏状态衰减导致长期遗忘以及低分辨率输出等问题。
- DVSS块通过多尺度卷积操作增强局部空间表征,并缓解长期遗忘问题。
- HRVMamba模型结合DVSS块和高分辨率架构,实现高效的高分辨率表示学习。
- HRVMamba模型在人体姿态估计、图像分类和语义分割任务上的表现具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


Compositional Zero-shot Learning via Progressive Language-based Observations
Authors:Lin Li, Guikun Chen, Zhen Wang, Jun Xiao, Long Chen
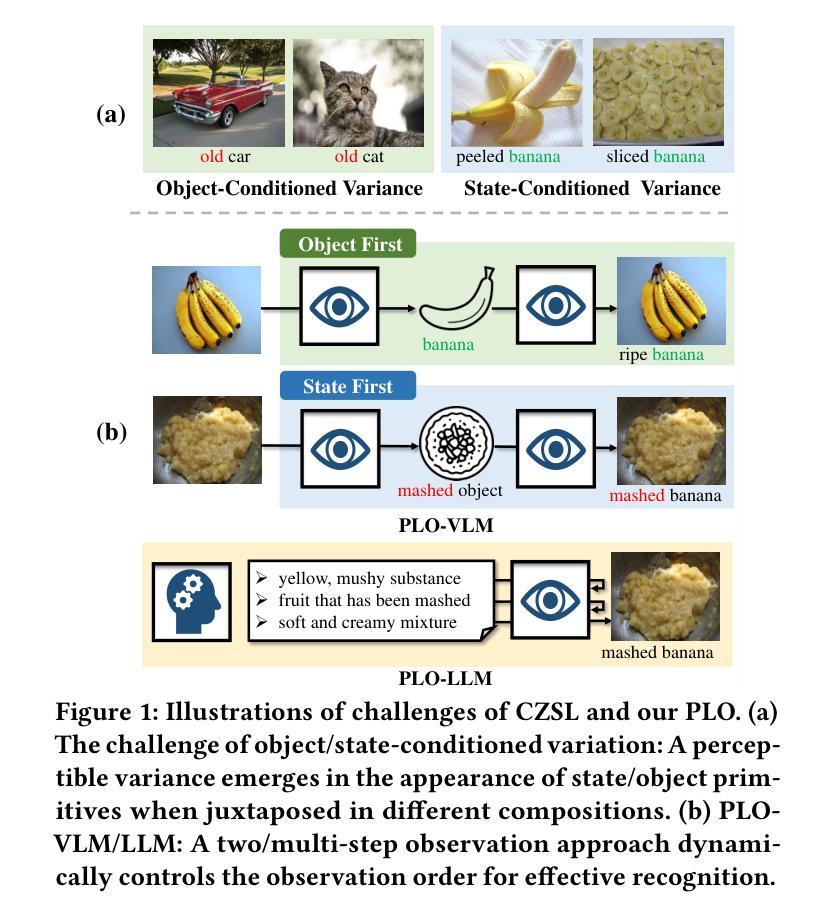
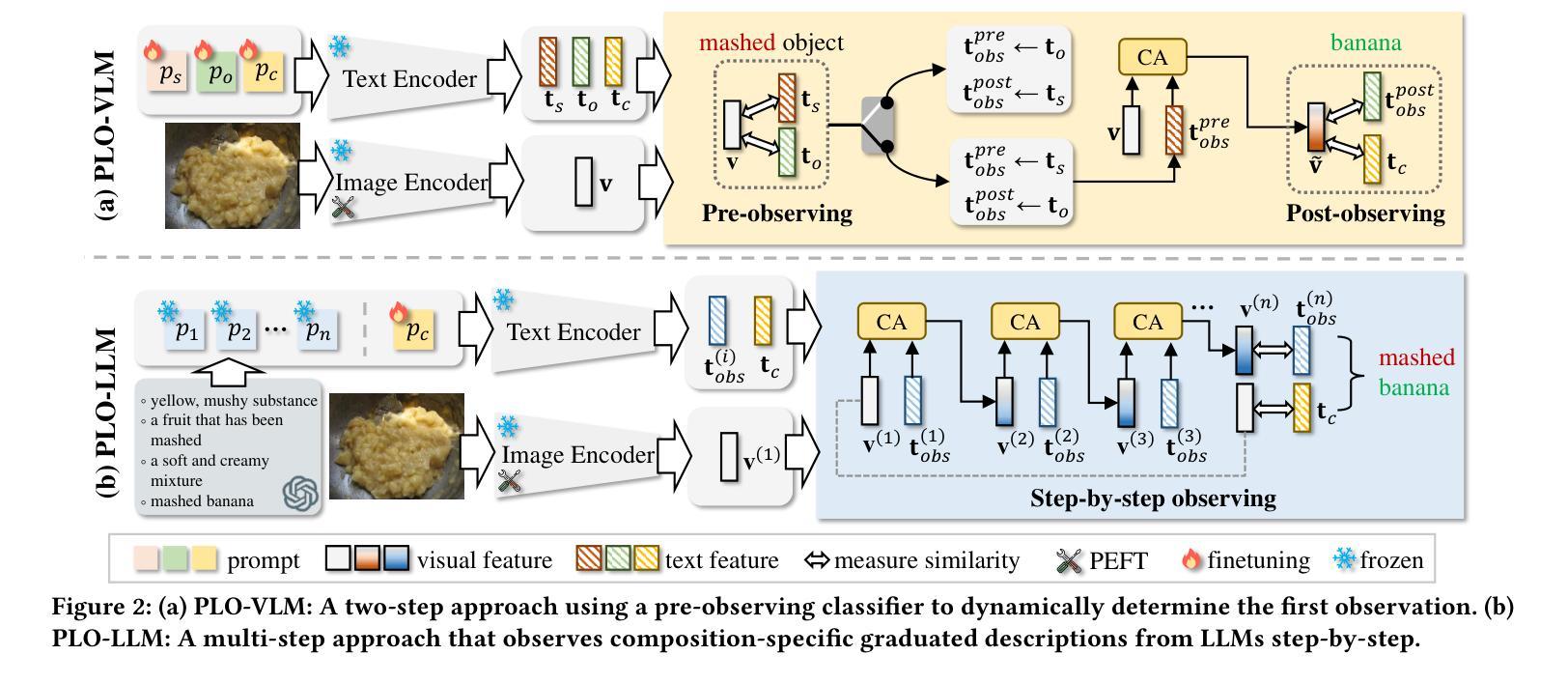
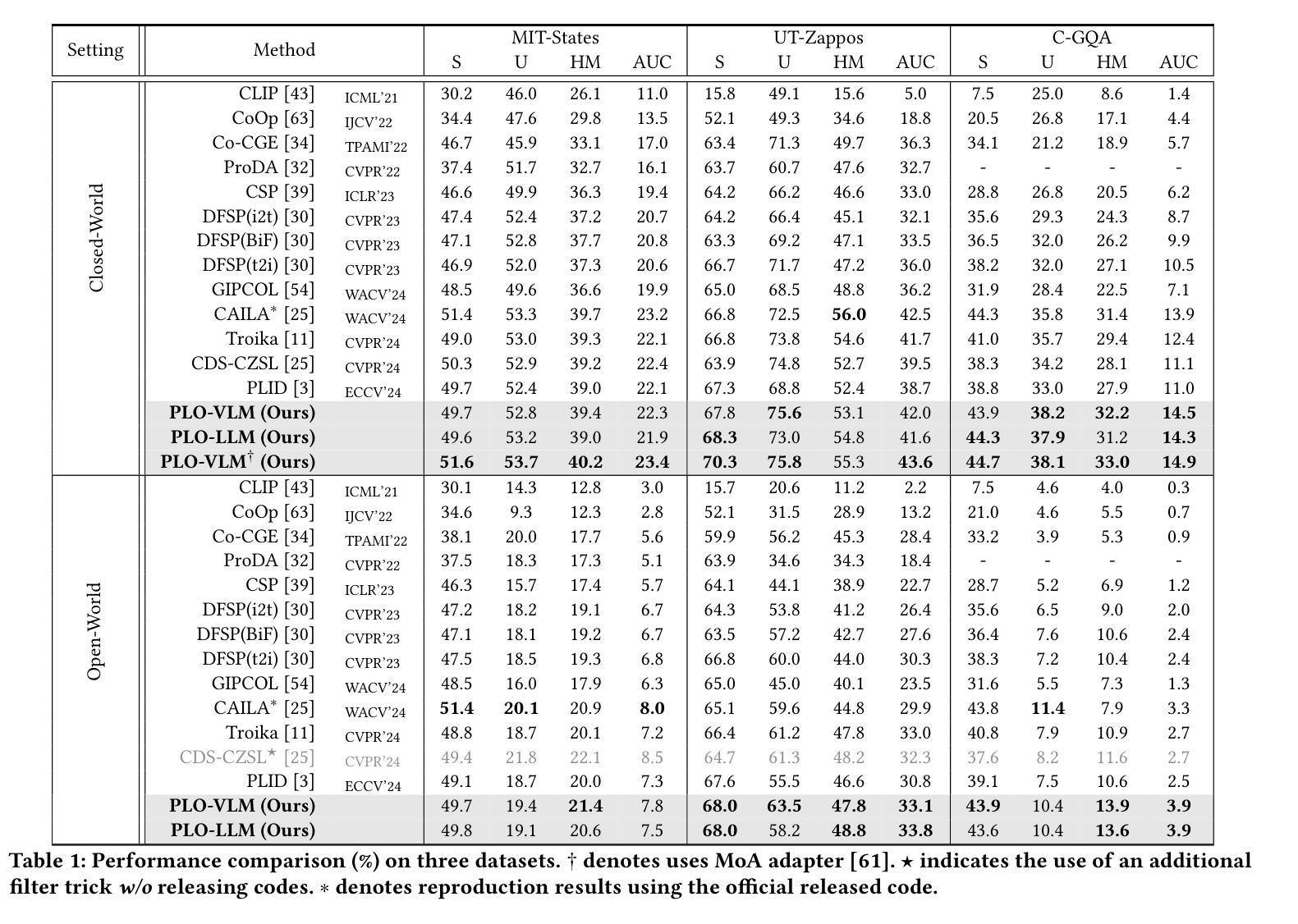
Compositional zero-shot learning aims to recognize unseen state-object compositions by leveraging known primitives (state and object) during training. However, effectively modeling interactions between primitives and generalizing knowledge to novel compositions remains a perennial challenge. There are two key factors: object-conditioned and state-conditioned variance, i.e., the appearance of states (or objects) can vary significantly when combined with different objects (or states). For instance, the state “old” can signify a vintage design for a “car” or an advanced age for a “cat”. In this paper, we argue that these variances