⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
HierAdaptMR: Cross-Center Cardiac MRI Reconstruction with Hierarchical Feature Adapters
Authors:Ruru Xu, Ilkay Oksuz
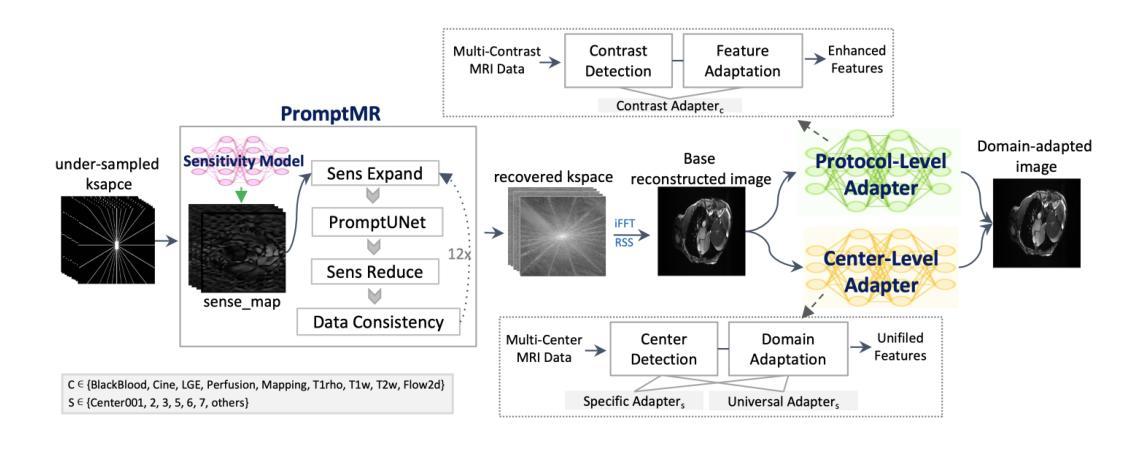
Deep learning-based cardiac MRI reconstruction faces significant domain shift challenges when deployed across multiple clinical centers with heterogeneous scanner configurations and imaging protocols. We propose HierAdaptMR, a hierarchical feature adaptation framework that addresses multi-level domain variations through parameter-efficient adapters. Our method employs Protocol-Level Adapters for sequence-specific characteristics and Center-Level Adapters for scanner-dependent variations, built upon a variational unrolling backbone. A Universal Adapter enables generalization to entirely unseen centers through stochastic training that learns center-invariant adaptations. The framework utilizes multi-scale SSIM loss with frequency domain enhancement and contrast-adaptive weighting for robust optimization. Comprehensive evaluation on the CMRxRecon2025 dataset spanning 5+ centers, 10+ scanners, and 9 modalities demonstrates superior cross-center generalization while maintaining reconstruction quality. code: https://github.com/Ruru-Xu/HierAdaptMR
基于深度学习的心脏MRI重建在跨多个临床中心部署时,面临因扫描仪配置和成像协议不同而导致的显著领域偏移挑战。我们提出了HierAdaptMR,这是一种分层特征适应框架,它通过参数高效的适配器解决多级领域变化问题。我们的方法采用协议级适配器处理序列特定特征,采用中心级适配器处理扫描仪相关变化,建立在可变滚动骨干网络上。通用适配器通过随机训练学习中心不变适应,实现对全新中心的泛化。该框架利用多尺度SSIM损失、频率域增强和对比度自适应加权进行稳健优化。在涵盖5个中心、10多个扫描仪和9种模态的CMRxRecon2025数据集上的全面评估表明,该框架在保持重建质量的同时,具有出色的跨中心泛化能力。代码地址:https://github.com/Ruru-Xu/HierAdaptMR
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025, CMRxRecon2025 Challenge paper
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的自适应心脏MRI重建框架HierAdaptMR,用于解决跨多个临床中心部署时面临的领域差异问题。该框架通过参数高效的适配器解决多层次领域变化问题,包括针对序列特定特性的协议级适配器和针对扫描仪相关变化的中心级适配器。此外,还有一个通用适配器通过随机训练学习中心不变适应,能够推广到完全未见过的中心。该框架利用多尺度结构相似性损失结合频域增强和对比度自适应加权进行优化,并在跨越多个中心、扫描仪和模态的CMRxRecon2025数据集上进行全面评估,展现出卓越的跨中心泛化能力和重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- HierAdaptMR是一个用于心脏MRI重建的深度学习方法,能够解决跨多个临床中心的领域差异问题。
- 通过参数高效的适配器实现多层次领域适应,包括协议级适配器和中心级适配器。
- 通用适配器通过随机训练学习中心不变适应,增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 框架结合了多尺度结构相似性损失、频域增强和对比度自适应加权,以实现稳健优化。
- 在跨越多个中心、扫描仪和模态的CMRxRecon2025数据集上进行了全面评估。
- HierAdaptMR在保持重建质量的同时展现出卓越的跨中心泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Fully Automated Segmentation of Fiber Bundles in Anatomic Tracing Data
Authors:Kyriaki-Margarita Bintsi, Yaël Balbastre, Jingjing Wu, Julia F. Lehman, Suzanne N. Haber, Anastasia Yendiki
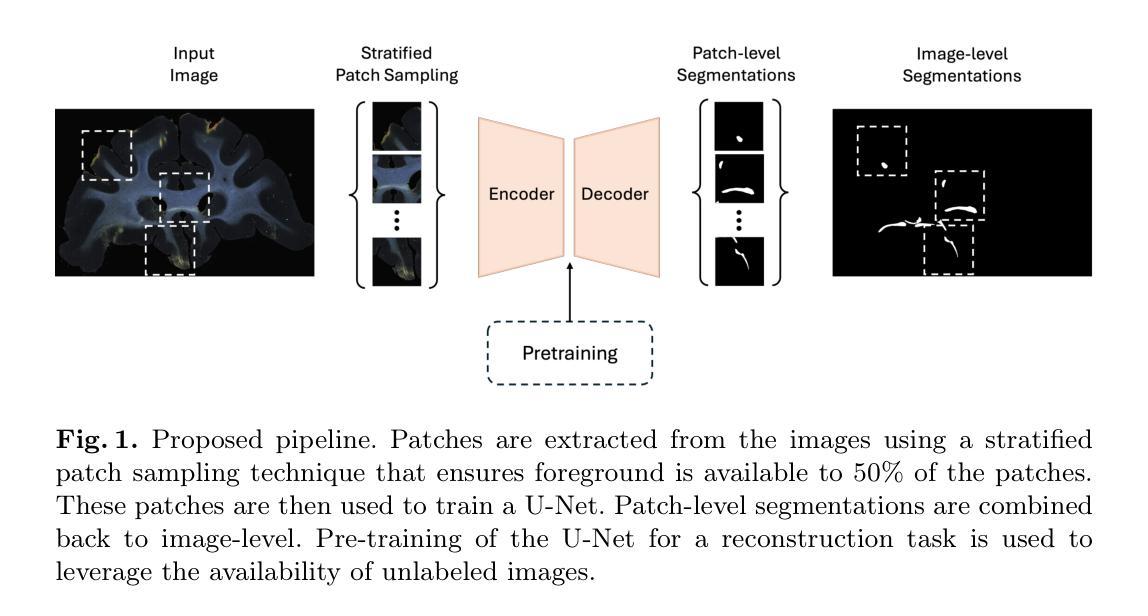
Anatomic tracer studies are critical for validating and improving diffusion MRI (dMRI) tractography. However, large-scale analysis of data from such studies is hampered by the labor-intensive process of annotating fiber bundles manually on histological slides. Existing automated methods often miss sparse bundles or require complex post-processing across consecutive sections, limiting their flexibility and generalizability. We present a streamlined, fully automated framework for fiber bundle segmentation in macaque tracer data, based on a U-Net architecture with large patch sizes, foreground aware sampling, and semisupervised pre-training. Our approach eliminates common errors such as mislabeling terminals as bundles, improves detection of sparse bundles by over 20% and reduces the False Discovery Rate (FDR) by 40% compared to the state-of-the-art, all while enabling analysis of standalone slices. This new framework will facilitate the automated analysis of anatomic tracing data at a large scale, generating more ground-truth data that can be used to validate and optimize dMRI tractography methods.
解剖追踪研究对于验证和改进扩散MRI(dMRI)图谱技术至关重要。然而,此类研究的数据大规模分析受到手动在组织切片上注释纤维束的劳动强度大的阻碍。现有的自动化方法经常会遗漏稀疏的束或需要在连续的切片上进行复杂的后处理,这限制了其灵活性和通用性。我们提出了一个简化的、完全自动化的框架,用于恒河猴追踪数据中的纤维束分割,该框架基于大补丁尺寸、前景感知采样和半监督预训练的U-Net架构。我们的方法消除了误标记终端为束的常见错误,提高了对稀疏束的检测精度超过20%,与最先进的方法相比,降低了40%的误报率(FDR),同时支持独立切片的分析。这一新框架将促进解剖追踪数据的自动化大规模分析,生成更多的真实数据,可用于验证和优化dMRI图谱技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CDMRI, MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于U-Net架构的自动化纤维束分割框架,适用于猕猴追踪数据。该方法采用大补丁尺寸、前景感知采样和半监督预训练,可消除误标记终端为束的错误,提高稀疏束检测率超过20%,并降低错误发现率(FDR)达40%,同时支持对独立切片的分析。这一新框架将促进大规模自动分析解剖追踪数据,生成更多可用于验证和优化dMRI追踪方法的地面真实数据。
Key Takeaways
- 解剖追踪研究对于验证和改进扩散MRI(dMRI)轨迹绘制至关重要。
- 现有手动注释纤维束的方法存在劳动强度大,难以应用于大规模数据分析的问题。
- 提出一种基于U-Net架构的自动化纤维束分割框架,具有大补丁尺寸、前景感知采样和半监督预训练的特点。
- 新方法能够消除误标记终端为束的错误,提高稀疏束检测率超过20%。
- 与现有方法相比,新框架可降低错误发现率(FDR)达40%。
- 新框架支持对独立切片的分析,增强了其灵活性和通用性。
点此查看论文截图

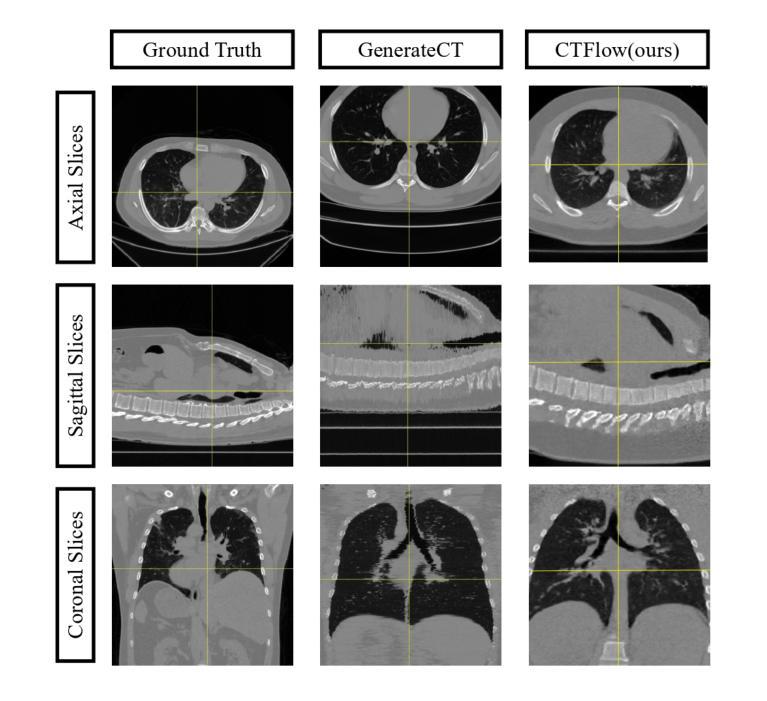
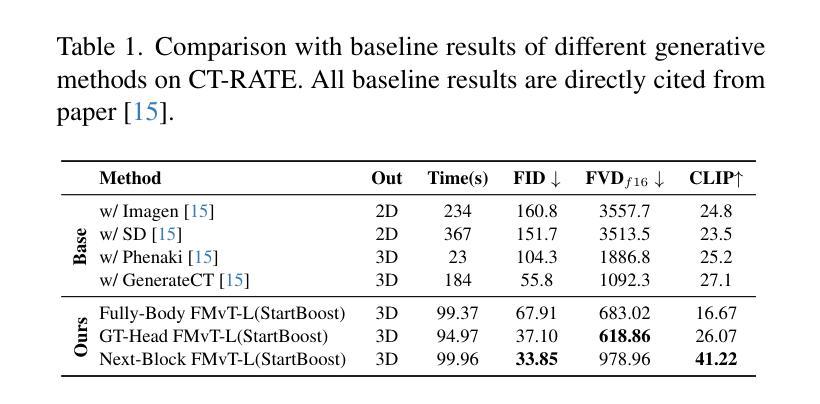
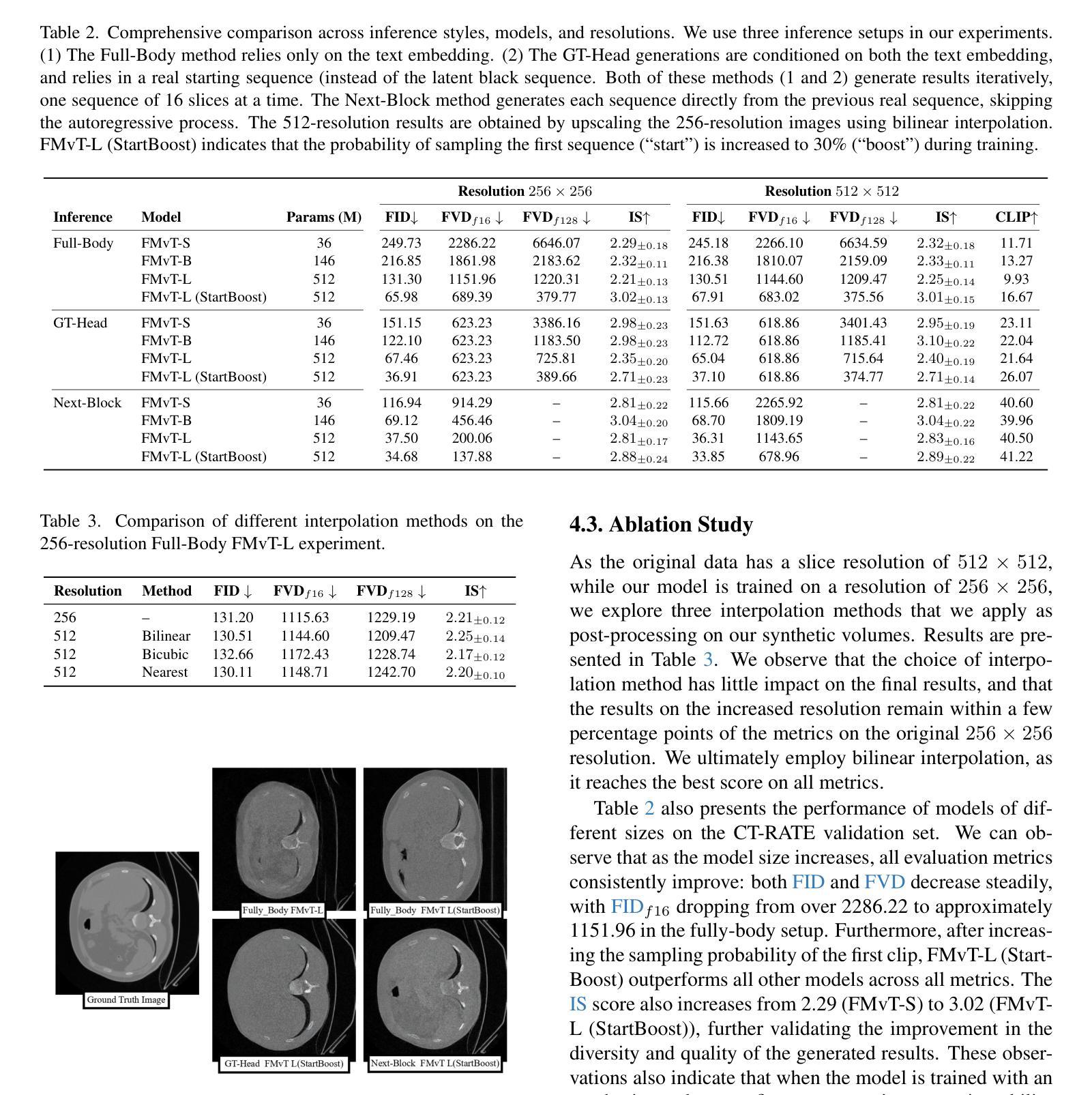
CTFlow: Video-Inspired Latent Flow Matching for 3D CT Synthesis
Authors:Jiayi Wang, Hadrien Reynaud, Franciskus Xaverius Erick, Bernhard Kainz
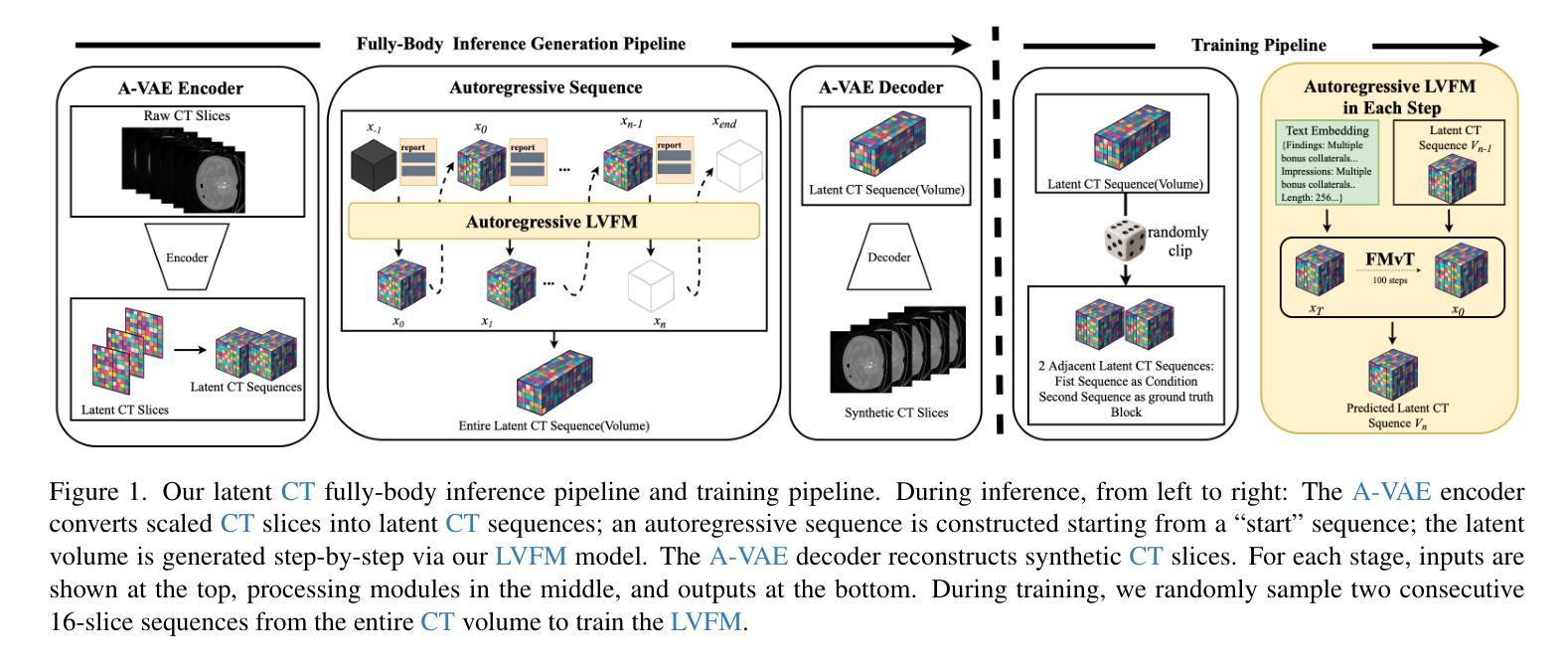
Generative modelling of entire CT volumes conditioned on clinical reports has the potential to accelerate research through data augmentation, privacy-preserving synthesis and reducing regulator-constraints on patient data while preserving diagnostic signals. With the recent release of CT-RATE, a large-scale collection of 3D CT volumes paired with their respective clinical reports, training large text-conditioned CT volume generation models has become achievable. In this work, we introduce CTFlow, a 0.5B latent flow matching transformer model, conditioned on clinical reports. We leverage the A-VAE from FLUX to define our latent space, and rely on the CT-Clip text encoder to encode the clinical reports. To generate consistent whole CT volumes while keeping the memory constraints tractable, we rely on a custom autoregressive approach, where the model predicts the first sequence of slices of the volume from text-only, and then relies on the previously generated sequence of slices and the text, to predict the following sequence. We evaluate our results against state-of-the-art generative CT model, and demonstrate the superiority of our approach in terms of temporal coherence, image diversity and text-image alignment, with FID, FVD, IS scores and CLIP score.
生成整个CT体积的模型以临床报告为条件,具有通过数据增强、隐私保护合成以及减少患者数据的监管约束来加速研究的潜力,同时保留诊断信号。随着大型三维CT体积与其相应临床报告的集合CT-RATE的发布,以文本为条件的CT体积生成模型训练变得可行。在这项工作中,我们介绍了CTFlow,这是一个以临床报告为条件的0.5B潜在流匹配变压器模型。我们利用FLUX中的A-VAE来定义我们的潜在空间,并依赖CT-Clip文本编码器对临床报告进行编码。为了在保持内存约束的同时生成一致完整的CT体积,我们采用了一种自定义的自回归方法,模型仅根据文本预测体积的第一序列切片,然后依赖于先前生成的切片序列和文本来预测后续的序列。我们与最先进的生成式CT模型进行了评估对比,通过FID、FVD、IS得分和CLIP得分,证明了我们的方法在时序一致性、图像多样性和文本-图像对齐方面的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于临床报告的整个CT体积生成模型具有加速研究、保护隐私、合成数据以及减少监管对患者数据的限制等潜力,同时保留诊断信号。借助新发布的CT-RATE大规模数据集——包含配对的3D CT体积及其临床报告,现在可实现大型文本条件CT体积生成模型的训练。在此工作中,我们介绍了CTFlow,这是一个基于临床报告的0.5B潜在流匹配转换器模型。我们利用FLUX中的A-VAE来定义我们的潜在空间,并依赖CT-Clip文本编码器对临床报告进行编码。为了在保持内存约束的同时生成一致的完整CT体积,我们采用了一种自定义的自回归方法,该方法使模型仅依靠文本预测体积的第一序列切片,然后依赖于先前生成的切片序列和文本来预测后续的切片。我们的结果经过先进的生成式CT模型评估,在时序连贯性、图像多样性和文本-图像对齐方面表现出优越性,通过FID、FVD、IS得分和CLIP得分验证。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式建模可以基于临床报告生成整个CT体积,有助于加速研究、保护隐私和减少监管约束。
- CT-RATE数据集的发布使得训练大型文本条件CT体积生成模型成为可能。
- CTFlow模型利用潜在空间定义和文本编码技术,生成与临床报告相匹配的CT体积。
- 采用自回归方法生成一致的完整CT体积,结合文本信息和已生成的切片序列进行预测。
- 与先进生成式CT模型相比,CTFlow在时序连贯性、图像多样性和文本-图像对齐方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

