⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
TiP4GEN: Text to Immersive Panorama 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Ke Xing, Hanwen Liang, Dejia Xu, Yuyang Yin, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
With the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of VR/AR technologies, there is a growing demand for the creation of high-quality, immersive dynamic scenes. However, existing generation works predominantly concentrate on the creation of static scenes or narrow perspective-view dynamic scenes, falling short of delivering a truly 360-degree immersive experience from any viewpoint. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{TiP4GEN}, an advanced text-to-dynamic panorama scene generation framework that enables fine-grained content control and synthesizes motion-rich, geometry-consistent panoramic 4D scenes. TiP4GEN integrates panorama video generation and dynamic scene reconstruction to create 360-degree immersive virtual environments. For video generation, we introduce a \textbf{Dual-branch Generation Model} consisting of a panorama branch and a perspective branch, responsible for global and local view generation, respectively. A bidirectional cross-attention mechanism facilitates comprehensive information exchange between the branches. For scene reconstruction, we propose a \textbf{Geometry-aligned Reconstruction Model} based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. By aligning spatial-temporal point clouds using metric depth maps and initializing scene cameras with estimated poses, our method ensures geometric consistency and temporal coherence for the reconstructed scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed designs and the superiority of TiP4GEN in generating visually compelling and motion-coherent dynamic panoramic scenes. Our project page is at https://ke-xing.github.io/TiP4GEN/.
随着虚拟现实/增强现实技术的迅速发展和广泛应用,对高质量沉浸式动态场景的创作需求日益增长。然而,现有的工作主要集中在创建静态场景或有限视角的动态场景,无法提供从任何视角的真正360度沉浸式体验。在本文中,我们介绍了TiP4GEN,这是一个先进的文本到动态全景场景生成框架,它能够实现精细的内容控制,并合成运动丰富、几何一致的全景4D场景。TiP4GEN集成了全景视频生成和动态场景重建,以创建360度沉浸式虚拟环境。对于视频生成,我们引入了一个双分支生成模型,包括全景分支和透视分支,分别负责全局和局部视图生成。双向交叉注意力机制促进了分支之间的全面信息交流。对于场景重建,我们提出了一个基于3D高斯拼贴的几何对齐重建模型。通过利用度量深度图对齐时空点云,并用估计的姿态初始化场景相机,我们的方法确保了重建场景的空间几何一致性和时间连贯性。大量实验证明了我们所提出设计的有效性以及TiP4GEN在生成视觉上吸引人且运动连贯的动态全景场景方面的优越性。我们的项目页面是https://ke-xing.github.io/TiP4GEN/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着VR/AR技术的迅速发展和广泛应用,对高质量、沉浸式动态场景的创作需求日益增长。然而,当前主要工作主要集中在静态场景或窄视角动态场景的创作上,无法提供真正的360度沉浸式体验。本文介绍了一种先进的文本到动态全景场景生成框架——TiP4GEN,它能够实现精细的内容控制,并合成运动丰富、几何一致的全景4D场景。TiP4GEN结合了全景视频生成和动态场景重建,创建出全方位的沉浸式虚拟环境。
Key Takeaways
- TiP4GEN框架能够实现高质量的动态全景场景生成,满足VR/AR技术的需求。
- 该框架通过结合全景视频生成和动态场景重建,创建出全方位的沉浸式虚拟环境。
- 提出了Dual-branch Generation Model,包括全景分支和透视分支,分别负责全局和局部视图生成。
- 双向交叉注意机制促进了分支之间的全面信息交流。
- 提出了基于3D高斯拼贴的Geometry-aligned Reconstruction Model,确保场景重建的几何一致性和时间连贯性。
- 实验证明,所提出的设计方案有效,TiP4GEN在生成视觉吸引、运动连贯的动态全景场景上具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


Improving Densification in 3D Gaussian Splatting for High-Fidelity Rendering
Authors:Xiaobin Deng, Changyu Diao, Min Li, Ruohan Yu, Duanqing Xu
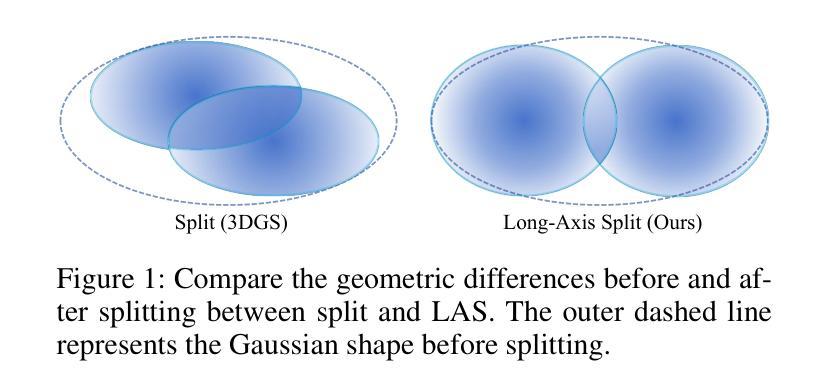
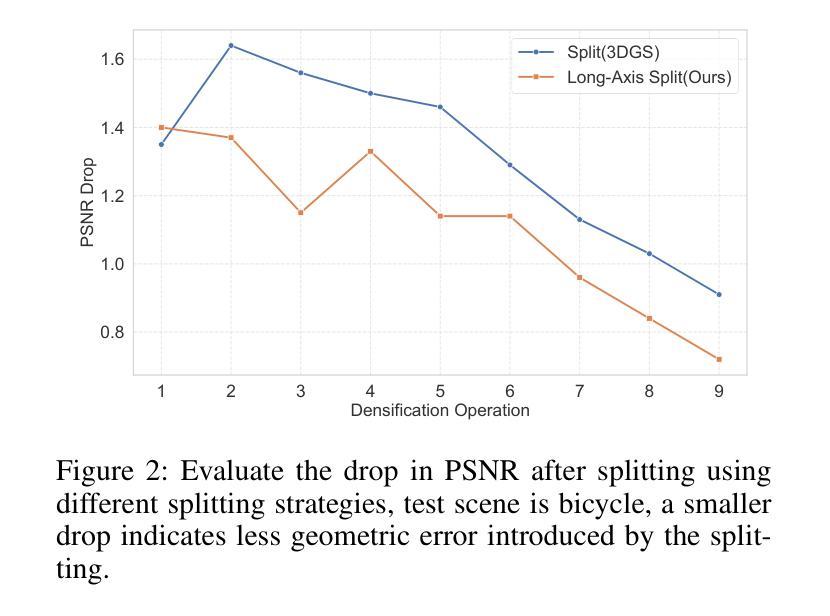
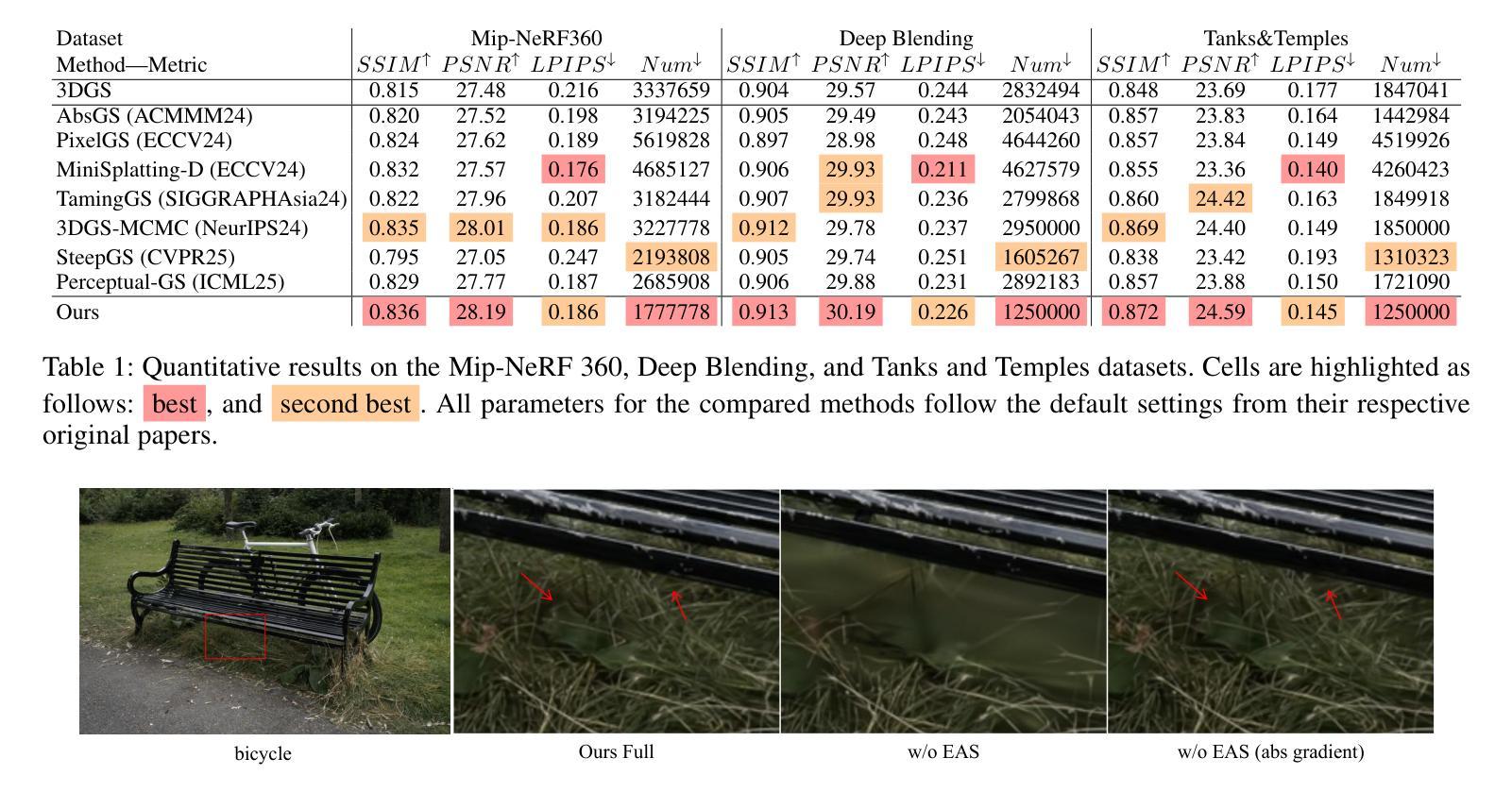
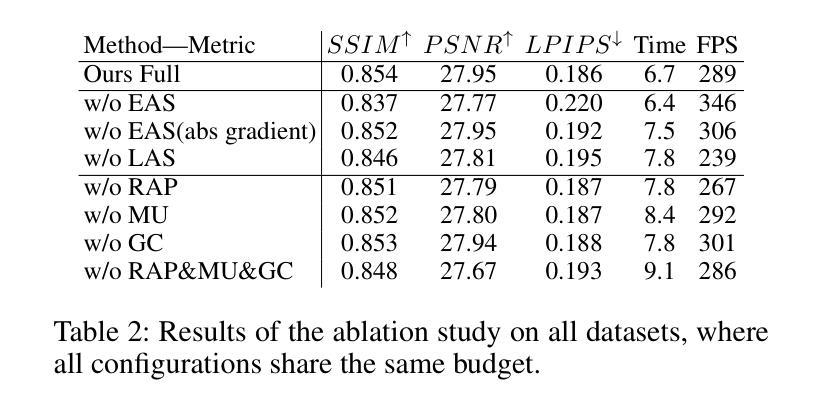
Although 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has achieved impressive performance in real-time rendering, its densification strategy often results in suboptimal reconstruction quality. In this work, we present a comprehensive improvement to the densification pipeline of 3DGS from three perspectives: when to densify, how to densify, and how to mitigate overfitting. Specifically, we propose an Edge-Aware Score to effectively select candidate Gaussians for splitting. We further introduce a Long-Axis Split strategy that reduces geometric distortions introduced by clone and split operations. To address overfitting, we design a set of techniques, including Recovery-Aware Pruning, Multi-step Update, and Growth Control. Our method enhances rendering fidelity without introducing additional training or inference overhead, achieving state-of-the-art performance with fewer Gaussians.
