⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
ASDFormer: A Transformer with Mixtures of Pooling-Classifier Experts for Robust Autism Diagnosis and Biomarker Discovery
Authors:Mohammad Izadi, Mehran Safayani
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition marked by disruptions in brain connectivity. Functional MRI (fMRI) offers a non-invasive window into large-scale neural dynamics by measuring blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signals across the brain. These signals can be modeled as interactions among Regions of Interest (ROIs), which are grouped into functional communities based on their underlying roles in brain function. Emerging evidence suggests that connectivity patterns within and between these communities are particularly sensitive to ASD-related alterations. Effectively capturing these patterns and identifying interactions that deviate from typical development is essential for improving ASD diagnosis and enabling biomarker discovery. In this work, we introduce ASDFormer, a Transformer-based architecture that incorporates a Mixture of Pooling-Classifier Experts (MoE) to capture neural signatures associated with ASD. By integrating multiple specialized expert branches with attention mechanisms, ASDFormer adaptively emphasizes different brain regions and connectivity patterns relevant to autism. This enables both improved classification performance and more interpretable identification of disorder-related biomarkers. Applied to the ABIDE dataset, ASDFormer achieves state-of-the-art diagnostic accuracy and reveals robust insights into functional connectivity disruptions linked to ASD, highlighting its potential as a tool for biomarker discovery.
自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)是一种复杂的神经发育性疾病,表现为大脑连接性的中断。功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)通过测量全脑的血氧水平依赖(BOLD)信号,为非侵入性地观察大规模神经动态提供了窗口。这些信号可以建模为感兴趣区域(ROI)之间的相互作用,这些区域根据其在脑功能中的基础作用被分组为功能社区。越来越多的证据表明,这些社区内部和之间的连接模式对ASD相关改变特别敏感。有效地捕捉这些模式并识别偏离典型发展的相互作用对于提高ASD诊断和治疗、促进生物标志物发现至关重要。在这项工作中,我们引入了ASDFormer,这是一种基于Transformer的架构,它结合了混合池化分类专家(MoE)来捕捉与ASD相关的神经特征。通过整合多个具有注意力机制的专门专家分支,ASDFormer自适应地强调与自闭症相关的不同大脑区域和连接模式。这既提高了分类性能,也提高了识别与疾病相关的生物标志物的解释性。应用于ABIDE数据集,ASDFormer达到了最先进的诊断准确性,并揭示了与ASD相关的功能性连接中断的稳健见解,突出了其作为生物标志物发现工具的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)是一种复杂的神经发育性疾病,表现为大脑连接性中断。功能磁共振成像(fMRI)通过测量大脑中的血氧水平依赖信号(BOLD信号)来观察大规模神经动态,为ASD相关的脑功能研究提供了非侵入性窗口。这项研究引入了一种基于Transformer的架构——ASDFormer,结合混合池化分类专家(MoE)来捕捉与ASD相关的神经特征。ASDFormer通过集成多个专业专家分支和注意力机制,自适应地强调与自闭症相关的不同大脑区域和连接模式,从而提高分类性能并更可解释地识别与疾病相关的生物标志物。
Key Takeaways
- 自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)是一种神经发育性疾病,涉及大脑连接性的中断。
- 功能磁共振成像(fMRI)是研究ASD脑功能的重要非侵入性工具。
- ASDFormer是一个基于Transformer的架构,用于捕捉与ASD相关的神经特征。
- MoE(混合池化分类专家)在ASDFormer中用于增强分类性能和识别疾病相关生物标志物的可解释性。
- ASDFormer通过自适应强调与自闭症相关的不同大脑区域和连接模式来提高诊断准确性。
- 在ABIDE数据集上应用ASDFormer达到了先进的诊断准确性。
点此查看论文截图

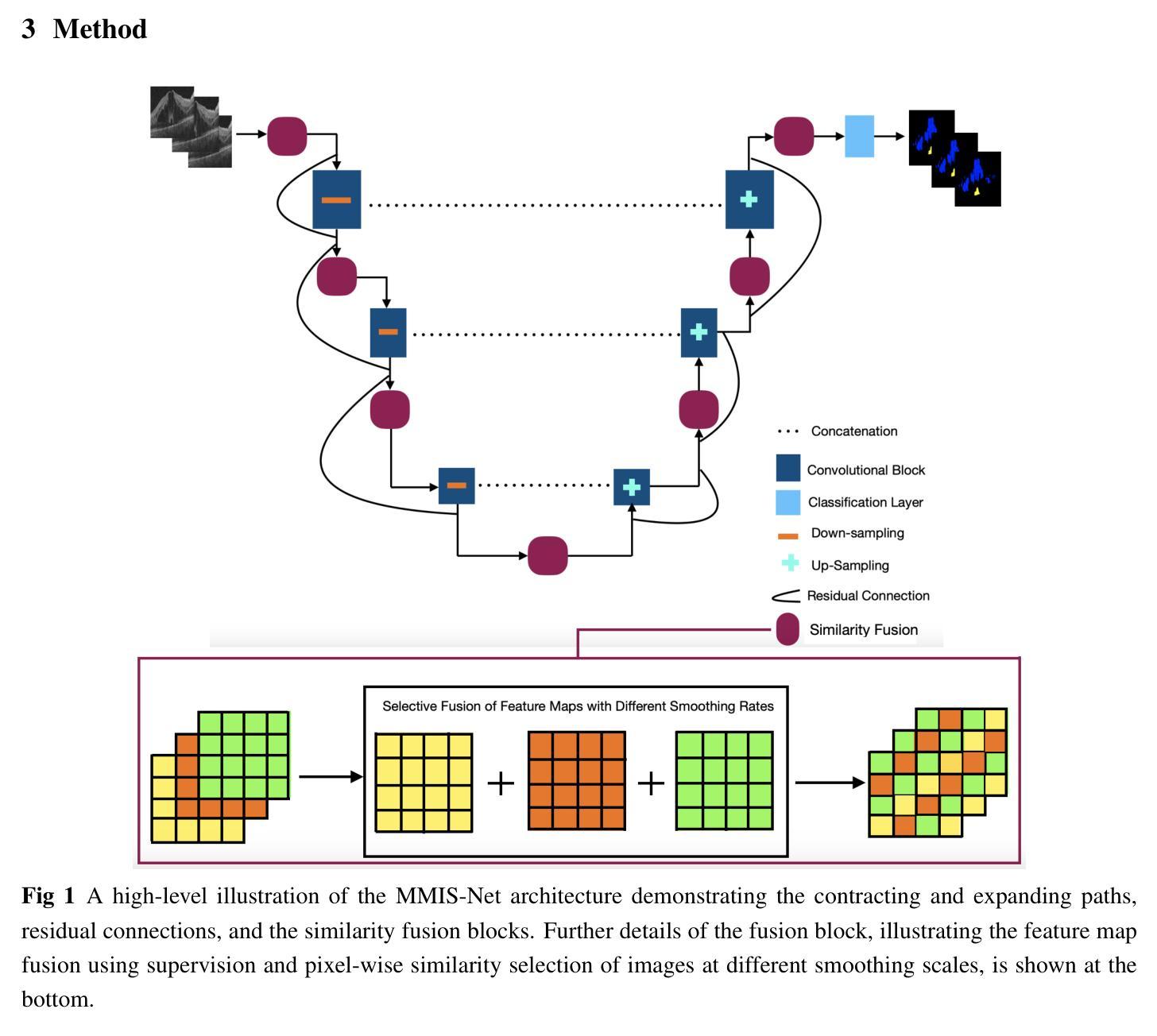
MMIS-Net for Retinal Fluid Segmentation and Detection
Authors:Nchongmaje Ndipenocha, Alina Mirona, Kezhi Wanga, Yongmin Li
Purpose: Deep learning methods have shown promising results in the segmentation, and detection of diseases in medical images. However, most methods are trained and tested on data from a single source, modality, organ, or disease type, overlooking the combined potential of other available annotated data. Numerous small annotated medical image datasets from various modalities, organs, and diseases are publicly available. In this work, we aim to leverage the synergistic potential of these datasets to improve performance on unseen data. Approach: To this end, we propose a novel algorithm called MMIS-Net (MultiModal Medical Image Segmentation Network), which features Similarity Fusion blocks that utilize supervision and pixel-wise similarity knowledge selection for feature map fusion. Additionally, to address inconsistent class definitions and label contradictions, we created a one-hot label space to handle classes absent in one dataset but annotated in another. MMIS-Net was trained on 10 datasets encompassing 19 organs across 2 modalities to build a single model. Results: The algorithm was evaluated on the RETOUCH grand challenge hidden test set, outperforming large foundation models for medical image segmentation and other state-of-the-art algorithms. We achieved the best mean Dice score of 0.83 and an absolute volume difference of 0.035 for the fluids segmentation task, as well as a perfect Area Under the Curve of 1 for the fluid detection task. Conclusion: The quantitative results highlight the effectiveness of our proposed model due to the incorporation of Similarity Fusion blocks into the network’s backbone for supervision and similarity knowledge selection, and the use of a one-hot label space to address label class inconsistencies and contradictions.
目的:深度学习在医学图像的分割和疾病检测方面已经取得了有前景的结果。然而,大多数方法都是在单一来源、模态、器官或疾病类型的数据上进行训练和测试的,忽略了其他可用注释数据的综合潜力。许多来自不同模态、器官和疾病的小型注释医学图像数据集都是公开发布的。在这项工作中,我们的目标是利用这些数据集的协同潜力来提高未见数据的性能。方法:为此,我们提出了一种新型算法MMIS-Net(多模态医学图像分割网络),它采用Similarity Fusion块,利用监督和像素级相似性知识选择进行特征图融合。此外,为了解决类定义不一致和标签矛盾的问题,我们创建了一个独热标签空间来处理在一个数据集中缺失但在另一个数据集中有注释的类。MMIS-Net在涵盖2种模态、涉及19个器官的10个数据集上进行训练,以构建单个模型。结果:该算法在RETOUCH挑战赛隐藏的测试集上进行了评估,在医学图像分割方面优于大型基础模型和其他最先进的算法。在流体分割任务中,我们获得了最佳的平均Dice得分0.83和绝对体积差异0.035;在流体检测任务中,我们获得了完美的曲线下面积1。结论:定量结果突出了我们提出的模型的有效性,这是由于将Similarity Fusion块集成到网络的主干中进行监督和相似性知识选择,以及使用独热标签空间来解决标签类的不一致性和矛盾。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度学习在医学图像分割和疾病检测方面展现出巨大潜力,但大多数方法仅针对单一来源、模态、器官或疾病类型的数据进行训练和测试,忽略了其他可用标注数据的潜力。本研究旨在利用多模态医学图像数据集的协同潜力来提高未见数据的性能。为此,我们提出了一种新型算法MMIS-Net(多模态医学图像分割网络),采用相似度融合块,利用监督信息和像素级相似度知识选择进行特征图融合。为解决类别定义不一致和标签矛盾问题,我们创建了一个独热标签空间来处理某一数据集缺失但另一数据集中已标注的类别。MMIS-Net在涵盖两种模态、涉及19个器官的10个数据集上进行训练,建立单一模型。算法在RETOUCH挑战赛隐藏测试集上的表现优于医学图像分割的大型基础模型和其他先进算法。在流体分割任务中,我们获得了最佳的平均Dice系数0.83和绝对体积差异0.035,以及在流体检测任务中完美的曲线下面积1。结论:定量结果突显了我们提出的模型的有效性,得益于网络主干中融入相似度融合块进行监督和相似度知识选择,以及使用独热标签空间解决标签类别不一致和矛盾问题。
关键见解
- 深度学习在医学图像分割和疾病检测中具有巨大潜力,但需跨多源数据提升性能。
- 提出MMIS-Net算法,融合多模态医学图像数据以提高未见数据性能。
- MMIS-Net采用相似度融合块,利用监督信息和像素级相似度知识选择进行特征图融合。
- 为解决类别定义不一致和标签矛盾问题,创建独热标签空间。
- MMIS-Net在涵盖多种模态、器官和数据集的广泛实验上表现出卓越性能。
- 在RETOUCH挑战赛隐藏测试集上,MMIS-Net表现优于其他先进算法。
- 定量结果突显MMIS-Net的有效性,特别是在流体分割和检测任务上。
点此查看论文截图

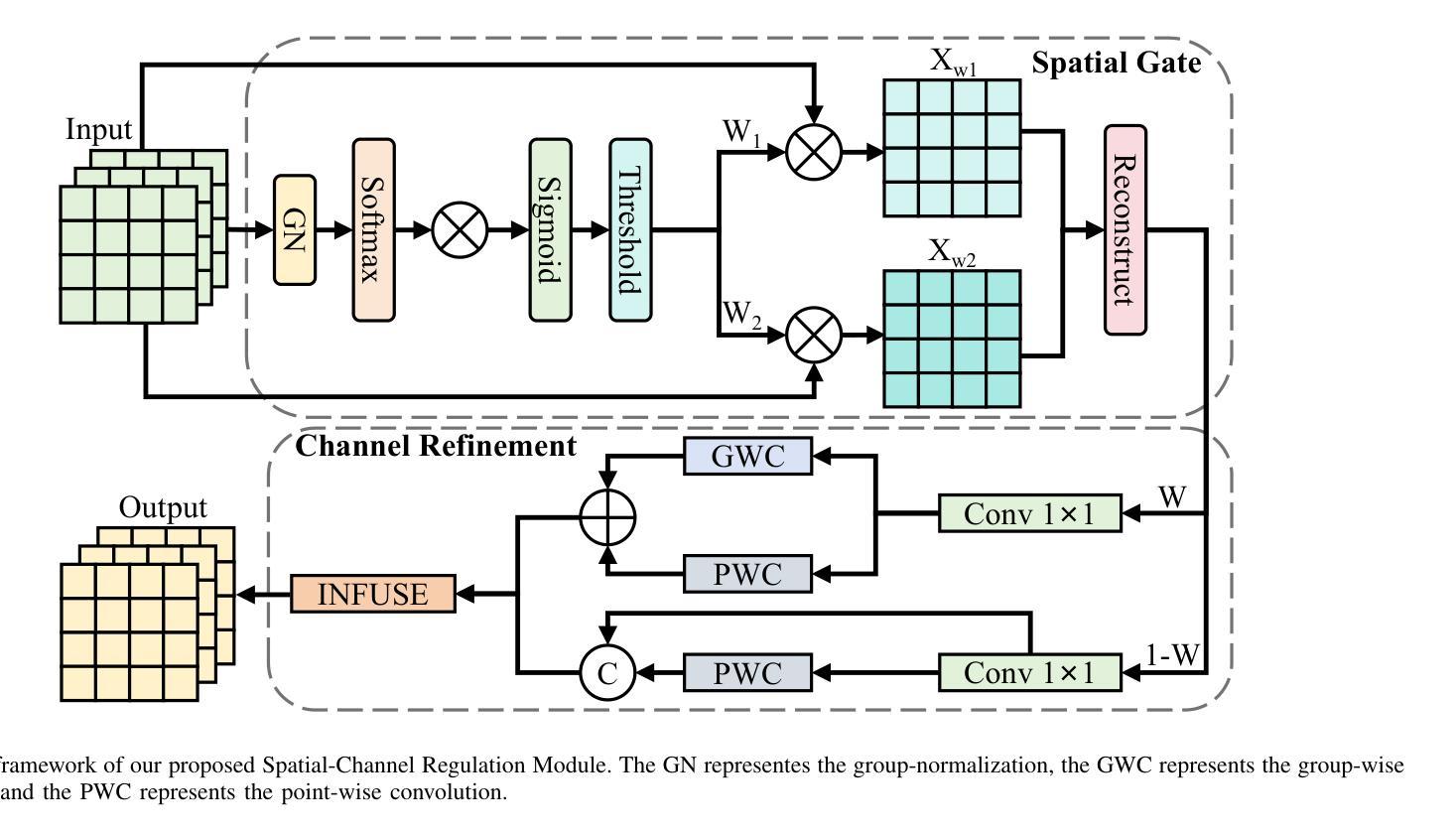
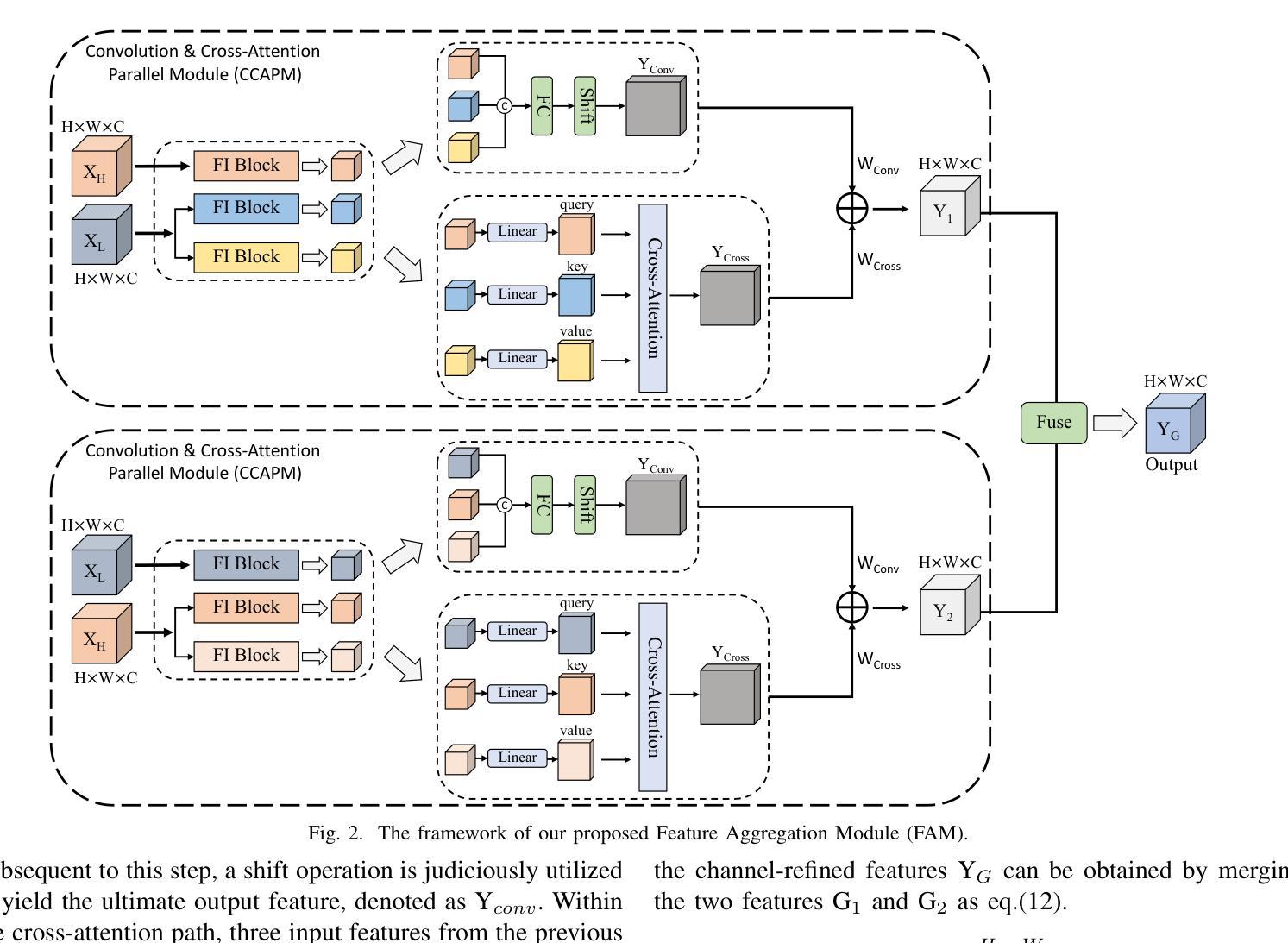
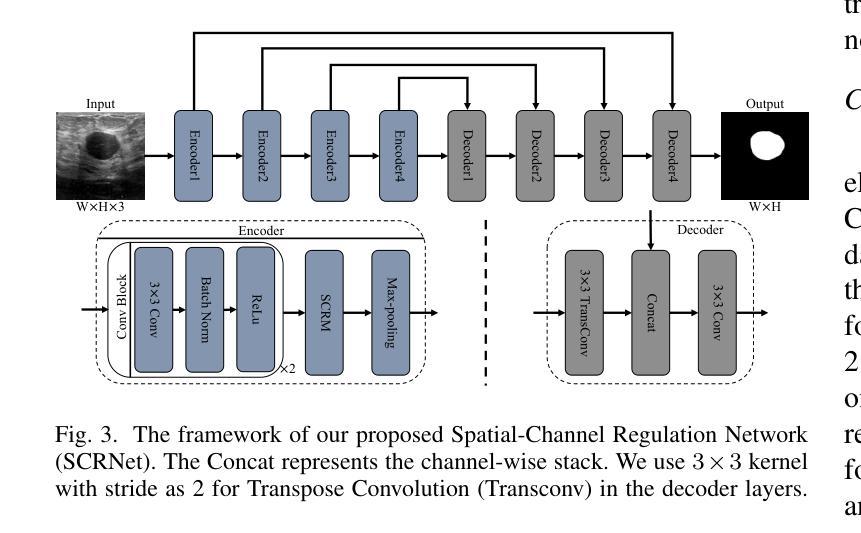
SCRNet: Spatial-Channel Regulation Network for Medical Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Weixin Xu, Ziliang Wang
Medical ultrasound image segmentation presents a formidable challenge in the realm of computer vision. Traditional approaches rely on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformer-based methods to address the intricacies of medical image segmentation. Nevertheless, inherent limitations persist, as CNN-based methods tend to disregard long-range dependencies, while Transformer-based methods may overlook local contextual information. To address these deficiencies, we propose a novel Feature Aggregation Module (FAM) designed to process two input features from the preceding layer. These features are seamlessly directed into two branches of the Convolution and Cross-Attention Parallel Module (CCAPM) to endow them with different roles in each of the two branches to help establish a strong connection between the two input features. This strategy enables our module to focus concurrently on both long-range dependencies and local contextual information by judiciously merging convolution operations with cross-attention mechanisms. Moreover, by integrating FAM within our proposed Spatial-Channel Regulation Module (SCRM), the ability to discern salient regions and informative features warranting increased attention is enhanced. Furthermore, by incorporating the SCRM into the encoder block of the UNet architecture, we introduce a novel framework dubbed Spatial-Channel Regulation Network (SCRNet). The results of our extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of SCRNet, which consistently achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to existing methods.
医学超声图像分割是计算机视觉领域的一个巨大挑战。传统的方法依赖于卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于Transformer的方法来解决医学图像分割的复杂性。然而,仍然存在固有的局限性,因为基于CNN的方法往往忽略了长期依赖关系,而基于Transformer的方法可能会忽视局部上下文信息。为了解决这些不足,我们提出了一种新型的特征聚合模块(FAM),用于处理来自前一层的两个输入特征。这些特征被无缝地引导到卷积和交叉注意并行模块(CCAPM)的两个分支中,在每个分支中赋予它们不同的角色,有助于建立两个输入特征之间的强连接。这一策略使我们的模块能够并专注于长期依赖关系和局部上下文信息,通过将卷积操作与交叉注意机制进行明智的融合。此外,通过将FAM集成在我们提出的空间通道调节模块(SCRM)中,增强了识别值得更多关注的显著区域和特征的能力。此外,通过将SCRM融入UNet架构的编码器块中,我们引入了一个名为空间通道调节网络(SCRNet)的新型框架。我们的广泛实验结果表明,SCRNet具有卓越的性能,与现有方法相比,始终达到最新水平(SOTA)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pagegs
Summary
医学超声图像分割是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战。传统方法主要依赖卷积神经网络和基于Transformer的方法,但仍存在CNN忽略长距离依赖和Transformer忽略局部上下文信息的局限性。为此,提出一种新型特征聚合模块(FAM),该模块能够处理来自前一层的两个输入特征,并通过卷积和交叉注意力并行模块(CCAPM)的两个分支赋予它们不同的角色,从而建立两个输入特征之间的强连接。此外,通过将FAM与空间通道调节模块(SCRM)集成,提高了辨别重要区域和需要更多关注的信息特征的能力。再将SCRM引入UNet架构的编码器块中,提出一种名为空间通道调节网络(SCRNet)的新型框架。实验结果表明,SCRNet性能卓越,与现有方法相比持续达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
1. 医学超声图像分割是计算机视觉领域的挑战。
2. 传统方法依赖CNN和Transformer,但存在局限性。
3. 新型特征聚合模块(FAM)能处理两个输入特征,建立强连接。
4. FAM结合卷积和交叉注意力机制,同时关注长距离依赖和局部上下文信息。
5. 空间通道调节模块(SCRM)增强辨别重要区域和信息特征的能力。
6. 将SCRM引入UNet架构,形成新型框架SCRNet。
点此查看论文截图

