⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
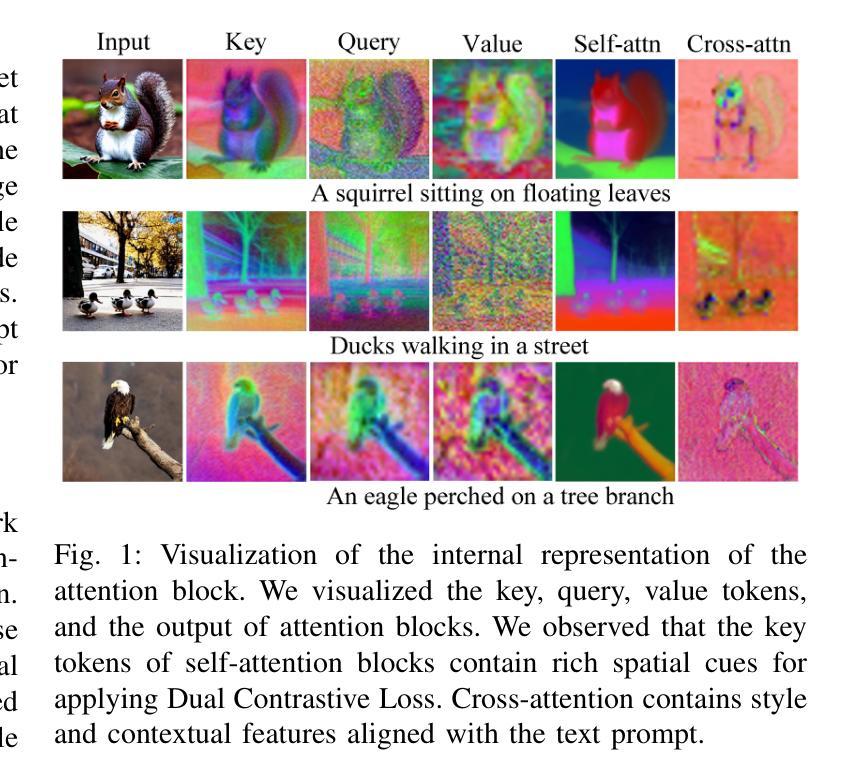
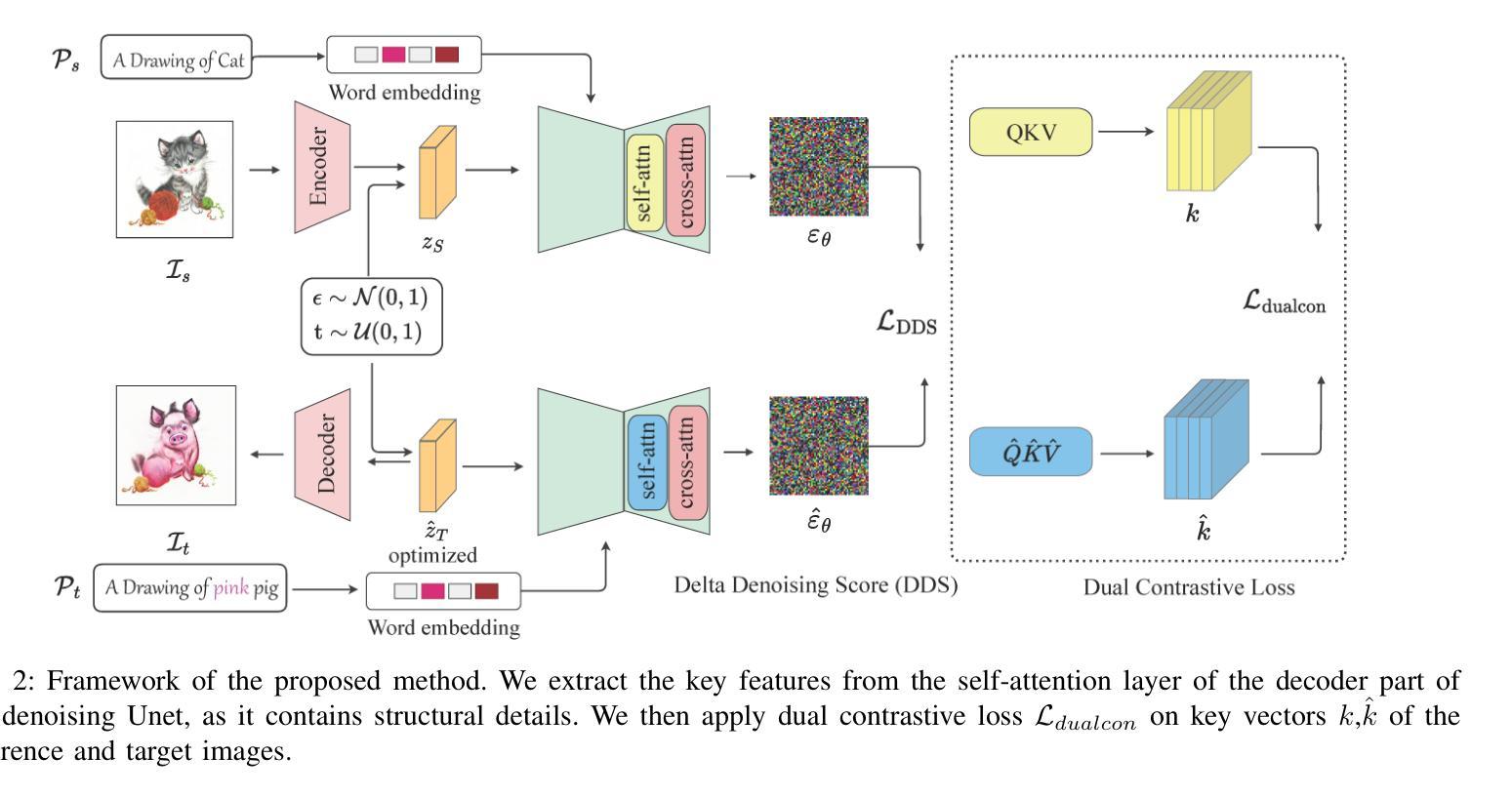
Single-Reference Text-to-Image Manipulation with Dual Contrastive Denoising Score
Authors:Syed Muhmmad Israr, Feng Zhao
Large-scale text-to-image generative models have shown remarkable ability to synthesize diverse and high-quality images. However, it is still challenging to directly apply these models for editing real images for two reasons. First, it is difficult for users to come up with a perfect text prompt that accurately describes every visual detail in the input image. Second, while existing models can introduce desirable changes in certain regions, they often dramatically alter the input content and introduce unexpected changes in unwanted regions. To address these challenges, we present Dual Contrastive Denoising Score, a simple yet powerful framework that leverages the rich generative prior of text-to-image diffusion models. Inspired by contrastive learning approaches for unpaired image-to-image translation, we introduce a straightforward dual contrastive loss within the proposed framework. Our approach utilizes the extensive spatial information from the intermediate representations of the self-attention layers in latent diffusion models without depending on auxiliary networks. Our method achieves both flexible content modification and structure preservation between input and output images, as well as zero-shot image-to-image translation. Through extensive experiments, we show that our approach outperforms existing methods in real image editing while maintaining the capability to directly utilize pretrained text-to-image diffusion models without further training.