尽管三维高斯斑点法(3DGS)在实时渲染方面取得了令人印象深刻的性能表现,但其稠化策略往往导致重建质量不佳。在这项工作中,我们从三个方面对3DGS的稠化流程进行了全面的改进:何时进行稠化、如何进行稠化以及如何缓解过度拟合问题。具体来说,我们提出了一种边缘感知得分(Edge-Aware Score),以有效地选择用于分割的高斯候选者。我们还引入了长轴分割策略(Long-Axis Split),以减少克隆和分割操作引入的几何失真。为解决过度拟合问题,我们设计了一系列技术,包括恢复感知修剪(Recovery-Aware Pruning)、多步更新(Multi-step Update)和生长控制(Growth Control)。我们的方法在提高了渲染保真度的同时,没有引入额外的训练或推理开销,使用更少的高斯实现了业界领先的性能表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://xiaobin2001.github.io/improved-gs-web
Summary
本文提出对3D高斯映射(3DGS)的密度增强流程的全面改进,从何时进行密度增强、如何进行密度增强以及如何缓解过拟合三个方面入手。通过引入边缘感知评分有效地选择候选高斯进行分割,采用长轴分割策略减少克隆和分割操作引起的几何失真。为解决过拟合问题,设计了一系列技术,包括恢复感知裁剪、多步更新和增长控制。该方法在不引入额外训练或推理开销的情况下提高了渲染保真度,实现了使用更少高斯数的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入Edge-Aware Score选择候选高斯进行分割,提高密度增强效率。
- 提出Long-Axis Split策略,减少克隆和分割操作引起的几何失真。
- 设计一系列技术解决过拟合问题,包括Recovery-Aware Pruning、Multi-step Update和Growth Control。
- 改进后的方法在渲染保真度上有所提升。
- 无需额外训练和推理开销。
- 使用更少的高斯数实现了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


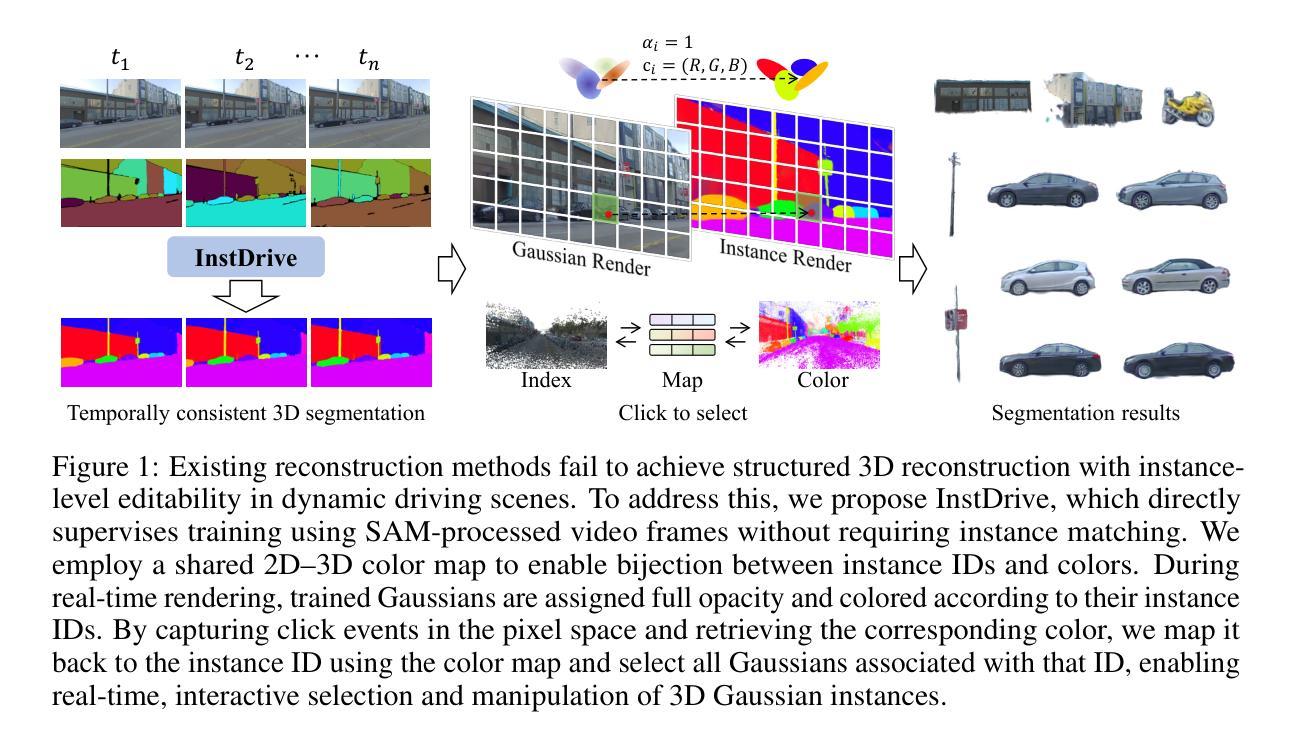
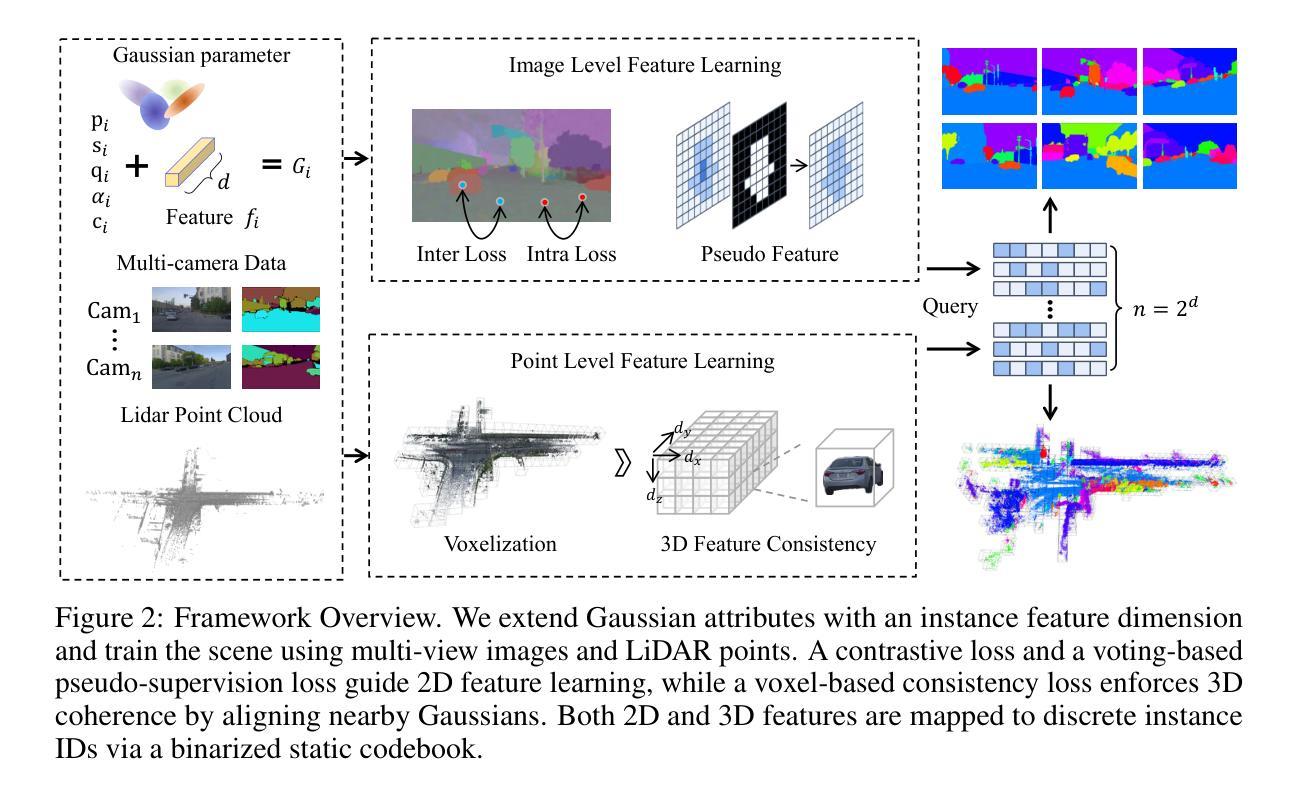
InstDrive: Instance-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting for Driving Scenes
Authors:Hongyuan Liu, Haochen Yu, Jianfei Jiang, Qiankun Liu, Jiansheng Chen, Huimin Ma
Reconstructing dynamic driving scenes from dashcam videos has attracted increasing attention due to its significance in autonomous driving and scene understanding. While recent advances have made impressive progress, most methods still unify all background elements into a single representation, hindering both instance-level understanding and flexible scene editing. Some approaches attempt to lift 2D segmentation into 3D space, but often rely on pre-processed instance IDs or complex pipelines to map continuous features to discrete identities. Moreover, these methods are typically designed for indoor scenes with rich viewpoints, making them less applicable to outdoor driving scenarios. In this paper, we present InstDrive, an instance-aware 3D Gaussian Splatting framework tailored for the interactive reconstruction of dynamic driving scene. We use masks generated by SAM as pseudo ground-truth to guide 2D feature learning via contrastive loss and pseudo-supervised objectives. At the 3D level, we introduce regularization to implicitly encode instance identities and enforce consistency through a voxel-based loss. A lightweight static codebook further bridges continuous features and discrete identities without requiring data pre-processing or complex optimization. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of InstDrive, and to the best of our knowledge, it is the first framework to achieve 3D instance segmentation in dynamic, open-world driving scenes.More visualizations are available at our project page.
从行车记录仪视频重建动态驾驶场景已经引起了越来越多的关注,这在自动驾驶和场景理解方面具有重要意义。虽然最近的进步已经取得了令人印象深刻的进展,但大多数方法仍然将所有背景元素统一到一个单一表示中,这阻碍了实例级别的理解和灵活的场景编辑。一些方法试图将2D分割提升到3D空间,但通常依赖于预处理的实例ID或复杂的管道来将连续特征映射到离散身份。此外,这些方法通常针对室内场景设计,视点丰富,使其不太适合室外驾驶场景。在本文中,我们提出了专为动态驾驶场景的交互式重建量身定制的实例感知3D高斯展平框架——InstDrive。我们使用SAM生成的蒙版作为伪真实标签,通过对比损失和伪监督目标来指导2D特征学习。在3D级别,我们引入正则化来隐式编码实例身份并通过基于体素的损失强制执行一致性。一个轻量级的静态编码本进一步连接连续特征和离散身份,无需数据预处理或复杂的优化。定量和定性实验证明了InstDrive的有效性,据我们所知,它是第一个实现在动态、开放世界驾驶场景中3D实例分割的框架。更多的可视化内容可在我们的项目页面查看。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文针对动态驾驶场景的重建展开研究,提出一个名为InstDrive的实例感知三维高斯溅泼框架,用于交互式重建动态驾驶场景。该研究利用SAM生成的掩膜作为伪真实标签,指导二维特征学习,并在三维层面引入正则化隐性编码实例身份,通过基于体素的损失进行一致性执行。框架适用于动态开放世界驾驶场景的3D实例分割,填补了现有技术的空白。
关键见解
- 动态驾驶场景的重建在自动驾驶和场景理解中具有重要性,吸引了越来越多的关注。
- 当前的方法在重建时将所有背景元素合并为一个单一表示,这影响了实例级别的理解和灵活的场景编辑。
- 本文提出的InstDrive框架利用实例感知进行重建,这有助于提高驾驶场景的理解和编辑能力。
- 使用SAM生成的掩膜作为伪真实标签,用于指导二维特征学习。
- 在三维层面引入正则化隐性编码实例身份,增强了框架的实例感知能力。
- 通过基于体素的损失进行一致性执行,提高了重建结果的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

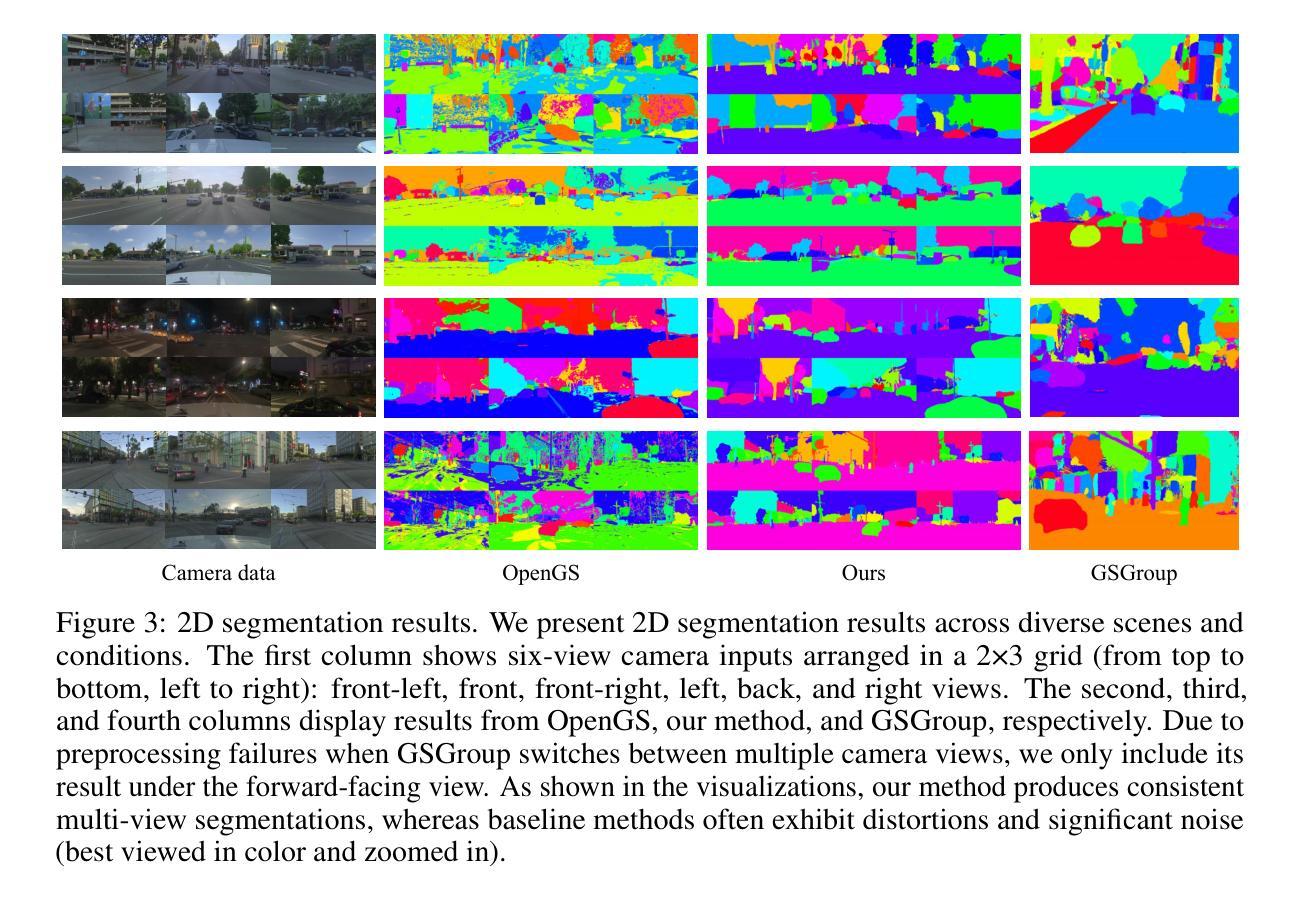
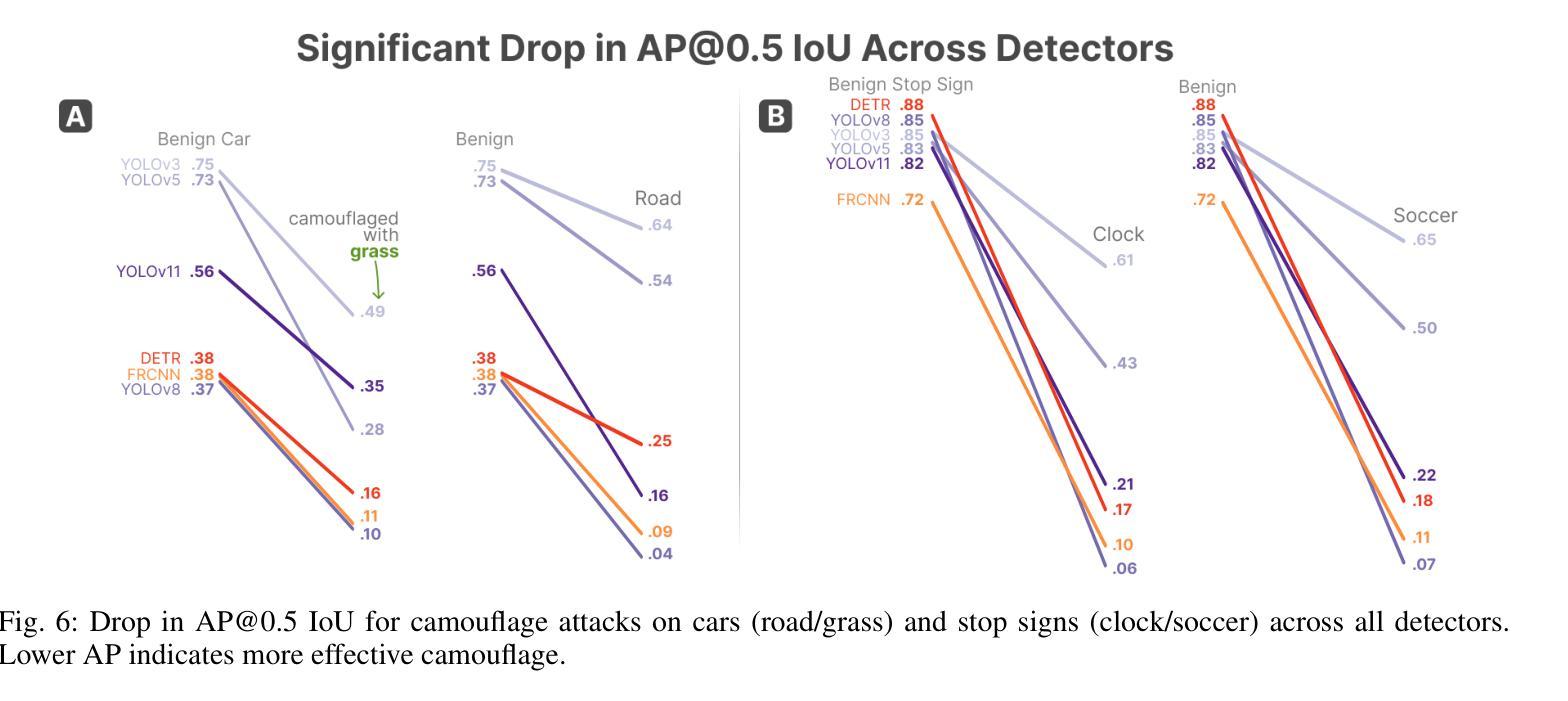
ComplicitSplat: Downstream Models are Vulnerable to Blackbox Attacks by 3D Gaussian Splat Camouflages
Authors:Matthew Hull, Haoyang Yang, Pratham Mehta, Mansi Phute, Aeree Cho, Haorang Wang, Matthew Lau, Wenke Lee, Wilian Lunardi, Martin Andreoni, Polo Chau
As 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) gains rapid adoption in safety-critical tasks for efficient novel-view synthesis from static images, how might an adversary tamper images to cause harm? We introduce ComplicitSplat, the first attack that exploits standard 3DGS shading methods to create viewpoint-specific camouflage - colors and textures that change with viewing angle - to embed adversarial content in scene objects that are visible only from specific viewpoints and without requiring access to model architecture or weights. Our extensive experiments show that ComplicitSplat generalizes to successfully attack a variety of popular detector - both single-stage, multi-stage, and transformer-based models on both real-world capture of physical objects and synthetic scenes. To our knowledge, this is the first black-box attack on downstream object detectors using 3DGS, exposing a novel safety risk for applications like autonomous navigation and other mission-critical robotic systems.
