⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-20 更新
LangVision-LoRA-NAS: Neural Architecture Search for Variable LoRA Rank in Vision Language Models
Authors:Krishna Teja Chitty-Venkata, Murali Emani, Venkatram Vishwanath
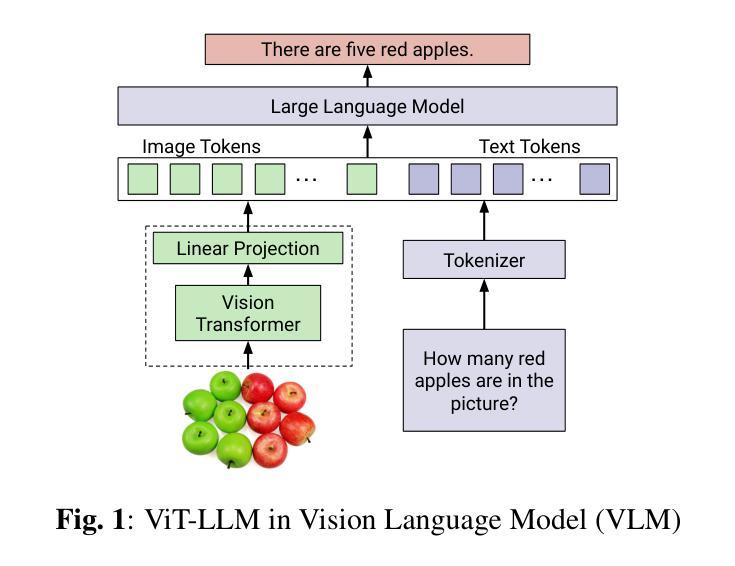
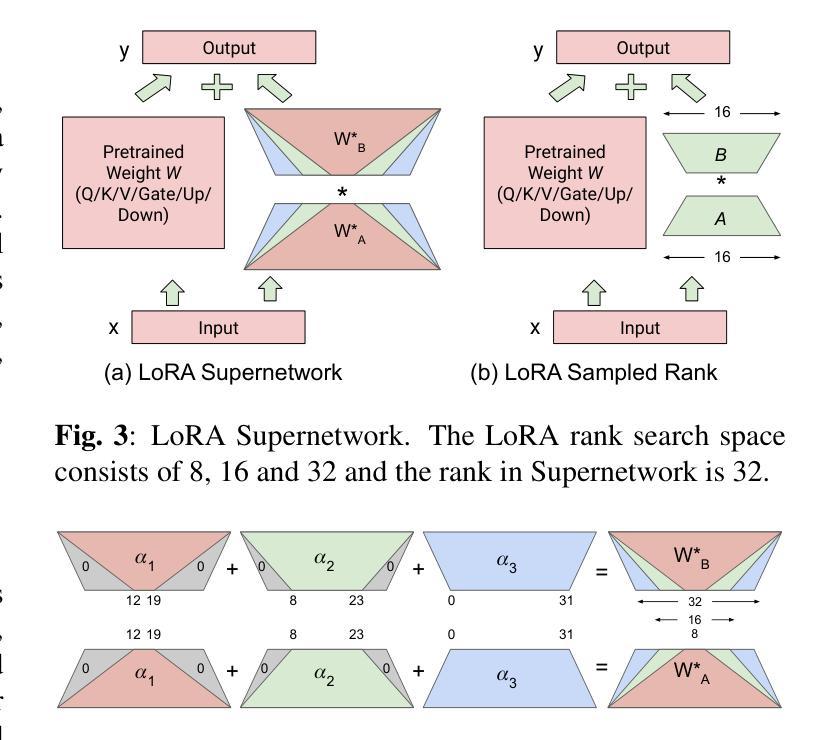
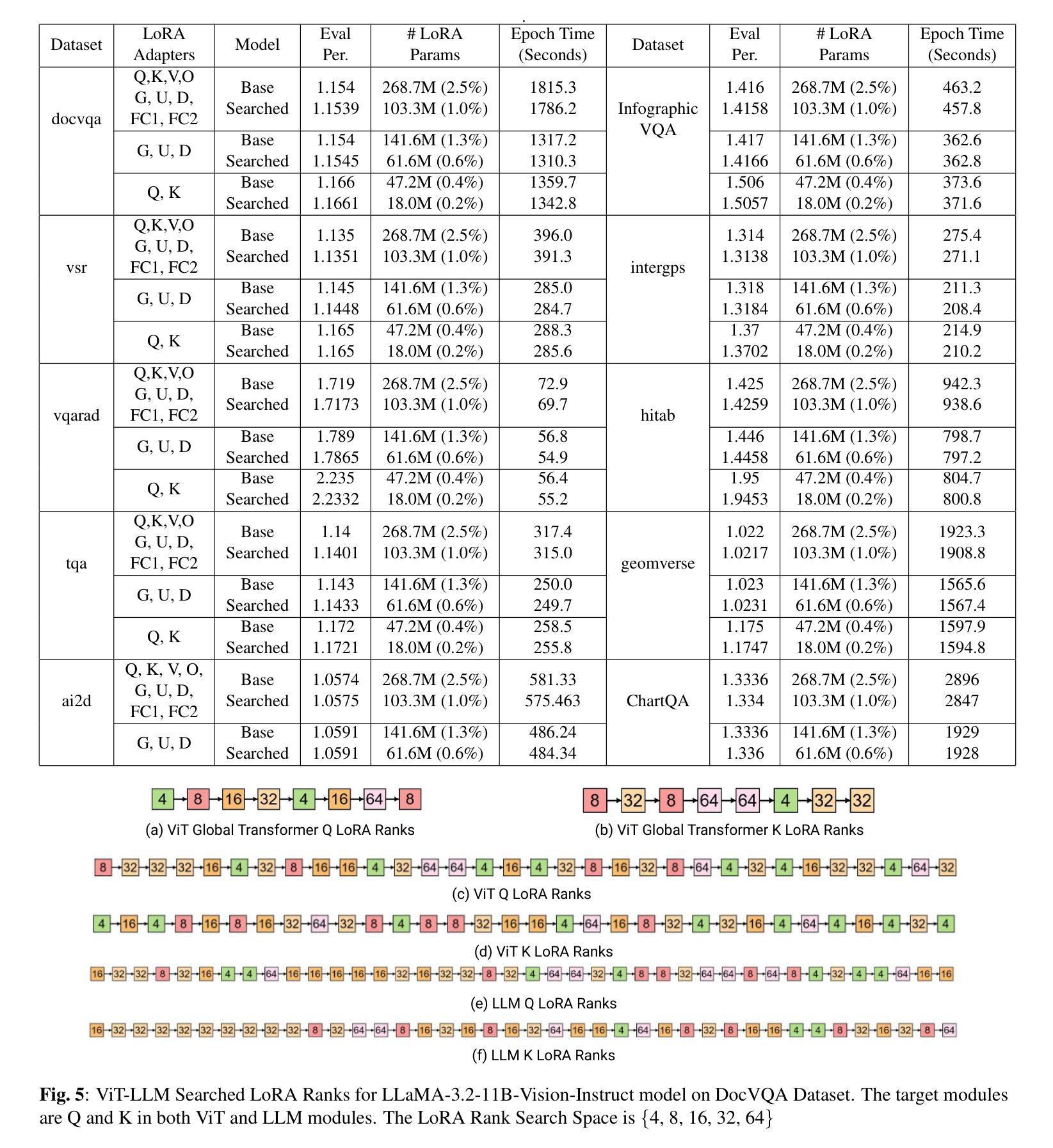
Vision Language Models (VLMs) integrate visual and text modalities to enable multimodal understanding and generation. These models typically combine a Vision Transformer (ViT) as an image encoder and a Large Language Model (LLM) for text generation. LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) is an efficient fine-tuning method to adapt pre-trained models to new tasks by introducing low-rank updates to their weights. While LoRA has emerged as a powerful technique for fine-tuning large models by introducing low-rank updates, current implementations assume a fixed rank, potentially limiting flexibility and efficiency across diverse tasks. This paper introduces \textit{LangVision-LoRA-NAS}, a novel framework that integrates Neural Architecture Search (NAS) with LoRA to optimize VLMs for variable-rank adaptation. Our approach leverages NAS to dynamically search for the optimal LoRA rank configuration tailored to specific multimodal tasks, balancing performance and computational efficiency. Through extensive experiments using the LLaMA-3.2-11B model on several datasets, LangVision-LoRA-NAS demonstrates notable improvement in model performance while reducing fine-tuning costs. Our Base and searched fine-tuned models on LLaMA-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct can be found \href{https://huggingface.co/collections/krishnateja95/llama-32-11b-vision-instruct-langvision-lora-nas-6786cac480357a6a6fcc59ee}{\textcolor{blue}{here}} and the code for LangVision-LoRA-NAS can be found \href{https://github.com/krishnateja95/LangVision-NAS}{\textcolor{blue}{here}}.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)结合了视觉和文本模态,以实现多模态理解和生成。这些模型通常将视觉转换器(ViT)作为图像编码器,并结合大型语言模型(LLM)进行文本生成。LoRA(低秩适应)是一种高效的微调方法,通过引入权重低秩更新,使预训练模型能够适应新任务。虽然LoRA已经成为通过引入低秩更新来微调大型模型的强大技术,但目前的实现都假设了一个固定的秩,这可能会限制其在不同任务中的灵活性和效率。本文介绍了\emph{LangVision-LoRA-NAS}这一新型框架,它将神经架构搜索(NAS)与LoRA相结合,以优化VLMs进行变秩适应。我们的方法利用NAS动态搜索针对特定多模态任务的最佳LoRA秩配置,在性能和计算效率之间取得平衡。