大规模文本到图像的生成模型已经显示出合成多样化和高质量图像的显著能力。然而,将这些模型直接应用于真实图像编辑仍然具有挑战性,原因有两点。首先,用户难以提出一个完美的文本提示来准确描述输入图像中的每个视觉细节。其次,虽然现有模型可以在某些区域引入理想的变化,但它们往往会剧烈改变输入内容,并在不需要的区域引入意想不到的变化。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Dual Contrastive Denoising Score(双对比降噪评分)框架,这是一个简单而强大的框架,利用文本到图像扩散模型的丰富生成先验知识。该框架受到非配对图像到图像转换的对比学习方法的启发,我们在所提出的框架中引入了直观的双对比损失。我们的方法利用潜在扩散模型中自注意力层中间表示的丰富空间信息,而无需依赖辅助网络。我们的方法实现了输入图像和输出图像之间的灵活内容修改和结构保留,以及零样本图像到图像的转换。通过大量实验,我们证明我们的方法在真实图像编辑方面优于现有方法,同时保持直接使用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的能力,无需进一步训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于对比学习的文本到图像生成模型编辑框架——Dual Contrastive Denoising Score。该框架解决了现有模型在编辑真实图像时面临的挑战,包括难以生成准确的文本提示和引入不必要的更改。通过利用对比学习方法和潜在扩散模型的自注意力层空间信息,该框架实现了灵活的内容修改和结构保留,以及零样本图像到图像的翻译。实验表明,该方法在真实图像编辑方面优于现有方法,并能直接使用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的文本到图像生成模型编辑框架——Dual Contrastive Denoising Score,用于解决真实图像编辑的挑战。
- 该框架利用对比学习方法进行无配对图像到图像的翻译,引入了一种简单的双重对比损失。
- 通过利用潜在扩散模型的自注意力层空间信息,实现了灵活的内容修改和结构保留。
- 该方法可以实现零样本图像到图像的翻译。
- 该方法在真实图像编辑方面表现出卓越的性能,优于现有的方法。
