⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
DictAS: A Framework for Class-Generalizable Few-Shot Anomaly Segmentation via Dictionary Lookup
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, ShiChen Qu, Xiaopei Zhang, Xingang Wang, Fei Shen, Zhengtao Zhang, Mukesh Prasad, Guiguang Ding
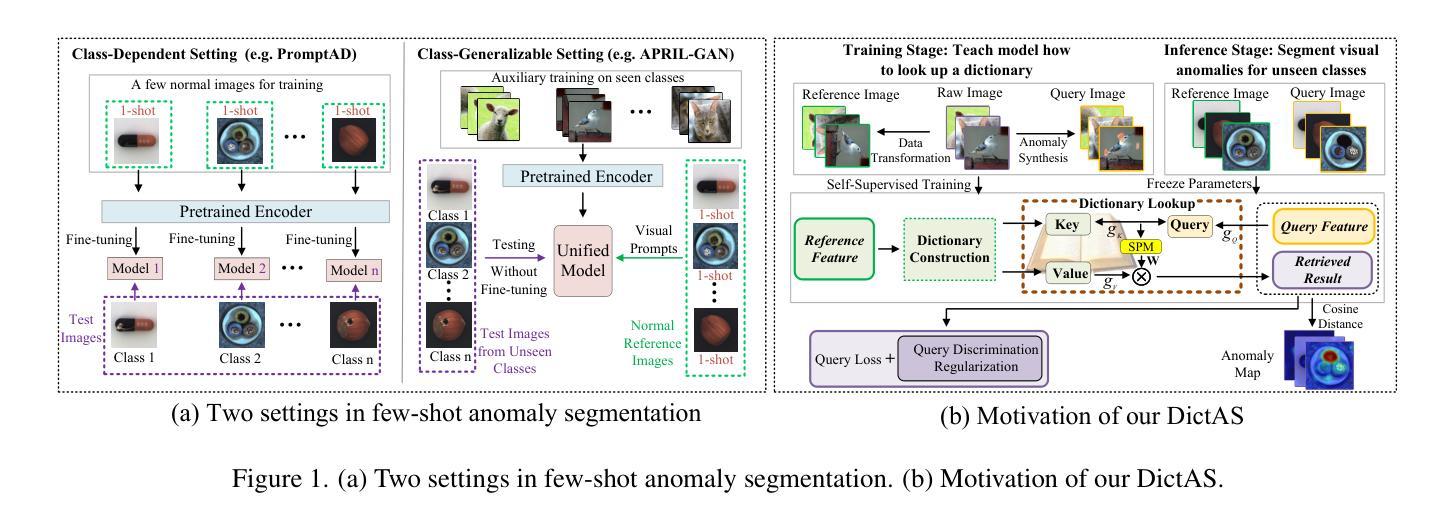
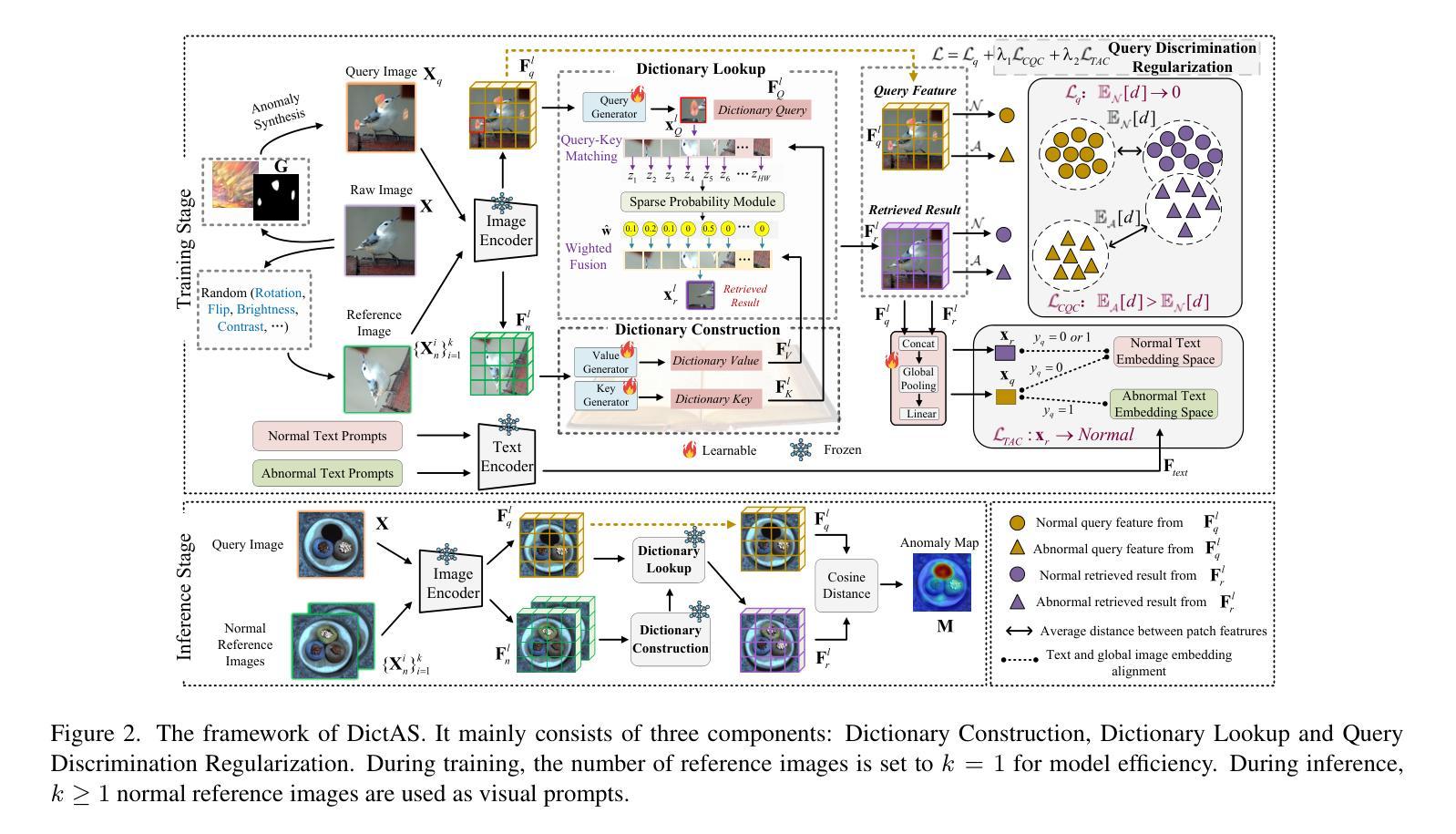
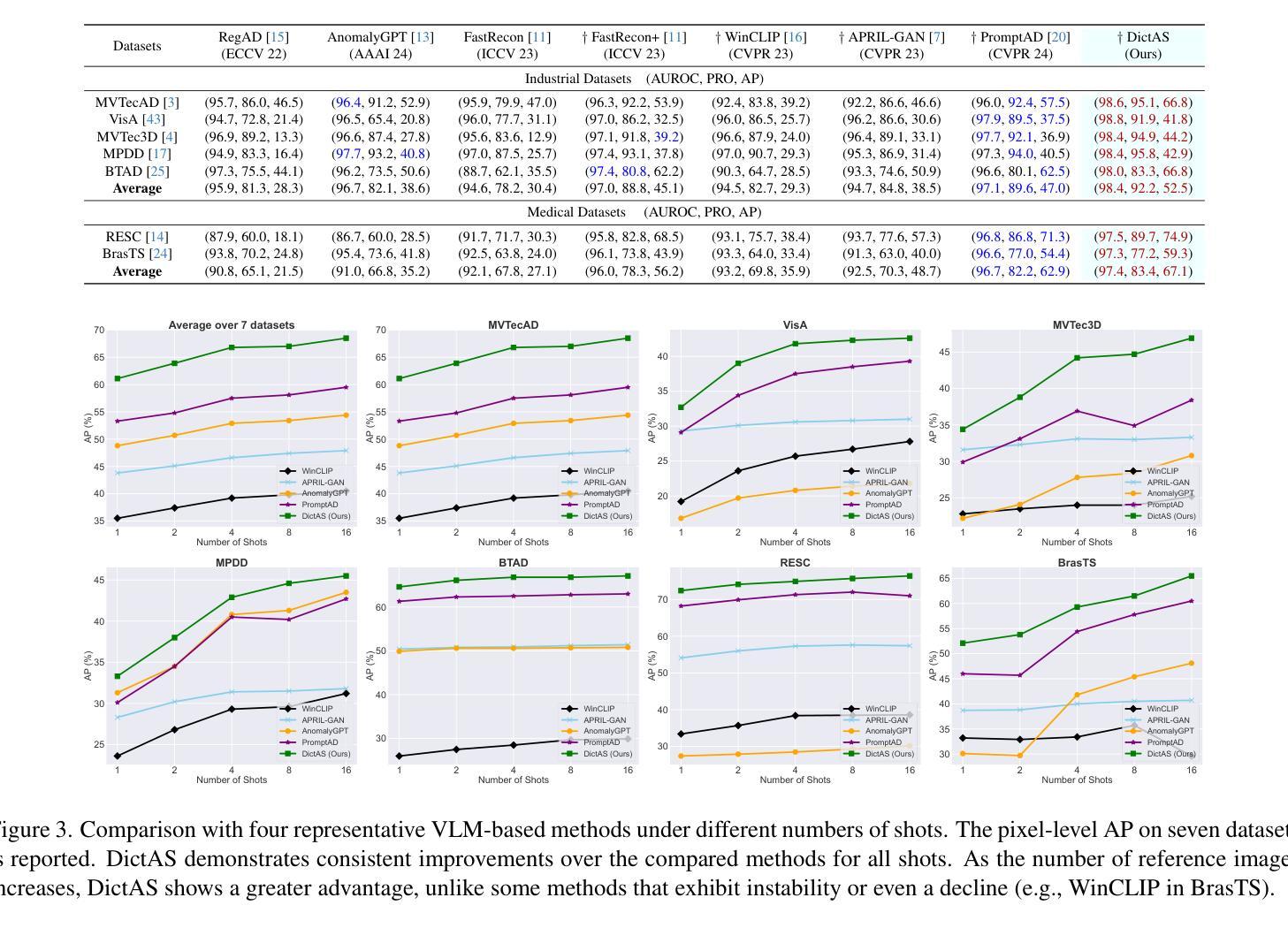
Recent vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable class-generalizable ability to unseen classes in few-shot anomaly segmentation (FSAS), leveraging supervised prompt learning or fine-tuning on seen classes. However, their cross-category generalization largely depends on prior knowledge of real seen anomaly samples. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, namely DictAS, which enables a unified model to detect visual anomalies in unseen object categories without any retraining on the target data, only employing a few normal reference images as visual prompts. The insight behind DictAS is to transfer dictionary lookup capabilities to the FSAS task for unseen classes via self-supervised learning, instead of merely memorizing the normal and abnormal feature patterns from the training set. Specifically, DictAS mainly consists of three components: (1) Dictionary Construction - to simulate the index and content of a real dictionary using features from normal reference images. (2) Dictionary Lookup - to retrieve queried region features from the dictionary via a sparse lookup strategy. When a query feature cannot be retrieved, it is classified as an anomaly. (3) Query Discrimination Regularization- to enhance anomaly discrimination by making abnormal features harder to retrieve from the dictionary. To achieve this, Contrastive Query Constraint and Text Alignment Constraint are further proposed. Extensive experiments on seven public industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that DictAS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FSAS methods.
最近的视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在少量异常分割(FSAS)中显示出对未见类别的类通用能力,这得益于对可见类别的有监督提示学习或微调。然而,它们的跨类别泛化在很大程度上依赖于真实可见异常样本的先验知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,即DictAS,它能够在未见对象类别中检测视觉异常,而无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练,仅使用少数正常参考图像作为视觉提示。DictAS的见解是通过自我监督学习将字典查找能力转移到未见类别的FSAS任务上,而不是仅仅从训练集中记忆正常和异常特征模式。具体来说,DictAS主要由三个组件组成:(1)字典构建——使用正常参考图像的特征模拟真实字典的索引和内容。(2)字典查找——通过稀疏查找策略从字典中检索查询区域特征。当无法检索查询特征时,它会被归类为异常。(3)查询判别正则化——通过使异常特征更难从字典中检索来提高异常判别力。为此,进一步提出了对比查询约束和文本对齐约束。在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验表明,DictAS始终优于最新的FSAS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, Project: https://github.com/xiaozhen228/DictAS
Summary
该论文提出了一种名为DictAS的新框架,用于在未训练的目标数据上检测未知对象类别中的视觉异常。它主要通过利用少数正常参考图像作为视觉提示来实现这一目标。DictAS的核心理念是通过自我监督学习将字典查找能力转移到少数拍摄异常分割任务上,而不是仅仅依靠训练集来记忆正常和异常的特征模式。经过大量实验证明,DictAS在多个公共工业数据集上的表现始终优于现有的少数拍摄异常分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- DictAS框架能在未重新训练目标数据的情况下,利用少数正常参考图像检测未知对象类别中的视觉异常。
- DictAS通过模拟真实字典的索引和内容,使用正常参考图像的特征进行字典构建。
- 通过稀疏查找策略从字典中检索查询区域特征,无法检索到的特征被分类为异常。
- Query Discrimination Regularization模块通过使异常特征更难从字典中检索出来,提高了异常识别的能力。
- 该框架引入了Contrastive Query Constraint和Text Alignment Constraint,进一步提高了模型的性能。
- 在七个公共工业数据集和医疗数据集上的实验表明,DictAS在少数拍摄异常分割任务上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

MAGNeT: Multimodal Adaptive Gaussian Networks for Intent Inference in Moving Target Selection across Complex Scenarios
Authors:Xiangxian Li, Yawen Zheng, Baiqiao Zhang, Yijia Ma, Xianhui Cao, Juan Liu, Yulong Bian, Jin Huang, Chenglei Yang
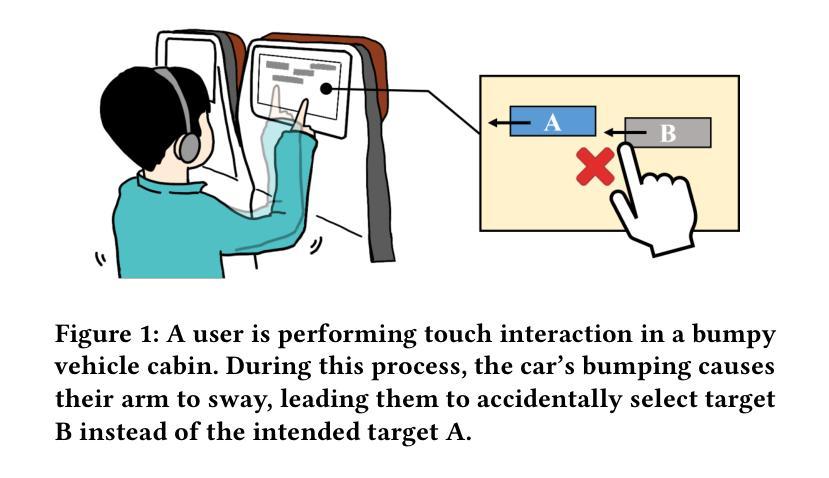
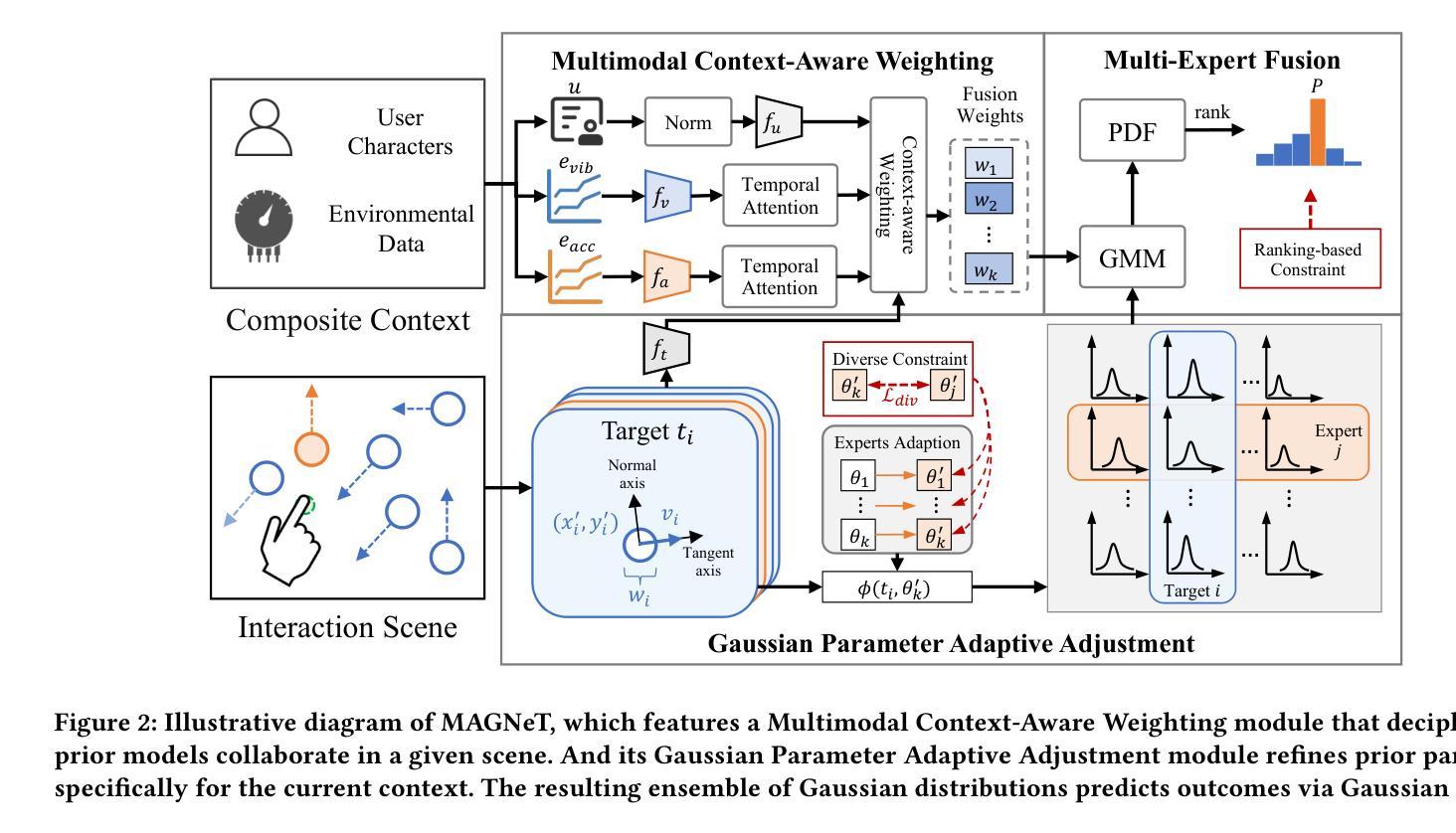
Moving target selection in multimedia interactive systems faces unprecedented challenges as users increasingly interact across diverse and dynamic contexts-from live streaming in moving vehicles to VR gaming in varying environments. Existing approaches rely on probabilistic models that relate endpoint distribution to target properties such as size and speed. However, these methods require substantial training data for each new context and lack transferability across scenarios, limiting their practical deployment in diverse multimedia environments where rich multimodal contextual information is readily available. This paper introduces MAGNeT (Multimodal Adaptive Gaussian Networks), which addresses these problems by combining classical statistical modeling with a context-aware multimodal method. MAGNeT dynamically fuses pre-fitted Ternary-Gaussian models from various scenarios based on real-time contextual cues, enabling effective adaptation with minimal training data while preserving model interpretability. We conduct experiments on self-constructed 2D and 3D moving target selection datasets under in-vehicle vibration conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MAGNeT achieves lower error rates with few-shot samples by applying context-aware fusion of Gaussian experts from multi-factor conditions.