通过对LLaMA-3.2-11B模型在多个数据集上进行的大量实验,LangVision-LoRA-NAS在模型性能上取得了显著的改进,同时降低了微调成本。我们的基础模型和经过搜索的微调模型都可以在LLaMA-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct上找到\href{https://huggingface.co/collections/krishnateja95/llama-32-11b-vision-instruct-langvision-lora-nas-6786cac480357a6a6fcc59ee}{\textcolor{blue}{此处}},而LangVision-LoRA-NAS的代码可以在\href{https://github.com/krishnateja95/LangVision-NAS}{\textcolor{blue}{此处}}找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICIP 2025 Conference
Summary
本文介绍了结合视觉和语言模型的集成方法,使用Vision Transformer作为图像编码器和大语言模型进行文本生成。针对预训练模型的微调问题,引入了LoRA技术,并通过Neural Architecture Search(NAS)进行优化,实现针对特定任务的低秩自适应调整。实验证明,LangVision-LoRA-NAS能够在降低微调成本的同时提高模型性能。其模型和代码已在相关链接中提供。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs融合视觉和文本模态以实现多模态理解和生成,通常结合Vision Transformer和大型语言模型。
- LoRA是一种有效的微调方法,通过引入低秩更新来适应预训练模型。
- 当前LoRA实现采用固定秩,可能限制了在不同任务中的灵活性和效率。
- LangVision-LoRA-NAS结合了NAS与LoRA技术,优化VLMs进行变秩自适应。
- NAS用于动态搜索针对特定多模态任务的最佳LoRA秩配置,平衡性能和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

Federated Cross-Modal Style-Aware Prompt Generation
Authors:Suraj Prasad, Navyansh Mahla, Sunny Gupta, Amit Sethi
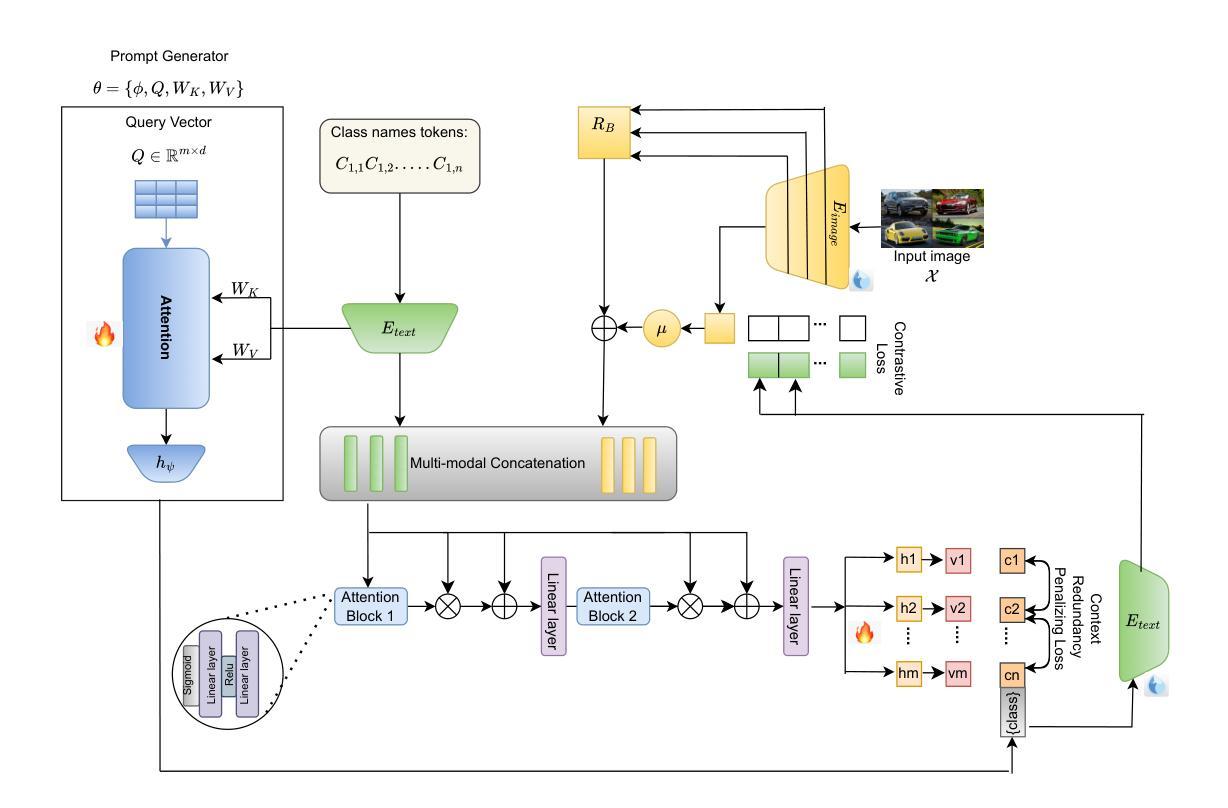
Prompt learning has propelled vision-language models like CLIP to excel in diverse tasks, making them ideal for federated learning due to computational efficiency. However, conventional approaches that rely solely on final-layer features miss out on rich multi-scale visual cues and domain-specific style variations in decentralized client data. To bridge this gap, we introduce FedCSAP (Federated Cross-Modal Style-Aware Prompt Generation). Our framework harnesses low, mid, and high-level features from CLIP’s vision encoder alongside client-specific style indicators derived from batch-level statistics. By merging intricate visual details with textual context, FedCSAP produces robust, context-aware prompt tokens that are both distinct and non-redundant, thereby boosting generalization across seen and unseen classes. Operating within a federated learning paradigm, our approach ensures data privacy through local training and global aggregation, adeptly handling non-IID class distributions and diverse domain-specific styles. Comprehensive experiments on multiple image classification datasets confirm that FedCSAP outperforms existing federated prompt learning methods in both accuracy and overall generalization.
