⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
Embodied-R1: Reinforced Embodied Reasoning for General Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Yifu Yuan, Haiqin Cui, Yaoting Huang, Yibin Chen, Fei Ni, Zibin Dong, Pengyi Li, Yan Zheng, Jianye Hao
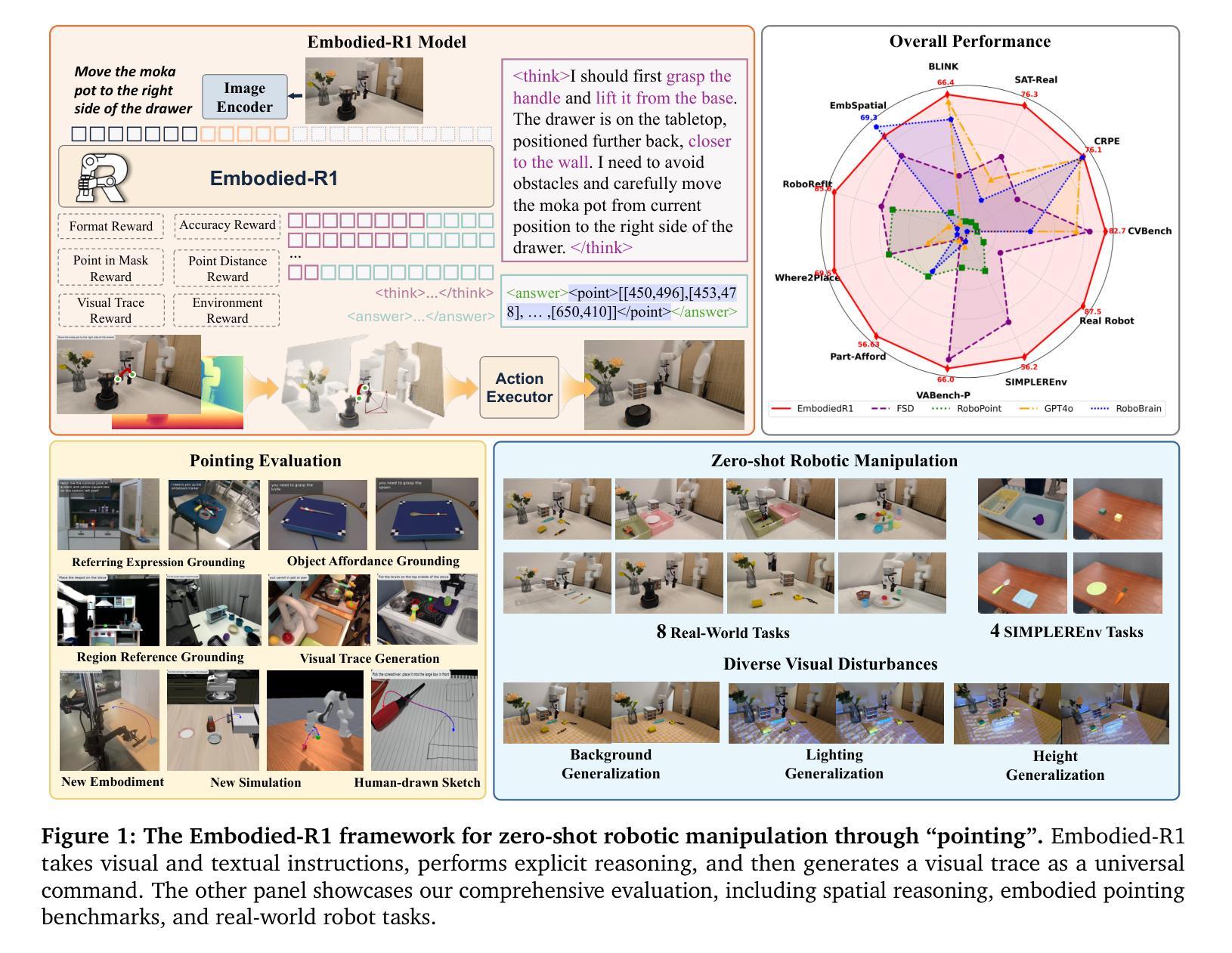
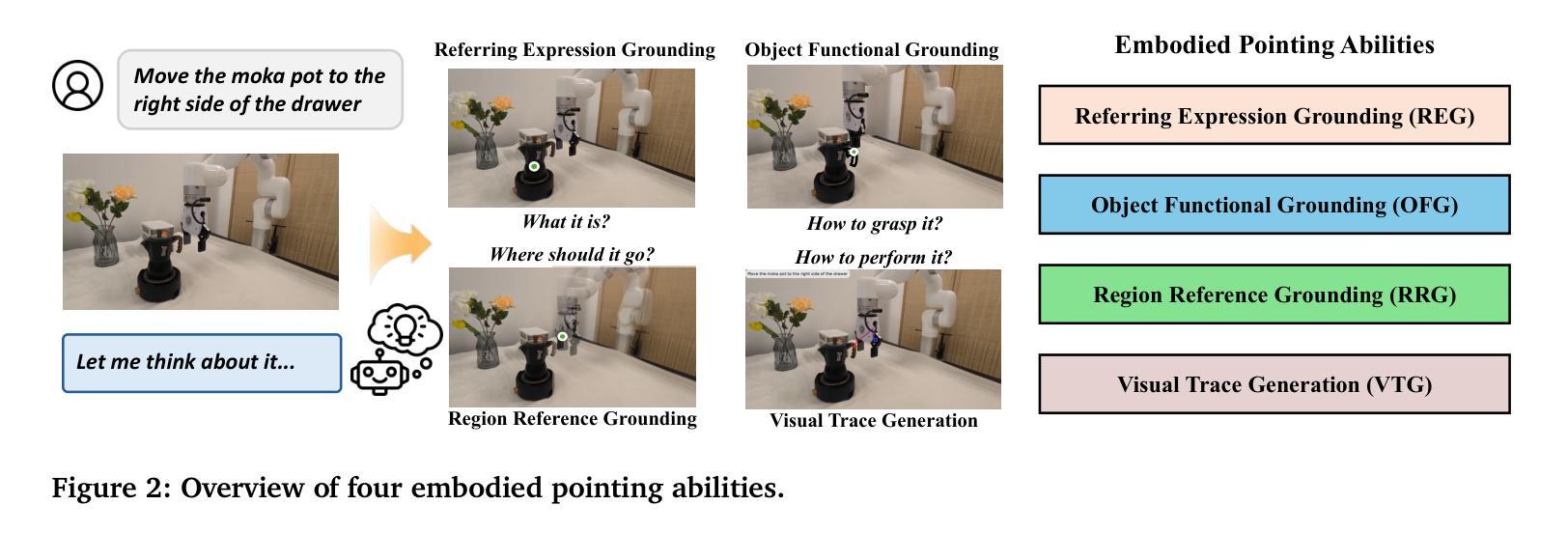
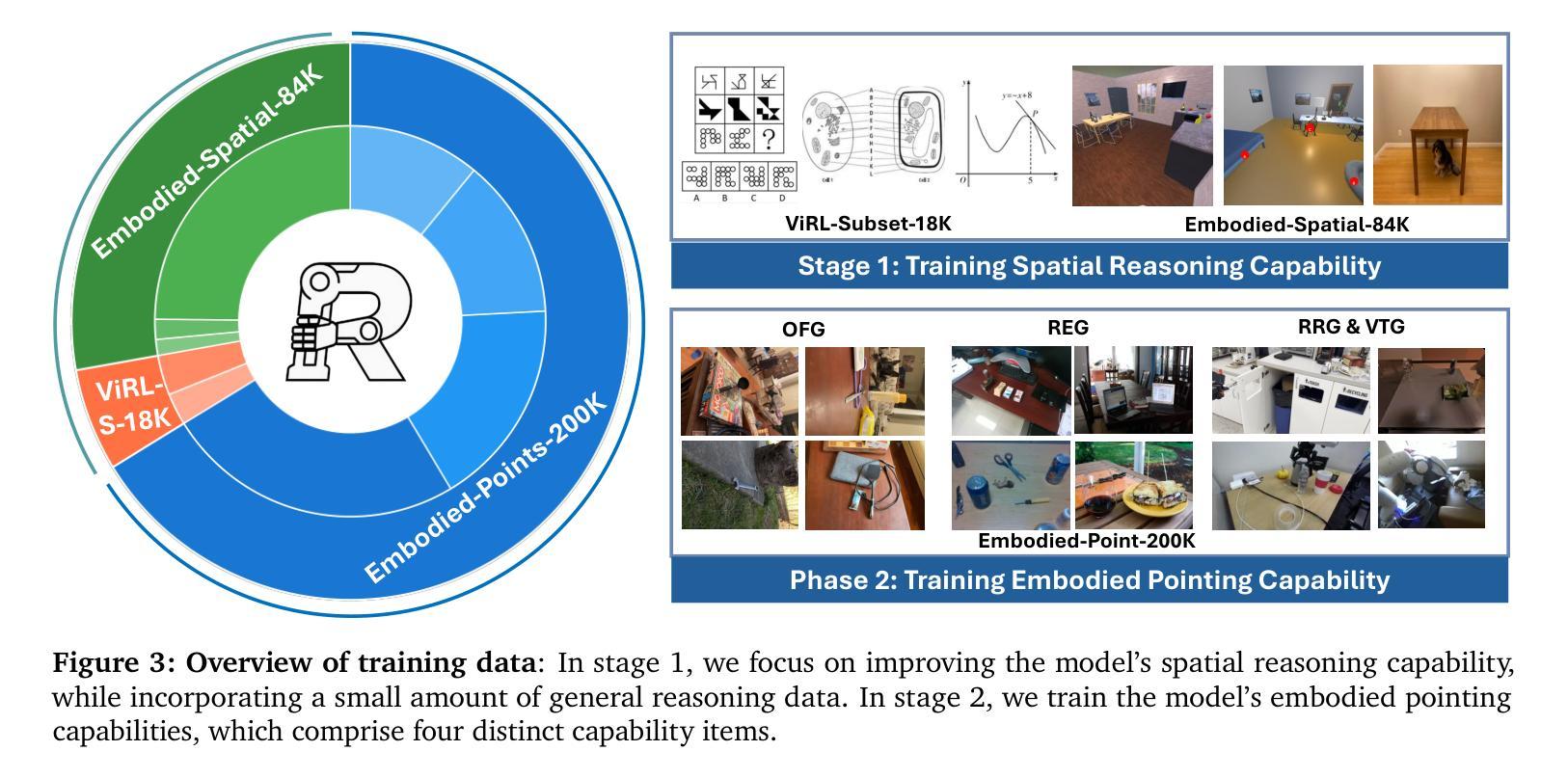
Generalization in embodied AI is hindered by the “seeing-to-doing gap,” which stems from data scarcity and embodiment heterogeneity. To address this, we pioneer “pointing” as a unified, embodiment-agnostic intermediate representation, defining four core embodied pointing abilities that bridge high-level vision-language comprehension with low-level action primitives. We introduce Embodied-R1, a 3B Vision-Language Model (VLM) specifically designed for embodied reasoning and pointing. We use a wide range of embodied and general visual reasoning datasets as sources to construct a large-scale dataset, Embodied-Points-200K, which supports key embodied pointing capabilities. We then train Embodied-R1 using a two-stage Reinforced Fine-tuning (RFT) curriculum with a specialized multi-task reward design. Embodied-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on 11 embodied spatial and pointing benchmarks. Critically, it demonstrates robust zero-shot generalization by achieving a 56.2% success rate in the SIMPLEREnv and 87.5% across 8 real-world XArm tasks without any task-specific fine-tuning, representing a 62% improvement over strong baselines. Furthermore, the model exhibits high robustness against diverse visual disturbances. Our work shows that a pointing-centric representation, combined with an RFT training paradigm, offers an effective and generalizable pathway to closing the perception-action gap in robotics.
泛在人工智能中的泛化能力受到“视觉到动作的差距”的制约,其根源在于数据稀缺和体现异质性。为了解决这个问题,我们首创了作为统一、不受体现限制的中间表示的“指向”,定义了四种核心体现指向能力,这些能力能够桥接高级视觉语言理解与低级动作原始形态。我们引入了专门为体现推理和指向而设计的Embodied-R1,这是一个3B的视觉语言模型(VLM)。我们使用各种体现和通用视觉推理数据集作为来源来构建大规模数据集Embodied-Points-200K,该数据集支持关键的体现指向能力。然后,我们使用两阶段强化微调(RFT)课程并使用特殊的多任务奖励设计来训练Embodied-R1。Embodied-R1在11个体现空间和指向基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。关键的是,它在SIMPLEREnv中实现了56.2%的成功率,并在不进行任何特定任务微调的情况下在8个真实世界的XArm任务中达到了87.5%的成功率,这代表了相比强大的基准线有62%的改进。此外,该模型对各种各样的视觉干扰表现出了很高的稳健性。我们的工作表明,以指向为中心的表示结合RFT训练范式,为缩小机器人感知-动作差距提供了一种有效且可推广的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Embodied-R1 technical report
Summary
本文探讨了有形体AI中的泛化问题,主要由于存在“看到即会操作”的鸿沟、数据稀缺和实体形态多样性等问题。为解决这些问题,本文提出了以“指向”为中心的统一、形态无关的表征方式,并定义了四种核心的有形体指向能力,以桥接高级视觉语言理解与低级动作原始形态。同时引入了专门用于有形体推理的Embodied-R1模型,通过大规模数据集Embodied-Points-200K的训练,采用两阶段强化微调(RFT)课程,实现有形体空间任务和指向任务的标杆性能。该模型展现出强大的零样本泛化能力,在未进行特定任务微调的情况下,在SIMPLEREnv任务中达到56.2%的成功率,并在XArm任务的8个真实世界场景中达到87.5%的成功率,相较于强大的基线模型有着62%的提升。此外,该模型对于各种视觉干扰也表现出高度的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 有形体AI的泛化受到“看到即会操作”鸿沟、数据稀缺和实体形态多样性的影响。
- 提出以“指向”为中心的统一、形态无关的表征方式,桥接高级视觉语言理解与低级动作原始形态。
- 介绍了Embodied-R1模型,该模型专门用于有形体推理。
- 通过大规模数据集Embodied-Points-200K训练Embodied-R1模型。
- 采用两阶段强化微调(RFT)课程,实现有形体空间任务和指向任务的标杆性能。
- Embodied-R1模型展现出强大的零样本泛化能力,具有较高的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

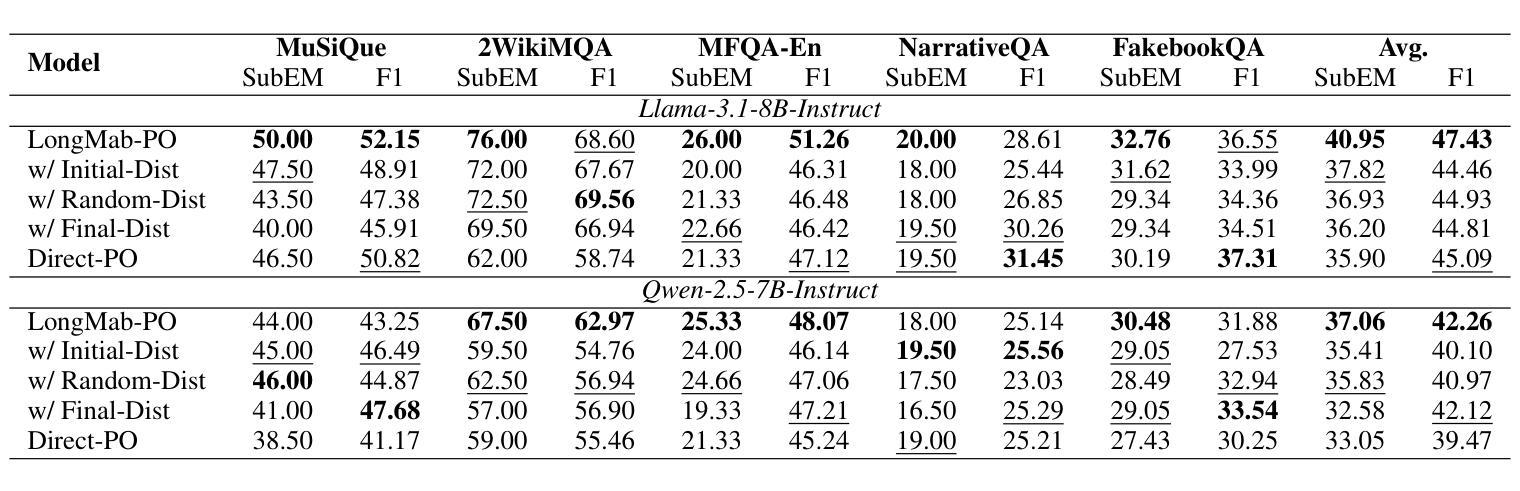
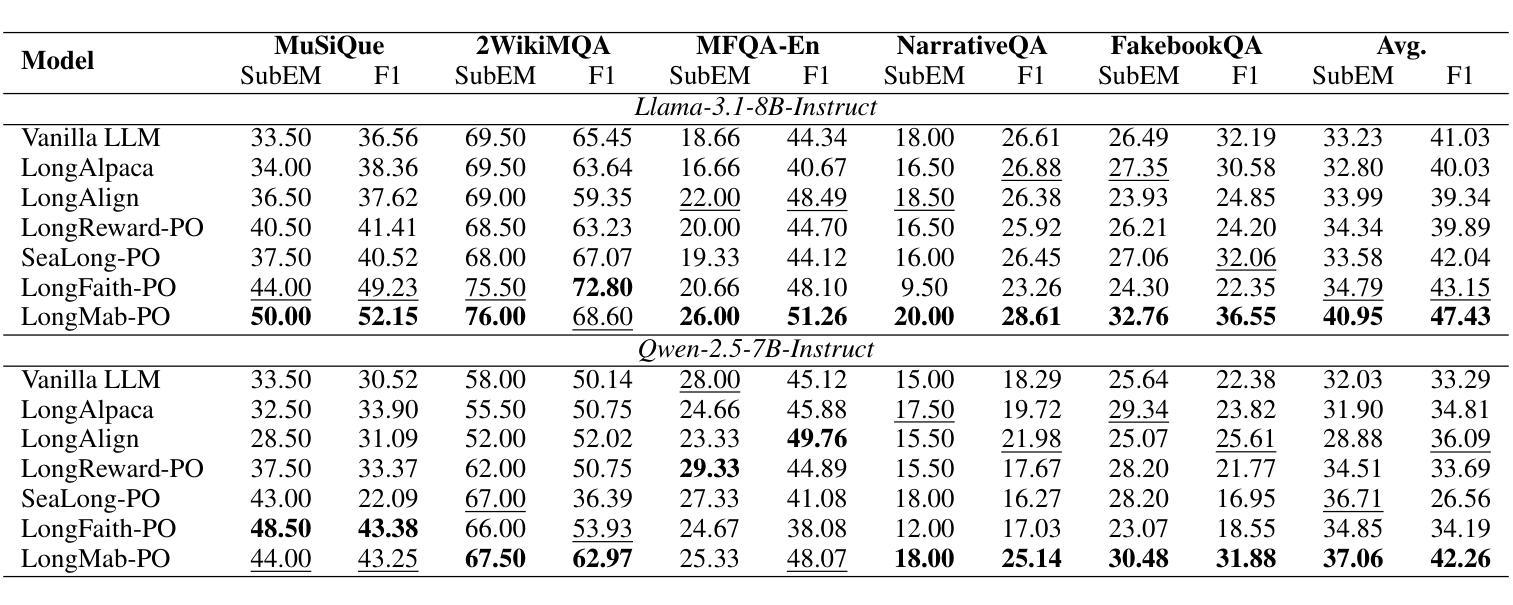
Chunks as Arms: Multi-Armed Bandit-Guided Sampling for Long-Context LLM Preference Optimization
Authors:Shaohua Duan, Xinze Li, Zhenghao Liu, Xiaoyuan Yi, Yukun Yan, Shuo Wang, Yu Gu, Ge Yu, Maosong Sun
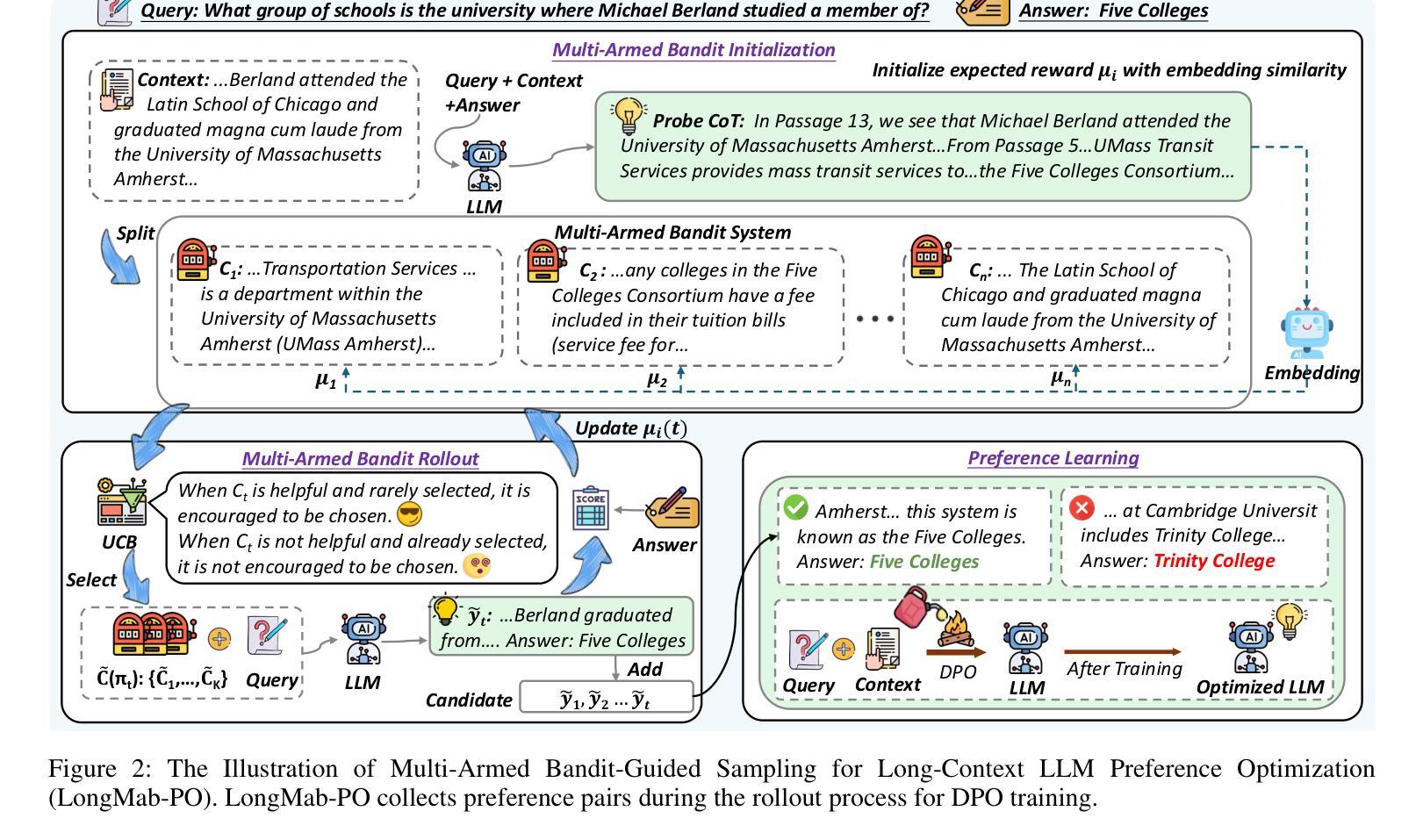
Long-context modeling is critical for a wide range of real-world tasks, including long-context question answering, summarization, and complex reasoning tasks. Recent studies have explored fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with synthetic data to enhance their long-context capabilities. However, the effectiveness of such approaches is often limited by the low diversity and factual inconsistencies in the generated data. To address these challenges, we propose LongMab-PO, a novel framework that leverages a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) rollout strategy to identify the most informative chunks from the given long context for sampling high-quality and diverse responses and constructing preference data pairs for Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) training. Specifically, we treat context chunks as arms of MAB, select chunks based on their expected reward scores to input into LLMs to generate responses, and iteratively update these scores based on reward feedback. This exploration and exploitation process enables the model to focus on the most relevant context segments, thereby generating and collecting high-quality and diverse responses. Finally, we collect these generated responses from the rollout process and apply the DPO method to further optimize the LLM. Experimental results show that LongMab-PO significantly improves the diversity and quality of preference data pairs, achieving state-of-the-art performance on long-context reasoning benchmarks. All code and data will be released on https://github.com/NEUIR/LongMab-PO.
长文本建模对于一系列现实世界任务至关重要,包括长文本问答、摘要和复杂推理任务等。近期的研究尝试通过合成数据微调大型语言模型(LLM)以增强其处理长文本的能力。然而,此类方法的效用往往受限于生成数据的多样性缺乏和事实性不一致。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了LongMab-PO这一新型框架,它运用多臂老虎机(MAB)滚动策略来识别给定长文本中最具信息量的部分,以采样高质量、多样化的答案,并构建偏好数据对用于直接偏好优化(DPO)训练。具体来说,我们将文本片段视为老虎机的臂膀,根据预期的奖励分数选择片段输入LLM生成答案,并根据反馈奖励迭代更新这些分数。这种探索与利用的过程使模型能够专注于最相关的文本片段,从而生成和收集高质量、多样化的答案。最后,我们收集这些生成答案并应用DPO方法来进一步优化LLM。实验结果表明,LongMab-PO显著提高了偏好数据对的多样性和质量,在长文本推理基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。所有代码和数据将在https://github.com/NEUIR/LongMab-PO上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
长语境建模对于包括长语境问答、摘要和复杂推理任务在内的多种实际任务至关重要。近期研究尝试通过合成数据微调大型语言模型(LLM)以增强其长语境能力,但这种方法的效果受限于生成数据的低多样性和事实性不一致。为此,我们提出LongMab-PO框架,利用多臂老虎机(MAB)策略识别最有信息量的长语境片段,以采样高质量、多样化的响应,并构建偏好数据对进行直接偏好优化(DPO)训练。实验结果显示,LongMab-PO能显著提高偏好数据对的多样性和质量,在长短语境推理基准测试中达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 长语境建模对于多种实际任务至关重要。
- 近期研究通过合成数据微调大型语言模型以增强其长语境能力,但存在生成数据多样性和事实性不一致的问题。
- 提出LongMab-PO框架,利用多臂老虎机策略识别最有信息量的长语境片段。
- 通过采样高质量、多样化的响应,构建偏好数据对进行直接偏好优化训练。
- LongMab-PO能显著提高偏好数据对的多样性和质量。
点此查看论文截图

