⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
Backdooring Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning by Noisy Alignment
Authors:Tuo Chen, Jie Gui, Minjing Dong, Ju Jia, Lanting Fang, Jian Liu
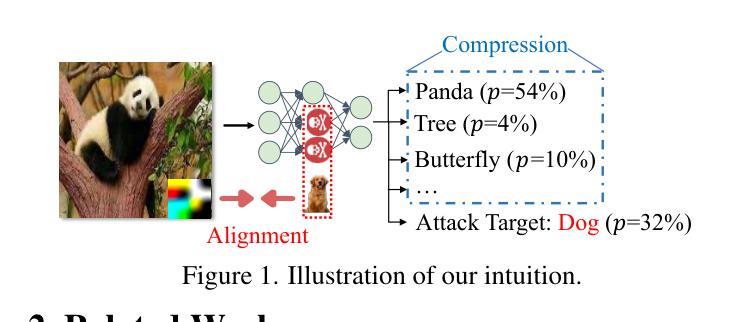
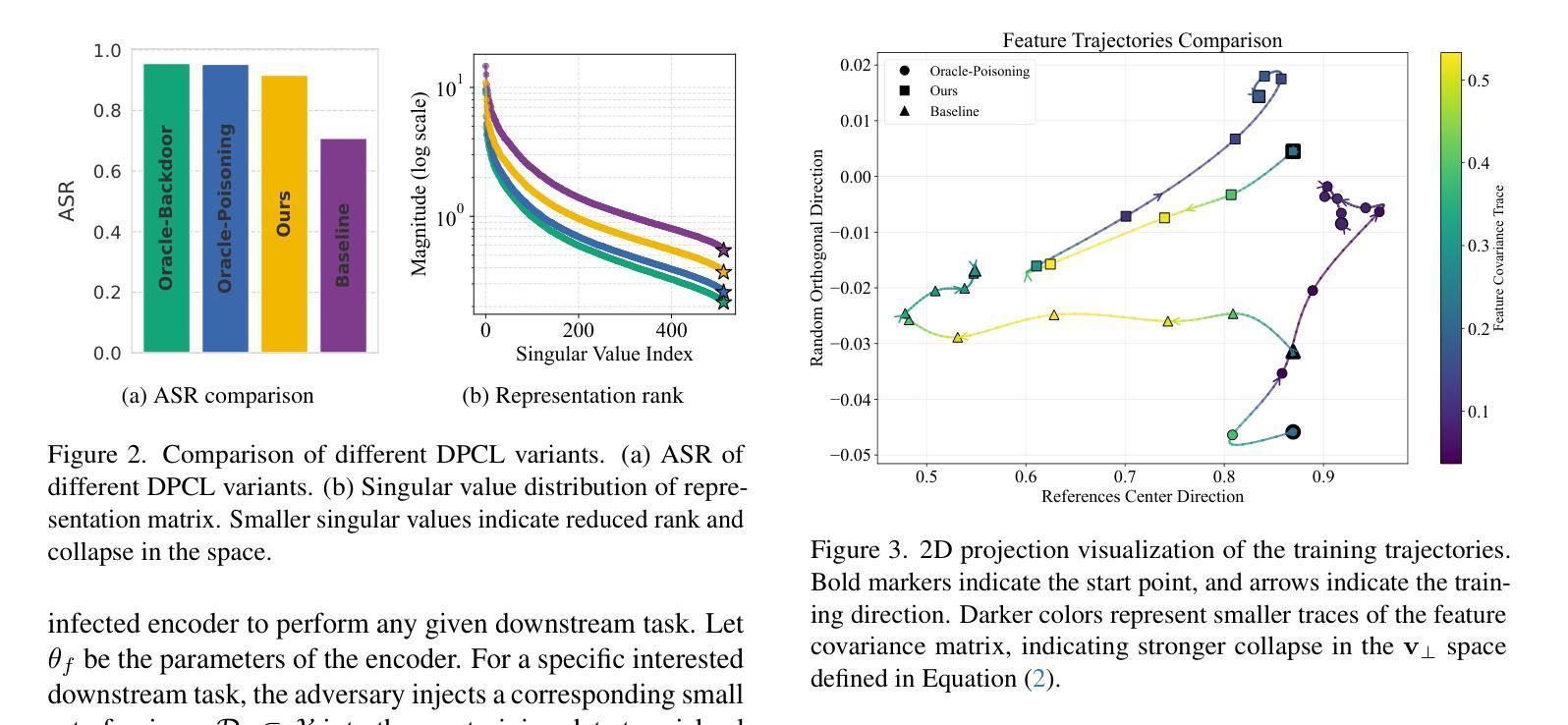
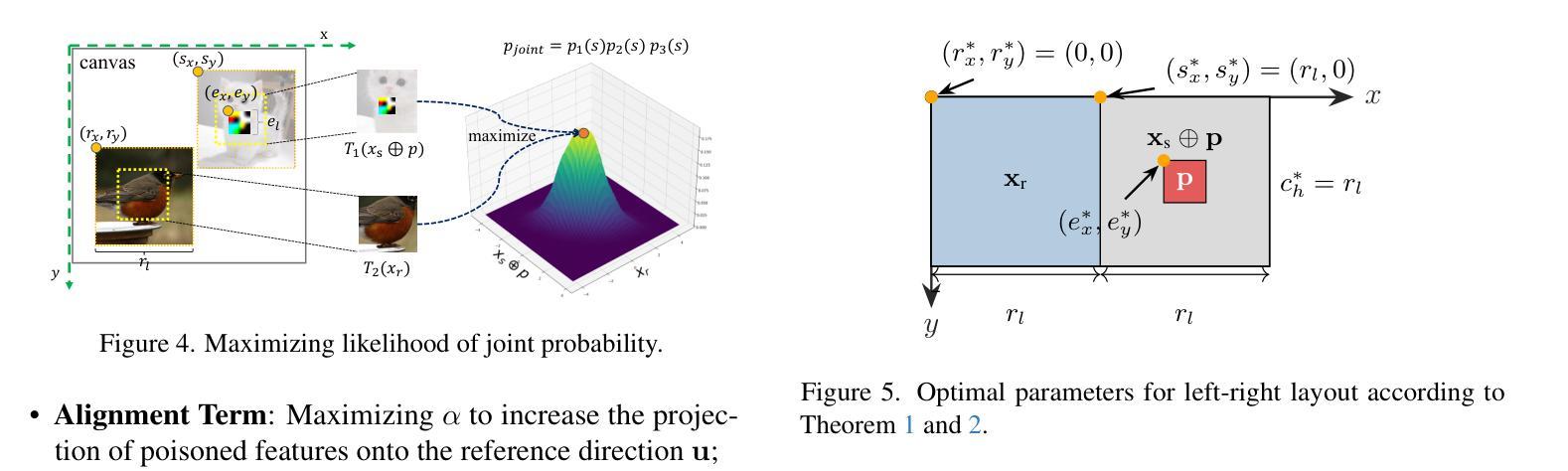
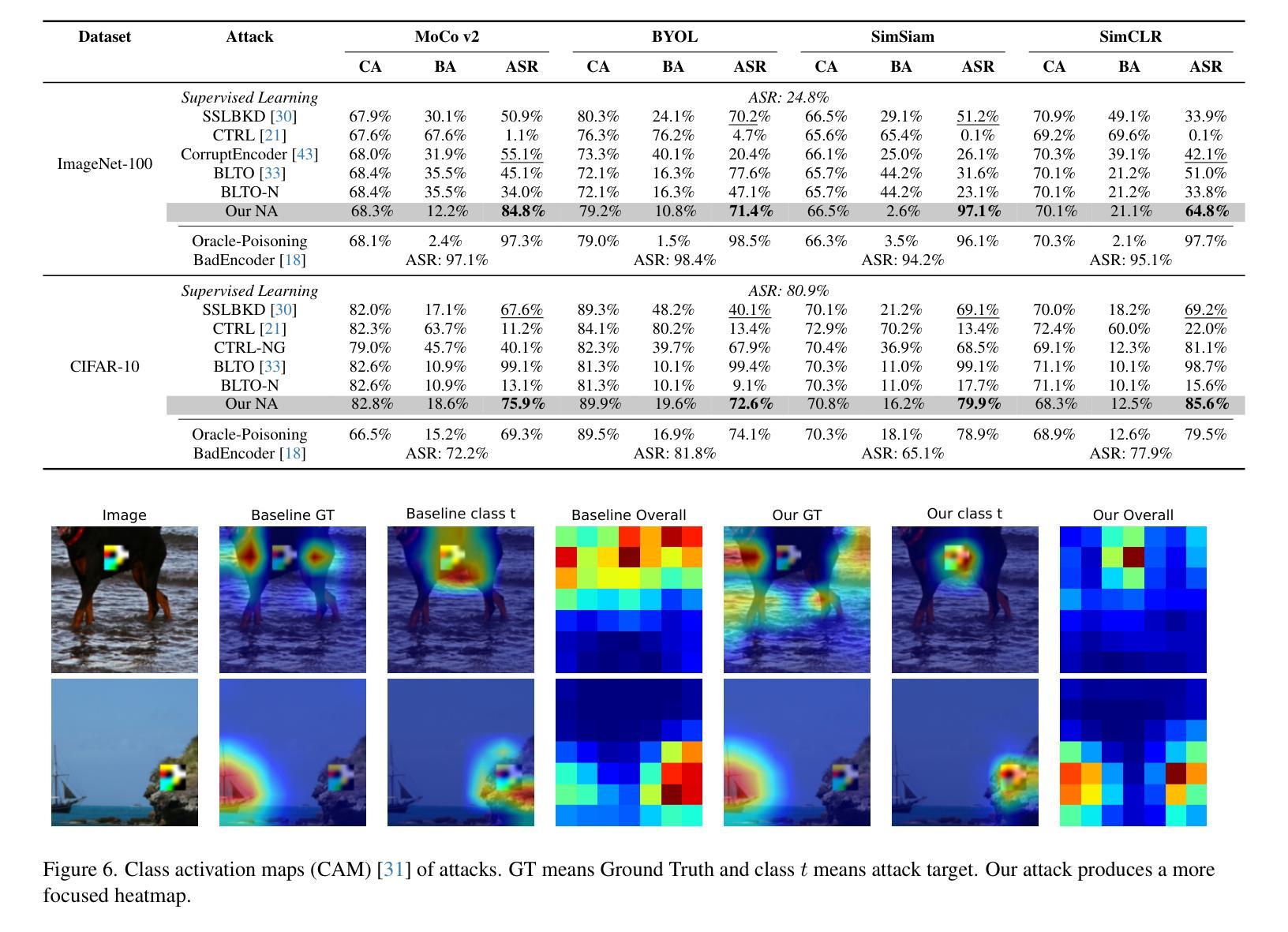
Self-supervised contrastive learning (CL) effectively learns transferable representations from unlabeled data containing images or image-text pairs but suffers vulnerability to data poisoning backdoor attacks (DPCLs). An adversary can inject poisoned images into pretraining datasets, causing compromised CL encoders to exhibit targeted misbehavior in downstream tasks. Existing DPCLs, however, achieve limited efficacy due to their dependence on fragile implicit co-occurrence between backdoor and target object and inadequate suppression of discriminative features in backdoored images. We