多媒体交互系统中的动态目标选择面临着前所未有的挑战,因为用户在不同的动态上下文中的交互日益增多,例如在移动车辆中进行直播或在不同的环境中进行VR游戏。现有方法依赖于概率模型,该模型将终点分布与目标的属性(如大小和速度)关联起来。然而,这些方法对于每种新上下文都需要大量的训练数据,并且在不同场景之间缺乏可迁移性,限制了它们在丰富的多媒体环境中进行实际部署的能力,在这些环境中,丰富的多模态上下文信息很容易获得。本文介绍了MAGNeT(多模态自适应高斯网络),它通过结合经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法来解决这些问题。MAGNeT根据实时的上下文线索动态融合来自各种场景的预先拟合的三元高斯模型,以最小的训练数据实现有效的适应,同时保持模型的可解释性。我们在自行构建的二维和三维移动目标选择数据集上进行了车内振动条件下的实验。大量实验表明,通过多因素条件下的高斯专家的上下文感知融合,MAGNeT在少数样本情况下实现了更低的错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
多媒体交互系统中移动目标选择面临前所未有的挑战,随着用户在不同动态上下文中的交互日益增多,如移动车辆中的直播到不同环境中的VR游戏。现有方法依赖于与目标属性(如大小和速度)相关的终端分布的概率模型。然而,这些方法需要为每个新上下文进行大量训练数据,并且缺乏跨场景的迁移能力,限制了它们在多媒体环境中的实际部署,那里拥有丰富的多模态上下文信息。本文介绍了MAGNeT(多模态自适应高斯网络),它通过结合经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法来解决这些问题。MAGNeT根据实时上下文线索动态融合来自各种场景的预先拟合的三元高斯模型,可在少量训练数据的情况下实现有效适应,同时保持模型的可解释性。我们在自行构建的二维和三维移动目标选择数据集上进行了实验,实验表明,MAGNeT通过应用上下文感知的高斯专家融合,在少数样本的情况下实现了较低的错误率。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体交互系统中移动目标选择面临挑战,尤其是在不同动态上下文中的交互。
- 现有方法依赖概率模型,需要为每种新上下文进行大量训练,且缺乏跨场景迁移能力。
- MAGNeT(多模态自适应高斯网络)结合经典统计建模和上下文感知的多模态方法来解决这些问题。
- MAGNeT根据实时上下文线索动态融合预拟合模型,实现有效适应并保留模型的可解释性。
- MAGNeT在移动目标选择方面表现出优异性能,特别是在少量训练数据的情况下。
- 实验证明MAGNeT在多种移动目标选择数据集上实现了较低的错误率。
点此查看论文截图



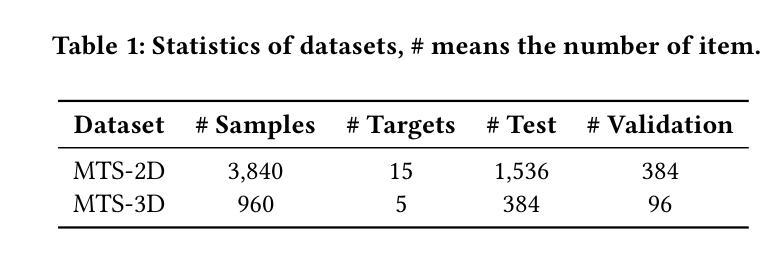
DCSCR: A Class-Specific Collaborative Representation based Network for Image Set Classification
Authors:Xizhan Gao, Wei Hu
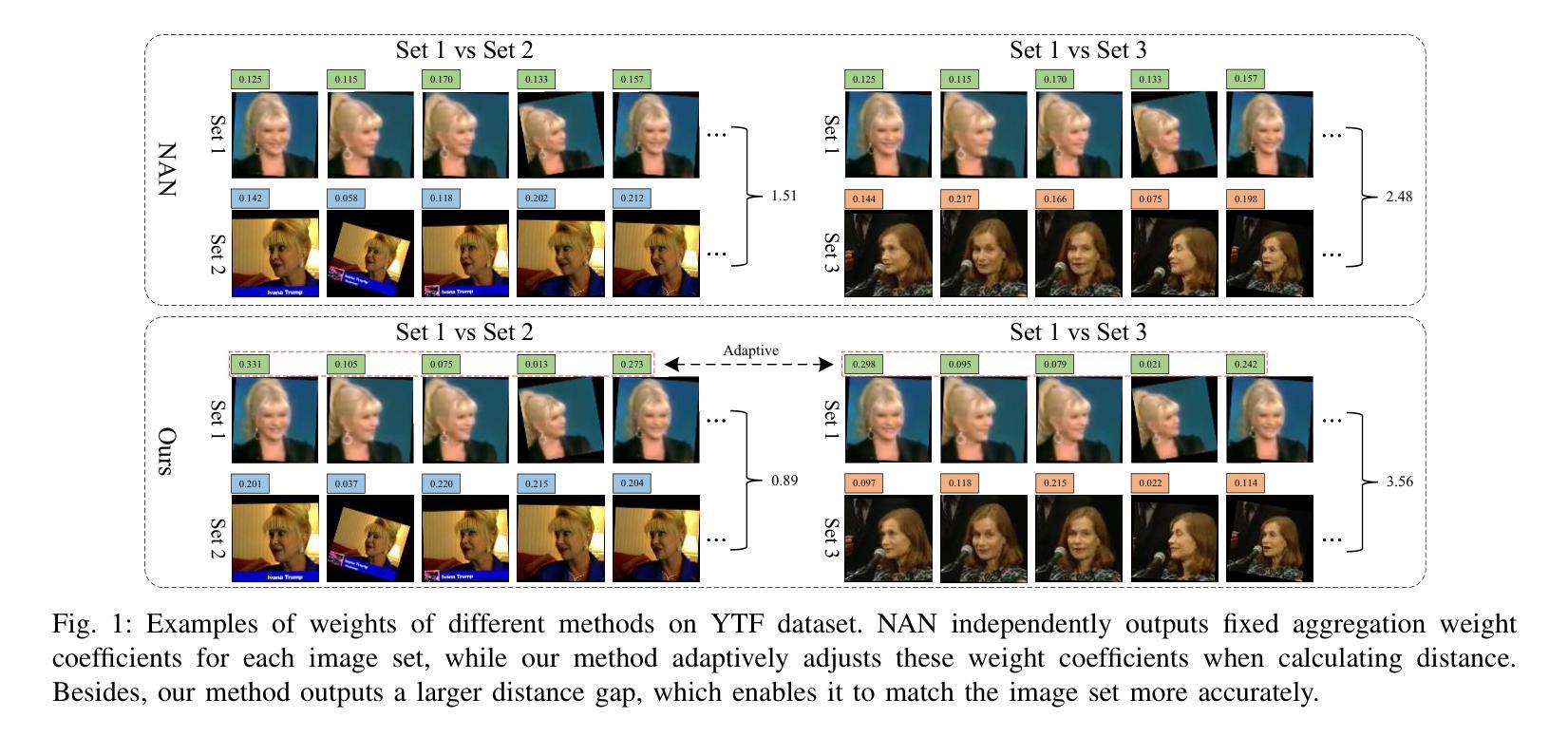
Image set classification (ISC), which can be viewed as a task of comparing similarities between sets consisting of unordered heterogeneous images with variable quantities and qualities, has attracted growing research attention in recent years. How to learn effective feature representations and how to explore the similarities between different image sets are two key yet challenging issues in this field. However, existing traditional ISC methods classify image sets based on raw pixel features, ignoring the importance of feature learning. Existing deep ISC methods can learn deep features, but they fail to adaptively adjust the features when measuring set distances, resulting in limited performance in few-shot ISC. To address the above issues, this paper combines traditional ISC methods with deep models and proposes a novel few-shot ISC approach called Deep Class-specific Collaborative Representation (DCSCR) network to simultaneously learn the frame- and concept-level feature representations of each image set and the distance similarities between different sets. Specifically, DCSCR consists of a fully convolutional deep feature extractor module, a global feature learning module, and a class-specific collaborative representation-based metric learning module. The deep feature extractor and global feature learning modules are used to learn (local and global) frame-level feature representations, while the class-specific collaborative representation-based metric learning module is exploit to adaptively learn the concept-level feature representation of each image set and thus obtain the distance similarities between different sets by developing a new CSCR-based contrastive loss function. Extensive experiments on several well-known few-shot ISC datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method compared with some state-of-the-art image set classification algorithms.