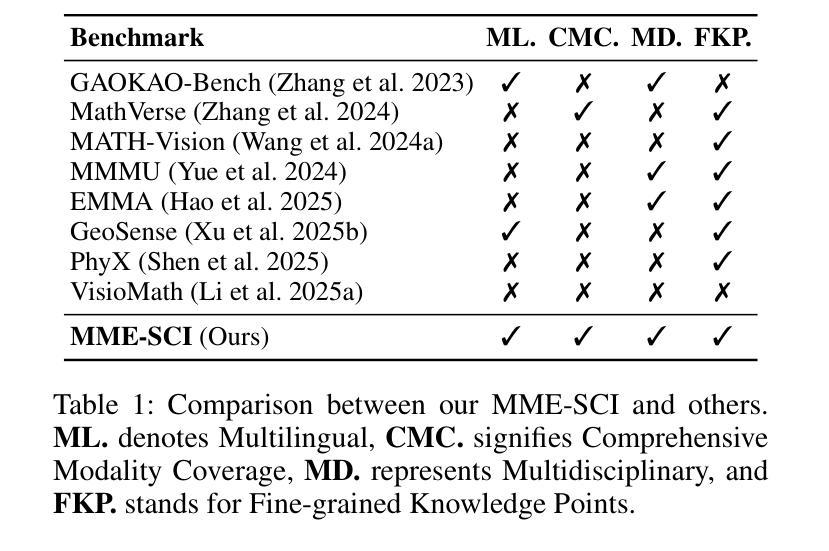
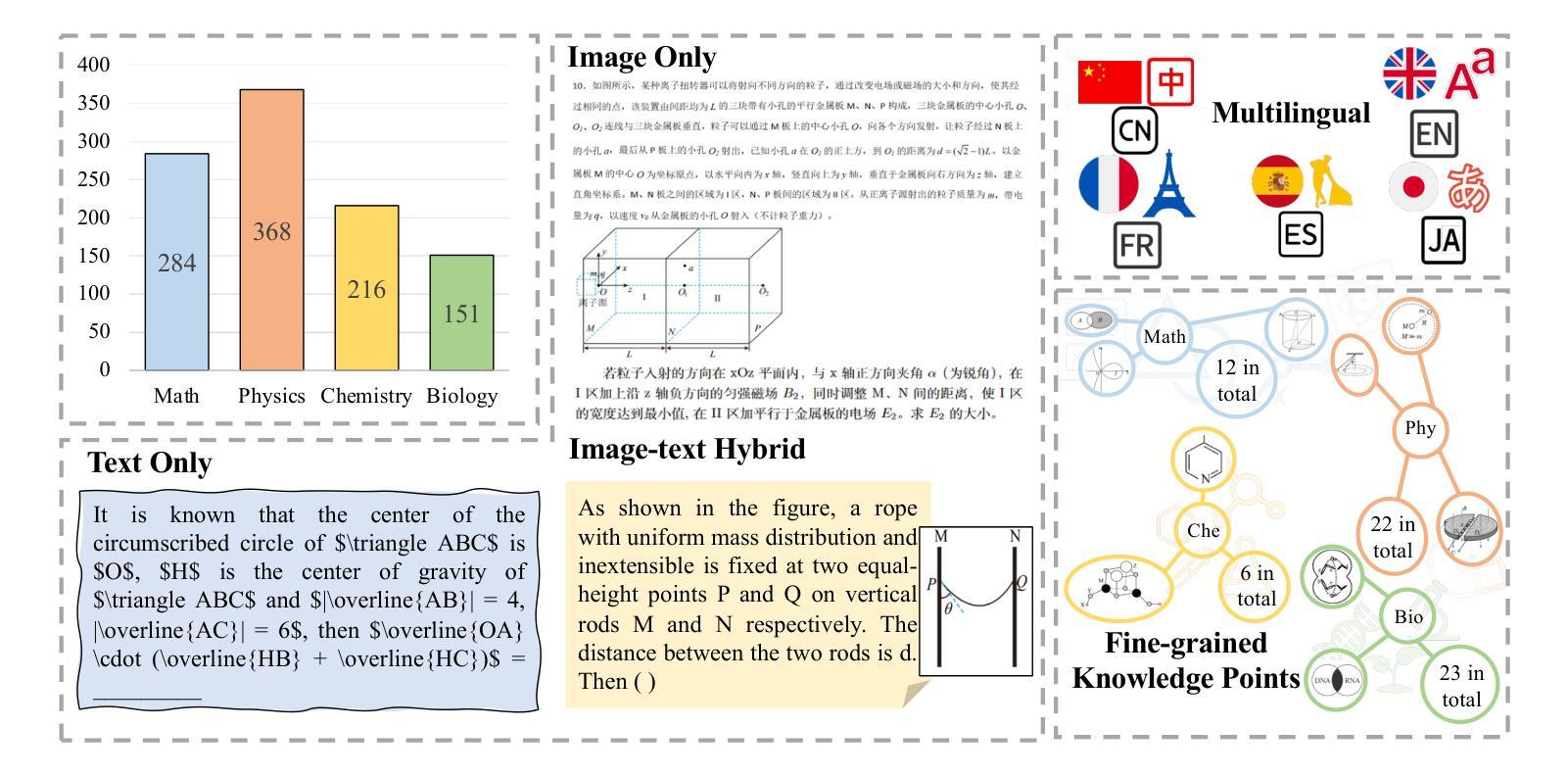
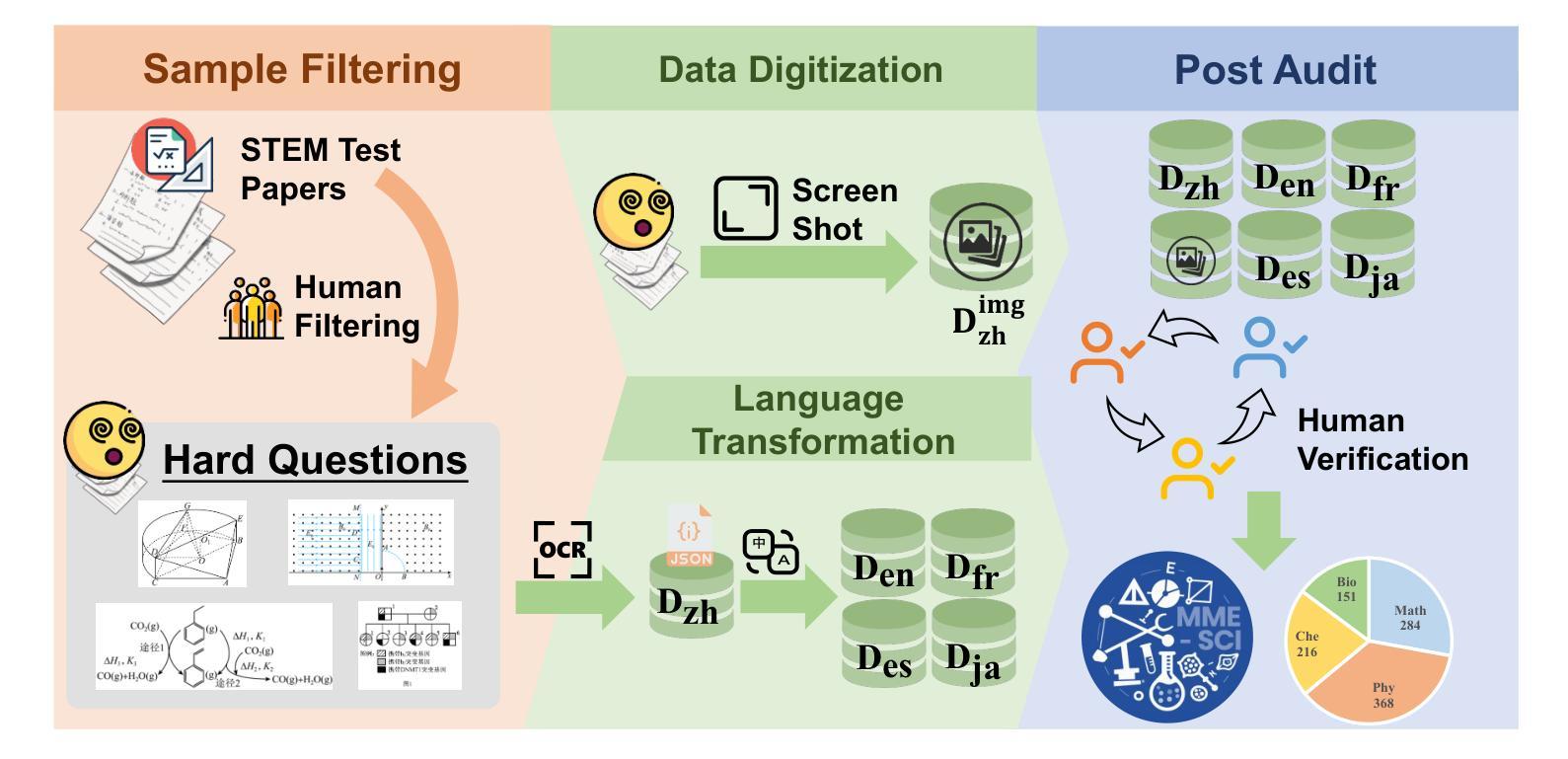
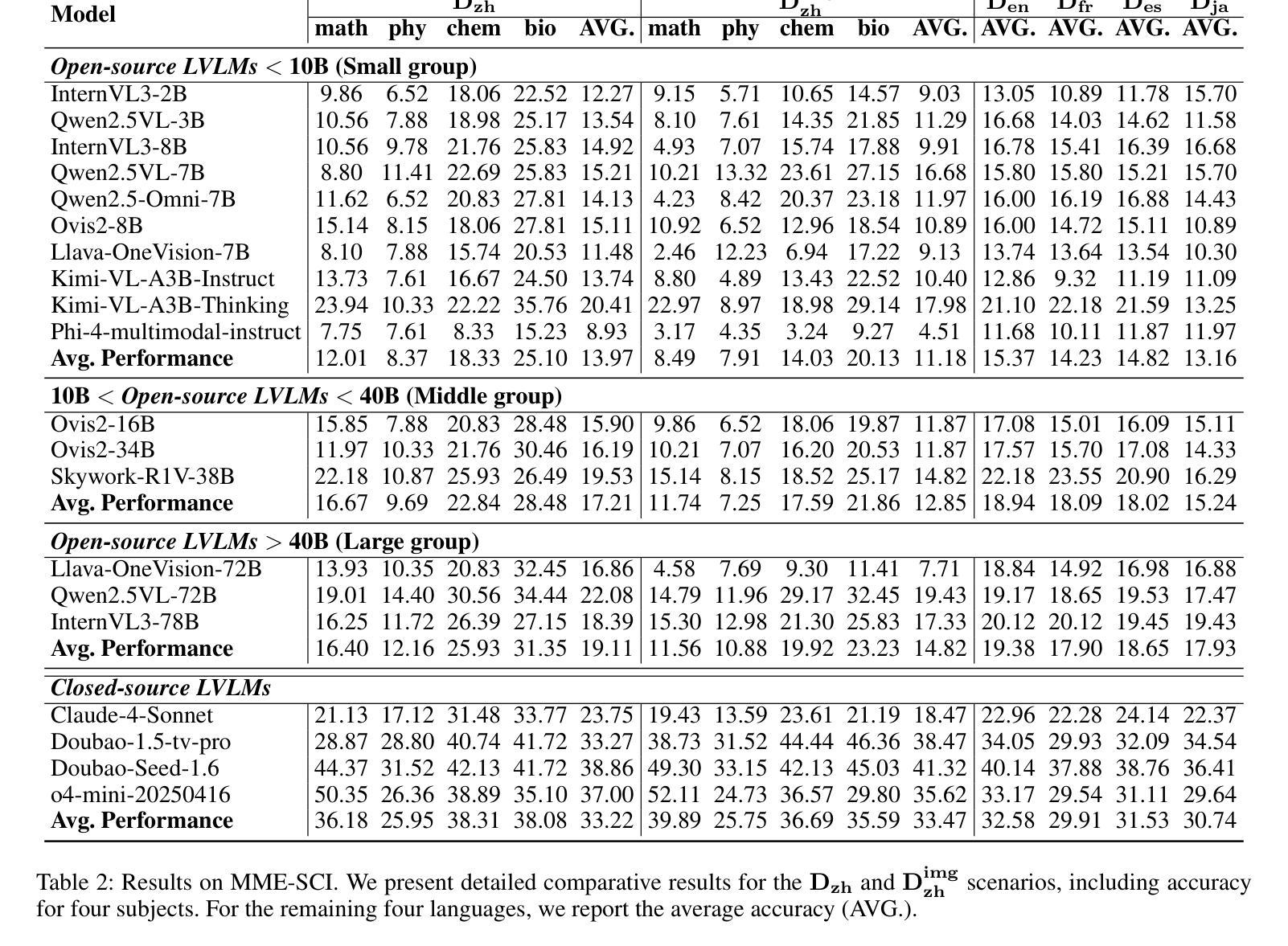
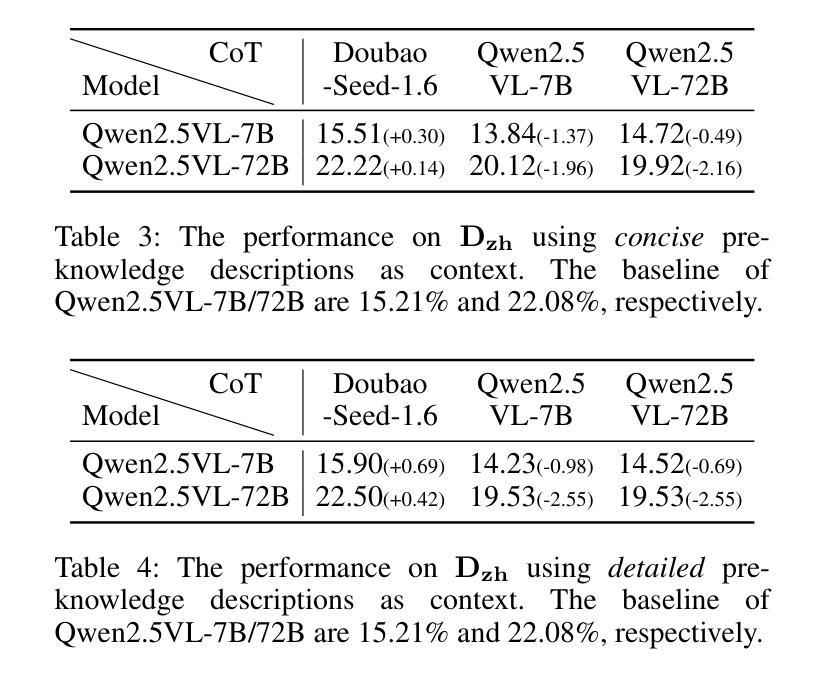
MME-SCI: A Comprehensive and Challenging Science Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Jiacheng Ruan, Dan Jiang, Xian Gao, Ting Liu, Yuzhuo Fu, Yangyang Kang
Recently, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved significant advancements across various domains, and corresponding evaluation benchmarks have been continuously refined and improved. In this process, benchmarks in the scientific domain have played an important role in assessing the reasoning capabilities of MLLMs. However, existing benchmarks still face three key challenges: 1) Insufficient evaluation of models’ reasoning abilities in multilingual scenarios; 2) Inadequate assessment of MLLMs’ comprehensive modality coverage; 3) Lack of fine-grained annotation of scientific knowledge points. To address these gaps, we propose MME-SCI, a comprehensive and challenging benchmark. We carefully collected 1,019 high-quality question-answer pairs, which involve 3 distinct evaluation modes. These pairs cover four subjects, namely mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology, and support five languages: Chinese, English, French, Spanish, and Japanese. We conducted extensive experiments on 16 open-source models and 4 closed-source models, and the results demonstrate that MME-SCI is widely challenging for existing MLLMs. For instance, under the Image-only evaluation mode, o4-mini achieved accuracy of only 52.11%, 24.73%, 36.57%, and 29.80% in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology, respectively, indicating a significantly higher difficulty level compared to existing benchmarks. More importantly, using MME-SCI’s multilingual and fine-grained knowledge attributes, we analyzed existing models’ performance in depth and identified their weaknesses in specific domains. The Data and Evaluation Code are available at https://github.com/JCruan519/MME-SCI.
最近,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各个领域都取得了显著的进展,相应的评估基准也在持续完善和改进。在这一过程中,科学领域的基准评估在评估MLLMs的推理能力方面发挥了重要作用。然而,现有基准仍面临三个关键挑战:1)在多语种场景下对模型的推理能力评估不足;2)对MLLMs的综合模态覆盖评估不足;3)科学知识点的精细标注缺乏。为了解决这些空白,我们提出了MME-SCI这一全面且具有挑战性的基准。我们精心收集了1019组高质量的问题答案对,涉及3种独特的评估模式。这些对涵盖了数学、物理、化学和生物四门学科,支持五种语言:中文、英文、法语、西班牙语和日语。我们对16个开源模型和4个闭源模型进行了广泛实验,结果表明MME-SCI对现有MLLMs具有广泛挑战性。例如,在仅图像评估模式下,o4-mini在数学、物理、化学和生物方面的准确率分别为52.11%、24.73%、36.57%和29.80%,表明其难度水平显著高于现有基准。更重要的是,使用MME-SCI的多语种和精细知识点属性,我们深入分析了现有模型的性能,并识别了它们在特定领域的弱点。数据和评估代码可通过https://github.com/JCruan519/MME-SCI获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, work in progress
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在科研领域的评估基准所面临的挑战,并提出了MME-SCI这一全面且具有挑战性的新基准。该基准收集了1019组高质量的问题答案对,涉及数学、物理、化学和生物四个学科,支持五种语言。实验结果显示,现有模型在MME-SCI基准下表现挑战,且通过该基准深入分析了模型的性能并识别了其弱点。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在科研领域评估基准上面临挑战。
- 现有基准在评估模型的跨语言推理能力、多模态覆盖完整性以及科学知识点的精细标注方面存在不足。
- MME-SCI基准被提出以解决现有挑战,包含1019组高质量问题答案对,覆盖数学、物理、化学和生物四个学科,支持五种语言。
- 广泛实验表明,MME-SCI基准对现有MLLMs具有挑战性。
- 在图像仅评价模式下,某些模型在数学、物理、化学和生物方面的准确率较低,表明难度较高。
- MME-SCI基准深入分析了现有模型的性能,并识别了其在特定领域的弱点。
点此查看论文截图

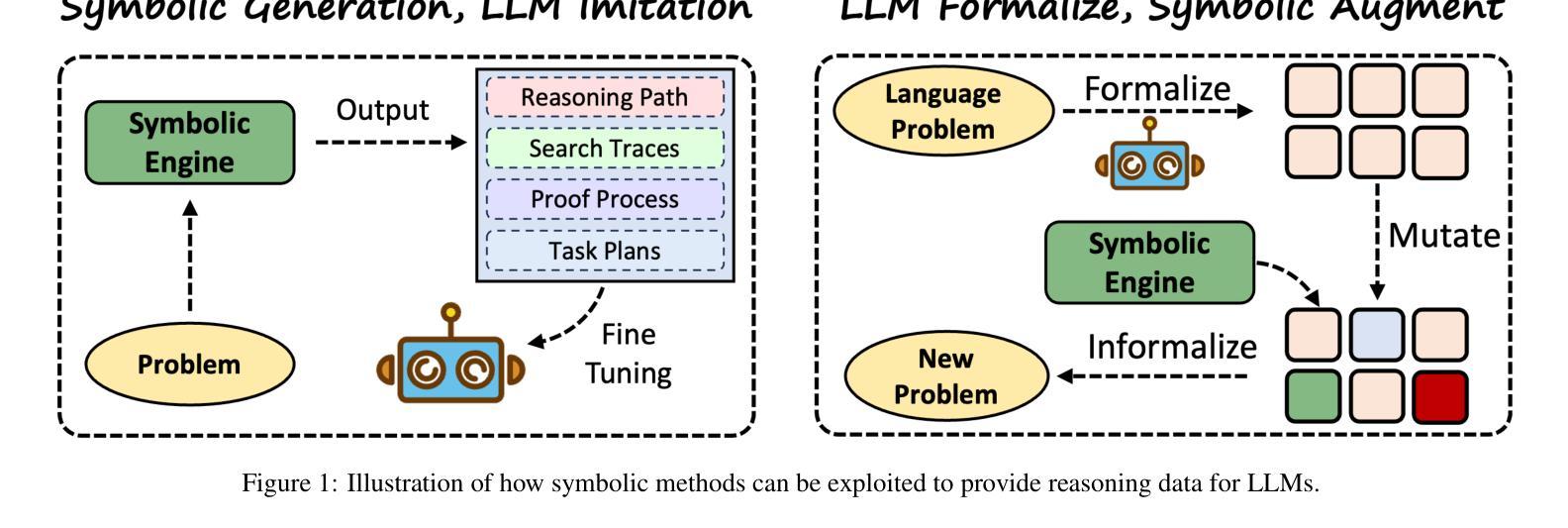
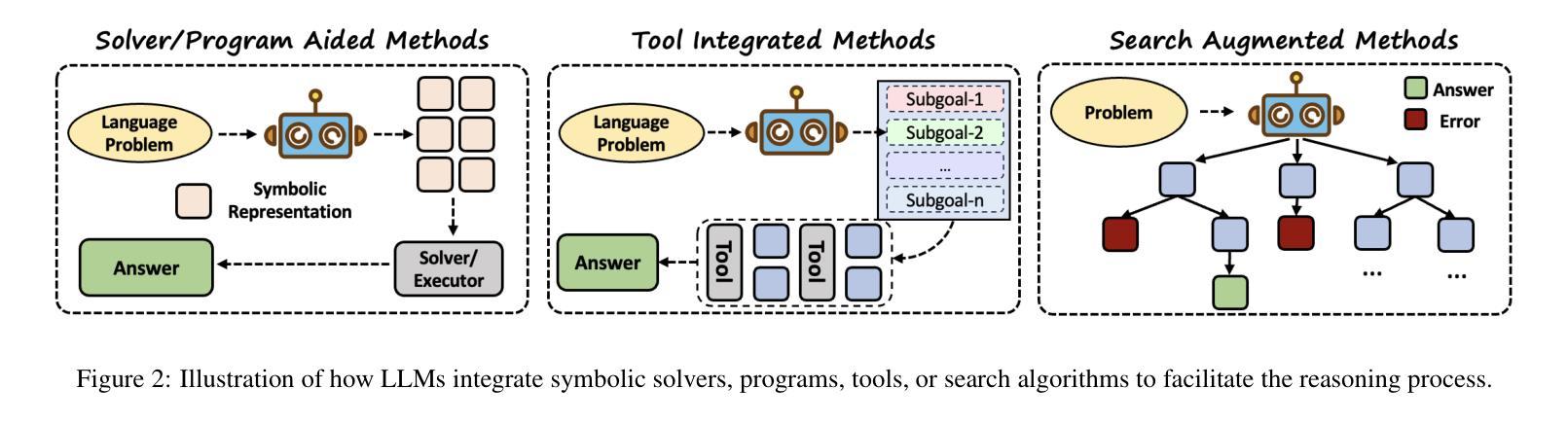
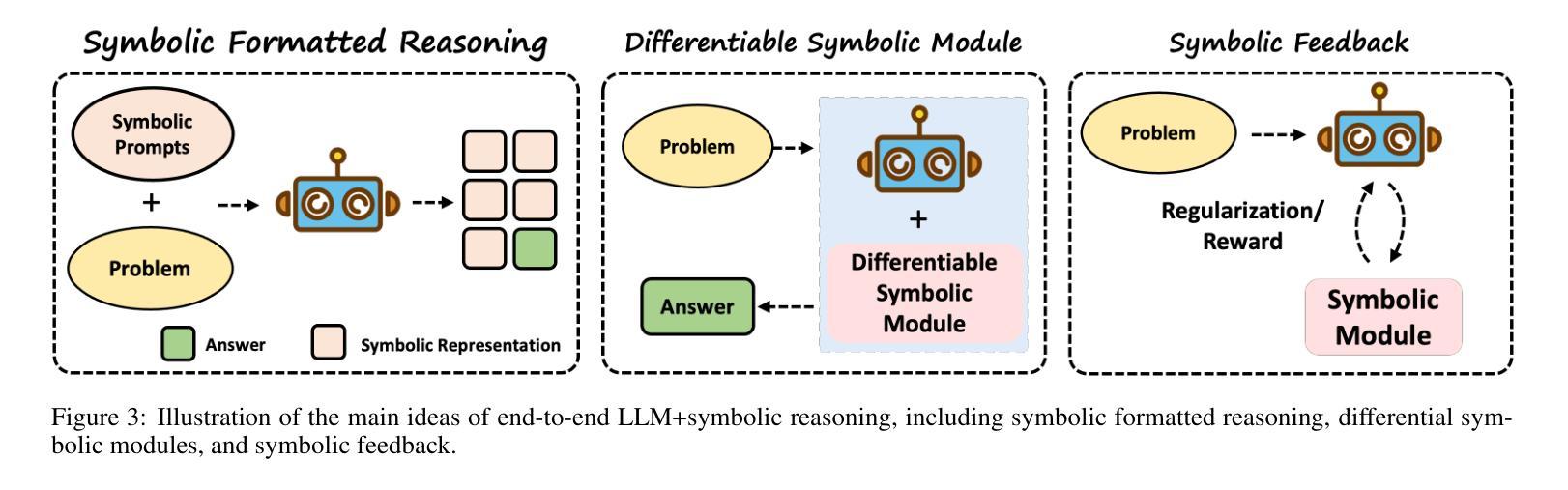
Neuro-Symbolic Artificial Intelligence: Towards Improving the Reasoning Abilities of Large Language Models
Authors:Xiao-Wen Yang, Jie-Jing Shao, Lan-Zhe Guo, Bo-Wen Zhang, Zhi Zhou, Lin-Han Jia, Wang-Zhou Dai, Yu-Feng Li
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promising results across various tasks, yet their reasoning capabilities remain a fundamental challenge. Developing AI systems with strong reasoning capabilities is regarded as a crucial milestone in the pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and has garnered considerable attention from both academia and industry. Various techniques have been explored to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, with neuro-symbolic approaches being a particularly promising way. This paper comprehensively reviews recent developments in neuro-symbolic approaches for enhancing LLM reasoning. We first present a formalization of reasoning tasks and give a brief introduction to the neurosymbolic learning paradigm. Then, we discuss neuro-symbolic methods for improving the reasoning capabilities of LLMs from three perspectives: Symbolic->LLM, LLM->Symbolic, and LLM+Symbolic. Finally, we discuss several key challenges and promising future directions. We have also released a GitHub repository including papers and resources related to this survey: https://github.com/LAMDASZ-ML/Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-with-NeSy.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在各种任务中展现出了有前景的结果,但它们的推理能力仍然是一个基本挑战。开发具有强大推理能力的AI系统被认为是实现通用人工智能(AGI)追求过程中的一个重要里程碑,并引起了学术界和工业界的极大关注。为了增强LLMs的推理能力,已经探索了各种技术,其中神经符号方法是一种特别有前景的方式。本文全面回顾了神经符号方法在提高LLM推理能力方面的最新发展。我们首先形式化推理任务,并简要介绍神经符号学习范式。然后,我们从符号到LLM、LLM到符号和LLM+符号三个角度,讨论神经符号方法在增强LLMs推理能力方面的应用。最后,我们讨论了几个关键挑战和未来的有前途的方向。我们还发布了一个GitHub仓库,包含与此调查相关的论文和资源:https://github.com/LAMDASZ-ML/Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-with-NeSy。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures, IJCAI 2025 Survey Track
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在各项任务中展现出良好性能,但其推理能力仍是核心挑战。开发具备强大推理能力的AI系统是迈向通用人工智能(AGI)的重要里程碑,引起学术界和工业界的广泛关注。为提升LLMs的推理能力,研究者探索了多种技术,其中神经符号方法前景特别光明。本文全面综述了近期用于增强LLM推理能力的神经符号方法。文章首先形式化推理任务,并简要介绍神经符号学习范式。接着,从符号到LLM、LLM到符号和LLM+符号三个角度,讨论提升LLM推理能力的神经符号方法。最后,文章还探讨了关键挑战和未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力是核心挑战。
- 开发具备强大推理能力的AI系统是迈向通用人工智能(AGI)的重要里程碑。
- 神经符号方法是一种提升LLMs推理能力的有前途的技术。
- 文章形式化推理任务,并介绍了神经符号学习范式。
- 神经符号方法可以从符号到LLM、LLM到符号和LLM+符号三个角度提升LLM的推理能力。
- 当前还存在一些关键挑战需要解决。
点此查看论文截图