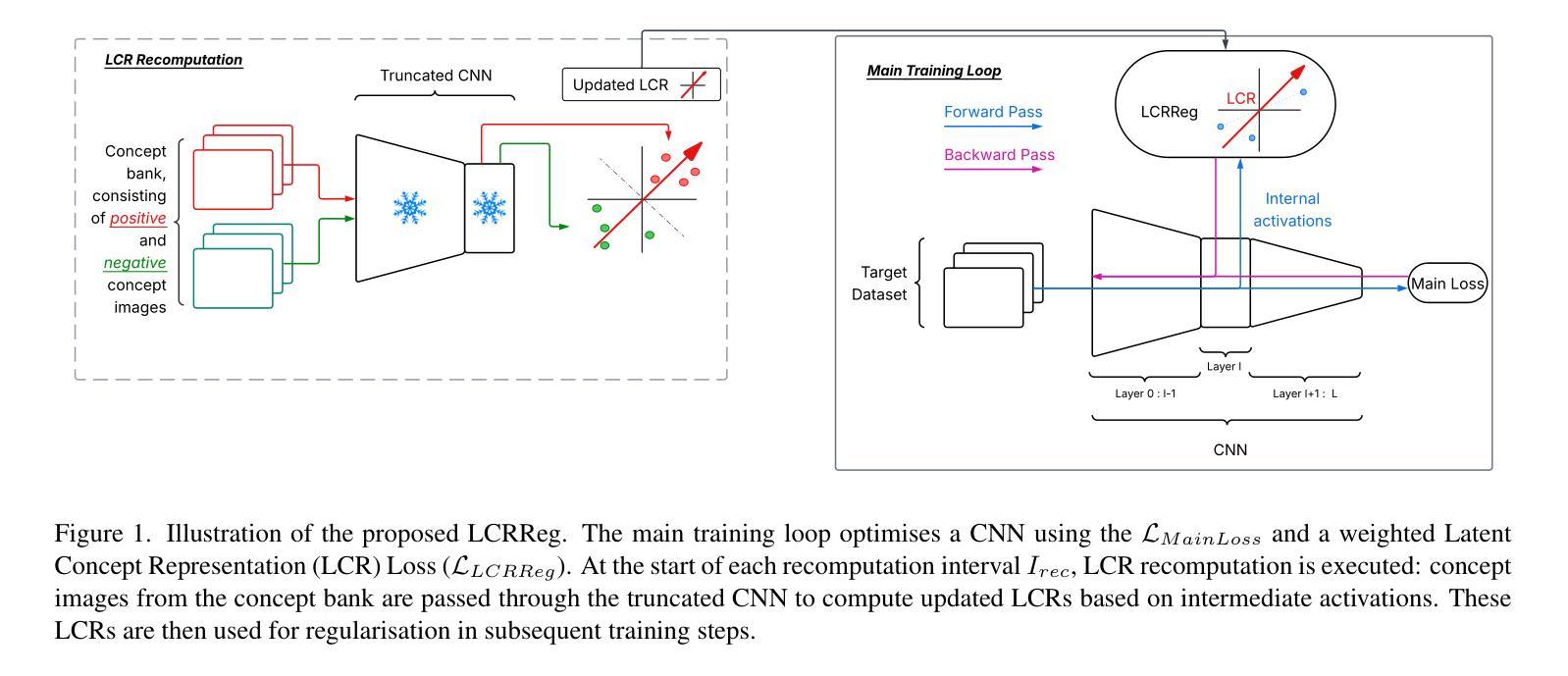
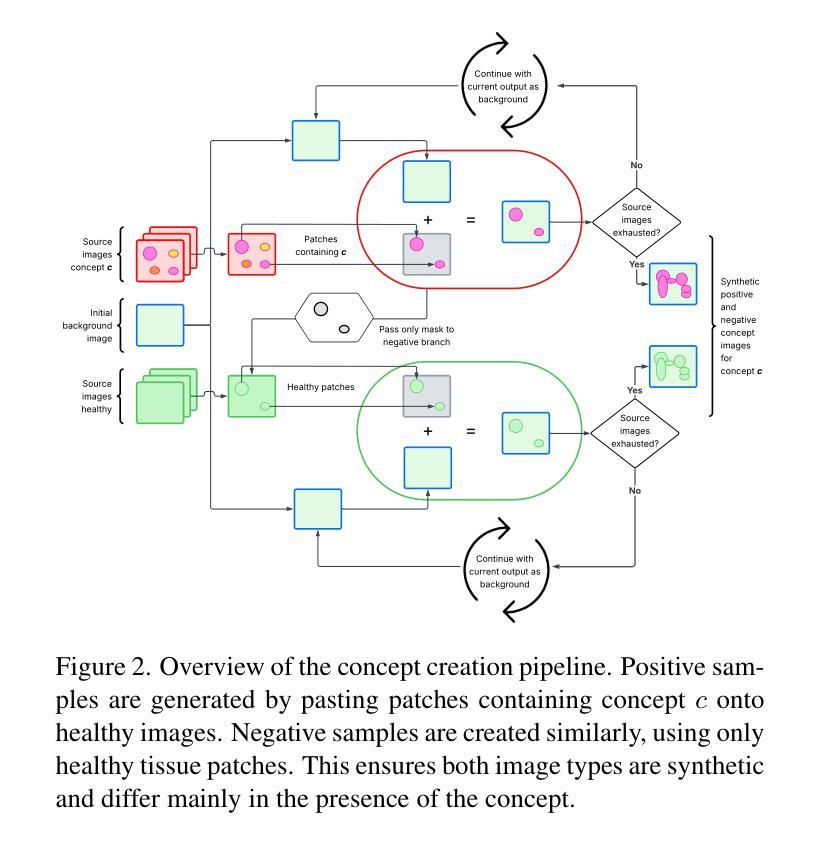
In-hoc Concept Representations to Regularise Deep Learning in Medical Imaging
Authors:Valentina Corbetta, Floris Six Dijkstra, Regina Beets-Tan, Hoel Kervadec, Kristoffer Wickstrøm, Wilson Silva
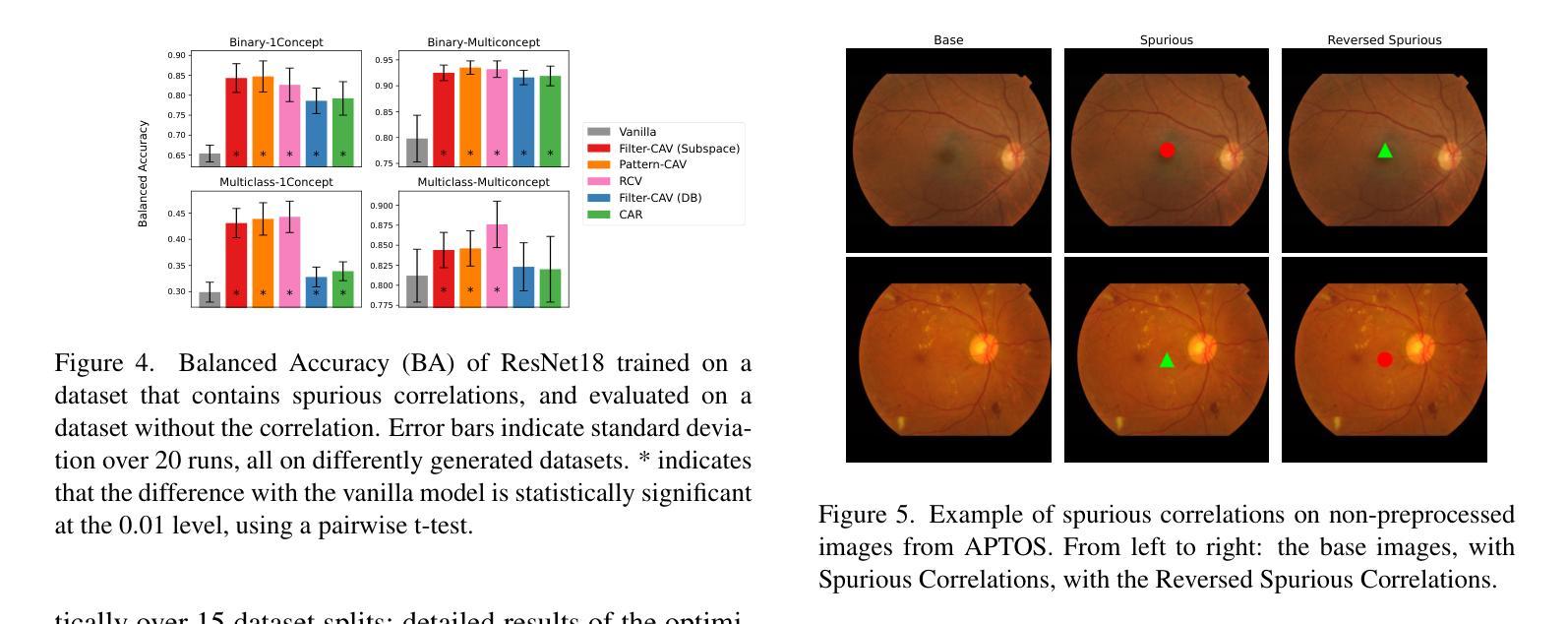
Deep learning models in medical imaging often achieve strong in-distribution performance but struggle to generalise under distribution shifts, frequently relying on spurious correlations instead of clinically meaningful features. We introduce LCRReg, a novel regularisation approach that leverages Latent Concept Representations (LCRs) (e.g., Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs)) to guide models toward semantically grounded representations. LCRReg requires no concept labels in the main training set and instead uses a small auxiliary dataset to synthesise high-quality, disentangled concept examples. We extract LCRs for predefined relevant features, and incorporate a regularisation term that guides a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to activate within latent subspaces associated with those concepts. We evaluate LCRReg across synthetic and real-world medical tasks. On a controlled toy dataset, it significantly improves robustness to injected spurious correlations and remains effective even in multi-concept and multiclass settings. On the diabetic retinopathy binary classification task, LCRReg enhances performance under both synthetic spurious perturbations and out-of-distribution (OOD) generalisation. Compared to baselines, including multitask learning, linear probing, and post-hoc concept-based models, LCRReg offers a lightweight, architecture-agnostic strategy for improving model robustness without requiring dense concept supervision. Code is available at the following link: https://github.com/Trustworthy-AI-UU-NKI/lcr\_regularization
在医学成像领域,深度学习模型往往能在内部数据分布上表现强劲,但在数据分布发生变化时却难以推广,经常依赖于偶然的关联而非具有临床意义的特征。我们引入了LCRReg,这是一种新型正则化方法,它利用潜在概念表示(LCRs)(例如概念激活向量(CAVs))来引导模型走向语义基础表示。LCRReg不需要主训练集中的概念标签,而是使用一个小型辅助数据集来合成高质量、解纠缠的概念示例。我们为预定义的相关特征提取LCRs,并引入一个正则化项,该正则化项可以引导卷积神经网络(CNN)在与这些概念相关的潜在子空间内激活。我们在合成和现实世界医学任务上评估了LCRReg。在一个受控的玩具数据集上,它显著提高了对注入的偶然关联的鲁棒性,即使在多概念和多类别环境中也依然有效。在糖尿病视网膜病变二分类任务中,LCRReg在合成偶然扰动和分布外(OOD)泛化的情况下提高了性能。与多任务学习、线性探测和后续概念模型等基线相比,LCRReg提供了一种轻便、架构中立的策略,可在不需要密集概念监督的情况下提高模型的稳健性。相关代码可在以下链接中找到:https://github.com/Trustworthy-AI-UU-NKI/lcr_regularization
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 13 figures, 2 tables, accepted at PHAROS-AFE-AIMI Workshop in conjunction with the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025. This is the submitted manuscript with added link to the github repo, funding acknowledgments and author names and affiliations, and a correction to numbers in Table 1. Final version not published yet
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的深度学习模型正则化方法LCRReg,该方法利用潜在概念表示(LCRs)引导模型学习语义化的特征表示,从而提高医学成像模型的通用性和稳健性。LCRReg通过利用辅助数据集合成高质量、解纠缠的概念示例来提取预定义的相关特征,并通过正则化项引导卷积神经网络(CNN)在相关概念的潜在子空间中进行激活。在合成和真实世界医学任务上的评估表明,LCRReg在应对注入的虚假关联和跨概念、跨类别的设置下,都能显著提高模型的稳健性。此外,在糖尿病视网膜病变的二分类任务中,LCRReg在应对合成虚假扰动和跨分布(OOD)泛化时,也增强了模型的性能。相比于多任务学习、线性探测和后验概念模型等基线方法,LCRReg提供了一种轻便、结构无关的策略,可在无需密集概念监督的情况下提高模型的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- LCRReg是一种新型的深度学习模型正则化方法,旨在提高医学成像模型的通用性和稳健性。
- LCRReg利用潜在概念表示(LCRs)来引导模型学习语义化的特征表示。
- LCRReg通过利用辅助数据集合成高质量、解纠缠的概念示例来提取预定义的相关特征。
- LCRReg通过正则化项引导卷积神经网络(CNN)在相关概念的潜在子空间中进行激活。
- 在合成和真实世界医学任务上的评估表明,LCRReg能显著提高模型的稳健性,特别是在处理虚假关联和跨类别问题时。
- 在糖尿病视网膜病变分类任务中,LCRReg增强了模型的性能,特别是在应对合成虚假扰动和跨分布泛化时。
点此查看论文截图

Improving Deep Learning for Accelerated MRI With Data Filtering
Authors:Kang Lin, Anselm Krainovic, Kun Wang, Reinhard Heckel
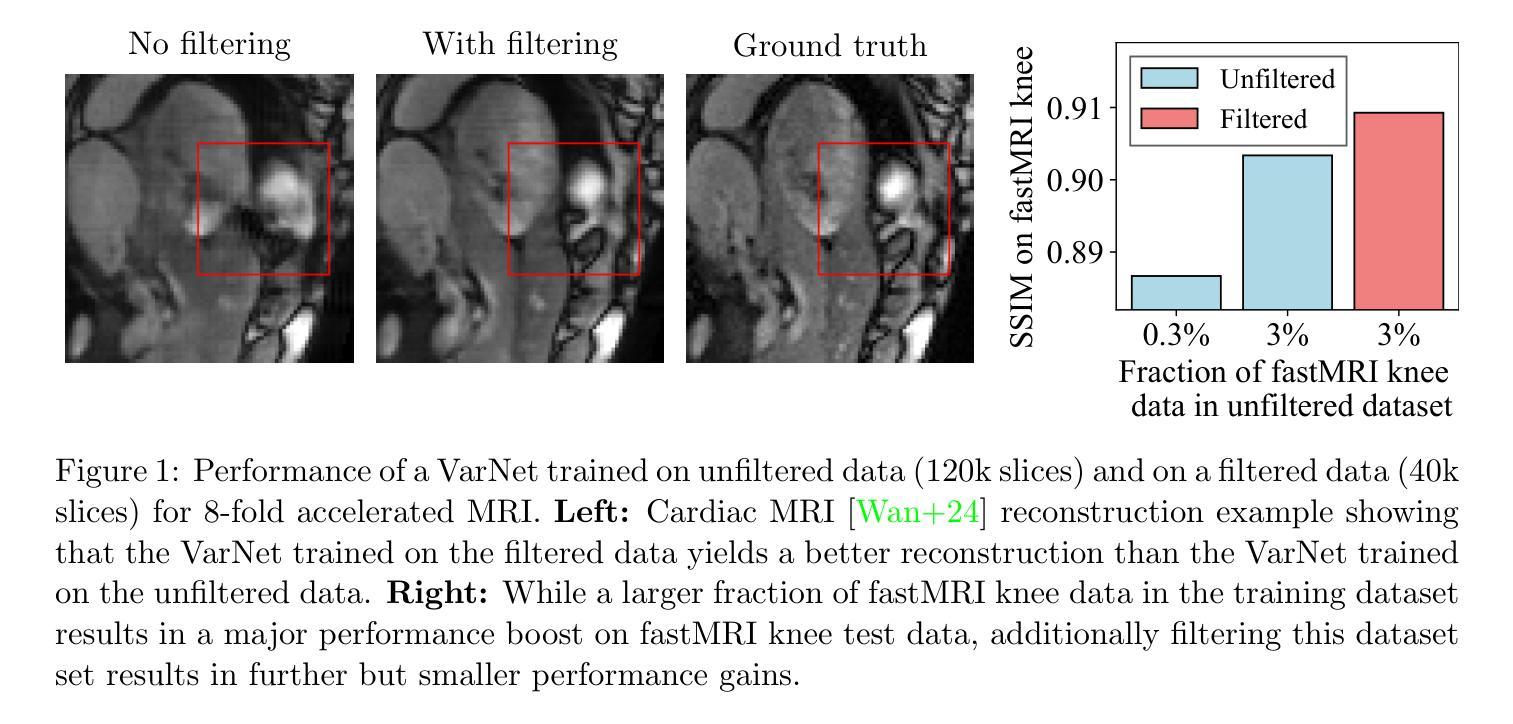
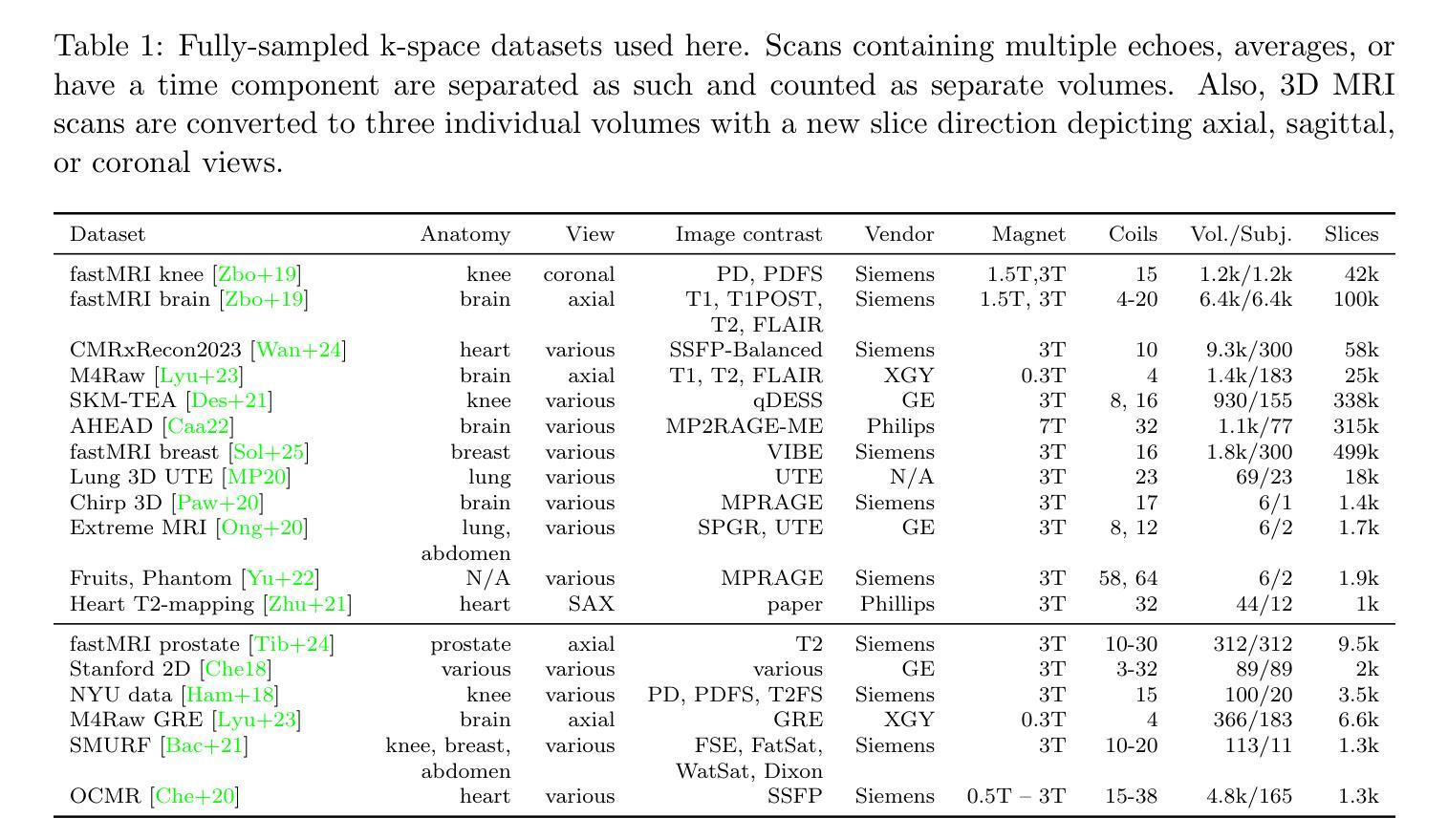
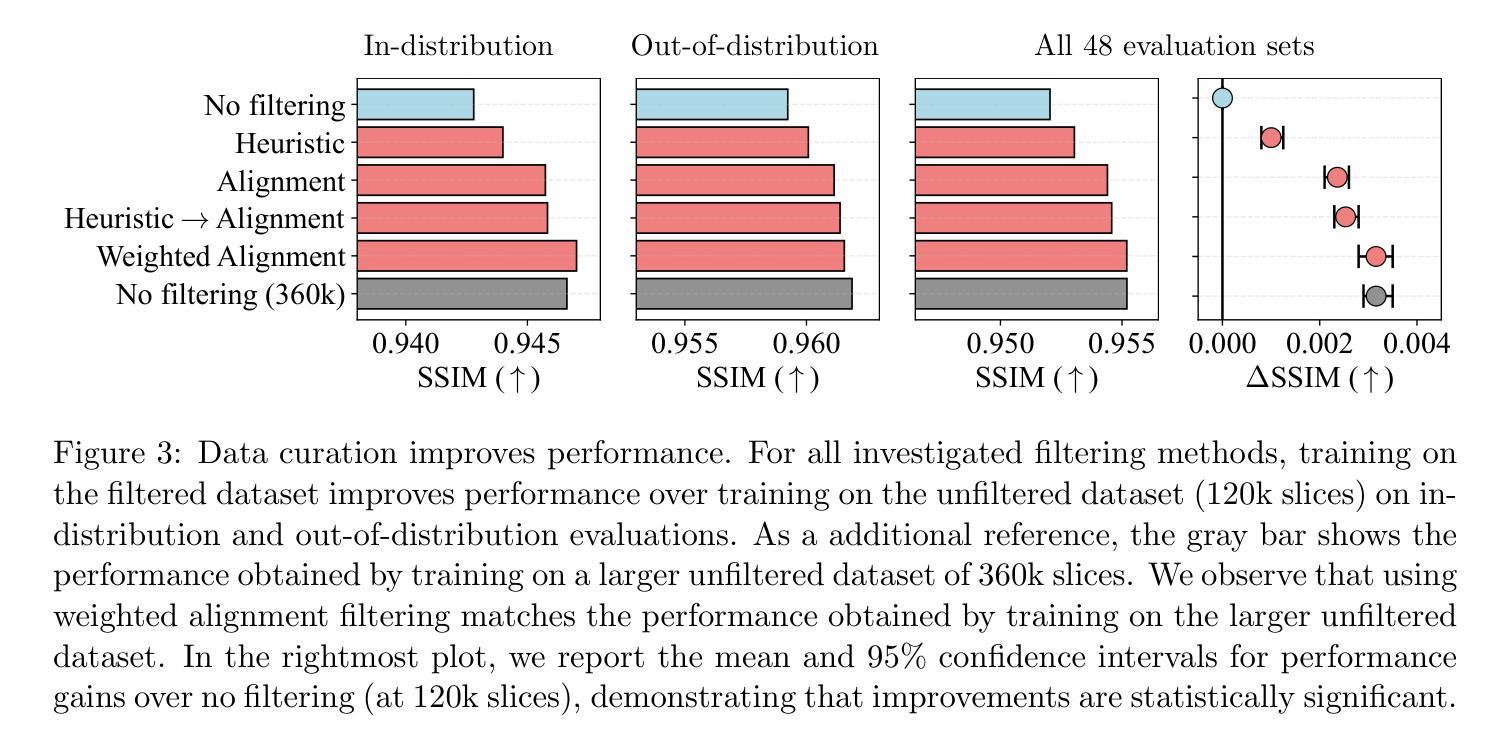
Deep neural networks achieve state-of-the-art results for accelerated MRI reconstruction. Most research on deep learning based imaging focuses on improving neural network architectures trained and evaluated on fixed and homogeneous training and evaluation data. In this work, we investigate data curation strategies for improving MRI reconstruction. We assemble a large dataset of raw k-space data from 18 public sources consisting of 1.1M images and construct a diverse evaluation set comprising 48 test sets, capturing variations in anatomy, contrast, number of coils, and other key factors. We propose and study different data filtering strategies to enhance performance of current state-of-the-art neural networks for accelerated MRI reconstruction. Our experiments show that filtering the training data leads to consistent, albeit modest, performance gains. These performance gains are robust across different training set sizes and accelerations, and we find that filtering is particularly beneficial when the proportion of in-distribution data in the unfiltered training set is low.
深度神经网络在加速MRI重建方面取得了最先进的成果。大多数基于深度学习的成像研究都集中在改进在固定和均匀的训练和评估数据上训练的神经网络架构。在这项工作中,我们研究了数据整理策略以改进MRI重建。我们从18个公共源中提取原始k空间数据,构建了一个包含约达一千万张图像的大型数据集,并建立一个多元化的评估集,包括有包含解剖学、对比度、线圈数量和其他关键因素的测试集共计有48套。我们提出并研究了不同的数据过滤策略来提高当前最先进神经网络用于加速MRI重建的性能。我们的实验表明,过滤训练数据可以带来一致但幅度适中的性能提升。这些性能提升在不同大小训练集和不同加速情况下均表现稳健,我们发现当未过滤训练集中分布内数据的比例较低时,过滤特别有益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了基于深度学习的MRI重建中的数据筛选策略。通过收集大量原始k空间数据并构建多样化的评估集,实验表明对训练数据进行筛选可以带来稳健的性能提升,特别是在未筛选的训练集中内部数据比例较低时更是如此。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注于深度学习在MRI重建中的数据筛选策略。
- 收集了大量原始k空间数据并构建了一个多样化的评估集。
- 通过对训练数据进行筛选,可以带来稳健的性能提升。
- 性能提升在不同训练集大小和加速情况下均存在。
- 数据筛选在训练集中内部数据比例较低时特别有益。
- 此方法可提高MRI重建的准确性和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

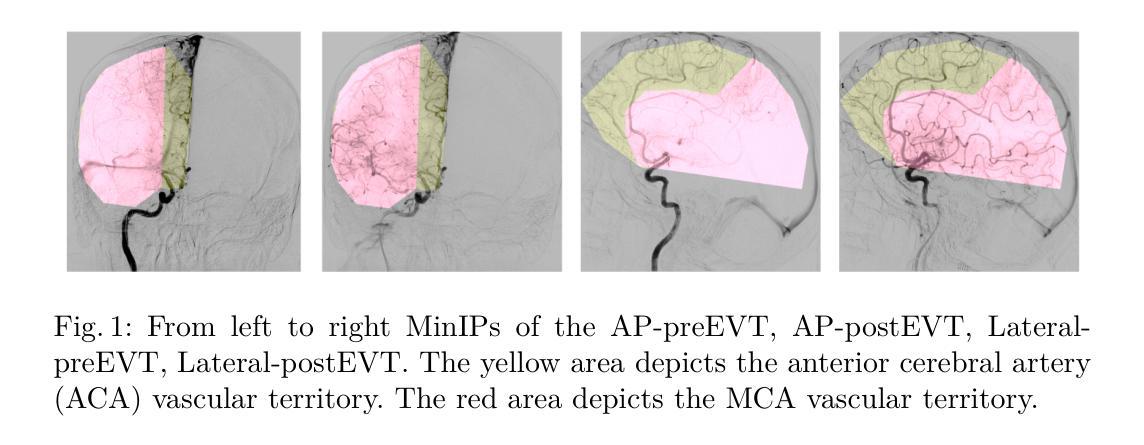
Direct vascular territory segmentation on cerebral digital subtraction angiography
Authors:P. Matthijs van der Sluijs, Lotte Strong, Frank G. te Nijenhuis, Sandra Cornelissen, Pieter Jan van Doormaal, Geert Lycklama a Nijeholt, Wim van Zwam, Ad van Es, Diederik Dippel, Aad van der Lugt, Danny Ruijters, Ruisheng Su, Theo van Walsum
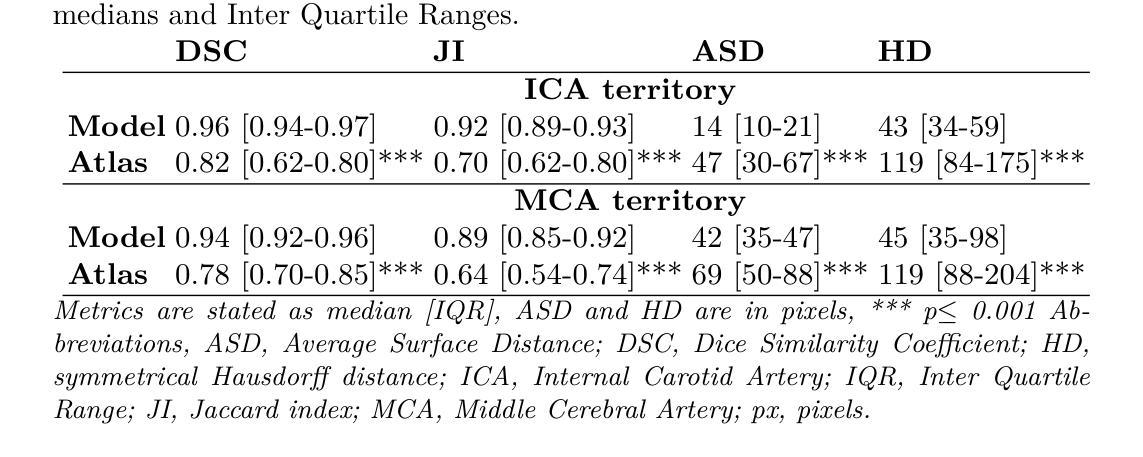
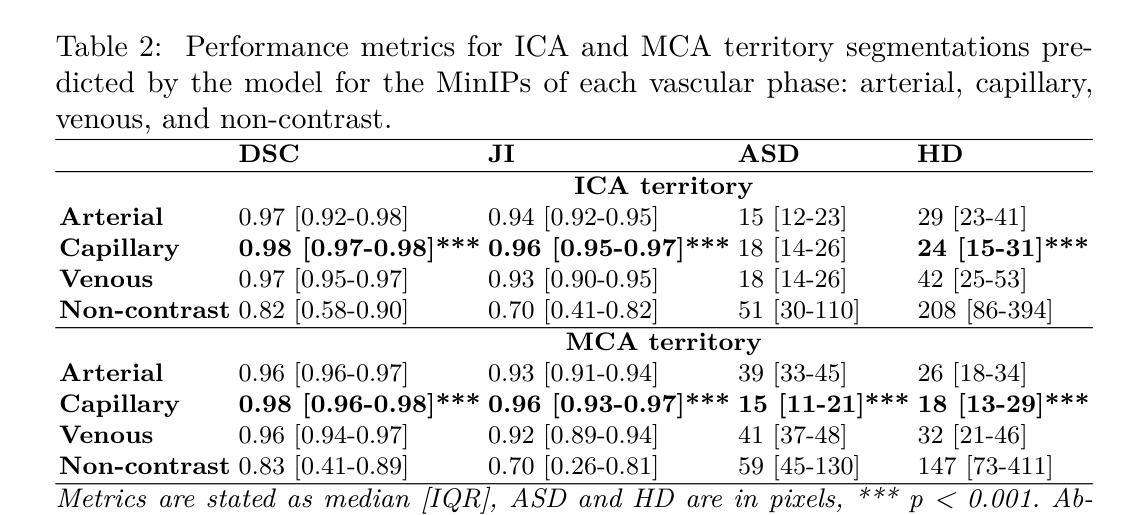
X-ray digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is frequently used when evaluating minimally invasive medical interventions. DSA predominantly visualizes vessels, and soft tissue anatomy is less visible or invisible in DSA. Visualization of cerebral anatomy could aid physicians during treatment. This study aimed to develop and evaluate a deep learning model to predict vascular territories that are not explicitly visible in DSA imaging acquired during ischemic stroke treatment. We trained an nnUNet model with manually segmented intracranial carotid artery and middle cerebral artery vessel territories on minimal intensity projection DSA acquired during ischemic stroke treatment. We compared the model to a traditional atlas registration model using the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and average surface distance (ASD). Additionally, we qualitatively assessed the success rate in both models using an external test. The segmentation model was trained on 1224 acquisitions from 361 patients with ischemic stroke. The segmentation model had a significantly higher DSC (0.96 vs 0.82, p<0.001) and lower ASD compared to the atlas model (13.8 vs 47.3, p<0.001). The success rate of the segmentation model (85%) was higher compared to the atlas registration model (66%) in the external test set. A deep learning method for the segmentation of vascular territories without explicit borders on cerebral DSA demonstrated superior accuracy and quality compared to the traditional atlas-based method. This approach has the potential to be applied to other anatomical structures for enhanced visualization during X-ray guided medical procedures. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/RuishengSu/autoTICI.
X射线数字减影血管造影术(DSA)在评估微创医学干预时经常被使用。DSA主要可视化血管,而软组织结构在DSA中可见度较低或不可见。可视化脑结构有助于医生在治疗过程中。本研究旨在开发并评估一种深度学习模型,以预测在缺血性中风治疗期间获得的DSA图像中未明确可见的血管区域。我们使用手动分割的颅内颈动脉和大脑中动脉血管区域,训练了一个nnUNet模型,该模型适用于缺血性中风治疗期间获得的最低强度投影DSA。我们将该模型与使用Dice相似系数(DSC)和平均表面距离(ASD)的传统图谱注册模型进行了比较。此外,我们还通过外部测试定性评估了两种模型的成功率。分割模型是在361名缺血性中风患者的1224次采集数据上进行训练的。与图谱模型相比,分割模型的DSC值显著更高(0.96比0.82,p<0.001),ASD值更低(13.8比47.3,p<0.001)。在外部测试集中,分割模型的成功率(85%)高于图谱注册模型(66%)。一种用于在脑DSA上分割无明确边界的血管区域的深度学习方法显示出比传统的基于图谱的方法更高的准确性和质量。这种方法有可能应用于其他解剖结构,以在X射线引导的手术过程中实现更好的可视化。代码可在https://github.com/RuishengSu/autoTICI上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to SWITCH 2025
摘要
本研究旨在开发并评估一种深度学习模型,用于预测在缺血性中风治疗中获得数字减影血管造影(DSA)中不可见的血管区域。研究使用nnUNet模型对颅内颈动脉和大脑中动脉血管区域进行手动分割,并与传统图谱注册模型的Dice相似系数(DSC)和平均表面距离(ASD)进行比较。结果显示,分割模型的DSC显著高于图谱模型(0.96 vs 0.82,p<0.001),ASD也较低(13.8 vs 47.3,p<0.001)。外部测试集中,分割模型的成功率(85%)也高于图谱注册模型(66%)。该研究提出的深度学习分割血管区域方法相比传统图谱方法具有更高的准确性和质量。该方法有望应用于其他解剖结构,以提高X光引导手术过程中的可视化效果。相关代码已公开发布在[网址链接]。
关键见解
- 研究使用深度学习模型预测DSA中不可见的血管区域,以提高缺血性中风治疗中的可视化效果。
- 对比了深度学习模型与传统图谱注册模型,显示深度学习模型在DSC和ASD方面表现更优。
- 深度学习模型在外部测试集中的成功率较高。
- 该方法有望应用于其他解剖结构的可视化,提高X光引导手术的效果。
- 相关代码已公开发布,便于他人使用与进一步研究。
- 本研究为医学图像分析提供了新思路,可能推动医学影像技术的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

