⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
Harnessing Group-Oriented Consistency Constraints for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation in CdZnTe Semiconductors
Authors:Peihao Li, Yan Fang, Man Liu, Huihui Bai, Anhong Wang, Yunchao Wei, Yao Zhao
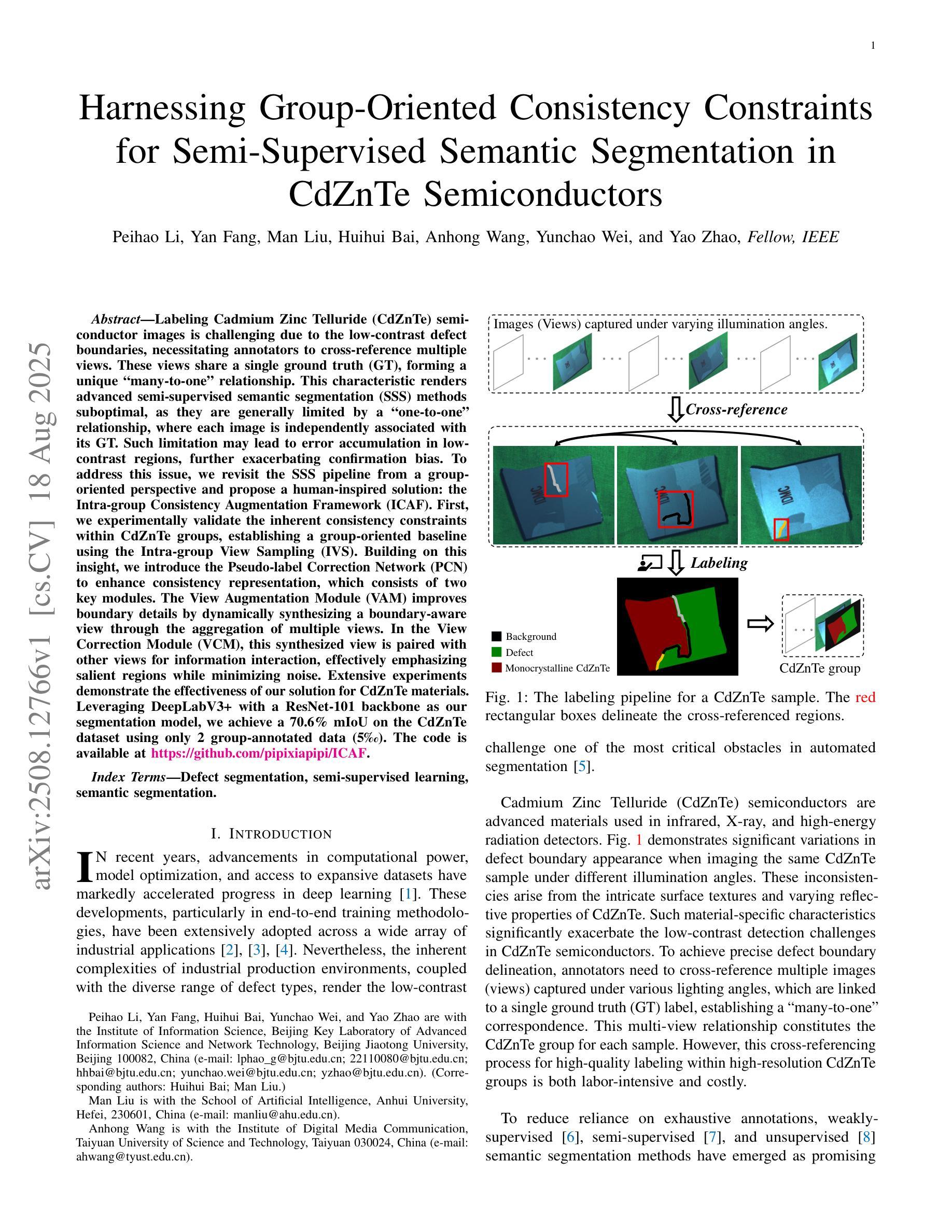
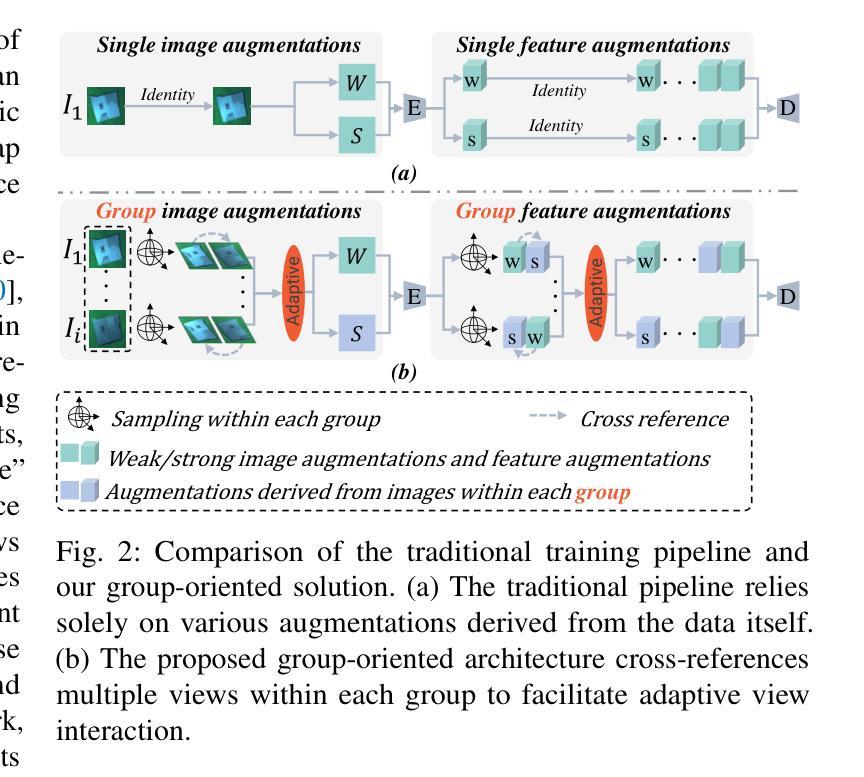
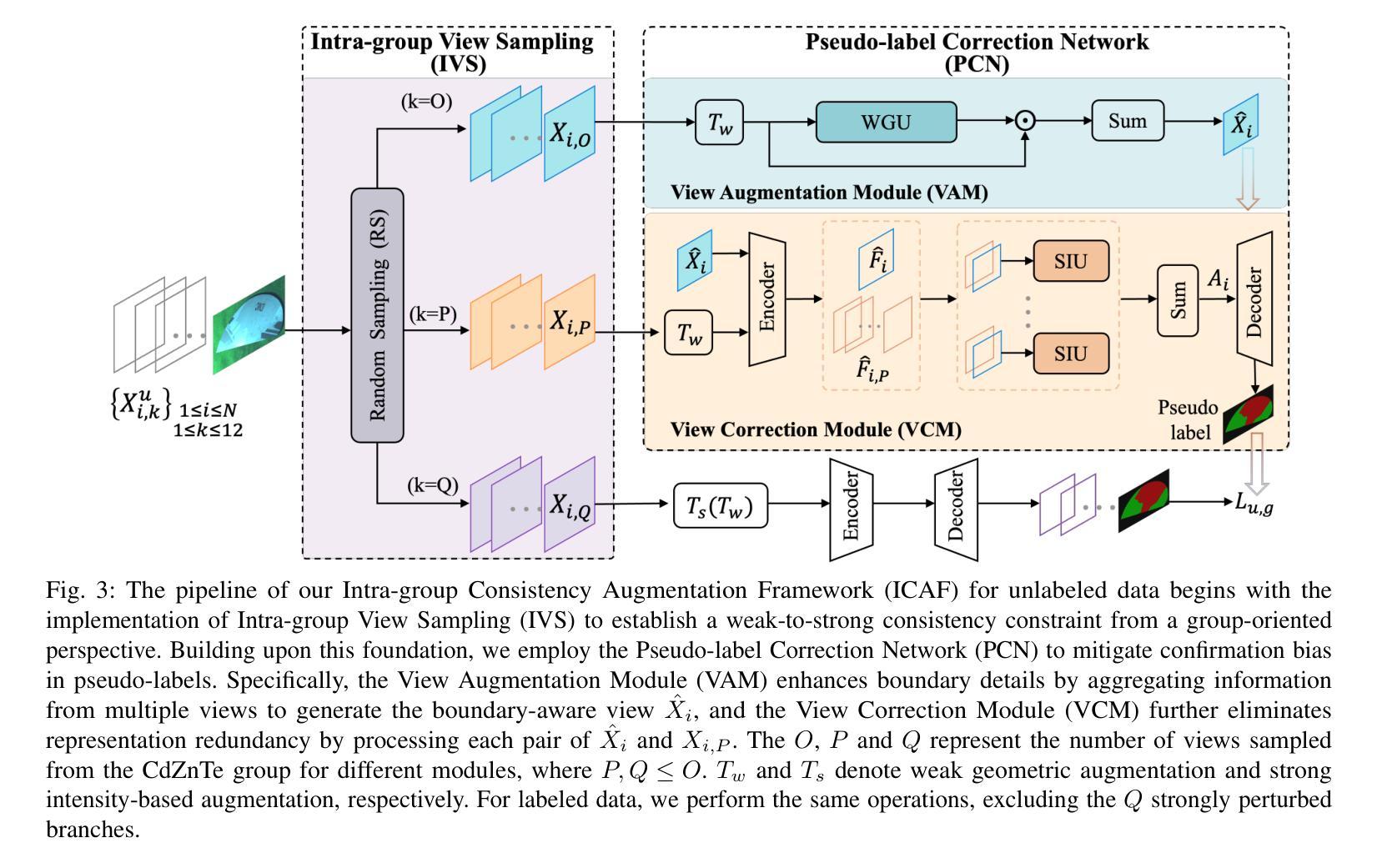
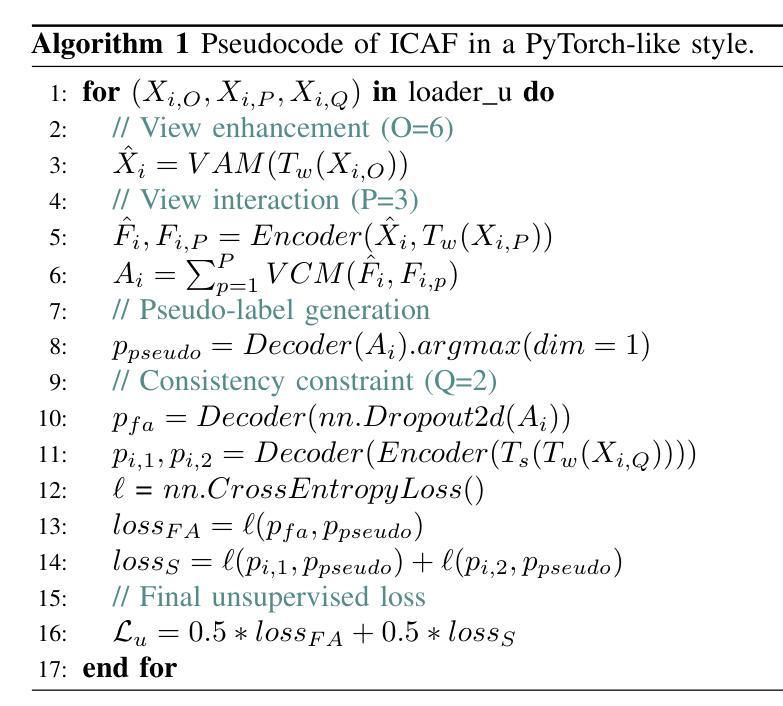
Labeling Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe) semiconductor images is challenging due to the low-contrast defect boundaries, necessitating annotators to cross-reference multiple views. These views share a single ground truth (GT), forming a unique many-to-one'' relationship. This characteristic renders advanced semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSS) methods suboptimal, as they are generally limited by a one-to-one’’ relationship, where each image is independently associated with its GT. Such limitation may lead to error accumulation in low-contrast regions, further exacerbating confirmation bias. To address this issue, we revisit the SSS pipeline from a group-oriented perspective and propose a human-inspired solution: the Intra-group Consistency Augmentation Framework (ICAF). First, we experimentally validate the inherent consistency constraints within CdZnTe groups, establishing a group-oriented baseline using the Intra-group View Sampling (IVS). Building on this insight, we introduce the Pseudo-label Correction Network (PCN) to enhance consistency representation, which consists of two key modules. The View Augmentation Module (VAM) improves boundary details by dynamically synthesizing a boundary-aware view through the aggregation of multiple views. In the View Correction Module (VCM), this synthesized view is paired with other views for information interaction, effectively emphasizing salient regions while minimizing noise. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our solution for CdZnTe materials. Leveraging DeepLabV3+ with a ResNet-101 backbone as our segmentation model, we achieve a 70.6% mIoU on the CdZnTe dataset using only 2 group-annotated data (5\textperthousand). The code is available at \href{https://github.com/pipixiapipi/ICAF}{https://github.com/pipixiapipi/ICAF}.