Input Time Scaling
Authors:Rapheal Huang, Weilong Guo
Current Large Language Models (LLMs) are usually post-trained on large-scale carefully curated datasets (data & training scaling) and doing reasoning in test time (inference time scaling). In this work, we present a new scaling paradigm, Input Time Scaling, to complement previous scaling methods by putting resources on queries (input time). During training and testing, we combine meta-knowledge from LLMs to refine inputs with different strategies. We also find a new phenomenon, training-testing co-design there. We need to apply query strategies during both training and testing. Only applying strategies on training or testing would seriously degrade the performance. We are also surprised to find that seemingly low data quality datasets can gain high performance. Adding irrelevant information to the queries, randomly selecting examples from a minimally filtered dataset, can even perform the best. These findings contradict the widely held inductive bias, “garbage in, garbage out”. Curating datasets with seemingly high-quality data can even potentially limit the performance ceiling. In addition, models trained on more data with similar quality (15k VS 1k) perform worse, simple dataset size scaling should also be carefully inspected. The good news is that our findings are compatible with the Less is More phenomenon. A small set of examples is enough to evoke high-level reasoning ability. With experiments on models trained on Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct, we are able to reach SOTA performance among 32B models on AIME24(76.7%) and AIME25(76.7%) pass@1. We can further achieve AIME24(76.7%) and AIME25(80%) with a majority vote of three models. Starting from DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B, the best result would be 86.7% on AIME24 and 76.7% on AIME25. To facilitate reproducibility and further research, we are working on open-source our datasets, data pipelines, evaluation results, and checkpoints.
当前的大型语言模型(LLM)通常是在大规模精心策划的数据集上进行后训练(数据与训练规模扩大),并在测试时间(推理时间规模)进行推理。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的扩展范式——输入时间扩展,以补充之前的扩展方法,将资源集中在查询(输入时间)上。在训练和测试过程中,我们采用LLM的元知识,通过不同的策略来优化输入。我们还发现了一个新现象,即训练与测试的协同设计。我们需要在训练和测试期间都应用查询策略。仅在训练或测试期间应用策略会严重降低性能。令人惊讶的是,我们发现即使是看似数据质量不高的数据集也能获得高性能。向查询中添加无关信息,从经过轻微过滤的数据集中随机选择示例,甚至可能表现最佳。这些发现与普遍存在的归纳偏见“垃圾进,垃圾出”相矛盾。使用看似高质量数据的数据集甚至可能限制性能上限。另外,在类似质量的更多数据上训练的模型(15k对1k)表现更差,因此也应谨慎检查简单的数据集规模扩展。好消息是,我们的研究与“少即是多”现象相吻合。少量示例足以激发高级推理能力。通过在Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct上训练的模型进行的实验,我们在32B模型的AIME24(76.7%)和AIME25(76.7%)上达到了最新性能。使用三个模型的大多数投票,我们可以进一步达到AIME24(76.7%)和AIME25(80%)。从DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B开始,AIME24的最佳结果将达到86.7%,AIME25的结果将达到76.7%。为了促进可重复性和进一步研究,我们正在开源我们的数据集、数据管道、评估结果和检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的缩放范式——输入时间缩放,以补充先前的缩放方法。通过查询(输入时间)分配资源,结合LLM的元知识对输入进行精细化处理。研究发现训练与测试的协同设计重要性,在两者中都应用查询策略才能取得最佳性能。此外,研究发现低质量数据集也能取得高性能,添加无关信息或随机选择例子可能效果更好,这与普遍偏见相反。模型在类似质量数据上的性能并非数据规模越大越好。实验证明,在小规模数据集上训练模型也能激发高级推理能力。通过开源数据集等资源促进复制性和进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了新的缩放范式——输入时间缩放,关注查询(输入时间)资源的分配,结合LLM的元知识优化输入。
- 发现训练与测试的协同设计重要性,需在两者中都应用查询策略。
- 低质量数据集也能取得高性能,添加无关信息或随机选择例子可能效果更好,挑战了“垃圾进,垃圾出”的偏见。
- 模型性能并非数据规模越大越好,类似质量数据的简单数据集规模缩放也需要谨慎检查。
- 小规模数据集能激发高级推理能力,与“少即是多”现象兼容。
- 使用Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct模型在AIME24和AIME25上取得了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Bounding Causal Effects and Counterfactuals
Authors:Tobias Maringgele
Causal inference often hinges on strong assumptions - such as no unmeasured confounding or perfect compliance - that are rarely satisfied in practice. Partial identification offers a principled alternative: instead of relying on unverifiable assumptions to estimate causal effects precisely, it derives bounds that reflect the uncertainty inherent in the data. Despite its theoretical appeal, partial identification remains underutilized in applied work, in part due to the fragmented nature of existing methods and the lack of practical guidance. This thesis addresses these challenges by systematically comparing a diverse set of bounding algorithms across multiple causal scenarios. We implement, extend, and unify state-of-the-art methods - including symbolic, optimization-based, and information-theoretic approaches - within a common evaluation framework. In particular, we propose an extension of a recently introduced entropy-bounded method, making it applicable to counterfactual queries such as the Probability of Necessity and Sufficiency (PNS). Our empirical study spans thousands of randomized simulations involving both discrete and continuous data-generating processes. We assess each method in terms of bound tightness, computational efficiency, and robustness to assumption violations. To support practitioners, we distill our findings into a practical decision tree for algorithm selection and train a machine learning model to predict the best-performing method based on observable data characteristics. All implementations are released as part of an open-source Python package, CausalBoundingEngine, which enables users to apply and compare bounding methods through a unified interface.
因果推断往往依赖于强有力的假设——如无未测量的混杂因素或完美遵循——这些假设在实践中很少得到满足。部分识别提供了一种有原则性的替代方案:它不再依赖无法验证的假设来精确估计因果关系的影响,而是推导出反映数据固有不确定性的边界。尽管它在理论上很有吸引力,但在实际应用中,部分识别仍然使用不足,部分原因是现有方法的碎片化以及缺乏实际指导。本论文通过系统地比较多个因果场景下一组多样化的边界算法来解决这些挑战。我们在一个统一的评估框架内实现了最先进的方法,对其进行扩展和统一,包括符号法、优化法和信息理论方法。特别是,我们对最近引入的熵边界方法进行了扩展,使其适用于必然性概率和充分性概率(PNS)等反事实查询。我们的实证研究涵盖了成千上万涉及离散和连续数据生成过程的随机模拟。我们根据边界紧密性、计算效率和违反假设的稳健性来评估每种方法。为了支持实践者,我们将研究结果总结成实用的决策树,用于算法选择,并训练机器学习模型,根据可观察的数据特征预测表现最佳的方法。所有实现都作为开源Python软件包的一部分发布,即因果边界引擎,它使用户能够通过统一接口应用和比较边界方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Bachelor’s thesis, Technical University of Munich, 2025. 102 pages, 20 figures
Summary
本文介绍了因果推断中基于假设的方法存在的问题,如假设难以满足等。部分识别作为一种替代方法,通过推导反映数据固有不确定性的边界来估计因果效应,而不是依赖无法验证的假设。尽管在理论上有其吸引力,部分识别在实际应用中仍然使用不足。本文主要解决了这个问题,系统性地比较了多种边界算法在多个因果场景下的表现,提出并完善了一种新发展的熵边界方法,使其适用于反事实查询等场景。通过大量的随机模拟评估了各种方法的边界紧密性、计算效率和假设违反的稳健性。同时,本文还提供了一种决策树和机器学习模型来支持从业者选择最佳算法。所有实现都被整合到一个开源的Python包中,便于用户应用和比较各种边界方法。
Key Takeaways
- 因果推断依赖于强假设,这些假设在实践中很少满足。
- 部分识别作为一种替代方法,通过推导反映数据不确定性的边界来估计因果效应。
- 本文系统地比较了多种边界算法在多个因果场景下的表现。
- 提出了一种改进的熵边界方法,适用于反事实查询等场景。
- 通过随机模拟评估了各种方法的性能。
- 提供了一种决策树和机器学习模型来帮助从业者选择最佳算法。
点此查看论文截图

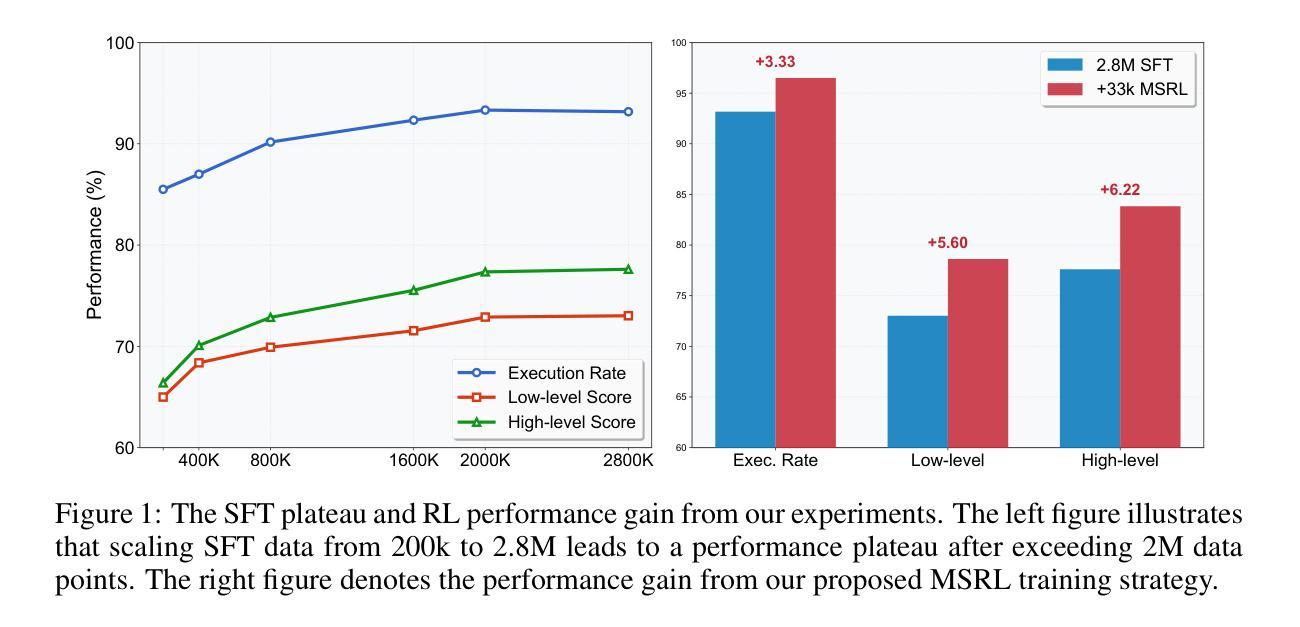
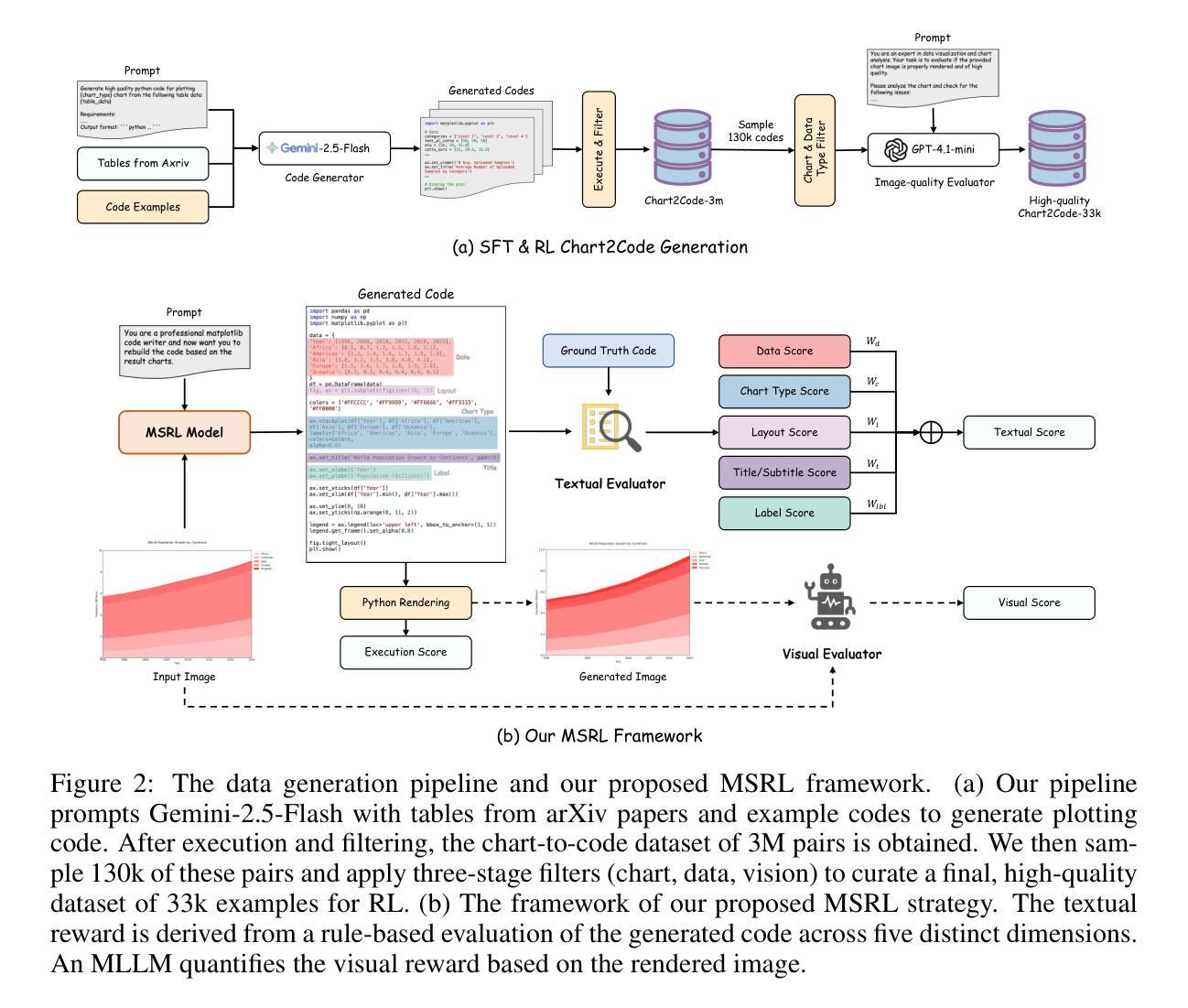
Breaking the SFT Plateau: Multimodal Structured Reinforcement Learning for Chart-to-Code Generation
Authors:Lei Chen, Xuanle Zhao, Zhixiong Zeng, Jing Huang, Liming Zheng, Yufeng Zhong, Lin Ma
While reinforcement learning (RL) has proven highly effective for general reasoning in vision-language models, its application to tasks requiring in-depth understanding of information-rich images and generation of structured outputs remains underexplored. Chart-to-code generation exemplifies this challenge, demanding complex reasoning over visual charts to generate structured code. Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) alone is often insufficient, highlighting the need for effective RL strategies that appropriately reward structured outputs. We systematically investigate the performance plateau in SFT through large-scale experiments and propose Multimodal Structured Reinforcement Learning (MSRL) for chart-to-code generation, which substantially breaks through this plateau. We construct the largest training corpus to date, containing 3 million chart-code pairs from real-world arXiv tables to mitigate simplistic patterns of prior synthetic data. Despite reaching state-of-the-art performance, our experiments show that scaling SFT data eventually hits a plateau where further increases yield negligible improvements. Our MSRL method leverages a multi-granularity structured reward system using multimodal textual and visual feedback. At the textual level, rule-based rewards validate fine-grained code details. At the visual level, model-based rewards assess structural similarity by rendering generated code into images and employing an evaluator model. We implement this within a two-stage curriculum for training stability. Results demonstrate that MSRL significantly breaks the SFT plateau, improving high-level metrics by 6.2% and 9.9% on ChartMimic and ReachQA benchmarks respectively, achieving competitive performance with advanced closed-source models.
虽然强化学习(RL)在视觉语言模型的通用推理中已被证明是非常有效的,但其在需要深入理解信息丰富的图像和生成结构化输出的任务中的应用仍然被探索得不够深入。图表到代码的生成就体现了这一挑战,它要求通过视觉图表进行复杂推理来生成结构化代码。仅仅使用监督微调(SFT)往往是不够的,这突显了需要有效的RL策略来适当奖励结构化输出的必要性。我们通过大规模实验系统地研究了SFT的性能瓶颈,并针对图表到代码生成提出了多模态结构化强化学习(MSRL),这实质性地突破了这一瓶颈。我们构建了迄今为止最大的训练语料库,包含来自现实世界arXiv表格的300万张图表和代码对,以减轻先前合成数据的简单模式。尽管达到了最先进的性能,我们的实验表明,扩大SFT数据最终会达到一个平台期,在此之后,进一步的增加只会带来微乎其微的改进。我们的MSRL方法利用多粒度结构化奖励系统,使用多模态文本和视觉反馈。在文本层面,基于规则的奖励验证了精细的代码细节。在视觉层面,基于模型的奖励通过将生成的代码呈现为图像并使用评估模型来评估结构相似性。我们在一个两阶段的课程中实现了这一点,以确保训练稳定性。结果表明,MSRL显著突破了SFT平台期,在ChartMimic和ReachQA基准测试上,高级指标的改进分别为6.2%和9.9%,与先进的封闭源代码模型相比具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF technical report
Summary
本文探讨了强化学习在视觉语言模型中的通用推理能力,尤其是在处理信息丰富的图像深度理解和生成结构化输出任务中的应用。针对图表到代码生成这一挑战,文章指出监督微调(SFT)的局限性,并介绍了多模态结构化强化学习(MSRL)的新方法。通过大规模实验,作者构建了包含真实arXiv表格的3百万图表代码对训练语料库,并采用多粒度结构化奖励系统,利用文本和视觉反馈。实验结果显示,MSRL方法在图表模仿和ReachQA基准测试上的高级指标分别提高了6.2%和9.9%,达到与先进封闭模型相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在视觉语言模型中的通用推理能力得到了验证,但在处理深度图像理解和生成结构化输出任务方面的应用仍然有限。
- 监督微调在处理复杂任务时存在局限性,需要更有效的强化学习策略来适当奖励结构化输出。
- 提出了一种新的多模态结构化强化学习(MSRL)方法,用于解决图表到代码生成等挑战性问题。
- 构建了一个包含真实arXiv表格的语料库,包含超过百万的图表代码对训练数据。
- MSRL方法采用多粒度结构化奖励系统,结合文本和视觉反馈,包括基于规则的奖励和基于模型的奖励。
- 实验结果表明,MSRL方法显著突破了监督微调的瓶颈,实现了高级指标的显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

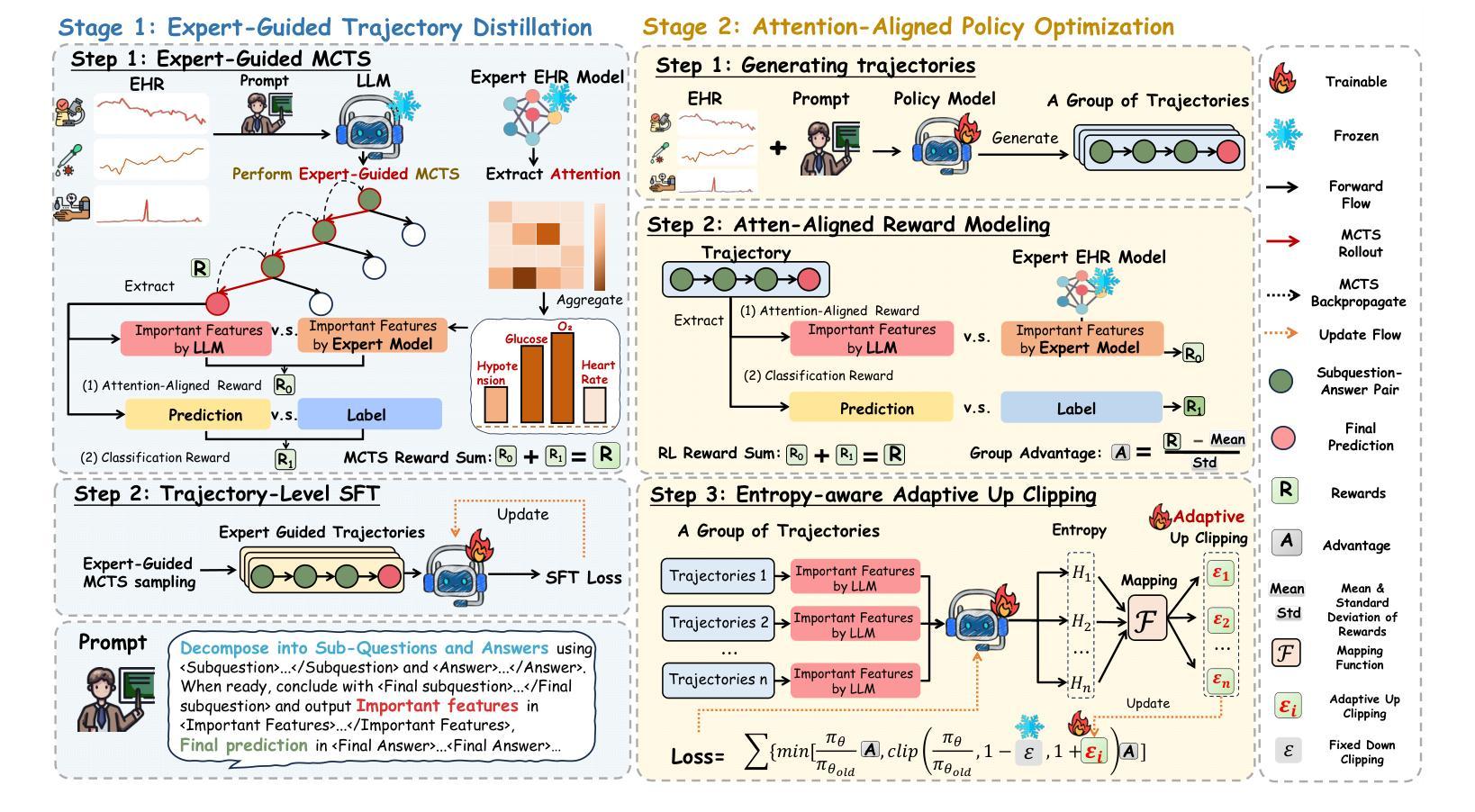
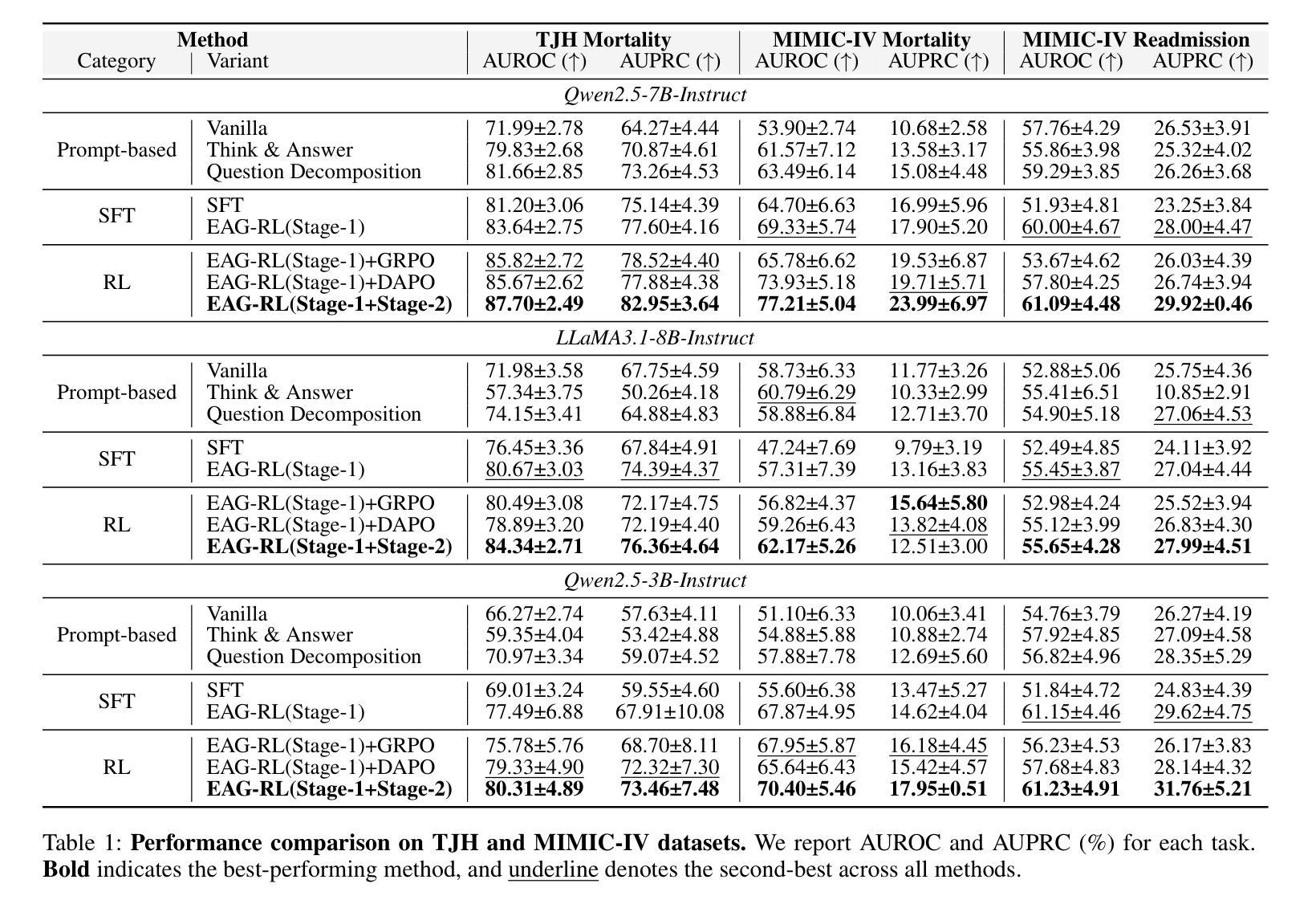
Toward Better EHR Reasoning in LLMs: Reinforcement Learning with Expert Attention Guidance
Authors:Yue Fang, Yuxin Guo, Jiaran Gao, Hongxin Ding, Xinke Jiang, Weibin Liao, Yongxin Xu, Yinghao Zhu, Zhibang Yang, Liantao Ma, Junfeng Zhao, Yasha Wang
Improving large language models (LLMs) for electronic health record (EHR) reasoning is essential for enabling accurate and generalizable clinical predictions. While LLMs excel at medical text understanding, they underperform on EHR-based prediction tasks due to challenges in modeling temporally structured, high-dimensional data. Existing approaches often rely on hybrid paradigms, where LLMs serve merely as frozen prior retrievers while downstream deep learning (DL) models handle prediction, failing to improve the LLM’s intrinsic reasoning capacity and inheriting the generalization limitations of DL models. To this end, we propose EAG-RL, a novel two-stage training framework designed to intrinsically enhance LLMs’ EHR reasoning ability through expert attention guidance, where expert EHR models refer to task-specific DL models trained on EHR data. Concretely, EAG-RL first constructs high-quality, stepwise reasoning trajectories using expert-guided Monte Carlo Tree Search to effectively initialize the LLM’s policy. Then, EAG-RL further optimizes the policy via reinforcement learning by aligning the LLM’s attention with clinically salient features identified by expert EHR models. Extensive experiments on two real-world EHR datasets show that EAG-RL improves the intrinsic EHR reasoning ability of LLMs by an average of 14.62%, while also enhancing robustness to feature perturbations and generalization to unseen clinical domains. These results demonstrate the practical potential of EAG-RL for real-world deployment in clinical prediction tasks. Our code have been available at https://github.com/devilran6/EAG-RL.
提升大型语言模型(LLM)在电子健康记录(EHR)推理中的能力,对于实现准确且可推广的临床预测至关重要。虽然大型语言模型在医疗文本理解方面表现出色,但在基于电子健康记录的预测任务中表现不佳,这是由于建模时序结构、高维数据的挑战所致。现有方法往往依赖于混合范式,其中大型语言模型仅作为冻结的先验检索器,而下游深度学习(DL)模型处理预测,这未能提升大型语言模型的内生推理能力,并继承了深度学习模型的泛化局限性。为此,我们提出了EAG-RL,这是一种新型的两阶段训练框架,旨在通过专家注意力指导内在提升大型语言模型的电子健康记录推理能力,其中专家电子健康记录模型是指基于电子健康记录数据训练的特定任务深度学习模型。具体来说,EAG-RL首先使用专家指导的蒙特卡洛树搜索构建高质量的、分步骤推理轨迹,以有效地初始化大型语言模型的策略。然后,EAG-RL通过强化学习进一步优化策略,使大型语言模型的注意力与专家电子健康记录模型识别的临床显著特征对齐。在两个真实世界的电子健康记录数据集上的大量实验表明,EAG-RL平均提升了大型语言模型的电子健康记录推理能力14.62%,同时提高了对特征扰动的稳健性和对未见临床领域的泛化能力。这些结果展示了EAG-RL在实际临床预测任务中的实用潜力。我们的代码已在https://github.com/devilran6/EAG-RL上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文着重介绍了如何提升大型语言模型(LLM)在电子健康记录(EHR)方面的推理能力,以实现准确且可推广的临床预测。针对LLM在处理结构化、高维度的EHR数据时面临的挑战,提出了一种名为EAG-RL的新型两阶段训练框架。该框架通过专家注意力引导增强LLM的内在EHR推理能力,并通过专家EHR模型指导的蒙特卡洛树搜索构建高质量的逐步推理轨迹,以初始化LLM的策略。然后通过强化学习进一步优化策略,使LLM的注意力与专家EHR模型识别的临床显著特征对齐。在两个真实的EHR数据集上的实验表明,EAG-RL提高了LLM的EHR推理能力平均达14.62%,同时提高了对特征扰动的稳健性和对未见临床领域的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提升大型语言模型(LLM)在电子健康记录(EHR)方面的推理能力是实现准确临床预测的关键。
- LLM在处理结构化、高维度的EHR数据时面临挑战。
- EAG-RL是一种新型两阶段训练框架,旨在通过专家注意力引导增强LLM的EHR推理能力。
- EAG-RL使用专家EHR模型指导的蒙特卡洛树搜索来初始化LLM的策略。
- 通过强化学习,EAG-RL进一步优化了LLM的策略,使其注意力与临床显著特征对齐。
- 在真实EHR数据集上的实验表明,EAG-RL提高了LLM的EHR推理能力达14.62%。
点此查看论文截图