Mechanism of Quercetin in Inhibiting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Regulating T Cell-Related Targets: An Analysis Based on Single-Cell Sequencing and Network Pharmacology
Authors:Ruiqi Chen, Liang Hang, Fengyun Wang
Objective: To investigate the mechanism by which quercetin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) through regulating T-cell-related targets, providing a novel strategy for TNBC immunotherapy.Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (GSE161529 dataset) and network pharmacology were integrated. PCA and UMAP clustering identified T-cell subsets and differentially expressed genes in TNBC microenvironment. TNBC-related targets were screened via CTD and OMIM databases, with functional pathways analyzed by GO/KEGG enrichment. Molecular docking and PPI networks validated interactions between quercetin and core targets.Results: Quercetin intersected with 79 TNBC targets, including AKT1, EGFR, and MMP9, enriched in EGFR inhibitor resistance and endocrine resistance pathways. Molecular docking revealed the highest affinity between quercetin and GSK3B (-13.2 kJ/mol). AKT1 and MMP9 expression correlated with patient survival.Conclusion: Quercetin may reverse TNBC immunosuppression by multi-target modulation of T-cell function, but clinical application requires solutions for its low bioavailability, such as delivery systems or combination therapies.
目标:通过调节T细胞相关靶点来研究槲皮素抑制三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)的机制,为TNBC免疫治疗提供新的策略。方法:整合单细胞RNA测序(GSE161529数据集)和网络药理学。主成分分析和UMAP聚类技术确定了T细胞亚群和TNBC微环境中差异表达的基因。通过CTD和OMIM数据库筛选TNBC相关靶点,利用GO/KEGG富集分析功能途径。分子对接和蛋白质相互作用网络验证了槲皮素与核心靶点之间的相互作用。结果:槲皮素与TNBC的79个靶点相互作用,包括AKT1、EGFR和MMP9等,这些靶点富集于EGFR抑制剂耐药和内分泌耐药途径。分子对接显示槲皮素与GSK3B之间的亲和力最高(-13.2kJ/mol)。AKT1和MMP9的表达与患者生存相关。结论:槲皮素可能通过多靶点调节T细胞功能逆转TNBC免疫抑制,但临床应用需要解决其生物利用度低的问题,如采用给药系统或联合疗法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
槲皮素可通过调节T细胞相关靶点抑制三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC),为TNBC免疫治疗提供新策略。研究通过单细胞RNA测序和网络药理学整合方法,识别T细胞亚群和TNBC微环境中的差异表达基因,筛选TNBC相关靶点,并验证槲皮素与核心靶点的相互作用。结果显示,槲皮素与79个TNBC靶点有交集,包括AKT1、EGFR和MMP9等,主要富集在EGFR抑制剂抗性和内分泌抗性途径中。分子对接显示槲皮素与GSK3B的亲和力最高。
Key Takeaways
- 槲皮素能够抑制三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)的发展,这一作用通过调节T细胞相关靶点实现。
- 研究采用了单细胞RNA测序和网络药理学方法,综合分析了T细胞亚群和TNBC微环境中的基因表达差异。
- 通过CTD和OMIM数据库筛选了TNBC相关靶点,并进行了GO/KEGG富集分析,明确了相关功能途径。
- 分子对接实验显示,槲皮素与核心靶点如GSK3B之间的亲和力较强。
- 槲皮素与多个TNBC靶点有交集,包括AKT1、EGFR和MMP9等。
- AKT1和MMP9的表达与患者生存相关,这提示了槲皮素治疗的可能临床意义。
点此查看论文截图


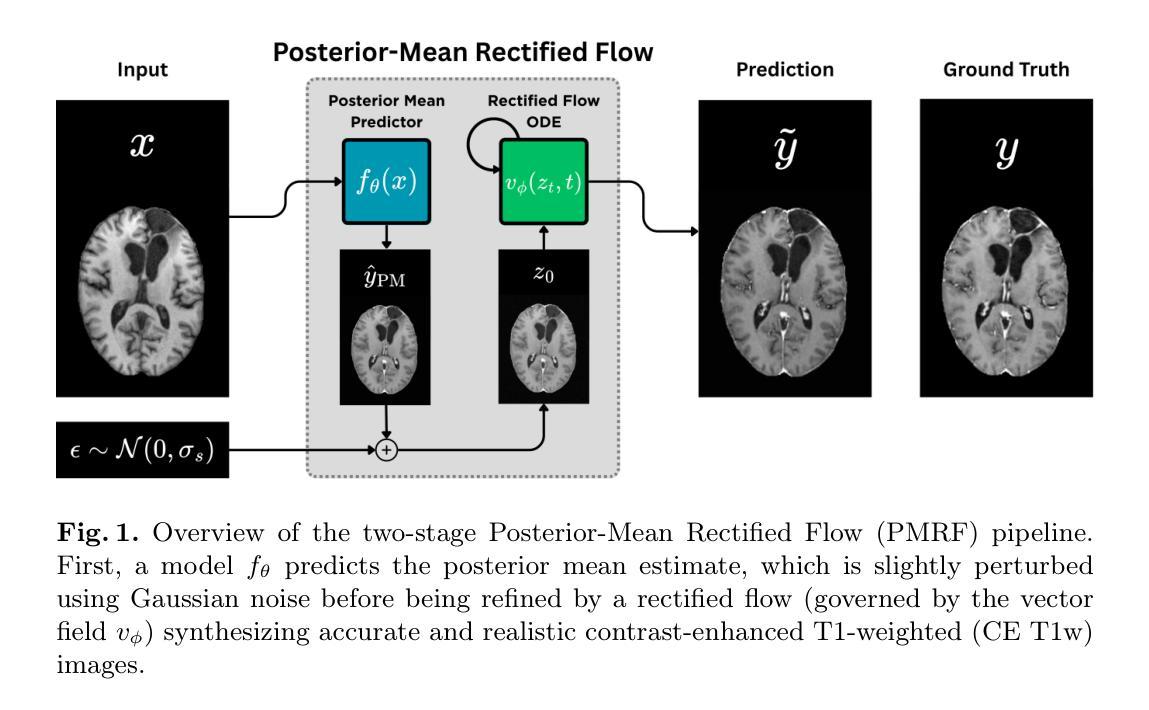
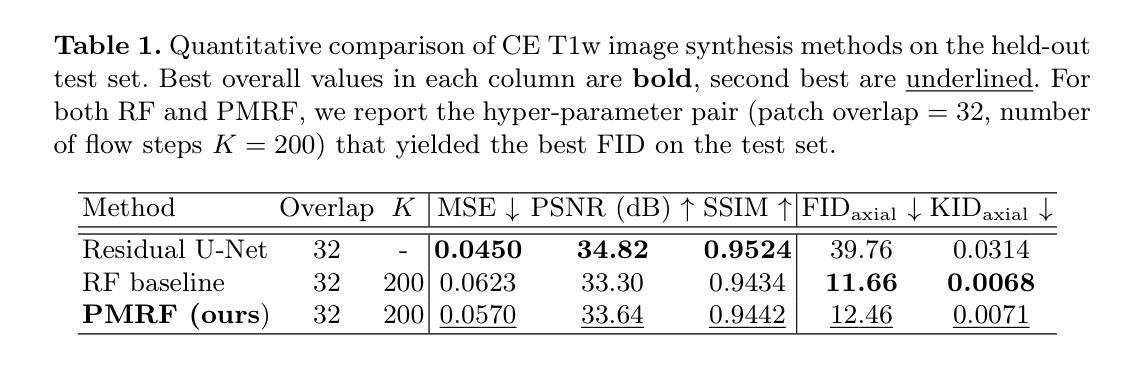
Synthesizing Accurate and Realistic T1-weighted Contrast-Enhanced MR Images using Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow
Authors:Bastian Brandstötter, Erich Kobler
Contrast-enhanced (CE) T1-weighted MRI is central to neuro-oncologic diagnosis but requires gadolinium-based agents, which add cost and scan time, raise environmental concerns, and may pose risks to patients. In this work, we propose a two-stage Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow (PMRF) pipeline for synthesizing volumetric CE brain MRI from non-contrast inputs. First, a patch-based 3D U-Net predicts the voxel-wise posterior mean (minimizing MSE). Then, this initial estimate is refined by a time-conditioned 3D rectified flow to incorporate realistic textures without compromising structural fidelity. We train this model on a multi-institutional collection of paired pre- and post-contrast T1w volumes (BraTS 2023-2025). On a held-out test set of 360 diverse volumes, our best refined outputs achieve an axial FID of $12.46$ and KID of $0.007$ ($\sim 68.7%$ lower FID than the posterior mean) while maintaining low volumetric MSE of $0.057$ ($\sim 27%$ higher than the posterior mean). Qualitative comparisons confirm that our method restores lesion margins and vascular details realistically, effectively navigating the perception-distortion trade-off for clinical deployment.
在神经肿瘤学诊断中,对比增强(CE)T1加权MRI是关键技术,但需要依赖钆基造影剂。这增加了成本和扫描时间,引发了环境担忧,并可能对患者构成风险。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种两阶段的后均值校正流(PMRF)管道,用于从非对比输入中合成体积CE脑MRI。首先,基于补丁的3D U-Net预测体素的后均值(最小化均方误差)。然后,通过时间调节的3D校正流对这个初步估计进行细化,以融入逼真的纹理而不损害结构保真度。我们的模型是在多个机构收集的配对的前后对比T1w体积集(BraTS 2023-2025)上进行训练的。在由360个不同体积组成的保留测试集上,我们最佳细化输出实现了轴向FID为12.46和KID为0.007(后均值FID降低了约68.7%),同时保持较低的体积均方误差为0.057(比后均值高大约27%)。定性比较证实,我们的方法能够逼真地恢复病灶边缘和血管细节,有效地解决了临床部署中的感知失真权衡问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 3 figures, MICCAI workshops (SASHIMI) 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于两阶段的合成对比增强(CE)T1加权MRI的方法,使用非对比增强输入数据。首先,基于补丁的3D U-Net预测体素级后验均值(最小化均方误差)。然后,通过时间调节的3D校正流对初始估计进行细化,以融入逼真的纹理而不损害结构保真度。该模型在多家机构的配对预对比和后对比T1w体积集上进行训练(BraTS 2023-2025)。在由360个不同体积组成的测试集上,最佳细化输出达到轴向FID为12.46和KID为0.007(与后验均值相比降低了约68.7%),同时保持较低的体积MSE为0.057(比后验均值高约27%)。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种两阶段的合成对比增强(CE)T1加权MRI的方法。
- 使用非对比增强输入数据进行预测。
- 第一阶段使用基于补丁的3D U-Net预测体素级后验均值。
- 第二阶段使用时间调节的3D校正流对初始估计进行细化。
- 模型训练数据来源于多机构的配对预和后对比T1w体积集(BraTS 2023-2025)。
- 测试结果显示最佳细化输出的FID和KID相较于后验均值有显著改善,同时保持了较低的MSE。
点此查看论文截图

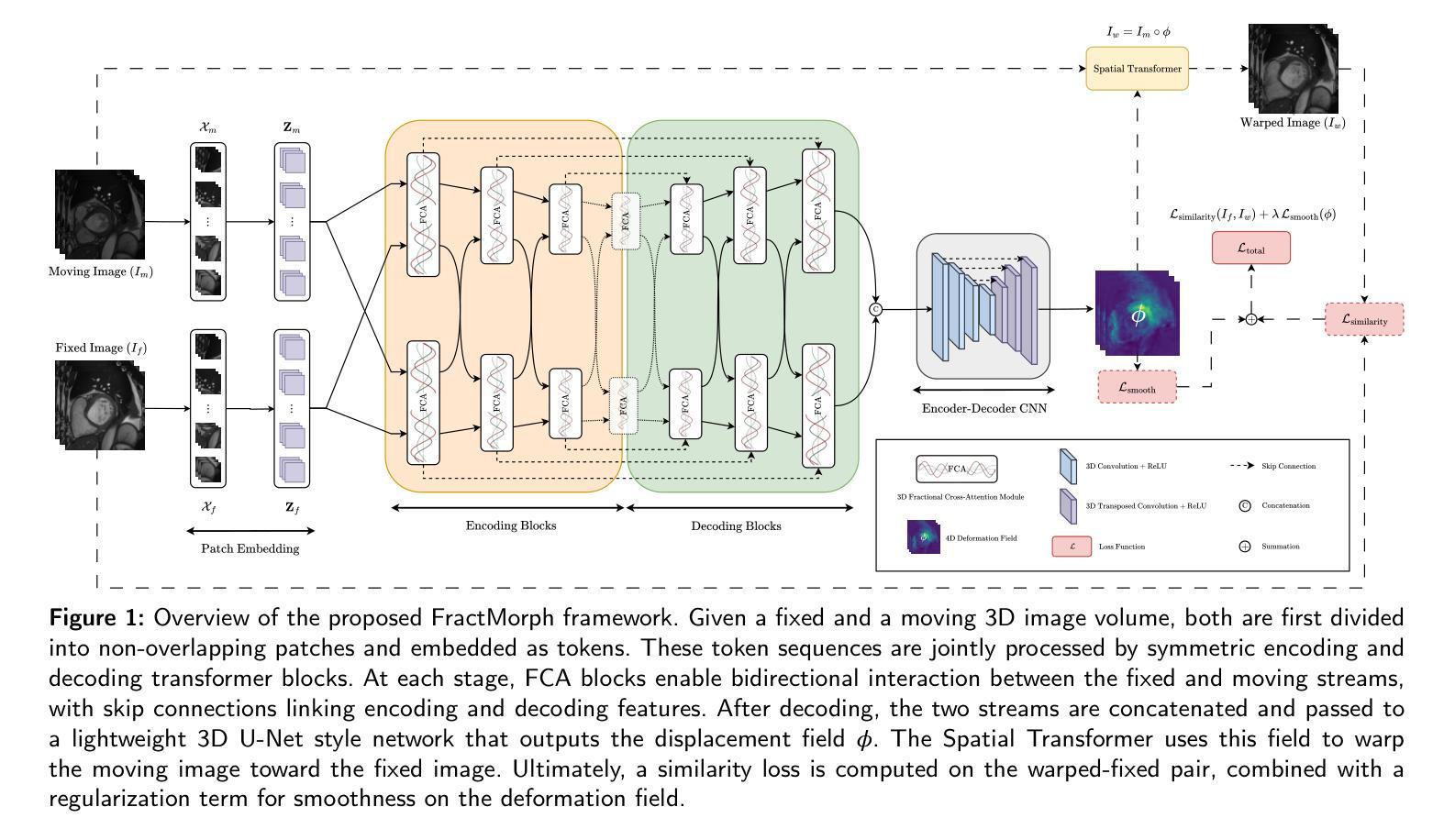
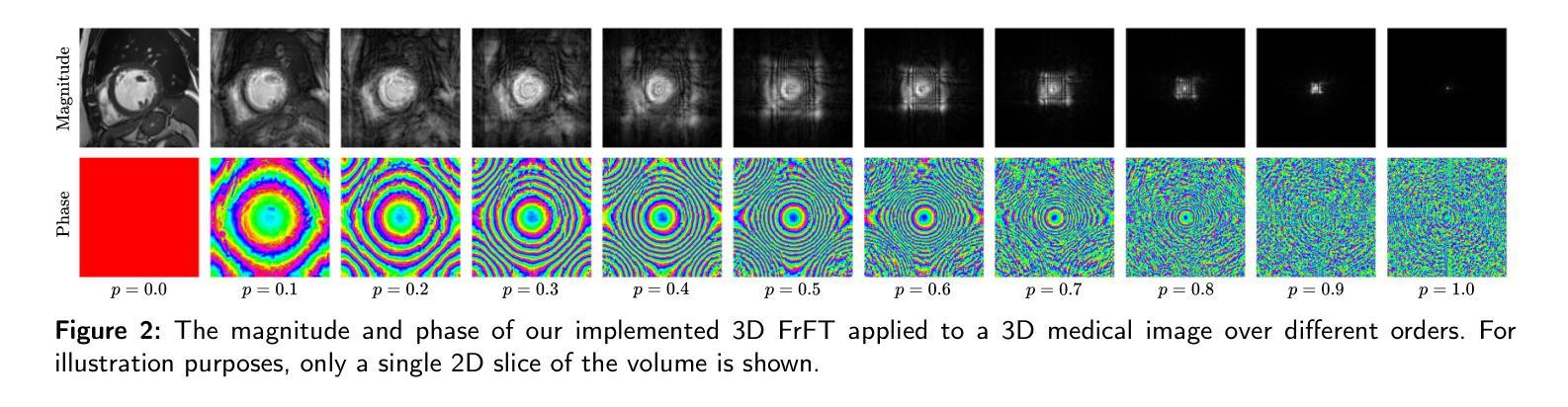
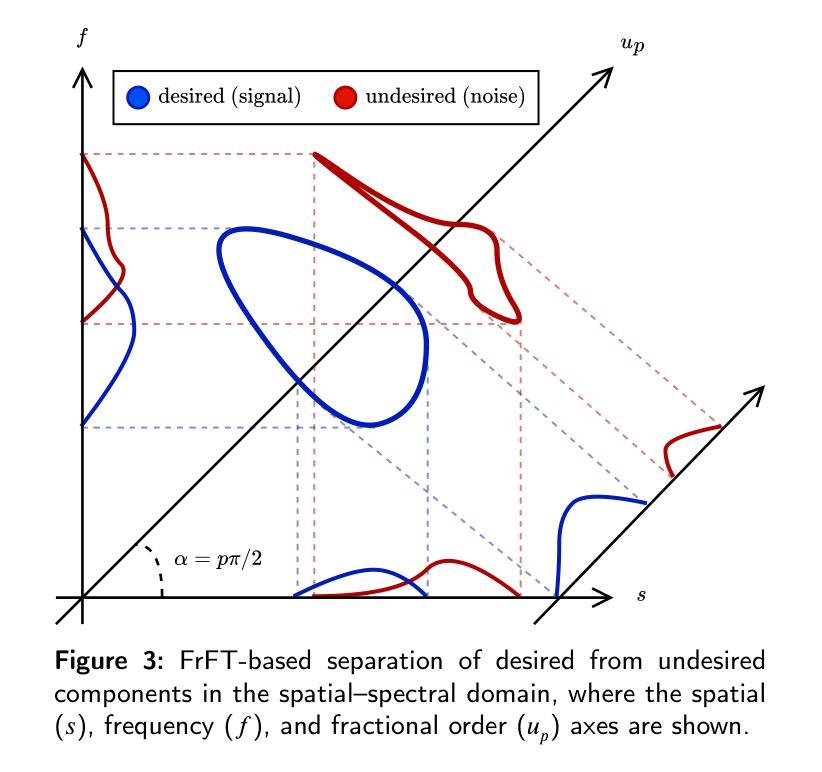
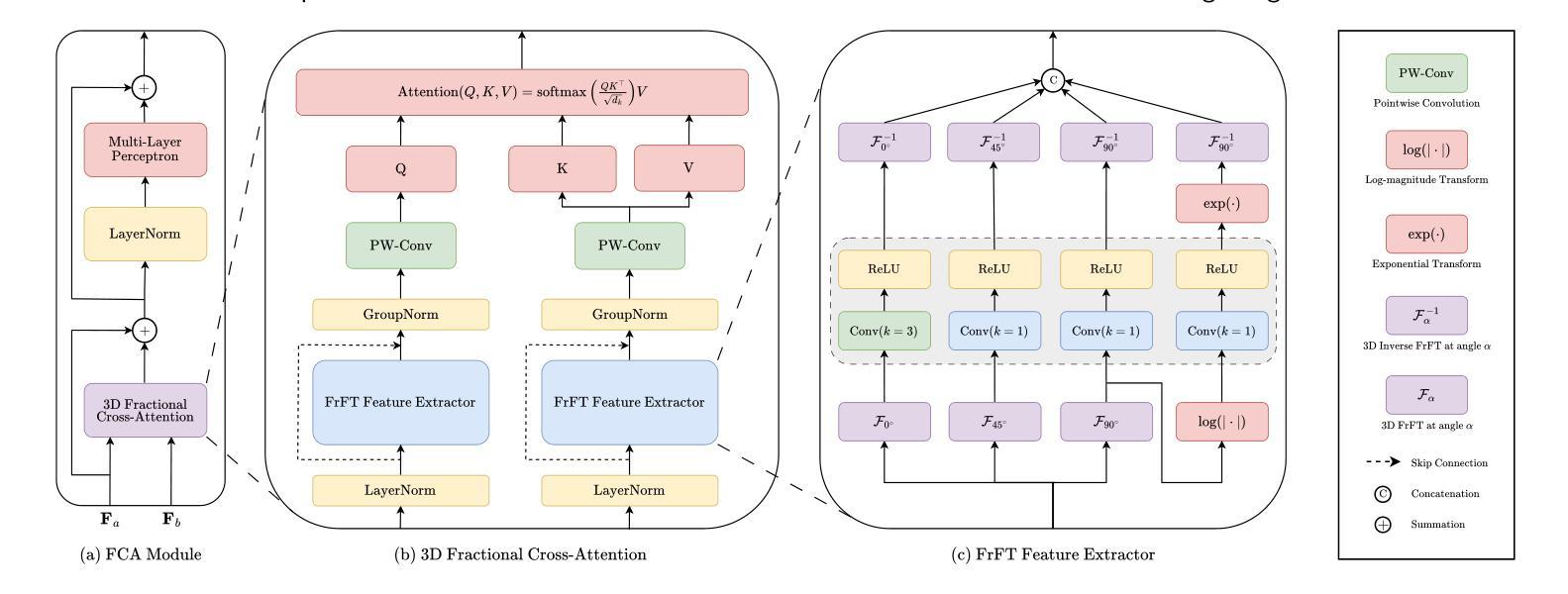
FractMorph: A Fractional Fourier-Based Multi-Domain Transformer for Deformable Image Registration
Authors:Shayan Kebriti, Shahabedin Nabavi, Ali Gooya
Deformable image registration (DIR) is a crucial and challenging technique for aligning anatomical structures in medical images and is widely applied in diverse clinical applications. However, existing approaches often struggle to capture fine-grained local deformations and large-scale global deformations simultaneously within a unified framework. We present FractMorph, a novel 3D dual-parallel transformer-based architecture that enhances cross-image feature matching through multi-domain fractional Fourier transform (FrFT) branches. Each Fractional Cross-Attention (FCA) block applies parallel FrFTs at fractional angles of 0{\deg}, 45{\deg}, 90{\deg}, along with a log-magnitude branch, to effectively extract local, semi-global, and global features at the same time. These features are fused via cross-attention between the fixed and moving image streams. A lightweight U-Net style network then predicts a dense deformation field from the transformer-enriched features. On the ACDC cardiac MRI dataset, FractMorph achieves state-of-the-art performance with an overall Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 86.45%, an average per-structure DSC of 75.15%, and a 95th-percentile Hausdorff distance (HD95) of 1.54 mm on our data split. We also introduce FractMorph-Light, a lightweight variant of our model with only 29.6M parameters, which maintains the superior accuracy of the main model while using approximately half the memory. Our results demonstrate that multi-domain spectral-spatial attention in transformers can robustly and efficiently model complex non-rigid deformations in medical images using a single end-to-end network, without the need for scenario-specific tuning or hierarchical multi-scale networks. The source code of our implementation is available at https://github.com/shayankebriti/FractMorph.
可变形图像配准(DIR)是医学图像中对齐解剖结构的关键且具挑战性的技术,广泛应用于各种临床应用中。然而,现有方法往往难以在一个统一的框架内同时捕获精细的局部变形和大规模的全局变形。我们提出了FractMorph,这是一种基于3D双平行transformer的新型架构,它通过多域分数阶傅里叶变换(FrFT)分支增强了跨图像特征匹配。每个分数交叉注意(FCA)块在0°、45°、90°的分数角度应用并行FrFT,以及一个对数幅度分支,以有效地同时提取局部、半全局和全局特征。这些特征通过固定图像流和移动图像流之间的交叉注意力进行融合。然后,一个轻量级的U-Net风格的网络从丰富的transformer特征中预测密集的变形场。在ACDC心脏MRI数据集上,FractMorph达到了最先进的性能,整体Dice相似度系数(DSC)为86.45%,平均每个结构的DSC为75.15%,在我们的数据拆分上,第95个百分位的Hausdorff距离(HD95)为1.54mm。我们还介绍了FractMorph-Light,这是我们模型的轻量级变体,仅有29.6M参数,它保持了主模型的优越准确性,同时大约使用了一半的内存。我们的结果表明,在transformer中的多域谱空间注意力可以稳健而有效地使用单个端到端网络对医学图像中的复杂非刚性变形进行建模,而无需针对场景进行特定调整或分层多尺度网络。我们的实现源代码可在[https://github.com/shayankebriti/FractMorph上找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的医学图像配准技术——FractMorph,它采用3D双平行变压器架构,通过多域分数傅立叶变换(FrFT)分支增强跨图像特征匹配。FractMorph能有效提取局部、半全局和全局特征,并在单一网络中实现复杂非刚性变形的稳健和高效建模,无需针对特定场景进行调整或分层多尺度网络。
Key Takeaways
- FractMorph是一种基于3D双平行变压器的新型医学图像配准技术。
- 通过多域分数傅立叶变换(FrFT)分支,增强跨图像特征匹配。
- FractMorph能同时提取局部、半全局和全局特征。
- FractMorph在ACDC心脏MRI数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
- FractMorph-Light是模型的轻量级变体,参数少,节省内存,同时保持了主模型的准确性。
- FractMorph采用单一端对端网络,无需针对特定场景调整或分层多尺度网络,即可对复杂非刚性变形进行稳健和高效建模。
点此查看论文截图