图像集分类(ISC)是一个比较无序的异质图像集之间相似性的任务,这些图像集具有可变的数量和品质,近年来引起了越来越多的研究关注。如何学习有效的特征表示以及如何探索不同图像集之间的相似性是该领域的两个关键且具有挑战性的问题。然而,现有的传统ISC方法基于原始像素特征对图像集进行分类,忽略了特征学习的重要性。现有的深度ISC方法可以学习深度特征,但在测量集合距离时无法自适应调整特征,导致在少样本ISC中的性能有限。为了解决上述问题,本文结合了传统ISC方法和深度模型,提出了一种新的少样本ISC方法,称为深度类特定协同表示(DCSCR)网络,可以同时学习每个图像集的框架和概念级别的特征表示以及不同集合之间的距离相似性。具体来说,DCSCR包括全卷积深度特征提取器模块、全局特征学习模块和基于类特定协同表示的度量学习模块。深度特征提取器和全局特征学习模块用于学习(局部和全局)框架级别的特征表示,而基于类特定的协同表示度量学习模块则用于自适应地学习每个图像集的概念级特征表示,并通过开发一种新的基于CSCR的对比损失函数来获得不同集合之间的距离相似性。在几个著名的少样本ISC数据集上的广泛实验表明,与一些最先进的图像集分类算法相比,所提出的方法具有有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注图像集分类(ISC)领域,针对如何学习有效的特征表示以及如何探索不同图像集之间的相似性两个关键问题,提出一种结合传统ISC方法和深度模型的新型少样本ISC方法——Deep Class-specific Collaborative Representation(DCSCR)网络。该网络能同时学习每个图像集的框架和概念级别的特征表示,以及不同集之间的距离相似性。通过一系列实验验证,该方法在几个知名的少样本ISC数据集上表现出优异的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 图像集分类(ISC)是近年来的研究热点,涉及如何学习有效的特征表示和探索不同图像集之间的相似性。
- 传统ISC方法基于原始像素特征进行分类,忽略了特征学习的重要性。
- 现有深度ISC方法虽然能学习深度特征,但在测量集间距离时无法自适应调整特征,导致在少样本ISC中的性能受限。
- DCSCR网络结合了传统ISC方法和深度模型,能同时学习每个图像集的框架和概念级别的特征表示。
- DCSCR网络包含全卷积深度特征提取模块、全局特征学习模块和基于类特定的协同表示度量学习模块。
- 通过开发新的CSCR对比损失函数,DCSCR网络能自适应地学习每个图像集的概念级别特征表示,并获取不同集之间的距离相似性。
点此查看论文截图


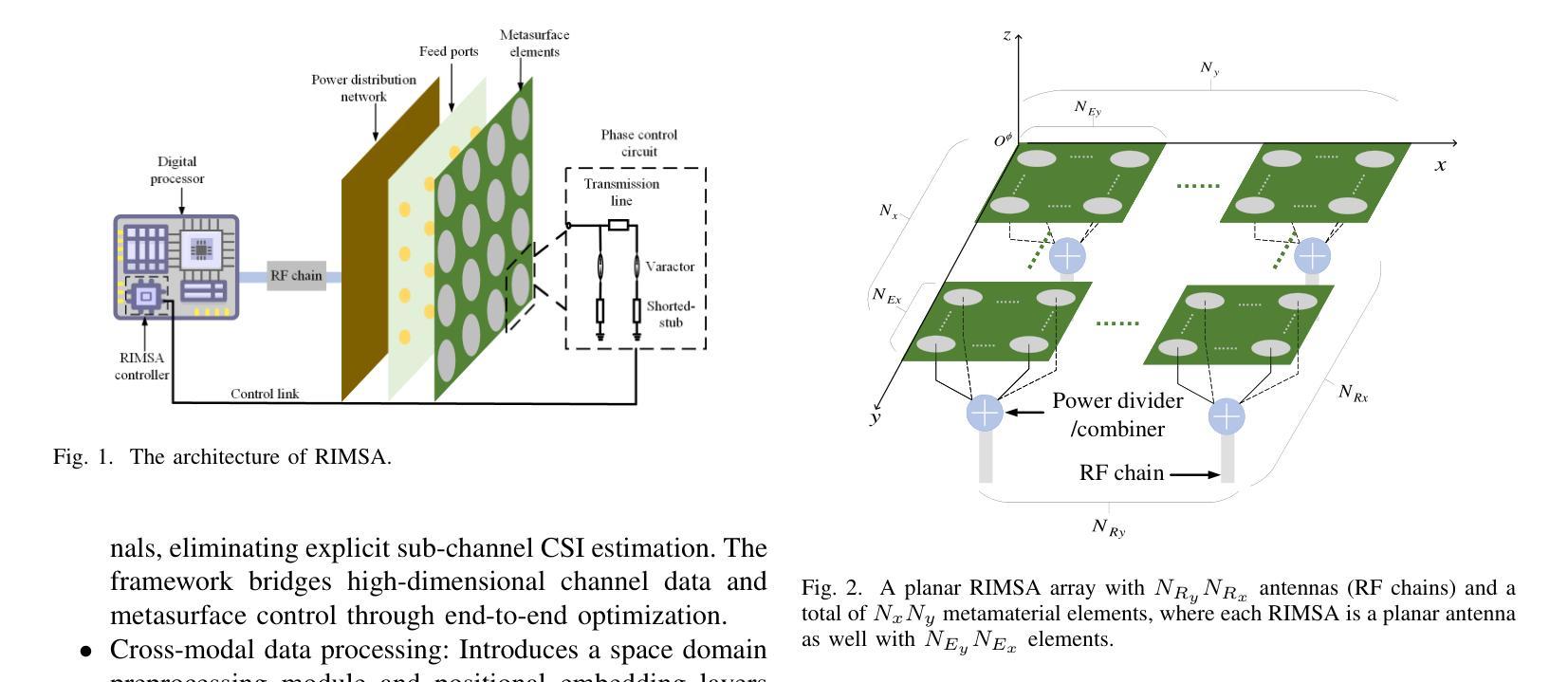
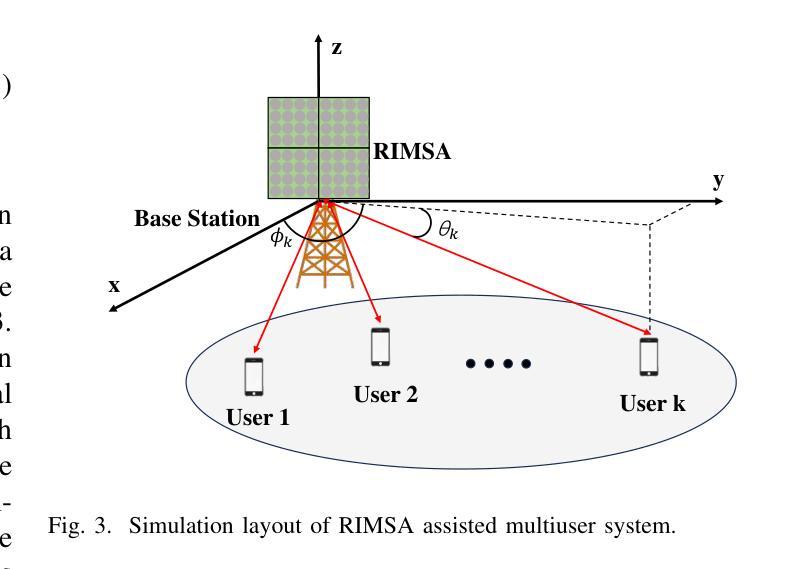
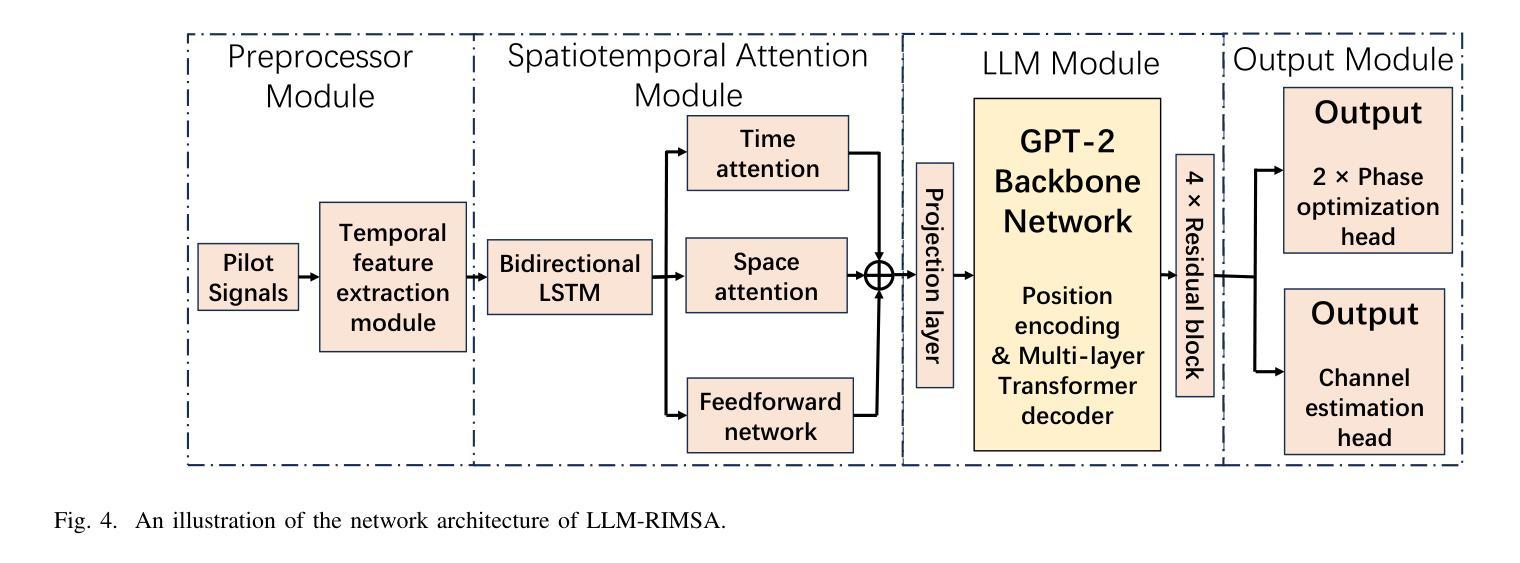
LLM-RIMSA: Large Language Models driven Reconfigurable Intelligent Metasurface Antenna Systems
Authors:Yunsong Huang, Hui-Ming Wang, Qingli Yan, Zhaowei Wang
The evolution of 6G networks demands ultra-massive connectivity and intelligent radio environments, yet existing reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) technologies face critical limitations in hardware efficiency, dynamic control, and scalability. This paper introduces LLM-RIMSA, a transformative framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with a novel reconfigurable intelligent metasurface antenna (RIMSA) architecture to address these challenges. Unlike conventional RIS designs, RIMSA employs parallel coaxial feeding and 2D metasurface integration, enabling each individual metamaterial element to independently adjust both its amplitude and phase. While traditional optimization and deep learning (DL) methods struggle with high-dimensional state spaces and prohibitive training costs for RIMSA control, LLM-RIMSA leverages pre-trained LLMs cross-modal reasoning and few-shot learning capabilities to dynamically optimize RIMSA configurations. Simulations demonstrate that LLM-RIMSA achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming conventional DL-based methods in sum rate while reducing training overhead. The proposed framework pave the way for LLM-driven intelligent radio environments.
6G网络的演进需要超大规模连接和智能无线电环境,然而现有的可重构智能表面(RIS)技术在硬件效率、动态控制和可扩展性方面面临关键挑战。本文介绍了LLM-RIMSA,这是一个创新性框架,它将大型语言模型(LLM)与新型的可重构智能超表面天线(RIMSA)架构相结合,以应对这些挑战。与传统的RIS设计不同,RIMSA采用并行同轴馈电和2D超表面集成,使每个单独的元材料元素都能独立调整其振幅和相位。传统的优化和深度学习(DL)方法在高维状态空间和RIMSA控制的昂贵训练成本方面遇到了困难,而LLM-RIMSA利用预训练的大型语言模型的跨模态推理和少量学习功能来动态优化RIMSA配置。模拟结果表明,LLM-RIMSA实现了最先进的性能,在总和速率上优于传统的基于DL的方法,同时降低了训练开销。所提出的框架为大型语言模型驱动的智能无线电环境铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM-RIMSA框架结合了大型语言模型(LLMs)和可重构智能超表面天线(RIMSA)架构,解决了现有可重构智能表面(RIS)技术在硬件效率、动态控制和可扩展性方面的局限。该框架采用并行同轴馈电和2D超表面集成,利用LLMs的跨模态推理和少量学习功能,动态优化RIMSA配置,实现超高连通性和智能无线电环境。
Key Takeaways
- 现有RIS技术面临硬件效率、动态控制和可扩展性的挑战。
- LLM-RIMSA框架结合了LLMs和RIMSA架构以应对这些挑战。
- RIMSA采用并行同轴馈电和2D超表面集成,使每个超材料元素能独立调整幅度和相位。
- 传统优化和深度学习方法在RIMSA控制上遇到高维状态空间和训练成本高昂的问题。
- LLM-RIMSA利用LLMs的跨模态推理和少量学习功能进行动态优化。
- 仿真显示LLM-RIMSA在总速率上实现了最先进的性能,优于传统的DL方法。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Large Language Models for Predictive Analysis of Human Misery
Authors:Bishanka Seal, Rahul Seetharaman, Aman Bansal, Abhilash Nandy
This study investigates the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for predicting human-perceived misery scores from natural language descriptions of real-world scenarios. The task is framed as a regression problem, where the model assigns a scalar value from 0 to 100 to each input statement. We evaluate multiple prompting strategies, including zero-shot, fixed-context few-shot, and retrieval-based prompting using BERT sentence embeddings. Few-shot approaches consistently outperform zero-shot baselines, underscoring the value of contextual examples in affective prediction. To move beyond static evaluation, we introduce the “Misery Game Show”, a novel gamified framework inspired by a television format. It tests LLMs through structured rounds involving ordinal comparison, binary classification, scalar estimation, and feedback-driven reasoning. This setup enables us to assess not only predictive accuracy but also the model’s ability to adapt based on corrective feedback. The gamified evaluation highlights the broader potential of LLMs in dynamic emotional reasoning tasks beyond standard regression. Code and data link: https://github.com/abhi1nandy2/Misery_Data_Exps_GitHub
本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)在根据真实世界场景的自然语言描述预测人类感知的痛苦分数方面的应用。该任务被构建为一个回归问题,模型为每条输入语句分配一个从0到100的标量值。我们评估了多种提示策略,包括零样本、固定上下文小样例和基于BERT句子嵌入的检索提示。小样例方法始终优于零样本基线,这凸显了上下文示例在情感预测中的价值。为了超越静态评估,我们推出了“苦难游戏秀”,这是一个受电视节目格式启发的新型游戏化框架。它通过涉及序数比较、二元分类、标量估计和反馈驱动推理的结构化回合来测试LLM。这种设置使我们不仅能够评估预测准确性,还能够评估模型根据纠正性反馈进行适应的能力。游戏化评估突显了LLM在超越标准回归的动态情绪推理任务中的更广泛潜力。代码和数据链接:https://github.com/abhi1nandy2/Misery_Data_Exps_GitHub
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)用于预测基于现实世界情境的自然语言描述的人类感知痛苦程度。研究采用回归问题框架,模型为每个输入语句分配一个从0到100的标量值。评估了多种提示策略,包括零样本、固定上下文少样本和基于BERT句子嵌入的检索提示。少样本方法始终优于零样本基线,突显了上下文实例在情感预测中的价值。为超越静态评估,研究引入了“痛苦游戏秀”这一新型游戏化框架,该框架以电视节目形式为灵感。通过有序比较、二元分类、标量估算和反馈驱动推理的结构性回合测试LLM,不仅评估其预测准确性,还评估其基于纠正反馈的适应能力。游戏化评估突显了LLM在动态情感推理任务中的更广泛潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可用于预测人类感知的痛苦程度,采用回归问题框架。
- 少样本方法在进行情感预测时表现优于零样本基线。
- 上下文实例在情感预测任务中具有重要作用。
- 引入了一种新型游戏化框架——“痛苦游戏秀”,用于评估LLM的动态情感推理能力。
- 该框架允许测试LLM的预测准确性以及基于纠正反馈的适应能力。
- 游戏化评估方法扩大了LLM在情感计算领域的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

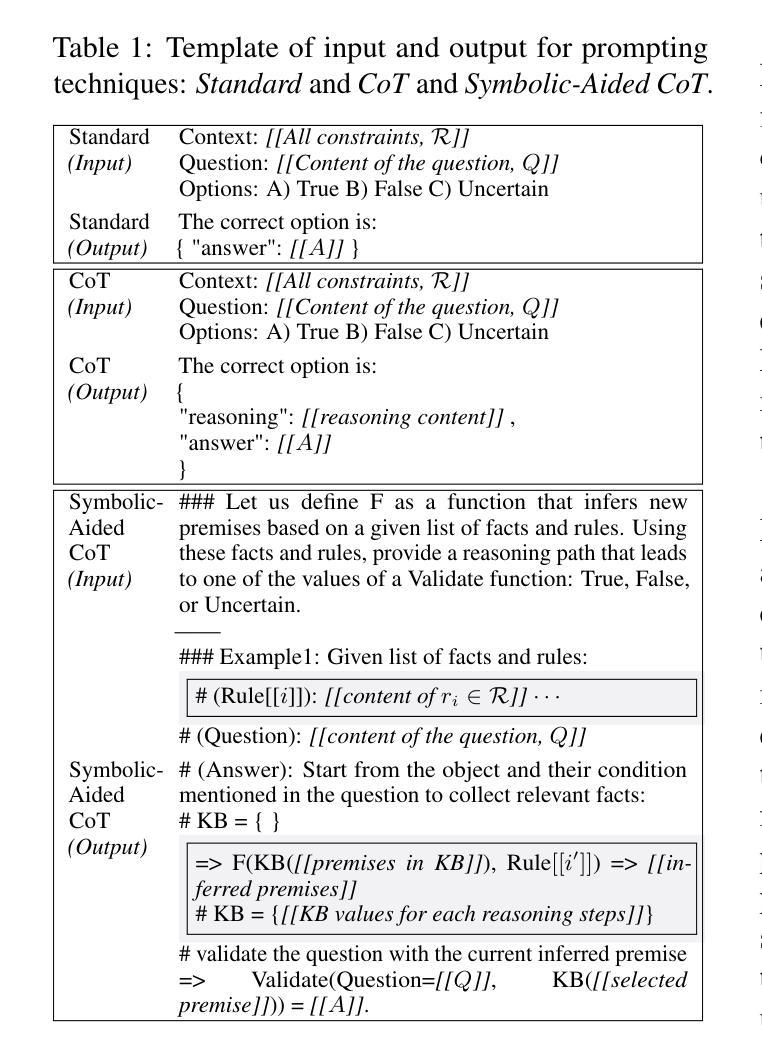
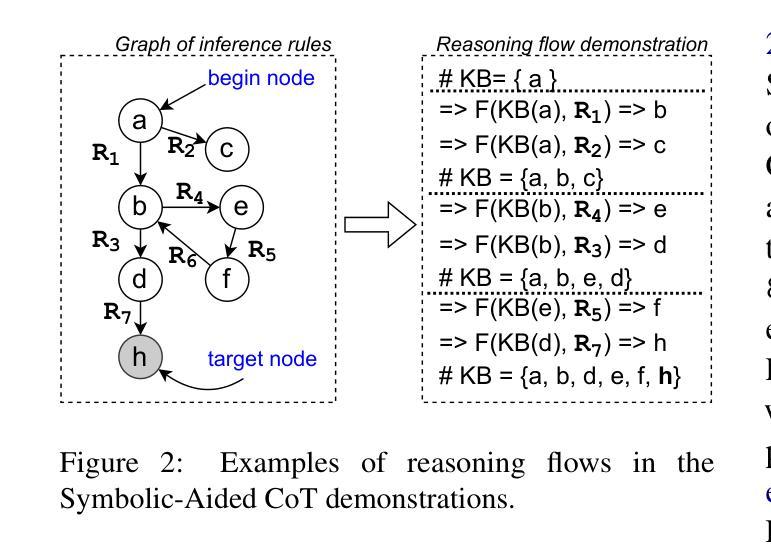
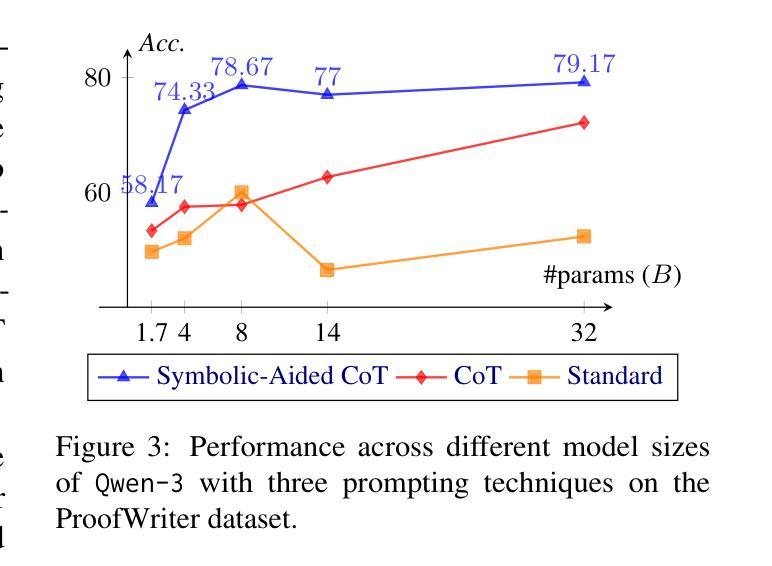
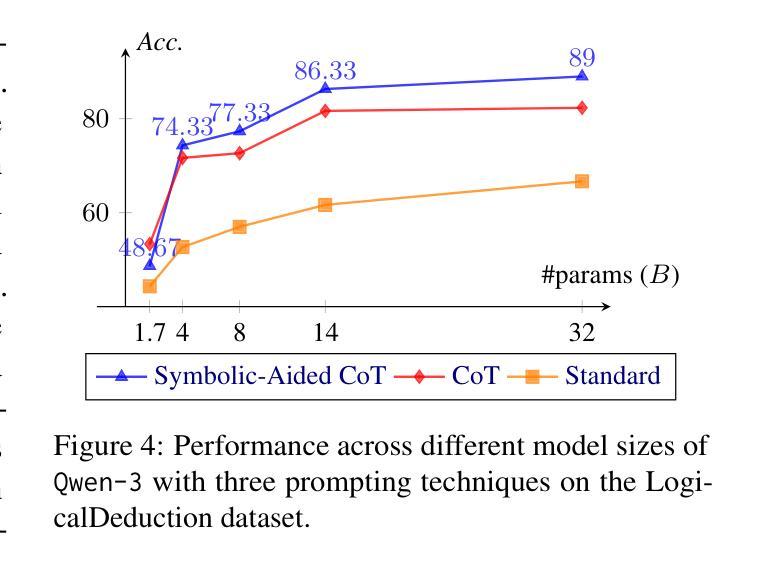
Non-Iterative Symbolic-Aided Chain-of-Thought for Logical Reasoning
Authors:Phuong Minh Nguyen, Tien Huu Dang, Naoya Inoue
This work introduces Symbolic-Aided Chain-of-Thought (CoT), an improved approach to standard CoT, for logical reasoning in large language models (LLMs). The key idea is to integrate lightweight symbolic representations into few-shot prompts, structuring the inference steps with a consistent strategy to make reasoning patterns more explicit within a non-iterative reasoning process. By incorporating these symbolic structures, our method preserves the generalizability of standard prompting techniques while enhancing the transparency, interpretability, and analyzability of LLM logical reasoning. Extensive experiments on four well-known logical reasoning benchmarks – ProofWriter, FOLIO, ProntoQA, and LogicalDeduction, which cover diverse reasoning scenarios – demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, particularly in complex reasoning tasks that require navigating multiple constraints or rules. Notably, Symbolic-Aided CoT consistently improves LLMs’ reasoning capabilities across various model sizes and significantly outperforms conventional CoT on three out of four datasets, ProofWriter, ProntoQA, and LogicalDeduction.