对碲化镉锌(CdZnTe)半导体图像进行标注是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为缺陷边界的对比度较低,需要标注者参照多个视角。这些视角共享一个真实值(GT),形成一种独特的“多对一”关系。这一特性使得先进的半监督语义分割(SSS)方法并不理想,因为它们通常受限于一对一的关系,即每张图像都独立地与其GT相关联。这种限制可能导致低对比度区域的误差累积,进一步加剧确认偏见。为了解决这个问题,我们从群体导向的视角重新审视SSS管道,并提出了一种人类启发式的解决方案:群组内部一致性增强框架(ICAF)。首先,我们通过实验验证了CdZnTe组内的固有一致性约束,并使用组内视图采样(IVS)建立了群体导向的基准线。在此基础上,我们引入了伪标签校正网络(PCN)以增强一致性表示,其中包括两个关键模块。视图增强模块(VAM)通过动态合成边界感知视图来改善边界细节,该视图是通过多个视图的聚合得到的。在视图校正模块(VCM)中,合成的视图与其他视图配对进行信息交互,从而有效地突出显著区域并最小化噪声。大量的实验表明,我们的解决方案对于CdZnTe材料非常有效。我们以DeepLabV3+作为分割模型,使用ResNet-101作为骨干网,在CdZnTe数据集上仅使用2组标注数据(千分之五)就达到了70.6%的mIoU。代码可在https://github.com/pipixiapipi/ICAF获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对CdZnTe半导体图像标注的挑战性问题,本文提出了一种基于群体一致性的增强框架(ICAF)的解决方法。通过群体导向的视角采样(IVS)和伪标签校正网络(PCN),提高了低对比度缺陷边界的标注准确性。实验结果显示,该方法在CdZnTe数据集上取得了70.6%的mIoU,仅使用2组标注数据(5%)。
Key Takeaways
- CdZnTe图像标注具有挑战性,因为缺陷边界对比度低,需要跨多个视角进行参考。
- 现有的半监督语义分割方法由于一对一关系限制,在低对比度区域容易出现误差累积。
- 本文从群体导向角度重新审视SSS管道,并提出一种基于群体一致性的增强框架(ICAF)的解决方法。
- 通过实验验证了CdZnTe群体内部的一致性约束,建立了群体导向的基线方法。
- 引入伪标签校正网络(PCN),包括视角增强模块(VAM)和视角校正模块(VCM),提高一致性表示和边界细节。
- 在CdZnTe数据集上,使用DeepLabV3+和ResNet-101作为分割模型,仅使用少量群体标注数据即可取得良好效果。
点此查看论文截图
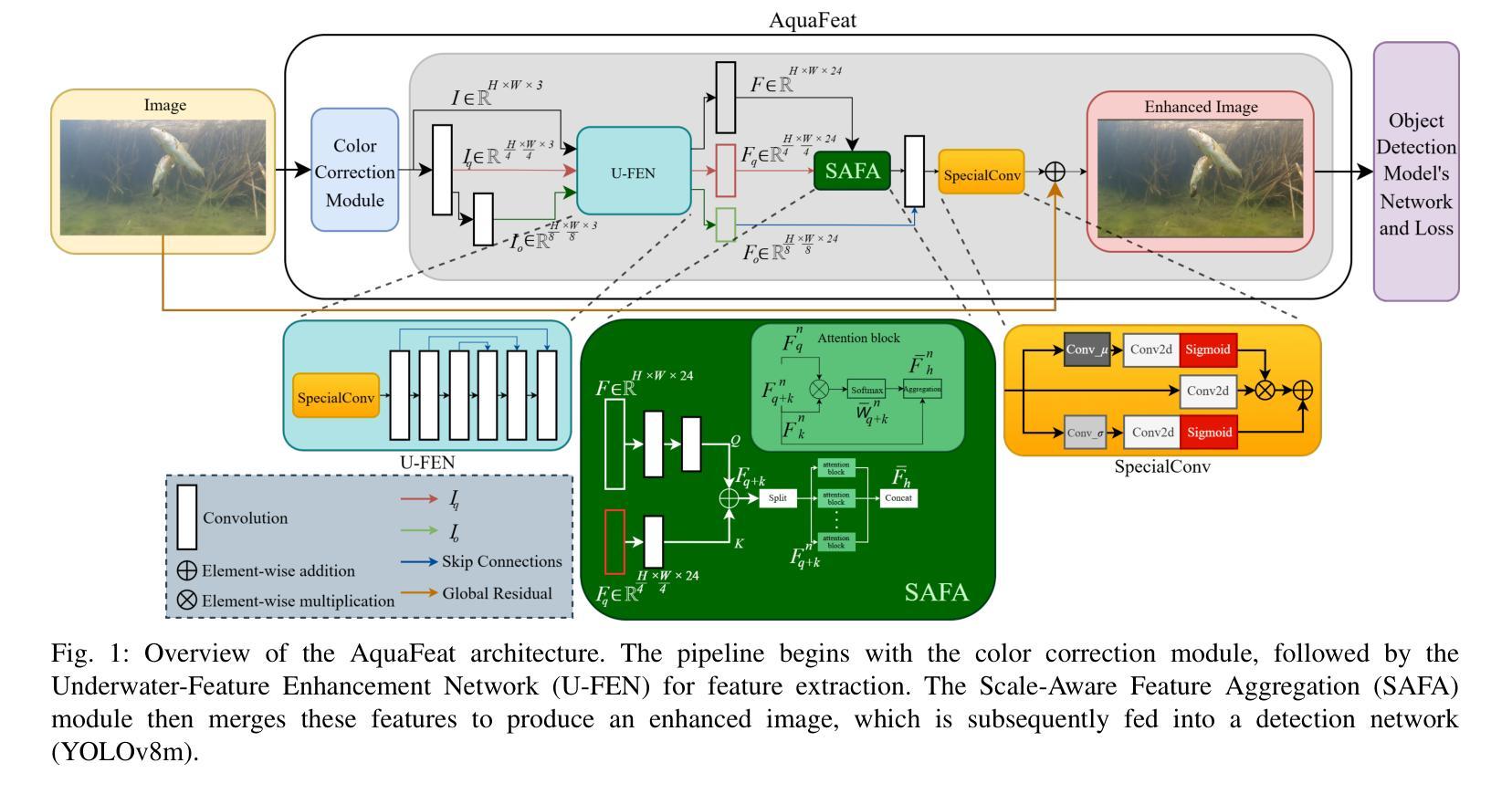
AquaFeat: A Features-Based Image Enhancement Model for Underwater Object Detection
Authors:Emanuel C. Silva, Tatiana T. Schein, Stephanie L. Brião, Guilherme L. M. Costa, Felipe G. Oliveira, Gustavo P. Almeida, Eduardo L. Silva, Sam S. Devincenzi, Karina S. Machado, Paulo L. J. Drews-Jr
The severe image degradation in underwater environments impairs object detection models, as traditional image enhancement methods are often not optimized for such downstream tasks. To address this, we propose AquaFeat, a novel, plug-and-play module that performs task-driven feature enhancement. Our approach integrates a multi-scale feature enhancement network trained end-to-end with the detector’s loss function, ensuring the enhancement process is explicitly guided to refine features most relevant to the detection task. When integrated with YOLOv8m on challenging underwater datasets, AquaFeat achieves state-of-the-art Precision (0.877) and Recall (0.624), along with competitive mAP scores (mAP@0.5 of 0.677 and mAP@[0.5:0.95] of 0.421). By delivering these accuracy gains while maintaining a practical processing speed of 46.5 FPS, our model provides an effective and computationally efficient solution for real-world applications, such as marine ecosystem monitoring and infrastructure inspection.