- 该方法能够直接使用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型,无需进一步训练。
点此查看论文截图


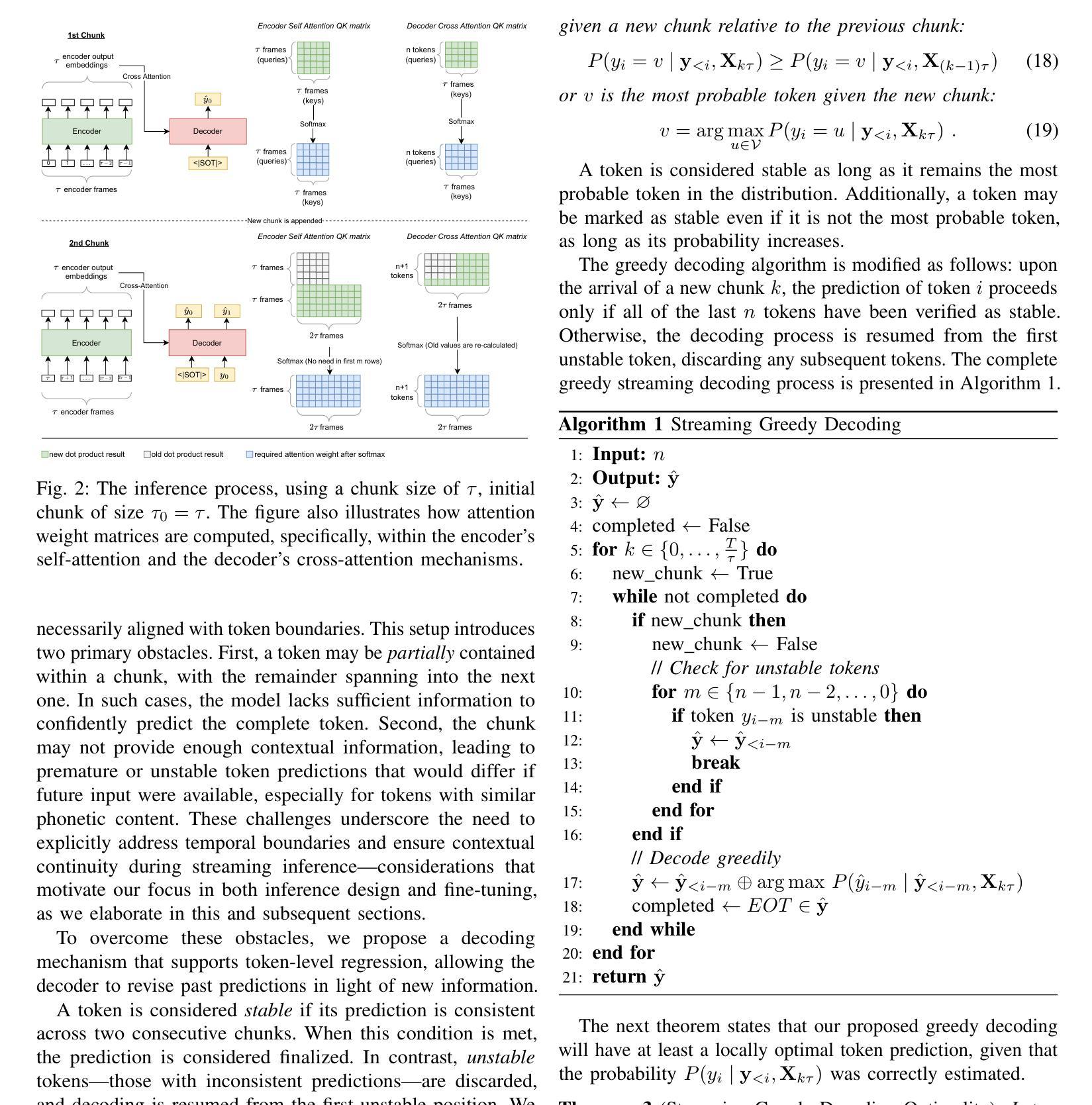
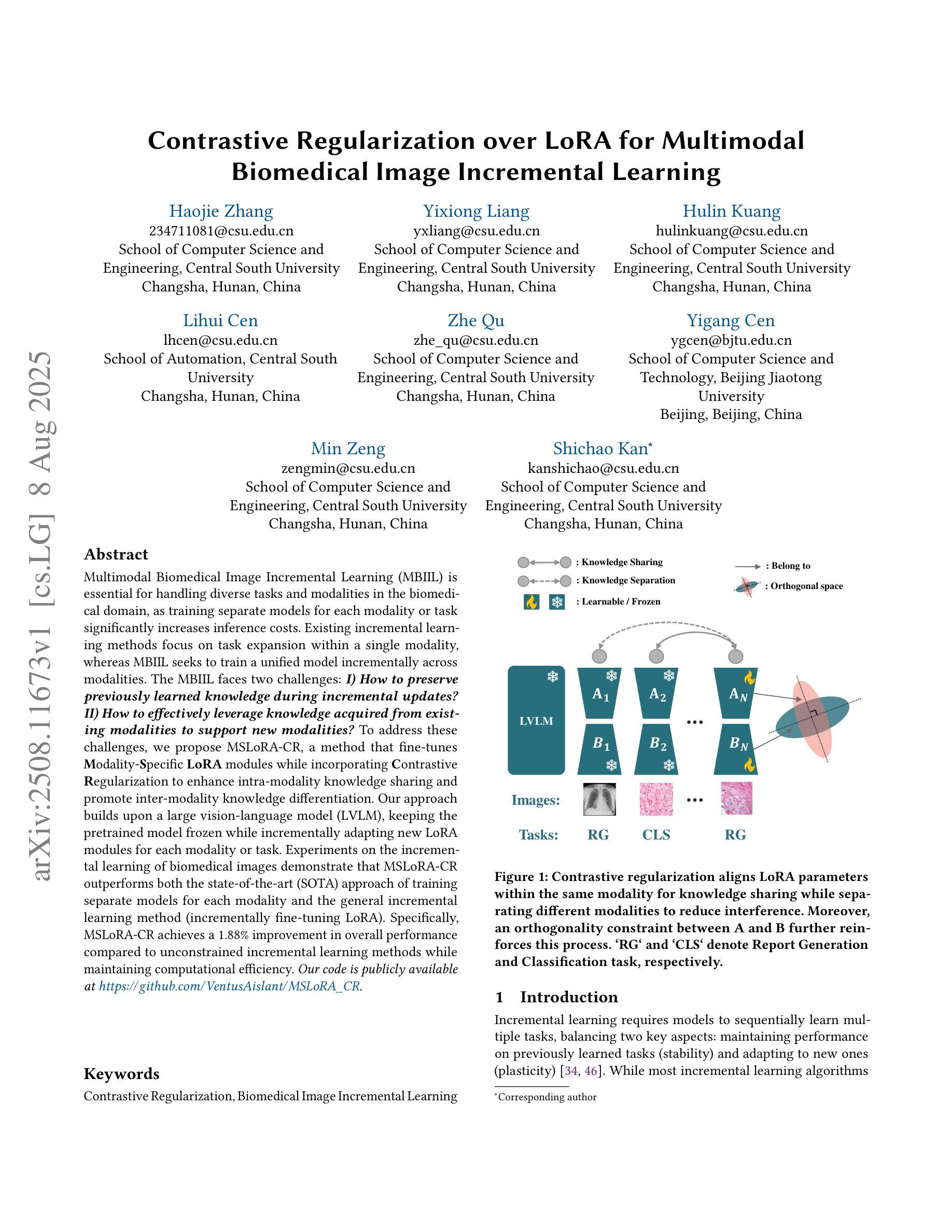
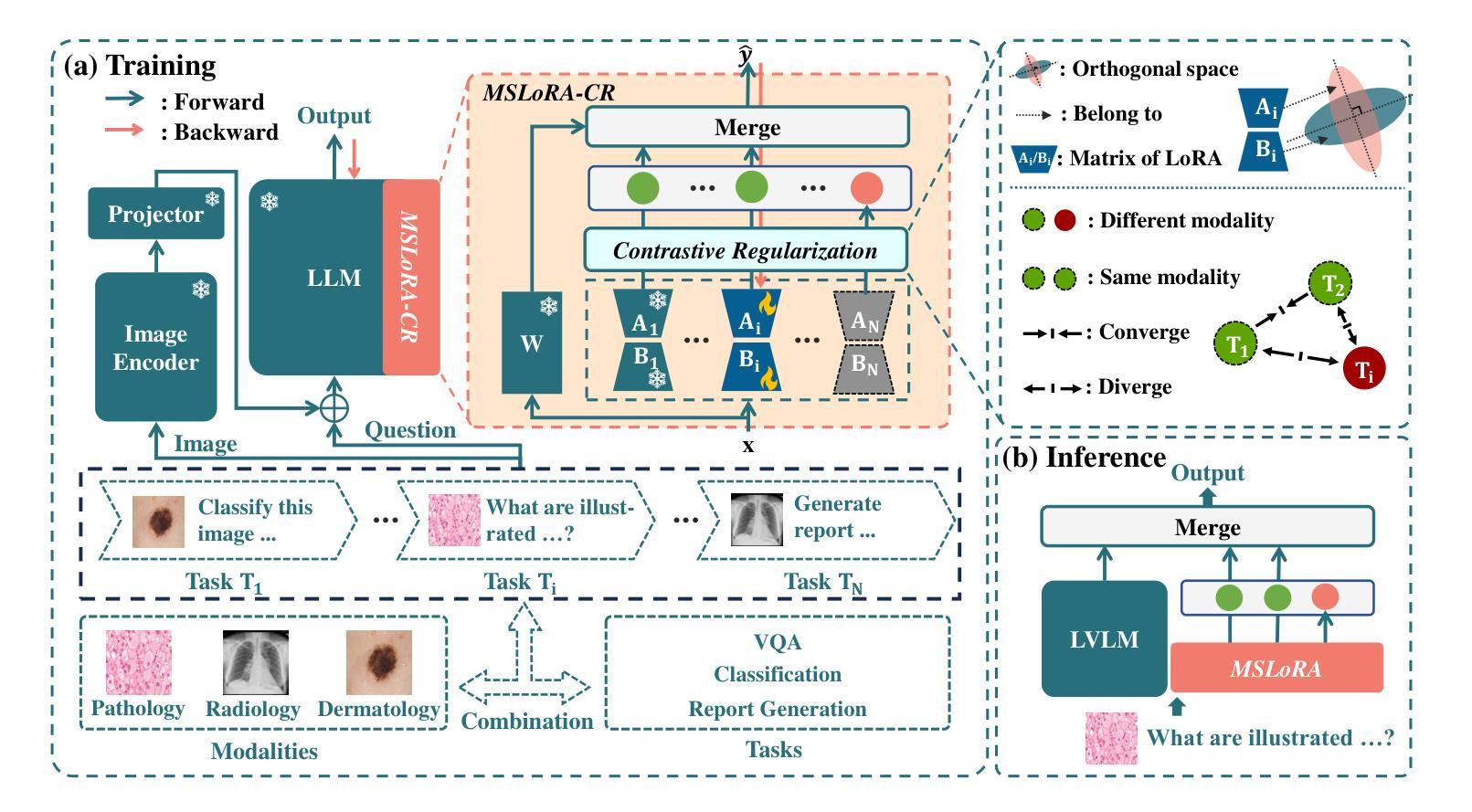
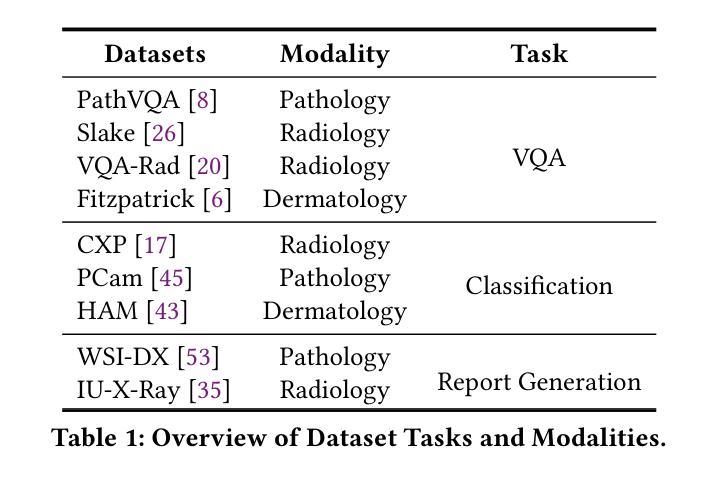
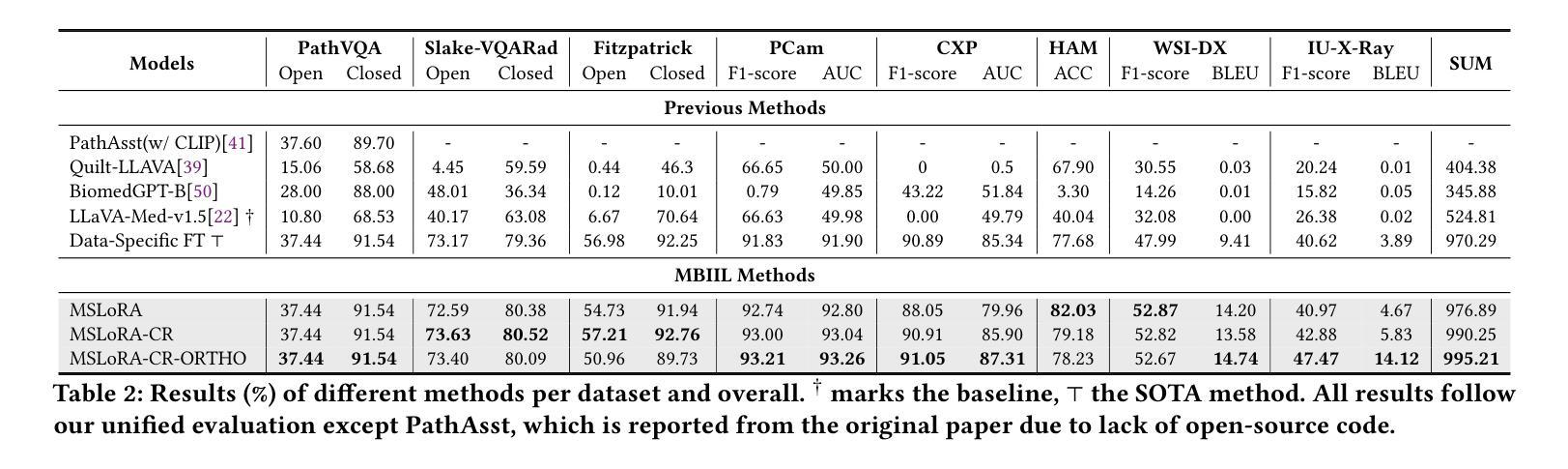
Contrastive Regularization over LoRA for Multimodal Biomedical Image Incremental Learning
Authors:Haojie Zhang, Yixiong Liang, Hulin Kuang, Lihui Cen, Zhe Qu, Yigang Cen, Min Zeng, Shichao Kan
Multimodal Biomedical Image Incremental Learning (MBIIL) is essential for handling diverse tasks and modalities in the biomedical domain, as training separate models for each modality or task significantly increases inference costs. Existing incremental learning methods focus on task expansion within a single modality, whereas MBIIL seeks to train a unified model incrementally across modalities. The MBIIL faces two challenges: I) How to preserve previously learned knowledge during incremental updates? II) How to effectively leverage knowledge acquired from existing