本文介绍了符号辅助思维链(CoT)方法,这是一种对标准思维链的改进方法,用于大型语言模型(LLM)的逻辑推理。其核心思想是将轻量级符号表示集成到少量提示中,使用一致的策略来结构化推理步骤,在一个非迭代推理过程中使推理模式更加明确。通过融入这些符号结构,我们的方法既保留了标准提示技术的通用性,又提高了LLM逻辑推理的透明度、可解释性和可分析性。在涵盖多种推理场景的四个知名逻辑推理基准测试——ProofWriter、FOLIO、ProntoQA和LogicalDeduction上的大量实验证明了所提出方法的有效性,特别是在需要应对多重约束或规则的复杂推理任务中。值得注意的是,符号辅助思维链方法在各种模型大小下都能持续提高LLM的推理能力,并在四个数据集中的三个(ProofWriter、ProntoQA和LogicalDeduction)上显著优于传统思维链方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
符号辅助思维链(Symbolic-Aided Chain-of-Thought,简称Symbolic-Aided CoT)是一种改进的思维链方法,用于提高大型语言模型(LLM)的逻辑推理能力。它通过整合轻量级符号表示进入少量提示,将推理步骤结构化,并采用一致策略,使非迭代推理过程中的推理模式更加明确。这种方法提高了LLM的逻辑推理的通用性、透明度、解释性和分析性。在涵盖多种推理场景的四个知名逻辑推理基准测试上进行的广泛实验表明,该方法在复杂推理任务中表现优异,特别是在涉及多个约束或规则的任务中表现尤为出色。该方法在各种模型尺寸上均提高了LLM的推理能力,并在三个基准测试上显著优于传统思维链方法。
Key Takeaways
- Symbolic-Aided CoT是思维链(CoT)的一种改进方法,用于增强大型语言模型(LLM)的逻辑推理能力。
- 该方法通过整合轻量级符号表示进入少量提示,提高推理的透明度、解释性和分析性。
- 实验表明,Symbolic-Aided CoT在复杂推理任务上表现优异,特别是在涉及多个约束或规则的任务中。
- 该方法在各种模型尺寸上都提高了LLM的推理能力。
- 与传统思维链方法相比,Symbolic-Aided CoT在三个基准测试上表现更佳。
- 这种方法保留了标准提示技术的通用性。
点此查看论文截图

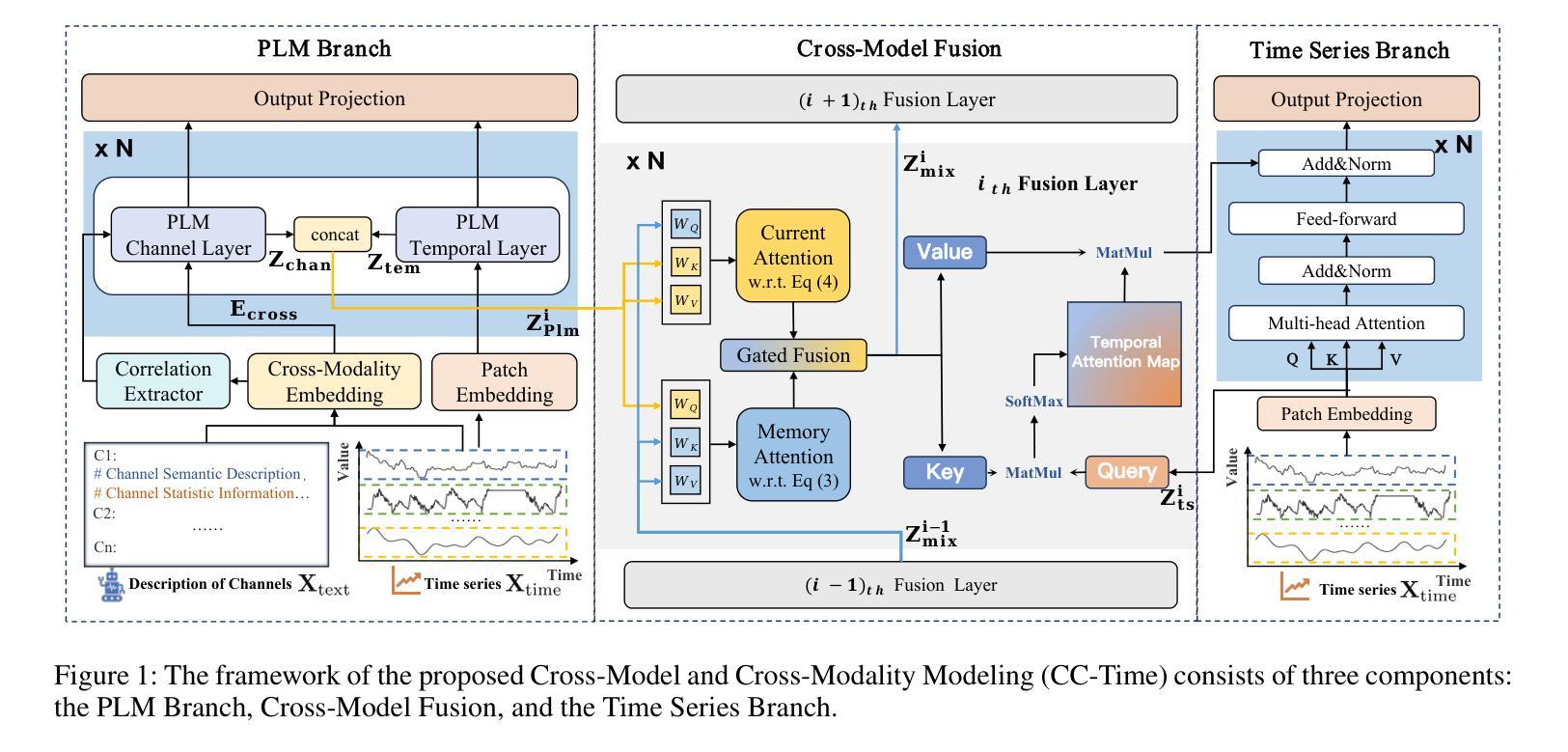
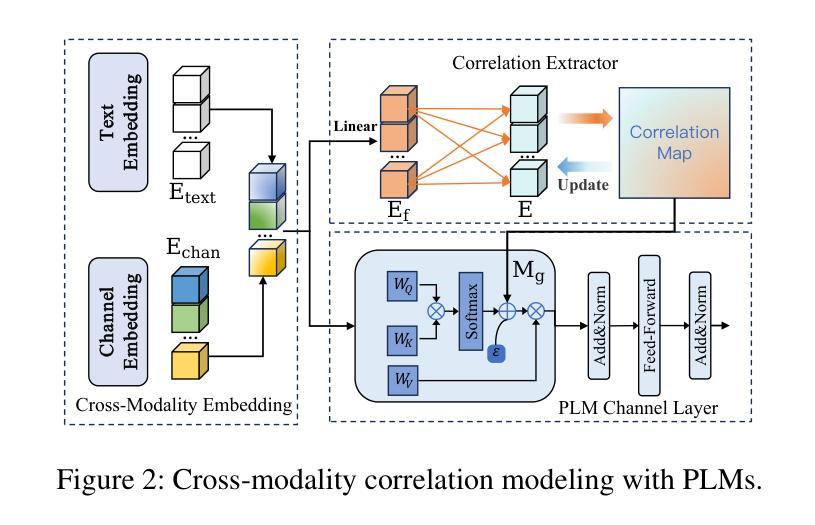
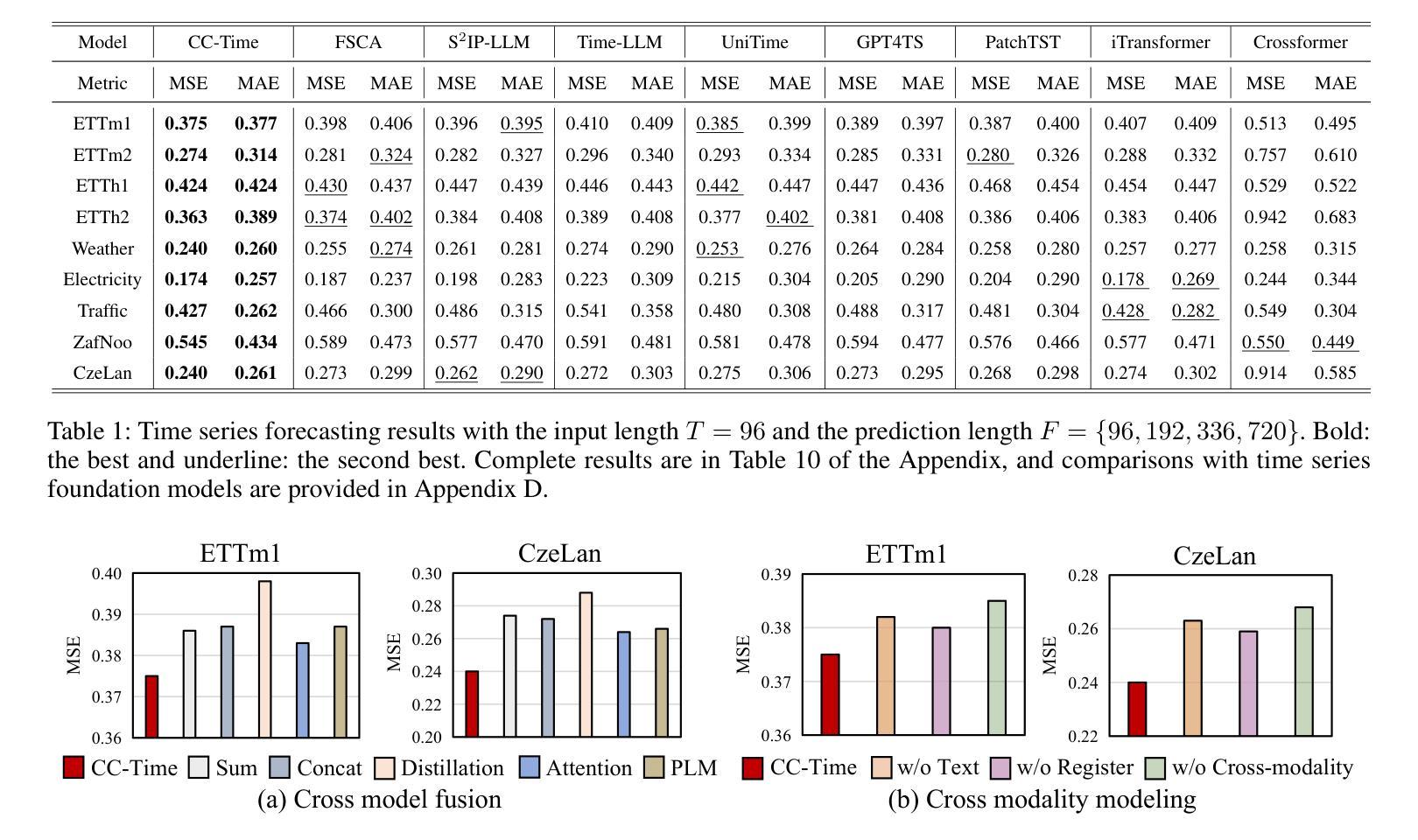
CC-Time: Cross-Model and Cross-Modality Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Peng Chen, Yihang Wang, Yang Shu, Yunyao Cheng, Kai Zhao, Zhongwen Rao, Lujia Pan, Bin Yang, Chenjuan Guo
With the success of pre-trained language models (PLMs) in various application fields beyond natural language processing, language models have raised emerging attention in the field of time series forecasting (TSF) and have shown great prospects. However, current PLM-based TSF methods still fail to achieve satisfactory prediction accuracy matching the strong sequential modeling power of language models. To address this issue, we propose Cross-Model and Cross-Modality Learning with PLMs for time series forecasting (CC-Time). We explore the potential of PLMs for time series forecasting from two aspects: 1) what time series features could be modeled by PLMs, and 2) whether relying solely on PLMs is sufficient for building time series models. In the first aspect, CC-Time incorporates cross-modality learning to model temporal dependency and channel correlations in the language model from both time series sequences and their corresponding text descriptions. In the second aspect, CC-Time further proposes the cross-model fusion block to adaptively integrate knowledge from the PLMs and time series model to form a more comprehensive modeling of time series patterns. Extensive experiments on nine real-world datasets demonstrate that CC-Time achieves state-of-the-art prediction accuracy in both full-data training and few-shot learning situations.