随着3D高斯贴图技术(3DGS)在静态图像高效合成新型视角的安全关键任务中得到迅速采用,对手如何篡改图像以造成危害?我们引入了ComplicitSplat技术,这是一种首次利用标准3DGS着色方法来创建视点特定迷彩的攻击技术——颜色和纹理会随着观察角度而改变——在场景对象中嵌入对抗内容,只有在特定视点才能看到这些场景对象,并且不需要访问模型架构或权重。我们的广泛实验表明,ComplicitSplat能够推广到攻击各种流行的检测器,包括单阶段、多阶段和基于变压器的模型,无论是在现实世界中对物理对象的捕获还是在合成场景中。据我们所知,这是利用3DGS对下游目标检测器的首次黑箱攻击,揭示了自动驾驶导航和其他关键任务机器人系统的应用中存在的新型安全风险。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了ComplicitSplat攻击,这是一种针对使用3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术的安全关键任务的新型攻击方法。该攻击利用标准3DGS着色方法创建视角特定伪装,在场景对象中添加对抗性内容,这些内容只在特定视角下可见。该攻击无需获取模型架构或权重信息即可实现攻击。实验表明,ComplicitSplat攻击能够成功攻击各种流行的检测器模型,包括单阶段、多阶段和基于转换器的模型,对现实世界捕获的物理对象和合成场景具有通用性。这是首次针对使用3DGS的下游对象检测器的黑箱攻击,暴露出自动驾驶和关键任务机器人系统等应用的全新安全风险。
Key Takeaways
- ComplicitSplat是一种针对3DGS技术的攻击方法,能够在场景对象中嵌入对抗性内容。
- 该攻击利用标准3DGS着色方法创建视角特定伪装,使得对抗性内容只在特定视角下可见。
- ComplicitSplat攻击无需获取模型架构或权重信息即可实现攻击。
- 该攻击方法能够成功攻击各种流行的检测器模型,包括单阶段、多阶段和基于转换器的模型。
- ComplicitSplat攻击具有在现实世界捕获的物理对象和合成场景中的通用性。
- 这是首次针对使用3DGS的下游对象检测器的黑箱攻击。
点此查看论文截图

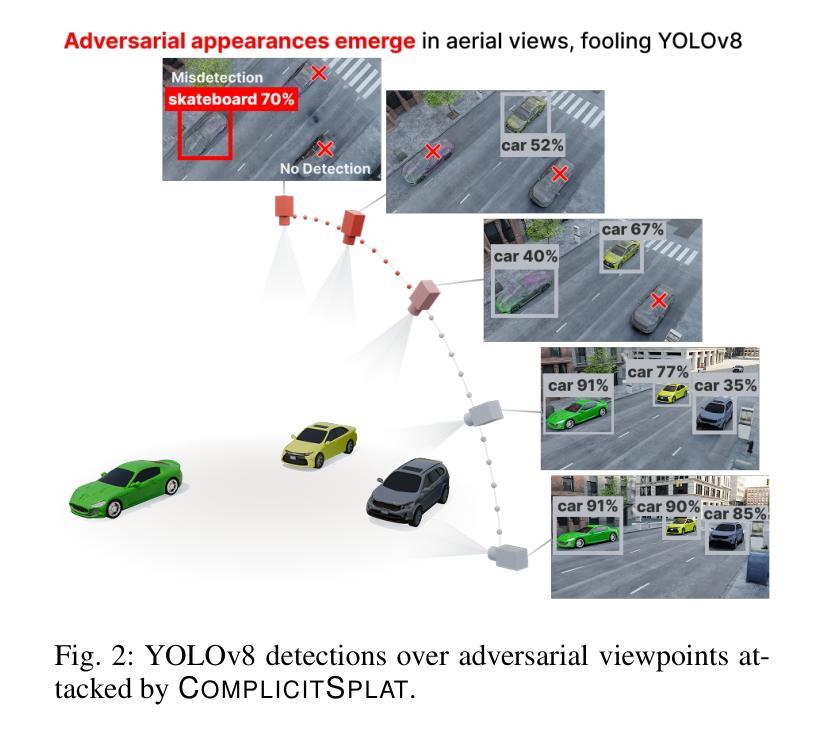
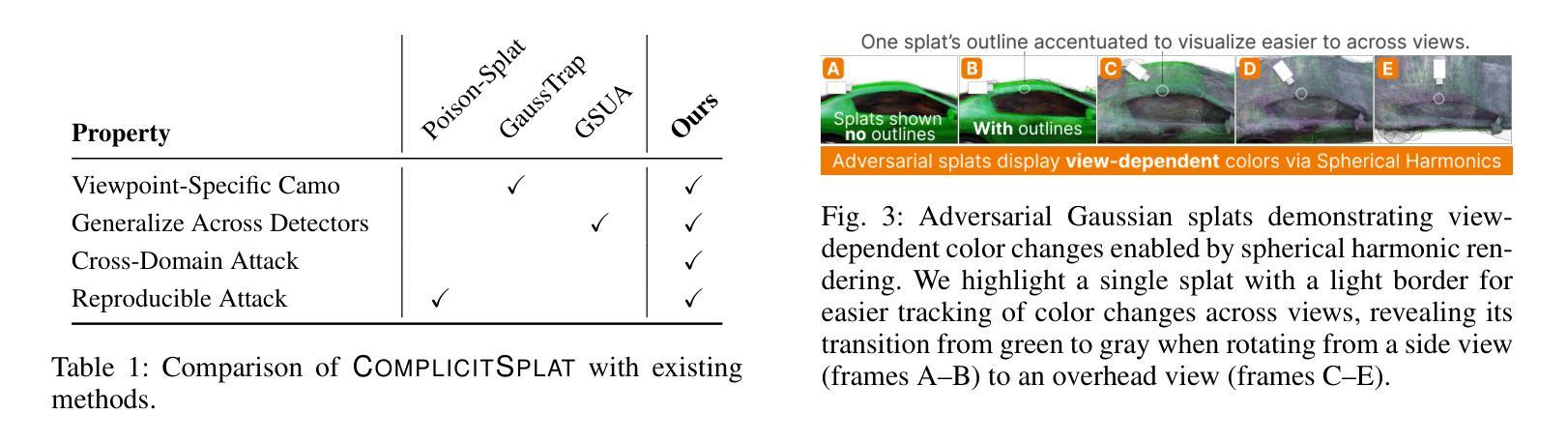
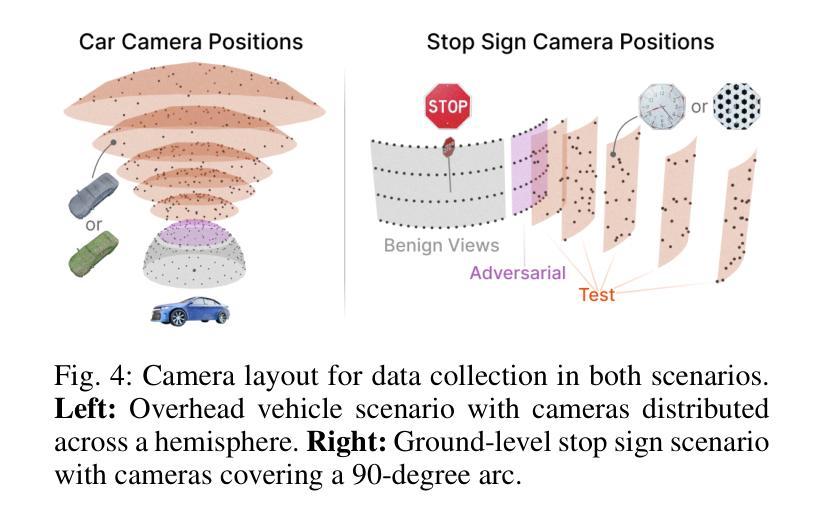

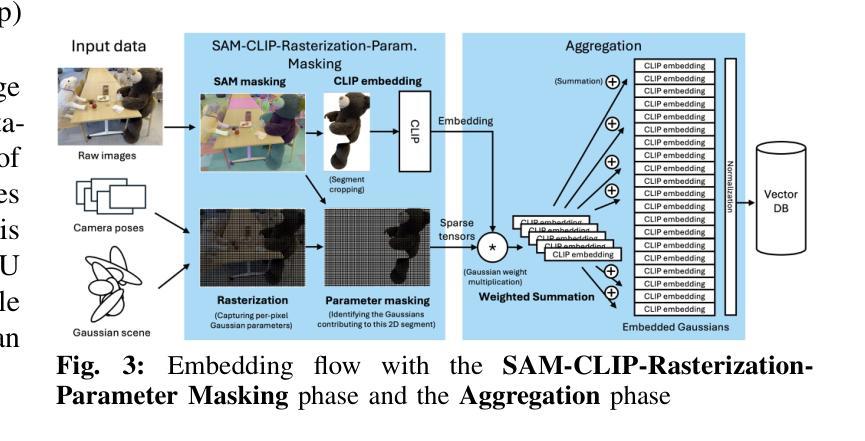
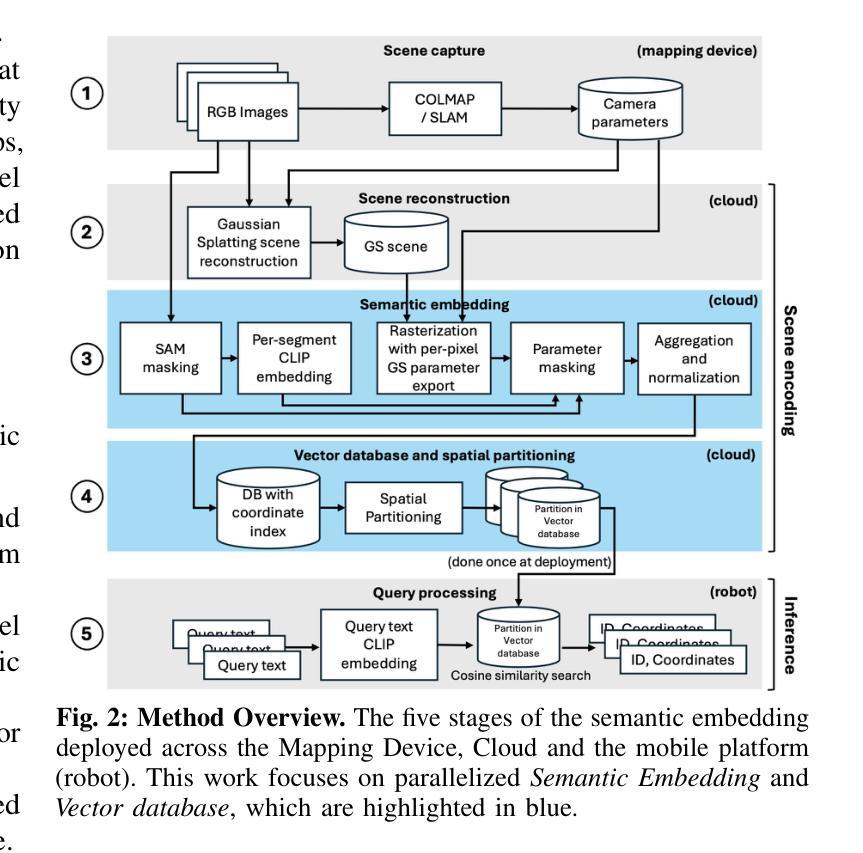
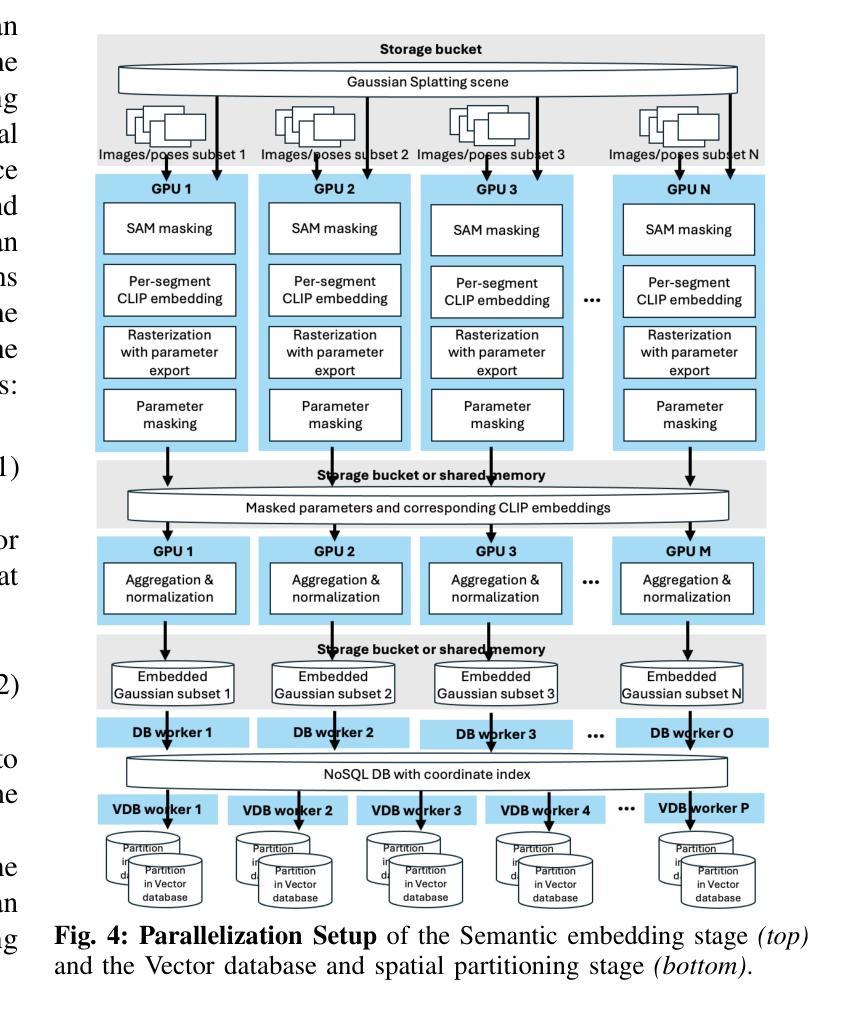
SLAG: Scalable Language-Augmented Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Laszlo Szilagyi, Francis Engelmann, Jeannette Bohg
Language-augmented scene representations hold great promise for large-scale robotics applications such as search-and-rescue, smart cities, and mining. Many of these scenarios are time-sensitive, requiring rapid scene encoding while also being data-intensive, necessitating scalable solutions. Deploying these representations on robots with limited computational resources further adds to the challenge. To address this, we introduce SLAG, a multi-GPU framework for language-augmented Gaussian splatting that enhances the speed and scalability of embedding large scenes. Our method integrates 2D visual-language model features into 3D scenes using SAM and CLIP. Unlike prior approaches, SLAG eliminates the need for a loss function to compute per-Gaussian language embeddings. Instead, it derives embeddings from 3D Gaussian scene parameters via a normalized weighted average, enabling highly parallelized scene encoding. Additionally, we introduce a vector database for efficient embedding storage and retrieval. Our experiments show that SLAG achieves an 18 times speedup in embedding computation on a 16-GPU setup compared to OpenGaussian, while preserving embedding quality on the ScanNet and LERF datasets. For more details, visit our project website: https://slag-project.github.io/.