水下环境中的严重图像退化损害了目标检测模型的性能,因为传统的图像增强方法通常没有针对此类下游任务进行优化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了AquaFeat,这是一种新型即插即用模块,可执行任务驱动的特征增强。我们的方法整合了一个多尺度特征增强网络,该网络通过端到端的方式与检测器的损失函数进行训练,确保增强过程明确指导并优化与检测任务最相关的特征。在与YOLOv8m集成于具有挑战性的水下数据集时,AquaFeat达到了最先进的精度(精确率为0.877,召回率为0.624),同时具有竞争力的mAP分数(在mAP@0.5为0.677,mAP@[0.5:0.95]为0.421)。在保持实际处理速度达到每秒46.5帧的同时实现了这些精度提升,我们的模型为实际应用(如海洋生态系统监测和基础设施检查)提供了有效且计算效率高的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在水下环境中,图像严重退化,影响目标检测模型的性能。针对这一问题,我们提出了AquaFeat,这是一种新型的即插即用模块,用于执行任务驱动的特征增强。该方法整合了一个多尺度特征增强网络,该网络与检测器的损失函数进行端到端的训练,确保增强过程明确指导,以优化与检测任务最相关的特征。当与YOLOv8m在水下数据集上进行集成时,AquaFeat达到了最先进的精度水平,包括精确度(0.877)和召回率(0.624),以及具有竞争力的mAP分数。在保证实际处理速度达到每秒46.5帧的同时,我们的模型为实际应用提供了有效且计算高效的解决方案,例如海洋生态系统监测和基础设施检测。
Key Takeaways
- 水下环境中的图像严重退化对目标检测模型产生影响。
- 传统图像增强方法通常不适用于下游任务。
- 提出了一种新型的即插即用模块AquaFeat,用于执行任务驱动的特征增强。
- 多尺度特征增强网络整合到检测器中,进行端到端的训练。
- AquaFeat与YOLOv8m集成后,在水下数据集上取得了最先进的性能表现。
- 模型在保证处理速度的同时提供了有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

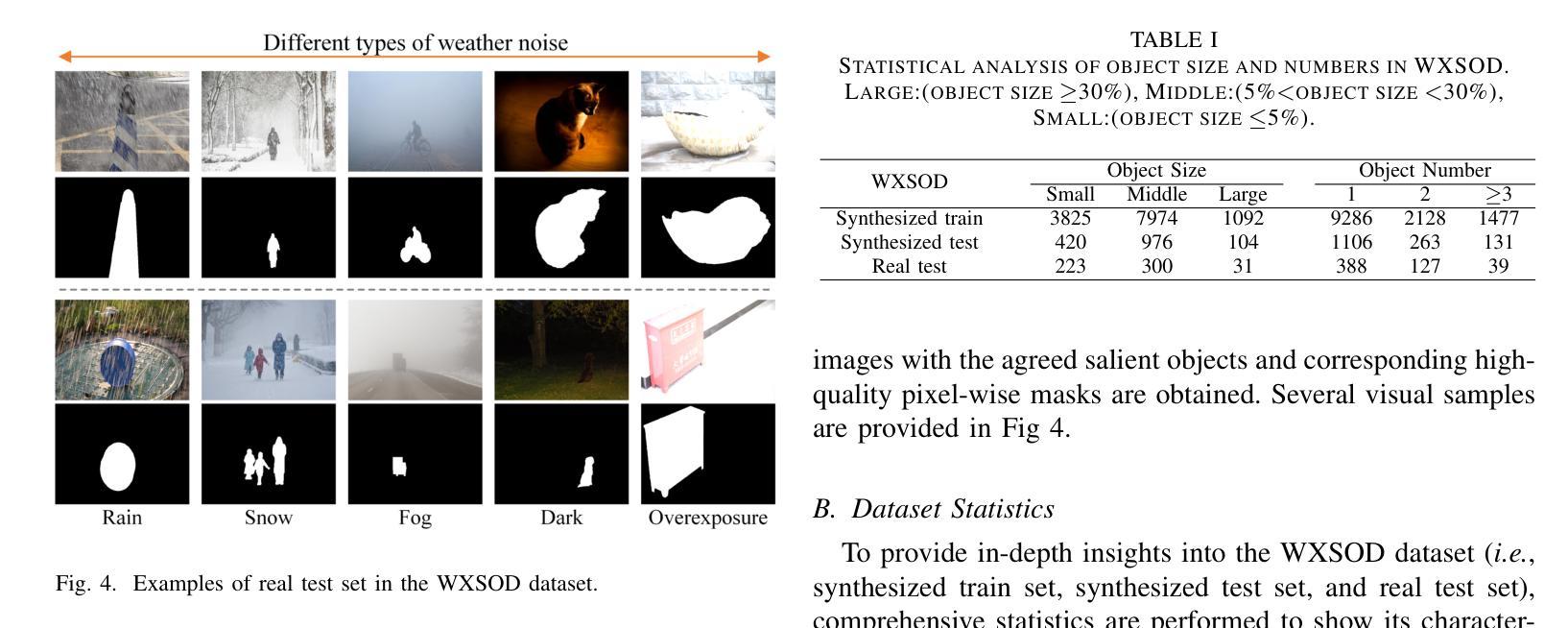
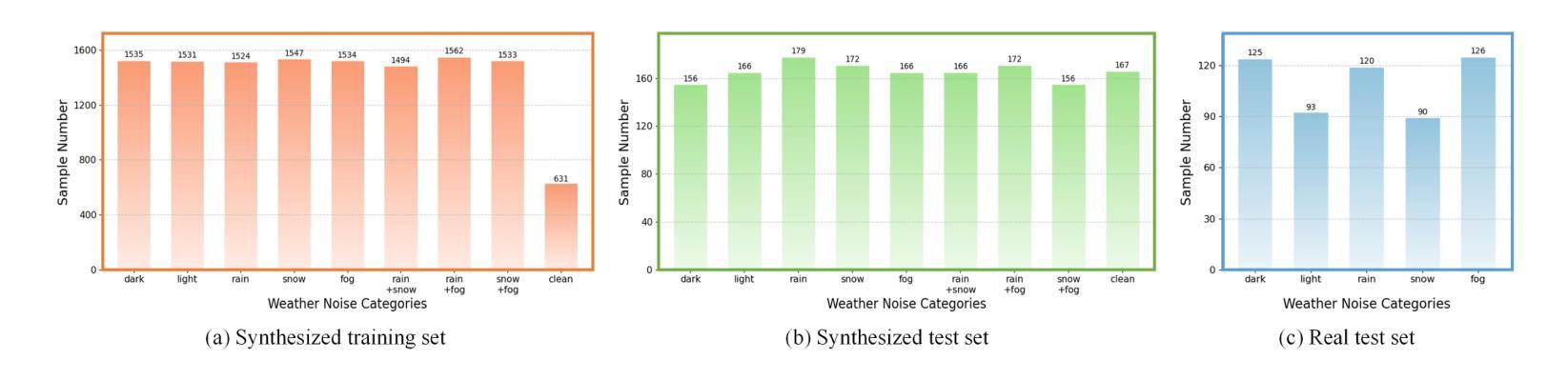
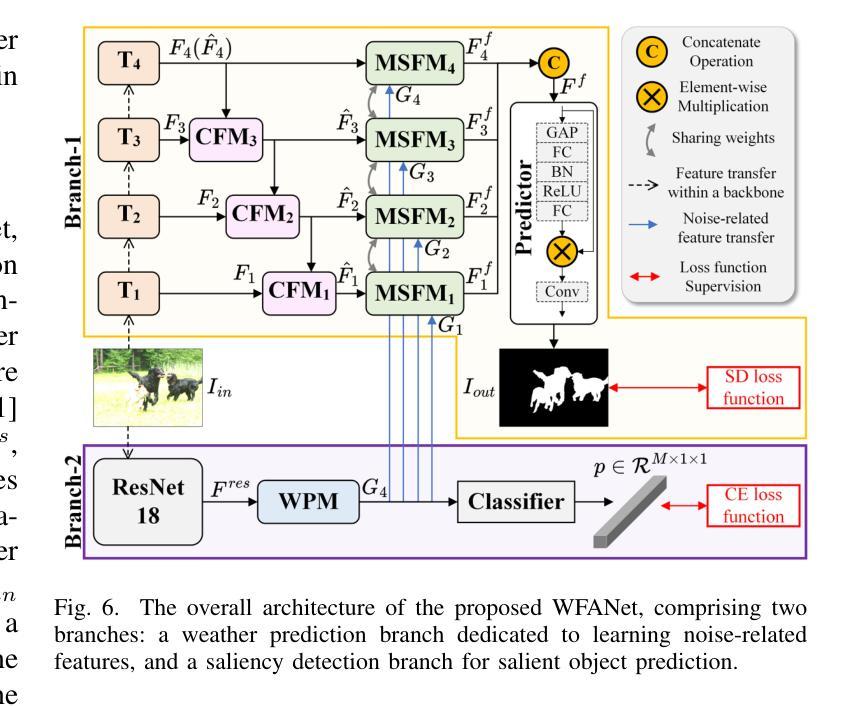
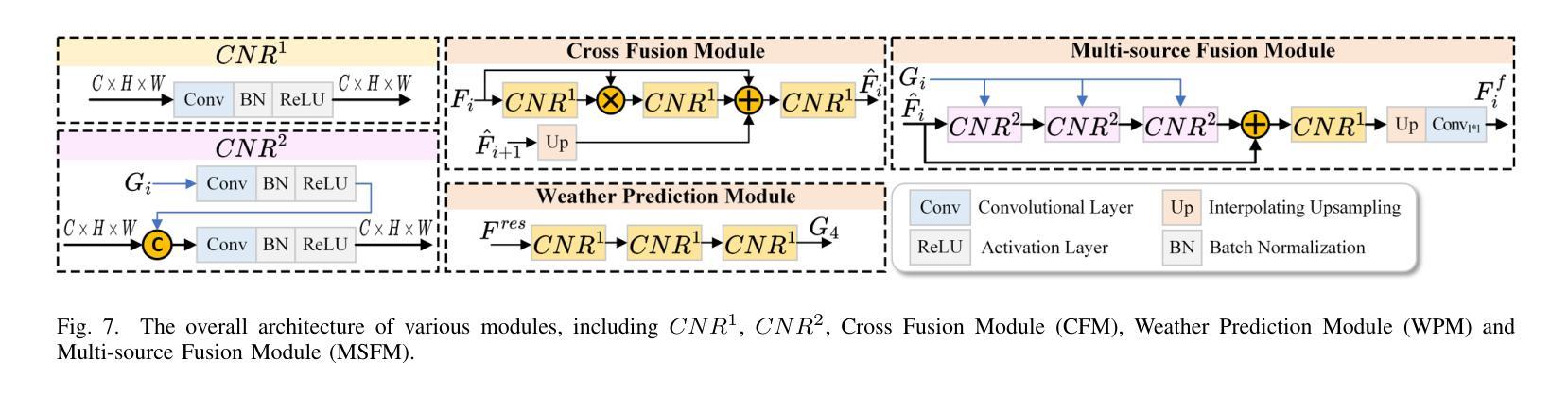
WXSOD: A Benchmark for Robust Salient Object Detection in Adverse Weather Conditions
Authors:Quan Chen, Xiong Yang, Rongfeng Lu, Qianyu Zhang, Yu Liu, Xiaofei Zhou, Bolun Zheng
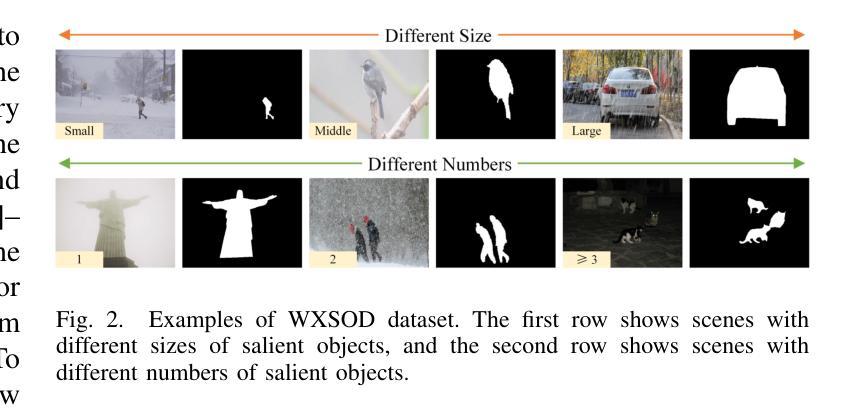
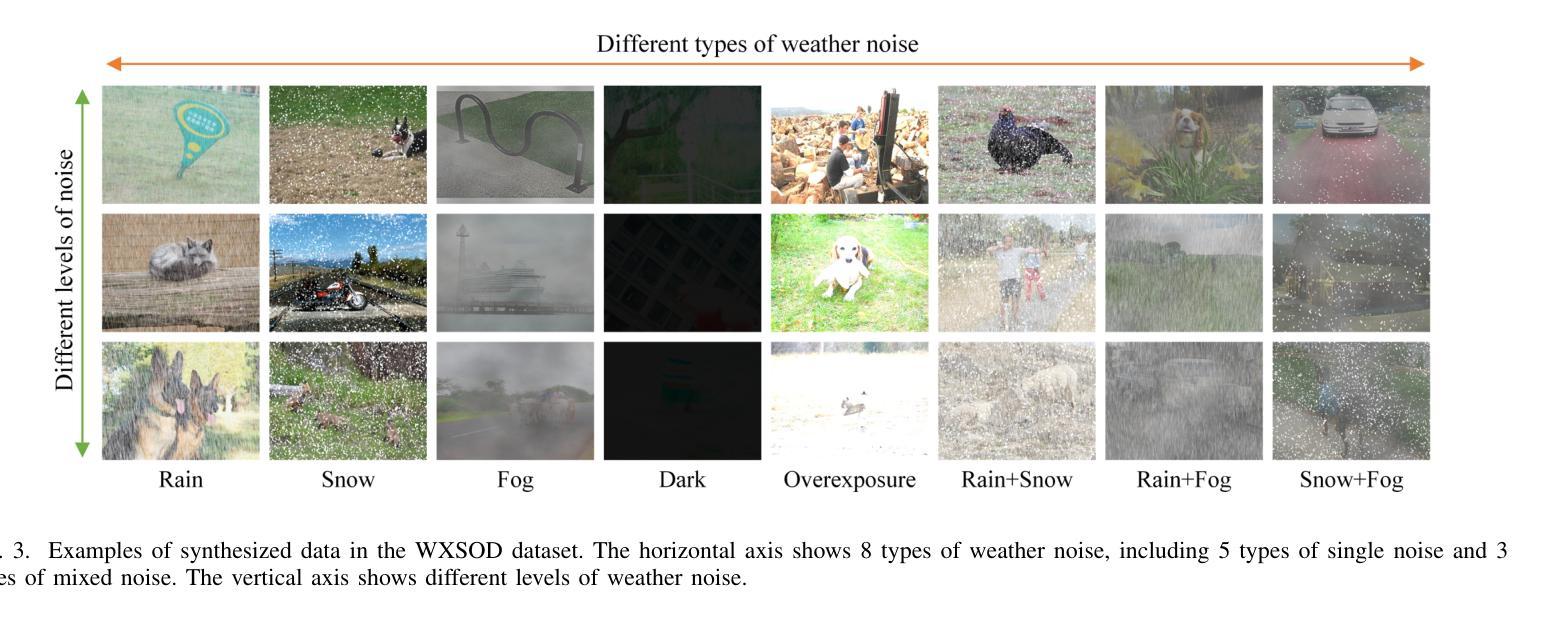
Salient object detection (SOD) in complex environments remains a challenging research topic. Most existing methods perform well in natural scenes with negligible noise, and tend to leverage multi-modal information (e.g., depth and infrared) to enhance accuracy. However, few studies are concerned with the damage of weather noise on SOD performance due to the lack of dataset with pixel-wise annotations. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a novel Weather-eXtended Salient Object Detection (WXSOD) dataset. It consists of 14,945 RGB images with diverse weather noise, along with the corresponding ground truth annotations and weather labels. To verify algorithm generalization, WXSOD contains two test sets, i.e., a synthesized test set and a real test set. The former is generated by adding weather noise to clean images, while the latter contains real-world weather noise. Based on WXSOD, we propose an efficient baseline, termed Weather-aware Feature Aggregation Network (WFANet), which adopts a fully supervised two-branch architecture. Specifically, the weather prediction branch mines weather-related deep features, while the saliency detection branch fuses semantic features extracted from the backbone with weather features for SOD. Comprehensive comparisons against 17 SOD methods shows that our WFANet achieves superior performance on WXSOD. The code and benchmark results will be made publicly available at https://github.com/C-water/WXSOD
在复杂环境中进行显著目标检测(SOD)仍然是一个具有挑战性的研究课题。大多数现有方法在自然场景中表现良好,几乎没有噪音干扰,并倾向于利用多模态信息(例如深度和红外)来提高准确性。然而,由于缺乏带有像素级注释的数据集,很少有研究关注天气噪声对SOD性能的影响。为了弥补这一空白,本文介绍了一个新的Weather-eXtended Salient Object Detection(WXSOD)数据集。它包含带有各种天气噪声的14945张RGB图像,以及相应的真实注释和天气标签。为了验证算法的通用性,WXSOD包含两个测试集,即合成测试集和真实测试集。前者是通过向干净图像添加天气噪声生成的,而后者则包含真实世界的天气噪声。基于WXSOD,我们提出了一种高效的基线模型,称为天气感知特征聚合网络(WFANet),它采用全监督的两分支架构。具体来说,天气预报分支挖掘与天气相关的深层特征,而显著性检测分支则将来自骨干网的语义特征与天气特征相融合用于SOD。与17种SOD方法的综合比较表明,我们的WFANet在WXSOD上取得了优越的性能。代码和基准测试结果将在https://github.com/C-water/WXSOD上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为WXSOD的新型天气扩展显著目标检测数据集,包含带有各种天气噪声的14,945张RGB图像,以及相应的地面真实注释和天气标签。为了验证算法的泛化能力,该数据集包含合成测试集和真实测试集。此外,还提出了一种基于WXSOD的有效基线方法——天气感知特征聚合网络(WFANet),采用全监督的两分支架构,能够在不同天气条件下实现鲁棒的显著目标检测。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一个新型数据集WXSOD,专门针对复杂环境中的显著目标检测。
- WXSOD包含大量带有天气噪声的RGB图像,并提供了相应的地面真实注释和天气标签。
- 数据集分为合成测试集和真实测试集,以验证算法的泛化能力。
- 提出了一种基于WXSOD的有效基线方法——WFANet。
- WFANet采用全监督的两分支架构,包括天气预测分支和显著性检测分支。
- 天气预测分支挖掘与天气相关的深度特征,而显著性检测分支融合来自骨干网的语义特征与天气特征,以实现鲁棒的显著目标检测。
点此查看论文截图

Automated Model Evaluation for Object Detection via Prediction Consistency and Reliablity
Authors:Seungju Yoo, Hyuk Kwon, Joong-Won Hwang, Kibok Lee
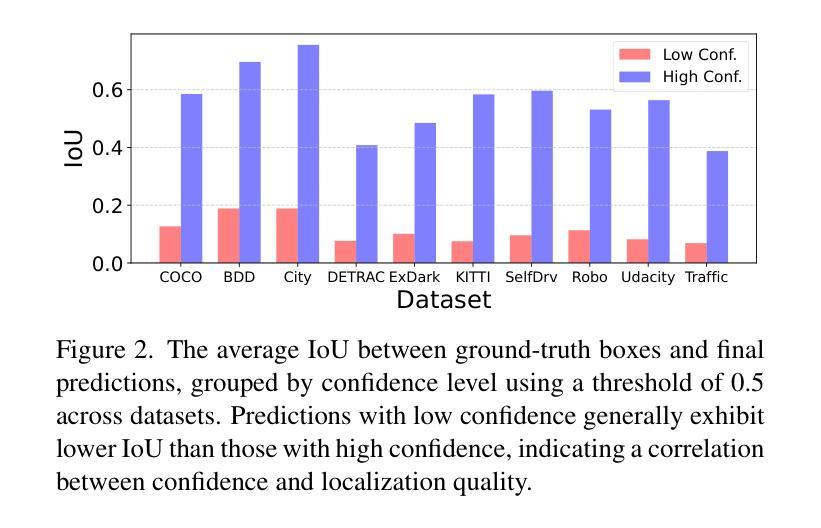
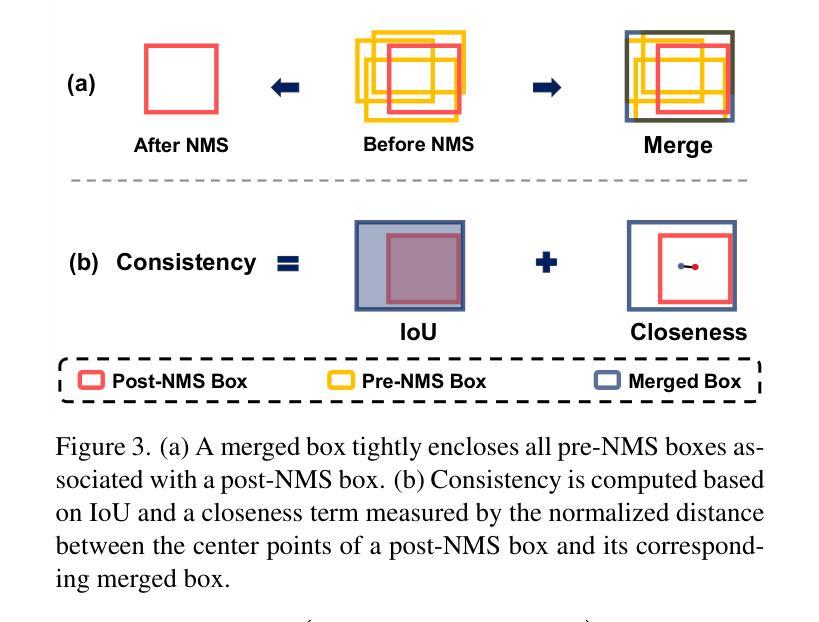
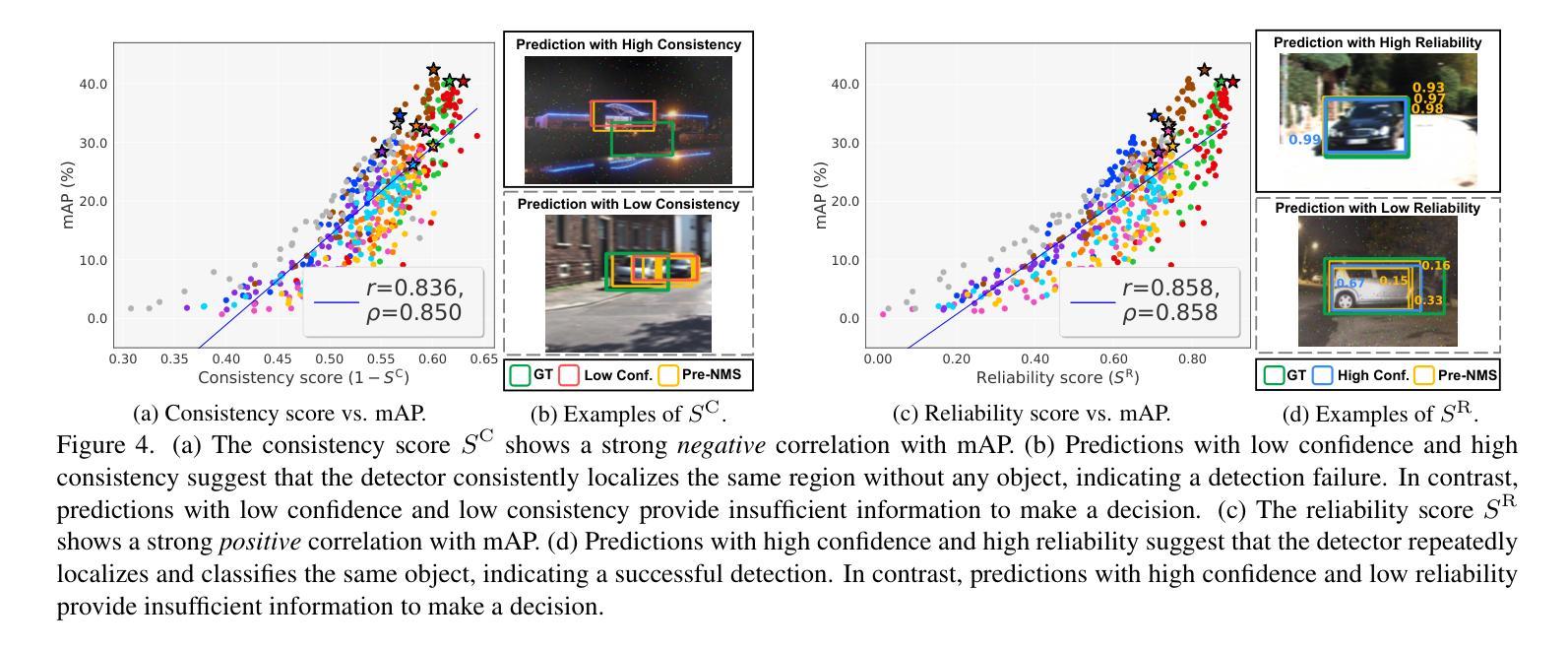
