⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
Latent Interpolation Learning Using Diffusion Models for Cardiac Volume Reconstruction
Authors:Niklas Bubeck, Suprosanna Shit, Chen Chen, Can Zhao, Pengfei Guo, Dong Yang, Georg Zitzlsberger, Daguang Xu, Bernhard Kainz, Daniel Rueckert, Jiazhen Pan
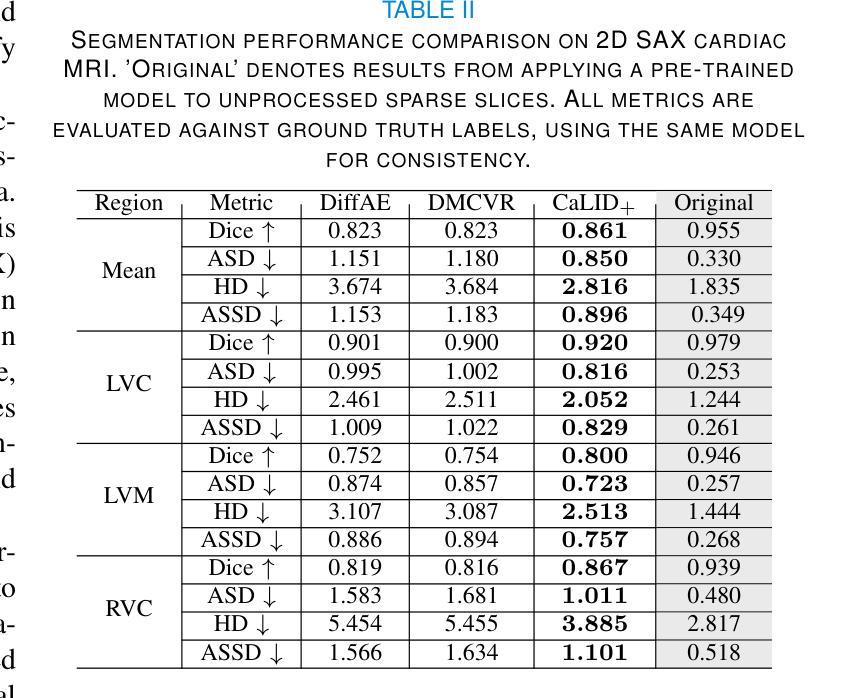
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging is a critical tool for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular disease, yet its utility is often limited by the sparse acquisition of 2D short-axis slices, resulting in incomplete volumetric information. Accurate 3D reconstruction from these sparse slices is essential for comprehensive cardiac assessment, but existing methods face challenges, including reliance on predefined interpolation schemes (e.g., linear or spherical), computational inefficiency, and dependence on additional semantic inputs such as segmentation labels or motion data. To address these limitations, we propose a novel \textbf{Ca}rdiac \textbf{L}atent \textbf{I}nterpolation \textbf{D}iffusion (CaLID) framework that introduces three key innovations. First, we present a data-driven interpolation scheme based on diffusion models, which can capture complex, non-linear relationships between sparse slices and improves reconstruction accuracy. Second, we design a computationally efficient method that operates in the latent space and speeds up 3D whole-heart upsampling time by a factor of 24, reducing computational overhead compared to previous methods. Third, with only sparse 2D CMR images as input, our method achieves SOTA performance against baseline methods, eliminating the need for auxiliary input such as morphological guidance, thus simplifying workflows. We further extend our method to 2D+T data, enabling the effective modeling of spatiotemporal dynamics and ensuring temporal coherence. Extensive volumetric evaluations and downstream segmentation tasks demonstrate that CaLID achieves superior reconstruction quality and efficiency. By addressing the fundamental limitations of existing approaches, our framework advances the state of the art for spatio and spatiotemporal whole-heart reconstruction, offering a robust and clinically practical solution for cardiovascular imaging.
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在心血管疾病的诊断和治疗中扮演着重要角色,但其应用常常受限于二维短轴切片的稀疏采集,导致体积信息不完整。从稀疏切片进行准确的3D重建对于全面的心脏评估至关重要,但现有方法面临挑战,包括依赖预定义的插值方案(例如线性或球形插值)、计算效率低下以及依赖于额外的语义输入(如分割标签或运动数据)。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种新颖的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架,它引入了三项关键创新。首先,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的数据驱动插值方案,该方案可以捕捉稀疏切片之间的复杂非线性关系,提高重建精度。其次,我们设计了一种在潜在空间运行的高效方法,将心脏3D上采样的时间加快了24倍,与以前的方法相比减少了计算开销。第三,我们的方法仅使用稀疏的二维CMR图像作为输入,与基线方法相比达到了最先进的性能,无需辅助输入(如形态指导),从而简化了工作流程。我们还将该方法扩展到二维+时间数据上,可以有效地模拟时空动态变化并确保时间连贯性。广泛的体积评估和下游分割任务表明,CaLID在重建质量和效率方面达到了先进技术水平。通过解决现有方法的基本局限性,我们的框架推动了空间和时间维度上心脏重建的最新技术前沿,为心血管成像提供了稳健且实用的临床解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在诊断和治疗心血管疾病中至关重要,但其效用常受限于二维短轴切片的稀疏采集,导致体积信息不完整。为解决现有方法在心脏潜在插值方面的局限,提出了全新的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架。此框架采用数据驱动插值方案,提高重建精度和计算效率,仅依赖稀疏的二维CMR图像即可实现卓越性能。此外,它还能处理二维加时间的时空动态数据,确保时间连贯性。综合体积评估和下游分割任务证明,CaLID框架具有出色的重建质量和效率,为心血管成像提供了稳健且实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- CMR成像在心血管疾病的诊断和管理中扮演重要角色,但受限于二维切片的稀疏采集造成的体积信息缺失问题。
- 提出一种新颖的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架,通过数据驱动的插值方案提高重建精度。
- CaLID框架能在潜在空间内操作并实现高效计算,显著缩短了三维心脏整体放大时间。
- 该框架无需额外的语义输入如分割标签或运动数据,仅依赖稀疏的二维CMR图像即可实现卓越性能。
- CaLID框架可扩展到二维加时间的时空数据处理,确保时间连贯性。
- 综合体积评估和下游分割任务显示,CaLID框架在时空全心脏重建方面取得了先进成果。
点此查看论文截图
Sketch3DVE: Sketch-based 3D-Aware Scene Video Editing
Authors:Feng-Lin Liu, Shi-Yang Li, Yan-Pei Cao, Hongbo Fu, Lin Gao
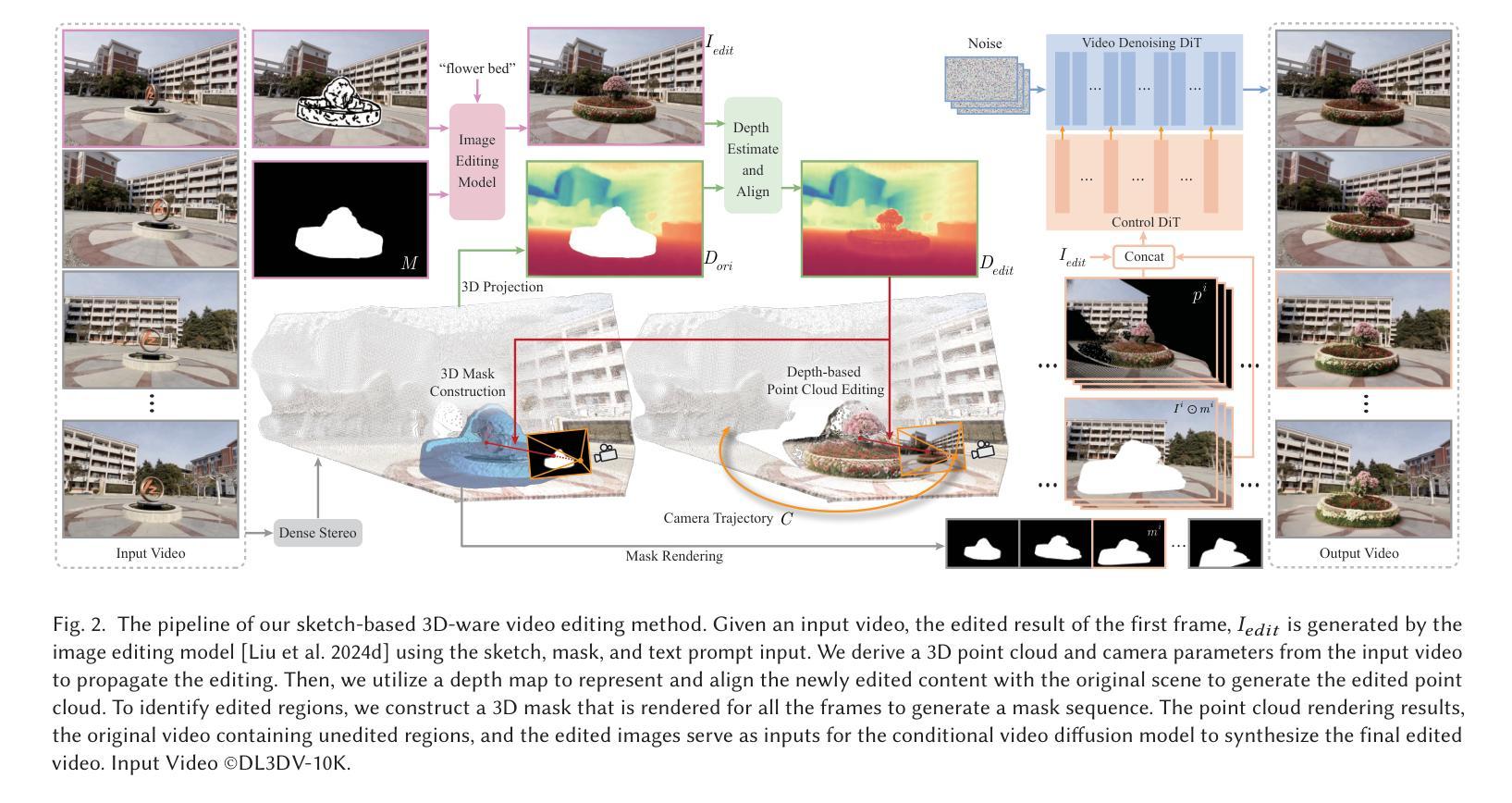
