⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
WebMall – A Multi-Shop Benchmark for Evaluating Web Agents
Authors:Ralph Peeters, Aaron Steiner, Luca Schwarz, Julian Yuya Caspary, Christian Bizer
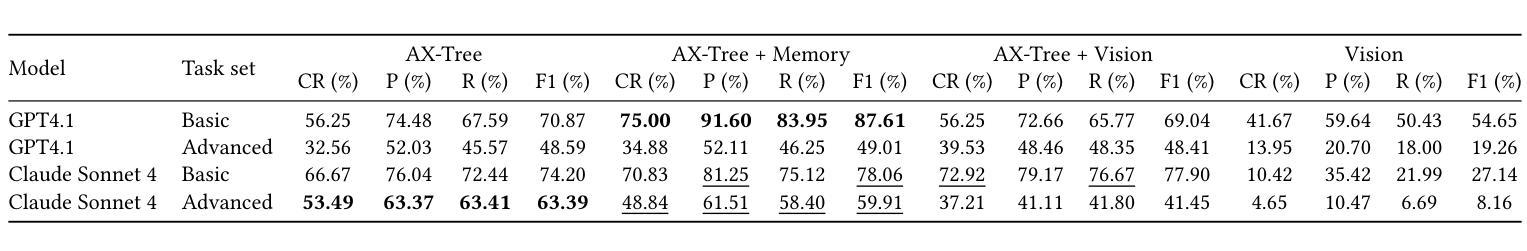
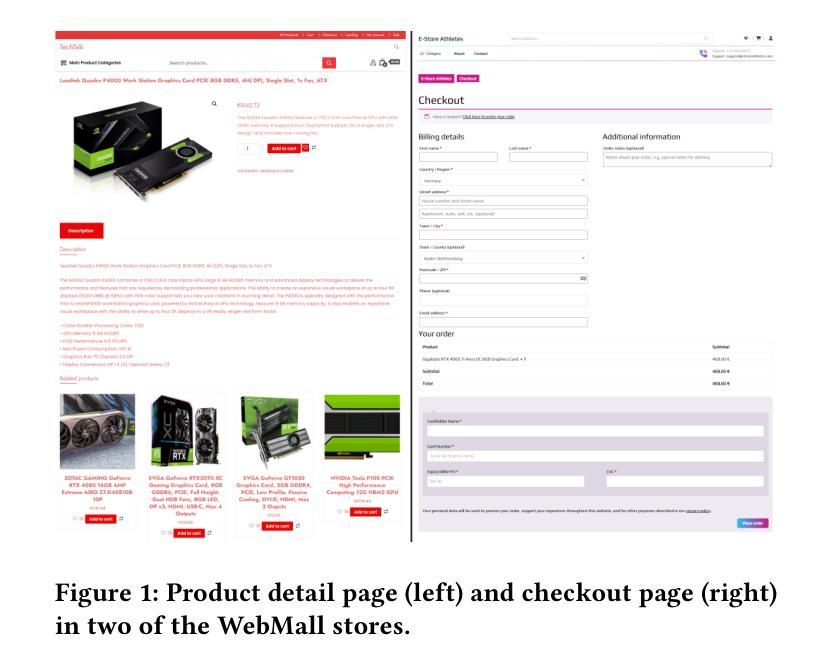
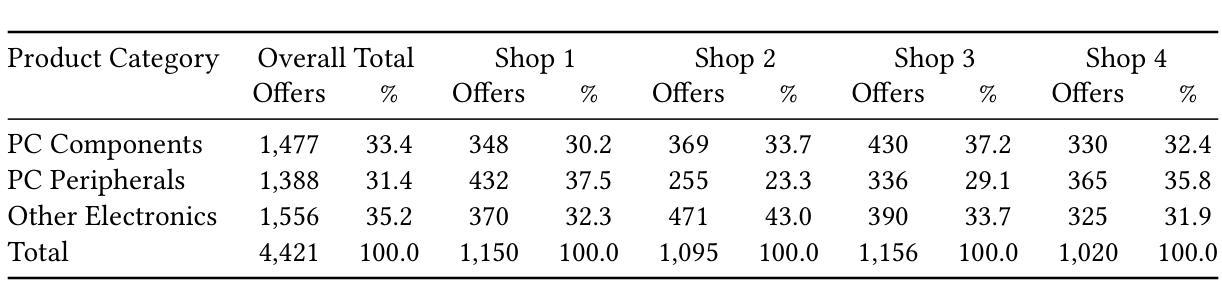
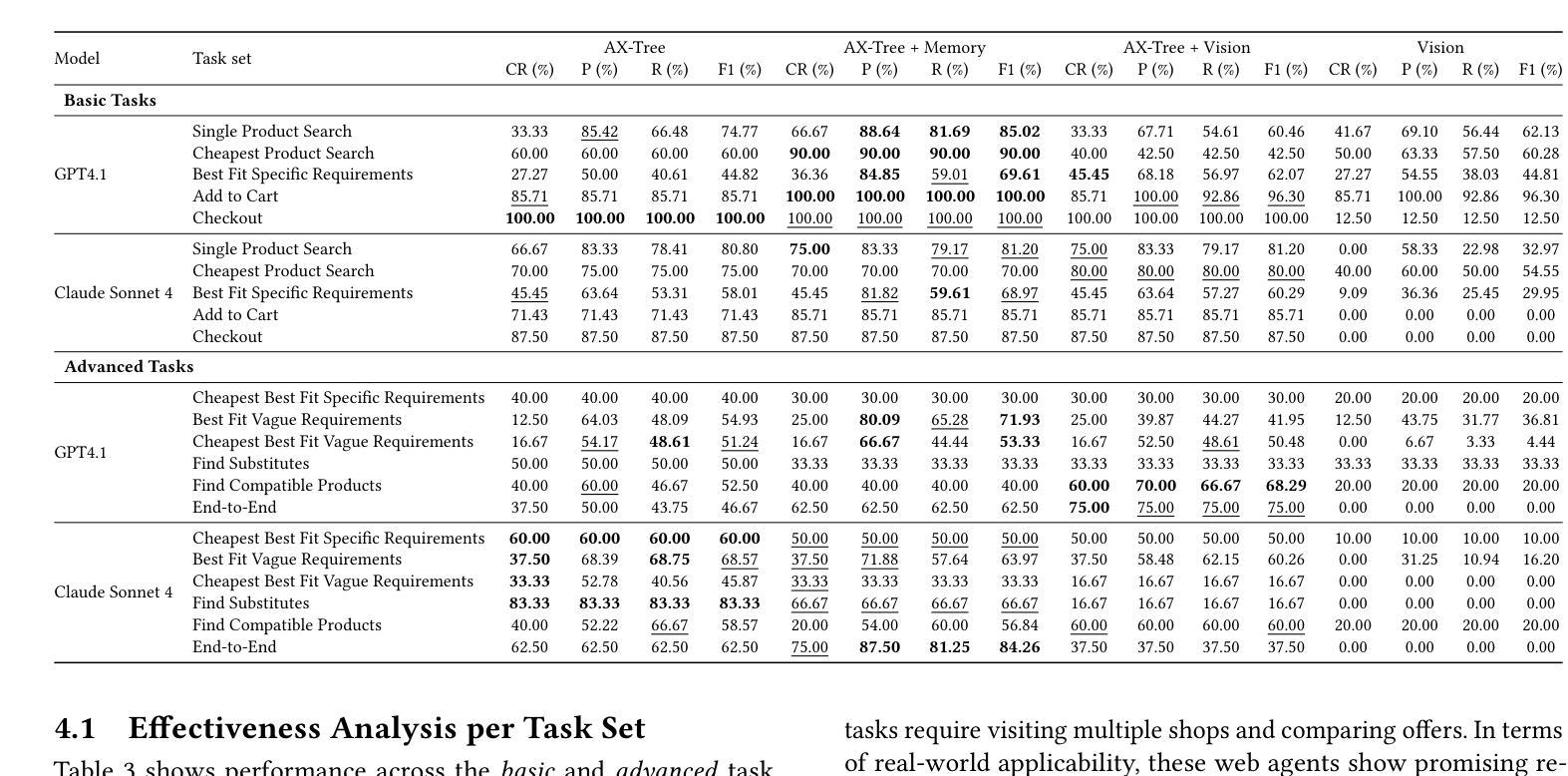
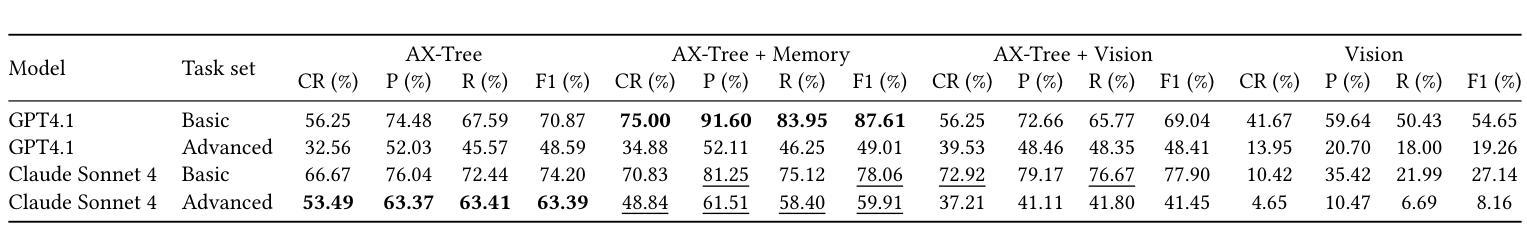
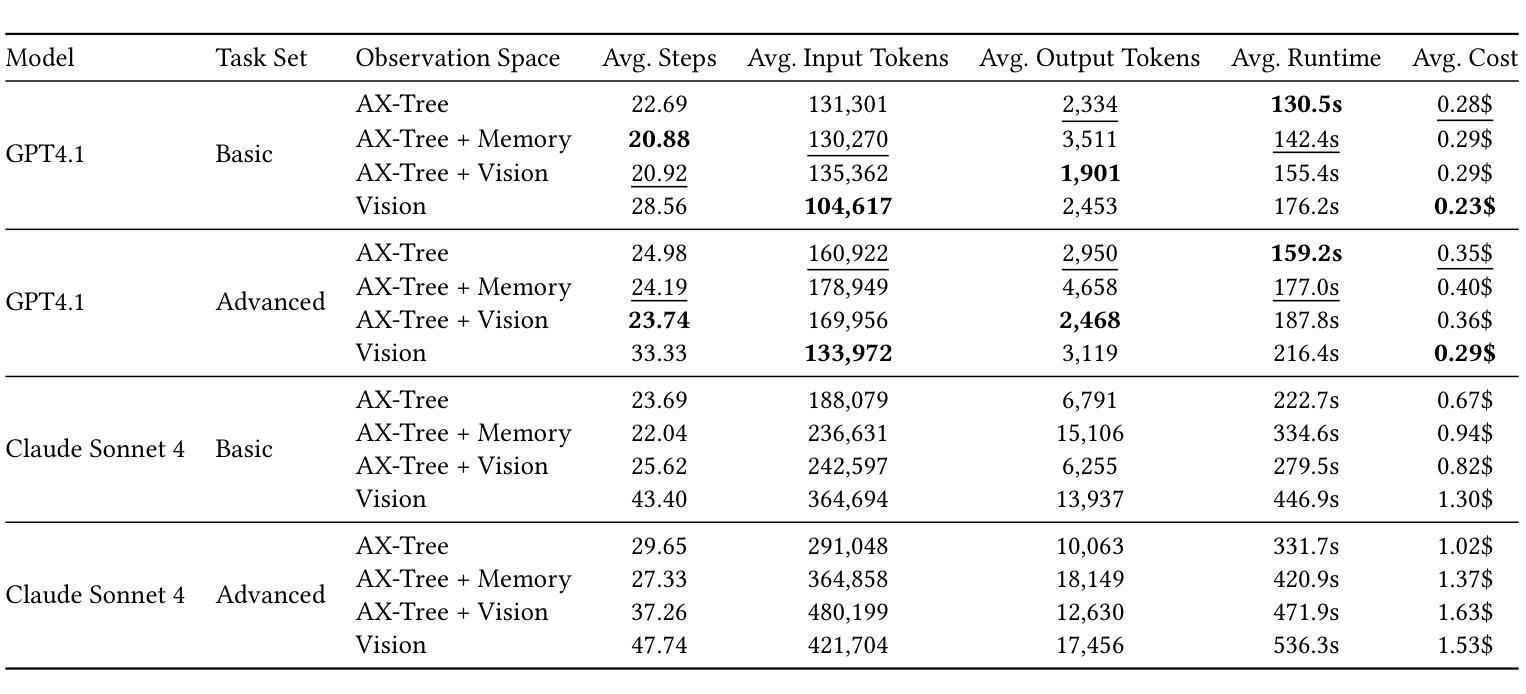
LLM-based web agents have the potential to automate long-running web tasks, such as finding offers for specific products in multiple online shops and subsequently ordering the cheapest products that meet the users needs. This paper introduces WebMall, a multi-shop online shopping benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of web agents for comparison-shopping. WebMall consists of four simulated online shops populated with authentic product offers sourced from the Common Crawl, alongside a suite of 91 cross-shop tasks. These tasks include basic tasks such as finding specific products in multiple shops, performing price comparisons, adding items to the shopping cart, and completing checkout. Advanced tasks involve searching for products based on vague requirements, identifying suitable substitutes, and finding compatible products. Compared to existing e-commerce benchmarks, such as WebShop or ShoppingBench, WebMall introduces comparison-shopping tasks across multiple shops. Furthermore, the product offers are more heterogeneous, as they originate from hundreds of distinct real-world shops. The tasks in WebMall require longer interaction trajectories than those in WebShop, while remaining representative of real-world shopping behaviors. We evaluate eight baseline agents on WebMall, varying in observation modality, memory utilization, and underlying large language model (GPT 4.1 and Claude Sonnet 4). The best-performing configurations achieve completion rates of 75% and 53%, and F1 scores of 87% and 63%, on the basic and advanced task sets, respectively. WebMall is publicly released to facilitate research on web agents and to promote advancements in navigation, reasoning, and efficiency within e-commerce scenarios.
基于LLM的Web代理具有自动化长期Web任务的潜力,例如在多间网上商店中寻找特定产品的优惠,然后订购符合用户需求的最低价格产品。本文介绍了WebMall,这是一个用于评估Web代理在比较购物中的有效性和效率的多店在线购物基准测试。WebMall由四个模拟在线商店组成,这些商店充满了来自Common Crawl的真实产品优惠信息,以及一套91个跨店任务。这些任务包括在多个商店中寻找特定产品、进行价格比较、将商品添加到购物车并完成结账等基本任务。高级任务包括根据模糊要求搜索产品、识别合适的替代品和寻找兼容产品。与现有的电子商务基准测试(如WebShop或ShoppingBench)相比,WebMall引入了跨多个商店的比较购物任务。此外,产品优惠更加多样化,因为它们来源于数百个不同的真实商店。WebMall中的任务需要比WebShop更长的交互轨迹,同时仍然代表真实世界的购物行为。我们在WebMall上评估了八种基线代理,它们在观察模式、内存利用和底层大型语言模型(GPT 4.1和Claude Sonnet 4)方面有所不同。表现最佳的配置在基本和高级任务集上的完成率分别为75%和53%,F1分数分别为87%和63%。WebMall公开发布,以促进对Web代理的研究,并推动电子商务场景中的导航、推理和效率方面的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM驱动的Web代理具备自动化长期Web任务的能力,如跨多个在线商店寻找特定产品的优惠并订购符合用户需求的最低价格产品。本文介绍了WebMall,这是一个在线购物基准测试平台,用于评估Web代理的比较购物效果与效率。WebMall包含四个模拟在线商店和91个跨店任务,用于评估代理在基本和高级任务上的表现。与现有电子商务基准测试相比,WebMall引入了跨多个商店的比较购物任务,产品来源更加多样化。我们对使用不同观察模式、记忆利用和大型语言模型(GPT 4.1和Claude Sonnet 4)的八种基准代理进行了评估,最佳配置在基本和高级任务集上的完成率分别为75%和53%,F1分数分别为87%和63%。WebMall已公开发布,以促进对Web代理的研究并推动电子商务场景中导航、推理和效率方面的进展。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based web agents具备自动化长期Web任务的能力,如跨多个在线商店进行比较购物。
- WebMall是一个多店在线购物基准测试平台,用于评估web代理在比较购物中的效果和效率。
- WebMall包含四个模拟在线商店和91个跨店任务,任务包括基本和高级任务,要求更长的交互轨迹。
- 与现有电子商务基准测试相比,WebMall的产品来源更加多样化,并引入了跨多个商店的比较购物任务。
- 评估的代理表现差异显著,最佳配置在任务完成率和F1分数方面表现较好。
- WebMall已公开发布,以促进对Web代理的研究。
点此查看论文截图


An LLM Agent-Based Complex Semantic Table Annotation Approach
Authors:Yilin Geng, Shujing Wang, Chuan Wang, Keqing He, Yanfei Lv, Ying Wang, Zaiwen Feng, Xiaoying Bai
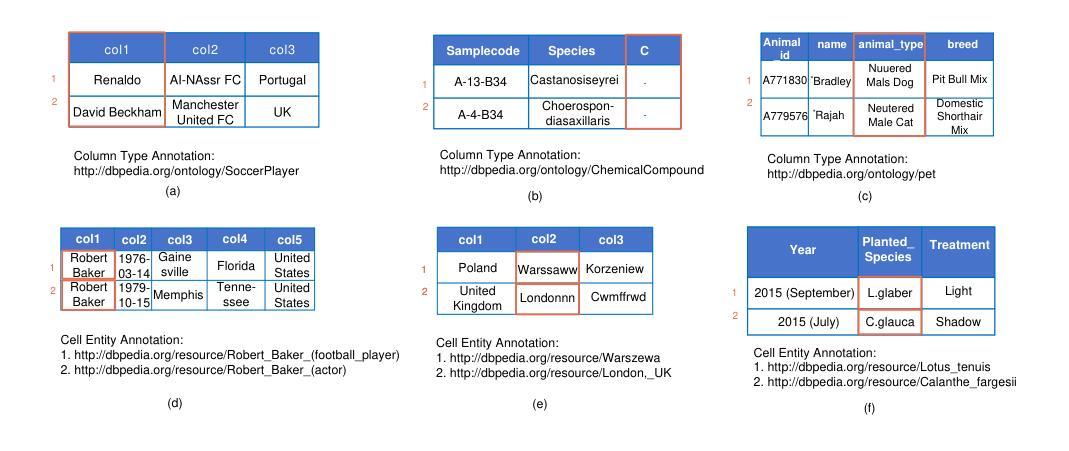
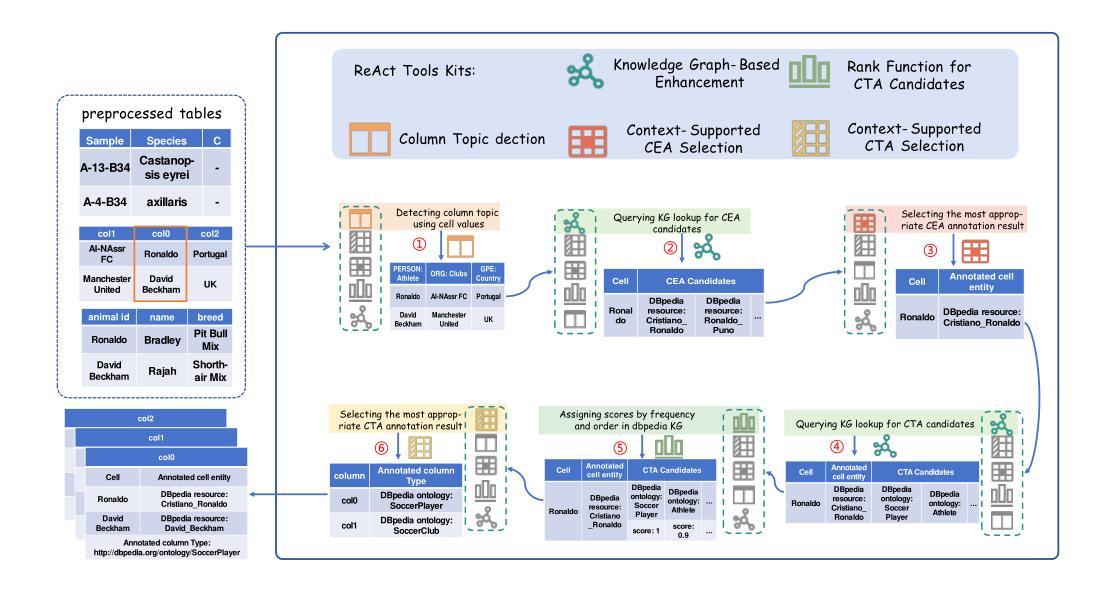
The Semantic Table Annotation (STA) task, which includes Column Type Annotation (CTA) and Cell Entity Annotation (CEA), maps table contents to ontology entities and plays important roles in various semantic applications. However, complex tables often pose challenges such as semantic loss of column names or cell values, strict ontological hierarchy requirements, homonyms, spelling errors, and abbreviations, which hinder annotation accuracy. To address these issues, this paper proposes an LLM-based agent approach for CTA and CEA. We design and implement five external tools with tailored prompts based on the ReAct framework, enabling the STA agent to dynamically select suitable annotation strategies depending on table characteristics. Experiments are conducted on the Tough Tables and BiodivTab datasets from the SemTab challenge, which contain the aforementioned challenges. Our method outperforms existing approaches across various metrics. Furthermore, by leveraging Levenshtein distance to reduce redundant annotations, we achieve a 70% reduction in time costs and a 60% reduction in LLM token usage, providing an efficient and cost-effective solution for STA.