提示学习推动了CLIP等视觉语言模型在各种任务中的卓越表现,使其成为联邦学习的理想选择,因为其在计算效率方面具有优势。然而,传统方法仅仅依赖最终层特征而忽略了去中心化客户端数据中丰富的多尺度视觉线索和特定领域的风格变化。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了FedCSAP(联邦跨模态风格感知提示生成)。我们的框架结合了CLIP视觉编码器的低、中、高级特征以及从批量级别统计派生的客户端特定风格指标。通过将复杂的视觉细节与文本上下文相结合,FedCSAP生成稳健的、具有上下文意识的提示令牌,这些令牌既独特又非冗余,从而提高了在已知和未知类别上的泛化能力。我们的方法遵循联邦学习模式,通过本地训练和全局聚合确保数据隐私,并能灵活处理非IID类分布和各种特定领域的风格。在多个图像分类数据集上的综合实验证实,FedCSAP在准确性和整体泛化方面优于现有的联邦提示学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了FedCSAP(Federated Cross-Modal Style-Aware Prompt Generation)框架,该框架结合了CLIP视觉编码器的多尺度特征和客户端特定的风格指标,生成稳健的上下文感知提示令牌,提高了跨已知和未知类别的泛化能力。在联邦学习范式内,FedCSAP确保了数据隐私,并擅长处理非IID类分布和不同的领域特定风格。实验证明,FedCSAP在准确性和整体泛化方面优于现有的联邦提示学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- FedCSAP框架结合了CLIP视觉编码器的多尺度特征,包括低、中、高级特征。
- 该框架利用客户端特定的风格指标,这些指标是从批量级别的统计数据中得出的。
- FedCSAP生成稳健的上下文感知提示令牌,这些令牌既独特又非冗余,提高了跨已知和未知类别的泛化能力。
- FedCSAP框架在联邦学习范式内运行,确保数据隐私,通过本地训练和全局聚合来处理非IID类分布和不同的领域特定风格。
- FedCSAP提高了视觉语言模型的效率,使其适用于联邦学习。
- 通过对多个图像分类数据集的综合实验,证明FedCSAP在准确性和整体泛化方面优于现有的联邦提示学习方法。
点此查看论文截图

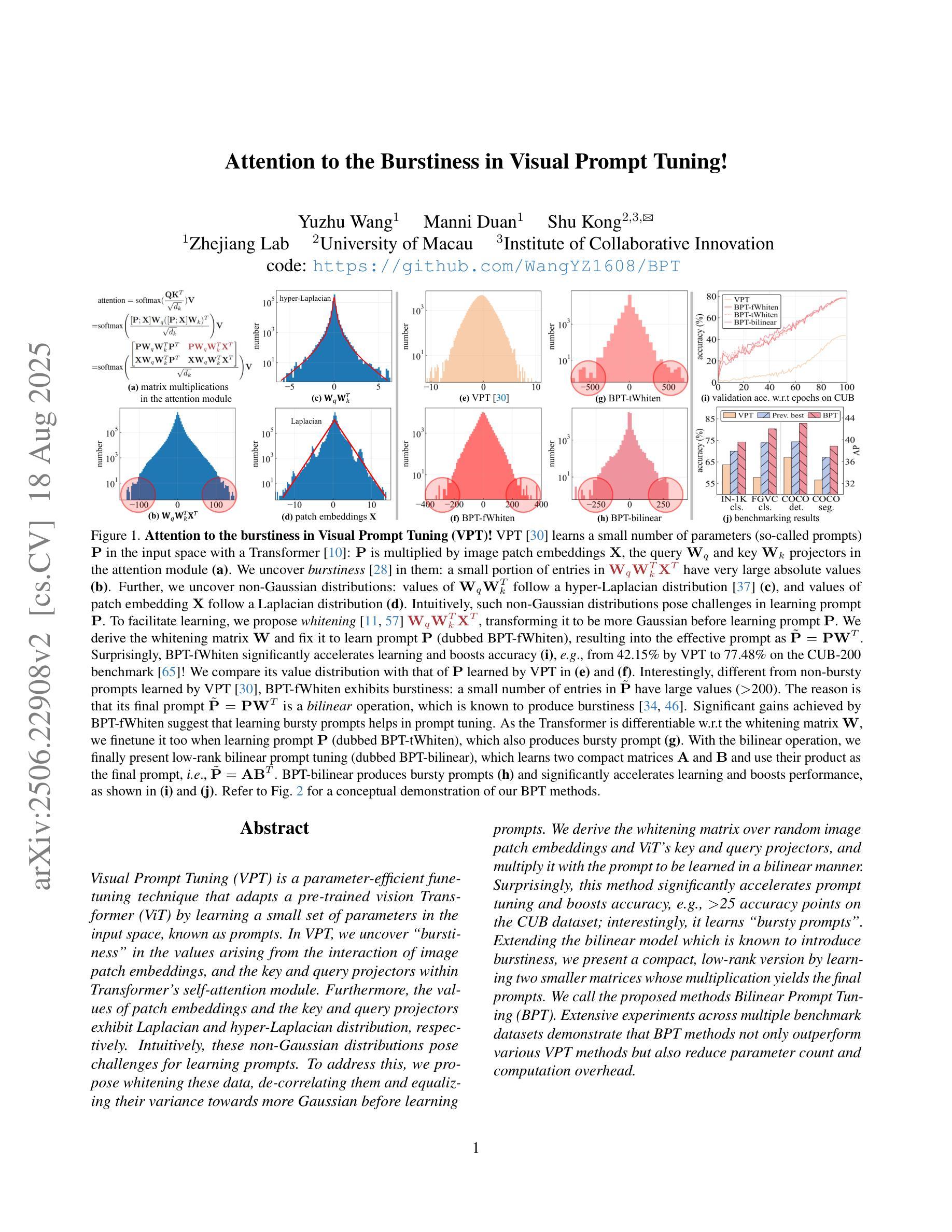
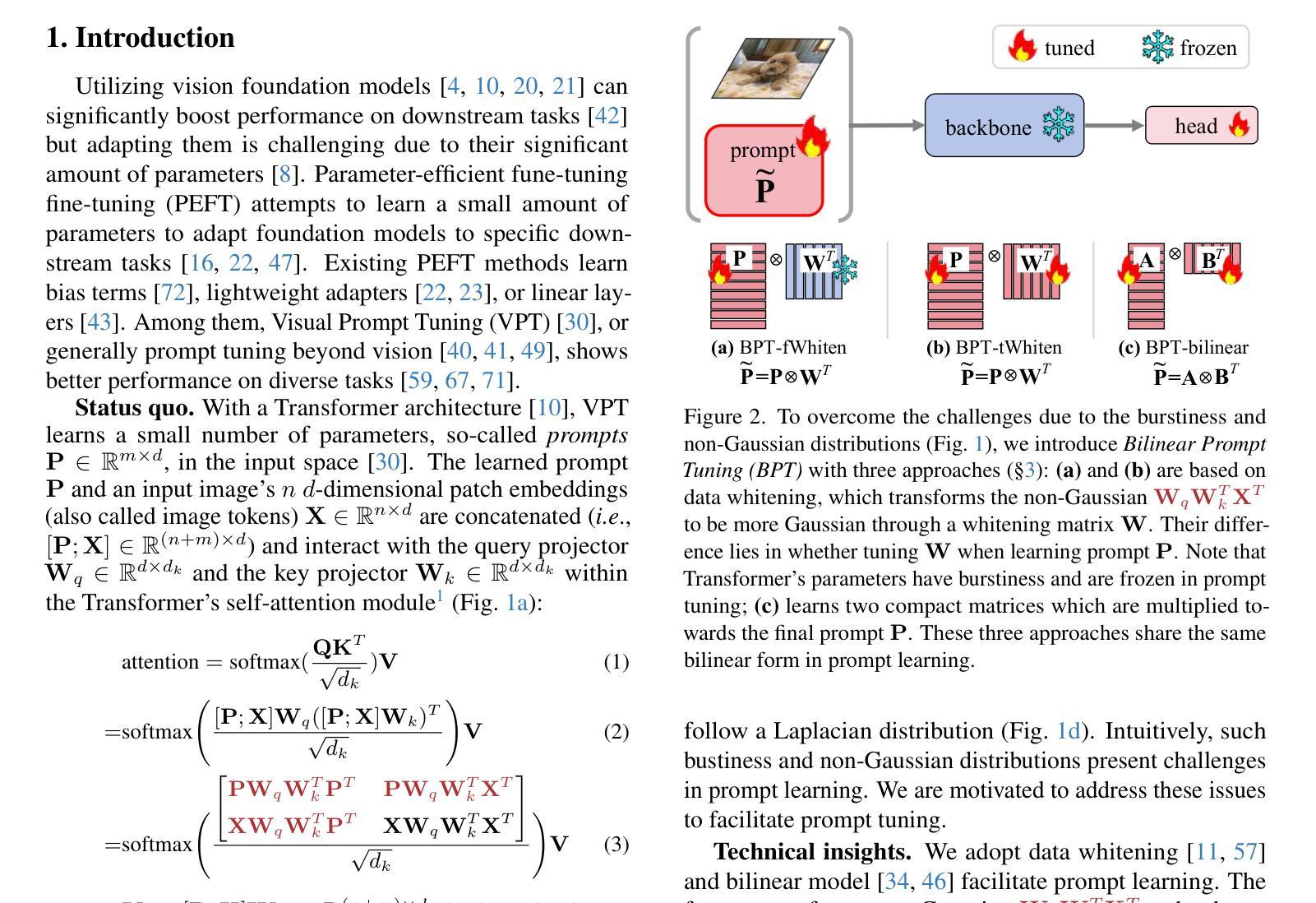
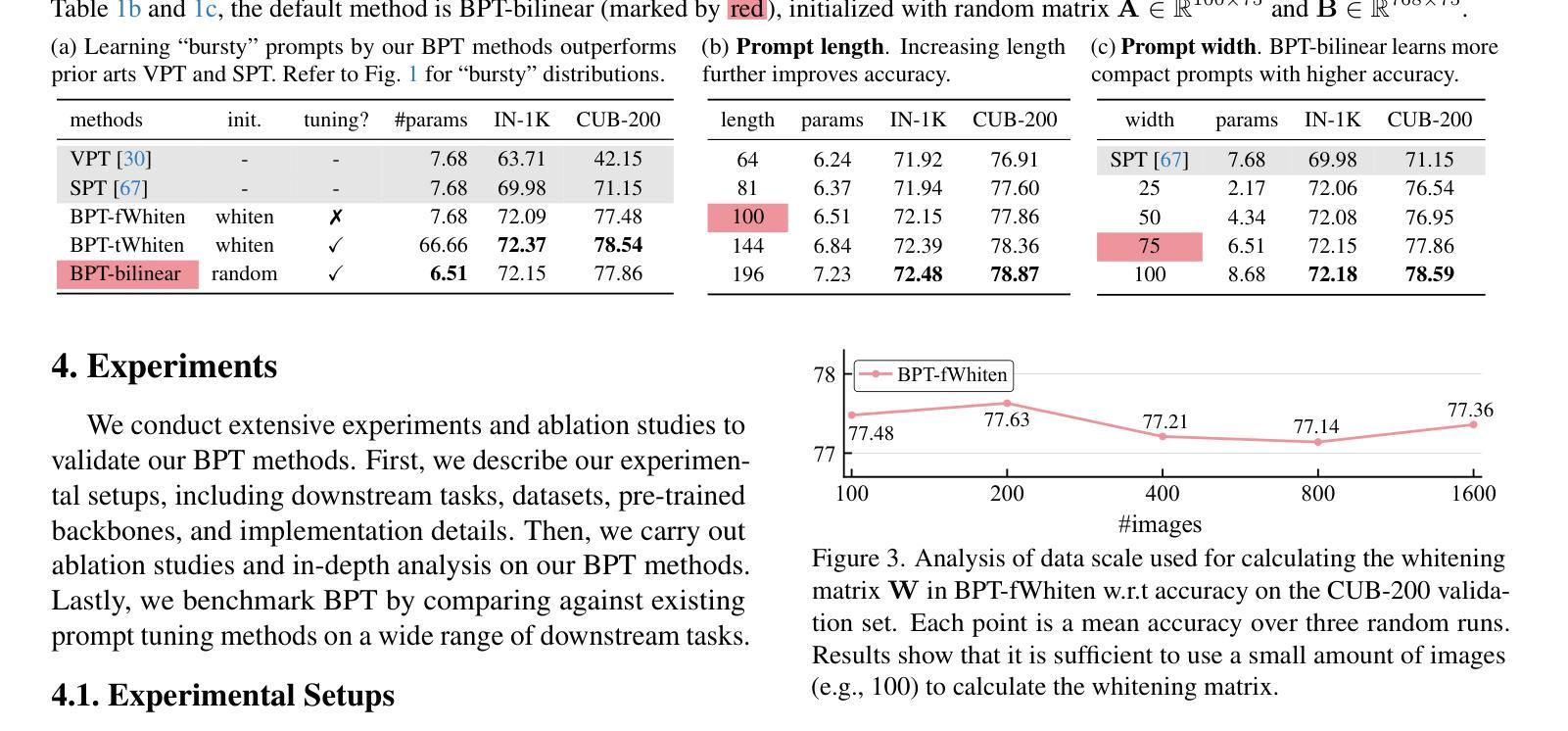
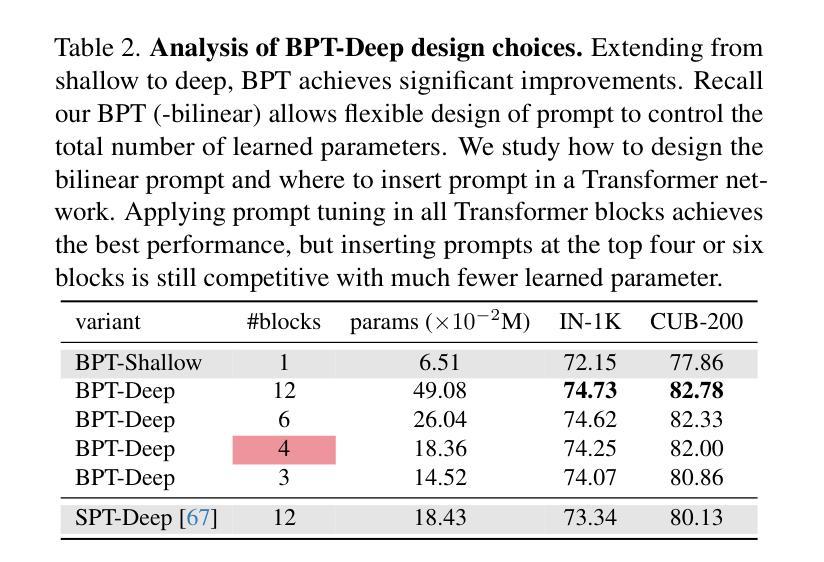
Attention to the Burstiness in Visual Prompt Tuning!
Authors:Yuzhu Wang, Manni Duan, Shu Kong
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) is a parameter-efficient fune-tuning technique that adapts a pre-trained vision Transformer (ViT) by learning a small set of parameters in the input space, known as prompts. In VPT, we uncover burstiness'' in the values arising from the interaction of image patch embeddings, and the key and query projectors within Transformer's self-attention module. Furthermore, the values of patch embeddings and the key and query projectors exhibit Laplacian and hyper-Laplacian distribution, respectively. Intuitively, these