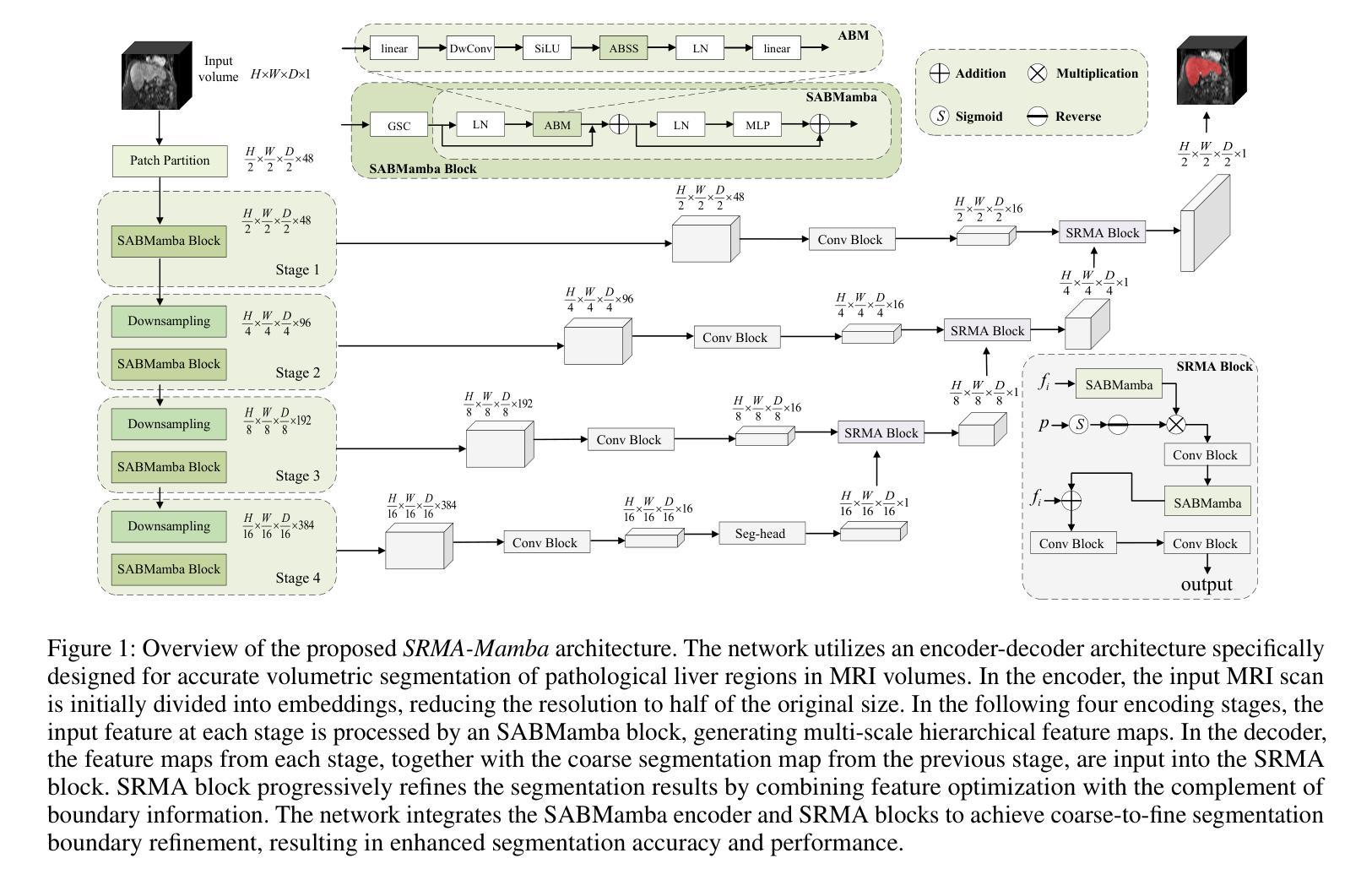
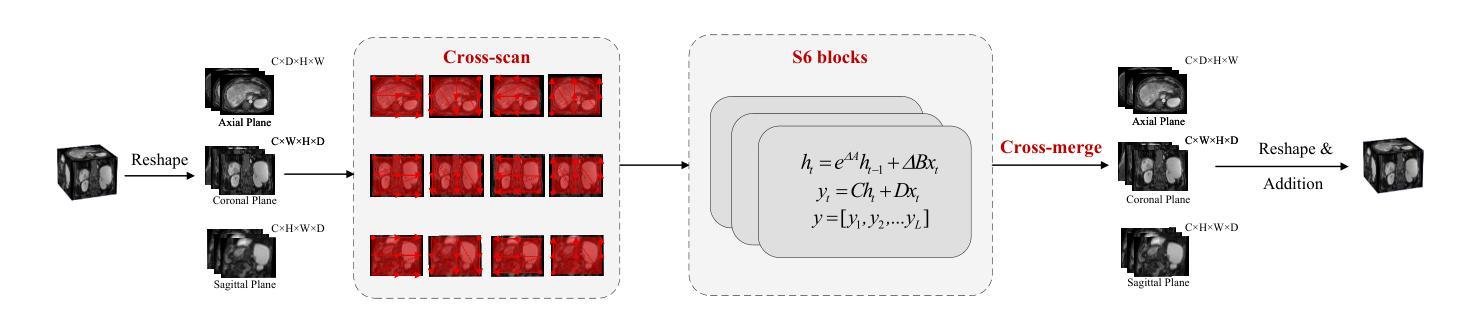
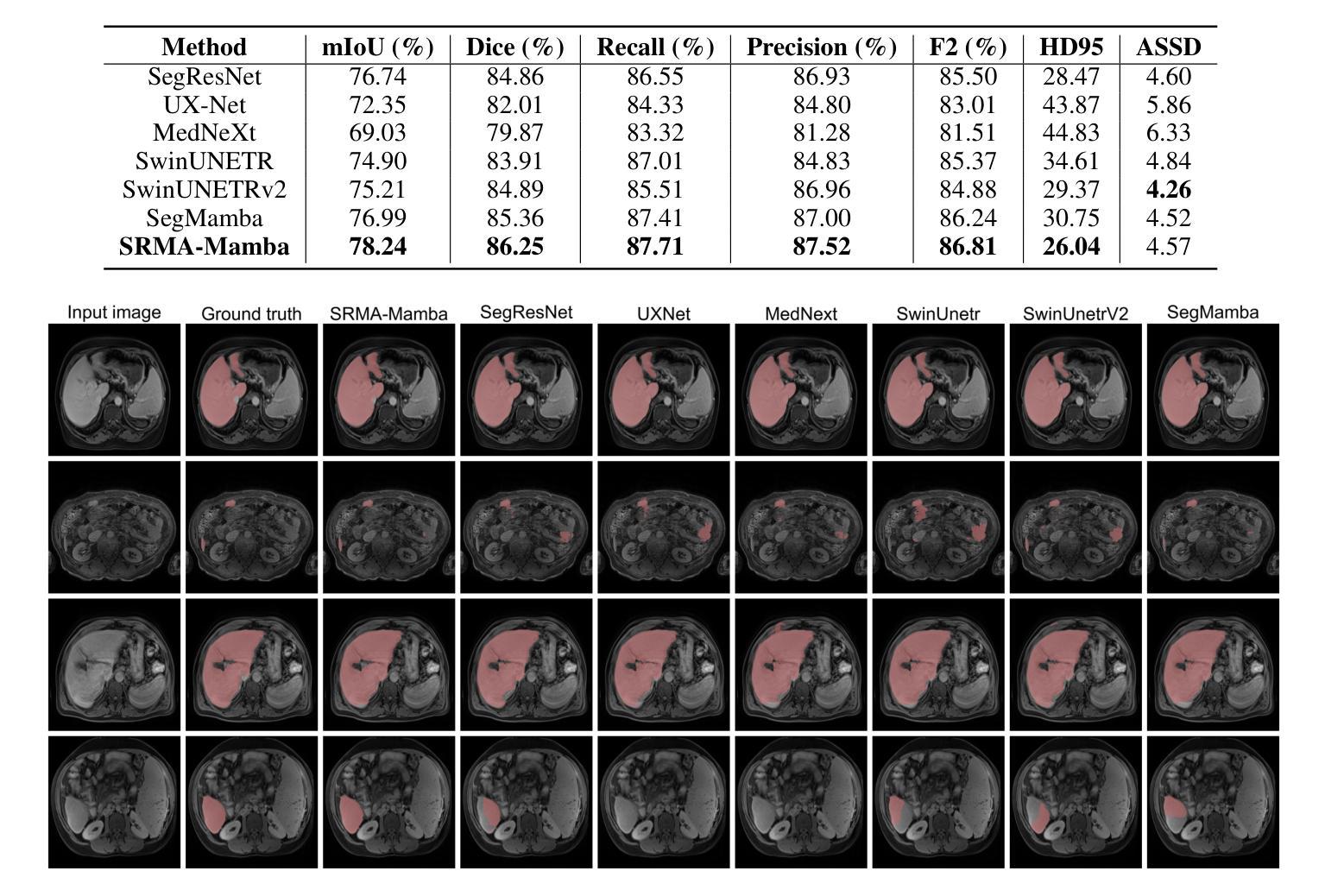
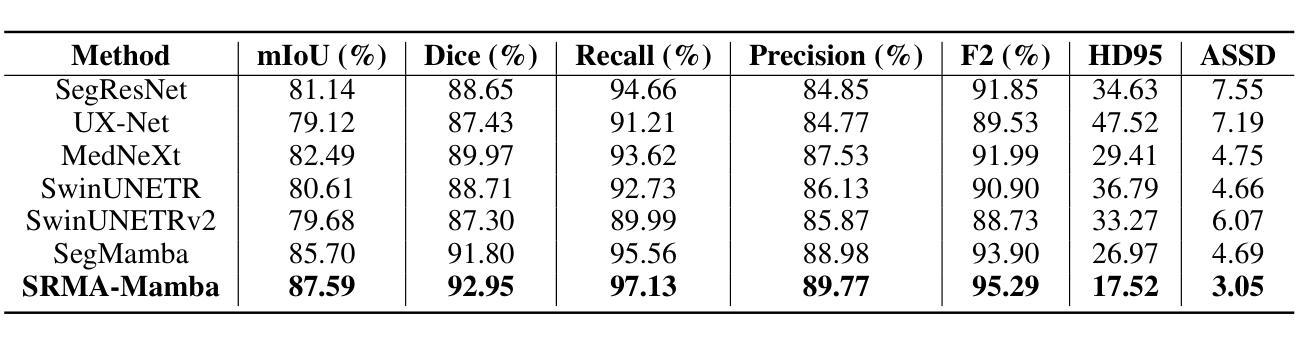
SRMA-Mamba: Spatial Reverse Mamba Attention Network for Pathological Liver Segmentation in MRI Volumes
Authors:Jun Zeng, Yannan Huang, Elif Keles, Halil Ertugrul Aktas, Gorkem Durak, Nikhil Kumar Tomar, Quoc-Huy Trinh, Deepak Ranjan Nayak, Ulas Bagci, Debesh Jha
Liver Cirrhosis plays a critical role in the prognosis of chronic liver disease. Early detection and timely intervention are critical in significantly reducing mortality rates. However, the intricate anatomical architecture and diverse pathological changes of liver tissue complicate the accurate detection and characterization of lesions in clinical settings. Existing methods underutilize the spatial anatomical details in volumetric MRI data, thereby hindering their clinical effectiveness and explainability. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel Mamba-based network, SRMA-Mamba, designed to model the spatial relationships within the complex anatomical structures of MRI volumes. By integrating the Spatial Anatomy-Based Mamba module (SABMamba), SRMA-Mamba performs selective Mamba scans within liver cirrhotic tissues and combines anatomical information from the sagittal, coronal, and axial planes to construct a global spatial context representation, enabling efficient volumetric segmentation of pathological liver structures. Furthermore, we introduce the Spatial Reverse Attention module (SRMA), designed to progressively refine cirrhotic details in the segmentation map, utilizing both the coarse segmentation map and hierarchical encoding features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SRMA-Mamba surpasses state-of-the-art methods, delivering exceptional performance in 3D pathological liver segmentation. Our code is available for public: {\color{blue}{https://github.com/JunZengz/SRMA-Mamba}}.
肝硬化在慢性肝病的预后中起着至关重要的作用。早期检测和及时干预是显著降低死亡率的关键。然而,肝脏组织的复杂解剖结构和多样化的病理变化使临床环境中病变的准确检测和特征描述变得复杂。现有方法未能充分利用体积MRI数据中的空间解剖细节,从而影响了它们的临床效果和可解释性。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了一种基于Mamba网络的新方法,即SRMA-Mamba,旨在模拟MRI体积中复杂解剖结构内的空间关系。通过集成基于空间解剖的Mamba模块(SABMamba),SRMA-Mamba在肝硬化组织内进行选择性Mamba扫描,并结合来自矢状面、冠状面和轴面的解剖信息,构建全局空间上下文表示,从而实现病理性肝结构的有效体积分割。此外,我们还引入了空间反向注意模块(SRMA),旨在利用粗分割图和分层编码特征,逐步精细调整肝硬化细节在分割图上的表现。大量实验表明,SRMA-Mamba超越了最先进的方法,在3D病理性肝脏分割方面表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码已公开发布在:{\color{blue}{https://github.com/JunZengz/SRMA-Mamba}}。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于Mamba网络的新型SRMA-Mamba模型在肝脏肝硬化组织病变的分割上表现优异。它通过整合空间解剖结构信息,建立全局空间上下文表示,实现了高效的三维肝脏病变分割。同时引入空间反向注意力模块SRMA,对硬化细节进行渐进精细化处理。SRMA-Mamba性能超越现有技术,代码已公开于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 肝脏肝硬化在慢性肝病预后中起关键作用,早期检测和及时干预能显著降低死亡率。
- 肝脏组织的复杂解剖结构和多变病理变化给临床准确检测与表征病变带来挑战。
- 现有方法未能充分利用MRI数据的空间解剖细节,影响其在临床的有效性和可解释性。
- SRMA-Mamba网络通过SABMamba模块对MRI体积内的复杂解剖结构进行空间关系建模。
- SRMA-Mamba结合三个平面(矢状面、冠状面和轴面)的解剖学信息,构建全局空间上下文表示,实现肝脏病变结构的高效三维分割。
- Spatial Reverse Attention模块(SRMA)用于逐步优化硬化细节,结合粗分割图和层次编码特征。
- 实验证明SRMA-Mamba性能超越现有技术,在三维肝脏病变分割上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

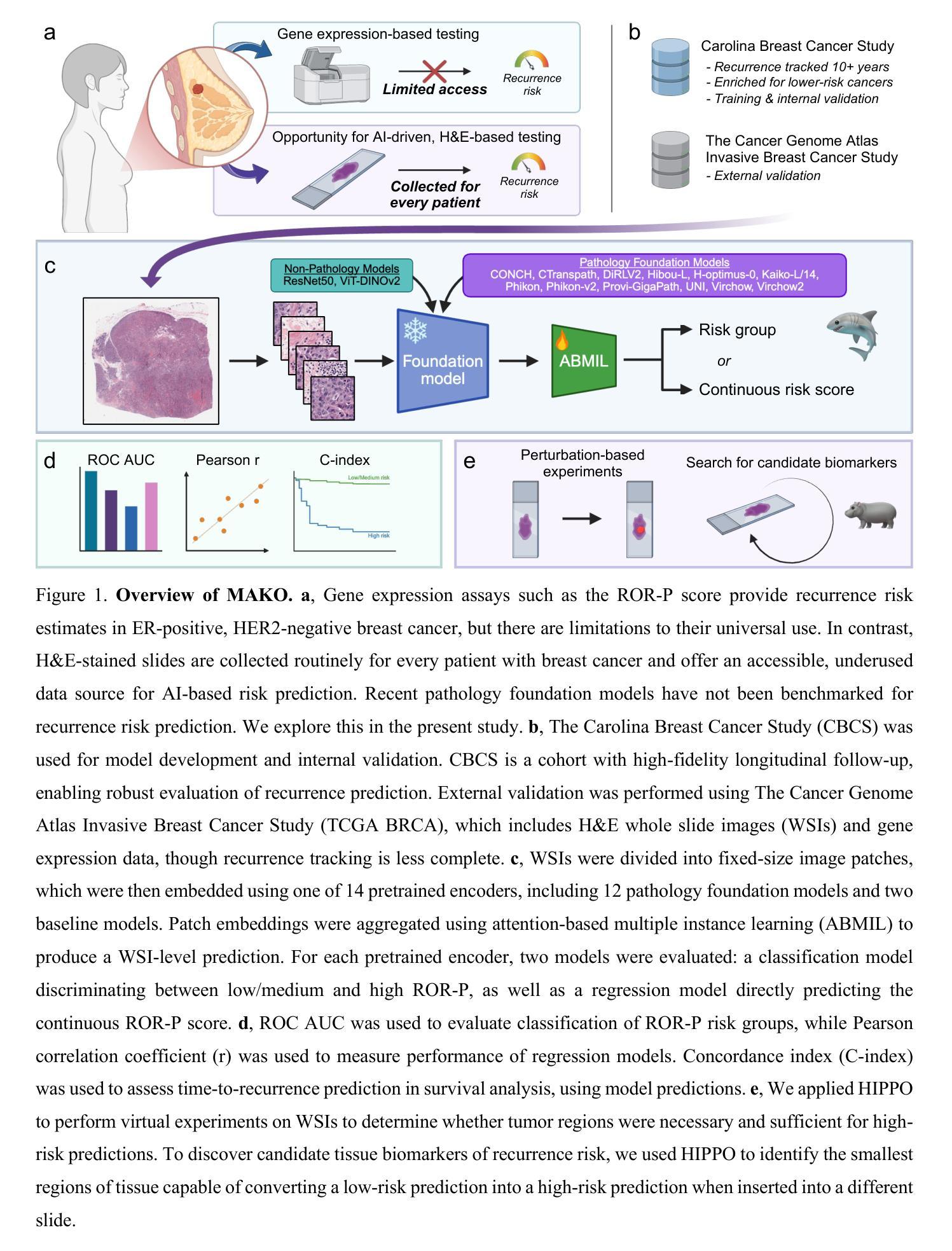
Towards interpretable prediction of recurrence risk in breast cancer using pathology foundation models
Authors:Jakub R. Kaczmarzyk, Sarah C. Van Alsten, Alyssa J. Cozzo, Rajarsi Gupta, Peter K. Koo, Melissa A. Troester, Katherine A. Hoadley, Joel H. Saltz
Transcriptomic assays such as the PAM50-based ROR-P score guide recurrence risk stratification in non-metastatic, ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer but are not universally accessible. Histopathology is routinely available and may offer a scalable alternative. We introduce MAKO, a benchmarking framework evaluating 12 pathology foundation models and two non-pathology baselines for predicting ROR-P scores from H&E-stained whole slide images using attention-based multiple instance learning. Models were trained and validated on the Carolina Breast Cancer Study and externally tested on TCGA BRCA. Several foundation models outperformed baselines across classification, regression, and survival tasks. CONCH achieved the highest ROC AUC, while H-optimus-0 and Virchow2 showed top correlation with continuous ROR-P scores. All pathology models stratified CBCS participants by recurrence similarly to transcriptomic ROR-P. Tumor regions were necessary and sufficient for high-risk predictions, and we identified candidate tissue biomarkers of recurrence. These results highlight the promise of interpretable, histology-based risk models in precision oncology.
基于PAM50的ROR-P评分等转录组检测对非转移性、ER阳性、HER2阴性乳腺癌的复发风险分层具有指导意义,但并非普遍适用。组织病理学是常规可用的,并可能提供一种可扩展的替代方案。我们介绍了MAKO,这是一个评估基准框架,对12个病理学基础模型以及两个非病理学基线进行了基准测试,它们使用基于注意力的多实例学习从H&E染色的全幻灯片图像中预测ROR-P评分。这些模型在卡罗莱纳乳腺癌研究(Carolina Breast Cancer Study)上进行了训练和验证,并在TCGA BRCA上进行了外部测试。在分类、回归和生存任务方面,多个基础模型的性能超过了基线水平。CONCH获得了最高的ROC AUC值,而H-optimus-0和Virchow2与连续的ROR-P评分表现出较高的相关性。所有病理学模型均能将CBCS参与者的复发情况与转录组ROR-P相似分层。肿瘤区域对于高风险预测是必要且充分的,我们确定了复发的候选组织生物标志物。这些结果突出了基于可解释组织学的风险模型在精准肿瘤学中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了MAKO这一评估框架,用于评价利用苏木精和伊红染色全切片图像预测ROR-P得分的病理基础模型。该研究在卡罗莱纳乳腺癌研究中进行模型训练和验证,并在TCGA BRCA上进行外部测试。一些病理基础模型在分类、回归和生存任务上的表现超过非病理基线。其中,CONCH模型ROC AUC最高,H-optimus-0和Virchow2与连续ROR-P得分的相关性最高。这些病理模型能够根据肿瘤区域预测高风险,并识别出复发候选组织生物标志物。该研究强调了可解释的、基于组织学的风险模型在精准肿瘤学中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用MAKO评估框架评价了预测ROR-P得分的病理基础模型表现。
- 研究在卡罗莱纳乳腺癌研究中对模型进行训练和验证,并在TCGA BRCA上进行外部测试。
- 某些病理基础模型在分类、回归和生存预测任务上的表现优于非病理基线。
- CONCH模型ROC AUC最高,H-optimus-0和Virchow2与ROR-P得分的连续性相关性最强。
- 病理模型能够根据肿瘤区域进行高风险预测,并提供可解释的预测依据。
- 研究发现了与肿瘤复发相关的组织生物标志物。
点此查看论文截图