语义表注解(STA)任务包括列类型注解(CTA)和单元格实体注解(CEA),其将表格内容映射到本体实体并在各种语义应用中扮演着重要角色。然而,复杂的表格往往带来挑战,如列名或单元格值的语义丢失、严格的本体层次结构要求、同义词、拼写错误和缩写,这些都会阻碍注释的准确性。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于大语言模型(LLM)的CTA和CEA代理方法。基于ReAct框架,我们设计并实现了五个外部工具,并使用针对性的提示使STA代理能够根据表格特性动态选择适当的注释策略。实验是在SemTab挑战中的Tough Tables和BiodivTab数据集上进行的,这些数据集包含了上述挑战。我们的方法在各项指标上均优于现有方法。此外,通过利用莱文斯坦距离减少冗余注释,我们实现了时间成本降低70%和大语言模型令牌使用量减少60%,为STA提供了高效且经济实惠的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:语义表注解任务包括列类型注解和单元格实体注解,它将表内容映射到本体实体上并在多种语义应用中发挥重要作用。针对复杂表格中的语义损失、严格的本体层次结构要求、同音词、拼写错误和缩写等问题,本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型的代理方法用于列类型注解和单元格实体注解。通过设计五个基于ReAct框架的外部工具与定制提示,该代理可以动态选择适合的策略来应对不同的表格特性。实验证明,该方法在SemTab挑战中的Tough Tables和BiodivTab数据集上的表现优于现有方法。此外,通过利用Levenshtein距离减少冗余注释,降低了时间成本和大型语言模型的令牌使用量,提供了一种高效且经济的语义表注解解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 语义表注解任务包括列类型注解和单元格实体注解,对表内容映射到本体实体上具有重要意义。
- 复杂表格存在语义损失、本体层次结构要求严格、同音词等挑战。
- 基于大型语言模型的代理方法被提出用于解决这些问题,并设计五个外部工具以应对不同表格特性。
- 在SemTab挑战中的实验证明该方法表现优于现有方法。
- 通过利用Levenshtein距离减少冗余注释,提高了效率并降低了时间和成本。
- 该方法提供了一种高效且经济的语义表注解解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

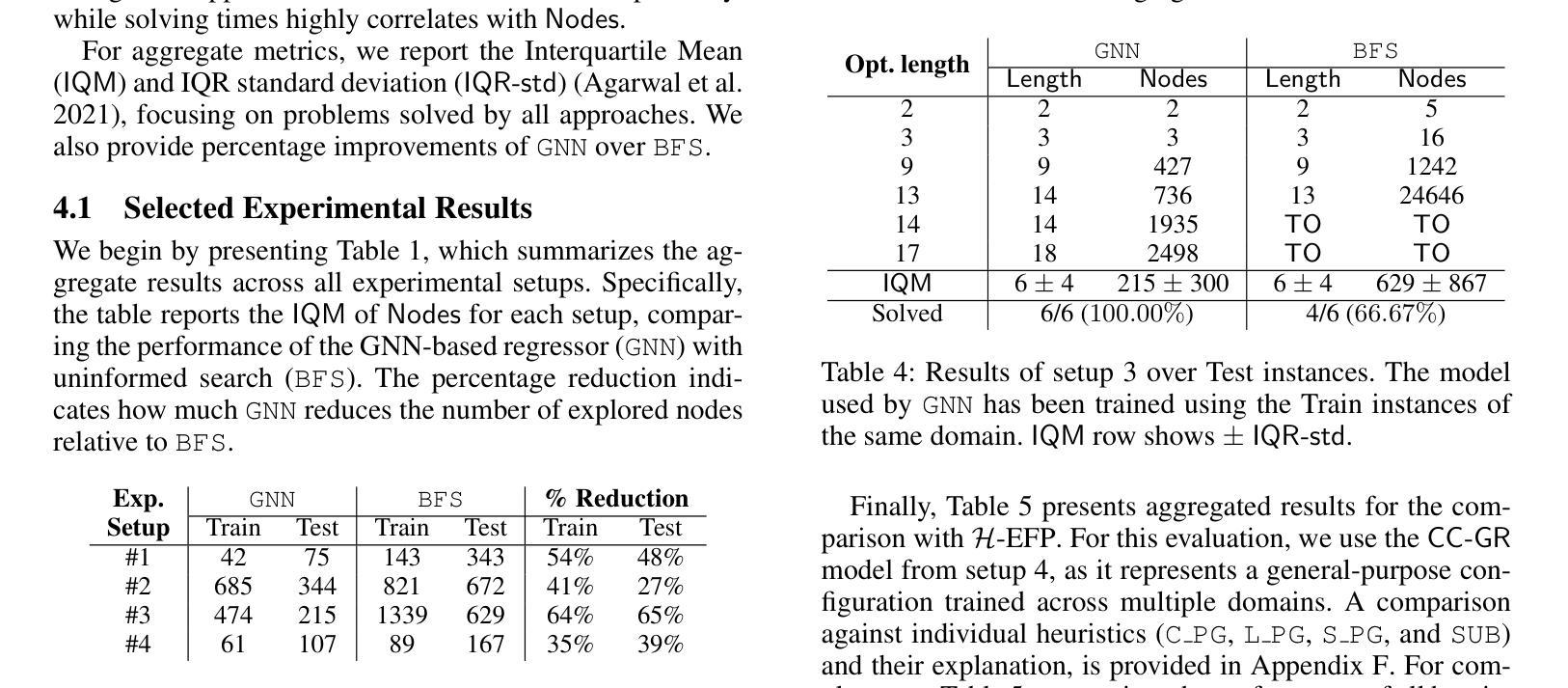
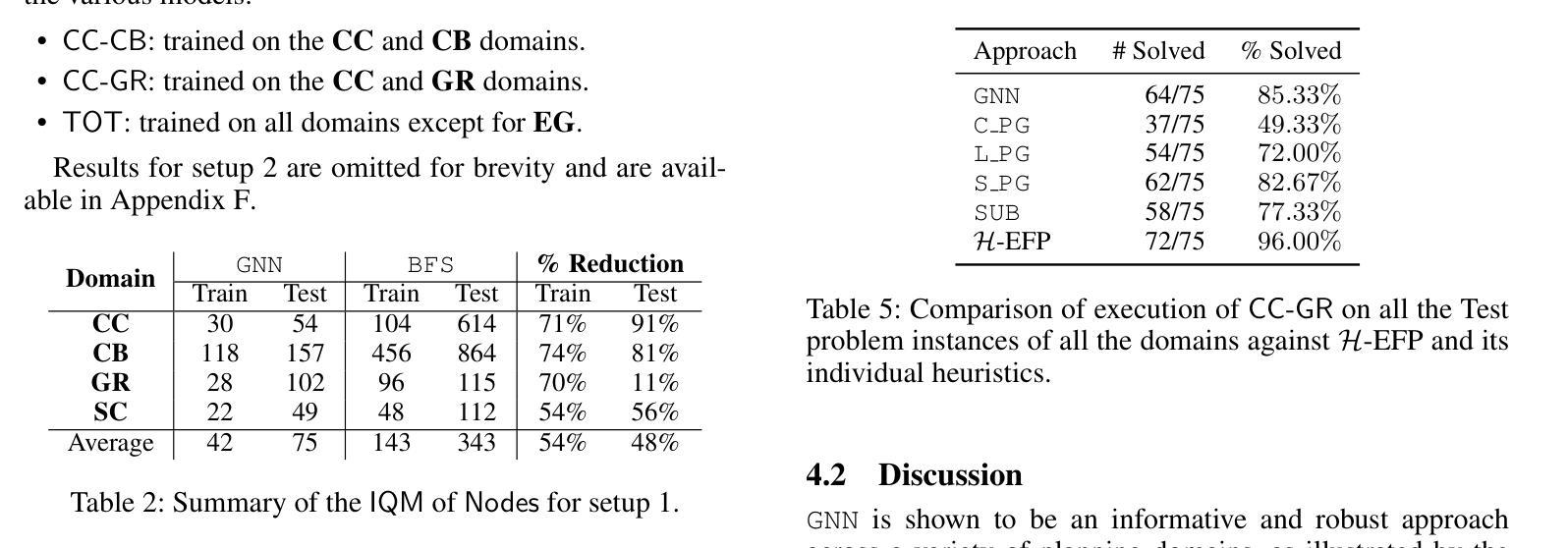
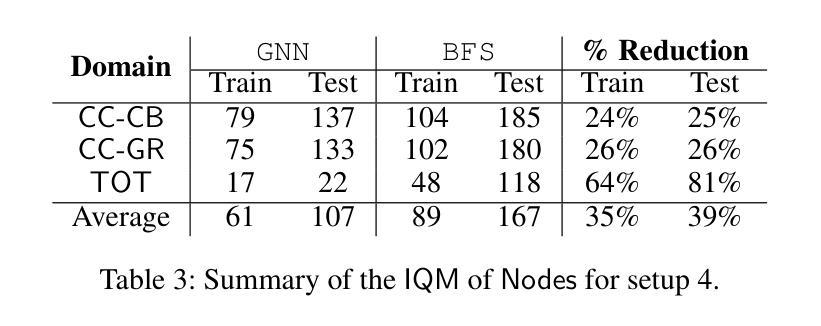
Scaling Multi-Agent Epistemic Planning through GNN-Derived Heuristics
Authors:Giovanni Briglia, Francesco Fabiano, Stefano Mariani
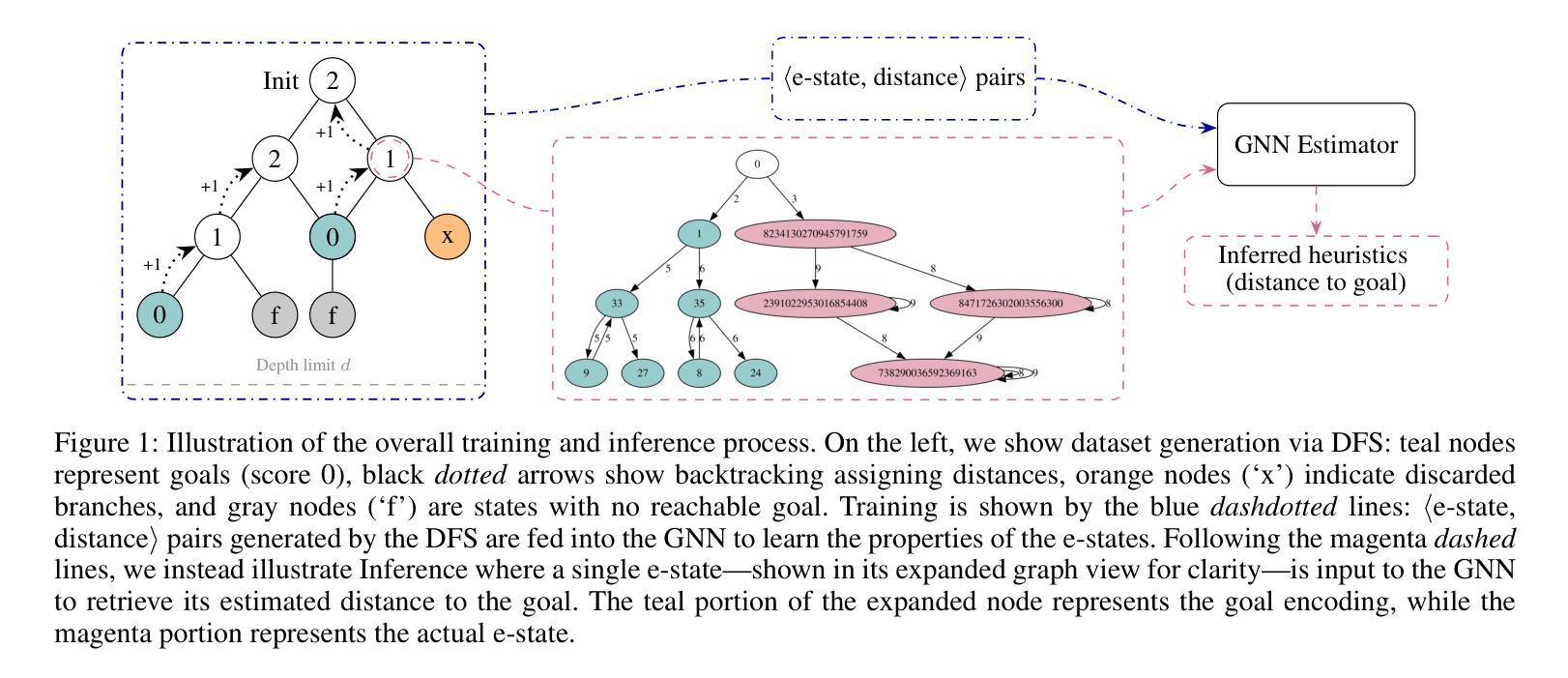
Multi-agent Epistemic Planning (MEP) is an autonomous planning framework for reasoning about both the physical world and the beliefs of agents, with applications in domains where information flow and awareness among agents are critical. The richness of MEP requires states to be represented as Kripke structures, i.e., directed labeled graphs. This representation limits the applicability of existing heuristics, hindering the scalability of epistemic solvers, which must explore an exponential search space without guidance, resulting often in intractability. To address this, we exploit Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to learn patterns and relational structures within epistemic states, to guide the planning process. GNNs, which naturally capture the graph-like nature of Kripke models, allow us to derive meaningful estimates of state quality – e.g., the distance from the nearest goal – by generalizing knowledge obtained from previously solved planning instances. We integrate these predictive heuristics into an epistemic planning pipeline and evaluate them against standard baselines, showing significant improvements in the scalability of multi-agent epistemic planning.
多智能体知识规划(MEP)是一个自主规划框架,能够推理物理世界和智能体的信念,适用于信息流和智能体之间的认知至关重要的领域。MEP的丰富性需要将状态表示为Kripke结构,即带有标签的有向图。这种表示方法限制了现有启发式方法的应用,阻碍了认知求解器的可扩展性,因为必须在没有指导的情况下进行指数搜索空间探索,这通常会导致难以解决。为解决这一问题,我们利用图神经网络(GNNs)学习认知状态中的模式和关系结构,以指导规划过程。图神经网络自然捕捉了Kripke模型的图形特征,允许我们通过推广从先前解决的规划实例中获得的知识来评估状态质量的有意义的估计——例如距离最近的目标的距离。我们将这些预测启发式集成到认知规划管道中,并与标准基线进行评估,显示出多智能体知识规划的扩展性得到了显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多主体认知规划(MEP)是一个自主规划框架,能够同时对物理世界和智能体的信念进行推理,在信息流动和智能体之间的意识至关重要的领域有广泛应用。MEP的丰富性需要将状态表示为Kripke结构,即带标签的有向图。这种表示限制了现有启发式方法的应用,阻碍了认知求解器的可扩展性,因为必须在没有指导的情况下进行指数搜索空间的探索,这通常会导致不可解性。为解决这一问题,我们利用图神经网络(GNNs)学习认知状态的模式和关系结构,以指导规划过程。通过捕捉Kripke模型的图形性质,GNNs允许我们从先前解决的规划实例中获得知识来推导有意义的状态质量估计——例如,离最近目标的距离。我们将这些预测性启发式方法整合到认知规划管道中,并进行标准基准测试,显示出多主体认知规划的扩展性得到了显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- MEP是一个用于自主规划的框架,能够处理物理世界和智能体信念的推理。
- MEP采用Kripke结构表示状态,限制了现有启发式方法的应用。
- GNNs被用来学习认知状态的模式和关系结构,以指导规划过程。
- GNNs能够捕捉Kripke模型的图形性质,从先前解决的规划实例中推导状态质量估计。
- 预测性启发式方法被整合到认知规划管道中。
- 与标准基准相比,整合后的方法在多主体认知规划的扩展性方面表现出显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

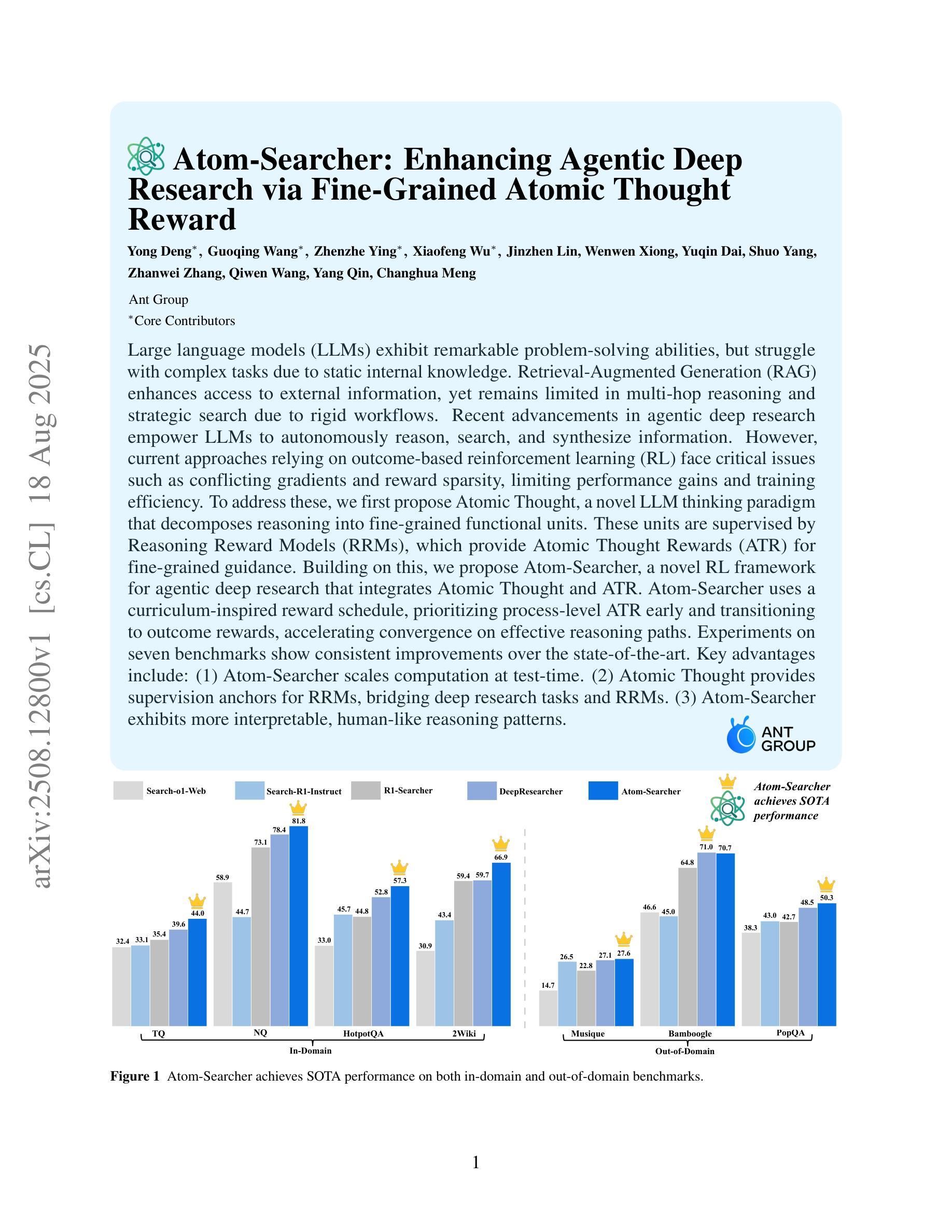
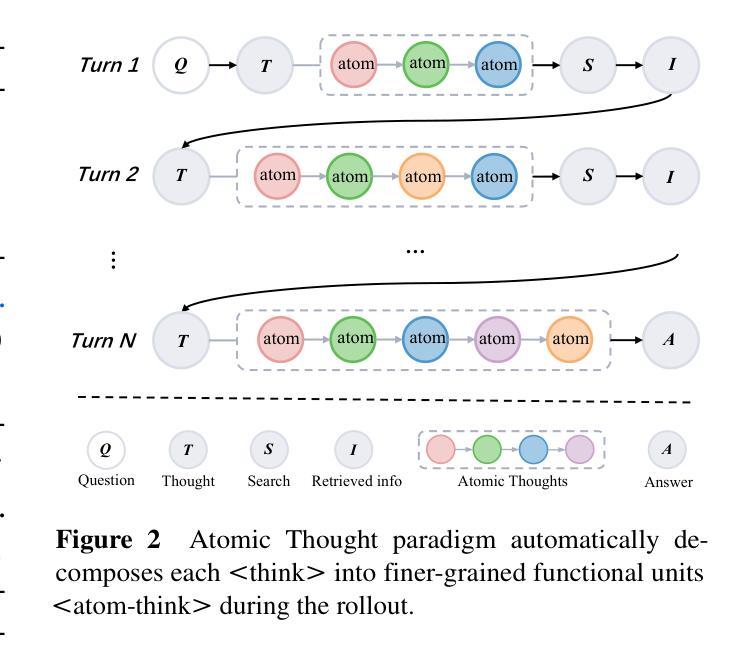
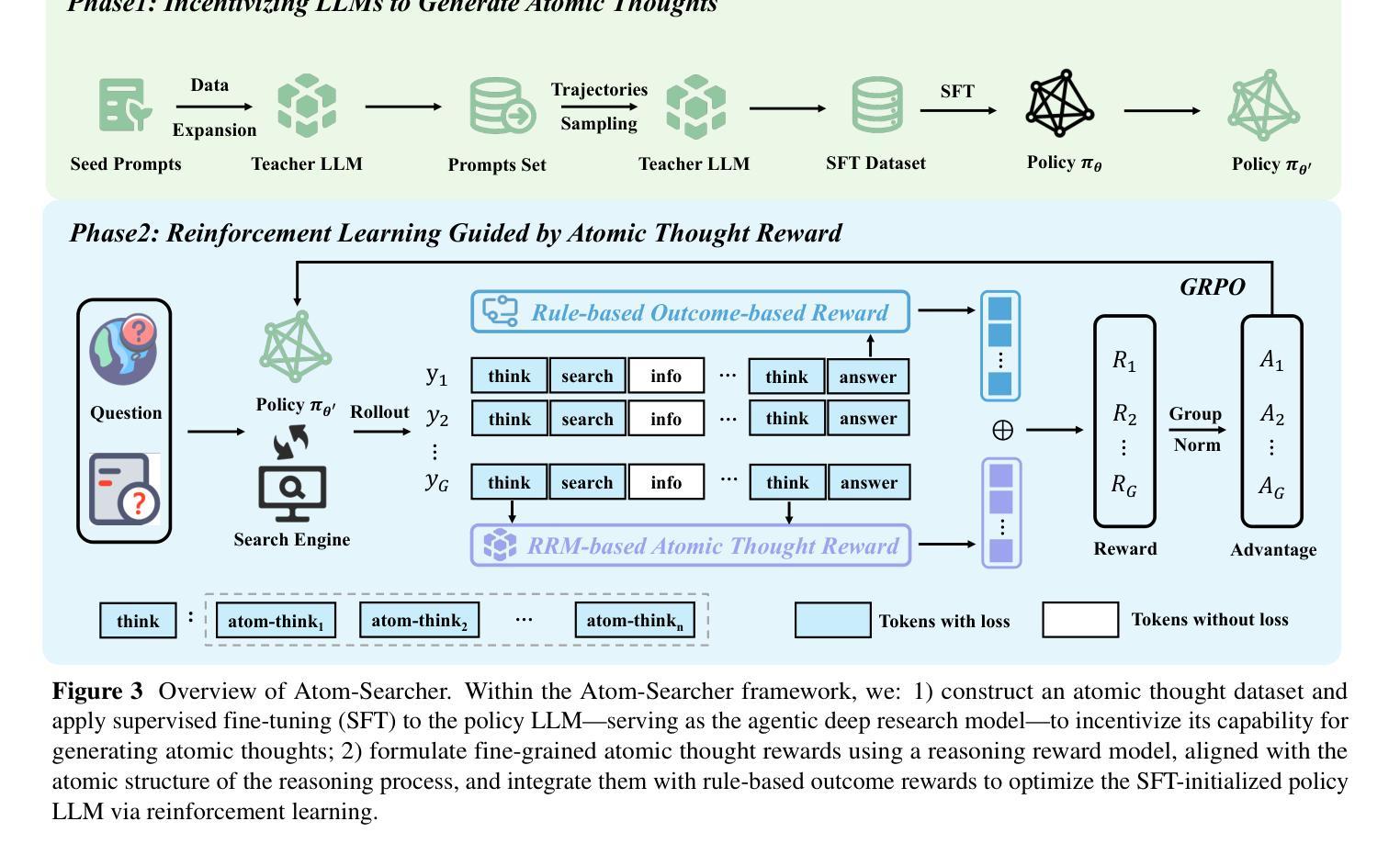
Atom-Searcher: Enhancing Agentic Deep Research via Fine-Grained Atomic Thought Reward
Authors:Yong Deng, Guoqing Wang, Zhenzhe Ying, Xiaofeng Wu, Jinzhen Lin, Wenwen Xiong, Yuqin Dai, Shuo Yang, Zhanwei Zhang, Qiwen Wang, Yang Qin, Changhua Meng
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable problem-solving abilities, but struggle with complex tasks due to static internal knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances access to external information, yet remains limited in multi-hop reasoning and strategic search due to rigid workflows. Recent advancements in agentic deep research empower LLMs to autonomously reason, search, and synthesize information. However, current approaches relying on outcome-based reinforcement learning (RL) face critical issues such as conflicting gradients and reward sparsity, limiting performance gains and training efficiency. To address these, we first propose Atomic Thought, a novel LLM thinking paradigm that decomposes reasoning into fine-grained functional units. These units are supervised by Reasoning Reward Models (RRMs), which provide Atomic Thought Rewards (ATR) for fine-grained guidance. Building on this, we propose Atom-Searcher, a novel RL framework for agentic deep research that integrates Atomic Thought and ATR. Atom-Searcher uses a curriculum-inspired reward schedule, prioritizing process-level ATR early and transitioning to outcome rewards, accelerating convergence on effective reasoning paths. Experiments on seven benchmarks show consistent improvements over the state-of-the-art. Key advantages include: (1) Atom-Searcher scales computation at test-time. (2) Atomic Thought provides supervision anchors for RRMs, bridging deep research tasks and RRMs. (3) Atom-Searcher exhibits more interpretable, human-like reasoning patterns.
