⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
MAGNeT: Multimodal Adaptive Gaussian Networks for Intent Inference in Moving Target Selection across Complex Scenarios
Authors:Xiangxian Li, Yawen Zheng, Baiqiao Zhang, Yijia Ma, XianhuiCao XianhuiCao, Juan Liu, Yulong Bian, Jin Huang, Chenglei Yang
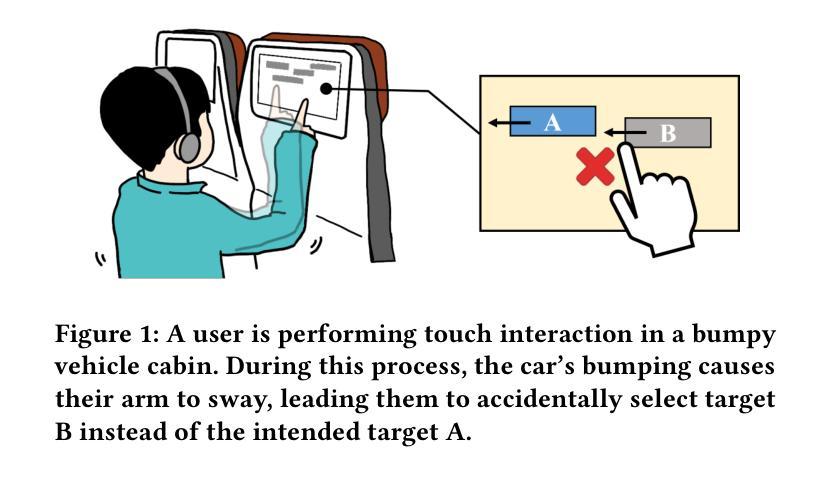
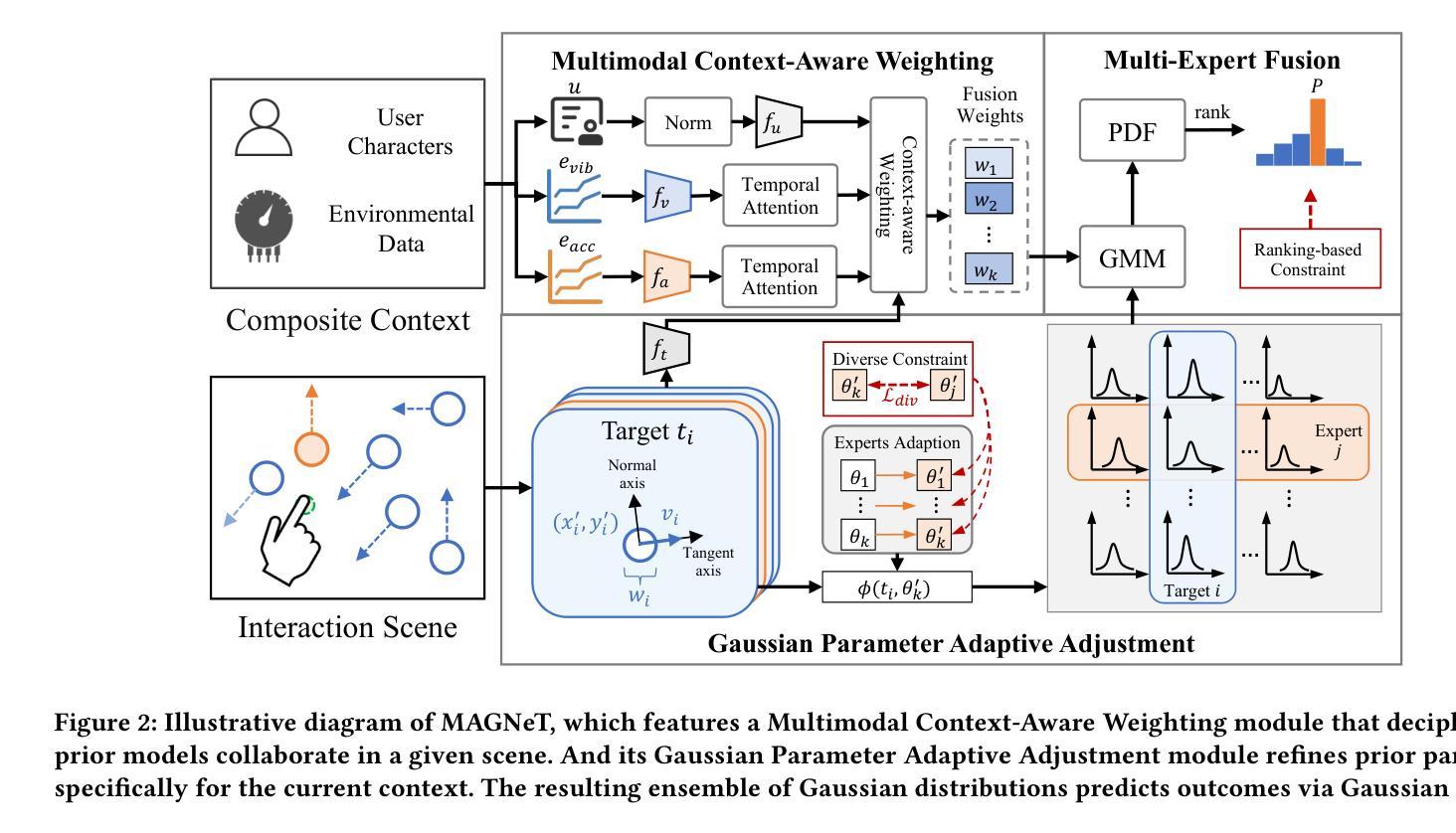
Moving target selection in multimedia interactive systems faces unprecedented challenges as users increasingly interact across diverse and dynamic contexts-from live streaming in moving vehicles to VR gaming in varying environments. Existing approaches rely on probabilistic models that relate endpoint distribution to target properties such as size and speed. However, these methods require substantial training data for each new context and lack transferability across scenarios, limiting their practical deployment in diverse multimedia environments where rich multimodal contextual information is readily available. This paper introduces MAGNeT (Multimodal Adaptive Gaussian Networks), which addresses these problems by combining classical statistical modeling with a context-aware multimodal method. MAGNeT dynamically fuses pre-fitted Ternary-Gaussian models from various scenarios based on real-time contextual cues, enabling effective adaptation with minimal training data while preserving model interpretability. We conduct experiments on self-constructed 2D and 3D moving target selection datasets under in-vehicle vibration conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MAGNeT achieves lower error rates with few-shot samples by applying context-aware fusion of Gaussian experts from multi-factor conditions.
