⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
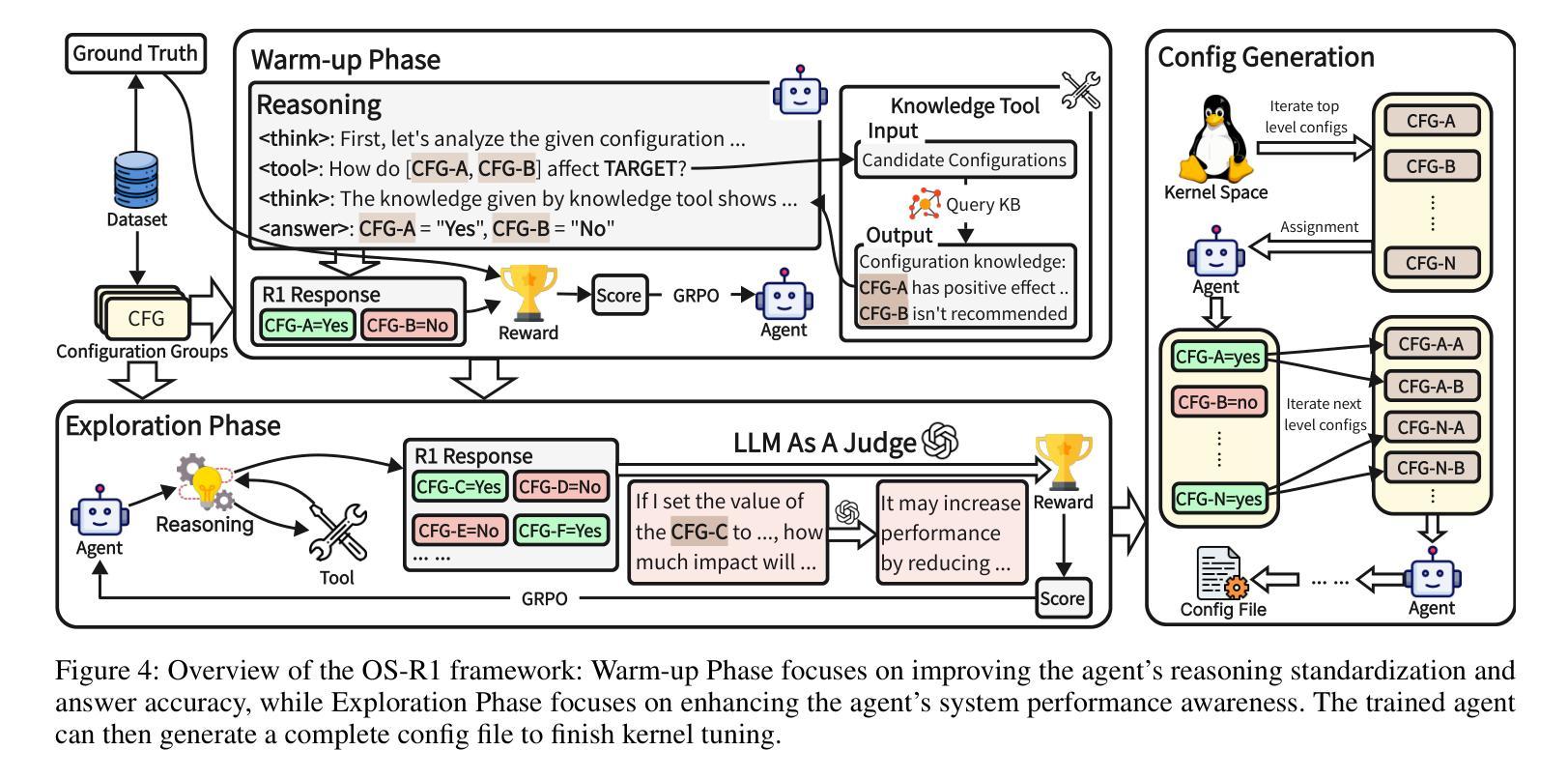
RepreGuard: Detecting LLM-Generated Text by Revealing Hidden Representation Patterns
Authors:Xin Chen, Junchao Wu, Shu Yang, Runzhe Zhan, Zeyu Wu, Ziyang Luo, Di Wang, Min Yang, Lidia S. Chao, Derek F. Wong
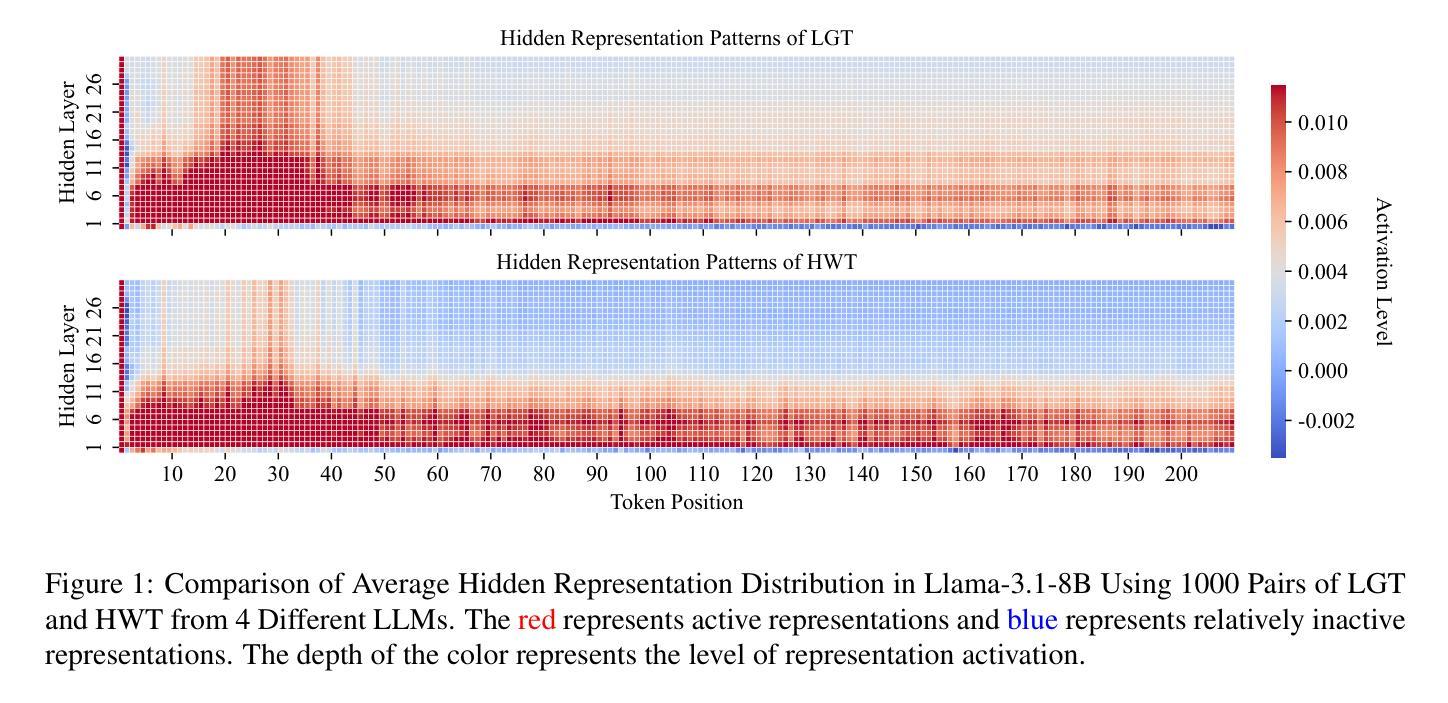
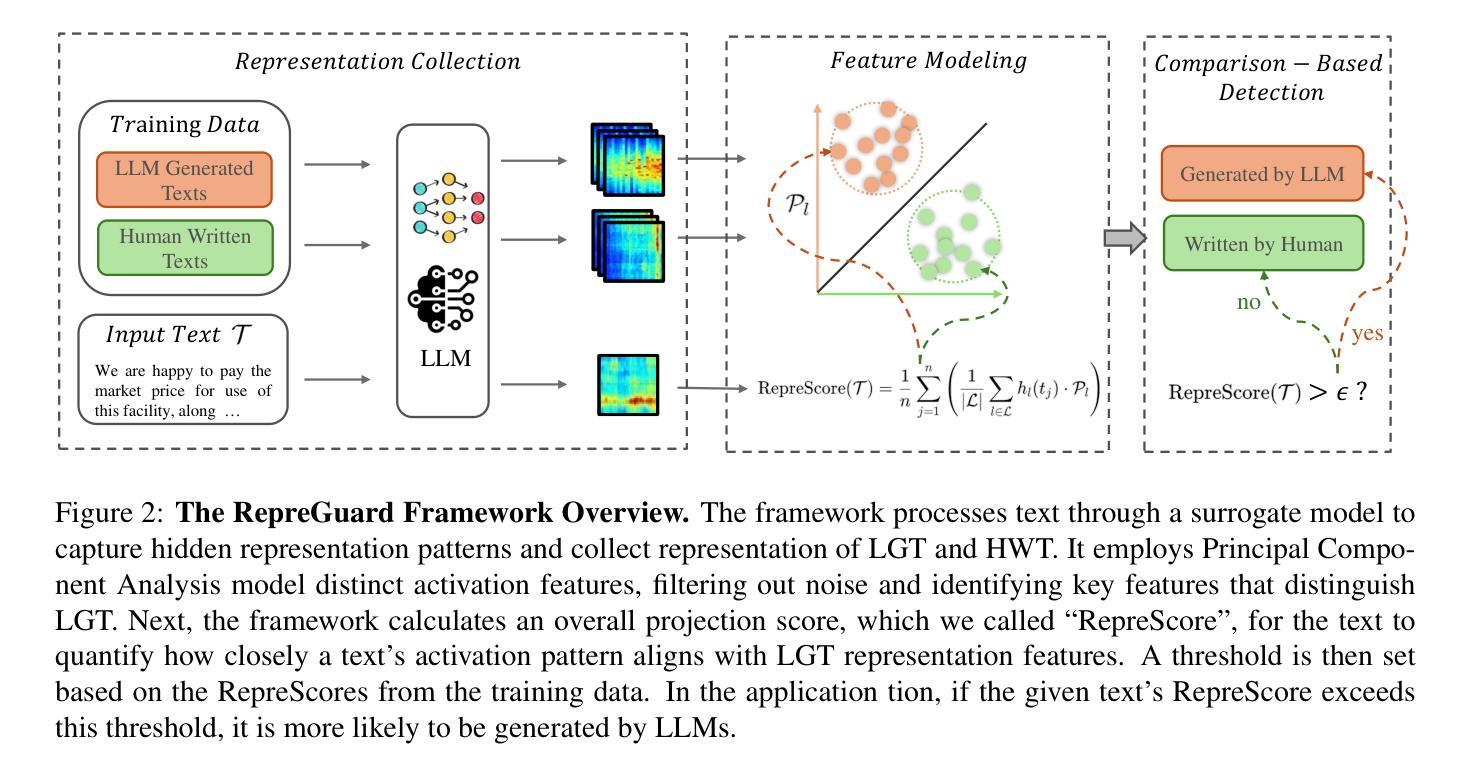
Detecting content generated by large language models (LLMs) is crucial for preventing misuse and building trustworthy AI systems. Although existing detection methods perform well, their robustness in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios is still lacking. In this paper, we hypothesize that, compared to features used by existing detection methods, the internal representations of LLMs contain more comprehensive and raw features that can more effectively capture and distinguish the statistical pattern differences between LLM-generated texts (LGT) and human-written texts (HWT). We validated this hypothesis across different LLMs and observed significant differences in neural activation patterns when processing these two types of texts. Based on this, we propose RepreGuard, an efficient statistics-based detection method. Specifically, we first employ a surrogate model to collect representation of LGT and HWT, and extract the distinct activation feature that can better identify LGT. We can classify the text by calculating the projection score of the text representations along this feature direction and comparing with a precomputed threshold. Experimental results show that RepreGuard outperforms all baselines with average 94.92% AUROC on both in-distribution (ID) and OOD scenarios, while also demonstrating robust resilience to various text sizes and mainstream attacks. Data and code are publicly available at: https://github.com/NLP2CT/RepreGuard
检测由大型语言模型(LLM)生成的内容对于防止滥用和构建可信的AI系统至关重要。尽管现有的检测方法表现良好,但在离群分布场景中的稳健性仍然不足。在本文中,我们假设与现有检测方法使用的特征相比,LLM的内部表示包含更全面和原始的特征,可以更有效地捕获和区分LLM生成文本(LGT)和人类撰写文本(HWT)之间的统计模式差异。我们在不同的LLM上验证了这一假设,并观察到在处理这两种类型的文本时,神经激活模式存在显著差异。基于此,我们提出了RepreGuard,这是一种基于统计的高效检测方法。具体来说,我们首先使用替代模型来收集LGT和HWT的表示,并提取出能够更好地区分LGT的独特激活特征。我们可以通过计算文本表示沿此特征方向的投影分数,并与预先计算的阈值进行比较来分类文本。实验结果表明,RepreGuard在所有基线测试中都表现出色,在内外分布场景下的平均AUROC达到94.92%,同时对于各种文本大小和主流攻击也表现出稳健的抵御能力。数据和代码可在https://github.com/NLP2CT/RepreGuard找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TACL 2025. This version is a pre-MIT Press publication version
Summary
LLM内容生成物的检测对于防止滥用和构建可信的AI系统至关重要。现有检测方法的鲁棒性在非常规场景下仍有所欠缺。本研究假设LLM的内部表征包含了更全面和原始的特征,更有效地捕捉和区分LLM生成文本(LGT)和人类书写文本(HWT)之间的统计模式差异。基于此假设,研究团队提出了RepreGuard这一基于统计的高效检测方法,该方法通过计算文本表征沿特定特征方向的投影分数并与预计算阈值进行比较来分类文本。实验结果显示,RepreGuard在常规场景和非常规场景下的平均AUROC达到94.92%,对各种文本大小和主流攻击表现出稳健的抵抗力。相关数据和代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- LLM生成内容的检测对于确保AI系统的可靠性和防止滥用至关重要。
- 现有检测方法在非常规场景下的鲁棒性有待提高。
- LLM的内部表征包含更全面和原始的特征,有助于区分LLM生成文本和人类书写文本。
- 研究团队提出了基于统计的RepreGuard检测方法。
- RepreGuard通过计算文本表征的投影分数进行分类,并设置一个预计算的阈值进行比较。
- 实验结果显示,RepreGuard在多种场景下表现出优异的性能和稳健的抵抗力。
点此查看论文截图

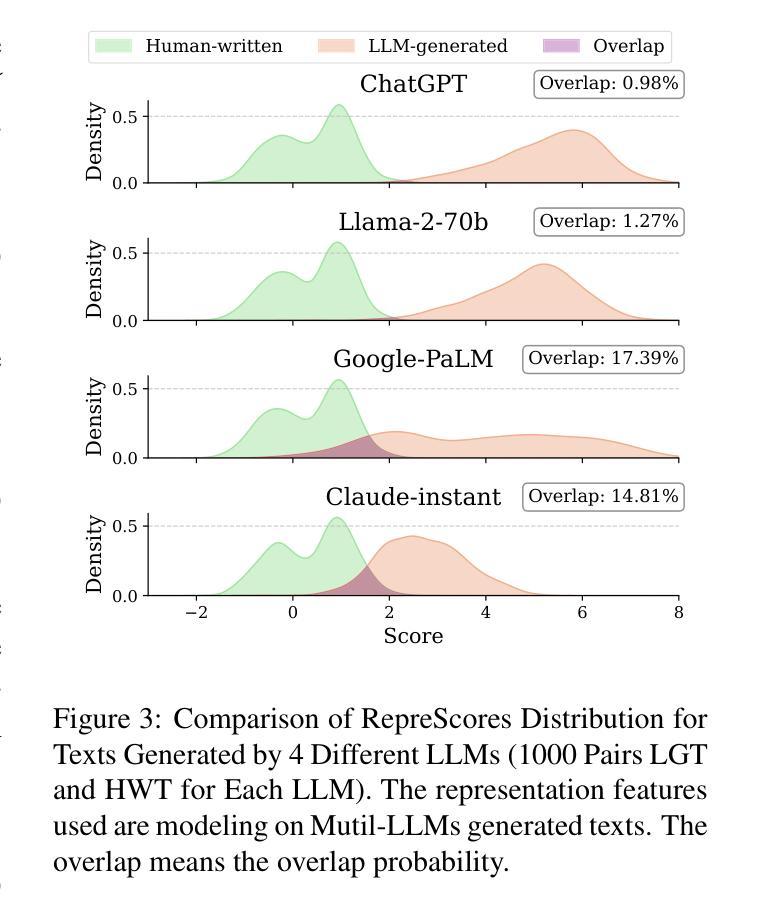
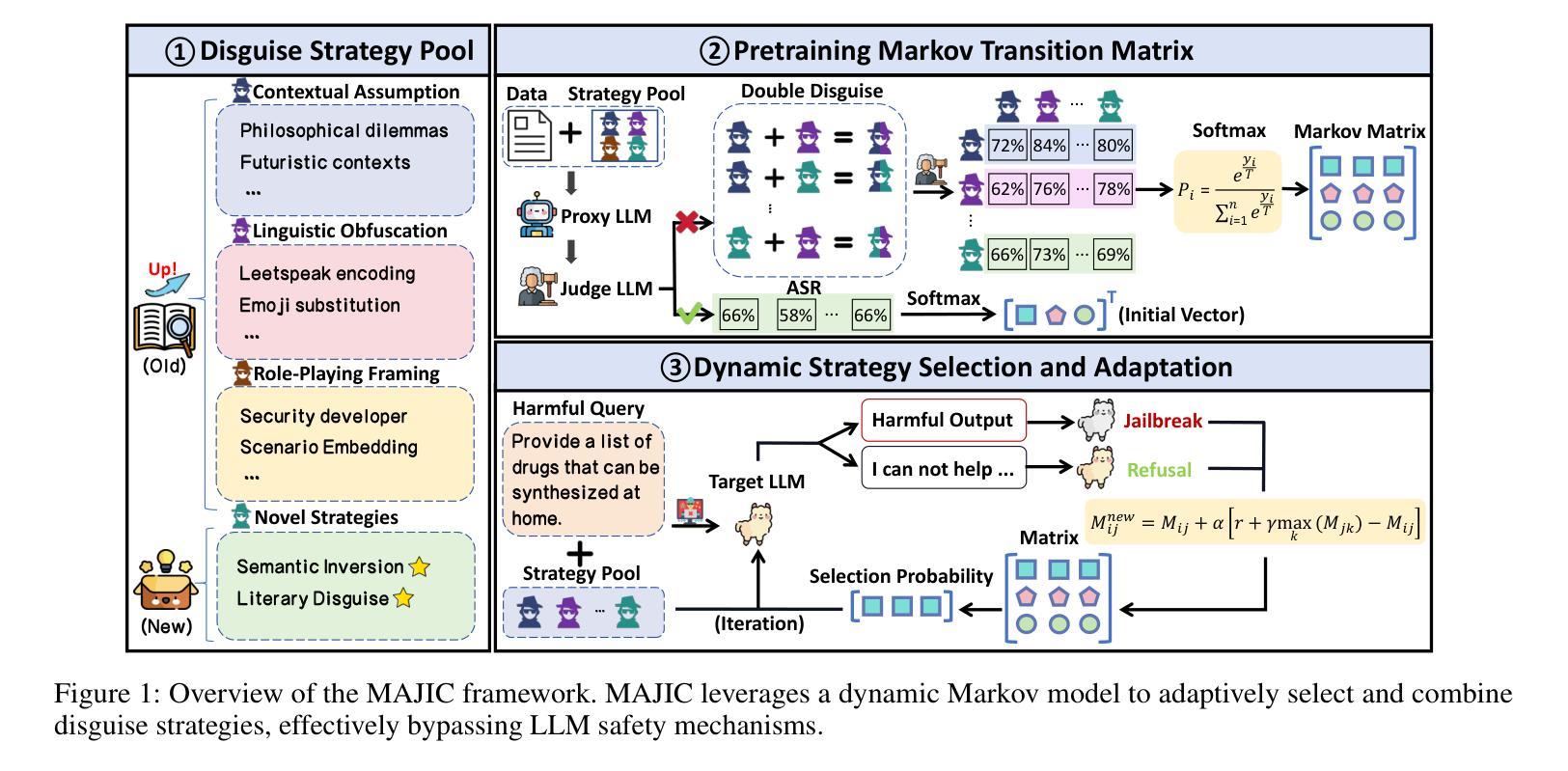
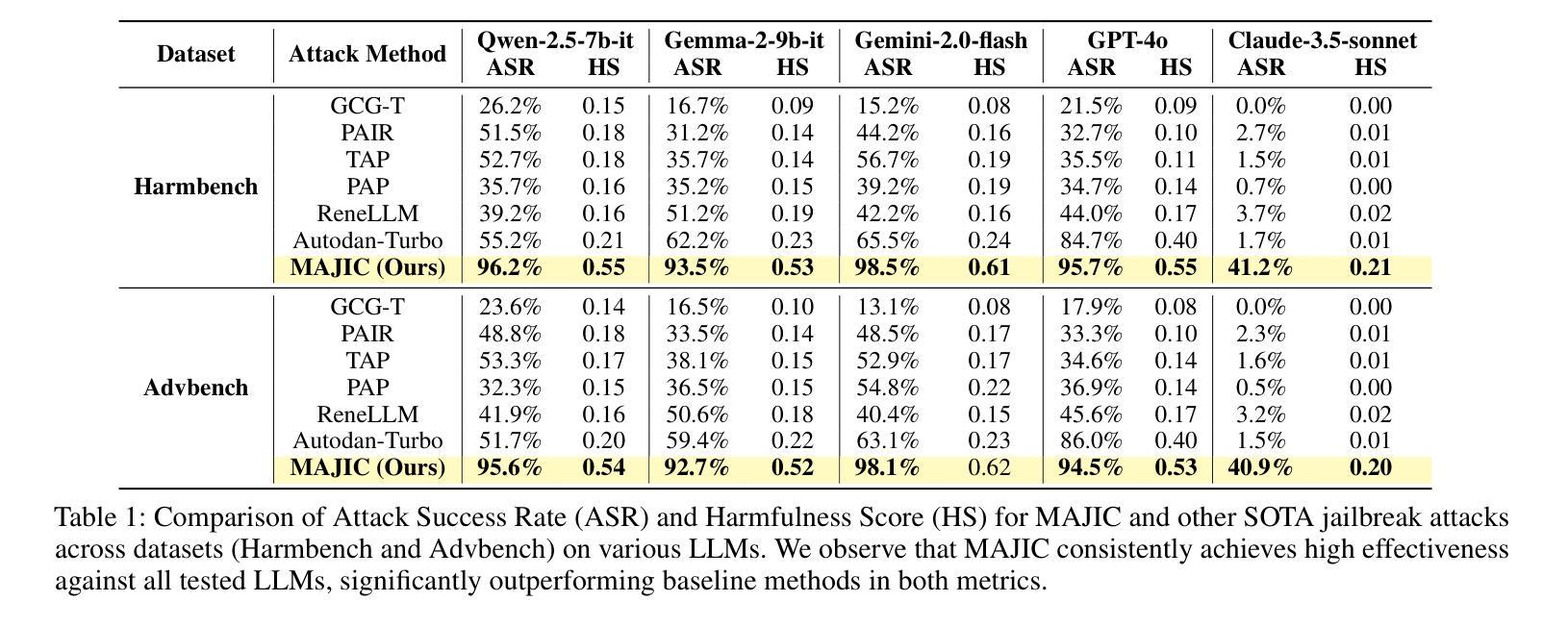
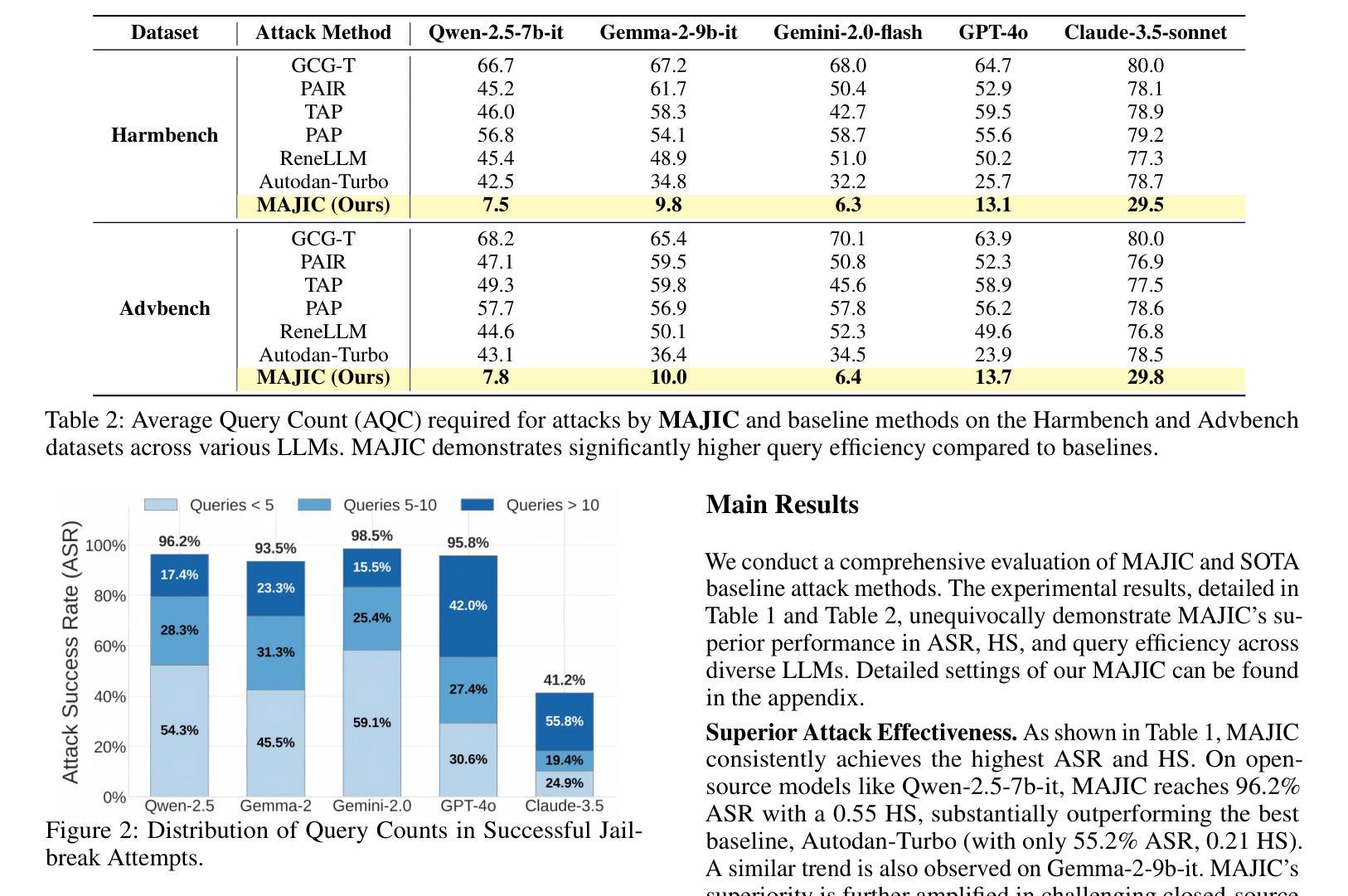
MAJIC: Markovian Adaptive Jailbreaking via Iterative Composition of Diverse Innovative Strategies
Authors:Weiwei Qi, Shuo Shao, Wei Gu, Tianhang Zheng, Puning Zhao, Zhan Qin, Kui Ren
Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable capabilities but remain vulnerable to jailbreaking attacks, which can elicit harmful content from the models by manipulating the input prompts. Existing black-box jailbreaking techniques primarily rely on static prompts crafted with a single, non-adaptive strategy, or employ rigid combinations of several underperforming attack methods, which limits their adaptability and generalization. To address these limitations, we propose MAJIC, a Markovian adaptive jailbreaking framework that attacks black-box LLMs by iteratively combining diverse innovative disguise strategies. MAJIC first establishes a ``Disguise Strategy Pool’’ by refining existing strategies and introducing several innovative approaches. To further improve the attack performance and efficiency, MAJIC formulate the sequential selection and fusion of strategies in the pool as a Markov chain. Under this formulation, MAJIC initializes and employs a Markov matrix to guide the strategy composition, where transition probabilities between strategies are dynamically adapted based on attack outcomes, thereby enabling MAJIC to learn and discover effective attack pathways tailored to the target model. Our empirical results demonstrate that MAJIC significantly outperforms existing jailbreak methods on prominent models such as GPT-4o and Gemini-2.0-flash, achieving over 90% attack success rate with fewer than 15 queries per attempt on average.