大型语言模型(LLM)展现出卓越的解决问题的能力,但由于静态内部知识,它们在处理复杂任务时遇到困难。检索增强生成(RAG)增强了对外部信息的访问,但由于僵化的工作流程,它在多跳推理和战略搜索方面仍然有限制。最近的代理深度研究进展使LLM能够自主推理、搜索和合成信息。然而,当前依赖结果基于强化学习(RL)的方法面临关键挑战,如梯度冲突和奖励稀疏,这限制了性能提升和训练效率。为了解决这些问题,我们首先提出原子思维,这是一种新的LLM思维范式,将推理分解成精细的功能单元。这些单元受到推理奖励模型(RRMs)的监督,为精细指导提供原子思维奖励(ATR)。在此基础上,我们提出了Atom-Searcher,这是一个用于代理深度研究的新型强化学习框架,它结合了原子思维和ATR。Atom-Searcher使用受课程启发的奖励时间表,早期优先提供过程级的ATR,然后过渡到结果奖励,从而加快对有效推理路径的收敛。在七个基准测试上的实验表明,与最新技术相比,它始终表现出一致的优势。主要优势包括:(1)Atom-Searcher在测试时扩展计算规模。(2)原子思维为RRMs提供了监督锚点,桥接了深度研究任务和RRMs。(3)Atom-Searcher展现出更具解释性、更人性化的推理模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)具有出色的解决问题的能力,但由于静态内部知识而难以应对复杂任务。检索增强生成(RAG)提高了对外部信息的访问能力,但由于工作流程僵化,它在多跳推理和战略搜索方面仍存在局限性。最近的深度研究中,赋能LLM自主推理、搜索和合成信息的进步显著。然而,依赖结果强化学习(RL)的方法面临梯度冲突和奖励稀疏等关键问题,限制了性能提升和训练效率。为解决这些问题,我们提出了原子思维这一新型LLM思维范式和基于它的推理奖励模型(RRM),通过精细的奖励引导进行原子思维奖励(ATR)。基于此,我们进一步提出了Atom-Searcher这一新型的深度研究RL框架,融合了原子思维和ATR。Atom-Searcher采用启发式教学奖励计划,早期侧重于过程级ATR,并逐步过渡到结果奖励,以加速在有效推理路径上的收敛。实验结果表明,相较于现有技术,Atom-Searcher具有持续的优势,如计算能力的扩展性、为RRM提供监督锚点以及更可解释的类似人类的推理模式。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)虽具备解决问题的能力,但在复杂任务方面存在由于静态内部知识的局限性。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)能提高对外部信息的访问,但在多跳推理和战略搜索方面的表现仍然受限。
- 目前依赖结果强化学习(RL)的方法面临梯度冲突和奖励稀疏的问题。
- 原子思维(Atomic Thought)是一种新型的LLM思维范式,通过将推理分解为精细的功能单元来提高性能。
- 推理奖励模型(RRM)用于提供原子思维奖励(ATR),为精细的推理过程提供指导。
- Atom-Searcher是一个结合了原子思维和ATR的新型RL框架,采用启发式教学奖励计划以加速收敛有效推理路径。
点此查看论文截图
A Taxonomy of Hierarchical Multi-Agent Systems: Design Patterns, Coordination Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications
Authors:David J. Moore
Hierarchical multi-agent systems (HMAS) organize collections of agents into layered structures that help manage complexity and scale. These hierarchies can simplify coordination, but they also can introduce trade-offs that are not always obvious. This paper proposes a multi-dimensional taxonomy for HMAS along five axes: control hierarchy, information flow, role and task delegation, temporal layering, and communication structure. The intent is not to prescribe a single “best” design but to provide a lens for comparing different approaches. Rather than treating these dimensions in isolation, the taxonomy is connected to concrete coordination mechanisms - from the long-standing contract-net protocol for task allocation to more recent work in hierarchical reinforcement learning. Industrial contexts illustrate the framework, including power grids and oilfield operations, where agents at production, maintenance, and supply levels coordinate to diagnose well issues or balance energy demand. These cases suggest that hierarchical structures may achieve global efficiency while preserving local autonomy, though the balance is delicate. The paper closes by identifying open challenges: making hierarchical decisions explainable to human operators, scaling to very large agent populations, and assessing whether learning-based agents such as large language models can be safely integrated into layered frameworks. This paper presents what appears to be the first taxonomy that unifies structural, temporal, and communication dimensions of hierarchical MAS into a single design framework, bridging classical coordination mechanisms with modern reinforcement learning and large language model agents.
分层多智能体系统(HMAS)将智能体集合组织成层次结构,有助于管理复杂性和规模。这些层次结构可以简化协调,但它们也可能引入并不总是明显的权衡。本文提出了一个沿着五个轴的多层次多维度分类法:控制层次结构、信息流、角色和任务委派、时间分层和通信结构。其目的并不是规定一个单一的“最佳”设计,而是提供一个比较不同方法的视角。这个分类法不仅孤立地处理这些维度,而且与具体的协调机制相关联——从长期的任务分配合同网协议到最新的分层强化学习工作。工业背景说明了该框架,包括电力网和油田操作,其中生产、维护和供应级别的智能体协调以诊断油井问题或平衡能源需求。这些案例表明,层次结构可能在实现全局效率的同时保留局部自主性,但平衡是微妙的。最后,论文指出了开放挑战:使分层决策对人类操作者具有可解释性、扩展到大量智能体以及评估基于学习的大型语言模型等智能体是否能安全地集成到分层框架中。本文似乎呈现了第一个将层次化MAS的结构、时间和通信维度统一到一个设计框架中的分类法,桥梁古典协调机制与现代的强化学习和大型语言模型智能体。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了层次化多智能体系统(HMAS)的五维分类方法,包括控制层次结构、信息流动、角色和任务委派、时间分层和通信结构。文章旨在提供一种比较不同层次化多智能体系统设计方法的透镜,旨在通过具体的协调机制实现全局效率和局部自主性的平衡。通过案例分析探讨了HMAS在实际工业环境中的实际应用和挑战。虽然本文提供了层次化决策的分类框架,但仍面临诸多挑战,如提高决策的可解释性、适应大规模智能体数量和评估基于学习模型的智能体的集成等。这看似是多智能体系统研究的重要一步,旨在跨越经典协调机制与当前强化学习和大型语言模型智能体的界限。
Key Takeaways
- HMAS通过分层结构管理复杂性和规模,简化协调,但也带来权衡。
- 提出一个五维分类法:控制层次结构、信息流动、角色和任务委派、时间分层和通信结构。
- 分类法旨在比较不同的HMAS设计方法,并强调具体的协调机制。
- HMAS在工业环境中可实现全局效率和局部自主性的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

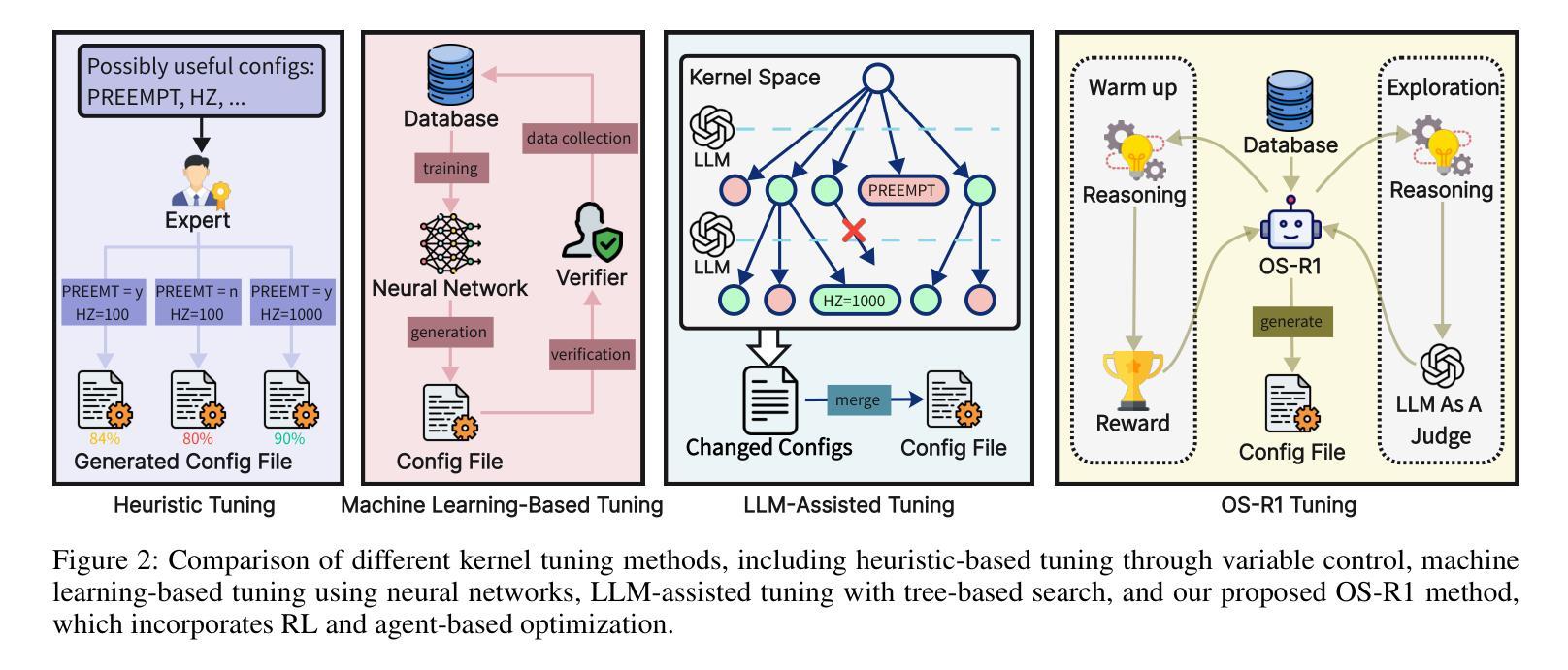
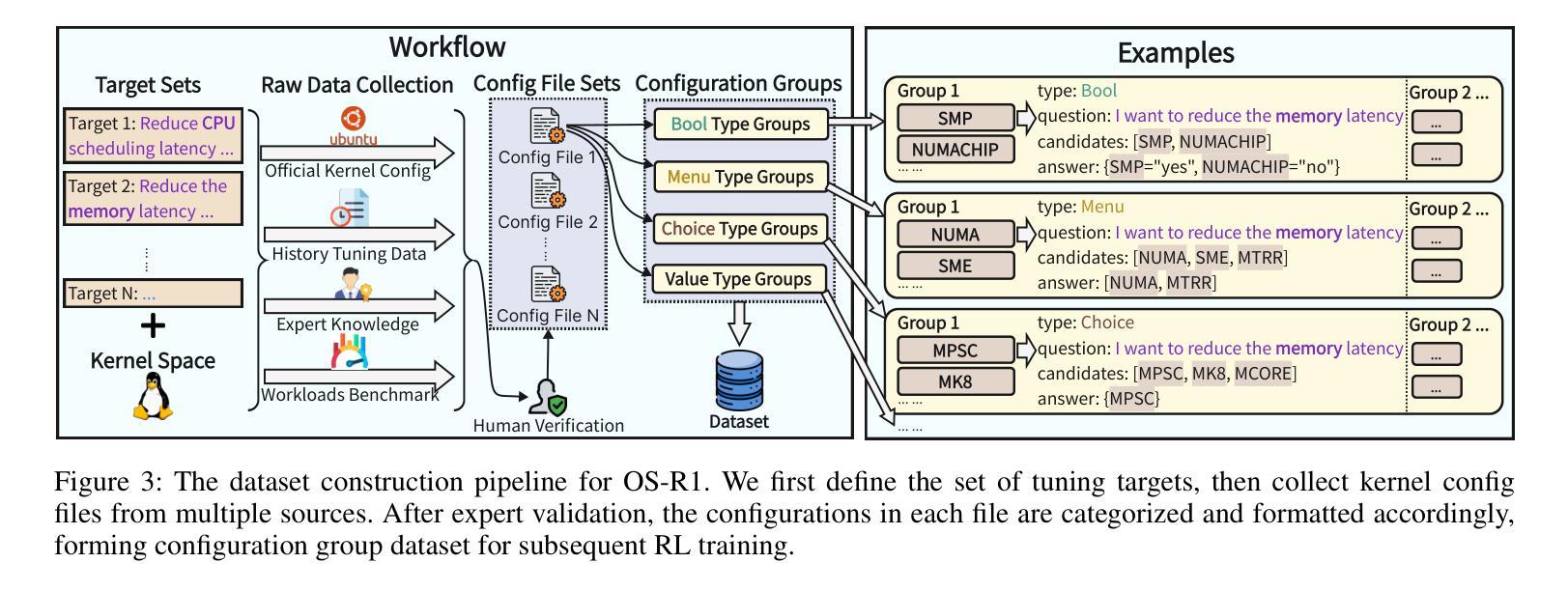
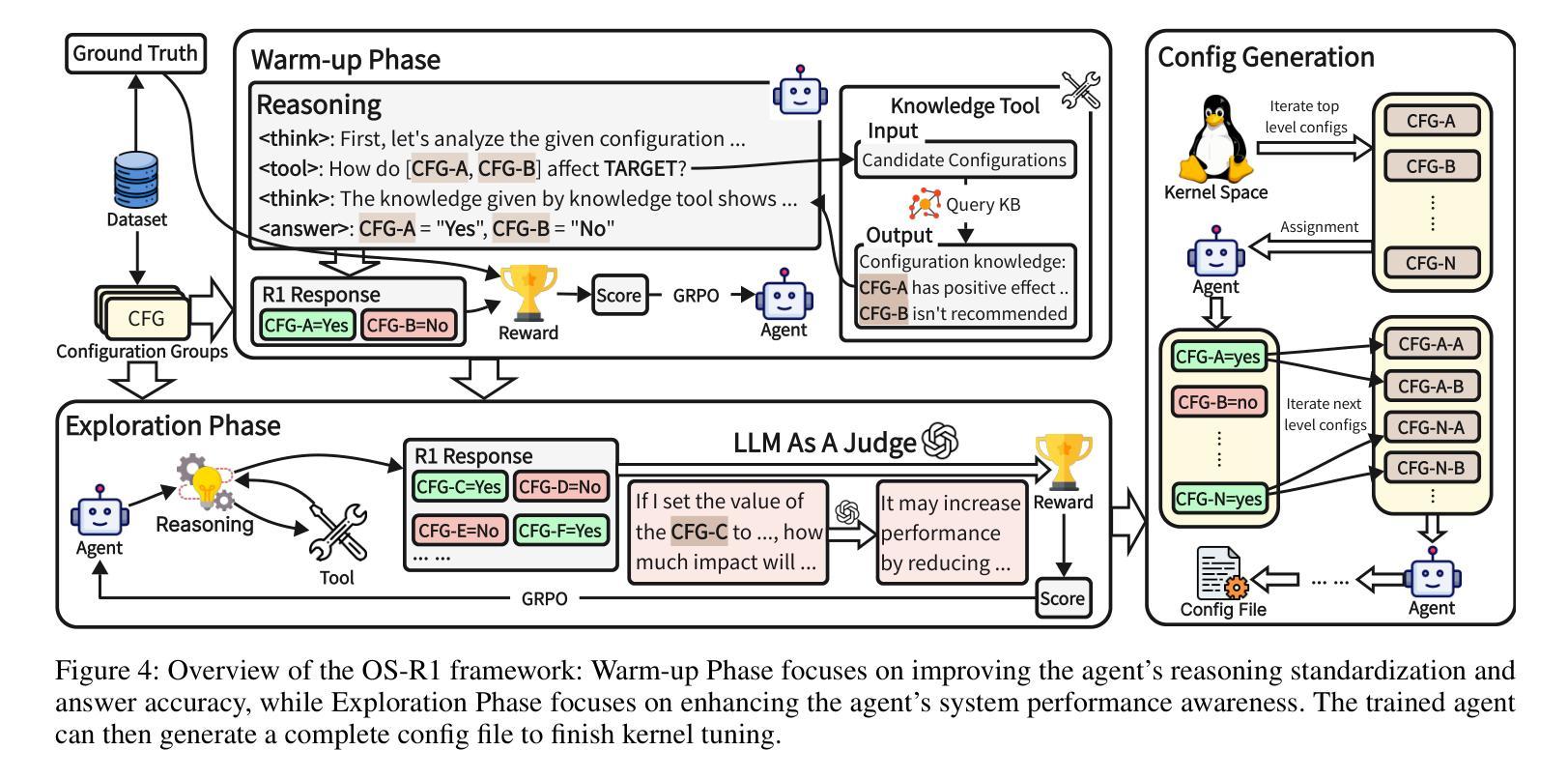
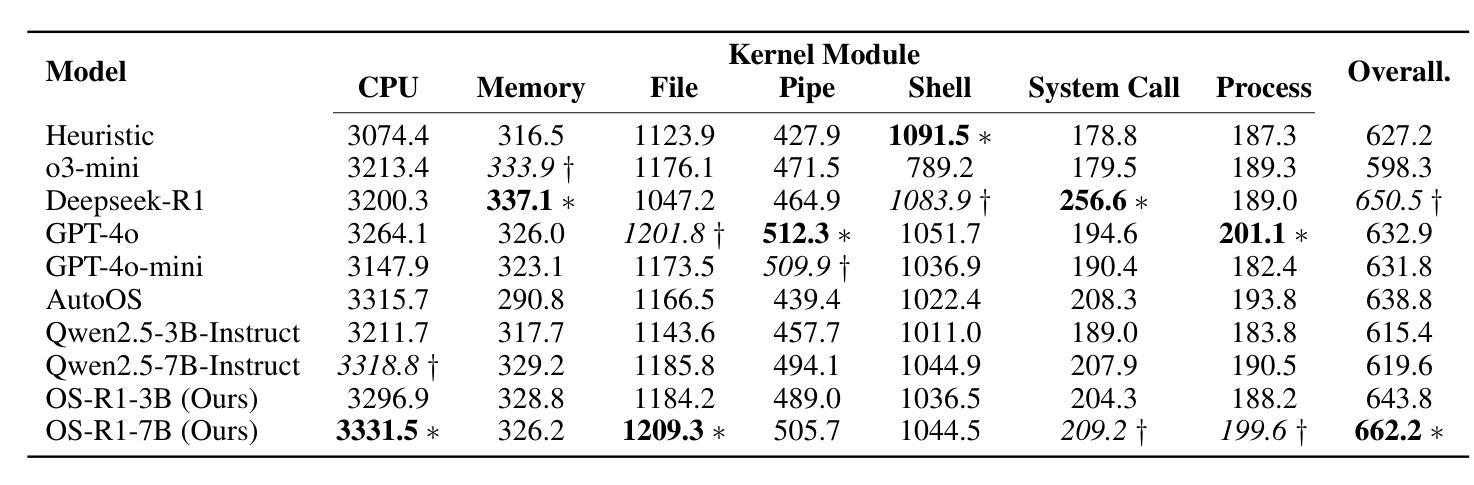
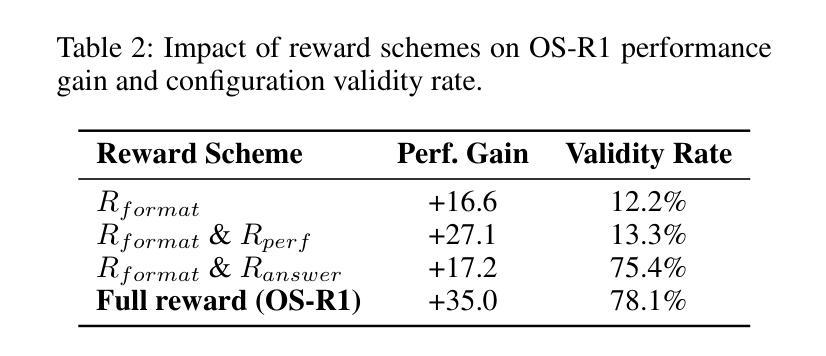
OS-R1: Agentic Operating System Kernel Tuning with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Hongyu Lin, Yuchen Li, Haoran Luo, Kaichun Yao, Libo Zhang, Mingjie Xing, Yanjun Wu
Linux kernel tuning is essential for optimizing operating system (OS) performance. However, existing methods often face challenges in terms of efficiency, scalability, and generalization. This paper introduces OS-R1, an agentic Linux kernel tuning framework powered by rule-based reinforcement learning (RL). By abstracting the kernel configuration space as an RL environment, OS-R1 facilitates efficient exploration by large language models (LLMs) and ensures accurate configuration modifications. Additionally, custom reward functions are designed to enhance reasoning standardization, configuration modification accuracy, and system performance awareness of the LLMs. Furthermore, we propose a two-phase training process that accelerates convergence and minimizes retraining across diverse tuning scenarios. Experimental results show that OS-R1 significantly outperforms existing baseline methods, achieving up to 5.6% performance improvement over heuristic tuning and maintaining high data efficiency. Notably, OS-R1 is adaptable across various real-world applications, demonstrating its potential for practical deployment in diverse environments. Our dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/LHY-24/OS-R1.