non-Gaussian distributions pose challenges for learning prompts. To address this, we propose whitening these data, de-correlating them and equalizing their variance towards more Gaussian before learning prompts. We derive the whitening matrix over random image patch embeddings and ViT's key and query projectors, and multiply it with the prompt to be learned in a bilinear manner. Surprisingly, this method significantly accelerates prompt tuning and boosts accuracy, e.g., $>$25 accuracy points on the CUB dataset; interestingly, it learns bursty prompts’’. Extending the bilinear model which is known to introduce burstiness, we present a compact, low-rank version by learning two smaller matrices whose multiplication yields the final prompts. We call the proposed methods Bilinear Prompt Tuning (BPT). Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that BPT methods not only outperform various VPT methods but also reduce parameter count and computation overhead.
视觉提示微调(VPT)是一种参数高效的微调技术,它通过在学习输入空间中的一小部分参数(称为提示)来适应预训练的视觉Transformer(ViT)。在VPT中,我们发现了图像补丁嵌入交互所产生的值中的“突发性”,以及Transformer自注意力模块中的键和查询投影器。此外,补丁嵌入的值和键以及查询投影器分别呈现出拉普拉斯和超拉普拉斯分布。直观地说,这些非高斯分布给学习提示带来了挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出对这些数据进行白化,去除其相关性,并在学习提示之前将其方差向更高斯的方向平衡。我们通过在随机图像补丁嵌入和ViT的键和查询投影器上推导白化矩阵,并将其与以双线性方式学习的提示相乘。令人惊讶的是,这种方法显著加速了提示调整并提高了准确性,例如在CUB数据集上的准确度提高了超过25个百分点;有趣的是,它学习了“突发性的提示”。通过扩展已知会引发突发性的双线性模型,我们提出了一个紧凑、低阶的版本,通过学习两个较小的矩阵,它们的乘积产生最终的提示。我们将所提出的方法称为双线性提示微调(BPT)。在多个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,BPT方法不仅优于各种VPT方法,而且减少了参数计数和计算开销。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025; v2: camera ready
Summary