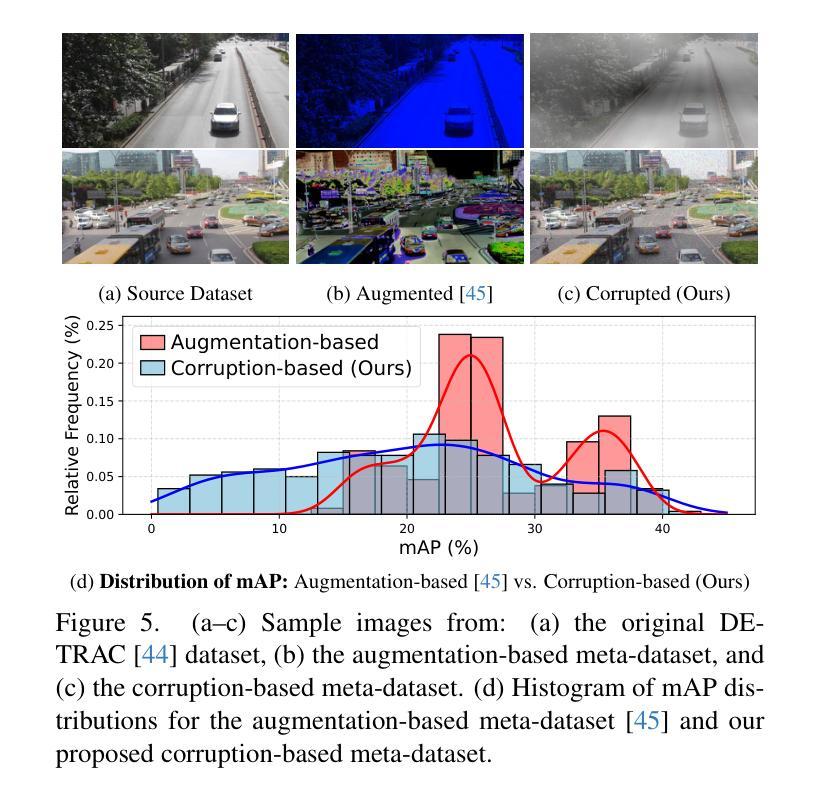
Recent advances in computer vision have made training object detectors more efficient and effective; however, assessing their performance in real-world applications still relies on costly manual annotation. To address this limitation, we develop an automated model evaluation (AutoEval) framework for object detection. We propose Prediction Consistency and Reliability (PCR), which leverages the multiple candidate bounding boxes that conventional detectors generate before non-maximum suppression (NMS). PCR estimates detection performance without ground-truth labels by jointly measuring 1) the spatial consistency between boxes before and after NMS, and 2) the reliability of the retained boxes via the confidence scores of overlapping boxes. For a more realistic and scalable evaluation, we construct a meta-dataset by applying image corruptions of varying severity. Experimental results demonstrate that PCR yields more accurate performance estimates than existing AutoEval methods, and the proposed meta-dataset covers a wider range of detection performance. The code is available at https://github.com/YonseiML/autoeval-det.
最近计算机视觉领域的进步使得训练目标检测器更加高效和有效;然而,评估它们在现实世界应用中的性能仍然依赖于昂贵的人工标注。为了解决这一局限性,我们为对象检测开发了一个自动化模型评估(AutoEval)框架。我们提出了预测一致性及可靠性(PCR),它利用传统检测器在非最大抑制(NMS)之前生成的多候选边界框。PCR通过联合测量1)NMS前后边界框的空间一致性,以及2)保留的框的可靠性,通过重叠框的置信度得分,无需真实标签即可估计检测性能。为了进行更现实和可扩展的评估,我们通过应用不同程度的数据图像损坏构建了元数据集。实验结果表明,PCR产生的性能估计比现有的AutoEval方法更准确,并且所提出的元数据集涵盖了更广泛的检测性能范围。代码可在https://github.com/YonseiML/autoeval-det找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Oral
Summary
近期计算机视觉技术的进步提高了目标检测器的训练效率和效果,但评估其在现实应用中的性能仍依赖于昂贵的人工标注。为解决这一局限性,我们开发了一种自动化模型评估(AutoEval)框架用于目标检测。我们提出预测一致性及可靠性(PCR),利用传统检测器在进行非极大值抑制(NMS)之前生成的多候选边界框进行评估。PCR通过联合测量1)NMS前后的边界框空间一致性,以及2)保留框的可靠性(通过重叠框的置信度评分),无需真实标签即可估计检测性能。为了进行更真实和可扩展的评估,我们通过应用不同严重程度的图像腐蚀构建了一个元数据集。实验结果表明,PCR较现有的AutoEval方法能更准确地估计性能,且所提元数据集覆盖了更广泛的检测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 近期计算机视觉技术提高了目标检测器的效率与效果。
- 评估目标检测器在现实应用中的性能仍然是一个挑战,需要自动化解决方案。
- 提出一种自动化模型评估(AutoEval)框架用于目标检测。
- 引入预测一致性及可靠性(PCR)方法,利用边界框的置信度和空间一致性评估检测性能。