Linux内核调优对于优化操作系统性能至关重要。然而,现有方法常常在效率、可扩展性和通用性方面面临挑战。本文介绍了一种名为OS-R1的基于规则的强化学习驱动的Linux内核调优框架。通过将内核配置空间抽象为强化学习环境,OS-R1便于大型语言模型进行高效探索,并确保准确的配置修改。此外,我们设计了自定义奖励函数,以提高大型语言模型的推理标准化、配置修改准确性和系统性能意识。此外,我们提出了一种两阶段训练过程,以加速收敛并减少不同调优场景下的再训练时间。实验结果表明,OS-R1显著优于现有基线方法,在启发式调优的基础上实现了高达5.6%的性能提升,并保持了较高的数据效率。值得注意的是,OS-R1可适应各种实际应用,展示了其在不同环境中实际部署的潜力。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/LHY-24/OS-R1公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
OS-R1,一个基于规则强化学习的Linux内核调优框架,通过抽象内核配置空间作为RL环境,提高了操作系统性能优化的效率与准确性。它利用大型语言模型进行高效探索,并通过自定义奖励函数增强标准化、修改准确性和系统性能意识。此外,提出的两阶段训练过程可加速收敛并减少不同调优场景下的再训练时间。实验表明,OS-R1显著优于现有方法,在性能上提高了5.6%,且具有良好的数据效率及跨实际应用环境的适应性。
Key Takeaways
- OS-R1引入了一种新的Linux内核调优框架,该框架结合规则强化学习技术以提高系统性能优化效率。
- 通过抽象内核配置空间作为强化学习环境,OS-R1使大型语言模型进行高效探索。
- 自定义奖励函数增强了标准化、配置修改准确性和系统性能意识。
- 两阶段训练过程加速模型收敛并减少在不同调优场景下的再训练时间。
- OS-R1在性能上显著优于现有方法,提高了高达5.6%。
- OS-R1具有良好的数据效率,可适应不同的实际应用程序和环境。
点此查看论文截图

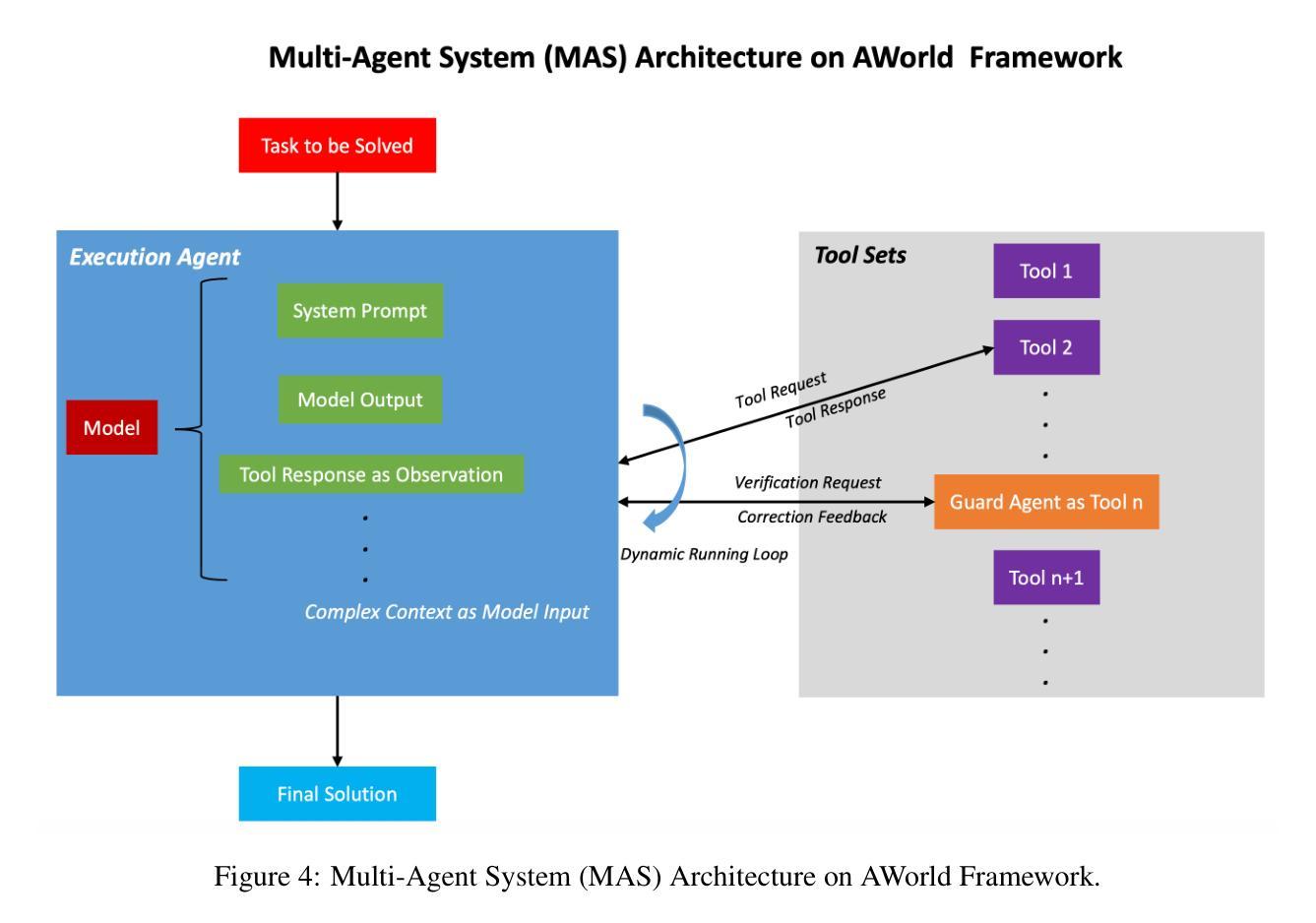
Dynamic Multi-Agent System with Stable Maneuvering for Robust GAIA Problem Solving by AWorld
Authors:Zhitian Xie, Qintong Wu, Chengyue Yu, Chenyi Zhuang, Jinjie Gu
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has empowered intelligent agents to leverage diverse external tools for solving complex real-world problems. However, as agents increasingly depend on multiple tools, they encounter new challenges: extended contexts from disparate sources and noisy or irrelevant tool outputs can undermine system reliability and accuracy. These challenges underscore the necessity for enhanced stability in agent-based systems. To address this, we introduce dynamic supervision and maneuvering mechanisms, constructing a robust and dynamic Multi-Agent System (MAS) architecture within the AWorld framework. In our approach, the Execution Agent invokes the Guard Agent at critical steps to verify and correct the reasoning process, effectively reducing errors arising from noise and bolstering problem-solving robustness. Extensive experiments on the GAIA test dataset reveal that our dynamic maneuvering mechanism significantly improves both the effectiveness and stability of solutions, outperforming single-agent system (SAS) and standard tool-augmented systems. As a result, our dynamic MAS system achieved first place among open-source projects on the prestigious GAIA leaderboard. These findings highlight the practical value of collaborative agent roles in developing more reliable and trustworthy intelligent systems.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,智能代理能够利用多种外部工具解决复杂的现实世界问题。然而,随着代理越来越依赖于多种工具,它们面临着新的挑战:来自不同来源的扩展上下文和嘈杂或无关的工具输出可能会破坏系统可靠性和准确性。这些挑战强调了提高基于代理的系统的稳定性的必要性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了动态监督和操作机制,在AWorld框架内构建了一个稳健且动态的多代理系统(MAS)架构。在我们的方法中,执行代理会在关键步骤调用防护代理来验证和纠正推理过程,有效地减少了由噪声引起的错误,增强了解决问题的稳健性。在GAIA测试数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的动态操作机制显著提高了解决方案的有效性和稳定性,优于单代理系统(SAS)和标准工具增强系统。因此,我们的动态MAS系统在著名的GAIA排行榜上获得开源项目第一名。这些发现凸显了协作代理角色在开发更可靠、更值得信赖的智能系统中的实际价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的快速发展使得智能代理能够利用多种外部工具解决复杂的现实世界问题。然而,随着代理越来越依赖于多种工具,他们面临新的挑战:来自不同来源的扩展上下文和嘈杂或无关的工具输出可能会破坏系统可靠性和准确性。为解决这些问题,我们引入动态监督和操控机制,在AWorld框架内构建稳健且动态的多代理系统(MAS)架构。执行代理在关键步骤调用守卫代理进行验证和校正推理过程,有效减少噪声引起的错误,增强解决问题的稳健性。在GAIA测试数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的动态操控机制显著提高了解决方案的有效性和稳定性,优于单代理系统(SAS)和标准工具增强系统。因此,我们的动态MAS系统在著名的GAIA排行榜上获得开源项目第一名。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的进步促进了智能代理利用外部工具解决复杂问题。
- 依赖多工具带来挑战,如上下文扩展、嘈杂工具输出影响系统可靠性。
- 引入动态监督和操控机制,构建多代理系统(MAS)以增强系统稳健性。
- 执行代理与守卫代理协同工作,减少错误,提高问题解决的稳健性。
- 在GAIA测试数据集上的实验表明,动态操控机制提高解决方案的有效性和稳定性。
- 与单代理系统和其他工具增强系统相比,动态MAS系统表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

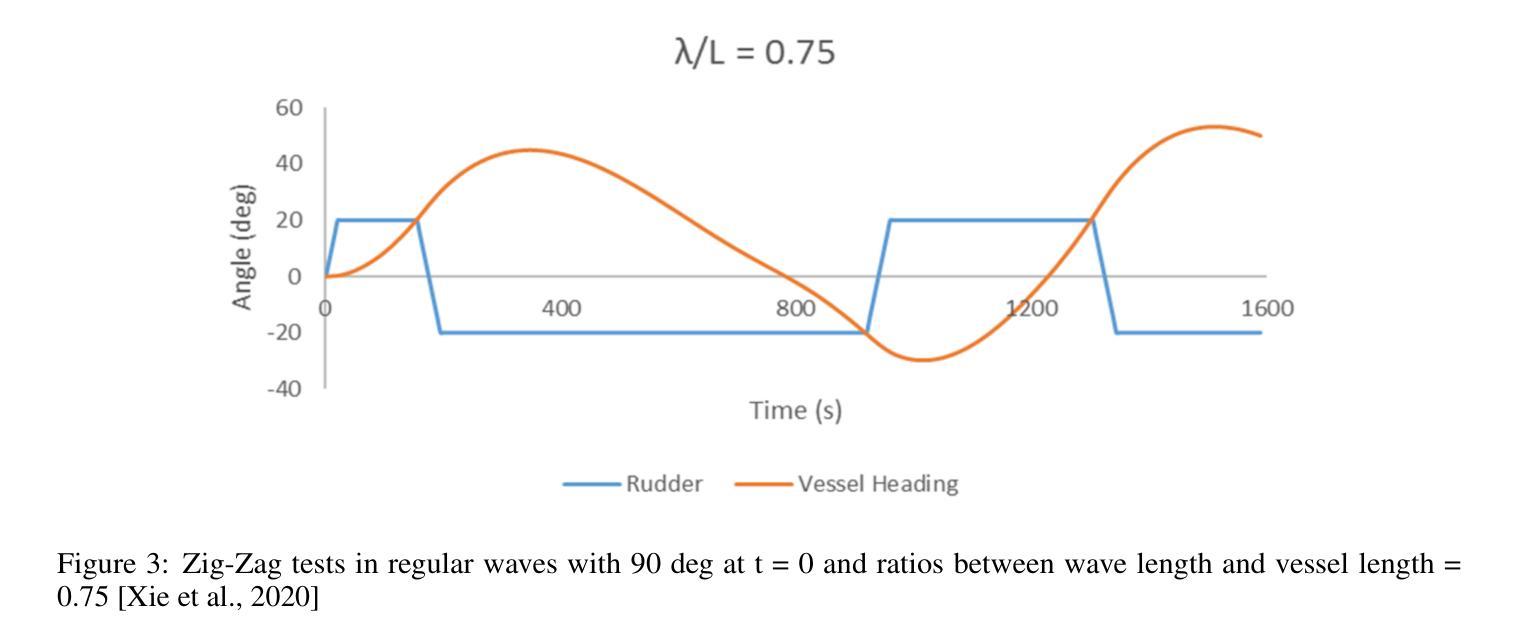
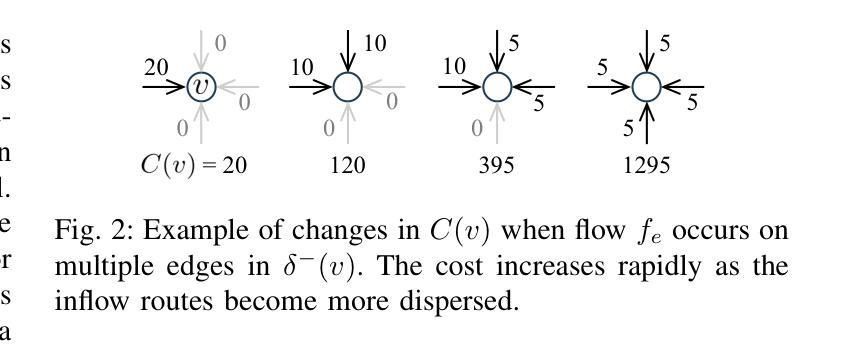
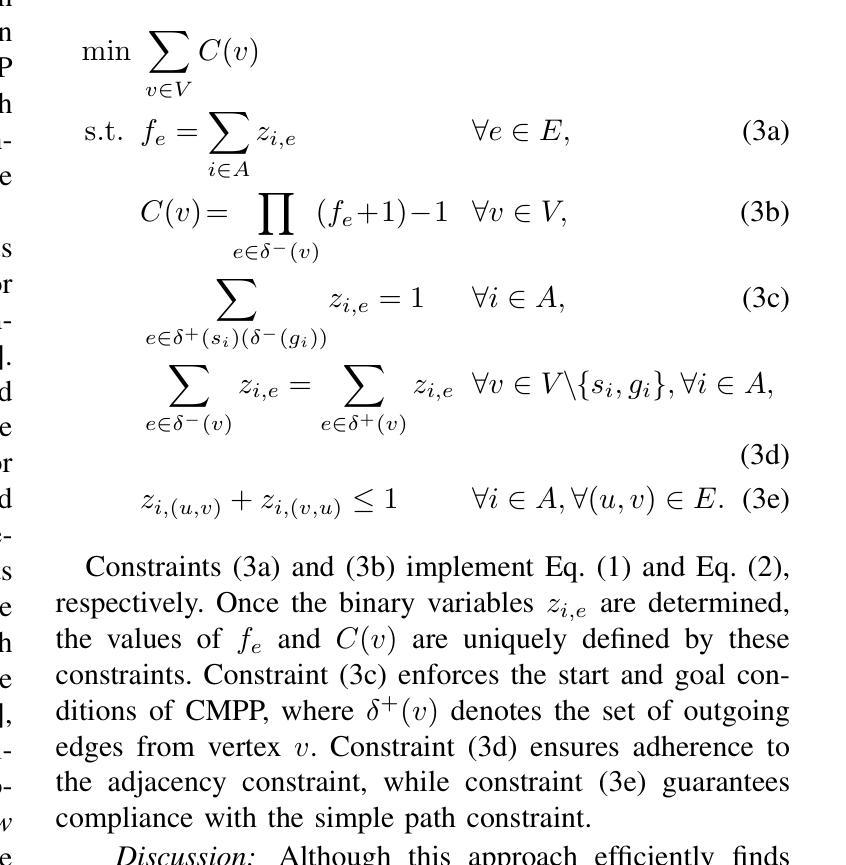
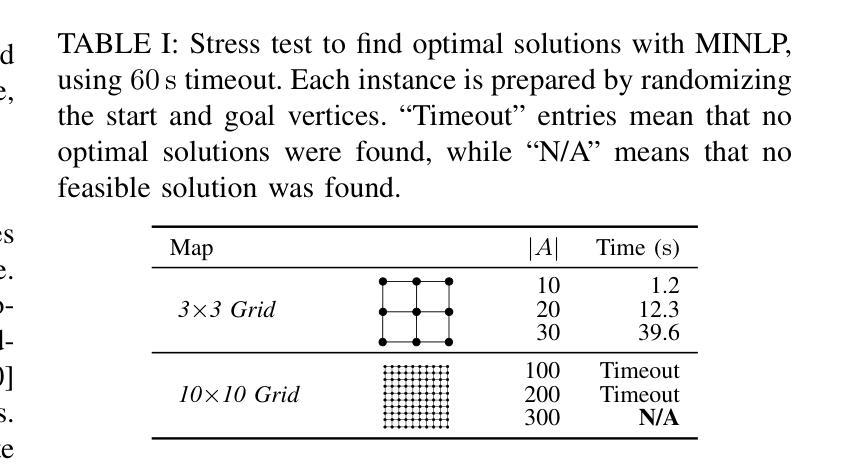
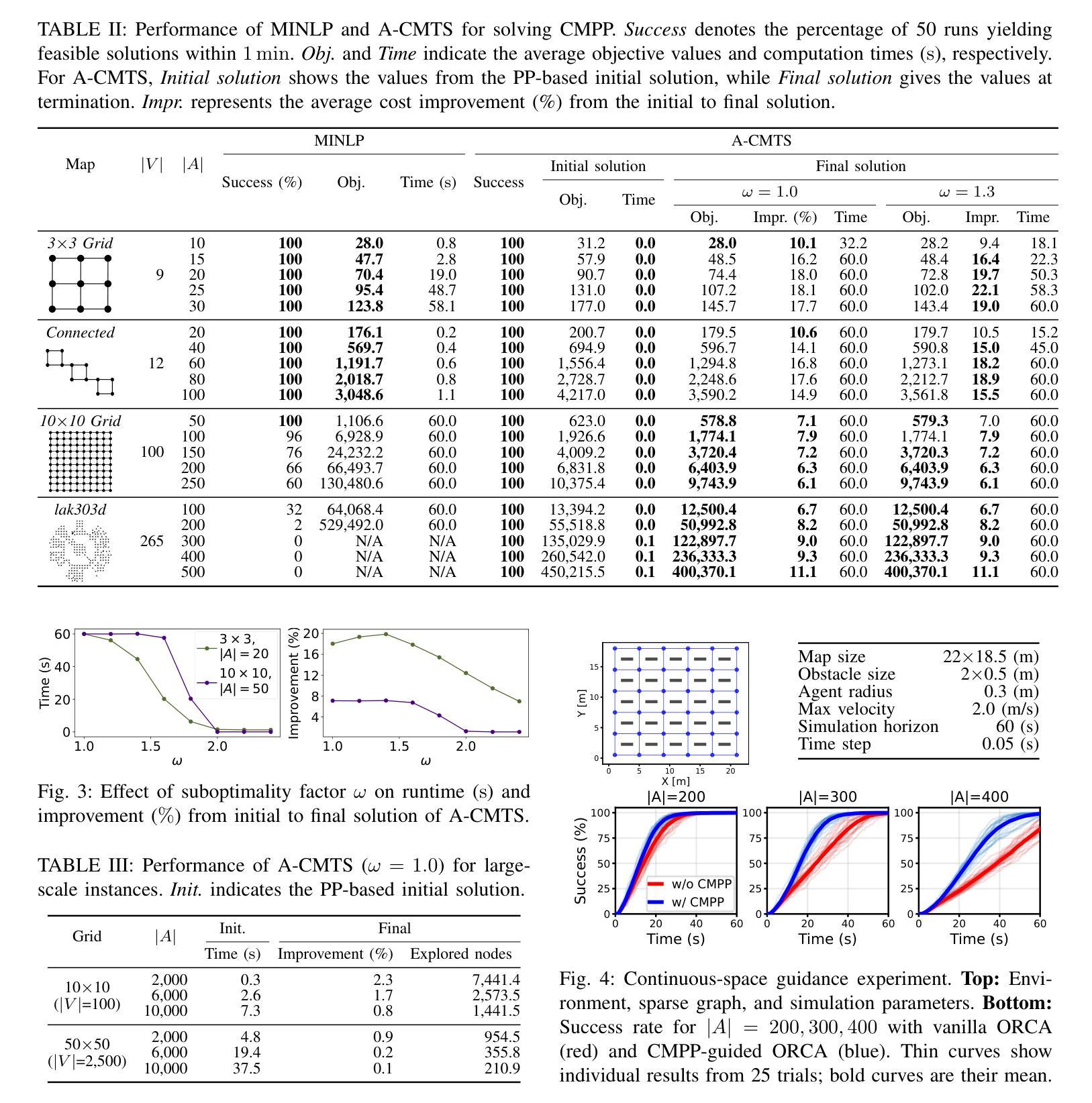
Congestion Mitigation Path Planning for Large-Scale Multi-Agent Navigation in Dense Environments
Authors:Takuro Kato, Keisuke Okumura, Yoko Sasaki, Naoya Yokomachi
In high-density environments where numerous autonomous agents move simultaneously in a distributed manner, streamlining global flows to mitigate local congestion is crucial to maintain overall navigation efficiency. This paper introduces a novel path-planning problem, congestion mitigation path planning (CMPP), which embeds congestion directly into the cost function, defined by the usage of incoming edges along agents’ paths. CMPP assigns a flow-based multiplicative penalty to each vertex of a sparse graph, which grows steeply where frequently-traversed paths intersect, capturing the intuition that congestion intensifies where many agents enter the same area from different directions. Minimizing the total cost yields a set of coarse-level, time-independent routes that autonomous agents can follow while applying their own local collision avoidance. We formulate the problem and develop two solvers: (i) an exact mixed-integer nonlinear programming solver for small instances, and (ii) a scalable two-layer search algorithm, A-CMTS, which quickly finds suboptimal solutions for large-scale instances and iteratively refines them toward the optimum. Empirical studies show that augmenting state-of-the-art collision-avoidance planners with CMPP significantly reduces local congestion and enhances system throughput in both discrete- and continuous-space scenarios. These results indicate that CMPP improves the performance of multi-agent systems in real-world applications such as logistics and autonomous-vehicle operations.