随着预训练语言模型(PLMs)在自然语言处理以外的各种应用领域的成功,语言模型在时间序列预测(TSF)领域引起了广泛的关注,并显示出巨大的潜力。然而,当前的基于PLM的时间序列预测方法仍然无法实现对时间序列模式进行强大建模的满意预测精度。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于PLM的时间序列预测交叉模型和多模态学习(CC-Time)。我们从两个方面探索PLM在时间序列预测中的潜力:1)PLM能够建模的时间序列特征是什么;以及是否仅靠PLM就能充分建立时间序列模型。在第一个方面,CC-Time结合多模态学习来建模语言模型中的时序依赖性和通道相关性,这来源于时间序列序列及其相应的文本描述。在第二个方面,CC-Time进一步提出了跨模型融合模块,以自适应地融合来自PLM和时序模型的知识,以实现对时间序列模式的更全面的建模。在九个真实数据集上的大量实验表明,CC-Time在全数据训练和少样本学习的情况下均达到了最先进的预测精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练语言模型(PLMs)在多个领域应用上的成功,其在时间序列预测(TSF)领域也展现出巨大潜力。为解决当前PLM在TSF预测精度上的不足,本文提出了跨模型与跨模态学习方法CC-Time,旨在提升语言模型在时序数据预测方面的能力。CC-Time从两个方面探索了语言模型在时序数据预测中的潜力,包括时序特征建模和单纯依赖语言模型构建时序模型的充分性。通过引入跨模态学习,CC-Time可以模拟语言模型中时间序列序列和时间序列描述之间的时间依赖关系和通道相关性。同时,通过跨模型融合技术自适应整合语言模型和时序模型的知识,构建更全面和精准的时序模式模型。实验表明,CC-Time在多个真实数据集上取得了领先的预测精度,无论是在全数据训练还是少样本学习情况下均表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练语言模型(PLMs)在多个领域应用上的成功引起了对时间序列预测(TSF)领域的关注。
- 当前PLM在TSF预测精度上仍有不足,需要新的方法提升其在时序数据预测方面的能力。
- CC-Time从时序特征建模和单纯依赖语言模型构建时序模型的充分性两个方面探索了语言模型在TSF中的潜力。
- CC-Time引入跨模态学习来模拟语言模型中时间序列序列和时间序列描述之间的关系。
- CC-Time通过跨模型融合技术整合语言模型和时序模型的知识,构建更全面和精准的时序模式模型。
- 实验表明,CC-Time在多个真实数据集上取得了领先的预测精度。
点此查看论文截图

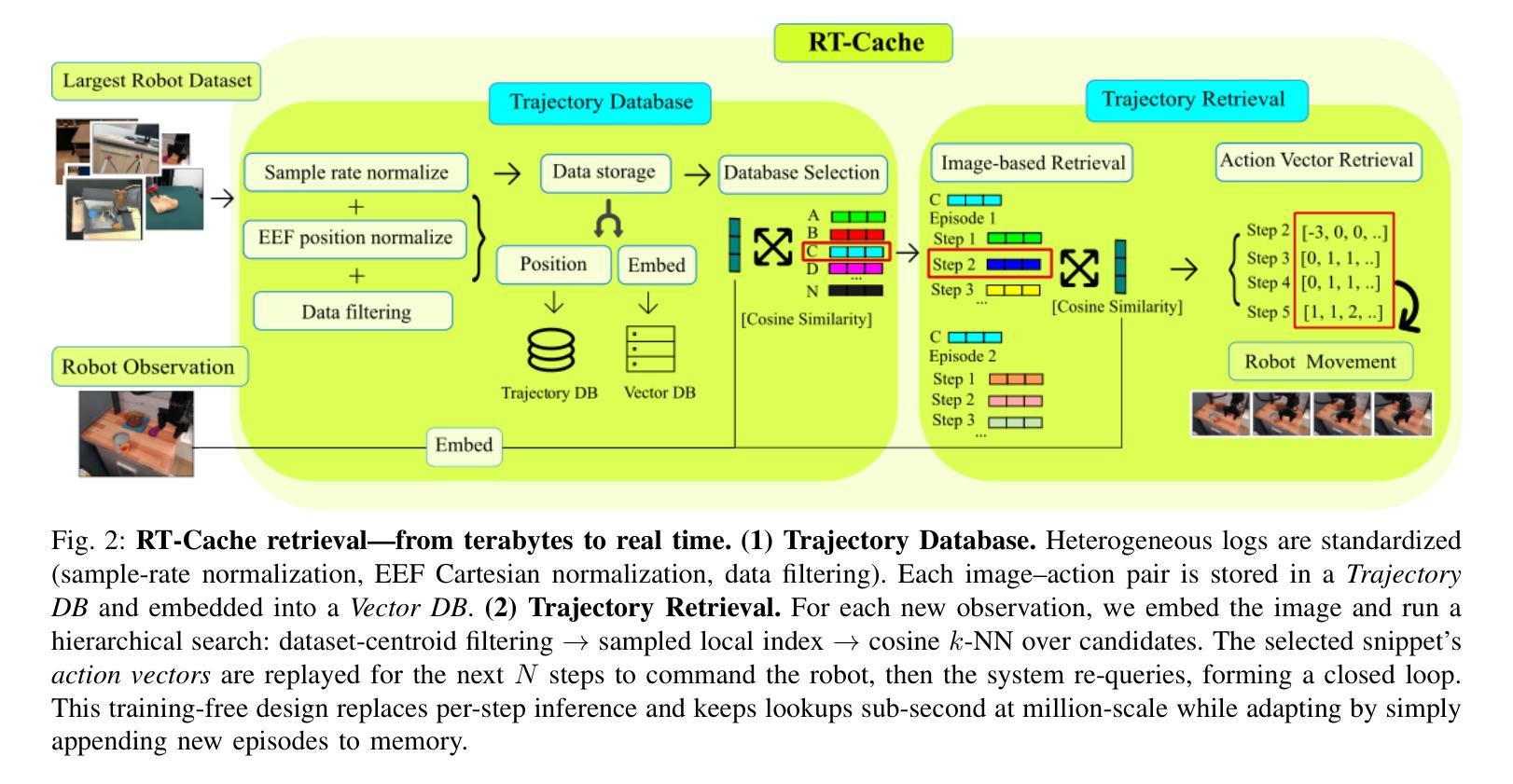
RT-Cache: Training-Free Retrieval for Real-Time Manipulation
Authors:Owen Kwon, Abraham George, Alison Bartsch, Amir Barati Farimani
Real robots are expected to repeat the same behavior in new environments with very little new data, yet modern controllers either incur heavy per-step inference or require deployment-time fine-tuning. We propose RT-Cache, a training-free retrieval-as-control pipeline that caches diverse image action trajectories in a unified vector memory and, at test time, embeds the current frame to retrieve and replay multi-step snippets, replacing per-step model calls. A hierarchical search keeps lookups sub-second at million scale, shifting cost from compute to storage and enabling real-time control on modest GPUs. Across real-robot tasks and large open logs, RT-Cache achieves higher success and lower completion time than strong retrieval baselines (approximately x2 higher success and ~30% faster in our settings), and a single-episode anchoring study shows immediate adaptation to a more complex, contact-rich task without fine-tuning. RT-Cache turns experience into an append-only memory, offering a simple, scalable path to few-shot deployment today and a foundation for multimodal keys and optional integration with high-level policies. Project page: https://rt-cache.github.io/.
现代机器人被期望在新的环境中使用很少的新数据就能重复执行相同的行为,然而现有的控制器要么在每一步推理时产生巨大的开销,要么需要在部署时进行微调。我们提出了RT-Cache,这是一种无需训练的回放控制管道,它可以在统一的向量内存中缓存各种图像行为轨迹。在测试时,它将当前帧嵌入其中,以检索和回放多步片段,从而替代每一步的模型调用。分层搜索使查找时间保持在子秒级别,即使在百万级别规模上也是如此,从而将成本从计算转移到存储,并在适度的GPU上实现实时控制。在真实机器人任务和大型开放日志中,RT-Cache的成功率高于强大的检索基线,完成时间更短(在我们的设置中,大约成功率提高两倍,速度提高约30%),一项单集锚定研究表明,它能够立即适应更复杂、接触丰富的任务而无需微调。RT-Cache将经验转化为一种附加式内存,为当今的少量部署提供了一条简单、可扩展的路径,并为多模式键和与高级政策的可选集成奠定了基础。项目页面:https://rt-cache.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