propose Noisy Alignment (NA), a DPCL method that explicitly suppresses noise components in poisoned images. Inspired by powerful training-controllable CL attacks, we identify and extract the critical objective of noisy alignment, adapting it effectively into data-poisoning scenarios. Our method implements noisy alignment by strategically manipulating contrastive learning’s random cropping mechanism, formulating this process as an image layout optimization problem with theoretically derived optimal parameters. The resulting method is simple yet effective, achieving state-of-the-art performance compared to existing DPCLs, while maintaining clean-data accuracy. Furthermore, Noisy Alignment demonstrates robustness against common backdoor defenses. Codes can be found at https://github.com/jsrdcht/Noisy-Alignment.
自监督对比学习(CL)能够从包含图像或图像文本对的无标签数据中有效地学习可迁移的表示,但容易受到数据中毒后门攻击(DPCLs)的影响。对手可以将中毒图像注入预训练数据集,导致受损的CL编码器在下游任务中表现出目标性错误行为。然而,现有的DPCLs由于依赖于后门和目标对象之间脆弱的隐含共现以及中毒图像中判别特征的抑制不足,其效果有限。我们提出了噪声对齐(NA),这是一种DPCL方法,可以明确地抑制中毒图像中的噪声成分。我们受到强大的训练可控CL攻击的启发,确定了噪声对齐的关键目标,并将其有效地适应到数据中毒场景中。我们的方法通过策略性地操作对比学习的随机裁剪机制来实现噪声对齐,将这一过程制定为一个图像布局优化问题,并理论推导出最优参数。该方法简单有效,与现有的DPCLs相比实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了干净数据的准确性。此外,噪声对齐表现出对抗常见后门防御的稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/jsrdcht/Noisy-Alignment找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了自监督对比学习(CL)在面临数据中毒后门攻击(DPCLs)时的脆弱性。针对此问题,提出了一种名为Noisy Alignment(NA)的DPCL方法,该方法通过战略性地操作对比学习的随机裁剪机制,明确地抑制了中毒图像中的噪声成分,实现了在数据中毒场景下的有效应对。该方法在理论上达到了最佳性能表现,并与现有DPCL相比表现出更好的效果。同时,它还对常见的后门防御表现出了稳健性。更多详情参见论文地址。https://github.com/jsrdcht/Noisy-Alignment。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督对比学习在面临数据中毒后门攻击时存在脆弱性。
- 数据中毒后门攻击可以通过注入中毒图像到预训练数据集中实现目标误行为。
- 现有DPCL方法受限于隐性共现和特征判别性抑制不足的问题。
- Noisy Alignment方法通过操作对比学习的随机裁剪机制抑制噪声成分,提高了DPCL的效能。
- Noisy Alignment方法实现了理论上的最佳参数优化,具有简单有效的特点。
- 与现有DPCL相比,Noisy Alignment在保持清洁数据准确性的同时达到了更好的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