多媒体交互系统中的动态目标选择面临着前所未有的挑战,因为用户在不同的动态上下文中的交互越来越频繁,从移动车辆中的直播到不同环境中的VR游戏。现有方法依赖于将端点分布与目标属性(如大小和速度)相关的概率模型。然而,这些方法需要针对每种新上下文的大量训练数据,并且在跨场景之间的迁移能力方面存在不足,从而限制了它们在丰富的多媒体环境中的实际部署,这些环境中丰富的多模态上下文信息很容易获得。本文介绍了MAGNeT(多模态自适应高斯网络),它通过结合经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法来解决这些问题。MAGNeT根据实时上下文线索动态融合来自各种场景的预先配置的三元高斯模型,通过最小的训练数据实现有效的适应,同时保持模型的可解释性。我们在自行构建的二维和三维移动目标选择数据集上进行了车内振动条件下的实验。大量实验表明,MAGNeT通过应用多因素条件下高斯专家的上下文感知融合,在少量样本的情况下实现了更低的错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
多媒体交互系统中移动目标选择面临前所未有的挑战,特别是在用户在不同动态环境中进行交互时。现有方法依赖于概率模型,将端点分布与目标属性关联,如大小和速度。但它们在面对新的上下文时需要大量训练数据,并且缺乏跨场景的迁移能力,限制了它们在丰富多媒体环境中的实际应用,这些环境中存在丰富的多模态上下文信息。本文提出MAGNeT(多模态自适应高斯网络),结合经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法来解决这些问题。MAGNeT根据实时上下文线索动态融合各种场景的预拟合三元高斯模型,在有限的训练数据基础上实现有效适应,同时保持模型的可解释性。通过实验验证了MAGNeT在低样本情况下实现较低错误率的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体交互系统中移动目标选择面临挑战,尤其是在动态环境中。
- 现有方法依赖于需要大量训练数据的概率模型,缺乏跨场景迁移能力。
- MAGNeT结合了经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法。
- MAGNeT根据实时上下文线索动态融合预拟合的三元高斯模型。
- MAGNeT在有限的训练数据上实现了有效适应,同时保持了模型的可解释性。
- 实验表明,MAGNeT在低样本情况下能够实现较低的错误率。
点此查看论文截图



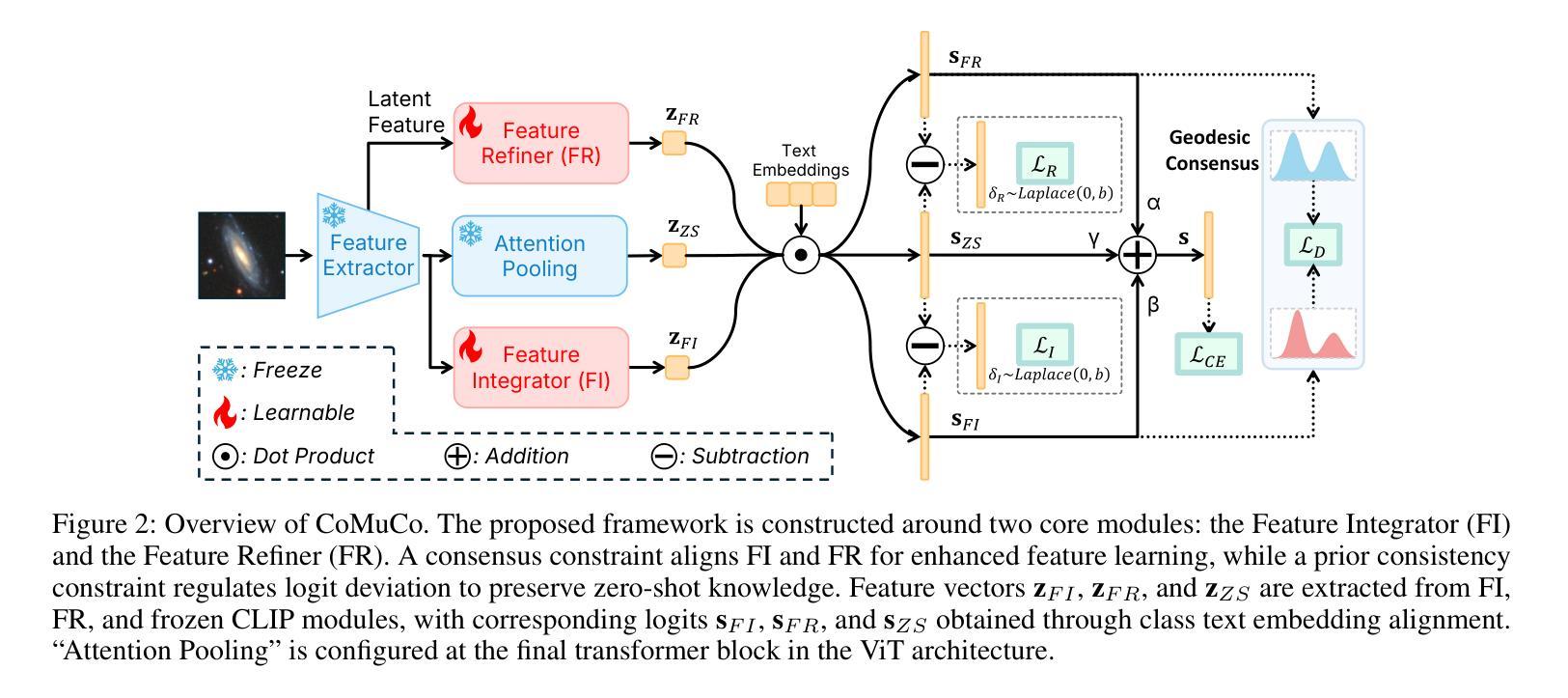
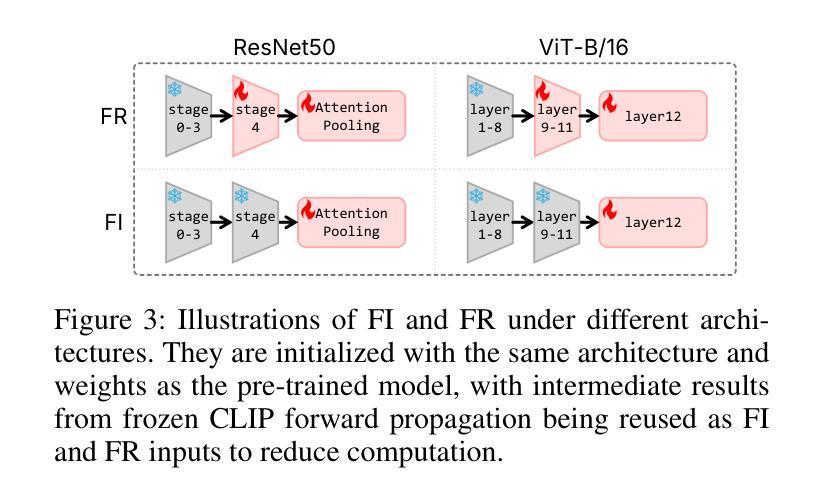
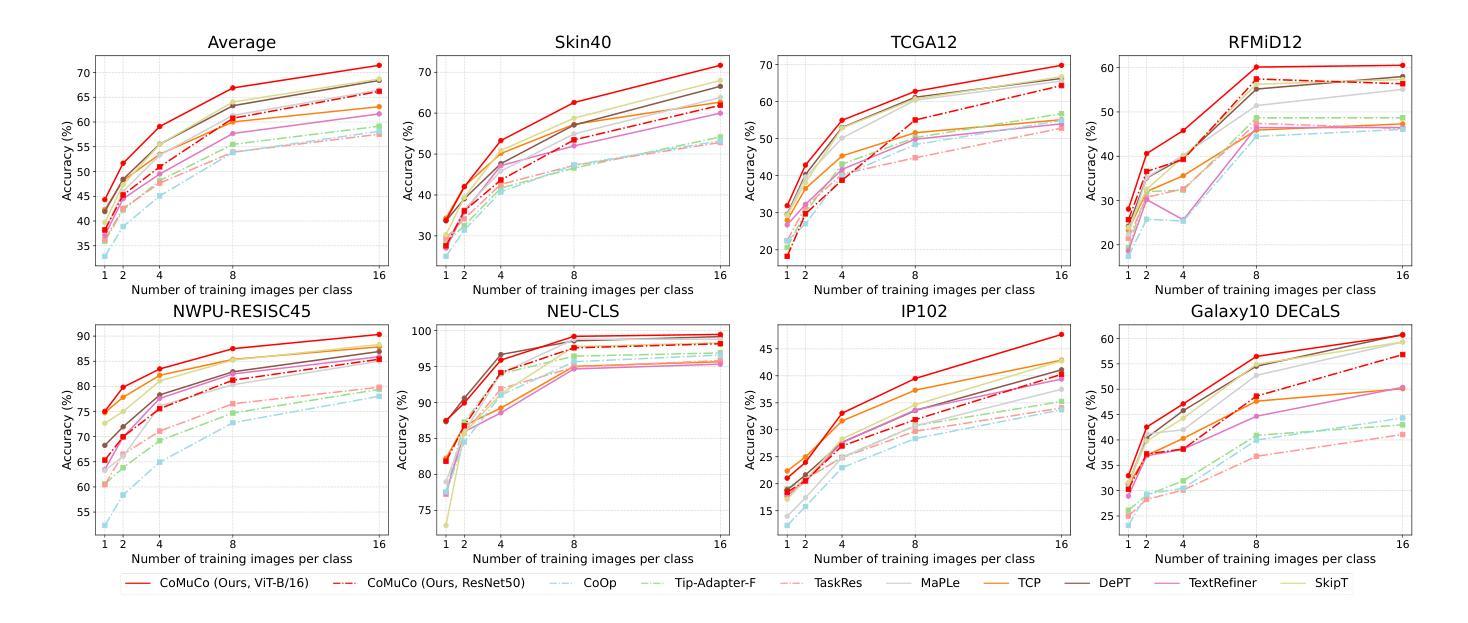
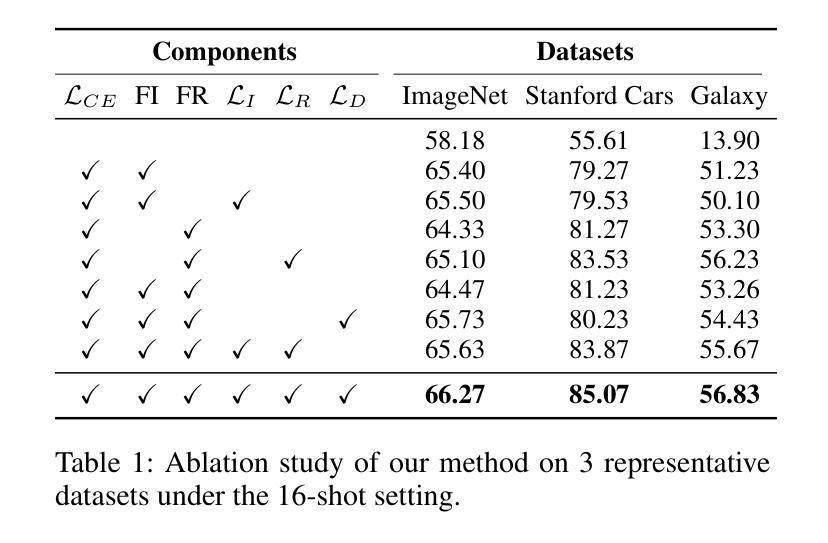
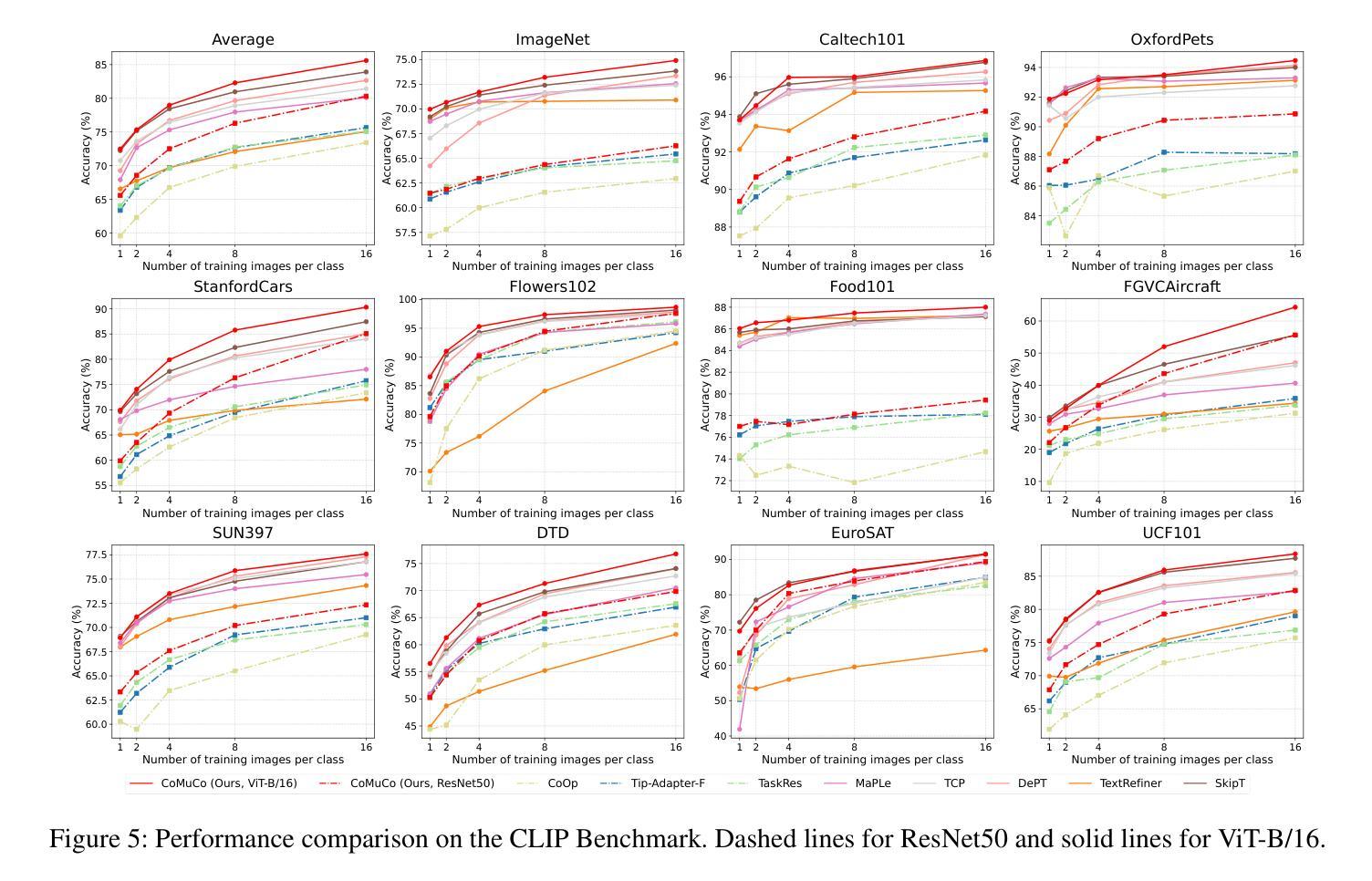
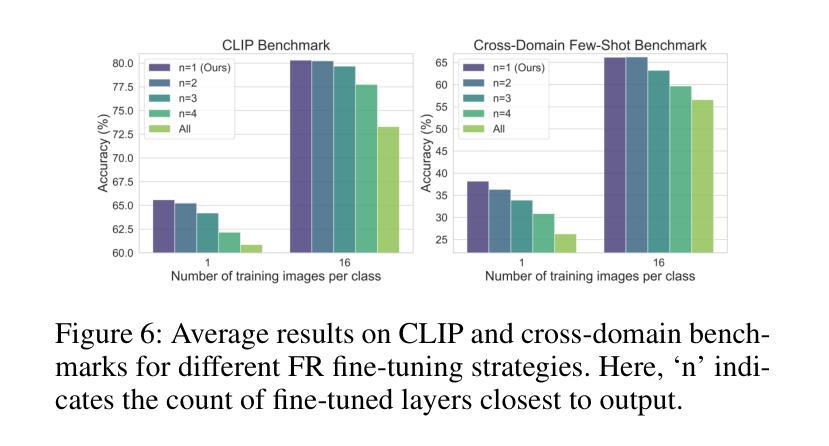