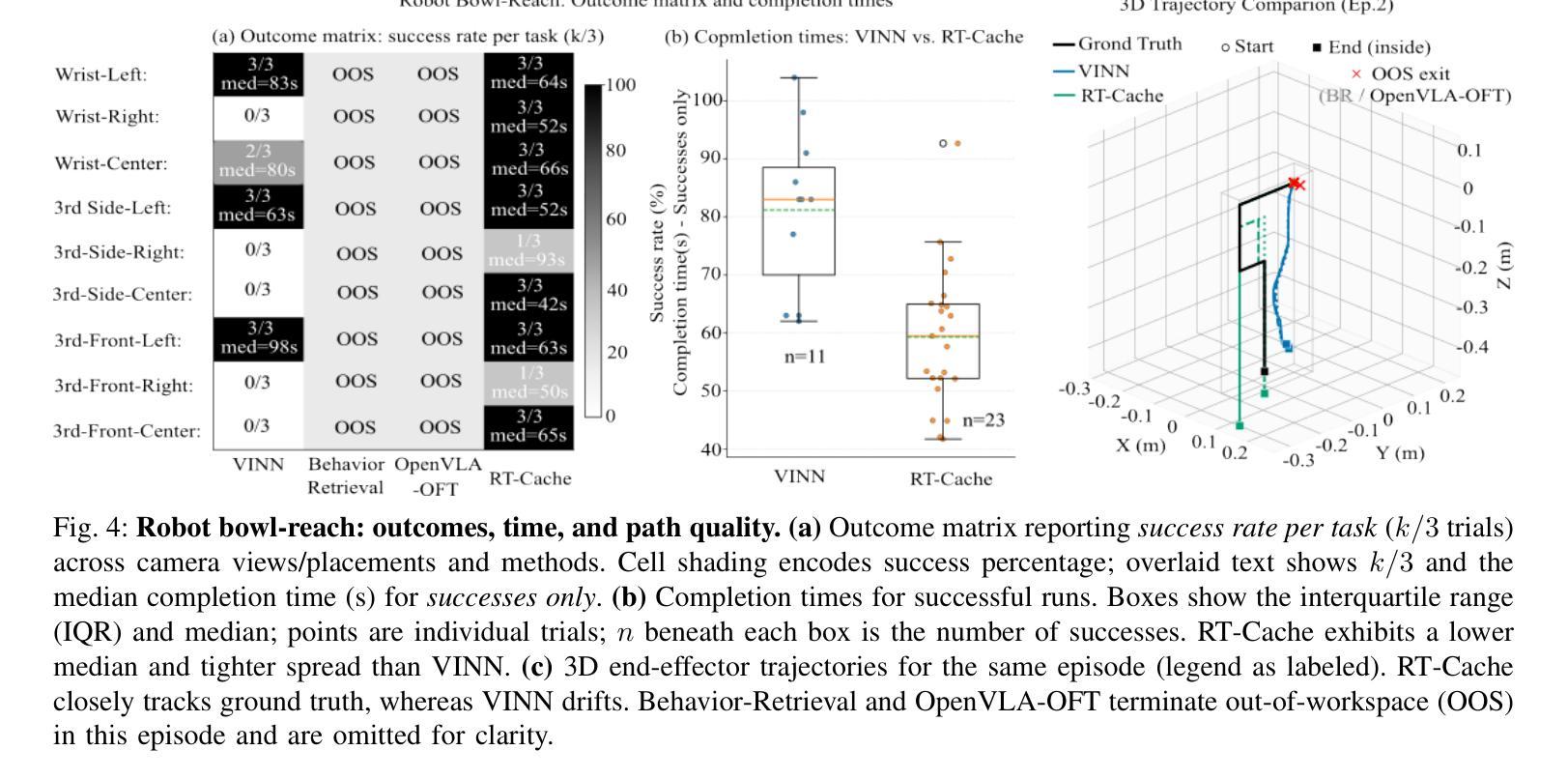
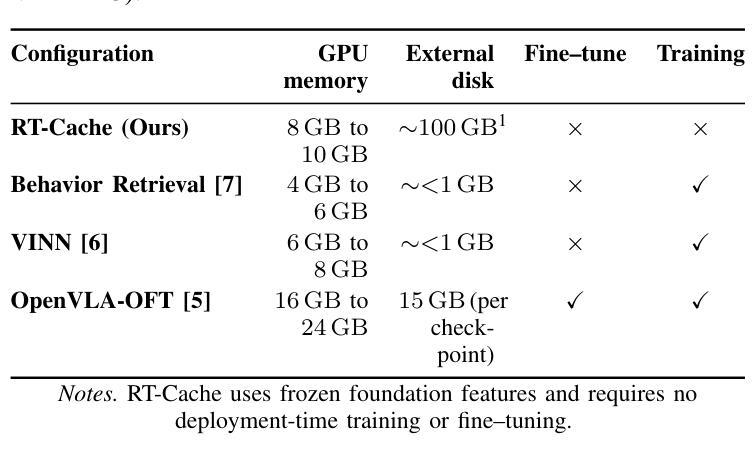
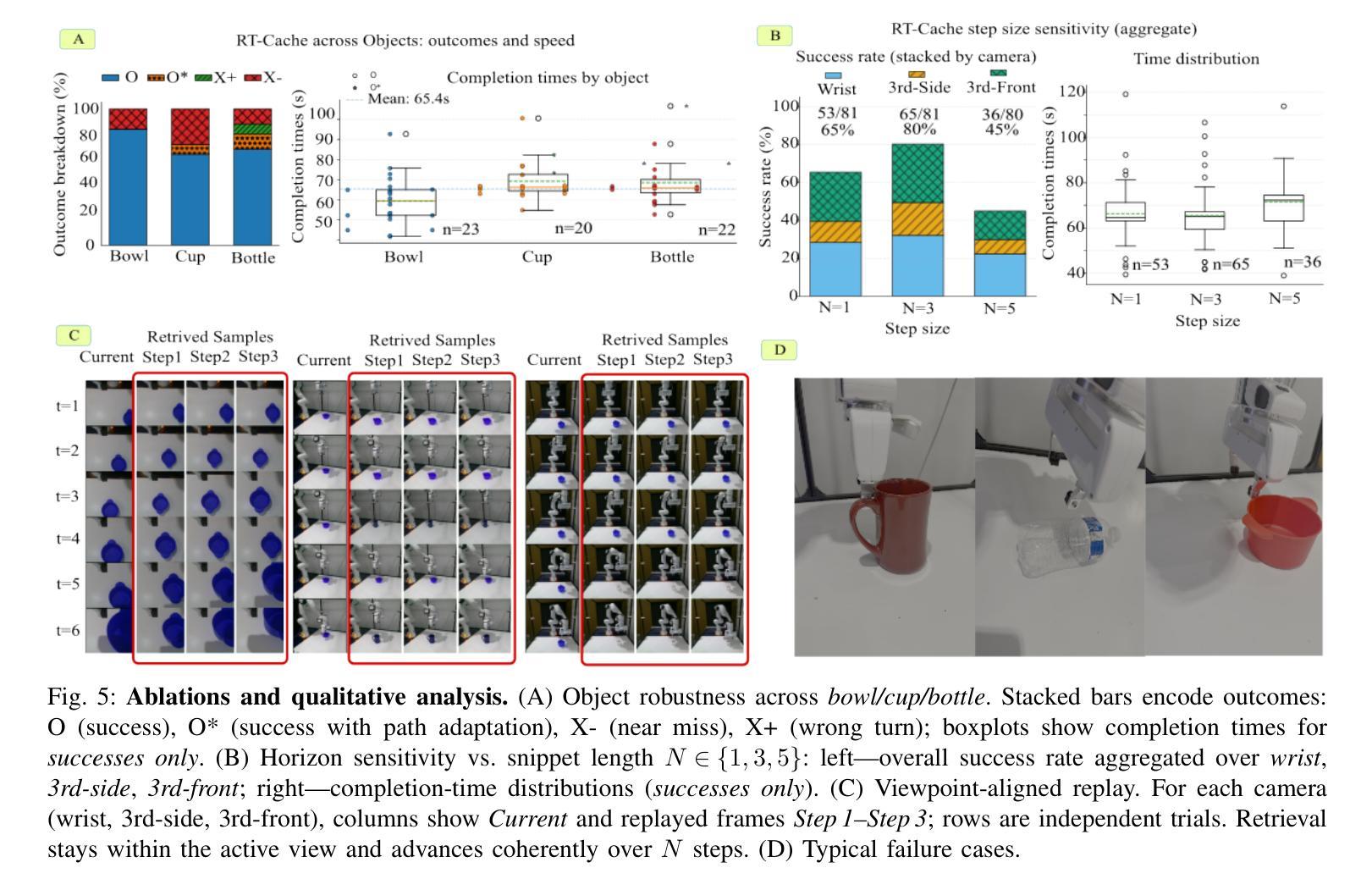
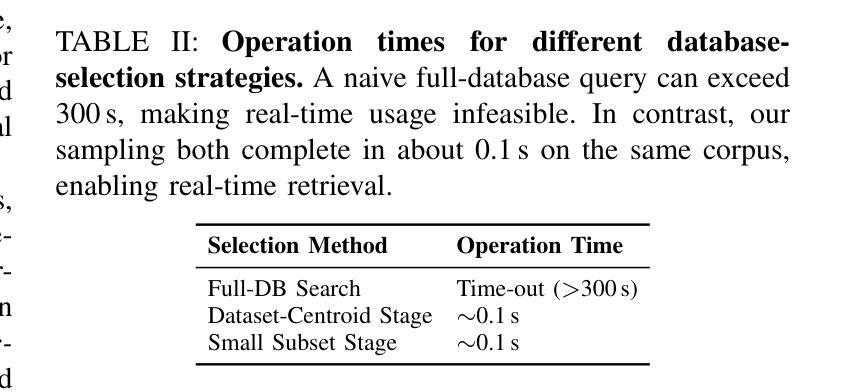
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures. Accepted to the 2025 IEEE-RAS 24th International Conference on Humanoid Robots
Summary
该文本介绍了RT-Cache系统,它采用无训练检索控制流程,通过缓存图像动作轨迹并在测试时嵌入当前帧来检索和回放多步片段,从而取代了分步模型调用。该系统采用分层搜索,在百万级规模上实现了亚秒级的查找速度,降低了计算成本并实现了实时控制。在真实机器人任务和大规模开放日志测试中,RT-Cache相较于强大的检索基线取得了更高的成功率和更快的完成时间。此外,其即时适应复杂接触密集型任务的能力,无需微调。
Key Takeaways
- RT-Cache系统采用无训练检索控制流程,适用于真实机器人场景中的快速适应任务。
- 通过缓存图像动作轨迹并嵌入当前帧进行检索和回放,实现高效率且不需要分步模型调用。
- 分层搜索技术使得查找速度在百万级规模上实现亚秒级响应。
- RT-Cache实现了实时控制,降低了计算成本。
- 在真实机器人任务和大规模开放日志测试中,RT-Cache比强大的检索基线表现出更高的成功率和更快的完成时间。
- 系统能够即时适应复杂的接触密集型任务,无需进行微调。
点此查看论文截图

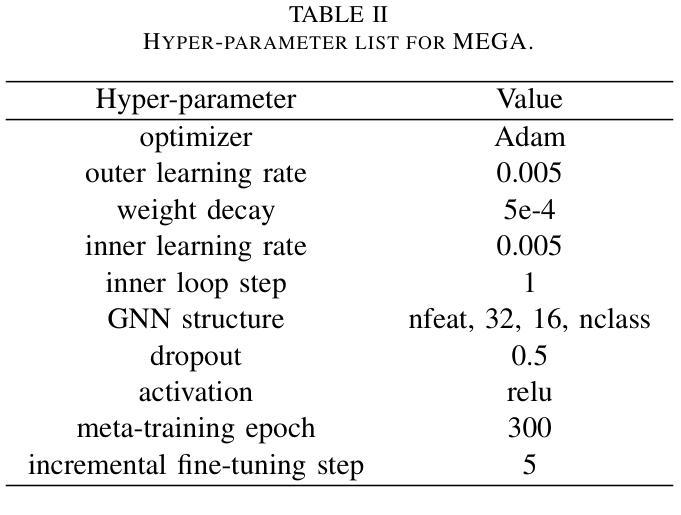
MEGA: Second-Order Gradient Alignment for Catastrophic Forgetting Mitigation in GFSCIL
Authors:Jinhui Pang, Changqing Lin, Hao Lin, Zhihui Zhang, Long Chen, Weiping Ding, Yu Liu, Xiaoshuai Hao
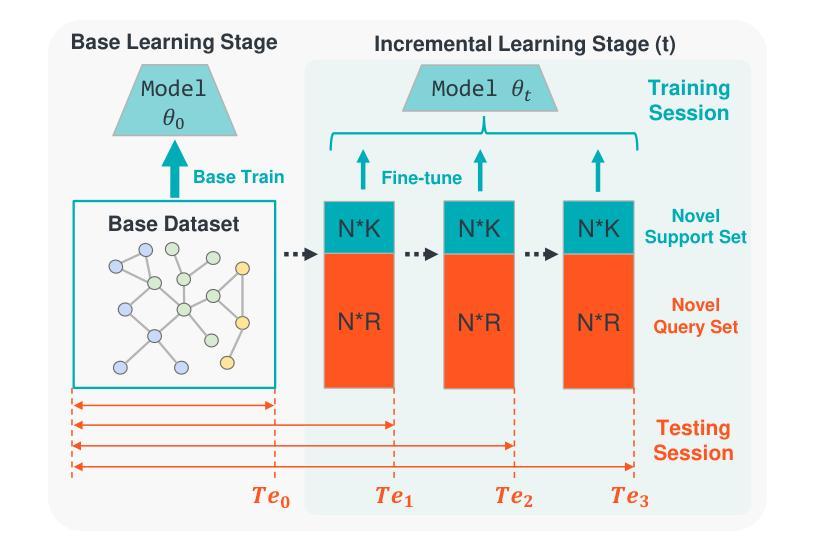
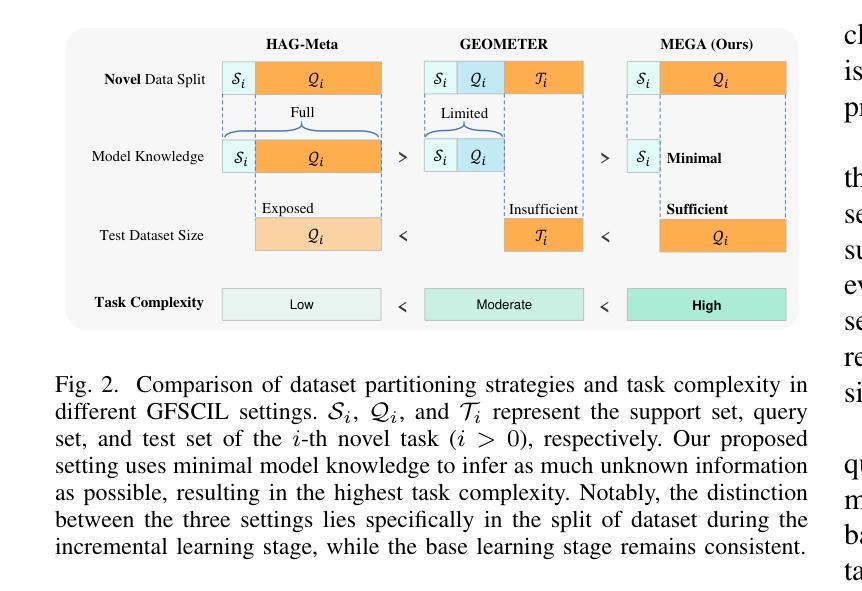
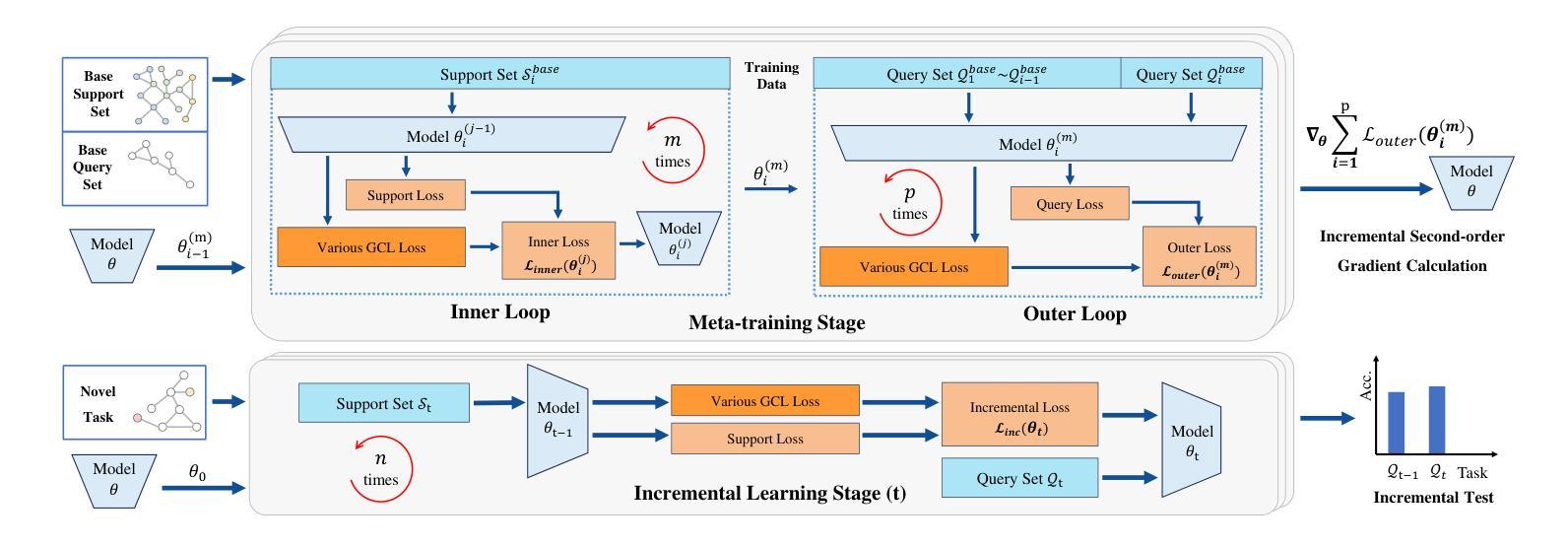
Graph Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (GFSCIL) enables models to continually learn from limited samples of novel tasks after initial training on a large base dataset. Existing GFSCIL approaches typically utilize Prototypical Networks (PNs) for metric-based class representations and fine-tune the model during the incremental learning stage. However, these PN-based methods oversimplify learning via novel query set fine-tuning and fail to integrate Graph Continual Learning (GCL) techniques due to architectural constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a more rigorous and practical setting for GFSCIL that excludes query sets during the incremental training phase. Building on this foundation, we introduce Model-Agnostic Meta Graph Continual Learning (MEGA), aimed at effectively alleviating catastrophic forgetting for GFSCIL. Specifically, by calculating the incremental second-order gradient during the meta-training stage, we endow the model to learn high-quality priors that enhance incremental learning by aligning its behaviors across both the meta-training and incremental learning stages. Extensive experiments on four mainstream graph datasets demonstrate that MEGA achieves state-of-the-art results and enhances the effectiveness of various GCL methods in GFSCIL. We believe that our proposed MEGA serves as a model-agnostic GFSCIL paradigm, paving the way for future research.