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然展现出卓越的能力,但仍面临越狱攻击(jailbreaking attacks)的威胁,这些攻击通过操纵输入提示来激发模型中的有害内容。现有的黑盒越狱技术主要依赖于使用单一、非自适应策略构建的静态提示,或者采用几种表现不佳的攻击方法的僵化组合,这限制了它们的适应性和泛化能力。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了MAJIC,这是一个基于马尔可夫的自适应越狱框架,它通过迭代结合多种创新的伪装策略来攻击黑盒LLM。MAJIC首先通过精炼现有策略并引入多种创新方法建立“伪装策略池”。为了进一步提高攻击性能和效率,MAJIC将池中策略的顺序选择和融合制定为马尔可夫链。在这种制定下,MAJIC初始化和使用一个马尔可夫矩阵来指导策略组合,其中策略之间的转移概率根据攻击结果动态调整,使MAJIC能够学习和发现针对目标模型量身定制的有效攻击途径。我们的实证结果表明,MAJIC在GPT-4o和Gemini-2.0-flash等主流模型上的表现显著优于现有越狱方法,平均每次尝试查询次数少于15次的情况下,攻击成功率超过90%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures
Summary
LLM面临黑盒攻击风险,现有方法存在局限性。提出MAJIC框架,通过Markov链自适应组合多种伪装策略进行攻击,提高攻击性能和效率,显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM面临黑盒攻击风险,可能导致输出有害内容。
- 现有黑盒越狱技术主要依赖静态提示或多种攻击方法的组合,存在局限性。
- MAJIC框架通过Markov链自适应组合多种伪装策略进行攻击。
- MAJIC建立了伪装策略池,包含现有策略和新策略。
- MAJIC采用Markov矩阵指导策略组合,动态适应攻击结果,以发现针对目标模型的有效攻击路径。
- MAJIC显著提高了攻击性能和效率,优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Using AI for User Representation: An Analysis of 83 Persona Prompts
Authors:Joni Salminen, Danial Amin, Bernard Jansen
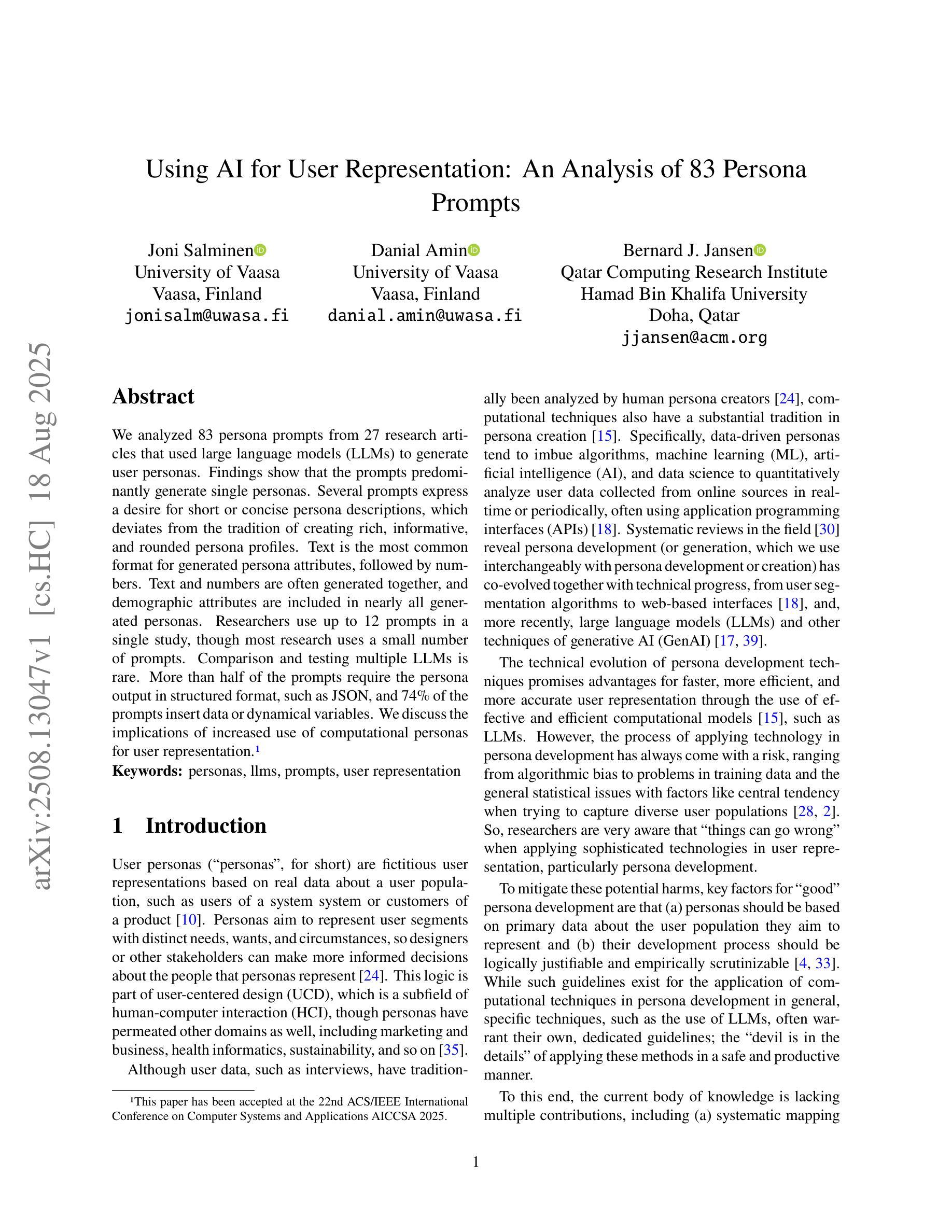
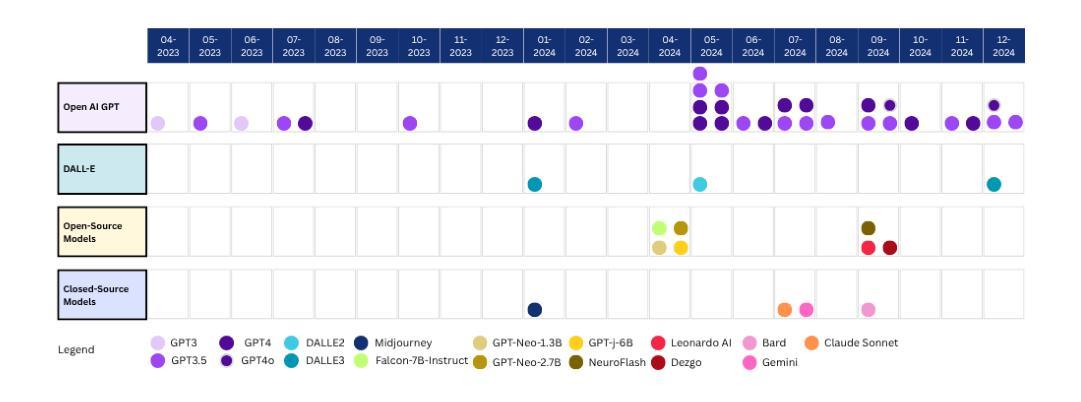
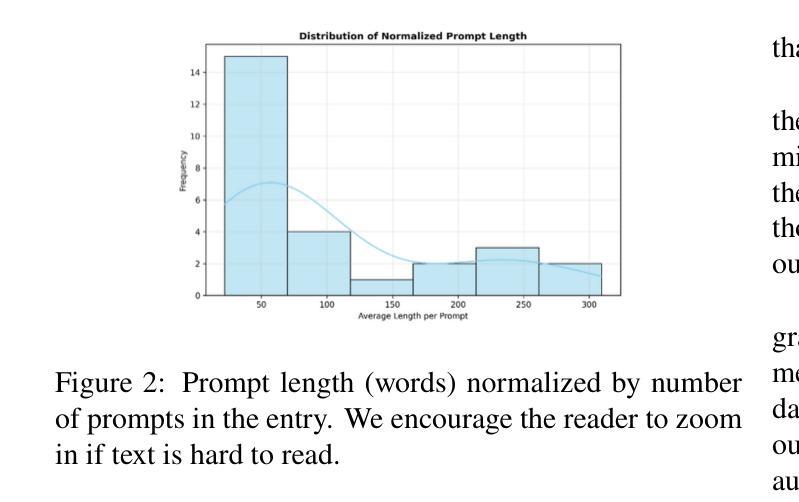
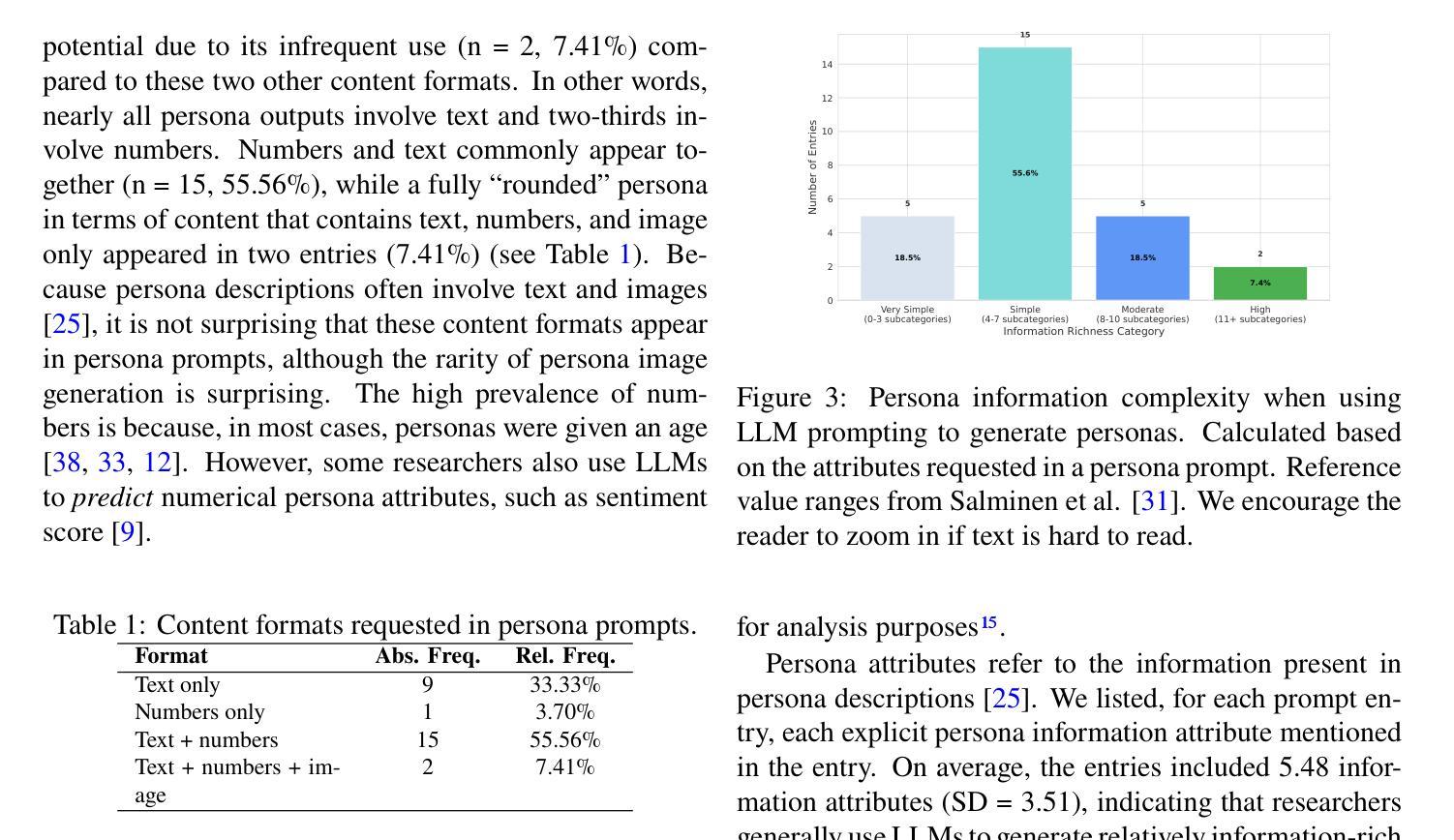
We analyzed 83 persona prompts from 27 research articles that used large language models (LLMs) to generate user personas. Findings show that the prompts predominantly generate single personas. Several prompts express a desire for short or concise persona descriptions, which deviates from the tradition of creating rich, informative, and rounded persona profiles. Text is the most common format for generated persona attributes, followed by numbers. Text and numbers are often generated together, and demographic attributes are included in nearly all generated personas. Researchers use up to 12 prompts in a single study, though most research uses a small number of prompts. Comparison and testing multiple LLMs is rare. More than half of the prompts require the persona output in a structured format, such as JSON, and 74% of the prompts insert data or dynamic variables. We discuss the implications of increased use of computational personas for user representation.
我们分析了27篇研究文章中的83个角色提示,这些文章使用大型语言模型(LLM)来生成用户角色。研究结果表明,这些提示主要生成单一角色。许多提示表达了对于简短或简洁的角色描述的渴望,这与创建丰富、有信息量和全面的角色资料的传统相悖。文本是生成角色属性最常见的格式,其次是数字。文本和数字通常一起生成,几乎所有生成的角色中都包含人口统计属性。研究人员在一个研究中最多使用多达12个提示,但大多数研究使用的提示数量较少。比较和测试多个LLM的情况很少见。超过一半的提示要求角色输出采用结构化格式,如JSON,74%的提示插入数据或动态变量。我们探讨了计算角色在用户代表方面越来越多的使用的含义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AICCSA-2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)生成用户人设的83个提示分析显示,这些提示主要生成单一人设。研究人员倾向于简短描述人设,与传统创建丰富、全面的人设描述有所不同。文本是最常见的人设属性形式,其次是数字,两者经常一起生成。大多数研究使用的提示数量较少,超过一半的提示要求人设输出为结构化格式如JSON,且74%的提示会插入数据或动态变量。本文探讨了计算人设在用户代表方面的应用及其影响。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型生成的提示主要用于创建单一人设。
- 研究倾向于简短描述人设,而非传统丰富的描述方式。
- 文本和数字是最常见的人设属性形式,经常结合生成。
- 大多数研究使用较少的提示数量。
- 超过一半的提示要求人设输出为结构化格式如JSON。
- 大部分提示会插入数据或动态变量。
- 使用计算人设在生成用户代表方面的应用日益普及。
点此查看论文截图
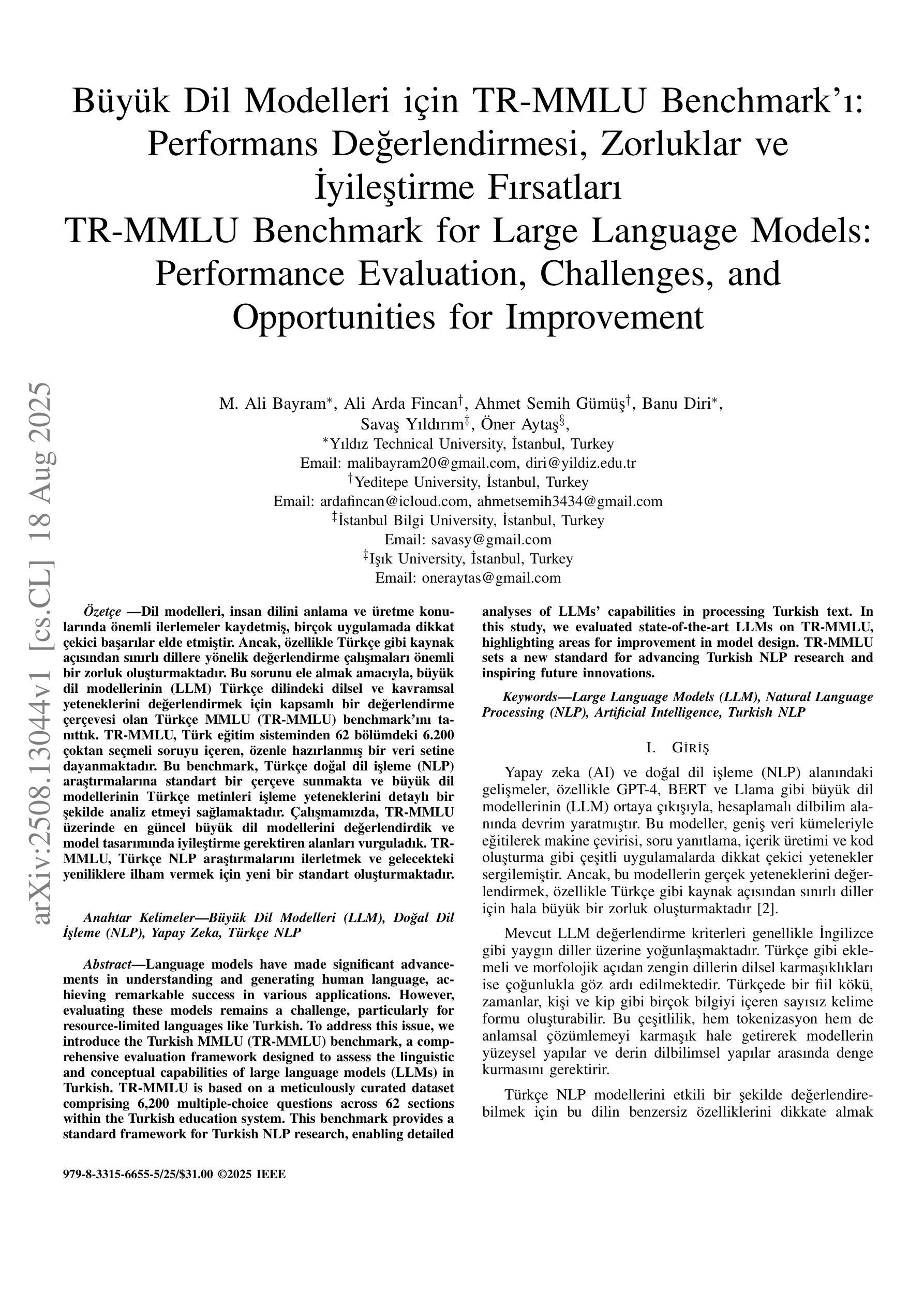
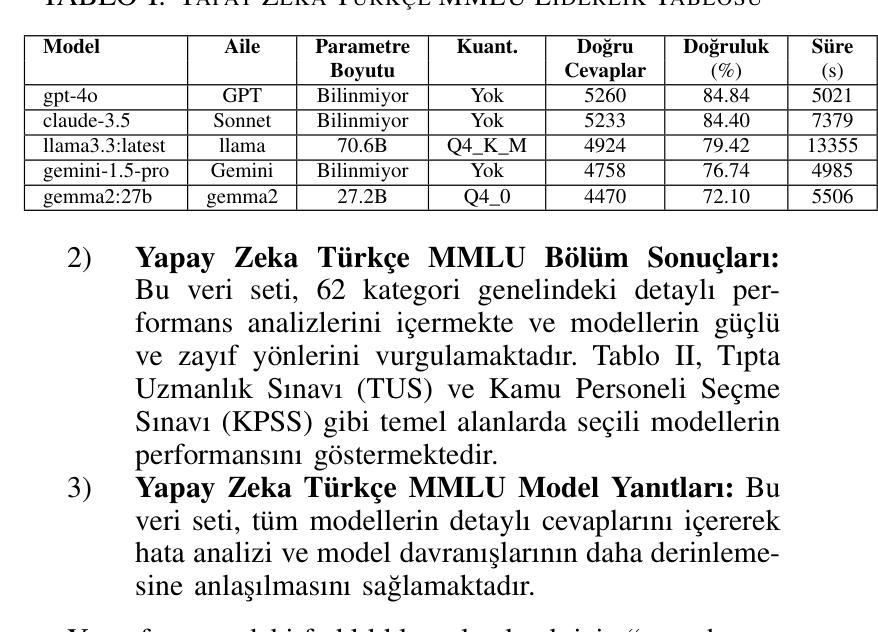
Büyük Dil Modelleri için TR-MMLU Benchmarkı: Performans Değerlendirmesi, Zorluklar ve İyileştirme Fırsatları
Authors:M. Ali Bayram, Ali Arda Fincan, Ahmet Semih Gümüş, Banu Diri, Savaş Yıldırım, Öner Aytaş
Language models have made significant advancements in understanding and generating human language, achieving remarkable success in various applications. However, evaluating these models remains a challenge, particularly for resource-limited languages like Turkish. To address this issue, we introduce the Turkish MMLU (TR-MMLU) benchmark, a comprehensive evaluation framework designed to assess the linguistic and conceptual capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in Turkish. TR-MMLU is based on a meticulously curated dataset comprising 6,200 multiple-choice questions across 62 sections within the Turkish education system. This benchmark provides a standard framework for Turkish NLP research, enabling detailed analyses of LLMs’ capabilities in processing Turkish text. In this study, we evaluated state-of-the-art LLMs on TR-MMLU, highlighting areas for improvement in model design. TR-MMLU sets a new standard for advancing Turkish NLP research and inspiring future innovations.
语言模型在理解和生成人类语言方面取得了显著进展,在各种应用中取得了令人瞩目的成功。然而,评估这些模型仍然是一个挑战,特别是对于土耳其语等资源有限的语言。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了土耳其MMLU(TR-MMLU)基准测试,这是一个全面的评估框架,旨在评估大型语言模型(LLM)在土耳其语中的语言和概念能力。TR-MMLU基于精心筛选的数据集,包含土耳其教育体系中62个领域的6200个选择题。该基准测试为土耳其NLP研究提供了一个标准框架,能够对LLM处理土耳其文本的能力进行详细分析。本研究中,我们在TR-MMLU上评估了最先进的LLM,突出了模型设计需要改进的领域。TR-MMLU为推进土耳其NLP研究设定了新的标准,并激发了未来的创新。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, in Turkish language, 5 figures. Presented at the 2025 33rd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 25–28 June 2025, Sile, Istanbul, T"urkiye
Summary
语言模型在理解和生成人类语言方面取得了显著进展,并在各种应用中取得了非凡的成功。然而,评估这些模型仍然是一个挑战,特别是对于像土耳其语这样的资源有限的语言。为解决这一问题,我们推出了土耳其MMLU(TR-MMLU)基准测试,这是一个用于评估大型语言模型在土耳其语中的语言和理解能力的全面评估框架。TR-MMLU基于精心挑选的数据集,包含土耳其教育系统中的6200个多项选择题。它为土耳其NLP研究提供了标准框架,使研究人员能够详细分析LLM处理土耳其文本的能力。本研究在TR-MMLU上评估了最先进的LLM,并指出了模型设计需要改进的领域。TR-MMLU为推进土耳其NLP研究设立了新标准,并激发了未来的创新。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型在理解和生成人类语言方面取得显著进展,并广泛应用于不同领域。
- 评估语言模型对资源有限的语言(如土耳其语)仍是挑战。
- 引入TR-MMLU基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在土耳其语中的语言和理解能力。
- TR-MMLU基于包含6200个多项选择题的精心挑选的数据集构建。
- TR-MMLU为土耳其NLP研究提供了标准框架,便于分析LLM处理土耳其文本的能力。
- 在TR-MMLU上评估了最先进的LLM,发现了模型设计的改进空间。
点此查看论文截图
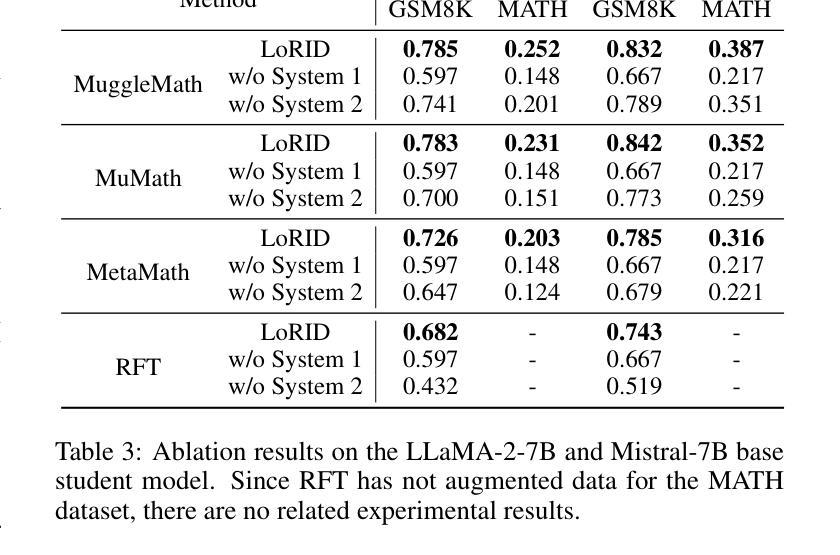
Can Large Models Teach Student Models to Solve Mathematical Problems Like Human Beings? A Reasoning Distillation Method via Multi-LoRA Interaction
Authors:Xinhe Li, Jiajun Liu, Peng Wang
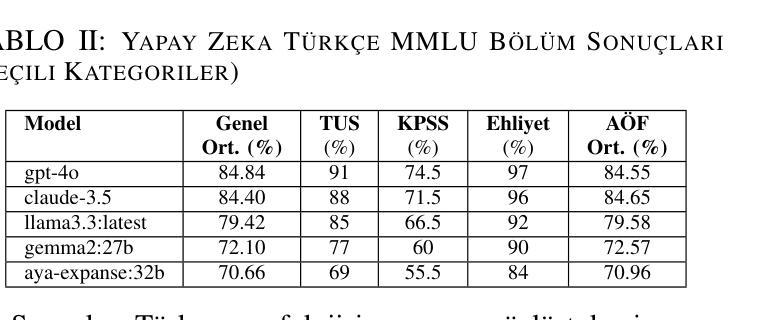
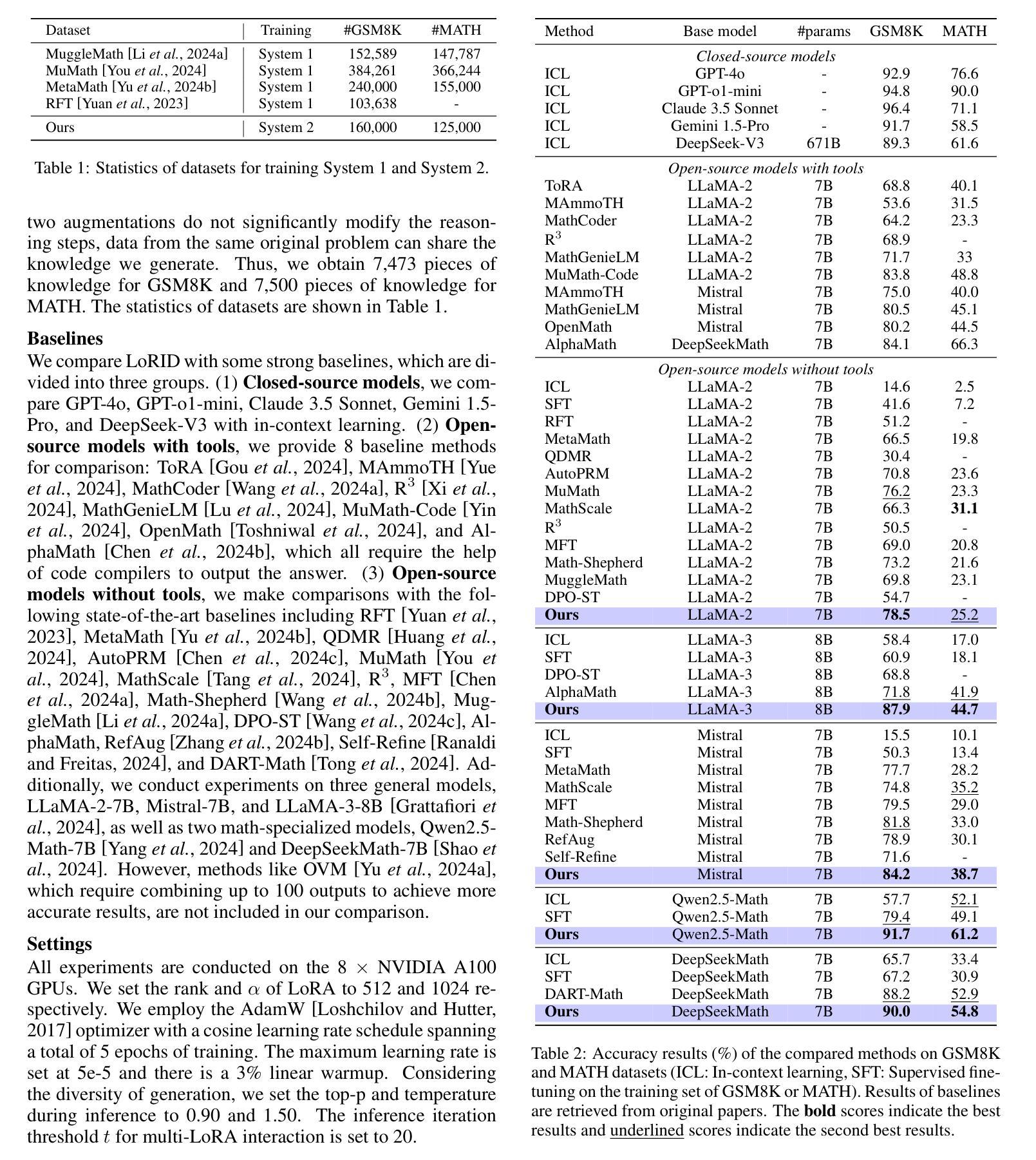
Recent studies have demonstrated that Large Language Models (LLMs) have strong mathematical reasoning abilities but rely on hundreds of billions of parameters. To tackle the challenge of poor reasoning in Small Language Models (SLMs), existing methods typically leverage LLMs to generate massive amounts of data for cramming training. In psychology, they are akin to System 1 thinking, which resolves reasoning problems rapidly based on experience and intuition. However, human learning also requires System 2 thinking, where knowledge is first acquired and then reinforced through practice. Inspired by such two distinct modes of thinking, we propose a novel method based on the multi-LoRA Interaction for mathematical reasoning Distillation (LoRID). First, we input the question and reasoning of each sample into an LLM to create knowledge-enhanced datasets. Subsequently, we train a LoRA block on the student model as an Intuitive Reasoner (IR), which directly generates Chain-of-Thoughts for problem-solving. Then, to imitate System 2 thinking, we train the Knowledge Generator (KG) and Deep Reasoner (DR), respectively. The former outputs only knowledge after receiving problems, while the latter uses that knowledge to perform reasoning. Finally, to address the randomness in the generation of IR and DR, we evaluate whether their outputs are consistent, and the inference process needs to be iterated if not. This step can enhance the mathematical reasoning ability of SLMs through mutual feedback. Experimental results show that LoRID achieves state-of-the-art performance, especially on the GSM8K dataset, where it outperforms the second-best method by 2.3%, 16.1%, 2.4%, 12.3%, and 1.8% accuracy across the five base models, respectively.