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning via Multi-View Collaborative Optimization with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Dexia Chen, Wentao Zhang, Qianjie Zhu, Ping Hu, Weibing Li, Tong Zhang, Ruixuan Wang
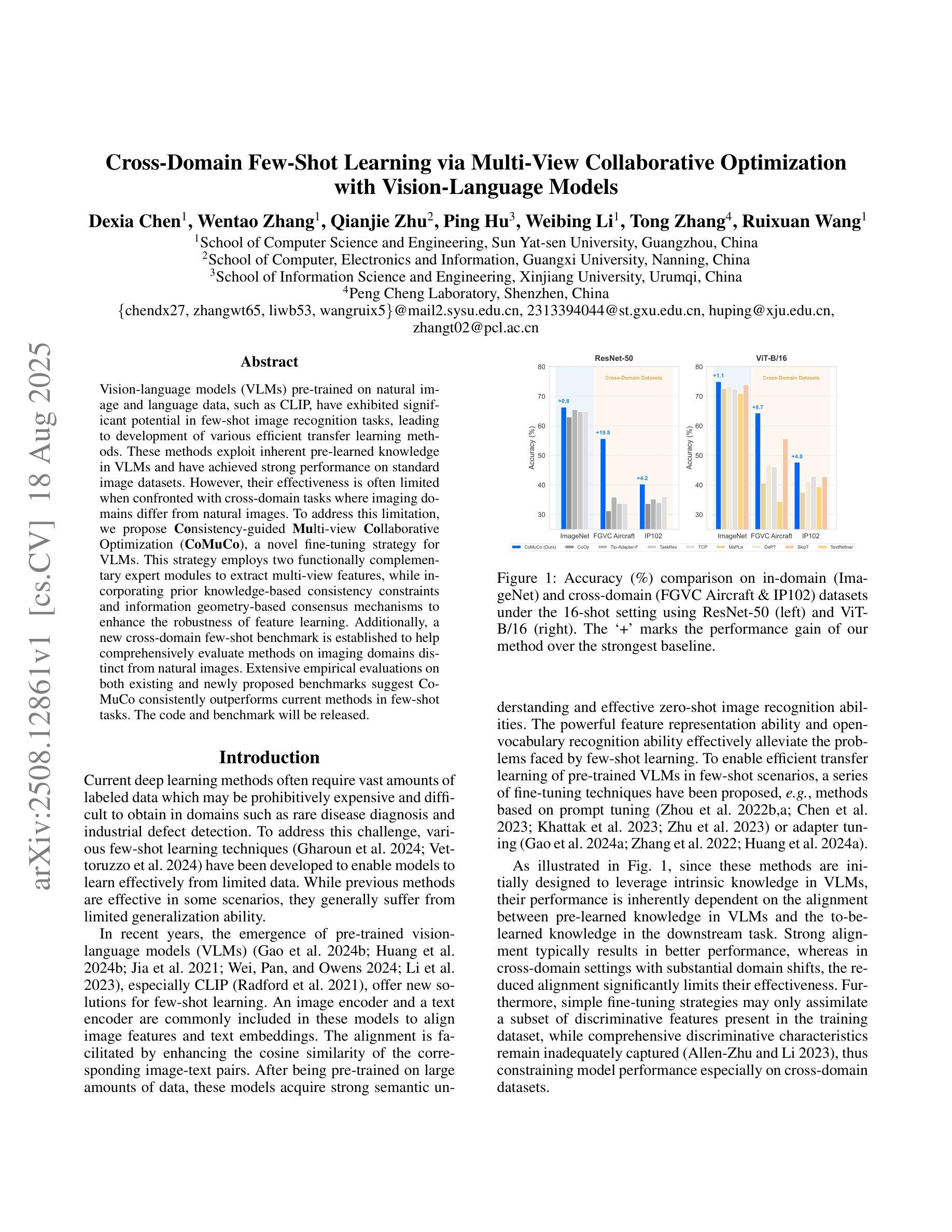
Vision-language models (VLMs) pre-trained on natural image and language data, such as CLIP, have exhibited significant potential in few-shot image recognition tasks, leading to development of various efficient transfer learning methods. These methods exploit inherent pre-learned knowledge in VLMs and have achieved strong performance on standard image datasets. However, their effectiveness is often limited when confronted with cross-domain tasks where imaging domains differ from natural images. To address this limitation, we propose Consistency-guided Multi-view Collaborative Optimization (CoMuCo), a novel fine-tuning strategy for VLMs. This strategy employs two functionally complementary expert modules to extract multi-view features, while incorporating prior knowledge-based consistency constraints and information geometry-based consensus mechanisms to enhance the robustness of feature learning. Additionally, a new cross-domain few-shot benchmark is established to help comprehensively evaluate methods on imaging domains distinct from natural images. Extensive empirical evaluations on both existing and newly proposed benchmarks suggest CoMuCo consistently outperforms current methods in few-shot tasks. The code and benchmark will be released.