图增量少样本类增量学习(GFSCIL)使模型能够在大量基础数据集上进行初步训练后,从新增任务的有限样本中持续学习。现有的GFSCIL方法通常利用原型网络(PNs)进行基于度量的类表示,并在增量学习阶段对模型进行微调。然而,这些基于PN的方法通过新的查询集微调来简化学习,并且由于架构约束,无法整合图持续学习(GCL)技术。为了解决这些挑战,我们为GFSCIL提出了一个更严格、更实用的设置,即在增量训练阶段排除查询集。在此基础上,我们引入了模型无关的元图持续学习(MEGA),旨在有效缓解GFSCIL的灾难性遗忘问题。具体来说,通过计算元训练阶段的增量二阶梯度,我们赋予模型学习高质量先验的能力,通过对齐元训练阶段和增量学习阶段的行为,增强增量学习效果。在四个主流图数据集上的大量实验表明,MEGA达到了最新的结果,提高了GFSCIL中各种GCL方法的有效性。我们相信,我们提出的MEGA作为一种模型无关的GFSCIL范式,为未来的研究铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
基于图数据的Few-Shot类增量学习(GFSCIL)能够让模型在初始时训练大量基础数据集后,继续学习新任务的小样本数据。现有的GFSCIL方法通常采用原型网络(PNs)进行基于度量的类表示,并在增量学习阶段微调模型。然而,基于PN的方法简化了通过新查询集进行微调的学习过程,并因架构约束未能整合图持续学习(GCL)技术。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了更严格和实用的GFSCIL设置,增量训练阶段排除查询集。在此基础上,我们引入了模型无关的元图持续学习(MEGA)方法,旨在有效缓解GFSCIL的灾难性遗忘问题。通过计算元训练阶段的二阶增量梯度,我们使模型学习高质量先验,增强元训练和增量学习阶段的行为一致性。在四个主流图数据集上的广泛实验表明,MEGA达到了最新水平的结果,提高了各种GCL方法在GFSCIL中的有效性。我们相信,我们提出的MEGA为GFSCIL提供了一个模型无关的解决方案,为未来的研究铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- Graph Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (GFSCIL) 允许模型在不断学习新任务的小样本数据的同时,保留在初始大量基础数据集上训练的结果。
- 现有GFSCIL方法主要使用原型网络(PNs)进行类表示和微调模型,但这种方法过于简化学习过程。
- 基于PN的方法未能充分利用图持续学习(GCL)技术,主要原因是架构上的限制。
- 为改进现有方法,提出了更严格和实用的GFSCIL设置,即在增量训练阶段排除查询集。
- 引入了一种新的方法——模型无关的元图持续学习(MEGA)——来缓解GFSCIL中的灾难性遗忘问题。
- MEGA通过计算元训练阶段的二阶增量梯度来学习高质量先验知识,增强了模型在元训练和增量学习阶段的行为一致性。
点此查看论文截图

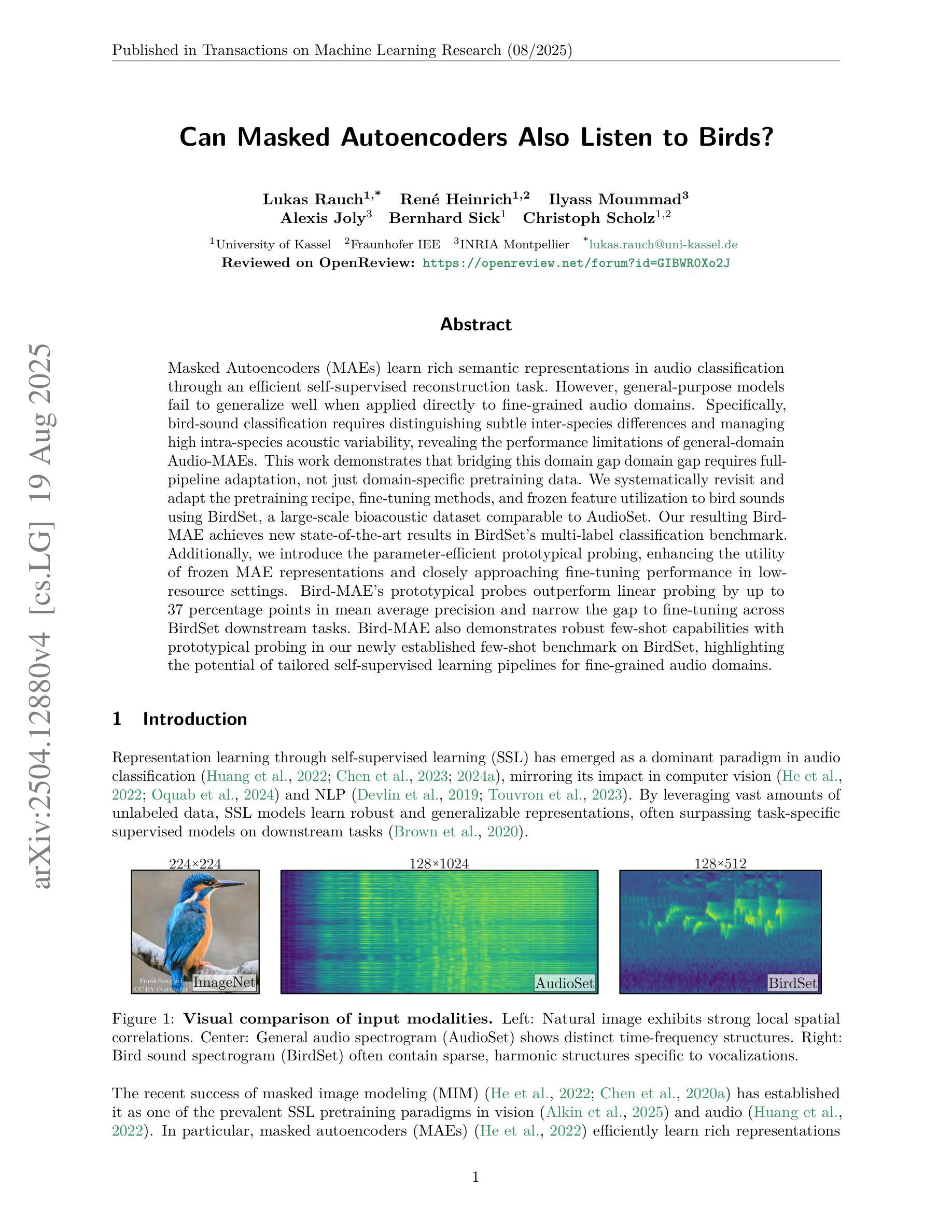
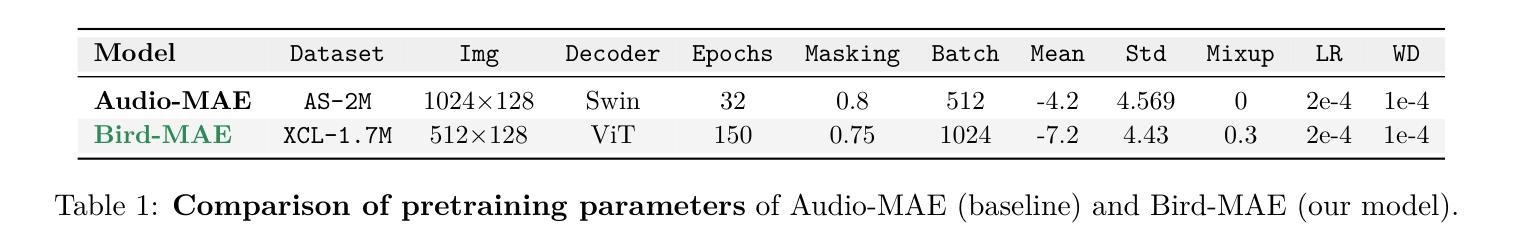
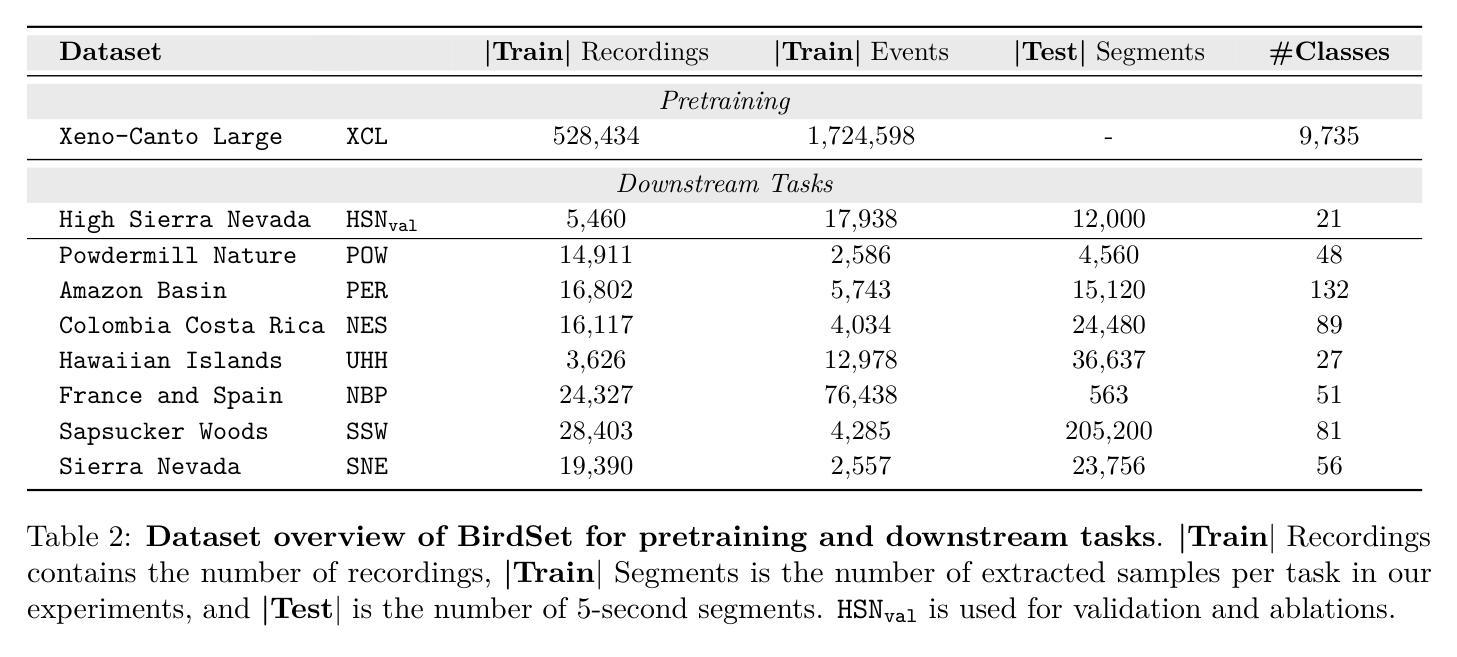
Can Masked Autoencoders Also Listen to Birds?
Authors:Lukas Rauch, René Heinrich, Ilyass Moummad, Alexis Joly, Bernhard Sick, Christoph Scholz
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) learn rich semantic representations in audio classification through an efficient self-supervised reconstruction task. However, general-purpose models fail to generalize well when applied directly to fine-grained audio domains. Specifically, bird-sound classification requires distinguishing subtle inter-species differences and managing high intra-species acoustic variability, revealing the performance limitations of general-domain Audio-MAEs. This work demonstrates that bridging this domain gap domain gap requires full-pipeline adaptation, not just domain-specific pretraining data. We systematically revisit and adapt the pretraining recipe, fine-tuning methods, and frozen feature utilization to bird sounds using BirdSet, a large-scale bioacoustic dataset comparable to AudioSet. Our resulting Bird-MAE achieves new state-of-the-art results in BirdSet’s multi-label classification benchmark. Additionally, we introduce the parameter-efficient prototypical probing, enhancing the utility of frozen MAE representations and closely approaching fine-tuning performance in low-resource settings. Bird-MAE’s prototypical probes outperform linear probing by up to 37 percentage points in mean average precision and narrow the gap to fine-tuning across BirdSet downstream tasks. Bird-MAE also demonstrates robust few-shot capabilities with prototypical probing in our newly established few-shot benchmark on BirdSet, highlighting the potential of tailored self-supervised learning pipelines for fine-grained audio domains.
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs)通过高效的自监督重建任务,在音频分类中学习丰富的语义表示。然而,当直接应用于细粒度音频域时,通用模型往往无法很好地推广。特别是,鸟类声音分类需要区分物种间的细微差异并处理高物种内部声学变化,这揭示了通用领域Audio-MAE的性能局限性。这项工作表明,弥合这一领域差距需要全管道适应,而不仅仅是领域特定的预训练数据。我们系统地回顾并适应了预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用鸟类声音,使用BirdSet——一个可与AudioSet相比的大规模生物声学数据集。我们得到的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中达到了最新水平。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,提高了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在平均精度均值方面比线性探针高出高达37个百分点,并缩小了在BirdSet下游任务中的微调差距。Bird-MAE还展示了我们新建立的BirdSet少样本基准测试中原型探针的稳健的少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频领域量身定制的自监督学习管道的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted @TMLR: https://openreview.net/forum?id=GIBWR0Xo2J
Summary
本文介绍了Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在音频分类中的丰富语义表示学习。然而,通用模型在精细粒度音频领域的应用中表现不佳。针对鸟类声音分类这一特定场景,本研究通过全管道适应方法,而非仅依赖特定领域的预训练数据来弥补领域差距。通过调整预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用方式,使用大规模生物声学数据集BirdSet,实现了对鸟类声音的新SOTA结果。此外,引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,提高了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在平均精度上最多高出线性探针37个百分点,并缩小了在BirdSet下游任务中的微调差距。同时,Bird-MAE在全新建立的BirdSet少样本基准测试中展现出强大的少样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) 能够有效学习音频分类的丰富语义表示。
- 通用模型在精细粒度音频领域(如鸟类声音分类)存在性能局限。
- 跨越领域差距需要全管道适应方法,不仅依赖特定领域的预训练数据。
- 通过调整预训练配方、微调方法和利用冻结特征,使用BirdSet数据集实现了鸟声分类的新SOTA结果。
- 引入参数高效的原型探测技术,提高冻结MAE表示的实用性,并接近低资源环境中的微调性能。
- Bird-MAE的原型探针在平均精度上有显著改进,缩小了与微调之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图
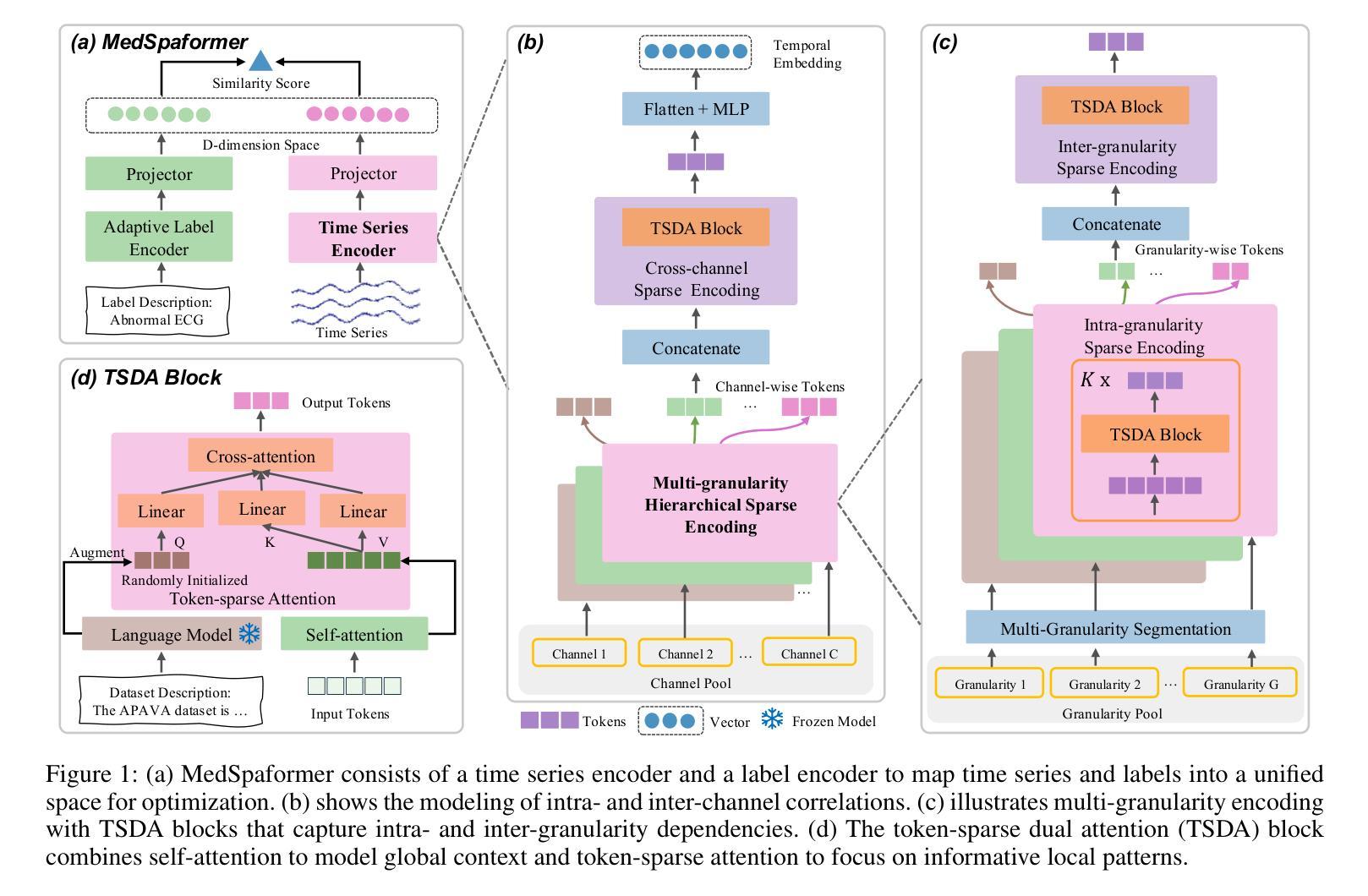
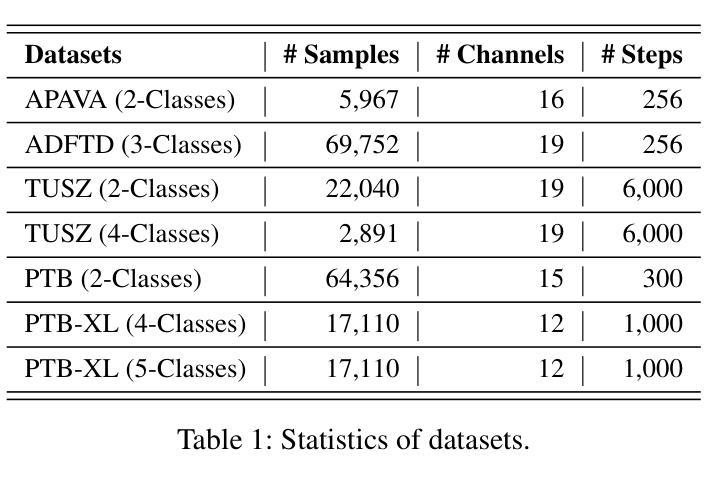
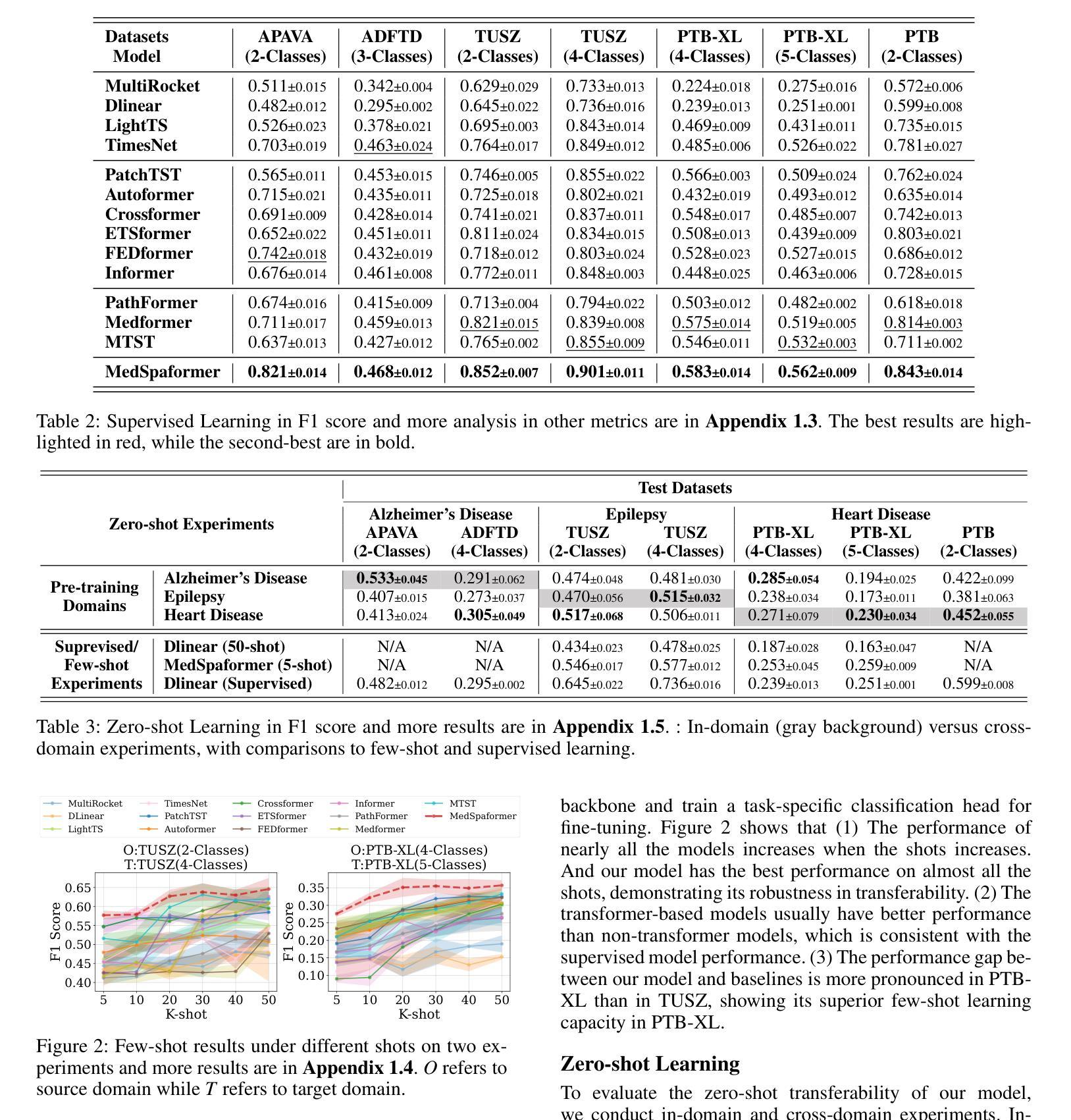
MedSpaformer: a Transferable Transformer with Multi-granularity Token Sparsification for Medical Time Series Classification
Authors:Jiexia Ye, Weiqi Zhang, Ziyue Li, Jia Li, Fugee Tsung
Accurate medical time series (MedTS) classification is essential for effective clinical diagnosis, yet remains challenging due to complex multi-channel temporal dependencies, information redundancy, and label scarcity. While transformer-based models have shown promise in time series analysis, most are designed for forecasting tasks and fail to fully exploit the unique characteristics of MedTS. In this paper, we introduce MedSpaformer, a transformer-based framework tailored for MedTS classification. It incorporates a sparse token-based dual-attention mechanism that enables global context modeling and token sparsification, allowing dynamic feature refinement by focusing on informative tokens while reducing redundancy. This mechanism is integrated into a multi-granularity cross-channel encoding scheme to capture intra- and inter-granularity temporal dependencies and inter-channel correlations, enabling progressive refinement of task-relevant patterns in medical signals. The sparsification design allows our model to flexibly accommodate inputs with variable lengths and channel dimensions. We also introduce an adaptive label encoder to extract label semantics and address cross-dataset label space misalignment. Together, these components enhance the model’s transferability across heterogeneous medical datasets, which helps alleviate the challenge of label scarcity. Our model outperforms 13 baselines across 7 medical datasets under supervised learning. It also excels in few-shot learning and demonstrates zero-shot capability in both in-domain and cross-domain diagnostics. These results highlight MedSpaformer’s robustness and its potential as a unified solution for MedTS classification across diverse settings.