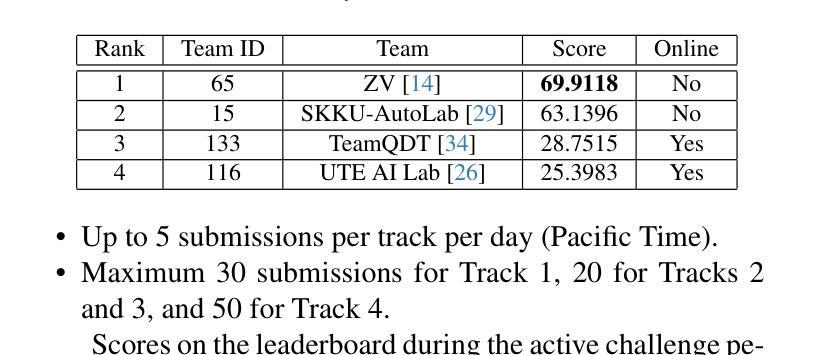
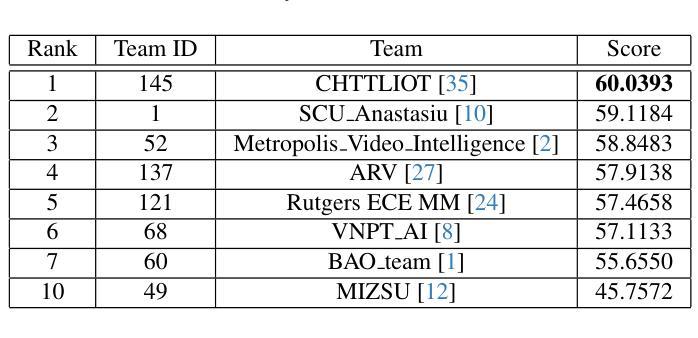
The 9th AI City Challenge
Authors:Zheng Tang, Shuo Wang, David C. Anastasiu, Ming-Ching Chang, Anuj Sharma, Quan Kong, Norimasa Kobori, Munkhjargal Gochoo, Ganzorig Batnasan, Munkh-Erdene Otgonbold, Fady Alnajjar, Jun-Wei Hsieh, Tomasz Kornuta, Xiaolong Li, Yilin Zhao, Han Zhang, Subhashree Radhakrishnan, Arihant Jain, Ratnesh Kumar, Vidya N. Murali, Yuxing Wang, Sameer Satish Pusegaonkar, Yizhou Wang, Sujit Biswas, Xunlei Wu, Zhedong Zheng, Pranamesh Chakraborty, Rama Chellappa
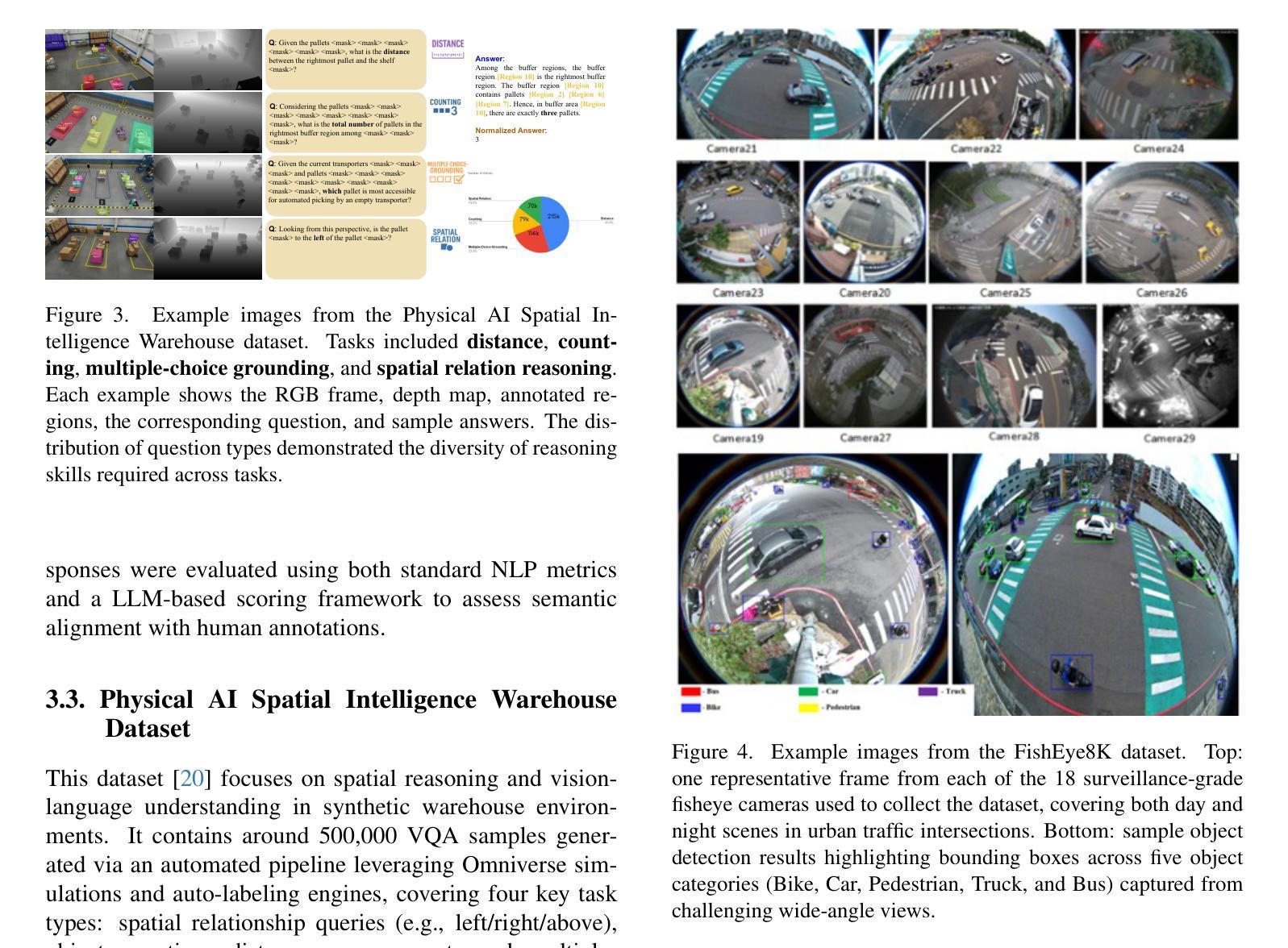
The ninth AI City Challenge continues to advance real-world applications of computer vision and AI in transportation, industrial automation, and public safety. The 2025 edition featured four tracks and saw a 17% increase in participation, with 245 teams from 15 countries registered on the evaluation server. Public release of challenge datasets led to over 30,000 downloads to date. Track 1 focused on multi-class 3D multi-camera tracking, involving people, humanoids, autonomous mobile robots, and forklifts, using detailed calibration and 3D bounding box annotations. Track 2 tackled video question answering in traffic safety, with multi-camera incident understanding enriched by 3D gaze labels. Track 3 addressed fine-grained spatial reasoning in dynamic warehouse environments, requiring AI systems to interpret RGB-D inputs and answer spatial questions that combine perception, geometry, and language. Both Track 1 and Track 3 datasets were generated in NVIDIA Omniverse. Track 4 emphasized efficient road object detection from fisheye cameras, supporting lightweight, real-time deployment on edge devices. The evaluation framework enforced submission limits and used a partially held-out test set to ensure fair benchmarking. Final rankings were revealed after the competition concluded, fostering reproducibility and mitigating overfitting. Several teams achieved top-tier results, setting new benchmarks in multiple tasks.
第九届AI城市挑战赛继续推动计算机视觉和人工智能在交通、工业自动化和公共安全领域的实际应用。2025年版比赛设有四个赛道,参赛人数增加了17%,评价服务器上有来自15个国家的245支队伍注册。挑战数据集公开发布后,至今下载量已超过3万次。第一赛道关注多类3D多相机跟踪,涉及人员、人形机器人、自主移动机器人和叉车,采用详细的校准和3D边界框注释。第二赛道解决了交通安全中的视频问答问题,通过多相机事件理解,辅以3D凝视标签。第三赛道解决动态仓库环境中的精细空间推理问题,需要AI系统解释RGB-D输入并回答结合感知、几何和语言的空间问题。第一赛道和第三赛道的数据集都是在NVIDIA Omniverse中生成的。第四赛道侧重于鱼眼相机的道路目标高效检测,支持在边缘设备的轻量级实时部署。评估框架强制执行提交限制,并使用部分隐藏的测试集以确保公平评估。在比赛结束后公布最终排名,促进可重复性和减轻过度拟合。多个团队取得顶尖成绩,在多个任务中创造新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Summary of the 9th AI City Challenge Workshop in conjunction with ICCV 2025
Summary
随着第九届人工智能城市挑战赛(AI City Challenge)的持续推进,计算机视觉和人工智能在交通、工业自动化和公共安全领域的应用不断发展。其中,2025年版本包含四个赛道,参赛队伍数量增加了17%,共有来自15个国家的245支队伍注册参赛。公开发布挑战数据集后,下载量已超过3万次。各赛道涵盖了多类别3D多相机跟踪、交通安全视频问答、精细空间推理和高效道路对象检测等任务,推动了人工智能在现实场景的应用和发展。
Key Takeaways
- 第九届人工智能城市挑战赛旨在推动计算机视觉和人工智能在交通、工业自动化和公共安全领域的实际应用。
- 2025年赛事规模扩大,参赛队伍数量增加17%,涉及多个国家的团队参与。
- 挑战数据集公开,下载量超过3万次,促进了数据共享和模型训练。
- 赛事包含四个赛道,分别关注多类别3D多相机跟踪、交通安全视频问答、精细空间推理和高效道路对象检测等任务。
- 部分赛道数据集采用NVIDIA Omniverse生成,贴近实际场景。
- 评价框架采用提交限制和部分未公开测试集,确保公平评估和模型泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


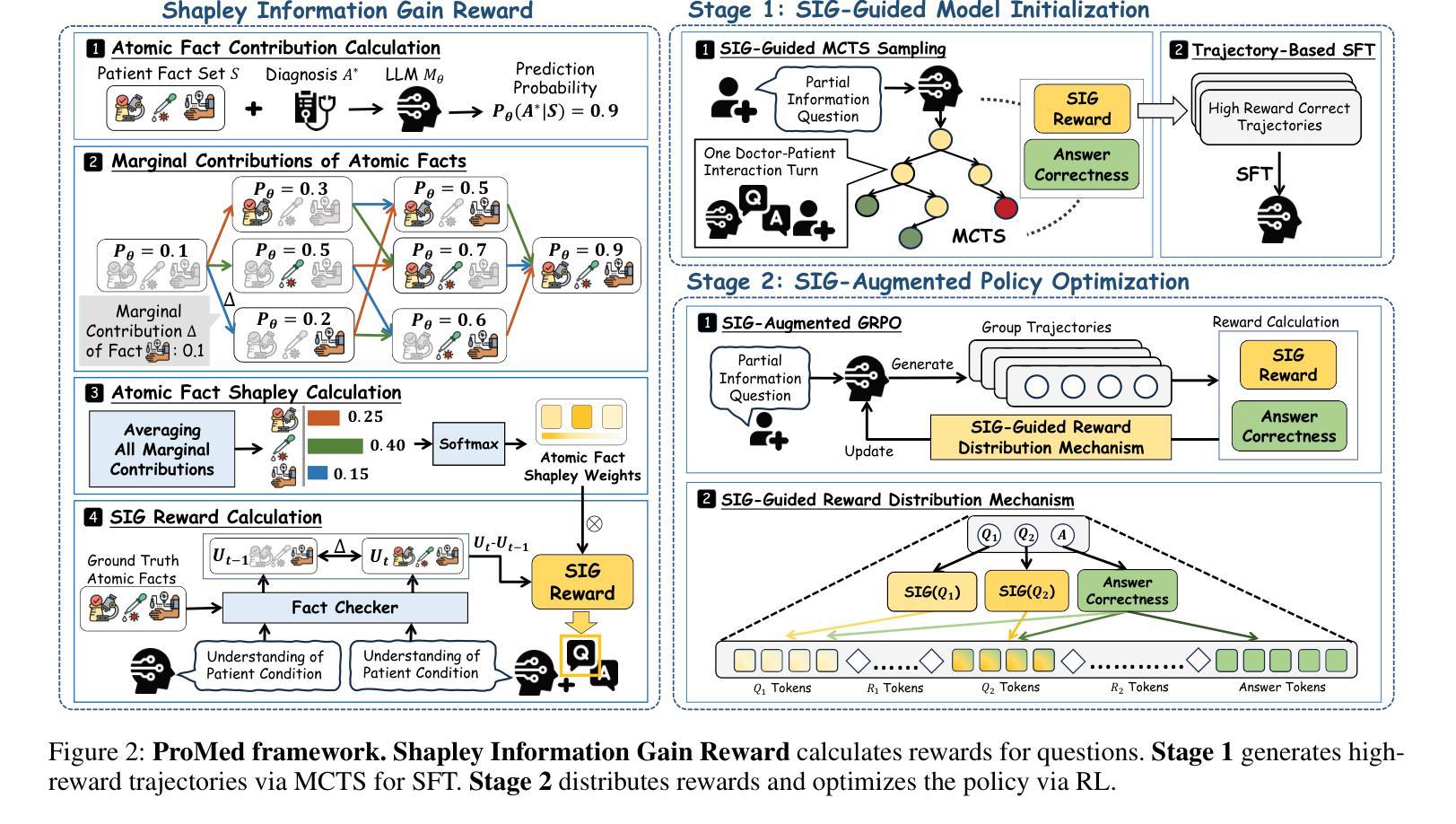
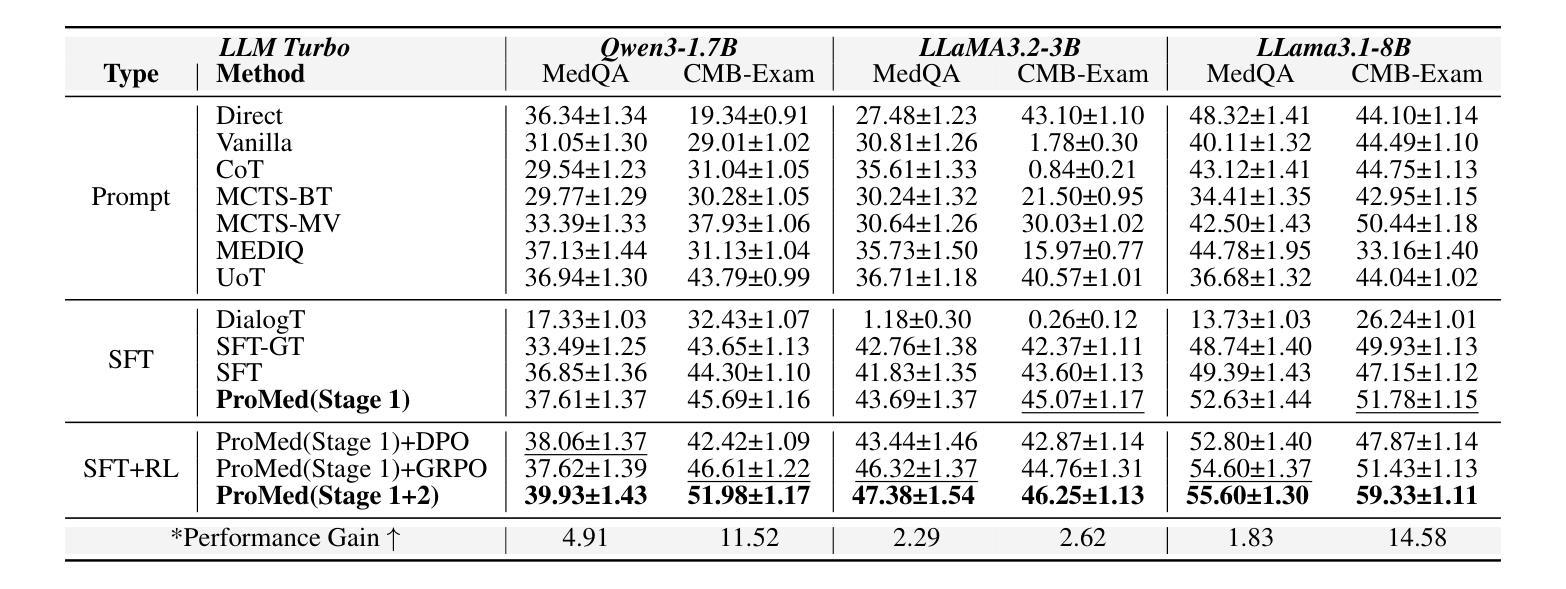
ProMed: Shapley Information Gain Guided Reinforcement Learning for Proactive Medical LLMs
Authors:Hongxin Ding, Baixiang Huang, Yue Fang, Weibin Liao, Xinke Jiang, Zheng Li, Junfeng Zhao, Yasha Wang
Interactive medical questioning is essential in real-world clinical consultations, where physicians must actively gather information from patients. While medical Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in static medical question answering, they predominantly operate under a reactive paradigm: generating answers directly without seeking additional information, which risks incorrect diagnoses in such interactive settings. To address this limitation, we propose ProMed, a reinforcement learning (RL) framework that transitions medical LLMs toward a proactive paradigm, equipping them with the ability to ask clinically valuable questions before decision-making. At the core of ProMed is the Shapley Information Gain (SIG) reward, which quantifies the clinical utility of each question by combining the amount of newly acquired information with its contextual importance, estimated via Shapley values. We integrate SIG into a two-stage training pipeline: (1) SIG-Guided Model Initialization uses Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to construct high-reward interaction trajectories to supervise the model, and (2) SIG-Augmented Policy Optimization, which integrates SIG and enhances RL with a novel SIG-guided Reward Distribution Mechanism that assigns higher rewards to informative questions for targeted optimization. Extensive experiments on two newly curated partial-information medical benchmarks demonstrate that ProMed significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods by an average of 6.29% and delivers a 54.45% gain over the reactive paradigm, while also generalizing robustly to out-of-domain cases.
互动医学提问在现实世界中的临床咨询中至关重要,医生必须主动从患者那里收集信息。虽然医疗大型语言模型(LLM)在静态医疗问题回答中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但它们主要遵循反应模式:直接生成答案而不寻求额外信息,这在交互式环境中可能导致误诊风险。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了ProMed,这是一个强化学习(RL)框架,使医疗LLM转向主动模式,赋予它们在决策前提出具有临床价值问题的能力。ProMed的核心是Shapley信息增益(SIG)奖励,它通过结合新获取的信息量和其上下文重要性来量化每个问题的临床效用,这些信息的重要性估计是通过Shapley值进行的。我们将SIG集成到一个两阶段训练管道中:(1)SIG引导模型初始化使用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)来构建高奖励交互轨迹以监督模型;(2)SIG增强策略优化,它将SIG与强化学习相结合,并通过新的SIG引导奖励分配机制来提高对信息性问题的奖励,以进行有针对性的优化。在两个新整理的部分信息医疗基准测试上的广泛实验表明,ProMed平均优于最新技术6.29%,并且在反应性模式上有54.45%的改进,同时对于离域情况也具有稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文指出互动医疗问诊在现实世界的临床咨询中的重要性,医生需主动收集病人的信息。尽管医疗领域的大型语言模型(LLM)在静态医疗问答中表现出令人印象深刻的能力,但它们主要遵循反应模式,即直接生成答案而不寻求额外信息,这可能在互动场景中导致误诊。为解决这一问题,提出ProMed,一个强化学习(RL)框架,使医疗LLM向主动模式转变,赋予它们在决策前提出具有临床价值问题的能力。ProMed的核心是Shapley信息增益(SIG)奖励,它结合了新获取的信息量和其上下文重要性来量化每个问题的临床实用性。我们将SIG集成到一个两阶段的训练管道中,第一阶段是SIG指导模型初始化,使用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)构建高奖励互动轨迹来监督模型;第二阶段是SIG增强策略优化,它结合了SIG和一个新的SIG指导奖励分配机制,为信息丰富的问题分配更高的奖励,以实现有针对性的优化。在全新整理的局部信息医疗基准测试上的实验表明,ProMed平均优于最新方法6.29%,相较于反应模式有54.45%的提升,并且在跨域案例中具有稳健的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 互动医疗问诊在现实世界的临床咨询中至关重要,医生需主动收集病人信息。
- 当前医疗大型语言模型(LLMs)主要遵循反应模式,可能导致误诊。
- ProMed是一个强化学习(RL)框架,使医疗LLM向主动模式转变,具备在决策前提出临床价值问题的能力。
- Shapley信息增益(SIG)奖励是ProMed的核心,它量化问题的临床实用性。
- ProMed采用两阶段训练管道:SIG指导模型初始化和SIG增强策略优化。
- Monte Carlo Tree Search(MCTS)用于构建高奖励互动轨迹来监督模型。
点此查看论文截图

Stands to Reason: Investigating the Effect of Reasoning on Idiomaticity Detection
Authors:Dylan Phelps, Rodrigo Wilkens, Edward Gow-Smith, Thomas Pickard, Maggie Mi, Aline Villavicencio
The recent trend towards utilisation of reasoning models has improved the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) across many tasks which involve logical steps. One linguistic task that could benefit from this framing is idiomaticity detection, as a potentially idiomatic expression must first be understood before it can be disambiguated and serves as a basis for reasoning. In this paper, we explore how reasoning capabilities in LLMs affect idiomaticity detection performance and examine the effect of model size. We evaluate, as open source representative models, the suite of DeepSeek-R1 distillation models ranging from 1.5B to 70B parameters across four idiomaticity detection datasets. We find the effect of reasoning to be smaller and more varied than expected. For smaller models, producing chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning increases performance from Math-tuned intermediate models, but not to the levels of the base models, whereas larger models (14B, 32B, and 70B) show modest improvements. Our in-depth analyses reveal that larger models demonstrate good understanding of idiomaticity, successfully producing accurate definitions of expressions, while smaller models often fail to output the actual meaning. For this reason, we also experiment with providing definitions in the prompts of smaller models, which we show can improve performance in some cases.
近期利用推理模型的趋势已提高大型语言模型(LLM)在涉及逻辑步骤的多个任务上的性能。可以从这种框架中受益的语言任务之一是习语检测,因为在一个习语表达式被理解之后,才能对其进行解歧,并作为推理的基础。在本文中,我们探讨了LLM中的推理能力如何影响习语检测性能,并研究了模型规模的影响。我们评估了作为开源代表模型的DeepSeek-R1蒸馏模型系列,这些模型参数从1.5B到70B不等,跨越四个习语检测数据集。我们发现推理的影响比预期的要小且更加多变。对于较小的模型,进行思维链(CoT)推理提高了数学调整中间模型的性能,但并未达到基础模型的水平,而较大的模型(14B、32B和70B)则显示出适度的改进。我们的深入分析表明,大型模型很好地理解了习语性,成功地对表达式给出了准确的定义,而小型模型往往无法输出实际含义。因此,我们还尝试在小型模型的提示中提供定义,我们证明在某些情况下这可以提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的推理模型趋势提升了逻辑任务上的表现。本文探讨了推理能力对语言模型在成语检测任务中的影响,并考察了模型规模的影响。通过对不同参数的DeepSeek-R1蒸馏模型在四个成语检测数据集上的评估,发现推理的影响较小且变化较大。对于较小的模型,通过链式思维(CoT)推理可以提高性能,但未达到基础模型的水平;而较大的模型显示出温和的提升。深入的分析表明,大模型能够更好地理解成语含义,成功给出准确的定义表达,而小模型则经常无法输出实际意义。为此,实验通过给小型模型的提示提供定义来提高性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的关键见解:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的推理模型趋势已提高了逻辑任务上的性能。
- 推理能力对语言模型在成语检测任务中的影响被研究。
- 模型规模对成语检测性能的影响被考察。
- 推理的影响较小且变化较大,小型模型的性能提升有限。
- 大模型能够更好地理解成语含义,给出准确的定义。
- 小模型在输出实际意义上经常失败。
点此查看论文截图

