⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
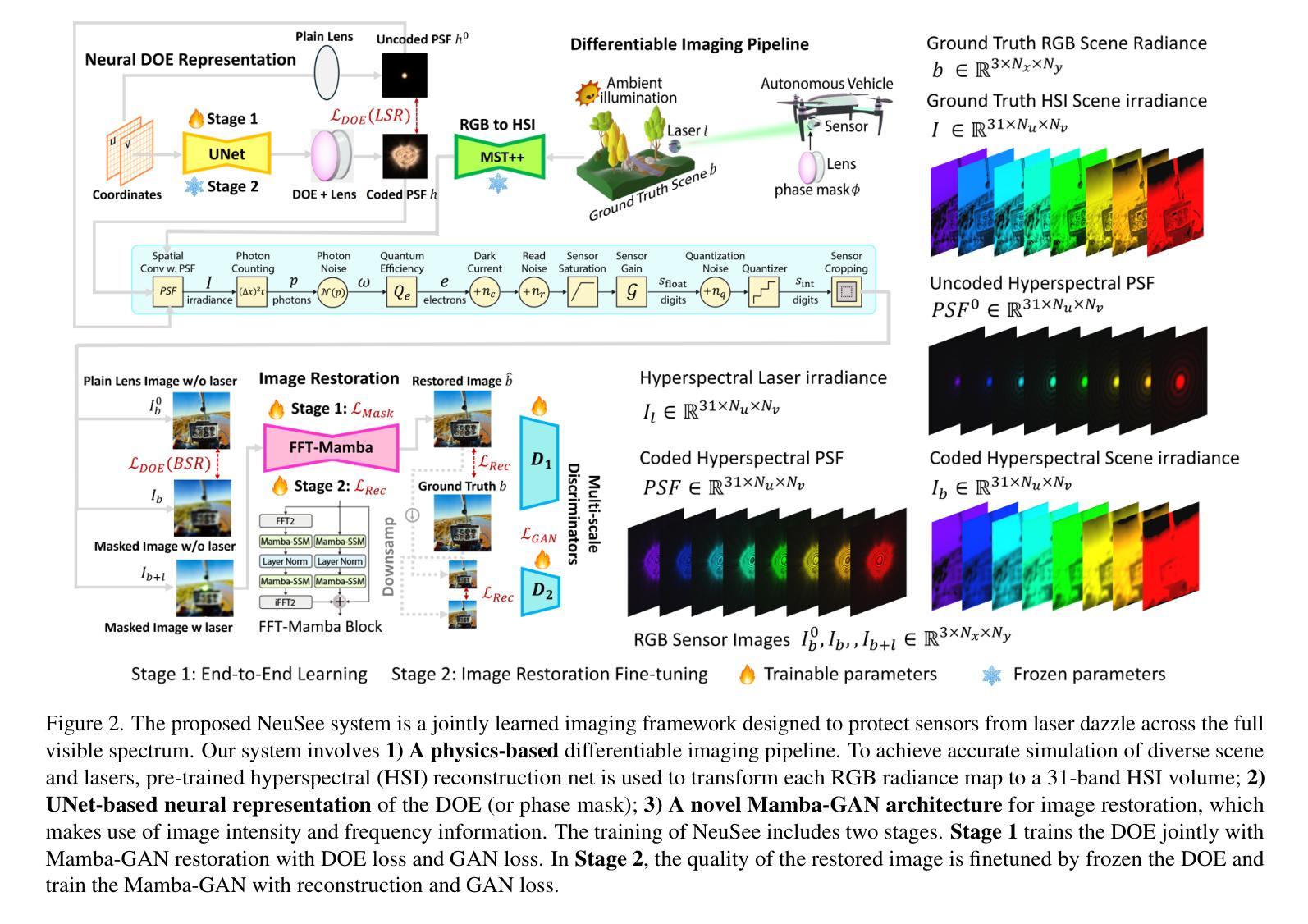
Learning to See Through Flare
Authors:Xiaopeng Peng, Heath Gemar, Erin Fleet, Kyle Novak, Abbie Watnik, Grover Swartzlander
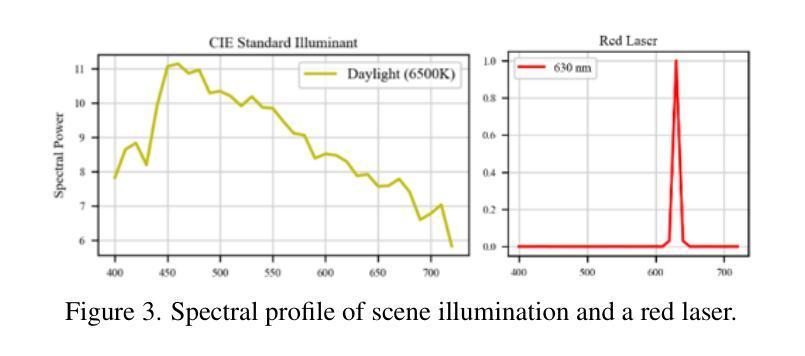
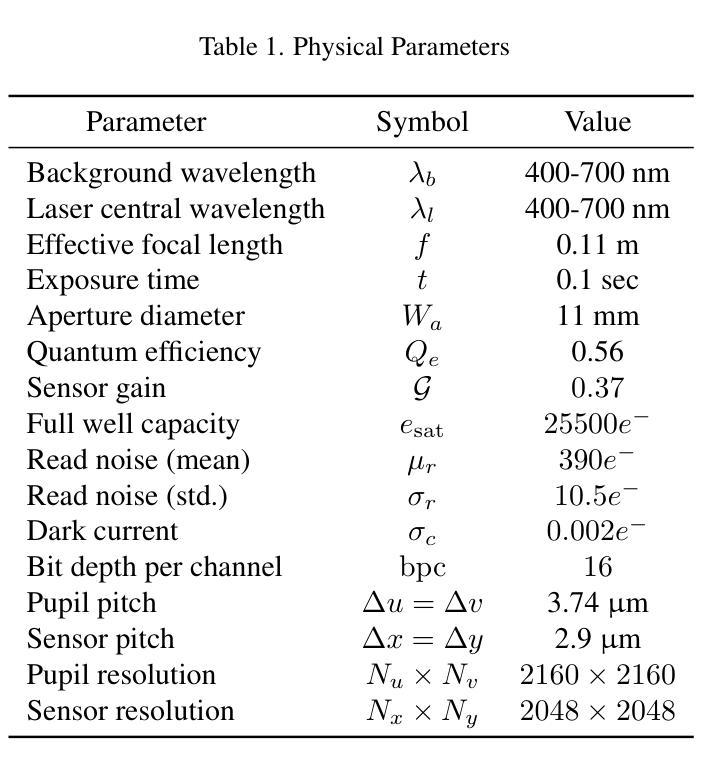
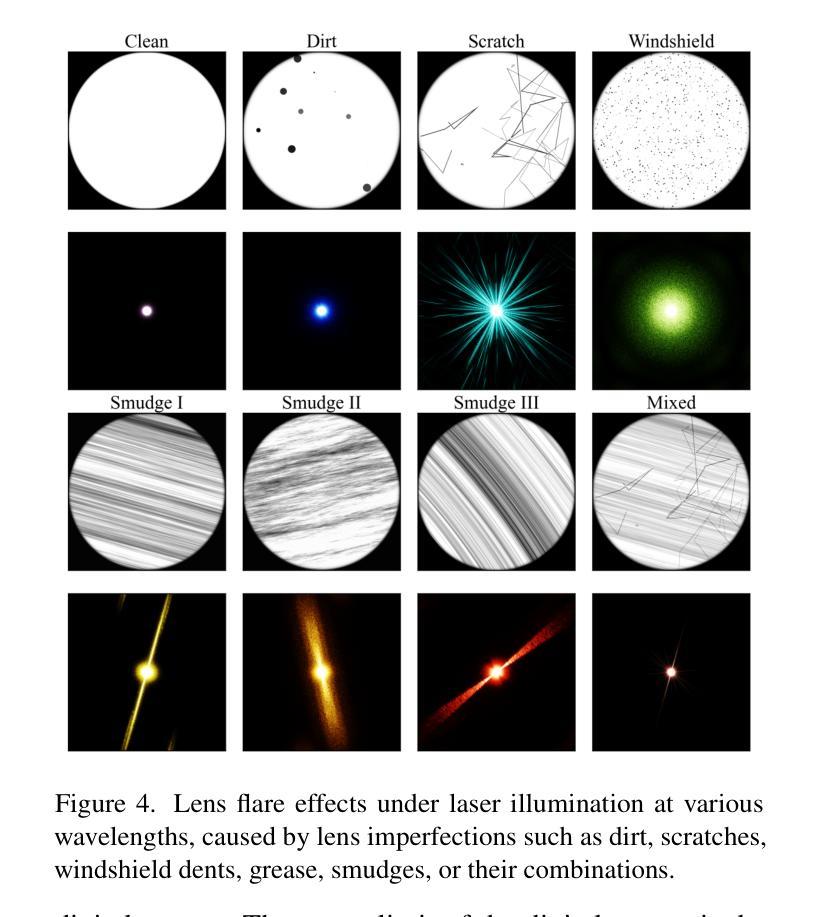
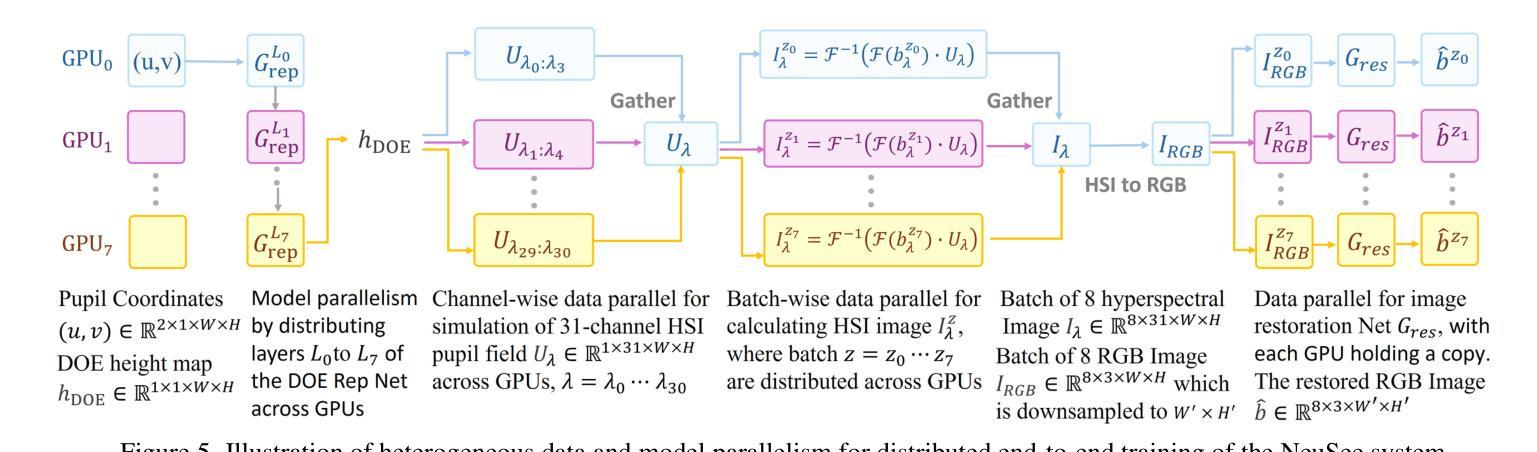
Machine vision systems are susceptible to laser flare, where unwanted intense laser illumination blinds and distorts its perception of the environment through oversaturation or permanent damage to sensor pixels. We introduce NeuSee, the first computational imaging framework for high-fidelity sensor protection across the full visible spectrum. It jointly learns a neural representation of a diffractive optical element (DOE) and a frequency-space Mamba-GAN network for image restoration. NeuSee system is adversarially trained end-to-end on 100K unique images to suppress the peak laser irradiance as high as $10^6$ times the sensor saturation threshold $I_{\textrm{sat}}$, the point at which camera sensors may experience damage without the DOE. Our system leverages heterogeneous data and model parallelism for distributed computing, integrating hyperspectral information and multiple neural networks for realistic simulation and image restoration. NeuSee takes into account open-world scenes with dynamically varying laser wavelengths, intensities, and positions, as well as lens flare effects, unknown ambient lighting conditions, and sensor noises. It outperforms other learned DOEs, achieving full-spectrum imaging and laser suppression for the first time, with a 10.1% improvement in restored image quality.