Recent video editing methods achieve attractive results in style transfer or appearance modification. However, editing the structural content of 3D scenes in videos remains challenging, particularly when dealing with significant viewpoint changes, such as large camera rotations or zooms. Key challenges include generating novel view content that remains consistent with the original video, preserving unedited regions, and translating sparse 2D inputs into realistic 3D video outputs. To address these issues, we propose Sketch3DVE, a sketch-based 3D-aware video editing method to enable detailed local manipulation of videos with significant viewpoint changes. To solve the challenge posed by sparse inputs, we employ image editing methods to generate edited results for the first frame, which are then propagated to the remaining frames of the video. We utilize sketching as an interaction tool for precise geometry control, while other mask-based image editing methods are also supported. To handle viewpoint changes, we perform a detailed analysis and manipulation of the 3D information in the video. Specifically, we utilize a dense stereo method to estimate a point cloud and the camera parameters of the input video. We then propose a point cloud editing approach that uses depth maps to represent the 3D geometry of newly edited components, aligning them effectively with the original 3D scene. To seamlessly merge the newly edited content with the original video while preserving the features of unedited regions, we introduce a 3D-aware mask propagation strategy and employ a video diffusion model to produce realistic edited videos. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of Sketch3DVE in video editing. Homepage and code: http://http://geometrylearning.com/Sketch3DVE/
最近的视频编辑方法在风格转换或外观修改方面取得了吸引人的成果。然而,编辑包含视点变化的3D场景的视频中的结构内容仍然是一个挑战,特别是在处理重大视点变化,如大幅度的相机旋转或缩放时。主要挑战包括生成与原始视频保持一致的新视图内容、保留未编辑区域,以及将稀疏的二维输入转化为逼真的三维视频输出。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Sketch3DVE,一种基于草图的三维视频编辑方法,实现对视点变化显著的视频的详细局部操作。为了解决稀疏输入带来的挑战,我们采用图像编辑方法为第一帧生成编辑结果,然后将这些结果传播到视频的其余帧。我们使用草图作为一种交互工具进行精确的几何控制,同时支持其他基于遮罩的图像编辑方法。为了处理视点变化,我们对视频中的三维信息进行详细的分析和操作。具体来说,我们采用密集立体方法估计点云和输入视频的相机参数。然后,我们提出了一种点云编辑方法,使用深度图来表示新编辑组件的三维几何形状,并将其有效地与原始三维场景对齐。为了无缝地将新编辑的内容与原始视频合并,同时保留未编辑区域的特点,我们引入了一种三维感知遮罩传播策略,并采用了视频扩散模型来生成逼真的编辑视频。大量实验表明,Sketch3DVE在视频编辑方面的优越性。主页和代码:http://geometrylearning.com/Sketch3DVE/(注:网址部分似乎有误重复,原文中的网址链接需要进一步检查并修正)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025
摘要
视频编辑中结构内容的编辑仍然是难点,特别是面对大视角变化时的编辑挑战重重。为实现精确的局部操作,提出了一种基于草图的3D感知视频编辑方法Sketch3DVE。利用图像编辑方法解决稀疏输入问题,利用草图作为交互工具进行精确的几何控制。通过密集立体法估计点云和输入视频的摄像机参数,提出一种点云编辑方法,使用深度图表示新编辑组件的3D几何结构,有效地与原始3D场景对齐。无缝融合新内容与原始视频,同时保留未编辑区域特征,采用视频扩散模型生成真实编辑视频。
关键见解
- 视频的结构内容编辑,特别是大视角变化的编辑,仍是研究的挑战。
- Sketch3DVE方法实现了基于草图的3D感知视频编辑,支持详细局部操作。
- 利用图像编辑方法解决稀疏输入问题,通过草图进行精确的几何控制。
- 采用密集立体法估计点云和摄像机参数,处理视角变化。
- 点云编辑方法使用深度图与原始3D场景对齐新编辑的3D几何结构。
- 利用视频扩散模型生成真实且无缝融合新内容与原始视频。
- Sketch3DVE在视频编辑方面的优越性得到了广泛实验的验证。
点此查看论文截图


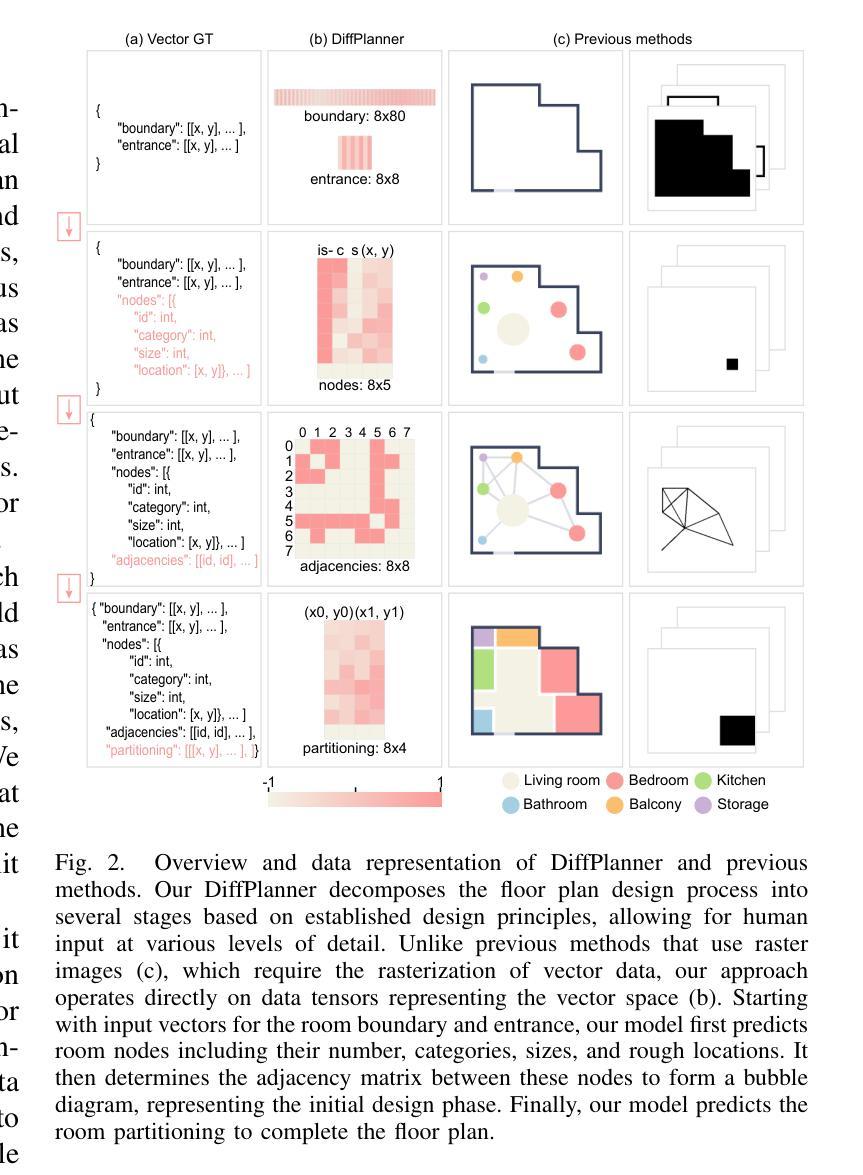
Eliminating Rasterization: Direct Vector Floor Plan Generation with DiffPlanner
Authors:Shidong Wang, Renato Pajarola
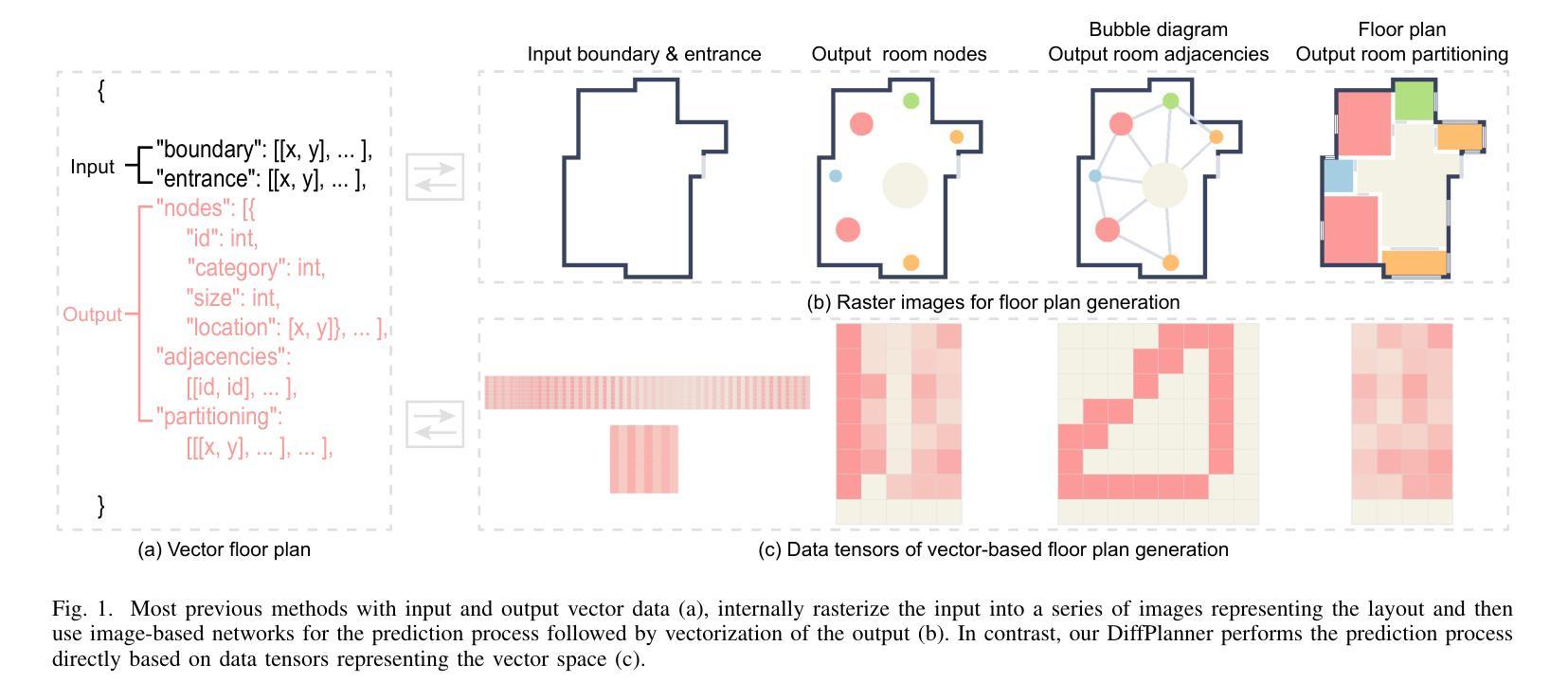
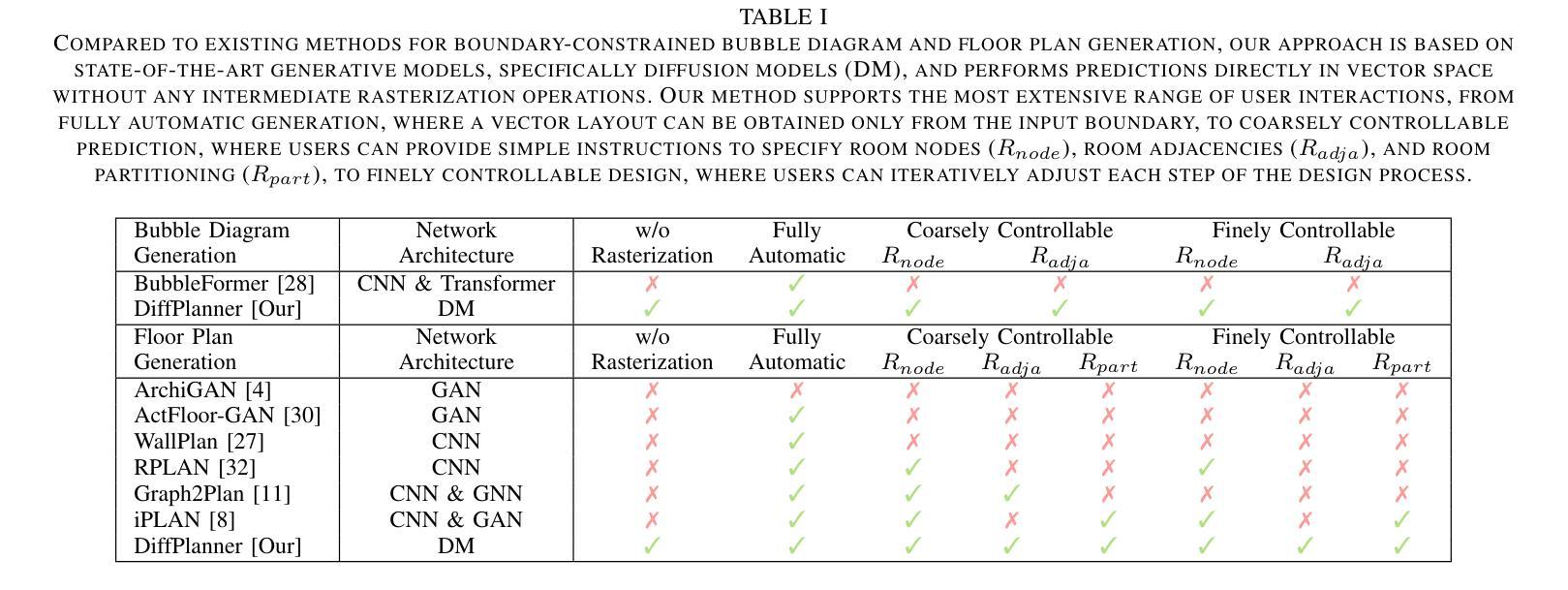
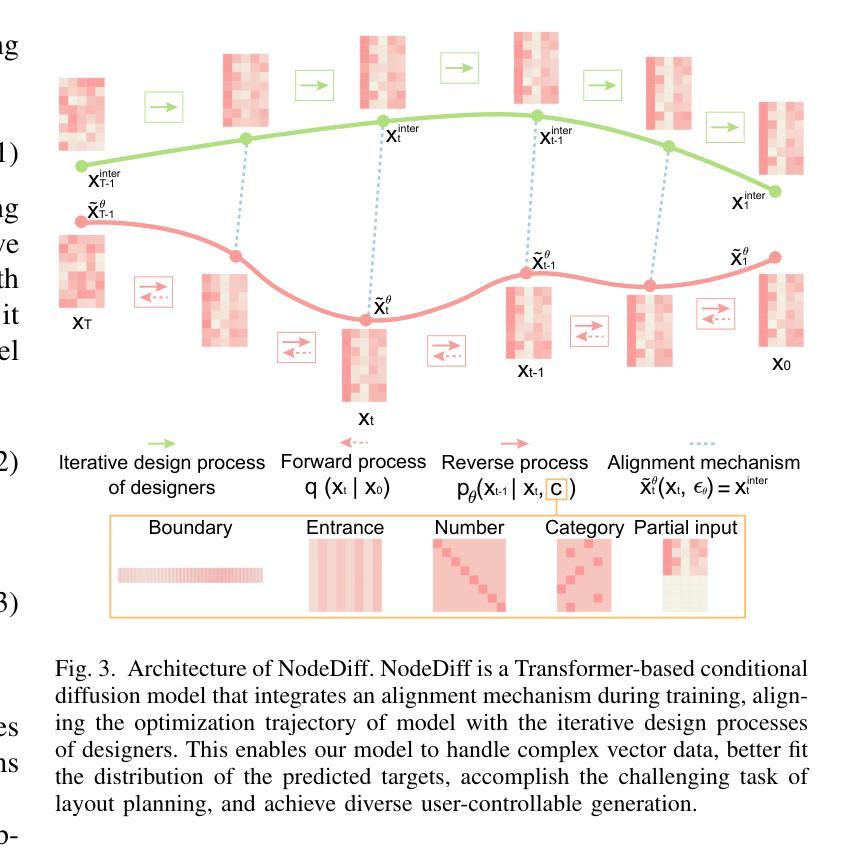
The boundary-constrained floor plan generation problem aims to generate the topological and geometric properties of a set of rooms within a given boundary. Recently, learning-based methods have made significant progress in generating realistic floor plans. However, these methods involve a workflow of converting vector data into raster images, using image-based generative models, and then converting the results back into vector data. This process is complex and redundant, often resulting in information loss. Raster images, unlike vector data, cannot scale without losing detail and precision. To address these issues, we propose a novel deep learning framework called DiffPlanner for boundary-constrained floor plan generation, which operates entirely in vector space. Our framework is a Transformer-based conditional diffusion model that integrates an alignment mechanism in training, aligning the optimization trajectory of the model with the iterative design processes of designers. This enables our model to handle complex vector data, better fit the distribution of the predicted targets, accomplish the challenging task of floor plan layout design, and achieve user-controllable generation. We conduct quantitative comparisons, qualitative evaluations, ablation experiments, and perceptual studies to evaluate our method. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiffPlanner surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in generating floor plans and bubble diagrams in the creative stages, offering more controllability to users and producing higher-quality results that closely match the ground truths.