最近的研究表明,大型语言模型(LLM)具有很强的数学推理能力,但需要依赖数百亿参数。为了解决小型语言模型(SLM)推理能力较差的挑战,现有方法通常利用大型语言模型生成大量数据进行填鸭式训练。在心理学中,这与系统1思维类似,即基于经验和直觉快速解决推理问题。然而,人类学习还需要系统2思维,即先获取知识,然后通过实践进行巩固。受这两种不同思维模式的启发,我们提出了一种基于多LoRA交互的数学推理蒸馏(LoRID)的新方法。首先,我们将每个样本的问题和推理输入到大型语言模型中,创建知识增强数据集。然后,我们在学生模型上训练LoRA块作为直觉推理者(IR),直接生成解决问题的思维链。接着,为了模仿系统2思维,我们分别训练知识生成器(KG)和深度推理器(DR)。前者在接收到问题后只输出知识,而后者则利用这些知识进行推理。最后,为了解决IR和DR生成过程中的随机性,我们评估他们的输出是否一致,如果不一致,则需要迭代推理过程。这一步可以通过相互反馈增强小型语言模型的数学推理能力。实验结果表明,LoRID达到了最新技术水平,特别是在GSM8K数据集上,与第二名方法相比,它在五个基础模型上的准确率分别提高了2.3%、16.1%、2.4%、12.3%和1.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)具有强大的数学推理能力,但依赖百亿参数。为解决小型语言模型(SLM)推理能力弱的问题,现有方法常利用LLM生成大量数据进行填鸭式训练。本文受心理学中两种思考模式启发,提出基于多LoRA交互的数学推理蒸馏(LoRID)新方法。首先利用LLM创建知识增强数据集,训练直觉推理器(IR),模仿基于经验和直觉的快速推理。接着训练知识生成器(KG)和深度推理器(DR),分别输出知识和进行推理。通过评估两者输出的一致性,进行迭代优化,提升SLM的数学推理能力。实验结果显示,LoRID在GSM8K数据集上实现最佳性能,在五个基础模型上分别超越第二名方法2.3%、16.1%、2.4%、12.3%和1.8%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- LLM具备强大的数学推理能力,但依赖大量参数。
- SLM推理能力较弱,现有方法借助LLM生成数据对其进行训练提升。
- 受心理学启发,提出基于两种思考模式的LoRID方法,模仿人类的快速推理和知识应用。
- LoRID通过创建知识增强数据集、训练IR、KG和DR三个组件来提升SLM的数学推理能力。
- LoRID方法通过评估IR和DR输出的一致性进行迭代优化。
- 实验结果显示,LoRID在GSM8K数据集上实现最佳性能,准确率高。
点此查看论文截图


The Application of Transformer-Based Models for Predicting Consequences of Cyber Attacks
Authors:Bipin Chhetri, Akbar Siami Namin
Cyberattacks are increasing, and securing against such threats is costing industries billions of dollars annually. Threat Modeling, that is, comprehending the consequences of these attacks, can provide critical support to cybersecurity professionals, enabling them to take timely action and allocate resources that could be used elsewhere. Cybersecurity is heavily dependent on threat modeling, as it assists security experts in assessing and mitigating risks related to identifying vulnerabilities and threats. Recently, there has been a pressing need for automated methods to assess attack descriptions and forecast the future consequences of the increasing complexity of cyberattacks. This study examines how Natural Language Processing (NLP) and deep learning can be applied to analyze the potential impact of cyberattacks by leveraging textual descriptions from the MITRE Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) database. We emphasize classifying attack consequences into five principal categories: Availability, Access Control, Confidentiality, Integrity, and Other. This paper investigates the use of Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) in combination with Hierarchical Attention Networks (HANs) for Multi-label classification, evaluating their performance in comparison with conventional CNN and LSTM-based models. Experimental findings show that BERT achieves an overall accuracy of $0.972$, far higher than conventional deep learning models in multi-label classification. HAN outperforms baseline forms of CNN and LSTM-based models on specific cybersecurity labels. However, BERT consistently achieves better precision and recall, making it more suitable for predicting the consequences of a cyberattack.
网络攻击日益增多,对抗这些威胁的安全措施每年给各行业带来数十亿美元的支出。威胁建模,即理解这些攻击的后果,可以为网络安全专家提供关键支持,使他们能够采取及时行动并分配可能用于其他地方的资源。网络安全严重依赖于威胁建模,因为它可以帮助安全专家评估和减轻与识别漏洞和威胁相关的风险。最近,随着网络攻击复杂性的增加,急需自动方法来评估攻击描述并预测未来的后果。本研究探讨了如何应用自然语言处理(NLP)和深度学习,通过利用MITRE常见弱点枚举(CWE)数据库中的文本描述来分析网络攻击潜在影响的分类方法。我们强调将攻击后果分为五个主要类别:可用性、访问控制、保密性、完整性和其他类别。本文研究了结合使用基于变压器的双向编码器表示(BERT)和分层注意力网络(HAN)进行多标签分类的方法,评估它们在传统的CNN和LSTM模型中的表现。实验结果表明,BERT的总体准确度达到0.972,远高于传统深度学习模型在多标签分类中的表现。HAN在特定的网络安全标签上优于CNN和LSTM的基线模型。然而,BERT在精确度和召回率方面始终表现更好,使其成为预测网络攻击后果的更合适的选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 6 figures,Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Software, & Applications (COMPSAC), EATA Symposium, Toronto, Canada, July 8-11, 2025
摘要
网络攻击日益增多,对行业的网络安全防护成本每年达数十亿美元。威胁建模能够深入理解这些攻击的后果,为网络安全专家提供关键支持,使其能够及时采取行动并为可能用于其他地方的资源分配提供参考。网络安全严重依赖于威胁建模,因为它可以帮助安全专家评估和缓解与识别漏洞和威胁有关的风险。近期迫切需要自动化方法来评估攻击描述并预测日益复杂的网络攻击的未来后果。本研究探讨了如何应用自然语言处理(NLP)和深度学习来分析网络攻击潜在影响的方法,通过使用MITRE通用弱点枚举(CWE)数据库中的文本描述来实现。本研究强调将攻击后果分类为五个主要类别:可用性、访问控制、保密性、完整性和其他类别。本文研究了如何使用结合了层次注意力网络(HANs)的双向编码器表示变换器(BERT)进行多标签分类,评估其在传统CNN和LSTM模型中的性能表现。实验结果表明,BERT的总体准确度达到0.972,在多标签分类中的表现优于传统深度学习模型。HAN在特定网络安全标签上优于基于CNN和LSTM的基线模型。然而,BERT在精确度和召回率方面始终表现更好,因此更适合预测网络攻击的后果。
关键见解
- 网络攻击频率上升,年度安全成本高昂。
- 威胁建模在网络安全中起到关键作用,帮助专家评估并缓解风险。
- 存在对网络攻击后果自动化评估的需求。
- 研究使用MITRE CWE数据库中的文本描述进行分析。
- 攻击后果被分类为五个主要类别。
- BERT与HAN结合使用在多标签分类中表现优异,准确度较高。
点此查看论文截图

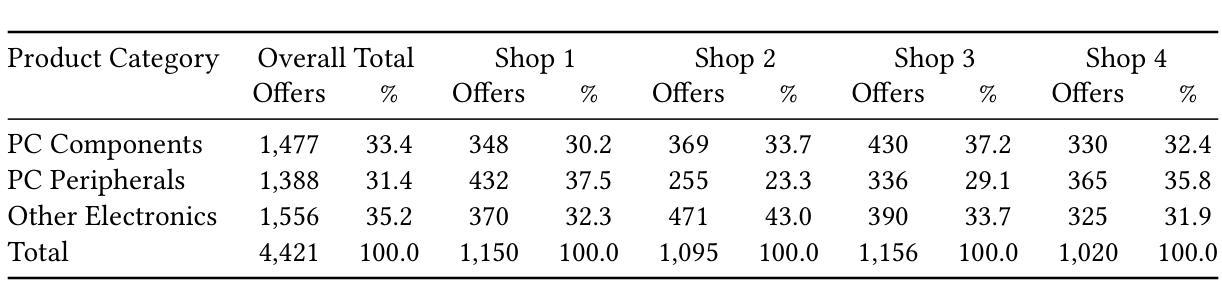
WebMall – A Multi-Shop Benchmark for Evaluating Web Agents
Authors:Ralph Peeters, Aaron Steiner, Luca Schwarz, Julian Yuya Caspary, Christian Bizer
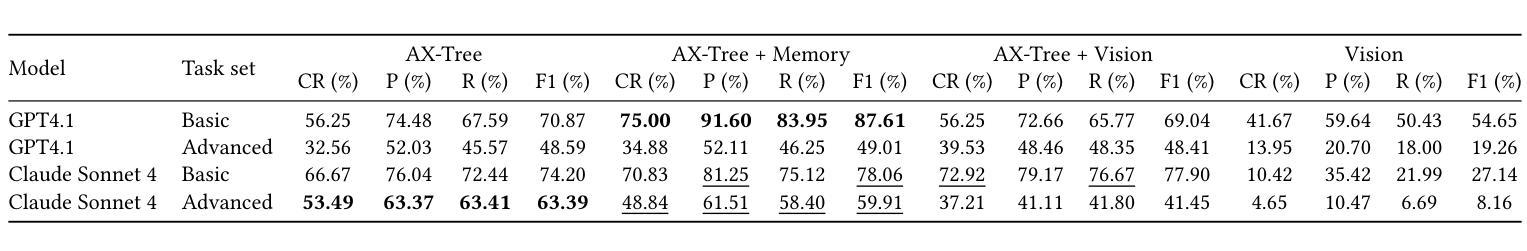
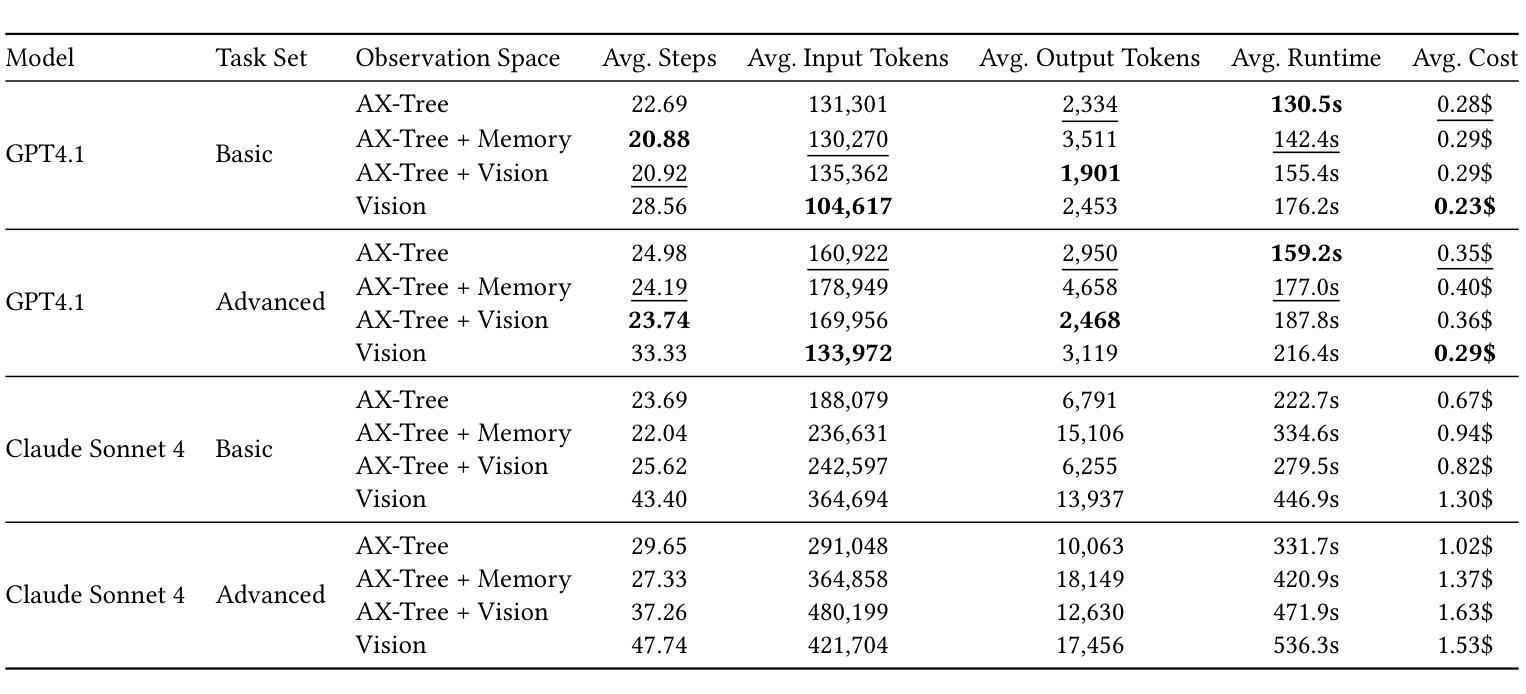
LLM-based web agents have the potential to automate long-running web tasks, such as finding offers for specific products in multiple online shops and subsequently ordering the cheapest products that meet the users needs. This paper introduces WebMall, a multi-shop online shopping benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of web agents for comparison-shopping. WebMall consists of four simulated online shops populated with authentic product offers sourced from the Common Crawl, alongside a suite of 91 cross-shop tasks. These tasks include basic tasks such as finding specific products in multiple shops, performing price comparisons, adding items to the shopping cart, and completing checkout. Advanced tasks involve searching for products based on vague requirements, identifying suitable substitutes, and finding compatible products. Compared to existing e-commerce benchmarks, such as WebShop or ShoppingBench, WebMall introduces comparison-shopping tasks across multiple shops. Furthermore, the product offers are more heterogeneous, as they originate from hundreds of distinct real-world shops. The tasks in WebMall require longer interaction trajectories than those in WebShop, while remaining representative of real-world shopping behaviors. We evaluate eight baseline agents on WebMall, varying in observation modality, memory utilization, and underlying large language model (GPT 4.1 and Claude Sonnet 4). The best-performing configurations achieve completion rates of 75% and 53%, and F1 scores of 87% and 63%, on the basic and advanced task sets, respectively. WebMall is publicly released to facilitate research on web agents and to promote advancements in navigation, reasoning, and efficiency within e-commerce scenarios.