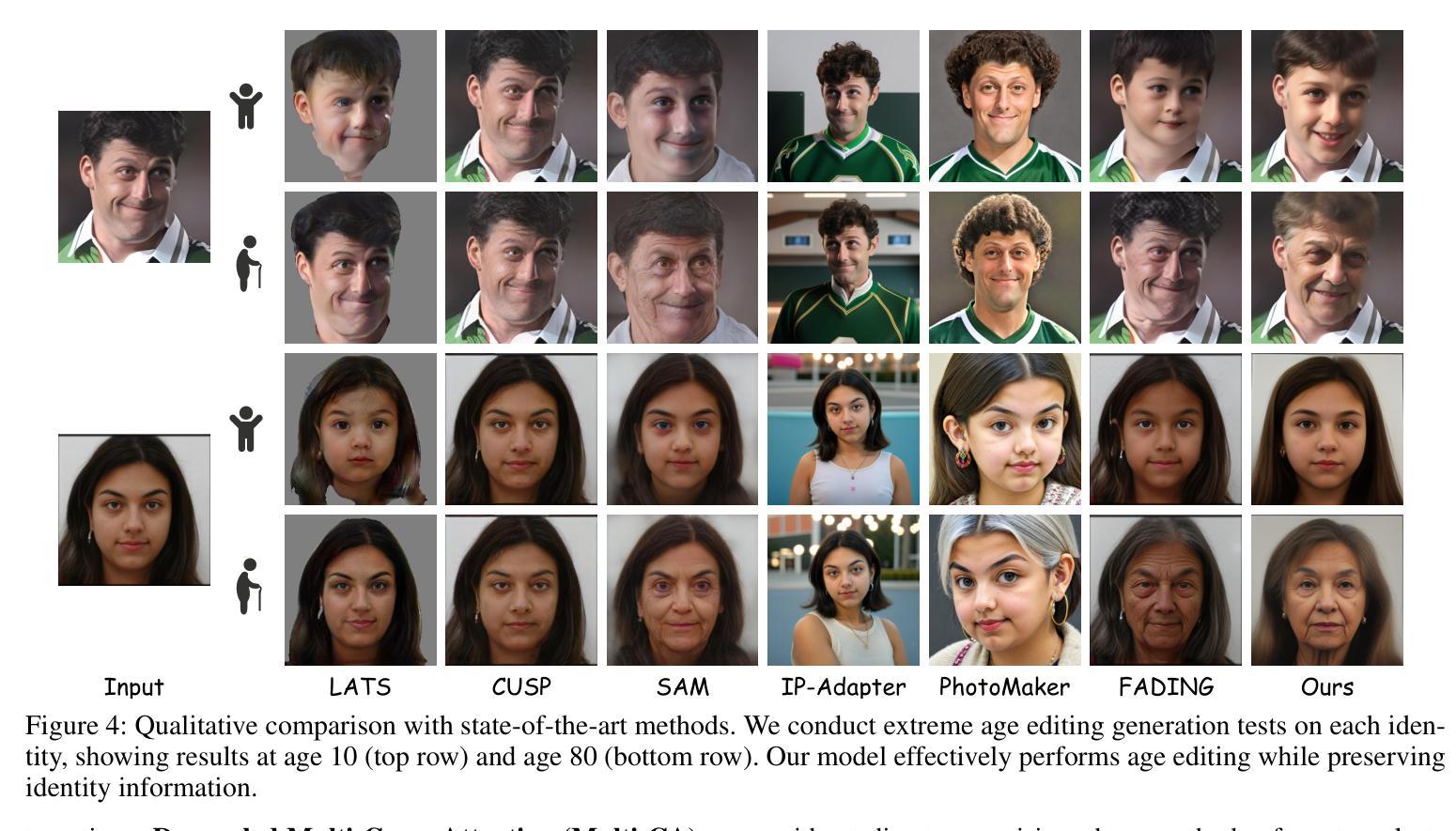
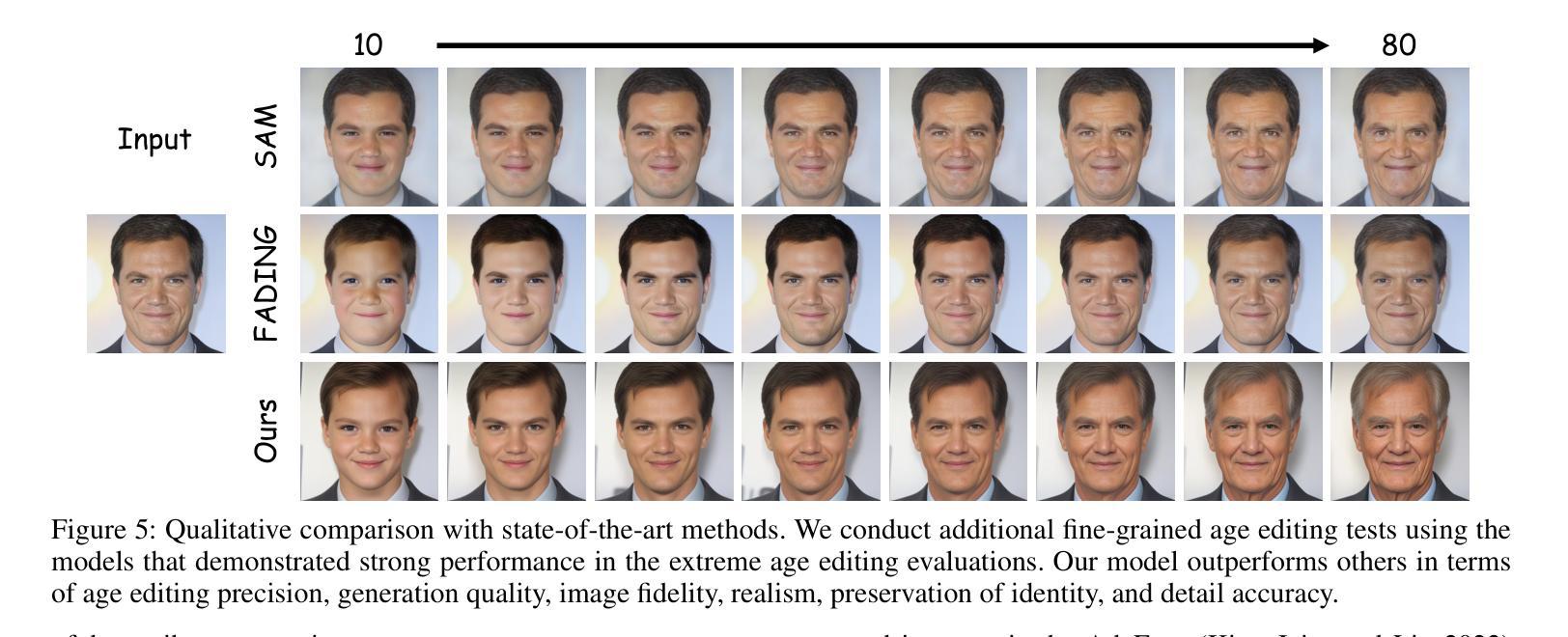
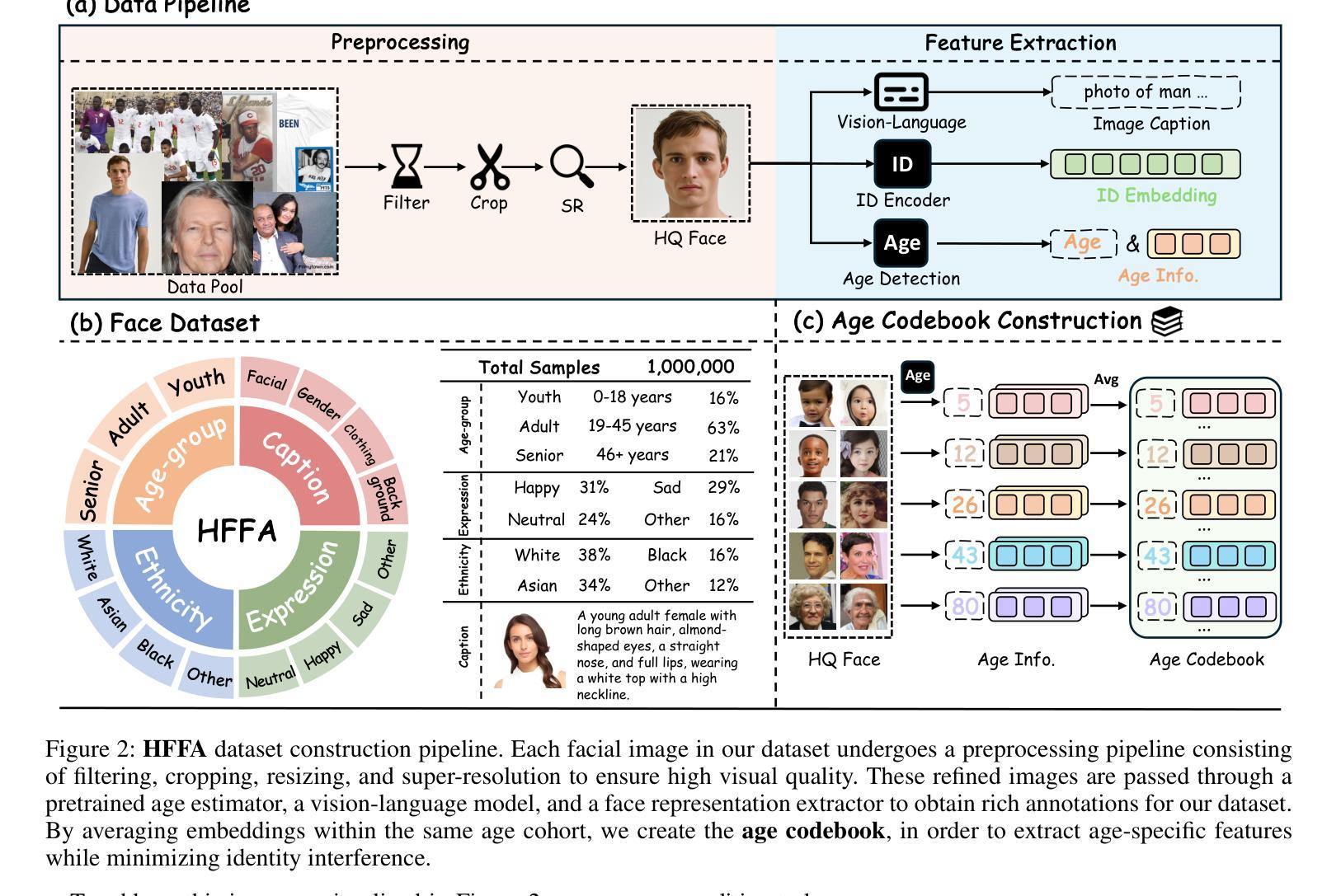
TimeMachine: Fine-Grained Facial Age Editing with Identity Preservation
Authors:Yilin Mi, Qixin Yan, Zheng-Peng Duan, Chunle Guo, Hubery Yin, Hao Liu, Chen Li, Chongyi Li
With the advancement of generative models, facial image editing has made significant progress. However, achieving fine-grained age editing while preserving personal identity remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose TimeMachine, a novel diffusion-based framework that achieves accurate age editing while keeping identity features unchanged. To enable fine-grained age editing, we inject high-precision age information into the multi-cross attention module, which explicitly separates age-related and identity-related features. This design facilitates more accurate disentanglement of age attributes, thereby allowing precise and controllable manipulation of facial aging. Furthermore, we propose an Age Classifier Guidance (ACG) module that predicts age directly in the latent space, instead of performing denoising image reconstruction during training. By employing a lightweight module to incorporate age constraints, this design enhances age editing accuracy by modest increasing training cost. Additionally, to address the lack of large-scale, high-quality facial age datasets, we construct a HFFA dataset (High-quality Fine-grained Facial-Age dataset) which contains one million high-resolution images labeled with identity and facial attributes. Experimental results demonstrate that TimeMachine achieves state-of-the-art performance in fine-grained age editing while preserving identity consistency.
随着生成模型的发展,面部图像编辑已经取得了重大进展。然而,在保持个人身份的同时实现精细年龄编辑仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们提出了TimeMachine,这是一种基于扩散的新型框架,能够在保持身份特征不变的同时实现精确的年龄编辑。为了实现精细年龄编辑,我们将高精度年龄信息注入多交叉注意模块,该模块显式地分离年龄相关和身份相关的特征。这种设计促进了年龄属性的更精确分离,从而允许精确且可控的面部衰老操作。此外,我们提出了年龄分类器指导(ACG)模块,该模块直接在潜在空间中预测年龄,而不是在训练过程中进行去噪图像重建。通过采用轻量级模块来融入年龄约束,这种设计在适度增加训练成本的情况下提高了年龄编辑的准确性。另外,为了解决缺乏大规模、高质量面部年龄数据集的问题,我们构建了HFFA数据集(高质量精细面部年龄数据集),其中包含一千万张高分辨率图像,并标有身份和面部属性。实验结果表明,TimeMachine在精细年龄编辑方面达到了先进性能,同时保持了身份一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着生成模型的进步,面部图像编辑已取得了显著进展,但在保持个人身份的同时实现精细年龄编辑仍是一项挑战。本文提出了TimeMachine,一种基于扩散的新型框架,可在准确编辑年龄的同时保持身份特征不变。通过向多交叉注意模块注入高精度年龄信息,实现年龄和身份特征的显式分离,从而促进年龄属性的精确解耦,从而实现面部衰老的精确可控操作。此外,还提出了一种年龄分类器引导(ACG)模块,直接在潜在空间中预测年龄,而不是在训练过程中进行去噪图像重建。通过采用轻量级模块来融入年龄约束,这种设计在适度增加训练成本的情况下提高了年龄编辑的准确性。另外,为解决缺乏大规模高质量面部年龄数据集的问题,构建了HFFA数据集(高质量精细面部年龄数据集),包含一千万张带有身份和面部属性标签的高分辨率图像。实验结果表明,TimeMachine在精细年龄编辑方面达到了领先水平,同时保持了身份一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的进步推动了面部图像编辑的发展。
- TimeMachine框架实现了在保持身份特征不变的情况下准确编辑年龄。
- 通过多交叉注意模块注入高精度年龄信息,实现年龄和身份特征的显式分离。
- 提出Age Classifier Guidance(ACG)模块,直接在潜在空间中预测年龄。
- ACG模块的设计通过适度增加训练成本提高了年龄编辑的准确性。
- 构建了HFFA数据集,包含一千万张带有身份和面部属性标签的高分辨率图像,用于面部年龄研究。
点此查看论文截图

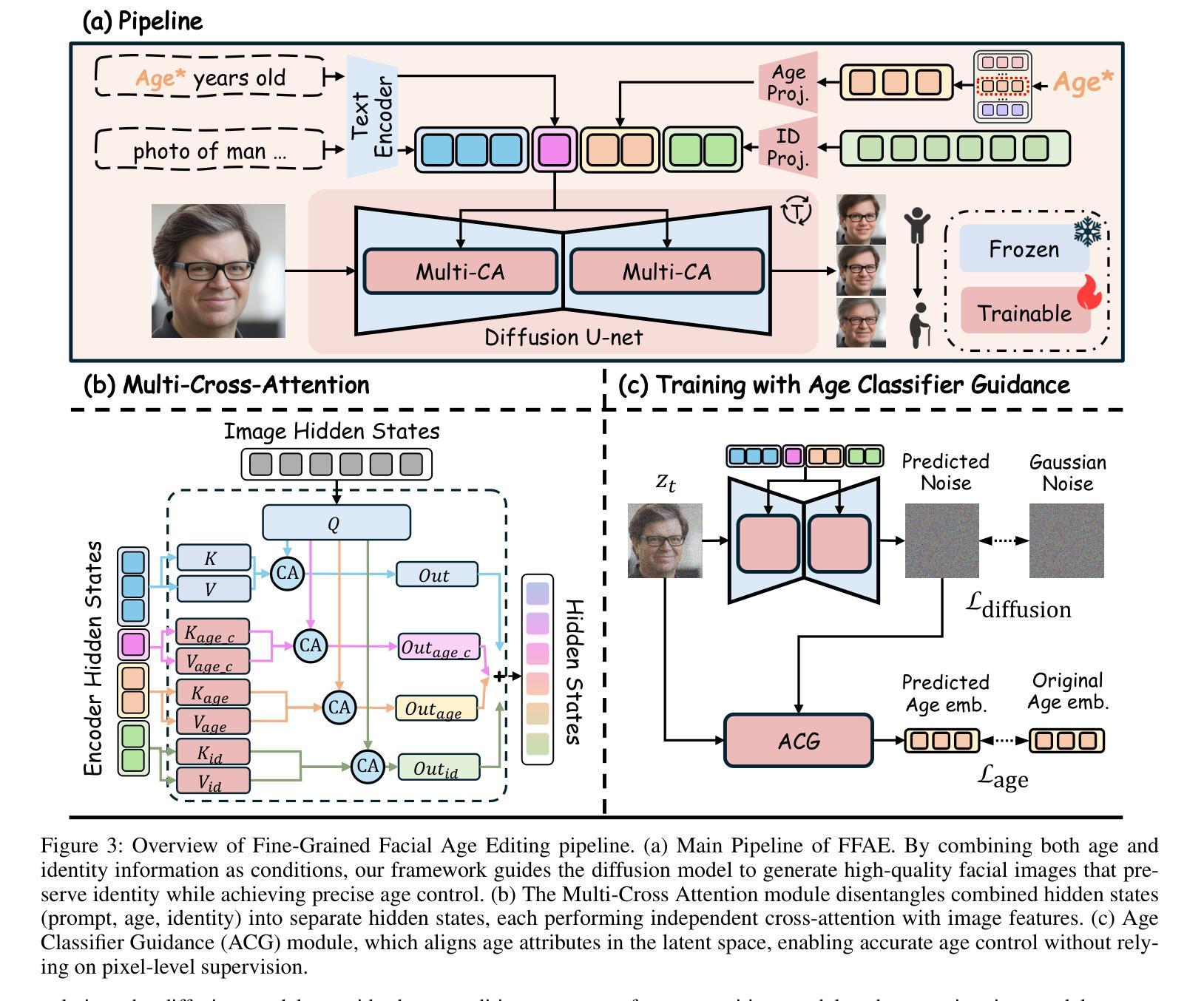


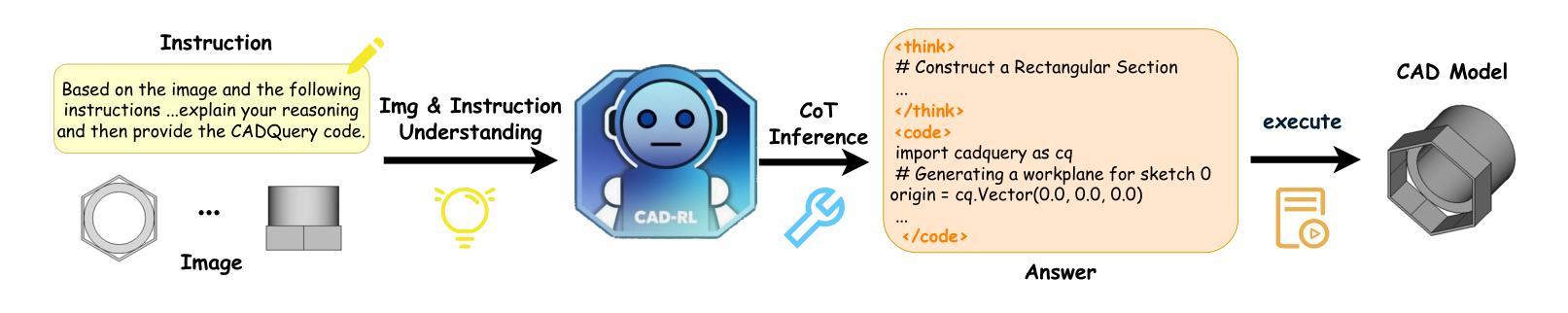
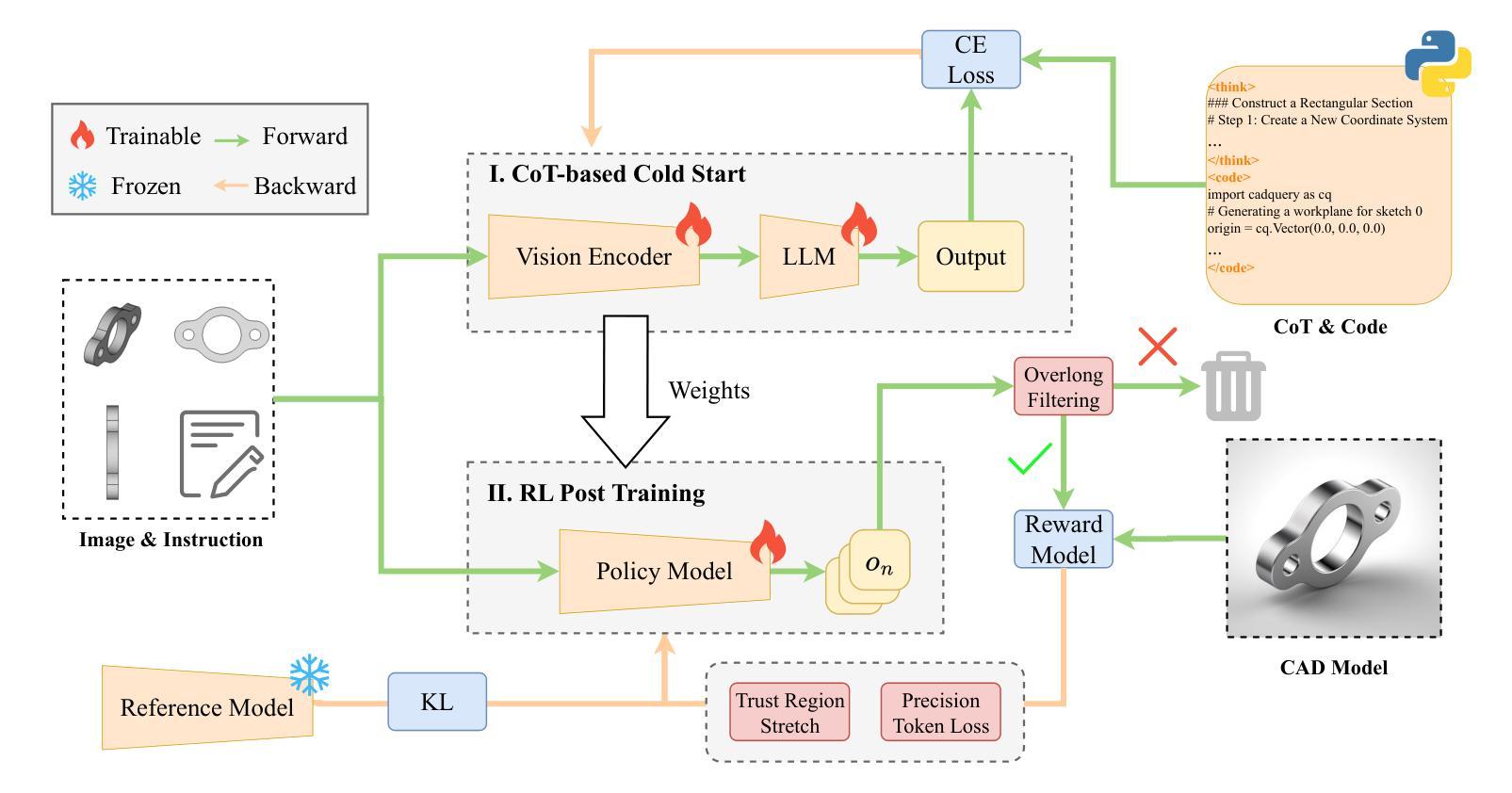
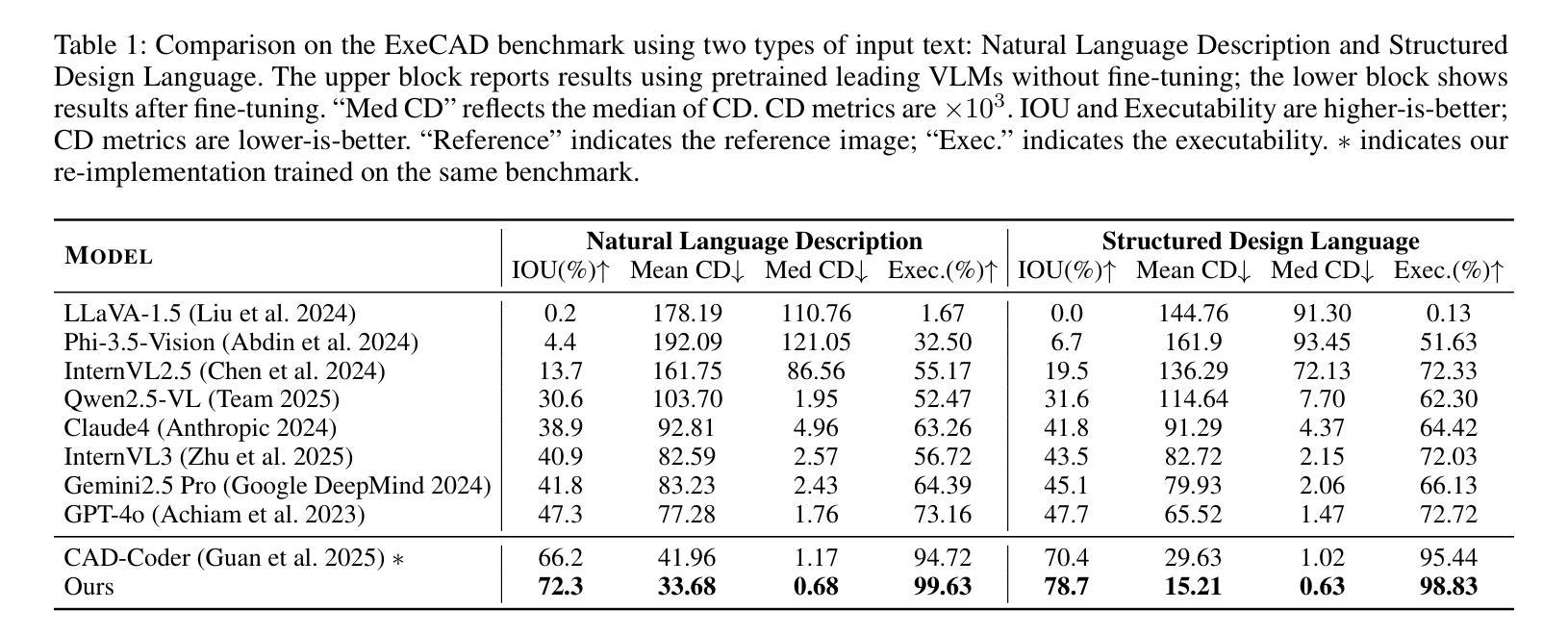
From Intent to Execution: Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reinforcement Learning for Precise CAD Code Generation
Authors:Ke Niu, Haiyang Yu, Zhuofan Chen, Mengyang Zhao, Teng Fu, Bin Li, Xiangyang Xue
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a vital role in engineering and manufacturing, yet current CAD workflows require extensive domain expertise and manual modeling effort. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have made it possible to generate code from natural language, opening new opportunities for automating parametric 3D modeling. However, directly translating human design intent into executable CAD code remains highly challenging, due to the need for logical reasoning, syntactic correctness, and numerical precision. In this work, we propose CAD-RL, a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) guided reinforcement learning post training framework for CAD modeling code generation. Our method combines CoT-based Cold Start with goal-driven reinforcement learning post training using three task-specific rewards: executability reward, geometric accuracy reward, and external evaluation reward. To ensure stable policy learning under sparse and high-variance reward conditions, we introduce three targeted optimization strategies: Trust Region Stretch for improved exploration, Precision Token Loss for enhanced dimensions parameter accuracy, and Overlong Filtering to reduce noisy supervision. To support training and benchmarking, we release ExeCAD, a noval dataset comprising 16,540 real-world CAD examples with paired natural language and structured design language descriptions, executable CADQuery scripts, and rendered 3D models. Experiments demonstrate that CAD-RL achieves significant improvements in reasoning quality, output precision, and code executability over existing VLMs.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造中扮演着至关重要的角色,然而当前的CAD工作流程需要广泛的专业知识和手动建模工作。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使得从自然语言生成代码成为可能,为自动化参数化3D建模带来了新的机会。然而,直接将人类的设计意图转化为可执行的CAD代码仍然面临巨大挑战,这需要进行逻辑推理、语法正确性和数值精确性。在这项工作中,我们提出了CAD-RL,这是一种用于CAD建模代码生成的多模态思维链(CoT)引导强化学习后训练框架。我们的方法结合了基于CoT的冷启动和基于目标导向的强化学习后训练,使用三种特定任务的奖励:可执行性奖励、几何精度奖励和外部评估奖励。为了确保在稀疏和高方差奖励条件下的策略学习稳定,我们引入了三种有针对性的优化策略:信任区域扩展以改善探索能力,精确令牌丢失以增强维度参数精度,以及长过滤以减少噪声监督。为了支持训练和基准测试,我们发布了ExeCAD数据集,该数据集包含16540个现实世界的CAD示例,每个示例都配有自然语言描述和结构化设计语言描述、可执行的CADQuery脚本以及渲染的3D模型。实验表明,在推理质量、输出精度和代码可执行性方面,CAD-RL相比现有的大型语言模型(VLMs)取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了计算机辅助设计(CAD)的重要性及其面临的挑战,如需要深厚的领域知识和手动建模。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为自动化参数化三维建模提供了新的机会。本文提出了一种基于强化学习的CAD建模代码生成方法——CAD-RL,该方法结合了基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的冷启动和面向目标强化学习训练,采用三种特定任务奖励来确保代码的可执行性、几何精度和外部评价。此外,为了稳定策略学习并引入三项有针对性的优化策略来提高模型性能。为支持训练和基准测试,发布了ExeCAD数据集。实验表明,CAD-RL在推理质量、输出精度和代码执行方面相较于现有的视觉语言模型有显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- CAD设计在工程和制造中起重要作用,但手动建模和深厚的领域知识需求使其具有挑战性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为自动化参数化三维建模提供了新的机会。
- CAD-RL方法结合了基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的冷启动和面向目标的强化学习训练。
- CAD-RL采用三种特定任务奖励确保代码的可执行性、几何精度和外部评价。
- 为稳定策略学习,引入了三项优化策略:Trust Region Stretch、Precision Token Loss和Overlong Filtering。
- 发布了一个名为ExeCAD的新数据集,用于训练和基准测试,包含配对自然语言描述和结构化设计语言的真实CAD示例。
点此查看论文截图