预训练于自然图像和语言数据上的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在少样本图像识别任务中展现出显著潜力,推动了各种高效的迁移学习方法的发展。这些方法利用视觉语言模型中的固有预学习知识,并在标准图像数据集上取得了强大的性能。然而,当面对成像域不同于自然图像的跨域任务时,其有效性往往受到限制。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了基于一致性引导的多视角协同优化(CoMuCo),这是一种用于视觉语言模型的新型微调策略。该策略采用两个功能上互补的专家模块来提取多视角特征,同时结合基于先验知识的一致性约束和基于信息几何的共识机制,以提高特征学习的稳健性。此外,还建立了一个新的跨域少样本基准测试,以帮助全面评估在不同于自然图像的成像域上的方法。对现有基准测试和新提出的基准测试的大量实证评估表明,CoMuCo在少样本任务中始终优于当前方法。代码和基准测试将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练在天然图像和语言数据上的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,在少量图像识别任务中展现出巨大潜力,并衍生出多种有效的迁移学习方法。这些少量样本学习方法利用VLMs中的预学习固有知识,在标准图像数据集上取得了强大的性能。然而,当面对成像域与天然图像不同的跨域任务时,其效果往往受限。为此,我们提出了名为“一致性导向多视角协同优化”(CoMuCo)的新微调策略。此策略利用两个功能上互补的专家模块提取多视角特征,并结合基于先验知识的一致性约束和基于信息几何的共识机制,以提高特征学习的稳健性。此外,我们还建立了一个新的跨域小样本基准测试,以全面评估在不同于自然图像的成像领域上的方法表现。对既有和新提出的基准测试进行的广泛实证评估表明,CoMuCo在少样本任务中的表现始终优于当前方法。代码和基准测试将公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在少量图像识别任务中具有显著潜力。
- 衍生出多种迁移学习方法,利用VLMs中的预学习固有知识。
- 跨域任务中VLMs性能受限,需要新方法应对成像域差异。
- 提出名为CoMuCo的新微调策略,利用专家模块和一致性约束提高特征学习稳健性。
- 建立新的跨域小样本基准测试,评估在不同于自然图像的成像领域上的方法表现。
- CoMuCo在少样本任务中的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
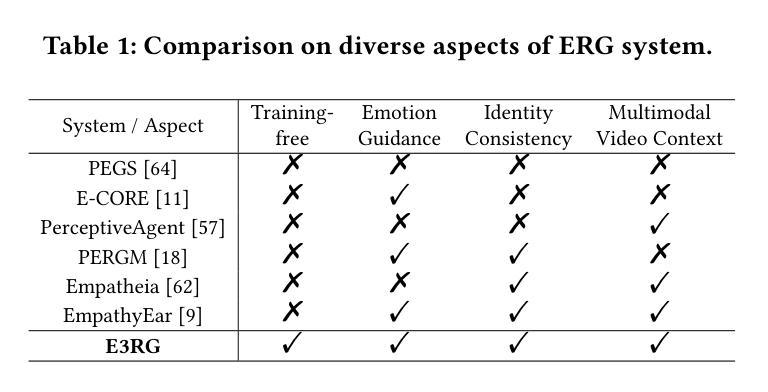
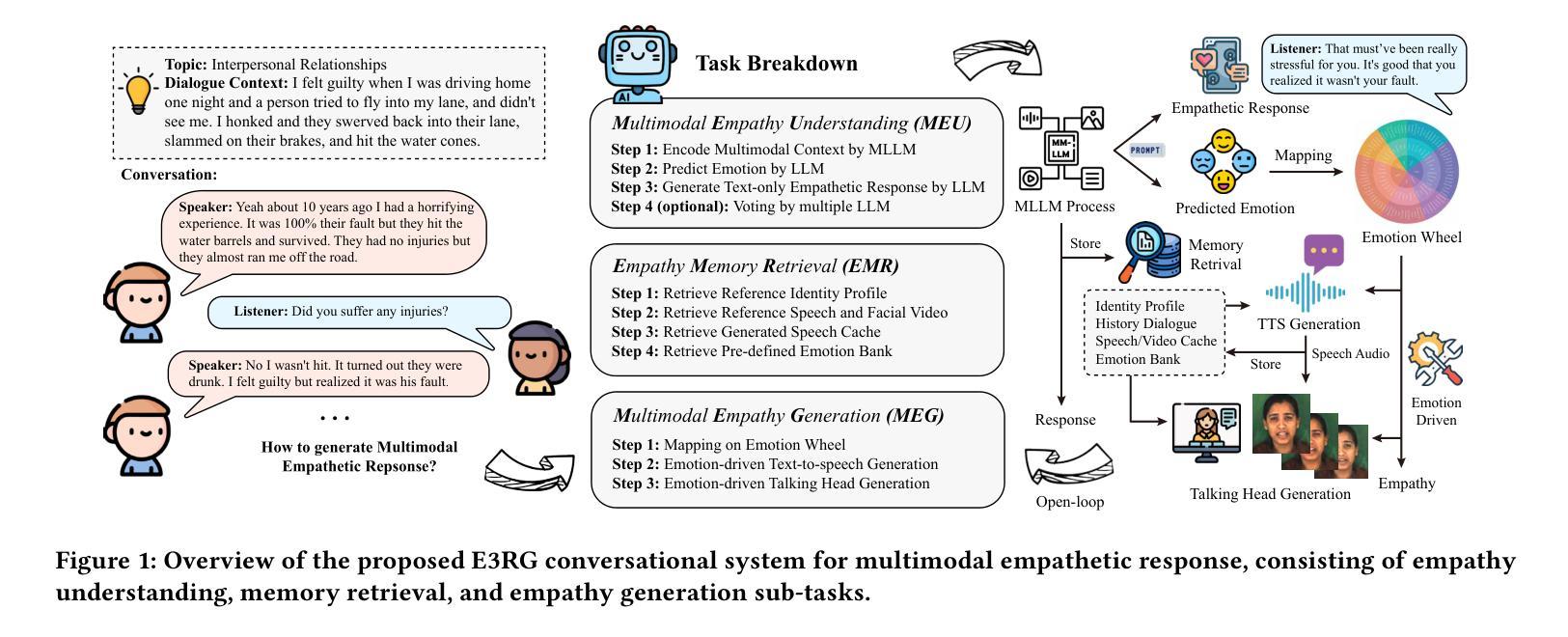
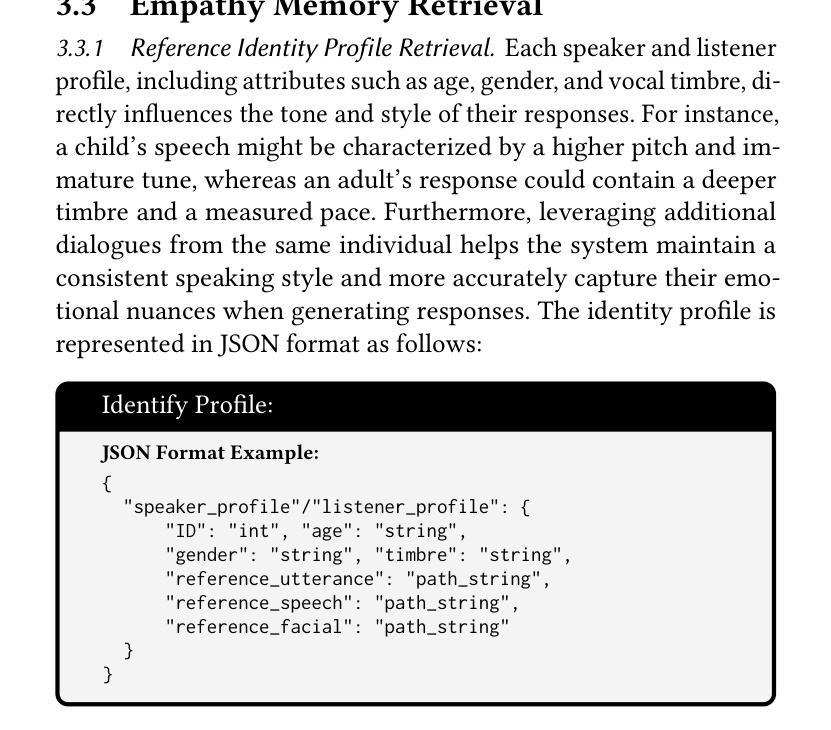
E3RG: Building Explicit Emotion-driven Empathetic Response Generation System with Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Ronghao Lin, Shuai Shen, Weipeng Hu, Qiaolin He, Aolin Xiong, Li Huang, Haifeng Hu, Yap-peng Tan
Multimodal Empathetic Response Generation (MERG) is crucial for building emotionally intelligent human-computer interactions. Although large language models (LLMs) have improved text-based ERG, challenges remain in handling multimodal emotional content and maintaining identity consistency. Thus, we propose E3RG, an Explicit Emotion-driven Empathetic Response Generation System based on multimodal LLMs which decomposes MERG task into three parts: multimodal empathy understanding, empathy memory retrieval, and multimodal response generation. By integrating advanced expressive speech and video generative models, E3RG delivers natural, emotionally rich, and identity-consistent responses without extra training. Experiments validate the superiority of our system on both zero-shot and few-shot settings, securing Top-1 position in the Avatar-based Multimodal Empathy Challenge on ACM MM 25. Our code is available at https://github.com/RH-Lin/E3RG.
