⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
Stereo-based 3D Anomaly Object Detection for Autonomous Driving: A New Dataset and Baseline
Authors:Shiyi Mu, Zichong Gu, Hanqi Lyu, Yilin Gao, Shugong Xu
3D detection technology is widely used in the field of autonomous driving, with its application scenarios gradually expanding from enclosed highways to open conventional roads. For rare anomaly categories that appear on the road, 3D detection models trained on closed sets often misdetect or fail to detect anomaly objects. To address this risk, it is necessary to enhance the generalization ability of 3D detection models for targets of arbitrary shapes and to possess the capability to filter out anomalies. The generalization of 3D detection is limited by two factors: the coupled training of 2D and 3D, and the insufficient diversity in the scale distribution of training samples. This paper proposes a Stereo-based 3D Anomaly object Detection (S3AD) algorithm, which decouples the training strategy of 3D and 2D to release the generalization ability for arbitrary 3D foreground detection, and proposes an anomaly scoring algorithm based on foreground confidence prediction, achieving target-level anomaly scoring. In order to further verify and enhance the generalization of anomaly detection, we use a 3D rendering method to synthesize two augmented reality binocular stereo 3D detection datasets which named KITTI-AR. KITTI-AR extends upon KITTI by adding 97 new categories, totaling 6k pairs of stereo images. The KITTI-AR-ExD subset includes 39 common categories as extra training data to address the sparse sample distribution issue. Additionally, 58 rare categories form the KITTI-AR-OoD subset, which are not used in training to simulate zero-shot scenarios in real-world settings, solely for evaluating 3D anomaly detection. Finally, the performance of the algorithm and the dataset is verified in the experiments. (Code and dataset can be obtained at https://github.com/shiyi-mu/S3AD-Code).
三维检测技术在自动驾驶领域得到了广泛应用,其应用场景已从封闭的高速公路逐渐扩展到开放的常规道路。对于道路上出现的罕见异常类别,在封闭集上训练的三维检测模型通常会出现误检或无法检测到异常对象的情况。为了解决这一风险,必须提高三维检测模型对任意形状的目标的泛化能力,并具备过滤异常值的能力。三维检测的泛化受到两个因素的限制:二维和三维的耦合训练,以及训练样本尺度分布多样性不足。
本文提出了一种基于立体视觉的3D异常对象检测(S3AD)算法,该算法解耦了三维和二维的训练策略,以释放对任意三维前景检测的泛化能力,并提出一种基于前景置信度预测的异常评分算法,实现目标级异常评分。
为了进一步验证和增强异常检测的泛化能力,我们采用了一种三维渲染方法来合成两个增强现实双目立体三维检测数据集,即KITTI-AR。KITTI-AR通过在KITTI的基础上添加97个新类别,总共生成了6000对立体图像。KITTI-AR-ExD子集包含39个常见类别作为额外训练数据,以解决样本分布稀疏的问题。此外,KITTI-AR-OoD子集包含了58个罕见类别,这些类别不用于训练,以模拟现实世界中的零样本场景,仅用于评估三维异常检测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
本文介绍了立体检测技术在自动驾驶领域的应用。针对封闭训练集中的三维检测模型在罕见异常类别上的误检或漏检问题,提出了一种基于立体视角的罕见异常物体检测算法S3AD。该算法采用三维与二维解耦的训练策略,提升了对任意三维前景的泛化能力,并提出了基于前景置信度预测的异常评分算法,实现目标级别的异常评分。此外,为验证并提升异常检测的泛化能力,利用三维渲染方法合成两个增强现实双目立体三维检测数据集KITTI-AR。其中,KITTI-AR扩展了KITTI数据集,新增了97个类别,总计生成了6千对立体图像。实验验证了算法和数据集的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D检测技术在自动驾驶领域应用广泛,从高速公路到开放道路,应用场景逐渐扩展。