Bridging AI Innovation and Healthcare Needs: Lessons Learned from Incorporating Modern NLP at The BC Cancer Registry
Authors:Lovedeep Gondara, Gregory Arbour, Raymond Ng, Jonathan Simkin, Shebnum Devji
Automating data extraction from clinical documents offers significant potential to improve efficiency in healthcare settings, yet deploying Natural Language Processing (NLP) solutions presents practical challenges. Drawing upon our experience implementing various NLP models for information extraction and classification tasks at the British Columbia Cancer Registry (BCCR), this paper shares key lessons learned throughout the project lifecycle. We emphasize the critical importance of defining problems based on clear business objectives rather than solely technical accuracy, adopting an iterative approach to development, and fostering deep interdisciplinary collaboration and co-design involving domain experts, end-users, and ML specialists from inception. Further insights highlight the need for pragmatic model selection (including hybrid approaches and simpler methods where appropriate), rigorous attention to data quality (representativeness, drift, annotation), robust error mitigation strategies involving human-in-the-loop validation and ongoing audits, and building organizational AI literacy. These practical considerations, generalizable beyond cancer registries, provide guidance for healthcare organizations seeking to successfully implement AI/NLP solutions to enhance data management processes and ultimately improve patient care and public health outcomes.
自动化从临床文档中提取数据,在医疗保健环境中具有显著提高效率的潜力。然而,部署自然语言处理(NLP)解决方案却存在实际挑战。本文基于我们在不列颠哥伦比亚省癌症登记处(BCCR)为信息提取和分类任务实施各种NLP模型的实践经验,分享项目生命周期中吸取的关键教训。我们强调,根据明确的业务目标而不是单纯的技术准确性来定义问题至关重要,采用迭代开发方法,并从一开始就促进跨学科的深度协作和协同设计,涉及领域专家、最终用户和机器学习专家。进一步的见解强调了实用模型选择的需要(包括混合方法和适当情况下的简化方法),对数据质量(代表性、漂移、注释)的严格关注,涉及人机循环验证和持续审计的稳健错误缓解策略,以及提高组织的人工智能素养。这些实际考虑因素,可推广应用于癌症登记以外的领域,为寻求成功实施人工智能/自然语言处理解决方案以改进数据管理流程并最终改善患者护理和公共卫生结果的医疗保健组织提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动化临床文档数据提取在提升医疗效率方面具有巨大潜力,但在部署自然语言处理(NLP)解决方案时面临实际挑战。本文依托在加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省癌症登记处(BCCR)实施各种NLP模型进行信息提取和分类任务的经验,分享项目生命周期中的重要教训。强调以明确的业务目标来定义问题的重要性而非单纯追求技术准确性,采取迭代式开发方法,并从一开始就促进跨学科合作和设计,包括领域专家、终端用户和机器学习专家的参与。此外,文章还强调了选择实用模型(包括混合方法和适当简化方法)、严格关注数据质量(代表性、漂移、注释)、构建包含人为循环验证和持续审计的错误缓解策略以及提高组织的人工智能素养的重要性。这些实际考量因素对于寻求成功实施人工智能/自然语言处理解决方案以改善数据管理流程并最终改善患者护理和公共卫生结果的医疗机构具有指导意义。
Key Takeaways
- 定义问题时需结合明确的业务目标,而非仅追求技术准确性。
- 采用迭代式开发方法,促进跨学科合作和参与。
- 需要根据实际问题和环境选择适合的NLP模型和方法。
- 严格关注数据质量,包括数据的代表性、漂移和注释。
- 实施包含人为循环验证和持续审计的错误缓解策略。
- 强调人工智能在组织中的应用和推广的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

NEUBORN: The Neurodevelopmental Evolution framework Using BiOmechanical RemodelliNg
Authors:Nashira Baena, Mariana da Silva, Irina Grigorescu, Aakash Saboo, Saga Masui, Jaques-Donald Tournier, Emma C. Robinson
Understanding individual cortical development is essential for identifying deviations linked to neurodevelopmental disorders. However, current normative modelling frameworks struggle to capture fine-scale anatomical details due to their reliance on modelling data within a population-average reference space. Here, we present a novel framework for learning individual growth trajectories from biomechanically constrained, longitudinal, diffeomorphic image registration, implemented via a hierarchical network architecture. Trained on neonatal MRI data from the Developing Human Connectome Project, the method improves the biological plausibility of warps, generating growth trajectories that better follow population-level trends while generating smoother warps, with fewer negative Jacobians, relative to state-of-the-art baselines. The resulting subject-specific deformations provide interpretable, biologically grounded mappings of development. This framework opens new possibilities for predictive modeling of brain maturation and early identification of malformations of cortical development.
了解个体皮层发育对于识别与神经发育障碍相关的偏差至关重要。然而,当前的规范性建模框架由于依赖于在人群平均参考空间内进行建模数据,难以捕获精细的解剖结构细节。在这里,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架通过层次网络架构实现,通过生物力学约束、纵向和形态图像配准来学习个体生长轨迹。该方法在发展中国家人类连接组计划的新生儿MRI数据上进行训练,提高了变形场的生物学合理性,生成的生长轨迹能更好地遵循人群水平趋势,同时生成更平滑的变形场,与最新基线相比具有更少的负雅可比行列式。这些特定的主体变形提供了可解释的、以生物学为基础的发育映射。该框架为预测大脑成熟模型和早期识别皮层发育畸形提供了新的可能性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的框架,用于通过基于生物力学约束的纵向微分图像配准技术学习个体生长轨迹。该框架采用层次网络架构实现,经过对发育人类连接组项目中的新生儿MRI数据的训练,能够生成更符合人口水平趋势的平滑变形映射,提高变形映射的生物合理性。这为预测大脑成熟和早期识别皮质发育畸形提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前规范性建模框架因依赖群体平均参考空间而无法捕捉精细的解剖细节。
- 介绍了一种新的框架,基于生物力学约束的纵向微分图像配准技术来学习个体生长轨迹。
- 新框架采用层次网络架构实现,经过新生儿MRI数据的训练。
- 与现有方法相比,新方法生成的变形映射更加符合人口水平趋势,并且更加平滑。
- 新方法提高了变形映射的生物合理性,并提供了可解释的、基于生物学的发育映射。
- 该框架为预测大脑成熟提供了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

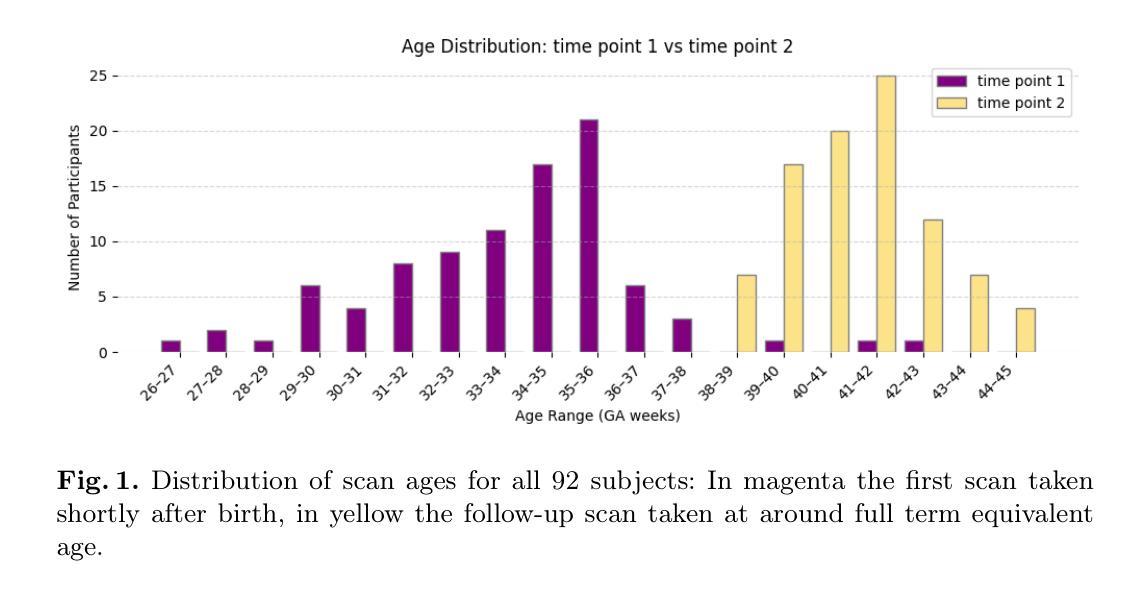
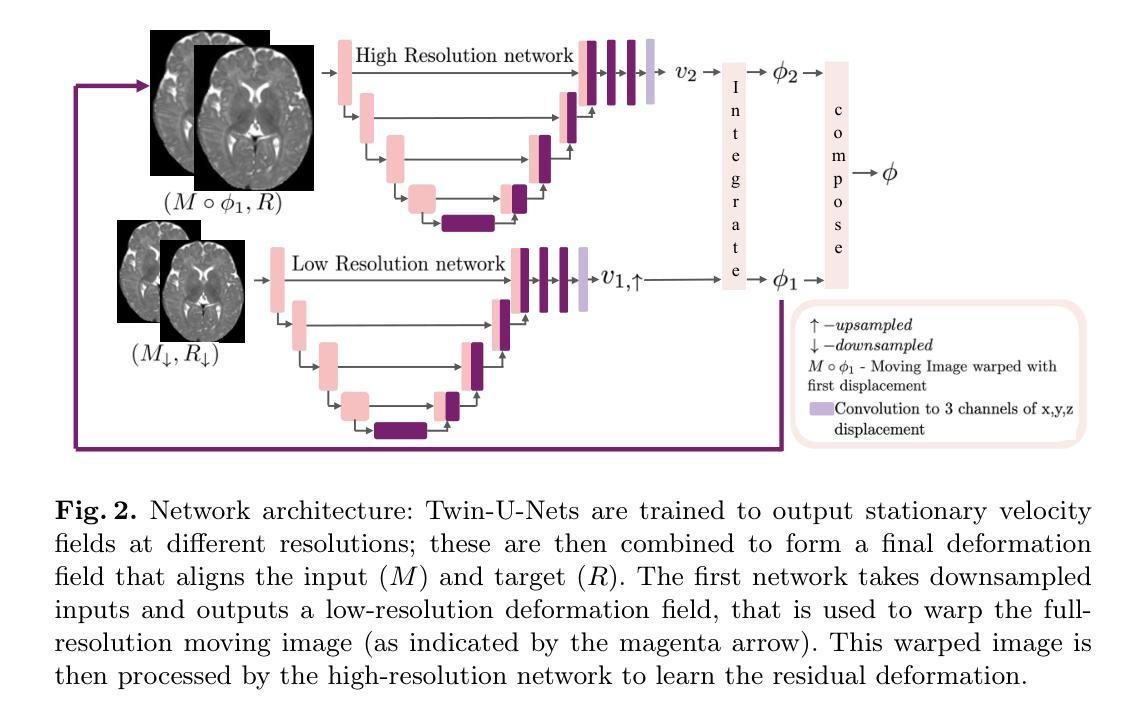
Unified and Semantically Grounded Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xin Wang, Yin Guo, Jiamin Xia, Kaiyu Zhang, Niranjan Balu, Mahmud Mossa-Basha, Linda Shapiro, Chun Yuan
Most prior unsupervised domain adaptation approaches for medical image segmentation are narrowly tailored to either the source-accessible setting, where adaptation is guided by source-target alignment, or the source-free setting, which typically resorts to implicit supervision mechanisms such as pseudo-labeling and model distillation. This substantial divergence in methodological designs between the two settings reveals an inherent flaw: the lack of an explicit, structured construction of anatomical knowledge that naturally generalizes across domains and settings. To bridge this longstanding divide, we introduce a unified, semantically grounded framework that supports both source-accessible and source-free adaptation. Fundamentally distinct from all prior works, our framework’s adaptability emerges naturally as a direct consequence of the model architecture, without the need for any handcrafted adaptation strategies. Specifically, our model learns a domain-agnostic probabilistic manifold as a global space of anatomical regularities, mirroring how humans establish visual understanding. Thus, the structural content in each image can be interpreted as a canonical anatomy retrieved from the manifold and a spatial transformation capturing individual-specific geometry. This disentangled, interpretable formulation enables semantically meaningful prediction with intrinsic adaptability. Extensive experiments on challenging cardiac and abdominal datasets show that our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in both settings, with source-free performance closely approaching its source-accessible counterpart, a level of consistency rarely observed in prior works. Beyond quantitative improvement, we demonstrate strong interpretability of the proposed framework via manifold traversal for smooth shape manipulation.
在医学图像分割中,大多数先前的无监督域自适应方法主要局限于源可访问设置,其中自适应由源目标对齐引导,或者无源的自由设置,这通常依赖于伪标签和模型蒸馏等隐式监督机制。这两种设置中的方法设计存在明显的分歧,暴露出内在缺陷:缺乏明确的、结构化构建的解剖学知识,这种知识能够自然地跨域和设置进行推广。为了弥合这一长期存在的分歧,我们引入了一个统一的、语义基础框架,支持源可访问和无源自适应。与所有先前的工作根本不同,我们框架的适应性是模型架构的直接结果,无需任何手工定制的自适应策略。具体来说,我们的模型学习一个域无关的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,反映人类建立视觉理解的方式。因此,每个图像的结构内容可以被解释为从流形中检索的规范解剖学以及捕获个体特定几何的空间变换。这种解耦、可解释的表达实现了具有内在适应性的语义上有意义的预测。在具有挑战性的心脏和腹部数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在这两种设置中均达到了最新水平的结果,无源性能接近其源可访问的对应物,这在以前的工作中很少观察到的一致性。除了定量改进之外,我们通过流形遍历展示了所提出框架的强大可解释性,以实现平滑的形状操纵。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种统一、语义化的框架,旨在支持有源可访问和无源自适应的医学图像分割。该框架无需任何手工定制的自适应策略,通过构建领域无关的概略流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,实现结构内容的解耦和可解释预测,具有内在的自适应性。在心脏和腹部数据集上的实验表明,该框架达到了两种设置下的最新技术水平,并且无源性能接近其有源对应物,这在以前的工作中很少观察到。此外,通过流形遍历进行平滑形状操纵,展示出了该框架的强可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种统一、语义化的框架,支持源可访问和源自由两种自适应医学图像分割方法。
- 框架通过构建领域无关的概略流形作为全局空间,实现解剖知识的结构化构建。
- 模型架构自然产生适应性,无需任何手工定制的自适应策略。
- 结构内容被解耦并表示为可解释的预测,包括通用解剖结构和个体特定几何的空间转换。
- 在心脏和腹部数据集上的实验结果表明,该框架在两种设置下均达到了最新技术水平。
- 源自由性能接近源可访问性能,展现了框架的高适应性和内在一致性。
点此查看论文截图
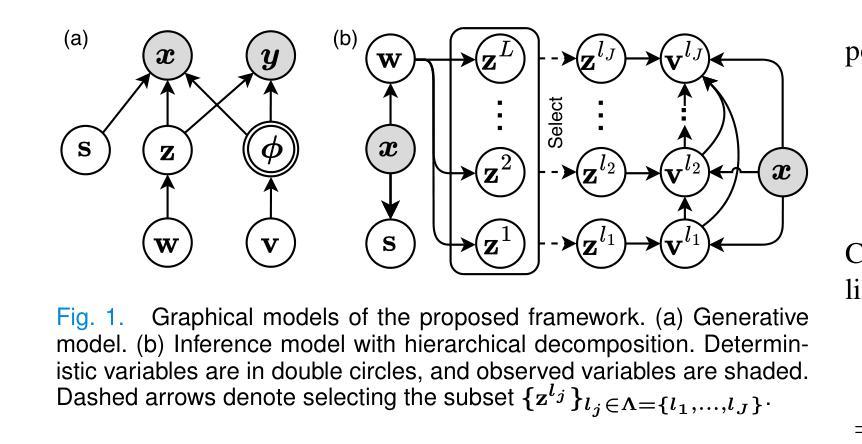
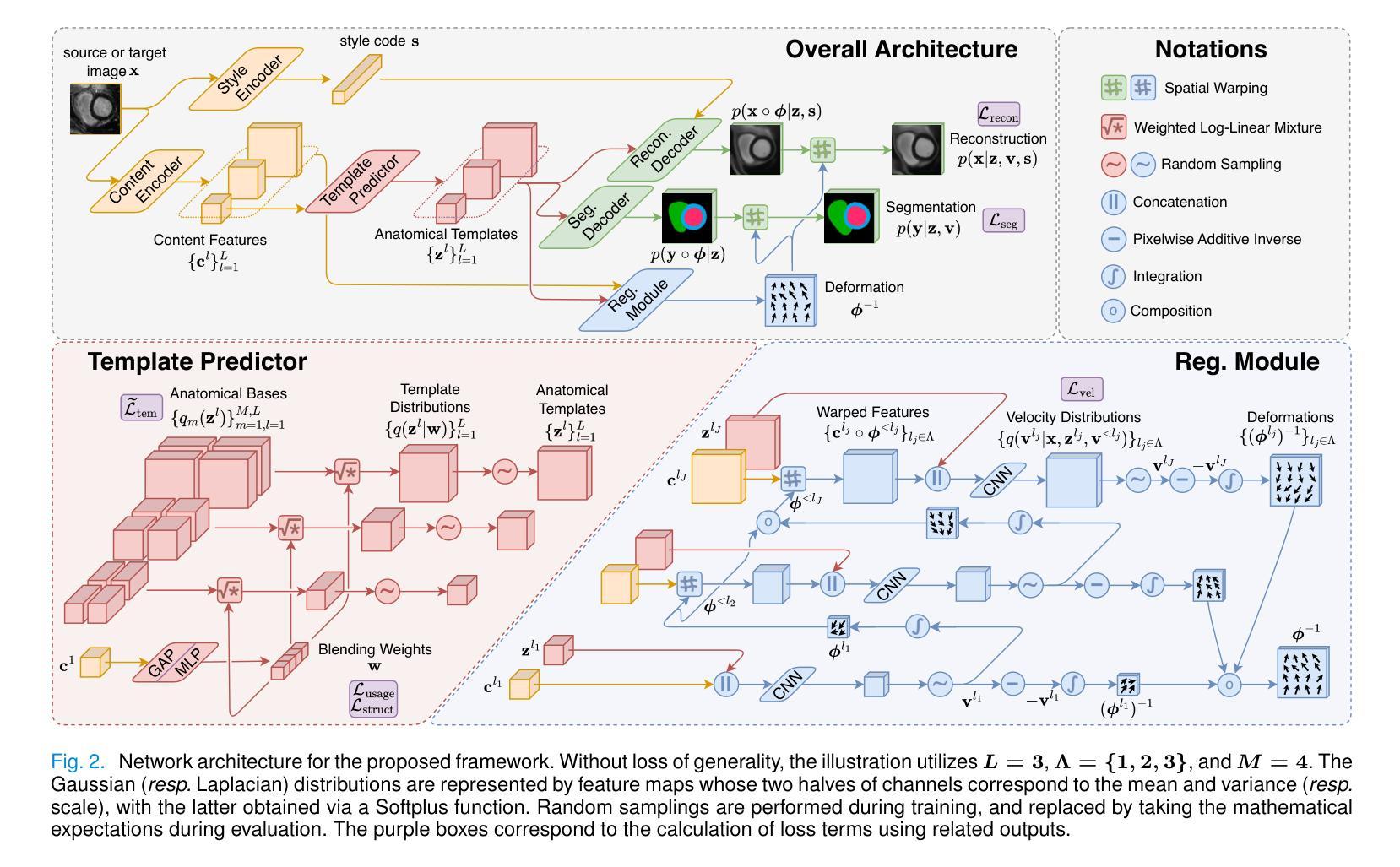
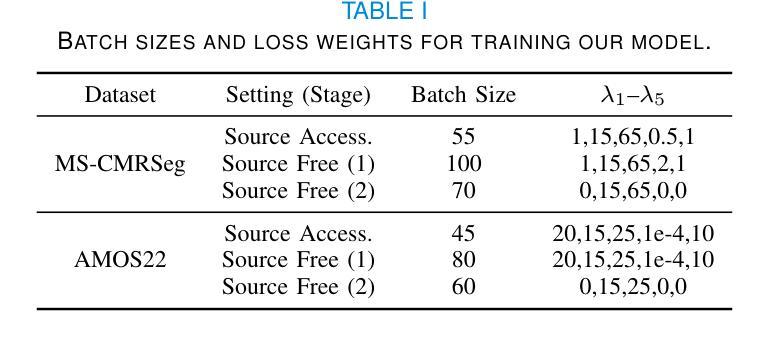
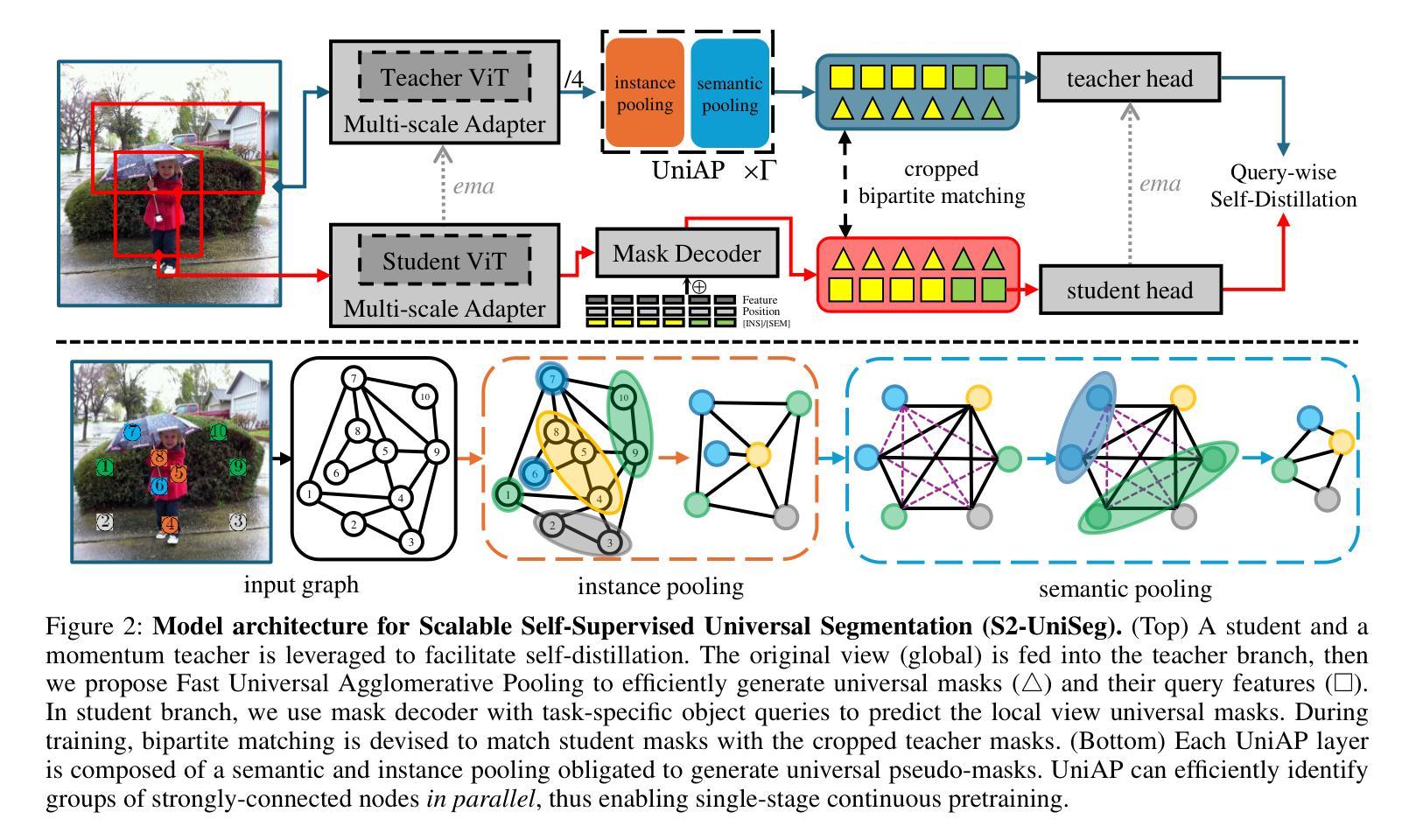
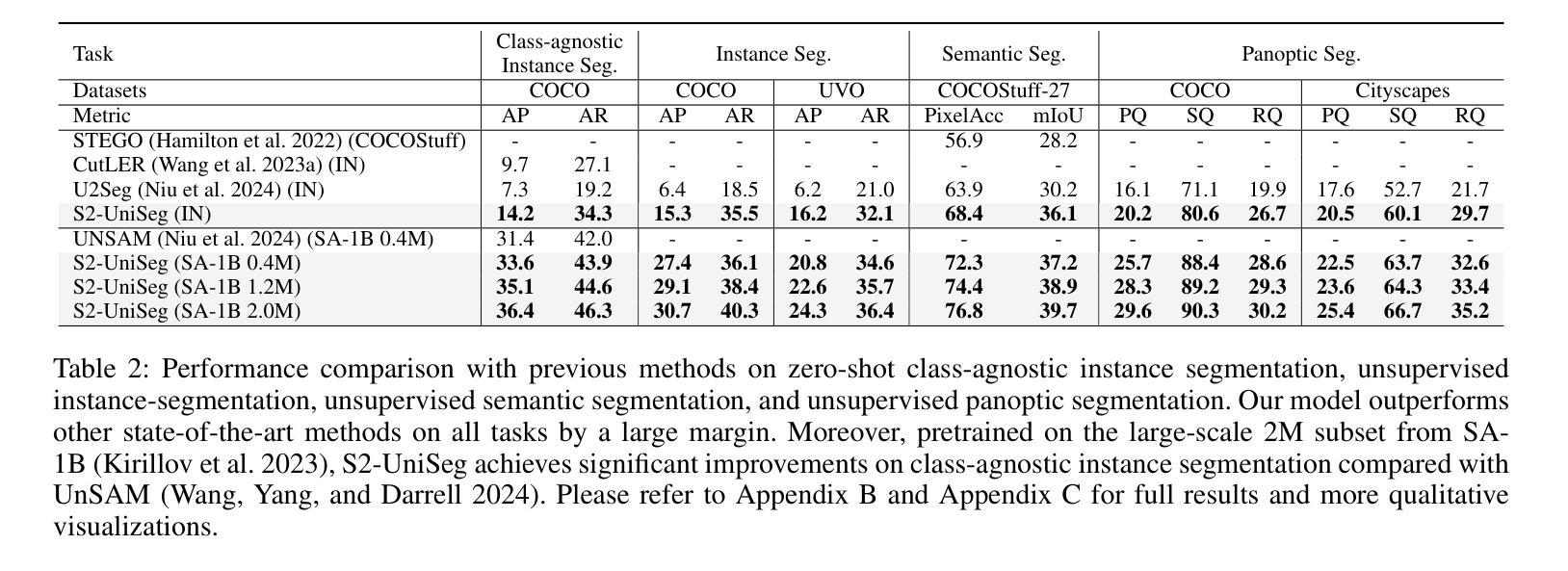
S2-UniSeg: Fast Universal Agglomerative Pooling for Scalable Segment Anything without Supervision
Authors:Huihui Xu, Jin Ye, Hongqiu Wang, Changkai Ji, Jiashi Lin, Ming Hu, Ziyan Huang, Ying Chen, Chenglong Ma, Tianbin Li, Lihao Liu, Junjun He, Lei Zhu
Recent self-supervised image segmentation models have achieved promising performance on semantic segmentation and class-agnostic instance segmentation. However, their pretraining schedule is multi-stage, requiring a time-consuming pseudo-masks generation process between each training epoch. This time-consuming offline process not only makes it difficult to scale with training dataset size, but also leads to sub-optimal solutions due to its discontinuous optimization routine. To solve these, we first present a novel pseudo-mask algorithm, Fast Universal Agglomerative Pooling (UniAP). Each layer of UniAP can identify groups of similar nodes in parallel, allowing to generate both semantic-level and instance-level and multi-granular pseudo-masks within ens of milliseconds for one image. Based on the fast UniAP, we propose the Scalable Self-Supervised Universal Segmentation (S2-UniSeg), which employs a student and a momentum teacher for continuous pretraining. A novel segmentation-oriented pretext task, Query-wise Self-Distillation (QuerySD), is proposed to pretrain S2-UniSeg to learn the local-to-global correspondences. Under the same setting, S2-UniSeg outperforms the SOTA UnSAM model, achieving notable improvements of AP+6.9 on COCO, AR+11.1 on UVO, PixelAcc+4.5 on COCOStuff-27, RQ+8.0 on Cityscapes. After scaling up to a larger 2M-image subset of SA-1B, S2-UniSeg further achieves performance gains on all four benchmarks. Our code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/bio-mlhui/S2-UniSeg
近期,自监督图像分割模型在语义分割和类别无关的实例分割方面取得了有前景的性能表现。然而,它们的预训练计划是多阶段的,需要在每个训练周期之间进行耗时的伪掩码生成过程。这种耗时的离线过程不仅难以随着训练数据集的大小进行扩展,而且由于其不连续的优化流程,还会导致次优解。为解决这些问题,我们首先提出了一种新型的伪掩码算法——快速通用聚合池化(UniAP)。UniAP的每一层都能并行识别出相似的节点组,从而能够在几秒钟内为一张图像生成语义级别和实例级别的多粒度伪掩码。基于快速的UniAP,我们提出了可扩展的自监督通用分割(S2-UniSeg),它采用学生和动量教师进行连续预训练。还提出了一种面向分割的预文本任务——查询级自蒸馏(QuerySD),用于预训练SSTrackSeg来学习局部到全局的对应关系。在相同设置下,S2-UniSeg优于UnSAM模型,在COCO上提高了AP+6.9,在UVO上提高了AR+11.1,在COCOStuff-27上提高了PixelAcc+4.5和在Cityscapes上提高了RQ+8.0。当扩大到更大的SA-1B的2M图像子集时,S2-UniSeg在四个基准测试上都取得了性能提升。我们的代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/bio-mlhui/S2-UniSeg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种新型伪掩膜算法——快速通用融合池化(UniAP),能够生成语义级别和实例级别的多粒度伪掩膜,大大提高了自监督图像分割模型的性能。基于快速UniAP,提出了可扩展自监督通用分割(S2-UniSeg)模型,采用学生和动量教师进行连续预训练。提出了一种新的面向分割的预文本任务——查询级自蒸馏(QuerySD),用于预训练S2-UniSeg学习局部到全局的对应关系。在相同设置下,S2-UniSeg优于当前最佳模型UnSAM,在COCO、UVO、COCOStuff-27和Cityscapes上的表现均有显著提高。在扩展到更大的SA-1B的2M图像子集后,S2-UniSeg在四个基准测试上的性能进一步提升。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的伪掩膜算法——快速通用融合池化(UniAP),可快速生成语义和实例级别的伪掩膜。
- 基于UniAP,提出了可扩展自监督通用分割模型(S2-UniSeg)。
- S2-UniSeg采用学生和动量教师的连续预训练方法。
- 提出了一种新的面向分割的预文本任务——查询级自蒸馏(QuerySD),帮助模型学习局部到全局的对应关系。
- S2-UniSeg相较于当前最佳模型UnSAM在多个基准测试上有显著提高。
- S2-UniSeg在扩展到更大的数据集后性能进一步提升。
点此查看论文截图