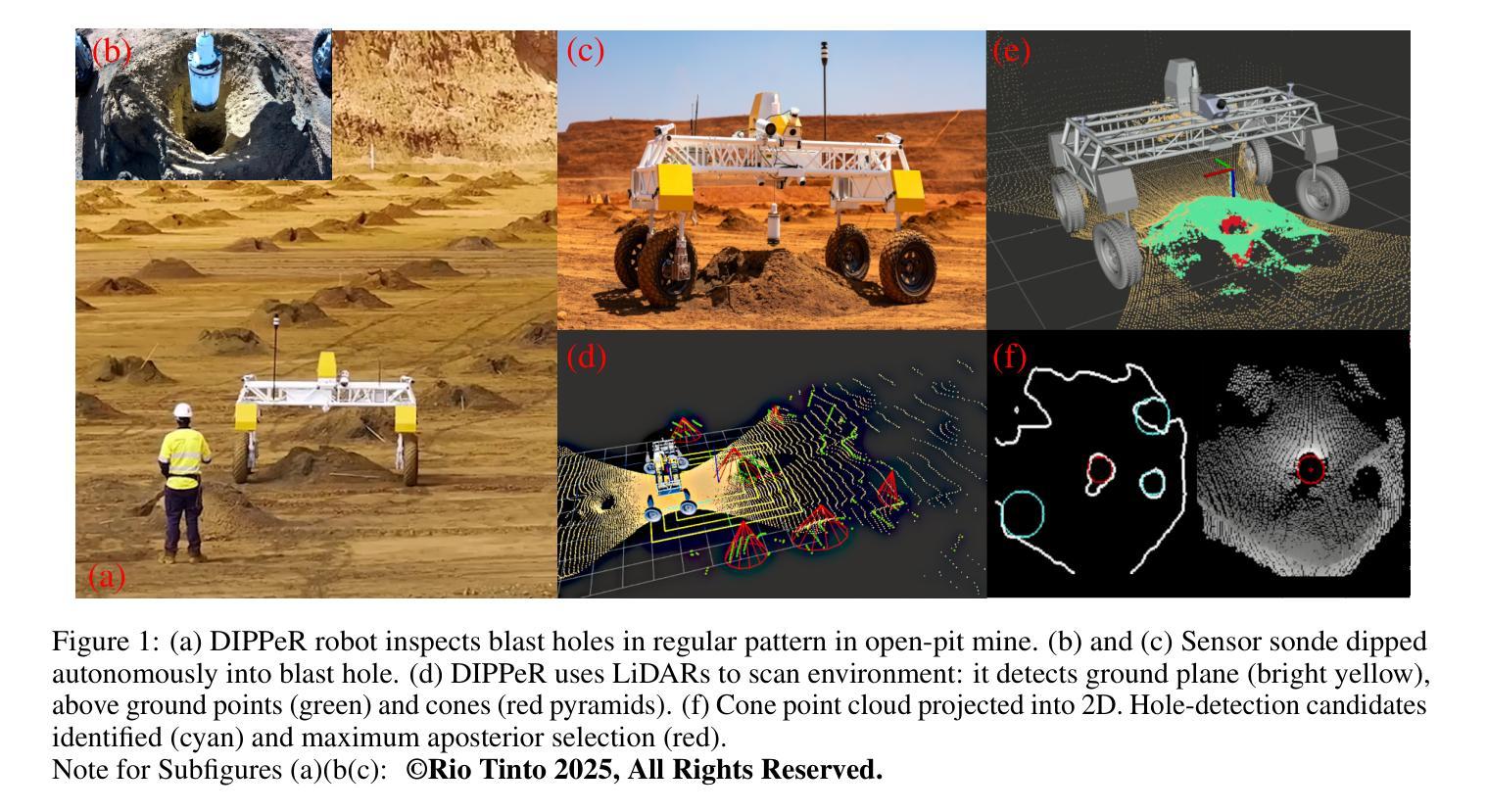
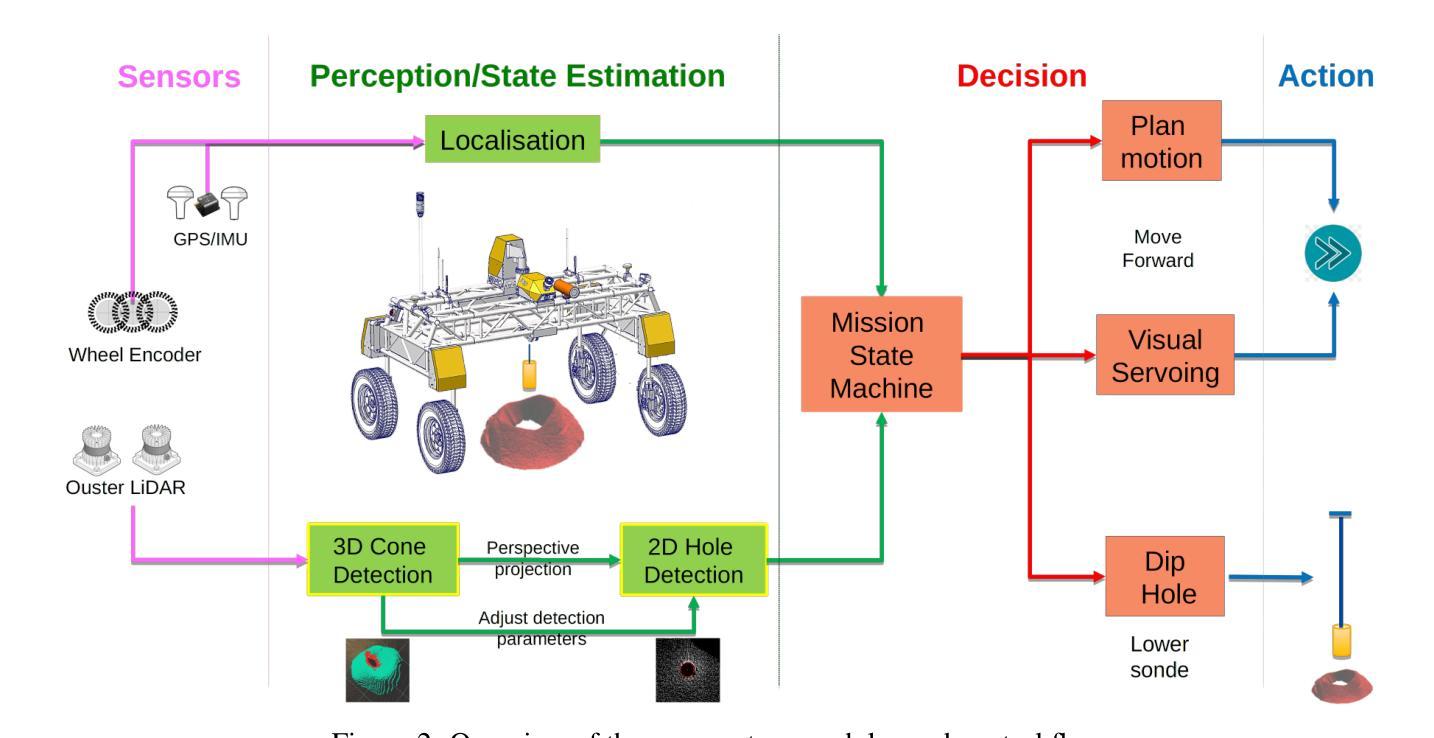
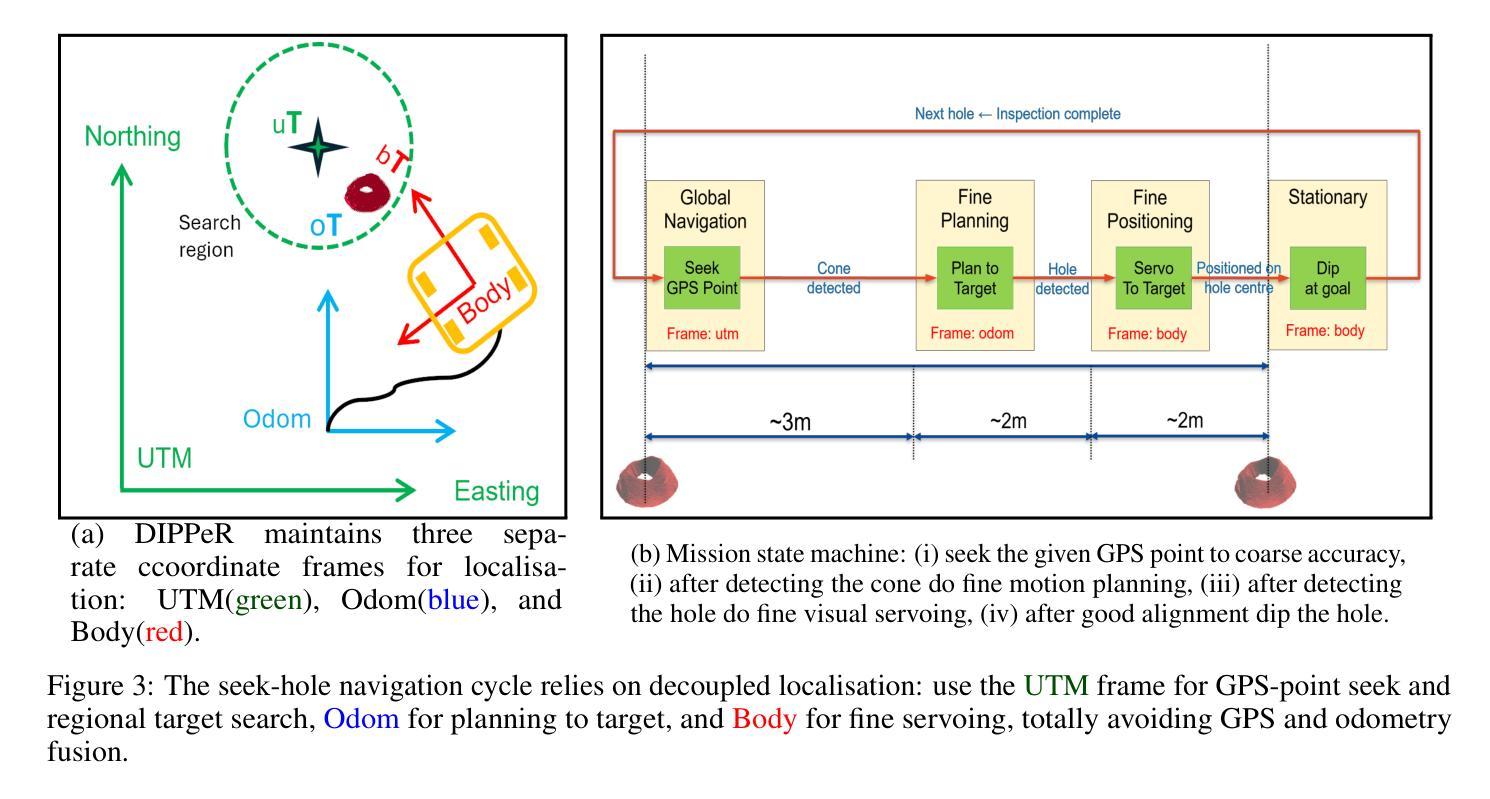
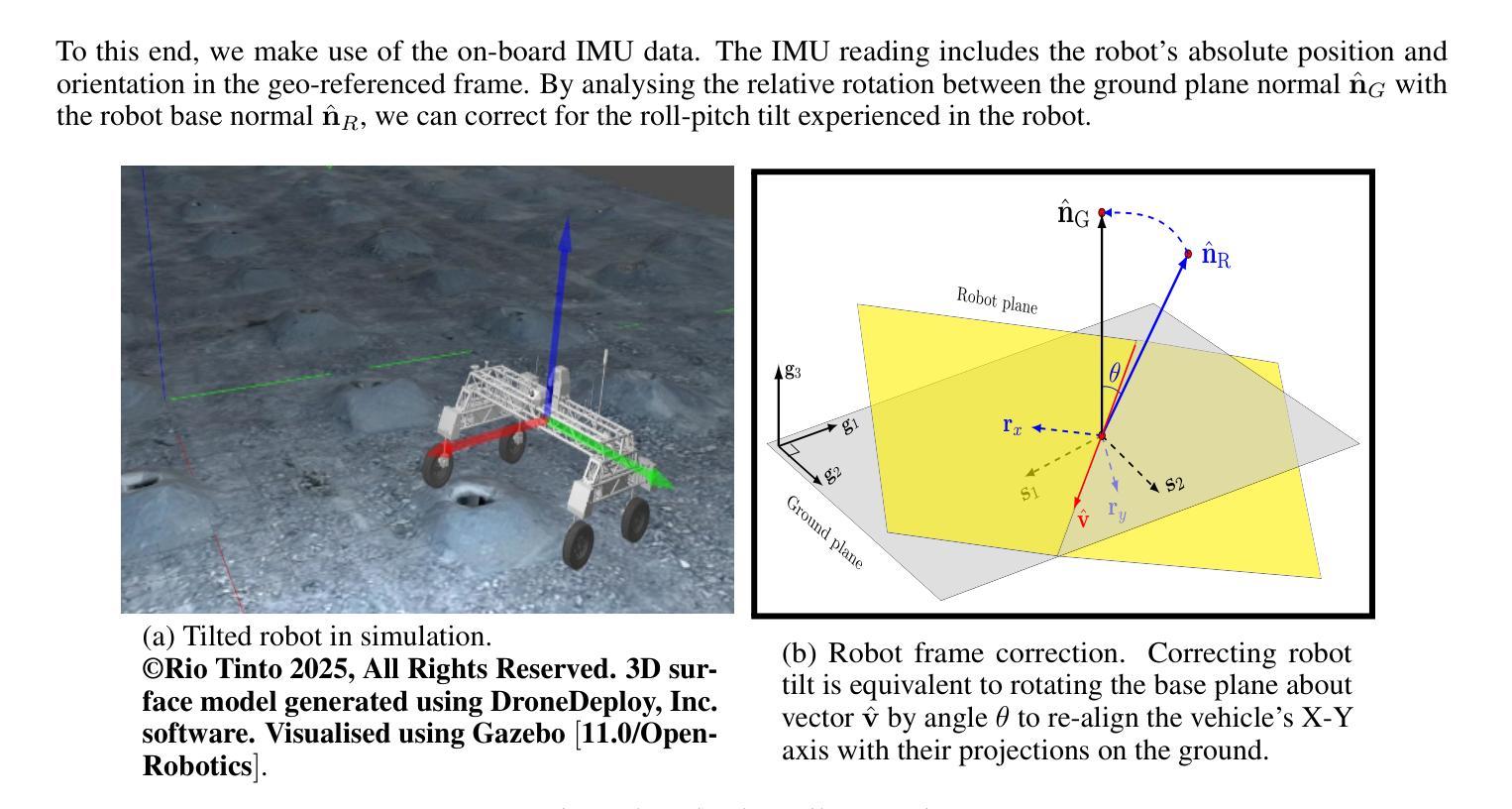
Blast Hole Seeking and Dipping – The Navigation and Perception Framework in a Mine Site Inspection Robot
Authors:Liyang Liu, Ehsan Mihankhah, Nathan Wallace, Javier Martinez, Andrew J. Hill
In open-pit mining, holes are drilled into the surface of the excavation site and detonated with explosives to facilitate digging. These blast holes need to be inspected internally for investigation of downhole material types and properties. Knowing these properties can lead to significant savings in material handling costs in downstream processes. Manual hole inspection is slow and expensive, with major limitations in revealing the geometric and geological properties of the holes and their contents. This has been the motivation for the development of our autonomous mine-site inspection robot - “DIPPeR”. In this paper, the automation aspect of the project is explained. We present a robust blast hole seeking and detection framework that enables target-based navigation and accurate down-hole sensor positioning. The pipeline first processes point-cloud data collected by the on-board LiDAR sensors, extracting the cone-shaped volume of drill-waste above the ground. By projecting the 3D cone points into a virtual depth image, segmentation is achieved in the 2D domain, yielding a circular hole at the image centre and a collared cone face. We then identify the hole centre using a robust detection module while suppressing non-maximum candidates, ensuring precise sensor placement for down-hole inspection and avoiding collisions with the cavity wall. To enable autonomous hole-seeking, the pipeline automatically adjusts its projection parameters during robot navigation to account for variations in point sparsity and hole opening size, ensuring a consistent hole appearance in 2D images. This allows continuous tracking of the target hole as the robot approaches the goal point. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our navigation and perception system in both high-fidelity simulation environments and on-site field tests. A demonstration video is available at “https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fRNbcBcaSqE“.
在露天采矿作业中,会在挖掘现场的表面钻孔,并使用炸药爆破以助于挖掘。这些爆破孔需要内部进行检查,以调查孔内材料的类型及属性。了解这些属性可以在后续流程中显著节省材料处理成本。手动孔内检查速度慢、成本高,并且在揭示孔的几何和地质属性及其内容方面存在主要局限。这激发了我们开发自主矿山检查机器人“DIPPeR”的动机。本文解释了该项目的自动化方面。我们提出了一个稳健的爆破孔搜寻和检测框架,该框架可实现基于目标的导航和准确的下孔传感器定位。该管道首先处理由车载激光雷达传感器收集的点云数据,提取出地面以上的钻渣形成的锥形体积。通过将3D锥形点投影到虚拟深度图像中,在2D领域实现分割,在图像中心形成一个圆形孔,周围是环形锥面。然后我们使用一个稳健的检测模块来识别孔的中心,同时抑制非最大候选目标,确保下孔检查的传感器精确放置,并避免与腔壁发生碰撞。为了实现自主寻孔,管道在机器人导航过程中会自动调整其投影参数,以应对点稀疏度和孔开口大小的变化,确保2D图像中孔的外观一致。这允许机器人在接近目标点时持续跟踪目标孔。我们在高保真模拟环境和现场测试中展示了我们的导航和感知系统的有效性。演示视频请访问:“https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fRNbcBcaSqE”。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种自主矿山检查机器人“DIPPeR”的自动化方面。机器人通过处理点云数据,实现钻孔搜寻与检测,能进行目标导航与精确的传感器定位。处理流程包括提取地面上的锥形废料体积、投影至虚拟深度图像以进行二维域分割,进而确定钻孔中心。此外,该流程能够调整投影参数以应对点稀疏度和开口大小的变化,确保二维图像中目标孔的一致性。该系统的导航和感知系统在高保真模拟环境和现场测试中均表现出了有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 自主矿山检查机器人“DIPPeR”可助力快速、经济地实现钻空检测与材料性质分析。
- 通过处理点云数据实现钻孔搜寻与检测,支持目标导航与精确传感器定位。
- 利用LiDAR传感器采集的点云数据进行锥形废料体积提取和虚拟深度图像投影。
- 通过二维域分割识别钻孔中心,确保精确传感器放置并避免与空洞壁碰撞。
- 系统能自动调整投影参数以应对不同环境条件下的钻孔特征变化。
- 在高保真模拟环境和现场测试中验证了导航和感知系统的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

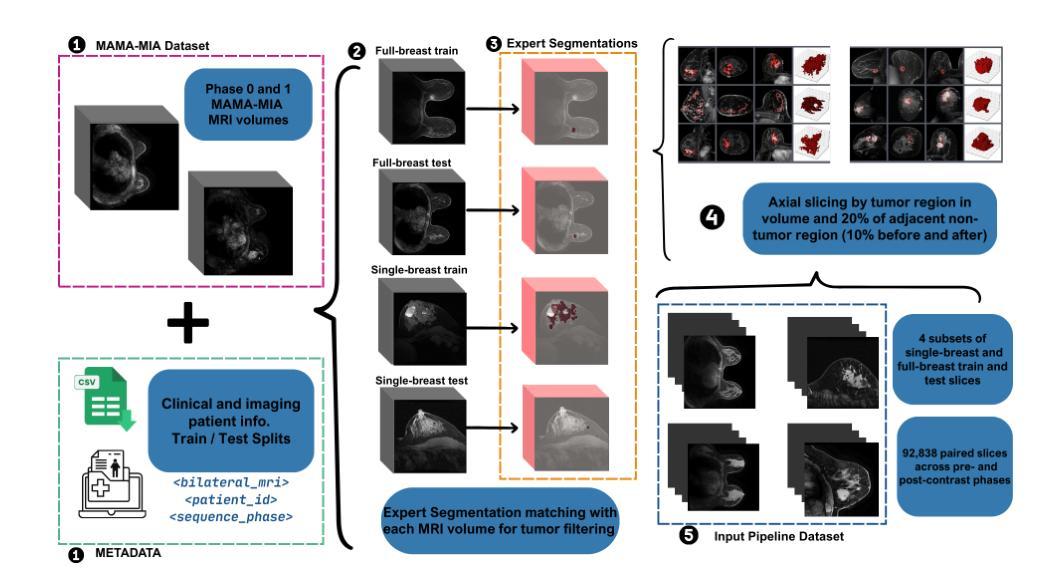
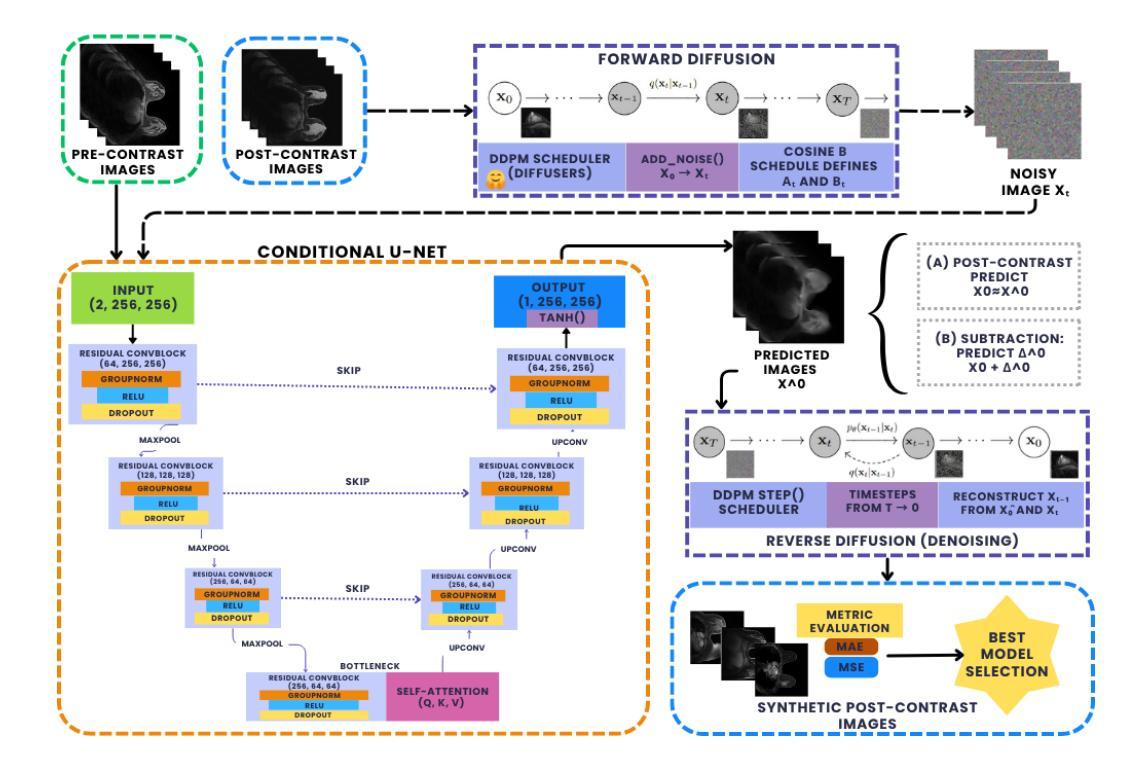
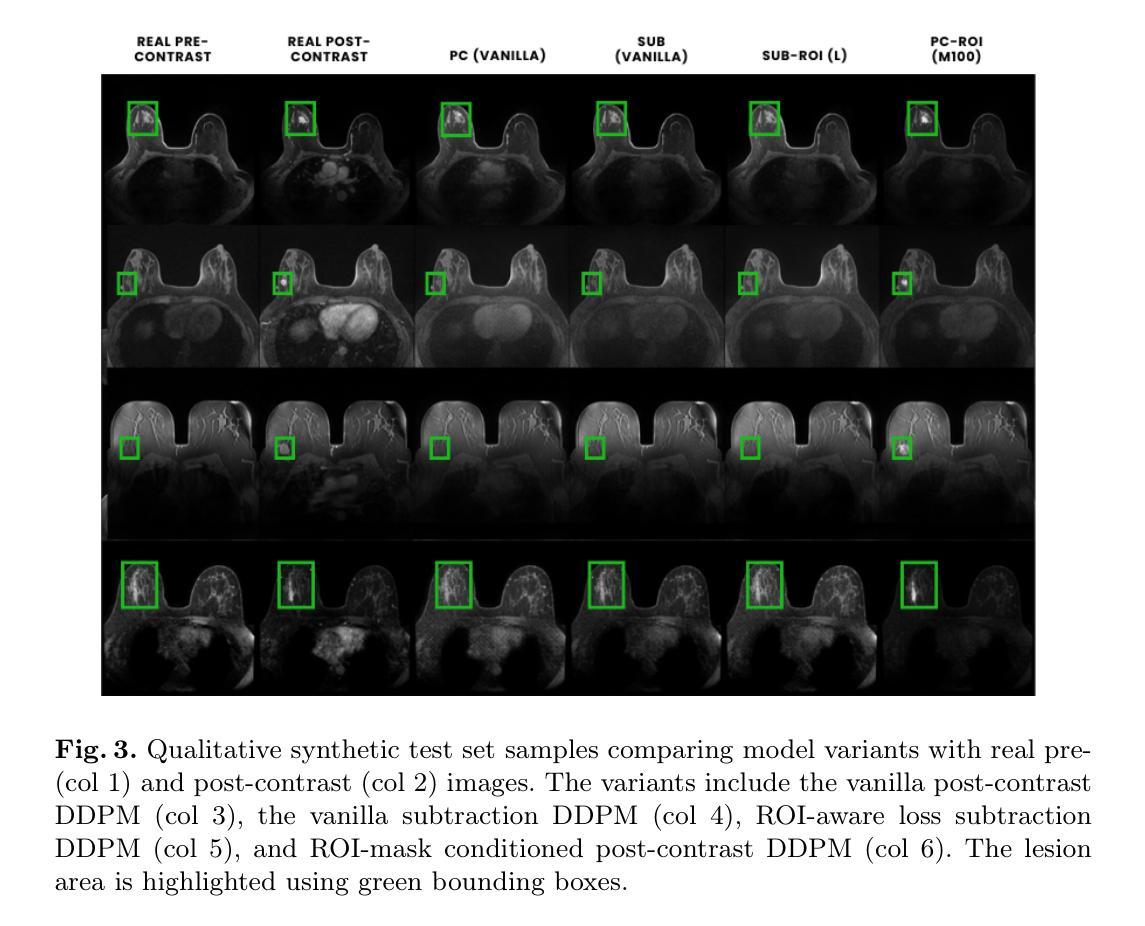
Comparing Conditional Diffusion Models for Synthesizing Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI from Pre-Contrast Images
Authors:Sebastian Ibarra, Javier del Riego, Alessandro Catanese, Julian Cuba, Julian Cardona, Nataly Leon, Jonathan Infante, Karim Lekadir, Oliver Diaz, Richard Osuala
Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI is essential for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. However, its reliance on contrast agents introduces safety concerns, contraindications, increased cost, and workflow complexity. To this end, we present pre-contrast conditioned denoising diffusion probabilistic models to synthesize DCE-MRI, introducing, evaluating, and comparing a total of 22 generative model variants in both single-breast and full breast settings. Towards enhancing lesion fidelity, we introduce both tumor-aware loss functions and explicit tumor segmentation mask conditioning. Using a public multicenter dataset and comparing to respective pre-contrast baselines, we observe that subtraction image-based models consistently outperform post-contrast-based models across five complementary evaluation metrics. Apart from assessing the entire image, we also separately evaluate the region of interest, where both tumor-aware losses and segmentation mask inputs improve evaluation metrics. The latter notably enhance qualitative results capturing contrast uptake, albeit assuming access to tumor localization inputs that are not guaranteed to be available in screening settings. A reader study involving 2 radiologists and 4 MRI technologists confirms the high realism of the synthetic images, indicating an emerging clinical potential of generative contrast-enhancement. We share our codebase at https://github.com/sebastibar/conditional-diffusion-breast-MRI.
动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在乳腺癌诊断和治疗中具有重要意义。然而,它对造影剂的依赖引发了安全性问题、禁忌症、成本增加和工作流程复杂等问题。为此,我们提出了基于预造影条件去噪扩散概率模型的DCE-MRI合成方法,在单乳和全乳环境中共介绍了22种生成模型并对其进行了评估和比较。为提高病灶保真度,我们引入了肿瘤感知损失函数和明确的肿瘤分割掩模条件。使用公共多中心数据集,与相应的预造影基线相比,我们发现基于减法图像的模型在五种互补评估指标上持续优于基于后造影的模型。除了对整个图像进行评估外,我们还对感兴趣区域进行了单独评估,其中肿瘤感知损失和分割掩模输入提高了评估指标。后者显著提高了定性结果,捕捉了造影剂摄取情况,尽管它假设能获取肿瘤定位输入,而在筛查环境中这是无法保证的。一项涉及两名放射科医生和四名MRI技术专家的读者研究证实了合成图像的高度逼真性,表明生成造影增强的临床潜力。我们已将我们的代码库共享至:https://github.com/sebastibar/conditional-diffusion-breast-MRI 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures, submitted and accepted to MICCAI Deepbreath workshop 2025
Summary
本文介绍了动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)在乳腺癌诊断和治疗中的重要性,但由于其依赖造影剂而带来安全顾虑、禁忌症、成本增加和工作流程复杂等问题。研究团队提出了基于预造影条件的去噪扩散概率模型来合成DCE-MRI图像,评估和比较了总共22种生成模型变体在单乳和全乳场景下的表现。为提高病灶保真度,研究引入了肿瘤感知损失函数和明确的肿瘤分割掩膜条件。通过公共多中心数据集的比较,基于减法图像模型的性能在五种互补评估指标上持续优于基于后造影模型。此外,对感兴趣区域的评估显示,肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入改善了评估指标。尽管需要假设存在肿瘤定位输入,这在筛查环境中可能无法保证,但包含肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入的模型在捕捉造影剂摄取方面显著提高了定性结果。通过涉及两名放射科医生和四名MRI技术专家的读者研究证实了合成图像的高度逼真性,表明生成对比增强技术的临床潜力。
Key Takeaways
- DCE-MRI在乳腺癌诊断和治疗中具有重要性,但依赖造影剂存在安全顾虑、禁忌症、成本和工作流程复杂等问题。
- 提出了基于预造影条件的去噪扩散概率模型来合成DCE-MRI图像,并评估和比较了多种生成模型。
- 为提高病灶保真度,引入了肿瘤感知损失函数和明确的肿瘤分割掩膜条件。
- 基于减法图像模型的性能优于基于后造影模型,这在一项涉及多种评估指标的公共多中心数据集的比较中得到了证实。
- 感兴趣区域的评估显示肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入改善了评估效果。
- 包含肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入的模型在捕捉造影剂摄取方面显著提高了定性结果,但需注意肿瘤定位输入可能无法保证。
点此查看论文截图