边界约束的平面图生成问题旨在生成给定边界内的一组房间的拓扑和几何属性。最近,基于学习的方法在生成逼真的平面图方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些方法需要将矢量数据转换为栅格图像,使用基于图像的生成模型,然后将结果转回矢量数据的工作流程。这个过程复杂且冗余,经常导致信息丢失。与矢量数据不同,栅格图像无法在不损失细节和精度的情况下进行缩放。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为DiffPlanner的新型深度学习框架,用于边界约束的平面图生成,它完全在矢量空间中进行操作。我们的框架是一个基于Transformer的条件扩散模型,在训练中集成了对齐机制,使模型的优化轨迹与设计师的迭代设计过程对齐。这使得我们的模型能够处理复杂的矢量数据,更好地适应预测目标分布,完成具有挑战性的平面图布局设计任务,并实现用户可控的生成。我们进行了定量比较、定性评估、剔除实验和感知研究来评估我们的方法。大量实验表明,DiffPlanner在创意阶段生成平面图和气泡图方面超越了现有最先进的方法,为用户提供更多可控性,并产生更接近真实的高质量结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
Summary
基于边界约束的平面图生成问题旨在生成给定边界内的一组房间的拓扑和几何属性。传统的基于学习的方法需要将矢量数据转换为栅格图像,使用基于图像的生成模型,然后再将结果转回矢量数据,这一过程复杂且冗余,常常导致信息丢失。为解决这些问题,我们提出了名为DiffPlanner的新型深度学习框架,用于在矢量空间内完全进行边界约束的平面图生成。通过集成对齐机制进行培训,DiffPlanner将模型优化轨迹与设计师的迭代设计过程对齐,从而更好地处理复杂矢量数据,更好地适应预测目标的分布,完成复杂的平面图布局设计任务,并实现用户可控的生成。实验证明,DiffPlanner在创意阶段的平面图生成和气泡图生成方面超过了现有最先进的方法,为用户提供更多控制力并产生更接近真实的高质量结果。
Key Takeaways
- 边界约束的平面图生成问题旨在生成给定边界内的房间拓扑和几何属性。
- 现有学习方法的转换流程复杂且冗余,存在信息丢失的问题。
- DiffPlanner是一个新型的深度学习框架,完全在矢量空间内进行边界约束的平面图生成。
- DiffPlanner集成了对齐机制进行培训,以优化模型处理复杂矢量数据的能力。
- DiffPlanner可以更好地适应预测目标的分布,完成复杂的平面图布局设计任务。
- DiffPlanner实现了用户可控的生成,为用户提供了更多控制力。
点此查看论文截图

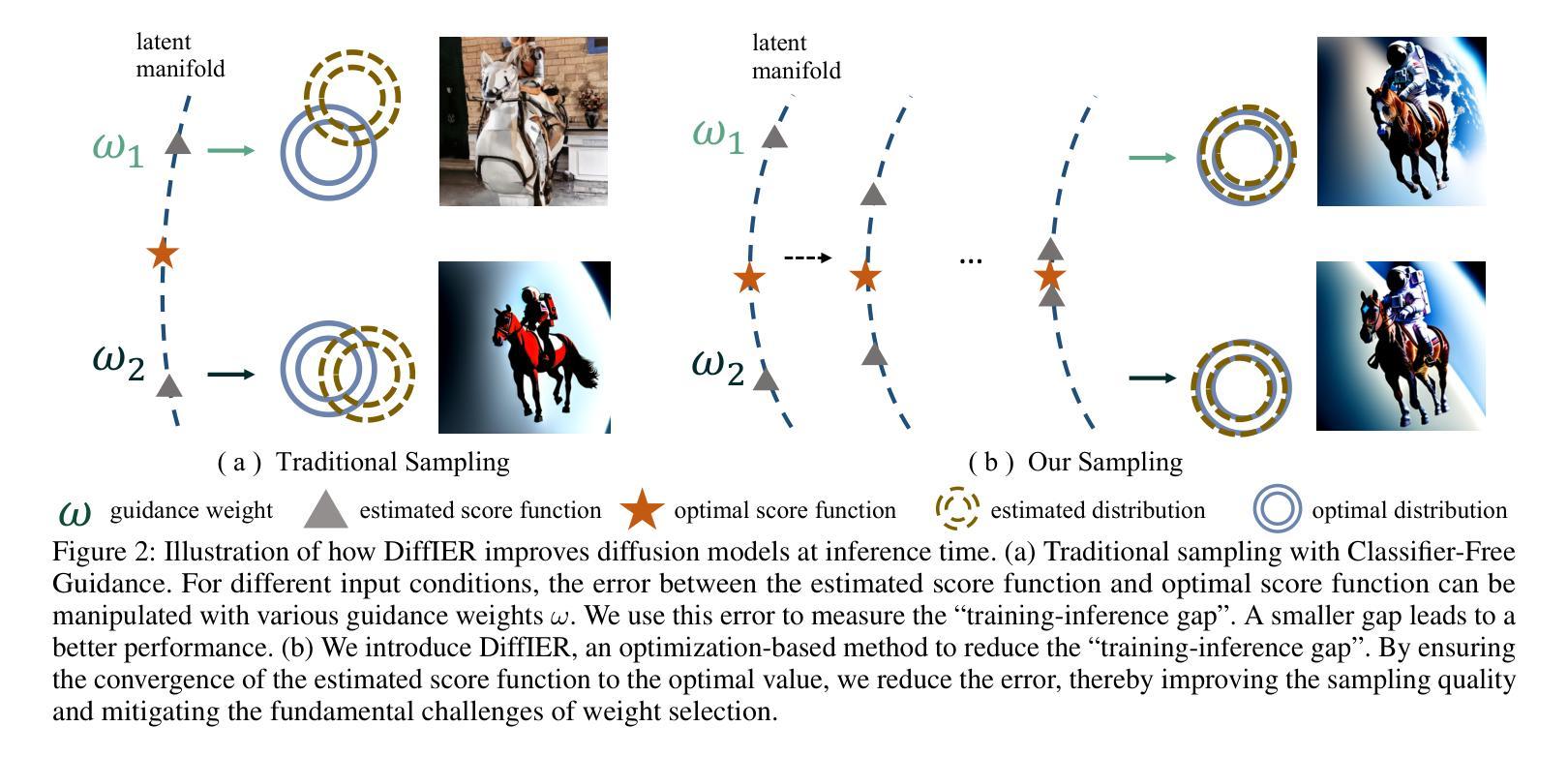
DiffIER: Optimizing Diffusion Models with Iterative Error Reduction
Authors:Ao Chen, Lihe Ding, Tianfan Xue
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality samples and enhancing performance across diverse domains through Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG). However, the quality of generated samples is highly sensitive to the selection of the guidance weight. In this work, we identify a critical ``training-inference gap’’ and we argue that it is the presence of this gap that undermines the performance of conditional generation and renders outputs highly sensitive to the guidance weight. We quantify this gap by measuring the accumulated error during the inference stage and establish a correlation between the selection of guidance weight and minimizing this gap. Furthermore, to mitigate this gap, we propose DiffIER, an optimization-based method for high-quality generation. We demonstrate that the accumulated error can be effectively reduced by an iterative error minimization at each step during inference. By introducing this novel plug-and-play optimization framework, we enable the optimization of errors at every single inference step and enhance generation quality. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms baseline approaches in conditional generation tasks. Furthermore, the method achieves consistent success in text-to-image generation, image super-resolution, and text-to-speech generation, underscoring its versatility and potential for broad applications in future research.
扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)在生成高质量样本和提高不同领域的性能方面表现出了卓越的能力。然而,生成样本的质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。在这项工作中,我们识别出了一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,我们认为正是这个差距影响了条件生成的表现,并使输出高度依赖于引导权重。我们通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这个差距,并建立了选择引导权重与最小化这个差距之间的关联。此外,为了缓解这一差距,我们提出了DiffIER,这是一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。我们证明,通过推理过程中每一步的迭代误差最小化,可以有效减少累积误差。通过引入这种新颖即插即用的优化框架,我们能够在每一个单独推理步骤中优化误差,提高生成质量。经验结果表明,我们提出的方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法。此外,该方法在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成方面取得了持续的成功,这突显了其在未来研究中的通用性和广泛应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成高质量样本和提升性能方面的显著能力,特别是通过无分类器引导(CFG)实现。然而,生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。本文识别出关键的“训练-推理差距”,并认为这一差距影响了条件生成性能,使输出对引导权重高度敏感。为减少这一差距,提出了DiffIER这一基于优化的高质量生成方法。通过迭代误差最小化,在推理阶段每一步优化误差,提高了生成质量。实验结果显示,该方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法,并在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成等任务中取得了持续的成功。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)展现出强大的生成能力。
- 生成的样本质量受引导权重选择的显著影响。
- 文中识别出“训练-推理差距”,这一差距影响条件生成性能。
- 提出DiffIER方法,通过优化减少推理阶段的误差积累。
- DiffIER方法通过迭代误差最小化,在推理每一步优化误差。
- DiffIER方法在条件生成任务上表现优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图




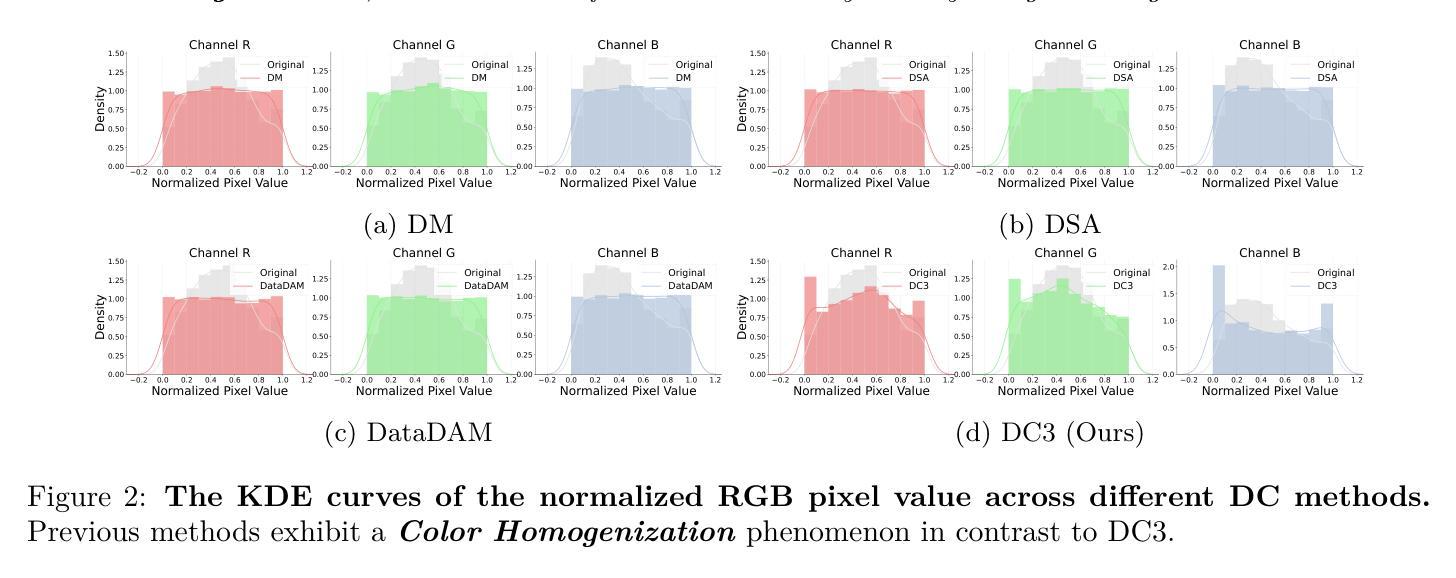
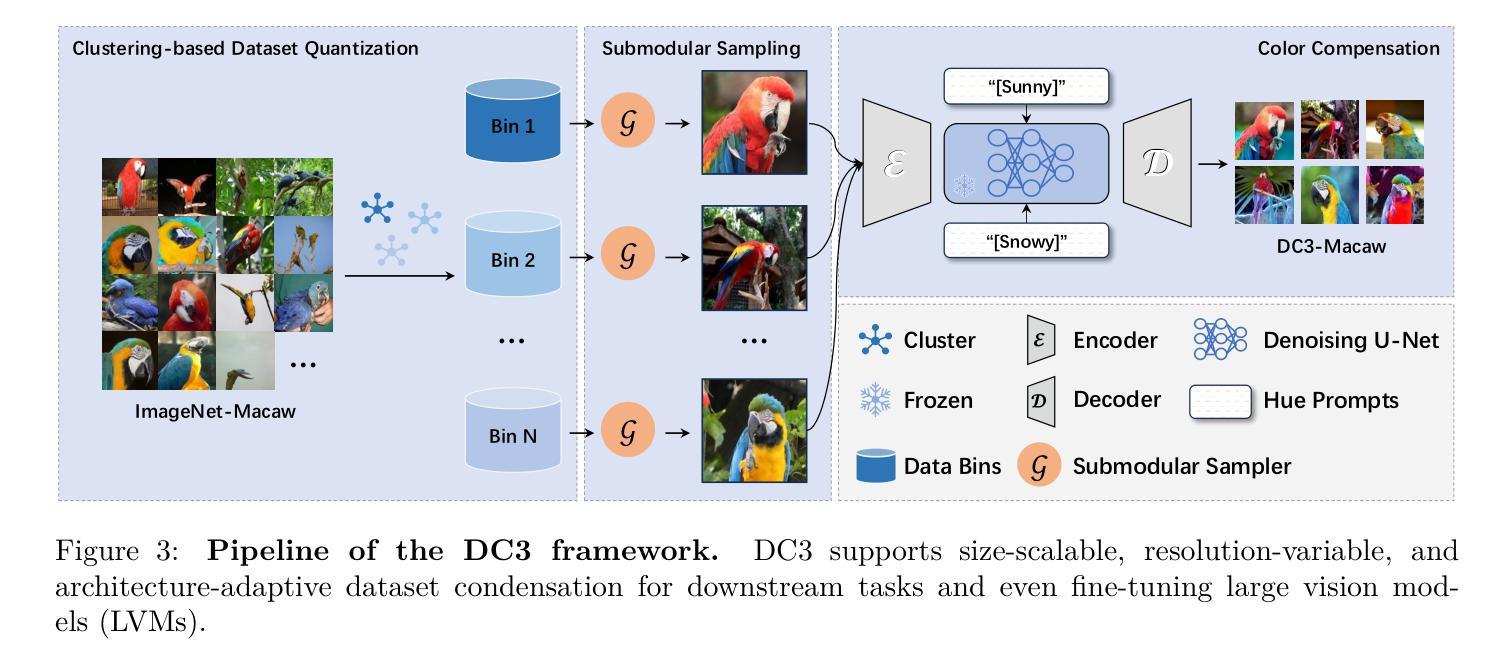
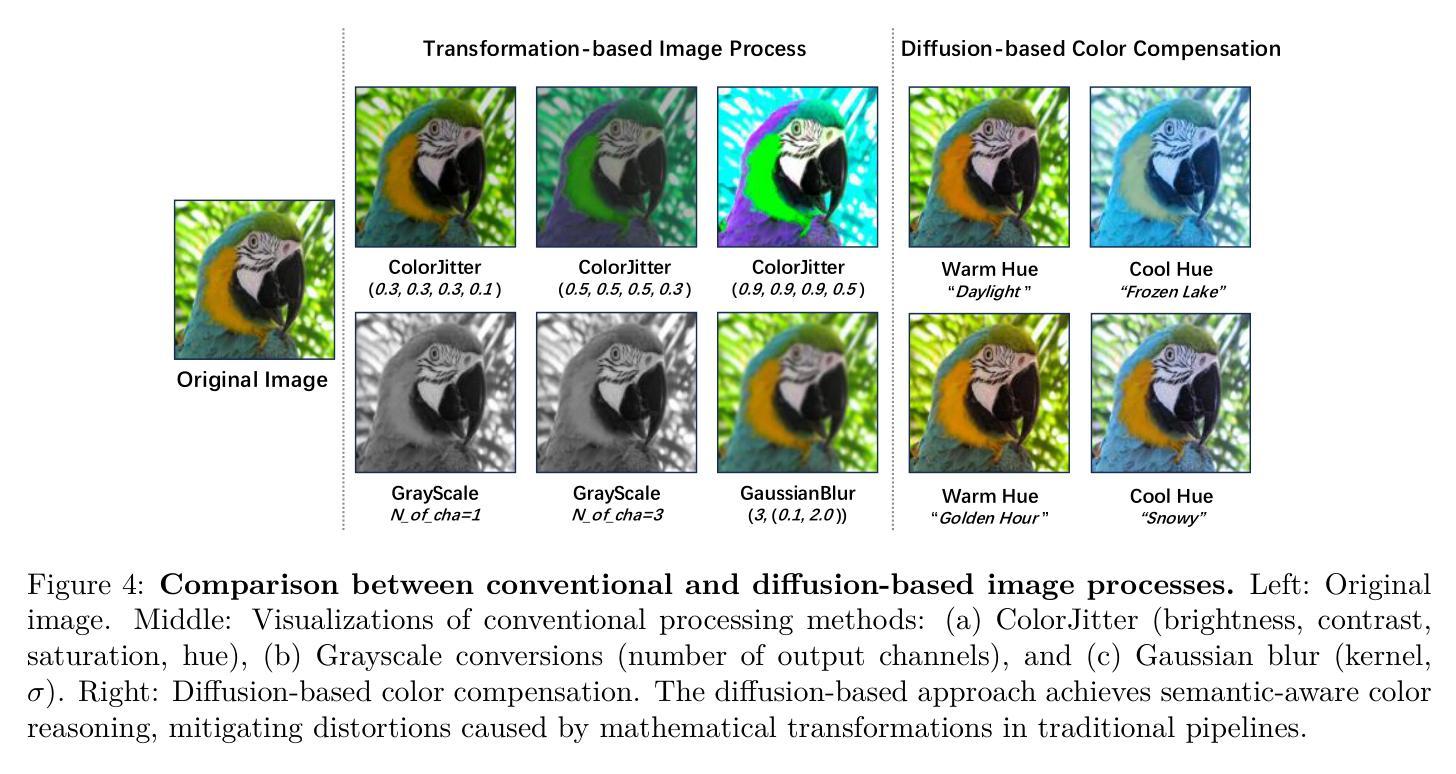
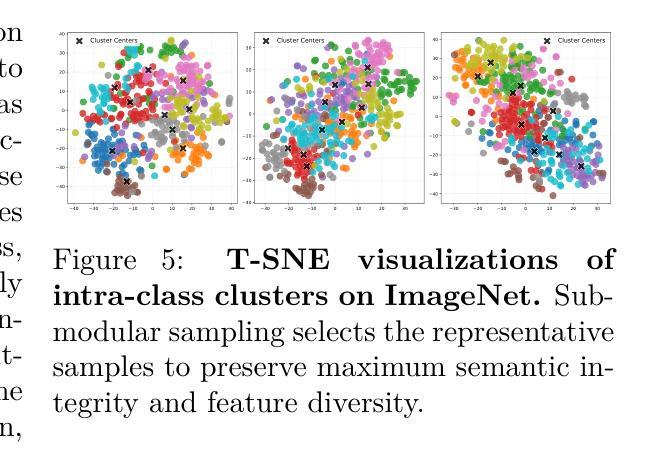
Dataset Condensation with Color Compensation
Authors:Huyu Wu, Duo Su, Junjie Hou, Guang Li
Dataset condensation always faces a constitutive trade-off: balancing performance and fidelity under extreme compression. Existing methods struggle with two bottlenecks: image-level selection methods (Coreset Selection, Dataset Quantization) suffer from inefficiency condensation, while pixel-level optimization (Dataset Distillation) introduces semantic distortion due to over-parameterization. With empirical observations, we find that a critical problem in dataset condensation is the oversight of color’s dual role as an information carrier and a basic semantic representation unit. We argue that improving the colorfulness of condensed images is beneficial for representation learning. Motivated by this, we propose DC3: a Dataset Condensation framework with Color Compensation. After a calibrated selection strategy, DC3 utilizes the latent diffusion model to enhance the color diversity of an image rather than creating a brand-new one. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance and generalization of DC3 that outperforms SOTA methods across multiple benchmarks. To the best of our knowledge, besides focusing on downstream tasks, DC3 is the first research to fine-tune pre-trained diffusion models with condensed datasets. The FID results prove that training networks with our high-quality datasets is feasible without model collapse or other degradation issues. Code and generated data are available at https://github.com/528why/Dataset-Condensation-with-Color-Compensation.