视觉提示微调(VPT)是一种参数高效的微调技术,它通过在学习输入空间中的一小部分参数(称为提示)来适应预训练的视觉Transformer(ViT)。在VPT中,我们发现了图像补丁嵌入值之间的“突发性”,以及Transformer自注意力模块中的键和查询投影与之的交互作用。针对这些非高斯分布带来的挑战,我们提出在学习提示之前对这些数据进行白化,去相关并均衡其方差以更接近高斯分布。通过推导随机图像补丁嵌入和ViT键查询投影的白化矩阵,并将其与要学习的提示相乘,此方法可显著加速提示调整并提升准确性,如在CUB数据集上的准确率超过25个点。我们进一步扩展了双线性模型,提出了一种紧凑、低秩的版本,通过学习两个较小的矩阵,其乘积产生最终的提示。我们称所提出的方法为双线性提示微调(BPT)。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,BPT方法不仅优于各种VPT方法,而且减少了参数计数和计算开销。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉提示微调(VPT)是一种针对预训练视觉Transformer的参数高效微调技术。
- VPT中发现图像补丁嵌入值与Transformer自注意力模块中的键和查询投影之间存在“突发性”。
- 针对非高斯分布带来的挑战,提出白化数据并均衡其方差以接近高斯分布再进行提示学习。
- 通过推导白化矩阵并与要学习的提示相乘,显著加速提示调整并提升准确性。
- 提出双线性提示微调(BPT),在多个基准数据集上表现优异,优于其他VPT方法。
- BPT方法减少参数计数和计算开销。
点此查看论文截图
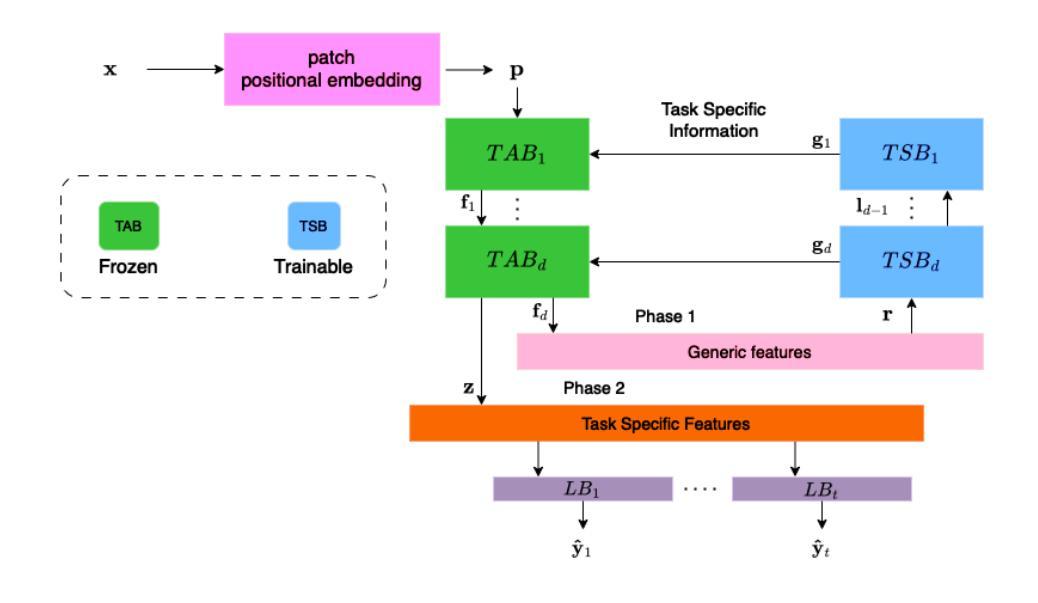
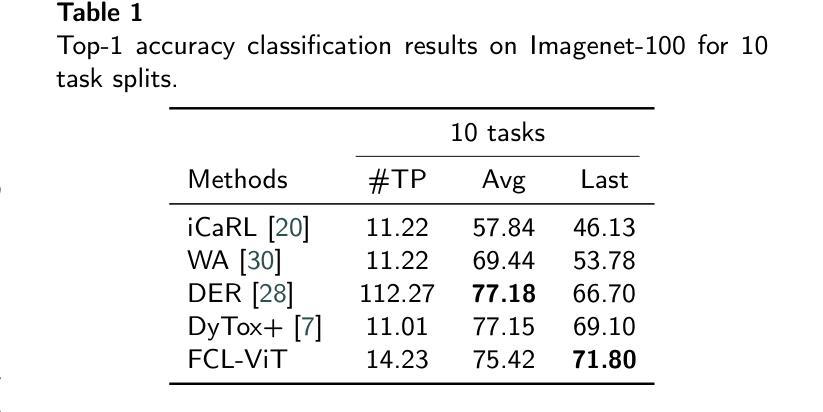
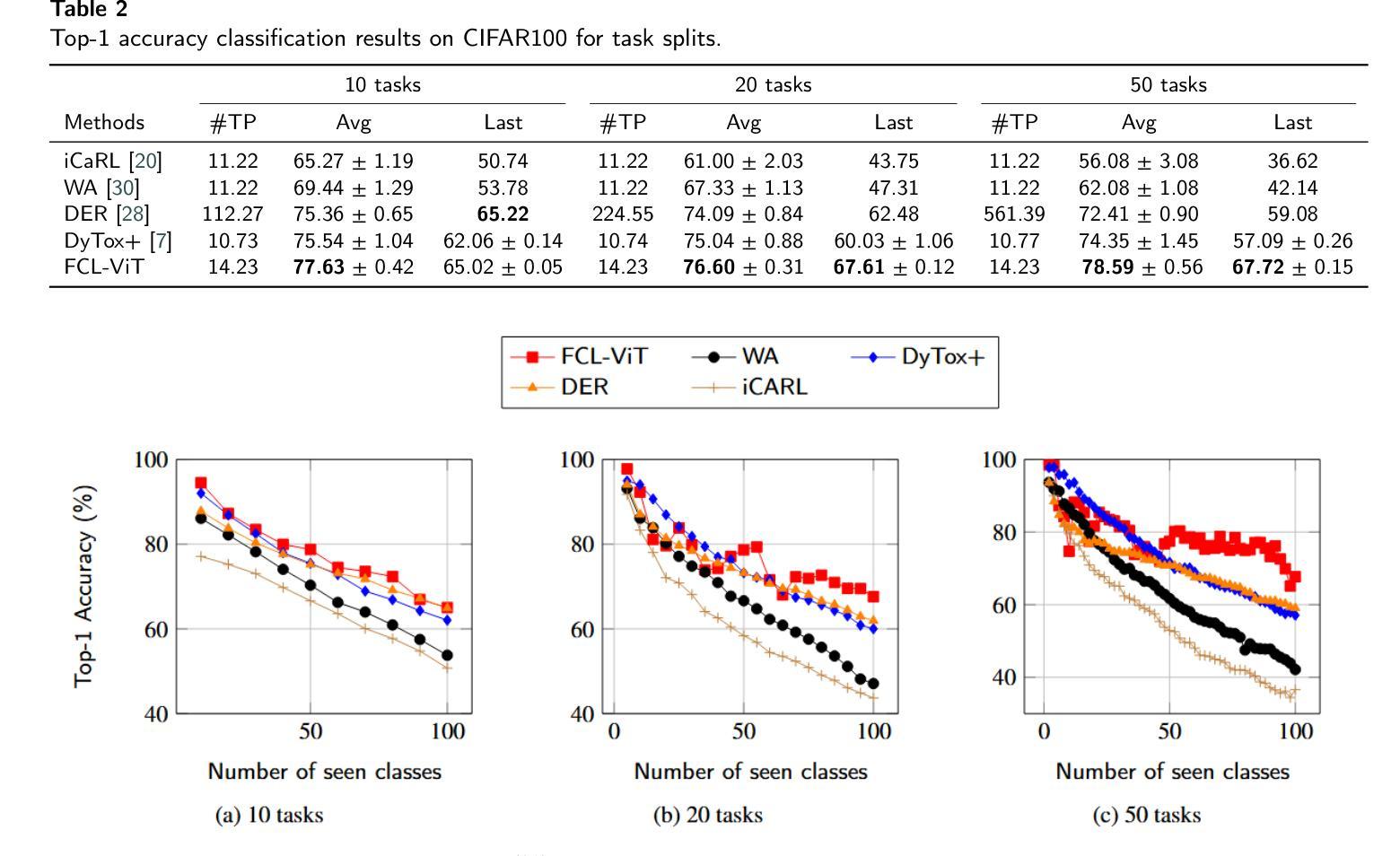
FCL-ViT: Task-Aware Attention Tuning for Continual Learning
Authors:Anestis Kaimakamidis, Ioannis Pitas
Continual Learning (CL) involves adapting the prior Deep Neural Network (DNN) knowledge to new tasks, without forgetting the old ones. However, modern CL techniques focus on provisioning memory capabilities to existing DNN models rather than designing new ones that are able to adapt according to the task at hand. This paper presents the novel Feedback Continual Learning Vision Transformer (FCL-ViT) that uses a feedback mechanism to generate real-time dynamic attention features tailored to the current task. The FCL-ViT operates in two Phases. In phase 1, the generic image features are produced and determine where the Transformer should attend on the current image. In phase 2, task-specific image features are generated that leverage dynamic attention. To this end, Tunable self-Attention Blocks (TABs) and Task Specific Blocks (TSBs) are introduced that operate in both phases and are responsible for tuning the TABs attention, respectively. The FCL-ViT surpasses state-of-the-art performance on Continual Learning compared to benchmark methods, while retaining a small number of trainable DNN parameters.