精确医疗时间序列(MedTS)分类对于有效的临床诊断至关重要,但由于复杂的跨通道时间依赖性、信息冗余和标签稀缺,它仍然是一个挑战。虽然基于变压器的模型在时间序列分析中显示出潜力,但大多数模型都是为预测任务而设计的,未能充分利用MedTS的独特特征。在本文中,我们介绍了针对MedTS分类的基于变压器的框架MedSpaformer。它采用了一种稀疏的基于标记的双重注意力机制,能够全局建模上下文并精简标记,通过关注信息丰富的标记进行动态特征细化,同时减少冗余。该机制被整合到多粒度跨通道编码方案中,以捕获粒度和跨粒度的时间依赖性以及通道间的相关性,从而逐步优化医疗信号中与任务相关的模式。精简设计使得我们的模型可以灵活地适应具有不同长度和通道维度的输入。我们还引入了一种自适应标签编码器来提取标签语义并解决跨数据集标签空间的不对齐问题。这些组件共同提高了模型在异质医疗数据集上的迁移能力,有助于缓解标签稀缺的挑战。我们的模型在7个医疗数据集上超越了13个基线模型,在监督学习中的表现尤为出色。在少量样本学习场景中,该模型表现出色,并在域内和跨域诊断中展示出零样本学习能力。这些结果凸显了MedSpaformer的稳健性以及其在多样环境下作为统一解决方案的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 figures, 9 pages, 4 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种针对医学时间序列(MedTS)分类的MedSpaformer框架。它通过稀疏令牌基础的双重注意力机制,实现了全局上下文建模和令牌稀疏化,减少了冗余信息并提升了特征精炼能力。同时集成多粒度跨通道编码方案,捕捉不同粒度的时序依赖性和跨通道相关性。通过引入自适应标签编码器解决跨数据集标签空间不一致性问题,增强模型在不同医疗数据集间的可迁移性。实验显示该模型在多个医学数据集上的表现优于其他基线模型,尤其在少样本学习方面表现优异,并具备零样本能力进行同域和跨域诊断。
Key Takeaways
- MedSpaformer是一种针对医学时间序列分类的变压器模型框架。
- 它采用了稀疏令牌基础的双重注意力机制以实现全局上下文建模和令牌稀疏化。
- 集成多粒度跨通道编码方案,有效捕捉时序数据的不同粒度依赖性和跨通道相关性。
- 自适应标签编码器用于提取标签语义并处理跨数据集标签空间不一致性问题。
- MedSpaformer模型在多个医学数据集上的表现优于其他基线模型。
- 该模型在少样本学习方面表现优异,并具备零样本能力进行诊断。
点此查看论文截图

Closed-Form Feedback-Free Learning with Forward Projection
Authors:Robert O’Shea, Bipin Rajendran
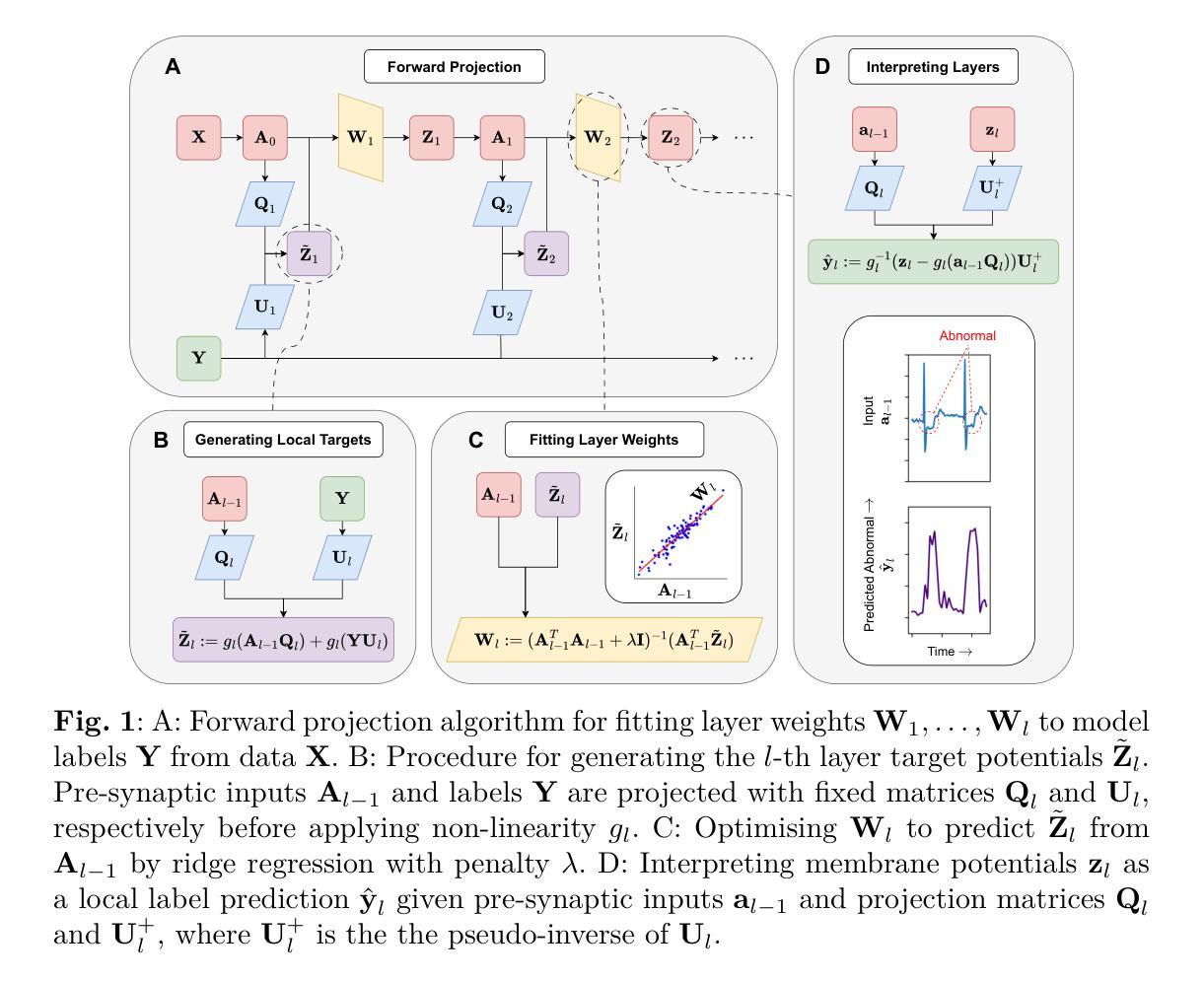
State-of-the-art methods for backpropagation-free learning employ local error feedback to direct iterative optimisation via gradient descent. In this study, we examine the more restrictive setting where retrograde communication from neuronal outputs is unavailable for pre-synaptic weight optimisation. To address this challenge, we propose Forward Projection (FP). This novel randomised closed-form training method requires only a single forward pass over the entire dataset for model fitting, without retrograde communication. Target values for pre-activation membrane potentials are generated layer-wise via nonlinear projections of pre-synaptic inputs and the labels. Local loss functions are optimised over pre-synaptic inputs using closed-form regression, without feedback from neuronal outputs or downstream layers. Interpretability is a key advantage of FP training; membrane potentials of hidden neurons in FP-trained networks encode information which is interpretable layer-wise as label predictions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of FP across four biomedical datasets. In few-shot learning tasks, FP yielded more generalisable models than those optimised via backpropagation. In large-sample tasks, FP-based models achieve generalisation comparable to gradient descent-based local learning methods while requiring only a single forward propagation step, achieving significant speed up for training. Interpretation functions defined on local neuronal activity in FP-based models successfully identified clinically salient features for diagnosis in two biomedical datasets. Forward Projection is a computationally efficient machine learning approach that yields interpretable neural network models without retrograde communication of neuronal activity during training.
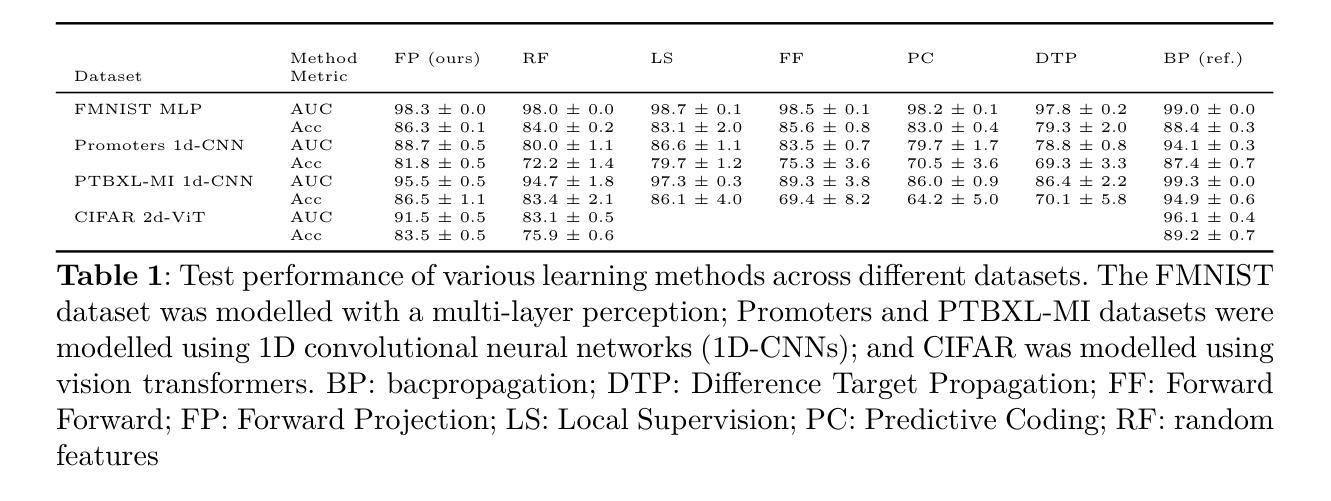
当前先进的不依赖反向传播的学习方法采用局部误差反馈来指导通过梯度下降法的迭代优化。在这项研究中,我们考察了一个更严格的设置环境,即当神经元输出的逆向通信无法用于突触前权重优化时的情况。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了“前向投影”(FP)。这种新颖的随机闭式训练方法仅在整个数据集上执行一次前向传递即可进行模型拟合,无需逆向通信。目标值逐层生成,通过突触前输入的非线性投影和标签实现。局部损失函数通过闭式回归在突触前输入上进行优化,无需神经元输出或下游层的反馈。可解释性是FP训练的关键优势;FP训练后的网络中隐藏神经元的膜电位编码的信息可以按层解读为标签预测。我们在四个生物医学数据集上展示了FP的有效性。在少量样本学习任务中,FP产生的模型比通过反向传播优化的模型更具泛化能力。在大样本任务中,FP模型基于的泛化能力与梯度下降法本地学习方法相当,但仅需一次前向传播步骤,大大加快了训练速度。在FP模型上定义的局部神经元活动的解释函数成功地在两个生物医学数据集中识别出了用于诊断的临床重要特征。前向投影是一种计算效率高的机器学习方法,可在训练过程中无需神经元活动的逆向通信即可产生可解释的神经网络模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 5 figures. Study code available at https://github.com/robertoshea/forward_projection. Study data available at https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/fb7xddyxs4/2
Summary
本研究提出了一种名为Forward Projection(FP)的新型随机闭式训练方法,该方法在无需逆向神经元输出通信的情况下,通过单次前向传播即可完成模型拟合。通过逐层生成目标预激活膜电位值,并利用闭式回归优化预突触输入的局部损失函数,FP训练提高了模型的解释性和预测性能。在四个生物医学数据集上的实验表明,FP在少样本学习任务中表现出更高的泛化能力,在大样本任务中也能实现与基于梯度下降的地方学习方法相当的泛化性能,同时只需一步前向传播,显著加快了训练速度。此外,FP模型中的解释函数能够成功识别两个生物医学数据集中的临床重要特征,为诊断提供了有力支持。总体而言,FP是一种高效且可解释的机器学习新方法,无需训练过程中的神经元活动逆向通信。
Key Takeaways
- Forward Projection(FP)是一种新型的随机闭式训练方法,无需逆向神经元输出通信即可完成模型拟合。
- FP通过逐层生成目标预激活膜电位值并利用闭式回归优化预突触输入的局部损失函数,提高模型的解释性和预测性能。
- 在少样本学习任务中,FP表现出更高的泛化能力。
- 在大样本任务中,FP模型的泛化性能与基于梯度下降的地方学习方法相当,但只需一步前向传播,加快了训练速度。
- FP模型中的解释函数能够识别临床重要特征,为诊断提供支持。
- FP训练提高了模型的解释性,使得膜电位信息可逐层解释为标签预测。
点此查看论文截图