数据集压缩始终面临一个基本的权衡:在极端压缩情况下平衡性能和保真度。现有方法面临两个瓶颈:图像级别的选择方法(核心集选择、数据集量化)存在压缩效率低下的问题,而像素级别的优化(数据集蒸馏)由于过度参数化而导致语义失真。通过经验观察,我们发现数据集压缩中的关键问题是忽视了颜色作为信息载体和基本语义表示单元的双重作用。我们认为提高浓缩图像的色彩丰富度对表示学习是有益的。受此启发,我们提出了DC3:一种具有颜色补偿的数据集压缩框架。经过校准的选择策略后,DC3利用潜在的扩散模型来提高图像的颜色多样性,而不是创建全新的图像。大量实验证明了DC3的卓越性能和泛化能力,它在多个基准测试上超越了最先进的方法。据我们所知,除了关注下游任务外,DC3是首次使用浓缩数据集对预训练扩散模型进行微调的研究。FID结果证明,使用我们高质量的数据集训练网络是可行的,不会出现模型崩溃或其他退化问题。代码和生成的数据可在https://github.com/528why/Dataset-Condensation-with-Color-Compensation找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了数据集压缩中颜色补偿的重要性,并提出了一种名为DC3的新的数据集压缩框架。该框架利用潜在扩散模型提高图像的颜色多样性,而非创建全新图像。实验证明,DC3在多个基准测试中表现优异,优于现有方法。此外,DC3还是首次尝试使用压缩数据集微调预训练扩散模型的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 数据集压缩面临性能与保真度之间的权衡。
- 现存方法面临两个瓶颈:图像级别的选择方法效率低下,像素级别的优化则会导致语义失真。
- 颜色在数据集压缩中被忽视,其作为信息载体和基本语义表示单元的双重角色至关重要。
- 提高压缩图像的色彩丰富性对表示学习有益。
- DC3框架利用潜在扩散模型增强图像颜色多样性,而非创建新图像。
- DC3在多个基准测试中表现优异,优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
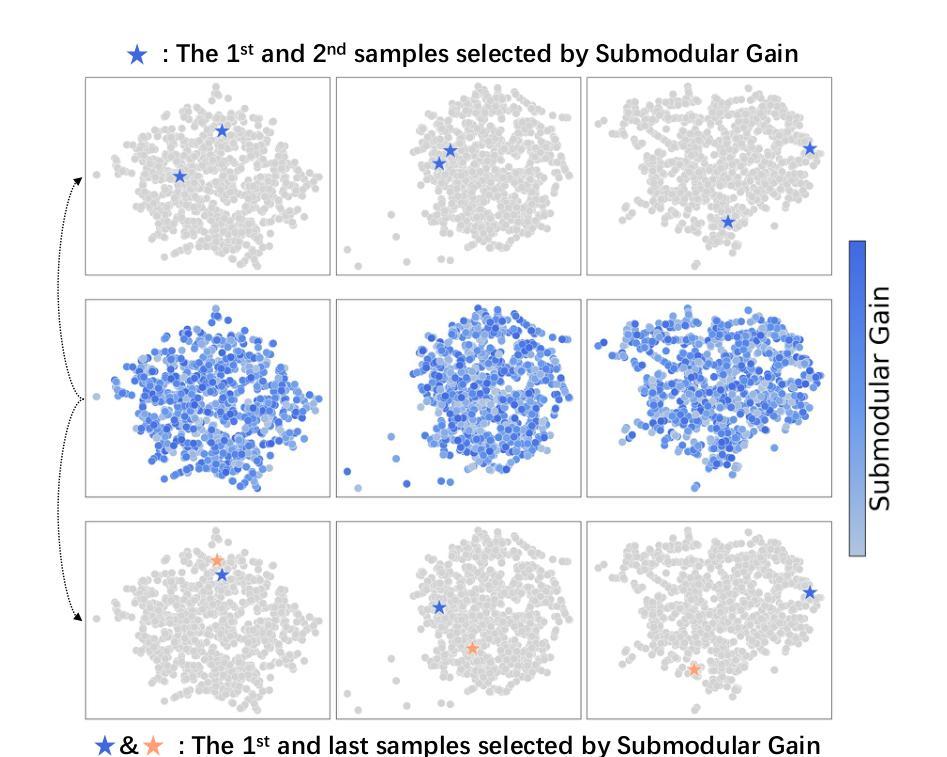
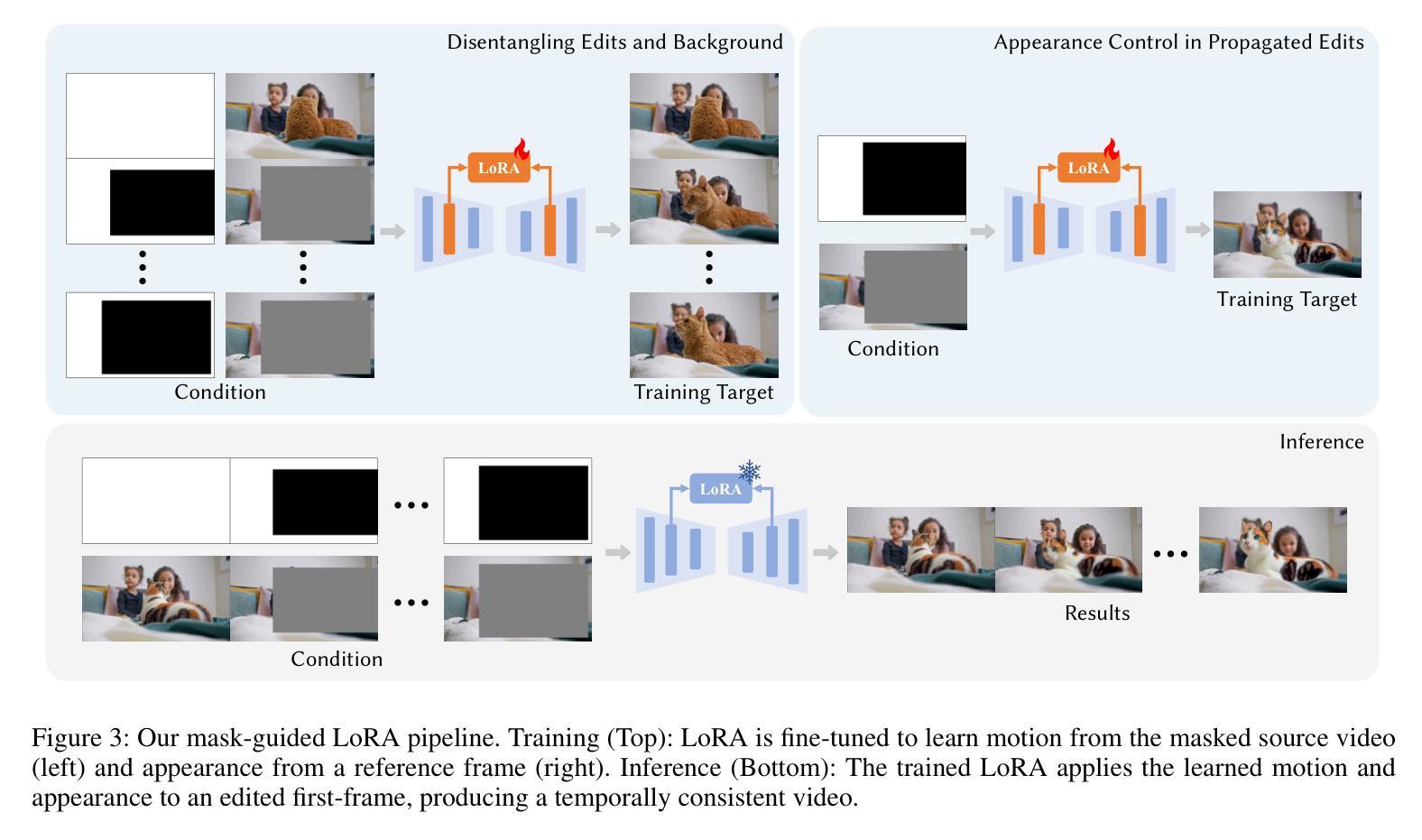
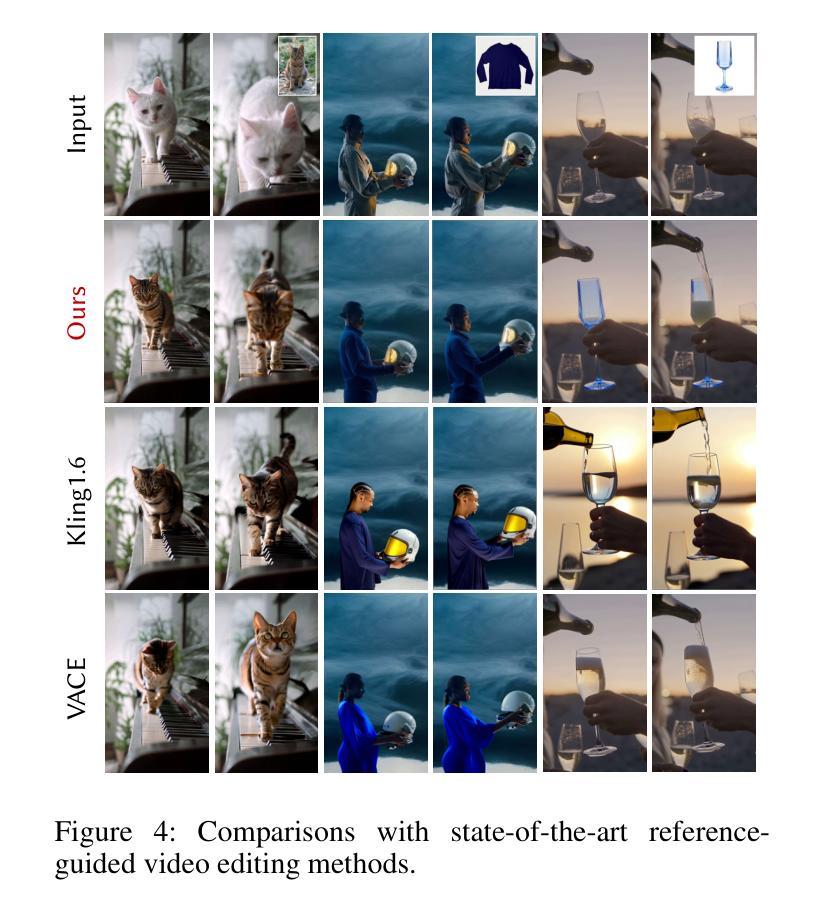
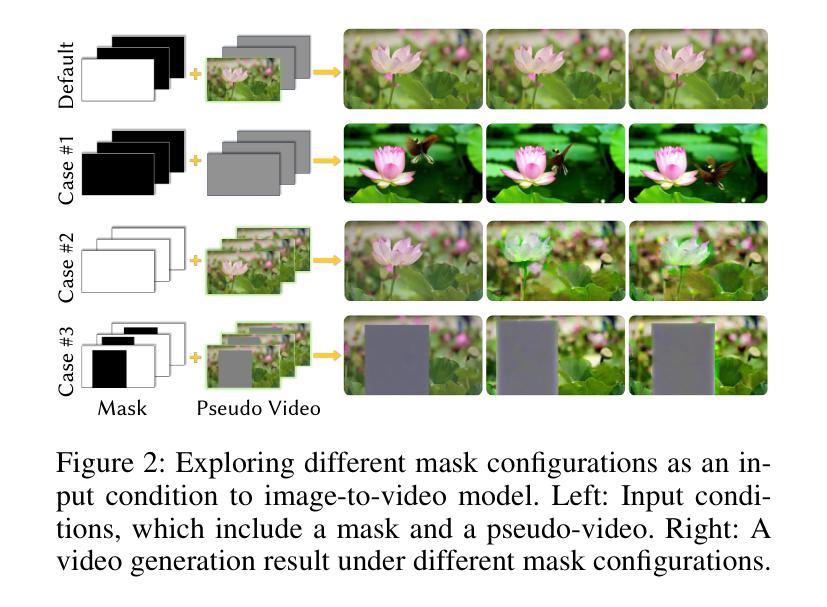
LoRA-Edit: Controllable First-Frame-Guided Video Editing via Mask-Aware LoRA Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chenjian Gao, Lihe Ding, Xin Cai, Zhanpeng Huang, Zibin Wang, Tianfan Xue
Video editing using diffusion models has achieved remarkable results in generating high-quality edits for videos. However, current methods often rely on large-scale pretraining, limiting flexibility for specific edits. First-frame-guided editing provides control over the first frame, but lacks flexibility over subsequent frames. To address this, we propose a mask-based LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) tuning method that adapts pretrained Image-to-Video (I2V) models for flexible video editing. Our key innovation is using a spatiotemporal mask to strategically guide the LoRA fine-tuning process. This teaches the model two distinct skills: first, to interpret the mask as a command to either preserve content from the source video or generate new content in designated regions. Second, for these generated regions, LoRA learns to synthesize either temporally consistent motion inherited from the video or novel appearances guided by user-provided reference frames. This dual-capability LoRA grants users control over the edit’s entire temporal evolution, allowing complex transformations like an object rotating or a flower blooming. Experimental results show our method achieves superior video editing performance compared to baseline methods. Project Page: https://cjeen.github.io/LoRAEdit
使用扩散模型进行视频编辑已经在为高质量视频生成编辑方面取得了显著成果。然而,当前的方法通常依赖于大规模预训练,这限制了特定编辑的灵活性。第一帧引导编辑提供了对第一帧的控制,但缺乏对后续帧的灵活性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,该方法可适应预训练的图生视频(I2V)模型,用于灵活视频编辑。我们的主要创新之处在于使用时空掩膜来战略性指导LoRA微调过程。这教会了模型两种独特技能:首先,将掩膜解释为来自源视频的指令,要么保留内容,要么在指定区域生成新内容。其次,对于这些生成的区域,LoRA学习合成从视频中继承的时间连贯运动或根据用户提供的参考帧引导的新外观。这种双功能的LoRA使用户能够控制整个时间轴的编辑过程,从而实现复杂的转换,如物体旋转或花朵绽放等。实验结果表明,我们的方法相较于基线方法实现了更出色的视频编辑性能。项目页面:https://cjeen.github.io/LoRAEdit 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
扩散模型在视频编辑领域已取得显著成果,能够生成高质量的视频编辑。但现有方法常依赖大规模预训练,对特定编辑的灵活性有限。为解决这一问题,我们提出基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,用于适应预训练的图生视频(I2V)模型以实现灵活的视频编辑。实验结果显示,该方法相较于基线方法实现了更优越的视频编辑性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在视频编辑中表现优异,能生成高质量编辑。
- 现有方法依赖大规模预训练,缺乏特定编辑的灵活性。
- 提出基于掩膜的LoRA调优方法,适应I2V模型进行灵活视频编辑。
- 使用时空掩膜指导LoRA微调过程,教会模型两种技能:保留源视频内容或在指定区域生成新内容。
- LoRA学会合成与视频一致的临时运动或根据用户提供的参考帧生成新外观。
- 双能力LoRA让用户控制整个时间演化的编辑,实现复杂转换。
点此查看论文截图




Hyperspectral Image Generation with Unmixing Guided Diffusion Model
Authors:Shiyu Shen, Bin Pan, Ziye Zhang, Zhenwei Shi
We address hyperspectral image (HSI) synthesis, a problem that has garnered growing interest yet remains constrained by the conditional generative paradigms that limit sample diversity. While diffusion models have emerged as a state-of-the-art solution for high-fidelity image generation, their direct extension from RGB to hyperspectral domains is challenged by the high spectral dimensionality and strict physical constraints inherent to HSIs. To overcome the challenges, we introduce a diffusion framework explicitly guided by hyperspectral unmixing. The approach integrates two collaborative components: (i) an unmixing autoencoder that projects generation from the image domain into a low-dimensional abundance manifold, thereby reducing computational burden while maintaining spectral fidelity; and (ii) an abundance diffusion process that enforces non-negativity and sum-to-one constraints, ensuring physical consistency of the synthesized data. We further propose two evaluation metrics tailored to hyperspectral characteristics. Comprehensive experiments, assessed with both conventional measures and the proposed metrics, demonstrate that our method produces HSIs with both high quality and diversity, advancing the state of the art in hyperspectral data generation.