can be mitigated by predicting composition categories based on pre-observed primitive. To this end, we propose Progressive Language-based Observations (PLO), which can dynamically determine a better observation order of primitives. These observations comprise a series of concepts or languages that allow the model to understand image content in a step-by-step manner. Specifically, PLO adopts pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) to empower the model with observation capabilities. We further devise two variants: 1) PLO-VLM: a two-step method, where a pre-observing classifier dynamically determines the observation order of two primitives. 2) PLO-LLM: a multi-step scheme, which utilizes large language models (LLMs) to craft composition-specific prompts for step-by-step observing. Extensive ablations on three challenging datasets demonstrate the superiority of PLO compared with state-of-the-art methods, affirming its abilities in compositional recognition.
组合零样本学习的目标是利用训练过程中的已知基本元素(状态和对象)来识别未见过的状态-对象组合。然而,有效地对基本元素之间的交互进行建模,并将知识推广到新的组合上,仍然是一个持久的挑战。有两个关键因素:对象条件变量和状态条件变量,即当与不同的对象(或状态)结合时,状态(或对象)的外观可能会有很大的变化。例如,“old”这个状态可能意味着一辆车的“复古设计”,或者一只猫的“年纪较大”。在本文中,我们认为可以通过基于预先观察到的基本元素来预测组合类别来减轻这些差异。为此,我们提出了基于语言的逐步观察(Progressive Language-based Observations,简称PLO),它能动态地确定一个更好的基本元素观察顺序。这些观察包含一系列的概念或语言,使模型能够以逐步的方式理解图像内容。具体来说,PLO使用预训练的视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models,简称VLMs)来为模型提供观察能力。我们还设计出了两种变体:1)PLO-VLM:一种两步方法,其中预观察分类器动态确定两个基本元素的观察顺序;2)PLO-LLM:一种多步方案,利用大型语言模型(Large Language Models,简称LLMs)为逐步观察创建特定的组合提示。在三个具有挑战性的数据集上的广泛实验证明了PLO相较于最先进的方法具有优越性,证实了其在组合识别方面的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Progressive Language-based Observations(PLO)的方法,用于缓解组成式零样本学习中的对象状态变化问题。此方法能够根据预观察到的原始动态确定观察顺序,以理解图像内容。采用预训练的视觉语言模型赋予模型观察能力,并进行两阶段和多阶段的方案变体实验,证实了该方法在组成式识别方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Compositional zero-shot learning致力于利用已知原始(状态和对象)来识别未见过的状态对象组合。
- 对象状态和对象之间的交互建模以及将知识推广到新的组合是长期存在的挑战。
- 本文提出PLO方法,通过预测基于预先观察到的原始的组成类别来减轻对象状态变化的问题。
- PLO能够动态确定原始的观察顺序,允许模型逐步理解图像内容。
- PLO利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)赋予模型观察能力。
- 方法包括两个变体:PLO-VLM(两阶段方法)和PLO-LLM(多阶段方案,利用大型语言模型为组成特定提示进行逐步观察)。
点此查看论文截图