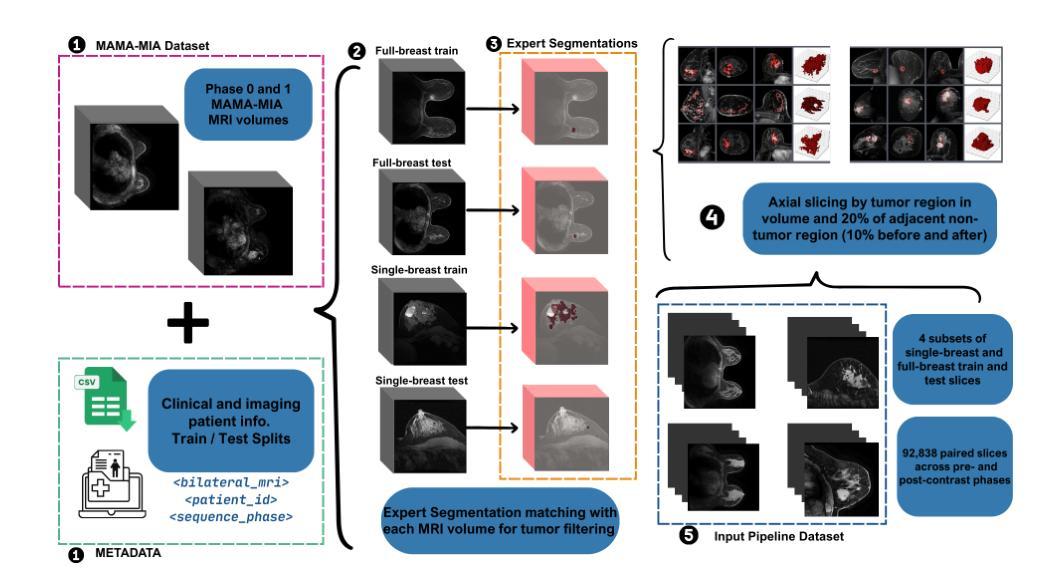
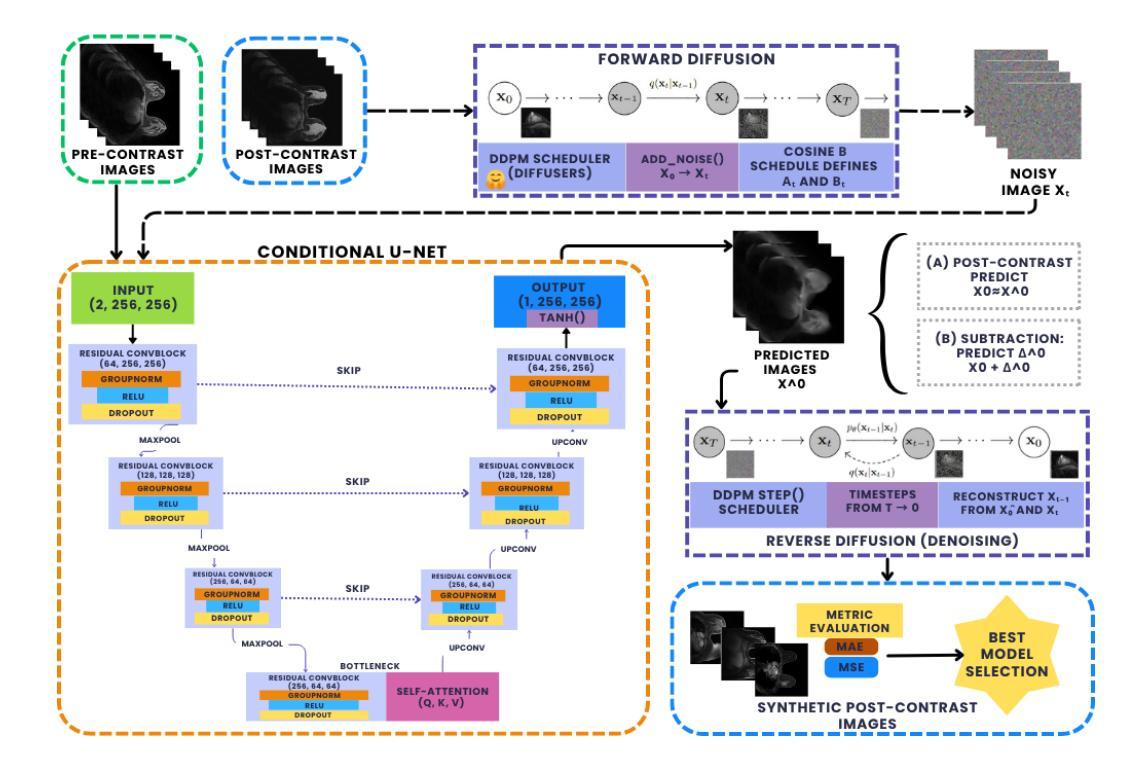
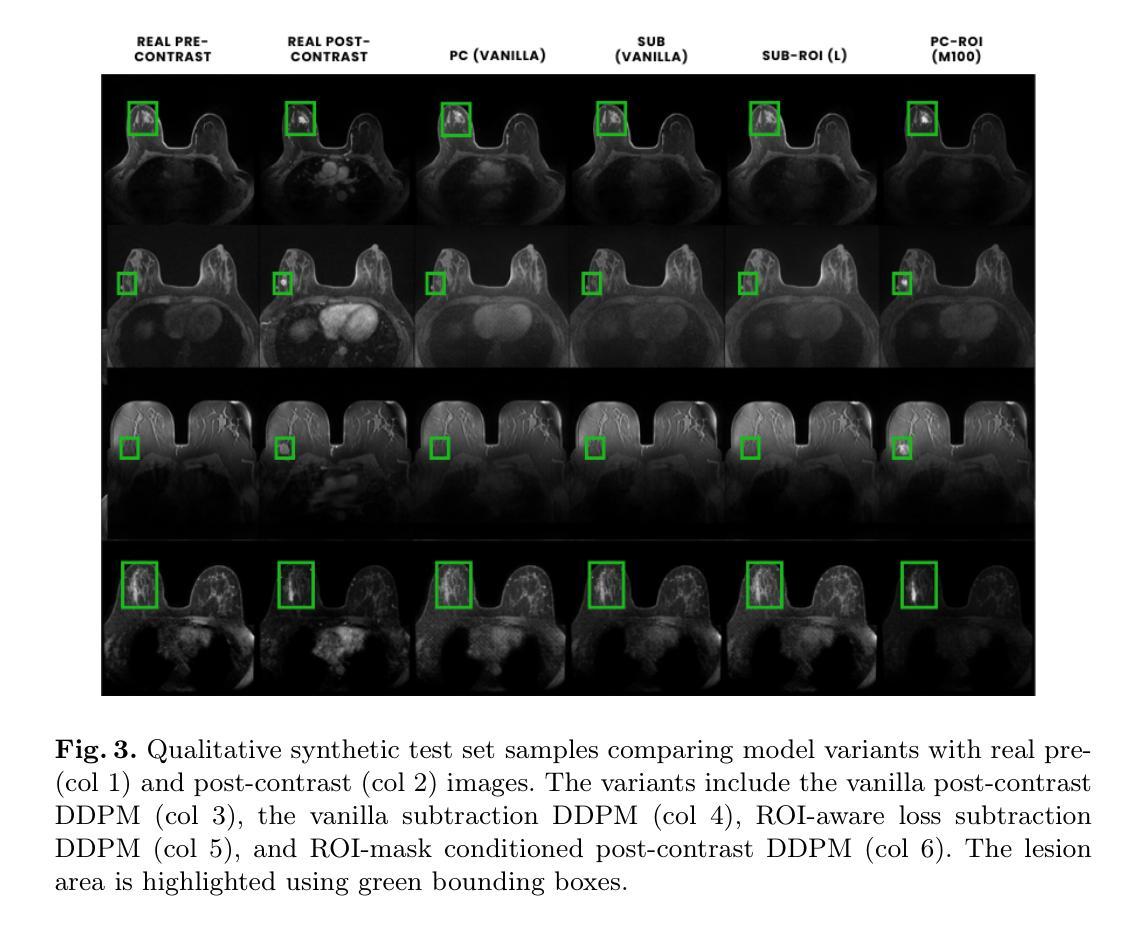
Comparing Conditional Diffusion Models for Synthesizing Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI from Pre-Contrast Images
Authors:Sebastian Ibarra, Javier del Riego, Alessandro Catanese, Julian Cuba, Julian Cardona, Nataly Leon, Jonathan Infante, Karim Lekadir, Oliver Diaz, Richard Osuala
Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI is essential for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. However, its reliance on contrast agents introduces safety concerns, contraindications, increased cost, and workflow complexity. To this end, we present pre-contrast conditioned denoising diffusion probabilistic models to synthesize DCE-MRI, introducing, evaluating, and comparing a total of 22 generative model variants in both single-breast and full breast settings. Towards enhancing lesion fidelity, we introduce both tumor-aware loss functions and explicit tumor segmentation mask conditioning. Using a public multicenter dataset and comparing to respective pre-contrast baselines, we observe that subtraction image-based models consistently outperform post-contrast-based models across five complementary evaluation metrics. Apart from assessing the entire image, we also separately evaluate the region of interest, where both tumor-aware losses and segmentation mask inputs improve evaluation metrics. The latter notably enhance qualitative results capturing contrast uptake, albeit assuming access to tumor localization inputs that are not guaranteed to be available in screening settings. A reader study involving 2 radiologists and 4 MRI technologists confirms the high realism of the synthetic images, indicating an emerging clinical potential of generative contrast-enhancement. We share our codebase at https://github.com/sebastibar/conditional-diffusion-breast-MRI.