语言增强的场景表示在大型机器人应用方面,如搜索和救援、智能城市和采矿等领域具有巨大潜力。许多这些场景都是时间敏感型的,需要快速场景编码,同时也是数据密集型的,需要可扩展的解决方案。在具有有限计算资源的机器人上部署这些表示形式进一步增加了挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了SLAG,这是一个用于语言增强高斯拼接的多GPU框架,它提高了嵌入大型场景的速度和可扩展性。我们的方法通过将2D视觉语言模型特征集成到3D场景中,使用SAM和CLIP。与以前的方法不同,SLAG不需要使用损失函数来计算每个高斯语言嵌入。相反,它通过归一化加权平均从3D高斯场景参数中提取嵌入,从而实现高度并行的场景编码。此外,我们还引入了一个向量数据库,用于有效地存储和检索嵌入。我们的实验表明,与OpenGaussian相比,SLAG在16 GPU设置上实现了嵌入计算的速度提升18倍,同时在ScanNet和LERF数据集上保持了嵌入质量。更多细节,请访问我们的项目网站:https://slag-project.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语言增强的场景表示在大型机器人应用,如搜救、智能城市和采矿等领域具有巨大潜力。为应对这些场景的时间敏感性和数据密集型特点,提出SLAG多GPU框架,采用语言增强的高斯点云技术,提高大场景嵌入的速度和可扩展性。该方法通过SAM和CLIP整合2D视觉语言模型特征到3D场景,无需损失函数计算每个高斯语言的嵌入。SLAG通过归一化加权平均从3D高斯场景参数中导出嵌入,实现高度并行的场景编码。此外,引入向量数据库,实现高效的嵌入存储和检索。实验表明,SLAG在16 GPU设置上实现了相对于OpenGaussian的18倍加速嵌入计算,同时在ScanNet和LERF数据集上保持了嵌入质量。
Key Takeaways
- 语言增强的场景表示在机器人应用中具有巨大潜力,特别是在大型、时间敏感、数据密集型的场景中。
- SLAG是一个多GPU框架,用于处理语言增强的高斯点云技术,提高大场景嵌入的速度和可扩展性。
- SLAG整合了2D视觉语言模型特征到3D场景,通过归一化加权平均导出嵌入,实现高度并行的场景编码。
- 与现有方法不同,SLAG无需损失函数计算语言嵌入。
- SLAG引入了向量数据库,实现了高效的嵌入存储和检索。
- 实验表明,SLAG在加速嵌入计算方面相对于OpenGaussian有显著优势,同时保持了嵌入质量。
点此查看论文截图

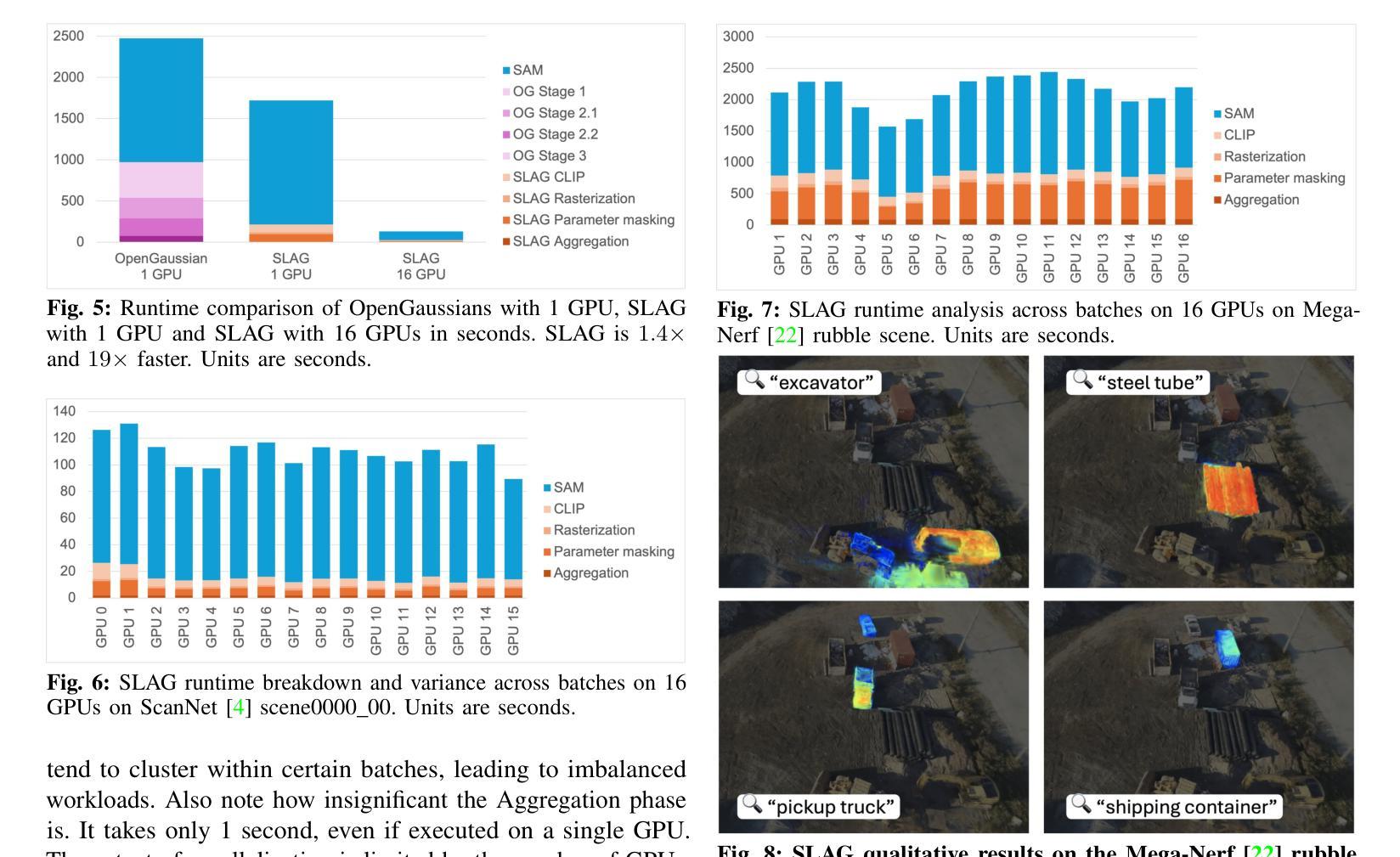
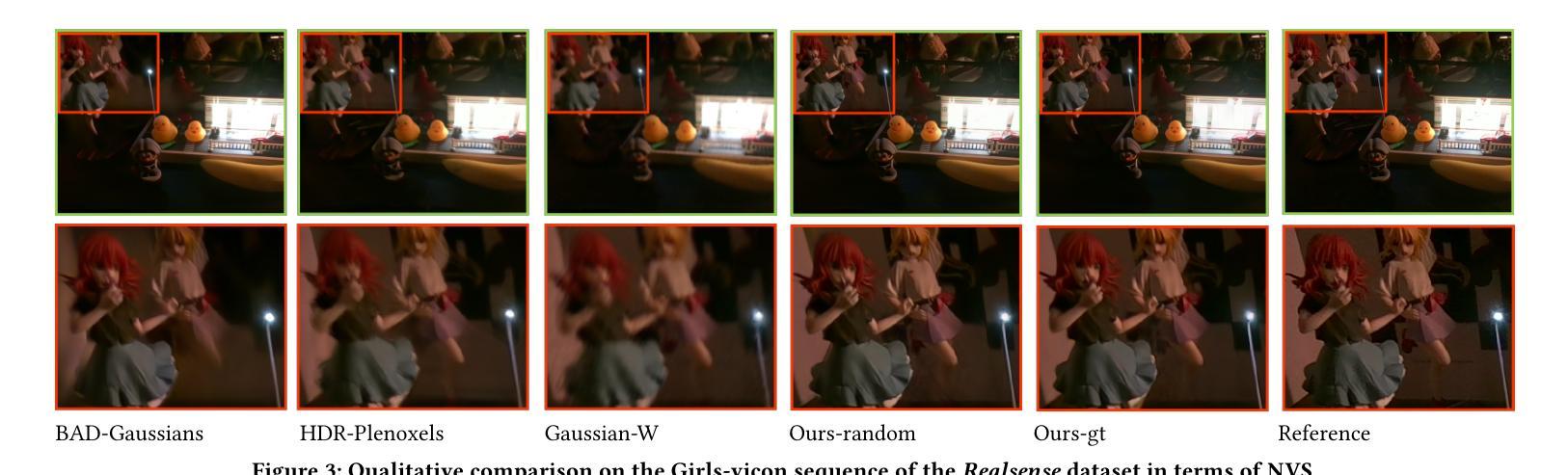
Casual3DHDR: Deblurring High Dynamic Range 3D Gaussian Splatting from Casually Captured Videos
Authors:Shucheng Gong, Lingzhe Zhao, Wenpu Li, Hong Xie, Yin Zhang, Shiyu Zhao, Peidong Liu
Photo-realistic novel view synthesis from multi-view images, such as neural radiance field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has gained significant attention for its superior performance. However, most existing methods rely on low dynamic range (LDR) images, limiting their ability to capture detailed scenes in high-contrast environments. While some prior works address high dynamic range (HDR) scene reconstruction, they typically require multi-view sharp images with varying exposure times captured at fixed camera positions, which is time-consuming and impractical. To make data acquisition more flexible, we propose \textbf{Casual3DHDR}, a robust one-stage method that reconstructs 3D HDR scenes from casually-captured auto-exposure (AE) videos, even under severe motion blur and unknown, varying exposure times. Our approach integrates a continuous-time camera trajectory into a unified physical imaging model, jointly optimizing exposure times, camera trajectory, and the camera response function (CRF). Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that \textbf{Casual3DHDR} outperforms existing methods in robustness and rendering quality. Our source code and dataset will be available at https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/