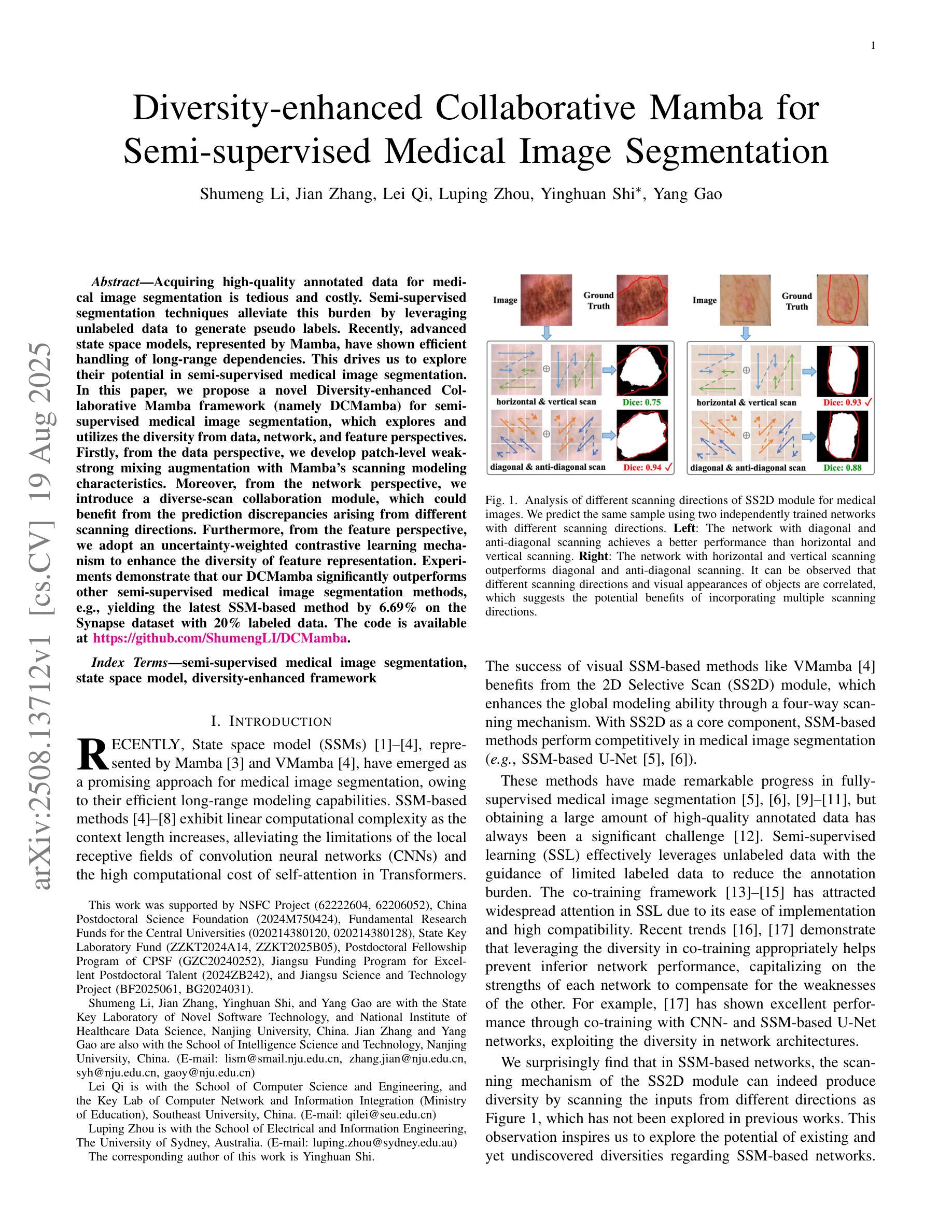
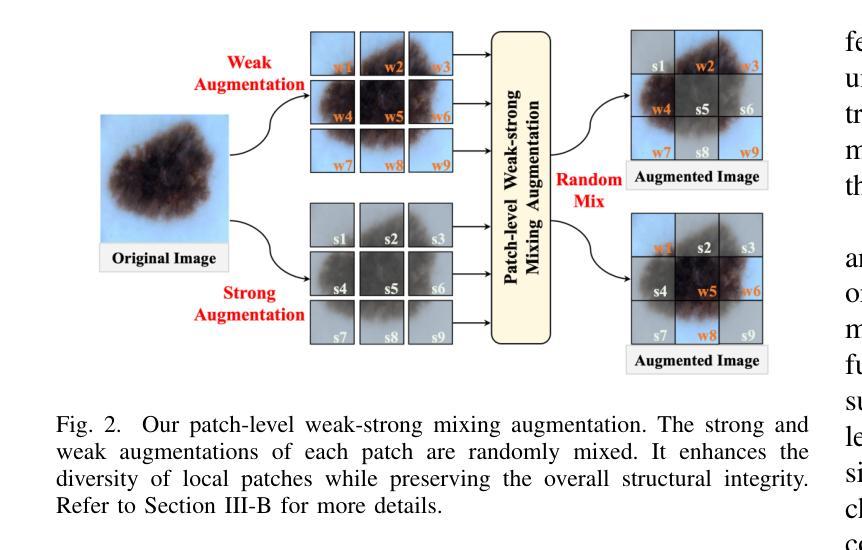
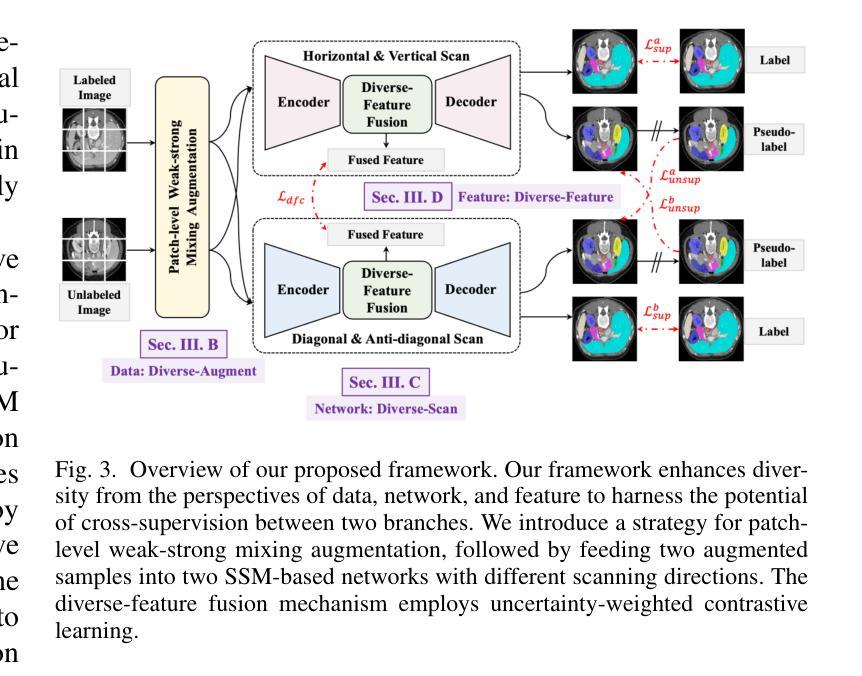
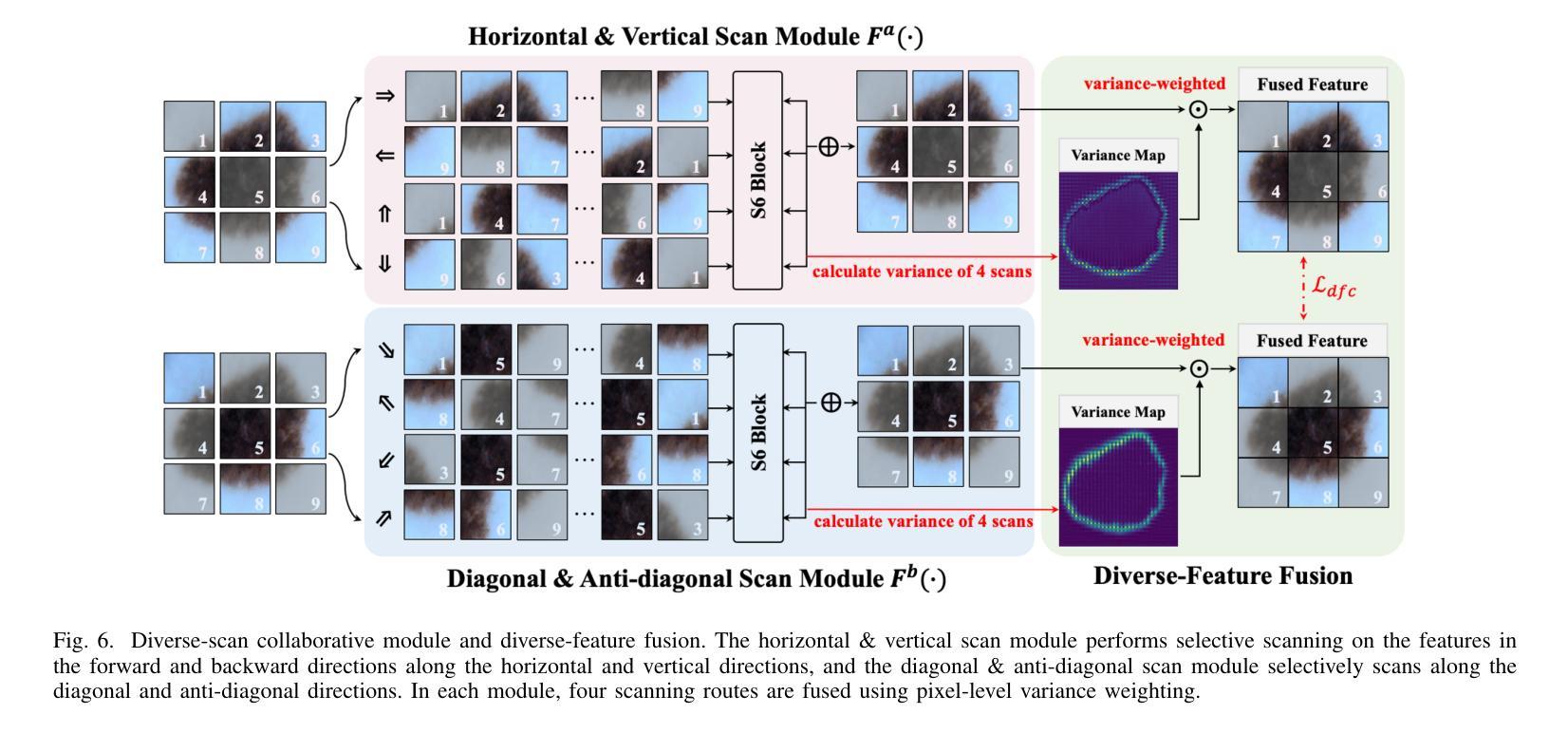
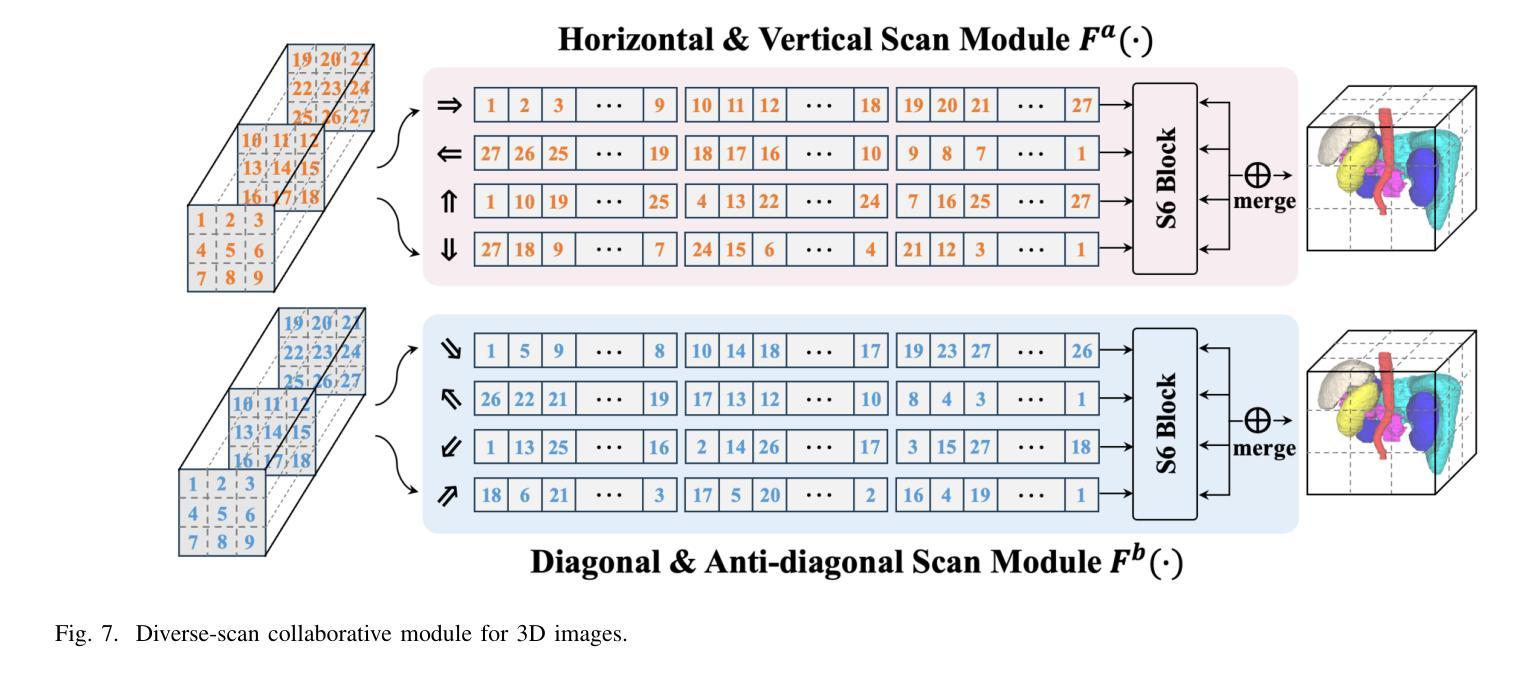
Diversity-enhanced Collaborative Mamba for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shumeng Li, Jian Zhang, Lei Qi, Luping Zhou, Yinghuan Shi, Yang Gao
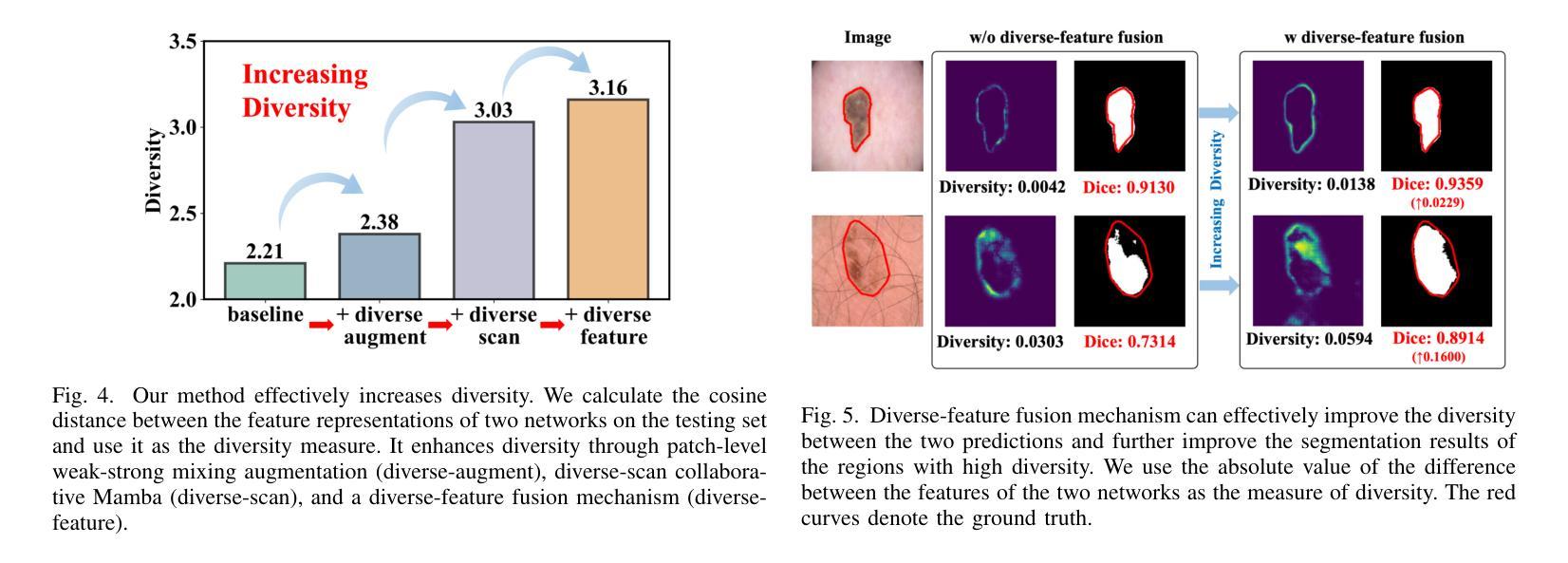
Acquiring high-quality annotated data for medical image segmentation is tedious and costly. Semi-supervised segmentation techniques alleviate this burden by leveraging unlabeled data to generate pseudo labels. Recently, advanced state space models, represented by Mamba, have shown efficient handling of long-range dependencies. This drives us to explore their potential in semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel Diversity-enhanced Collaborative Mamba framework (namely DCMamba) for semi-supervised medical image segmentation, which explores and utilizes the diversity from data, network, and feature perspectives. Firstly, from the data perspective, we develop patch-level weak-strong mixing augmentation with Mamba’s scanning modeling characteristics. Moreover, from the network perspective, we introduce a diverse-scan collaboration module, which could benefit from the prediction discrepancies arising from different scanning directions. Furthermore, from the feature perspective, we adopt an uncertainty-weighted contrastive learning mechanism to enhance the diversity of feature representation. Experiments demonstrate that our DCMamba significantly outperforms other semi-supervised medical image segmentation methods, e.g., yielding the latest SSM-based method by 6.69% on the Synapse dataset with 20% labeled data.
获取高质量标注数据对于医学图像分割而言既繁琐又成本高昂。半监督分割技术通过利用未标注数据生成伪标签,减轻了这一负担。最近,以Mamba为代表的高级状态空间模型显示出对长距离依赖关系的有效处理。这促使我们探索其在半监督医学图像分割中的潜力。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于半监督医学图像分割的新型多样性增强协同Mamba框架(即DCMamba),该框架从数据、网络和特征角度探索并利用多样性。首先,从数据角度,我们结合Mamba的扫描建模特性,开发出基于补丁级别的弱强混合增强技术。此外,从网络角度看,我们引入了一个多样化的扫描协作模块,可以利用不同扫描方向产生的预测差异。进一步地,从特征角度,我们采用一种基于不确定性的对比学习机制,以增强特征表示的多样性。实验表明,我们的DCMamba在半监督医学图像分割方法上明显优于其他方法,例如,在Synapse数据集上使用20%的标注数据,相较于最新的SSM方法提升了6.69%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督医学图像分割技术利用未标注数据生成伪标签,减轻标注负担。本文提出一种基于先进状态空间模型(如Mamba)的半监督医学图像分割框架DCMamba,从数据、网络和特征三个角度探索和利用多样性。实验证明,DCMamba显著优于其他半监督医学图像分割方法,如在Synapse数据集上,使用20%标注数据的情况下,比最新SSM方法高出6.69%。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割技术利用未标注数据生成伪标签,减轻高成本和高难度的标注工作。
- DCMamba框架基于先进状态空间模型(如Mamba),有效处理长距离依赖关系。
- DCMamba从数据、网络和特征三个角度探索和利用多样性。
- 数据层面,利用弱强混合增强技术与Mamba扫描建模特性结合。
- 网络层面,引入多样扫描协作模块,利用不同扫描方向产生的预测差异。
- 特征层面,采用加权不确定性对比学习机制,提高特征表示的多样性。
点此查看论文截图

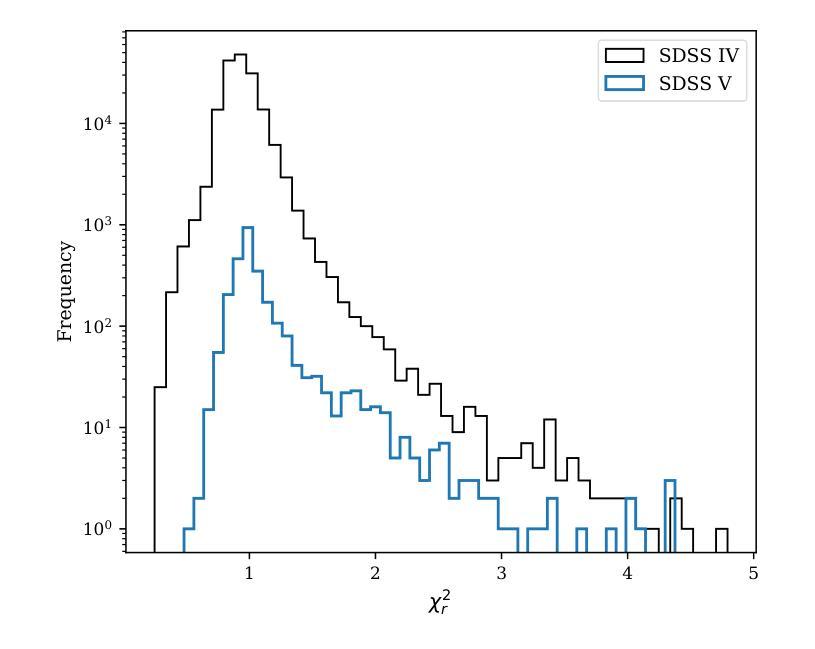
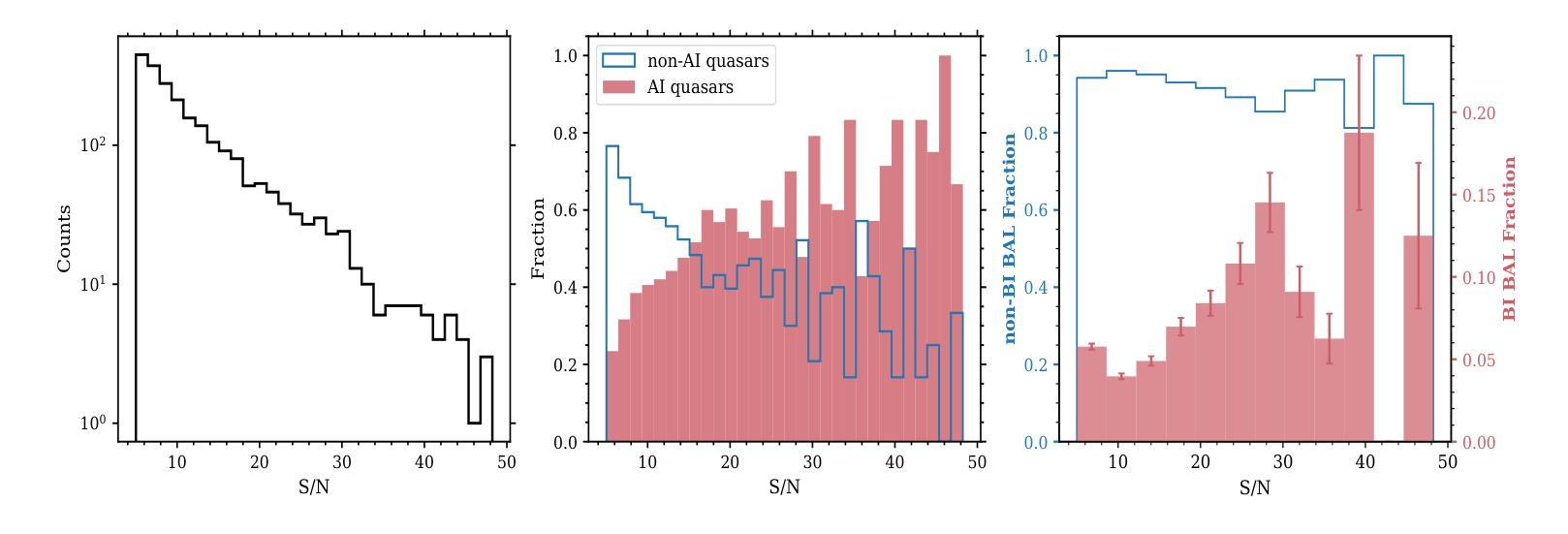
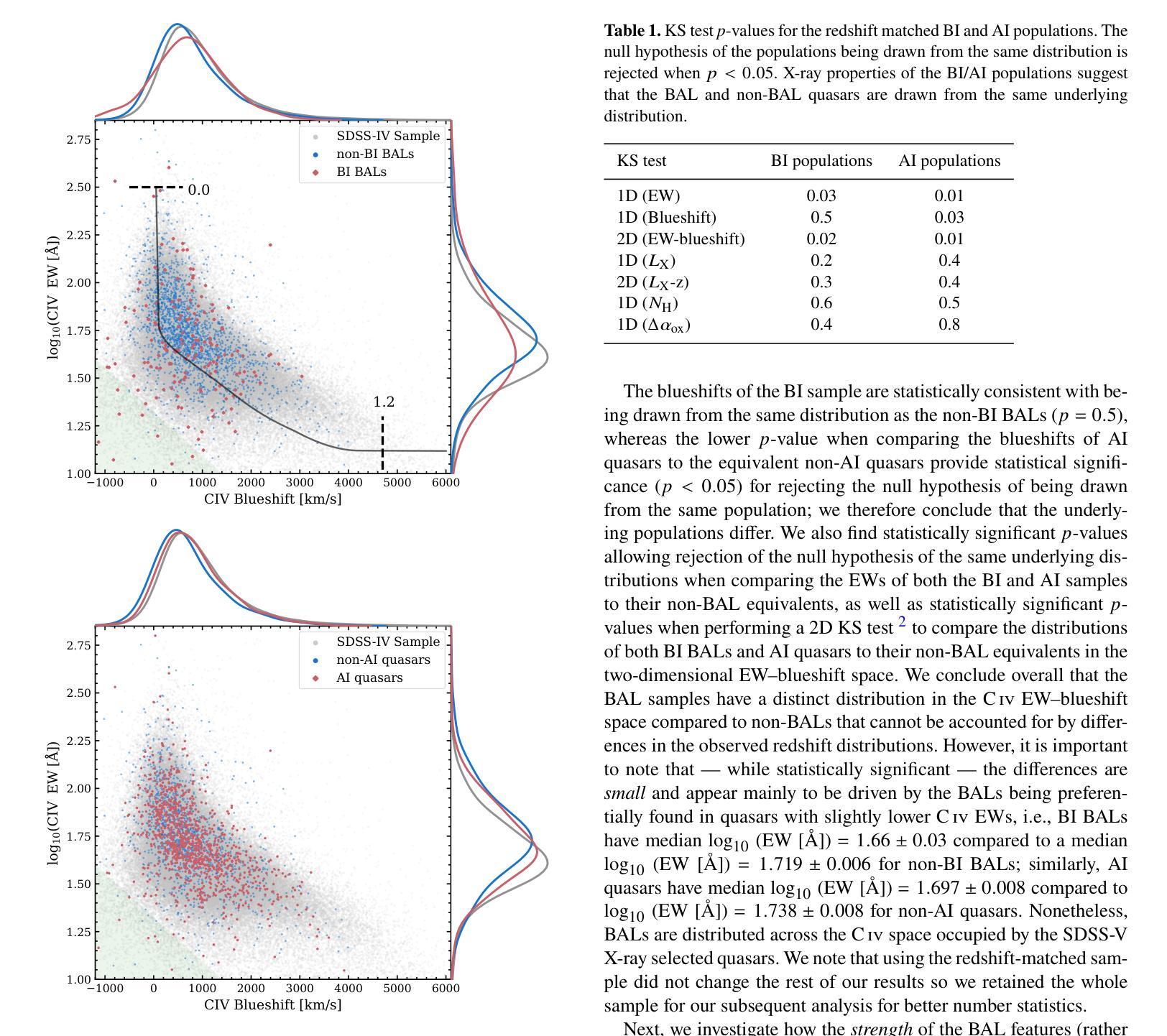
X-ray selected broad absorption line quasars in SDSS-V: BALs and non-BALs span the same range of X-ray properties
Authors:Pranavi Hiremath, Amy L. Rankine, James Aird, W. N. Brandt, Paola Rodríguez Hidalgo, Scott F. Anderson, Catarina Aydar, Claudio Ricci, Donald P. Schneider, M. Vivek, Zsofi Igo, Sean Morrison, Mara Salvato
Broad absorption line (BAL) quasars are often considered X-ray weak relative to their optical/UV luminosity, whether intrinsically (i.e., the coronal emission is fainter) or due to large column densities of absorbing material. The SDSS-V is providing optical spectroscopy for samples of quasar candidates identified by eROSITA as well as Chandra, XMM or Swift, making the resulting datasets ideal for characterising the BAL quasar population within an X-ray selected sample. We use the Balnicity Index (BI) to identify the BAL quasars based on absorption of the CIV $\lambda,1549$ emission line in the optical spectra, finding 143 BAL quasars in our sample of 2317 X-ray selected quasars within $1.5\le z \le3.5$. This observed BAL fraction of $\approx$ 6 per cent is comparable to that found in optically selected samples. We also identify absorption systems via the Absorption Index (AI) which includes mini-BALs and NALs, finding 954 quasars with AI $>0$. We consider the CIV emission space (equivalent width vs. blueshift) to study the BAL outflows within the context of the radiatively driven accretion disc-wind model. X-ray selection excludes the highest outflow velocities in emission but includes the full range of absorption velocities which we suggest is consistent with the BAL gas being located further from the X-ray corona than the emitting gas. We observe both X-ray weak and X-ray strong BALs (via the optical-to-X-ray spectral slope, $\alpha_\text{ox}$) and detect little evidence for differing column densities between the BAL and non-BAL quasars, suggesting the BALs and non-BALs have the same shielding gas and intrinsic X-ray emission.
巴尔(Broad Absorption Line,简称BAL)类星体通常被认为在X射线相对于其光学/紫外光度较弱,无论这是其固有特性(即冕发射较弱),还是由于吸收材料的大柱密度所致。SDSS-V为eROSITA以及Chandra、XMM或Swift识别的类星体候选样本提供了光学光谱,这使得数据集非常适合于表征X射线选定样本中的巴尔类星体。我们使用巴尔指数(Balnicity Index,简称BI)来识别基于光学光谱中CIV λ 1549发射线的吸收而存在的巴尔类星体,在我们的样本中找到了处于红移范围 $1.5\le z \le3.5$ 的2317个X射线选定类星体中的143个巴尔类星体。观察到的巴尔占比约为百分之六,与光学选定样本中观察到的结果相当。我们还通过包括微巴尔和NAL的吸光度指数(Absorption Index,简称AI)来识别吸收系统,发现AI大于零的类星体有954个。我们考虑CIV发射空间(等效宽度与蓝移)来研究巴尔流出在辐射驱动吸积盘风模型中的背景。X射线选择排除了发射中的最高流出速度,但包括了完整的吸收速度范围,我们认为这与巴尔气体位于远离X射线冕的发射气体之外是一致的。我们观察到既有X射线弱的巴尔类星体也有X射线强的巴尔类星体(通过光学到X射线的光谱斜率 $\alpha_\text{ox}$ ),并且在巴尔类星体和非巴尔类星体之间发现了柱密度几乎没有差异的证据,这表明它们具有相同的屏蔽气体和固有X射线发射。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 16 figures, 3 appendices, accepted for publication in MNRAS
Summary
在X射线选择的样本中,巴尔末尔(BAL)类奎萨(quasar)表现出相对较弱的光谱特征。通过对SDSS-V光学光谱数据的分析,利用巴尔末尔指数(BI)识别出因CIV λ 1549发射线吸收而产生的巴尔末尔类奎萨。研究发现在样本中观察到约6%的巴尔末尔类奎萨,与光学选择的样本相当。此外,通过吸收指数(AI)发现了包含微型巴尔末尔和NALs的吸收系统。对CIV发射空间的研究表明,辐射驱动型吸积盘风模型中的巴尔末尔流出物表现出多样化的外流速度特性。X射线选择排除了最高的发射外流速度,但包含了完整的吸收速度范围,暗示巴尔末尔气体位于X射线冕之外。同时观察到既有X射线弱的也有X射线强的巴尔末尔类奎萨,且未发现BAL和非BAL奎萨之间的列密度差异,暗示它们可能有相同的屏蔽气体和内在X射线发射。
Key Takeaways
- 巴尔末尔(BAL)类奎萨在X射线光谱上相对较弱。
- 通过SDSS-V光学光谱数据识别了巴尔末尔类奎萨。
- 在X射线选择的样本中观察到的巴尔末尔类奎萨比例约为6%。
- 通过吸收指数发现了包含微型巴尔末尔和NALs的吸收系统。
- 辐射驱动型吸积盘风模型中的巴尔末尔流出物具有多样化的特性。
- X射线选择样本中,巴尔末尔气体可能位于X射线冕之外。
点此查看论文截图