- 对于道路上出现的罕见异常类别,现有的3D检测模型在封闭训练集上容易出现误检或漏检。
- 提出了一种基于立体视角的罕见异常物体检测算法S3AD,通过解耦三维与二维的训练,提高模型的泛化能力。
- S3AD算法采用基于前景置信度预测的异常评分机制,实现目标级别的异常评分。
- 为验证和增强异常检测的泛化能力,使用3D渲染方法合成KITTI-AR数据集,包含两个子集:KITTI-AR-ExD和KITTI-AR-OoD。
- KITTI-AR数据集扩展了KITTI数据集,新增97个类别,总计生成6千对立体图像,用于验证算法性能。
点此查看论文截图

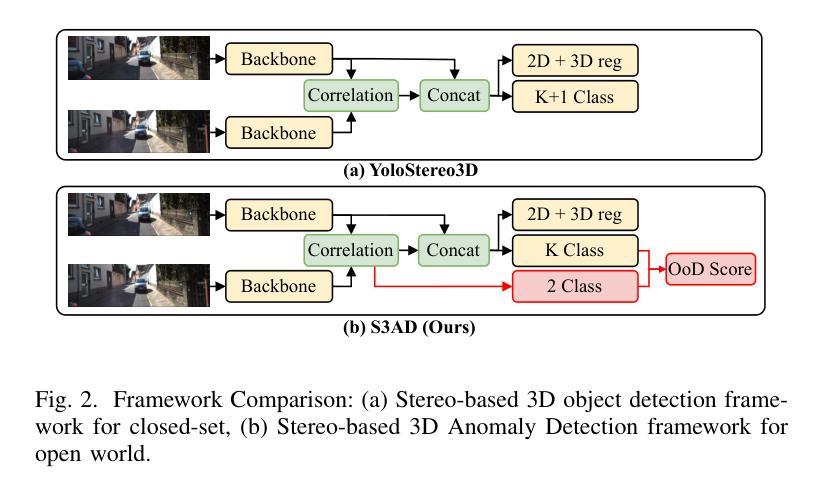
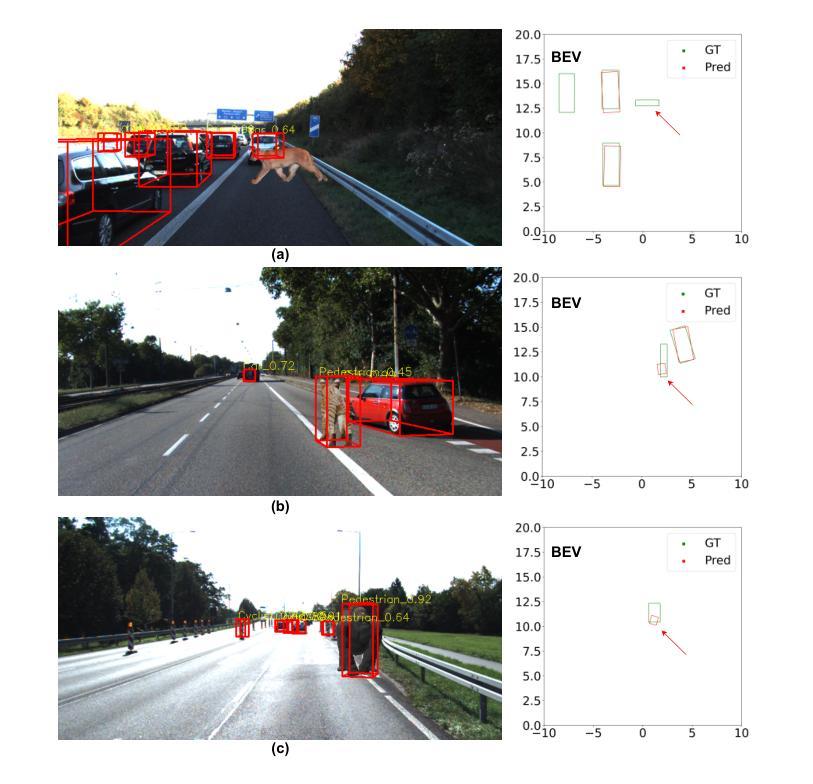
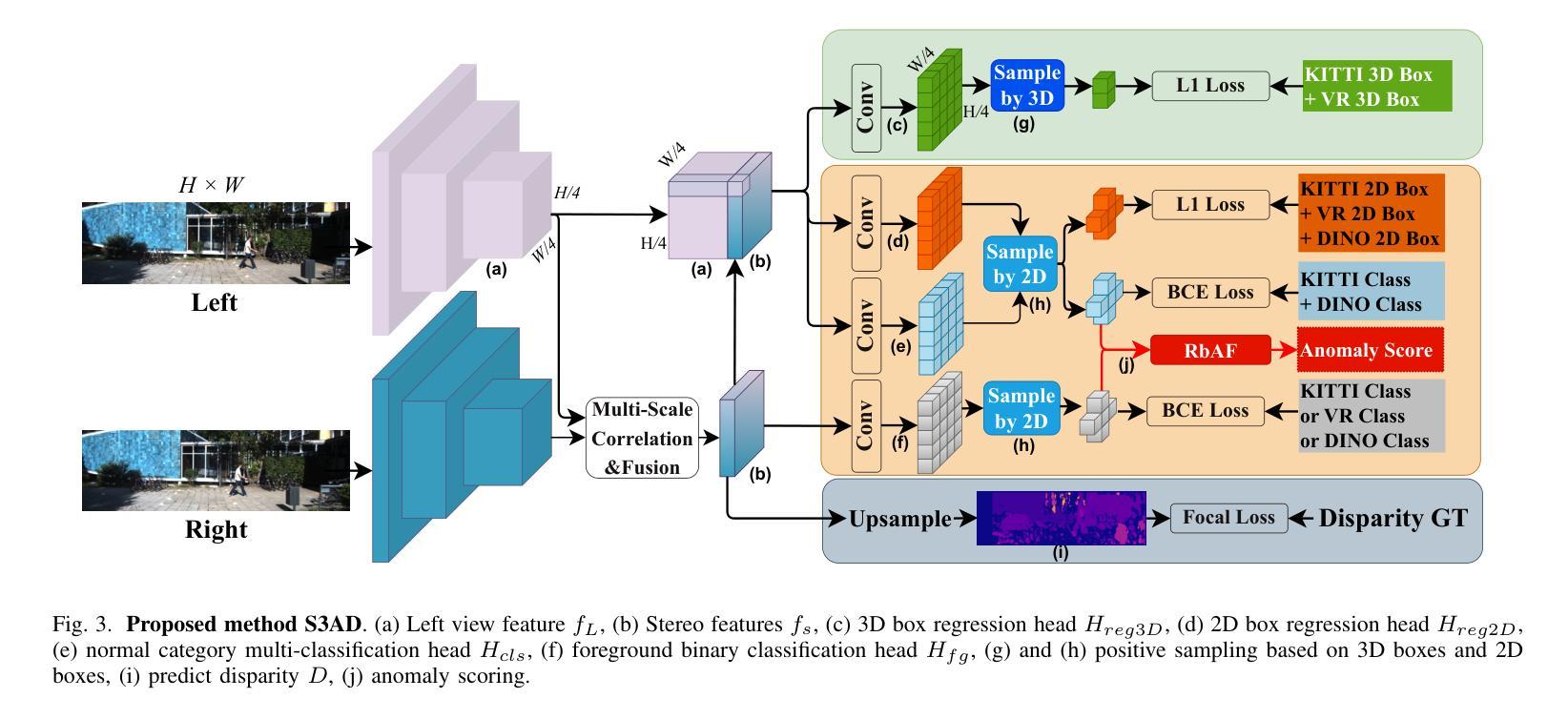
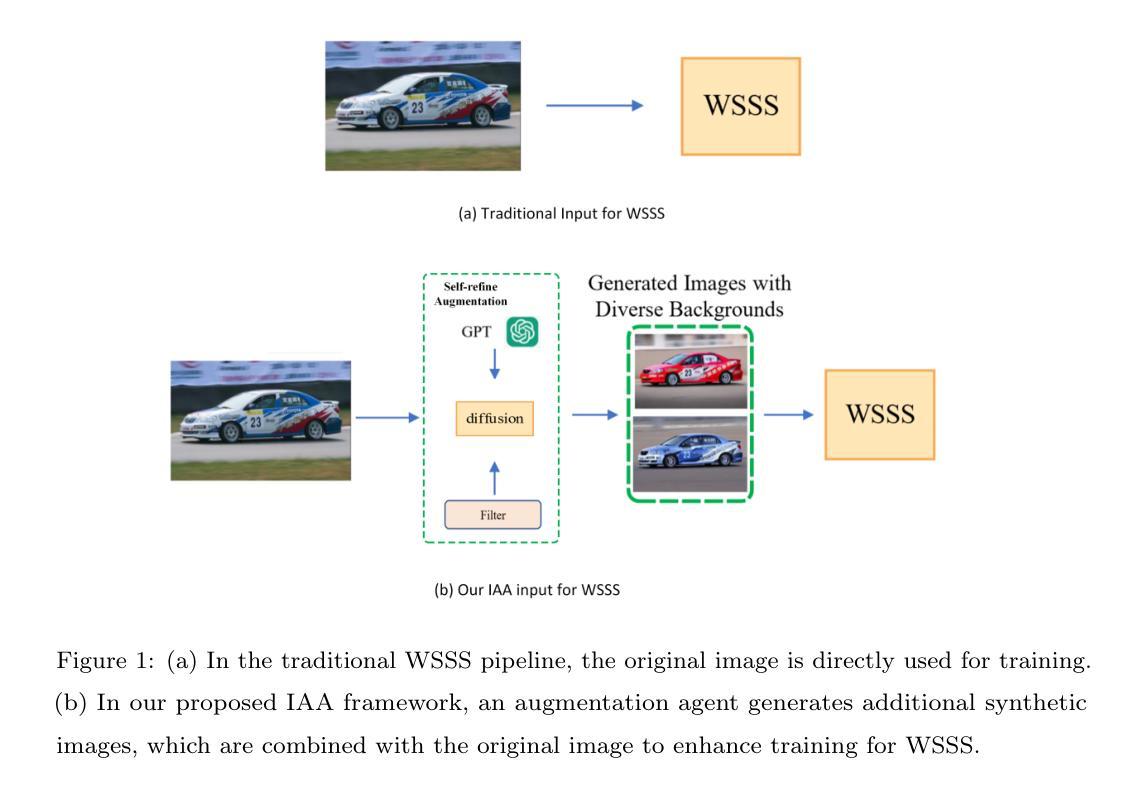
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要集中在设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更准确的密集标签,忽视了固定数据集带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像的多样性可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM生成提示的不稳定性,我们开发了一种提示自我完善机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的表现远远超过了最新的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Neurocomputing 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度改进了弱监督语义分割(WSSS)。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外的图像,增强了WSSS的性能。同时,通过开发一种提示自我完善机制和在线过滤器,提高了生成的图像的质量和平衡性。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- IAA方法从数据生成的角度改进了弱监督语义分割(WSSS)。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外图像以增强WSSS性能。
- 开发了一种提示自我完善机制,提高生成的提示的合理性。
- 通过在线过滤器动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡性。
- 实验结果表明,IAA方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
点此查看论文截图