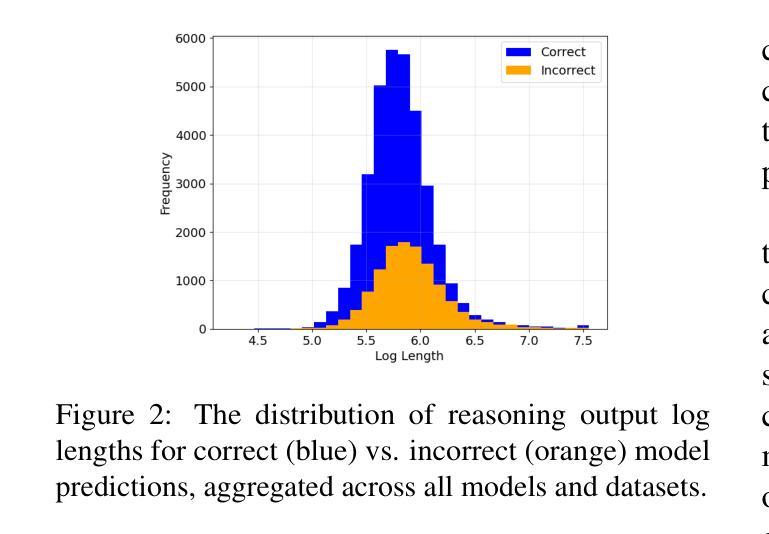
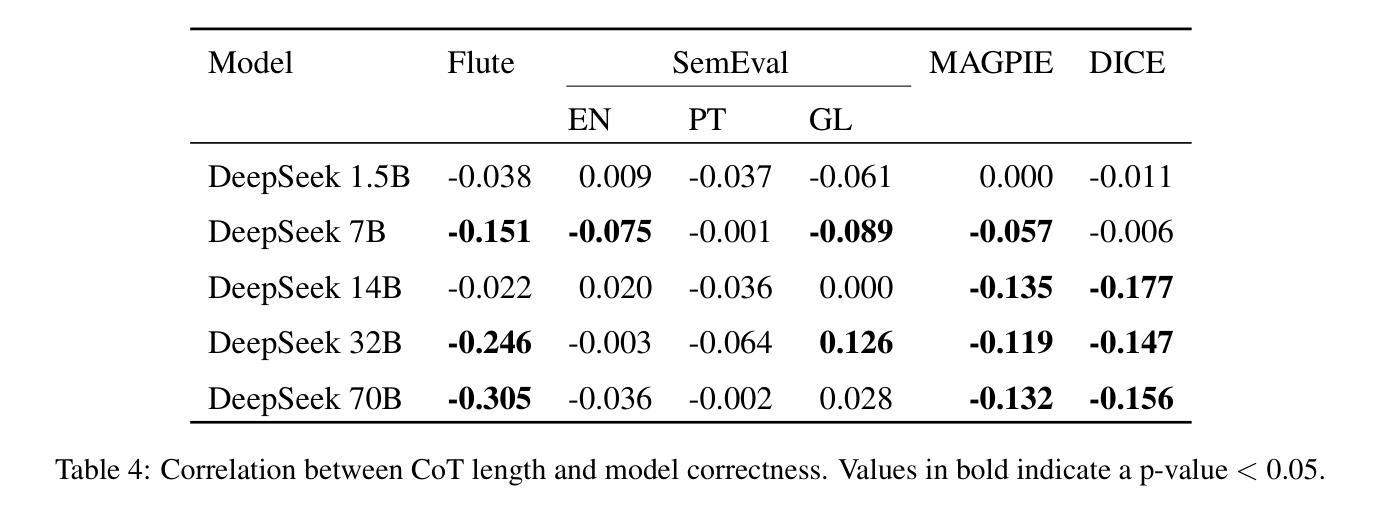
Explicit v.s. Implicit Memory: Exploring Multi-hop Complex Reasoning Over Personalized Information
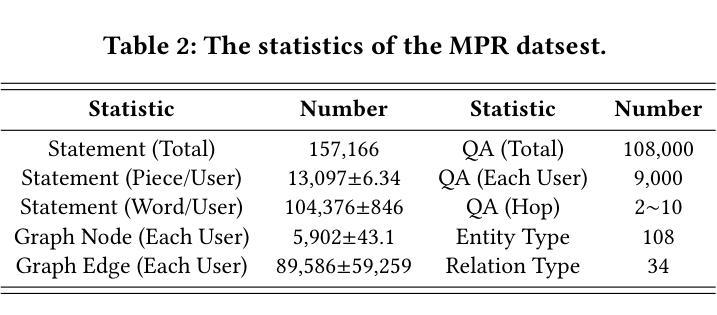
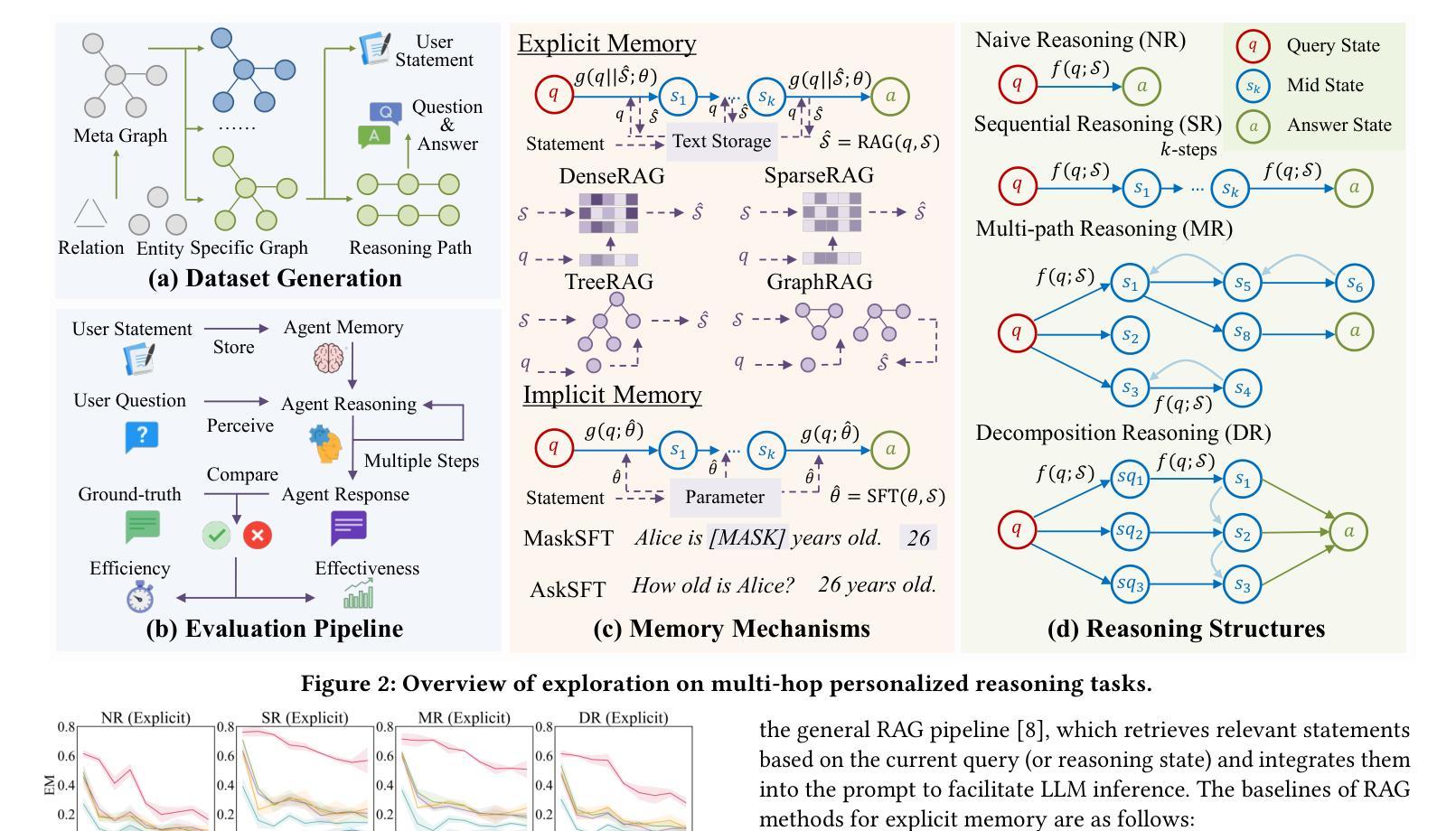
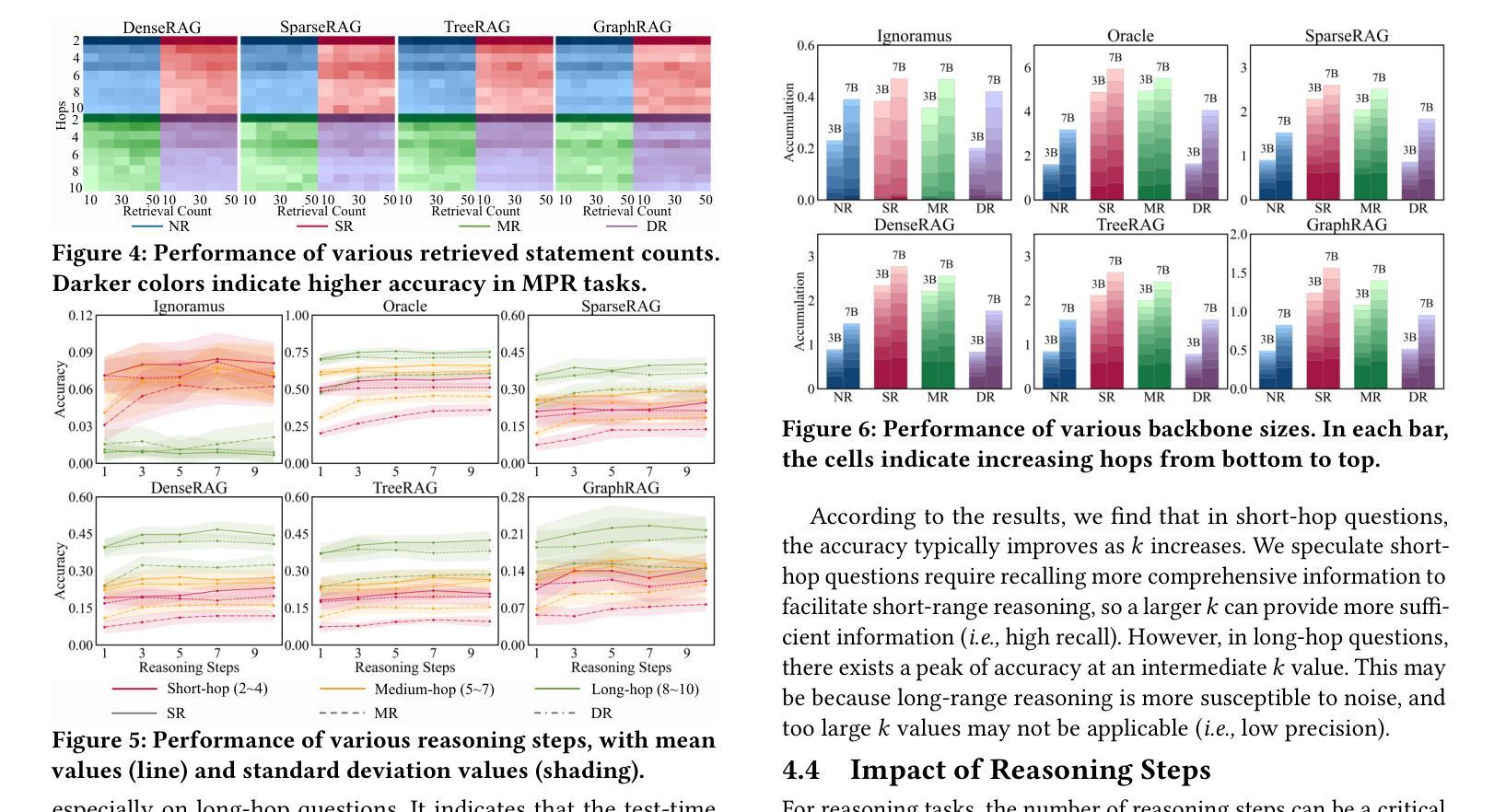
Authors:Zeyu Zhang, Yang Zhang, Haoran Tan, Rui Li, Xu Chen
In large language model-based agents, memory serves as a critical capability for achieving personalization by storing and utilizing users’ information. Although some previous studies have adopted memory to implement user personalization, they typically focus on preference alignment and simple question-answering. However, in the real world, complex tasks often require multi-hop reasoning on a large amount of user information, which poses significant challenges for current memory approaches. To address this limitation, we propose the multi-hop personalized reasoning task to explore how different memory mechanisms perform in multi-hop reasoning over personalized information. We explicitly define this task and construct a dataset along with a unified evaluation framework. Then, we implement various explicit and implicit memory methods and conduct comprehensive experiments. We evaluate their performance on this task from multiple perspectives and analyze their strengths and weaknesses. Besides, we explore hybrid approaches that combine both paradigms and propose the HybridMem method to address their limitations. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model through extensive experiments. To benefit the research community, we release this project at https://github.com/nuster1128/MPR.
在基于大型语言模型的代理中,记忆对于通过存储和利用用户信息来实现个性化至关重要。虽然一些早期的研究已经采用记忆来实现用户个性化,但它们通常侧重于偏好对齐和简单问答。然而,在现实世界,复杂的任务通常需要利用大量用户信息进行多跳推理,这对当前记忆方法构成了重大挑战。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了多跳个性化推理任务,以探索不同记忆机制在个性化信息上的多跳推理表现。我们明确定义了此任务,并构建了一个数据集以及一个统一的评估框架。然后,我们实现了多种显式记忆方法和隐式记忆方法,并进行了全面的实验。我们从多个角度评估了他们在这一任务上的表现,并分析了他们的优缺点。此外,我们还探索了结合这两种方法的混合方法,并提出了HybridMem方法来解决它们的局限性。我们通过大量实验证明了所提出模型的有效性。为了造福研究社区,我们在https://github.com/nuster1128/MPR上发布了此项目。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 13 figures, 3 tables
Summary
大型语言模型中的记忆能力对于实现个性化至关重要,它通过存储和利用用户信息来实现个性化。先前的研究虽然采用了记忆实现用户个性化的方法,但它们主要集中在偏好对齐和简单问答上。现实世界中的复杂任务需要多跳推理,这对当前记忆方法提出了挑战。为应对这一挑战,本文提出了多跳个性化推理任务,探索不同记忆机制在个性化信息上的多跳推理表现。本文定义了这个任务,构建了数据集和统一评估框架,实现了各种显性和隐性记忆方法,并进行了综合实验评估。此外,还探索了结合两种方法的混合方法,并提出了HybridMem方法来解决其局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 记忆能力在大型语言模型中的重要作用:存储和利用用户信息以实现个性化。
- 先前研究主要集中在简单问答和偏好对齐上,对于复杂任务的多跳推理挑战应对不足。
- 提出多跳个性化推理任务,以探索记忆机制在个性化信息上的多跳推理表现。
- 构建了数据集和统一评估框架,以支持该任务的研究。
- 实现了多种显性和隐性记忆方法,并进行了综合实验评估其性能。
- 提出混合方法结合两种记忆方法,解决其局限性。
点此查看论文截图

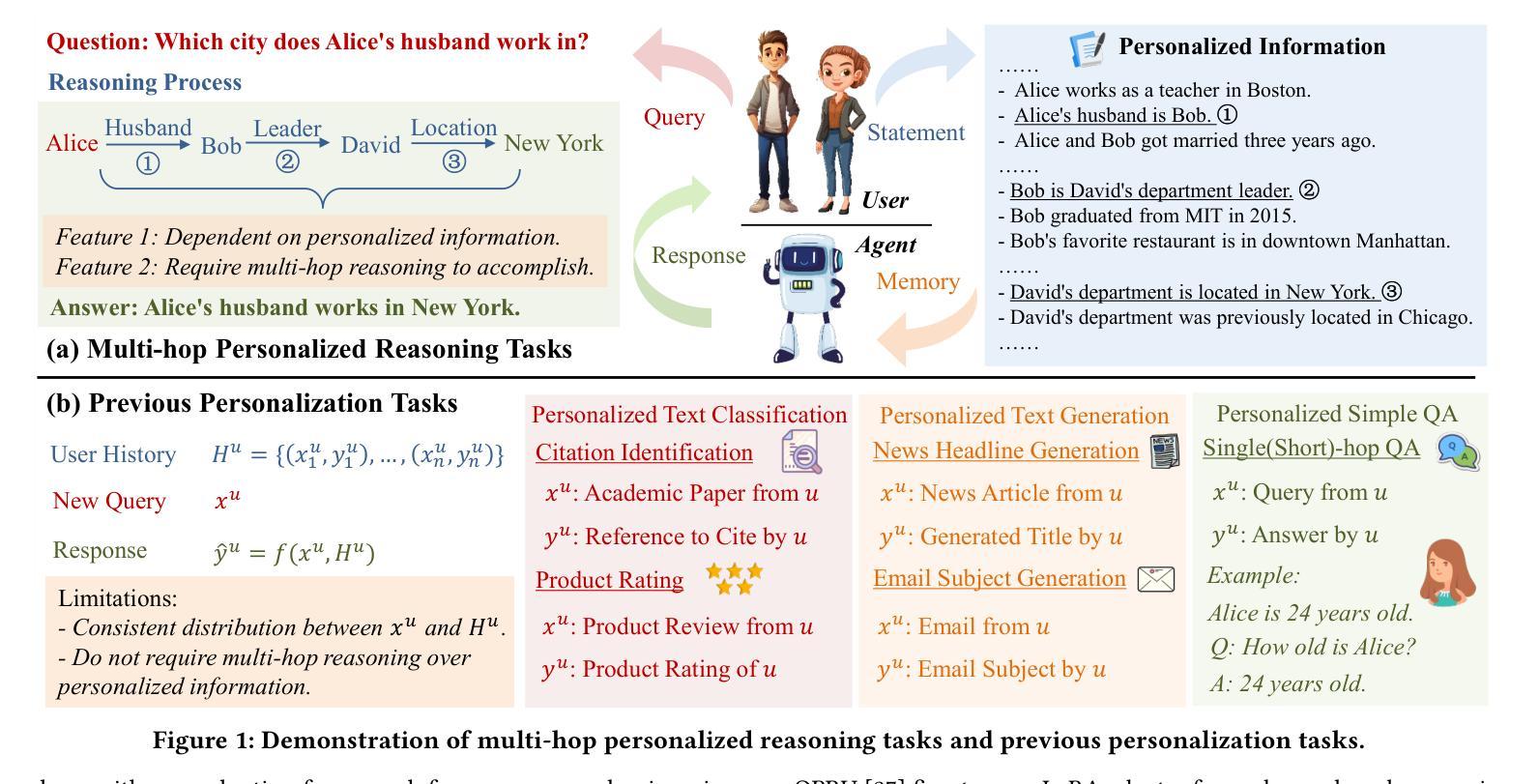
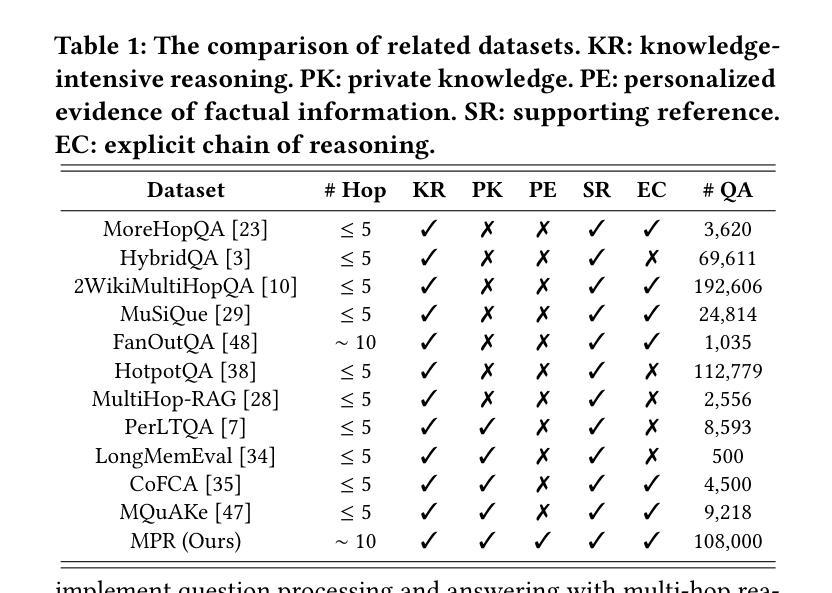
RISE: Enhancing VLM Image Annotation with Self-Supervised Reasoning
Authors:Suhang Hu, Wei Hu, Yuhang Su, Fan Zhang
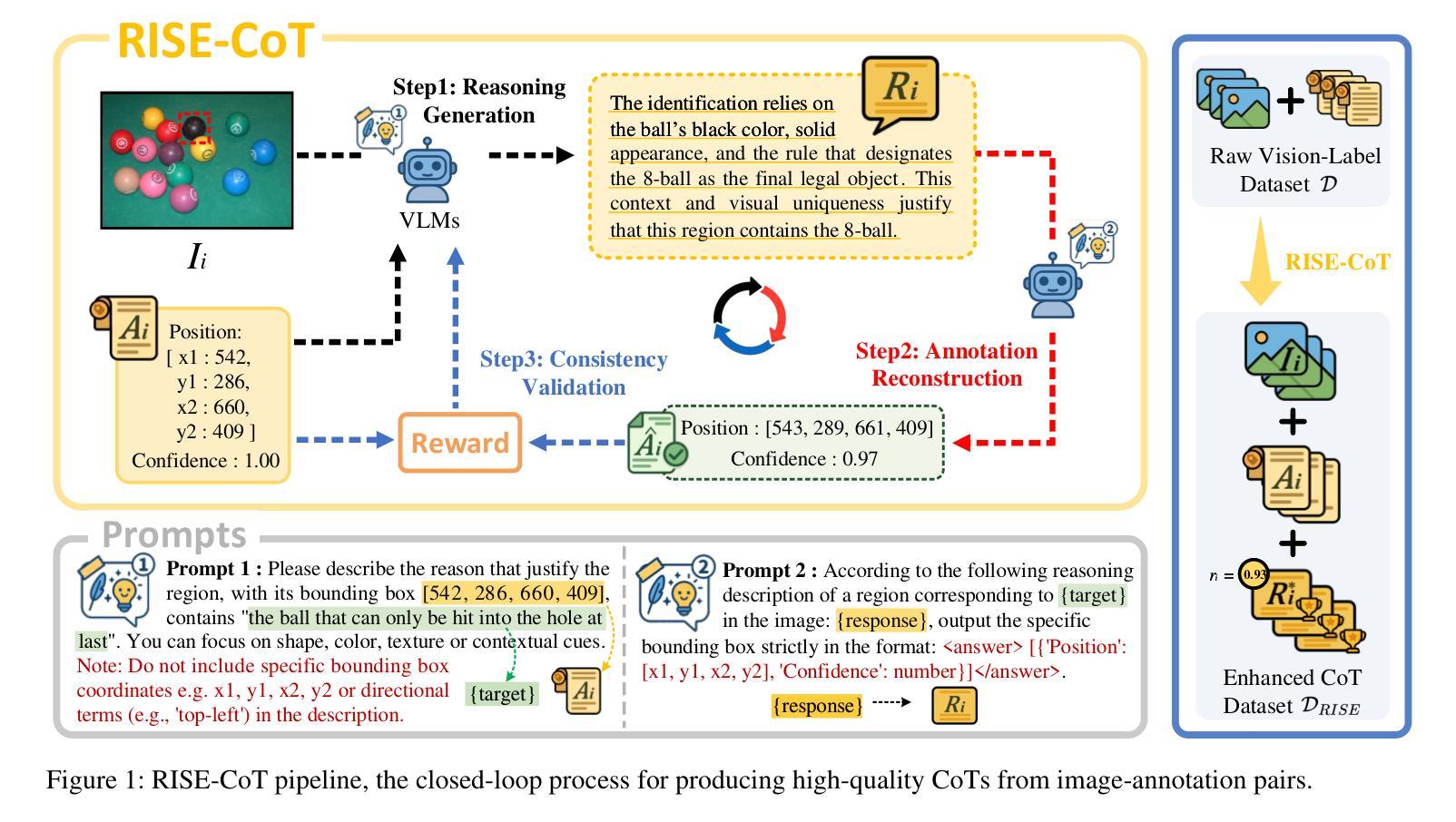
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) struggle with complex image annotation tasks, such as emotion classification and context-driven object detection, which demand sophisticated reasoning. Standard Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) focuses solely on annotation outcomes, ignoring underlying rationales, while Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (Visual-RFT) produces inconsistent Chains of Thought (CoTs) due to the absence of high-quality, verified CoTs during pre-training. We introduce RISE (Reason-Inspire-Strengthen-Expertise), a two-stage framework to overcome these limitations. In the Reason stage (RISE-CoT), a reinforcement learning-driven “annotation-reasoning-annotation” closed-loop generates visually grounded, logically consistent CoTs by verifying their ability to reconstruct original annotations without direct leakage. The Inspire and Strengthen stage (RISE-R1) leverages a high-quality CoT subset, filtered by RISE-CoT rewards, for supervised fine-tuning, followed by reinforcement fine-tuning to produce interpretable reasoning and accurate annotations, achieving Expertise in complex visual tasks. Evaluated on complex and simple image annotation tasks, RISE-trained Qwen2-VL-2B outperforms SFT and Visual-RFT, achieving robust performance and enhanced explainability. RISE offers a self-supervised solution for advancing VLM reasoning without requiring manually annotated CoTs.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在处理复杂的图像标注任务时面临挑战,例如情感分类和上下文驱动的对象检测等需要复杂推理的任务。标准监督微调(SFT)只关注标注结果,忽略了潜在的推理过程,而视觉强化微调(Visual-RFT)则由于预训练期间缺乏高质量、经过验证的推理链(CoTs),产生了不一致的推理链。我们引入了RISE(Reason-Inspire-Strengthen-Expertise),这是一个两阶段的框架,旨在克服这些限制。在推理阶段(RISE-CoT),一个强化学习驱动的“标注-推理-标注”闭环通过验证其重建原始标注的能力,生成视觉基础、逻辑一致的推理链,而无需直接泄露信息。在激励和强化阶段(RISE-R1)则利用RISE-CoT奖励过滤出的高质量推理链子集进行有监督微调,然后进行强化微调,以产生可解释的推理和准确的标注,在复杂视觉任务中实现专业级表现。在复杂和简单的图像标注任务上,经过RISE训练的Qwen2-VL-2B超越了SFT和Visual-RFT,实现了稳健的性能和增强的可解释性。RISE提供了一种自监督的解决方案,无需手动注释的推理链即可推动VLM的推理能力进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Vision-Language Models(VLMs)在处理复杂图像标注任务时的挑战,如情感分类和上下文驱动的目标检测。为解决标准监督微调(SFT)和视觉强化微调(Visual-RFT)的局限性,提出了一种名为RISE的两阶段框架。该框架通过生成视觉基础、逻辑一致的Chains of Thought(CoTs)来提高VLMs的推理能力,并在复杂视觉任务中实现专业性能。经过RISE训练的Qwen2-VL-2B在复杂和简单的图像标注任务上表现出卓越的性能和增强的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在处理复杂图像标注任务时面临挑战,需要高级推理能力。
- 标准监督微调(SFT)和视觉强化微调(Visual-RFT)存在局限性,无法完全满足这些需求。
- RISE框架通过生成视觉基础、逻辑一致的Chains of Thought(CoTs)来提高VLMs的推理能力。
- RISE框架包括两个阶段:Reason阶段(RISE-CoT)生成验证后的CoTs,Inspire和Strengthen阶段(RISE-R1)利用高质量的CoTs子集进行监督和强化微调。
- RISE训练后的模型在复杂和简单的图像标注任务上表现出卓越性能。
- RISE框架提供了一种自监督的解决方案,可推动VLM推理的进步,无需手动注释的CoTs。
点此查看论文截图