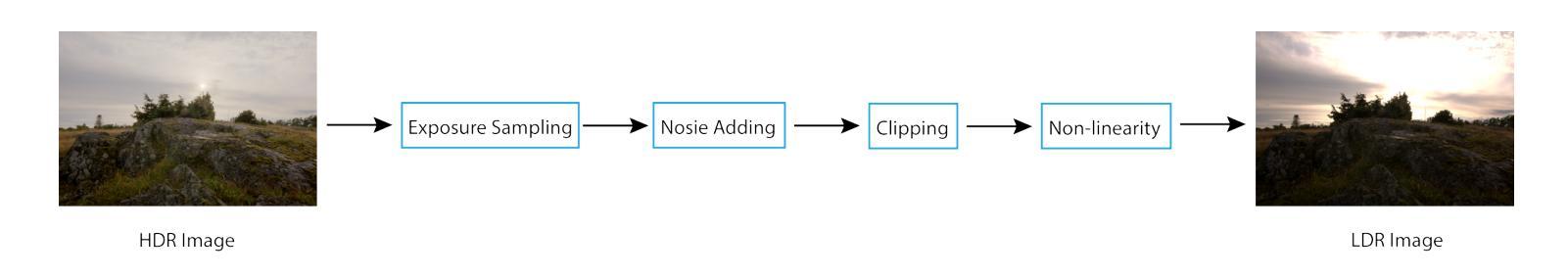
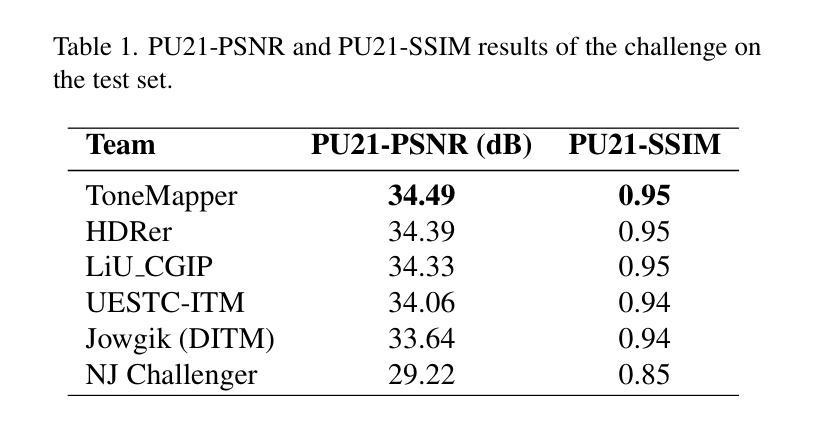
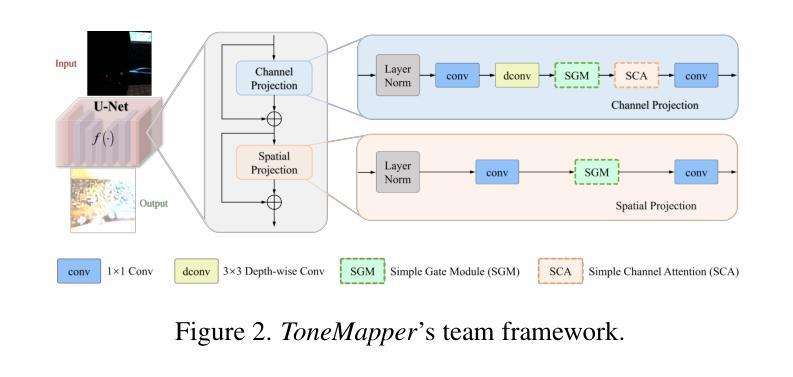
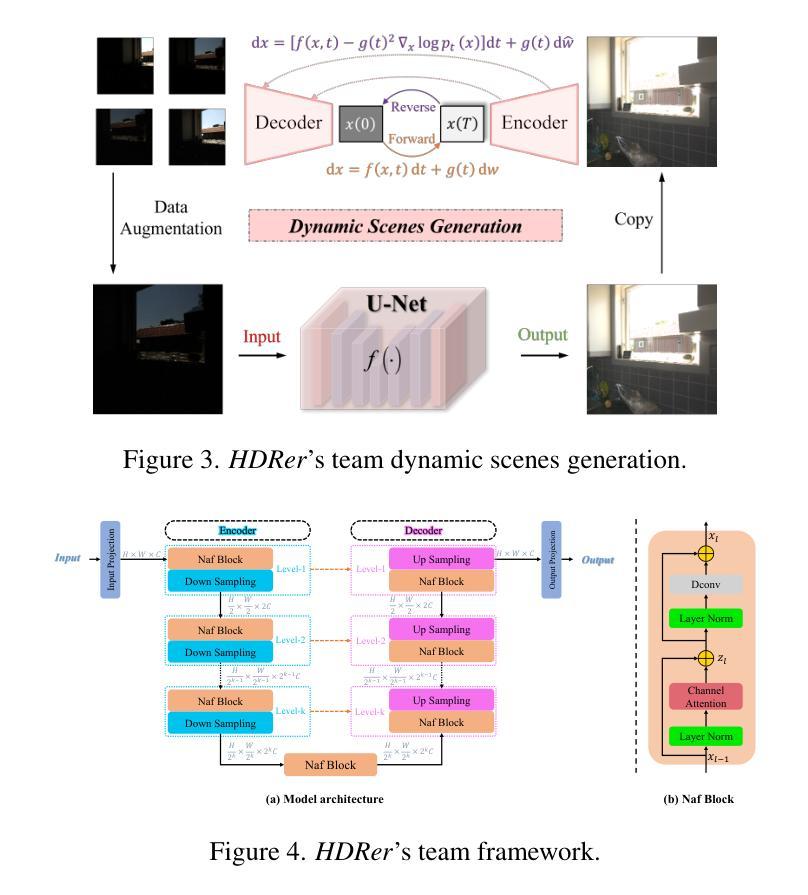
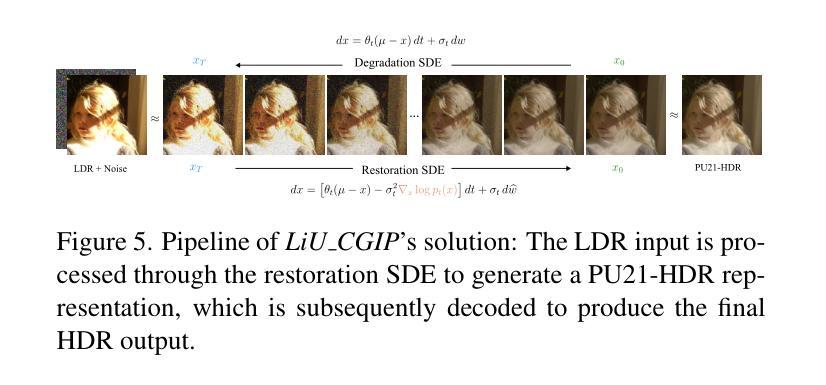
AIM 2025 challenge on Inverse Tone Mapping Report: Methods and Results
Authors:Chao Wang, Francesco Banterle, Bin Ren, Radu Timofte, Xin Lu, Yufeng Peng, Chengjie Ge, Zhijing Sun, Ziang Zhou, Zihao Li, Zishun Liao, Qiyu Kang, Xueyang Fu, Zheng-Jun Zha, Zhijing Sun, Xingbo Wang, Kean Liu, Senyan Xu, Yang Qiu, Yifan Ding, Gabriel Eilertsen, Jonas Unger, Zihao Wang, Ke Wu, Jinshan Pan, Zhen Liu, Zhongyang Li, Shuaicheng Liu, S. M Nadim Uddin
This paper presents a comprehensive review of the AIM 2025 Challenge on Inverse Tone Mapping (ITM). The challenge aimed to push forward the development of effective ITM algorithms for HDR image reconstruction from single LDR inputs, focusing on perceptual fidelity and numerical consistency. A total of \textbf{67} participants submitted \textbf{319} valid results, from which the best five teams were selected for detailed analysis. This report consolidates their methodologies and performance, with the lowest PU21-PSNR among the top entries reaching 29.22 dB. The analysis highlights innovative strategies for enhancing HDR reconstruction quality and establishes strong benchmarks to guide future research in inverse tone mapping.
本文全面回顾了AIM 2025关于逆色调映射(ITM)的挑战。该挑战旨在推动从单一LDR输入构建有效的ITM算法的发展,侧重于感知保真度和数值一致性。共有\textbf{67}名参与者提交了\textbf{319}份有效结果,从中选择了五支顶尖团队进行详细分析。本报告总结了他们的方法和性能,其中最佳作品的PU21-PSNR最低值达到29.22 dB。分析突出了提高HDR重建质量的创新策略,并建立了强有力的基准,为未来的逆色调映射研究提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文全面评述了AIM 2025挑战赛中的逆色调映射(ITM)技术。该挑战赛旨在推动从单一LDR输入实现HDR图像重建的有效ITM算法的发展,重点关注感知保真度和数值一致性。共有67支队伍提交了319个有效结果,其中前五支队伍被选中进行详细分析。本文总结了这些队伍的方法和表现,最佳队伍的PU21-PSNR达到29.22 dB。分析突出了提高HDR重建质量的创新策略,并为未来的逆色调映射研究提供了强有力的基准。
Key Takeaways
- AIM 2025挑战赛聚焦于逆色调映射(ITM)技术的HDR图像重建。
- 挑战赛有67支队伍参与,提交了319个有效结果。
- 前五名队伍的方法和表现被详细分析并总结。
- 最佳队伍的PU21-PSNR达到29.22 dB。
- 分析强调了提高HDR重建质量的创新策略。
- 报告为未来的逆色调映射研究提供了强有力的基准。
点此查看论文截图