在高密度环境中,众多自主代理以分布式方式同时移动,理顺全局流程以缓解局部拥堵对于维持整体导航效率至关重要。本文引入了一种新的路径规划问题,即拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP),它将拥堵直接嵌入到成本函数中,该成本函数由代理路径上的传入边使用定义。CMPP为每个稀疏图的顶点分配基于流量的乘法惩罚,该惩罚在频繁穿越的路径交叉处急剧增长,直觉地反映了拥堵的加剧,即许多代理从不同方向进入同一区域。最小化总成本产生了一组粗略的、时间独立的路线,自主代理可以遵循这些路线并应用其自己的本地避障策略。我们制定问题并开发了两个求解器:(i)针对小实例的精确混合整数非线性规划求解器,(ii)可扩展的两层搜索算法A-CMTS,该算法可以快速为大规模实例找到次优解,并迭代地对其进行优化以达到最优。实证研究表明,使用CMPP增强最新的避障规划器可以显著减少局部拥堵,并在离散和连续空间场景中提高系统吞吐量。这些结果表明,CMPP在物流和自动驾驶等实际应用中提高了多代理系统的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2025. (C) 2025 IEEE. CC BY 4.0 license. Supplementary videos will be accessible via IEEE Xplore upon publication
摘要
在存在众多以分布式方式自主移动的智能体的高密度环境中,优化全局流程以缓解局部拥堵对于维持整体导航效率至关重要。本文引入了一种新型路径规划问题——拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP),它将拥堵直接嵌入到成本函数中,该成本函数由智能体路径上的传入边决定。CMPP为每个稀疏图的顶点分配基于流量的乘法惩罚,这在频繁穿越的路径交汇处急剧增长,捕捉到一个直觉,即当许多智能体从不同方向进入同一区域时,拥堵加剧。最小化总成本产生一组粗略的、时间独立的路线,自主智能体可以在遵循这些路线的同时应用其自身的局部防撞功能。我们建立了这个问题,并开发了两种求解器:(i)一种精确的混合整数非线性规划求解器用于小型实例,(ii)一种快速为大型实例找到次优解决方案的可扩展两层搜索算法A-CMTS,并朝着最优方向迭代改进它们。实证研究表明,通过将最新防撞规划器与CMPP相结合,可在离散空间和连续空间场景中显著降低局部拥堵并提高系统吞吐量。这些结果表明,CMPP在物流和自动驾驶车辆操作等实际应用中提高了多智能体系统的性能。
关键要点
- 在高密度环境中,缓解局部拥堵对维持多智能体系统整体导航效率至关重要。
- 提出了新型的拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP)问题,将拥堵直接纳入成本函数。
- CMPP为稀疏图的每个顶点分配基于流量的乘法惩罚,在频繁交汇的路径交汇处惩罚更高。
- 最小化总成本得到自主智能体可遵循的粗略时间独立路线。
- 开发了两种求解器:一种是精确的非线性规划求解器适用于小规模问题;另一种是快速找到大规模问题的次优解并迭代优化的两层搜索算法A-CMTS。
点此查看论文截图


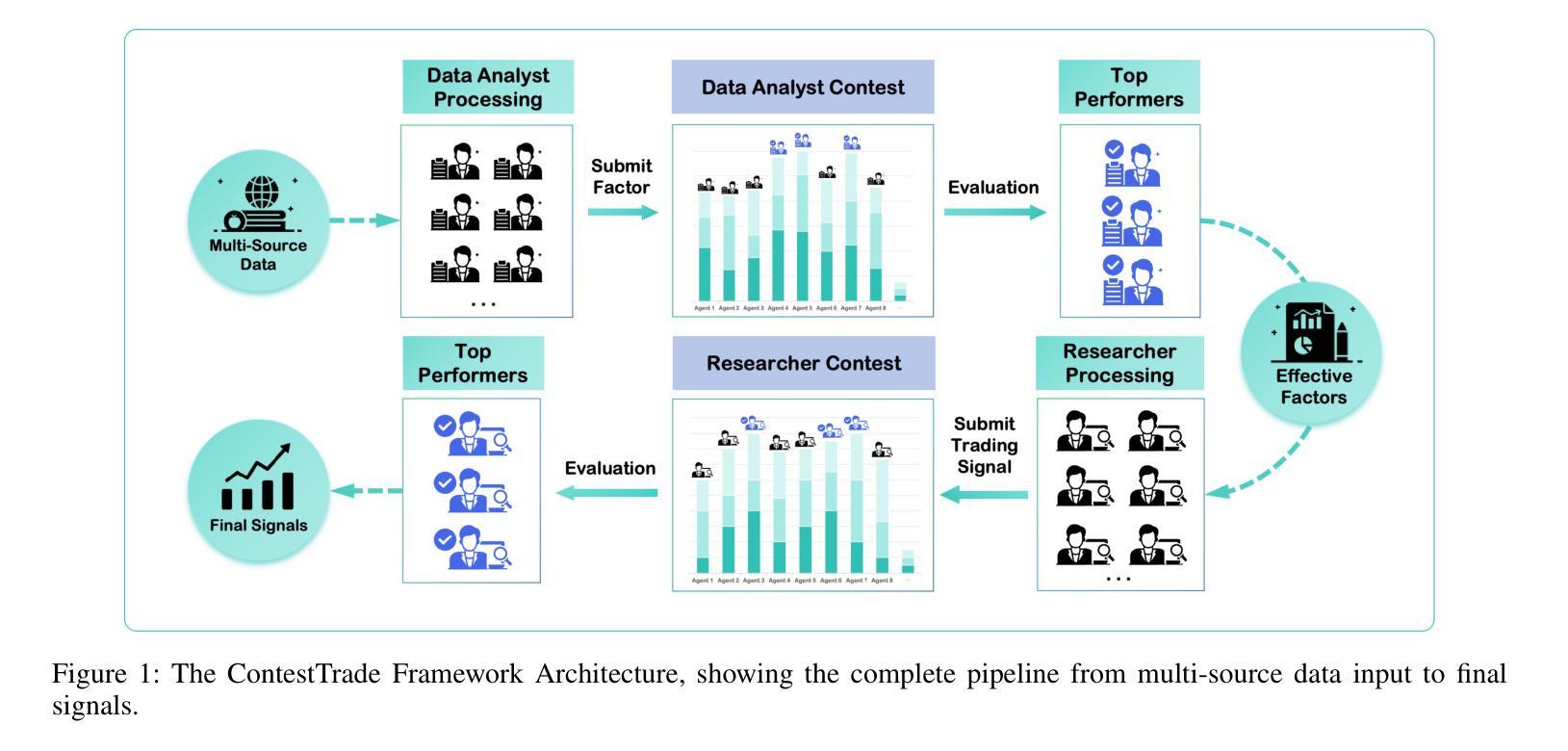
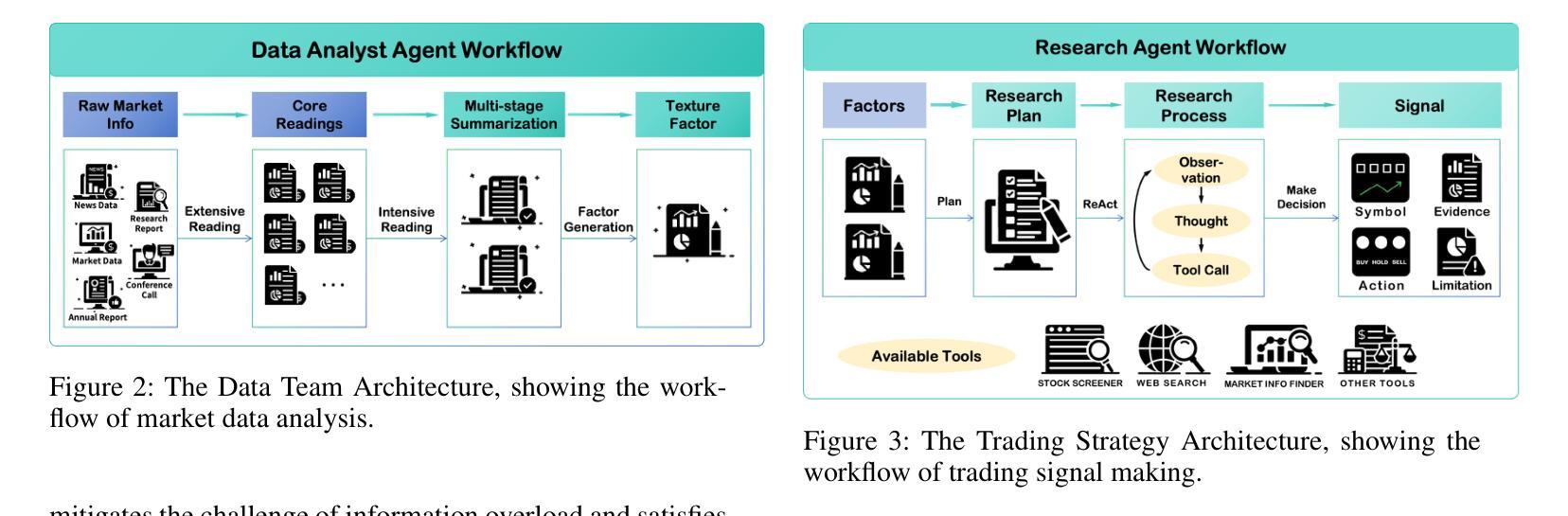
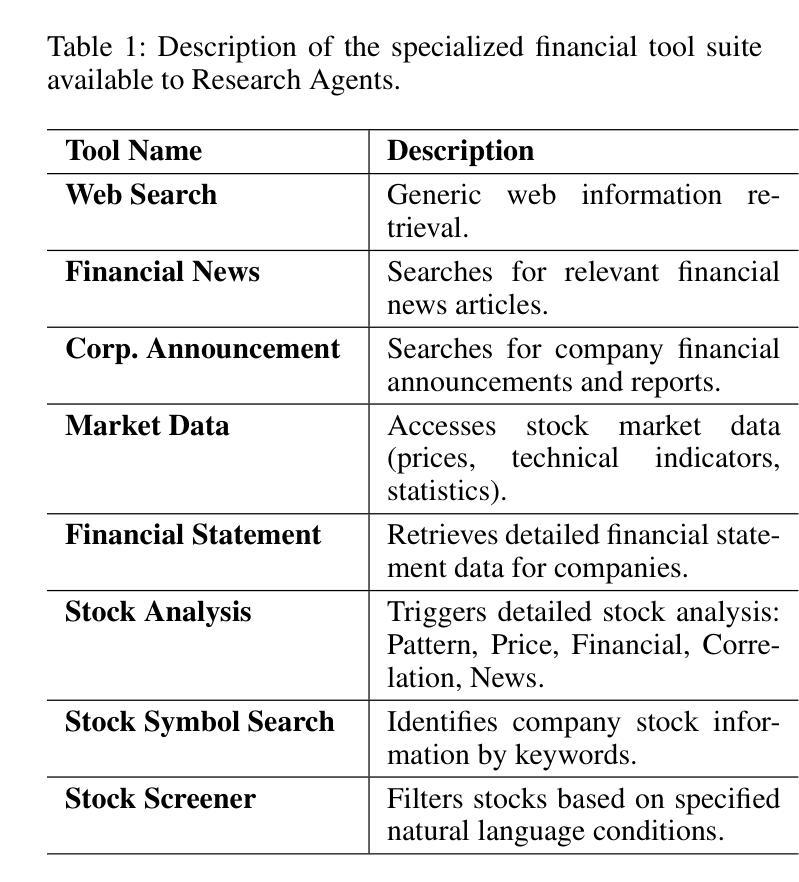
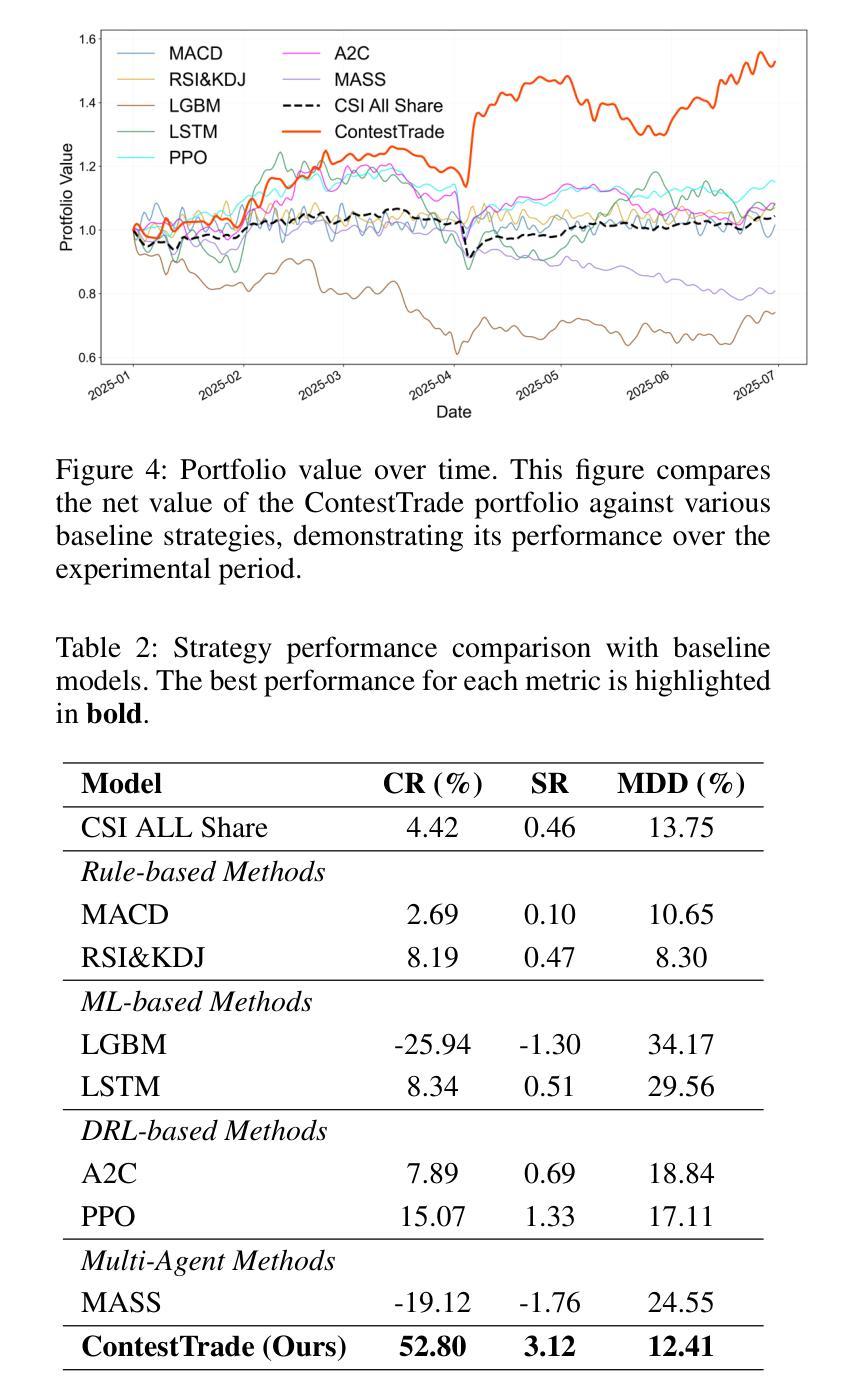
ContestTrade: A Multi-Agent Trading System Based on Internal Contest Mechanism
Authors:Li Zhao, Rui Sun, Zuoyou Jiang, Bo Yang, Yuxiao Bai, Mengting Chen, Xinyang Wang, Jing Li, Zuo Bai
In financial trading, large language model (LLM)-based agents demonstrate significant potential. However, the high sensitivity to market noise undermines the performance of LLM-based trading systems. To address this limitation, we propose a novel multi-agent system featuring an internal competitive mechanism inspired by modern corporate management structures. The system consists of two specialized teams: (1) Data Team - responsible for processing and condensing massive market data into diversified text factors, ensuring they fit the model’s constrained context. (2) Research Team - tasked with making parallelized multipath trading decisions based on deep research methods. The core innovation lies in implementing a real-time evaluation and ranking mechanism within each team, driven by authentic market feedback. Each agent’s performance undergoes continuous scoring and ranking, with only outputs from top-performing agents being adopted. The design enables the system to adaptively adjust to dynamic environment, enhances robustness against market noise and ultimately delivers superior trading performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed system significantly outperforms prevailing multi-agent systems and traditional quantitative investment methods across diverse evaluation metrics. ContestTrade is open-sourced on GitHub at https://github.com/FinStep-AI/ContestTrade.