多模态共情响应生成(MERG)对于构建具有情感智能的人机交互至关重要。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)已经改进了基于文本的ERG,但在处理多模态情感内容和保持身份一致性方面仍存在挑战。因此,我们提出了基于多模态LLM的显式情感驱动共情响应生成系统E3RG,它将MERG任务分解为三部分:多模态共情理解、共情记忆检索和多模态响应生成。通过集成先进的表达性语音和视频生成模型,E3RG无需额外训练即可提供自然、情感丰富且符合身份一致的响应。实验验证了我们系统在零样本和少样本设置上的优越性,在ACM MM 25的基于Avatar的多模态共情挑战中获得了第一名。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/RH-Lin/E3RG获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACM MM 2025 Grand Challenge
Summary
多模态共情反应生成(MERG)对于构建具有情感智能的人机交互至关重要。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)已经提高了基于文本的ERG能力,但在处理多模态情感内容和保持身份一致性方面仍存在挑战。因此,我们提出了基于多模态LLM的显式情感驱动共情反应生成系统E3RG,它将MERG任务分解为三个部分:多模态共情理解、共情记忆检索和多模态反应生成。通过整合先进的表达性语音和视频生成模型,E3RG能够在无需额外训练的情况下产生自然、情感丰富且身份一致的反应。实验验证了我们系统在零样本和少样本设置上的优越性,并在ACM MM 25的基于Avatar的多模态共情挑战中获得第一名。相关代码可通过https://github.com/RH-Lin/E3RG获取。
Key Takeaways
- MERG(多模态共情反应生成)是构建情感智能人机交互的核心。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在文本基础的ERG上已有显著提升,但在处理多模态情感内容和维持身份一致性上仍有挑战。
- E3RG系统是一个显式情感驱动的共情反应生成系统,基于多模态LLM。
- E3RG将MERG任务分为三个核心部分:多模态共情理解、共情记忆检索和多模态反应生成。
- E3RG集成了先进的表达性语音和视频生成模型,以产生自然、情感丰富和身份一致的反应。
- 实验证明,E3RG在零样本和少样本设置上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图



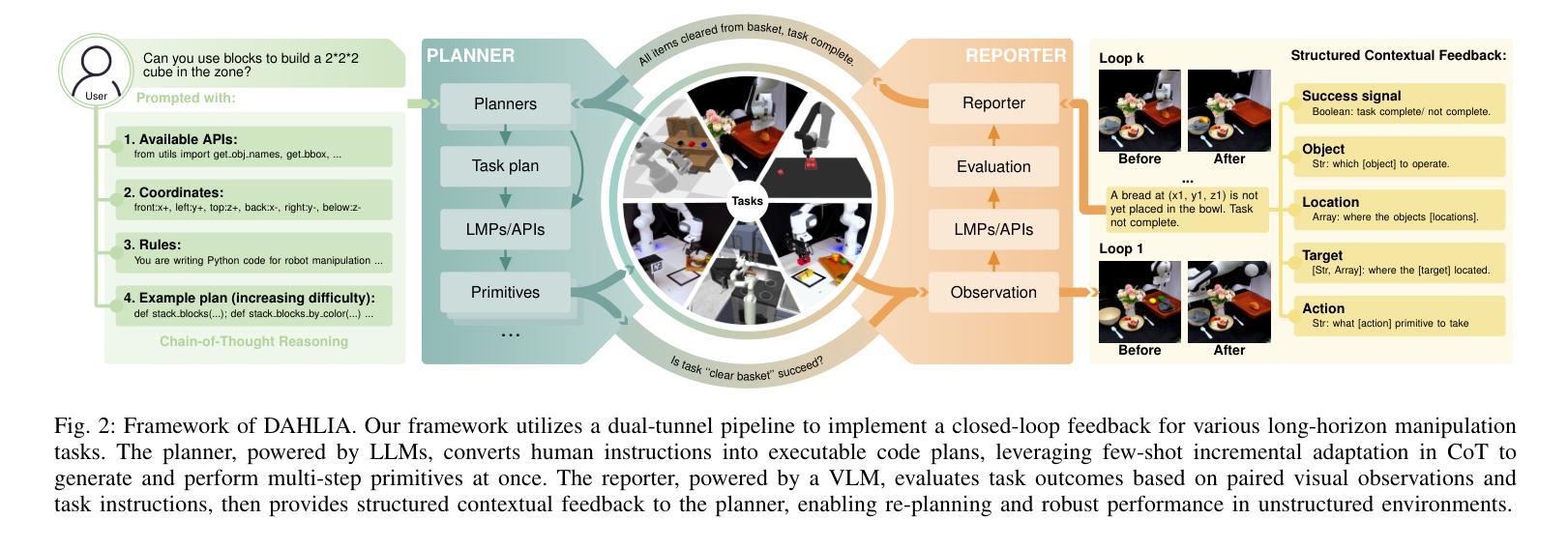
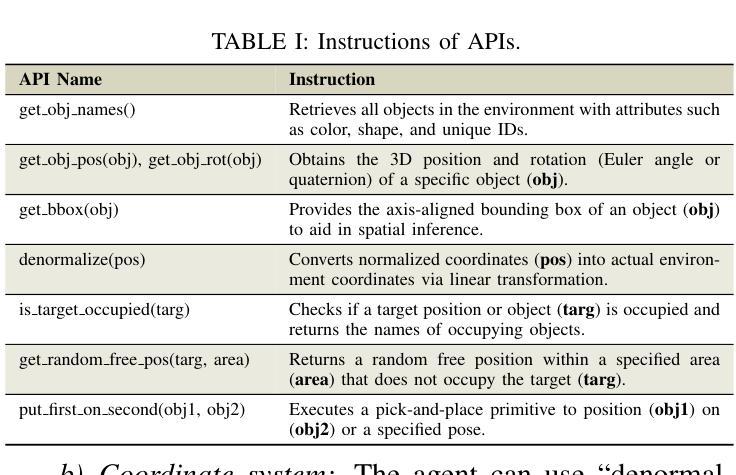
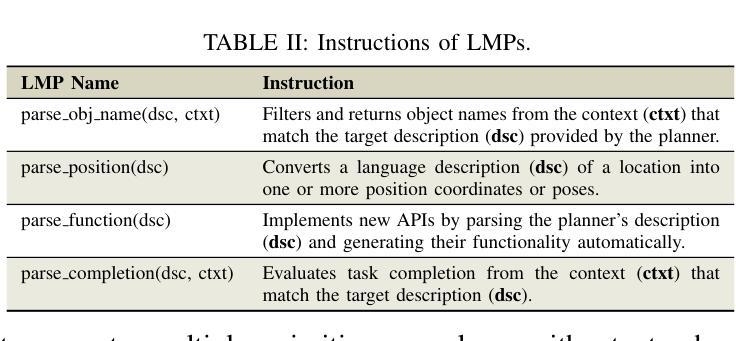
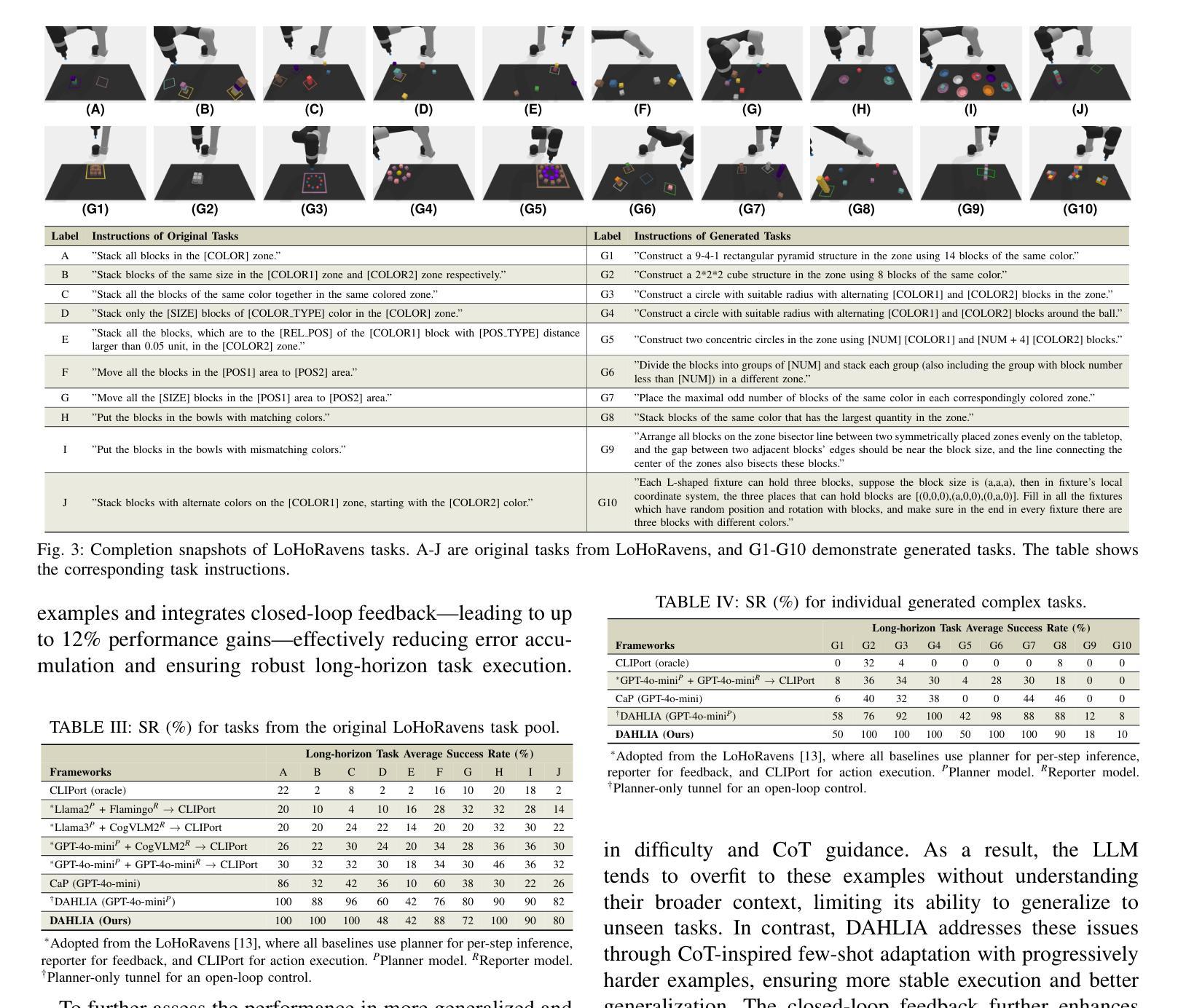
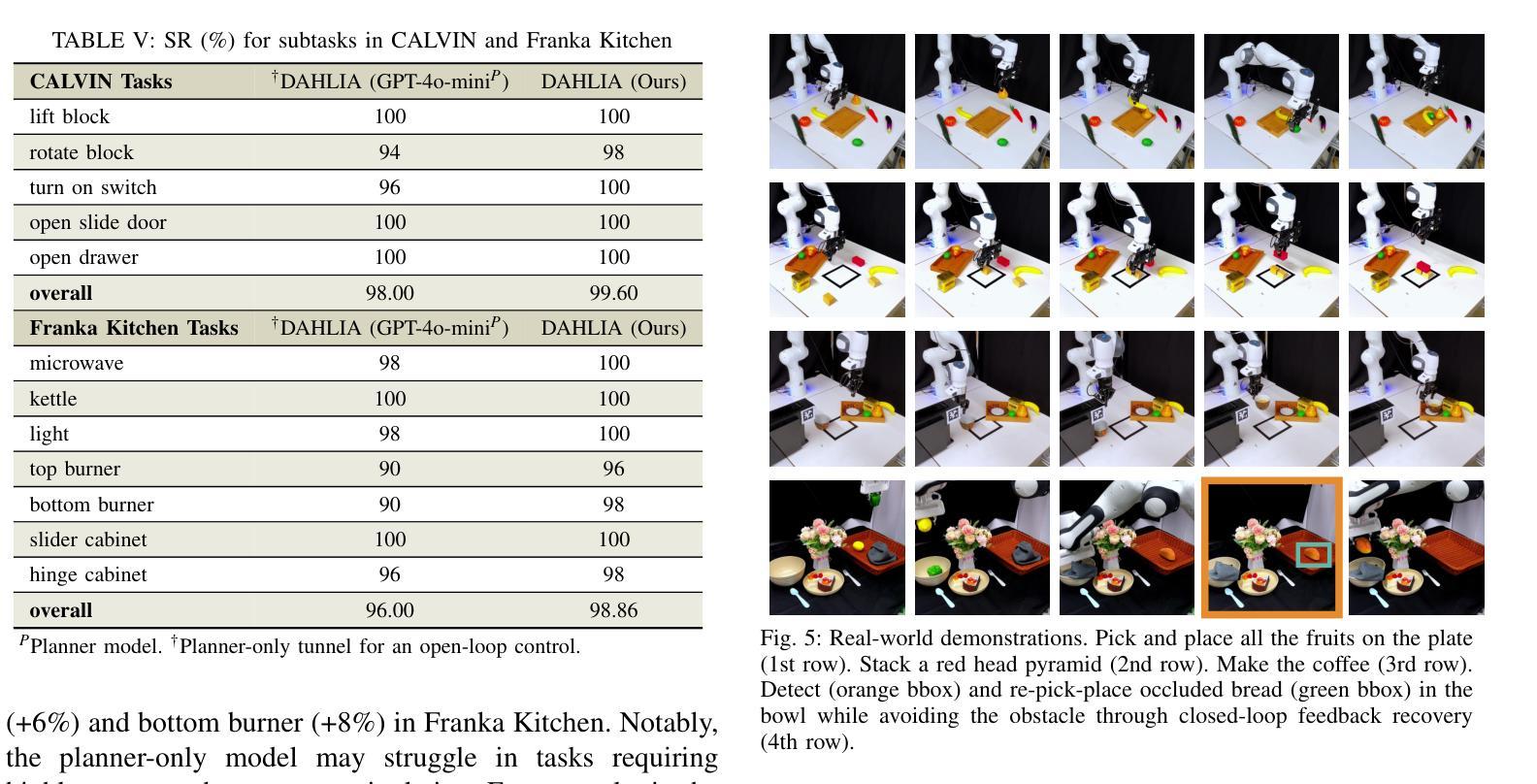
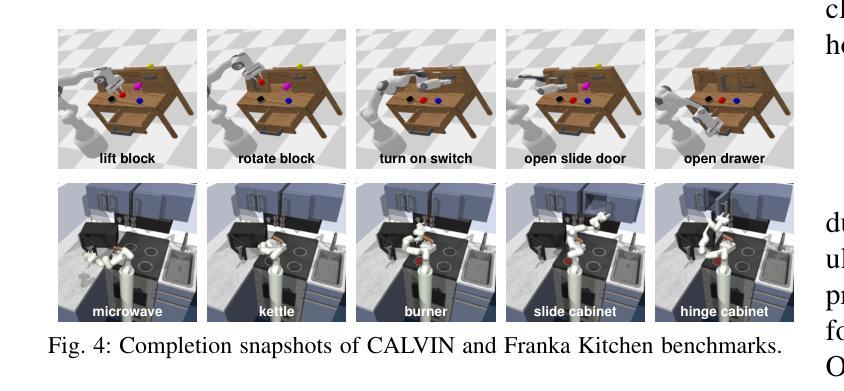
Embodied Long Horizon Manipulation with Closed-loop Code Generation and Incremental Few-shot Adaptation
Authors:Yuan Meng, Xiangtong Yao, Haihui Ye, Yirui Zhou, Shengqiang Zhang, Zhenguo Sun, Zhenshan Bing, Alois Knoll
Embodied long-horizon manipulation requires robotic systems to process multimodal inputs-such as vision and natural language-and translate them into executable actions. However, existing learning-based approaches often depend on large, task-specific datasets and struggle to generalize to unseen scenarios. Recent methods have explored using large language models (LLMs) as high-level planners that decompose tasks into subtasks using natural language and guide pretrained low-level controllers. Yet, these approaches assume perfect execution from low-level policies, which is unrealistic in real-world environments with noise or suboptimal behaviors. To overcome this, we fully discard the pretrained low-level policy and instead use the LLM to directly generate executable code plans within a closed-loop framework. Our planner employs chain-of-thought (CoT)-guided few-shot learning with incrementally structured examples to produce robust and generalizable task plans. Complementing this, a reporter evaluates outcomes using RGB-D and delivers structured feedback, enabling recovery from misalignment and replanning under partial observability. This design eliminates per-step inference, reduces computational overhead, and limits error accumulation that was observed in previous methods. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on 30+ diverse seen and unseen long-horizon tasks across LoHoRavens, CALVIN, Franka Kitchen, and cluttered real-world settings.
具有长期视野的操作需要机器人系统处理多模式输入,如视觉和自然语言,并将其转化为可执行的行动。然而,现有的基于学习的方法通常依赖于大型、特定的任务数据集,在未见场景中的泛化能力较差。最近的方法已经尝试使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为高级规划器,利用自然语言将任务分解为子任务,并引导预训练的低级控制器。然而,这些方法假设低级策略的执行是完美的,这在充满噪声或次优行为的现实环境中是不现实的。为了克服这一问题,我们完全抛弃了预训练的低级策略,而是使用LLM直接在闭环框架内生成可执行代码计划。我们的规划器采用增量结构化示例引导的思维链(CoT)小样本学习,生成稳健且可泛化的任务计划。作为补充,一个报告者使用RGB-D评估结果并提供结构化反馈,实现在部分可观察性下的偏差恢复和重新规划。这种设计消除了逐步推理,减少了计算开销,并限制了之前在方法中观察到的误差累积。我们的框架在LoHoRavens、CALVIN、Frank Kitchen和杂乱的真实世界环境中实现了超过30种多样化和未见过的长期任务的最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF update ICRA 6 page
Summary
本论文探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)作为高层次的计划制定者来解决长视野操纵的问题。鉴于真实世界中的噪音或次优行为问题,论文提出了一种全新的方法,即利用LLM直接生成可执行代码计划,而不是依赖预先训练的低层次策略。论文通过思维链引导少数实例学习来制定稳健且通用的任务计划,并使用RGB-D评估结果,以实现偏差恢复和不完全可观测下的重新规划。该方法避免了分步推理的复杂性和误差累积的问题,实现了跨多个场景的长远任务的出色表现。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的关键见解要点:
- 论文聚焦于使用大型语言模型(LLMs)作为机器人系统的任务规划器来解决长视野操纵问题。
- 针对真实世界中的噪音和次优行为问题,论文提出了一种新方法,即不使用预先训练的低层次策略,直接使用LLM生成可执行代码计划。
- 论文提出通过思维链(CoT)引导少数实例学习的方法,使得机器人能够在各种场景中稳健地制定任务计划。
- RGB-D用于评估任务执行的结果,这有助于系统对可能的偏差进行反馈并调整规划。这种反馈机制可以在不完全可观测的条件下提高系统的恢复能力。
点此查看论文截图

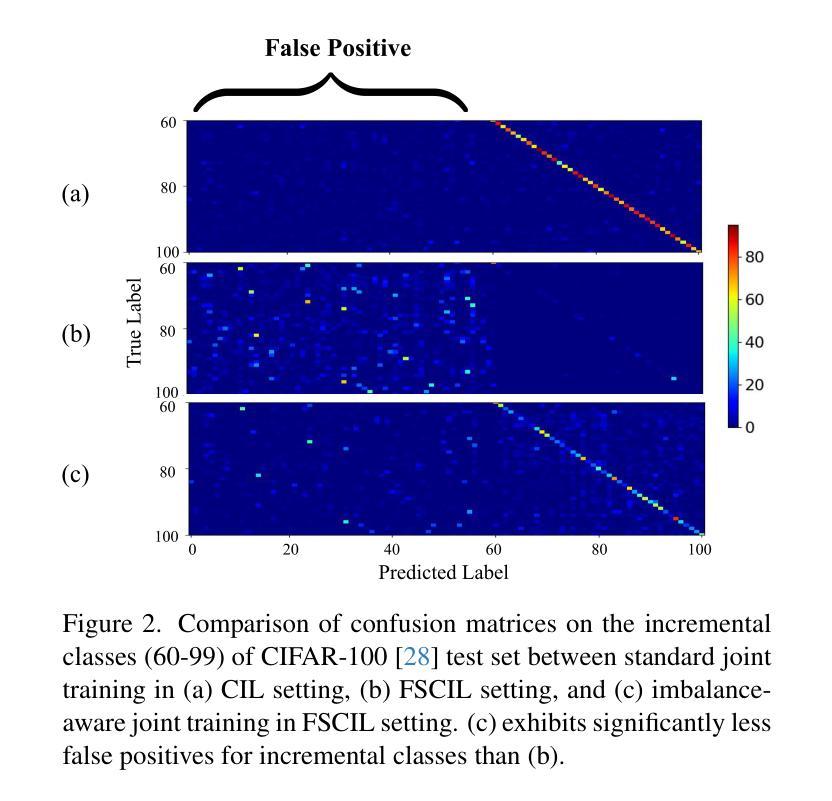
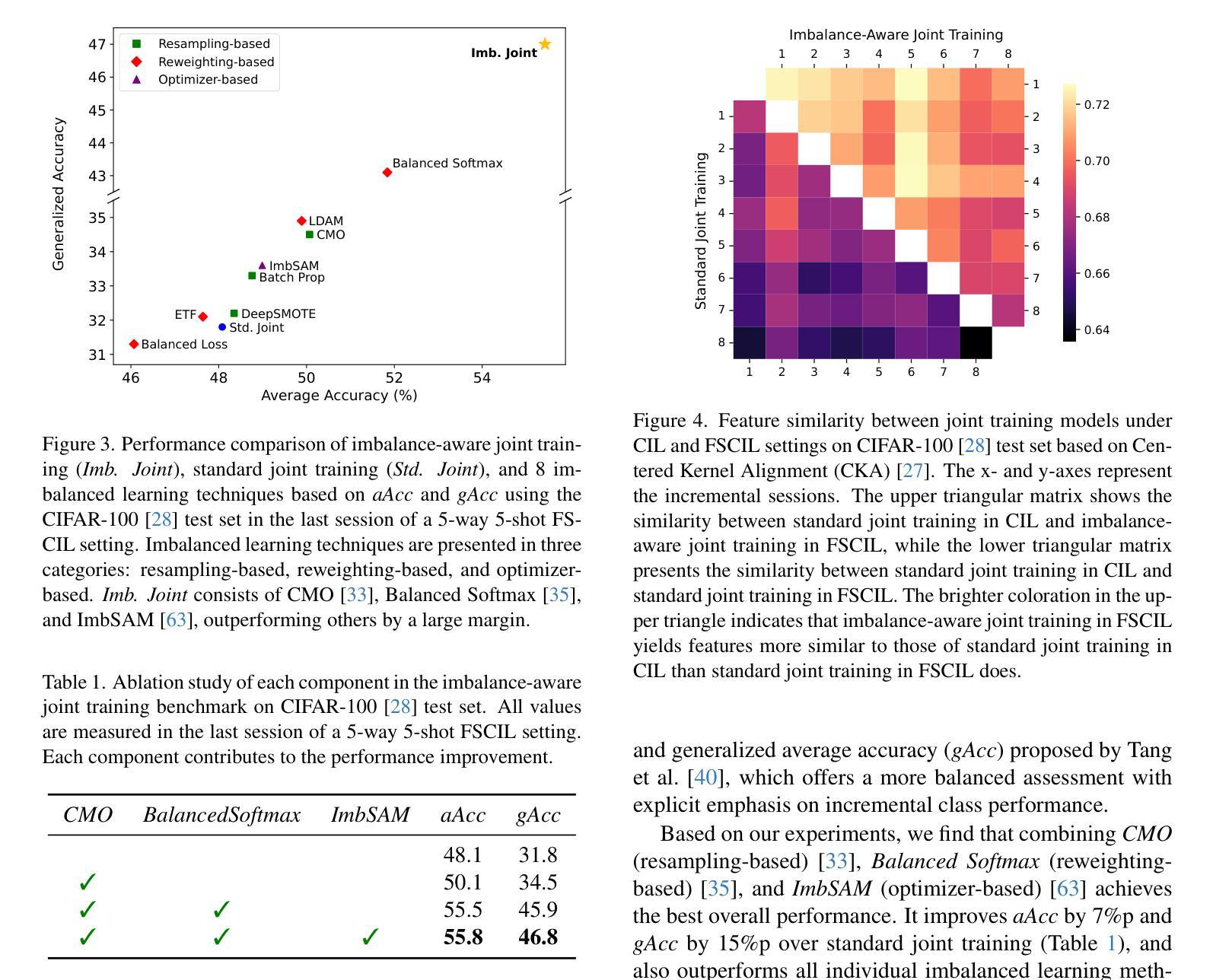
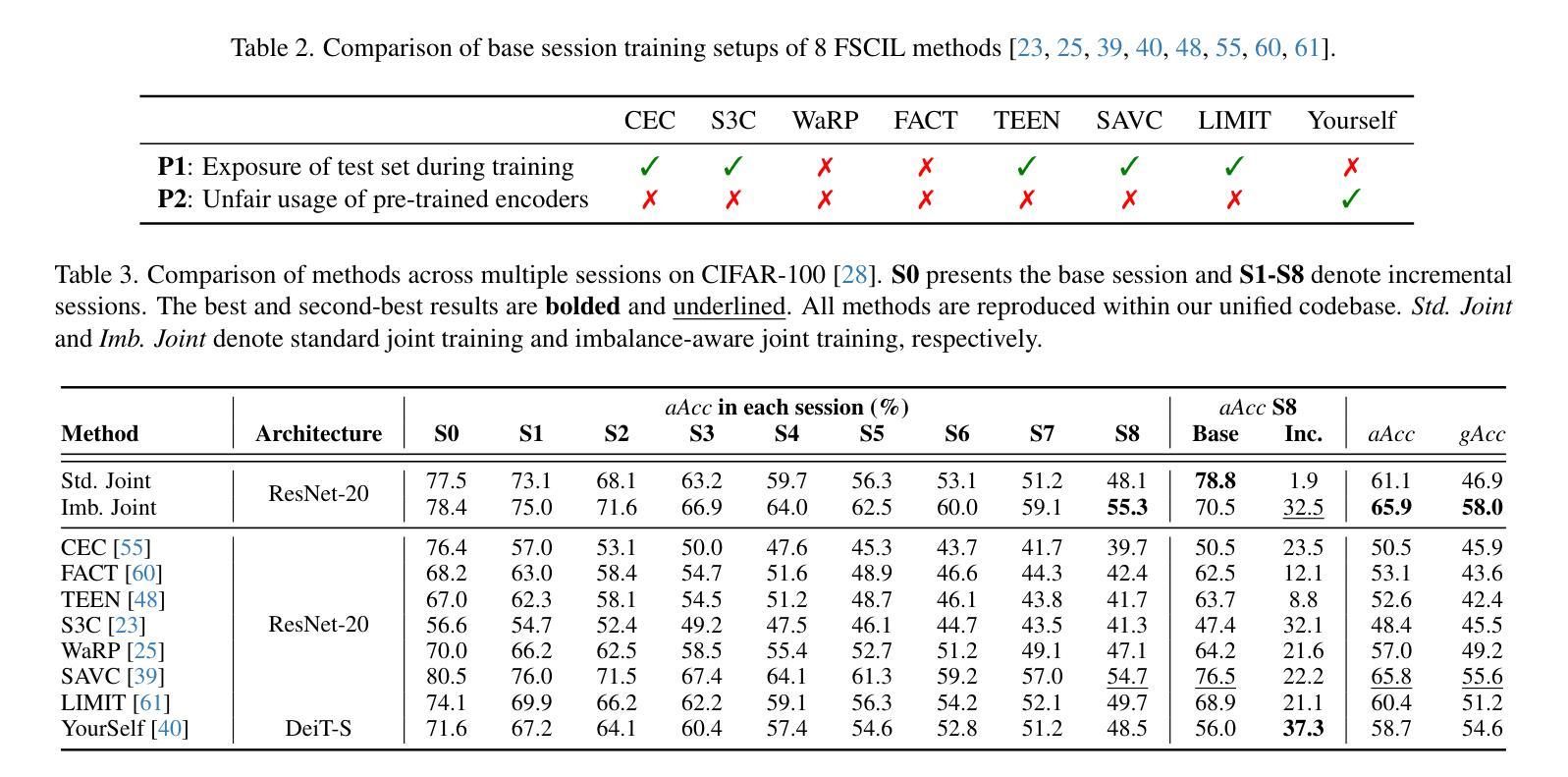
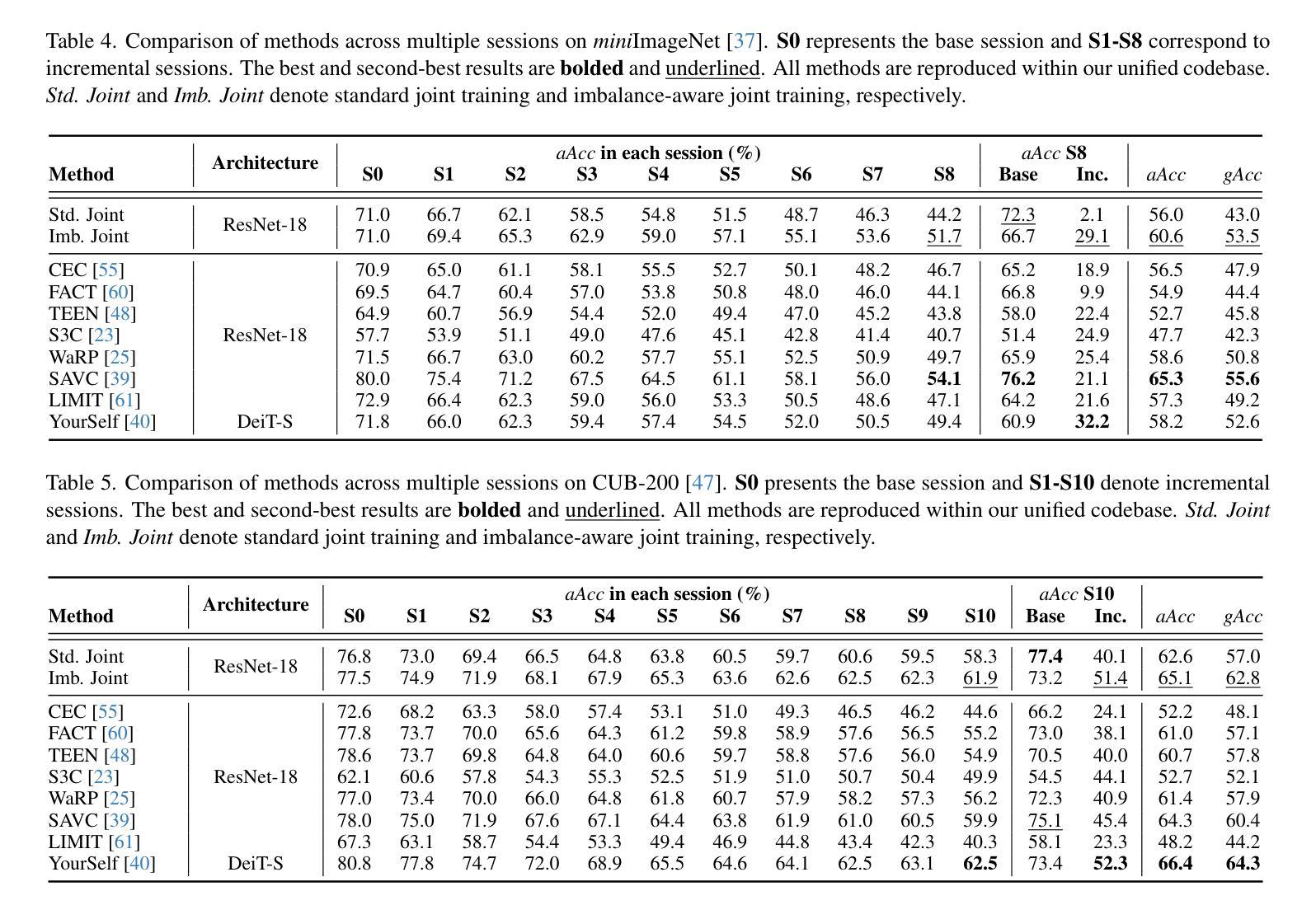
Does Prior Data Matter? Exploring Joint Training in the Context of Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Shiwon Kim, Dongjun Hwang, Sungwon Woo, Rita Singh
Class-incremental learning (CIL) aims to adapt to continuously emerging new classes while preserving knowledge of previously learned ones. Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) presents a greater challenge that requires the model to learn new classes from only a limited number of samples per class. While incremental learning typically assumes restricted access to past data, it often remains available in many real-world scenarios. This raises a practical question: should one retrain the model on the full dataset (i.e., joint training), or continue updating it solely with new data? In CIL, joint training is considered an ideal benchmark that provides a reference