基于多视角图像的光照真实感新型视图合成,例如神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),因其卓越性能而受到广泛关注。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于低动态范围(LDR)图像,限制了它们在高对比度环境中捕捉精细场景的能力。虽然一些早期的工作解决了高动态范围(HDR)场景重建问题,但它们通常需要固定相机位置拍摄的多视角清晰图像,这些图像具有不同的曝光时间,既耗时又不切实际。为了使数据采集更加灵活,我们提出了一种稳健的一次性方法\textbf{Casual3DHDR},可从随意捕获的自动曝光(AE)视频中重建3D HDR场景,即使在严重运动模糊和未知、变化的曝光时间下也可实现。我们的方法将连续时间相机轨迹集成到一个统一的物理成像模型中,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数(CRF)。在合成和真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,\textbf{Casual3DHDR}在鲁棒性和渲染质量方面优于现有方法。我们的源代码和数据集将在https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2025. Project page: https://lingzhezhao.github.io/CasualHDRSplat/
Summary
该文介绍了基于神经辐射场和3D高斯贴图技术的真实小说视角合成技术。针对现有方法在低动态范围图像上的局限性,提出一种名为Casual3DHDR的新方法,能够从非专业拍摄的自拍视频重建出三维高动态范围场景,并在严重运动模糊和未知、变化曝光时间下表现优异。该方法整合连续时间相机轨迹至统一物理成像模型,联合优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数。实验证明Casual3DHDR在稳健性和渲染质量上超越现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 真实小说视角合成技术结合神经辐射场和3D高斯贴图技术受到关注。
- 现有方法主要依赖低动态范围图像,难以捕捉高对比场景细节。
- 提出Casual3DHDR方法,能从非专业拍摄的自拍视频重建三维高动态范围场景。
- Casual3DHDR在严重运动模糊和未知、变化曝光时间下表现优异。
- 方法整合连续时间相机轨迹至物理成像模型,优化曝光时间、相机轨迹和相机响应函数。
- 实验证明Casual3DHDR在稳健性和渲染质量上超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
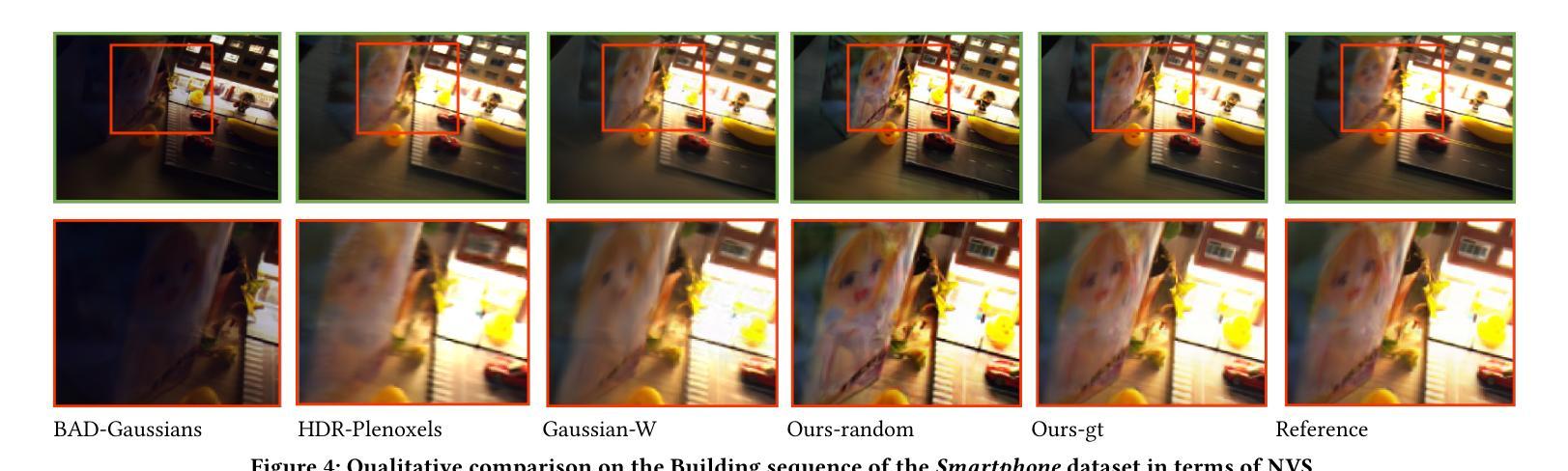
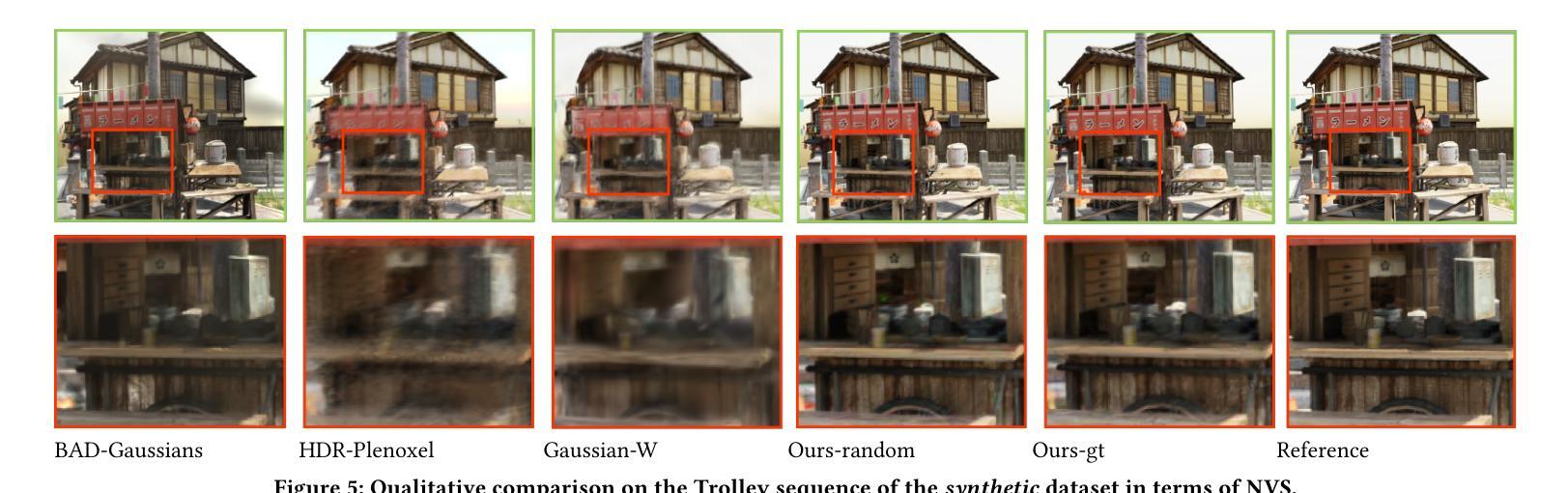

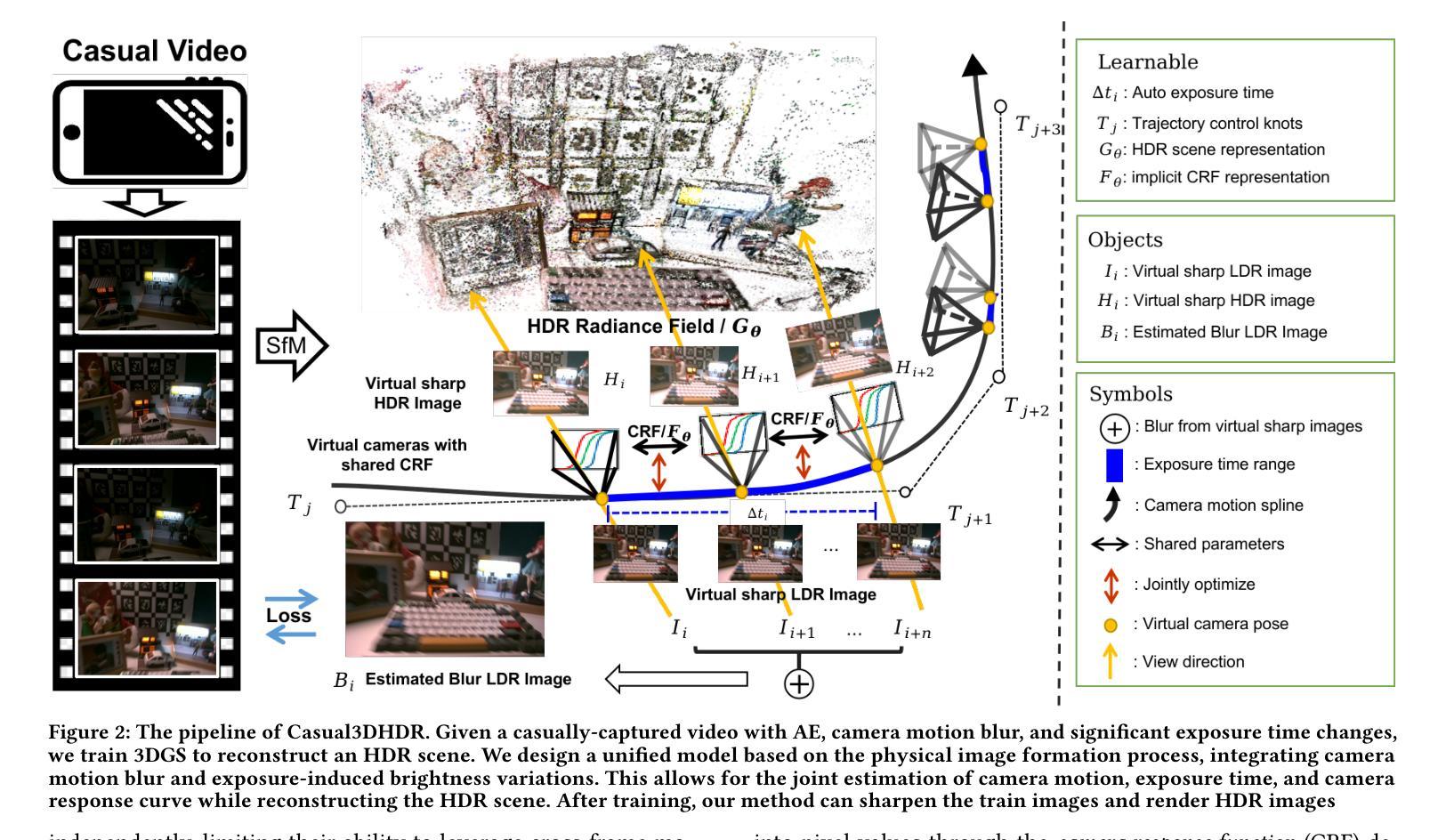




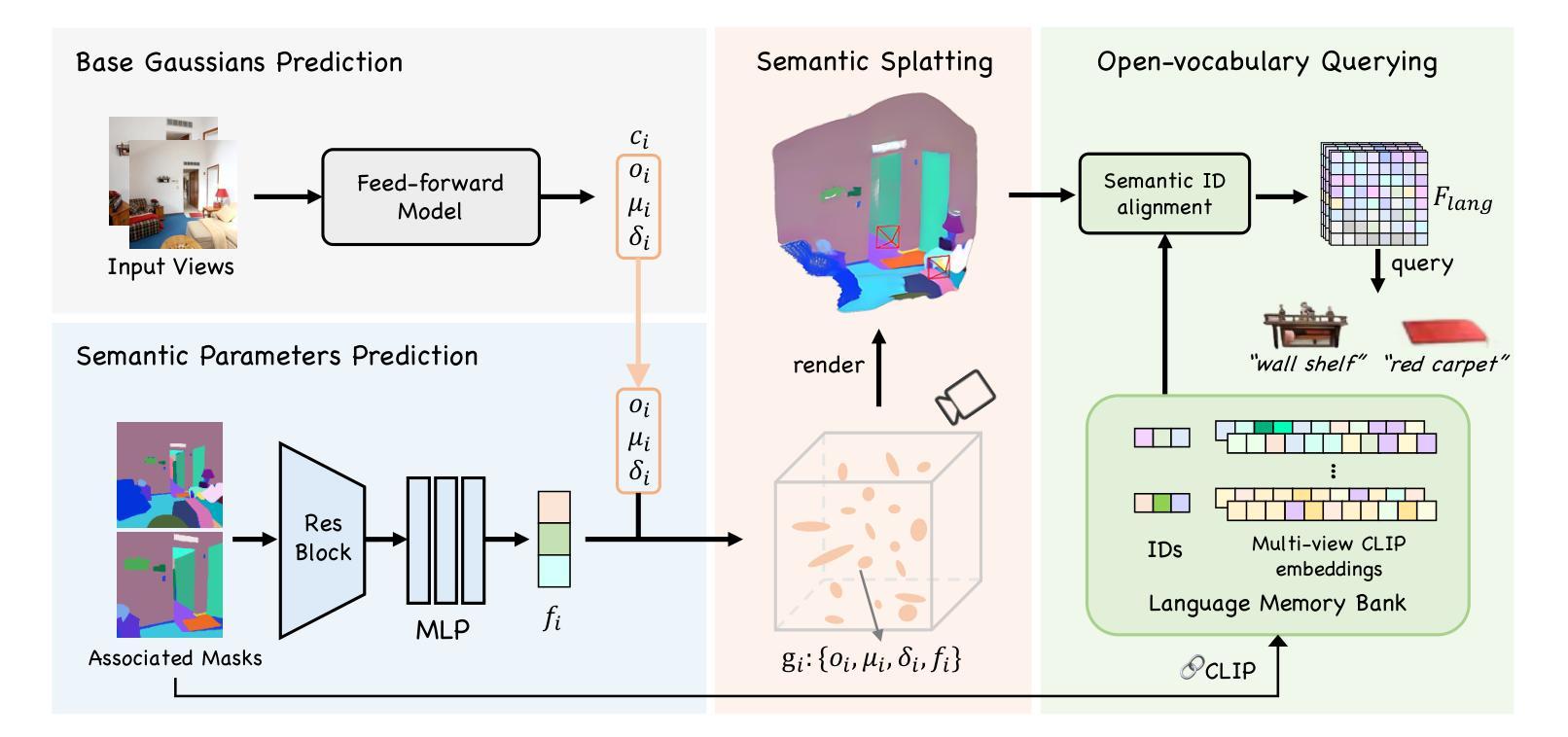
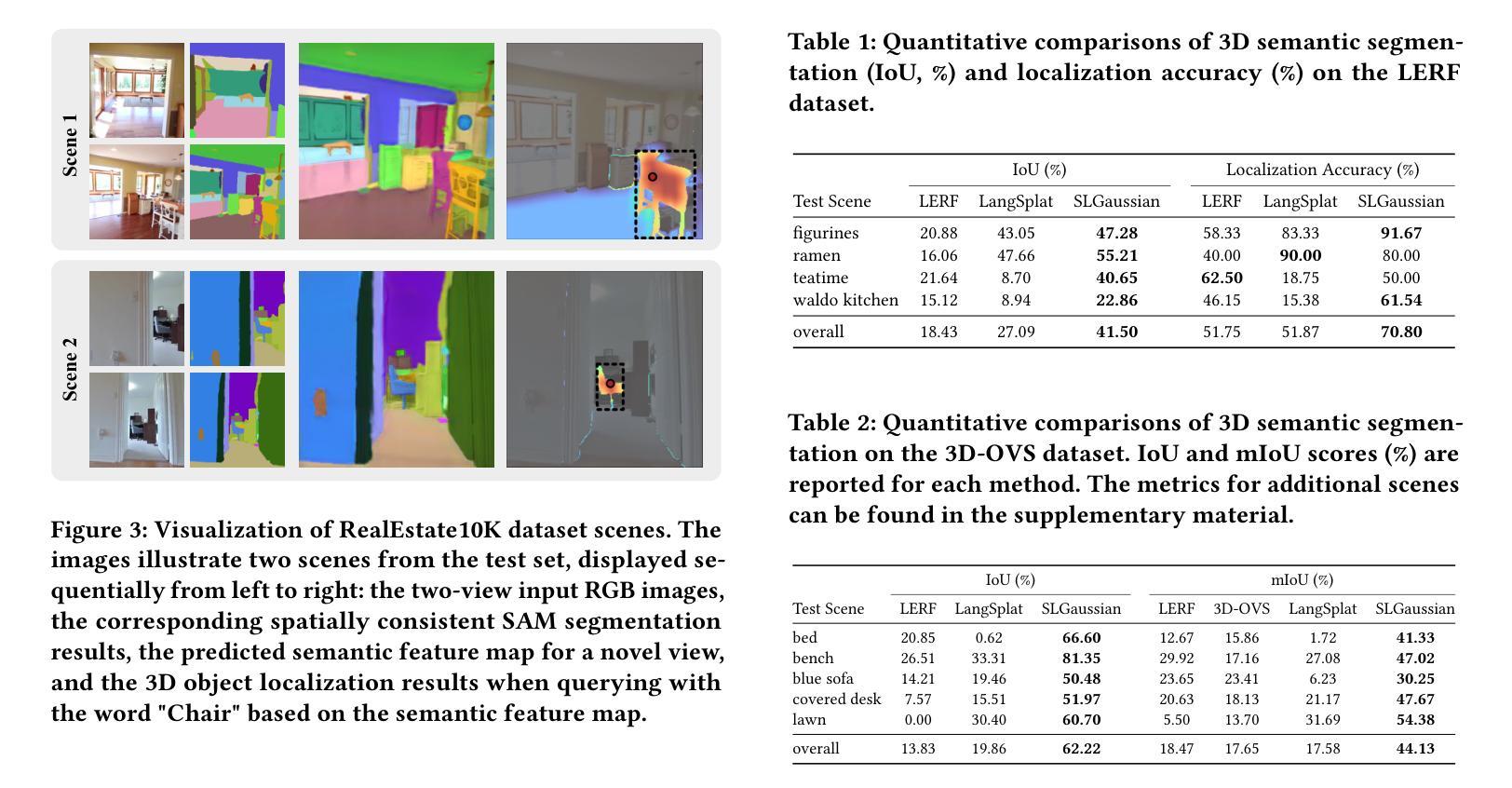
SLGaussian: Fast Language Gaussian Splatting in Sparse Views
Authors:Kangjie Chen, BingQuan Dai, Minghan Qin, Dongbin Zhang, Peihao Li, Yingshuang Zou, Haoqian Wang
3D semantic field learning is crucial for applications like autonomous navigation, AR/VR, and robotics, where accurate comprehension of 3D scenes from limited viewpoints is essential. Existing methods struggle under sparse view conditions, relying on inefficient per-scene multi-view optimizations, which are impractical for many real-world tasks. To address this, we propose SLGaussian, a feed-forward method for constructing 3D semantic fields from sparse viewpoints, allowing direct inference of 3DGS-based scenes. By ensuring consistent SAM segmentations through video tracking and using low-dimensional indexing for high-dimensional CLIP features, SLGaussian efficiently embeds language information in 3D space, offering a robust solution for accurate 3D scene understanding under sparse view conditions. In experiments on two-view sparse 3D object querying and segmentation in the LERF and 3D-OVS datasets, SLGaussian outperforms existing methods in chosen IoU, Localization Accuracy, and mIoU. Moreover, our model achieves scene inference in under 30 seconds and open-vocabulary querying in just 0.011 seconds per query.