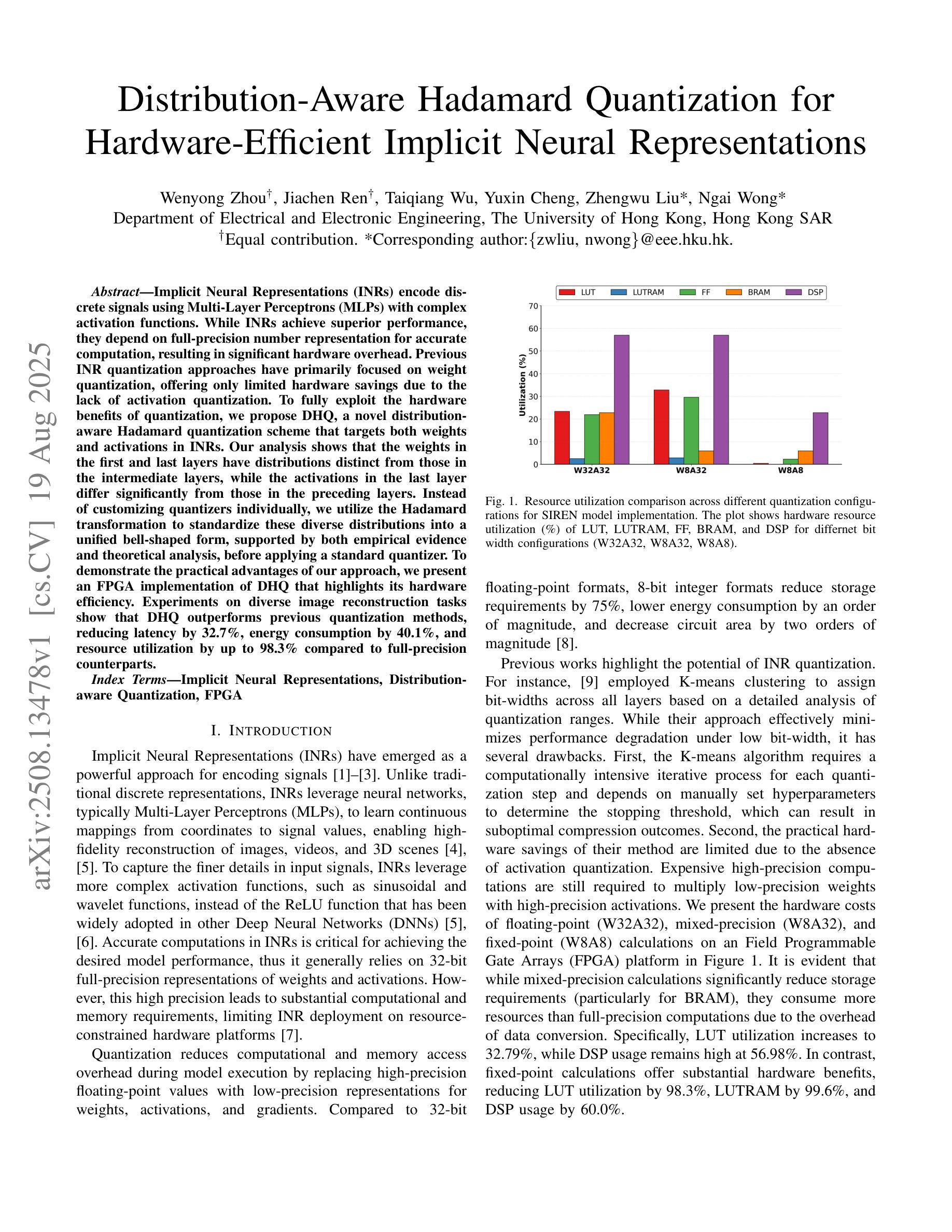
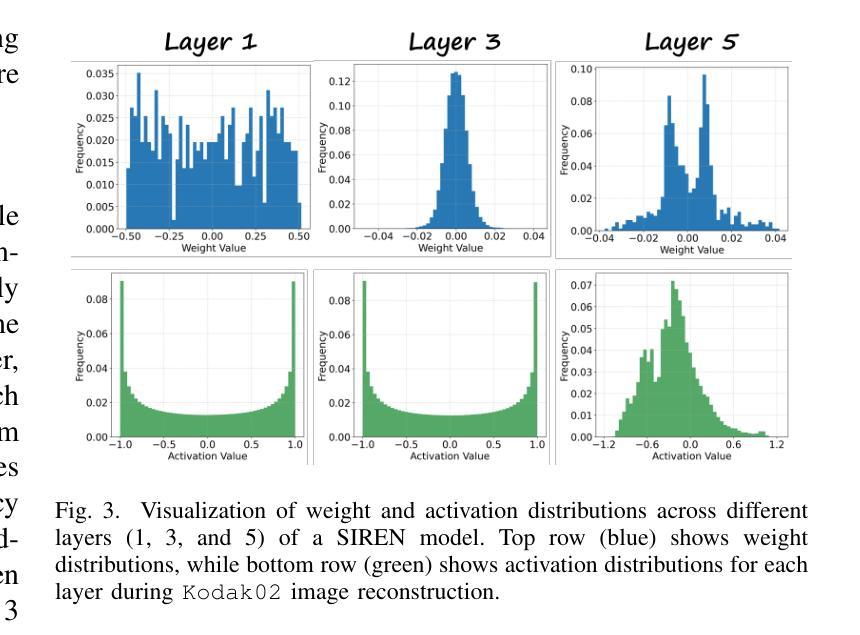
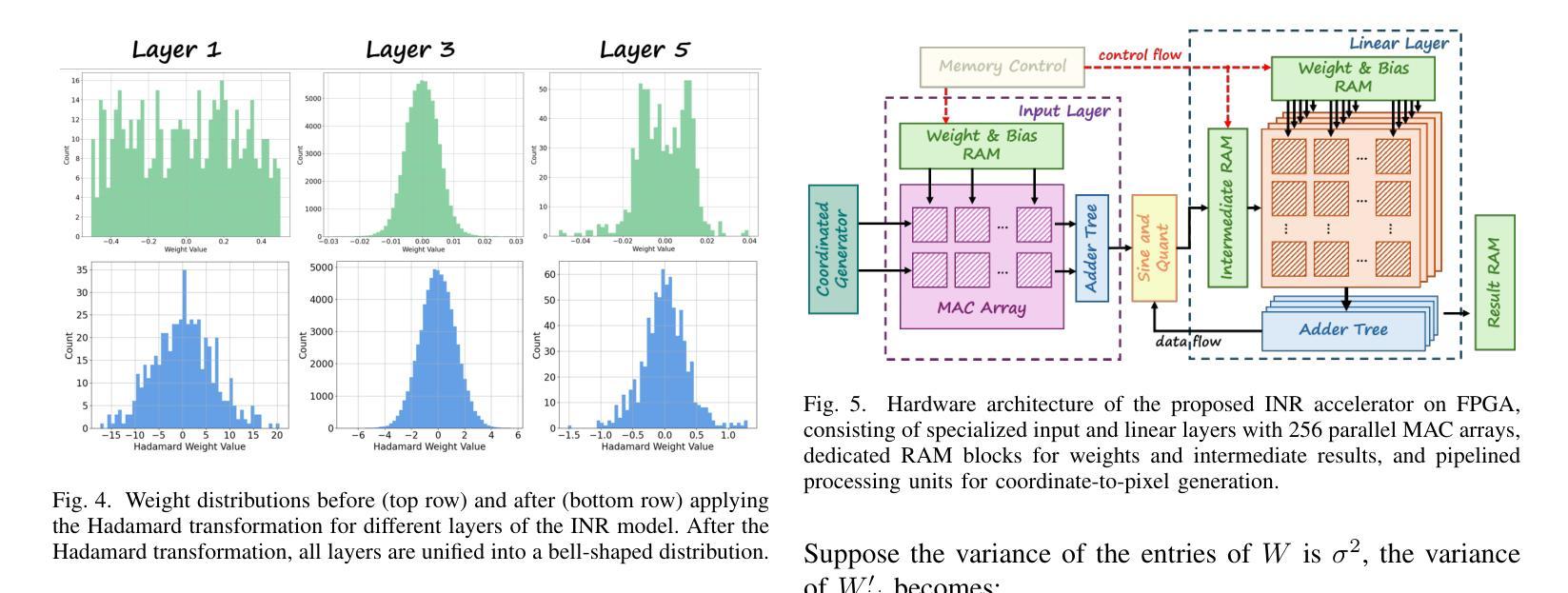
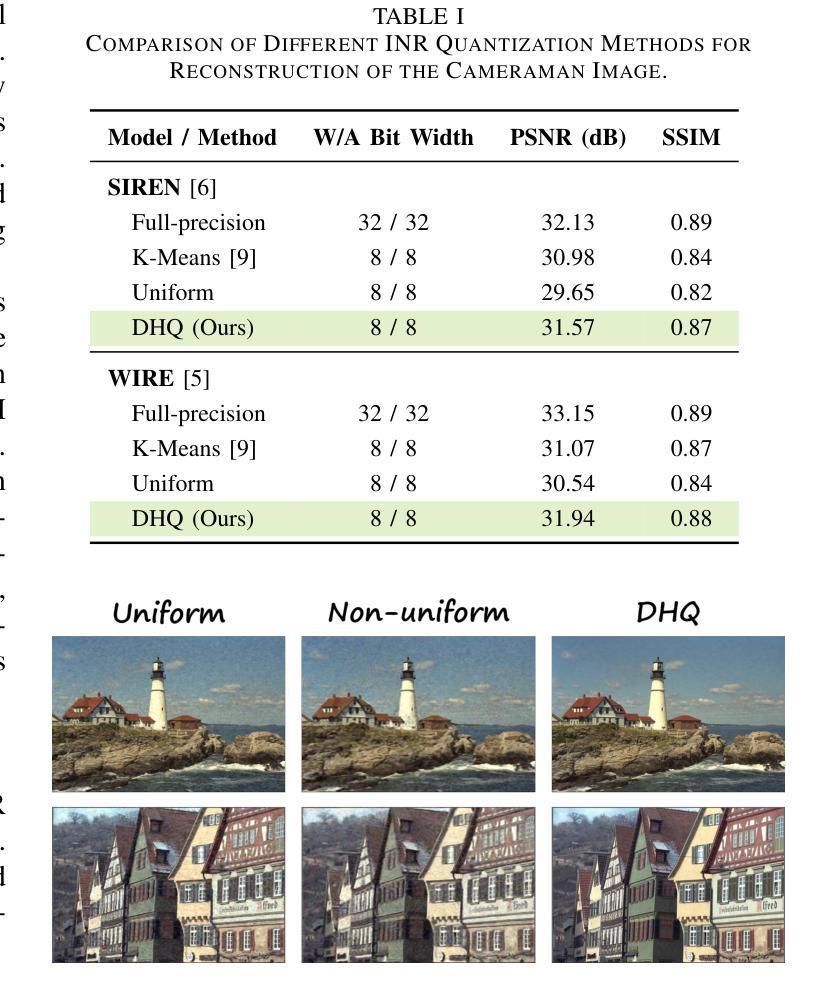
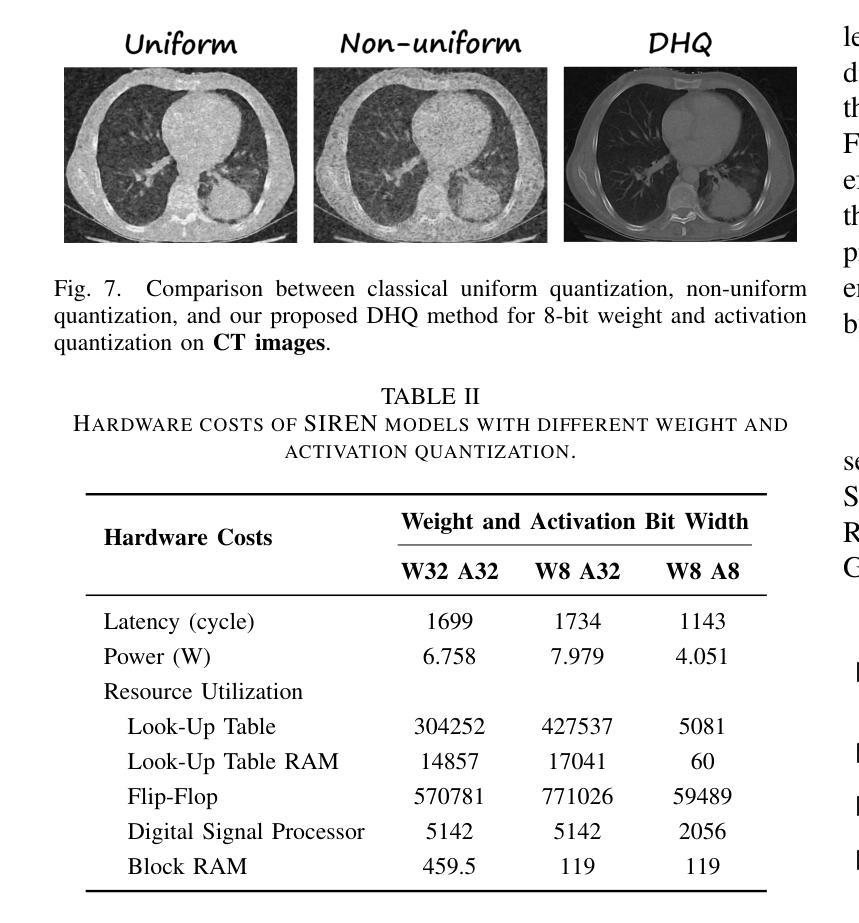
Distribution-Aware Hadamard Quantization for Hardware-Efficient Implicit Neural Representations
Authors:Wenyong Zhou, Jiachen Ren, Taiqiang Wu, Yuxin Cheng, Zhengwu Liu, Ngai Wong
Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) encode discrete signals using Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) with complex activation functions. While INRs achieve superior performance, they depend on full-precision number representation for accurate computation, resulting in significant hardware overhead. Previous INR quantization approaches have primarily focused on weight quantization, offering only limited hardware savings due to the lack of activation quantization. To fully exploit the hardware benefits of quantization, we propose DHQ, a novel distribution-aware Hadamard quantization scheme that targets both weights and activations in INRs. Our analysis shows that the weights in the first and last layers have distributions distinct from those in the intermediate layers, while the activations in the last layer differ significantly from those in the preceding layers. Instead of customizing quantizers individually, we utilize the Hadamard transformation to standardize these diverse distributions into a unified bell-shaped form, supported by both empirical evidence and theoretical analysis, before applying a standard quantizer. To demonstrate the practical advantages of our approach, we present an FPGA implementation of DHQ that highlights its hardware efficiency. Experiments on diverse image reconstruction tasks show that DHQ outperforms previous quantization methods, reducing latency by 32.7%, energy consumption by 40.1%, and resource utilization by up to 98.3% compared to full-precision counterparts.
隐式神经网络表示(INR)使用多层感知器(MLP)和复杂的激活函数来编码离散信号。尽管INR达到了优越的性能,但它们依赖于全精度数字表示来进行精确计算,导致了显著的硬件开销。先前的INR量化方法主要集中在权重量化上,由于缺乏激活量化,只能提供有限的硬件节省。为了充分利用量化的硬件优势,我们提出了DHQ,这是一种新型分布感知的Hadamard量化方案,旨在针对INR中的权重和激活。我们的分析表明,第一层和最后一层的权重分布与中间层的分布不同,而最后一层的激活与前几层的激活有很大差异。我们并不针对每种量化器进行单独定制,而是利用Hadamard变换将多样化的分布标准化为统一的钟形形式,为后续应用标准量化器提供了可能,这一过程得到了实验证据和理论分析的支撑。为了展示我们的方法的实际优势,我们展示了DHQ的FPGA实现,突出了其硬件效率。在多种图像重建任务上的实验表明,DHQ优于先前的量化方法,与全精度相比,延迟降低了32.7%,能耗降低了40.1%,资源利用率提高了高达98.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 7 figures
Summary
基于隐神经表示(INRs)使用多层感知器(MLPs)和复杂激活函数编码离散信号的方法取得了优越的性能,但其计算依赖于全精度数字表示,导致硬件开销较大。为充分利用量化的硬件优势,本文提出了一种新型分布感知哈达玛量化方案DHQ,同时针对INRs中的权重和激活进行量化。DHQ利用哈达玛变换将不同分布标准化为统一的钟形形式,再应用标准量化器。实验表明,DHQ在图像重建任务上优于先前的量化方法,降低了延迟、能耗和资源利用率。
Key Takeaways
- 隐神经表示(INRs)使用多层感知器(MLPs)和复杂激活函数编码离散信号。
- INRs的计算依赖于全精度数字表示,导致硬件开销大。
- 现有的INR量化方法主要集中在权重量化上,忽略了激活量化。
- DHQ是一种新型的分布感知哈达玛量化方案,针对INRs中的权重和激活进行量化。
- DHQ利用哈达玛变换将不同分布标准化为统一的钟形形式。
- DHQ在图像重建任务上表现出优越的性能,相较于全精度计算降低了延迟、能耗和资源利用率。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking GPT-5 for Zero-Shot Multimodal Medical Reasoning in Radiology and Radiation Oncology
Authors:Mingzhe Hu, Zach Eidex, Shansong Wang, Mojtaba Safari, Qiang Li, Xiaofeng Yang
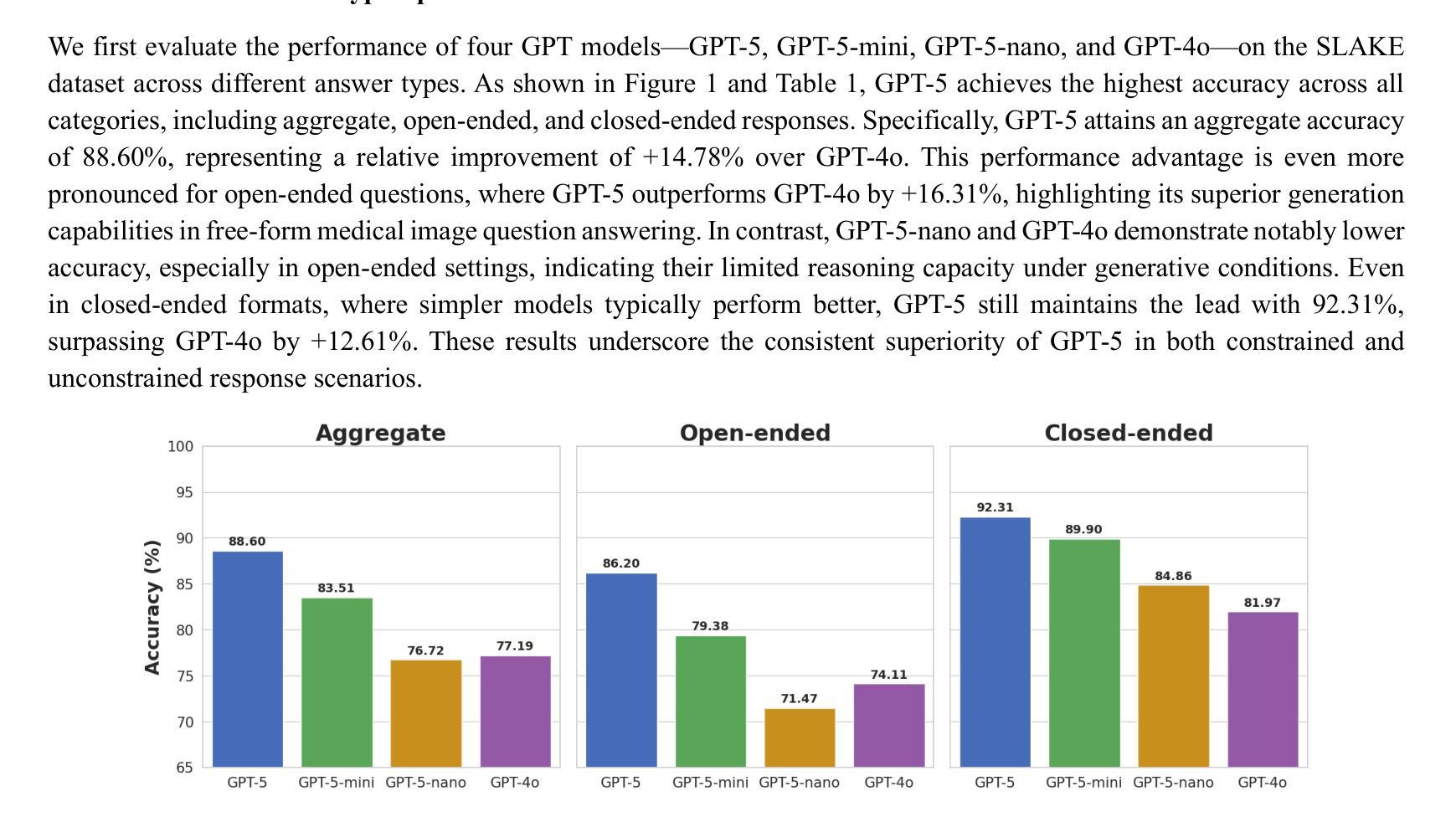
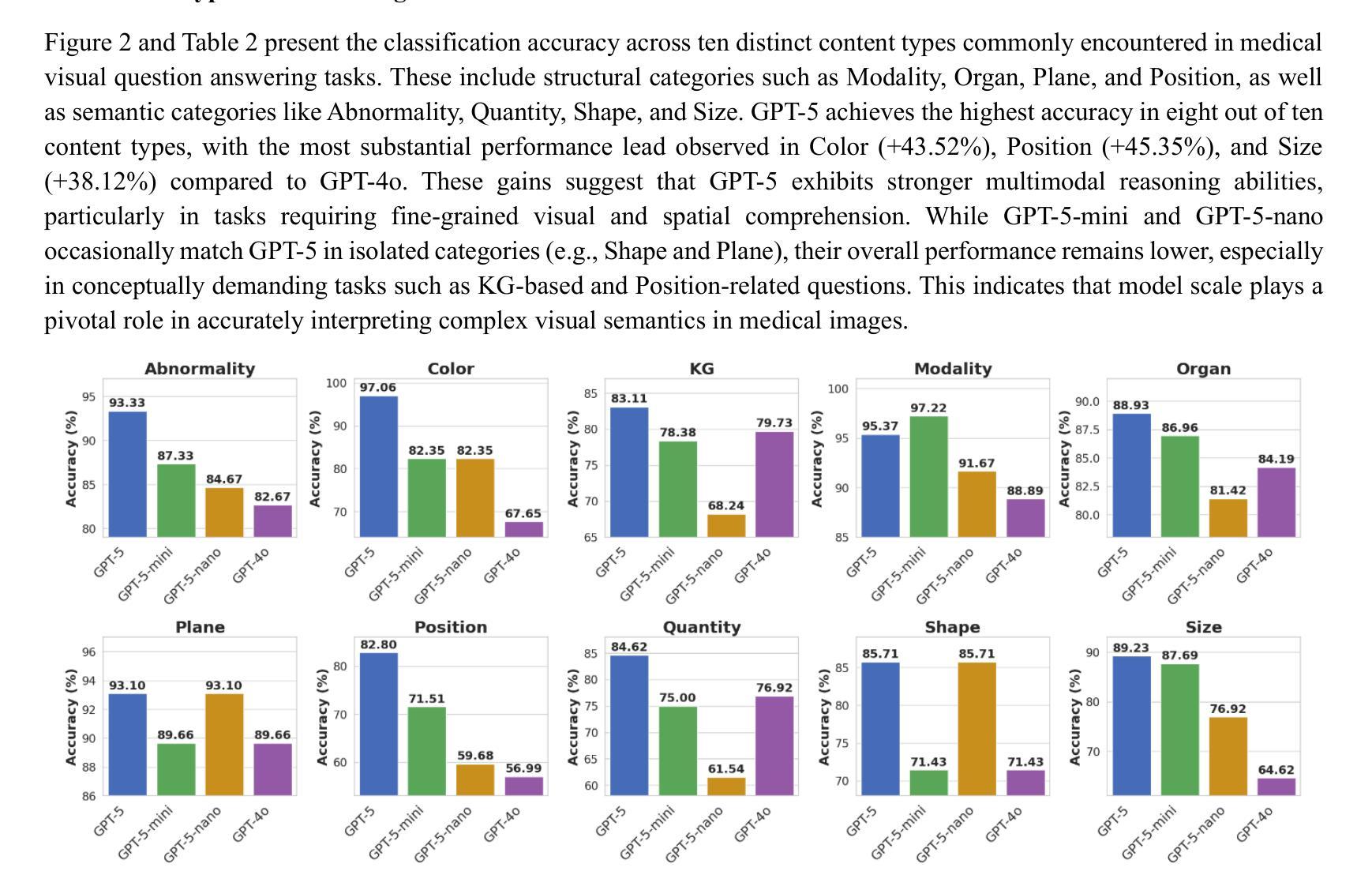
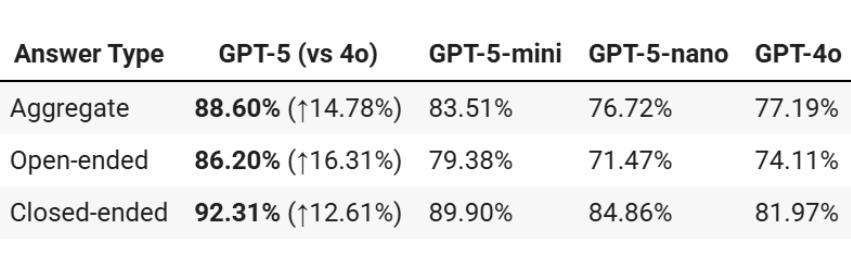
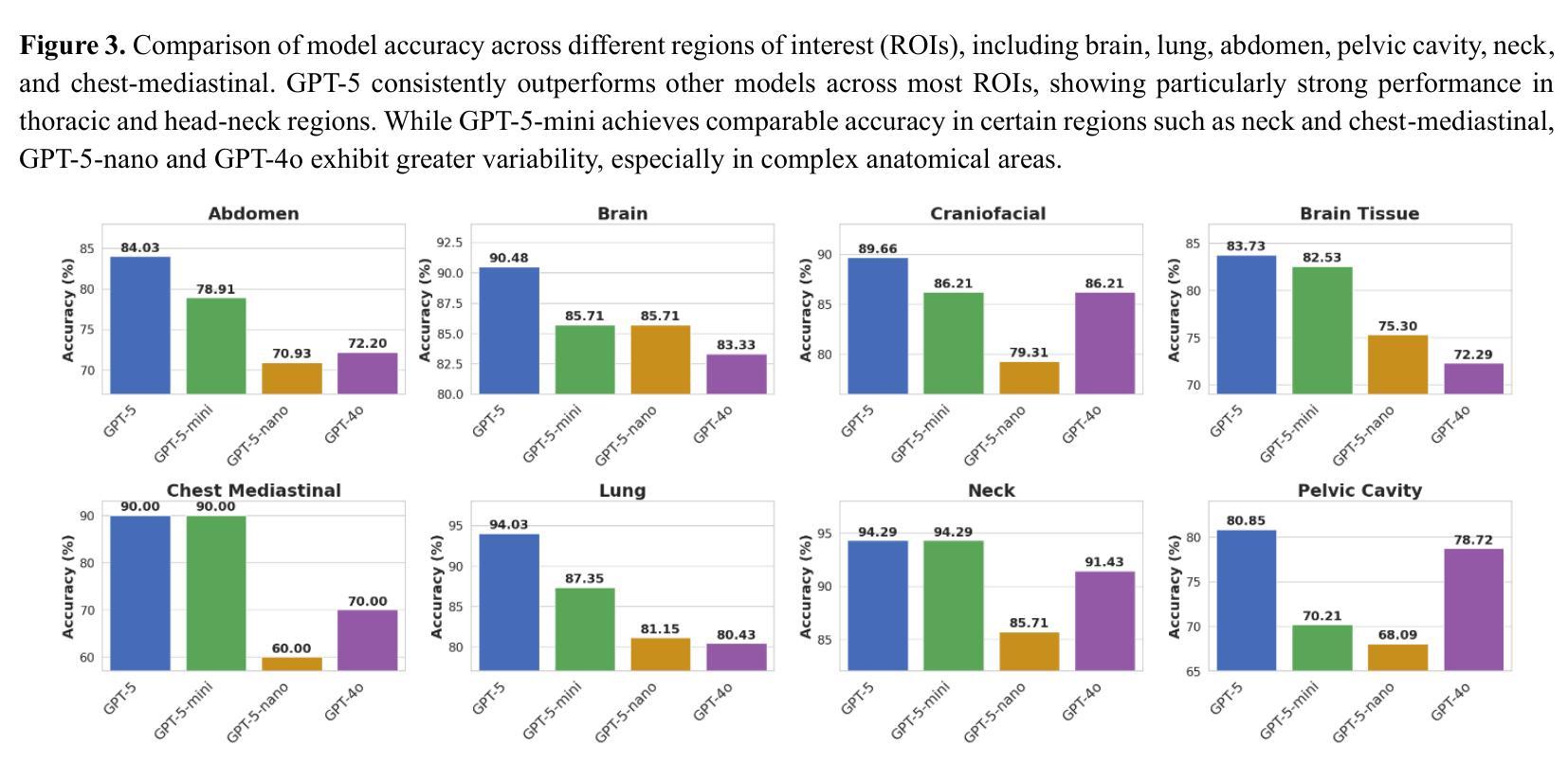
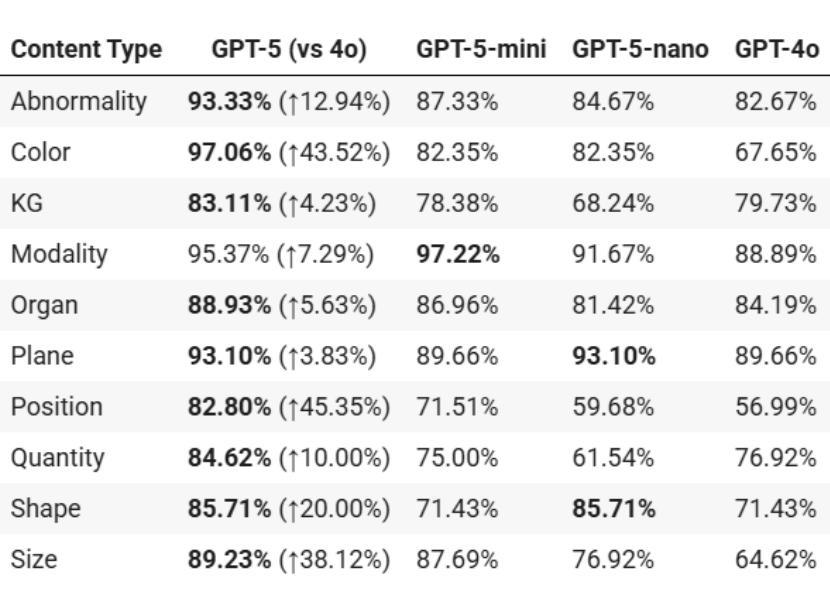
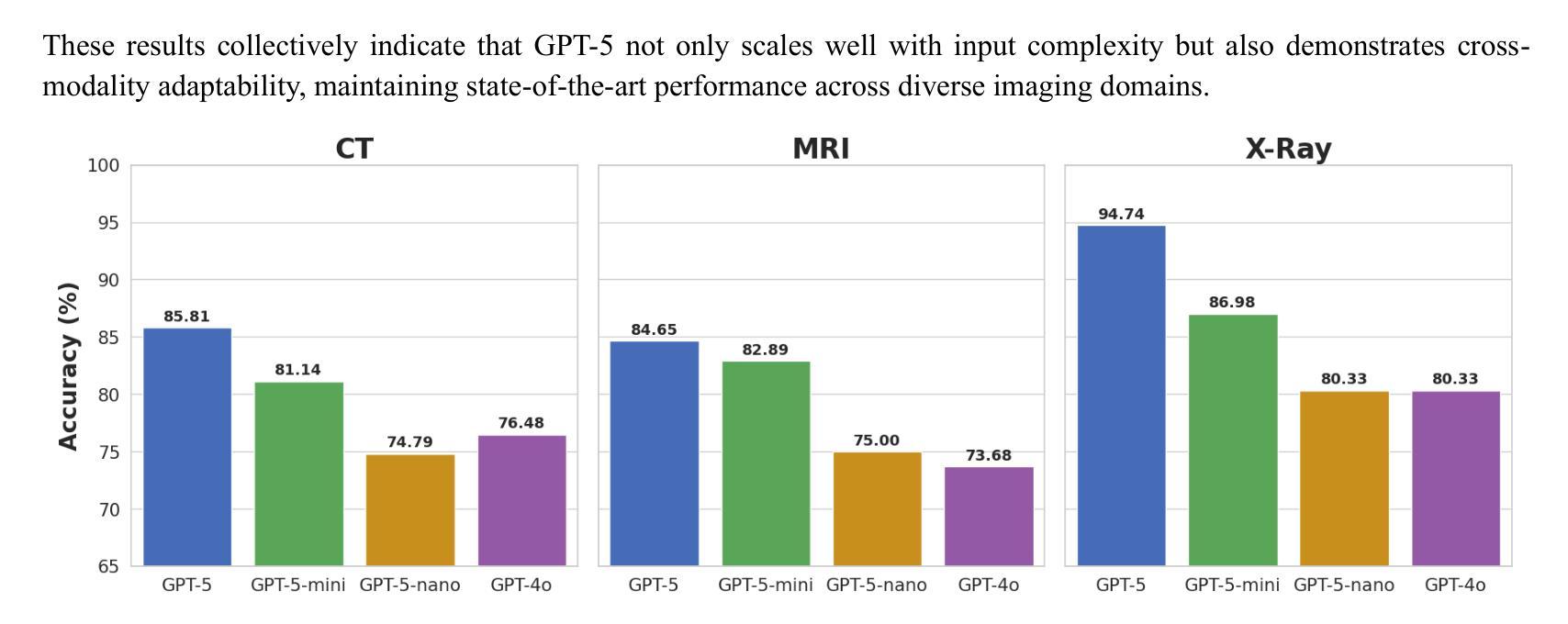
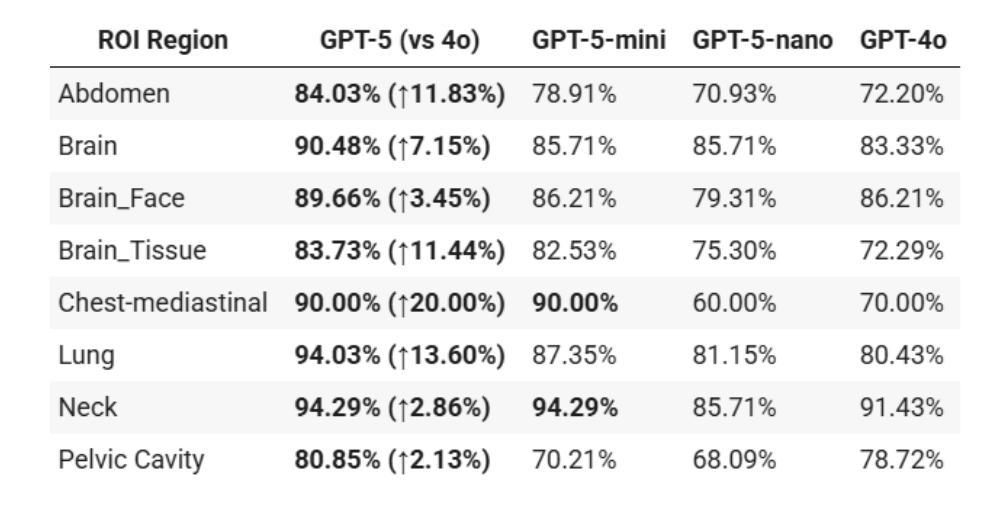
Radiology, radiation oncology, and medical physics require decision-making that integrates medical images, textual reports, and quantitative data under high-stakes conditions. With the introduction of GPT-5, it is critical to assess whether recent advances in large multimodal models translate into measurable gains in these safety-critical domains. We present a targeted zero-shot evaluation of GPT-5 and its smaller variants (GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano) against GPT-4o across three representative tasks. We present a targeted zero-shot evaluation of GPT-5 and its smaller variants (GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano) against GPT-4o across three representative tasks: (1) VQA-RAD, a benchmark for visual question answering in radiology; (2) SLAKE, a semantically annotated, multilingual VQA dataset testing cross-modal grounding; and (3) a curated Medical Physics Board Examination-style dataset of 150 multiple-choice questions spanning treatment planning, dosimetry, imaging, and quality assurance. Across all datasets, GPT-5 achieved the highest accuracy, with substantial gains over GPT-4o up to +20.00% in challenging anatomical regions such as the chest-mediastinal, +13.60% in lung-focused questions, and +11.44% in brain-tissue interpretation. On the board-style physics questions, GPT-5 attained 90.7% accuracy (136/150), exceeding the estimated human passing threshold, while GPT-4o trailed at 78.0%. These results demonstrate that GPT-5 delivers consistent and often pronounced performance improvements over GPT-4o in both image-grounded reasoning and domain-specific numerical problem-solving, highlighting its potential to augment expert workflows in medical imaging and therapeutic physics.
放射学、放射肿瘤学和医学物理学需要在高风险的条件下,结合医学图像、文本报告和定量数据进行决策。随着GPT-5的推出,评估近期大型多模式模型的进展是否能为这些安全关键的领域带来可衡量的收益至关重要。我们针对三项代表性任务,对GPT-5及其小型变体(GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano)与GPT-4o进行了有针对性的零样本评估。
一是VQA-RAD,这是放射学中视觉问答的基准测试;二是SLAKE,这是一个语义注释、多语言问答数据集,用于测试跨模态定位;三是精选的医学物理委员会考试风格数据集,包含150道关于治疗计划、剂量测定、成像和质量保证的多项选择题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要评估了GPT-5及其小型版本(GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano)在放射学、放射肿瘤学和医学物理等领域内的决策能力,通过与GPT-4o的比较,展示了GPT-5在这些安全关键领域中的显著性能提升。在视觉问答、跨模态接地测试以及医学物理考试风格的数据集上,GPT-5均表现出最高准确度,且在特定区域和问题上较GPT-4o有显著提高。最终,研究表明GPT-5具有增强医学影像和医治物理工作流程的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-5在放射学、放射肿瘤学和医学物理等领域展现出强大的决策能力。
- GPT-5及其小型版本在多个代表性任务中表现出比GPT-4o更高的准确性。
- 在视觉问答、跨模态接地测试和医学物理考试风格的数据集上,GPT-5达到最高准确度。
- GPT-5在特定区域和问题上较GPT-4o有显著提高,如在挑战区域解剖学、肺部问题和脑组织解释方面。
- GPT-5在医学物理考试风格的问题中达到90.7%的准确率,超过估计的人类及格门槛。
- GPT-4o在多个任务中的表现不及GPT-5,尤其在复杂问题上。
点此查看论文截图

Fully Automated Segmentation of Fiber Bundles in Anatomic Tracing Data
Authors:Kyriaki-Margarita Bintsi, Yaël Balbastre, Jingjing Wu, Julia F. Lehman, Suzanne N. Haber, Anastasia Yendiki
Anatomic tracer studies are critical for validating and improving diffusion MRI (dMRI) tractography. However, large-scale analysis of data from such studies is hampered by the labor-intensive process of annotating fiber bundles manually on histological slides. Existing automated methods often miss sparse bundles or require complex post-processing across consecutive sections, limiting their flexibility and generalizability. We present a streamlined, fully automated framework for fiber bundle segmentation in macaque tracer data, based on a U-Net architecture with large patch sizes, foreground aware sampling, and semisupervised pre-training. Our approach eliminates common errors such as mislabeling terminals as bundles, improves detection of sparse bundles by over 20% and reduces the False Discovery Rate (FDR) by 40% compared to the state-of-the-art, all while enabling analysis of standalone slices. This new framework will facilitate the automated analysis of anatomic tracing data at a large scale, generating more ground-truth data that can be used to validate and optimize dMRI tractography methods.
解剖追踪研究对于验证和改进扩散MRI(dMRI)图谱技术至关重要。然而,此类研究的数据大规模分析受到手动在组织切片上注释纤维束的劳动强度大的阻碍。现有的自动化方法往往会遗漏稀疏的束或需要在连续的切片上进行复杂的后处理,这限制了其灵活性和通用性。我们提出了一个在猕猴追踪数据中纤维束分割的简化、全自动框架,该框架基于具有大补丁大小、前景感知采样和半监督预训练的U-Net架构。我们的方法消除了常见的错误,如将终端误标记为束,提高了对稀疏束的检测率超过20%,并且与最新技术相比,降低了40%的误报率(FDR),同时支持单独切片的分析。这一新框架将促进解剖追踪数据的自动大规模分析,生成更多的真实数据,可用于验证和优化dMRI图谱技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CDMRI, MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于U-Net架构、大补丁尺寸、前景感知采样和半监督预训练,提出一个简化、全自动化的框架,用于猕猴追踪数据的纤维束分割。该方法消除了误标记终端为束的常见错误,提高了稀疏束的检测率,降低了误报率,并能够实现独立切片的分析。此新框架将促进大规模自动分析解剖追踪数据,生成更多可用于验证和优化扩散MRI成像方法的地面真实数据。
Key Takeaways
- U-Net架构结合了大规模数据处理的能力与前瞳感知采样技术用于纤维束分割。
- 此方法实现了全自动化的纤维束分割,提高了检测稀疏纤维束的效率。
- 与现有技术相比,新方法降低了误报率(FDR)并消除了误标记终端为纤维束的错误。
- 新框架适用于独立切片的分析,增强了其灵活性和通用性。
- 该方法有助于大规模自动分析解剖追踪数据,生成更多地面真实数据。
- 这些地面真实数据可用于验证和优化扩散MRI成像(dMRI)的追踪方法。
点此查看论文截图