- PCR方法无需真实标签即可估计检测性能。
- 构建了一个元数据集,通过应用不同严重程度的图像腐蚀以进行更全面的评估。
点此查看论文截图

Unified and Semantically Grounded Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xin Wang, Yin Guo, Jiamin Xia, Kaiyu Zhang, Niranjan Balu, Mahmud Mossa-Basha, Linda Shapiro, Chun Yuan
Most prior unsupervised domain adaptation approaches for medical image segmentation are narrowly tailored to either the source-accessible setting, where adaptation is guided by source-target alignment, or the source-free setting, which typically resorts to implicit supervision mechanisms such as pseudo-labeling and model distillation. This substantial divergence in methodological designs between the two settings reveals an inherent flaw: the lack of an explicit, structured construction of anatomical knowledge that naturally generalizes across domains and settings. To bridge this longstanding divide, we introduce a unified, semantically grounded framework that supports both source-accessible and source-free adaptation. Fundamentally distinct from all prior works, our framework’s adaptability emerges naturally as a direct consequence of the model architecture, without the need for any handcrafted adaptation strategies. Specifically, our model learns a domain-agnostic probabilistic manifold as a global space of anatomical regularities, mirroring how humans establish visual understanding. Thus, the structural content in each image can be interpreted as a canonical anatomy retrieved from the manifold and a spatial transformation capturing individual-specific geometry. This disentangled, interpretable formulation enables semantically meaningful prediction with intrinsic adaptability. Extensive experiments on challenging cardiac and abdominal datasets show that our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in both settings, with source-free performance closely approaching its source-accessible counterpart, a level of consistency rarely observed in prior works. Beyond quantitative improvement, we demonstrate strong interpretability of the proposed framework via manifold traversal for smooth shape manipulation.