三维语义场学习对于自主导航、AR/VR和机器人等应用至关重要,这些应用需要准确理解从有限视角观察到的三维场景。现有方法在稀疏视角条件下表现不佳,依赖于不切实际的场景多视角优化,这在许多现实世界任务中并不实用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SLGaussian方法,这是一种前馈方法,可以从稀疏视角构建三维语义场,允许直接推断基于3DGS的场景。通过确保通过视频跟踪的一致性SAM分割,并使用低维索引处理高维CLIP特征,SLGaussian有效地将语言信息嵌入三维空间,为稀疏视角条件下的准确三维场景理解提供了稳健的解决方案。在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的两视角稀疏三维对象查询和分割实验表明,SLGaussian在选定的IoU、定位精度和mIoU方面优于现有方法。此外,我们的模型能够在不到30秒内实现场景推断,每次查询的开放词汇查询时间仅为0.011秒。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025. Project page: https://chenkangjie1123.github.io/SLGaussian.github.io/
摘要
SLGaussian能够从稀疏视角构建三维语义场,解决真实场景中有限视角下的三维场景理解问题。该方法将语言信息嵌入三维空间,并通过视频跟踪确保SAM分割的一致性,采用高维CLIP特征的低维索引实现高效嵌入。在稀疏两视图三维物体查询和分割实验中,SLGaussian在IoU、定位精度和mIoU等方面优于现有方法,场景推理时间小于30秒,开放词汇查询每秒可达0.01次。该方法对自主导航、AR/VR和机器人等应用具有重要意义。
关键见解
- SLGaussian解决了现有方法在稀疏视角条件下对三维场景理解的困难。
- 通过高效嵌入语言信息至三维空间实现了精准的三维场景理解。
- 利用视频跟踪确保SAM分割的一致性,增强模型性能。
- 采用低维索引处理高维CLIP特征,提升效率。
- 在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的实验显示,SLGaussian在IoU、定位精度和mIoU等方面优于现有方法。
- SLGaussian可实现快速场景推理(小于30秒)。
点此查看论文截图
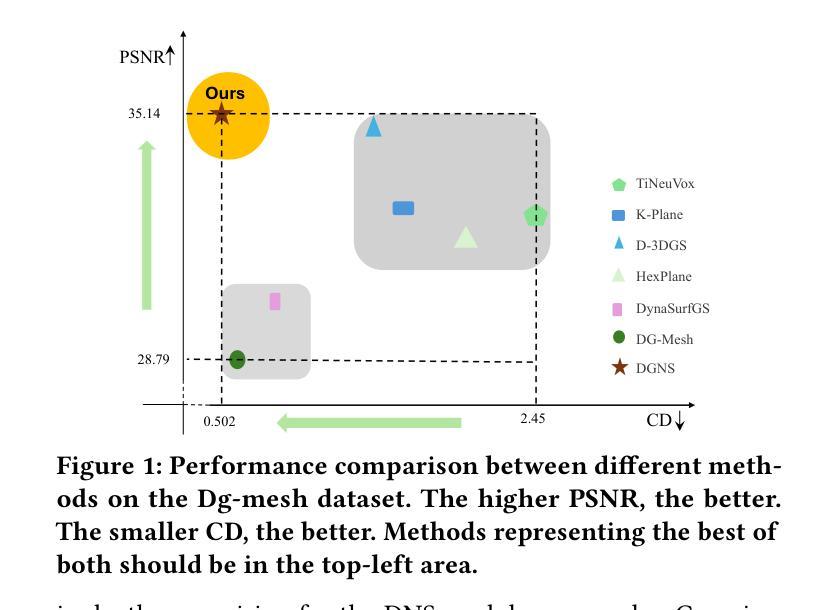
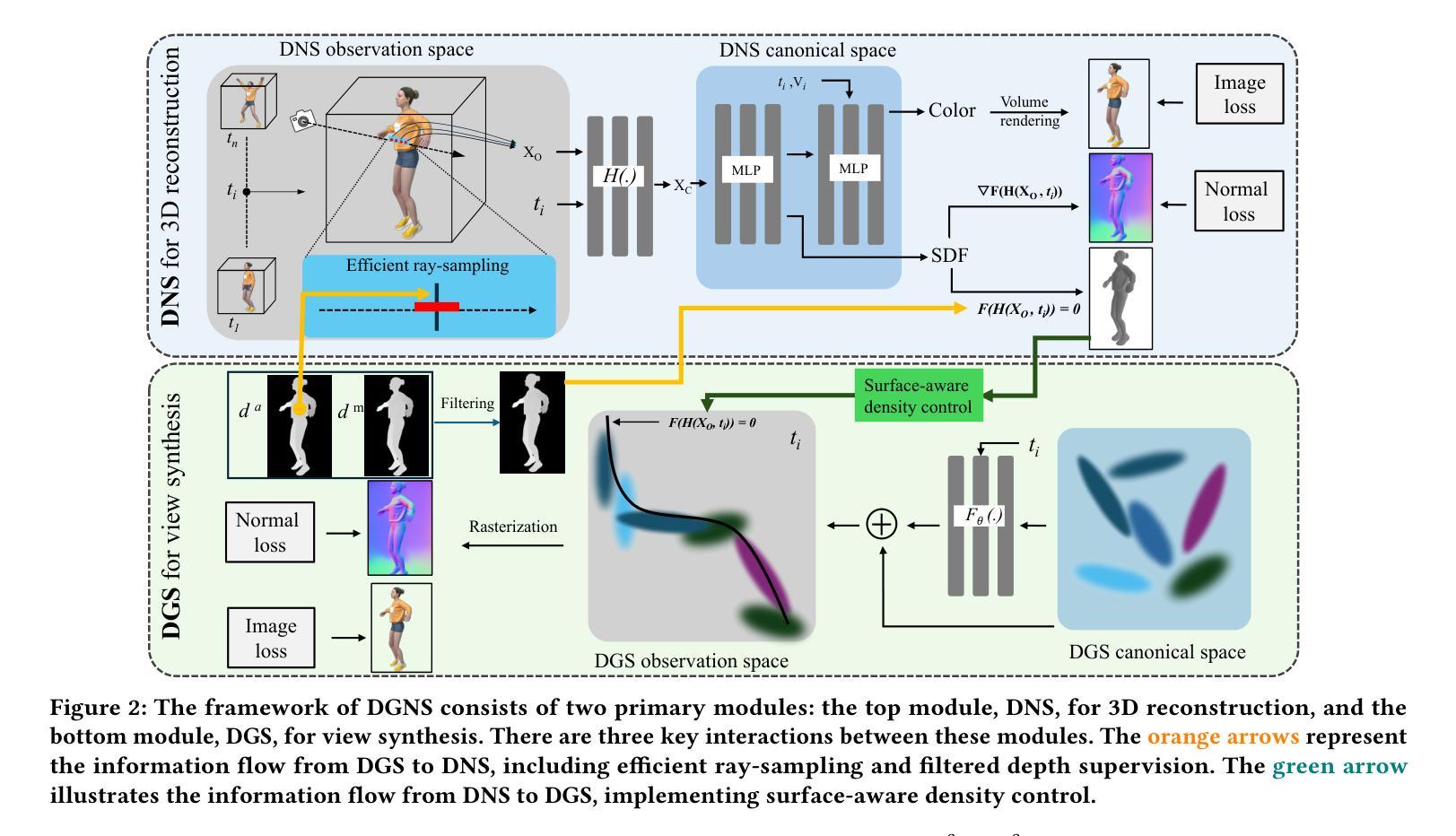
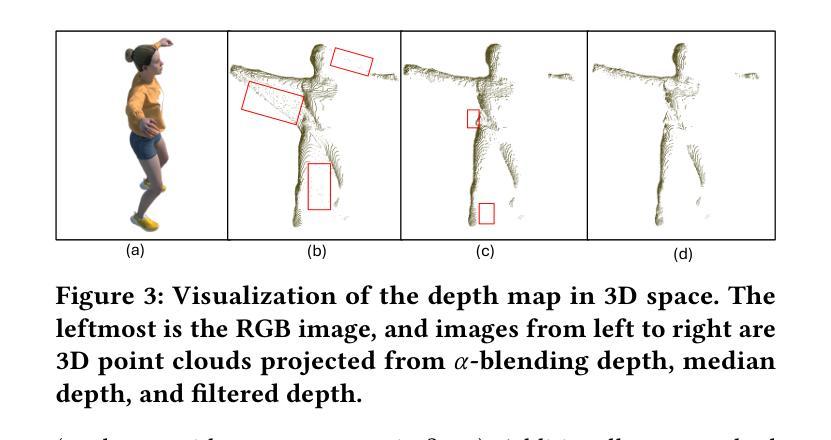
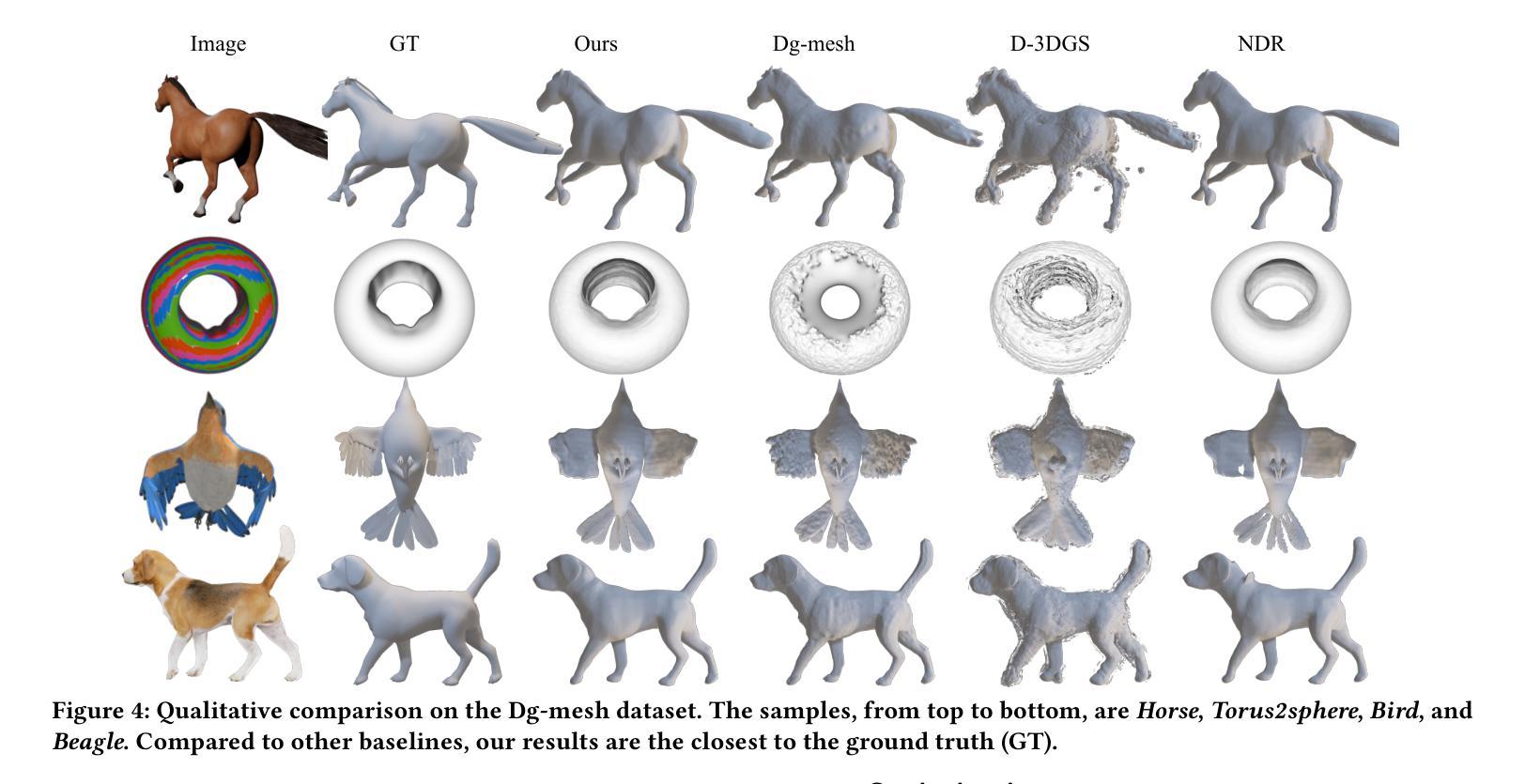
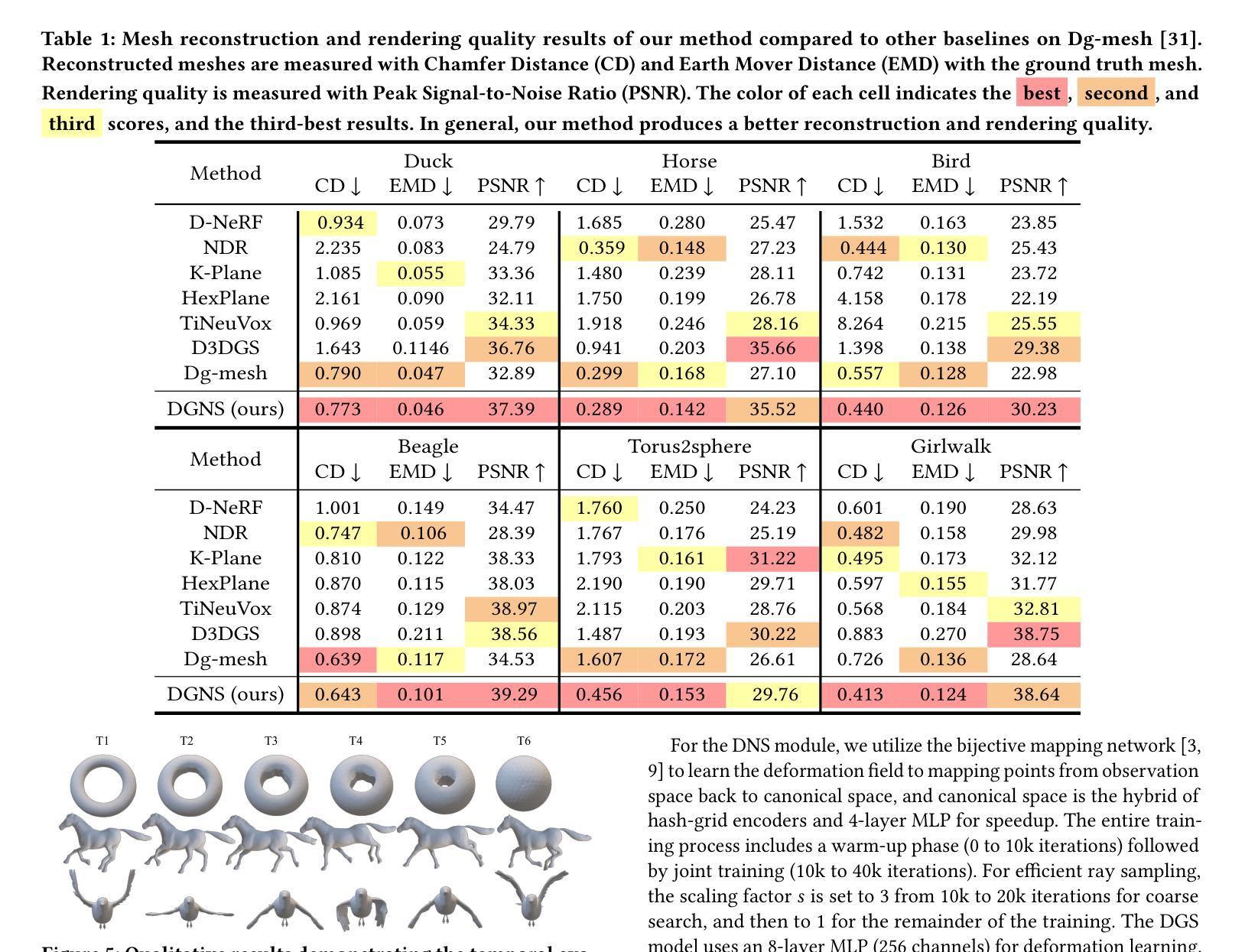
DGNS: Deformable Gaussian Splatting and Dynamic Neural Surface for Monocular Dynamic 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Xuesong Li, Jinguang Tong, Jie Hong, Vivien Rolland, Lars Petersson
Dynamic scene reconstruction from monocular video is essential for real-world applications. We introduce DGNS, a hybrid framework integrating \underline{D}eformable \underline{G}aussian Splatting and Dynamic \underline{N}eural \underline{S}urfaces, effectively addressing dynamic novel-view synthesis and 3D geometry reconstruction simultaneously. During training, depth maps generated by the deformable Gaussian splatting module guide the ray sampling for faster processing and provide depth supervision within the dynamic neural surface module to improve geometry reconstruction. Conversely, the dynamic neural surface directs the distribution of Gaussian primitives around the surface, enhancing rendering quality. In addition, we propose a depth-filtering approach to further refine depth supervision. Extensive experiments conducted on public datasets demonstrate that DGNS achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D reconstruction, along with competitive results in novel-view synthesis.