modalities to support new modalities? To address these challenges, we propose MSLoRA-CR, a method that fine-tunes Modality-Specific LoRA modules while incorporating Contrastive Regularization to enhance intra-modality knowledge sharing and promote inter-modality knowledge differentiation. Our approach builds upon a large vision-language model (LVLM), keeping the pretrained model frozen while incrementally adapting new LoRA modules for each modality or task. Experiments on the incremental learning of biomedical images demonstrate that MSLoRA-CR outperforms both the state-of-the-art (SOTA) approach of training separate models for each modality and the general incremental learning method (incrementally fine-tuning LoRA). Specifically, MSLoRA-CR achieves a 1.88% improvement in overall performance compared to unconstrained incremental learning methods while maintaining computational efficiency. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/VentusAislant/MSLoRA_CR.
多模态生物医学图像增量学习(MBIIL)对于处理生物医学领域中的多样任务和模态至关重要,因为为每个模态或任务单独训练模型会显著增加推理成本。现有的增量学习方法侧重于单一模态内的任务扩展,而MBIIL则寻求跨模态训练一个统一模型的增量方式。MBIIL面临两大挑战:一、如何在增量更新中保持已学习到的知识?二、如何有效利用从现有模态中获取的知识来支持新模态?为解决这些挑战,我们提出了MSLoRA-CR方法,该方法可以微调模态特定LoRA模块,同时结合对比正则化,以增强模态内知识共享并促进模态间知识差异化。我们的方法基于大型视觉语言模型(LVLM),保持预训练模型冻结,同时增量适应每个模态或任务的新LoRA模块。在生物医学图像增量学习方面的实验表明,MSLoRA-CR在性能上优于为每个模态分别训练的最先进方法和通用增量学习方法(增量微调LoRA)。具体来说,与无约束的增量学习方法相比,MSLoRA-CR在总体性能上实现了1.88%的提升,同时保持了计算效率。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/VentusAislant/MSLoRA_CR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, submitted to ACM Multimedia 2025
Summary
本文介绍了多模态生物医学图像增量学习(MBIIL)的重要性,并指出其面临的主要挑战是:如何在增量更新过程中保持已学知识以及如何有效利用不同模态的知识支持新模态的学习。为此,文章提出了MSLoRA-CR方法,通过微调模态特定LoRA模块并结合对比正则化,增强模态内知识共享并促进模态间知识区分。实验证明,MSLoRA-CR在生物医学图像增量学习上优于单独为每种模态训练模型的方法和一般的增量学习方法,总体性能提升达到1.88%。
Key Takeaways
- MBIIL对于处理生物医学领域中的多样任务和模态至关重要,统一模型增量跨模态训练能降低推理成本。
- MBIIL面临两大挑战:保持增量更新中的先前知识和利用现有模态知识支持新模态学习。
- MSLoRA-CR方法通过微调模态特定LoRA模块并结合对比正则化来解决这些挑战。
- MSLoRA-CR方法建立于大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)之上,保持预训练模型冻结,并增量适应每个模态或任务的LoRA模块。