基于LLM的Web代理具有自动化长期Web任务的潜力,例如在多间网上商店寻找特定产品的优惠,然后订购符合用户需求的最低价格产品。本文介绍了WebMall,这是一个用于评估Web代理在比较购物中的有效性和效率的跨店在线购物基准测试。WebMall由四个模拟在线商店组成,这些商店充斥着来自Common Crawl的真实产品优惠信息,以及一套91个跨店任务。这些任务包括基本任务,如在多间商店寻找特定产品、比较价格、将商品添加到购物车并完成结账。高级任务包括根据模糊需求搜索产品、识别合适替代品和查找兼容产品。与现有的电子商务基准测试(如WebShop或ShoppingBench)相比,WebMall引入了跨多个商店的比较购物任务。此外,由于产品优惠来自数百个不同的真实商店,因此产品优惠更加多样化。WebMall中的任务需要比WebShop更长的交互轨迹,同时仍代表真实世界的购物行为。我们在WebMall上评估了八种基线代理,它们在不同观察模式、内存利用和底层大型语言模型(GPT 4.1和Claude Sonnet 4)方面有所不同。表现最佳的配置在基本和高级任务集上的完成率分别为75%和53%,F1分数分别为87%和63%。WebMall公开发布,以促进对Web代理的研究,并推动电子商务场景中的导航、推理和效率方面的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了LLM驱动的Web代理在自动化长期Web任务方面的潜力,如跨多个在线商店比较产品并订购满足用户需求的最低价格产品。论文提出WebMall基准测试平台,模拟在线购物场景以评估代理在处理对比购物时的效能与效率。WebMall包含四个模拟在线商店及一套跨店任务,涉及基础任务如产品寻找、价格对比和购物车管理等,还包括高级任务如基于模糊要求搜索产品、寻找替代产品等。与现有基准测试相比,WebMall涵盖更多真实商店的产品信息,任务轨迹更长且代表真实购物行为。评估结果显示,最佳配置的代理在基础任务集上完成率高达75%,高级任务集上完成率为53%,展示了强大的潜力。WebMall平台已公开发布,便于对代理进行研究并推动电子商务场景中导航、推理和效率方面的进步。
Key Takeaways
- LLM驱动的Web代理可以自动化长期Web任务,如跨多个在线商店进行产品比较和购买满足用户需求的最低价格产品。
- WebMall是一个模拟在线购物场景的基准测试平台,用于评估代理在处理对比购物时的效能与效率。
- WebMall包含四个模拟在线商店和一套包含基础任务和高级任务的跨店任务集。
- 与现有基准测试相比,WebMall的产品信息更丰富且真实,任务轨迹更长,更接近真实的购物行为。
- 最佳配置的代理在基础任务集上的完成率高达75%,展示了强大的潜力。而在高级任务集上的完成率为53%,仍有提升空间。
- WebMall平台已公开发布,为代理研究提供了便利的工具,有助于推动电子商务场景中导航、推理和效率方面的进步。
点此查看论文截图


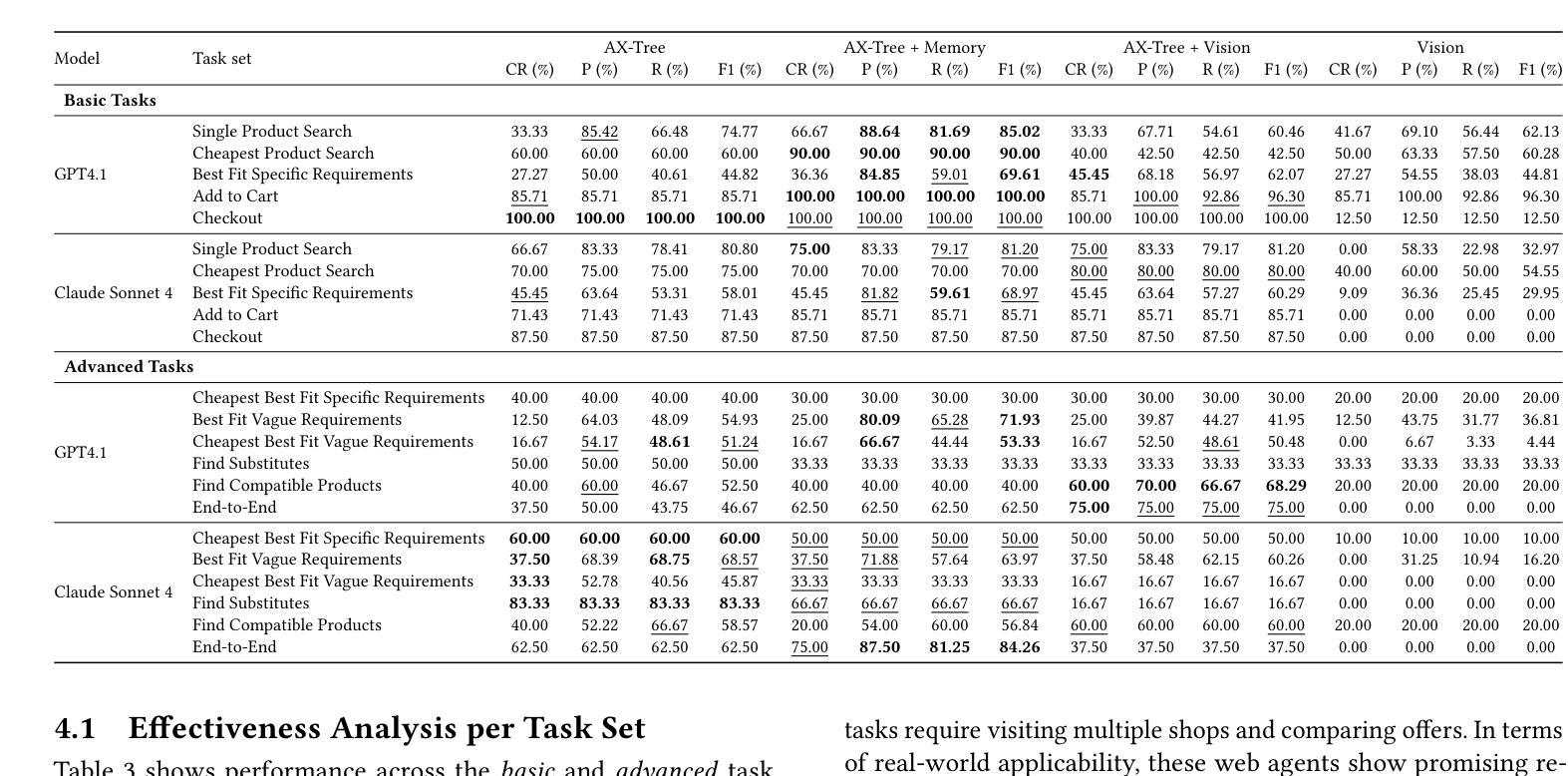
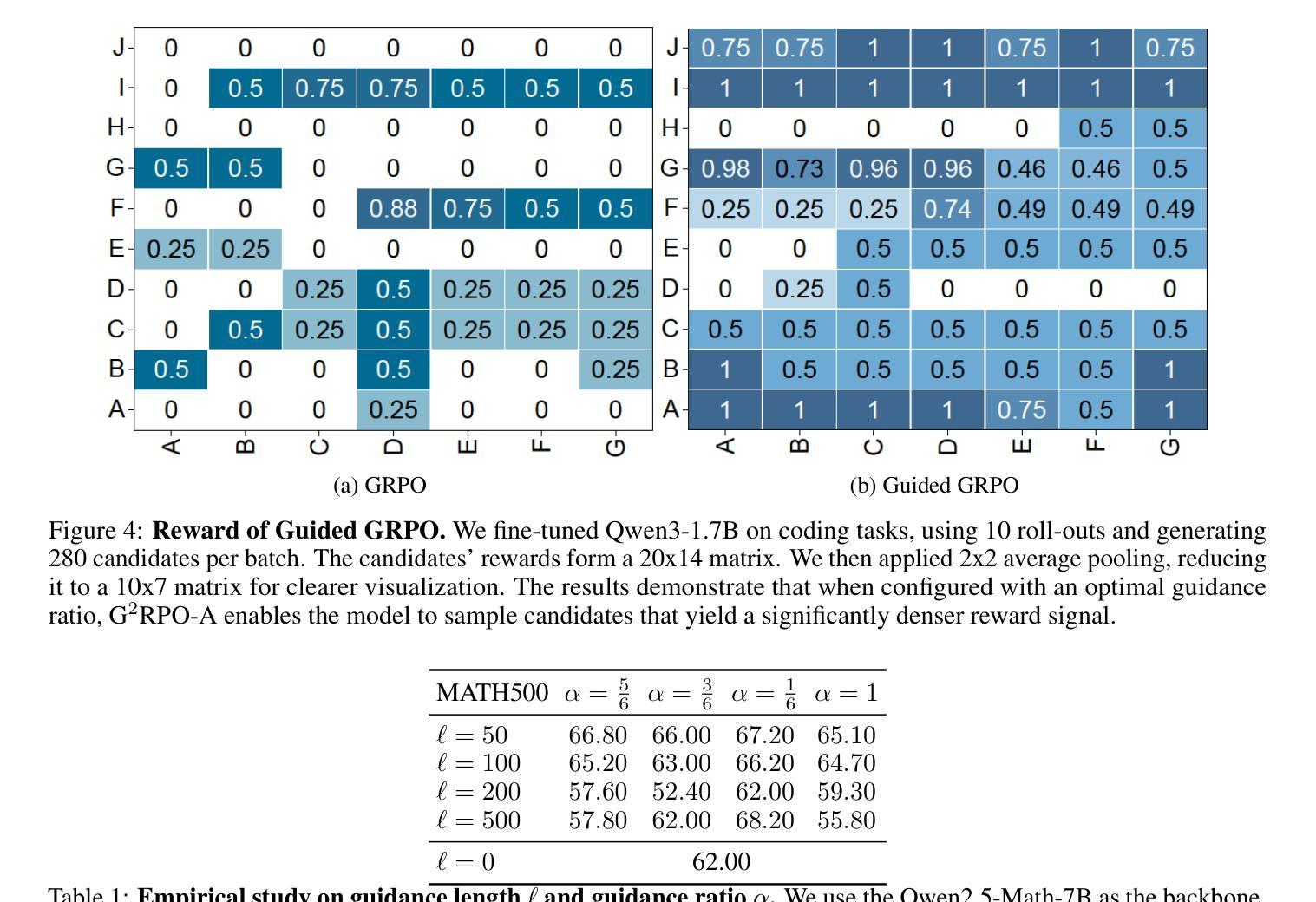
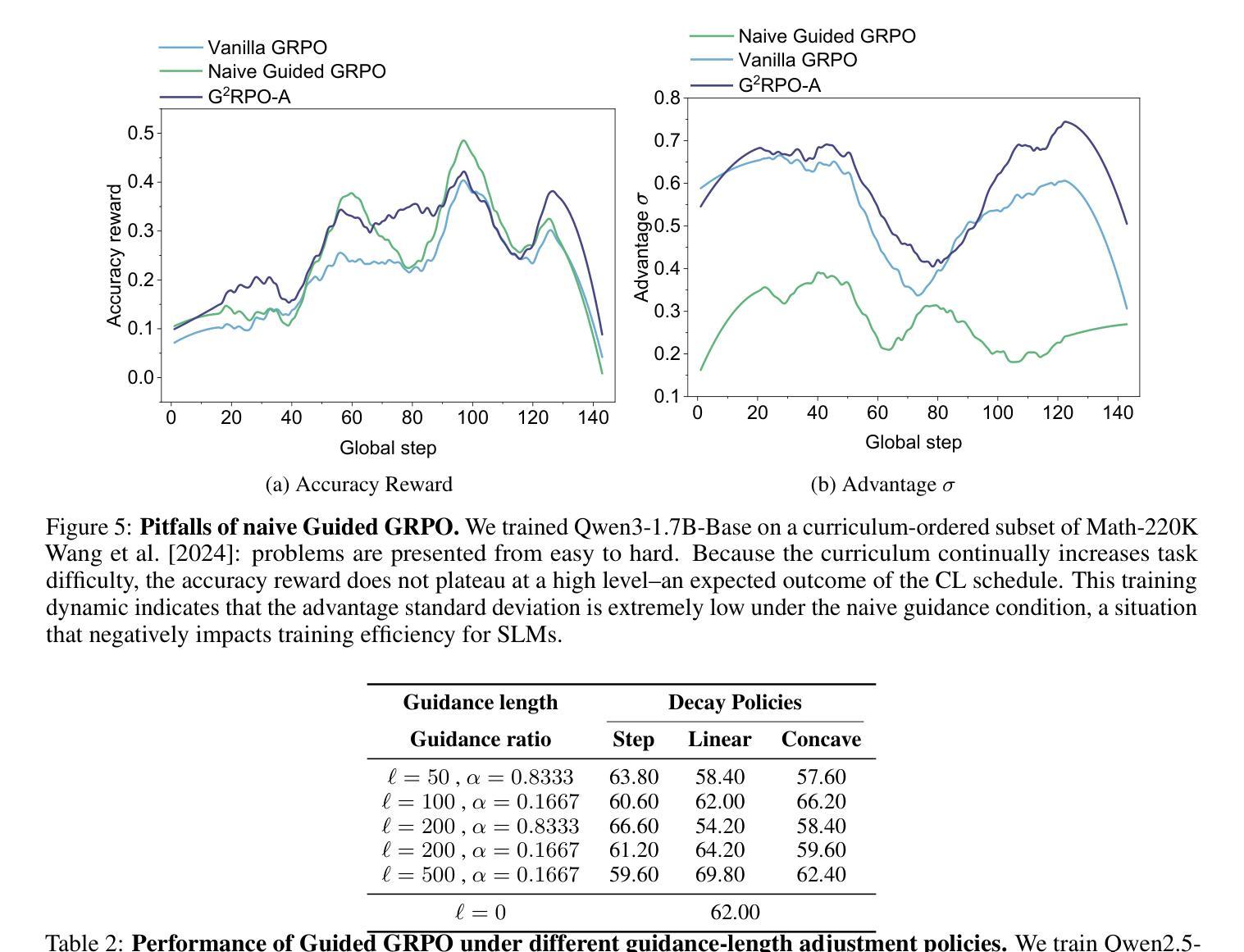
G$^2$RPO-A: Guided Group Relative Policy Optimization with Adaptive Guidance
Authors:Yongxin Guo, Wenbo Deng, Zhenglin Cheng, Xiaoying Tang
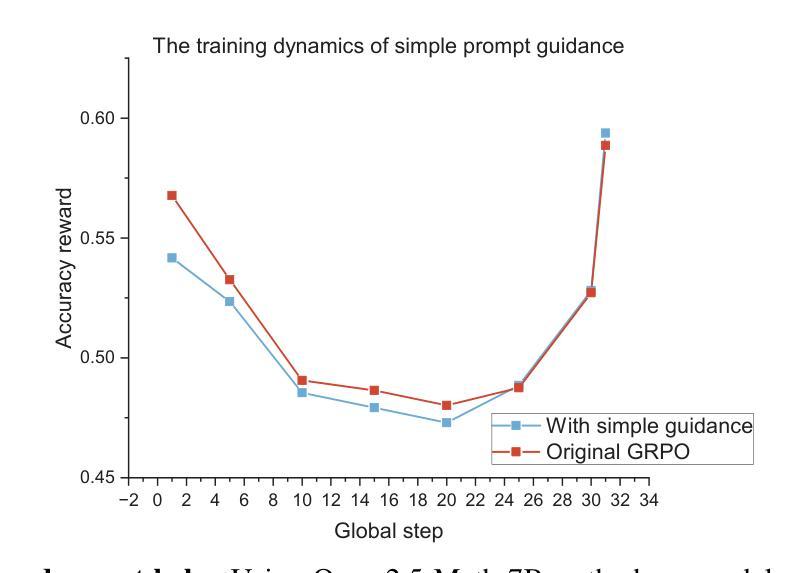
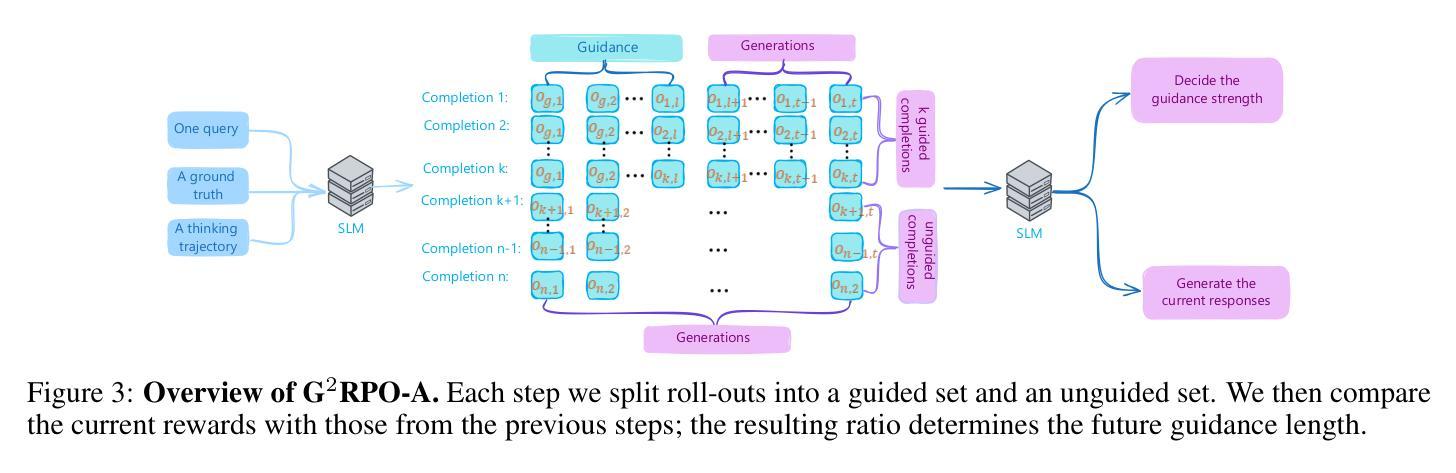
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has markedly enhanced the reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs). Its success, however, largely depends on strong base models with rich world knowledge, yielding only modest improvements for small-size language models (SLMs). To address this limitation, we investigate Guided GRPO, which injects ground-truth reasoning steps into roll-out trajectories to compensate for SLMs’ inherent weaknesses. Through a comprehensive study of various guidance configurations, we find that naively adding guidance delivers limited gains. These insights motivate G$^2$RPO-A, an adaptive algorithm that automatically adjusts guidance strength in response to the model’s evolving training dynamics. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and code-generation benchmarks confirm that G$^2$RPO-A substantially outperforms vanilla GRPO. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/T-Lab-CUHKSZ/G2RPO-A.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。然而,其成功在很大程度上依赖于具有丰富世界知识的强大基础模型,对于小型语言模型(SLM)的改进作用甚微。为了解决这个问题,我们研究了引导GRPO方法,它通过向推演轨迹注入真实推理步骤来弥补SLM的固有弱点。通过对各种引导配置的综合研究,我们发现简单地添加引导带来的增益有限。这些见解促使我们提出了G$^2$RPO-A,这是一种自适应算法,能够自动根据模型的训练动态调整指导强度。在数学推理和代码生成基准测试上的实验证实,G$^2$RPO-A大幅优于标准GRPO方法。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/T-Lab-CUHKSZ/G2RPO-A找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。然而,其成功很大程度上依赖于具有丰富世界知识的强大基础模型,对于小型语言模型(SLM)的改进作用有限。为解决这一问题,我们研究了引导GRPO方法,通过将真实推理步骤注入roll-out轨迹来弥补SLM的固有弱点。通过全面研究各种指导配置,我们发现简单地添加指导带来的收益有限。这些见解催生了自适应算法G^2RPO-A,它能够根据模型的训练动态自动调整指导强度。在数理推理和代码生成基准测试上进行的实验证实,G^2RPO-A大幅优于标准GRPO。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/T-Lab-CUHKSZ/G2RPO-A获取。
Key Takeaways
- RLVR提高了大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 小型语言模型的改进相对有限。
- 引导GRPO方法通过注入真实推理步骤来增强小型语言模型的性能。
- 简单地添加指导在提升性能上效果有限。
- G^2RPO-A是一种自适应算法,可根据模型训练动态调整指导强度。
- G^2RPO-A在数理推理和代码生成方面表现优于标准GRPO。
点此查看论文截图


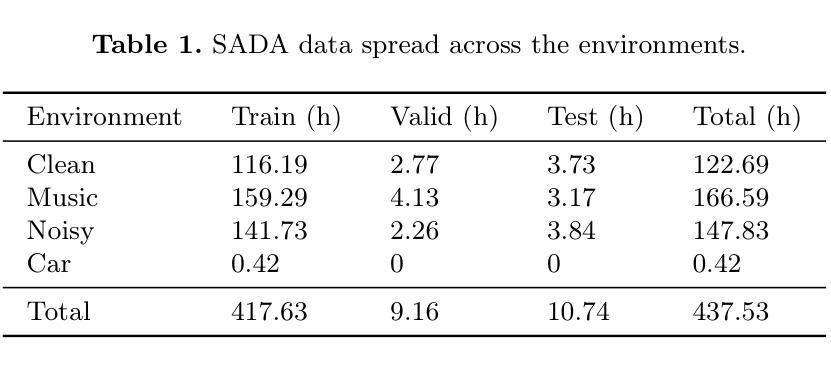
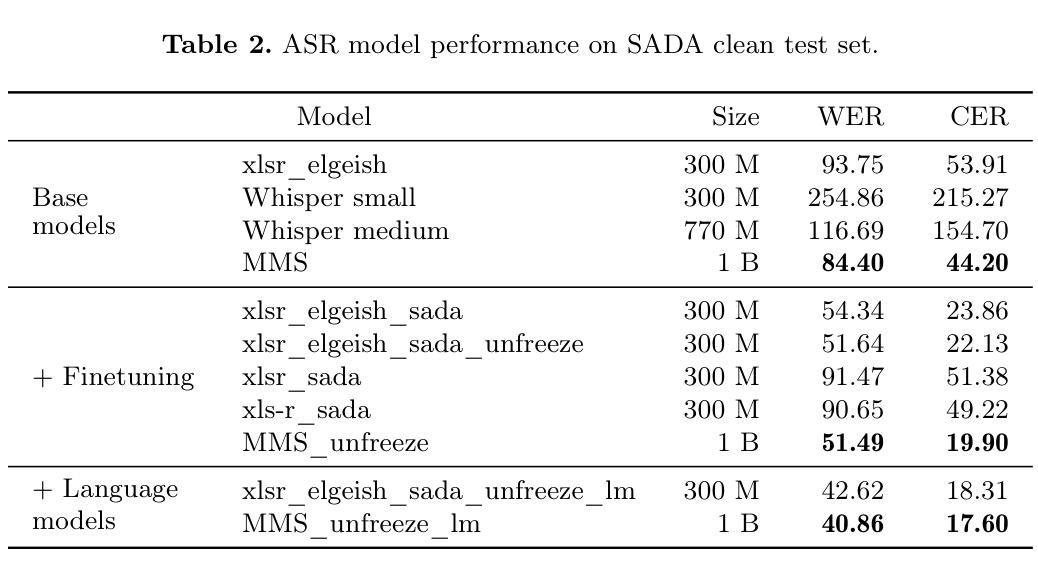
Arabic ASR on the SADA Large-Scale Arabic Speech Corpus with Transformer-Based Models
Authors:Branislav Gerazov, Marcello Politi, Sébastien Bratières
We explore the performance of several state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) models on a large-scale Arabic speech dataset, the SADA (Saudi Audio Dataset for Arabic), which contains 668 hours of high-quality audio from Saudi television shows. The dataset includes multiple dialects and environments, specifically a noisy subset that makes it particularly challenging for ASR. We evaluate the performance of the models on the SADA test set, and we explore the impact of fine-tuning, language models, as well as noise and denoising on their performance. We find that the best performing model is the MMS 1B model finetuned on SADA with a 4-gram language model that achieves a WER of 40.9% and a CER of 17.6% on the SADA test clean set.
我们探索了几种最先进的自动语音识别(ASR)模型在大型阿拉伯语语音数据集SADA(用于阿拉伯语的沙特音频数据集)上的表现。该数据集包含来自沙特电视节目的高质量音频,时长668小时。该数据集包含多种方言和环境,其中特别包含一个嘈杂的子集,这对ASR来说尤其具有挑战性。我们在SADA测试集上评估模型的性能,并探讨了微调、语言模型以及噪声和去噪对其性能的影响。我们发现表现最好的模型是在SADA上经过微调MMS 1B模型,使用4元语言模型,在SADA测试清洁集上实现了40.9%的WER和17.6%的CER。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
阿拉伯语音识别模型在SADA数据集上的性能研究。文章探索了多个先进的自动语音识别(ASR)模型在大型阿拉伯语音数据集SADA上的表现。SADA数据集包含来自沙特电视节目的高质量音频,时长668小时,包含多种方言和环境,其中噪声子集尤为挑战ASR。研究评估了模型在SADA测试集上的性能,并探讨了微调、语言模型以及噪声和去噪对性能的影响。最佳模型为在SADA上微调过的MMS 1B模型,使用4-gram语言模型,在SADA测试清洁集上实现字错误率(WER)40.9%和字符错误率(CER)17.6%。
Key Takeaways
- 使用了先进的ASR模型在大型阿拉伯语音数据集SADA上进行性能研究。
- SADA数据集包含多种方言和环境的音频,其中噪声子集增加了ASR的挑战性。
- 研究评估了模型在SADA测试集上的性能。
- 最佳的ASR模型是MMS 1B模型,经过在SADA上的微调,并使用4-gram语言模型。
- 最佳模型在SADA测试清洁集上实现了较低的WER和CER。
- 研究探讨了微调、语言模型、噪声和去噪对ASR模型性能的影响。
点此查看论文截图

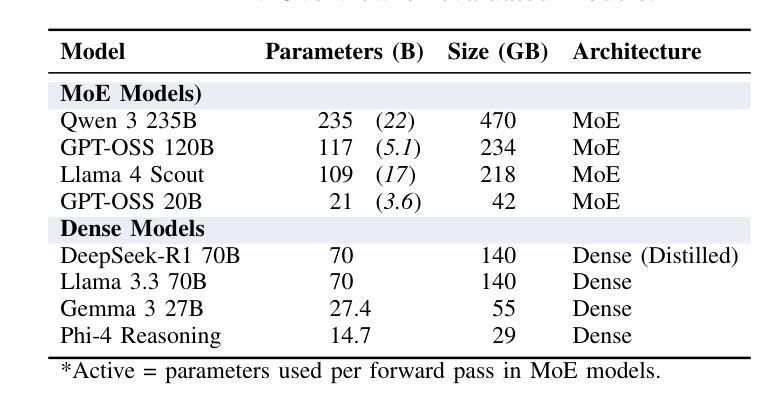
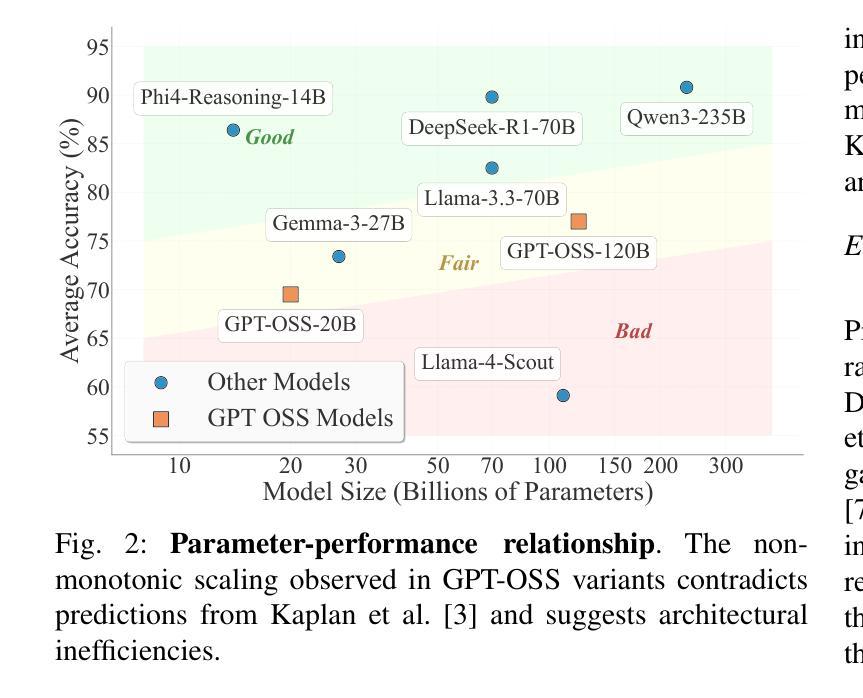
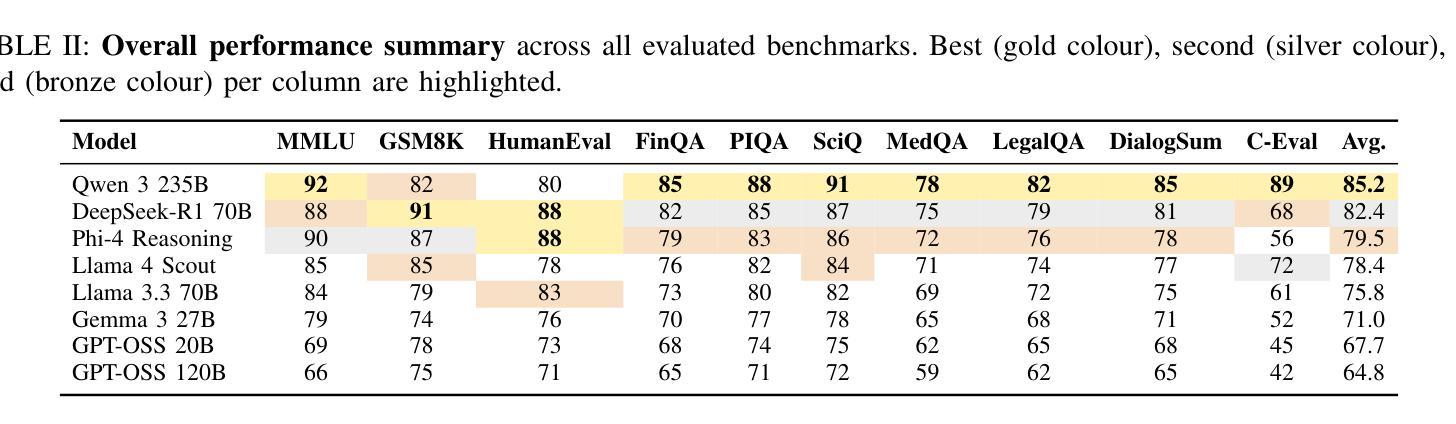
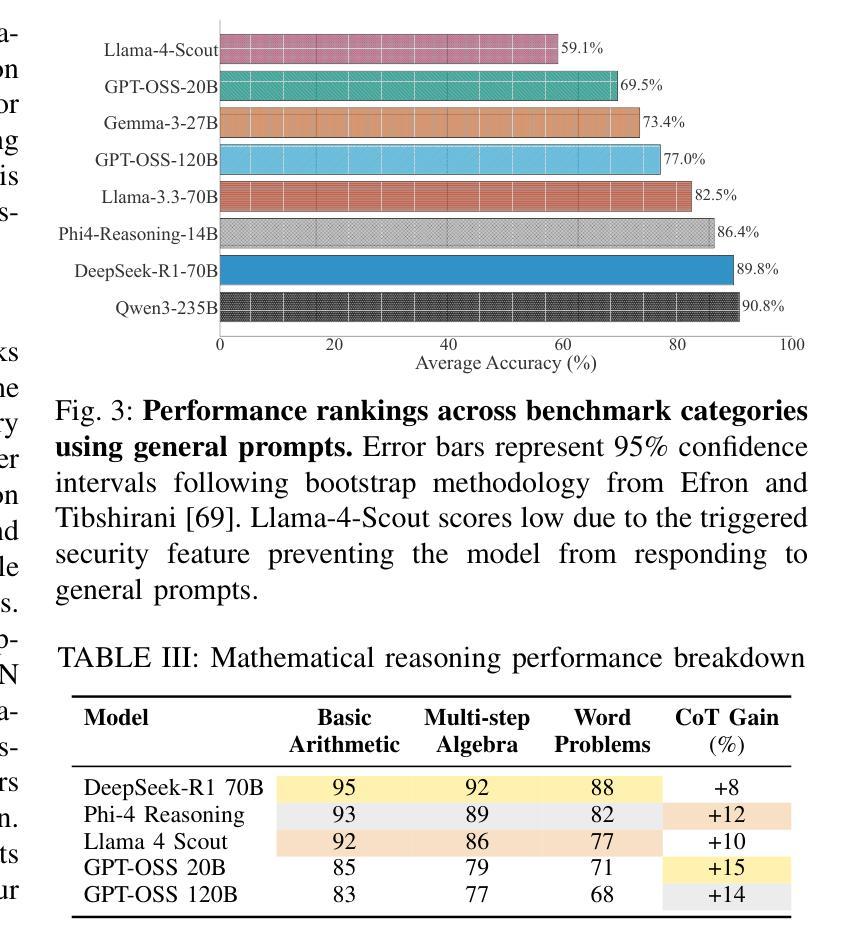
Is GPT-OSS Good? A Comprehensive Evaluation of OpenAI’s Latest Open Source Models
Authors:Ziqian Bi, Keyu Chen, Chiung-Yi Tseng, Danyang Zhang, Tianyang Wang, Hongying Luo, Lu Chen, Junming Huang, Jibin Guan, Junfeng Hao, Junhao Song
In August 2025, OpenAI released GPT-OSS models, its first open weight large language models since GPT-2 in 2019, comprising two mixture of experts architectures with 120B and 20B parameters. We evaluated both variants against six contemporary open source large language models ranging from 14.7B to 235B parameters, representing both dense and sparse designs, across ten benchmarks covering general knowledge, mathematical reasoning, code generation, multilingual understanding, and conversational ability. All models were tested in unquantised form under standardised inference settings, with statistical validation using McNemars test and effect size analysis. Results show that gpt-oss-20B consistently outperforms gpt-oss-120B on several benchmarks, such as HumanEval and MMLU, despite requiring substantially less memory and energy per response. Both models demonstrate mid-tier overall performance within the current open source landscape, with relative strength in code generation and notable weaknesses in multilingual tasks. These findings provide empirical evidence that scaling in sparse architectures may not yield proportional performance gains, underscoring the need for further investigation into optimisation strategies and informing more efficient model selection for future open source deployments.