我们关注高光谱图像(HSI)的合成问题。这一问题虽然引起了越来越多的兴趣,但仍受到有条件生成范式的约束,这些范式限制了样本的多样性。虽然扩散模型已成为高保真图像生成的最先进解决方案,但它们从RGB直接扩展到高光谱领域却面临着高光谱维度高和HSI固有的严格物理约束的挑战。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了一个由高光谱解混明确指导的扩散框架。该方法结合了两个协作组件:(i)一个解混自编码器,将图像域的生成投影到低维丰度流形上,从而在保持光谱保真度的同时减少计算负担;(ii)一个丰度扩散过程,强制执行非负性和总和为一的约束,确保合成数据的物理一致性。我们还提出了两个针对高光谱特性定制的评价指标。通过常规度量方法和所提出的指标进行的综合实验表明,我们的方法生成的高光谱图像质量高、多样性好,推动了高光谱数据生成的最新技术进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
针对高光谱图像(HSI)合成问题,由于条件生成范式限制了样本多样性,虽然扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面表现出卓越性能,但其直接扩展到高光谱领域面临高光谱维度和严格物理约束的挑战。为克服这些挑战,我们提出了一个由高光谱解混引导的扩散框架,该框架包括两个协作组件:一)解混自编码器将图像域的生成投射到低维丰度流形上,以减少计算负担并保持光谱保真度;二)丰度扩散过程强制实施非负性和总和为一的约束,以确保合成数据的物理一致性。我们的方法生成的高光谱图像具有高质量和多样性,推动了高光谱数据生成的最新技术。
Key Takeaways:
- 高光谱图像合成问题受限于条件生成范式的样本多样性。
- 扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面具有卓越性能,但直接应用于高光谱领域面临挑战。
- 提出的扩散框架由高光谱解混引导,包括解混自编码器和丰度扩散过程两个协作组件。
- 解混自编码器将图像生成投射到低维丰度流形上,以维持光谱保真度并降低计算负担。
- 丰度扩散过程确保合成数据的物理一致性,通过实施非负性和总和为一的约束。
- 提出的方法生成的高光谱图像具有高质量和多样性。
点此查看论文截图
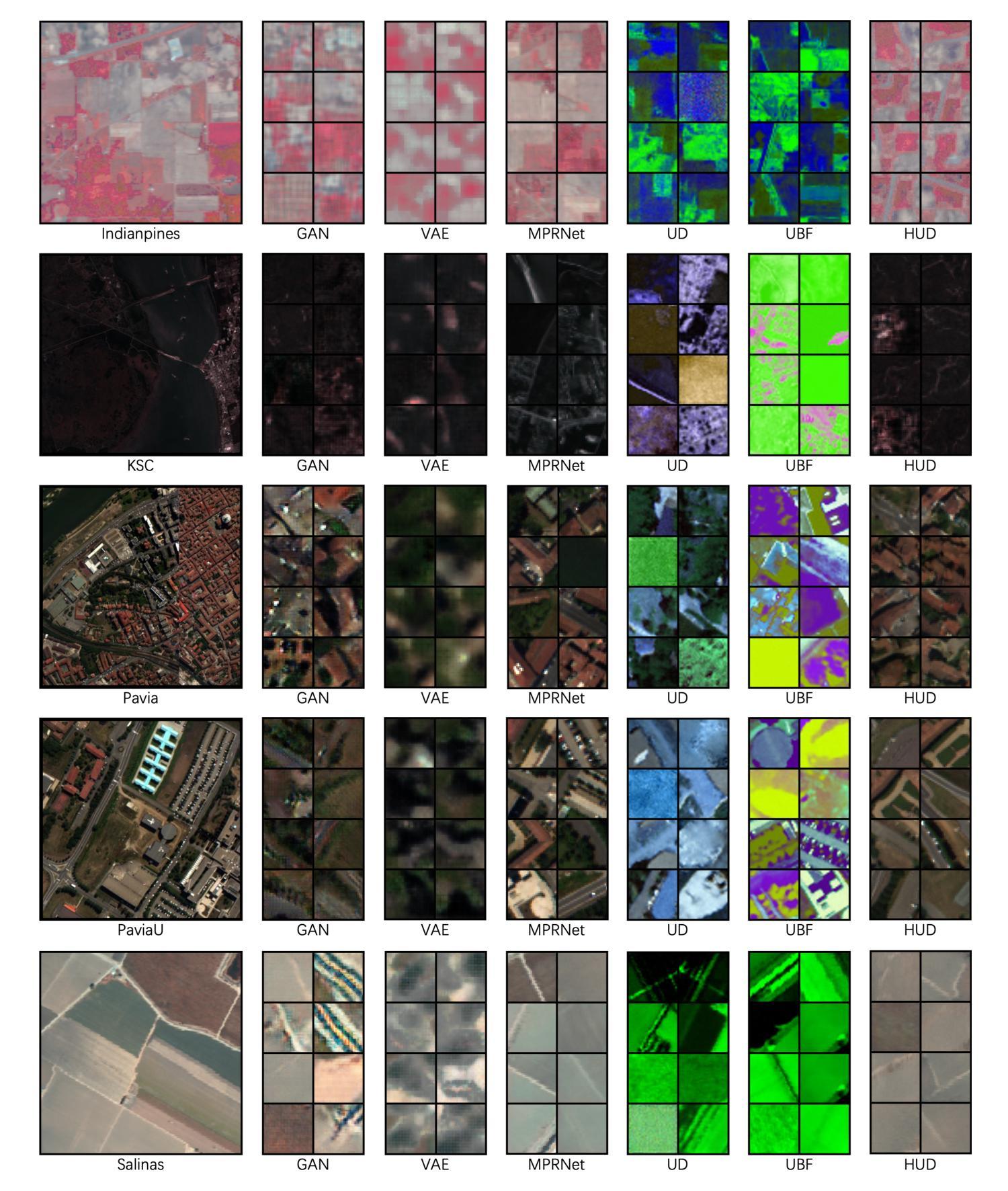

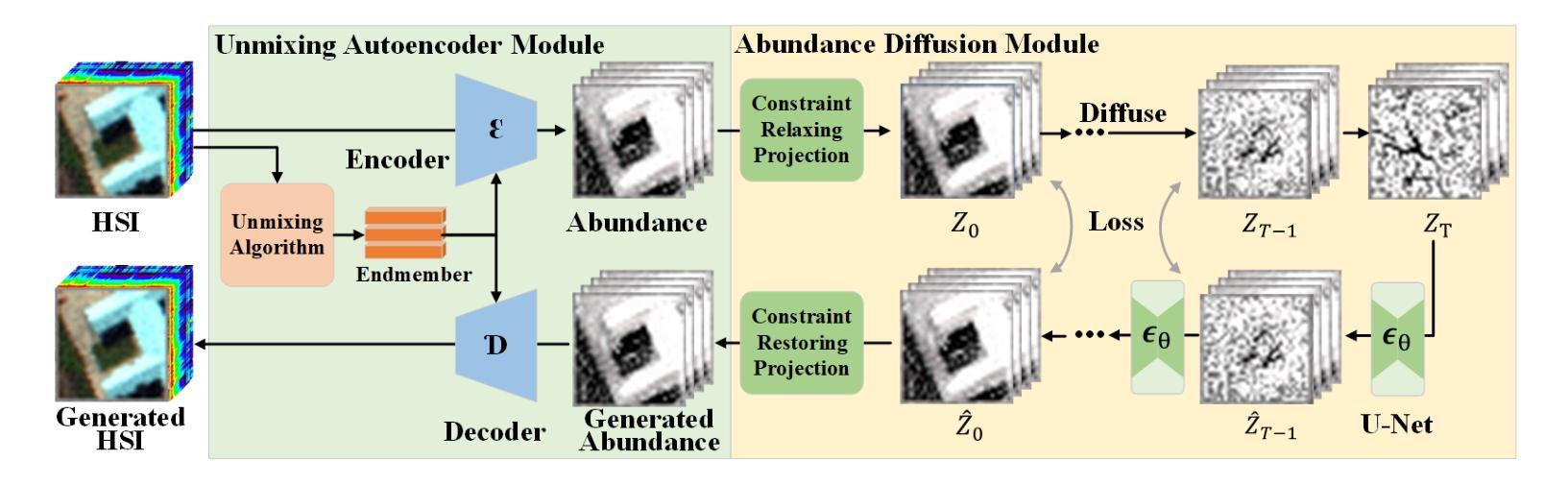

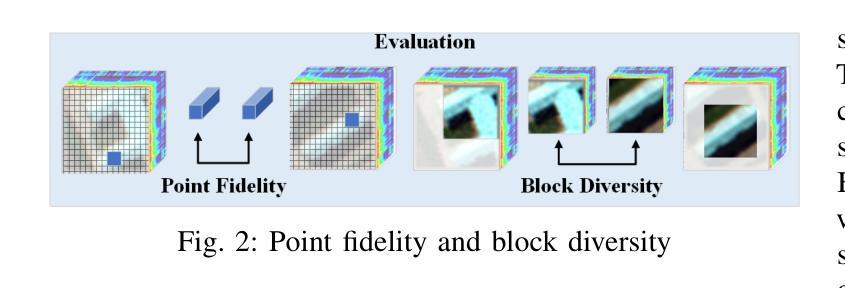

Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要集中在设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更准确的密集标签,忽视了固定数据集所带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像的多样性可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们引入了一种新方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM提示生成中的不稳定问题,我们开发了一种提示自我优化机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成的图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最先进的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Neurocomputing 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的性能。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外的图像,增强WSSS的训练图像多样性。同时,为解决LLMs在生成提示时的不稳定性问题,提出了提示自我优化机制,并通过在线过滤器确保生成图像的质量和平衡性。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- IAA方法从数据生成角度提升WSSS性能,通过自动生成额外图像增加训练图像多样性。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型实现图像自动生成。
- 提出提示自我优化机制,解决LLMs在生成提示时的不稳定性问题。
- 通过在线过滤器确保生成图像的质量和平衡性。
- IAA方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上表现优异,显著超越现有WSSS方法。
- 该方法丰富了语义信息,有助于模型理解更全面的语义模式。
点此查看论文截图

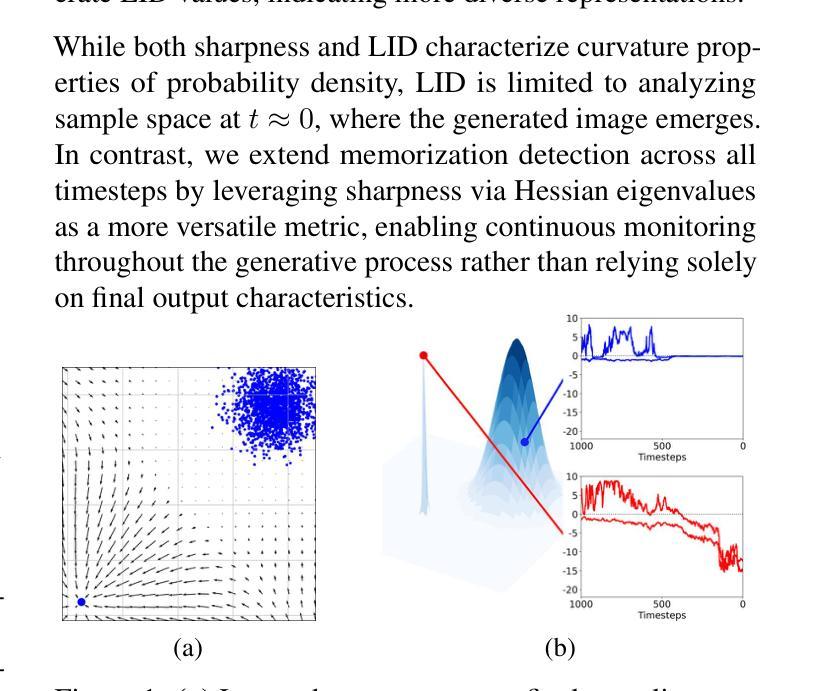
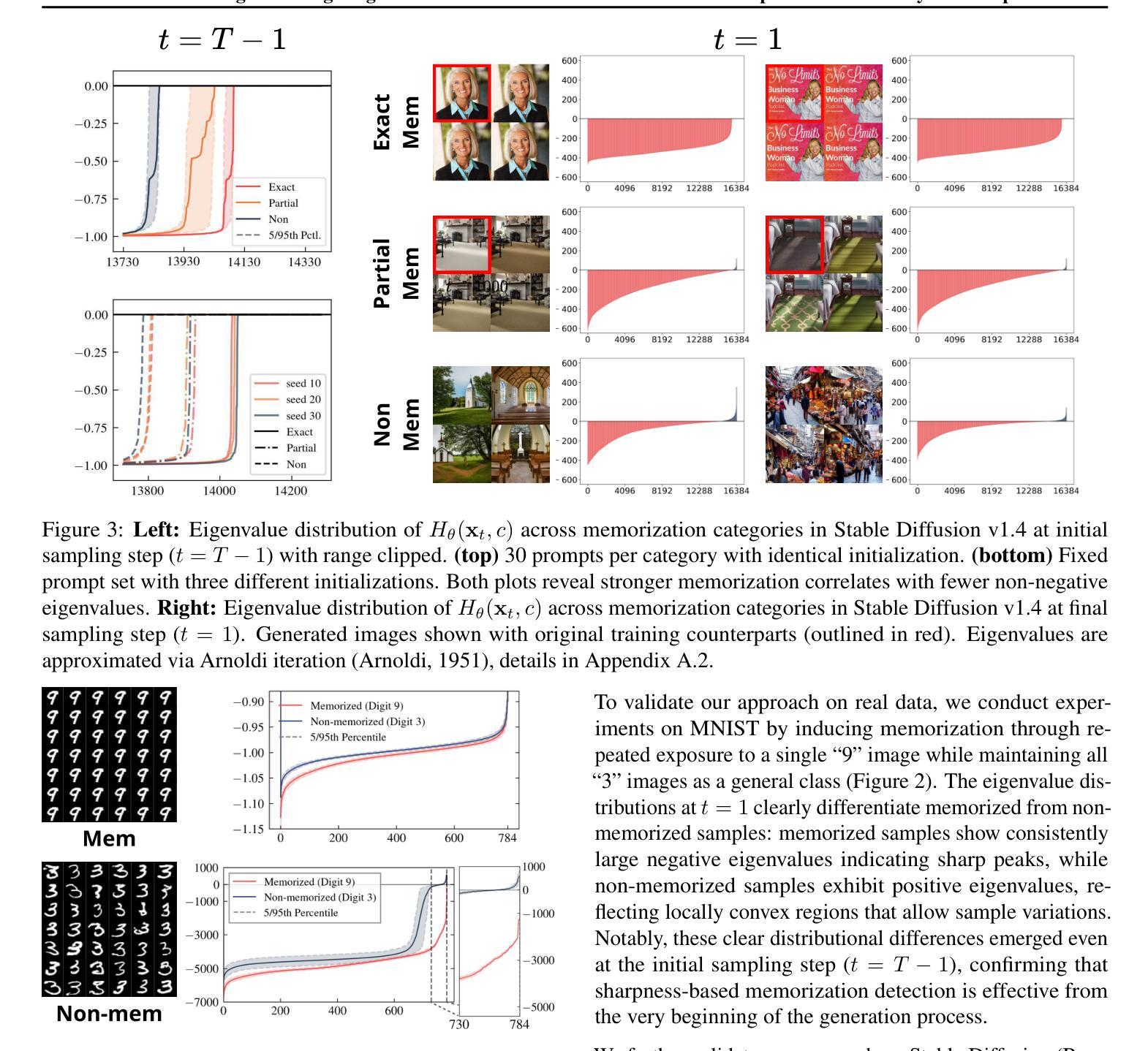
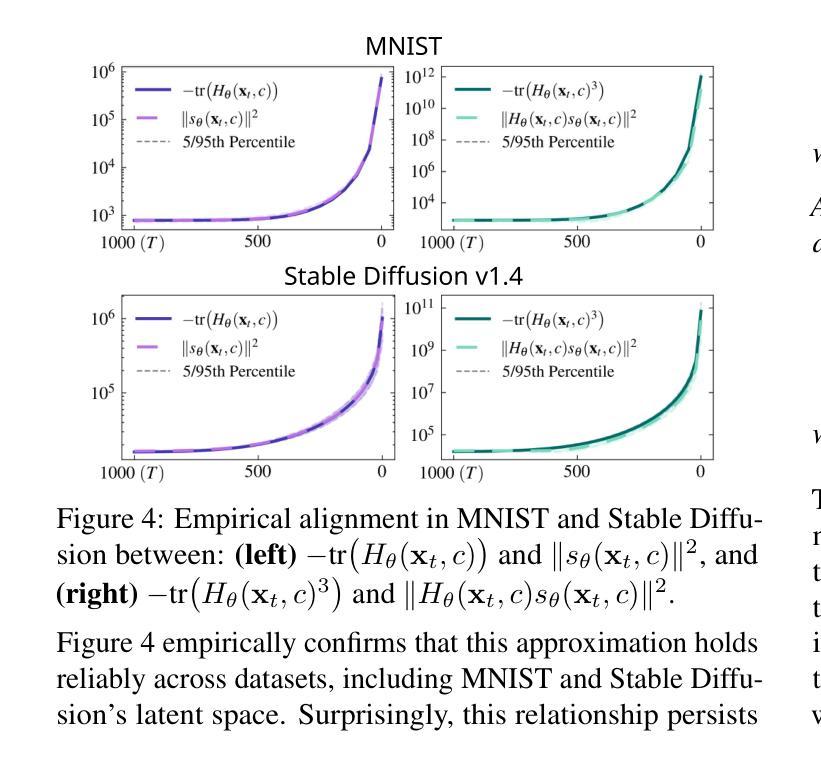
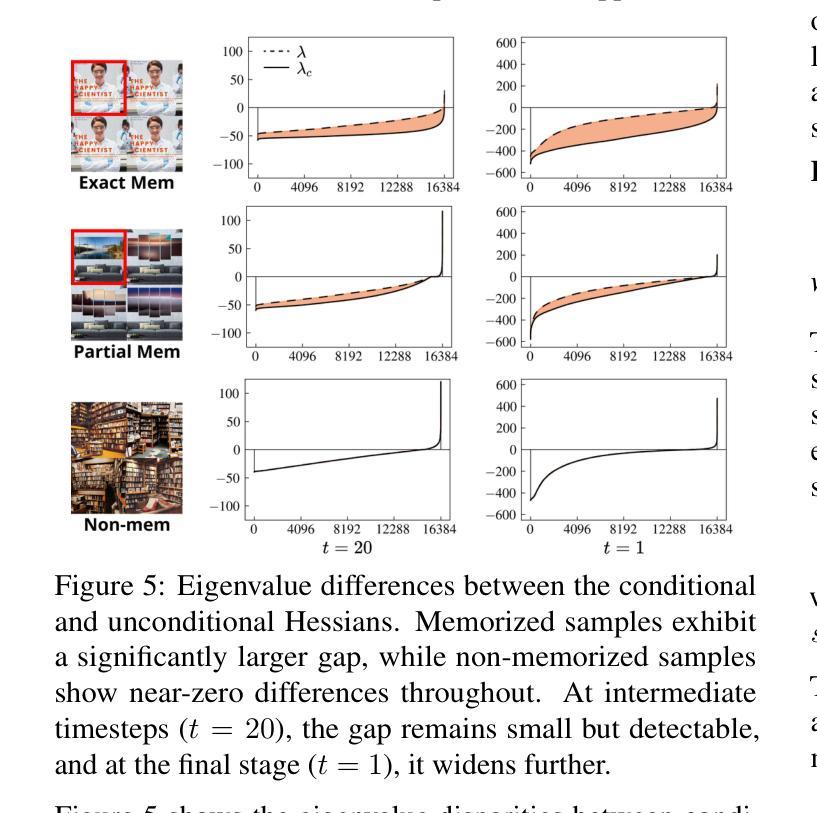
Understanding and Mitigating Memorization in Generative Models via Sharpness of Probability Landscapes
Authors:Dongjae Jeon, Dueun Kim, Albert No