- 实验表明,MSLoRA-CR在生物医学图像增量学习上较现有方法有所提升,总体性能提升达1.88%。
- MSLoRA-CR方法在保证计算效率的同时实现了性能的提升。
点此查看论文截图
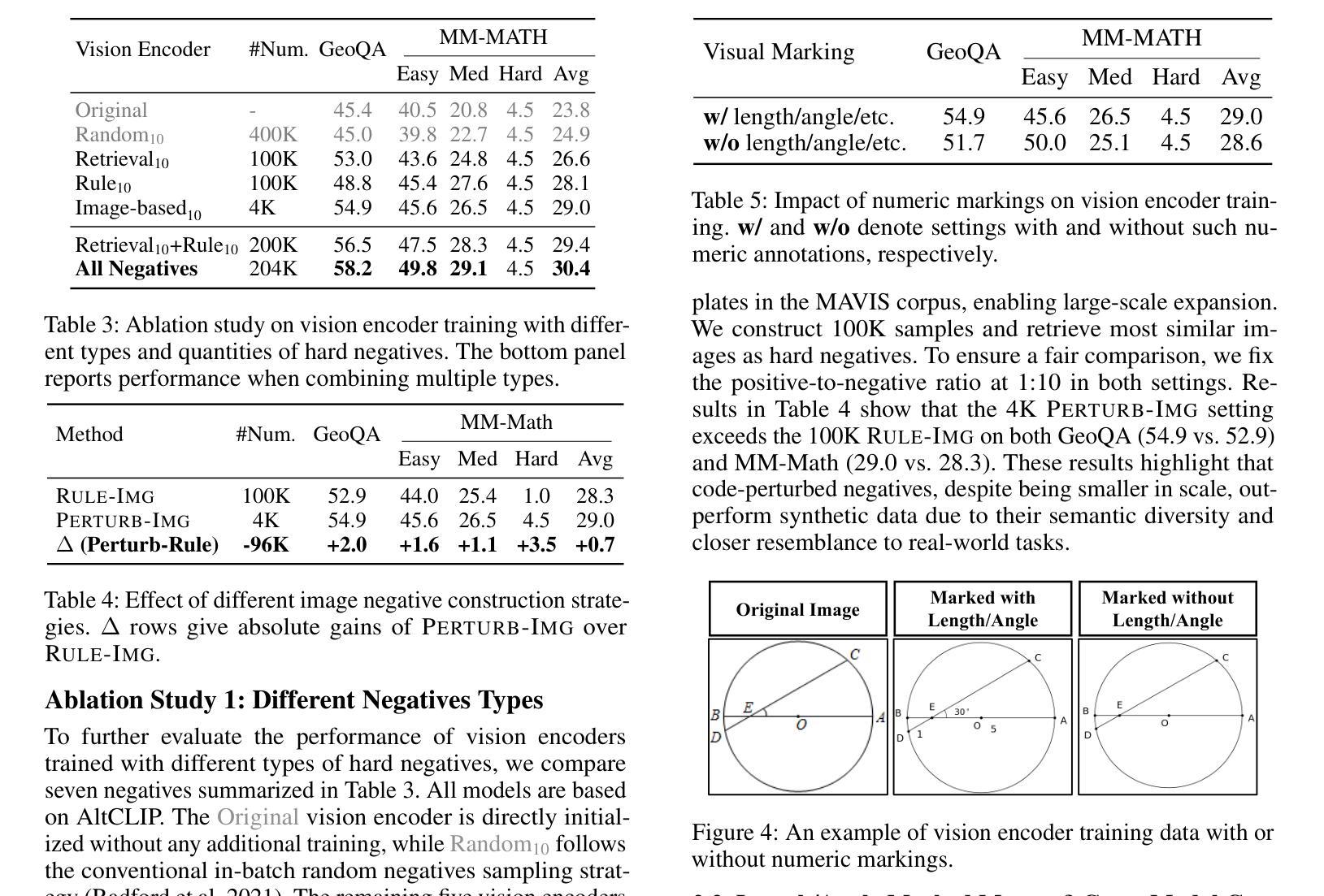
Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Fine-Grained Geometric Understanding in Large Multimodal Models
Authors:Kai Sun, Yushi Bai, Zhen Yang, Jiajie Zhang, Ji Qi, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
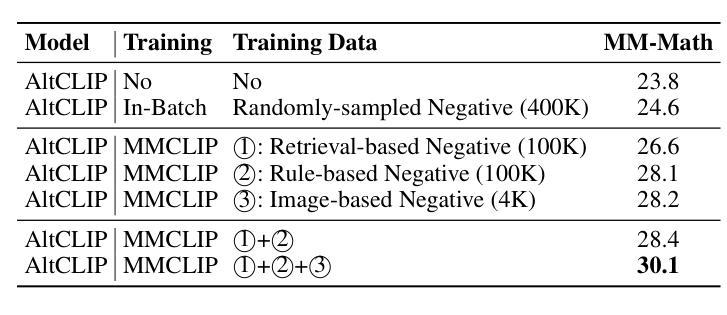
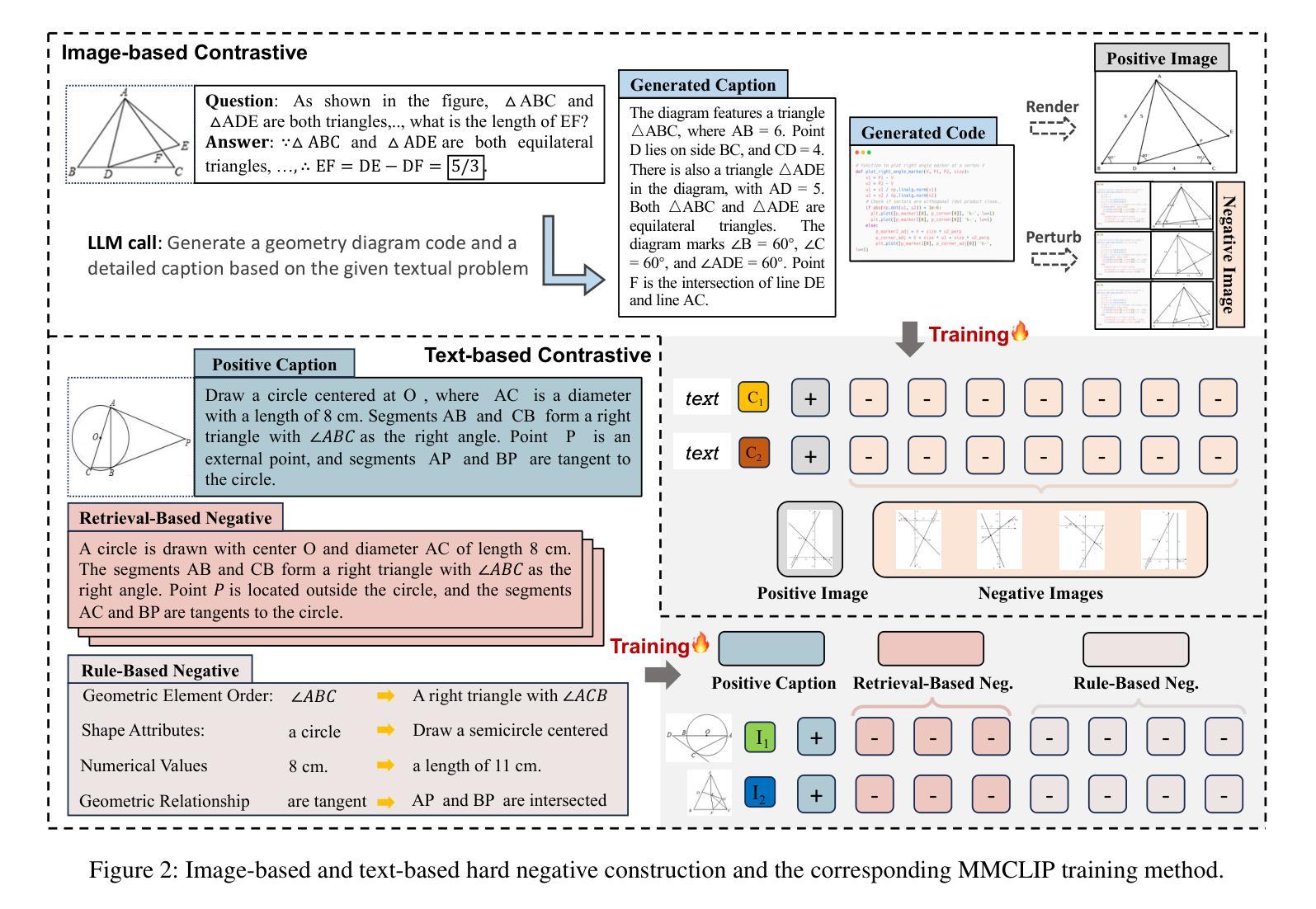
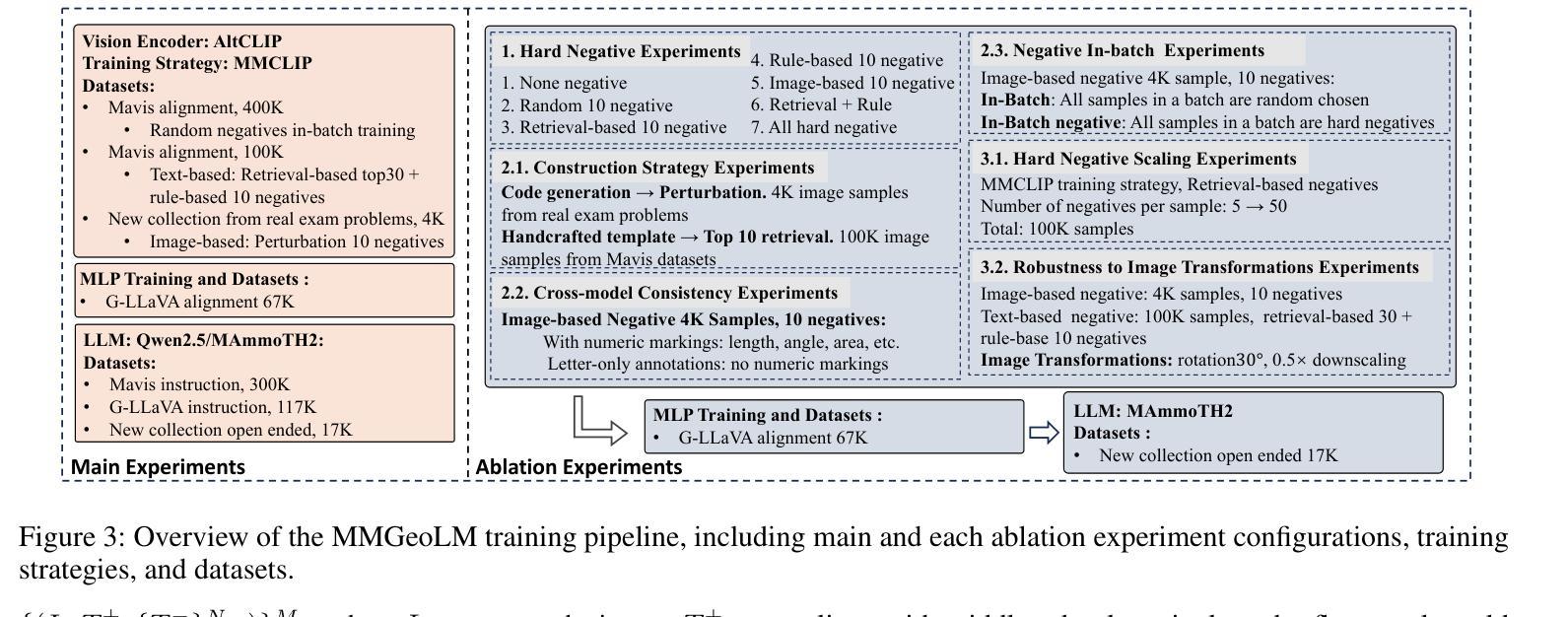
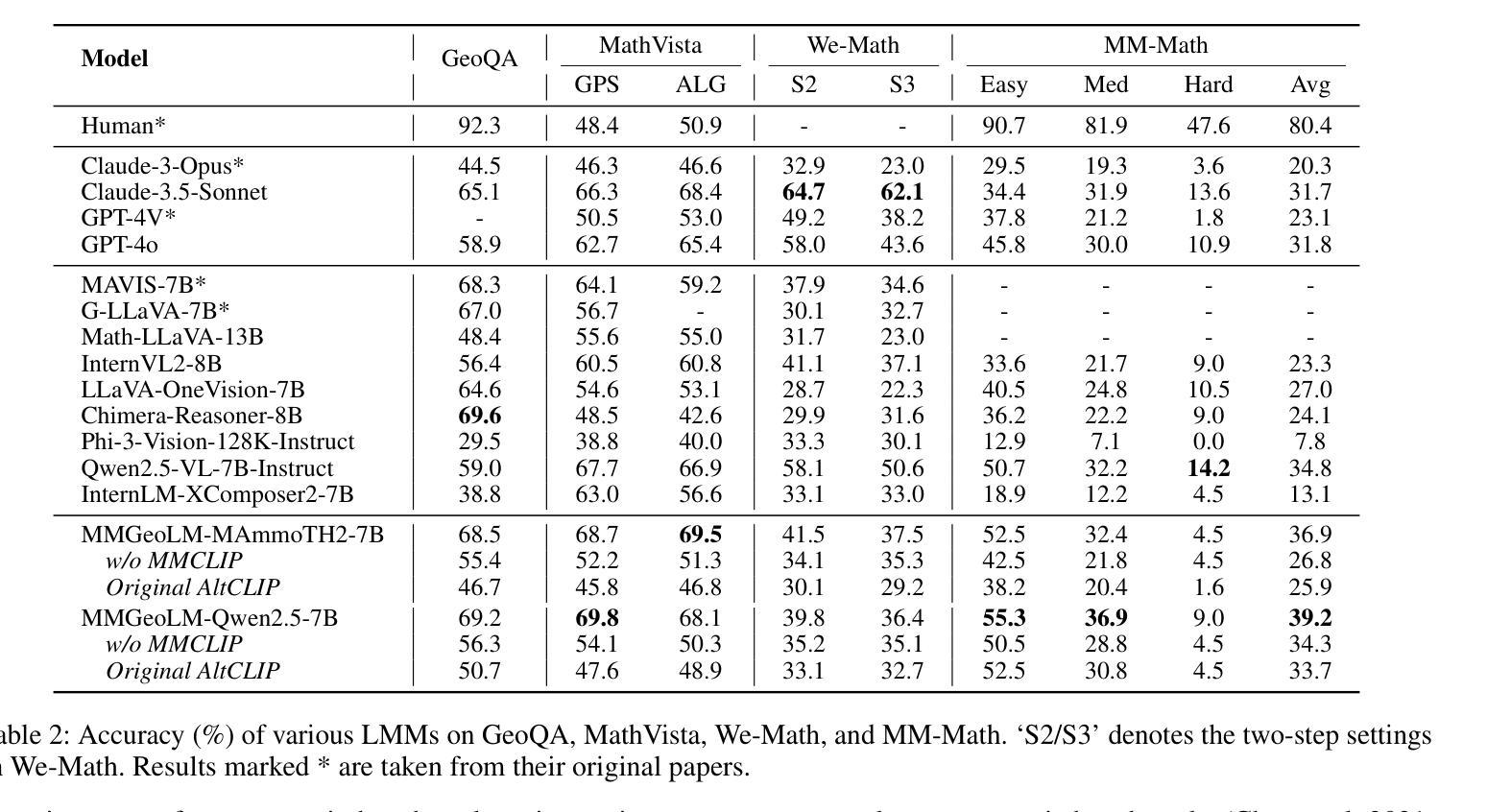
Benefiting from contrastively trained visual encoders on large-scale natural scene images, Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable performance across various visual perception tasks. However, the inherent limitations of contrastive learning upon summarized descriptions fundamentally restrict the capabilities of models in meticulous reasoning, particularly in crucial scenarios of geometric problem-solving. To enhance geometric understanding, we propose a novel hard negative contrastive learning framework for the