动态对比增强(DCE)MRI对乳腺癌诊断和治疗至关重要。然而,它对造影剂的依赖引发了安全性担忧、禁忌症、成本增加和工作流程复杂等问题。为此,我们提出了基于预造影条件去噪扩散概率模型的DCE-MRI合成方法,在单乳和全乳环境中介绍、评估和比较了总共22种生成模型变体。为了提高病灶保真度,我们引入了肿瘤感知损失函数和明确的肿瘤分割掩膜条件。使用公共多中心数据集,与相应的预造影基线相比,我们发现基于减法图像的模型在五种互补评估指标上持续优于基于后造影的模型。除了评估整个图像外,我们还单独评估了感兴趣区域,其中肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入改善了评估指标。后者显著提高了定性结果捕捉造影剂吸收的情况,尽管它假定存在肿瘤定位输入,但在筛查环境中这些输入不能保证可用。涉及两名放射学家和四名MRI技术人员的读者研究证实了合成图像的高度逼真性,表明生成对比增强具有新兴的临床潜力。我们在https://github.com/sebastibar/conditional-diffusion-breast-MRI分享我们的代码库。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures, submitted and accepted to MICCAI Deepbreath workshop 2025
Summary:
基于动态对比增强(DCE)MRI在乳腺癌诊断和治疗中的重要性,该研究采用预对比条件下的降噪扩散概率模型来合成DCE-MRI图像。通过引入肿瘤感知损失函数和明确的肿瘤分割掩膜条件,该研究在单乳和全乳环境下对总计22种生成模型变体进行了介绍、评估和比较。利用公共多中心数据集并与相应的预对比基线进行比较,发现基于减法图像的模型在五个补充评价指标上持续优于基于对比后的模型。单独评估感兴趣区域时,肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入同样提高了评价指标。尽管需要假设具备肿瘤定位输入,这在筛查环境中并不总能保证,但这些增强技术能够捕捉对比剂的吸收过程。包含两名放射科医生和四名MRI技术人员的读者研究证实了合成图像的高度逼真性,表明生成对比增强技术的临床潜力正在显现。研究者的代码库已公开分享在https://github.com/sebastibar/conditional-diffusion-breast-MRI上。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究采用了预对比条件下的降噪扩散概率模型来合成动态对比增强(DCE)MRI图像,以辅助乳腺癌的诊断和治疗。
- 通过引入肿瘤感知损失函数和肿瘤分割掩膜条件,提高了模型的性能。
- 对比了多种生成模型变体,并在单乳和全乳环境下进行了评估。
- 使用公共多中心数据集进行的实验表明,基于减法图像的模型在评价指标上优于基于对比后的模型。
- 在评估感兴趣区域时,使用肿瘤感知损失和分割掩膜输入进一步提高了模型的性能。这些技术虽然依赖于肿瘤定位输入,但有助于捕捉对比剂的吸收过程。
- 读者研究证实了合成图像的高度逼真性,这表明生成对比增强技术具有潜在的临床应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

Refining Contrastive Learning and Homography Relations for Multi-Modal Recommendation
Authors:Shouxing Ma, Yawen Zeng, Shiqing Wu, Guandong Xu