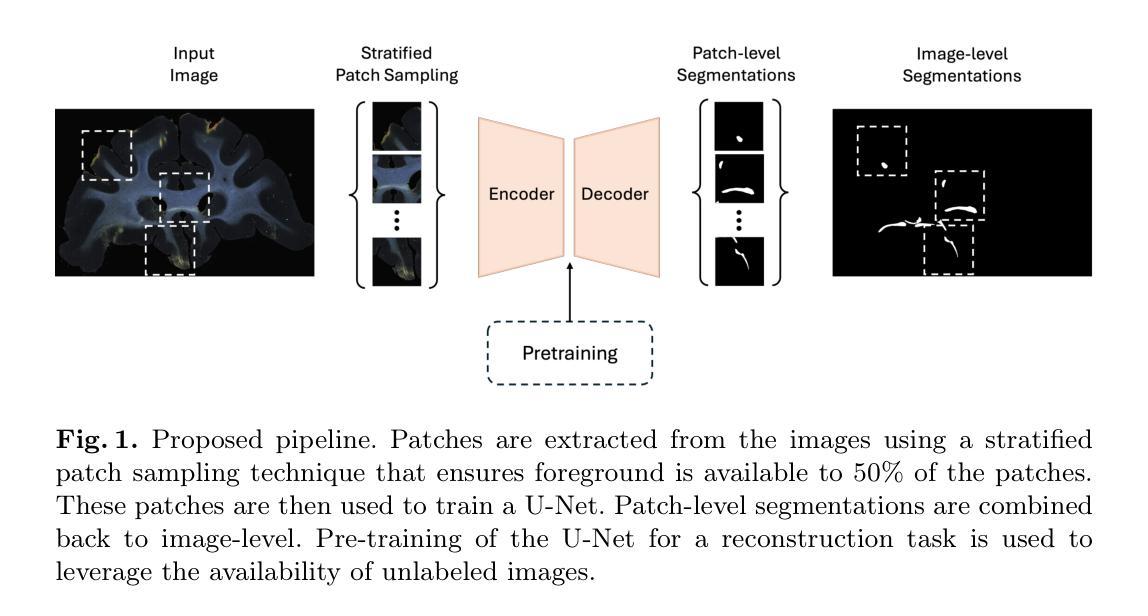
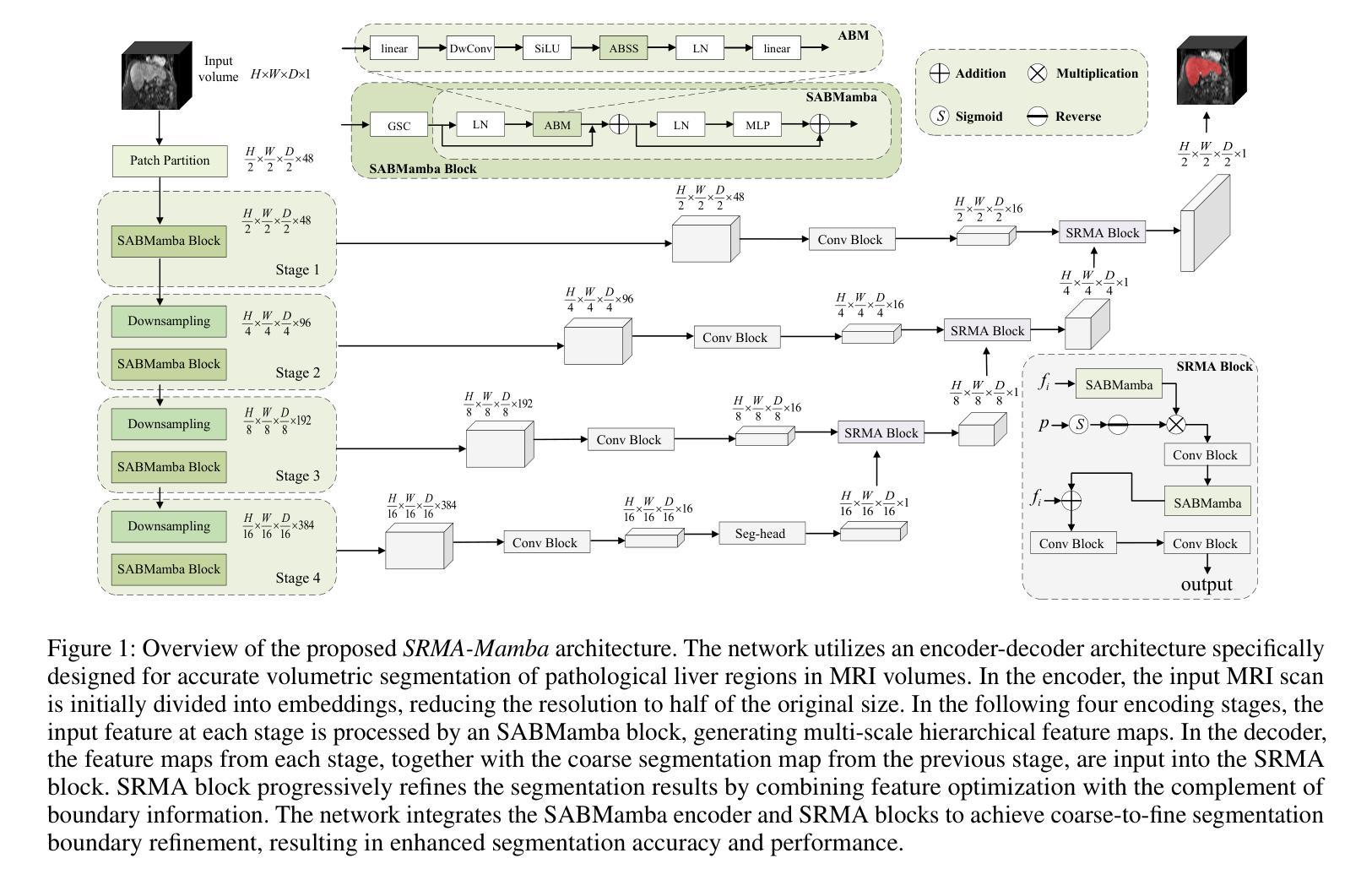
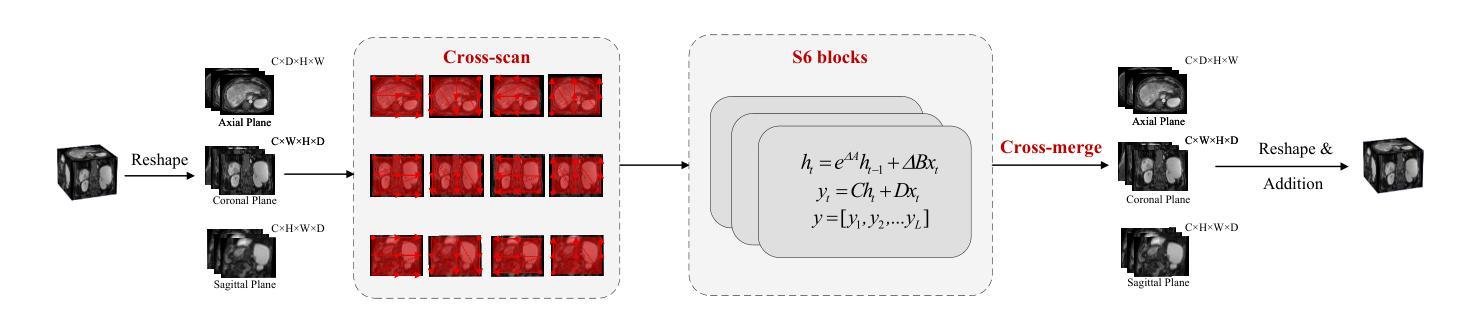
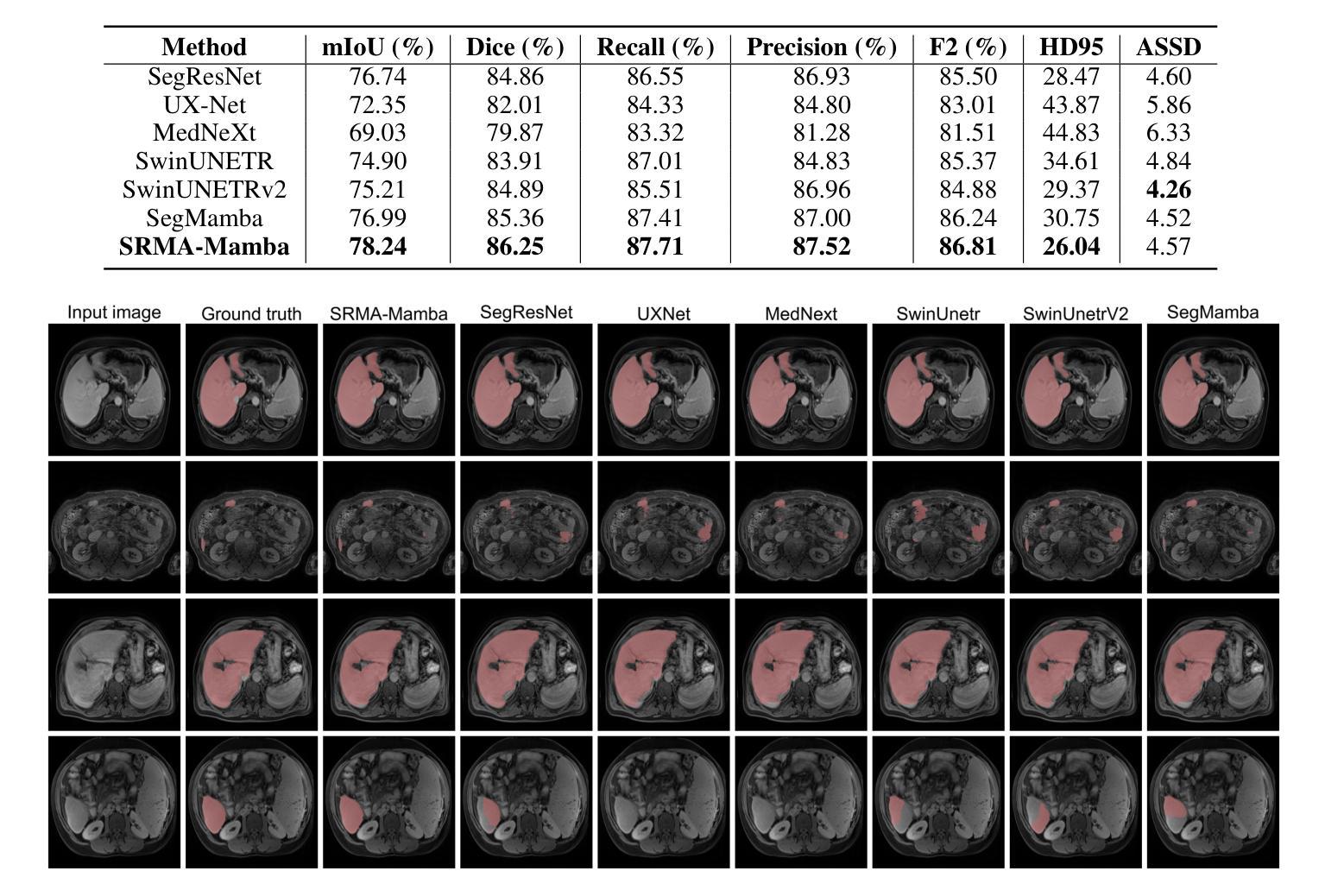
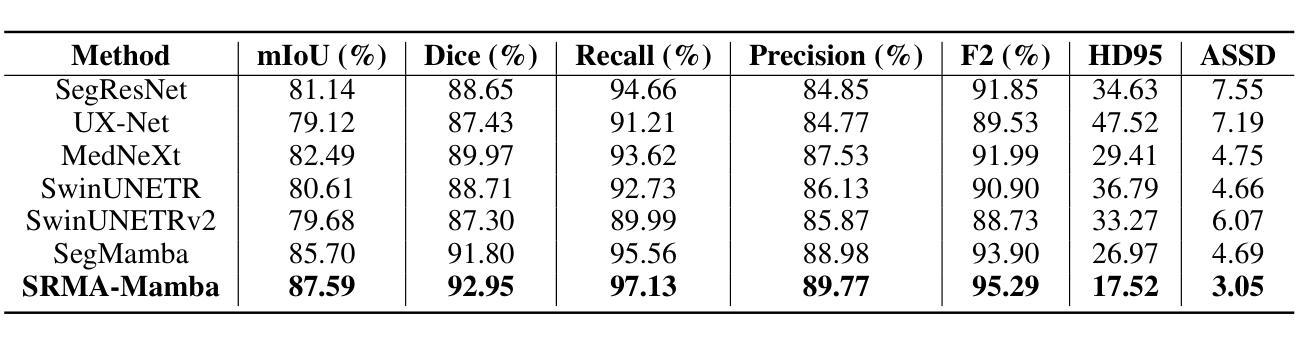
SRMA-Mamba: Spatial Reverse Mamba Attention Network for Pathological Liver Segmentation in MRI Volumes
Authors:Jun Zeng, Yannan Huang, Elif Keles, Halil Ertugrul Aktas, Gorkem Durak, Nikhil Kumar Tomar, Quoc-Huy Trinh, Deepak Ranjan Nayak, Ulas Bagci, Debesh Jha
Liver Cirrhosis plays a critical role in the prognosis of chronic liver disease. Early detection and timely intervention are critical in significantly reducing mortality rates. However, the intricate anatomical architecture and diverse pathological changes of liver tissue complicate the accurate detection and characterization of lesions in clinical settings. Existing methods underutilize the spatial anatomical details in volumetric MRI data, thereby hindering their clinical effectiveness and explainability. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel Mamba-based network, SRMA-Mamba, designed to model the spatial relationships within the complex anatomical structures of MRI volumes. By integrating the Spatial Anatomy-Based Mamba module (SABMamba), SRMA-Mamba performs selective Mamba scans within liver cirrhotic tissues and combines anatomical information from the sagittal, coronal, and axial planes to construct a global spatial context representation, enabling efficient volumetric segmentation of pathological liver structures. Furthermore, we introduce the Spatial Reverse Attention module (SRMA), designed to progressively refine cirrhotic details in the segmentation map, utilizing both the coarse segmentation map and hierarchical encoding features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SRMA-Mamba surpasses state-of-the-art methods, delivering exceptional performance in 3D pathological liver segmentation. Our code is available for public: https://github.com/JunZengz/SRMA-Mamba.
肝硬化在慢性肝病的预后中扮演着重要角色。早期检测和及时干预是显著降低死亡率的关键。然而,肝脏组织的复杂解剖结构和多样的病理变化使临床环境中病变的准确检测和特征描述变得复杂。现有方法未能充分利用体积MRI数据中的空间解剖细节,从而阻碍了其在临床上的效果和可解释性。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了一种新型的基于Mamba的网络,名为SRMA-Mamba,旨在模拟MRI体积中复杂解剖结构内的空间关系。通过集成基于空间解剖的Mamba模块(SABMamba),SRMA-Mamba在肝硬化组织内进行选择性Mamba扫描,并结合来自矢状面、冠状面和轴面的解剖信息,构建全局空间上下文表示,从而实现病理肝脏结构的高效体积分割。此外,我们还引入了空间反向注意力模块(SRMA),旨在利用粗分割图和分层编码特征逐步优化肝硬化细节在分割图上的表现。大量实验表明,SRMA-Mamba超越了最先进的方法,在3D病理肝脏分割方面表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码已公开:https://github.com/JunZengz/SRMA-Mamba。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了肝脏硬化在慢性肝病预后中的重要作用,强调早期检测和及时干预对降低死亡率的重要性。针对肝脏组织复杂解剖结构和多变病理变化导致的临床准确检测和表征病灶的困难,提出了一种基于Mamba网络的新方法SRMA-Mamba。该方法通过整合空间解剖基础上的Mamba模块(SABMamba),能够在肝脏硬化组织中进行选择性Mamba扫描,并结合矢状面、冠状面和轴面的解剖信息构建全局空间上下文表示,实现病理肝脏结构的高效三维分割。此外,还引入了空间反向注意力模块(SRMA),用于逐步优化分割图中的肝硬化细节。实验表明,SRMA-Mamba超越了最新方法,在三维病理肝脏分割中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 肝脏硬化在慢性肝病预后中起关键作用,强调早期检测和及时干预的重要性。
- 现有方法未能充分利用MRI数据的空间解剖细节,影响临床效果和解释性。
- 提出了一种新的基于Mamba网络的SRMA-Mamba方法,用于建模MRI体积内复杂解剖结构的空间关系。
- SABMamba模块实现选择性Mamba扫描,结合多平面解剖信息构建全局空间上下文表示。
- SRMA模块用于逐步优化分割图中的肝硬化细节,提高分割性能。
- SRMA-Mamba在三维病理肝脏分割方面表现出卓越性能,超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

KonfAI: A Modular and Fully Configurable Framework for Deep Learning in Medical Imaging
Authors:Valentin Boussot, Jean-Louis Dillenseger
KonfAI is a modular, extensible, and fully configurable deep learning framework specifically designed for medical imaging tasks. It enables users to define complete training, inference, and evaluation workflows through structured YAML configuration files, without modifying the underlying code. This declarative approach enhances reproducibility, transparency, and experimental traceability while reducing development time. Beyond the capabilities of standard pipelines, KonfAI provides native abstractions for advanced strategies including patch-based learning, test-time augmentation, model ensembling, and direct access to intermediate feature representations for deep supervision. It also supports complex multi-model training setups such as generative adversarial architectures. Thanks to its modular and extensible architecture, KonfAI can easily accommodate custom models, loss functions, and data processing components. The framework has been successfully applied to segmentation, registration, and image synthesis tasks, and has contributed to top-ranking results in several international medical imaging challenges. KonfAI is open source and available at \href{https://github.com/vboussot/KonfAI}{https://github.com/vboussot/KonfAI}.
KonfAI是一个专为医学成像任务设计的模块化、可扩展和可完全配置的深度学习框架。它使用户能够通过结构化的YAML配置文件定义完整的训练、推理和评估工作流程,而无需修改底层代码。这种声明式方法提高了可重复性、透明度和实验可追溯性,同时减少了开发时间。除了标准管道的功能外,KonfAI还提供本地抽象以支持高级策略,包括基于补丁的学习、测试时增强、模型集成和深度监督的直接访问中间特征表示。它还支持复杂的多模型训练设置,如生成对抗架构。由于其模块化和可扩展的架构,KonfAI可以轻松容纳自定义模型、损失函数和数据处理组件。该框架已成功应用于分割、注册和图像合成任务,并为多个国际医学成像挑战带来了排名靠前的结果。KonfAI是开源的,可在[https://github.com/vboussot/KonfAI]处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/vboussot/KonfAI
Summary
康菲AI是一个模块化、可扩展且可配置的深度学习框架,专为医学影像任务设计。它使用户能够通过结构化YAML配置文件定义完整的训练、推理和评估流程,无需修改底层代码。这一声明式方法提高了重复性、透明性和实验可追溯性,并缩短了开发时间。此外,康菲AI还提供原生抽象,支持高级策略如基于补丁的学习、测试时增强、模型集成和深度监督的直接访问中间特征表示,并支持复杂的多模型训练设置,如生成对抗架构。其模块化可扩展架构可轻松容纳自定义模型、损失函数和数据处理组件。该框架已成功应用于分割、注册和图像合成任务,并在多个国际医学影像挑战中取得名列前茅的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 康菲AI是一个用于医学影像任务的深度学习框架。
- 它通过结构化YAML配置文件进行配置,用户无需修改底层代码。
- 康菲AI采用声明式方法,提高重复性、透明性和实验可追溯性。
- 该框架支持高级策略,如基于补丁的学习、测试时增强和模型集成。
- 康菲AI提供对中间特征表示的深度监督的直接访问。
- 它支持复杂的多模型训练设置,包括生成对抗架构。
点此查看论文截图



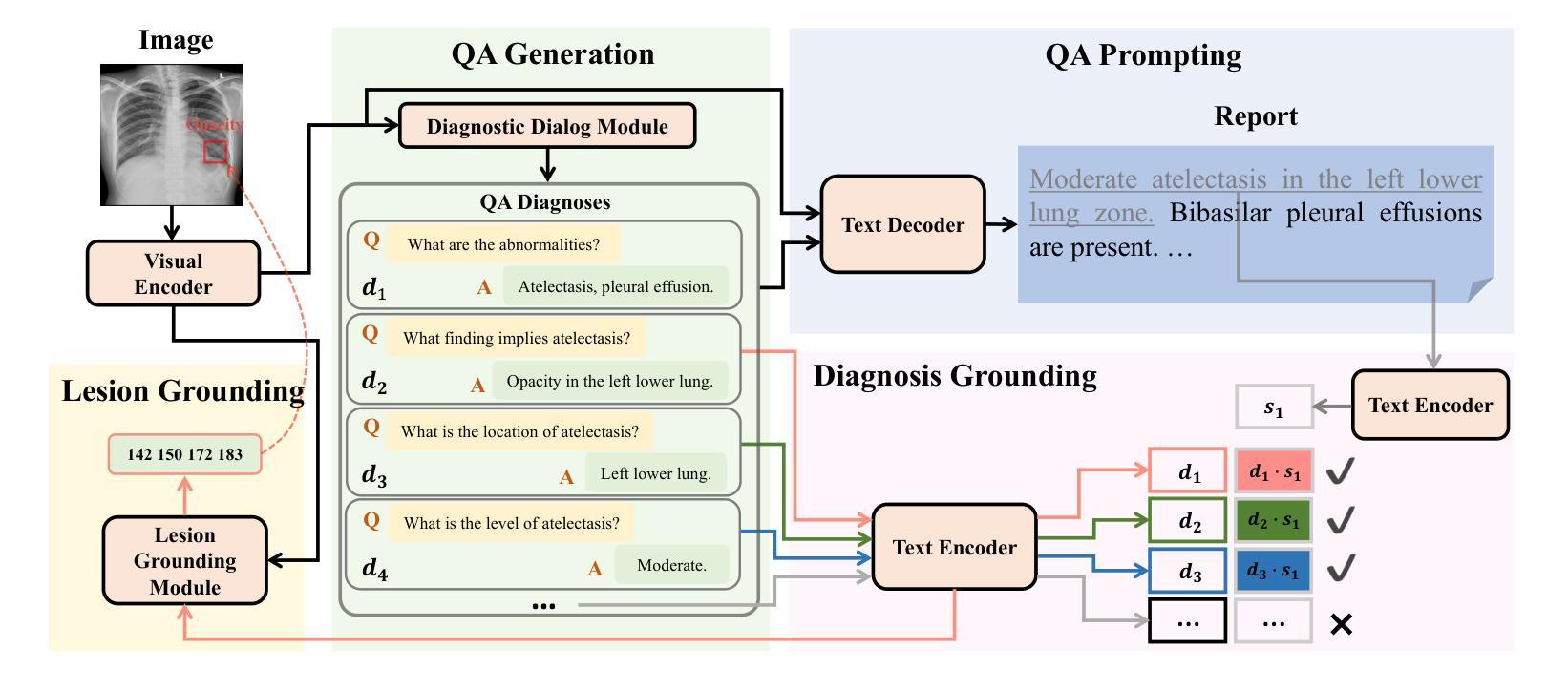
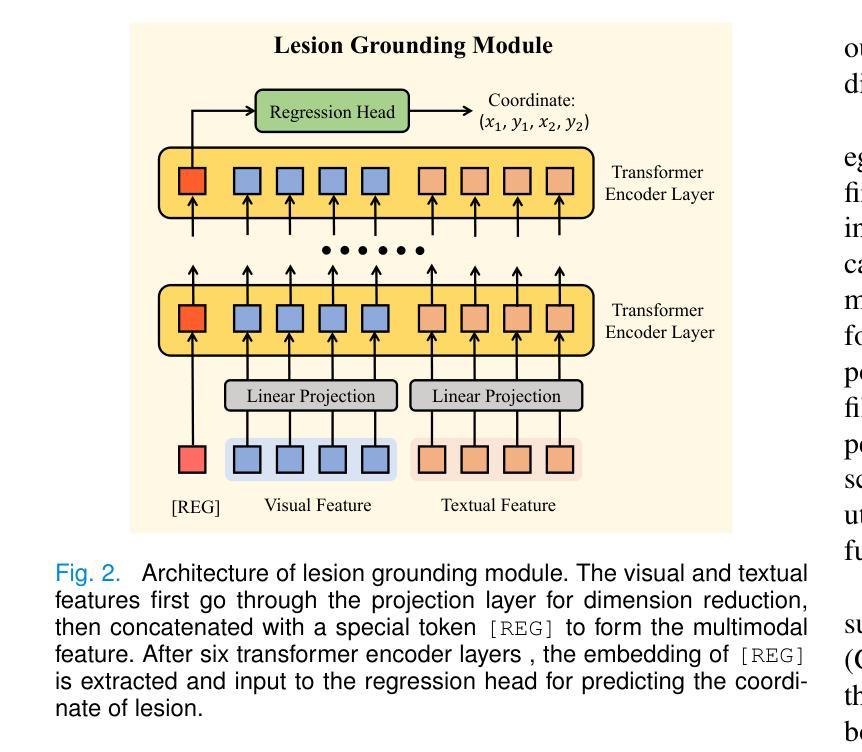
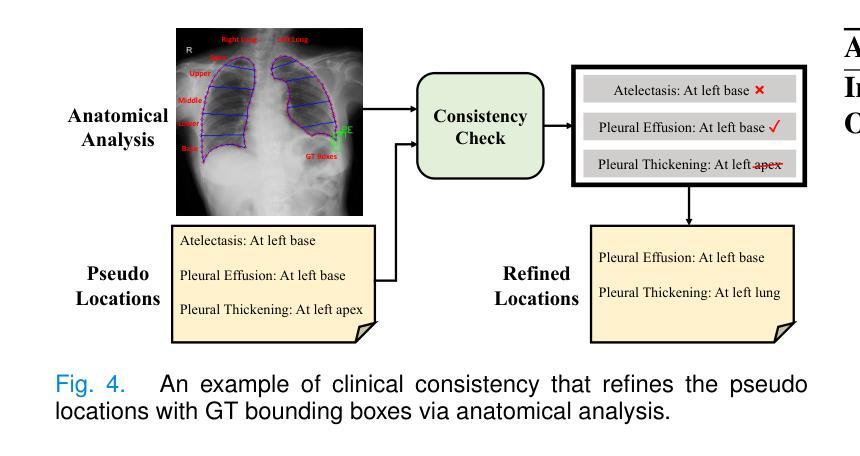
A Chain of Diagnosis Framework for Accurate and Explainable Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Haibo Jin, Haoxuan Che, Sunan He, Hao Chen
Despite the progress of radiology report generation (RRG), existing works face two challenges: 1) The performances in clinical efficacy are unsatisfactory, especially for lesion attributes description; 2) the generated text lacks explainability, making it difficult for radiologists to trust the results. To address the challenges, we focus on a trustworthy RRG model, which not only generates accurate descriptions of abnormalities, but also provides basis of its predictions. To this end, we propose a framework named chain of diagnosis (CoD), which maintains a chain of diagnostic process for clinically accurate and explainable RRG. It first generates question-answer (QA) pairs via diagnostic conversation to extract key findings, then prompts a large language model with QA diagnoses for accurate generation. To enhance explainability, a diagnosis grounding module is designed to match QA diagnoses and generated sentences, where the diagnoses act as a reference. Moreover, a lesion grounding module is designed to locate abnormalities in the image, further improving the working efficiency of radiologists. To facilitate label-efficient training, we propose an omni-supervised learning strategy with clinical consistency to leverage various types of annotations from different datasets. Our efforts lead to 1) an omni-labeled RRG dataset with QA pairs and lesion boxes; 2) a evaluation tool for assessing the accuracy of reports in describing lesion location and severity; 3) extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of CoD, where it outperforms both specialist and generalist models consistently on two RRG benchmarks and shows promising explainability by accurately grounding generated sentences to QA diagnoses and images.
尽管放射学报告生成(RRG)有所进展,但现有工作面临两大挑战:1)在临床效果方面的表现不尽如人意,特别是在病灶属性描述方面;2)生成的文本缺乏可解释性,使放射科医生难以信任结果。为了应对这些挑战,我们专注于一个可信赖的RRG模型,该模型不仅能生成异常情况的准确描述,还能为预测提供依据。为此,我们提出了一个名为“诊断链”(CoD)的框架,它保持诊断过程的连续性,以实现临床准确和可解释的RRG。首先,它通过诊断对话生成问答(QA)对,以提取关键发现。然后,使用QA诊断提示大型语言模型进行准确生成。为了提高可解释性,设计了一个诊断接地模块来匹配QA诊断和生成的句子,其中诊断作为参考。此外,还设计了一个病灶定位模块,用于在图像中定位异常,进一步提高放射科医生的工作效率。为了促进标签高效训练,我们提出了一种具有临床一致性的全监督学习策略,以利用不同数据集的各种类型的注释。我们的努力带来了以下成果:1)一个带有QA对和病灶框的全标签RRG数据集;2)一个评估报告描述病灶位置和严重程度准确性的评估工具;3)大量实验证明了CoD的有效性,它在两个RRG基准测试上始终优于专业模型和通用模型,并通过将生成的句子准确地对接到QA诊断和图像上,显示出有前景的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE TMI
Summary
本文提出一个名为诊断链(CoD)的可信放射学报告生成(RRG)模型框架,旨在解决现有工作中的两大挑战:临床效果不佳和生成文本缺乏解释性。CoD通过生成问答(QA)对来提取关键发现,并使用QA诊断提示大型语言模型进行准确生成。为提高解释性,设计了诊断接地模块来匹配QA诊断和生成的句子,同时设计病灶定位模块以提高放射科医生的工作效率。此外,还提出了一种利用多种类型注释和不同数据集的全监督学习策略,以实现标签效率训练。该框架能生成具有问答对和病灶框的全方位标记RRG数据集,并提供评估报告描述病灶位置和严重性的准确性工具。实验证明,CoD在两种RRG基准测试上表现优于专业模型和通用模型,且通过准确地将生成的句子与QA诊断和图像进行匹配,展现出良好的解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有放射学报告生成工作存在临床效果不佳和生成文本缺乏解释性的挑战。
- 提出的诊断链(CoD)模型框架旨在解决这些问题,实现准确且可解释的放射学报告生成。
- CoD通过生成问答对来提取关键发现,并使用QA诊断提示大型语言模型进行文本生成。
- 诊断接地模块和病灶定位模块的设计提高了模型的解释性和工作效率。
- 采用了全监督学习策略,利用多种类型注释和不同数据集进行标签效率训练。
- CoD能生成具有问答对和病灶框的全方位标记RRG数据集。
点此查看论文截图