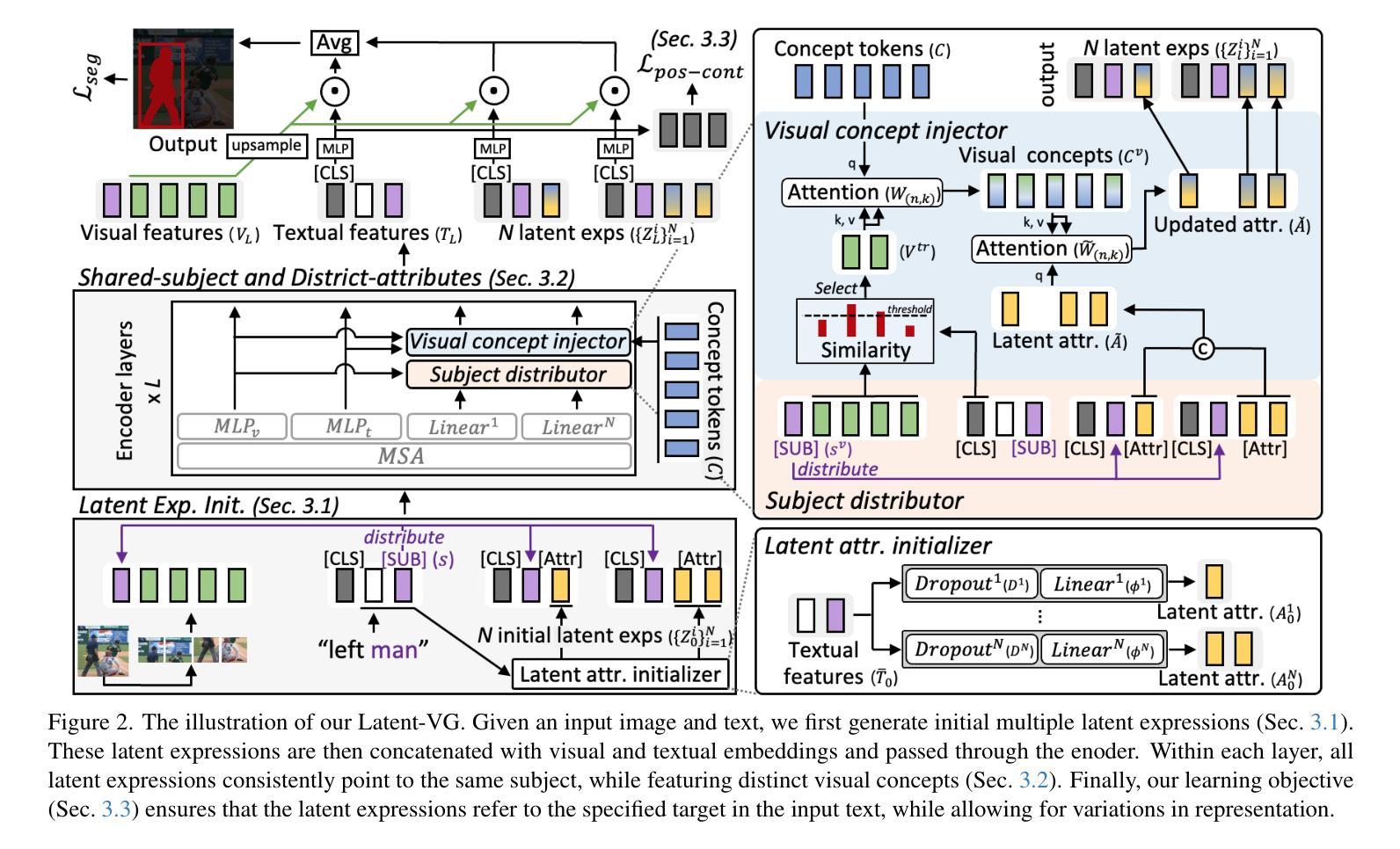
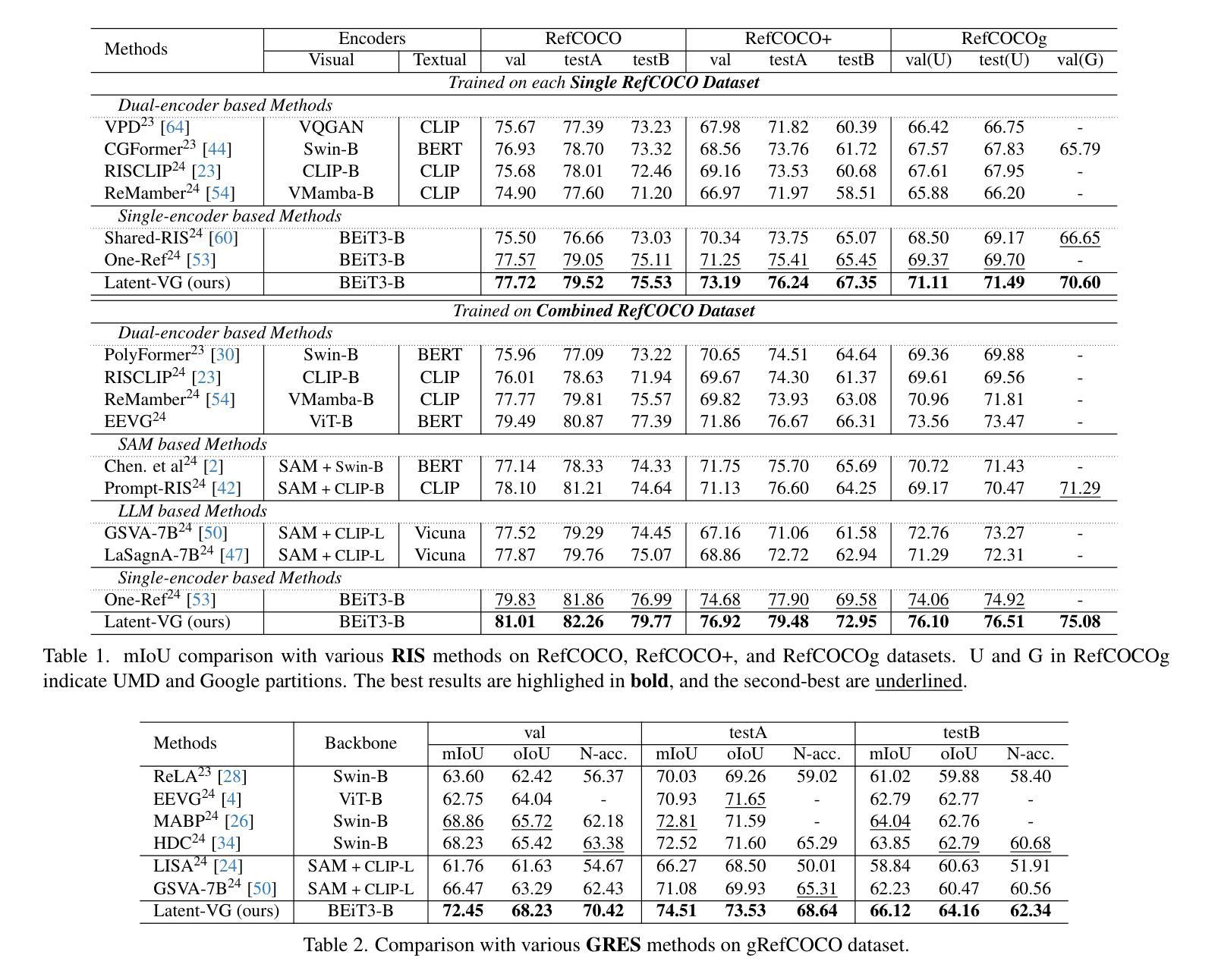
Latent Expression Generation for Referring Image Segmentation and Grounding
Authors:Seonghoon Yu, Junbeom Hong, Joonseok Lee, Jeany Son
Visual grounding tasks, such as referring image segmentation (RIS) and referring expression comprehension (REC), aim to localize a target object based on a given textual description. The target object in an image can be described in multiple ways, reflecting diverse attributes such as color, position, and more. However, most existing methods rely on a single textual input, which captures only a fraction of the rich information available in the visual domain. This mismatch between rich visual details and sparse textual cues can lead to the misidentification of similar objects. To address this, we propose a novel visual grounding framework that leverages multiple latent expressions generated from a single textual input by incorporating complementary visual details absent from the original description. Specifically, we introduce subject distributor and visual concept injector modules to embed both shared-subject and distinct-attributes concepts into the latent representations, thereby capturing unique and target-specific visual cues. We also propose a positive-margin contrastive learning strategy to align all latent expressions with the original text while preserving subtle variations. Experimental results show that our method not only outperforms state-of-the-art RIS and REC approaches on multiple benchmarks but also achieves outstanding performance on the generalized referring expression segmentation (GRES) benchmark.
视觉定位任务,如引用图像分割(RIS)和引用表达式理解(REC),旨在根据给定的文本描述定位目标对象。图像中的目标对象可以用多种方式描述,反映诸如颜色、位置等多样化的属性。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于单个文本输入,这只能捕获视觉域中丰富信息的一部分。丰富视觉细节和稀疏文本线索之间的不匹配可能导致相似对象的误识别。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,该框架利用单个文本输入产生的多个潜在表达式,并融入原始描述中缺失的互补视觉细节。具体来说,我们引入了主体分配器和视觉概念注入模块,将共享主体和独特属性概念嵌入到潜在表示中,从而捕获独特且目标特定的视觉线索。我们还提出了一种正边距对比学习策略,将所有潜在表达式与原始文本对齐,同时保留细微变化。实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅在多个基准测试上超越了最先进的RIS和REC方法,而且在广义引用表达式分割(GRES)基准测试上也取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
这是一篇关于视觉定位任务的研究论文,主要介绍了如何通过结合多种潜在表达和视觉细节来解决单一文本输入导致的视觉与文本信息不匹配的问题。论文提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,通过引入主体分配器和视觉概念注入器模块来嵌入共享主体和独特属性概念,并使用正面间隔对比学习策略来对齐所有潜在表达和原始文本。该方法的优势在于能在多个基准测试中表现优秀,并且在广义参照表达式分割任务上也表现出出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉定位任务包括参照图像分割和参照表达理解,旨在根据给定的文本描述定位目标对象。
- 现有方法大多依赖于单一的文本输入,无法充分利用视觉领域的丰富信息。
- 论文提出了一种新的视觉定位框架,结合了来自单一文本输入的多种潜在表达,并引入了视觉细节来补充原始描述的不足。
- 引入主体分配器和视觉概念注入器模块,以嵌入共享主体和独特属性概念。
- 使用正面间隔对比学习策略,以对齐所有潜在表达和原始文本,同时保留细微变化。
- 该方法在多个基准测试中表现优秀,超越了现有的参照图像分割和参照表达理解方法。
点此查看论文截图