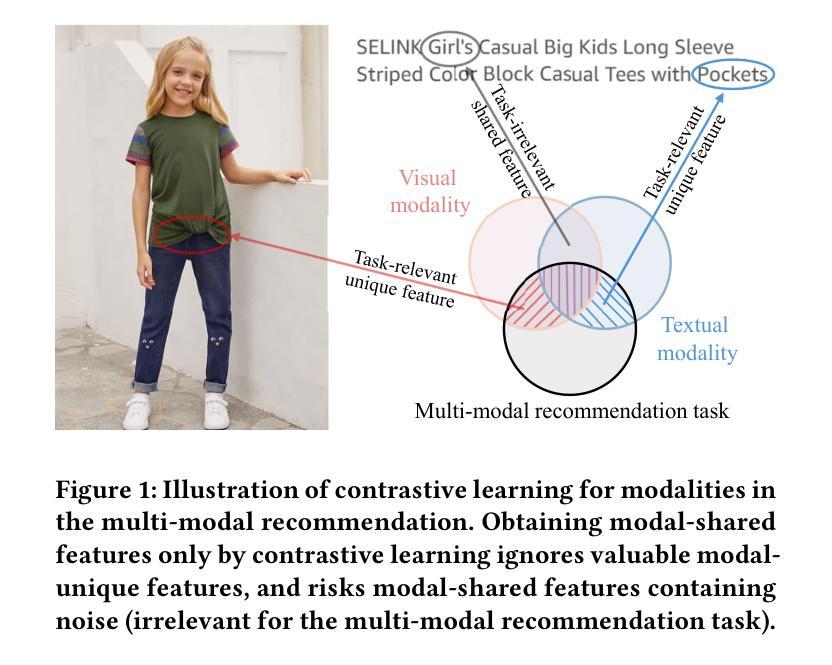
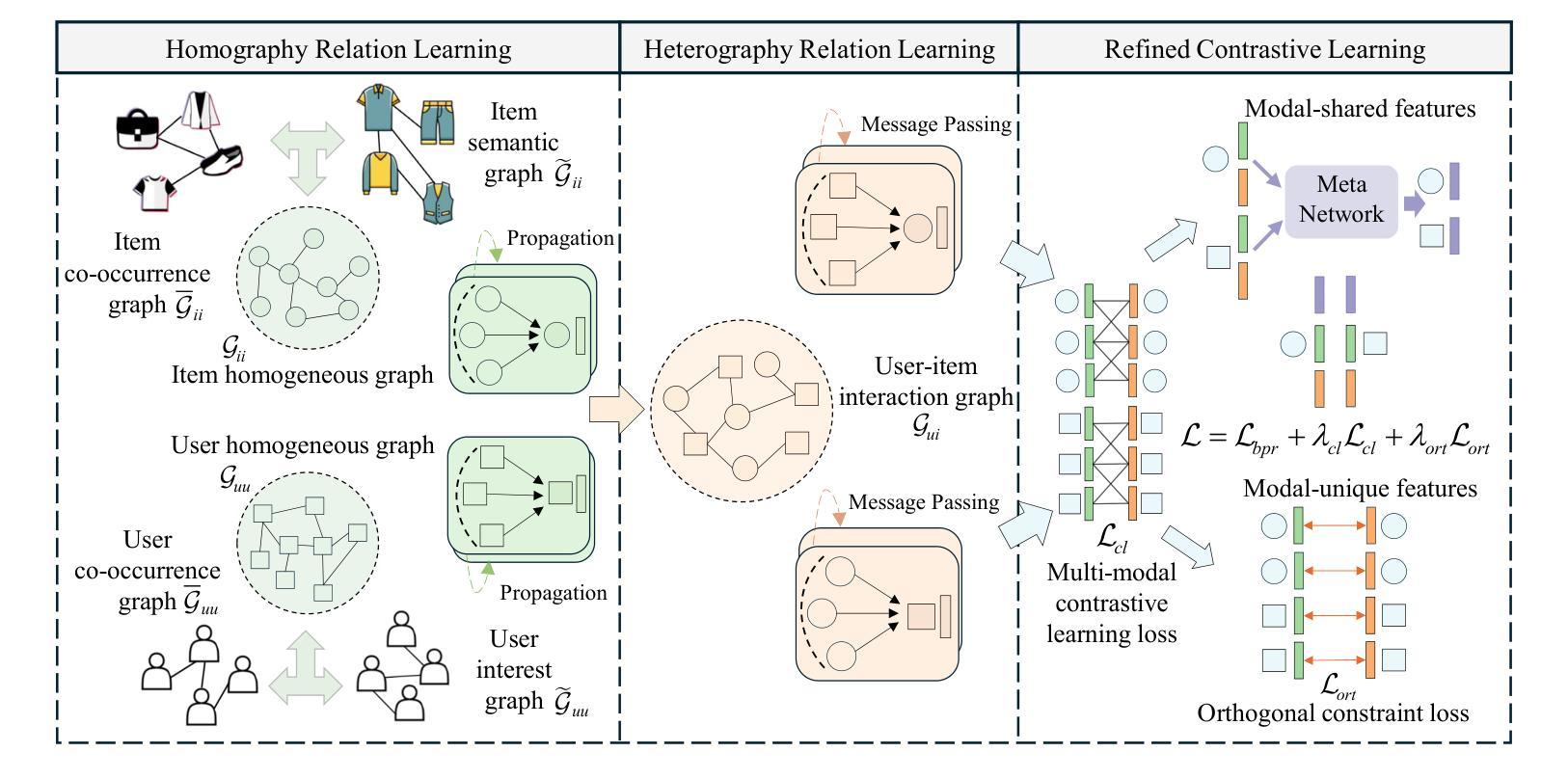
Multi-modal recommender system focuses on utilizing rich modal information ( i.e., images and textual descriptions) of items to improve recommendation performance. The current methods have achieved remarkable success with the powerful structure modeling capability of graph neural networks. However, these methods are often hindered by sparse data in real-world scenarios. Although contrastive learning and homography ( i.e., homogeneous graphs) are employed to address the data sparsity challenge, existing methods still suffer two main limitations: 1) Simple multi-modal feature contrasts fail to produce effective representations, causing noisy modal-shared features and loss of valuable information in modal-unique features; 2) The lack of exploration of the homograph relations between user interests and item co-occurrence results in incomplete mining of user-item interplay. To address the above limitations, we propose a novel framework for \textbf{R}\textbf{E}fining multi-mod\textbf{A}l cont\textbf{R}astive learning and ho\textbf{M}ography relations (\textbf{REARM}). Specifically, we complement multi-modal contrastive learning by employing meta-network and orthogonal constraint strategies, which filter out noise in modal-shared features and retain recommendation-relevant information in modal-unique features. To mine homogeneous relationships effectively, we integrate a newly constructed user interest graph and an item co-occurrence graph with the existing user co-occurrence