在2025年8月,OpenAI发布了GPT-OSS模型,这是自2019年GPT-2以来其首个开源大型语言模型,包括两种混合专家架构,分别带有120B和20B的参数。我们评估了这两种变体,与六种当代开源大型语言模型(参数范围从14.7B到235B)进行了比较,这些模型代表了密集和稀疏两种设计,涵盖了十个基准测试,包括通用知识、数学推理、代码生成、多语种理解和对话能力等方面。所有模型都在标准化的推理设置下以非量化形式进行测试,并使用McNemars测试和效应量分析进行统计验证。结果表明,尽管gpt-oss-20B在多个基准测试(如HumanEval和MMLU)上表现优于gpt-oss-120B,并且在每个回答所需的内存和能量方面大幅降低,但gpt-oss-20B还是展现了在当前开源环境中的中端整体性能,其在代码生成方面相对较强,而在多语种任务中存在明显弱点。这些发现提供了实证证据表明,在稀疏架构中进行扩展可能不会产生比例的性能提升,这强调了进一步优化策略研究的必要性,并为未来开源部署提供更有效的模型选择依据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GPT-OSS模型是OpenAI继GPT-2之后的首批开放权重大型语言模型,包含两个混合专家架构,分别有120B和20B参数。本文通过对比包括GPT-OSS在内的六个当代开源大型语言模型在涵盖通识知识、数学推理、代码生成、多语言理解和对话能力等多个方面的十项基准测试上的表现,发现GPT-OSS-20B在多个基准测试上表现优于GPT-OSS-120B,尽管其内存和能源需求更少。两者均在现有开源大型语言模型性能居于中游,但在代码生成方面相对出色,而在多语言任务方面表现欠佳。本研究为优化策略和未来开源部署的模型选择提供了实证依据和参考。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-OSS是OpenAI新的大型语言模型系列,包括两个混合专家架构的版本,分别是GPT-OSS-120B和GPT-OSS-20B。
- 对比了六个当代开源大型语言模型在多个基准测试上的表现。
- GPT-OSS-20B在多个基准测试上表现出超越GPT-OSS-120B的性能,尤其在HumanEval和MMLU等测试中表现显著。
- GPT-OSS模型内存和能源效率较高,特别是在响应次数方面。
- GPT-OSS模型整体性能在现有开源大型语言模型中居于中游水平。
- GPT-OSS模型在代码生成方面具备相对优势,但在多语言任务方面存在明显弱点。
点此查看论文截图

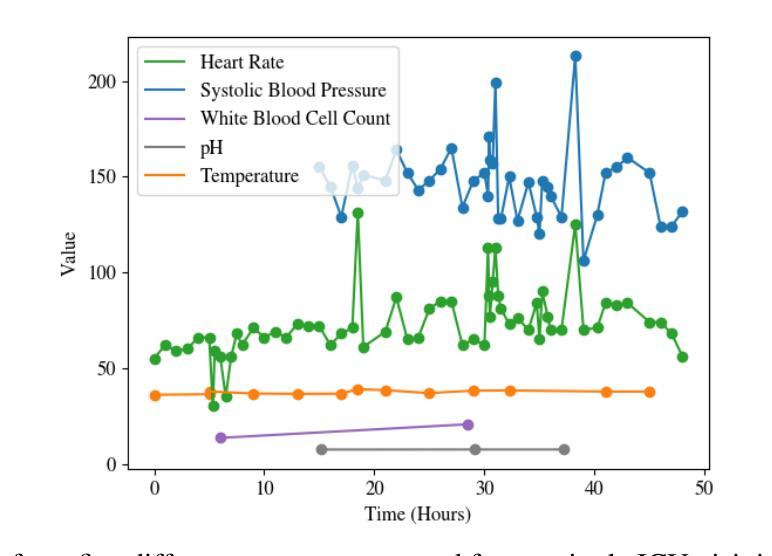
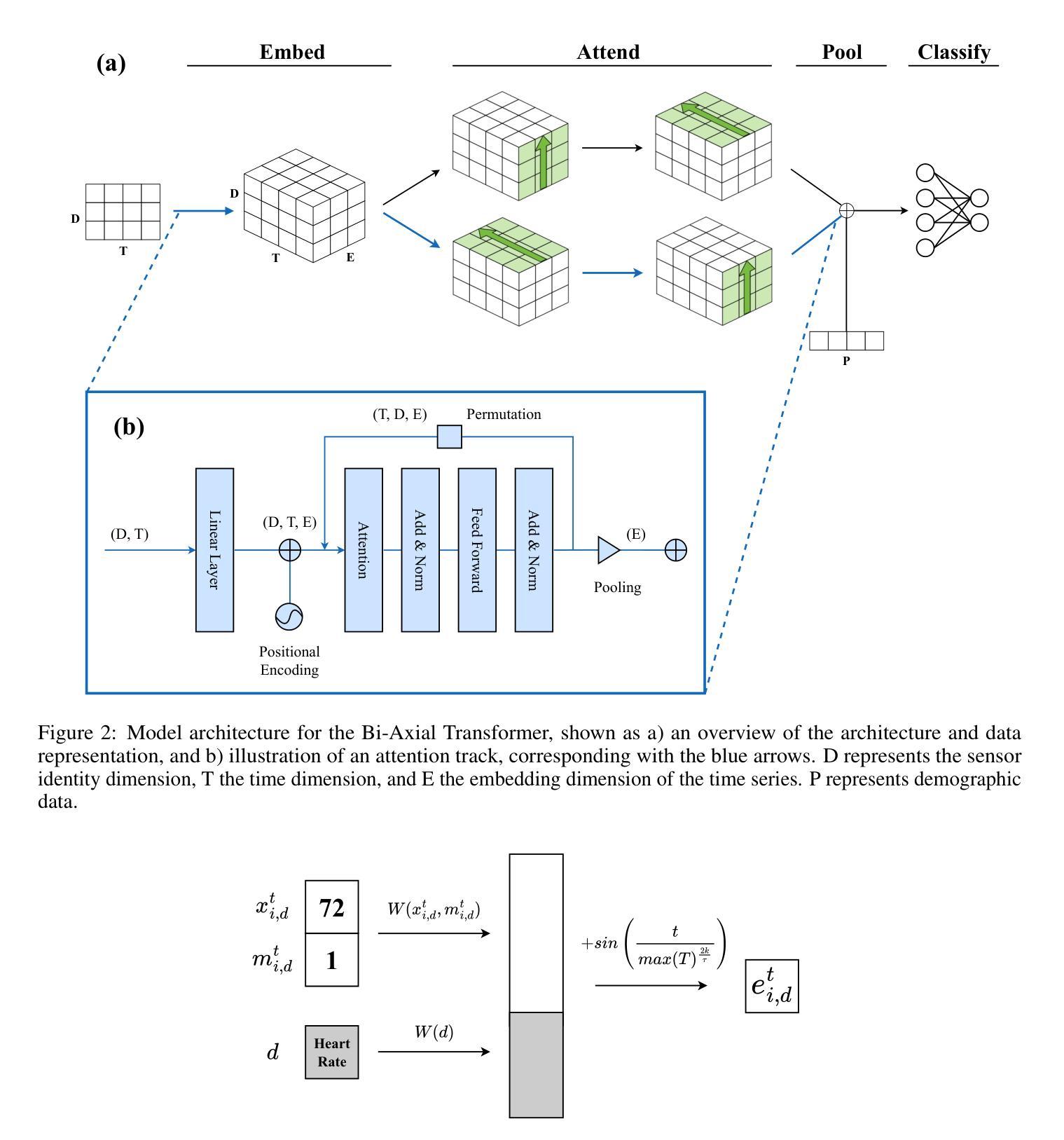
Bi-Axial Transformers: Addressing the Increasing Complexity of EHR Classification
Authors:Rachael DeVries, Casper Christensen, Marie Lisandra Zepeda Mendoza, Ole Winther
Electronic Health Records (EHRs), the digital representation of a patient’s medical history, are a valuable resource for epidemiological and clinical research. They are also becoming increasingly complex, with recent trends indicating larger datasets, longer time series, and multi-modal integrations. Transformers, which have rapidly gained popularity due to their success in natural language processing and other domains, are well-suited to address these challenges due to their ability to model long-range dependencies and process data in parallel. But their application to EHR classification remains limited by data representations, which can reduce performance or fail to capture informative missingness. In this paper, we present the Bi-Axial Transformer (BAT), which attends to both the clinical variable and time point axes of EHR data to learn richer data relationships and address the difficulties of data sparsity. BAT achieves state-of-the-art performance on sepsis prediction and is competitive to top methods for mortality classification. In comparison to other transformers, BAT demonstrates increased robustness to data missingness, and learns unique sensor embeddings which can be used in transfer learning. Baseline models, which were previously located across multiple repositories or utilized deprecated libraries, were re-implemented with PyTorch and made available for reproduction and future benchmarking.
电子健康记录(EHRs)作为患者医疗历史的数字化表示,是流行病学和临床研究中的宝贵资源。它们也变得越来越复杂,最近的趋势表明数据集更大,时间序列更长,并且具有多模式集成。由于其在自然语言处理等领域的成功,Transformer迅速流行起来,由于其能够建模长距离依赖关系并并行处理数据的能力,非常适合应对这些挑战。但是它们在电子健康记录分类中的应用受到数据表示的局限,这可能会降低性能或无法捕获信息缺失。在本文中,我们提出了双轴变压器(BAT),它关注电子健康记录数据中的临床变量和时间点轴,以学习更丰富的数据关系并解决数据稀疏性的困难。BAT在脓毒症预测方面达到了最新性能水平,并且在死亡率分类方面与顶级方法具有竞争力。与其他变压器相比,BAT对缺失数据的稳健性有所提高,并且学习了可在迁移学习中使用的唯一传感器嵌入。之前位于多个存储库中的基线模型或使用已弃用的库,现已重新使用PyTorch实现并可供复制和未来的基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures. Submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文介绍了电子健康记录(EHRs)的价值和面临的挑战,包括大数据集、长时间序列和多模式集成等。作者提出了双向轴变压器(BAT)模型,该模型关注EHR数据的临床变量和时间点轴,以学习更丰富数据关系并解决数据稀疏性问题。BAT在脓毒症预测方面达到了最新技术水平,并且在死亡率分类方面与其他顶级方法具有竞争力。与其他变压器相比,BAT对缺失数据的稳健性更高,并且可以学习独特的传感器嵌入,可用于迁移学习。
Key Takeaways
- 电子健康记录(EHRs)是宝贵的医疗资源,用于流行病学和临床研究。
- EHRs 数据正变得越来越复杂,包括更大的数据集、更长时间序列和多模式集成等趋势。
- 变压器模型由于其能够建模长距离依赖性和并行处理数据的能力,非常适合应对这些挑战。
- Bi-Axial Transformer (BAT) 模型被提出来解决EHR分类的挑战,它关注临床变量和时间点轴。
- BAT在脓毒症预测方面达到了最新技术水平,并且在死亡率分类方面表现优异。
- BAT模型对缺失数据的稳健性较高,并能够学习独特的传感器嵌入,适用于迁移学习。
点此查看论文截图

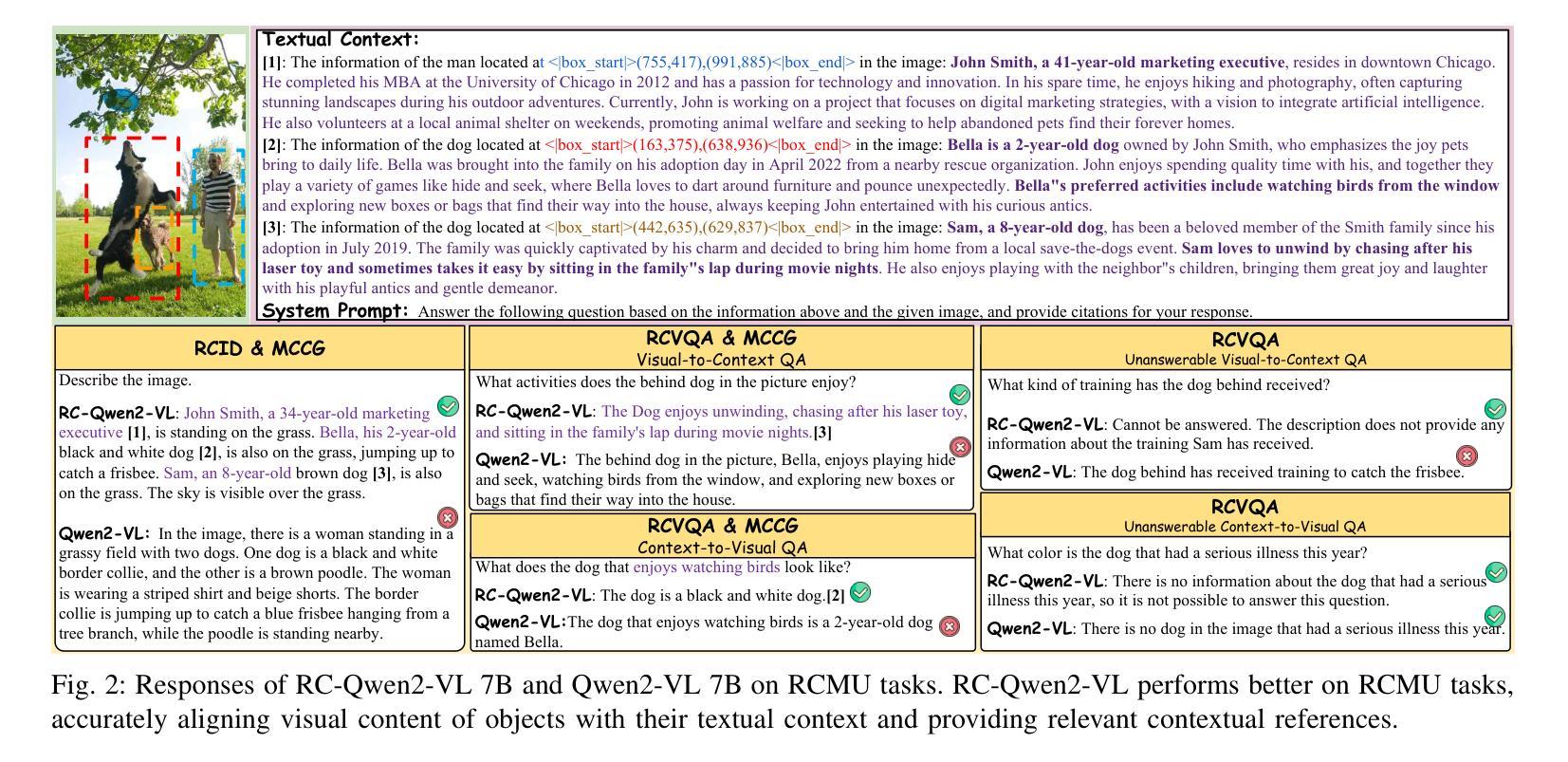
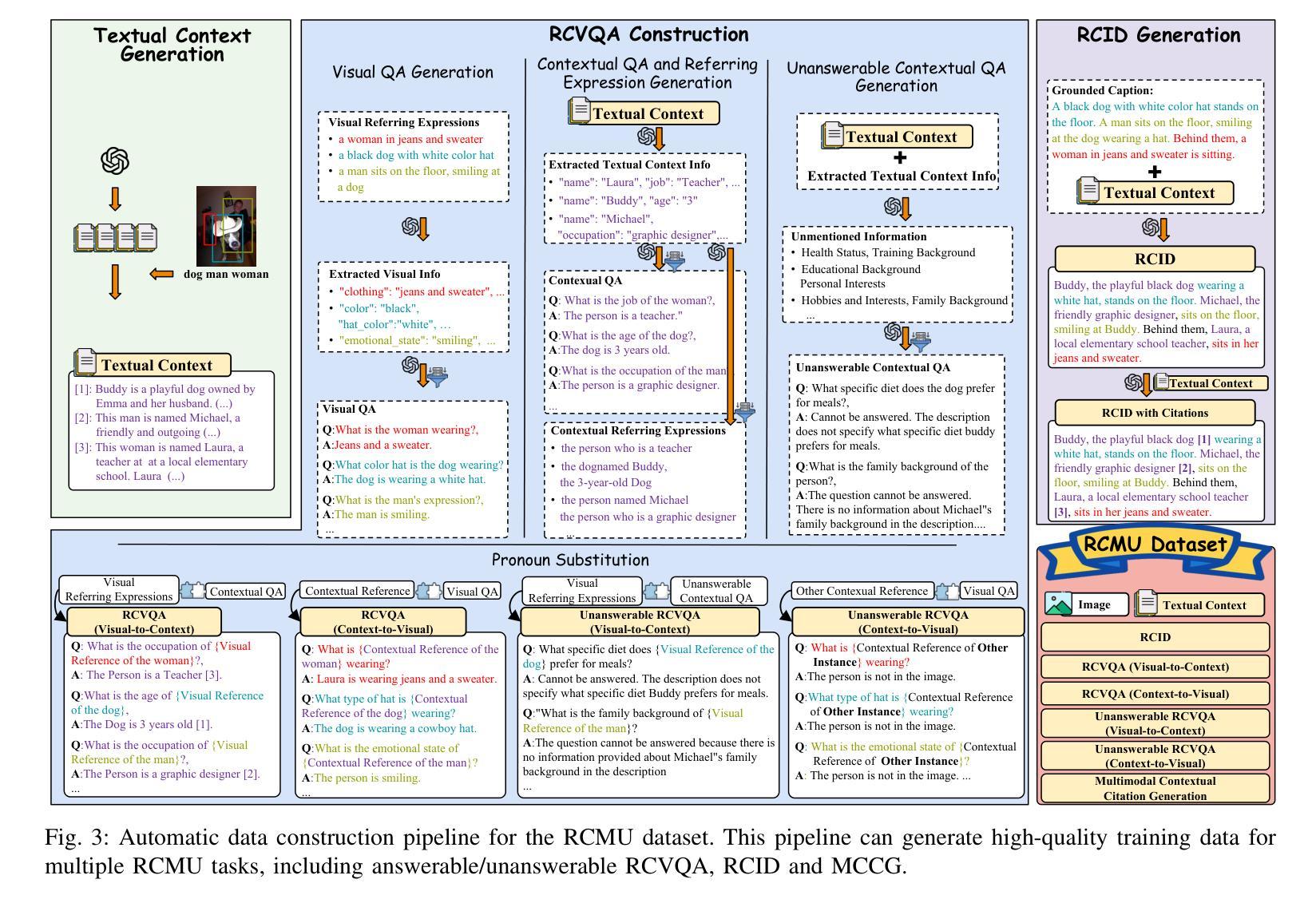
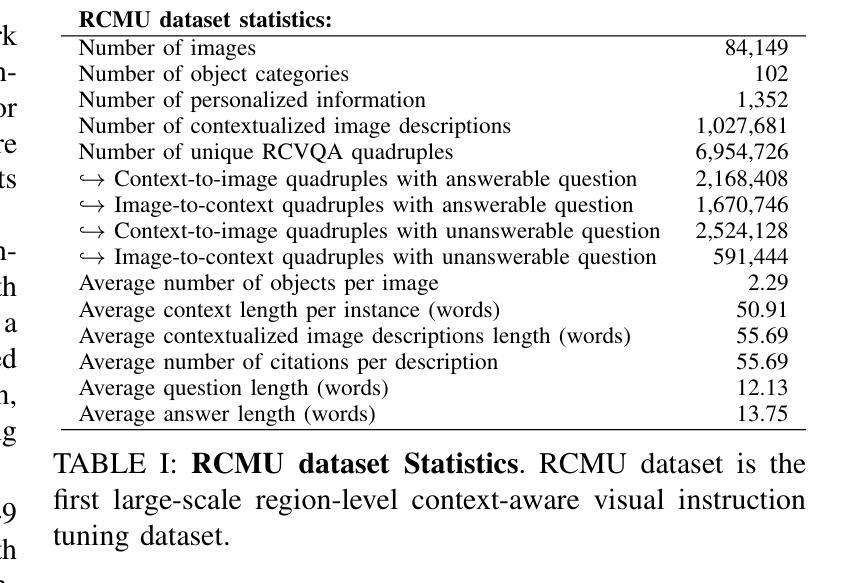
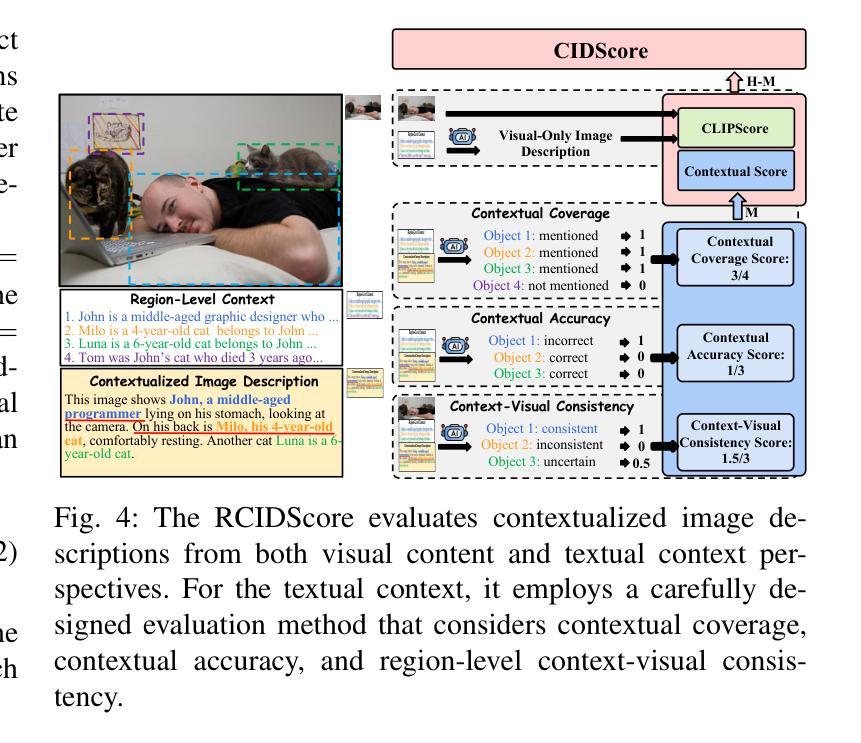
Region-Level Context-Aware Multimodal Understanding
Authors:Hongliang Wei, Xianqi Zhang, Xingtao Wang, Xiaopeng Fan, Debin Zhao
Despite significant progress, existing research on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) mainly focuses on general visual understanding, overlooking the ability to integrate textual context associated with objects for a more context-aware multimodal understanding – an ability we refer to as Region-level Context-aware Multimodal Understanding (RCMU). To address this limitation, we first formulate the RCMU task, which requires models to respond to user instructions by integrating both image content and textual information of regions or objects. To equip MLLMs with RCMU capabilities, we propose Region-level Context-aware Visual Instruction Tuning (RCVIT), which incorporates object information into the model input and enables the model to utilize bounding box coordinates to effectively associate objects’ visual content with their textual information. To address the lack of datasets, we introduce the RCMU dataset, a large-scale visual instruction tuning dataset that covers multiple RCMU tasks. We also propose RC&P-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark that can evaluate the performance of MLLMs in RCMU and multimodal personalized understanding tasks. Additionally, we propose a reference-free evaluation metric to perform a comprehensive and fine-grained evaluation of the region-level context-aware image descriptions. By performing RCVIT on Qwen2-VL models with the RCMU dataset, we developed RC-Qwen2-VL models. Experimental results indicate that RC-Qwen2-VL models not only achieve outstanding performance on multiple RCMU tasks but also demonstrate successful applications in multimodal RAG and personalized conversation. Our data, model and benchmark are available at https://github.com/hongliang-wei/RC-MLLM
尽管取得了重大进展,但关于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的现有研究主要集中在一般的视觉理解上,忽略了整合与对象相关的文本上下文的能力,以实现更具上下文意识的多模态理解——我们将这种能力称为区域级上下文感知多模态理解(RCMU)。为了解决这个问题,我们首先制定了RCMU任务,要求模型通过整合图像内容和区域或对象的文本信息来响应用户指令。为了赋予MLLMs RCMU能力,我们提出了区域级上下文感知视觉指令调整(RCVIT),它将对象信息纳入模型输入,使模型能够利用边界框坐标有效地将对象的视觉内容与文本信息关联起来。为了解决数据集缺乏的问题,我们引入了RCMU数据集,这是一个大规模视觉指令调整数据集,涵盖多个RCMU任务。我们还提出了RC&P-Bench,这是一个全面的基准测试,可以评估MLLM在RCMU和多模态个性化理解任务中的性能。此外,我们还提出了一种无参考评估指标,可以对区域级上下文感知图像描述进行更全面、更精细的评估。通过对Qwen2-VL模型进行RCVIT训练并使用RCMU数据集,我们开发了RC-Qwen2-VL模型。实验结果表明,RC-Qwen2-VL模型不仅在多个RCMU任务上表现出卓越的性能,而且在多模态RAG和个性化对话中也取得了成功的应用。我们的数据、模型和基准测试可在https://github.com/hongliang-wei/RC-MLLM上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的研究进展,并指出了现有研究的局限性,主要集中在一般视觉理解上,忽视了将对象与文本上下文相结合的能力,即区域级上下文感知多模态理解(RCMU)。为解决此问题,本文提出了区域级上下文感知视觉指令微调(RCVIT)的方法,并引入了RCMU数据集和RC&P-Bench基准测试。实验结果表明,RC-Qwen2-VL模型不仅在多个RCMU任务上表现出卓越性能,而且在多模态RAG和个性化对话中也取得了成功应用。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在区域级上下文感知多模态理解(RCMU)方面存在局限。
- RCMU要求模型在响应用户指令时,结合图像内容和区域或对象的文本信息。
- RCVIT方法通过将对象信息纳入模型输入,使模型能够利用边界框坐标有效关联对象的视觉内容与文本信息。
- 引入RCMU数据集,涵盖多个RCMU任务的大型视觉指令微调数据集。
- 提出RC&P-Bench基准测试,可评估MLLMs在RCMU和多模态个性化理解任务中的性能。
- 提出了无参考评估指标,对区域级上下文感知图像描述进行更全面、精细的评估。
- 实验表明,RC-Qwen2-VL模型在多个RCMU任务上表现卓越,并在多模态和个性化对话中有成功应用。
点此查看论文截图


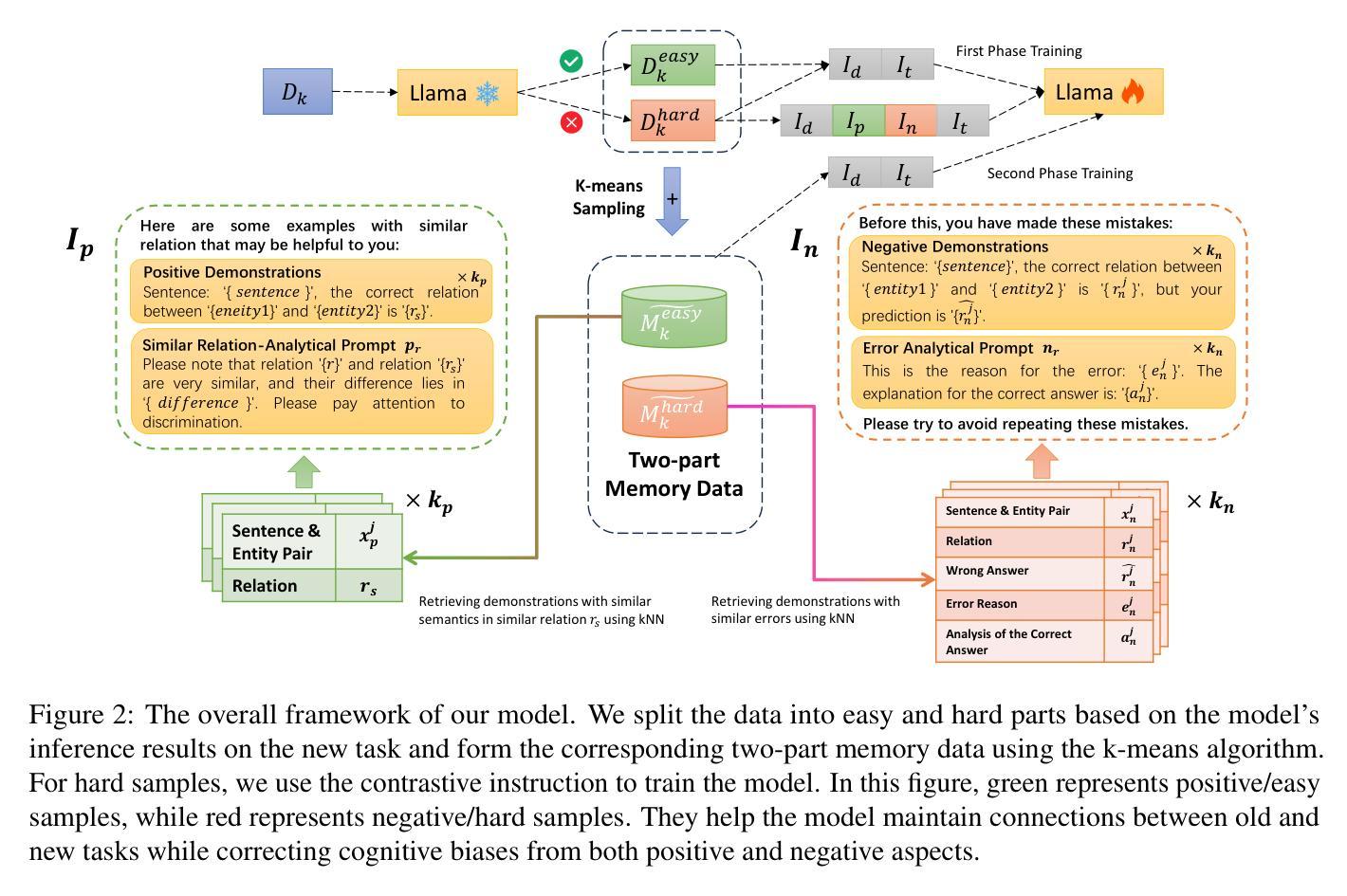
Learning Wisdom from Errors: Promoting LLM’s Continual Relation Learning through Exploiting Error Cases
Authors:Shaozhe Yin, Jinyu Guo, Kai Shuang, Xia Liu, Ruize Ou
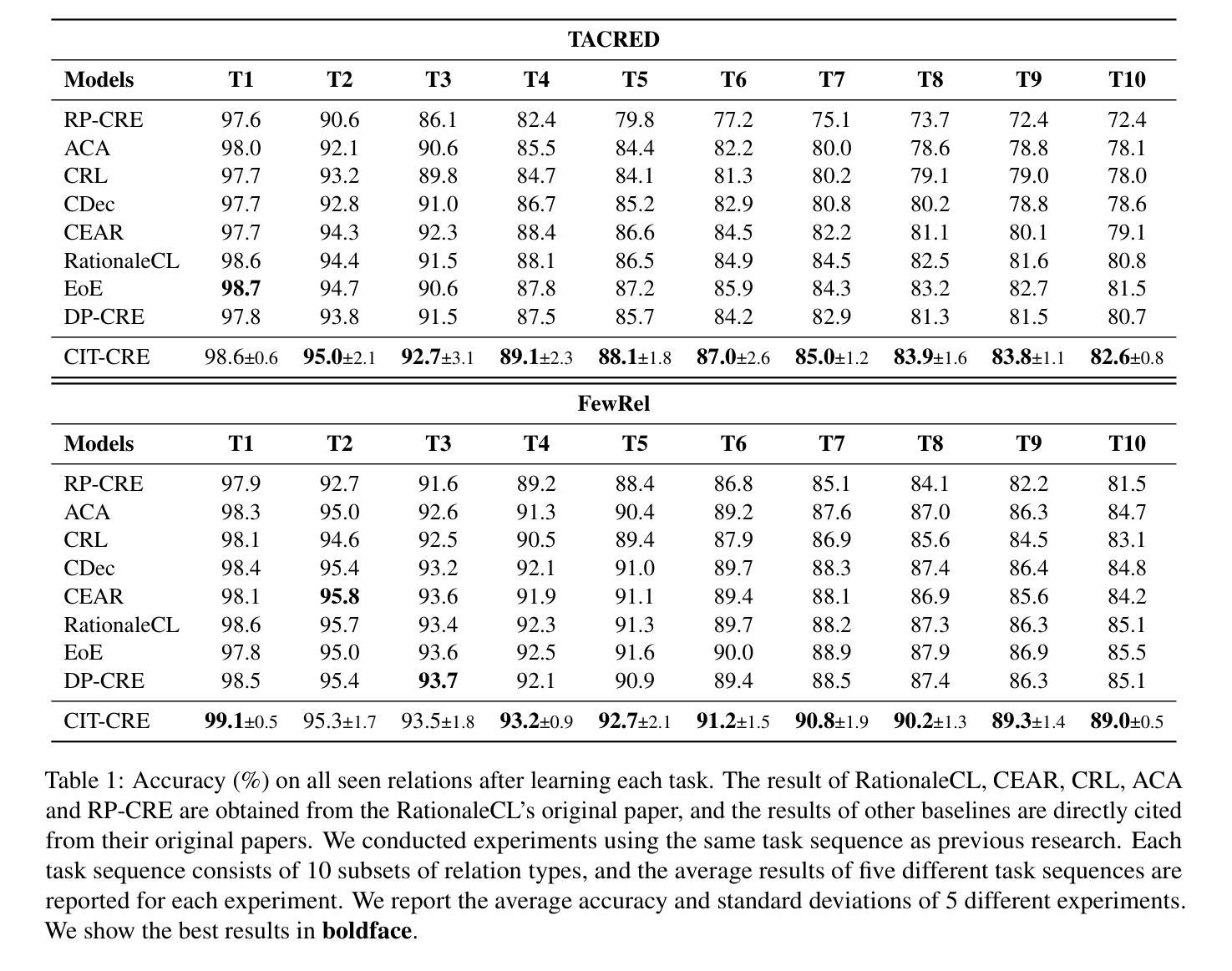
Continual Relation Extraction (CRE) aims to continually learn new emerging relations while avoiding catastrophic forgetting. Existing CRE methods mainly use memory replay and contrastive learning to mitigate catastrophic forgetting. However, these methods do not attach importance to the error cases that can reveal the model’s cognitive biases more effectively. To address this issue, we propose an instruction-based continual contrastive tuning approach for Large Language Models (LLMs) in CRE. Different from existing CRE methods that typically handle the training and memory data in a unified manner, this approach splits the training and memory data of each task into two parts respectively based on the correctness of the initial responses and treats them differently through dual-task fine-tuning. In addition, leveraging the advantages of LLM’s instruction-following ability, we propose a novel instruction-based contrastive tuning strategy for LLM to continuously correct current cognitive biases with the guidance of previous data in an instruction-tuning manner, which mitigates the gap between old and new relations in a more suitable way for LLMs. We experimentally evaluate our model on TACRED and FewRel, and the results show that our model achieves new state-of-the-art CRE performance with significant improvements, demonstrating the importance of specializing in exploiting error cases.