持续学习(CL)涉及将先前的深度神经网络(DNN)知识适应于新任务,同时不忘旧任务。然而,现代CL技术更注重为现有DNN模型提供记忆能力,而不是设计能够根据当前任务进行适应的新模型。本文提出了一种新型的反馈持续学习视觉转换器(FCL-ViT),它使用反馈机制生成实时动态注意力特征,这些特征针对当前任务量身定制。FCL-ViT有两个工作阶段。在阶段1中,生成通用图像特征,并确定转换器应在当前图像上关注的位置。在阶段2中,生成特定于任务的图像特征,这些特征利用动态注意力。为此,引入了可调自注意力块(TABs)和任务特定块(TSBs),它们在两个阶段中都起作用,分别负责调整TABs的注意力。与基准方法相比,FCL-ViT在持续学习方面的性能超过了最新技术水平,同时保持了较少的可训练DNN参数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种新型的反馈持续学习视觉转换器(FCL-ViT),它利用反馈机制生成针对当前任务的实时动态注意力特征。FCL-ViT分为两个阶段:第一阶段产生通用图像特征,确定转换器在当前图像上应该关注的位置;第二阶段生成特定任务的图像特征,利用动态注意力。通过引入可调自注意力块(TABs)和任务特定块(TSBs),在两个阶段中操作,分别调整TABs的注意力。FCL-ViT在持续学习方面的性能超过了现有技术,同时减少了可训练的DNN参数数量。
Key Takeaways
- FCL-ViT是一种新型的持续学习视觉转换器。
- 它利用反馈机制生成针对当前任务的实时动态注意力特征。
- FCL-ViT分为两个阶段:通用图像特征阶段和特定任务图像特征阶段。
- 引入了可调自注意力块(TABs)和任务特定块(TSBs)来操作这两个阶段。
- TABs负责生成动态注意力特征,而TSBs则负责生成特定任务的图像特征。
- FCL-ViT在持续学习方面的性能超过了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

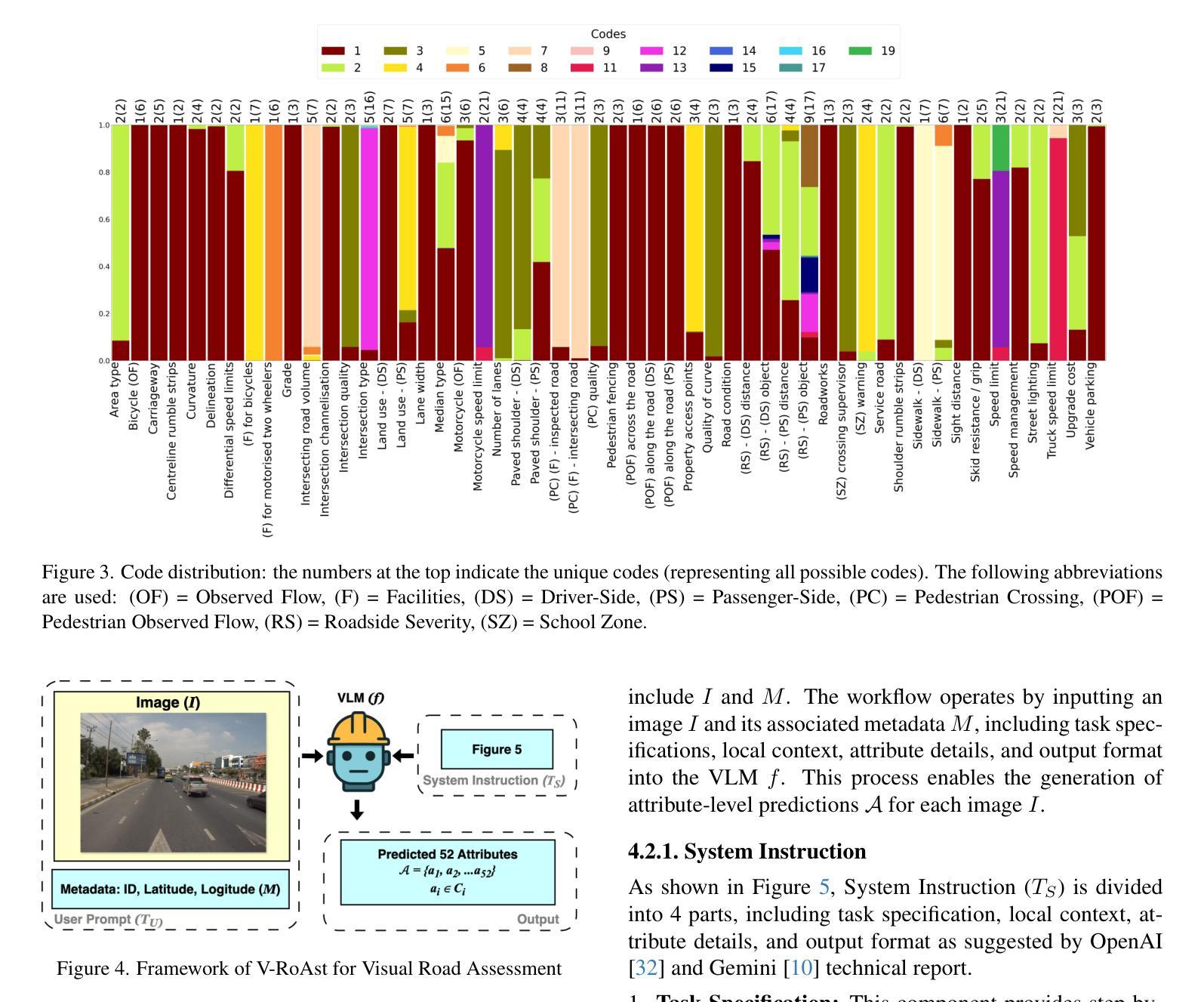
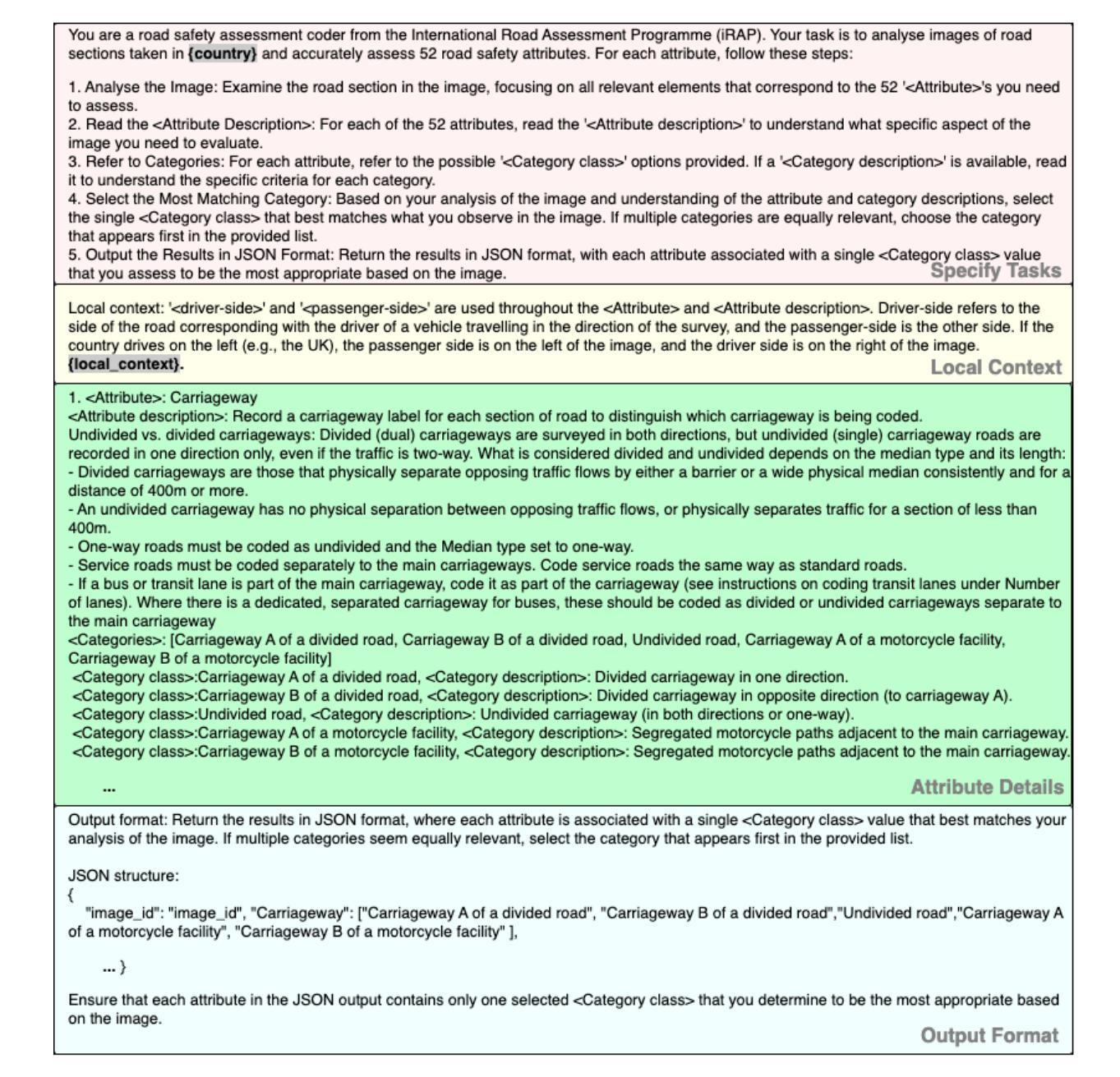
V-RoAst: Visual Road Assessment. Can VLM be a Road Safety Assessor Using the iRAP Standard?