and item semantic graphs for graph learning. The extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of REARM to various state-of-the-art baselines. Our visualization further shows an improvement made by REARM in distinguishing between modal-shared and modal-unique features. Code is available \href{https://github.com/MrShouxingMa/REARM}{here}.
多模态推荐系统主要利用物品的丰富模态信息(例如图像和文本描述)来提高推荐性能。当前的方法已经借助图神经网络的强大结构建模能力取得了显著的成功。然而,这些方法在现实场景中的数据稀疏问题上往往受到限制。尽管对比学习和同构(即同类型图)被用来解决数据稀疏性的挑战,但现有方法仍存在两个主要局限性:1)简单的多模态特征对比无法产生有效的表示,导致模态共享特征中的噪声和模态唯一特征中有价值信息的损失;2)在用户兴趣和物品共现之间的同图关系探索不足,导致对用户-物品互动的不完全挖掘。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一个新颖的框架,即细化多模态对比学习和同构关系的REARM框架。具体来说,我们通过采用元网络和正交约束策略来补充多模态对比学习,以过滤模态共享特征中的噪声并保留模态唯一特征中与推荐相关的信息。为了有效地挖掘同构关系,我们将新构建的用户兴趣图和物品共现图与现有的用户共现和物品语义图相结合,进行图学习。在三个真实数据集上的大量实验表明,REARM优于各种最新基线。我们的可视化进一步显示了REARM在区分模态共享和模态唯一特征方面的改进。代码可用here:https://github.com/MrShouxingMa/REARM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted as a full paper at ACM MM 2025
Summary
多模态推荐系统通过利用物品的丰富模态信息(如图像和文本描述)提高推荐性能。现有方法已借助图神经网络的强大结构建模能力取得显著成功,但在真实场景中的数据稀疏性问题仍然是一个挑战。针对简单多模态特征对比产生的无效表示、模态共享特征的噪声以及模态特有特征信息的丢失等问题,以及用户兴趣与物品共现之间的同图关系挖掘不足的问题,我们提出了一个名为REARM的新框架。通过元网络和正交约束策略补充多模态对比学习,同时结合用户兴趣图和物品共现图进行图学习,有效挖掘同构关系。在三个真实数据集上的实验表明,REARM优于各种最新基线方法。我们的可视化结果进一步证明了REARM在区分模态共享和模态特有特征方面的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态推荐系统利用物品的图像和文本描述等丰富模态信息提高推荐性能。
- 当前方法借助图神经网络的强大结构建模能力取得显著成果,但数据稀疏性问题仍是挑战。
- 现有方法存在简单多模态特征对比产生的无效表示、模态共享特征的噪声及模态特有信息丢失的问题。
- REARM框架通过元网络和正交约束策略补充多模态对比学习,提高性能。
- REARM结合用户兴趣图和物品共现图进行有效图学习,挖掘同构关系。
- 在三个真实数据集上的实验证明REARM优于其他最新方法。
点此查看论文截图