In this paper, we introduce a geometric framework to analyze memorization in diffusion models through the sharpness of the log probability density. We mathematically justify a previously proposed score-difference-based memorization metric by demonstrating its effectiveness in quantifying sharpness. Additionally, we propose a novel memorization metric that captures sharpness at the initial stage of image generation in latent diffusion models, offering early insights into potential memorization. Leveraging this metric, we develop a mitigation strategy that optimizes the initial noise of the generation process using a sharpness-aware regularization term. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Dongjae0324/sharpness_memorization_diffusion.
本文介绍了一个基于几何的框架,通过对数概率密度的尖锐程度来分析扩散模型中的记忆化。我们通过证明其在量化尖锐度方面的有效性,为之前提出的基于分数差异的记忆化度量提供了数学依据。此外,我们提出了一个新的记忆化度量标准,该标准能够捕捉潜在扩散模型的图像生成初始阶段的尖锐度,为潜在的记忆化提供早期见解。利用这一度量标准,我们开发了一种缓解策略,通过采用尖锐度感知正则化项来优化生成过程的初始噪声。代码公开在https://github.com/Dongjae0324/sharpness_memorization_diffusion。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025 (Spotlight). Code: https://github.com/Dongjae0324/sharpness_memorization_diffusion
Summary:
本论文通过几何框架分析了扩散模型中的记忆能力,主要通过概率密度对数的锐度进行阐述。文章从数学角度证明了一个基于评分差异的记忆力指标的有效性,并展示其在量化锐度方面的作用。此外,文章还提出了一种新的记忆力指标,用于捕捉图像生成初期在潜在扩散模型中的锐度,为潜在记忆力提供早期洞察。利用这一指标,研究团队开发了一种优化生成过程初始噪声的策略,即采用锐度感知的正则化项。相关代码已公开在https://github.com/Dongjae0324/sharpness_memorization_diffusion。
Key Takeaways:
- 引入几何框架分析扩散模型中的记忆力。
- 通过概率密度对数的锐度进行阐述。
- 数学证明了基于评分差异的记忆力指标的有效性。
- 提出新的记忆力指标,捕捉图像生成初期的锐度。
- 利用新的记忆力指标开发了一种优化生成过程的方法。
- 优化策略聚焦于初始噪声的优化。
点此查看论文截图

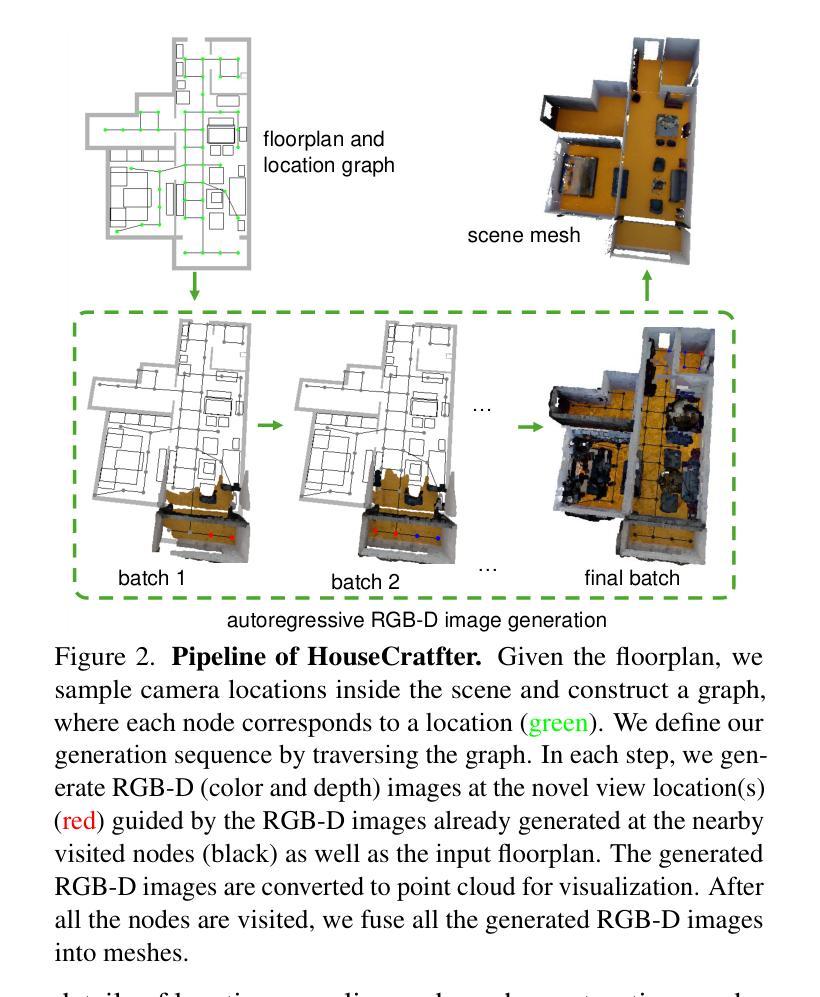
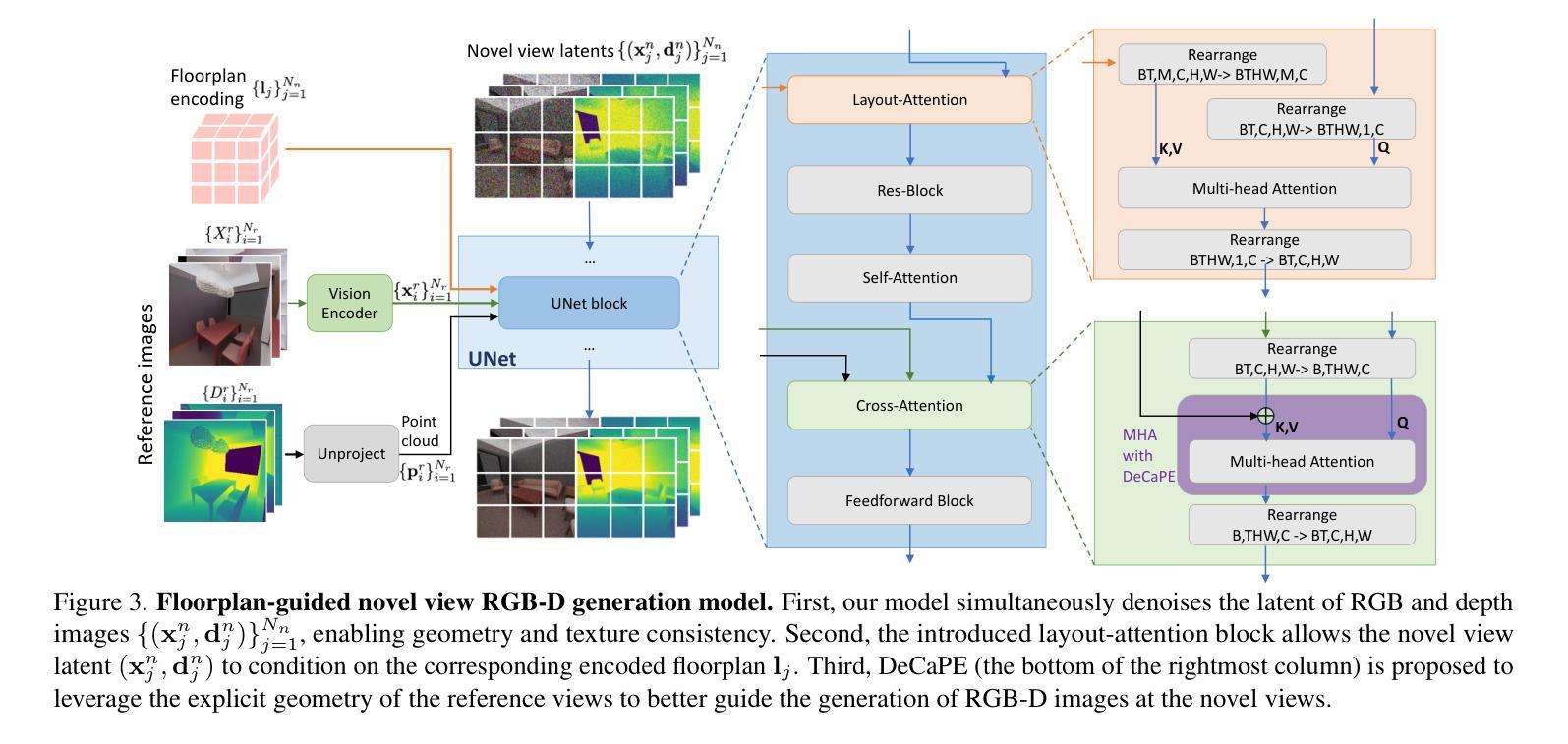
HouseCrafter: Lifting Floorplans to 3D Scenes with 2D Diffusion Model
Authors:Hieu T. Nguyen, Yiwen Chen, Vikram Voleti, Varun Jampani, Huaizu Jiang
We introduce HouseCrafter, a novel approach that can lift a floorplan into a complete large 3D indoor scene (e.g., a house). Our key insight is to adapt a 2D diffusion model, which is trained on web-scale images, to generate consistent multi-view color (RGB) and depth (D) images across different locations of the scene. Specifically, the RGB-D images are generated autoregressively in a batch-wise manner along sampled locations based on the floorplan, where previously generated images are used as condition to the diffusion model to produce images at nearby locations. The global floorplan and attention design in the diffusion model ensures the consistency of the generated images, from which a 3D scene can be reconstructed. Through extensive evaluation on the 3D-Front dataset, we demonstrate that HouseCraft can generate high-quality house-scale 3D scenes. Ablation studies also validate the effectiveness of different design choices. We will release our code and model weights. Project page: https://neu-vi.github.io/houseCrafter/