在金融交易领域,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理展现出了巨大的潜力。然而,对市场噪声的高度敏感性削弱了LLM交易系统的性能。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型的多代理系统,该系统以现代企业管理结构为灵感,具备内部竞争机制。该系统由两个专业团队组成:(1)数据团队——负责处理和压缩大量市场数据,形成多样化的文本因素,确保它们符合模型的限制语境。(2)研究团队——根据深度研究方法制定并行多路径交易决策。核心创新在于在每个团队内部实施实时评估和排名机制,以真实的市场反馈为驱动。每个代理的表现都会进行持续评分和排名,只有表现最佳的代理的输出才会被采用。这种设计使系统能够自适应地调整动态环境,增强对市场噪声的稳健性,并最终实现优越的交易性能。实验结果表明,我们提出的系统在多种评价指标上显著优于现有的多代理系统和传统的量化投资方法。ContestTrade已在GitHub上开源,地址为:https://github.com/FinStep-AI/ContestTrade。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的金融交易代理展现出巨大潜力,但易受市场噪音影响。为此,我们提出一种新型多代理系统,该系统由数据团队和研究团队组成,借鉴现代企业管理结构中的竞争机制。通过实时评估和排名机制,系统能够自适应调整环境、增强对市场噪音的稳健性并提升交易性能。该系统已在GitHub上开源,性能优越。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在金融交易领域展现出巨大潜力。
- 市场噪音对LLM交易系统性能影响较大。
- 提出一种新型多代理系统,包含数据团队和研究团队。
- 系统借鉴现代企业管理结构中的竞争机制。
- 系统通过实时评估和排名机制自适应调整环境。
- 系统增强了对市场噪音的稳健性并提升了交易性能。
点此查看论文截图

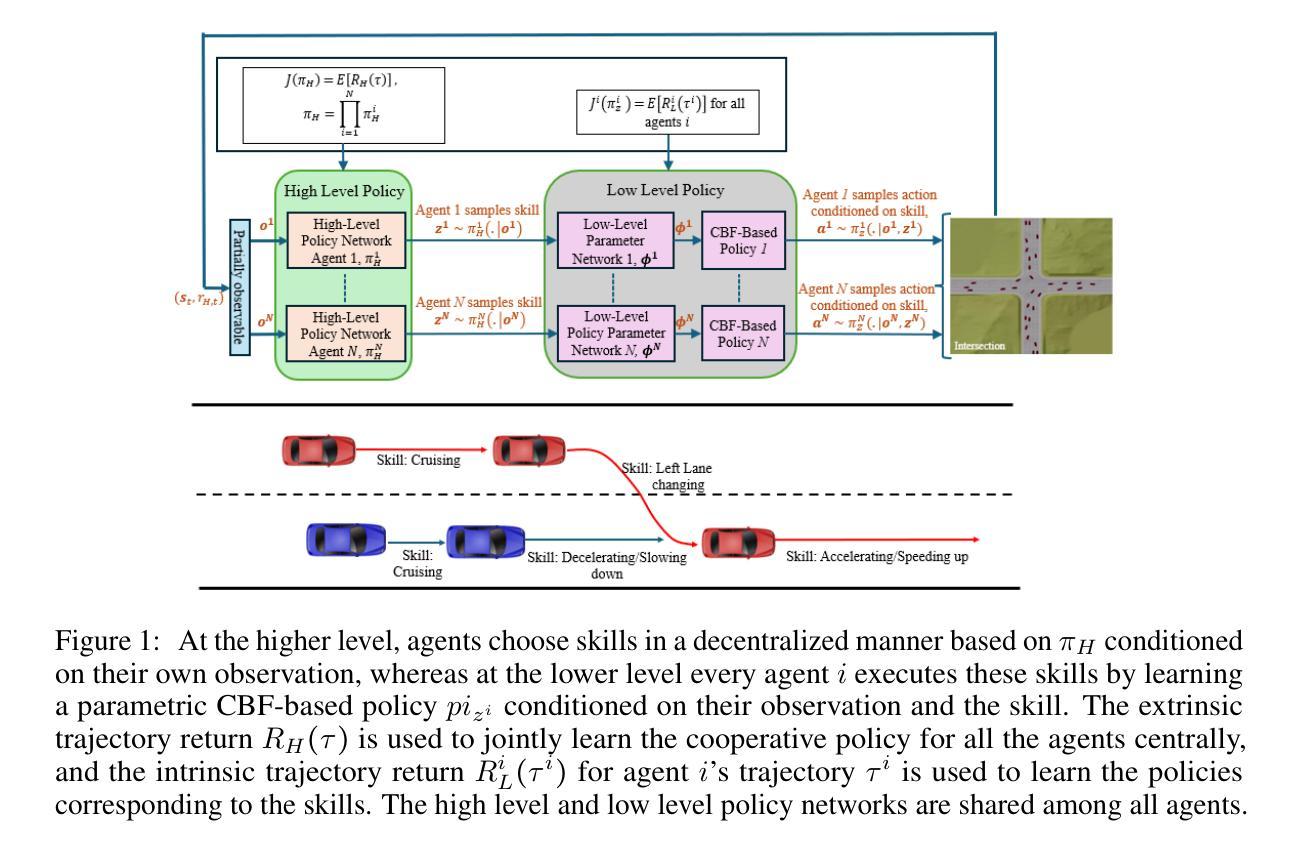
Hierarchical Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Control Barrier Functions for Safety-Critical Autonomous Systems
Authors:H. M. Sabbir Ahmad, Ehsan Sabouni, Alexander Wasilkoff, Param Budhraja, Zijian Guo, Songyuan Zhang, Chuchu Fan, Christos Cassandras, Wenchao Li
We address the problem of safe policy learning in multi-agent safety-critical autonomous systems. In such systems, it is necessary for each agent to meet the safety requirements at all times while also cooperating with other agents to accomplish the task. Toward this end, we propose a safe Hierarchical Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (HMARL) approach based on Control Barrier Functions (CBFs). Our proposed hierarchical approach decomposes the overall reinforcement learning problem into two levels learning joint cooperative behavior at the higher level and learning safe individual behavior at the lower or agent level conditioned on the high-level policy. Specifically, we propose a skill-based HMARL-CBF algorithm in which the higher level problem involves learning a joint policy over the skills for all the agents and the lower-level problem involves learning policies to execute the skills safely with CBFs. We validate our approach on challenging environment scenarios whereby a large number of agents have to safely navigate through conflicting road networks. Compared with existing state of the art methods, our approach significantly improves the safety achieving near perfect (within 5%) success/safety rate while also improving performance across all the environments.
我们解决多智能体安全关键自主系统中的安全策略学习问题。在这种系统中,每个智能体必须随时满足安全要求,同时与其他智能体合作完成任务。为此,我们提出了一种基于控制屏障函数(CBF)的安全分层多智能体强化学习(HMARL)方法。我们提出的分层方法将整体的强化学习问题分解为两个层次的学习:在较高层次上学习联合合作行为,在较低层次或智能体层面上学习以高级策略为条件的安全个体行为。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于技能的HMARL-CBF算法,其中高级问题涉及学习所有智能体的技能联合策略,而低级问题涉及使用CBF安全执行技能的学习策略。我们在具有挑战性的环境场景中验证了我们的方法,其中大量智能体必须通过冲突的道路网络进行安全导航。与现有最先进的相比,我们的方法显著提高了安全性,实现了近完美的(在5%以内)成功/安全率,同时提高了所有环境中的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
安全多智能体强化学习在关键自主系统中的研究。针对此类系统中各智能体需全天候满足安全需求且与其他智能体合作完成任务的问题,提出了一种基于控制屏障函数的安全分层多智能体强化学习(HMARL)方法。该方法将整体强化学习问题分解为两个层次的学习问题:高层学习联合合作行为,低层或智能体层次则在高层策略条件下学习安全个体行为。提出一种基于技能的HMARL-CBF算法,高层问题涉及学习所有智能体的技能联合策略,低层问题则涉及利用CBF学习安全执行技能的政策。在充满挑战的环境中验证了该方法的有效性,大量智能体在冲突道路网络上安全导航,相较于现有方法显著提高安全性,接近完美的成功/安全率(在5%以内),同时提高所有环境的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决多智能体安全关键自主系统中的安全策略学习问题。
- 提出一种基于控制屏障函数的安全分层多智能体强化学习(HMARL)方法。
- 将整体强化学习问题分解为两个层次的学习问题:联合合作行为和个人安全行为。
- 提出一种基于技能的HMARL-CBF算法,其中高层学习所有智能体的技能联合策略,低层学习安全执行技能的政策。
- 在复杂环境中验证了该方法的有效性,大量智能体在冲突道路网络上安全导航。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法显著提高安全性,达到近乎完美的成功/安全率(在5%以内)。
点此查看论文截图

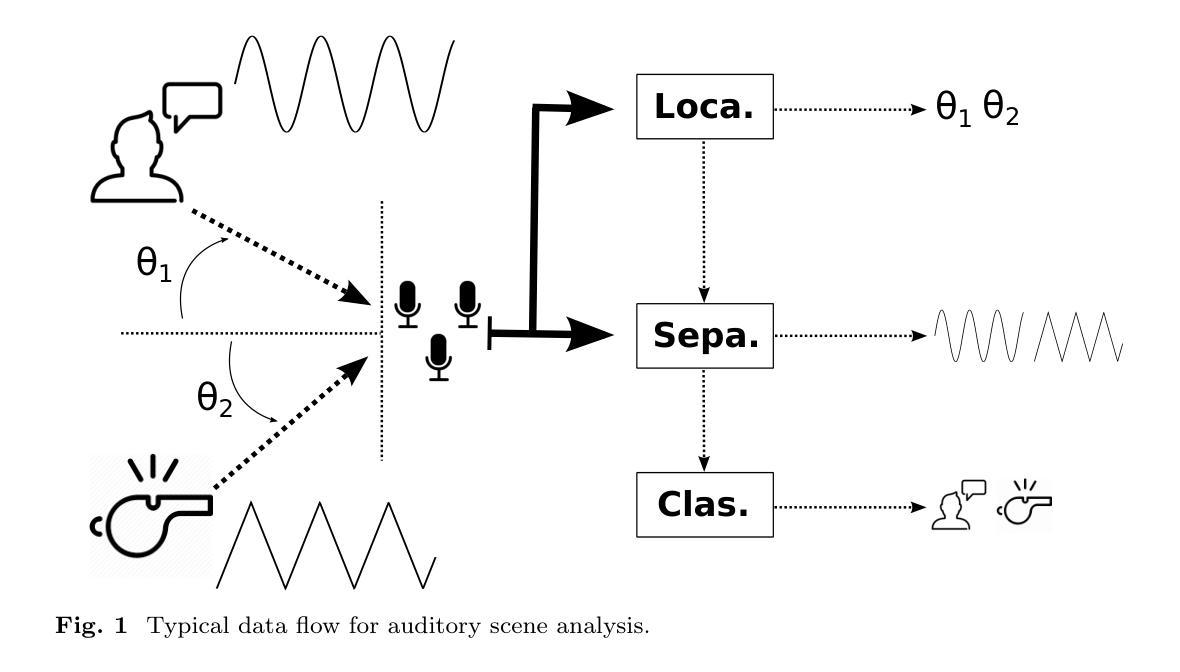
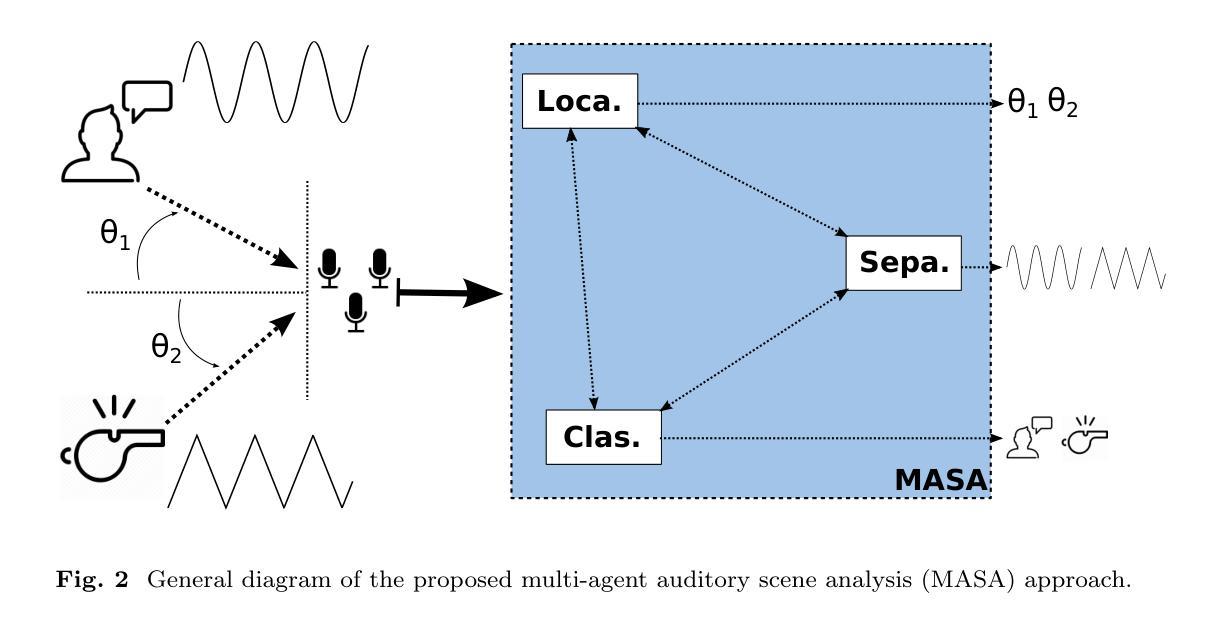
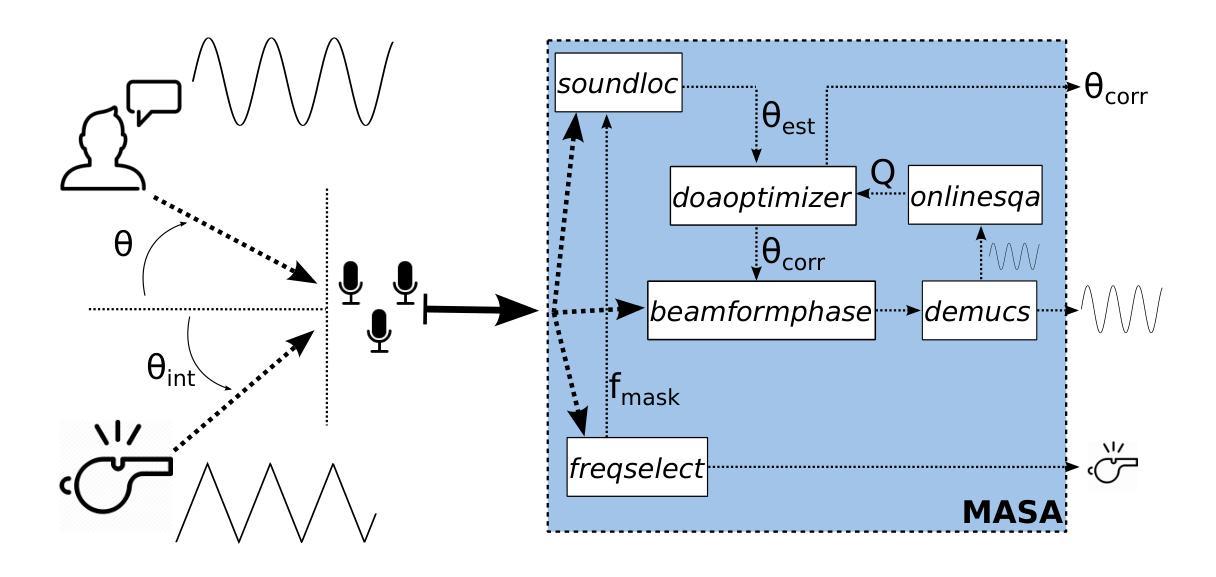
Multi-agent Auditory Scene Analysis
Authors:Caleb Rascon, Luis Gato-Diaz, Eduardo García-Alarcón
Auditory scene analysis (ASA) aims to retrieve information from the acoustic environment, by carrying out three main tasks: sound source location, separation, and classification. These tasks are traditionally executed with a linear data flow, where the sound sources are first located; then, using their location, each source is separated into its own audio stream; from each of which, information is extracted that is relevant to the application scenario (audio event detection, speaker identification, emotion classification, etc.). However, running these tasks linearly increases the overall response time, while making the last tasks (separation and classification) highly sensitive to errors of the first task (location). A considerable amount of effort and computational complexity has been employed in the state-of-the-art to develop techniques that are the least error-prone possible. However, doing so gives rise to an ASA system that is non-viable in many applications that require a small computational footprint and a low response time, such as bioacoustics, hearing-aid design, search and rescue, human-robot interaction, etc. To this effect, in this work, a multi-agent approach is proposed to carry out ASA where the tasks are run in parallel, with feedback loops between them to compensate for local errors, such as: using the quality of the separation output to correct the location error; and using the classification result to reduce the localization’s sensitivity towards interferences. The result is a multi-agent auditory scene analysis (MASA) system that is robust against local errors, without a considerable increase in complexity, and with a low response time. The complete proposed MASA system is provided as a framework that uses open-source tools for sound acquisition and reproduction (JACK) and inter-agent communication (ROS2), allowing users to add their own agents.