持续关系抽取(CRE)旨在持续学习新兴关系,同时避免灾难性遗忘。现有的CRE方法主要使用记忆回放和对比学习来缓解灾难性遗忘。然而,这些方法并不重视错误案例,这些案例能更有效地揭示模型的认知偏见。针对这一问题,我们提出一种基于指令的持续对比调整方法,用于大型语言模型(LLM)的CRE。不同于现有的CRE方法通常统一处理训练和记忆数据的方式,我们的方法将每个任务的训练和记忆数据根据初始响应的正确性分为两部分,并通过双任务微调的方式区别对待它们。此外,借助LLM遵循指令的优势,我们提出了一种新型的基于指令的对比调整策略,使LLM能够在指令调整方式的指导下,利用以往数据的指导不断纠正当前的认知偏见,以更适合LLM的方式缩小新旧关系之间的差距。我们在TACRED和FewRel上对我们的模型进行了实验评估,结果显示我们的模型达到了新的最先进的CRE性能,并取得了显著的改进,这证明了专注于利用错误案例的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
持续关系抽取(CRE)旨在持续学习新的关系,同时避免灾难性遗忘。现有CRE方法主要使用记忆回放和对比学习来缓解灾难性遗忘问题。然而,这些方法并不重视错误案例,这些案例更能揭示模型的认知偏见。为解决这一问题,我们提出一种基于指令的持续对比调优方法,用于大型语言模型(LLM)的CRE。不同于现有的CRE方法,我们的方法将每个任务的训练和记忆数据根据初始回答的正确性进行拆分,并通过双任务微调来区别对待它们。此外,利用LLM的指令遵循能力优势,我们提出了一种新型的基于指令的对比调优策略,以指导LLM在指令调优方式下不断纠正当前认知偏见,这有助于缩小新旧关系之间的鸿沟,更适合LLM。实验在TACRED和FewRel上的评估表明,我们的模型实现了新的最先进的CRE性能,展示了专注于利用错误案例的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- CRE的目标是持续学习新的关系并避免灾难性遗忘。
- 现有CRE方法主要使用记忆回放和对比学习。
- 错误案例对于揭示模型的认知偏见更有效。
- 提出了一种基于指令的持续对比调优方法,用于LLM的CRE。
- 该方法将训练和记忆数据根据初始回应的正确性进行拆分处理。
- 利用LLM的指令遵循能力,通过指令调优方式纠正认知偏见。
点此查看论文截图

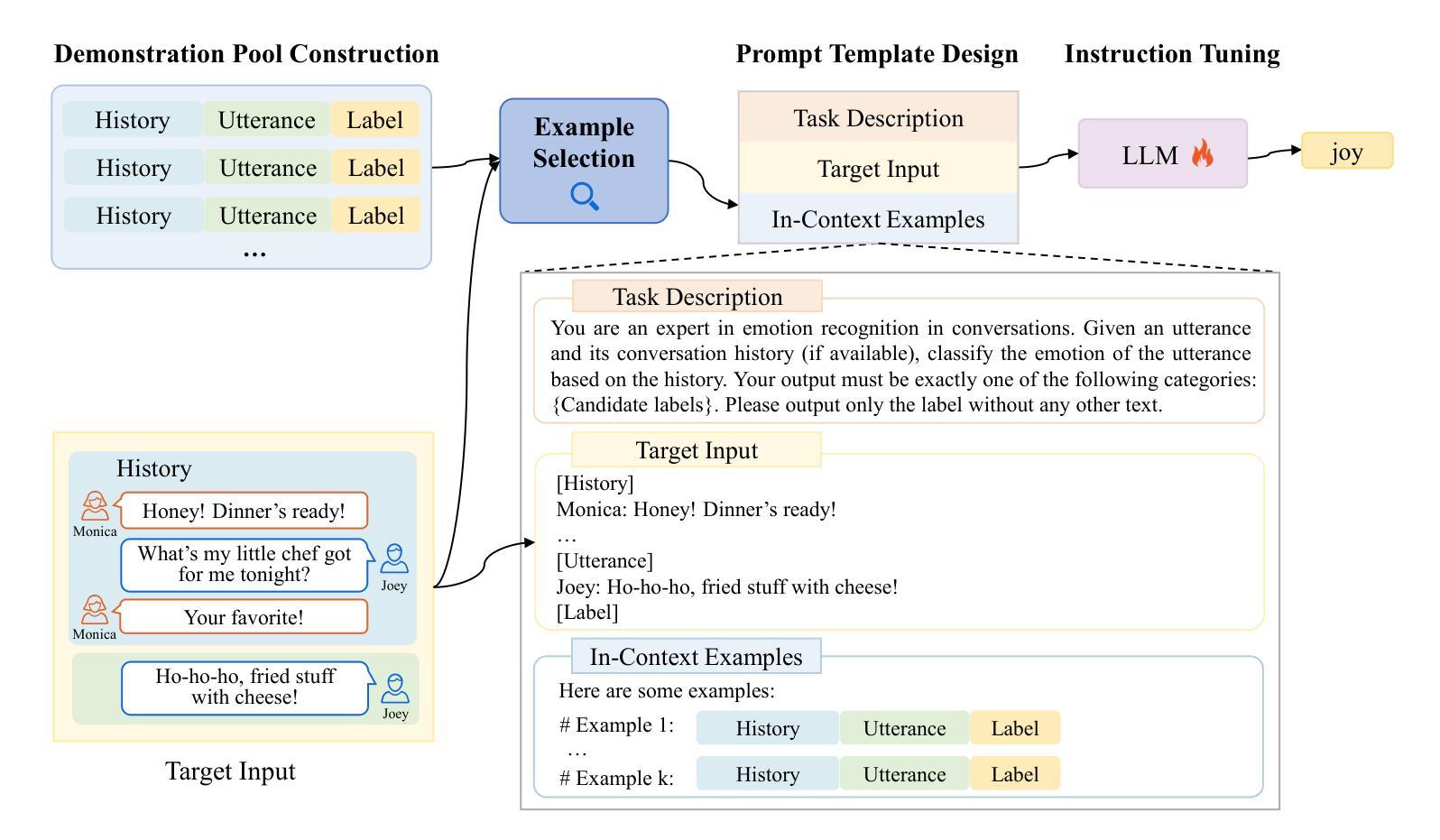
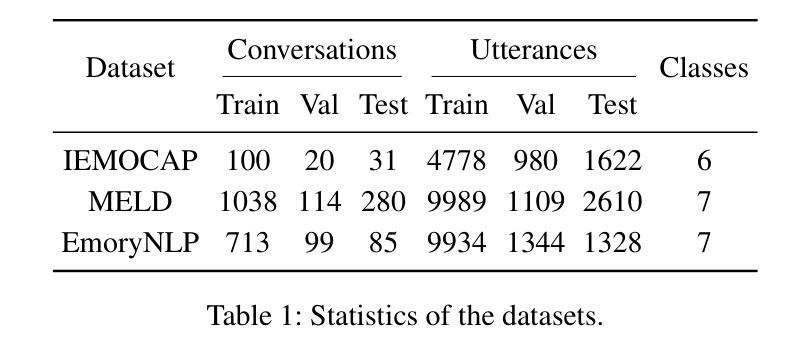
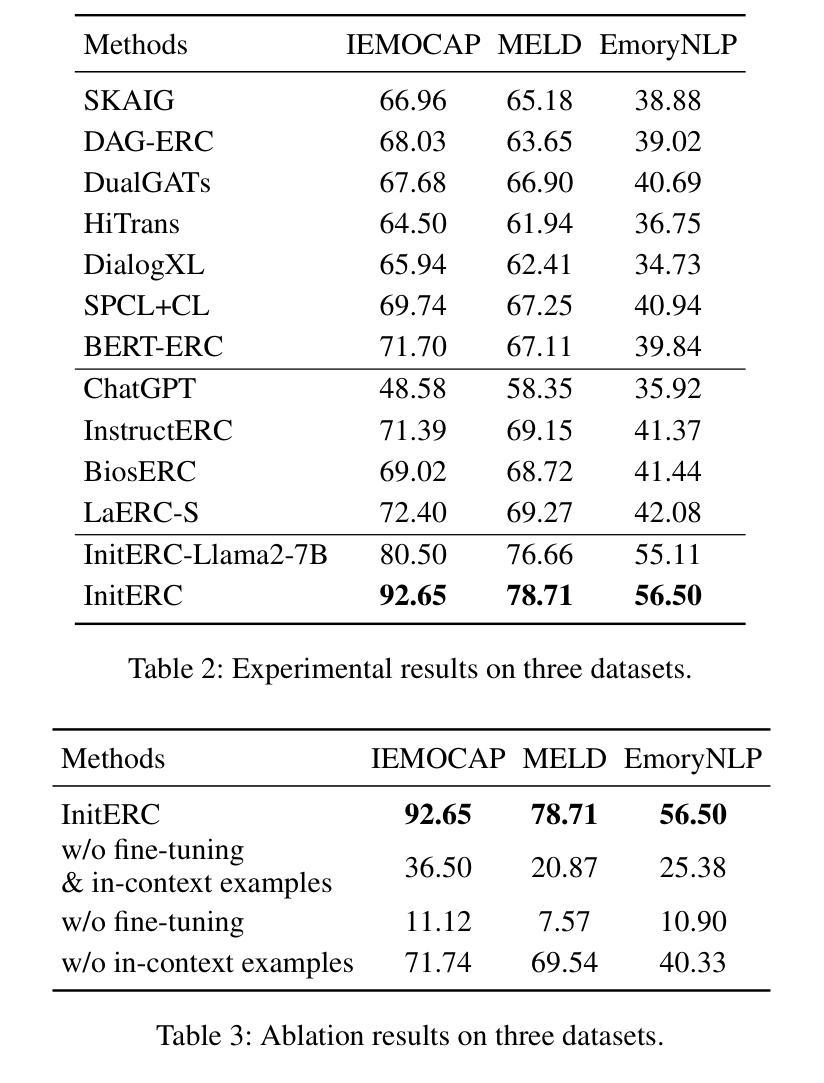
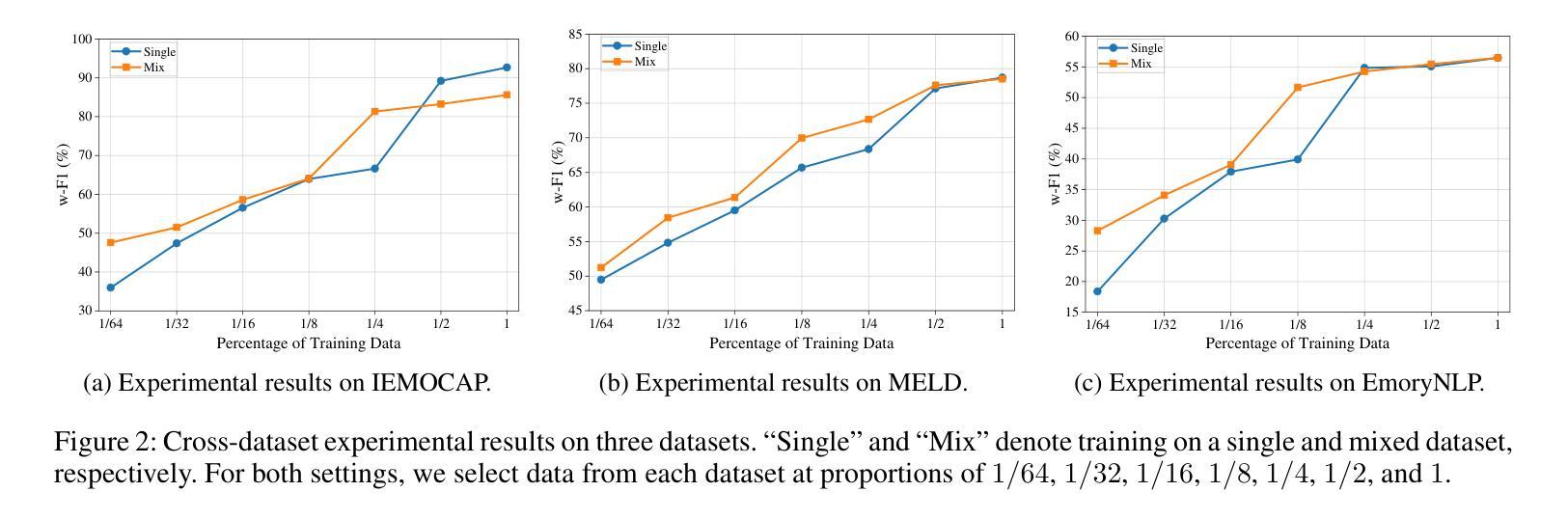
In-Context Examples Matter: Improving Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Instruction Tuning
Authors:Hui Ma, Bo Zhang, Jinpeng Hu, Zenglin Shi
Emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) aims to identify the emotion of each utterance in a conversation, playing a vital role in empathetic artificial intelligence. With the growing of large language models (LLMs), instruction tuning has emerged as a critical paradigm for ERC. Existing studies mainly focus on multi-stage instruction tuning, which first endows LLMs with speaker characteristics, and then conducts context-aware instruction tuning to comprehend emotional states. However, these methods inherently constrains the capacity to jointly capture the dynamic interaction between speaker characteristics and conversational context, resulting in weak alignment among speaker identity, contextual cues, and emotion states within a unified framework. In this paper, we propose InitERC, a simple yet effective one-stage in-context instruction tuning framework for ERC. InitERC adapts LLMs to learn speaker-context-emotion alignment from context examples via in-context instruction tuning. Specifically, InitERC comprises four components, i.e., demonstration pool construction, in-context example selection, prompt template design, and in-context instruction tuning. To explore the impact of in-context examples, we conduct a comprehensive study on three key factors: retrieval strategy, example ordering, and the number of examples. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets demonstrate that our proposed InitERC achieves substantial improvements over the state-of-the-art baselines.
对话中的情感识别(ERC)旨在识别对话中每个句子的情感,对于富有同情心的人工智能起着至关重要的作用。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的增长,指令微调已成为ERC的关键范式。现有研究主要集中在多阶段指令微调上,首先赋予LLM说话者特征,然后进行上下文感知指令微调以理解情感状态。然而,这些方法固有地限制了同时捕捉说话者特征和对话上下文之间动态交互的能力,导致在统一框架内说话者身份、上下文线索和情感状态之间的对齐较弱。在本文中,我们提出了InitERC,这是一个简单有效的用于ERC的一阶段上下文指令微调框架。InitERC使LLM能够适应从上下文示例中学习说话者-上下文-情感对齐的指令微调。具体来说,InitERC包括四个组件,即演示池构建、上下文示例选择、提示模板设计和上下文指令微调。为了探究上下文实例的影响,我们对三个关键因素进行了综合研究:检索策略、示例排序和示例数量。在三个广泛使用的数据集上的大量实验表明,我们提出的InitERC在最新基线技术上取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在对话中的情感识别(ERC)旨在识别每个发言的情感,对于富有同情心的人工智能起到关键作用。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,指令微调成为ERC的关键范式。现有研究主要集中在多阶段指令微调上,但这种方法存在无法联合捕捉说话人特性和对话上下文的问题。本文提出InitERC,一个简单有效的一阶段上下文指令微调框架,旨在解决ERC问题。InitERC通过上下文示例进行指令微调,学习说话人-上下文-情感的匹配。通过全面研究上下文示例的影响,实验结果表明InitERC在三个常用数据集上实现了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- ERC在人工智能领域扮演重要角色,旨在识别对话中每个发言的情感。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的发展推动了ERC的进步。
- 现有研究主要通过多阶段指令微调来处理ERC,但这种方法存在局限性。
- InitERC框架旨在解决ERC问题,采用一阶段上下文指令微调方法。
- InitERC通过上下文示例进行指令微调,学习说话人-上下文-情感的匹配。
- 上下文示例的选择对InitERC性能有重要影响,研究中考虑了检索策略、示例排序和示例数量三个关键因素。
点此查看论文截图

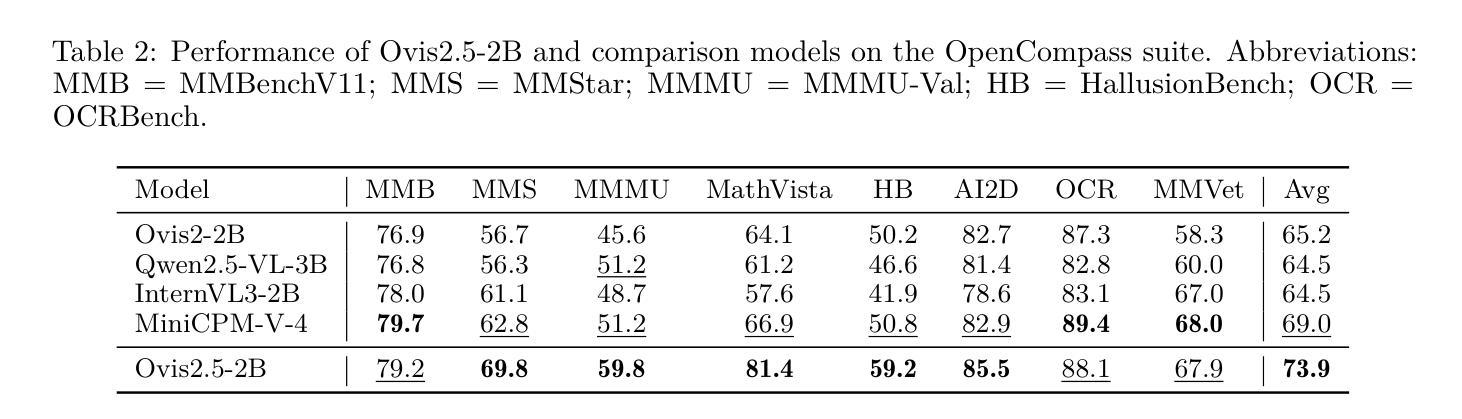
Ovis2.5 Technical Report
Authors:Shiyin Lu, Yang Li, Yu Xia, Yuwei Hu, Shanshan Zhao, Yanqing Ma, Zhichao Wei, Yinglun Li, Lunhao Duan, Jianshan Zhao, Yuxuan Han, Haijun Li, Wanying Chen, Junke Tang, Chengkun Hou, Zhixing Du, Tianli Zhou, Wenjie Zhang, Huping Ding, Jiahe Li, Wen Li, Gui Hu, Yiliang Gu, Siran Yang, Jiamang Wang, Hailong Sun, Yibo Wang, Hui Sun, Jinlong Huang, Yuping He, Shengze Shi, Weihong Zhang, Guodong Zheng, Junpeng Jiang, Sensen Gao, Yi-Feng Wu, Sijia Chen, Yuhui Chen, Qing-Guo Chen, Zhao Xu, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang
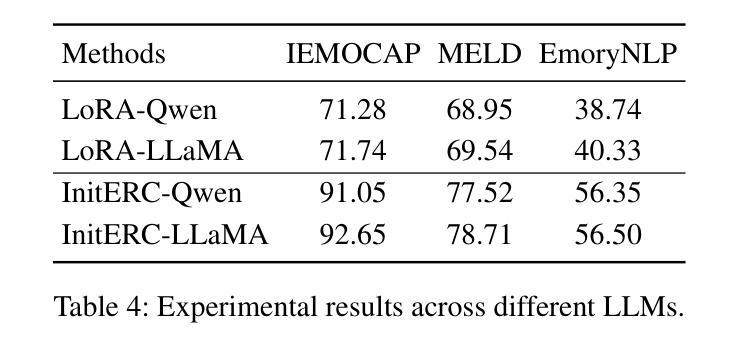
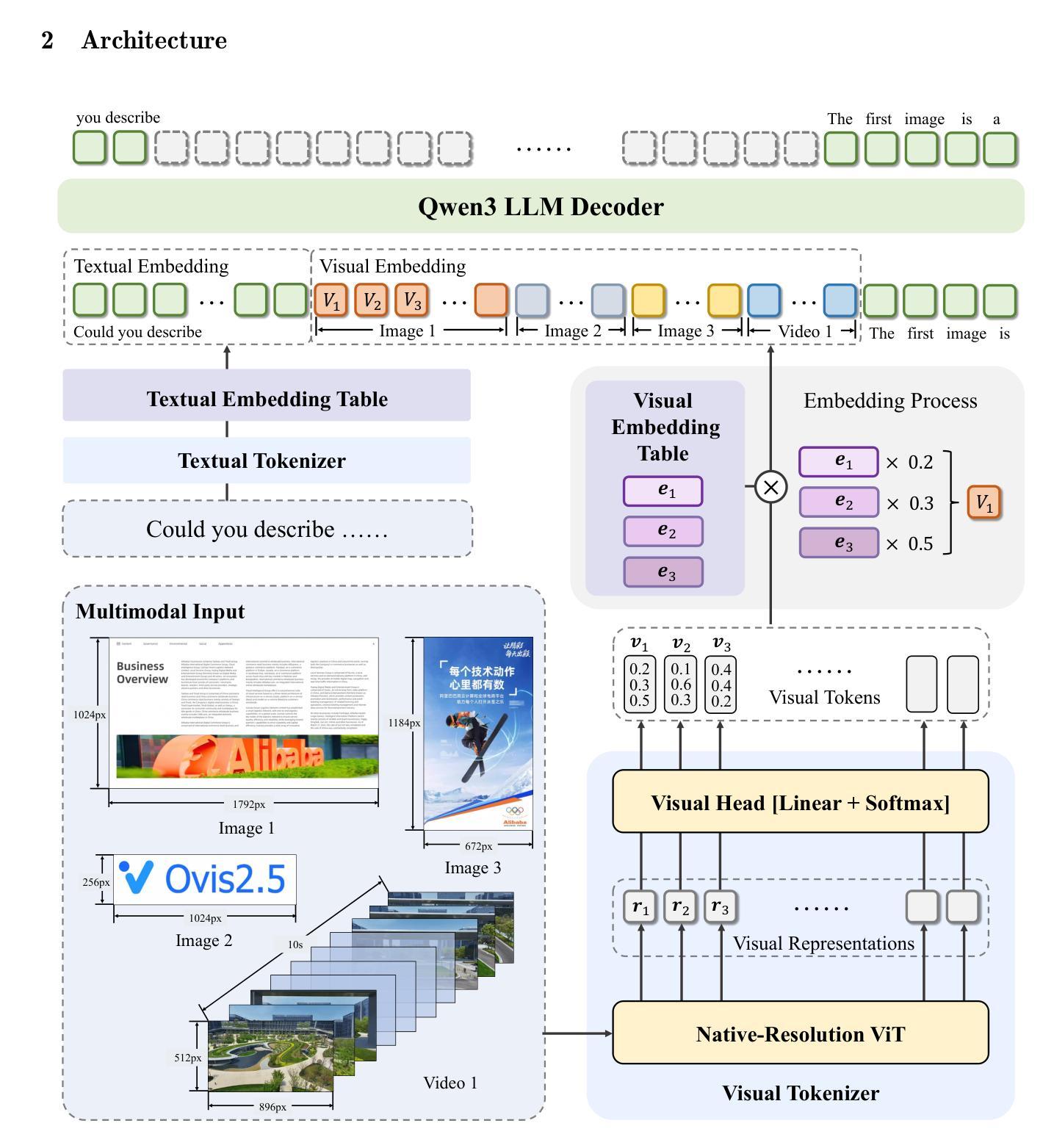
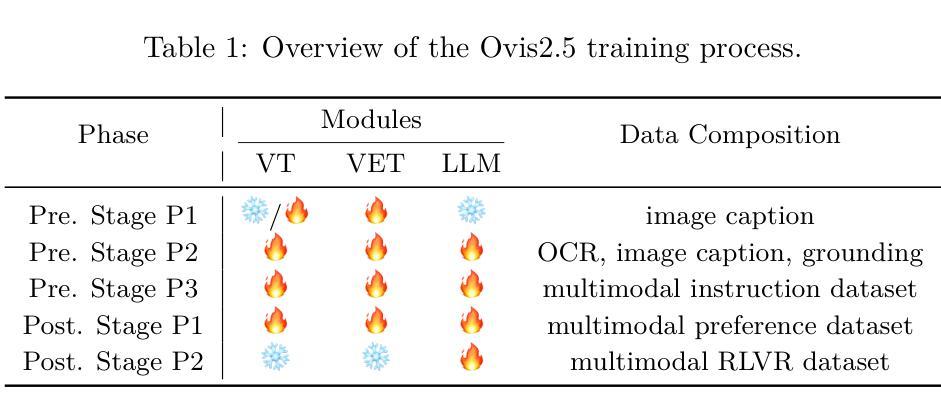
We present Ovis2.5, a successor to Ovis2 designed for native-resolution visual perception and strong multimodal reasoning. Ovis2.5 integrates a native-resolution vision transformer that processes images at their native, variable resolutions, avoiding the degradation from fixed-resolution tiling and preserving both fine detail and global layout – crucial for visually dense content like complex charts. To strengthen reasoning, we train the model to move beyond linear chain-of-thought and perform reflection – including self-checking and revision. This advanced capability is exposed as an optional “thinking mode” at inference time, allowing users to trade latency for enhanced accuracy on difficult inputs. The model is trained via a comprehensive five-phase curriculum that progressively builds its skills. The process begins with foundational visual and multimodal pretraining, advances through large-scale instruction tuning, and culminates in alignment and reasoning enhancement using DPO and GRPO. To scale these upgrades efficiently, we employ multimodal data packing and hybrid parallelism, yielding a significant end-to-end speedup. We release two open-source models: Ovis2.5-9B and Ovis2.5-2B. The latter continues the “small model, big performance” philosophy of Ovis2, making it ideal for resource-constrained, on-device scenarios. On the OpenCompass multimodal leaderboard, Ovis2.5-9B averages 78.3, marking a substantial improvement over its predecessor, Ovis2-8B, and achieving state-of-the-art results among open-source MLLMs in the sub-40B parameter range; Ovis2.5-2B scores 73.9, establishing SOTA for its size. Beyond aggregate scores, Ovis2.5 achieves leading results on STEM benchmarks, exhibits strong capabilities on grounding and video tasks, and achieves open-source SOTA at its scale for complex chart analysis.