Authors:Natchapon Jongwiriyanurak, Zichao Zeng, June Moh Goo, Xinglei Wang, Ilya Ilyankou, Kerkritt Sriroongvikrai, Nicola Christie, Meihui Wang, Huanfa Chen, James Haworth
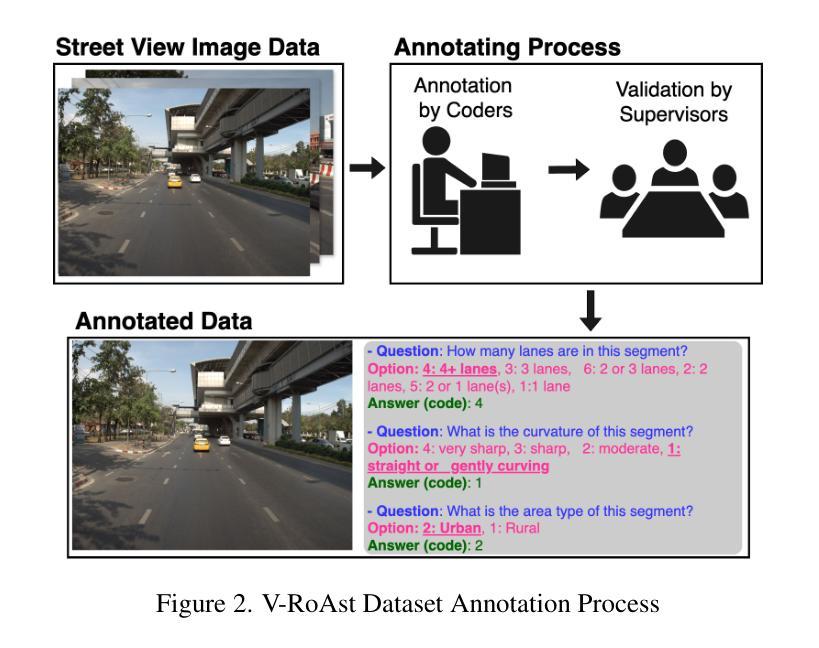
Road safety assessments are critical yet costly, especially in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), where most roads remain unrated. Traditional methods require expert annotation and training data, while supervised learning-based approaches struggle to generalise across regions. In this paper, we introduce \textit{V-RoAst}, a zero-shot Visual Question Answering (VQA) framework using Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to classify road safety attributes defined by the iRAP standard. We introduce the first open-source dataset from ThaiRAP, consisting of over 2,000 curated street-level images from Thailand annotated for this task. We evaluate Gemini-1.5-flash and GPT-4o-mini on this dataset and benchmark their performance against VGGNet and ResNet baselines. While VLMs underperform on spatial awareness, they generalise well to unseen classes and offer flexible prompt-based reasoning without retraining. Our results show that VLMs can serve as automatic road assessment tools when integrated with complementary data. This work is the first to explore VLMs for zero-shot infrastructure risk assessment and opens new directions for automatic, low-cost road safety mapping. Code and dataset: https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst.
道路安全评估至关重要,但成本高昂,特别是在中低收入国家(LMICs),那里大多数道路都未进行评估。传统方法需要专家标注和训练数据,而基于监督学习的方法在跨地区推广时面临困难。在本文中,我们介绍了使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的零样本视觉问答(VQA)框架V-RoAst,用于根据iRAP标准对道路安全属性进行分类。我们首次推出开源数据集ThaiRAP,其中包含超过2000张为此任务标注的泰国街道级图像。我们在数据集上评估了Gemini-1.5-flash和GPT-4o-mini的性能,并与VGGNet和ResNet基准测试进行了比较。虽然VLM在空间感知方面表现不佳,但它们对未见类别具有良好的泛化能力,并提供灵活的基于提示的推理而无需重新训练。我们的结果表明,当与补充数据结合时,VLM可以作为自动道路评估工具。本文首次探索了用于零样本基础设施风险评估的VLM,为自动、低成本的道路安全地图绘制开辟了新的方向。代码和数据集:https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种基于零样本的视觉问答框架V-RoAst,利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)对道路安全属性进行分类。该研究引入了ThaiRAP的首个开源数据集,包含超过2000张针对此任务标注的泰国街头图像。评估了Gemini-1.5-flash和GPT-4o-mini在该数据集上的性能,与VGGNet和ResNet基准测试相比,VLMs在空间感知方面表现不佳,但在未见类别上具有良好的泛化能力,并提供灵活的基于提示的推理而无需重新训练。研究结果表明,将VLMs与补充数据相结合可作为自动道路评估工具。本研究是首次探索用于零样本基础设施风险评估的VLMs,为自动、低成本道路安全映射开辟了新方向。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新的零样本视觉问答框架V-RoAst,用于道路安全属性的分类。
- 引入了ThaiRAP的首个开源数据集,包含标注的泰国街头图像,为道路安全评估提供数据支持。