听觉场景分析(ASA)旨在通过执行三个主要任务从声学环境中检索信息:声源定位、分离和分类。这些任务通常是按线性数据流执行的,首先定位声源;然后,利用它们的位置,将每个声源分离成各自的音频流;从每个音频流中提取与应用场景相关的信息(如音频事件检测、说话人识别、情感分类等)。然而,按线性方式运行这些任务会增加总体响应时间,同时使最后的任务(分离和分类)对第一个任务(定位)的错误高度敏感。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Applied Soft Computing
Summary
多智能体听觉场景分析(MASA)采用并行执行任务的方式,通过反馈环路补偿局部错误,如利用分离质量校正定位误差和利用分类结果减少干扰对定位的影响。MASA系统对局部错误具有鲁棒性,且复杂度增加不大,响应时间快。
Key Takeaways
- 听觉场景分析(ASA)主要从声学环境中提取信息,包括声音源定位、分离和分类三个主要任务。
- 传统线性执行这些任务的方法会增加总体响应时间,并使后续任务对前面任务的错误更加敏感。
- 在本研究中,提出了一种多智能体听觉场景分析(MASA)方法,该方法采用并行执行任务,并在任务间建立反馈环路以补偿局部错误。
- MASA系统利用分离质量校正定位误差,并使用分类结果来减少干扰对定位的影响,从而增强了对局部错误的鲁棒性。
- MASA系统的复杂度增加不大,且具备快速的响应时间,使其适用于对计算足迹和响应时间有严格要求的应用。
- MASA系统框架利用开源工具进行声音采集和复制(JACK)以及智能体间通信(ROS2),用户可添加自己的智能体。
- MASA系统框架的提供为研究者提供了一个实现多智能体听觉场景分析的平台。
点此查看论文截图

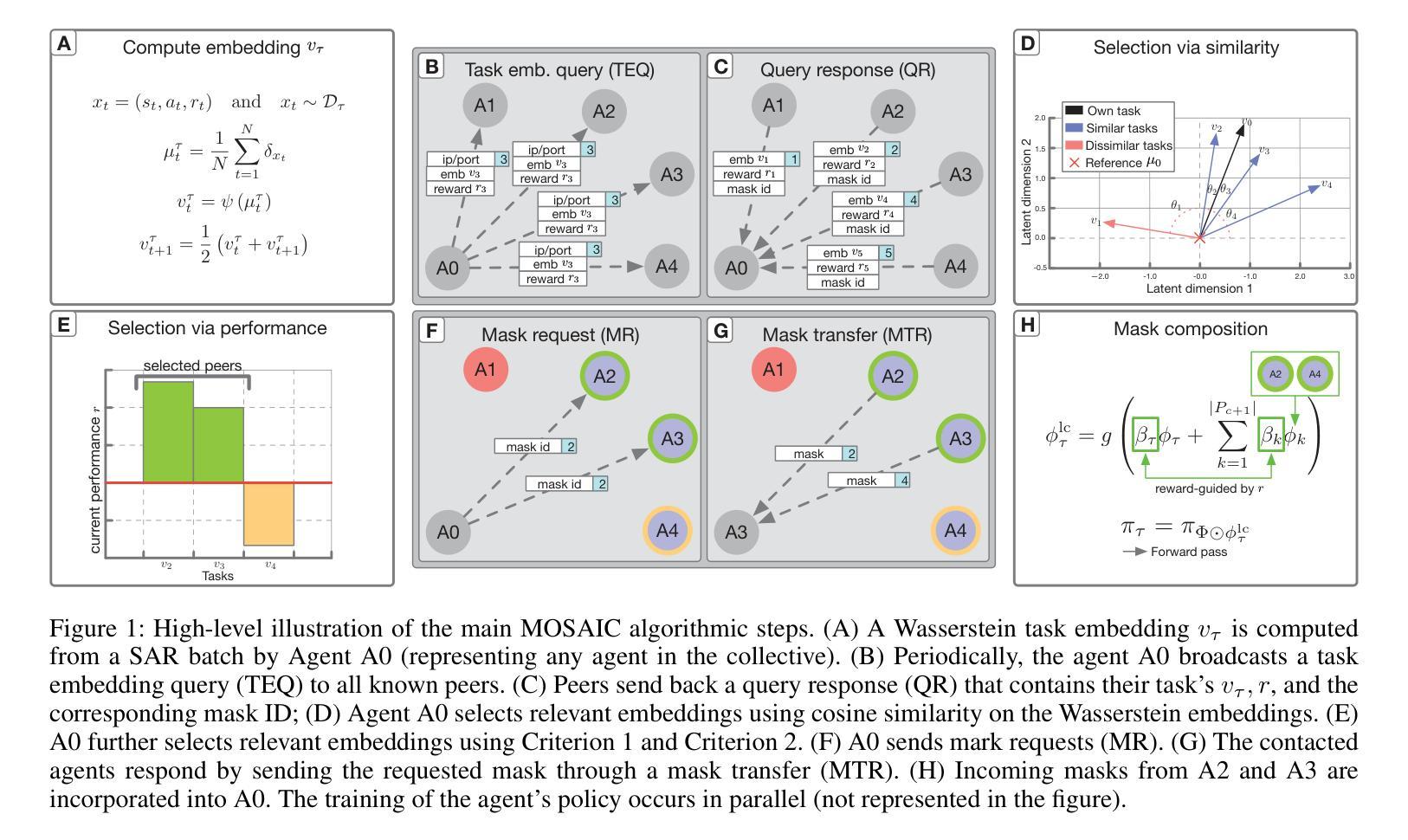
Policy Search, Retrieval, and Composition via Task Similarity in Collaborative Agentic Systems
Authors:Saptarshi Nath, Christos Peridis, Eseoghene Benjamin, Xinran Liu, Soheil Kolouri, Peter Kinnell, Zexin Li, Cong Liu, Shirin Dora, Andrea Soltoggio
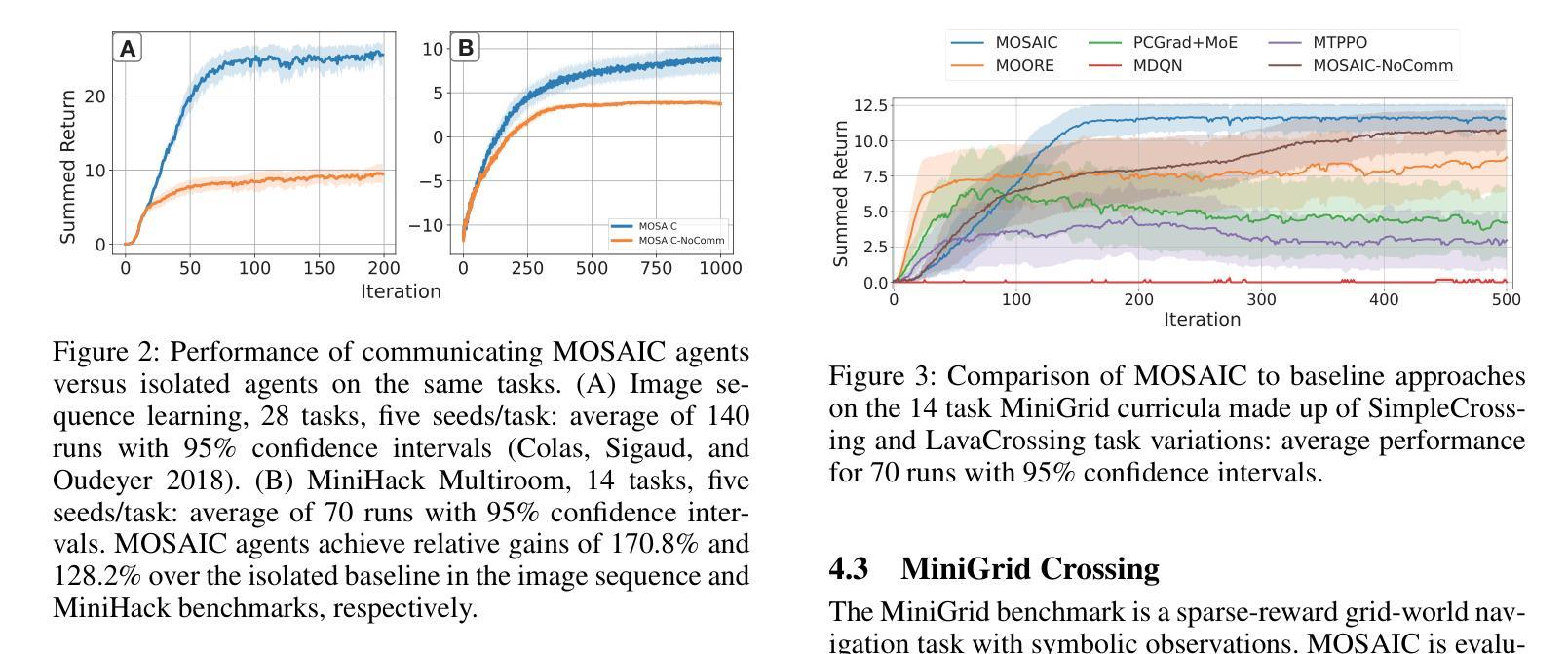
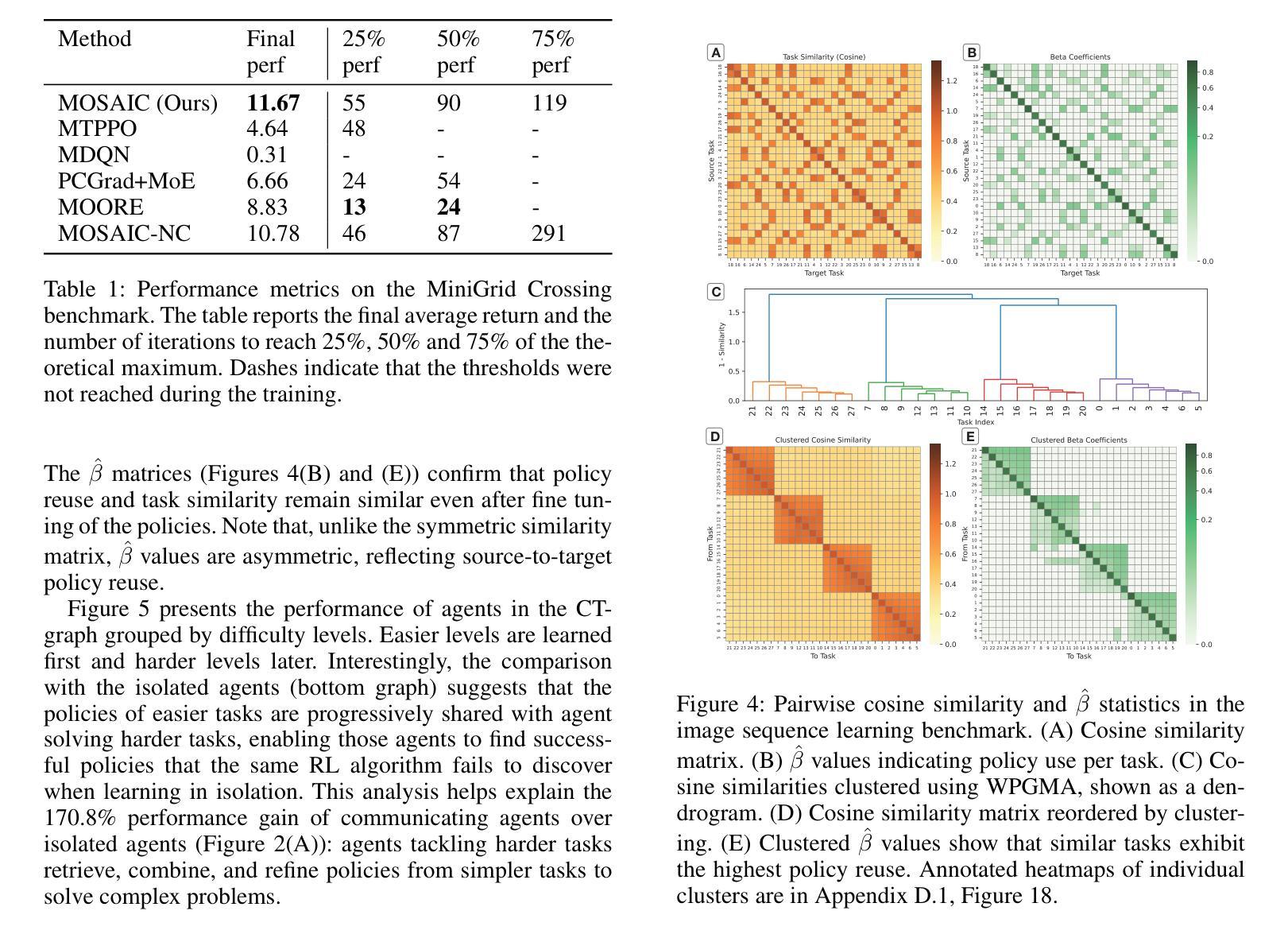
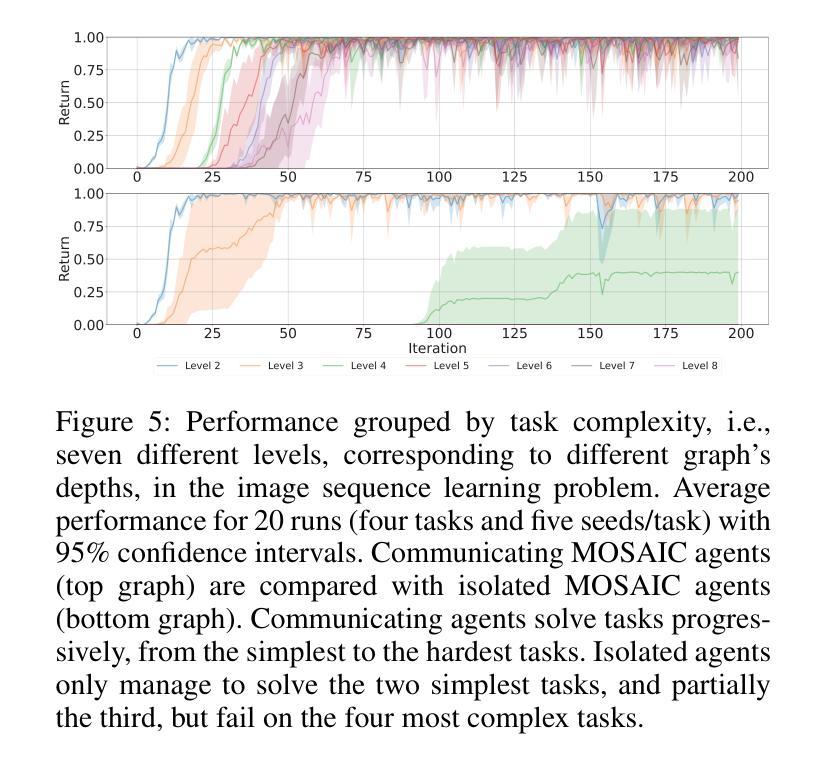
Agentic AI aims to create systems that set their own goals, adapt proactively to change, and refine behavior through continuous experience. Recent advances suggest that, when facing multiple and unforeseen tasks, agents could benefit from sharing machine-learned knowledge and reuse policies that have already been fully or partially learned by other agents. However, how to query, select, and retrieve policies from a pool of agents, and how to integrate such policies remains a largely unexplored area. This study explores how an agent decides what knowledge to select, from whom, and when and how to integrate it in its own policy in order to accelerate its own learning. The proposed algorithm, \emph{Modular Sharing and Composition in Collective Learning} (MOSAIC), improves learning in agentic collectives by combining (1) knowledge selection using performance signals and cosine similarity on Wasserstein task embeddings, (2) modular and transferable neural representations via masks, and (3) policy integration, composition and fine-tuning. MOSAIC outperforms isolated learners and global sharing approaches in both learning speed and overall performance, and in some cases solves tasks that isolated agents cannot. The results also demonstrate that selective, goal-driven reuse leads to less susceptibility to task interference. We also observe the emergence of self-organization, where agents solving simpler tasks accelerate the learning of harder ones through shared knowledge.
人工智能Agent旨在创建能够自主设定目标、主动适应变化并通过持续经验调整行为的系统。最近的进展表明,在面对多个和未曾预见的任务时,agents可以通过共享机器学习的知识和重用其他agents已经完全或部分学习的策略来获益。然而,如何从多个agents的池中查询、选择和检索策略,以及如何整合这些策略仍然是一个尚未完全探索的领域。本研究探讨了agent如何决定选择哪些知识、从谁那里获取、以及何时以及如何将其整合到自身的策略中,以加速其自身的学习。提出的算法“集体学习中的模块化共享与组合”(MOSAIC),通过以下三个方面改进了集体学习中的学习:1)使用性能信号和Wasserstein任务嵌入上的余弦相似性进行知识选择;2)通过掩码实现模块化可迁移的神经表征;以及3)策略集成、组合和微调。MOSAIC在学习速度和整体性能上均优于孤立学习者和全局共享方法,在某些情况下,可以解决孤立agents无法解决的问题。结果还表明,选择性、目标驱动的重用降低了对任务干扰的敏感性。我们还观察到自我组织的出现,其中解决简单任务的agents通过共享知识来加速解决更复杂任务的学习。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 20 figures, 6 tables. Preprint
Summary
人工智能代理系统通过学习设定自身目标、主动适应变化并通过持续经验优化行为。面对多重和未曾预见的任务时,代理之间共享机器学到的知识和重用其他代理已完全或部分学到的策略可带来好处。然而,如何查询、选择和检索代理池中的策略,以及如何整合这些策略仍是一个待探索的领域。本研究探讨了代理如何决定选择哪些知识、从谁那里获取、以及何时和如何将其整合到自身策略中,以加速自身学习。提出的算法“集体学习中的模块化共享与组合(MOSAIC)”通过结合知识选择、模块化可转移的神经表征和策略整合,提高了代理集体的学习效率。MOSAIC在学习速度和整体性能上超越了孤立学习者和全局共享方法,并在某些情况下解决了孤立代理无法解决的问题。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic AI系统能自主设定目标、适应变化,并通过经验持续优化行为。
- 面对多重任务时,代理之间共享知识和策略带来益处。
- 知识选择、模块化可转移的神经表征和策略整合是提高代理学习效率的关键。
- MOSAIC算法通过结合性能信号和余弦相似性在Wasserstein任务嵌入中进行知识选择。
- MOSAIC在学习速度和整体性能上优于孤立学习者和全局共享方法。
- 选择性、目标驱动的重用策略减少了任务干扰的易感性。
点此查看论文截图

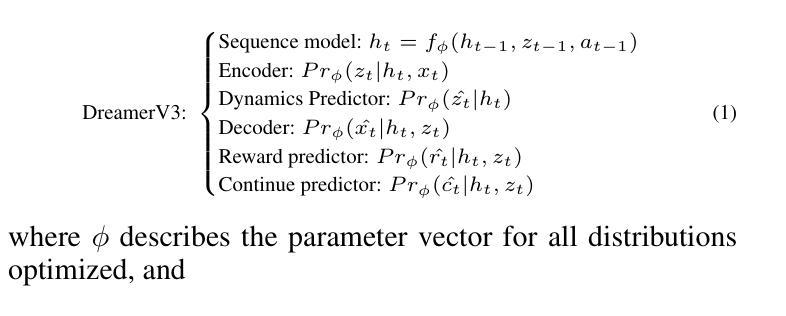
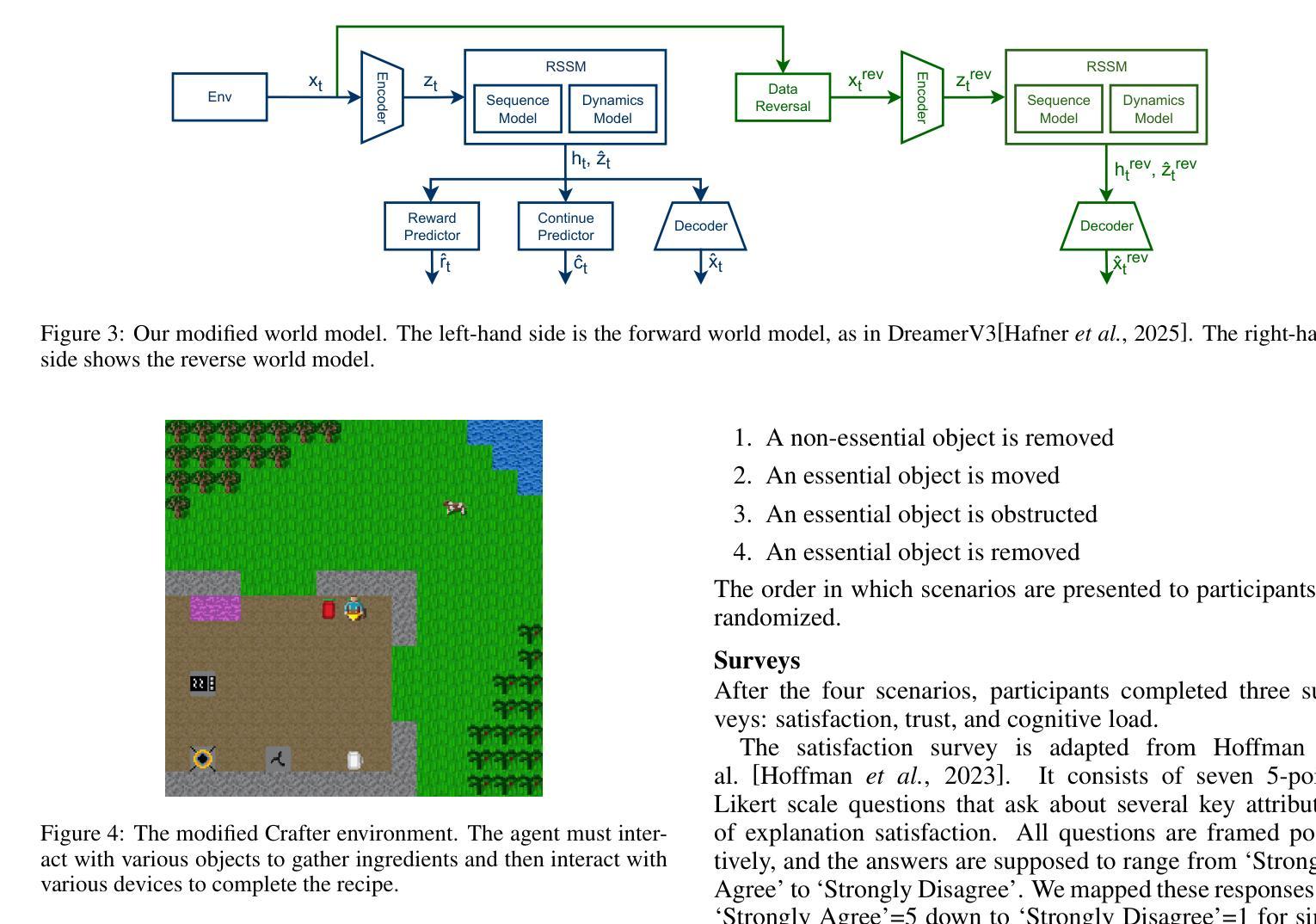
Explainable Reinforcement Learning Agents Using World Models
Authors:Madhuri Singh, Amal Alabdulkarim, Gennie Mansi, Mark O. Riedl
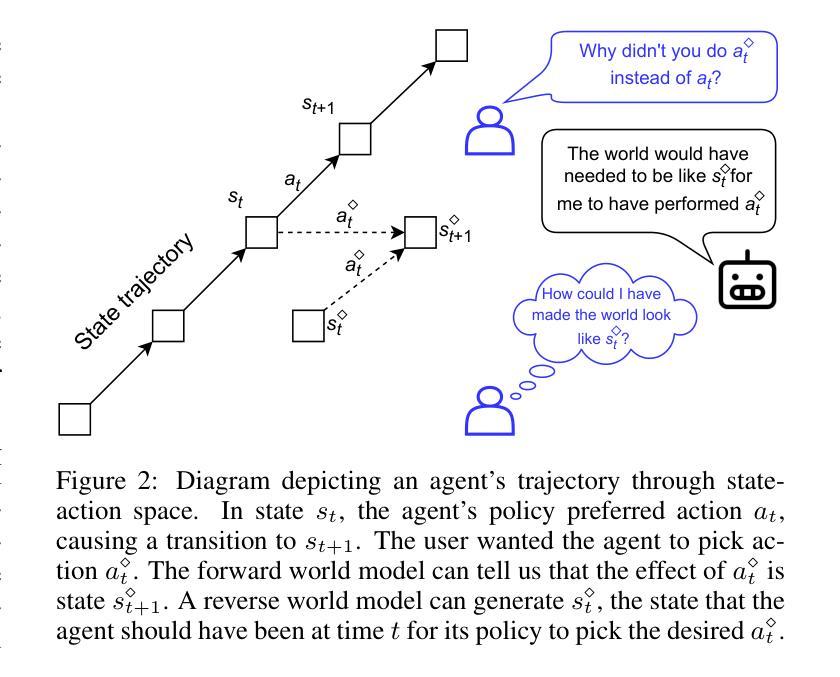
Explainable AI (XAI) systems have been proposed to help people understand how AI systems produce outputs and behaviors. Explainable Reinforcement Learning (XRL) has an added complexity due to the temporal nature of sequential decision-making. Further, non-AI experts do not necessarily have the ability to alter an agent or its policy. We introduce a technique for using World Models to generate explanations for Model-Based Deep RL agents. World Models predict how the world will change when actions are performed, allowing for the generation of counterfactual trajectories. However, identifying what a user wanted the agent to do is not enough to understand why the agent did something else. We augment Model-Based RL agents with a Reverse World Model, which predicts what the state of the world should have been for the agent to prefer a given counterfactual action. We show that explanations that show users what the world should have been like significantly increase their understanding of the agent policy. We hypothesize that our explanations can help users learn how to control the agents execution through by manipulating the environment.