机器视觉系统容易受到激光眩光的影响,其中不希望的强烈激光照明会通过过饱和或对传感器像素的永久损坏来干扰其对环境的感知。我们引入了NeuSee,这是全光谱高保真传感器保护的首个计算成像框架。它联合学习了一个衍射光学元件(DOE)的神经表征和频率空间的Mamba-GAN网络,用于图像恢复。NeuSee系统在10万张独特图像上进行端到端的对抗训练,可抑制高达$10^6$倍的峰值激光辐照度,超过传感器饱和阈值$I_{\textrm{sat}}$,即在没有DOE的情况下相机传感器可能会损坏的点。我们的系统利用异构数据和模型并行性进行分布式计算,整合超光谱信息和多个神经网络进行真实模拟和图像恢复。NeuSee考虑了开放世界场景,动态变化的激光波长、强度和位置,以及镜头眩光效应、未知的照明条件和传感器噪声。它优于其他学习的DOE,首次实现全光谱成像和激光抑制,恢复图像质量提高了10.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICCVW 2025
Summary
机器视觉系统易受激光眩光影响,导致环境感知失真或传感器像素永久损坏。我们推出NeuSee,这是首个全光谱高保真传感器保护计算成像框架。它联合学习衍射光学元件的神经表征和频率空间的Mamba-GAN网络进行图像恢复。NeuSee系统采用端到端的对抗训练模式,能够在传感器饱和阈值$I_{\text{sat}}$的基础上抑制高达$10^6$倍的激光峰值辐射。我们的系统利用异构数据和模型并行性进行分布式计算,整合超光谱信息和多个神经网络进行真实模拟和图像恢复。NeuSee考虑开放世界场景,动态适应激光波长、强度、位置的变化,以及镜头眩光效应、未知的环境照明条件和传感器噪声。相较于其他学习的衍射光学元件,NeuSee首次实现了全光谱成像和激光抑制,恢复图像质量提高了10.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 机器视觉系统易受激光眩光影响,可能导致环境感知失真或传感器像素永久损坏。
- NeuSee是首个全光谱高保真传感器保护计算成像框架。
- NeuSee联合学习衍射光学元件的神经表征和频率空间的Mamba-GAN网络进行图像恢复。
- 系统能够在传感器饱和阈值的基础上抑制高达$10^6$倍的激光峰值辐射。
- 采用异构数据和模型并行性进行分布式计算,以整合超光谱信息和多个神经网络进行真实模拟和图像恢复。
- NeuSee适应多种开放世界场景,包括动态变化的激光属性和环境照明条件。
点此查看论文截图

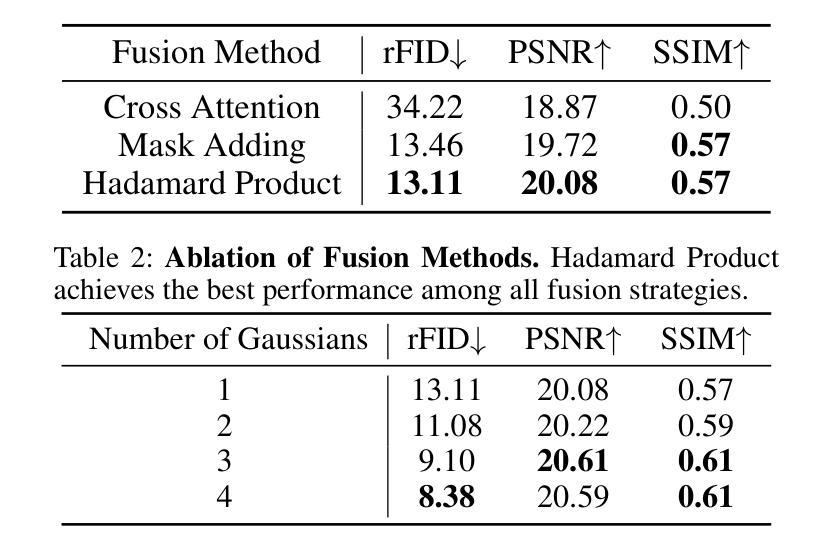
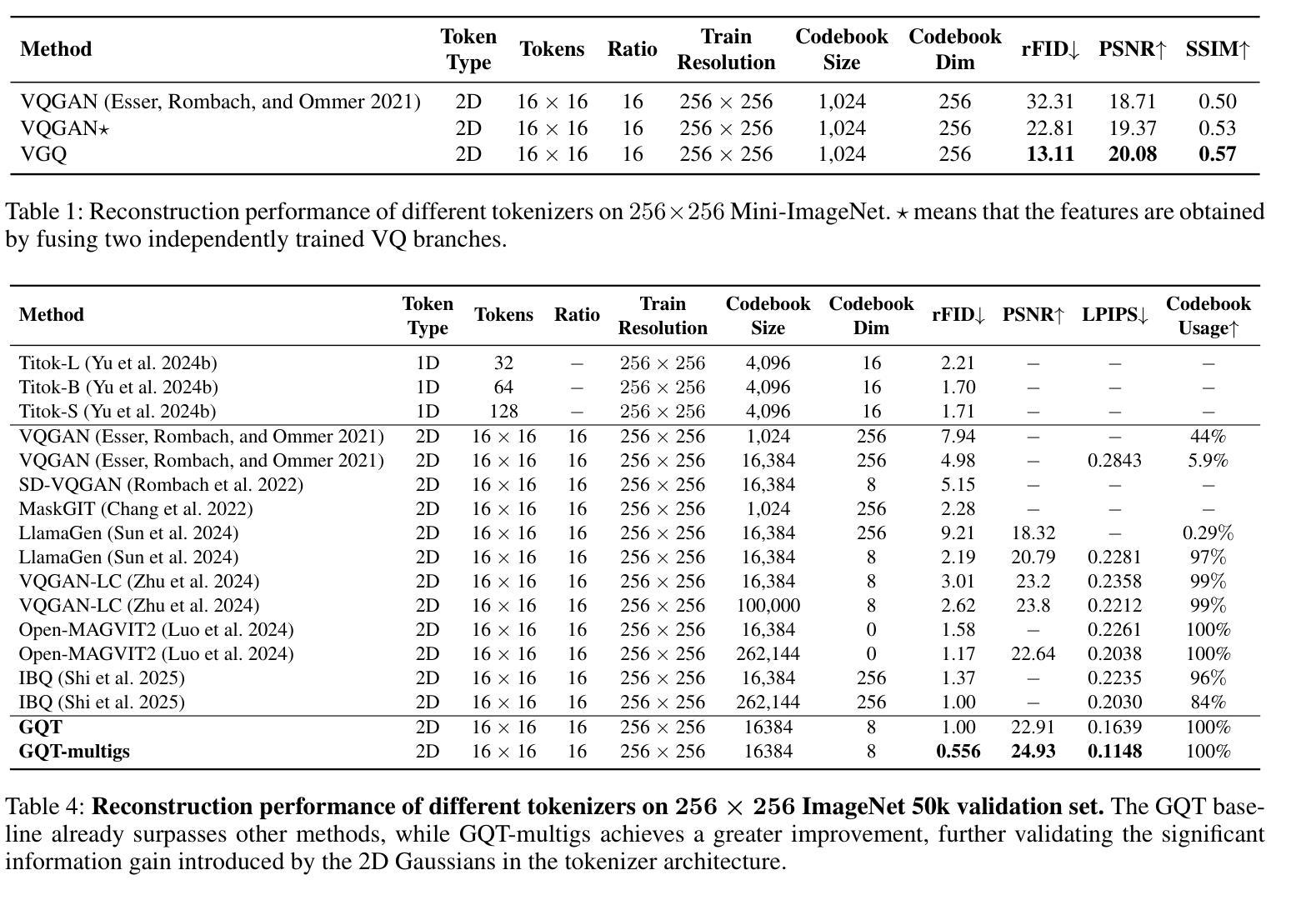
2D Gaussians Meet Visual Tokenizer
Authors:Yiang Shi, Xiaoyang Guo, Wei Yin, Mingkai Jia, Qian Zhang, Xiaolin Hu, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wan