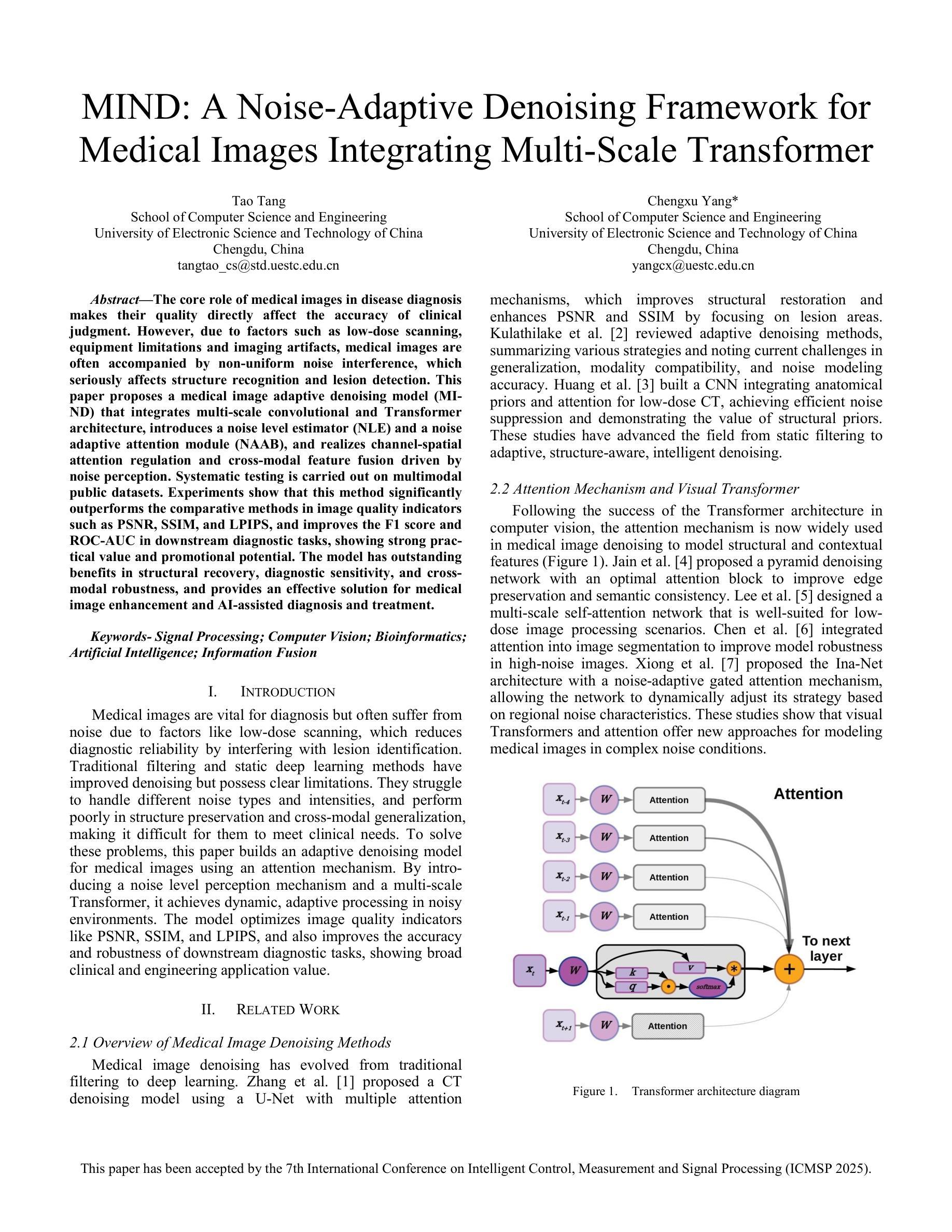
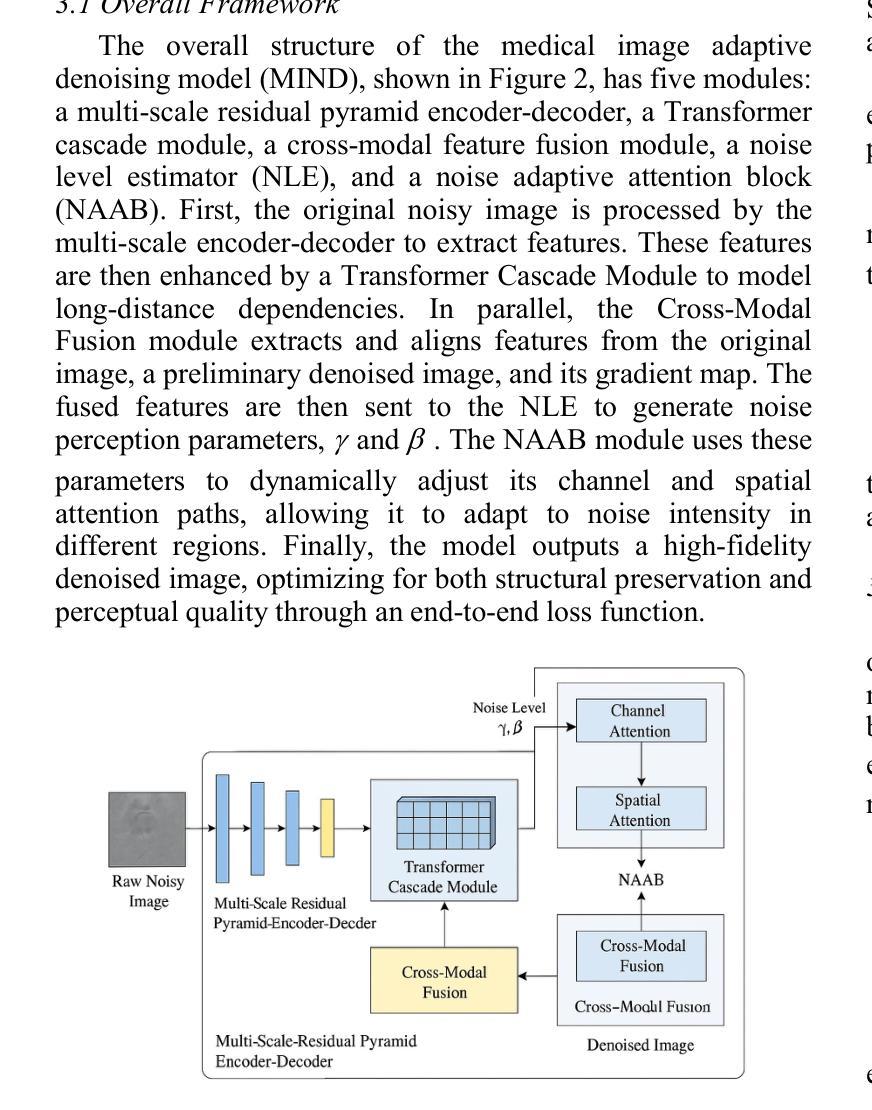
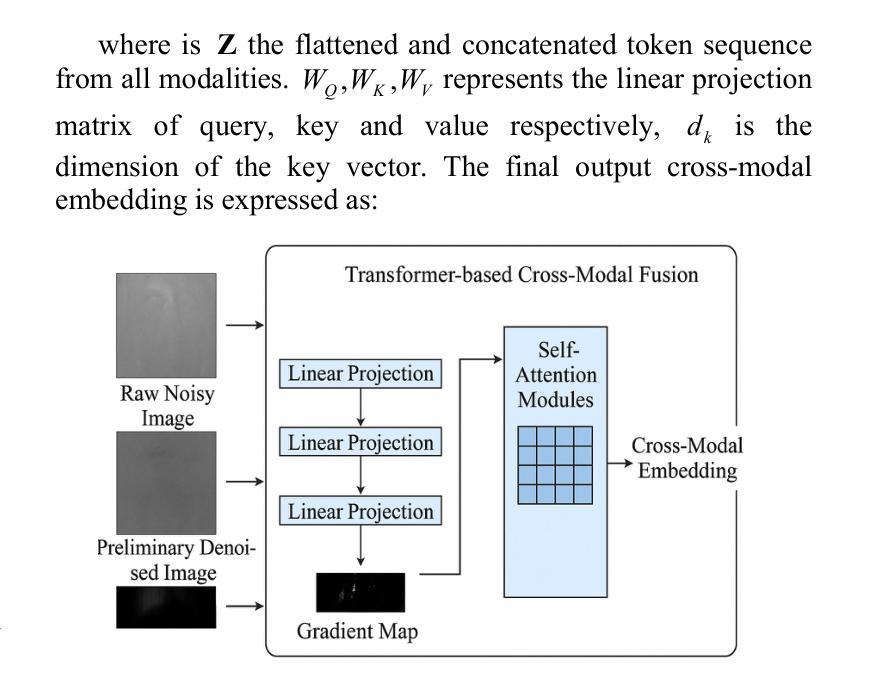
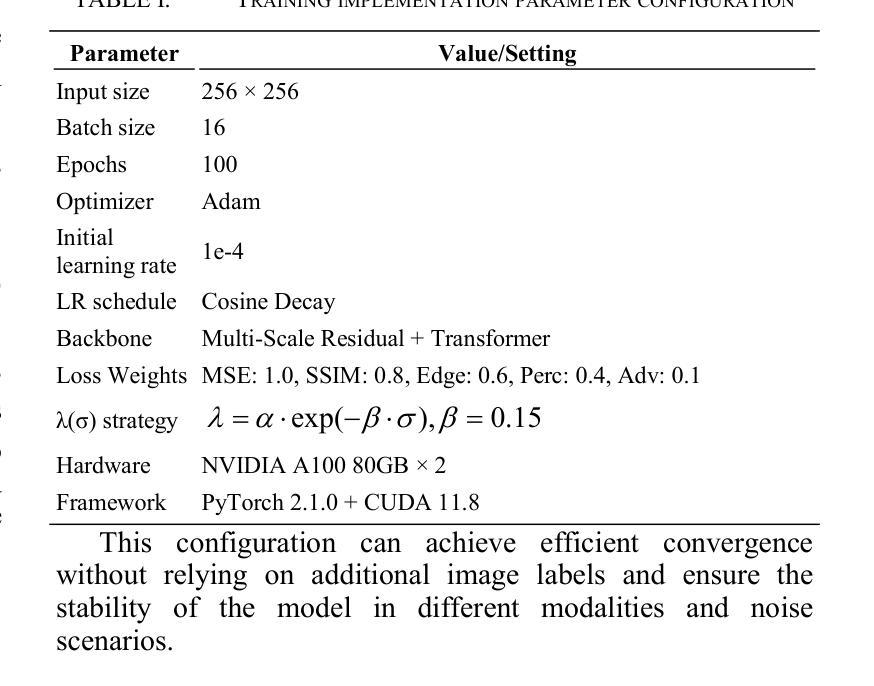
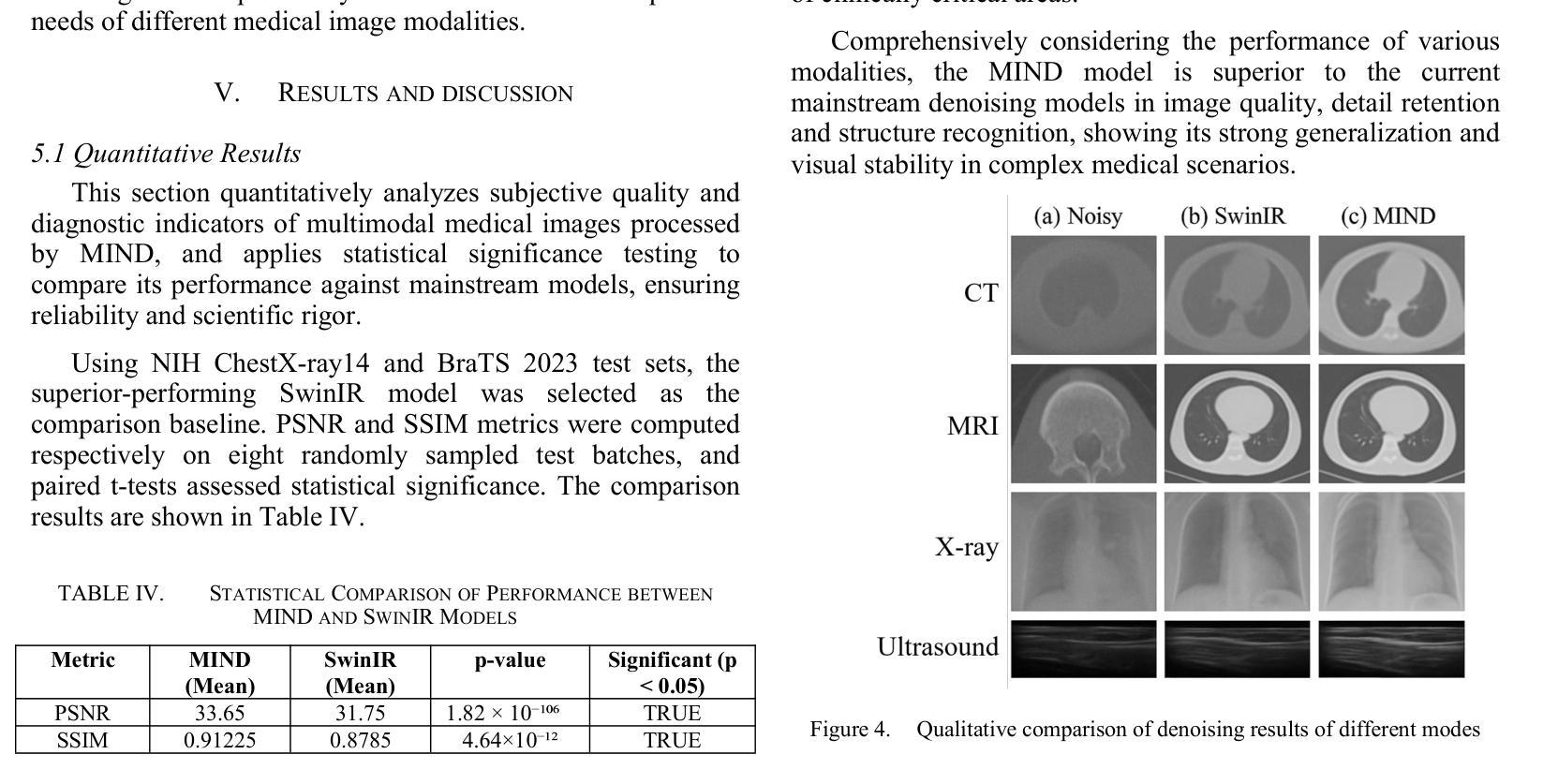
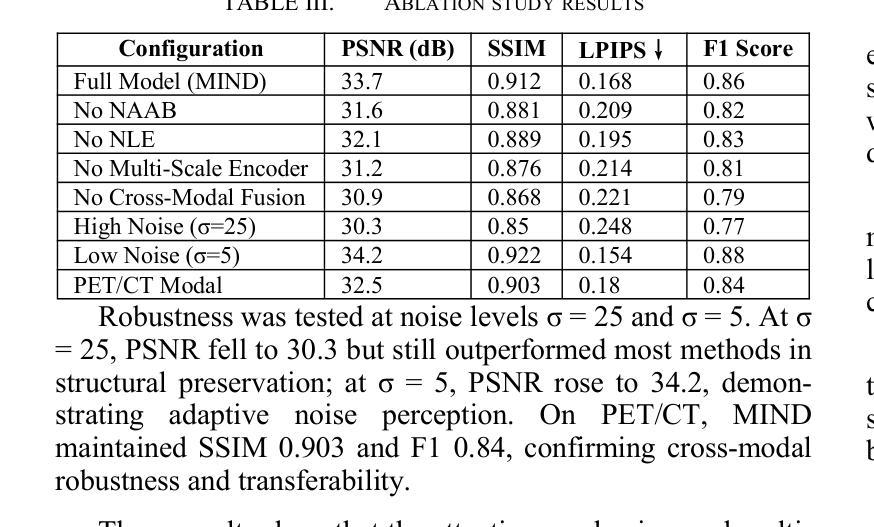
MIND: A Noise-Adaptive Denoising Framework for Medical Images Integrating Multi-Scale Transformer
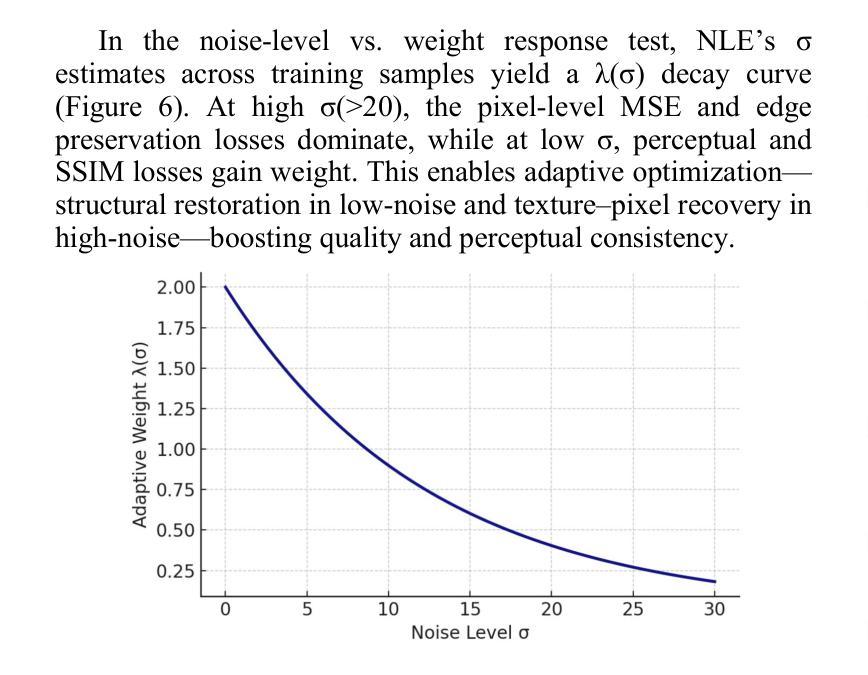
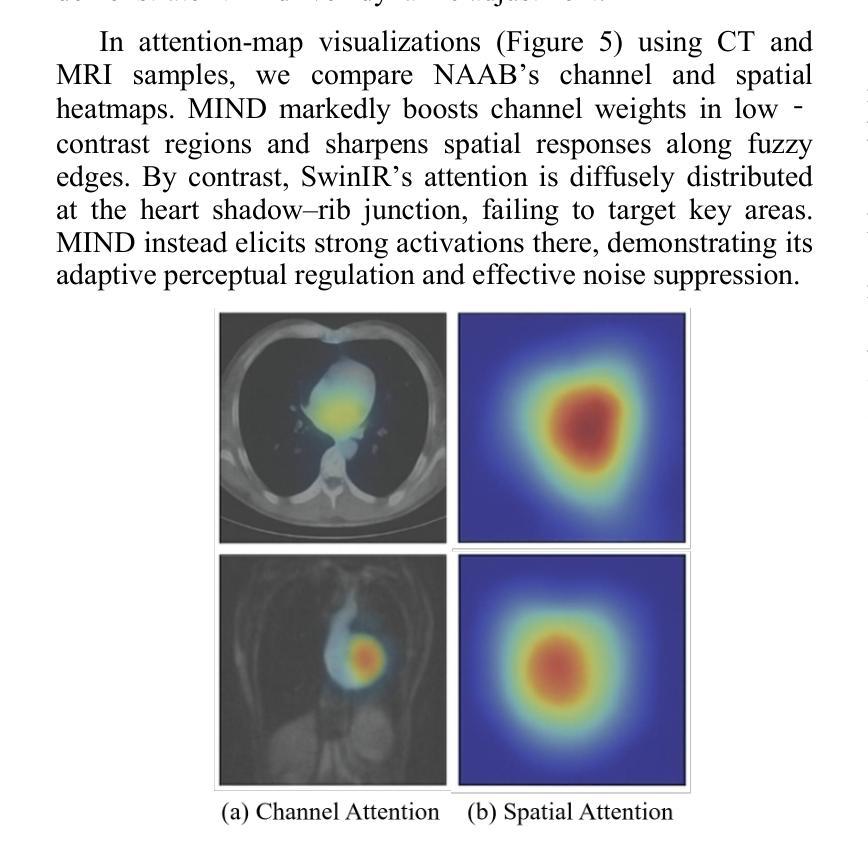
Authors:Tao Tang, Chengxu Yang
The core role of medical images in disease diagnosis makes their quality directly affect the accuracy of clinical judgment. However, due to factors such as low-dose scanning, equipment limitations and imaging artifacts, medical images are often accompanied by non-uniform noise interference, which seriously affects structure recognition and lesion detection. This paper proposes a medical image adaptive denoising model (MI-ND) that integrates multi-scale convolutional and Transformer architecture, introduces a noise level estimator (NLE) and a noise adaptive attention module (NAAB), and realizes channel-spatial attention regulation and cross-modal feature fusion driven by noise perception. Systematic testing is carried out on multimodal public datasets. Experiments show that this method significantly outperforms the comparative methods in image quality indicators such as PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS, and improves the F1 score and ROC-AUC in downstream diagnostic tasks, showing strong prac-tical value and promotional potential. The model has outstanding benefits in structural recovery, diagnostic sensitivity, and cross-modal robustness, and provides an effective solution for medical image enhancement and AI-assisted diagnosis and treatment.
医疗图像在疾病诊断中的核心作用使其质量直接影响临床判断的准确性。然而,由于低剂量扫描、设备限制和成像伪影等因素,医疗图像通常伴随着非均匀噪声干扰,这严重影响结构识别和病灶检测。本文针对这一问题,提出了一种结合多尺度卷积和Transformer架构的医疗图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND)。该模型引入了噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB),实现了基于噪声感知的通道空间注意力调节和跨模态特征融合。在多模态公共数据集上进行了系统测试。实验表明,该方法在图像质量指标(如PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS)上显著优于对比方法,并在下游诊断任务中提高了F1分数和ROC-AUC,表现出较强的实用价值和推广潜力。该模型在结构恢复、诊断敏感度和跨模态稳健性方面表现出显著优势,为医疗图像增强和AI辅助诊断和治疗提供了有效解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Control, Measurement and Signal Processing (ICMSP 2025). 6 pages, 6 figures
Summary
医疗图像在疾病诊断中的核心作用要求其质量直接影响临床判断的准确性。本文提出一种结合多尺度卷积和Transformer架构的医疗图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND),通过引入噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB),实现通道-空间注意力调节和噪声感知驱动的跨模态特征融合。该模型在多模态公共数据集上进行系统测试,实验结果表明该方法在图像质量指标PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS上显著优于对比方法,并在下游诊断任务中提高F1分数和ROC-AUC,表现出强大的实用价值和应用潜力。该模型在结构恢复、诊断敏感性和跨模态稳健性方面具有显著优势,为医疗图像增强和AI辅助诊断和治疗提供了有效解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像质量直接影响疾病诊断的准确性。
- 提出的医疗图像自适应去噪模型(MI-ND)结合了多尺度卷积和Transformer架构。
- MI-ND模型包括噪声水平估计器(NLE)和噪声自适应注意力模块(NAAB)。
- MI-ND模型实现了通道-空间注意力调节和跨模态特征融合。
- 系统测试表明MI-ND模型在图像质量指标上优于其他方法。
- MI-ND模型在下游诊断任务中提高了F1分数和ROC-AUC。
点此查看论文截图

Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer Using Multimodal Learning on Electronic Health Records
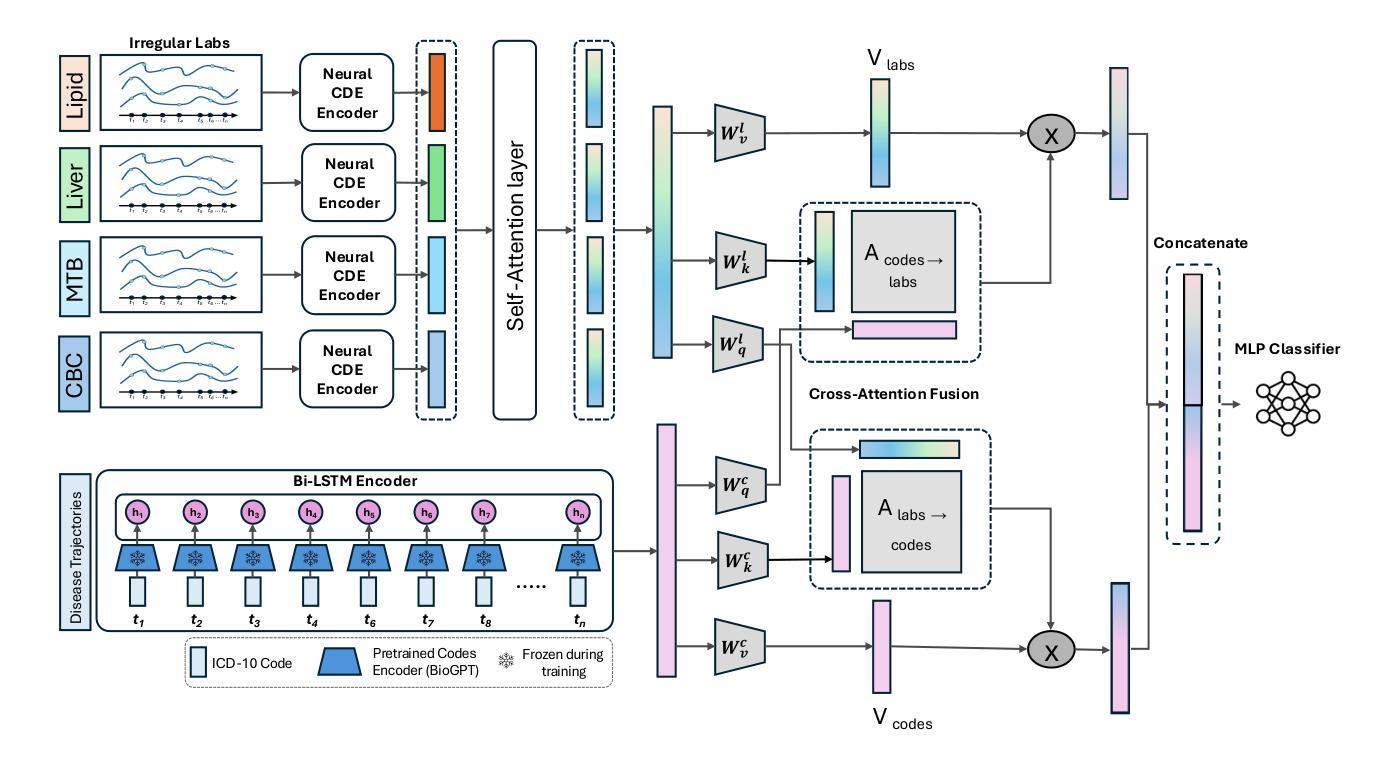
Authors:Mosbah Aouad, Anirudh Choudhary, Awais Farooq, Steven Nevers, Lusine Demirkhanyan, Bhrandon Harris, Suguna Pappu, Christopher Gondi, Ravishankar Iyer
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest cancers, and early detection remains a major clinical challenge due to the absence of specific symptoms and reliable biomarkers. In this work, we propose a new multimodal approach that integrates longitudinal diagnosis code histories and routinely collected laboratory measurements from electronic health records to detect PDAC up to one year prior to clinical diagnosis. Our method combines neural controlled differential equations to model irregular lab time series, pretrained language models and recurrent networks to learn diagnosis code trajectory representations, and cross-attention mechanisms to capture interactions between the two modalities. We develop and evaluate our approach on a real-world dataset of nearly 4,700 patients and achieve significant improvements in AUC ranging from 6.5% to 15.5% over state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, our model identifies diagnosis codes and laboratory panels associated with elevated PDAC risk, including both established and new biomarkers. Our code is available at https://github.com/MosbahAouad/EarlyPDAC-MML.
胰腺癌导管腺癌(PDAC)是最致命的癌症之一,由于缺少特定症状和可靠生物标志物,早期检测仍然是临床上的一个主要挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的多模式方法,该方法结合了纵向诊断代码历史记录和电子健康记录中常规收集的实验室测量值,可在临床诊断前一年检测到PDAC。我们的方法结合了神经控制微分方程来模拟不规则实验室时间序列数据、预训练语言模型和循环网络来学习诊断代码轨迹表示,以及交叉注意力机制来捕捉两种模式之间的交互。我们在近4700名患者的实际数据集上开发和评估了我们的方法,与最先进的方法相比,AUC有6.5%至15.5%的显著提高。此外,我们的模型还确定了与胰腺癌风险增加相关的诊断代码和实验室检测板,包括已知和新生物标志物。我们的代码可在https://github.com/MosbahAouad/EarlyPDAC-MML找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的多模式方法,通过整合纵向诊断代码历史和电子健康记录中常规收集的实验室测量数据,可在临床确诊前一年预测胰腺癌。该方法使用神经网络控制微分方程对不规则实验室时间序列进行建模,并结合预训练的语言模型和循环网络来学习诊断代码轨迹表示,同时使用交叉注意机制捕捉两种模式之间的互动。在接近4700名患者的真实数据集上开发和评估该方法,较最新方法显著提高了AUC值(从6.5%到15.5%)。此外,该模型确定了与胰腺癌风险增加的相关的诊断代码和实验室检测板,包括已知和新生物标志物。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的多模式方法用于胰腺癌早期检测。
- 通过整合诊断代码历史和实验室测量数据,可在临床确诊前一年进行预测。
- 使用神经网络控制微分方程对不规则实验室时间序列进行建模。
- 结合预训练的语言模型和循环网络学习诊断代码轨迹表示。
- 使用交叉注意机制捕捉诊断代码和实验室数据间的互动。
- 在真实数据集上的评估结果显示,较最新方法显著提高AUC值。
点此查看论文截图

Segment Anything in Pathology Images with Natural Language
Authors:Zhixuan Chen, Junlin Hou, Liqi Lin, Yihui Wang, Yequan Bie, Xi Wang, Yanning Zhou, Ronald Cheong Kin Chan, Hao Chen
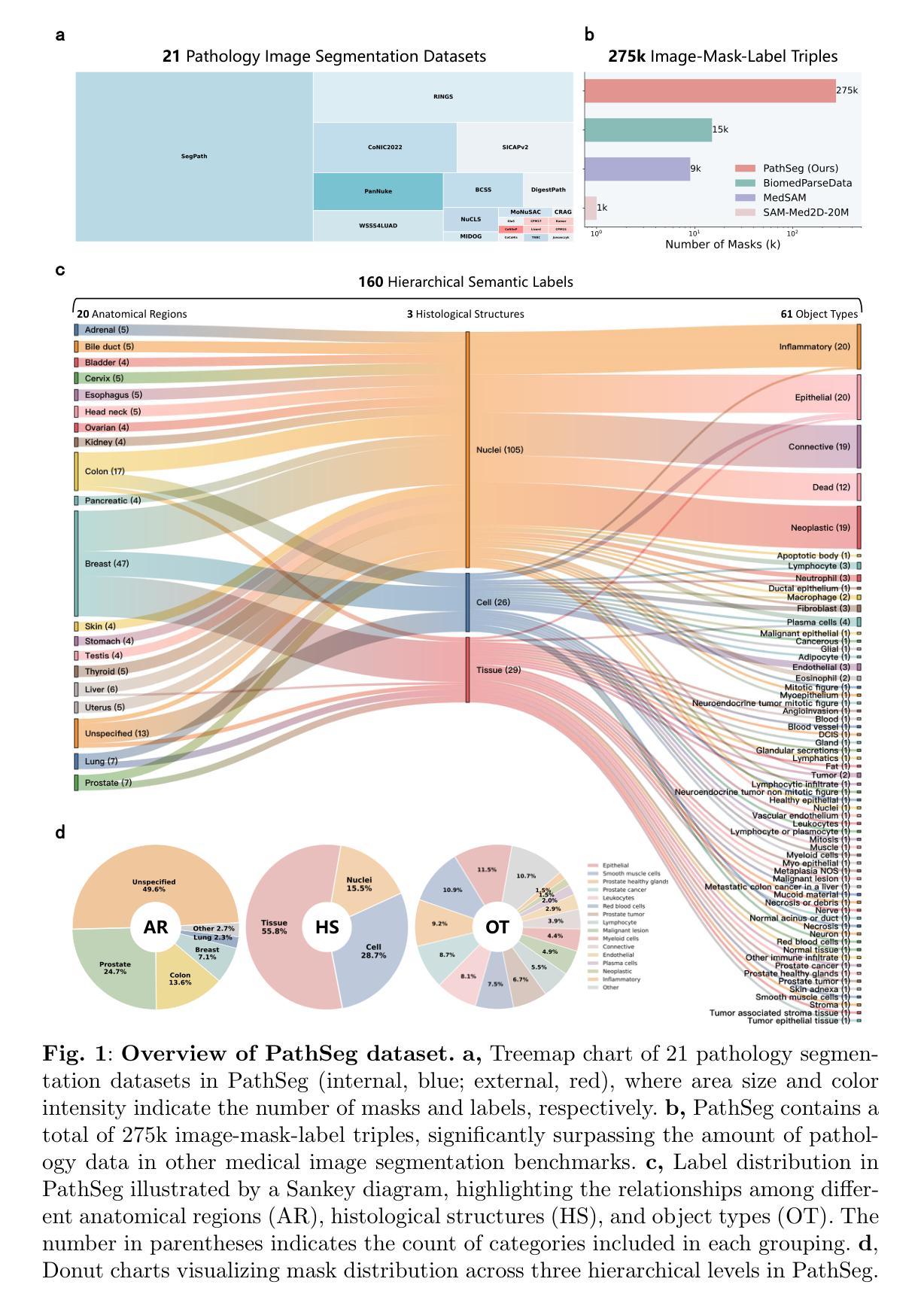
Pathology image segmentation is crucial in computational pathology for analyzing histological features relevant to cancer diagnosis and prognosis. However, current methods face major challenges in clinical applications due to limited annotated data and restricted category definitions. To address these limitations, we propose PathSegmentor, the first text-prompted segmentation foundation model designed specifically for pathology images. We also introduce PathSeg, the largest and most comprehensive dataset for pathology segmentation, built from 21 public sources and containing 275k image-mask-label triples across 160 diverse categories. With PathSegmentor, users can perform semantic segmentation using natural language prompts, eliminating the need for laborious spatial inputs such as points or boxes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PathSegmentor outperforms specialized models with higher accuracy and broader applicability, while maintaining a compact architecture. It significantly surpasses existing spatial- and text-prompted models by 0.145 and 0.429 in overall Dice scores, respectively, showing strong robustness in segmenting complex structures and generalizing to external datasets. Moreover, PathSegmentor’s outputs enhance the interpretability of diagnostic models through feature importance estimation and imaging biomarker discovery, offering pathologists evidence-based support for clinical decision-making. This work advances the development of explainable AI in precision oncology.
病理学图像分割在计算病理学中对分析与癌症诊断和预后相关的组织学特征至关重要。然而,由于标注数据有限和类别定义受限,当前方法在临床应用方面面临重大挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了PathSegmentor,这是专门为病理学图像设计的首个文本提示分割基础模型。我们还介绍了PathSeg,这是最大的最全面的病理学分割数据集,由21个公共来源构建,包含160多个类别的27.5万张图像-掩膜-标签三元组。使用PathSegmentor,用户可以使用自然语言提示执行语义分割,无需繁琐的空间输入,如点或框。大量实验表明,PathSegmentor在准确度和适用性方面超越了专业模型,同时保持了紧凑的架构。在总体Dice得分方面,它分别以0.145和0.429的优势超越了现有的空间提示模型和文本提示模型,在分割复杂结构和适应外部数据集方面表现出强大的稳健性。此外,PathSegmentor的输出通过特征重要性评估和成像生物标志物发现,增强了诊断模型的解释性,为病理学家提供基于证据的支持,有助于临床决策。这项工作推动了精准肿瘤学中可解释人工智能的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了病理图像分割在计算病理学中的重要性,并指出了当前方法在临床应用中的挑战。为应对这些挑战,提出了PathSegmentor模型,这是首个针对病理图像设计的文本提示分割基础模型。同时引入了PathSeg数据集,用于广泛的病理分割任务。PathSegmentor允许用户利用自然语言提示进行语义分割,无需繁琐的空间输入。实验表明,PathSegmentor在准确性和适用性方面优于专业模型,同时在总体Dice得分上超越现有空间提示和文本提示模型。此外,PathSegmentor的输出通过特征重要性估计和成像生物标志物发现提高了诊断模型的解释性,为病理医师提供循证支持,推动精准肿瘤学中的可解释人工智能的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 病理图像分割在计算病理学领域对于癌症诊断和治疗至关重要。
- 当前方法在应用中面临有限标注数据和限制类别定义的挑战。
- PathSegmentor模型是首个针对病理图像设计的文本提示分割基础模型,解决了上述挑战。
- PathSeg数据集是最大的综合数据集,包含多个数据来源和不同类别的分割图像。
- PathSegmentor模型无需繁琐的空间输入,可以利用自然语言提示进行语义分割。
- 实验结果显示PathSegmentor模型在准确性方面显著优于其他模型,具有更强的稳健性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图