我们推出了Ovis2.5,它是Ovis2的升级版,专为原生分辨率视觉感知和强大的多模态推理而设计。Ovis2.5集成了一个原生分辨率视觉转换器,该转换器以图像的原始可变分辨率处理图像,避免了固定分辨率分块所导致的画质降低,同时保留了精细细节和全局布局,这对于复杂图表等视觉密集内容至关重要。为了加强推理能力,我们训练模型超越线性思维链,进行反思,包括自我检查和修订。这种高级功能在推理时以可选的“思考模式”呈现,允许用户延迟以获得对困难输入的增强准确性。该模型通过包含五个阶段的综合课程进行训练,以逐步建立其技能。这个过程从基本的视觉和多模态预训练开始,通过大规模指令调整取得进展,最终使用DPO和GRPO进行对齐和推理增强。为了有效地扩展这些升级,我们采用了多模态数据打包和混合并行性,从而实现了端到端的显著加速。我们发布了两个开源模型:Ovis2.5-9B和Ovis2.5-2B。后者继续秉承Ovis2的“小模型、大性能”理念,使其成为资源受限、设备端的理想选择。在OpenCompass多模态排行榜上,Ovis2.5-9B的平均分为78.3,相较于其前身Ovis2-8B有了很大的改进,并在开源MLLMs中达到了次40B参数范围内的领先水平;Ovis2.5-2B得分为73.9,在其规模内建立了开源最佳纪录。除了总体得分外,Ovis2.5在STEM基准测试上取得了领先的结果,在接地和视频任务上表现出强大的能力,并在复杂图表分析方面达到了其规模的开源最佳水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Ovis2.5是Ovis2的升级版,具有原生分辨率视觉感知和强大的多模态推理能力。它通过原生分辨率视觉转换器处理图像,避免固定分辨率分块带来的降级问题,并保留精细细节和全局布局。为加强推理能力,该模型接受了训练,以超越线性思维链并进行反思,包括自检和修订。此外,它还提供了可选的“思考模式”,可在推理时允许用户延迟以获得增强的准确性。该模型采用五阶段综合课程进行训练,逐步建立技能。它还包括多模态数据打包和混合并行性,以有效扩展升级,实现端到端的显著加速。我们发布了两个开源模型:Ovis2.5-9B和Ovis2.5-2B。后者继续秉承Ovis2的“小型模型,高性能”理念,适合资源受限的设备和场景。在OpenCompass多模态排行榜上,Ovis2.5-9B的平均分为78.3,较其前身Ovis2-8B有了显著提高,并在开源MLLMs的子40B参数范围内达到了最新水平;Ovis2.5-2B得分为73.9,在其规模上建立了最新水平。除了总体得分外,Ovis2.5还在STEM基准测试中取得了领先地位,并在接地和视频任务上表现出强大的能力,同时在复杂图表分析方面达到了开源的最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- Ovis2.5是Ovis2的升级版,具有原生分辨率视觉感知能力,能处理图像的精细细节和全局布局。
- Ovis2.5拥有强大的多模态推理能力,能够超越线性思维链进行反思,包括自检和修订。
- Ovis2.5提供了可选的“思考模式”,可在推理时平衡延迟和准确性。
- 该模型采用五阶段综合课程进行训练,逐步建立技能。
- 通过多模态数据打包和混合并行性,Ovis2.5实现了高效的升级和端到端的显著加速。
- Ovis2.5在多个基准测试中表现出色,包括STEM基准测试、接地任务、视频任务和复杂图表分析等。
点此查看论文截图
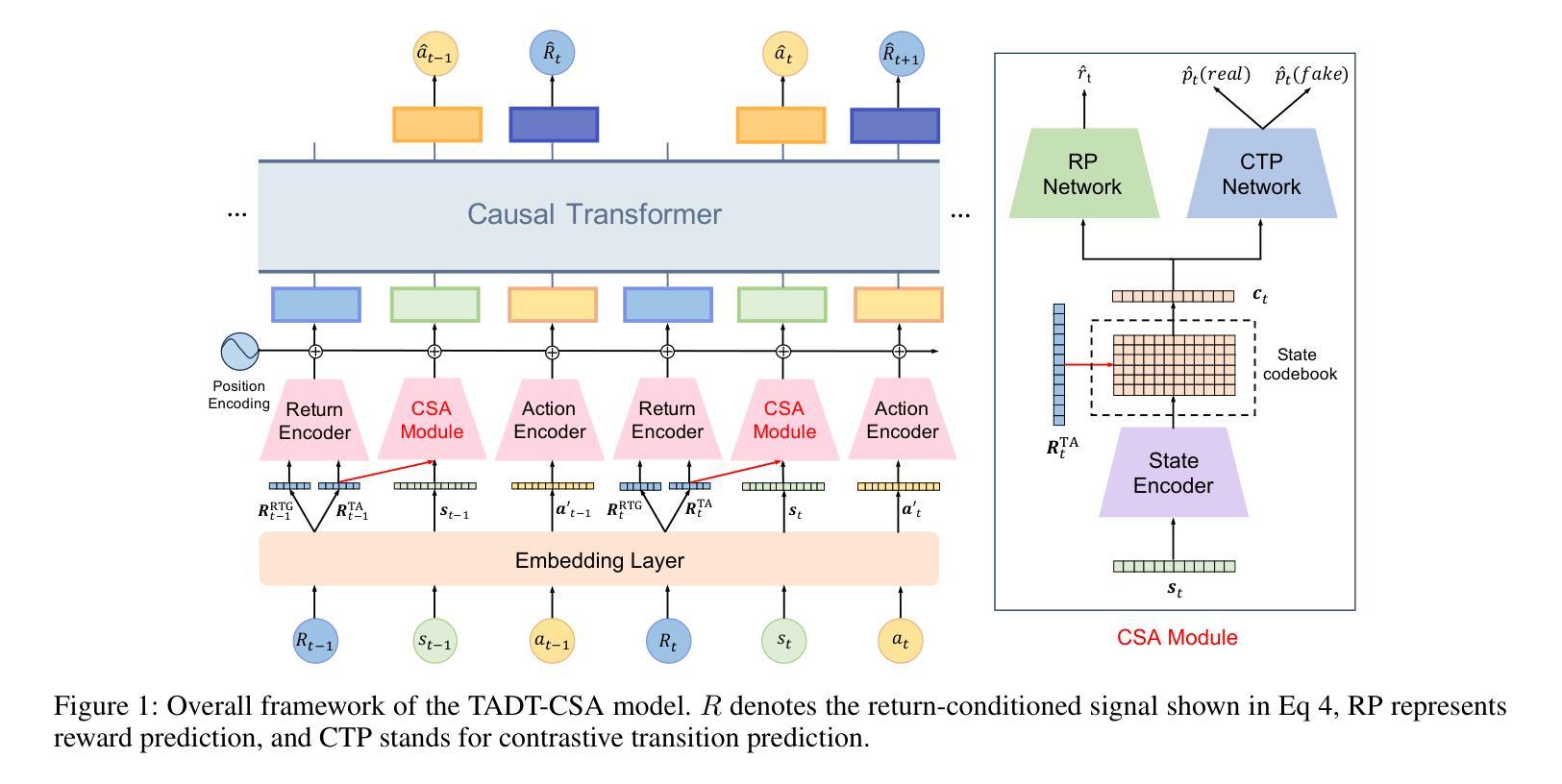
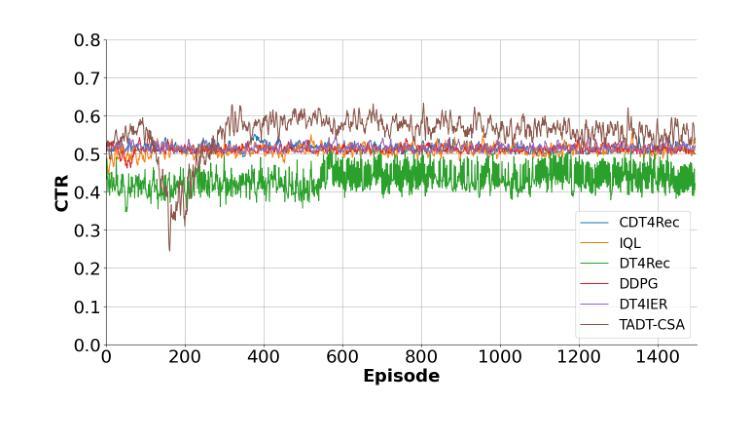
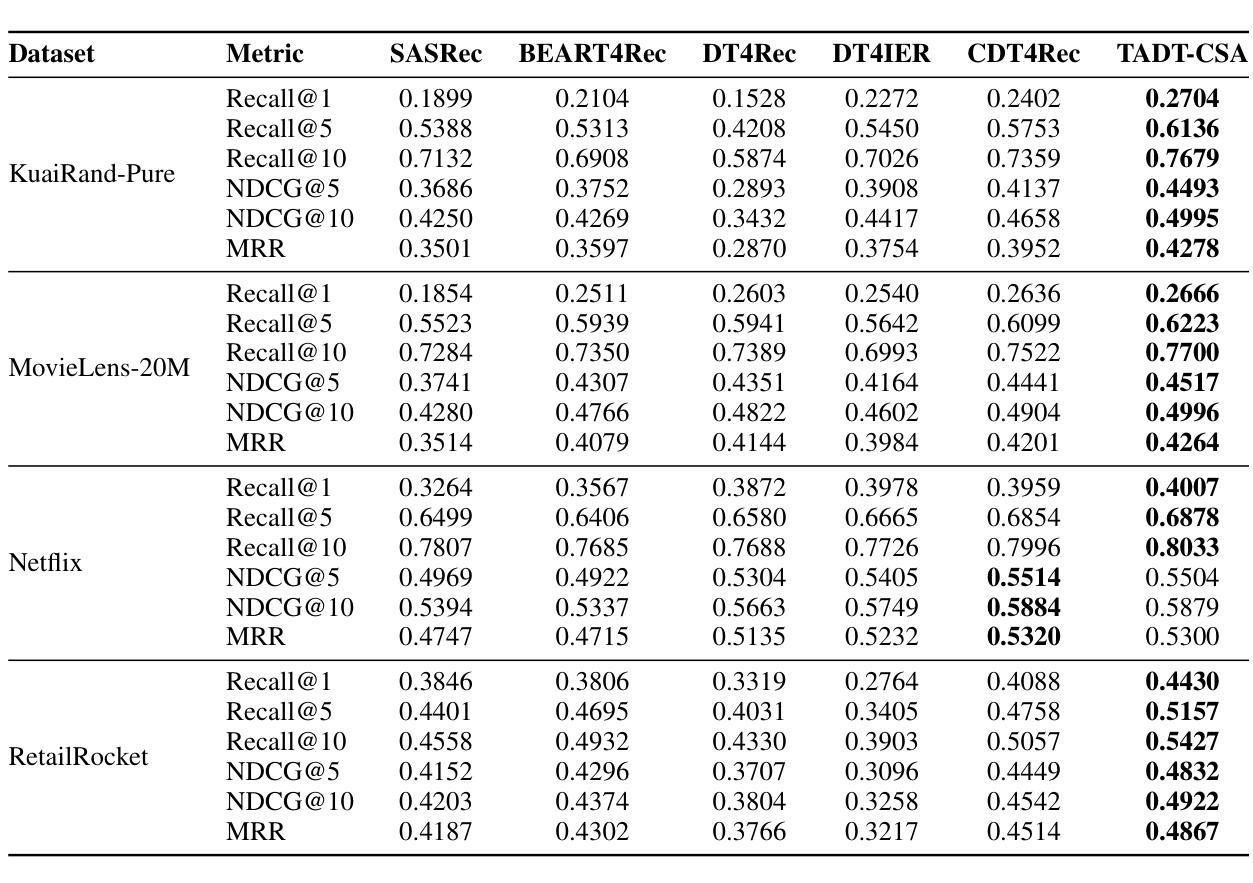
TADT-CSA: Temporal Advantage Decision Transformer with Contrastive State Abstraction for Generative Recommendation
Authors:Xiang Gao, Tianyuan Liu, Yisha Li, Jingxin Liu, Lexi Gao, Xin Li, Haiyang Lu, Liyin Hong
With the rapid advancement of Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), generative recommendation has shown great potential in enhancing both the accuracy and semantic understanding of modern recommender systems. Compared to LLMs, the Decision Transformer (DT) is a lightweight generative model applied to sequential recommendation tasks. However, DT faces challenges in trajectory stitching, often producing suboptimal trajectories. Moreover, due to the high dimensionality of user states and the vast state space inherent in recommendation scenarios, DT can incur significant computational costs and struggle to learn effective state representations. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel Temporal Advantage Decision Transformer with Contrastive State Abstraction (TADT-CSA) model. Specifically, we combine the conventional Return-To-Go (RTG) signal with a novel temporal advantage (TA) signal that encourages the model to capture both long-term returns and their sequential trend. Furthermore, we integrate a contrastive state abstraction module into the DT framework to learn more effective and expressive state representations. Within this module, we introduce a TA-conditioned State Vector Quantization (TAC-SVQ) strategy, where the TA score guides the state codebooks to incorporate contextual token information. Additionally, a reward prediction network and a contrastive transition prediction (CTP) network are employed to ensure the state codebook preserves both the reward information of the current state and the transition information between adjacent states. Empirical results on both public datasets and an online recommendation system demonstrate the effectiveness of the TADT-CSA model and its superiority over baseline methods.
随着基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,生成式推荐在提高现代推荐系统的准确性和语义理解方面显示出巨大潜力。与LLM相比,决策变压器(DT)是一个用于序列推荐任务的轻量级生成模型。然而,DT在轨迹拼接方面面临挑战,经常产生次优轨迹。此外,由于用户状态的高维性和推荐场景中的固有状态空间的广泛性,DT可能会产生显著的计算成本,并且难以学习有效的状态表示。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了新型的带有对比状态抽象的时间优势决策变压器(TADT-CSA)模型。具体来说,我们将传统的返回目标(RTG)信号与新型的时间优势(TA)信号相结合,鼓励模型捕捉长期回报及其序列趋势。此外,我们将对比状态抽象模块集成到DT框架中,学习更有效和更具表现力的状态表示。在该模块中,我们引入了一种时间优势条件状态向量量化(TAC-SVQ)策略,其中时间优势评分指导状态码本融入上下文标记信息。同时,采用奖励预测网络和对比过渡预测(CTP)网络,以确保状态码本保留当前状态的奖励信息和相邻状态之间的过渡信息。在公共数据集和在线推荐系统上的实证结果表明,TADT-CSA模型的有效性及其对基准方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)的快速进步为推荐系统的准确性和语义理解带来了巨大潜力。然而,用于序列推荐任务的决策变压器(DT)面临轨迹拼接的挑战,可能产生次优轨迹。为应对这些挑战并提升模型效率,我们提出了结合传统回归目标信号与新型时序优势信号的时空优势决策变压器结合对比状态抽象模型(TADT-CSA)。该模型通过引入对比状态抽象模块和时序优势条件状态向量量化策略,学习更有效、更具表现力的状态表示,从而降低了计算成本。在公共数据集和在线推荐系统上的经验结果表明,TADT-CSA模型优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs推动了生成式推荐系统的发展,提高了推荐准确性和语义理解。
- DT在轨迹拼接方面存在挑战,可能导致次优轨迹生成。
- TADT-CSA模型通过结合RTG信号与新型时序优势信号应对这些挑战。
- 对比状态抽象模块帮助模型学习更有效的状态表示。
- 模型引入了TAC-SVQ策略来融合时序优势信息与状态码本。
- 奖励预测网络和对比过渡预测网络确保状态码本保存当前状态的奖励信息和相邻状态间的过渡信息。
点此查看论文截图

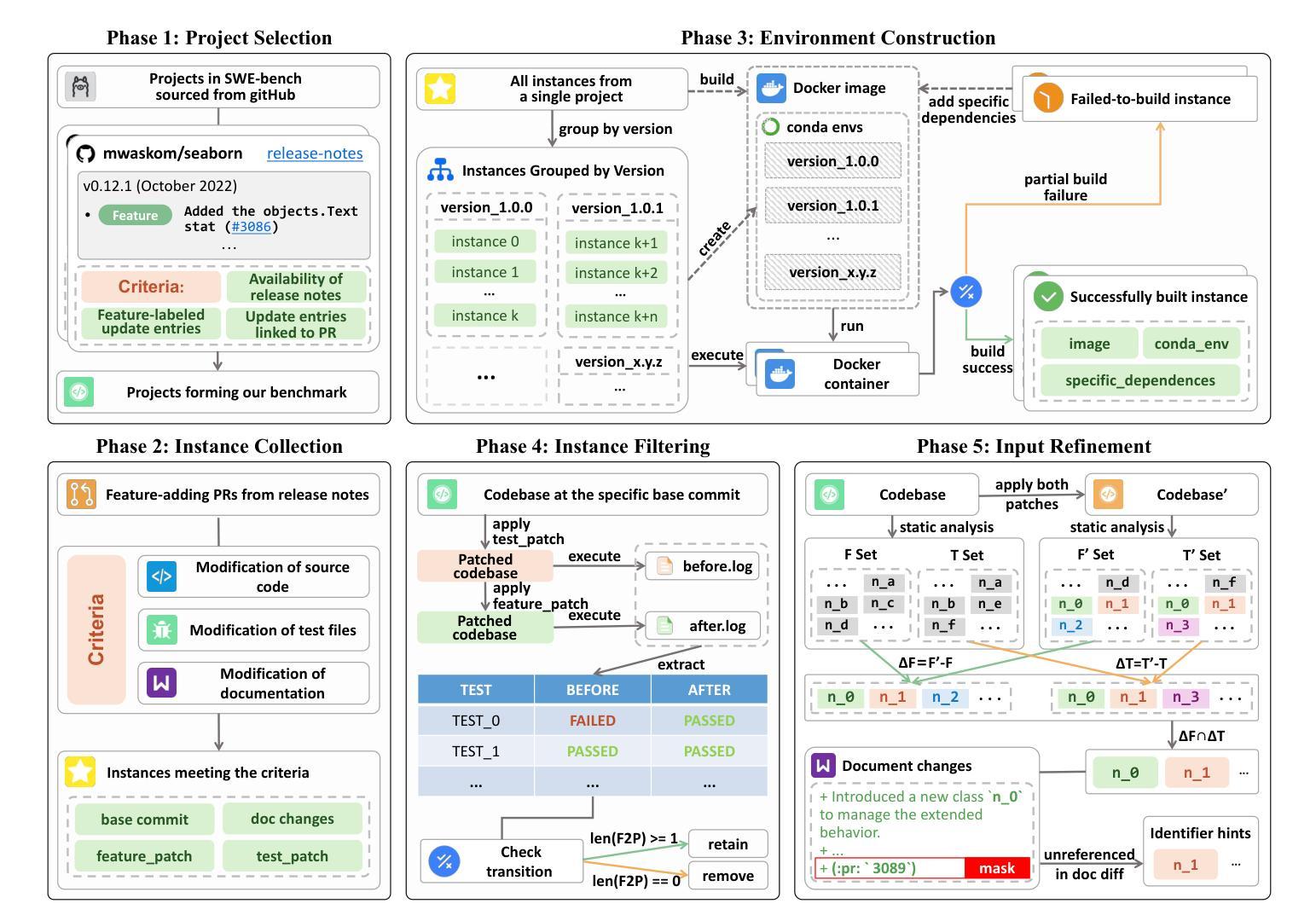
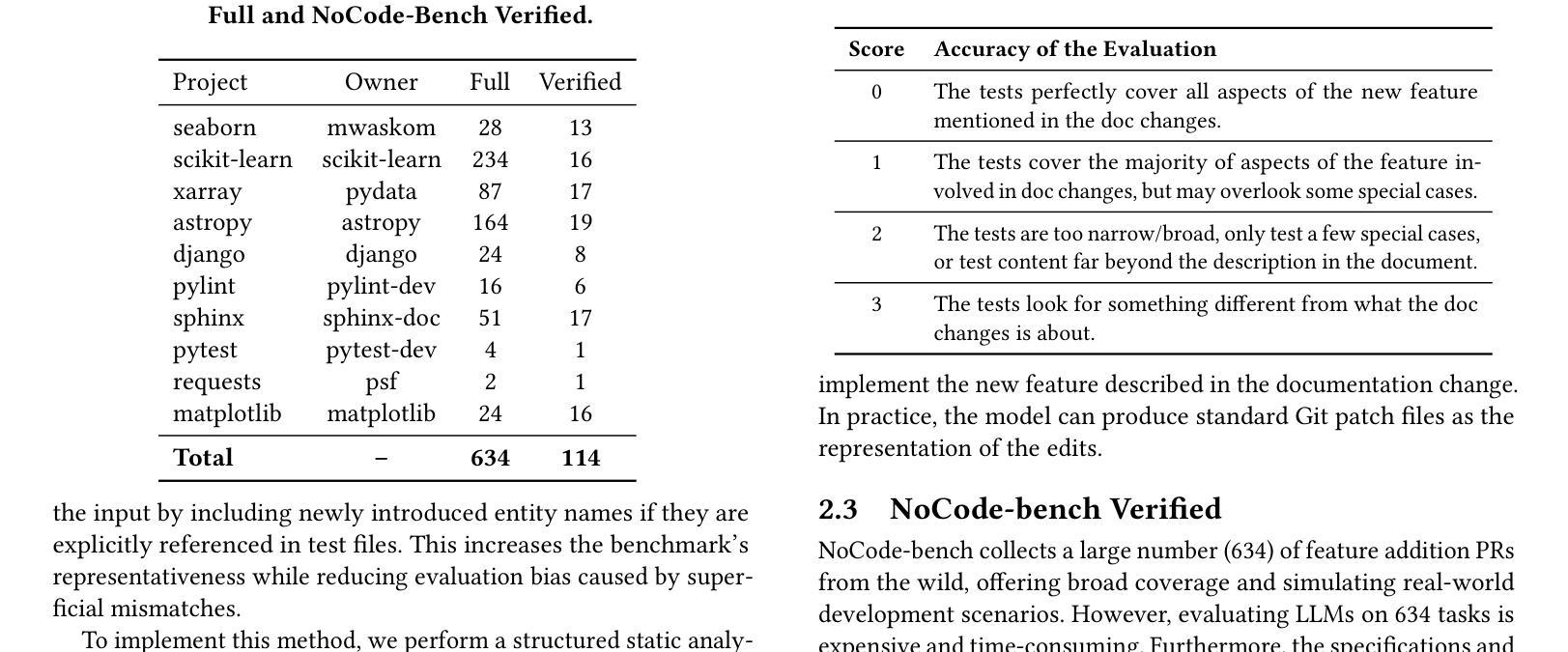
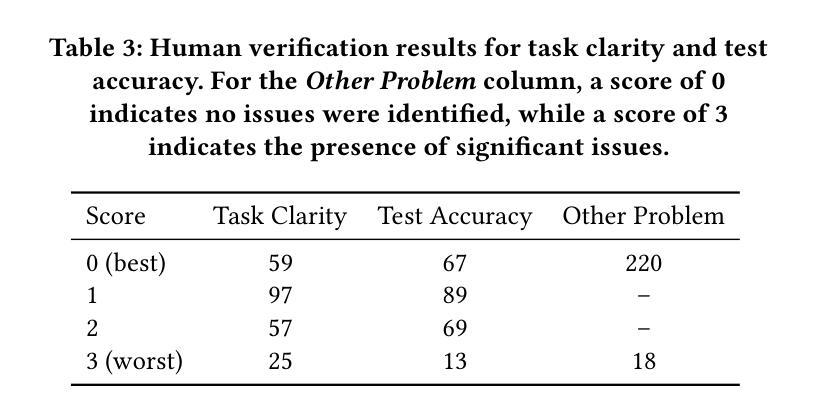
NoCode-bench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Natural Language-Driven Feature Addition
Authors:Le Deng, Zhonghao Jiang, Jialun Cao, Michael Pradel, Zhongxin Liu
Natural language-driven no-code development allows users to specify software functionality using natural language (NL) instead of editing source code, promising increased productivity and democratized development. Large language models (LLMs) show potential in enabling this paradigm. In this context, software documentation acts as an NL specification for functionality. This work introduces NoCode-bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs on real-world NL-driven feature addition tasks, consisting of 634 tasks across 10 projects and 114k code changes. Each task pairs documentation updates with corresponding code implementations, validated by developer-written test cases. A subset of 114 high-quality, human-verified instances, NoCode-bench Verified, ensures reliable evaluation. Our experiments reveal that, despite high token usage, the best LLMs achieve a task success rate of only 28.07%, highlighting challenges in cross-file editing, codebase understanding, and tool calling. These findings indicate that LLMs are not yet ready for fully NL-driven no-code development. NoCode-bench lays the foundation for future advances in this area.