从单目视频中重建动态场景对于实际应用至关重要。我们引入了DGNS,这是一个混合框架,集成了可变形的高斯喷绘(Deformable Gaussian Splatting)和动态神经网络表面(Dynamic Neural Surfaces),可以有效地同时处理动态新颖视图合成和3D几何重建。在训练过程中,由可变形高斯喷绘模块生成的深度图引导光线采样以实现更快的处理速度,并在动态神经网络模块内部提供深度监督,以提高几何重建的效果。相反,动态神经网络表面指导高斯原始元素在表面周围的分布,从而提高渲染质量。此外,我们还提出了一种深度过滤方法来进一步优化深度监督。在公共数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,DGNS在3D重建方面达到了最新技术水平,同时在新颖视图合成方面也取得了具有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代动态场景重建技术DGNS融合变形高斯喷溅和动态神经网络表面,能有效实现动态新视角合成和3D几何重建。DGNS通过深度图指导光线采样以提高处理速度,同时改进几何重建;动态神经网络表面则能提升渲染质量。采用深度过滤方法进一步优化深度监督,在公共数据集上取得最先进的3D重建性能及新视角合成竞争力表现。
Key Takeaways
- DGNS是一个融合变形高斯喷溅和动态神经网络表面的混合框架,用于动态场景重建。
- DGNS能有效实现动态新视角合成和3D几何重建。
- 深度图在DGNS中起到重要作用,指导光线采样以提高处理速度,并改进几何重建。
- 动态神经网络表面能提升渲染质量,通过引导高斯原始数据的分布来实现。
- 采用深度过滤方法进一步优化深度监督,提高性能。
- DGNS在公共数据集上实现了先进的3D重建性能。
点此查看论文截图

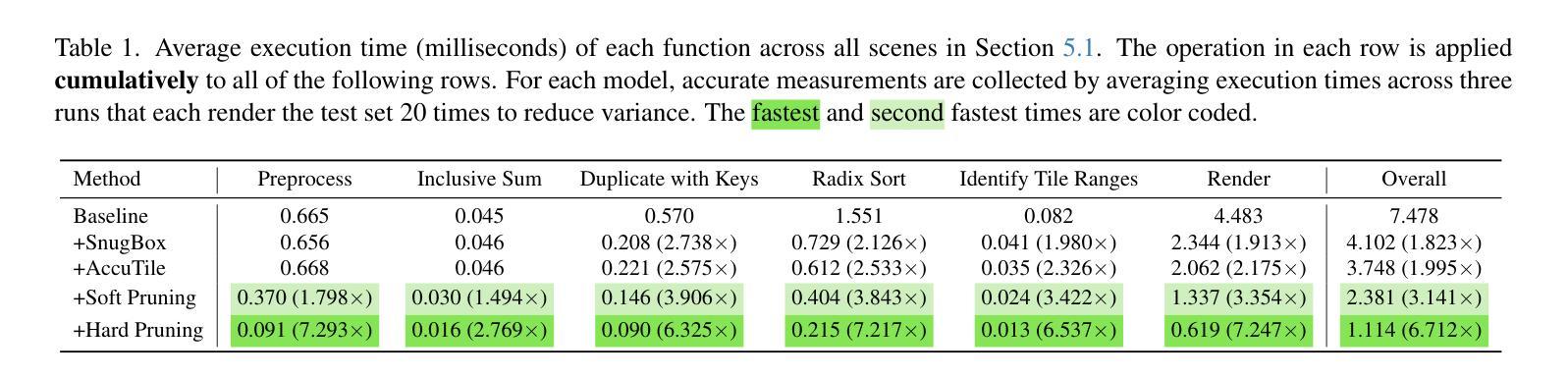
Speedy-Splat: Fast 3D Gaussian Splatting with Sparse Pixels and Sparse Primitives
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Geng Lin, Vasu Singla, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) is a recent 3D scene reconstruction technique that enables real-time rendering of novel views by modeling scenes as parametric point clouds of differentiable 3D Gaussians. However, its rendering speed and model size still present bottlenecks, especially in resource-constrained settings. In this paper, we identify and address two key inefficiencies in 3D-GS to substantially improve rendering speed. These improvements also yield the ancillary benefits of reduced model size and training time. First, we optimize the rendering pipeline to precisely localize Gaussians in the scene, boosting rendering speed without altering visual fidelity. Second, we introduce a novel pruning technique and integrate it into the training pipeline, significantly reducing model size and training time while further raising rendering speed. Our Speedy-Splat approach combines these techniques to accelerate average rendering speed by a drastic $\mathit{6.71\times}$ across scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
3D高斯展开技术(3D-GS)是一种最新的三维场景重建技术,它通过把场景建模为可微分的三维高斯参数点云来实现实时渲染新颖视角。然而,其渲染速度和模型大小仍然面临瓶颈,特别是在资源受限的环境中。在这篇论文中,我们识别并解决了在3D-GS中的两个关键低效问题,以显著提高渲染速度。这些改进还带来了模型大小和训练时间减少的辅助效益。首先,我们优化了渲染流程,精确地将高斯定位在场景中,以提高渲染速度而不影响视觉保真度。其次,我们引入了一种新型修剪技术并将其集成到训练流程中,在进一步提高了渲染速度的同时显著减少了模型大小和训练时间。我们的Speedy-Splat方法结合了这些技术,在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集的场景中平均渲染速度提高了惊人的6.71倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://speedysplat.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了针对实时渲染瓶颈的改进版三维高斯点云渲染技术。通过优化渲染管道和引入新型修剪技术,该技术显著提高了渲染速度,同时减小了模型大小并缩短了训练时间。这些改进使场景渲染速度大幅提升,平均提升幅度达到$\times 6.71$倍。该技术的实施对场景重建领域具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了新的三维高斯点云渲染技术改进版本。此技术提高了实时渲染性能。
- 优化渲染管道以提高渲染速度,且不影响视觉保真度。这种优化能大幅提高渲染效率。
- 引入了一种新型修剪技术并将其集成到训练管道中,显著减小模型大小并缩短训练时间。这种修剪技术进一步提高了渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图

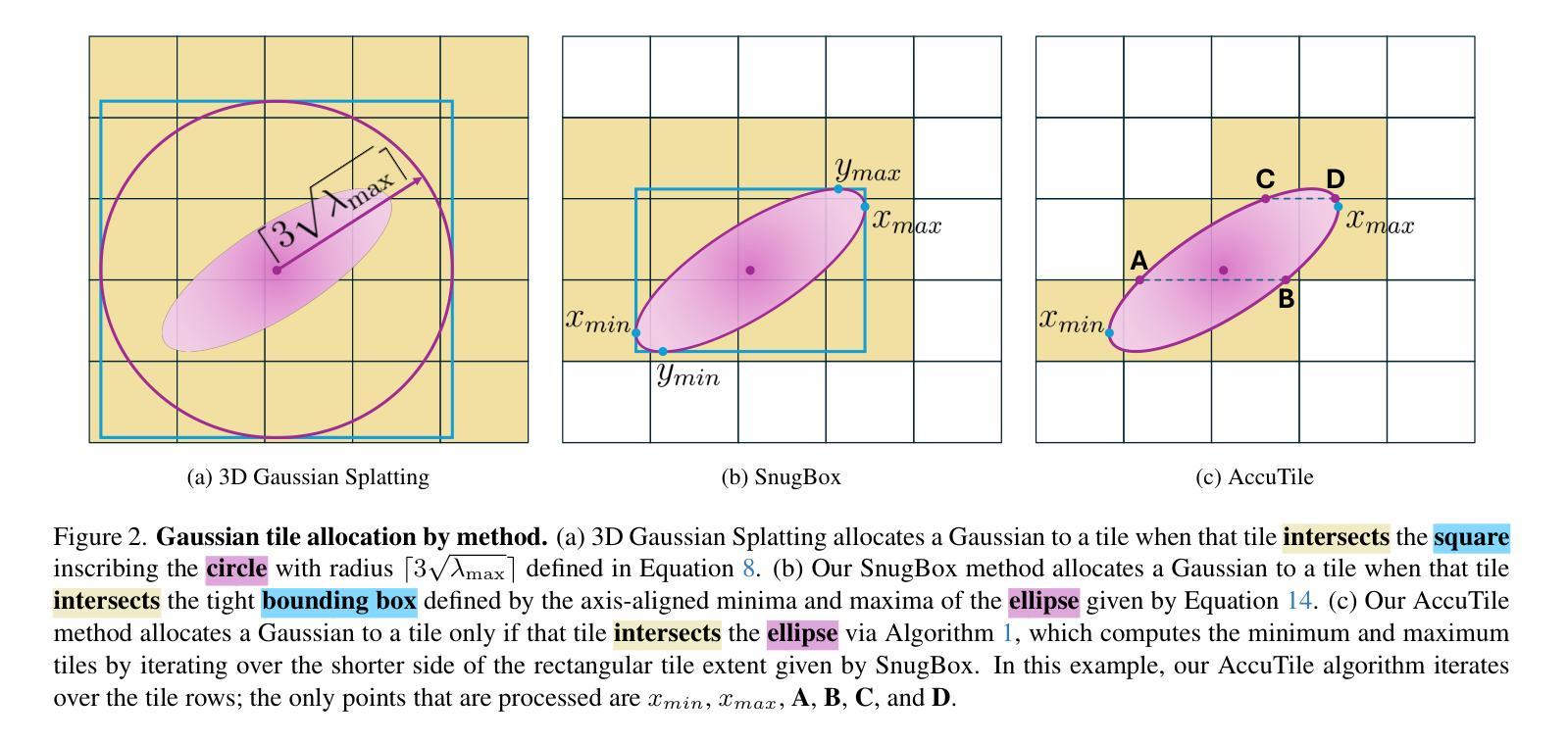

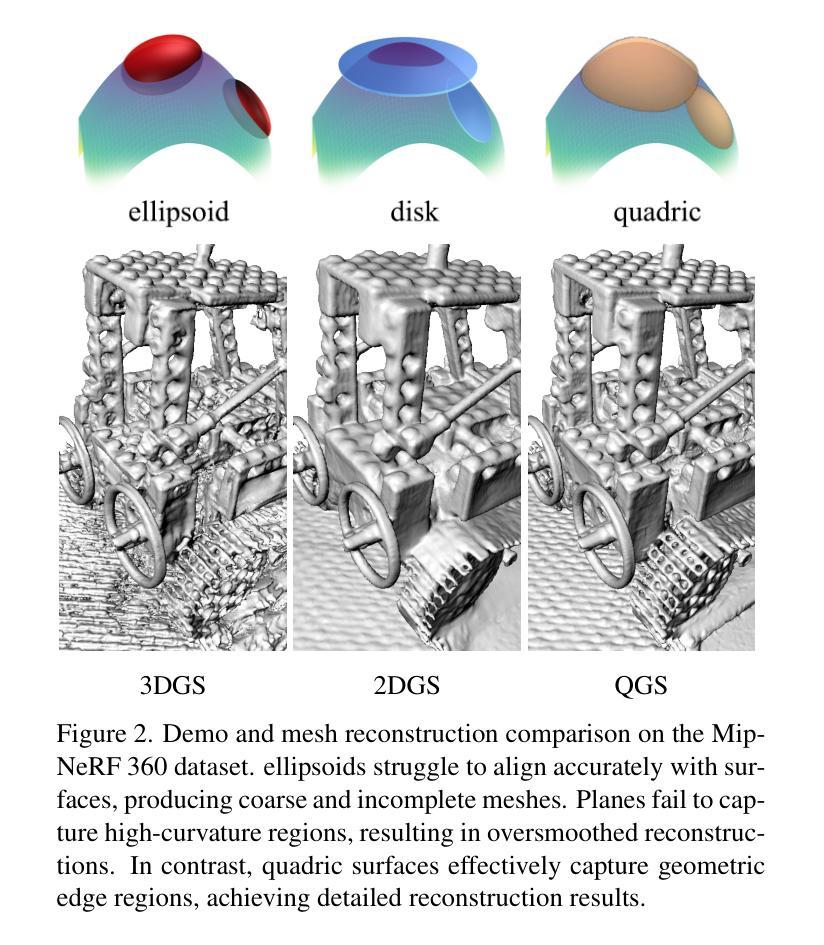
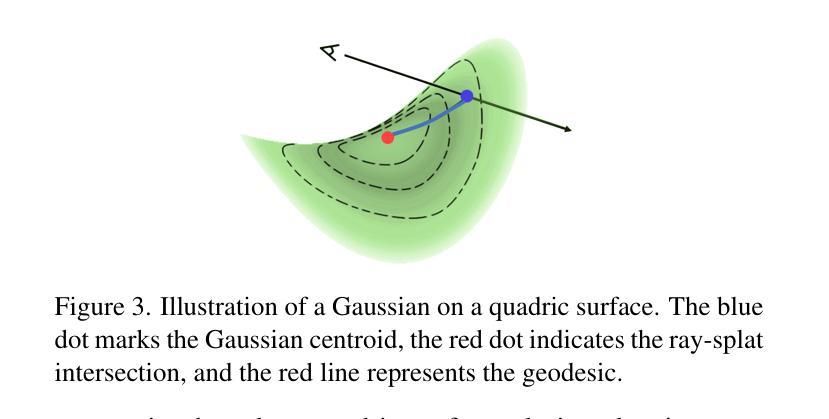
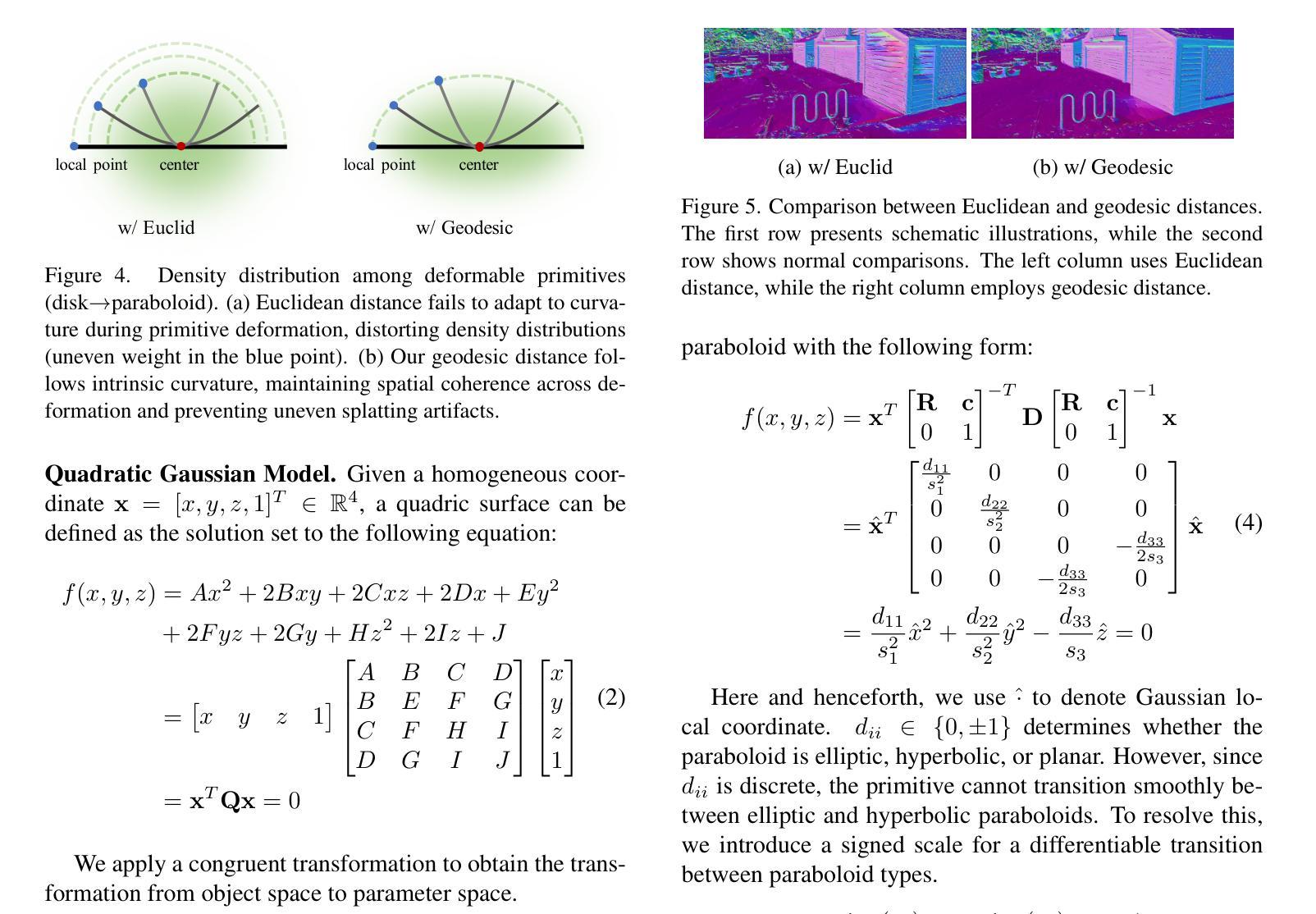
Quadratic Gaussian Splatting: High Quality Surface Reconstruction with Second-order Geometric Primitives
Authors:Ziyu Zhang, Binbin Huang, Hanqing Jiang, Liyang Zhou, Xiaojun Xiang, Shunhan Shen
We propose Quadratic Gaussian Splatting (QGS), a novel representation that replaces static primitives with deformable quadric surfaces (e.g., ellipse, paraboloids) to capture intricate geometry. Unlike prior works that rely on Euclidean distance for primitive density modeling–a metric misaligned with surface geometry under deformation–QGS introduces geodesic distance-based density distributions. This innovation ensures that density weights adapt intrinsically to the primitive curvature, preserving consistency during shape changes (e.g., from planar disks to curved paraboloids). By solving geodesic distances in closed form on quadric surfaces, QGS enables surface-aware splatting, where a single primitive can represent complex curvature that previously required dozens of planar surfels, potentially reducing memory usage while maintaining efficient rendering via fast ray-quadric intersection. Experiments on DTU, Tanks and Temples, and MipNeRF360 datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art surface reconstruction, with QGS reducing geometric error (chamfer distance) by 33% over 2DGS and 27% over GOF on the DTU dataset. Crucially, QGS retains competitive appearance quality, bridging the gap between geometric precision and visual fidelity for applications like robotics and immersive reality.