我们介绍了HouseCrafter这一新方法,它能够将平面地板设计转化为一个完整的大型室内三维场景(例如房子)。我们的主要见解是适应二维扩散模型,该模型在网页规模图像上进行训练,以生成不同场景位置的一致的多视角彩色(RGB)和深度(D)图像。具体而言,基于地板设计,沿着采样位置以批量方式生成RGB-D图像,其中先前生成的图像被用作扩散模型的调节条件以产生邻近位置的图像。全局的地板设计和扩散模型中的注意力机制确保了生成图像的一致性,从而可以从这些图像重建三维场景。我们在3D-Front数据集上进行了广泛评估,证明了HouseCraft可以生成高质量的房子规模三维场景。消融研究也验证了不同设计选择的有效性。我们将发布我们的代码和模型权重。项目页面:[链接](待填写具体链接地址)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:我们推出HouseCrafter,这是一种新颖的方法,能将平面图提升为完整的大型室内三维场景(例如房屋)。我们的关键见解是适应二维扩散模型,该模型在网页规模图像上进行训练,以生成场景不同位置的连续多视图彩色(RGB)和深度(D)图像。具体来说,基于平面图采样的位置以批处理方式自动生成RGB-D图像,其中先前生成的图像用作扩散模型的条件来生成附近位置的图像。扩散模型中的全局平面图和注意力设计确保了生成图像的一致性,从中可以重建三维场景。在3D-Front数据集上的广泛评估表明,HouseCraft可以生成高质量的房子规模三维场景。
Key Takeaways:
- HouseCrafter是一种将平面图转化为完整大型室内三维场景的新方法。
- 该方法利用二维扩散模型,在网页规模图像上进行训练。
- HouseCrafter能生成场景不同位置的连续多视图彩色(RGB)和深度(D)图像。
- RGB-D图像是基于平面图采样的位置以批处理方式生成的。
- 先前生成的图像被用作条件来生成附近位置的图像,确保了一致性。
- 通过全局平面图和扩散模型中的注意力设计,生成了连贯的三维场景。
点此查看论文截图

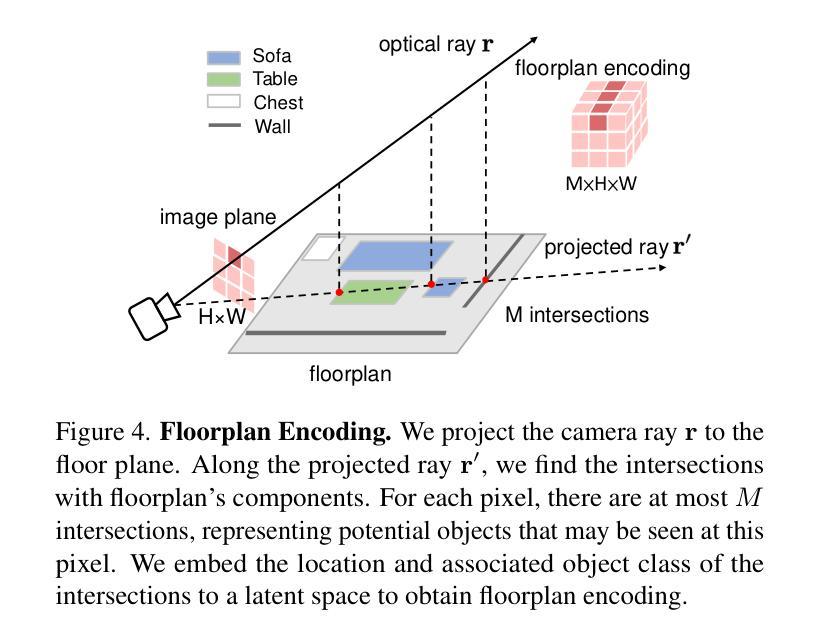

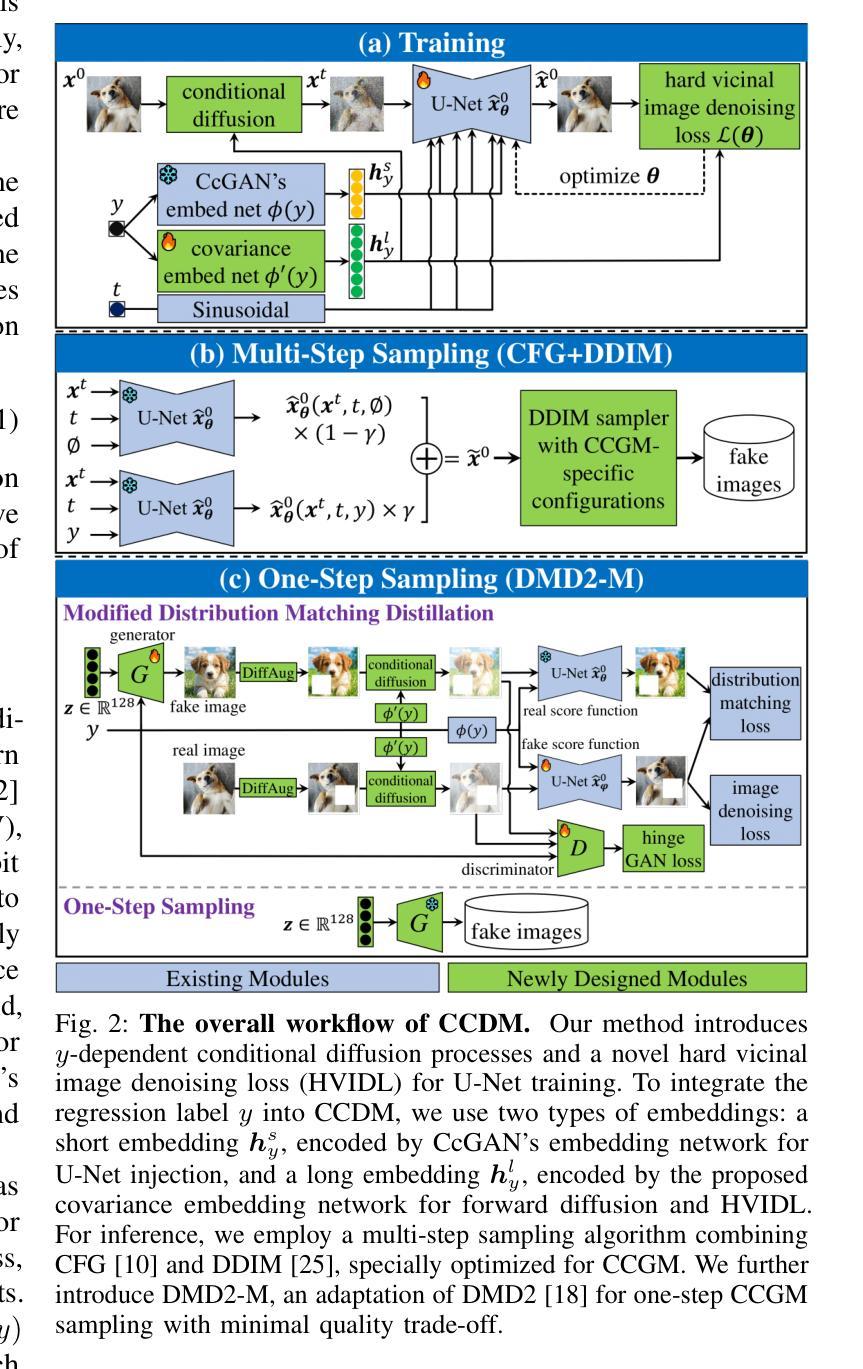
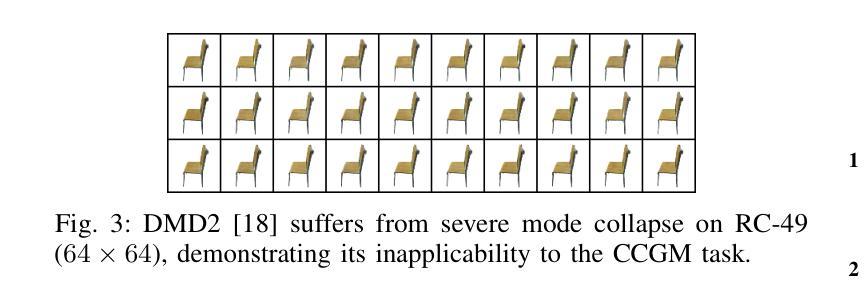
CCDM: Continuous Conditional Diffusion Models for Image Generation
Authors:Xin Ding, Yongwei Wang, Kao Zhang, Z. Jane Wang
Continuous Conditional Generative Modeling (CCGM) estimates high-dimensional data distributions, such as images, conditioned on scalar continuous variables (aka regression labels). While Continuous Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CcGANs) were designed for this task, their instability during adversarial learning often leads to suboptimal results. Conditional Diffusion Models (CDMs) offer a promising alternative, generating more realistic images, but their diffusion processes, label conditioning, and model fitting procedures are either not optimized for or incompatible with CCGM, making it difficult to integrate CcGANs’ vicinal approach. To address these issues, we introduce Continuous Conditional Diffusion Models (CCDMs), the first CDM specifically tailored for CCGM. CCDMs address existing limitations with specially designed conditional diffusion processes, a novel hard vicinal image denoising loss, a customized label embedding method, and efficient conditional sampling procedures. Through comprehensive experiments on four datasets with resolutions ranging from 64x64 to 192x192, we demonstrate that CCDMs outperform state-of-the-art CCGM models, establishing a new benchmark. Ablation studies further validate the model design and implementation, highlighting that some widely used CDM implementations are ineffective for the CCGM task. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/UBCDingXin/CCDM.