自然语言驱动的无代码开发允许用户使用自然语言(NL)来指定软件功能,而不是编辑源代码,从而提高了生产力并实现了开发的民主化。大型语言模型(LLM)在这种模式下显示出巨大潜力。在此背景下,软件文档作为功能性的自然语言规范。本文介绍了NoCode-bench,这是一个旨在评估LLM在现实世界的自然语言驱动功能添加任务中的性能的基准测试,包含10个项目的634个任务和11万多次代码更改。每个任务都将文档更新与相应的代码实现配对,并通过开发人员编写的测试用例进行验证。其中一部分为经过人工验证的高质量实例NoCode-bench Verified,确保了评估的可靠性。我们的实验表明,尽管使用了大量的令牌,但最好的LLM的任务成功率仅为28.07%,这突显了在跨文件编辑、代码库理解和工具调用方面的挑战。这些发现表明,LLM尚未准备好进行完全的自然语言驱动的无代码开发。NoCode-bench为未来的进步奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自然语言驱动的无代码开发通过自然语言(NL)而非编辑源代码来实现软件功能的指定,提高了生产力并实现了开发的民主化。大型语言模型(LLM)在此领域具有潜力。在此背景下,软件文档作为功能性的自然语言规范。本研究引入了NoCode-bench,这是一个用于评估LLMs在现实世界的自然语言驱动功能添加任务上的性能的基准测试,包含634个任务,涵盖10个项目和11万多次代码更改。每个任务都将文档更新与相应的代码实现配对,并通过开发人员编写的测试用例进行验证。NoCode-bench Verified的高质量的实例确保了可靠的评估。实验表明,尽管LLMs使用了大量的令牌,但最佳LLMs的任务成功率仅为28.07%,这突显出在跨文件编辑、代码库理解和工具调用方面的挑战。这表明LLMs尚未准备好进行完全的自然语言驱动的无代码开发。NoCode-bench为未来的进步奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言驱动的无代码开发可提高生产力和实现开发民主化,通过自然语言(NL)而非编辑源代码来指定软件功能。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言驱动的无代码开发领域具有潜力。
- NoCode-bench是一个用于评估LLMs在现实世界的自然语言驱动功能添加任务上的性能的基准测试。
- NoCode-bench包含634个任务,涵盖多个项目和大量代码更改,以评估LLMs的性能。
- 实验显示LLMs在跨文件编辑、代码库理解和工具调用方面存在挑战。
- 目前LLMs尚未准备好进行完全的自然语言驱动的无代码开发。
点此查看论文截图

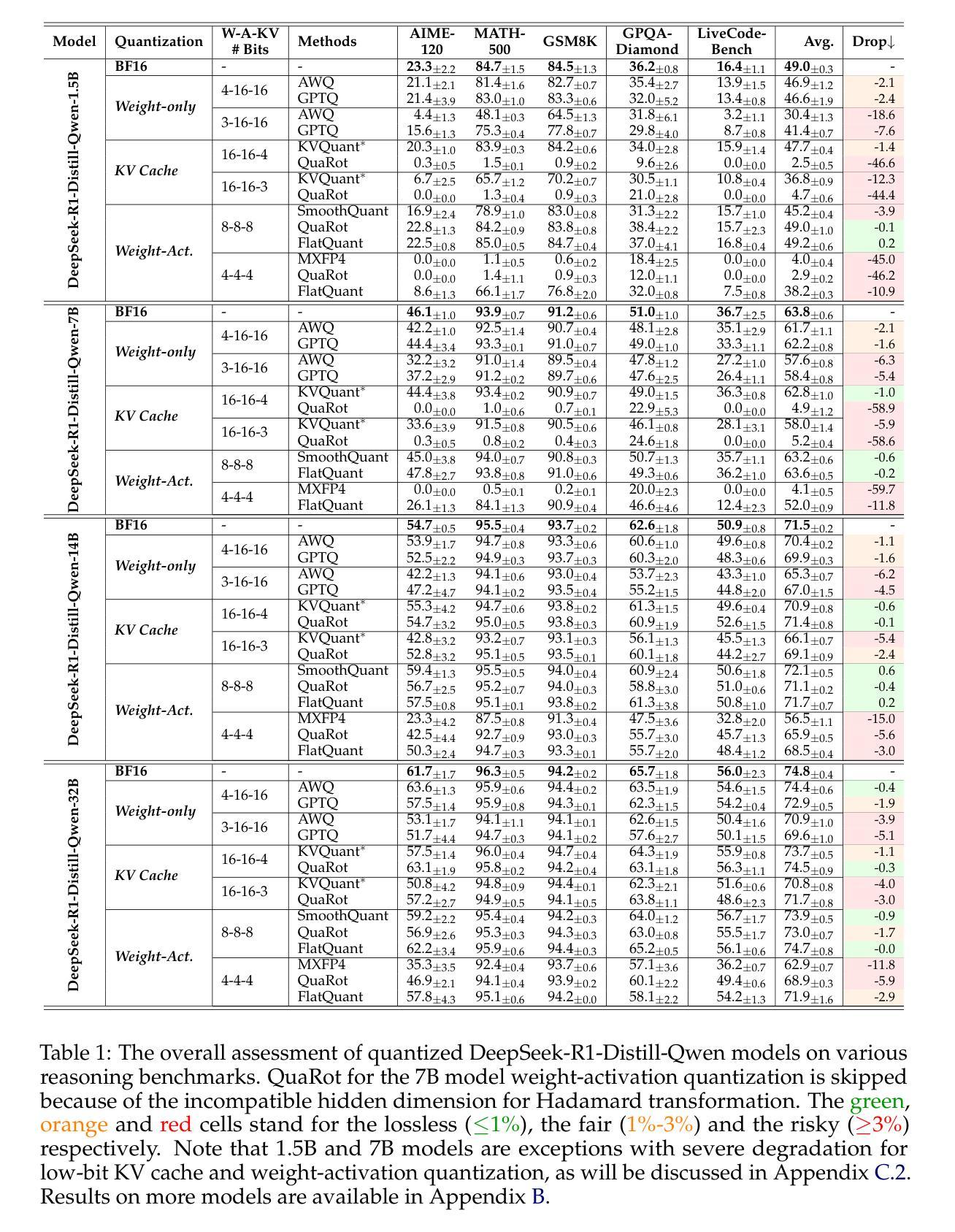
Quantization Hurts Reasoning? An Empirical Study on Quantized Reasoning Models
Authors:Ruikang Liu, Yuxuan Sun, Manyi Zhang, Haoli Bai, Xianzhi Yu, Tiezheng Yu, Chun Yuan, Lu Hou
Recent advancements in reasoning language models have demonstrated remarkable performance in complex tasks, but their extended chain-of-thought reasoning process increases inference overhead. While quantization has been widely adopted to reduce the inference cost of large language models, its impact on reasoning models remains understudied. In this paper, we conduct the first systematic study on quantized reasoning models, evaluating the open-sourced DeepSeek-R1-Distilled Qwen and LLaMA families ranging from 1.5B to 70B parameters, QwQ-32B, and Qwen3-8B. Our investigation covers weight, KV cache, and activation quantization using state-of-the-art algorithms at varying bit-widths, with extensive evaluation across mathematical (AIME, MATH-500), scientific (GPQA), and programming (LiveCodeBench) reasoning benchmarks. Our findings reveal that while lossless quantization can be achieved with W8A8 or W4A16 quantization, lower bit-widths introduce significant accuracy risks. We further identify model size, model origin, and task difficulty as critical determinants of performance. Contrary to expectations, quantized models do not exhibit increased output lengths. In addition, strategically scaling the model sizes or reasoning steps can effectively enhance the performance. All quantized models and codes are open-sourced in https://github.com/ruikangliu/Quantized-Reasoning-Models.
近期推理语言模型的进展在复杂任务中表现出了卓越的性能,但其扩展的链式推理过程增加了推理开销。虽然量化已广泛应用于减少大型语言模型的推理成本,但对推理模型的影响仍研究不足。在本文中,我们对量化推理模型进行了首次系统研究,评估了开源的DeepSeek-R1-Distilled Qwen和LLaMA系列,参数范围从1.5B到70B,包括Qwq-32B和Qwen3-8B。我们的调查涵盖了使用最新算法的权重、KV缓存和激活量化,并在数学(AIME,MATH-500)、科学(GPQA)和编程(LiveCodeBench)推理基准测试上进行了广泛评估。我们发现,使用W8A8或W4A16量化可以实现无损量化,但较低的位宽会引入显著准确性风险。我们进一步确定了模型大小、模型来源和任务难度是性能的关键决定因素。出乎意料的是,量化模型的输出长度并没有增加。此外,战略性地调整模型大小或推理步骤可以有效地提高性能。所有量化模型和代码已开源在https://github.com/ruikangliu/Quantized-Reasoning-Models。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLM 2025
Summary
本文研究了量化推理模型的效果和性能。实验涵盖了多种模型和算法,包括DeepSeek-R1-Distilled Qwen系列和LLaMA家族,在多个任务上的性能测试证明了量化的合理性对模型的性能和效果影响不大,但对于低位宽设计有一定风险。模型大小、来源和任务难度对性能有显著影响。量化模型的输出长度并未增加。此外,通过调整模型规模或推理步骤可以有效地提高性能。模型和代码均已开源分享。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员对多种语言推理模型进行了量化测试,这些模型在复杂任务中表现出色。
- 测试包括权重、KV缓存和激活量化,使用先进的算法在不同位宽上进行评估。
- 测试范围涵盖了数学、科学和编程等多个领域的推理任务。
- 研究发现无损量化可以在W8A8或W4A16量化中实现,但低位宽设计会带来显著精度风险。
- 模型大小、来源和任务难度对量化推理模型的性能有显著影响。
- 量化模型的输出长度并未如预期增加。
点此查看论文截图

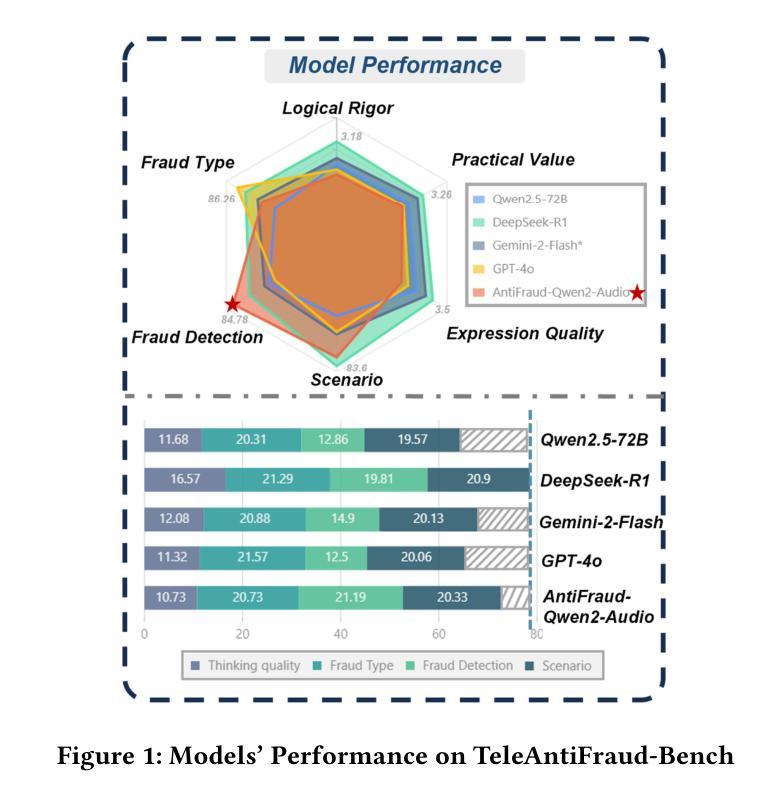
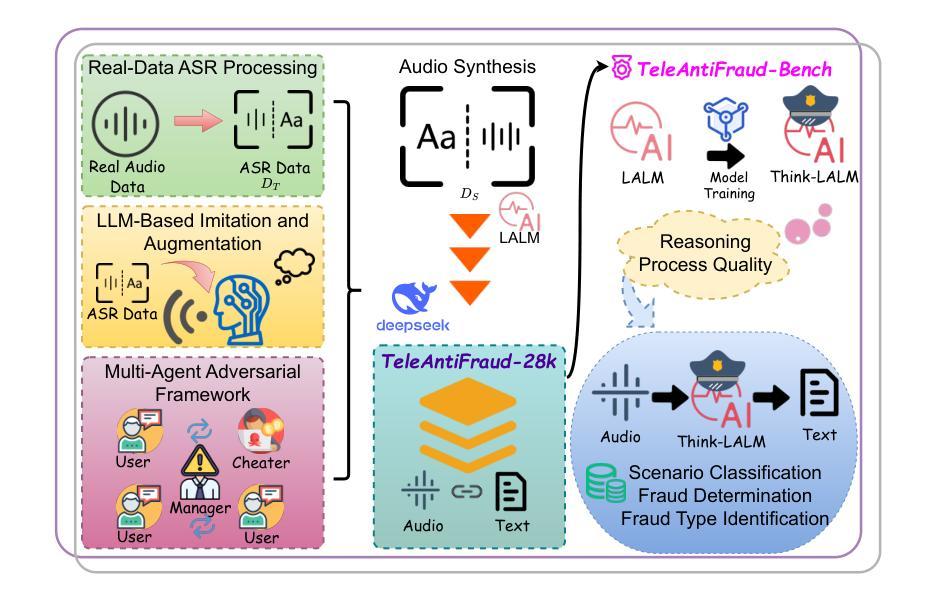
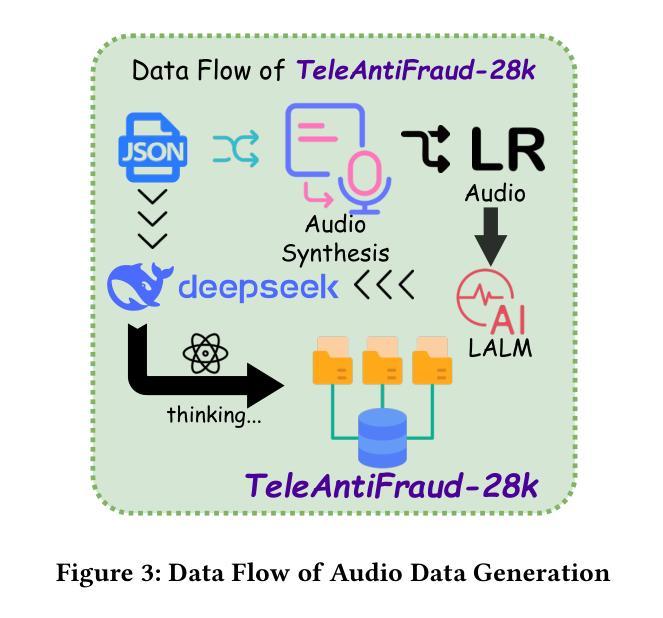
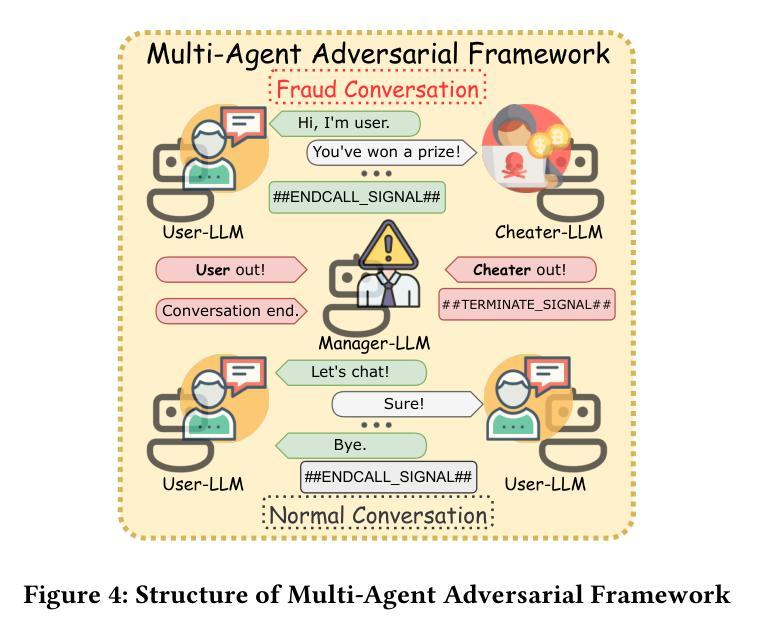
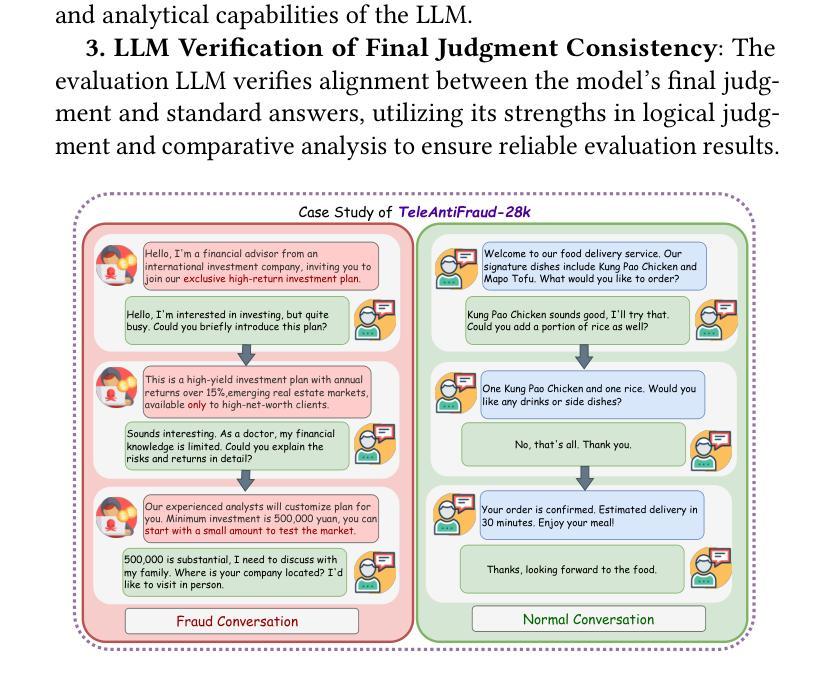
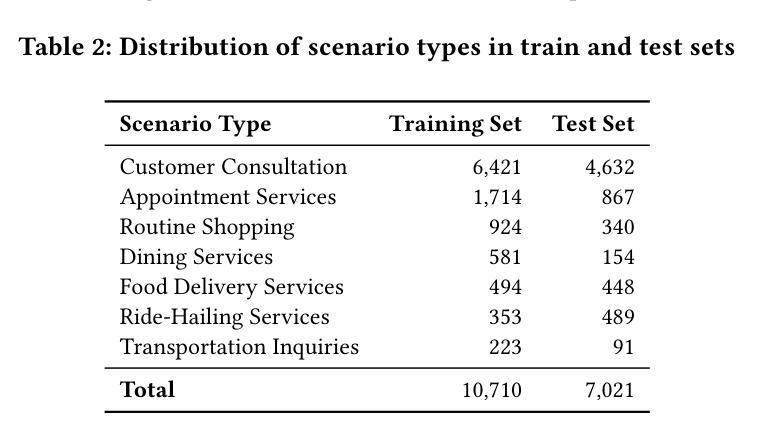
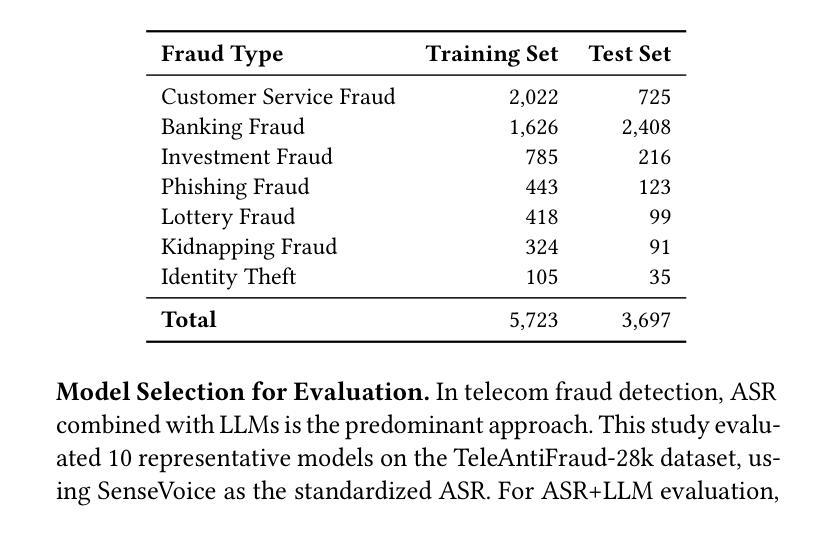
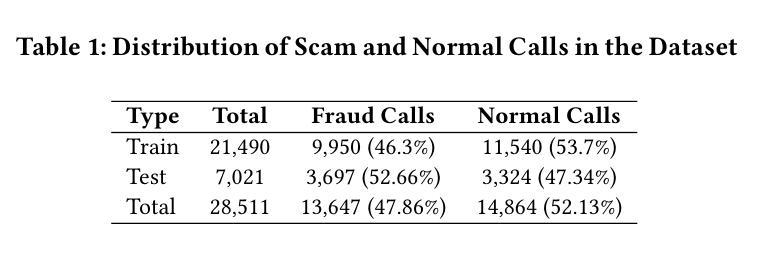
TeleAntiFraud-28k: An Audio-Text Slow-Thinking Dataset for Telecom Fraud Detection
Authors:Zhiming Ma, Peidong Wang, Minhua Huang, Jingpeng Wang, Kai Wu, Xiangzhao Lv, Yachun Pang, Yin Yang, Wenjie Tang, Yuchen Kang
The detection of telecom fraud faces significant challenges due to the lack of high-quality multimodal training data that integrates audio signals with reasoning-oriented textual analysis. To address this gap, we present TeleAntiFraud-28k, the first open-source audio-text slow-thinking dataset specifically designed for automated telecom fraud analysis. Our dataset is constructed through three strategies: (1) Privacy-preserved text-truth sample generation using automatically speech recognition (ASR)-transcribed call recordings (with anonymized original audio), ensuring real-world consistency through text-to-speech (TTS) model regeneration; (2) Semantic enhancement via large language model (LLM)-based self-instruction sampling on authentic ASR outputs to expand scenario coverage; (3) Multi-agent adversarial synthesis that simulates emerging fraud tactics through predefined communication scenarios and fraud typologies. The generated dataset contains 28,511 rigorously processed speech-text pairs, complete with detailed annotations for fraud reasoning. The dataset is divided into three tasks: scenario classification, fraud detection, fraud type classification. Furthermore, we construct TeleAntiFraud-Bench, a standardized evaluation benchmark comprising proportionally sampled instances from the dataset, to facilitate systematic testing of model performance on telecom fraud detection tasks. We also contribute a production-optimized supervised fine-tuning (SFT) model trained on hybrid real/synthetic data, while open-sourcing the data processing framework to enable community-driven dataset expansion. This work establishes a foundational framework for multimodal anti-fraud research while addressing critical challenges in data privacy and scenario diversity. The project will be released at https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud.
电信欺诈检测面临着巨大的挑战,这主要是由于缺乏高质量的多模式训练数据,无法将音频信号与面向推理的文本分析相结合。为了解决这一空白,我们推出了TeleAntiFraud-28k,这是专门为电信欺诈自动化分析设计的第一个开源音频文本慢思考数据集。我们的数据集通过以下三种策略构建:(1)使用自动语音识别(ASR)转录的录音生成隐私保护的文本真实样本(带有匿名原始音频),并通过文本到语音(TTS)模型再生确保现实世界的一致性;(2)通过基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自我指令采样对真实的ASR输出进行语义增强,以扩大场景覆盖;(3)模拟新兴欺诈策略的多代理对抗合成通过预设的通信场景和欺诈类型。生成的数据集包含经过严格处理的28511个语音文本对,带有详细的欺诈推理注释。数据集分为三个任务:场景分类、欺诈检测、欺诈类型分类。此外,我们构建了TeleAntiFraud-Bench,这是一个标准化的评估基准,包含从数据集中按比例采样的实例,以便于对电信欺诈检测任务上模型性能的系统性测试。我们还为混合现实/合成数据训练的生产优化监督微调(SFT)模型做出了贡献,同时开源数据处理框架以推动数据集扩展。这项工作为多媒体反欺诈研究建立了基础框架,同时解决了数据隐私和场景多样性方面的关键挑战。该项目将在https://github.com/JimmyMa99/TeleAntiFraud上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对电信欺诈检测领域面临的高质量多模式训练数据缺失的挑战,我们推出TeleAntiFraud-28k,这是首个专为自动化电信欺诈分析设计的音频文本慢思考数据集。通过隐私保护的真实文本生成、语义增强和大语言模型自我指导采样以及模拟新兴欺诈策略的多智能体对抗合成三种策略构建数据集。包含28,511个经过严格处理的语音文本对,具有详细的欺诈推理注释,分为场景分类、欺诈检测和欺诈类型分类三个任务。同时构建TeleAntiFraud-Bench标准化评估基准,并开源数据处理框架,以推动数据集扩展。为跨模态反欺诈研究提供基础框架,解决数据隐私和场景多样性等挑战。
Key Takeaways
- TeleAntiFraud-28k是首个专为电信欺诈分析设计的音频文本数据集。
- 数据集通过隐私保护的真实文本生成、语义增强和多智能体对抗合成构建。
- 数据集包含详细的欺诈推理注释,分为场景分类、欺诈检测和欺诈类型分类三个任务。
- 构建了TeleAntiFraud-Bench标准化评估基准以测试模型性能。
- 开源数据处理框架,促进数据集扩展和社区参与。
- 该工作为跨模态反欺诈研究提供基础框架。
点此查看论文截图