for evaluating the trade-offs between performance and computational cost. However, in FSCIL, joint training becomes less reliable due to severe imbalance between base and incremental classes. This results in the absence of a practical baseline, making it unclear which strategy is preferable for practitioners. To this end, we revisit joint training in the context of FSCIL by incorporating imbalance mitigation techniques, and suggest a new imbalance-aware joint training benchmark for FSCIL. We then conduct extensive comparisons between this benchmark and FSCIL methods to analyze which approach is most suitable when prior data is accessible. Our analysis offers realistic insights and guidance for selecting training strategies in real-world FSCIL scenarios. Code is available at: https://github.com/shiwonkim/Joint_FSCIL
类增量学习(CIL)旨在适应不断涌现的新类,同时保留对先前学习知识的记忆。小样本类增量学习(FSCIL)呈现出一个更大的挑战,需要模型仅从每类的有限样本中学习新类别。虽然增量学习通常假设对过去数据的访问受到限制,但在许多现实场景中,它通常仍然可用。这引发了一个实际问题:是否应在整个数据集上重新训练模型(即联合训练),还是继续使用新数据进行更新?在CIL中,联合训练被认为是一个理想的基准,为评估性能和计算成本之间的权衡提供了参考。然而,在FSCIL中,由于基础类和增量类之间的严重不平衡,联合训练变得不那么可靠。这导致缺乏实用的基准,使得从业者不清楚哪种策略更为可取。为此,我们通过融入不平衡缓解技术,重新审视了FSCIL中的联合训练,并提出了一个新的不平衡感知联合训练基准用于FSCIL。然后,我们对此基准和FSCIL方法进行了广泛的比较,分析了当可以访问先前数据时,哪种方法最为适合。我们的分析为现实世界的FSCIL场景中选择训练策略提供了切实的见解和指导。代码可用在:https://github.com/shiwonkim/Joint_FSCIL
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇文本讨论了类增量学习(CIL)和少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)的挑战,其中FSCIL需要从有限的样本中学习新类别。文本探讨了在实际场景中是否应该使用联合训练(即重新训练整个数据集)或仅使用新数据进行更新。对于FSCIL,由于基础类和增量类之间的严重不平衡,联合训练变得不那么可靠。为此,文本引入了不平衡感知的联合训练基准测试,并与FSCIL方法进行了广泛的比较,以分析在可访问先验数据的情况下哪种方法最适合实际应用场景。为此提供了对选择现实世界中FSCIL场景的训练策略的实际见解和指导。
Key Takeaways
以下是从文本中提取的关键要点,以简化和清晰的方式呈现:
- 类增量学习(CIL)旨在适应不断出现的新类别,同时保留对先前学习知识的记忆。
- 少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)是一个更大挑战,要求模型从每个类别的有限样本中学习新类别。
- 联合训练在CIL中被视为理想基准,但在FSCIL中变得不那么可靠,因为基础类和增量类之间存在严重不平衡。
- 引入了一种新的不平衡感知联合训练基准测试,以应对FSCIL的挑战。
- 对比分析了新的不平衡感知联合训练基准与FSCIL方法,以了解在可访问先验数据的情况下哪种方法最有效。
- 分析提供了对选择现实世界中FSCIL场景的训练策略的实际见解和指导。
点此查看论文截图

SGPT: Few-Shot Prompt Tuning for Signed Graphs
Authors:Zian Zhai, Sima Qing, Xiaoyang Wang, Wenjie Zhang
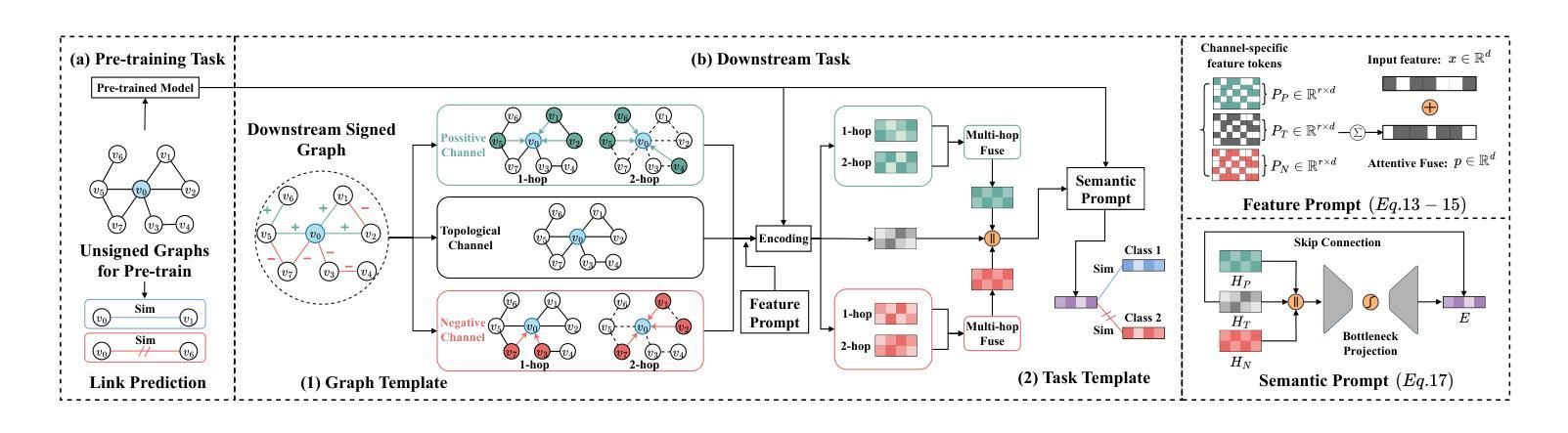
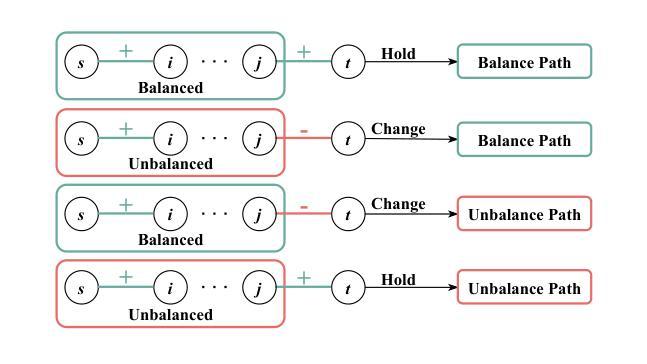