The image tokenizer is a critical component in AR image generation, as it determines how rich and structured visual content is encoded into compact representations. Existing quantization-based tokenizers such as VQ-GAN primarily focus on appearance features like texture and color, often neglecting geometric structures due to their patch-based design. In this work, we explored how to incorporate more visual information into the tokenizer and proposed a new framework named Visual Gaussian Quantization (VGQ), a novel tokenizer paradigm that explicitly enhances structural modeling by integrating 2D Gaussians into traditional visual codebook quantization frameworks. Our approach addresses the inherent limitations of naive quantization methods such as VQ-GAN, which struggle to model structured visual information due to their patch-based design and emphasis on texture and color. In contrast, VGQ encodes image latents as 2D Gaussian distributions, effectively capturing geometric and spatial structures by directly modeling structure-related parameters such as position, rotation and scale. We further demonstrate that increasing the density of 2D Gaussians within the tokens leads to significant gains in reconstruction fidelity, providing a flexible trade-off between token efficiency and visual richness. On the ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, VGQ achieves strong reconstruction quality with an rFID score of 1.00. Furthermore, by increasing the density of 2D Gaussians within the tokens, VGQ gains a significant boost in reconstruction capability and achieves a state-of-the-art reconstruction rFID score of 0.556 and a PSNR of 24.93, substantially outperforming existing methods. Codes will be released soon.