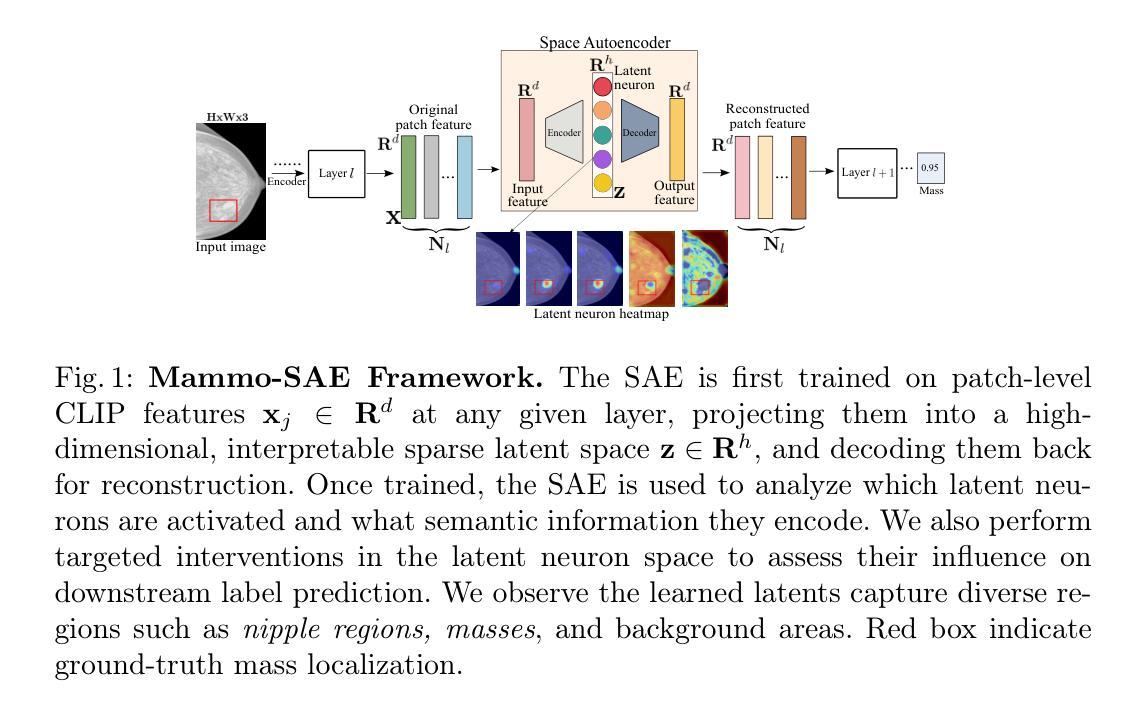
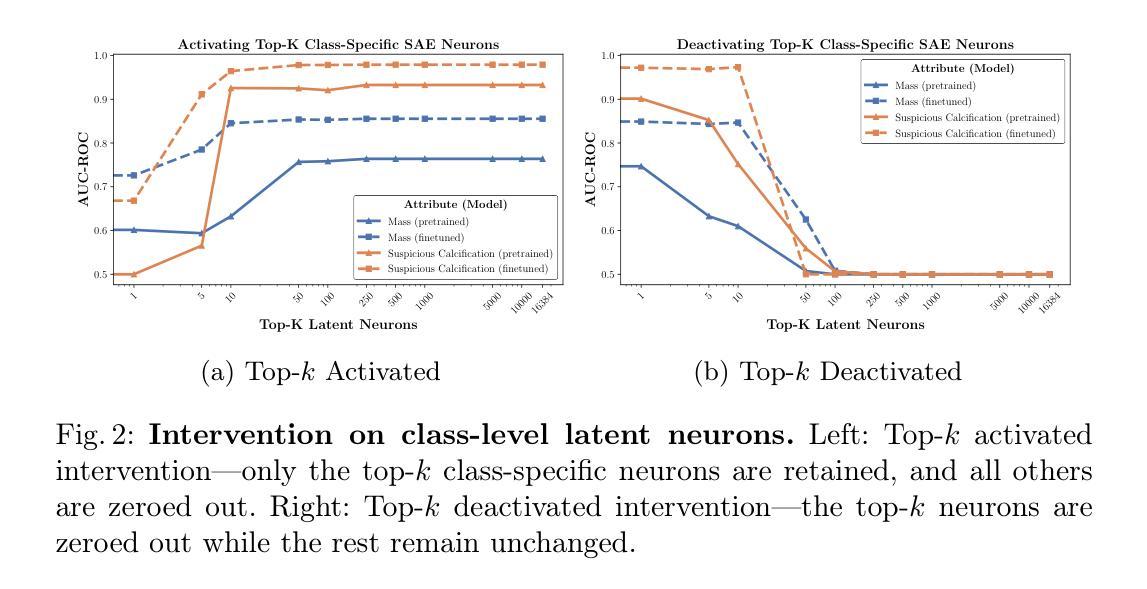
Mammo-SAE: Interpreting Breast Cancer Concept Learning with Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Krishna Kanth Nakka
Interpretability is critical in high-stakes domains such as medical imaging, where understanding model decisions is essential for clinical adoption. In this work, we introduce Sparse Autoencoder (SAE)-based interpretability to breast imaging by analyzing {Mammo-CLIP}, a vision–language foundation model pretrained on large-scale mammogram image–report pairs. We train a patch-level \texttt{Mammo-SAE} on Mammo-CLIP to identify and probe latent features associated with clinically relevant breast concepts such as \textit{mass} and \textit{suspicious calcification}. Our findings reveal that top activated class level latent neurons in the SAE latent space often tend to align with ground truth regions, and also uncover several confounding factors influencing the model’s decision-making process. Additionally, we analyze which latent neurons the model relies on during downstream finetuning for improving the breast concept prediction. This study highlights the promise of interpretable SAE latent representations in providing deeper insight into the internal workings of foundation models at every layer for breast imaging. The code will be released at https://krishnakanthnakka.github.io/MammoSAE/
在医学影像等高风险领域,可解释性对于模型的决策理解至关重要,这对于临床采纳至关重要。在这项工作中,我们通过分析基于大规模乳腺X光图像报告对预训练的视觉语言基础模型Mammo-CLIP,引入基于稀疏自动编码器(SAE)的可解释性来对乳腺影像进行解读。我们在Mammo-CLIP上训练了一个基于补丁级别的Mammo-SAE,以识别和探测与临床相关的乳腺概念(如肿块和可疑钙化)相关的潜在特征。我们的研究结果表明,SAE潜在空间中顶部激活的类别级别潜在神经元往往与真实区域对齐,并揭示了影响模型决策过程的几个混淆因素。此外,我们还分析了模型在进行下游微调以改善乳腺概念预测时依赖哪些潜在神经元。这项研究突出了可解释的SAE潜在表示在深入了解每一层基础模型内部工作原理方面的潜力,特别是在乳腺成像方面。代码将在https://krishnakanthnakka.github.io/MammoSAE/发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Deep Breast Imaging workshop, MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在医学成像等高风险领域中解释性的重要性,并针对乳腺成像引入了基于稀疏自动编码器(SAE)的解释性方法。通过对Mammo-CLIP的的分析和研究,发现SAE潜在空间中的顶层激活类潜在神经元往往与真实区域对齐,并且揭示了影响模型决策过程的几个混杂因素。此外,还分析了模型在进行下游微调以改善乳腺癌概念预测时依赖哪些潜在神经元。此研究强调了可解释的SAE潜在表达在乳腺成像中对基础模型内部工作的深入了解方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 解释性在医学成像领域至关重要,特别是在高风险情境如乳腺成像中。
- 研究者引入了基于稀疏自动编码器(SAE)的解释性方法,以增强对模型决策过程的理解。
- 对Mammo-CLIP模型的分析显示,SAE潜在空间中的顶层激活类潜在神经元与真实区域对齐。
- 研究揭示了影响模型决策过程的混杂因素。
- 分析了模型在进行下游微调时依赖的潜在神经元,以提高乳腺癌概念预测的准确性。
- 研究结果强调了可解释的SAE潜在表达对深入了解乳腺成像基础模型内部工作的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


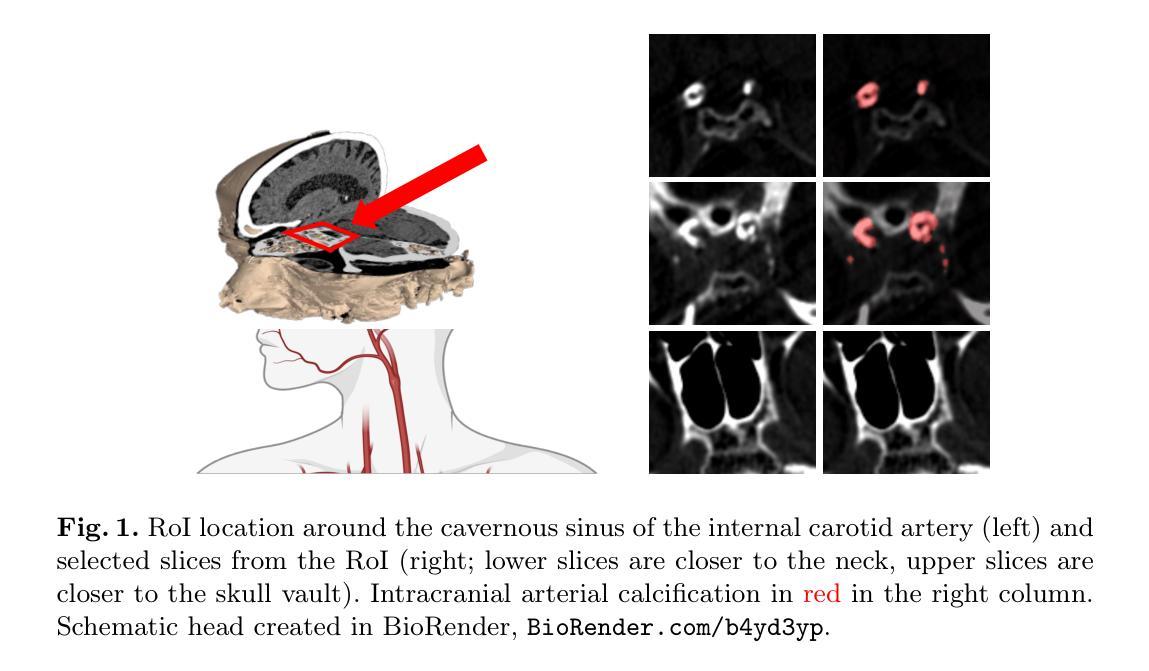
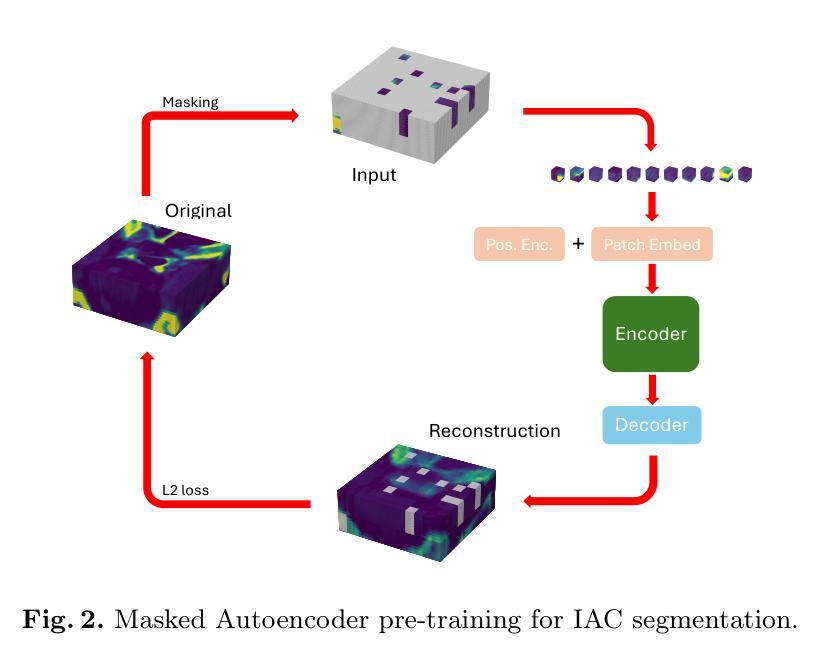
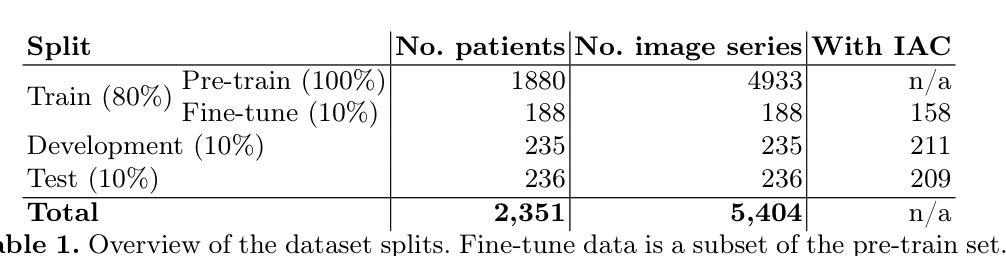
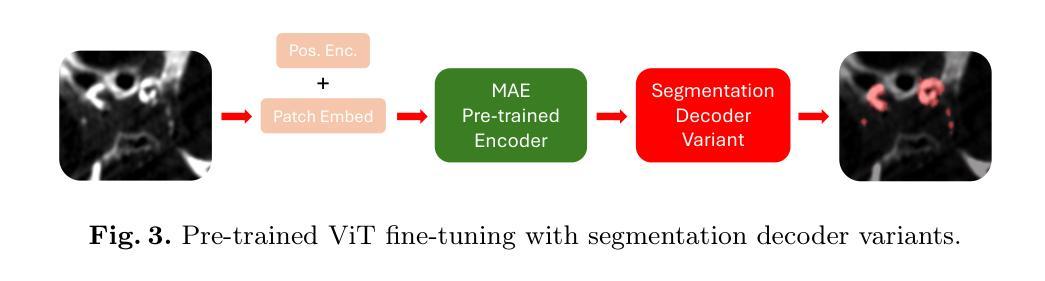
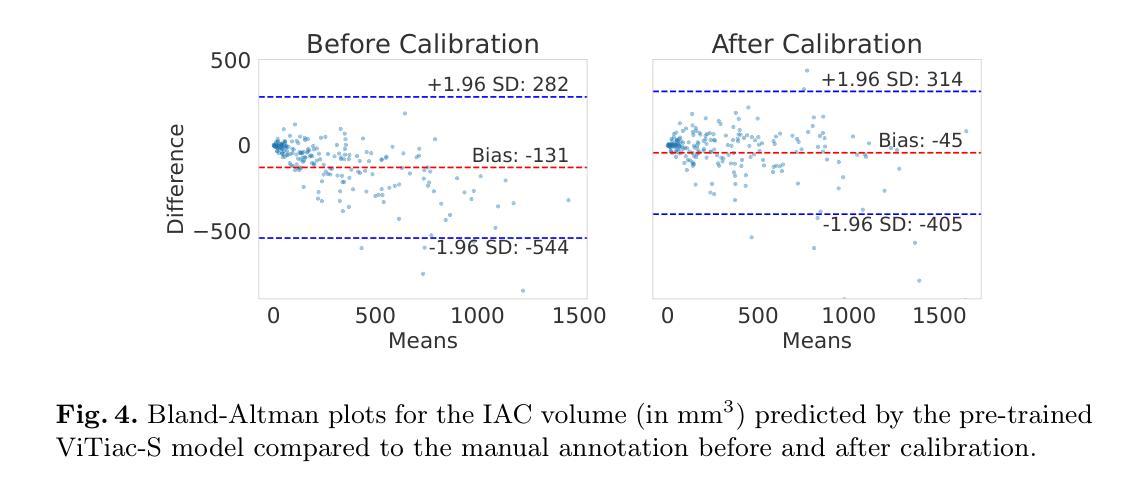
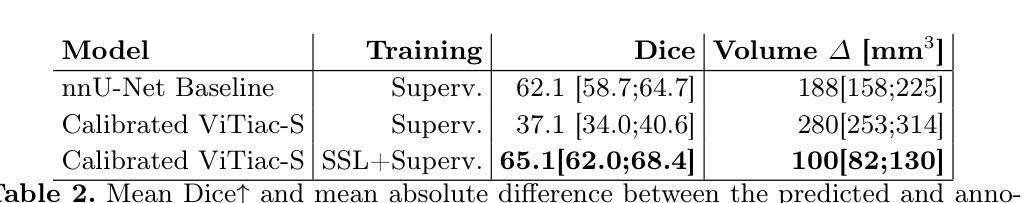
Calibrated Self-supervised Vision Transformers Improve Intracranial Arterial Calcification Segmentation from Clinical CT Head Scans
Authors:Benjamin Jin, Grant Mair, Joanna M. Wardlaw, Maria del C. Valdés Hernández
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have gained significant popularity in the natural image domain but have been less successful in 3D medical image segmentation. Nevertheless, 3D ViTs are particularly interesting for large medical imaging volumes due to their efficient self-supervised training within the masked autoencoder (MAE) framework, which enables the use of imaging data without the need for expensive manual annotations. Intracranial arterial calcification (IAC) is an imaging biomarker visible on routinely acquired CT scans linked to neurovascular diseases such as stroke and dementia, and automated IAC quantification could enable their large-scale risk assessment. We pre-train ViTs with MAE and fine-tune them for IAC segmentation for the first time. To develop our models, we use highly heterogeneous data from a large clinical trial, the third International Stroke Trial (IST-3). We evaluate key aspects of MAE pre-trained ViTs in IAC segmentation, and analyse the clinical implications. We show: 1) our calibrated self-supervised ViT beats a strong supervised nnU-Net baseline by 3.2 Dice points, 2) low patch sizes are crucial for ViTs for IAC segmentation and interpolation upsampling with regular convolutions is preferable to transposed convolutions for ViT-based models, and 3) our ViTs increase robustness to higher slice thicknesses and improve risk group classification in a clinical scenario by 46%. Our code is available online.
Vision Transformers(ViTs)在自然图像领域已经获得了极大的受欢迎程度,但在3D医学图像分割方面的成功较小。然而,对于大型医学成像体积而言,3D ViTs特别有趣,因为它们能在masked autoencoder(MAE)框架内进行高效的自我监督训练,这允许使用成像数据而无需昂贵的手动注释。颅内动脉钙化(IAC)是一个在常规获得的CT扫描上可见的成像生物标志物,与中风和痴呆等神经血管疾病有关,自动化IAC定量能够进行大规模风险评估。我们首次使用MAE对ViTs进行预训练,并对其进行微调以进行IAC分割。为了开发我们的模型,我们使用了来自大型临床试验的具有高度异质性的数据——第三次国际中风试验(IST-3)。我们评估了MAE预训练的ViTs在IAC分割方面的关键方面,并分析了其临床意义。我们的结果显示:1)我们的校准自监督ViT比强大的监督型nnU-Net基线高出3.2 Dice点;2)对于IAC分割的ViTs而言,小补丁尺寸至关重要,对于基于ViT的模型,使用常规卷积进行插值上采样比转置卷积更可取;3)我们的ViTs提高了对较厚切片的鲁棒性,并在临床场景中提高了风险组分类的准确率,达到46%。我们的代码可在网上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 3rd Data Engineering in Medical Imaging workshop @ MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Vision Transformers(ViTs)在自然图像领域的广泛应用,以及在3D医学图像分割中的挑战。研究团队首次使用Masked Autoencoder(MAE)框架预训练ViTs,并将其微调用于颅内动脉钙化(IAC)分割。实验结果显示,经过校准的自我监督ViT在IAC分割方面优于强大的监督型nnU-Net基准模型,且低补丁大小和插值上采样对于ViT在IAC分割中的表现至关重要。此外,ViTs能提高对较高切片厚度的稳健性,并在临床环境中提高风险分组分类的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在自然图像领域广泛应用,但在医学图像分割中应用相对较少。
- ViTs 在大型医疗影像体积中特别受欢迎,其基于Masked Autoencoder (MAE)框架的自我监督训练能够实现影像数据的使用,无需昂贵的手动标注。
- 首次使用MAE框架预训练ViTs并将其微调用于颅内动脉钙化(IAC)分割。
- 实验结果表明,经过校准的自我监督ViT在IAC分割方面优于nnU-Net基准模型。
- 低补丁大小和插值上采样对于ViT在IAC分割中的表现至关重要。
- ViTs能提高对较高切片厚度的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