Signed Graph Neural Networks (SGNNs) are effective in learning expressive representations for signed graphs but typically require substantial task-specific labels, limiting their applicability in label-scarce industrial scenarios. In contrast, unsigned graph structures are abundant and can be readily leveraged to pre-train Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), offering a promising solution to reduce supervision requirements in downstream signed graph tasks. However, transferring knowledge from unsigned to signed graphs is non-trivial due to the fundamental discrepancies in graph types and task objectives between pre-training and downstream phases. To address this challenge, we propose Signed Graph Prompt Tuning (SGPT), a novel graph prompting framework that adapts pre-trained unsigned GNNs to few-shot signed graph tasks. We first design a graph template based on balance theory to disentangle mixed node relationships introduced by negative links, mitigating the structural mismatches between unsigned and signed graphs. We further introduce a task template that reformulates downstream signed tasks into a unified link prediction objective, aligning their optimization goals with the pre-training task. Furthermore, we develop feature prompts that align downstream semantic spaces with the feature spaces learned during pre-training, and semantic prompts to integrate link sign semantics in a task-aware manner. We conduct extensive experiments on seven benchmark signed graph datasets, demonstrating that SGPT significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, establishing a powerful and generalizable solution for few-shot signed graph learning.
有符号图神经网络(SGNNs)在学习有符号图的表现力表示方面非常有效,但通常需要大量的特定任务标签,这在标签稀缺的工业场景中限制了其应用。相比之下,无符号图结构非常丰富,可以很容易地用于预训练图神经网络(GNNs),为解决下游有符号图任务中的监督需求减少提供了有前途的解决方案。然而,从无符号图到签名图的知识转移并不简单,因为预训练阶段和下游阶段之间的图形类型和任务目标之间存在基本差异。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了有符号图提示调整(SGPT),这是一种新型的图提示框架,用于将预训练的无符号GNNs适应于少量有符号图任务。我们首先根据平衡理论设计了一个图模板,以解开由负链接引入的混合节点关系,减轻无符号图和有符号图之间的结构不匹配问题。我们还引入了任务模板,将下游有符号任务重新制定为统一的链接预测目标,使它们的优化目标与预训练任务的目标保持一致。此外,我们开发了特征提示,使下游语义空间与预训练过程中学习的特征空间保持一致,以及语义提示,以任务感知的方式整合链接符号语义。我们在七个基准有符号图数据集上进行了广泛实验,结果表明SGPT显著优于现有最先进的方法,为少量有符号图学习建立了强大且通用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CIKM’25
Summary
本文提出了Signed Graph Prompt Tuning(SGPT)框架,该框架适应于预训练的unsigned GNNs并应用于少量的signed graph任务。通过设计基于平衡理论的图模板解决结构不匹配问题,引入任务模板统一下游signed任务为链接预测目标,同时开发特征提示和语义提示来增强预训练和下游任务的语义对齐。在七个基准signed graph数据集上的实验表明,SGPT显著优于现有先进技术,为少量signed graph学习提供了强大且通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Signed Graph Neural Networks (SGNNs) 在学习signed图表示时有效,但在标签稀缺的工业场景中适用性受限。
- Unsigned图结构丰富,可预训练Graph Neural Networks(GNNs),为解决下游signed图任务的监督要求提供有前途的解决方案。
- 从unsigned图到signed图的知诺转移是非平凡的,因为预训练和下流阶段在图形类型和任务目标上的根本差异。
- 提出了Signed Graph Prompt Tuning (SGPT) 框架,该框架通过图模板、任务模板、特征提示和语义提示来解决这一问题。
- 图模板基于平衡理论设计,以解决unsigned和signed图之间的结构不匹配问题。
- 任务模板将下游signed任务重新制定为统一的链接预测目标,与预训练任务优化目标对齐。
点此查看论文截图