连续条件生成模型(CCGM)用于估计高维数据分布,如图像,并根据标量连续变量(即回归标签)进行条件化。虽然连续条件生成对抗网络(CcGANs)是为这一任务而设计的,但它们在对抗学习过程中的不稳定性往往导致结果不尽人意。条件扩散模型(CDMs)提供了一个有前景的替代方案,能够生成更逼真的图像,但它们的扩散过程、标签条件和模型拟合程序并未针对CCGM进行优化或不兼容,这使得难以融入CcGANs的邻近方法。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了连续条件扩散模型(CCDMs),这是专门为CCGM设计的第一个CDM。CCDMs通过特殊设计的条件扩散过程、新颖的硬邻近图像去噪损失、定制的标签嵌入方法和高效的条件采样程序,解决了现有限制。我们在四个不同分辨率(从64x64到192x192)的数据集上进行了全面的实验,证明CCDMs超越了最新的CCGM模型,建立了新的基准。消融研究进一步验证了模型设计和实现,强调一些广泛使用的CDM实现对于CCGM任务无效。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/UBCDingXin/CCDM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
连续条件生成模型(CCGM)用于估计图像等高维数据分布,该分布受标量连续变量(即回归标签)的制约。虽然连续条件生成对抗网络(CcGANs)被设计用于此任务,但其对抗学习过程中的不稳定性常常导致结果不尽人意。条件扩散模型(CDMs)提供了一个前景可观的替代方案,能生成更真实的图像,但它们对扩散过程、标签制约和模型拟合程序的设计并不优化甚至与CCGM不兼容。为解决这些问题,我们推出专门面向CCGM设计的连续条件扩散模型(CCDMs)。CCDMs解决了现有限制,具备特殊设计的条件扩散过程、新颖的硬vicinal图像去噪损失、定制化的标签嵌入方法和高效的条件采样程序。在四个不同分辨率(从64x64到192x192)的数据集上进行的综合实验表明,CCDMs的表现优于最先进的状态CCGM模型,并建立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 连续条件生成模型(CCGM)旨在估计高维数据分布,如图像,受连续变量(回归标签)制约。
- 连续条件生成对抗网络(CcGANs)虽然为此任务设计,但对抗学习过程中的不稳定性导致结果不佳。
- 条件扩散模型(CDMs)能生成更真实的图像,但对CCGM的扩散过程、标签制约和模型拟合程序并未优化或不兼容。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了连续条件扩散模型(CCDMs),针对CCGM进行了特殊设计。
- CCDMs通过特殊的扩散过程、新的硬vicinal图像去噪损失、定制化的标签嵌入方法和高效的采样程序解决了现有问题。
- 综合实验证明,CCDMs在多个数据集上的表现优于其他先进CCGM模型,建立了新的性能基准。
点此查看论文截图


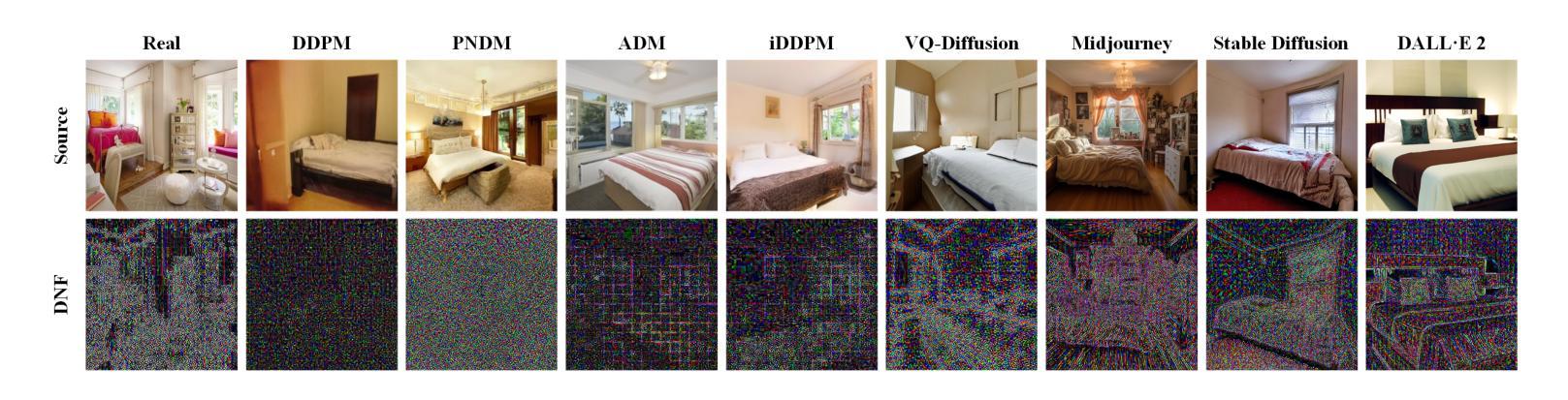
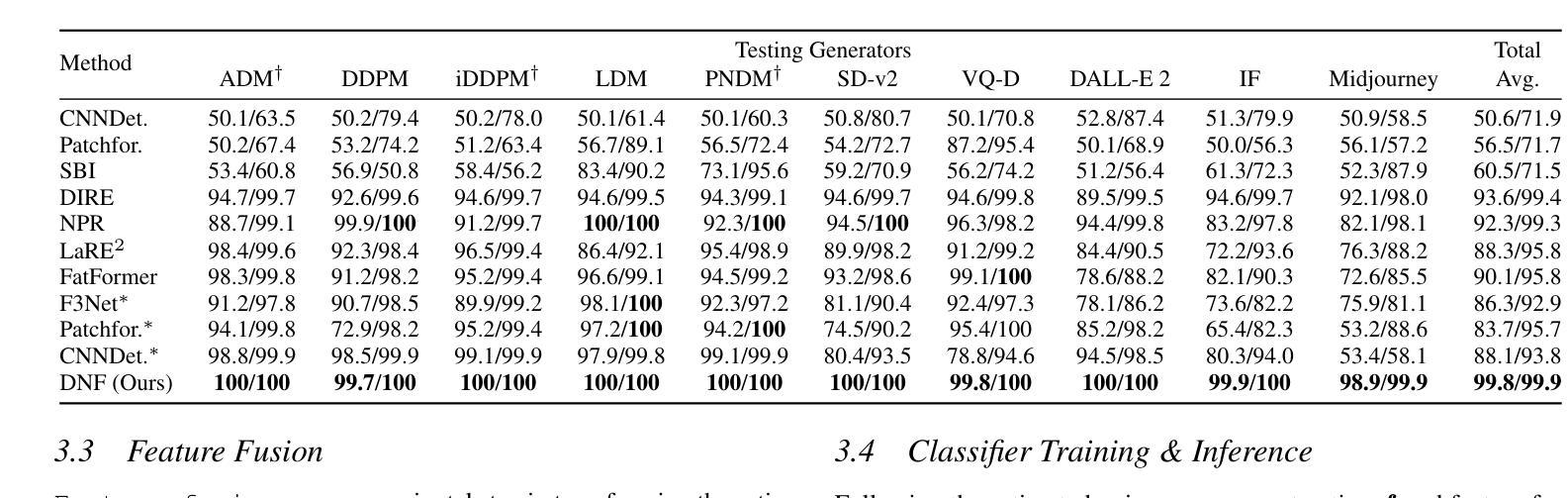
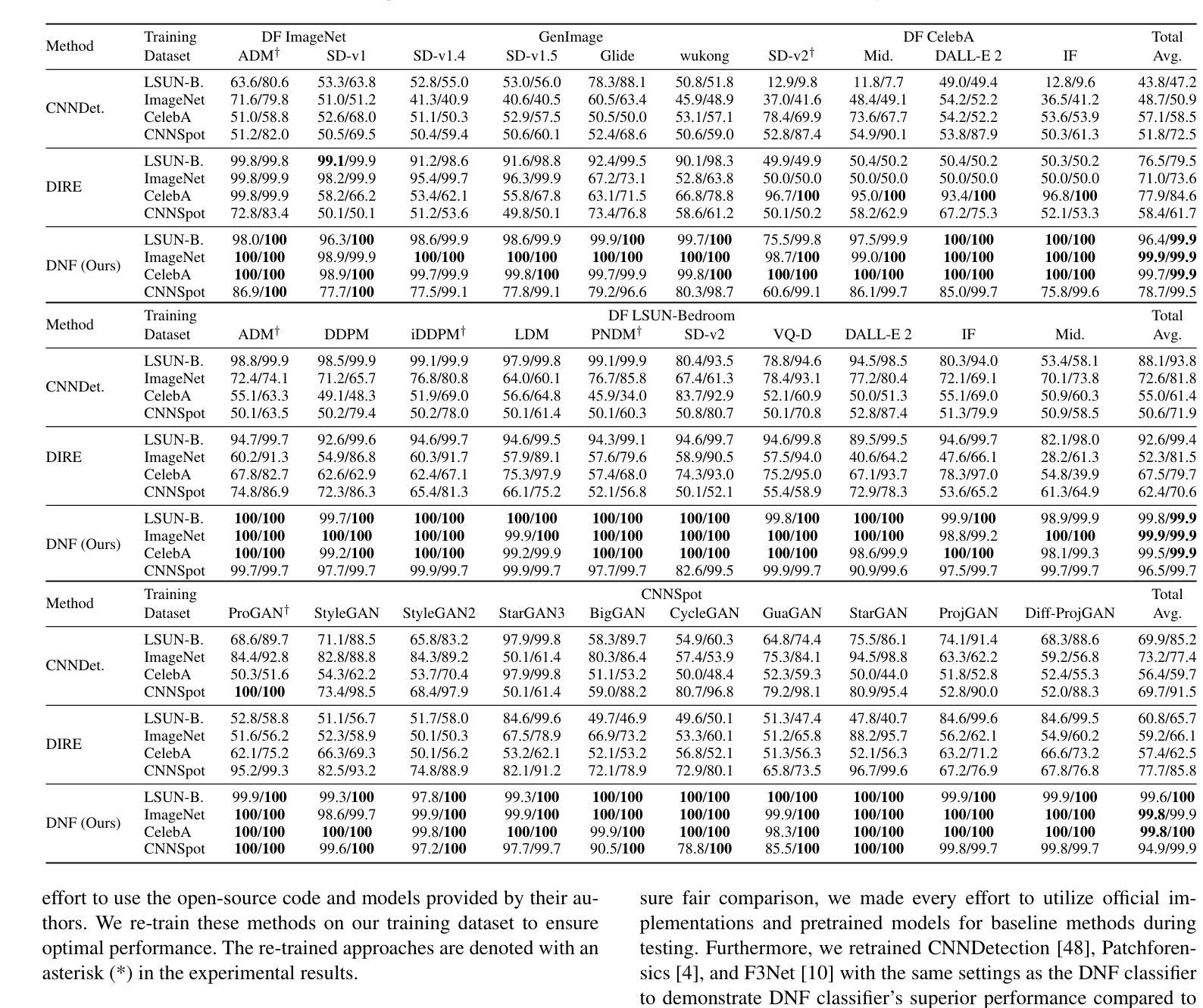
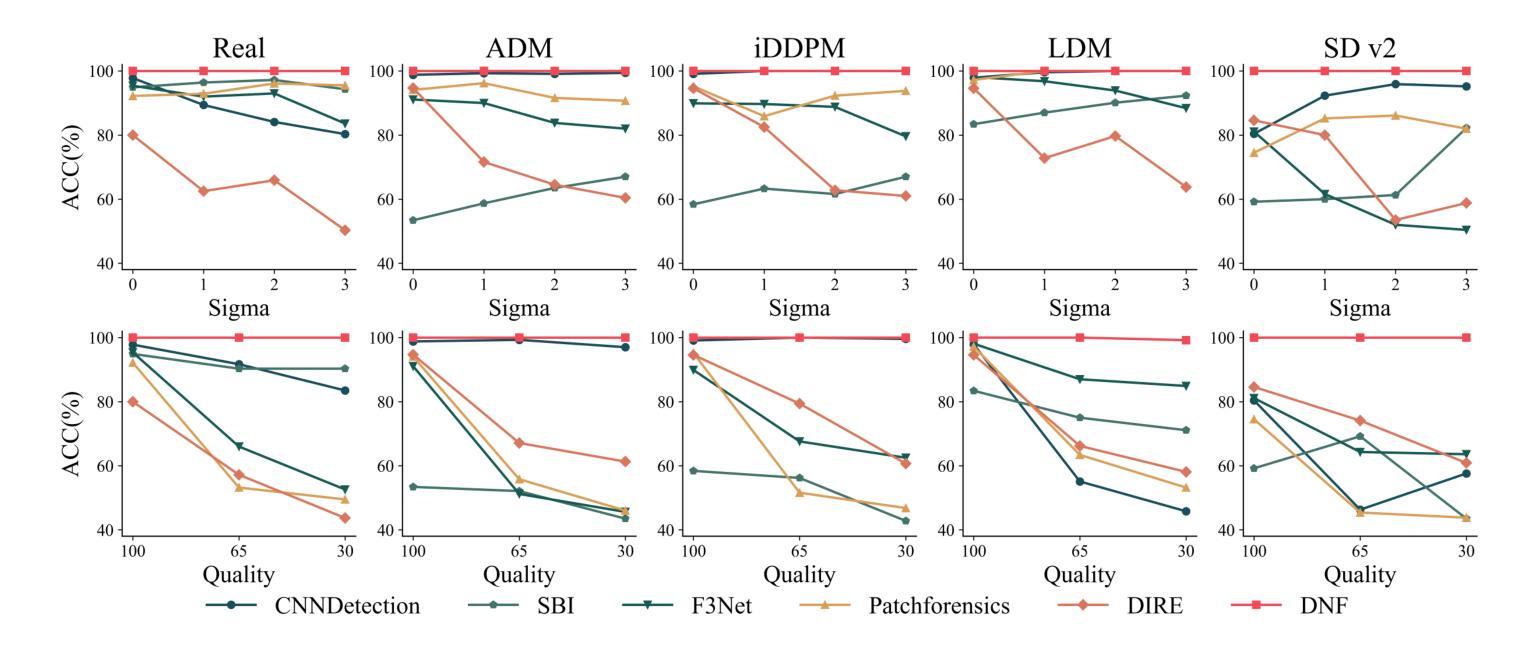
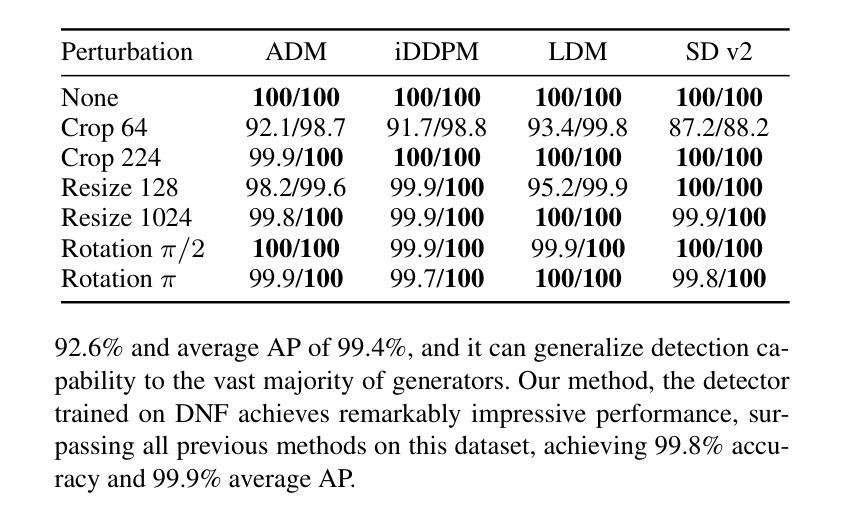
Diffusion Noise Feature: Accurate and Fast Generated Image Detection
Authors:Yichi Zhang, Xiaogang Xu
Generative models now produce images with such stunning realism that they can easily deceive the human eye. While this progress unlocks vast creative potential, it also presents significant risks, such as the spread of misinformation. Consequently, detecting generated images has become a critical research challenge. However, current detection methods are often plagued by low accuracy and poor generalization. In this paper, to address these limitations and enhance the detection of generated images, we propose a novel representation, Diffusion Noise Feature (DNF). Derived from the inverse process of diffusion models, DNF effectively amplifies the subtle, high-frequency artifacts that act as fingerprints of artificial generation. Our key insight is that real and generated images exhibit distinct DNF signatures, providing a robust basis for differentiation. By training a simple classifier such as ResNet-50 on DNF, our approach achieves remarkable accuracy, robustness, and generalization in detecting generated images, including those from unseen generators or with novel content. Extensive experiments across four training datasets and five test sets confirm that DNF establishes a new state-of-the-art in generated image detection. The code is available at https://github.com/YichiCS/Diffusion-Noise-Feature.
生成模型现在能够生成如此逼真的图像,以至于它们可以轻松欺骗人眼。虽然这一进展释放了巨大的创造力,但也带来了显著的风险,例如误导信息的传播。因此,检测生成图像已成为一项重要的研究挑战。然而,当前的检测方法往往存在准确性低和泛化能力差的困扰。针对这些局限性并增强对生成图像的检测能力,本文提出了一种新的表示方法:扩散噪声特征(DNF)。DNF来源于扩散模型的逆过程,有效地放大了作为人工生成指纹的微妙高频伪影。我们的关键见解是,真实和生成的图像表现出不同的DNF签名,这为区分它们提供了坚实的基础。通过在DNF上训练像ResNet-50这样的简单分类器,我们的方法在检测生成图像时实现了令人印象深刻的准确性、稳健性和泛化能力,包括来自未见过的生成器或具有新内容的情况。在四个训练数据集和五个测试集上进行的广泛实验证实,DNF在生成图像检测方面建立了最新的最先进的水平。代码可用在https://github.com/YichiCS/Diffusion-Noise-Feature。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型图像检测策略,即扩散噪声特征(DNF),用以识别生成模型的图像。该策略利用扩散模型的逆过程提取特征,有效放大生成图像的高频伪影,从而实现精准识别。实验证明,DNF在检测不同生成器甚至新型内容的生成图像时,具有出色的准确性、稳健性和泛化能力,为生成图像检测领域树立了新的标杆。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的图像具有逼真的现实主义效果,但同时也存在传播误导信息的重大风险。
- 当前图像检测方法的准确性和泛化能力有待提高。
- 扩散噪声特征(DNF)是从扩散模型的逆过程中提取的新型表示方法。
- DNF能有效放大生成图像的高频伪影,这些伪影作为人工生成的指纹。
- DNF显示真实和生成图像之间的明显差异,为区分它们提供了稳健的基础。
- 通过使用如ResNet-50等简单分类器进行训练,DNF策略在检测生成图像方面取得了突破性成果。
点此查看论文截图