- 评估了多种模型在数据集上的性能,发现VLMs在空间感知方面相对较弱。
- VLMs在未见类别上具有良好的泛化能力,并能提供灵活的基于提示的推理。
- 结合补充数据,VLMs可作为自动道路评估工具。
- 本研究是首次探索将VLMs应用于零样本基础设施风险评估。
点此查看论文截图

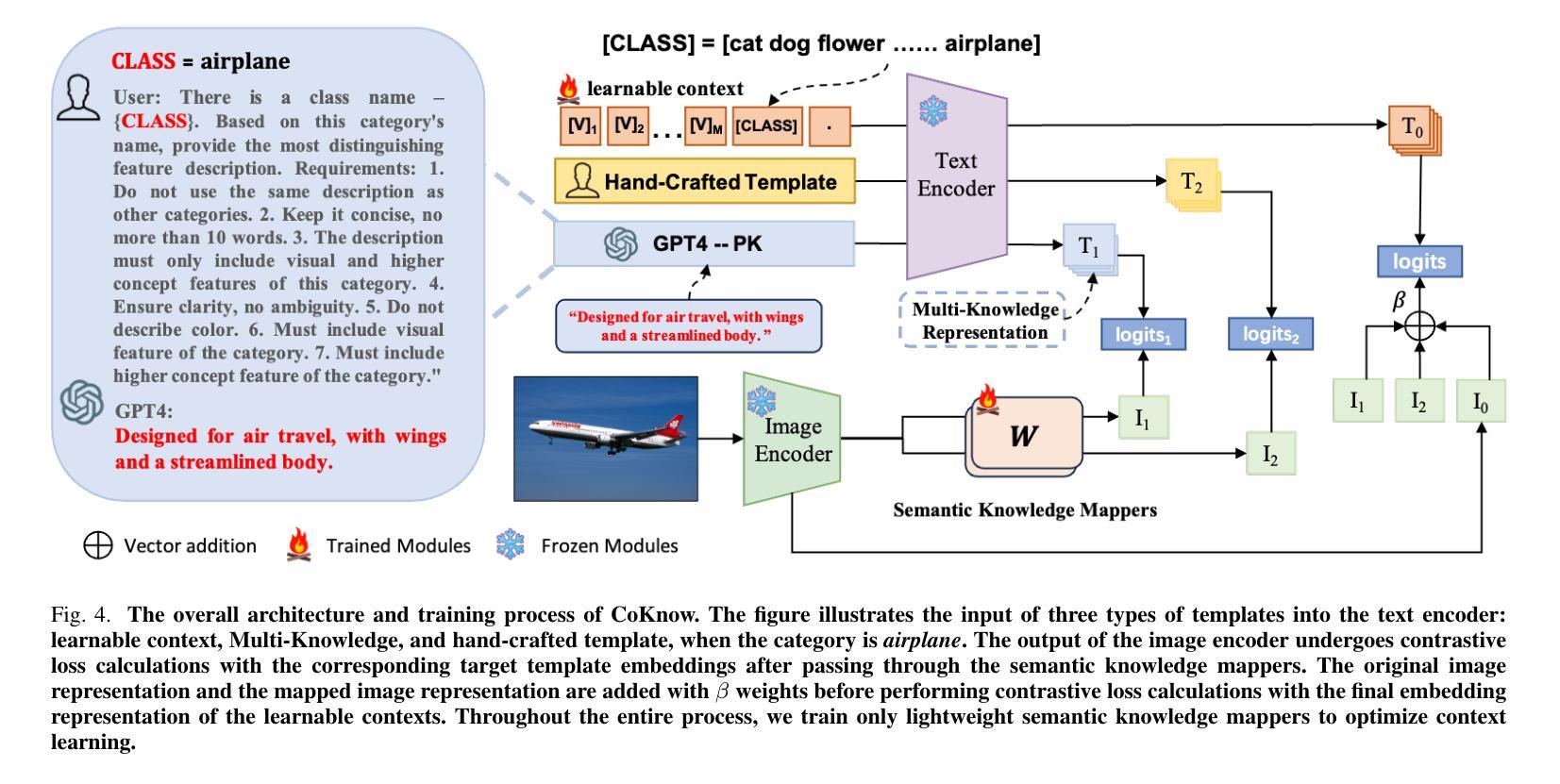
Optimization of Prompt Learning via Multi-Knowledge Representation for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Enming Zhang, Bingke Zhu, Yingying Chen, Qinghai Miao, Ming Tang, Jinqiao Wang
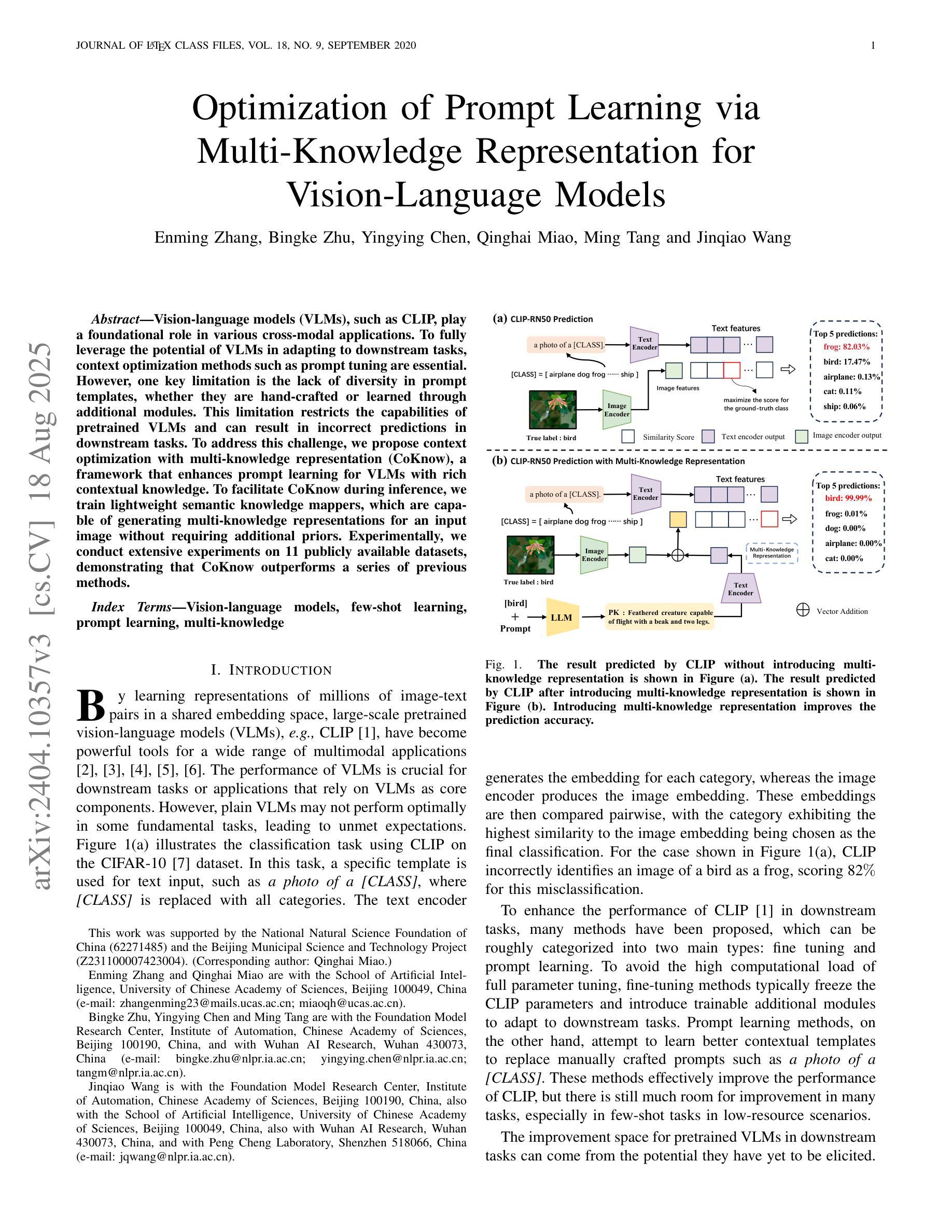
Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as CLIP, play a foundational role in various cross-modal applications. To fully leverage VLMs’ potential in adapting to downstream tasks, context optimization methods like Prompt Tuning are essential. However, one key limitation is the lack of diversity in prompt templates, whether they are hand-crafted or learned through additional modules. This limitation restricts the capabilities of pretrained VLMs and can result in incorrect predictions in downstream tasks. To address this challenge, we propose Context Optimization with Multi-Knowledge Representation (CoKnow), a framework that enhances Prompt Learning for VLMs with rich contextual knowledge. To facilitate CoKnow during inference, we trained lightweight semantic knowledge mappers, which are capable of generating Multi-Knowledge Representation for an input image without requiring additional priors. Experimentally, We conducted extensive experiments on 11 publicly available datasets, demonstrating that CoKnow outperforms a series of previous methods.
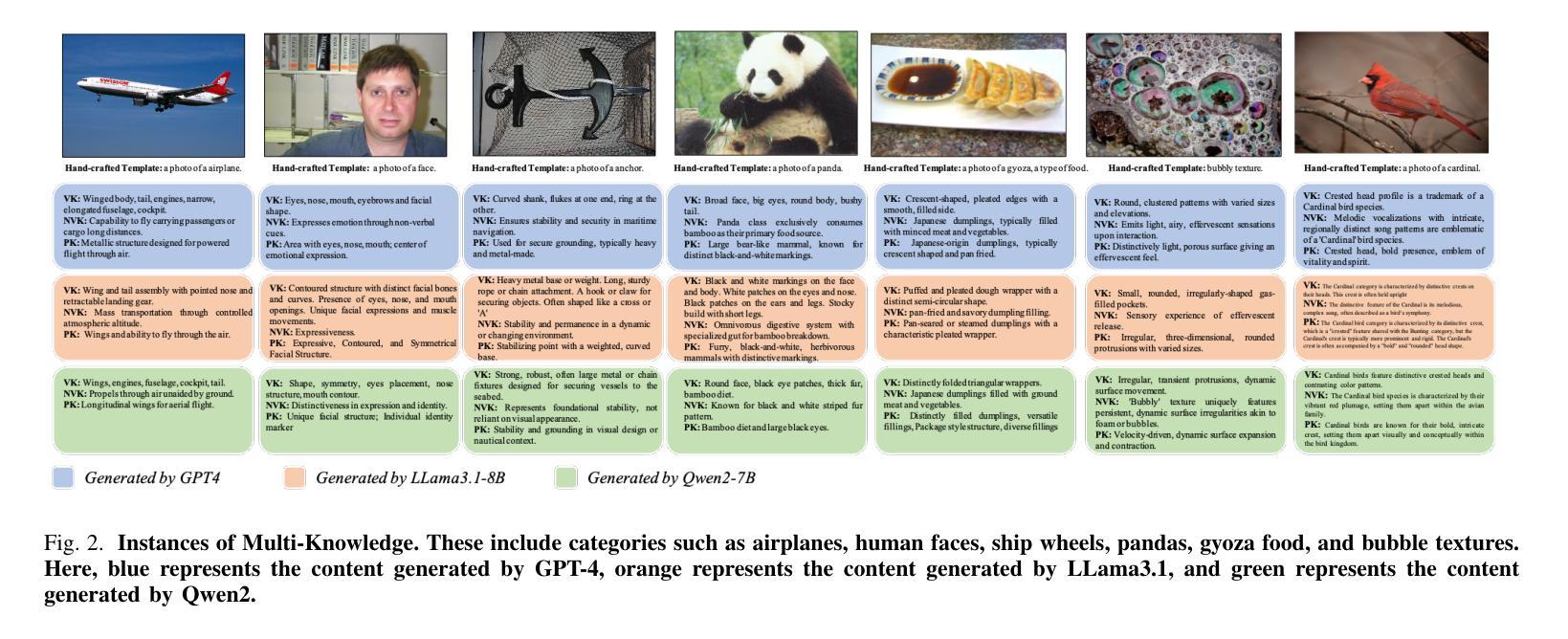
视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在各种跨模态应用中发挥着基础性的作用。为了充分利用视觉语言模型适应下游任务的潜力,语境优化方法(如提示微调)至关重要。然而,一个关键的局限性在于提示模板的缺乏多样性,无论是手工制作的,还是通过附加模块学习的。这一局限性限制了预训练视觉语言模型的能力,并可能导致下游任务预测错误。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了基于多知识表示的语境优化(CoKnow)框架,该框架通过丰富的上下文知识增强视觉语言模型的提示学习。为了在推理过程中促进CoKnow的应用,我们训练了轻量级的语义知识映射器,它们能够为输入图像生成多知识表示,而无需额外的先验知识。通过实验,我们在11个公开数据集上进行了大量实验,证明了CoKnow优于一系列之前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在跨模态应用中的重要作用,以及针对其局限性提出的改进方案。为提高预训练VLMs在下游任务中的适应能力,作者提出了使用多知识表示(CoKnow)框架来增强提示学习的方法。CoKnow通过训练轻量级语义知识映射器,能够在不需要额外先验知识的情况下为输入图像生成多知识表示。实验结果显示,CoKnow在多个公开数据集上的表现优于一系列先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在多模态应用中发挥重要作用,但仍面临在下游任务中的适应性问题。
- 提示学习是一种解决该问题的方法,但现有的提示模板缺乏多样性限制了其效果。
- 作者提出了使用多知识表示(CoKnow)框架来增强提示学习,丰富语境知识。
- CoKnow训练了轻量级语义知识映射器,无需额外先验知识即可生成多知识表示。
- CoKnow在不同数据集上的表现优于先前的方法。
- 多知识表示能提高模型对图像的理解和预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图