图像标记器是AR图像生成中的关键组件,因为它决定了丰富且结构化的视觉内容如何被编码成紧凑的表示形式。现有的基于量化的标记器(例如VQ-GAN)主要关注纹理和颜色等外观特征,但由于其基于补丁的设计,往往忽略了几何结构。在这项工作中,我们探讨了如何将更多的视觉信息融入标记器,并提出了一种名为视觉高斯量化(VGQ)的新框架。这是一种新颖的标记器范式,通过在传统视觉代码本量化框架中集成二维高斯值,显式地增强结构建模。我们的方法解决了朴素量化方法(如VQ-GAN)的固有局限性。由于基于补丁的设计和对纹理和颜色的重视,这些方法难以对结构化视觉信息进行建模。相比之下,VGQ将图像潜在值编码为二维高斯分布,通过直接建模与结构相关的参数(例如位置、旋转和尺度)来有效地捕获几何和空间结构。我们还证明,通过在标记中增加二维高斯值的密度,可以实现重建保真度的显着提高,在标记效率和视觉丰富性之间提供灵活的权衡。在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中,VGQ的重建质量强大,rFID得分为1.00。此外,通过增加标记中的二维高斯值密度,VGQ的重建能力得到显着提升,实现了最新的重建rFID得分0.556和PSNR 24.93,大幅超越了现有方法。代码很快会发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了图像分词器在AR图像生成中的重要性,并探讨了如何将其改进以更好地编码图像的结构信息。提出了一种名为视觉高斯量化的新型分词器框架(VGQ),它将二维高斯分布引入传统视觉代码本量化框架中,以提高对结构化信息的建模能力。通过编码图像潜在信息为二维高斯分布,VGQ能够捕捉几何和空间结构,并在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中取得了优秀的重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分词器是AR图像生成中的关键组件,负责将丰富的视觉内容编码为紧凑表示。
- 现有基于量化的分词器如VQ-GAN主要关注外观特征(如纹理和颜色),但忽略了图像的结构信息。
- VGQ框架通过整合二维高斯分布到传统视觉代码本量化框架中,旨在解决现有量化方法的局限性并增强结构建模能力。
- VGQ框架能捕捉几何和时空结构信息,通过建模结构相关参数如位置、旋转和尺度来实现。
- 增加二维高斯在令牌内的密度可显著提高重建保真度,并在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中实现了出色的重建质量。
- VGQ达到了先进的重建FID分数0.556和PSNR分数24.93,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图