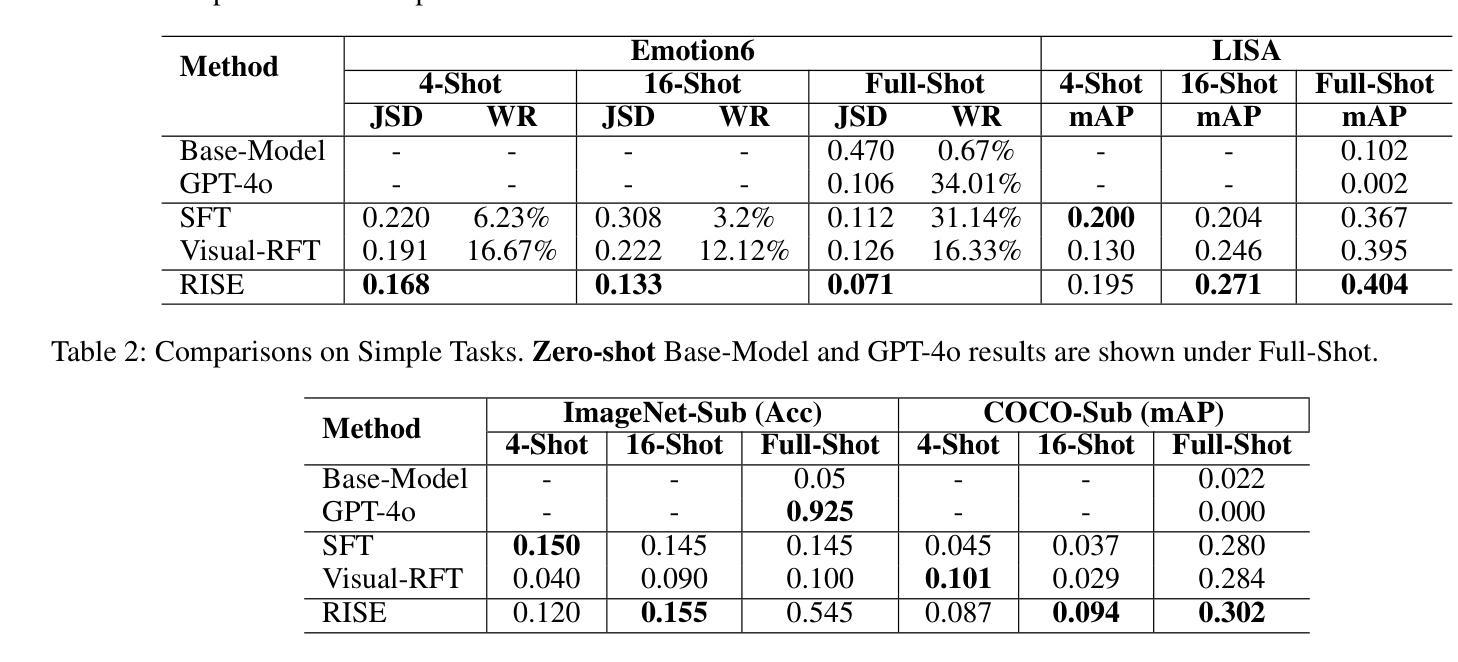
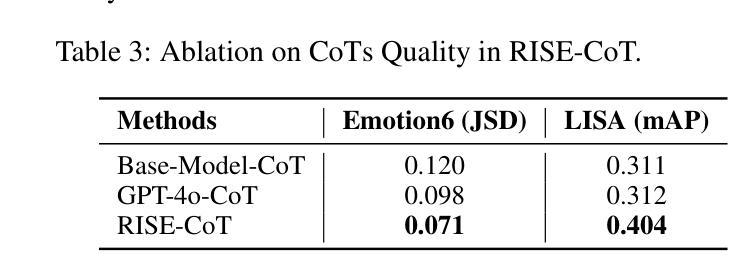
PC-Sampler: Position-Aware Calibration of Decoding Bias in Masked Diffusion Models
Authors:Pengcheng Huang, Shuhao Liu, Zhenghao Liu, Yukun Yan, Shuo Wang, Zulong Chen, Tong Xiao
Recent advances in masked diffusion models (MDMs) have established them as powerful non-autoregressive alternatives for sequence generation. Nevertheless, our preliminary experiments reveal that the generation quality of MDMs is still highly sensitive to the choice of decoding strategy. In particular, widely adopted uncertainty-based samplers suffer from two key limitations: a lack of global trajectory control and a pronounced bias toward trivial tokens in the early stages of decoding. These shortcomings restrict the full potential of MDMs. In this work, we introduce Position-Aware Confidence-Calibrated Sampling (PC-Sampler), a novel decoding strategy that unifies global trajectory planning with content-aware informativeness maximization. PC-Sampler incorporates a position-aware weighting mechanism to regulate the decoding path and a calibrated confidence score to suppress the premature selection of trivial tokens. Extensive experiments on three advanced MDMs across seven challenging benchmarks-including logical reasoning and planning tasks-demonstrate that PC-Sampler consistently outperforms existing MDM decoding strategies by more than 10% on average, significantly narrowing the performance gap with state-of-the-art autoregressive models. All codes are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/PC-Sampler.
近期,掩膜扩散模型(MDMs)的进展为序列生成提供了强大的非自回归替代方案。然而,我们的初步实验表明,MDMs的生成质量对解码策略的选择仍然高度敏感。特别是广泛采用的基于不确定性的采样器存在两大局限:缺乏全局轨迹控制和在解码早期阶段对平凡标记的明显偏向。这些缺点限制了MDMs的潜力。在这项工作中,我们引入了位置感知置信校准采样(PC-Sampler),这是一种新的解码策略,它将全局轨迹规划与内容感知的信息最大化相结合。PC-Sampler采用位置感知加权机制来调节解码路径,并使用校准置信度来抑制平凡标记的过早选择。在三个先进的MDMs和七个具有挑战性的基准测试(包括逻辑推理和任务规划)上的广泛实验表明,PC-Sampler在平均意义上始终优于现有的MDM解码策略,超过10%,显著缩小了与最新自回归模型之间的性能差距。所有代码可在https://github.com/NEUIR/PC-Sampler找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages,13 figures
Summary
近期,掩码扩散模型(MDMs)成为非自回归序列生成任务的强大工具。但初步实验表明,MDMs的生成质量对解码策略的选择非常敏感。当前广泛采用的不确定性采样器存在全局轨迹控制不足和早期解码阶段明显偏向平凡代币的两大局限。本研究提出位置感知置信校准采样(PC-Sampler)这一新颖解码策略,结合全局轨迹规划与内容感知信息量最大化。PC-Sampler通过位置感知加权机制调控解码路径,并用校准置信度得分抑制平凡代币的过早选择。在多个先进MDMs和七个挑战性基准上的实验表明,PC-Sampler平均性能超出现有MDM解码策略10%以上,显著缩小了与顶尖自回归模型的性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- 掩码扩散模型(MDMs)已成为非自回归序列生成的有力工具。
- 初步实验发现,MDMs的生成质量对解码策略选择敏感。
- 现有不确定性采样器存在全局轨迹控制不足和早期解码阶段偏向平凡代币的问题。
- 提出新的解码策略——位置感知置信校准采样(PC-Sampler)。
- PC-Sampler结合全局轨迹规划与内容感知信息量最大化。
- PC-Sampler通过位置感知加权和校准置信度得分解决现有采样器的缺陷。
- 实验表明,PC-Sampler在多个基准测试中性能显著优于现有MDM解码策略。
点此查看论文截图

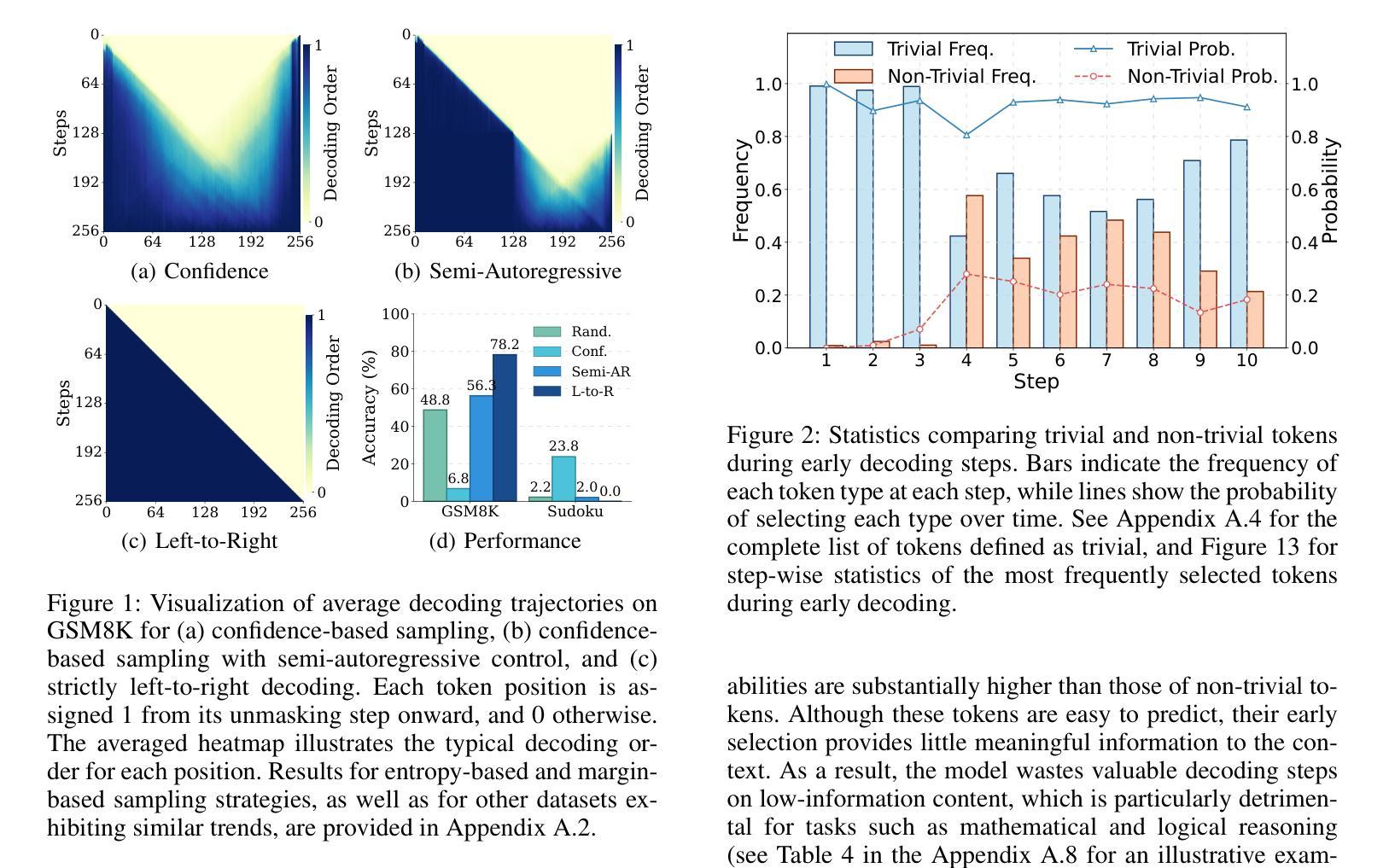
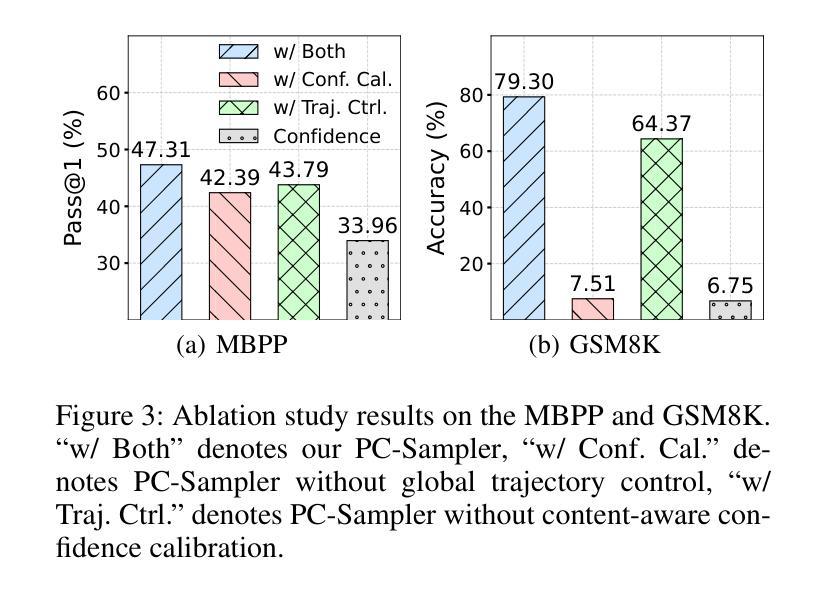
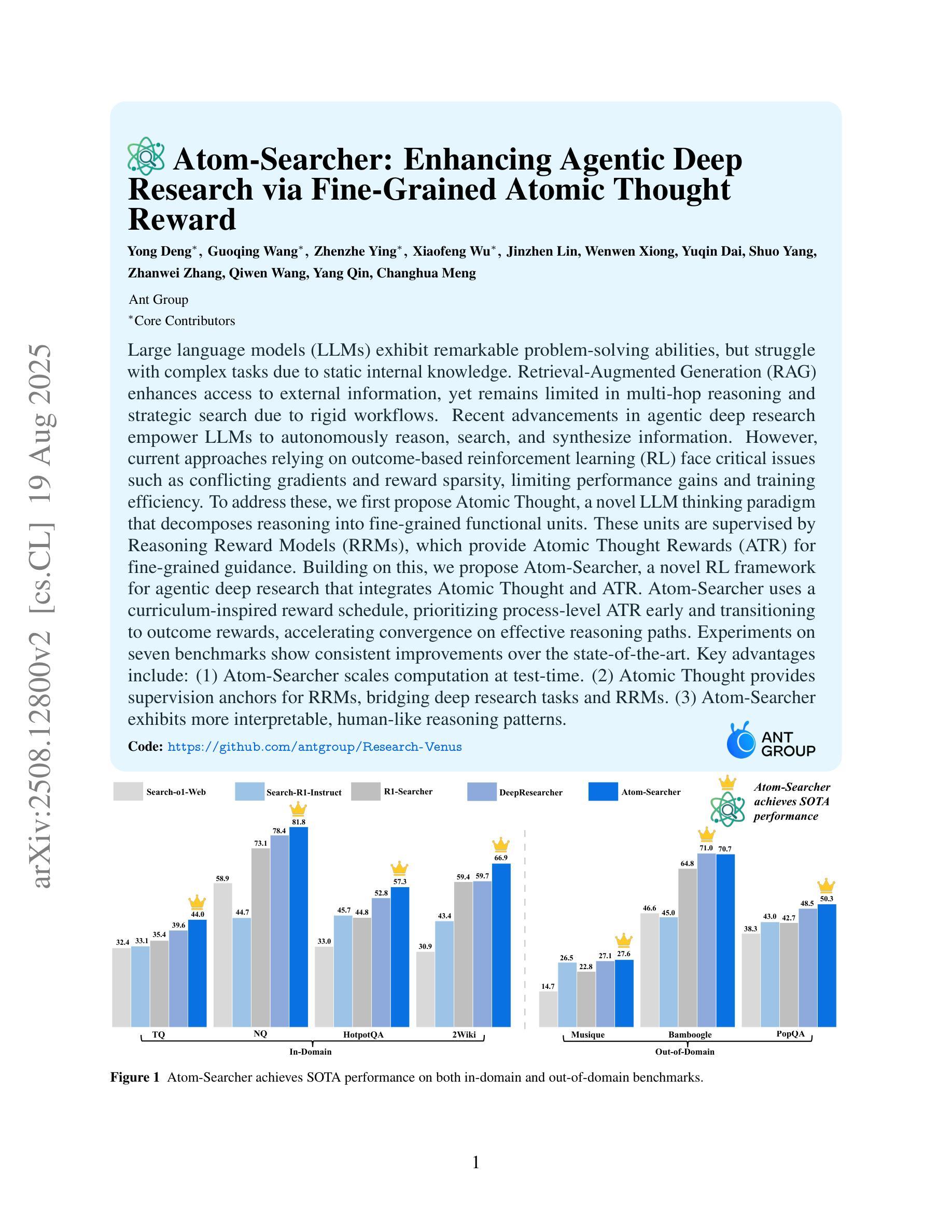
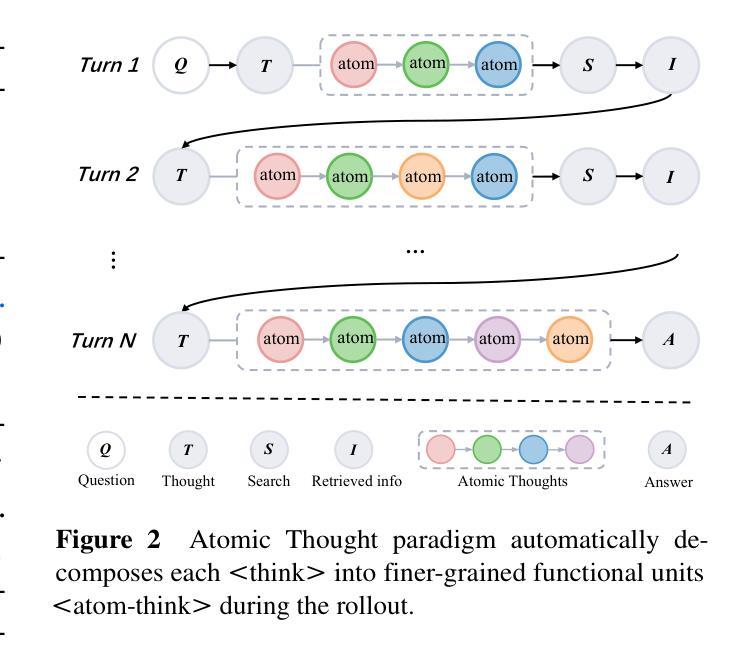
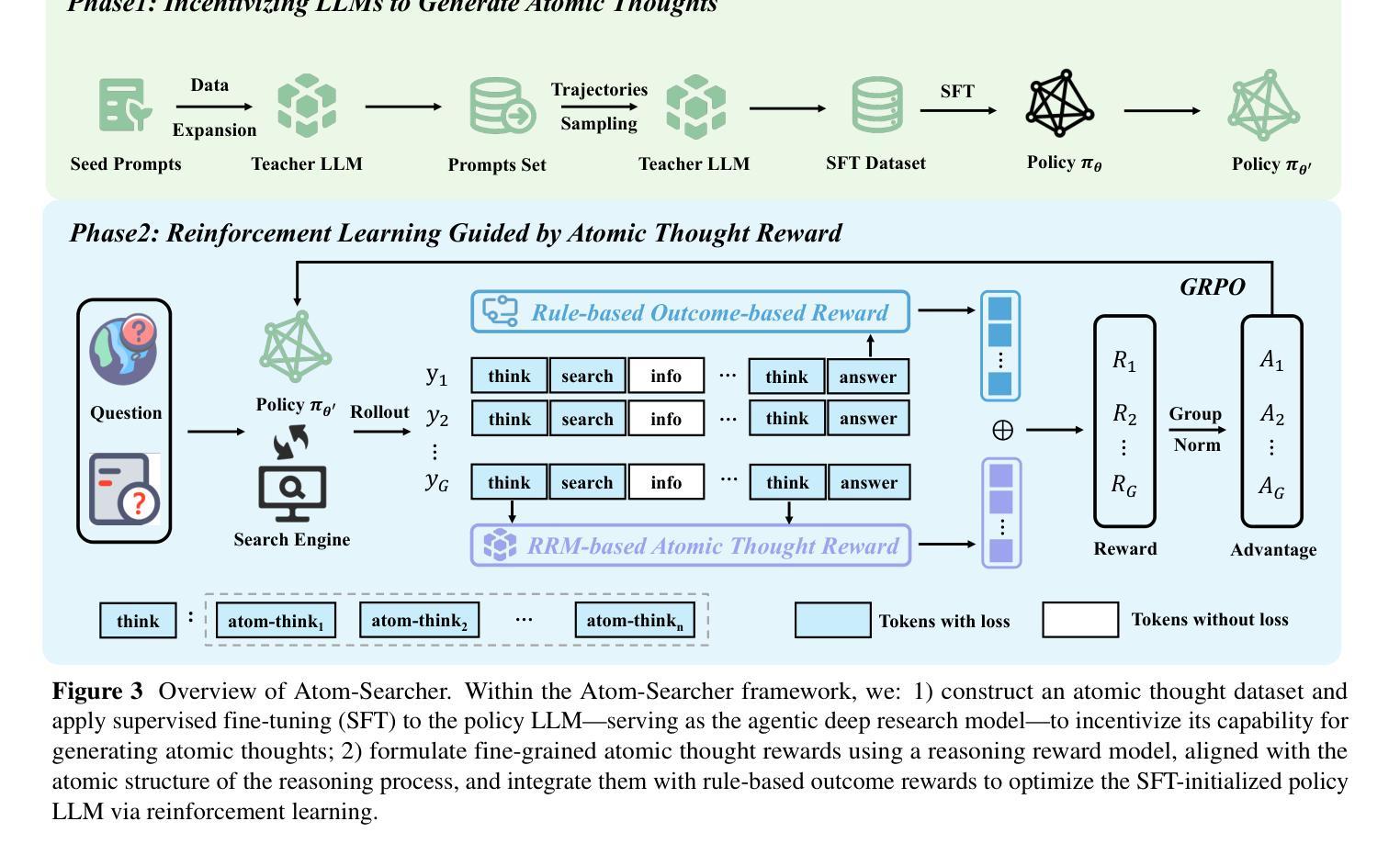
Atom-Searcher: Enhancing Agentic Deep Research via Fine-Grained Atomic Thought Reward
Authors:Yong Deng, Guoqing Wang, Zhenzhe Ying, Xiaofeng Wu, Jinzhen Lin, Wenwen Xiong, Yuqin Dai, Shuo Yang, Zhanwei Zhang, Qiwen Wang, Yang Qin, Changhua Meng
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable problem-solving abilities, but struggle with complex tasks due to static internal knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances access to external information, yet remains limited in multi-hop reasoning and strategic search due to rigid workflows. Recent advancements in agentic deep research empower LLMs to autonomously reason, search, and synthesize information. However, current approaches relying on outcome-based reinforcement learning (RL) face critical issues such as conflicting gradients and reward sparsity, limiting performance gains and training efficiency. To address these, we first propose Atomic Thought, a novel LLM thinking paradigm that decomposes reasoning into fine-grained functional units. These units are supervised by Reasoning Reward Models (RRMs), which provide Atomic Thought Rewards (ATR) for fine-grained guidance. Building on this, we propose Atom-Searcher, a novel RL framework for agentic deep research that integrates Atomic Thought and ATR. Atom-Searcher uses a curriculum-inspired reward schedule, prioritizing process-level ATR early and transitioning to outcome rewards, accelerating convergence on effective reasoning paths. Experiments on seven benchmarks show consistent improvements over the state-of-the-art. Key advantages include: (1) Atom-Searcher scales computation at test-time. (2) Atomic Thought provides supervision anchors for RRMs, bridging deep research tasks and RRMs. (3) Atom-Searcher exhibits more interpretable, human-like reasoning patterns.
大型语言模型(LLM)展现出卓越的解决问题能力,但由于内部知识的静态性,在应对复杂任务时遇到困难。检索增强生成(RAG)增强了对外部信息的访问能力,但由于工作流程僵化,在多层次推理和策略搜索方面仍存在局限。最近的深度研究代理进步使LLM能够自主推理、搜索和合成信息。然而,当前依赖结果基于增强学习(RL)的方法面临关键性问题,如梯度冲突和奖励稀疏,这限制了性能提升和训练效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)具有出色的问题解决能力,但在复杂任务方面存在静态知识限制。检索增强生成(RAG)提高了对外部信息的访问能力,但在多跳推理和策略搜索方面仍存在刚性工作流程的限制。最近的研究进展使得LLM能够自主推理、搜索和合成信息。然而,当前依赖结果基于强化学习(RL)的方法面临关键挑战,如梯度冲突和奖励稀疏性,限制了性能提升和培训效率。为解决这些问题,我们提出了原子思维这一新型LLM思考范式,将推理分解为精细的功能单元,并由推理奖励模型(RRM)提供原子思维奖励(ATR)进行精细指导。在此基础上,我们提出了Atom-Searcher这一新型的RL框架,融合了原子思维和ATR。Atom-Searcher采用课程式奖励时间表,早期侧重于过程级的ATR,然后过渡到结果奖励,加速在有效推理路径上的收敛。在七个基准测试上的实验表明,与最新技术相比,Atom-Searcher具有一致的改进优势。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务方面存在静态知识限制。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)在增强对外部信息的访问能力的同时,仍面临多跳推理和策略搜索的刚性工作流程限制。
- 最新研究进展使得LLM能够自主推理、搜索和合成信息。
- 当前强化学习方法面临梯度冲突和奖励稀疏性挑战。
- 原子思维是一种新型的LLM思考范式,将推理分解为精细的功能单元,由推理奖励模型(RRM)提供奖励进行指导。
- Atom-Searcher是融合了原子思维和ATR的RL框架,采用课程式奖励时间表以加速收敛。
点此查看论文截图
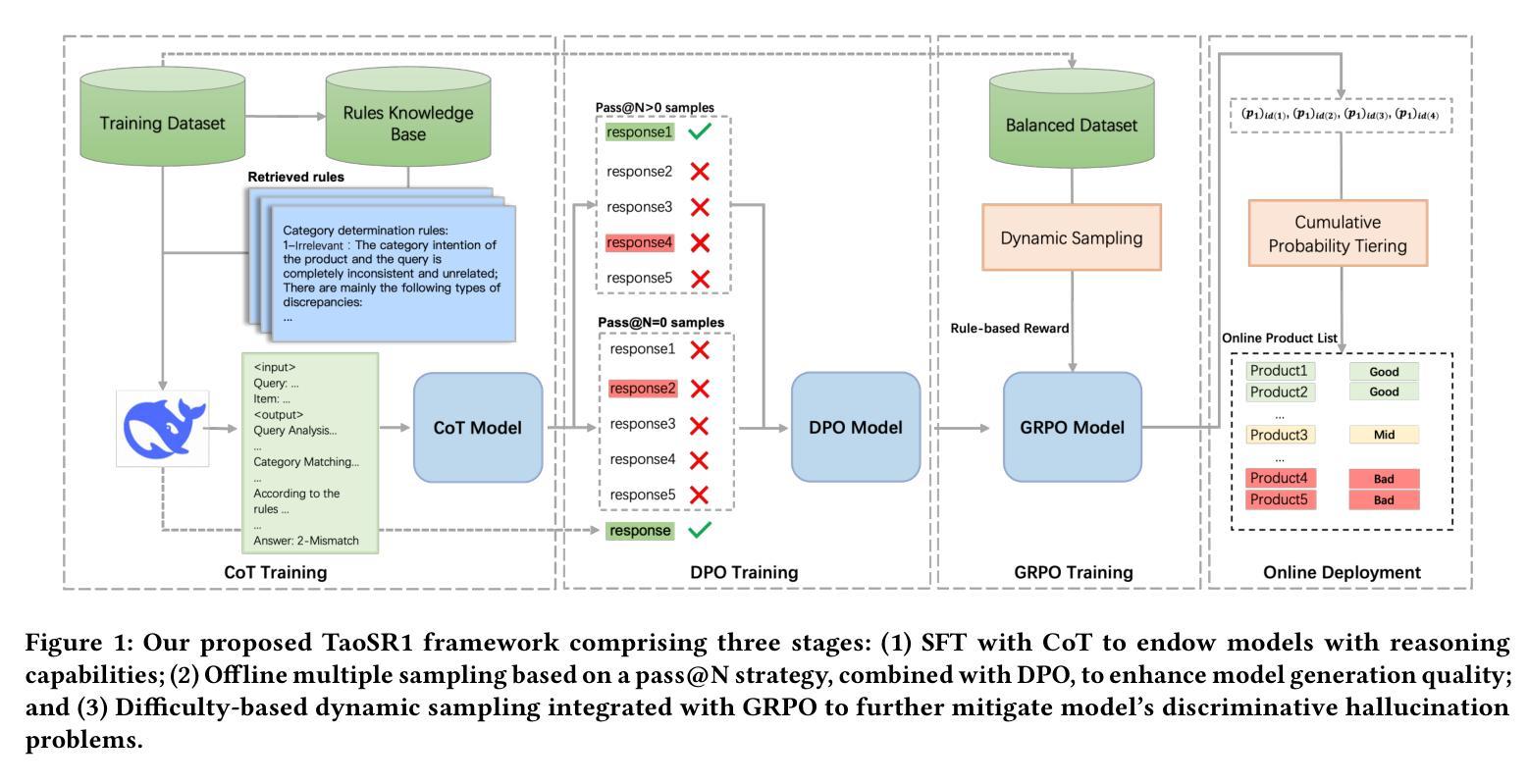
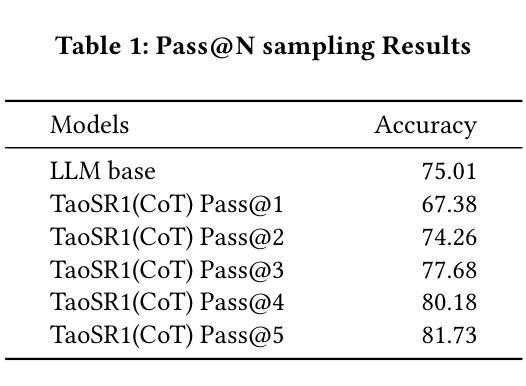
TaoSR1: The Thinking Model for E-commerce Relevance Search
Authors:Chenhe Dong, Shaowei Yao, Pengkun Jiao, Jianhui Yang, Yiming Jin, Zerui Huang, Xiaojiang Zhou, Dan Ou, Haihong Tang
Query-product relevance prediction is a core task in e-commerce search. BERT-based models excel at semantic matching but lack complex reasoning capabilities. While Large Language Models (LLMs) are explored, most still use discriminative fine-tuning or distill to smaller models for deployment. We propose a framework to directly deploy LLMs for this task, addressing key challenges: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) error accumulation, discriminative hallucination, and deployment feasibility. Our framework, TaoSR1, involves three stages: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with CoT to instill reasoning; (2) Offline sampling with a pass@N strategy and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to improve generation quality; and (3) Difficulty-based dynamic sampling with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to mitigate discriminative hallucination. Additionally, post-CoT processing and a cumulative probability-based partitioning method enable efficient online deployment. TaoSR1 significantly outperforms baselines on offline datasets and achieves substantial gains in online side-by-side human evaluations, introducing a novel paradigm for applying CoT reasoning to relevance classification.
查询商品相关性预测是电子商务搜索中的核心任务。基于BERT的模型擅长语义匹配,但缺乏复杂的推理能力。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)已被探索,但大多数仍使用判别微调或蒸馏到较小的模型进行部署。我们提出了一种直接部署LLM来完成此任务框架,解决了关键挑战:思维链(CoT)误差累积、判别性幻觉和部署可行性。我们的框架TaoSR1包含三个阶段:(1)使用CoT进行有监督微调(SFT)以灌输推理能力;(2)采用pass@N策略和直接偏好优化(DPO)进行离线采样,以提高生成质量;(3)基于难度的动态采样与群体相对策略优化(GRPO),以减轻判别性幻觉。此外,CoT处理后的基于累积概率的分区方法能够实现有效的在线部署。TaoSR1在离线数据集上的表现远超基线,在线并行人类评估中也取得了实质性进步,为将CoT推理应用于相关性分类引入了一种新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为TaoSR1的框架,用于在电子商务搜索中的查询产品相关性预测任务中直接部署大型语言模型(LLMs)。该框架解决了链式思维(CoT)误差累积、判别式幻觉和部署可行性等关键挑战。通过监督微调(SFT)赋予模型推理能力,采用离线采样和直接偏好优化提高生成质量,并通过难度基础上的动态采样优化组相对策略,缓解判别式幻觉问题。此外,框架还包括后CoT处理和基于累积概率的分区方法,以实现高效在线部署。TaoSR1在离线数据集上显著优于基线,并在在线实时人类评估中取得实质性进步,为应用CoT推理于相关性分类任务开创了新范式。
Key Takeaways
- BERT模型在语义匹配方面表现出色,但缺乏复杂推理能力。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在查询产品相关性预测任务中具有潜力。
- 提出的TaoSR1框架旨在解决链式思维(CoT)误差累积、判别式幻觉和部署可行性等挑战。
- TaoSR1框架包括三个阶段:监督微调(SFT)赋予推理能力,离线采样和直接偏好优化提高生成质量,难度基础上的动态采样优化组相对策略。
- TaoSR1框架采用后CoT处理和基于累积概率的分区方法,实现高效在线部署。
- TaoSR1在离线数据集上显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