可解释的AI(XAI)系统已经被提出,以帮助人们理解AI系统如何产生输出和行为。由于时序决策的自然属性,可解释的强化学习(XRL)增加了额外的复杂性。此外,非AI专家并不一定具备改变代理或其策略的能力。我们引入了一种使用世界模型来为基于模型的深度强化学习代理生成解释的技术。世界模型预测了当执行动作时世界将如何变化,从而可以生成反事实轨迹。然而,仅仅确定用户希望代理执行的操作并不足以理解为什么代理执行了其他操作。我们用反向世界模型增强基于模型的RL代理,该模型预测世界状态应该是怎样的,才能使代理偏好给定的反事实动作。我们表明,向用户展示世界应该是怎样的样子的解释,能显著提高他们对代理策略的理解。我们假设我们的解释可以帮助用户学习如何通过操纵环境来控制代理的执行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Workshop on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) at IJCAI 2025
Summary
本摘要介绍了可解释的强化学习(XRL)的复杂性及其对于时序决策制定的挑战。为解决这一问题,我们引入了使用世界模型(World Models)为基于模型的深度强化学习(Model-Based Deep RL)代理生成解释的技术。通过预测世界在执行动作时的变化,世界模型可以生成反事实轨迹。然而,仅仅了解用户希望代理执行的动作并不足以理解代理的实际行为原因。因此,我们增强了基于模型的RL代理的反向世界模型(Reverse World Model),它预测对于代理偏好给定的反事实动作时世界的状态应该是什么样的。实验表明,解释用户看到的世界应该是怎样的,可以显著提高他们对代理策略的理解。我们假设这些解释可以帮助用户学习如何通过操纵环境来控制代理的执行。
Key Takeaways
- 可解释的强化学习(XRL)面临复杂性和挑战,特别是时序决策的问题。
- 世界模型技术被用来为基于模型的深度强化学习代理生成解释。
- 世界模型可以生成反事实轨迹,预测世界在执行动作时的变化。
- 仅知道用户希望代理执行的动作不足以理解代理的实际行为原因。
- 反向世界模型增强了基于模型的RL代理,预测在给定反事实动作下世界的状态。
- 显示给用户的世界模型解释能显著提高他们对代理策略的理解。
点此查看论文截图

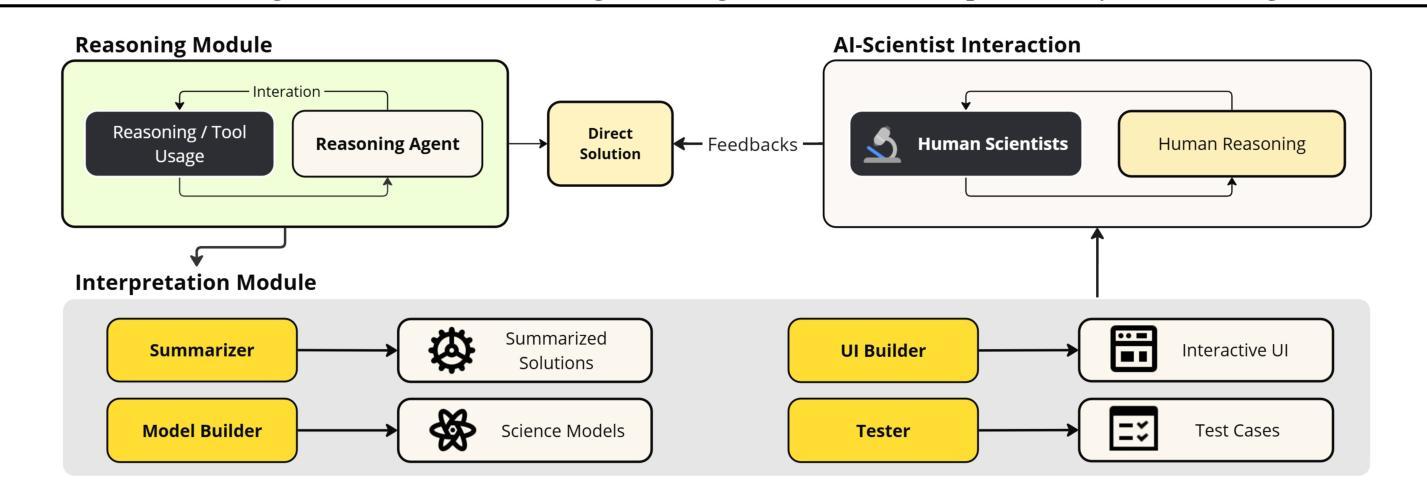
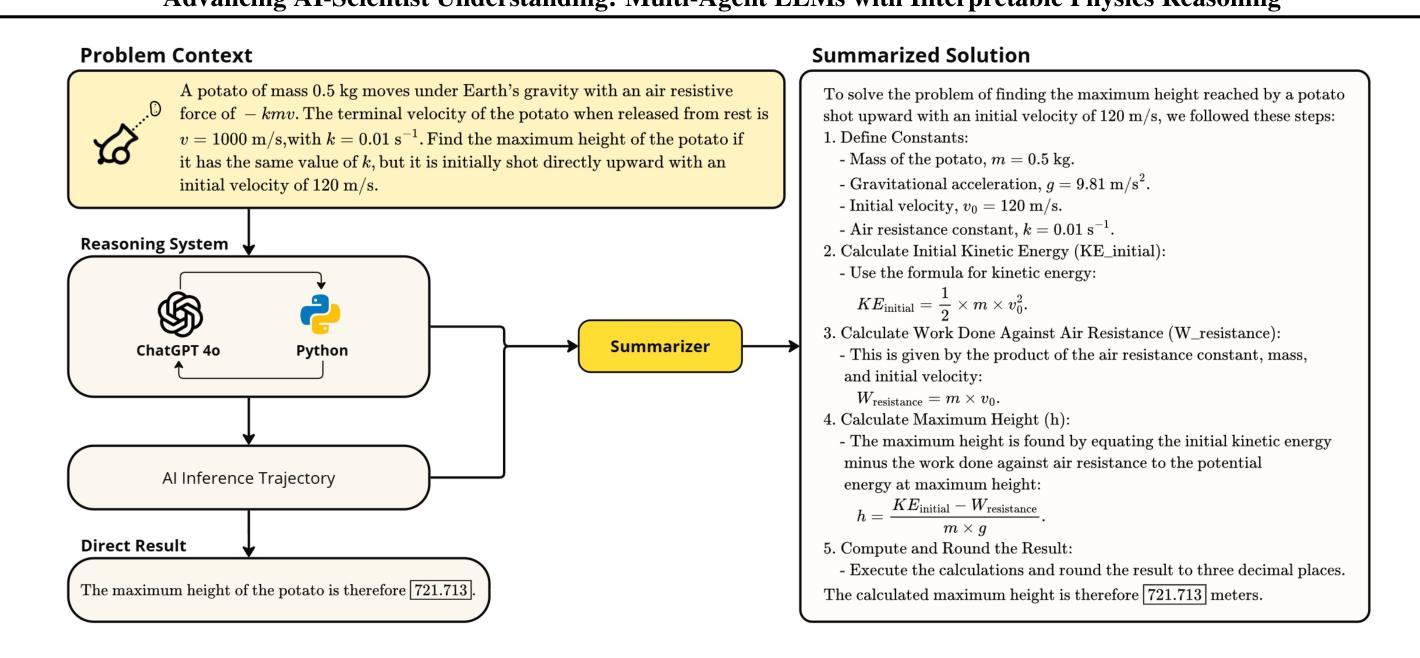
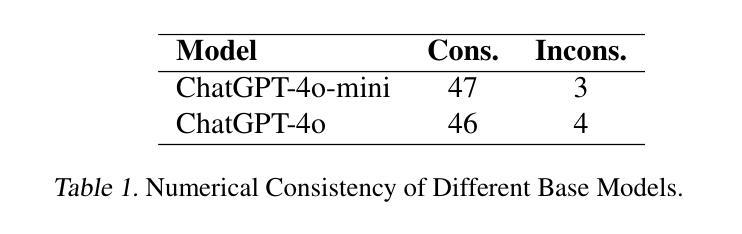
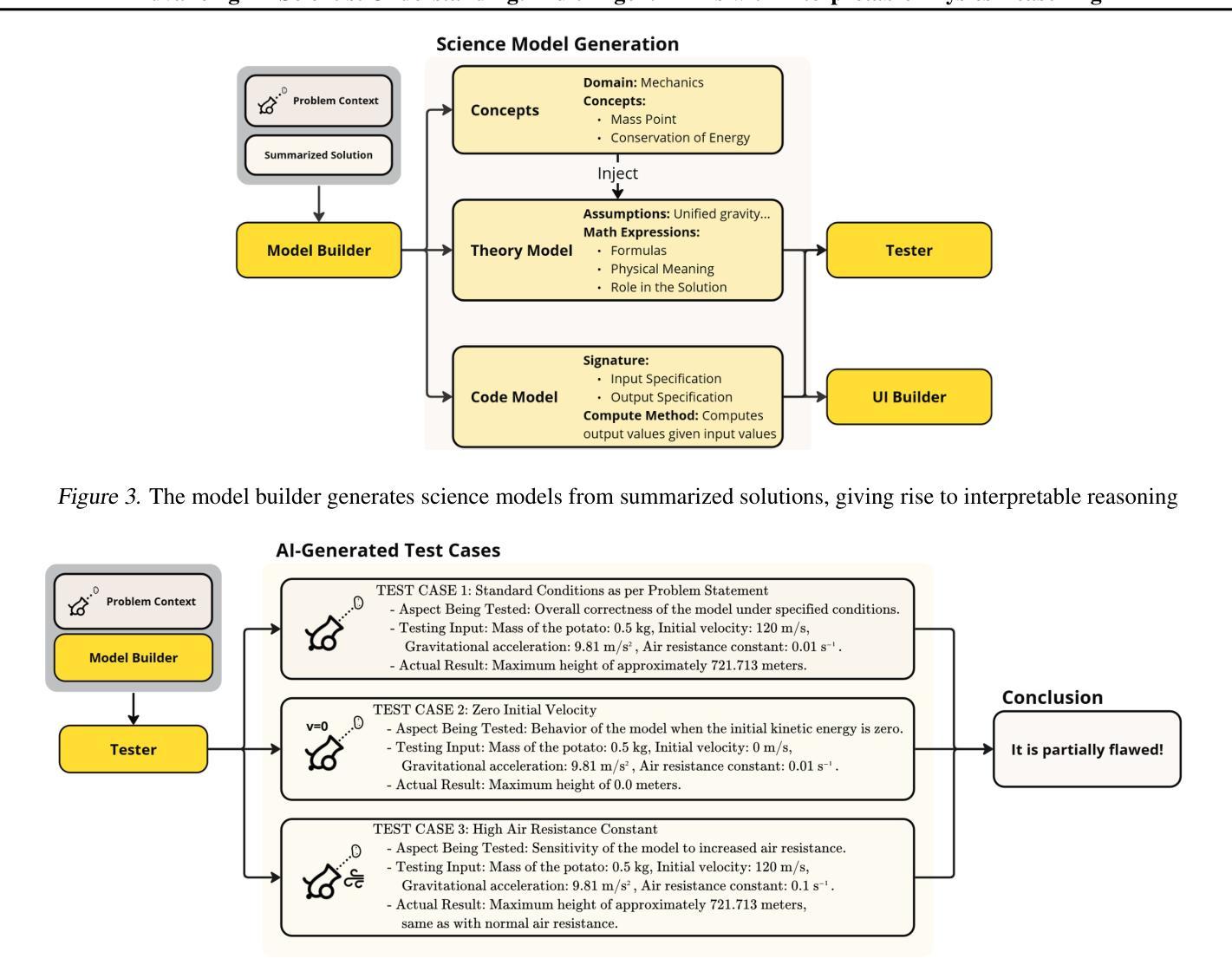
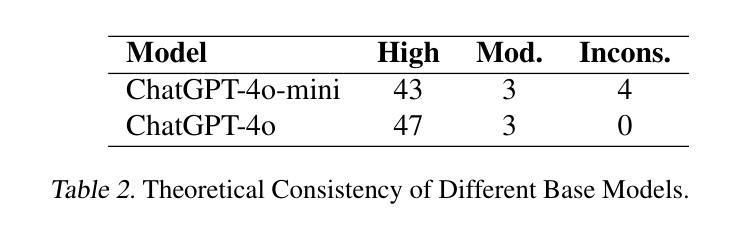
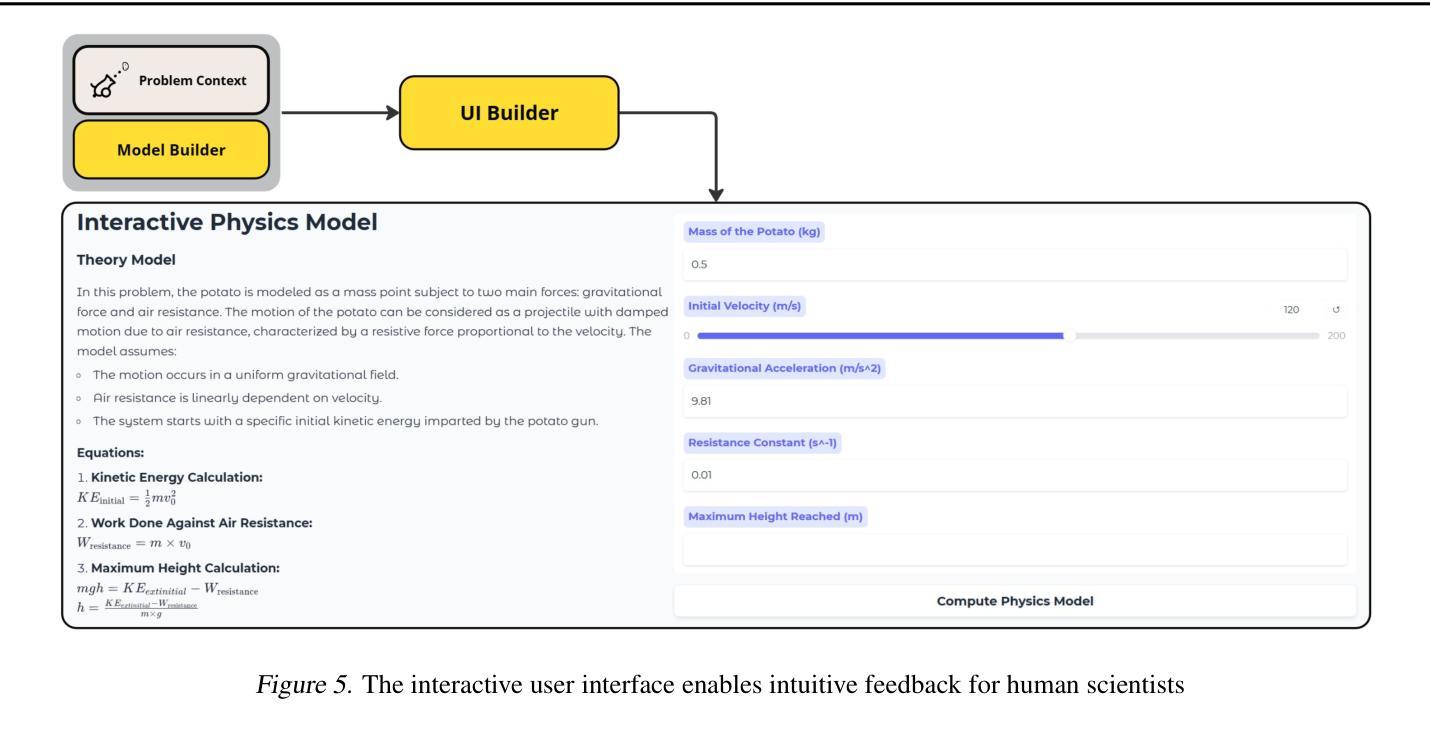
Advancing AI-Scientist Understanding: Multi-Agent LLMs with Interpretable Physics Reasoning
Authors:Yinggan Xu, Hana Kimlee, Yijia Xiao, Di Luo
Large Language Models (LLMs) are playing an increasingly important role in physics research by assisting with symbolic manipulation, numerical computation, and scientific reasoning. However, ensuring the reliability, transparency, and interpretability of their outputs remains a major challenge. In this work, we introduce a novel multi-agent LLM physicist framework that fosters collaboration between AI and human scientists through three key modules: a reasoning module, an interpretation module, and an AI-scientist interaction module. Recognizing that effective physics reasoning demands logical rigor, quantitative accuracy, and alignment with established theoretical models, we propose an interpretation module that employs a team of specialized LLM agents-including summarizers, model builders, visualization tools, and testers-to systematically structure LLM outputs into transparent, physically grounded science models. A case study demonstrates that our approach significantly improves interpretability, enables systematic validation, and enhances human-AI collaboration in physics problem-solving and discovery. Our work bridges free-form LLM reasoning with interpretable, executable models for scientific analysis, enabling more transparent and verifiable AI-augmented research.
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在物理研究中的作用越来越重要,它们可以协助进行符号操作、数值计算和科学推理。然而,确保这些输出的可靠性、透明度和可解释性仍然是一个主要挑战。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新型的多智能体LLM物理学家框架,该框架通过三个关键模块:推理模块、解释模块和人机互动模块,来培养人工智能与人类科学家之间的协作。我们认识到有效的物理推理需要逻辑严谨、定量准确并与既定的理论模型相符,因此,我们提出了一种解释模块,该模块采用一组专业的LLM智能体,包括摘要撰写者、模型构建者、可视化工具和测试者等,以系统地构建透明的、基于物理的科学模型。一项案例研究表明,我们的方法显著提高了可解释性,实现了系统的验证,并增强了人类在解决物理问题和发现方面的能力。我们的工作将自由的LLM推理与可解释、可执行的模型相结合,用于科学分析,实现了更透明、可验证的人工智能辅助研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Workshop on MAS
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在物理研究中的作用日益重要,可协助进行符号操作、数值计算和科学研究推理。然而,确保输出的可靠性、透明度和可解释性是一大挑战。本研究介绍了一种新型的多智能体LLM物理学家框架,通过推理模块、解释模块和人机互动模块三个核心模块促进人工智能与人类科学家的合作。该框架采用专业LLM智能体团队进行结构化输出,以建立透明、基于物理的科学模型,显著提高了解释性,实现系统验证,并强化了人类与人工智能在解决物理问题和发现方面的合作。该研究将自由形式的LLM推理与可解释、可执行的模型相结合,实现了更透明和可验证的人工智能辅助研究。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在物理研究中发挥着重要作用,涵盖符号操作、数值计算和科学研究推理。
- LLM在物理研究中的可靠性、透明度和可解释性仍是挑战。
- 引入了一种新型的多智能体LLM物理学家框架,包含推理模块、解释模块和人机互动模块。
- 解释模块采用专业LLM智能体团队进行结构化输出,建立透明、基于物理的科学模型。
- 该框架提高了LLM输出的解释性,实现了系统验证。
- 强化了人类与人工智能在解决物理问题和发现方面的合作。
点此查看论文截图