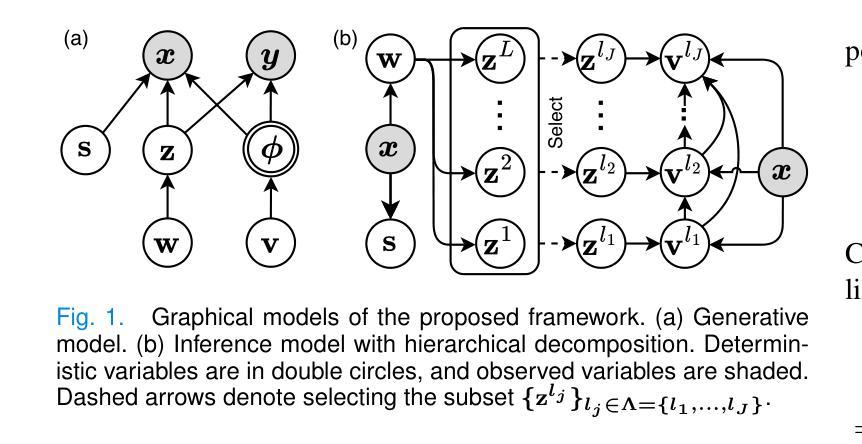
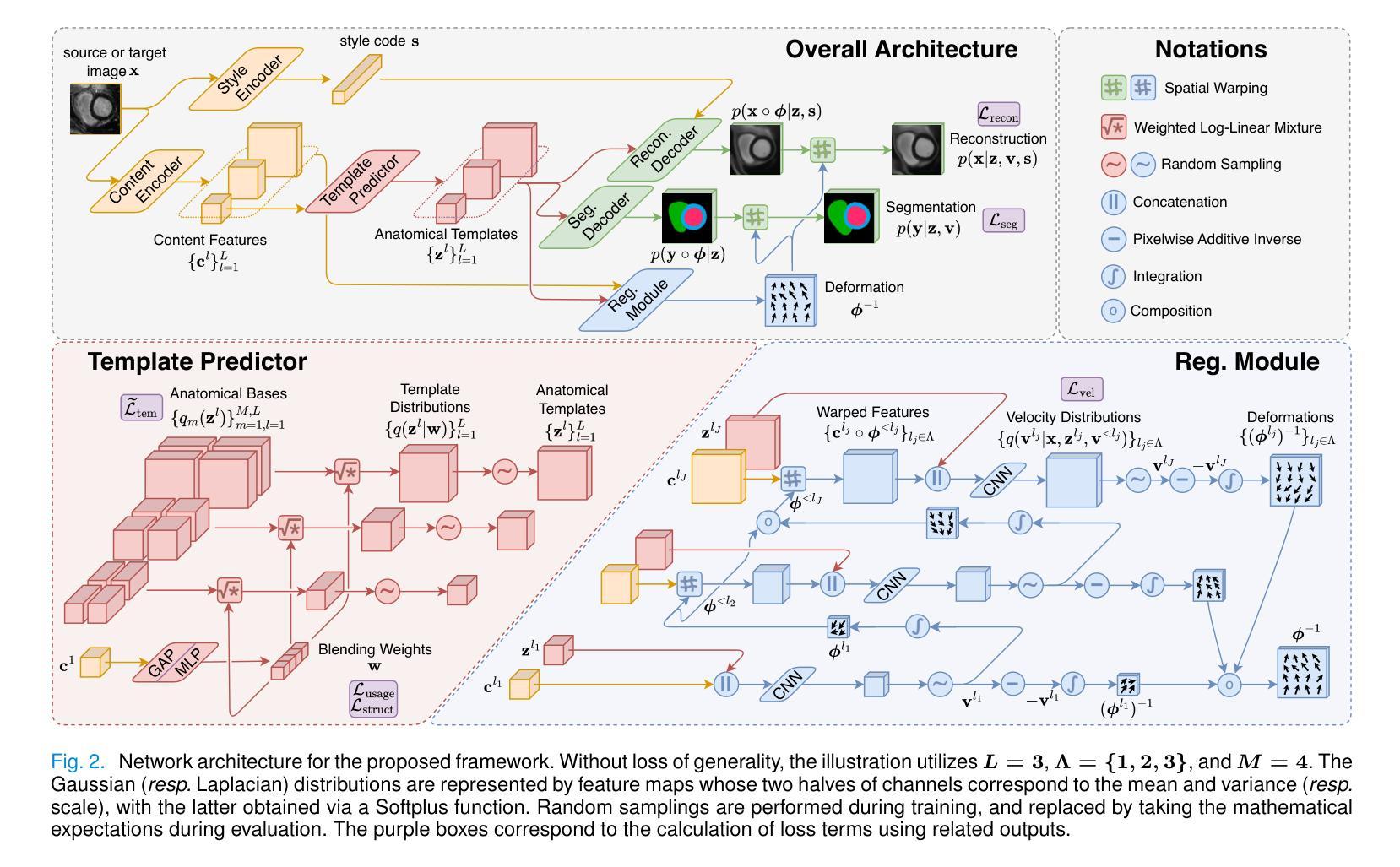
大部分以前的针对医学图像分割的无监督域适应方法都只局限于源数据可访问的场景,其中适应过程是通过源目标对齐来引导的,或者无源的情景,这通常依赖于隐式监督机制,如伪标签和模型蒸馏。这两种情景之间在方法论设计上的巨大差异揭示了一个固有缺陷:缺乏一个明确的结构化的解剖知识构建,该构建能自然地跨域和场景进行推广。为了弥合这一长期分歧,我们引入了一个统一的、语义基础的框架,支持源数据可访问和无源适应。我们的框架与所有先前的工作有着根本的不同,其适应性是模型架构的直接结果,无需任何手工定制的适应策略。具体来说,我们的模型学习一个域无关的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,这反映了人类如何建立视觉理解。因此,图像中的结构内容可以被解释为从流形中检索出的标准解剖结构和捕捉个体特定几何的空间变换。这种解耦、可解释的公式能够实现具有内在适应性的语义上有意义的预测。在具有挑战性的心脏和腹部数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的框架在这两种场景中均达到了最新水平的结果,无源的绩效接近其源数据可访问的对应物,这在以前的工作中很少观察到的一致性。除了定量改进之外,我们还通过流形遍历进行平滑形状操纵来展示所提出框架的强大可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种统一、语义基础框架,支持有源可访问和无源自由适应两种情况下的医学图像分割。该框架学习一个领域不可知的概率流形作为解剖规律的全局空间,模拟人类建立视觉理解的方式。通过解耦和可解释的形式化,实现了具有内在适应性的语义上有意义的预测。在心脏和腹部数据集上的实验表明,该框架在两种情况下均达到最新水平,其中无源性能接近其有源对应的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种统一框架,同时支持有源可访问和无源自由适应的医学图像分割。
- 框架的核心是学习一个领域不可知的概率流形,作为解剖规律的全局空间。
- 模型的架构自然产生了适应性,无需任何手工定制的策略。
- 通过解耦和可解释的形式化,实现语义上有意义的预测。
- 在心脏和腹部数据集上的实验表现出卓越性能,达到最新水平。
- 无源性能接近有源对应的表现,展示了强大的框架一致性。
点此查看论文截图