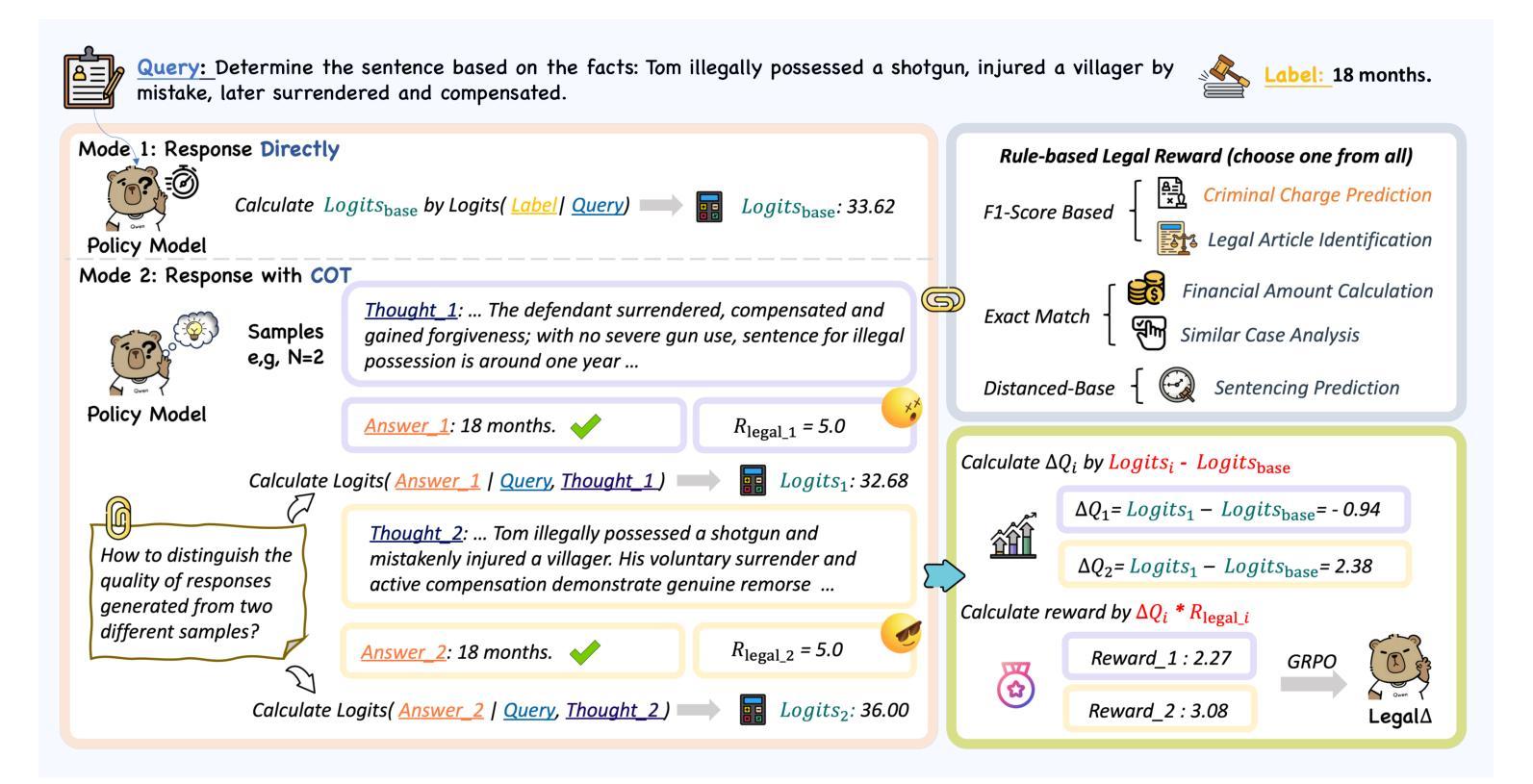
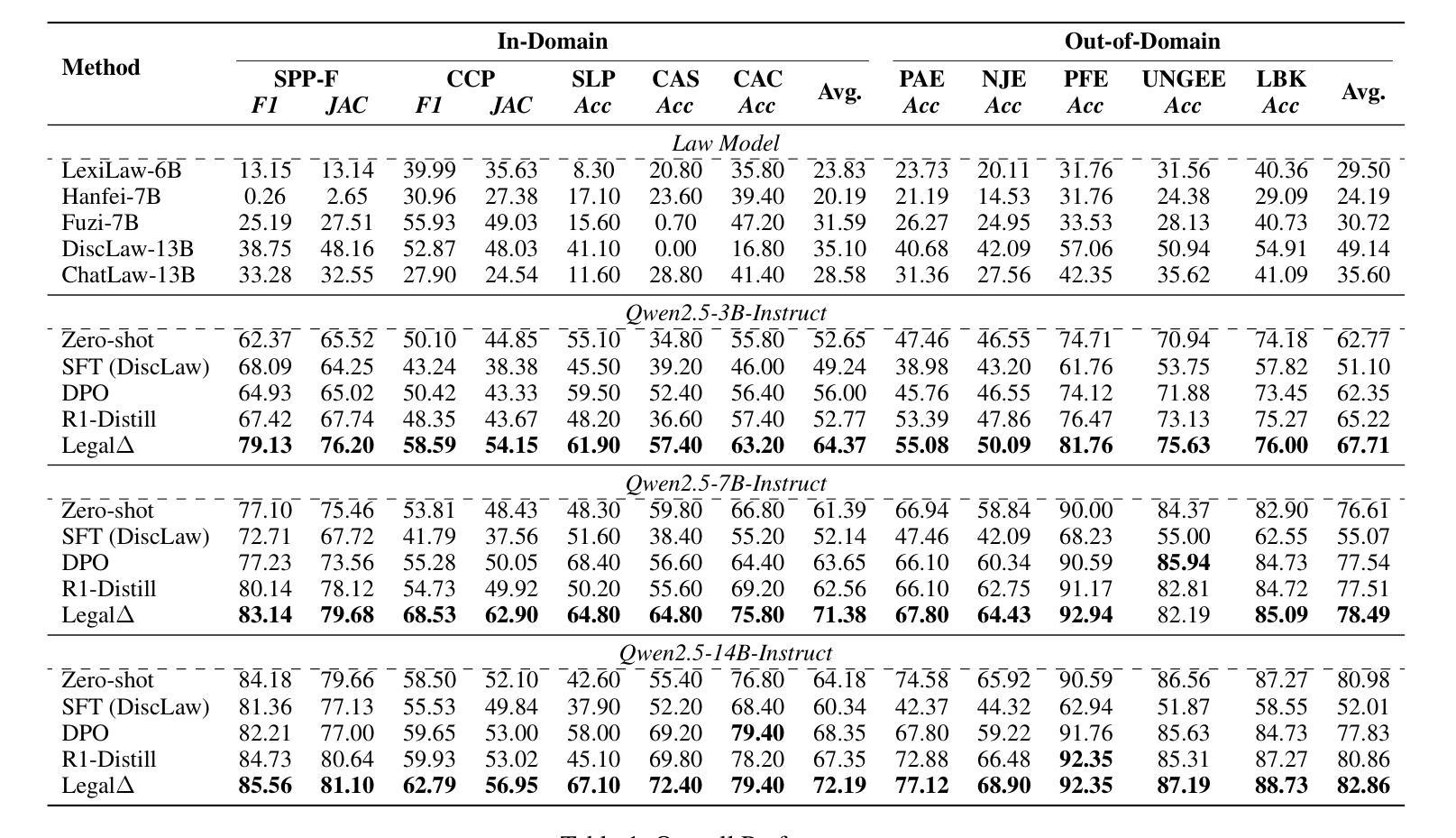
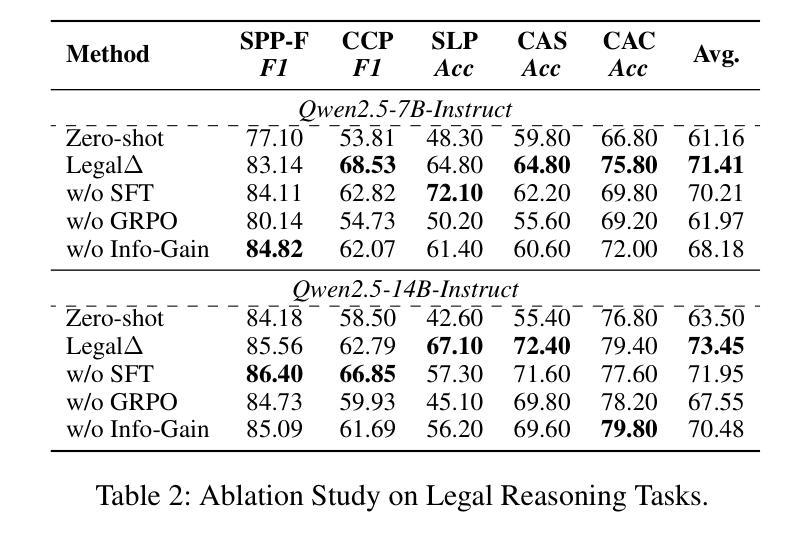
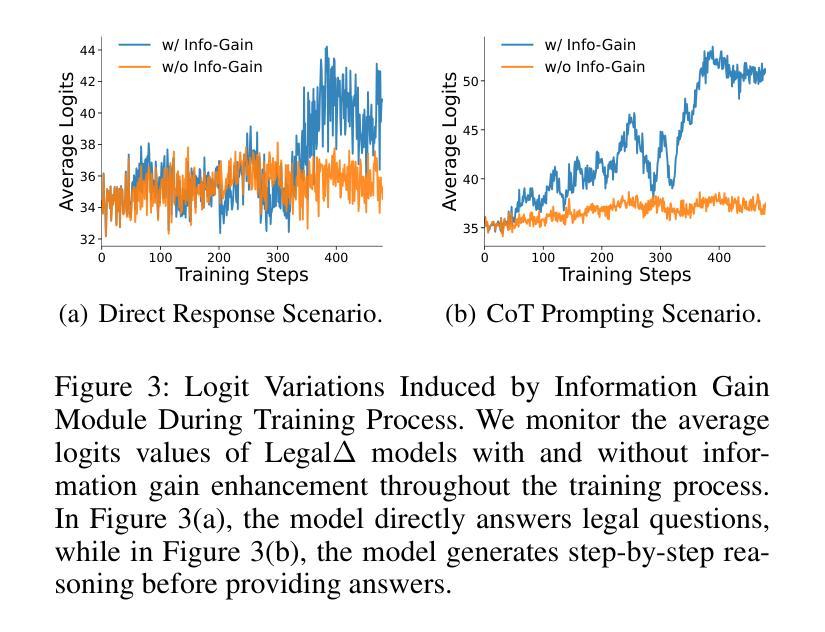
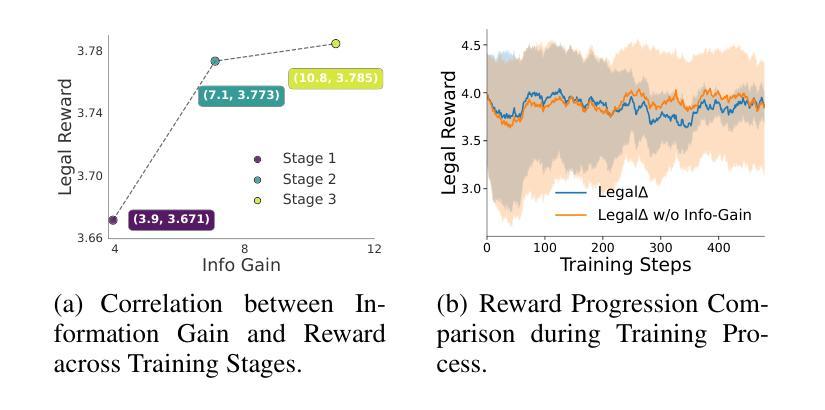
Legal$Δ$: Enhancing Legal Reasoning in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning with Chain-of-Thought Guided Information Gain
Authors:Xin Dai, Buqiang Xu, Zhenghao Liu, Yukun Yan, Huiyuan Xie, Xiaoyuan Yi, Shuo Wang, Ge Yu
Legal Artificial Intelligence (LegalAI) has achieved notable advances in automating judicial decision-making with the support of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing legal LLMs still struggle to generate reliable and interpretable reasoning processes. They often default to fast-thinking behavior by producing direct answers without explicit multi-step reasoning, limiting their effectiveness in complex legal scenarios that demand rigorous justification. To address this challenge, we propose Legal$\Delta$, a reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance legal reasoning through chain-of-thought guided information gain. During training, Legal$\Delta$ employs a dual-mode input setup-comprising direct answer and reasoning-augmented modes-and maximizes the information gain between them. This encourages the model to acquire meaningful reasoning patterns rather than generating superficial or redundant explanations. Legal$\Delta$ follows a two-stage approach: (1) distilling latent reasoning capabilities from a powerful Large Reasoning Model (LRM), DeepSeek-R1, and (2) refining reasoning quality via differential comparisons, combined with a multidimensional reward mechanism that assesses both structural coherence and legal-domain specificity. Experimental results on multiple legal reasoning tasks demonstrate that Legal$\Delta$ outperforms strong baselines in both accuracy and interpretability. It consistently produces more robust and trustworthy legal judgments without relying on labeled preference data. All code and data will be released at https://github.com/NEUIR/LegalDelta.
法律人工智能(LegalAI)在大型语言模型(LLM)的支持下,在自动化司法决策方面取得了显著进展。然而,现有的法律LLM在生成可靠且可解释的推理过程方面仍然存在困难。它们通常采取快速思考的行为,直接给出答案,而没有明确的多步骤推理,这在需要严格证明的复杂法律场景中限制了它们的有效性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了LegalΔ,一个通过思维链引导信息增益来增强法律推理的强化学习框架。在训练过程中,LegalΔ采用双模式输入设置,包括直接答案模式和推理增强模式,并最大化两者之间的信息增益。这鼓励模型获取有意义的推理模式,而不是产生肤浅或冗余的解释。LegalΔ采用两阶段方法:(1)从强大的大型推理模型(LRM)DeepSeek-R1中提炼潜在的推理能力;(2)通过差异比较和结合评估结构连贯性和法律领域特异性的多维奖励机制来优化推理质量。在多个法律推理任务上的实验结果表明,LegalΔ在准确性和可解释性方面超越了强大的基准测试。它在不依赖标记偏好数据的情况下,始终产生更稳健和可信的法律判断。所有代码和数据将在https://github.com/NEUIR/LegalDelta上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
法律人工智能(LegalAI)借助大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化司法决策制定方面取得显著进展,但在复杂法律场景中,现有法律LLMs在生成可靠且可解释的推理过程方面仍存在困难。它们往往采用快速思考行为,直接给出答案,缺乏明确的多步骤推理,难以应对需要严格论证的法律情境。为应对这一挑战,提出了LegalΔ强化学习框架,通过链式思维引导的信息增益来提升法律推理能力。LegalΔ采用双模式输入设置,鼓励模型获取有意义的推理模式,而非生成肤浅或冗余的解释。实验结果表明,LegalΔ在多个法律推理任务上的准确性和可解释性均优于强基线,能够产生更稳健和可信赖的法律判断,且无需依赖标记偏好数据。
Key Takeaways
- LegalAI借助LLMs在自动化司法决策中取得进展。
- 现有法律LLMs在复杂法律场景中面临生成可靠和可解释推理的挑战。
- LegalΔ强化学习框架通过链式思维引导的信息增益提升法律推理。
- LegalΔ采用双模式输入设置,鼓励模型获取有意义推理模式。
- LegalΔ通过两阶段方法:从强大的LRM中提炼潜在推理能力,并通过差异比较和多维度奖励机制提高推理质量。
- LegalΔ在多个法律推理任务上的准确性和可解释性优于强基线。
点此查看论文截图

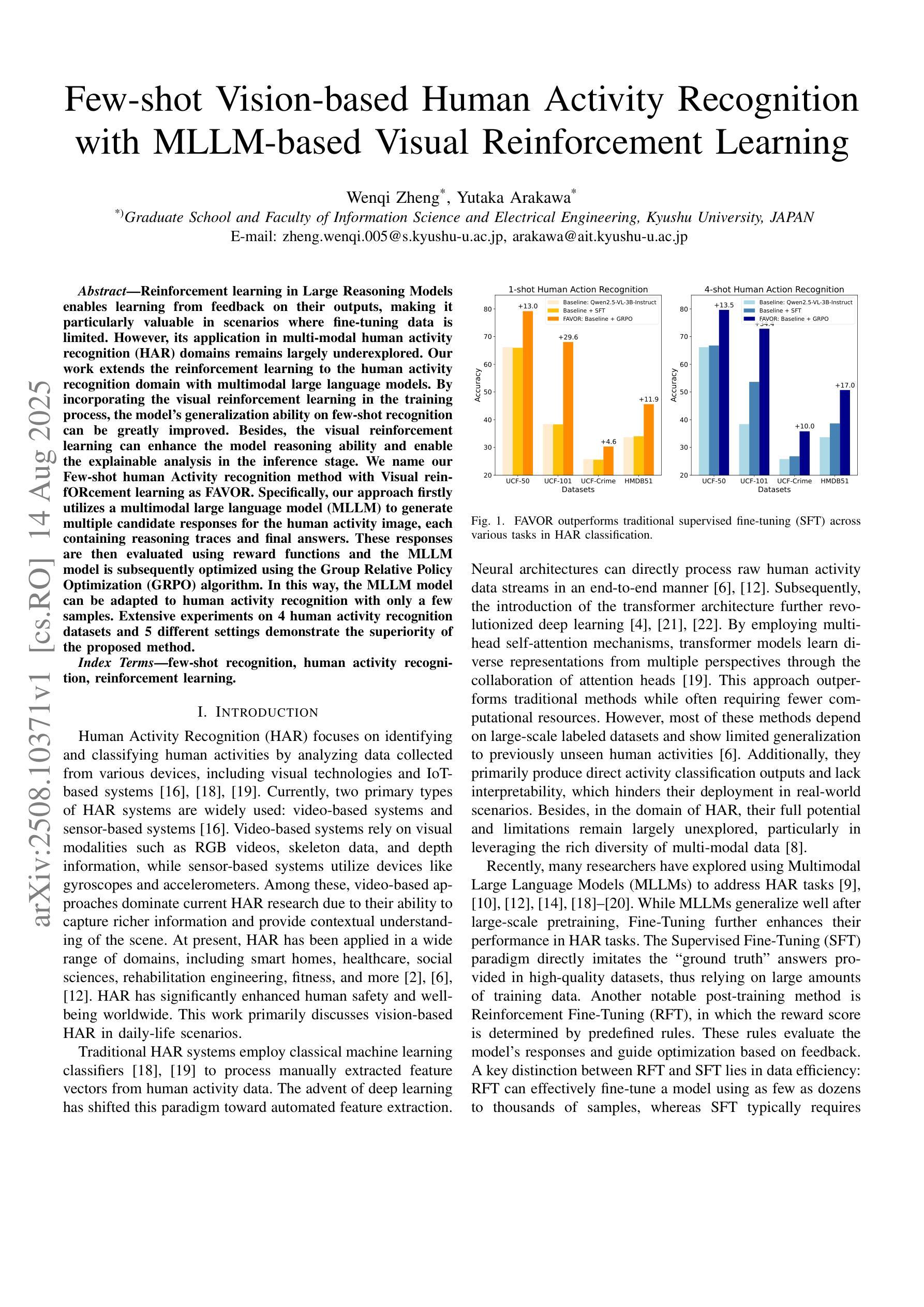
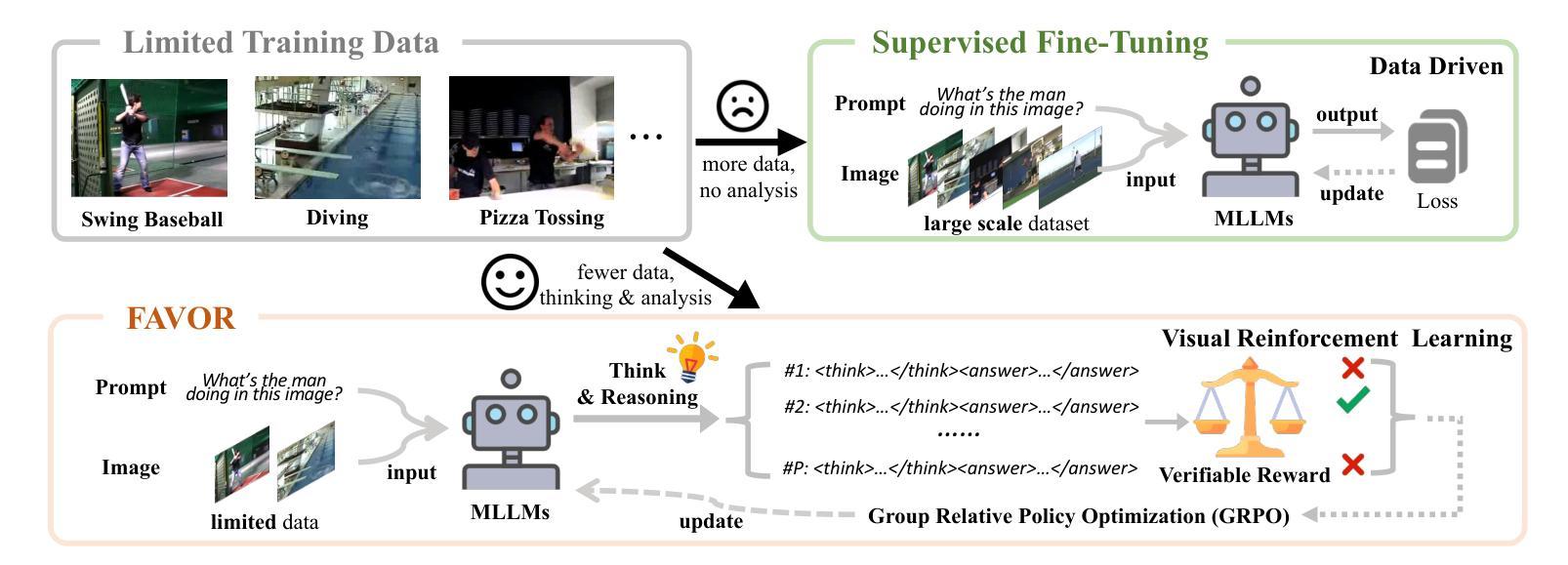
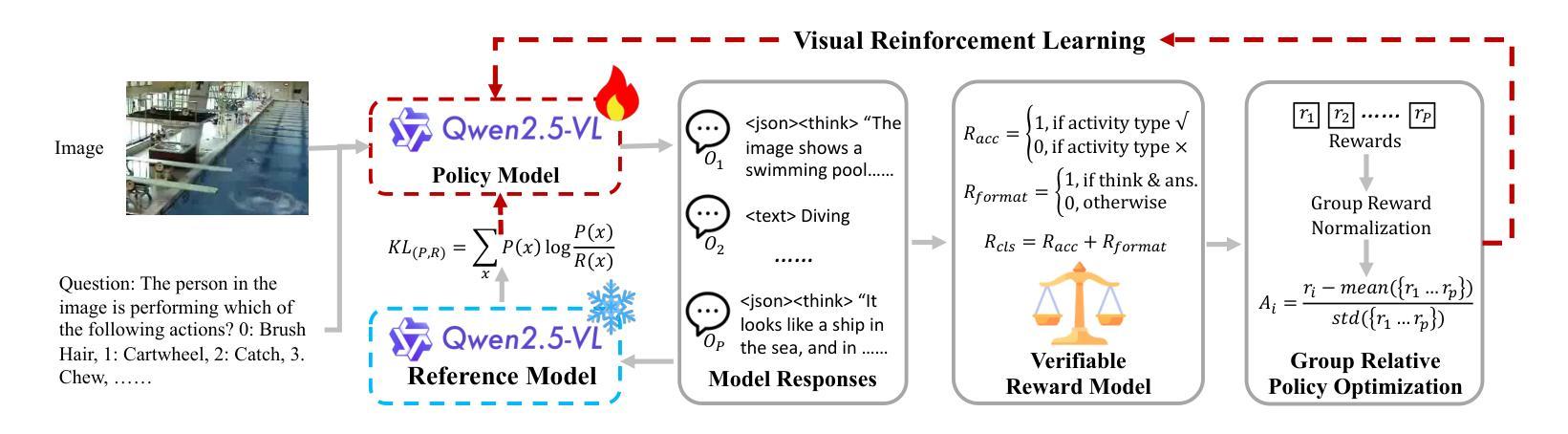
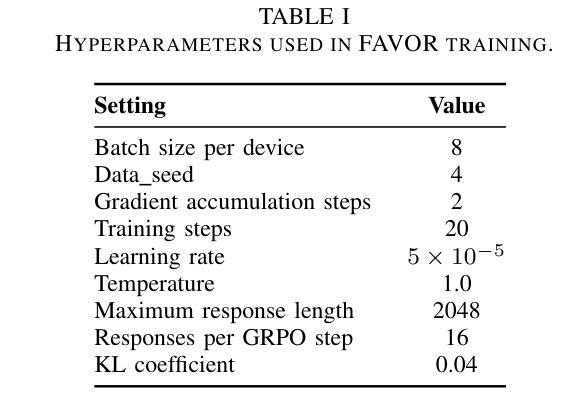
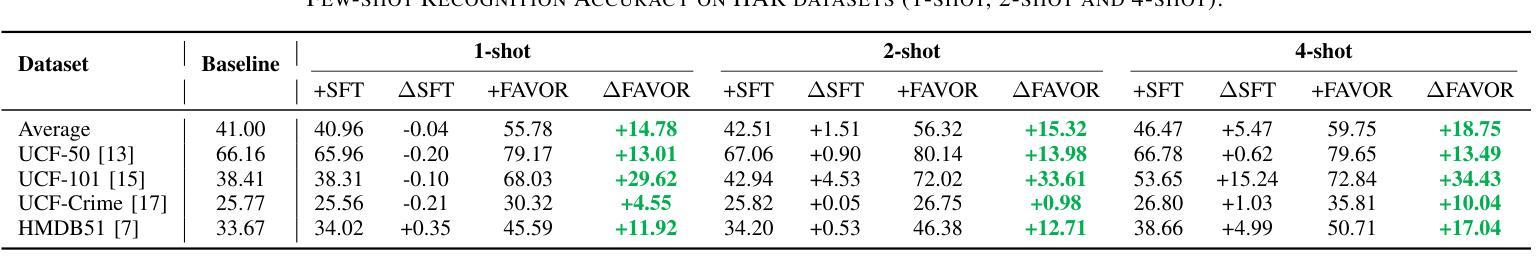
Few-shot Vision-based Human Activity Recognition with MLLM-based Visual Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wenqi Zheng, Yutaka Arakawa
Reinforcement learning in large reasoning models enables learning from feedback on their outputs, making it particularly valuable in scenarios where fine-tuning data is limited. However, its application in multi-modal human activity recognition (HAR) domains remains largely underexplored. Our work extends reinforcement learning to the human activity recognition domain with multimodal large language models. By incorporating visual reinforcement learning in the training process, the model’s generalization ability on few-shot recognition can be greatly improved. Additionally, visual reinforcement learning can enhance the model’s reasoning ability and enable explainable analysis in the inference stage. We name our few-shot human activity recognition method with visual reinforcement learning FAVOR. Specifically, our approach first utilizes a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to generate multiple candidate responses for the human activity image, each containing reasoning traces and final answers. These responses are then evaluated using reward functions, and the MLLM model is subsequently optimized using the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm. In this way, the MLLM model can be adapted to human activity recognition with only a few samples. Extensive experiments on four human activity recognition datasets and five different settings demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
强化学习在大型推理模型中的应用使得模型能够根据输出反馈进行学习,这在精细调整数据有限的情况下尤为有价值。然而,其在多模态人类活动识别(HAR)领域的应用仍被大大忽视。我们的工作将强化学习扩展到人类活动识别领域,并引入多模态大型语言模型。通过在训练过程中融入视觉强化学习,可以大大提高模型在少样本识别方面的泛化能力。此外,视觉强化学习还可以增强模型的推理能力,并在推理阶段实现可解释性分析。我们将采用视觉强化学习的少样本人类活动识别方法命名为FAVOR。具体来说,我们的方法首先利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)为人体活动图像生成多个候选响应,每个响应都包含推理轨迹和最终答案。然后,使用奖励函数对这些响应进行评估,随后使用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法对MLLM模型进行优化。通过这种方式,MLLM模型可以适应仅使用少量样本的人类活动识别。在四个人类活动识别数据集和五种不同设置下的广泛实验证明了所提出方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习在大规模推理模型中的应用可以从输出反馈中学习,这在精细调整数据有限的情况下尤其有价值。本研究将强化学习扩展到了人类活动识别领域,并结合多模态大型语言模型。通过引入视觉强化学习,模型在少量样本识别上的泛化能力大大提高,同时增强了模型的推理能力,并在推理阶段实现了可解释性分析。本研究提出的基于视觉强化学习的少量人类活动识别方法命名为FAVOR。该方法利用多模态大型语言模型生成人类活动图像的多响应候选,利用奖励函数进行评估,并使用集团相对策略优化算法对模型进行优化。在四个数据集和五种不同设置下的实验表明,该方法具有优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习可应用于大规模推理模型,并从输出反馈中学习。
- 视觉强化学习被引入到人类活动识别领域,与多模态大型语言模型结合。
- 视觉强化学习可显著提高模型在少量样本识别上的泛化能力。
- 视觉强化学习增强了模型的推理能力,并实现了推理阶段的可解释性分析。
- 提出了一种基于视觉强化学习的少量人类活动识别方法,名为FAVOR。
- FAVOR方法利用多模态大型语言模型生成多个响应候选,并使用奖励函数和集团相对策略优化算法进行优化。
点此查看论文截图