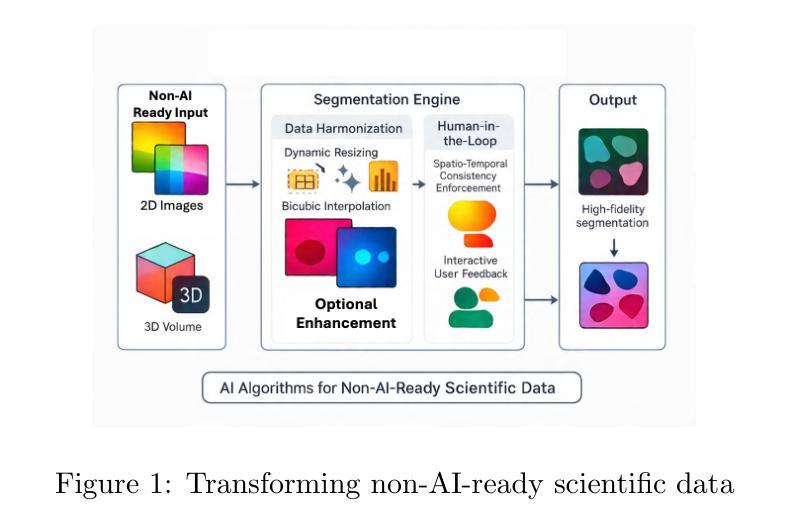
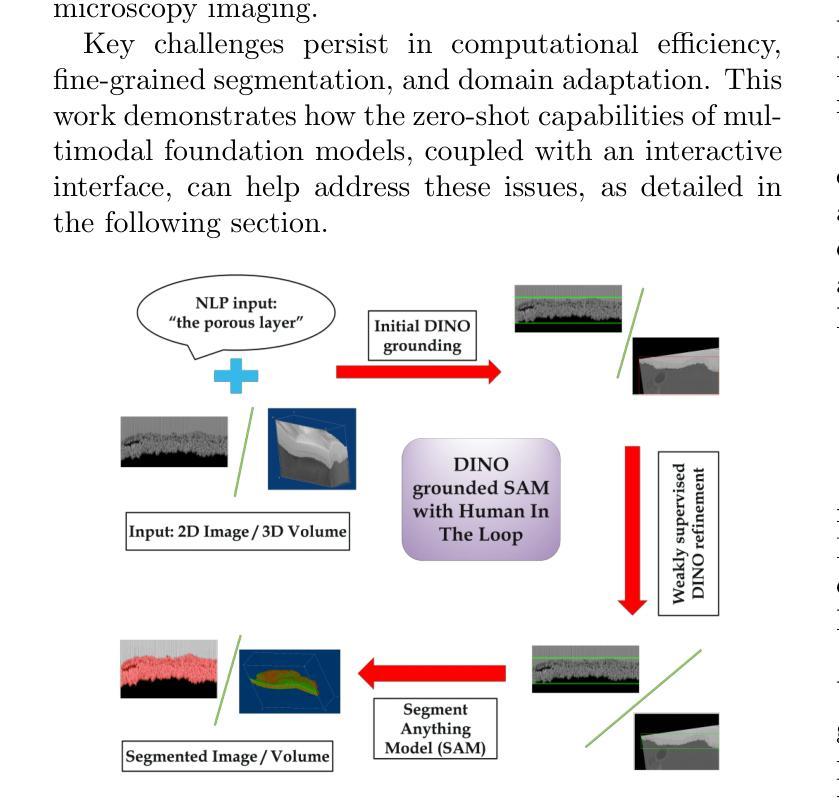
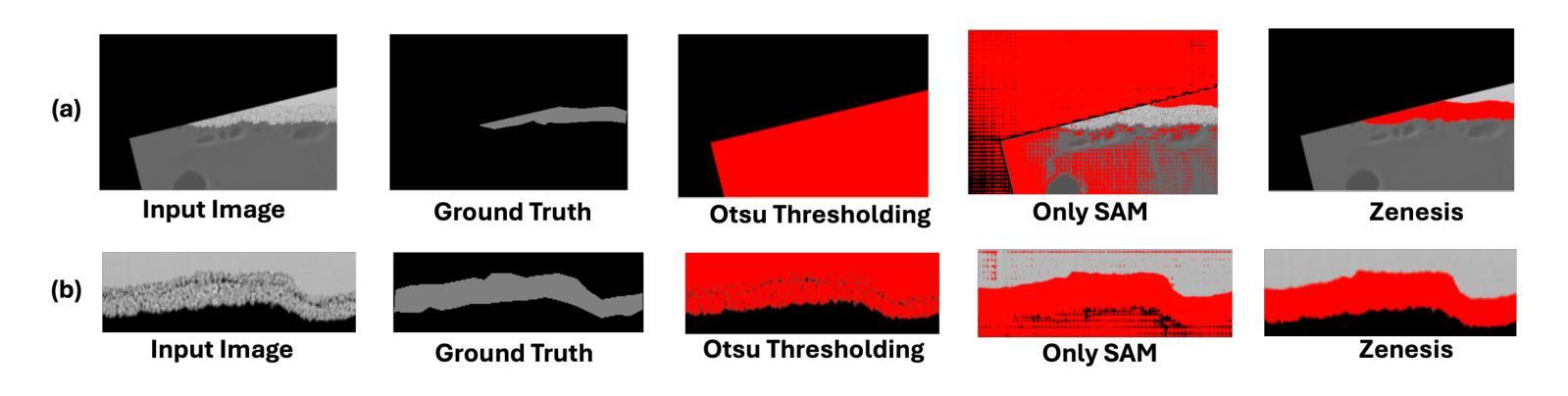
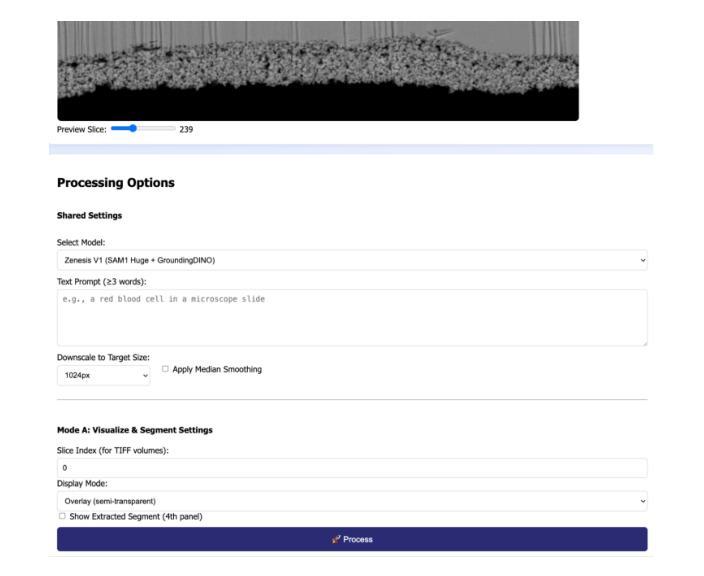
Foundation Models for Zero-Shot Segmentation of Scientific Images without AI-Ready Data
Authors:Shubhabrata Mukherjee, Jack Lang, Obeen Kwon, Iryna Zenyuk, Valerie Brogden, Adam Weber, Daniela Ushizima
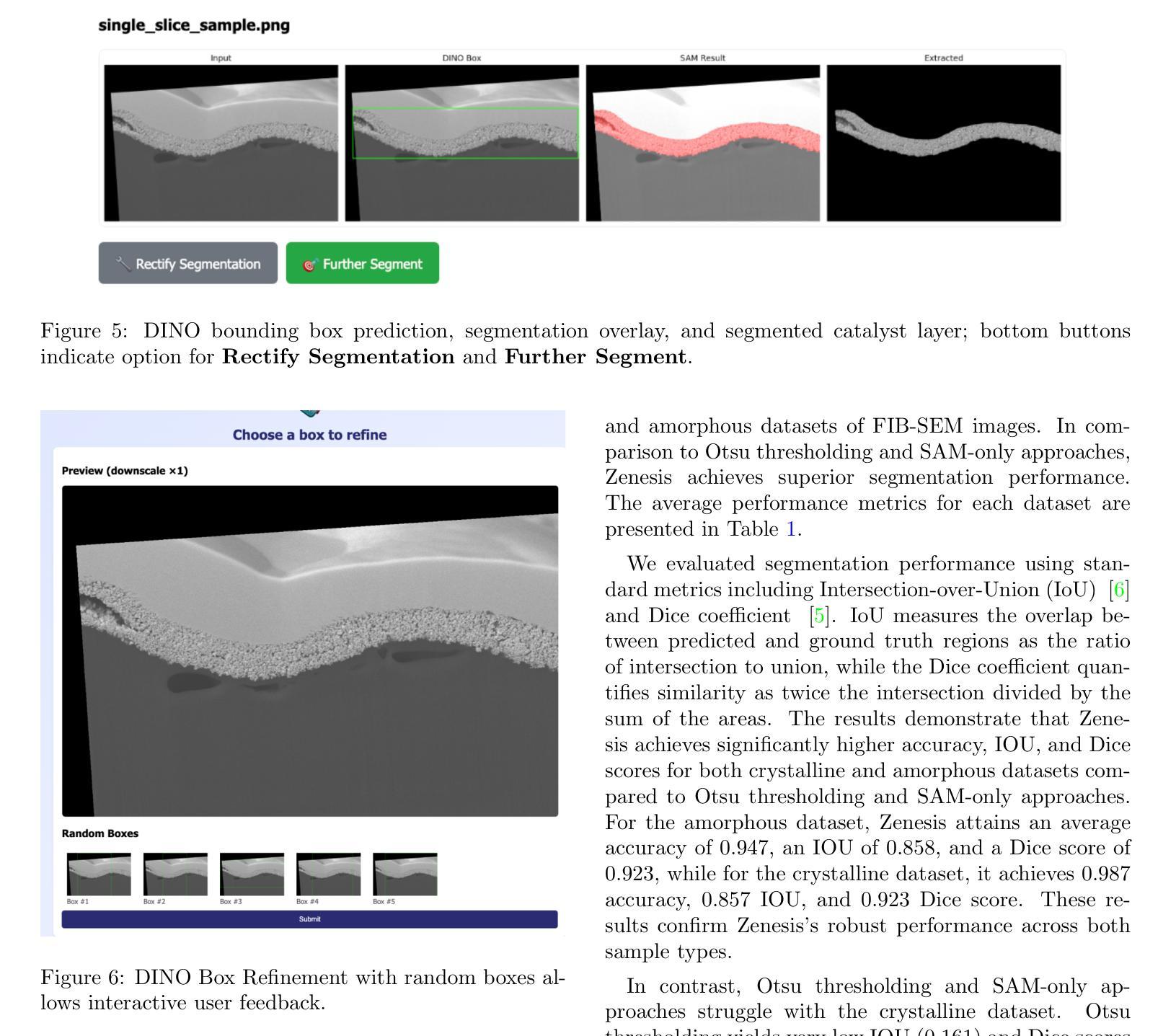
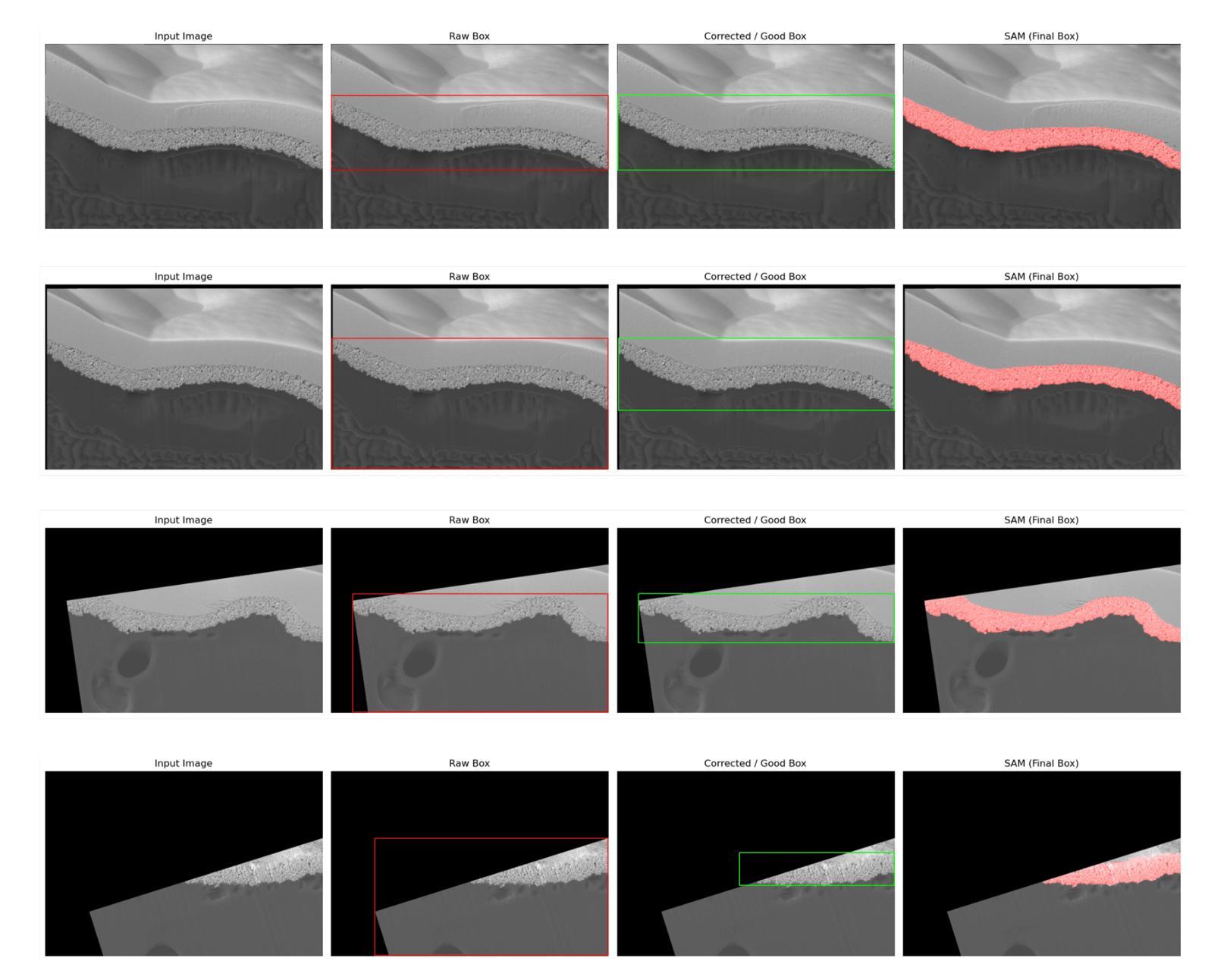
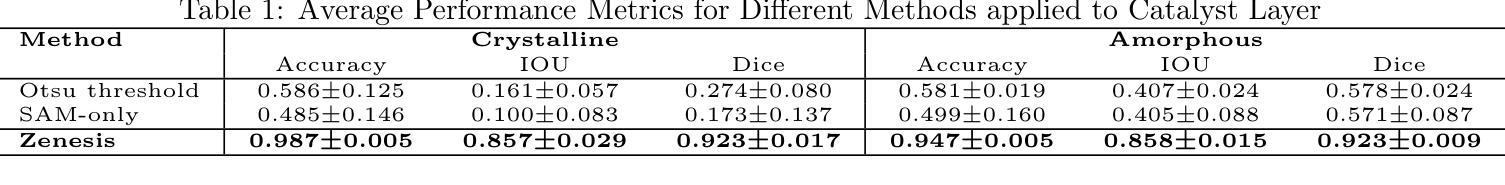
Zero-shot and prompt-based models have excelled at visual reasoning tasks by leveraging large-scale natural image corpora, but they often fail on sparse and domain-specific scientific image data. We introduce Zenesis, a no-code interactive computer vision platform designed to reduce data readiness bottlenecks in scientific imaging workflows. Zenesis integrates lightweight multimodal adaptation for zero-shot inference on raw scientific data, human-in-the-loop refinement, and heuristic-based temporal enhancement. We validate our approach on Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) datasets of catalyst-loaded membranes. Zenesis outperforms baselines, achieving an average accuracy of 0.947, Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.858, and Dice score of 0.923 on amorphous catalyst samples; and 0.987 accuracy, 0.857 IoU, and 0.923 Dice on crystalline samples. These results represent a significant performance gain over conventional methods such as Otsu thresholding and standalone models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Zenesis enables effective image segmentation in domains where annotated datasets are limited, offering a scalable solution for scientific discovery.
零样本和基于提示的模型通过利用大规模的自然图像语料库在视觉推理任务上表现出色,但它们通常在稀疏和特定领域的科学图像数据上表现不佳。我们推出了Zenesis,这是一个无代码交互式计算机视觉平台,旨在减少科学成像工作流程中的数据准备瓶颈。Zenesis集成了轻量级的跨模态适应,用于在原始科学数据上进行零样本推理,还有人为驱动的循环优化和基于启发式的临时增强功能。我们在催化剂负载膜的聚焦离子束扫描电子显微镜(FIB-SEM)数据集上验证了我们的方法。Zenesis的表现优于基线,在无序催化剂样本上达到了平均准确率0.947、交并比(IoU)为0.858以及Dice系数为0.923;在结晶样本上的准确率达到了0.987、IoU为0.857以及Dice系数为0.923。相较于传统方法(如Otsu阈值法)和独立模型(如Anything模型)等,这些结果代表了显著的性能提升。Zenesis在标注数据集有限的领域实现了有效的图像分割,为科学发现提供了可伸缩的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted for presentation at the 59th International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP 2025), DRAI workshop
Summary
Zenesis是一个无代码的交互式计算机视觉平台,专为解决科学成像工作流程中的数据准备瓶颈而设计。它集成了轻量级的多模式适应技术,用于在原始科学数据上进行零射击推断,以及人机交互优化和基于启发式的时间增强功能。在Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM)数据集上验证,Zenesis在催化剂负载膜的无定形和结晶样品上取得了显著成绩,性能优于传统方法和单一模型。它为科学发现提供了有效的图像分割解决方案,特别是在标注数据集有限的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- Zenesis是一个针对科学成像的计算机视觉平台,旨在解决数据准备瓶颈问题。
- 平台集成了轻量级的多模式适应技术,用于在原始科学数据上进行零射击推断。
- Zenesis支持人机交互优化和基于启发式的时间增强功能。
- 在FIB-SEM数据集上,Zenesis对催化剂负载膜的无定形和结晶样品进行了验证,并取得了卓越的性能。
- 与传统方法和单一模型相比,Zenesis表现出更高的性能。
- 该平台特别适用于标注数据集有限的情况下的图像分割任务。
点此查看论文截图

Patient-Specific Deep Reinforcement Learning for Automatic Replanning in Head-and-Neck Cancer Proton Therapy
Authors:Malvern Madondo, Yuan Shao, Yingzi Liu, Jun Zhou, Xiaofeng Yang, Zhen Tian
Anatomical changes during intensity-modulated proton therapy (IMPT) for head-and-neck cancer (HNC) can shift Bragg peaks, risking tumor underdosing and organ-at-risk overdosing. Treatment replanning is often required to maintain clinically acceptable treatment quality. However, current manual replanning processes are resource-intensive and time-consuming. We propose a patient-specific deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework for automated IMPT replanning, with a reward-shaping mechanism based on a $150$-point plan quality score addressing competing clinical objectives. We formulate the planning process as a reinforcement learning problem where agents learn control policies to adjust optimization priorities, maximizing plan quality. Unlike population-based approaches, our framework trains agents for each patient using their planning Computed Tomography (CT) and augmented anatomies simulating anatomical changes (tumor progression and regression). This patient-specific approach leverages anatomical similarities along the treatment course, enabling effective plan adaptation. We implemented two DRL algorithms, Deep Q-Network and Proximal Policy Optimization, using dose-volume histograms (DVHs) as state representations and a $22$-dimensional action space of priority adjustments. Evaluation on eight HNC patients using actual replanning CT data showed that both agents improved initial plan scores from $120.78 \pm 17.18$ to $139.59 \pm 5.50$ (DQN) and $141.50 \pm 4.69$ (PPO), surpassing the replans manually generated by a human planner ($136.32 \pm 4.79$). Clinical validation confirms that improvements translate to better tumor coverage and OAR sparing across diverse anatomical changes. This work highlights DRL’s potential in addressing geometric and dosimetric complexities of adaptive proton therapy, offering efficient offline adaptation solutions and advancing online adaptive proton therapy.
在头颈癌(HNC)的强度调制质子疗法(IMPT)过程中,解剖结构的变化可能会导致布拉格峰偏移,从而存在肿瘤剂量不足和危及器官剂量过大的风险。为了保持临床上可接受的治疗质量,经常需要进行治疗再计划。然而,当前的再计划流程需要大量资源和时间。针对此,我们提出了一种基于深度强化学习(DRL)的患者特异性自动IMPT再计划框架。该框架具有基于$150$点计划质量分数的奖励塑造机制,以解决相互竞争的临床目标。我们将规划过程制定为一个强化学习问题,其中智能体学习控制策略来调整优化优先级,以最大化计划质量。不同于基于人群的方法,我们的框架使用患者的规划计算机断层扫描(CT)和模拟解剖结构变化的增强解剖结构来训练每个患者的智能体(如肿瘤进展和消退)。这种患者特异性方法利用了治疗过程中的解剖结构相似性,能够实现有效的计划适应。我们实现了两种DRL算法,深度Q网络和近端策略优化,使用剂量体积直方图作为状态表示和$22$维的优先级调整动作空间。对使用实际再计划CT数据的八名HNC患者的评估显示,两种智能体都将初始计划得分从$120.78 \pm 17.18$提高到DQN的$139.59 \pm 5.50$和PPO的$141.50 \pm 4.69$,超过了人工规划师手动生成的再计划($136.32 \pm 4.79$)。临床验证证实,这些改进转化为更好的肿瘤覆盖率和OAR保护,跨越各种解剖结构变化。这项工作突出了DRL在解决自适应质子疗法的几何和剂量学复杂性方面的潜力,为在线自适应质子疗法提供有效的离线适应解决方案并推动其发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research (PMLR) 298; accepted at Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference (MLHC) 2025
Summary
基于深度强化学习的自适应质子治疗计划调整框架,通过模拟解剖变化训练个体,以优化治疗计划并应对解剖变化带来的风险。该框架采用深度Q网络和近端策略优化算法,在状态表示和动作空间方面进行了创新设计,提高了治疗计划的质量。
Key Takeaways
- 在强度调制质子疗法(IMPT)中,解剖变化可能导致布拉格峰偏移,增加肿瘤欠剂量和器官风险超剂量的风险。
- 治疗再计划是维持临床治疗质量的关键,但当前的手动再计划过程资源密集且耗时。
- 提议使用基于深度强化学习(DRL)的自动化IMPT再计划框架,通过奖励机制调整优化优先级,以最大化计划质量。
- 该框架采用患者特定的训练方式,利用规划计算机断层扫描(CT)和模拟解剖变化进行训练。
- 实施了两种DRL算法:深度Q网络和近端策略优化,使用剂量体积直方图作为状态表示和具有22维动作空间的优先级调整。
- 在实际再计划CT数据上对8名头颈癌患者的评估显示,该框架显著提高了初始计划质量,超过了人类规划师手动生成的重计划。
点此查看论文截图

Point or Line? Using Line-based Representation for Panoptic Symbol Spotting in CAD Drawings
Authors:Xingguang Wei, Haomin Wang, Shenglong Ye, Ruifeng Luo, Yanting Zhang, Lixin Gu, Jifeng Dai, Yu Qiao, Wenhai Wang, Hongjie Zhang
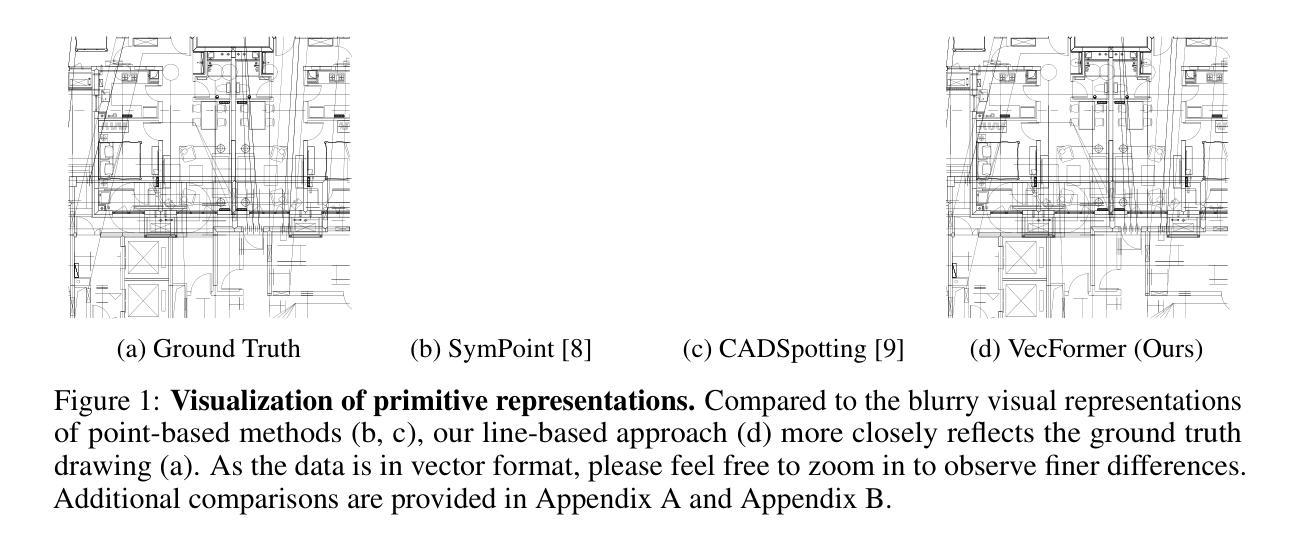
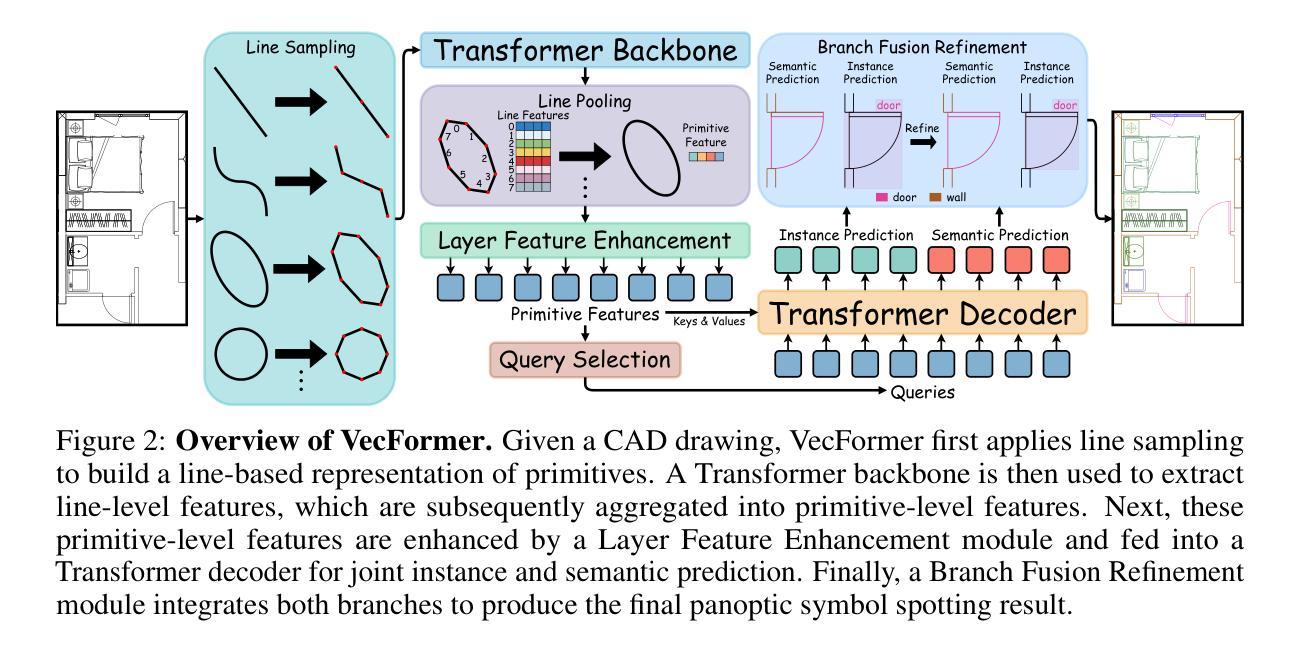
We study the task of panoptic symbol spotting, which involves identifying both individual instances of countable things and the semantic regions of uncountable stuff in computer-aided design (CAD) drawings composed of vector graphical primitives. Existing methods typically rely on image rasterization, graph construction, or point-based representation, but these approaches often suffer from high computational costs, limited generality, and loss of geometric structural information. In this paper, we propose VecFormer, a novel method that addresses these challenges through line-based representation of primitives. This design preserves the geometric continuity of the original primitive, enabling more accurate shape representation while maintaining a computation-friendly structure, making it well-suited for vector graphic understanding tasks. To further enhance prediction reliability, we introduce a Branch Fusion Refinement module that effectively integrates instance and semantic predictions, resolving their inconsistencies for more coherent panoptic outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method establishes a new state-of-the-art, achieving 91.1 PQ, with Stuff-PQ improved by 9.6 and 21.2 points over the second-best results under settings with and without prior information, respectively, highlighting the strong potential of line-based representation as a foundation for vector graphic understanding.
我们研究了全景符号识别任务,该任务涉及识别计算机辅助设计(CAD)绘图中的可计数事物的单个实例和不可计数内容的语义区域,这些绘图由矢量图形原始元素组成。现有方法通常依赖于图像矢量化、图构建或基于点的表示,但这些方法往往存在计算成本高、通用性有限以及几何结构信息丢失等问题。在本文中,我们提出了VecFormer这一新方法,它通过基于线条的原始元素表示来解决这些挑战。这种设计保留了原始元素的几何连续性,能够在保持计算友好的结构的同时实现更准确的形状表示,使其非常适合矢量图形理解任务。为了进一步提高预测可靠性,我们引入了分支融合细化模块,该模块有效地集成了实例和语义预测,解决它们的不一致性,以获得更连贯的全景输出。大量实验表明,我们的方法创造了新的最佳水平,实现了91.1个PQ值,其中Stuff-PQ在有无先验信息的设置下分别提高了9.6和21.2个点,这突显了基于线条的表示作为矢量图形理解基础的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了计算机辅助设计(CAD)绘图中的全景符号识别任务。针对现有方法在计算成本高、通用性有限以及几何结构信息丢失等方面的问题,提出了基于线条表示的VecFormer方法。该方法通过保留原始几何连续性,实现了更精确的形状表示,同时保持了计算友好的结构,非常适合矢量图形理解任务。为进一步提高了预测可靠性,引入了分支融合细化模块,有效地结合了实例和语义预测,解决了它们的不一致性,为全景输出提供了更连贯的结果。实验表明,该方法建立了一个新的世界纪录,在有/无先验信息的情况下,实现了超过第二名结果高达9.6和21.2点的Stuff-PQ提升。
Key Takeaways
- VecFormer解决了CAD绘图全景符号识别任务中计算成本高、通用性有限和信息丢失等问题。
- VecFormer采用基于线条的表示方法,保留了原始几何连续性,实现了更精确的形状表示。
- VecFormer具有计算友好的结构,适合矢量图形理解任务。
- 分支融合细化模块结合了实例和语义预测,解决了预测不一致性问题。
- VecFormer在全景符号识别任务上取得了新的世界纪录。
- 在有先验信息的情况下,VecFormer的Stuff-PQ提升了9.6点。
点此查看论文截图