vision encoder, which combines image-based contrastive learning using generation-based hard negatives created by perturbing diagram generation code, and text-based contrastive learning using rule-based negatives derived from modified geometric descriptions and retrieval-based negatives selected based on caption similarity. We train CLIP using our hard negative learning method, namely MMCLIP (Multimodal Math CLIP), and subsequently train an LMM for geometric problem-solving. Experiments show that our trained model, MMGeoLM, significantly outperforms other open-source models on three geometric reasoning benchmarks. Even with a size of 7B, it can rival powerful closed-source models like GPT-4o. We further conduct ablation studies to analyze three key factors: hard negative types, the efficiency of image-based negatives, and training configurations. These analyses yield important insights into optimizing hard negative strategies for geometric reasoning tasks.
得益于在大规模自然场景图像上进行对比训练的视觉编码器,大型多模态模型(LMMs)在各种视觉感知任务中取得了显著的性能。然而,对比学习在摘要描述上的固有局限性,从根本上限制了模型在精细推理方面的能力,特别是在解决几何问题的关键场景中。为了增强几何理解能力,我们提出了一种新型的硬负对比学习框架,该框架结合了基于图像对比学习和基于生成的硬负样本,通过扰动图表生成代码创建这些样本,以及基于文本对比学习和通过规则生成的负样本,这些负样本来源于修改后的几何描述和基于检索的负样本,这些负样本是根据字幕相似性选择的。我们使用我们的硬负学习方法训练CLIP,即MMCLIP(多模态数学CLIP),然后训练一个用于解决几何问题的LMM。实验表明,我们训练的MMGeoLM模型在三个几何推理基准测试中显著优于其他开源模型。即使其规模达到7B,也能与强大的闭源模型如GPT-4o相抗衡。我们还进行了消除研究,分析了三种关键因素:硬负样本类型、基于图像的负样本效率和训练配置。这些分析为我们优化几何推理任务的硬负策略提供了重要见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于对比学习训练的大型多模态模型(LMMs)在自然场景图像上取得了显著的视觉感知性能。然而,对比学习的固有局限性影响了模型的精细推理能力,特别是在解决几何问题的关键场景中。为增强模型的几何理解能力,我们提出了全新的硬负对比学习框架,该框架结合了基于图像和文本的对比学习。通过扰动图表生成代码生成基于生成的硬负样本,以及基于规则和检索的负样本。我们使用MMCLIP(多模态数学CLIP)训练CLIP,并进一步训练用于几何问题解决的LMM。实验表明,我们的训练模型MMGeoLM在三个几何推理基准测试中显著优于其他开源模型,甚至能与强大的闭源模型如GPT-4o相抗衡。
Key Takeaways
- Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) 利用对比学习在大型自然场景图像上取得了突出的视觉感知性能。
- 对比学习的固有局限性影响了模型在精细推理,尤其是几何问题处理方面的性能。
- 提出了一种新的硬负对比学习框架,结合了图像和文本对比学习,以改进模型的几何理解能力。
- 通过扰动图表生成代码生成基于生成的硬负样本,以及使用规则调整和基于检索的负样本。
- 使用MMCLIP训练的模型MMGeoLM在几何推理基准测试中表现优异,甚至可与强大的闭源模型相抗衡。
- 消融研究分析了硬负样本类型、图像负样本效率和训练配置等三个关键因素。
点此查看论文截图