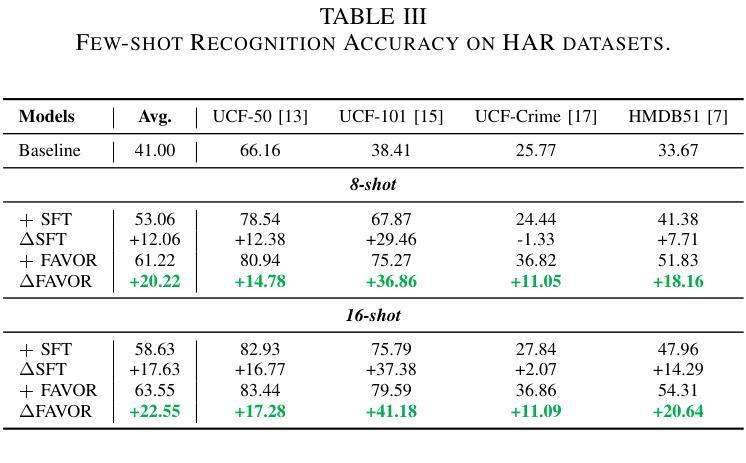
Making Qwen3 Think in Korean with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Jungyup Lee, Jemin Kim, Sang Park, SeungJae Lee
We present a two-stage fine-tuning approach to make the large language model Qwen3 14B “think” natively in Korean. In the first stage, supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on a high-quality Korean reasoning dataset establishes a strong foundation in Korean logical reasoning, yielding notable improvements in Korean-language tasks and even some gains in general reasoning ability. In the second stage, we employ reinforcement learning with a customized Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm to further enhance both Korean reasoning alignment and overall problem-solving performance. We address critical stability challenges in GRPO training - such as reward hacking and policy collapse - by introducing an oracle judge model that calibrates the reward signal. Our approach achieves stable learning (avoiding the collapse observed in naive GRPO) and leads to steady, incremental performance gains. The final RL-tuned model demonstrates substantially improved results on advanced reasoning benchmarks (particularly math and coding tasks) while maintaining knowledge and language proficiency, successfully conducting its internal chain-of-thought entirely in Korean.
我们提出了一种两阶段的微调方法,使大型语言模型Qwen3 14B能够“以韩语母语思考”。在第一阶段,通过高质量韩语推理数据集的有监督微调(SFT)为韩语逻辑推理建立了坚实的基础,在韩语任务中取得了显著的改进,甚至在一般推理能力上也有所提升。在第二阶段,我们使用强化学习与自定义的Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)算法进一步提高了韩语推理对齐和整体解决问题的能力。我们通过引入校准奖励信号的专家裁判模型来解决GRPO训练中的关键稳定性挑战,如奖励破解和政策崩溃等。我们的方法实现了稳定的学习(避免了幼稚GRPO中观察到的崩溃),并带来了稳定的、增量式的性能提升。最终经过RL调参的模型在高级推理基准测试(尤其是数学和编码任务)上取得了显著改进的结果,同时保持了知识和语言技能,成功地以韩语完全完成了其内部思考链。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型Qwen3 14B通过两阶段微调使其“天生”具备韩语思考能力。第一阶段通过高质量韩语推理数据集进行有监督微调(SFT),为韩语逻辑推理打下了坚实基础,在韩语任务上取得了显著改进,甚至在通用推理能力上也有所提升。第二阶段采用强化学习,结合自定义的组相对策略优化(GRPO)算法,进一步提高韩语推理对齐和整体问题解决能力。通过引入校准奖励信号的oracle判断模型,解决了GRPO训练中的关键稳定性挑战,如奖励黑客和策略崩溃。该方法实现了稳定学习,带来了稳定的性能提升。最终通过强化学习调整的模型在高级推理基准测试(尤其是数学和编码任务)上取得了显著改善,同时保持了知识和语言技能,并成功以韩语完成了内部思维链条。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个两阶段微调方法,使大型语言模型Qwen3 14B能够“以韩语思考”。
- 第一阶段通过高质量韩语推理数据集进行有监督微调,提高了韩语任务和通用推理能力。
- 第二阶段采用强化学习和自定义的GRPO算法进一步提高韩语推理和问题解决能力。
- 引入oracle判断模型解决GRPO训练中的稳定性挑战。
- 方法实现了稳定学习,并带来性能上的持续提高。
- 最终模型在高级推理测试中表现优异,特别是在数学和编码任务上。
点此查看论文截图

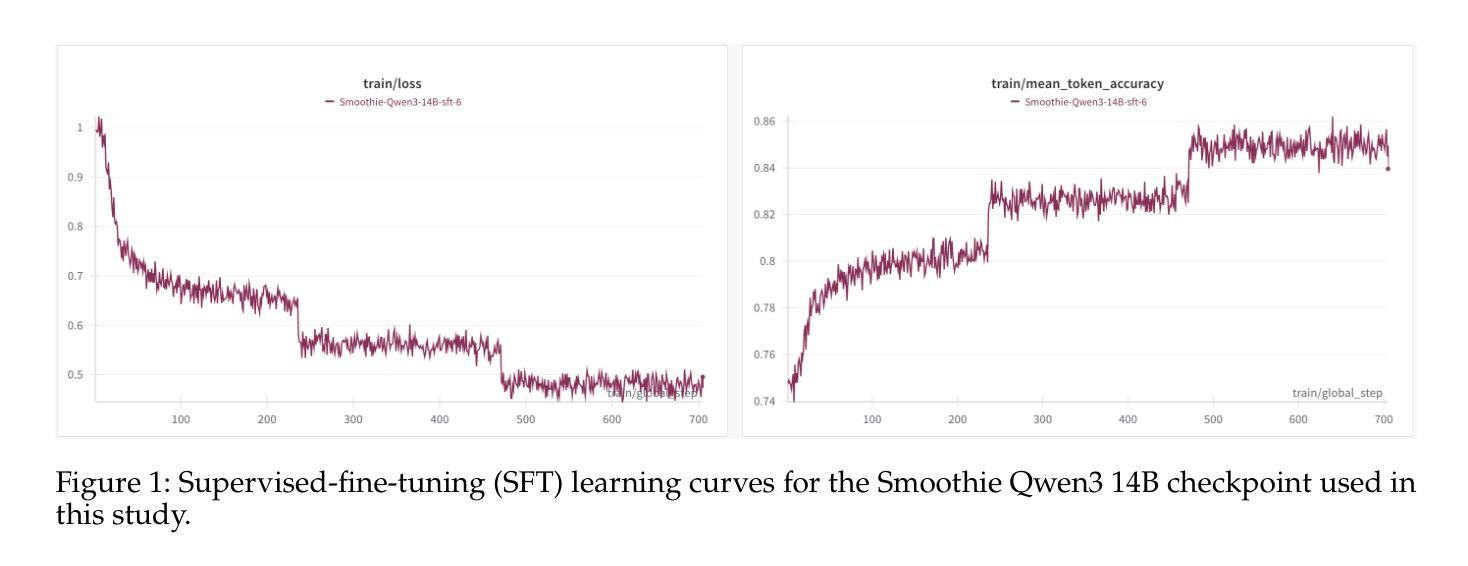
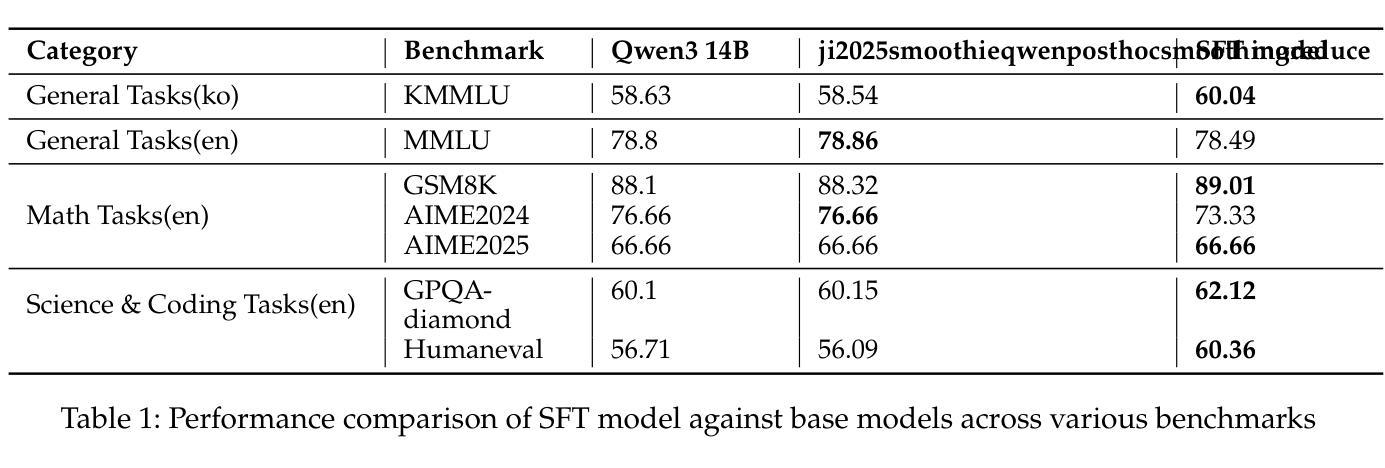
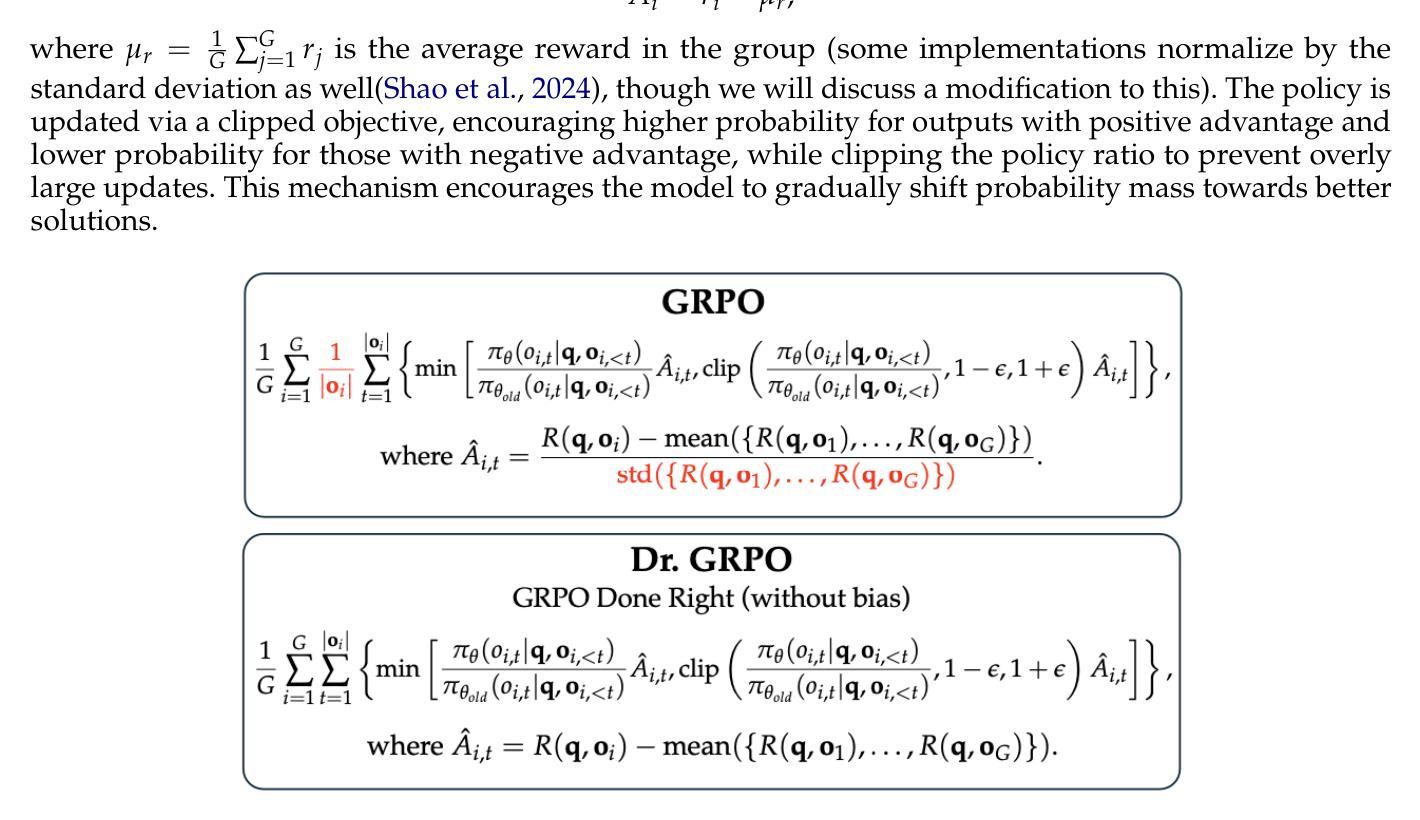
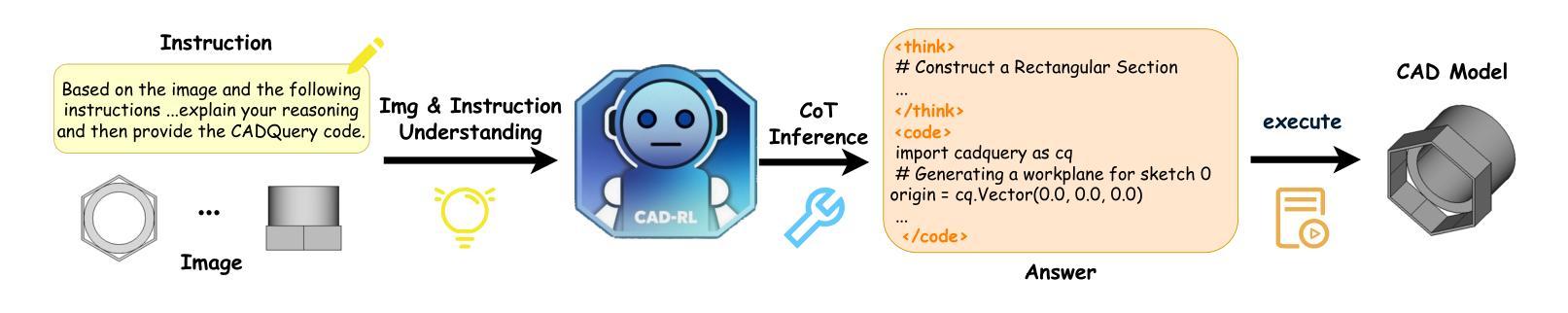
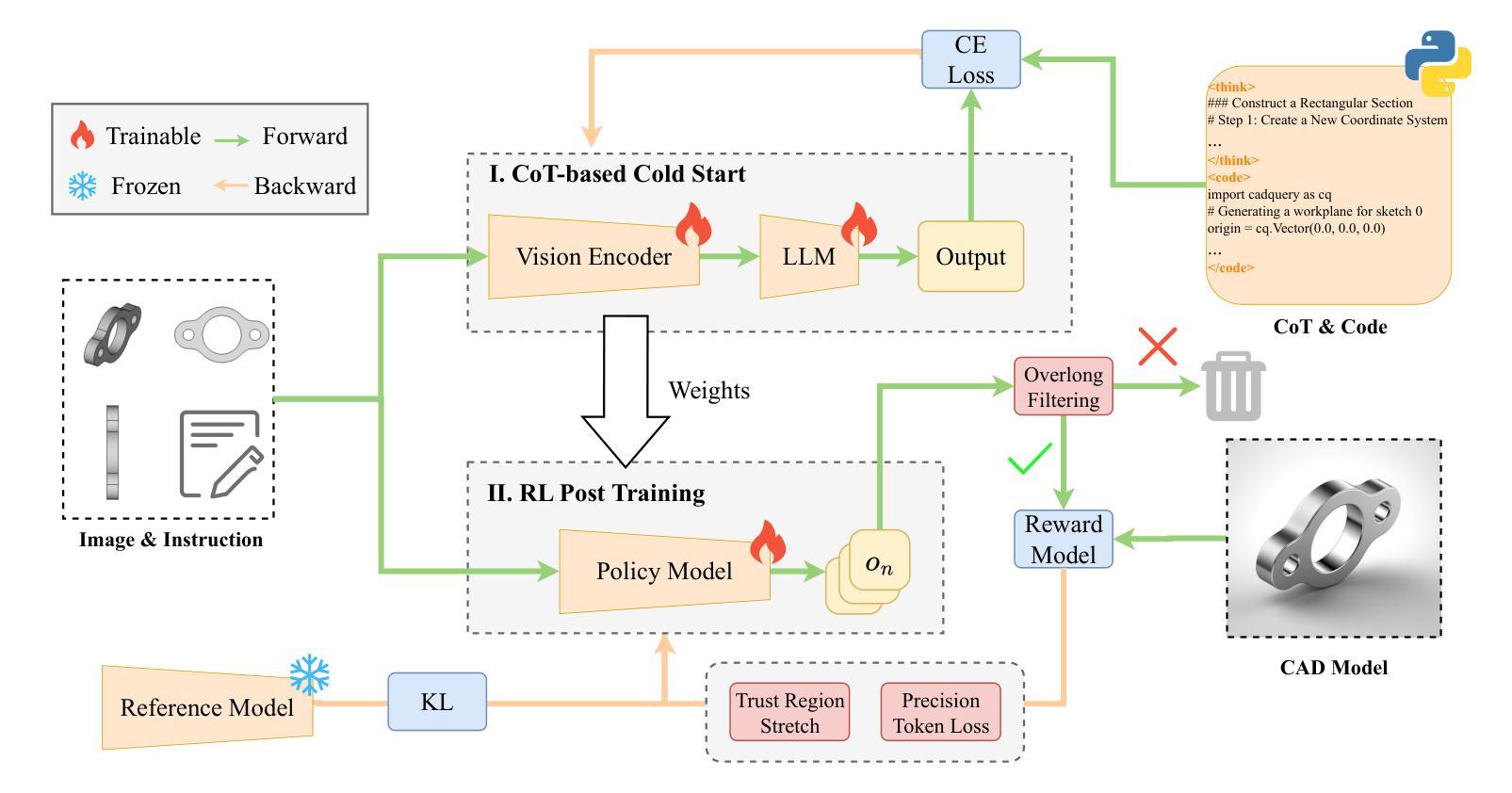
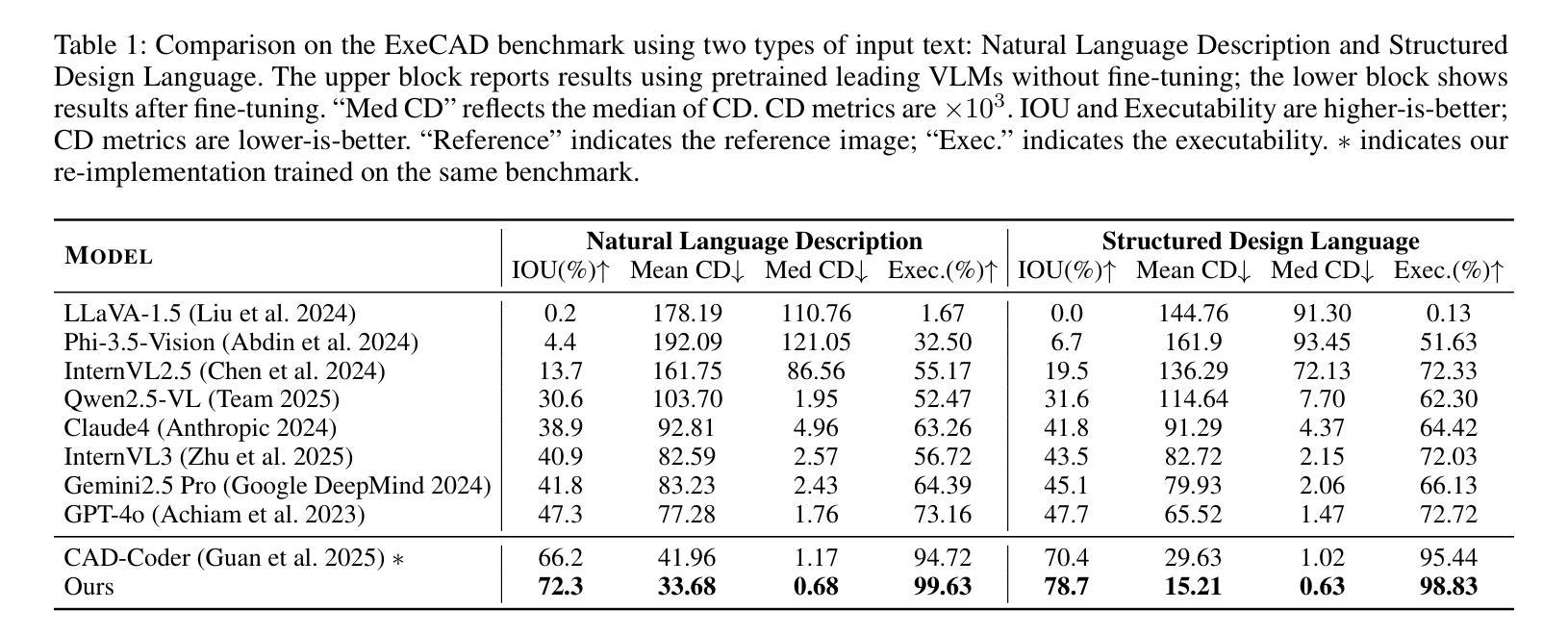
From Intent to Execution: Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reinforcement Learning for Precise CAD Code Generation
Authors:Ke Niu, Haiyang Yu, Zhuofan Chen, Mengyang Zhao, Teng Fu, Bin Li, Xiangyang Xue
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a vital role in engineering and manufacturing, yet current CAD workflows require extensive domain expertise and manual modeling effort. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have made it possible to generate code from natural language, opening new opportunities for automating parametric 3D modeling. However, directly translating human design intent into executable CAD code remains highly challenging, due to the need for logical reasoning, syntactic correctness, and numerical precision. In this work, we propose CAD-RL, a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) guided reinforcement learning post training framework for CAD modeling code generation. Our method combines CoT-based Cold Start with goal-driven reinforcement learning post training using three task-specific rewards: executability reward, geometric accuracy reward, and external evaluation reward. To ensure stable policy learning under sparse and high-variance reward conditions, we introduce three targeted optimization strategies: Trust Region Stretch for improved exploration, Precision Token Loss for enhanced dimensions parameter accuracy, and Overlong Filtering to reduce noisy supervision. To support training and benchmarking, we release ExeCAD, a noval dataset comprising 16,540 real-world CAD examples with paired natural language and structured design language descriptions, executable CADQuery scripts, and rendered 3D models. Experiments demonstrate that CAD-RL achieves significant improvements in reasoning quality, output precision, and code executability over existing VLMs.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造中扮演着至关重要的角色,然而当前的CAD工作流程需要广泛的专业知识和手动建模工作。自然语言生成代码的最新进展为自动化参数化三维建模提供了新的机会。然而,直接将人类的设计意图转化为可执行的CAD代码仍然面临巨大的挑战,这包括逻辑理解、语法正确和数值精确的需求。在这项工作中,我们提出了CAD-RL,这是一种用于CAD建模代码生成的多模态思维链引导强化学习训练后框架。我们的方法结合了基于思维链的冷启动和目标驱动强化学习训练后使用三种特定任务奖励:可执行性奖励、几何精度奖励和外部评估奖励。为确保在稀疏和高方差奖励条件下稳定学习政策,我们引入了三项有针对性的优化策略:用于改进探索的信任区域扩展、用于提高维度参数精度的精确令牌丢失以及用于减少噪声监督的长过滤。为了支持训练和基准测试,我们发布了ExeCAD数据集,该数据集包含现实世界中的CAD示例共16,540个,每个示例配备自然语言描述和结构化设计语言描述、可执行的CADQuery脚本以及渲染的3D模型。实验表明,在推理质量、输出精度和代码可执行性方面,CAD-RL相较于现有的大型语言模型取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程师和制造行业扮演着至关重要的角色,但其流程需要大量专业知识和技能进行手动建模。随着自然语言到代码生成技术的进步,全自动的三维参数建模有了新机遇。然而,将人类的设计意图直接转化为可执行的CAD代码仍面临逻辑理解、语法正确性和数值精确性的挑战。本研究提出了CAD-RL模型,采用多模态思维链指导强化学习对CAD建模代码生成进行后训练。该模型结合了思维链的冷启动技术,以目标驱动强化学习进行后训练,并使用三个特定任务奖励:可执行性奖励、几何精度奖励和外部评价奖励。在稀疏且多变的奖励条件下确保稳定学习,本研究还推出了三大针对性优化策略。同时公开了一个支持训练和基准测试的新数据集ExeCAD,它包含了现实世界中CAD建模的例子和配套的自然语言描述、结构化的设计语言以及可执行脚本等。实验结果证明了CAD-RL模型在推理质量、输出精确度和代码可执行性方面取得了显著进步。
Key Takeaways
- CAD在工程师和制造行业中的重要性及其手动建模的需求。
- 自然语言到代码生成技术在全自动三维参数建模中的应用及挑战。
- CAD-RL模型的提出,结合了多模态思维链(CoT)和强化学习用于CAD建模代码生成。
- CAD-RL模型采用三种任务特定奖励和三大优化策略来提高性能。
- 发布了一个新的数据集ExeCAD,用于训练和基准测试。
- CAD-RL模型在推理质量、输出精确度和代码可执行性方面的显著改善。
点此查看论文截图