我们提出了二次高斯贴图(Quadratic Gaussian Splatting,简称QGS)这一新型表达方式,它以可变形的二次曲面(如椭圆、抛物线等)替代静态的原始图形,以捕捉复杂的几何结构。不同于先前依赖欧几里得距离进行原始密度建模的作品——这一度量方式与变形下的表面几何结构不匹配——QGS引入了基于测地距离(geodesic distance)的密度分布。这一创新确保了密度权重能够自适应于原始曲率,在形状变化(例如从平面圆盘到弯曲的抛物线)过程中保持一致性。通过在二次曲面上解决封闭形式的测地距离问题,QGS能够实现表面感知贴图,其中单个原始图形可以代表之前需要数十个平面表面的复杂曲率,从而在保持高效渲染(通过快速的射线与二次曲面相交)的同时,可能减少内存使用。在DTU、Tanks and Temples以及MipNeRF360数据集上的实验表明,QGS在表面重建方面达到了最先进的水平,相对于二维几何贴图(2DGS)减少了33%的几何误差(混错距离),相对于GOF在DTU数据集上减少了27%。关键的是,QGS保持了竞争力的外观质量,在机器人和沉浸式现实等应用中,在几何精度和视觉保真度之间架起了桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16pages,18figures
Summary
一种名为Quadratic Gaussian Splatting(QGS)的新型表示方法,通过引入可变形的二次曲面(如椭圆、抛物线等)来捕捉复杂的几何形状,替换静态的原始模型。该方法创新性地采用基于测地距离(geodesic distance)的密度分布,使密度权重能够自适应原始曲率的变形,保证形状变化时的一致性。通过解决二次曲面上的测地距离问题,QGS实现了表面感知的拼接技术,单个原始模型可以代表复杂的曲面,可能大大减少内存使用,同时保持高效的渲染速度。实验证明,QGS在表面重建上具有最佳状态,减少了几何误差,并在某些数据集上超越了其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- QGS引入可变形二次曲面捕捉复杂几何形状,替换静态原始模型。
- 采用基于测地距离的密度分布,确保形状变化时密度权重的一致性。
- QGS实现表面感知的拼接技术,提高内存效率和渲染速度。
- QGS在表面重建上表现最佳状态,减少几何误差。
- QGS在DTU数据集上相比其他方法减少了几何错误约33%。
- QGS在保持几何精度的同时,具有优秀的视觉效果,适用于机器人和沉浸式现实等应用。
点此查看论文截图

Reconstructing Satellites in 3D from Amateur Telescope Images
Authors:Zhiming Chang, Boyang Liu, Yifei Xia, Youming Guo, Boxin Shi, He Sun
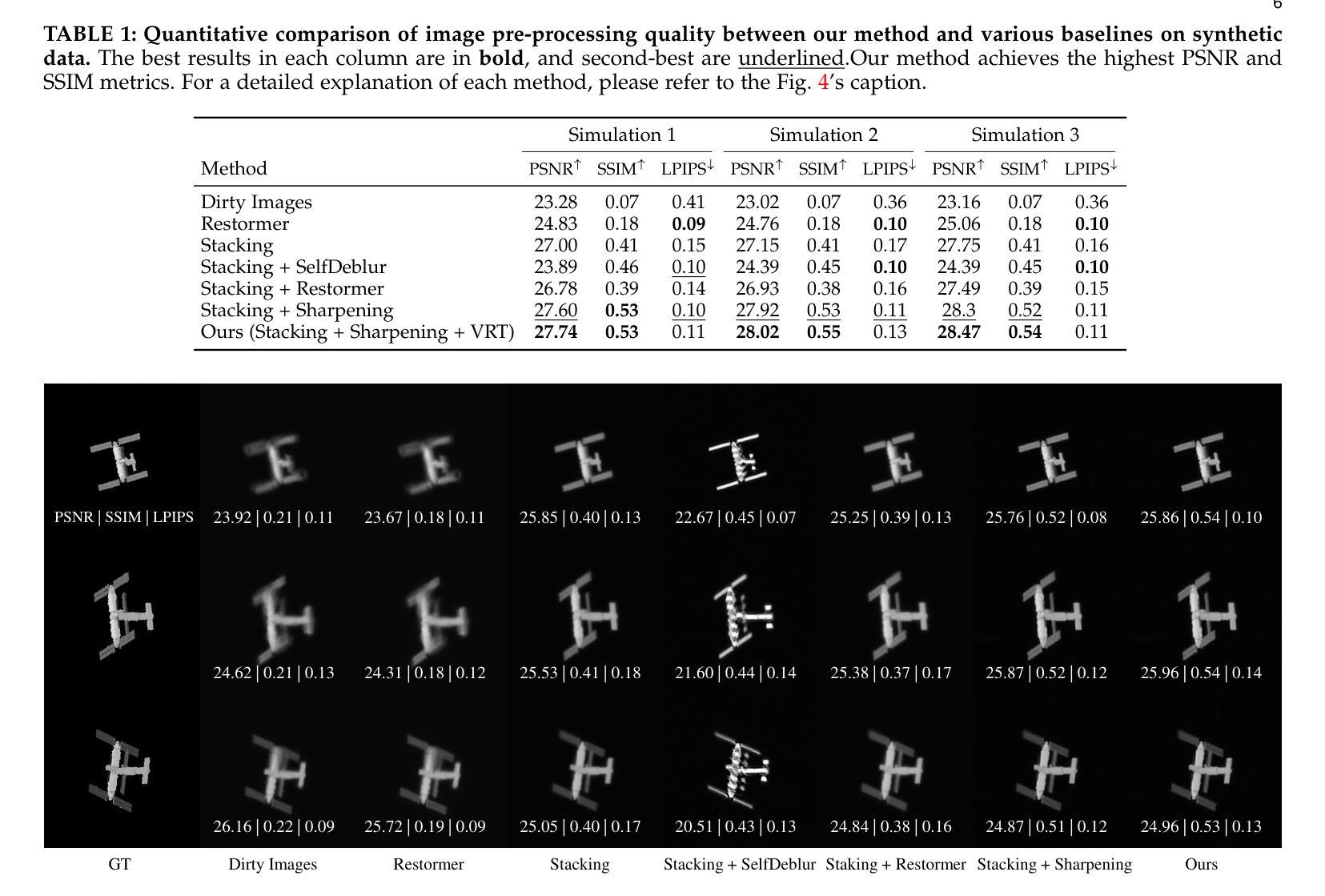
Monitoring space objects is crucial for space situational awareness, yet reconstructing 3D satellite models from ground-based telescope images is challenging due to atmospheric turbulence, long observation distances, limited viewpoints, and low signal-to-noise ratios. In this paper, we propose a novel computational imaging framework that overcomes these obstacles by integrating a hybrid image pre-processing pipeline with a joint pose estimation and 3D reconstruction module based on controlled Gaussian Splatting (GS) and Branch-and-Bound (BnB) search. We validate our approach on both synthetic satellite datasets and on-sky observations of China’s Tiangong Space Station and the International Space Station, achieving robust 3D reconstructions of low-Earth orbit satellites from ground-based data. Quantitative evaluations using SSIM, PSNR, LPIPS, and Chamfer Distance demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based approaches, and ablation studies confirm the critical role of each component. Our framework enables high-fidelity 3D satellite monitoring from Earth, offering a cost-effective alternative for space situational awareness. Project page: https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
对空间目标进行监测是获取太空态势感知的关键,然而,由于大气湍流、长观测距离、有限的观测视角以及信噪比低等因素,从地面望远镜图像重建卫星三维模型是一项挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,通过集成混合图像预处理管道和基于受控的高斯Splatting(GS)和分支界定(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和三维重建模块来克服这些障碍。我们在合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站以及国际空间站的实时天文观测上验证了我们的方法,实现了从地面数据对低地球轨道卫星的稳健三维重建。使用结构相似性度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)和Chamfer距离进行的定量评估表明,我们的方法优于最新的基于NeRF的方法,并且消融研究证实了每个组件的关键作用。我们的框架能够实现从地球的高保真三维卫星监测,为太空态势感知提供经济高效的替代方案。项目页面:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,通过整合混合图像预处理管道与基于受控高斯散斑(GS)和分支定界(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和三维重建模块,克服了从地面望远镜图像重建卫星三维模型的诸多挑战。该研究对合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站及国际空间站的实地观测进行了验证,实现了从地面数据稳健重建低地球轨道卫星的三维模型。定量评估表明,该方法优于现有的NeRF技术,各组件的作用至关重要。该研究为从地球进行的高保真三维卫星监测提供了成本效益高的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 监测空间物体对于空间态势感知至关重要,但从地面望远镜图像重建卫星三维模型具有挑战性。
- 本文提出了一种新型计算成像框架,整合了混合图像预处理管道和基于受控高斯散斑与分支定界搜索的联合姿态估计和三维重建模块。
- 该方法实现了对合成卫星数据集和真实卫星观测的稳健三维重建。
- 定量评估表明,该方法优于现有的NeRF技术。
- 消融研究证实了框架中每个组件的关键作用。
- 该框架为从地球进行的高保真三维卫星监测提供了可能。
点此查看论文截图