⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
MMAU-Pro: A Challenging and Comprehensive Benchmark for Holistic Evaluation of Audio General Intelligence
Authors:Sonal Kumar, Šimon Sedláček, Vaibhavi Lokegaonkar, Fernando López, Wenyi Yu, Nishit Anand, Hyeonggon Ryu, Lichang Chen, Maxim Plička, Miroslav Hlaváček, William Fineas Ellingwood, Sathvik Udupa, Siyuan Hou, Allison Ferner, Sara Barahona, Cecilia Bolaños, Satish Rahi, Laura Herrera-Alarcón, Satvik Dixit, Siddhi Patil, Soham Deshmukh, Lasha Koroshinadze, Yao Liu, Leibny Paola Garcia Perera, Eleni Zanou, Themos Stafylakis, Joon Son Chung, David Harwath, Chao Zhang, Dinesh Manocha, Alicia Lozano-Diez, Santosh Kesiraju, Sreyan Ghosh, Ramani Duraiswami
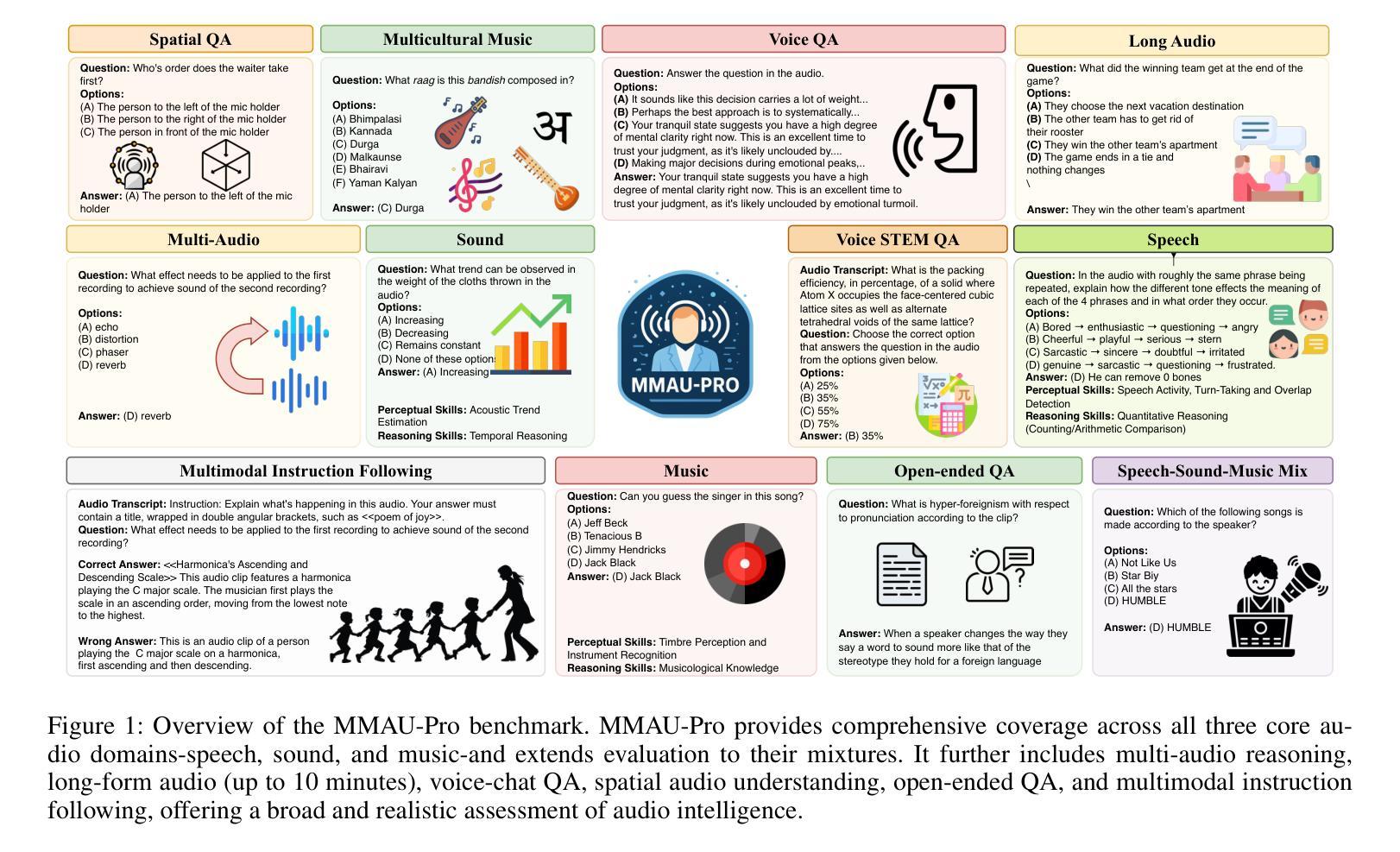
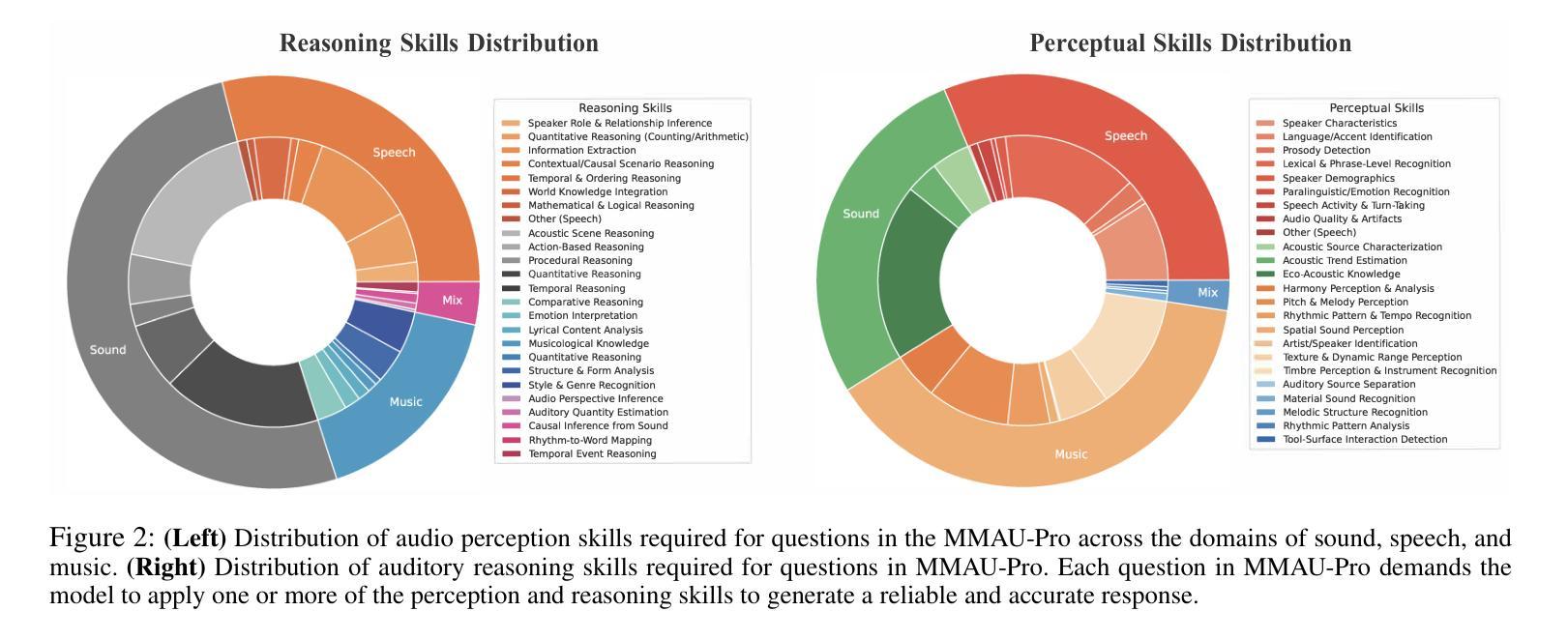
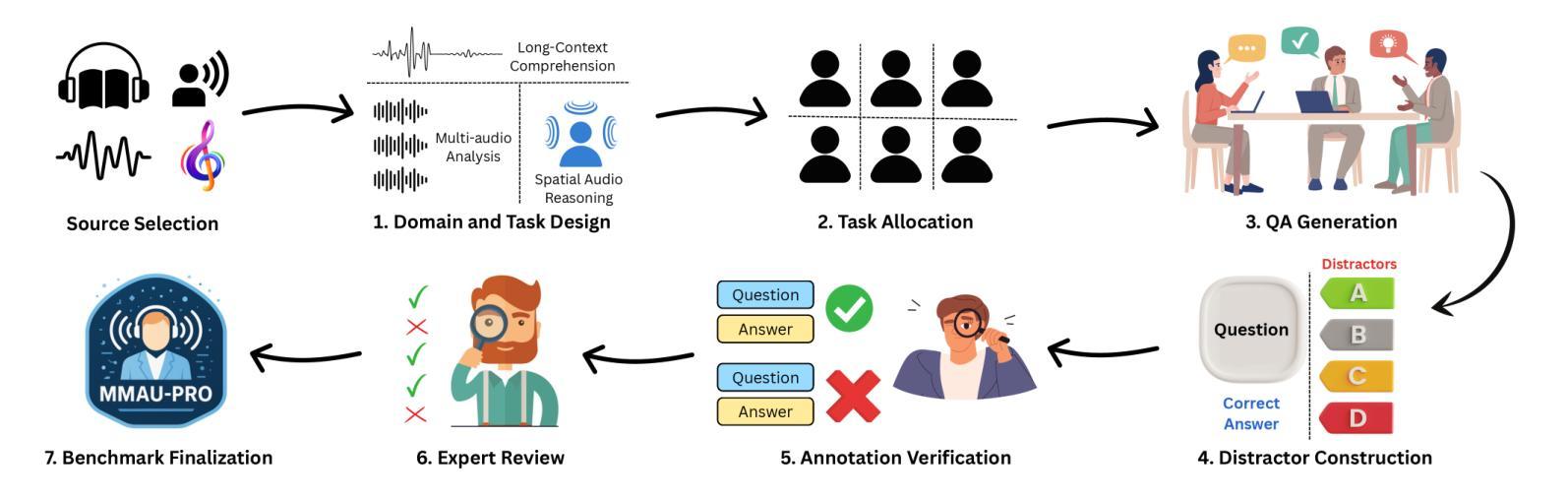
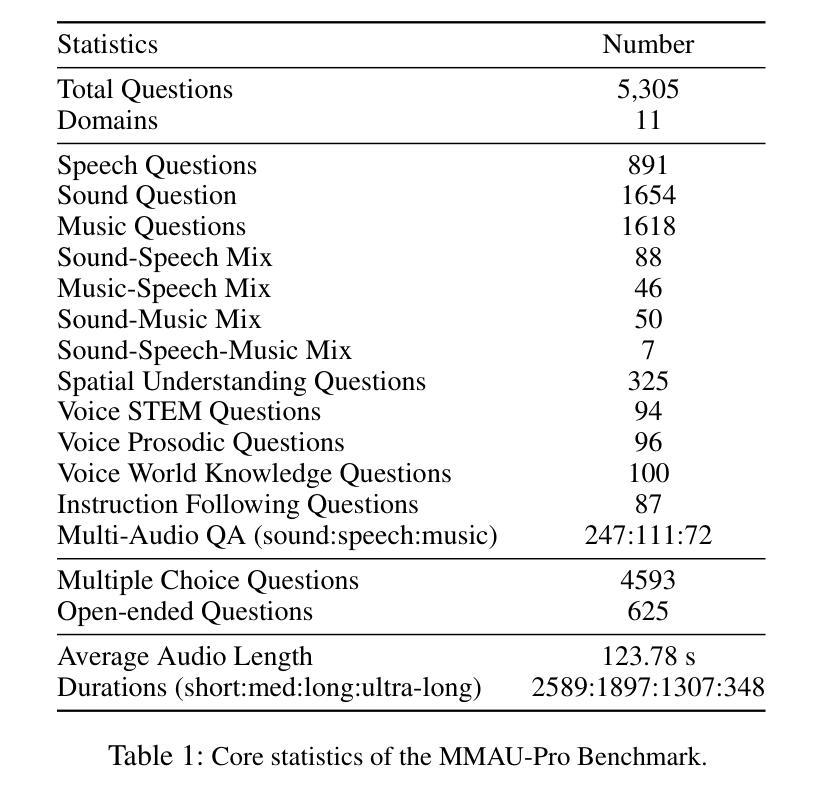
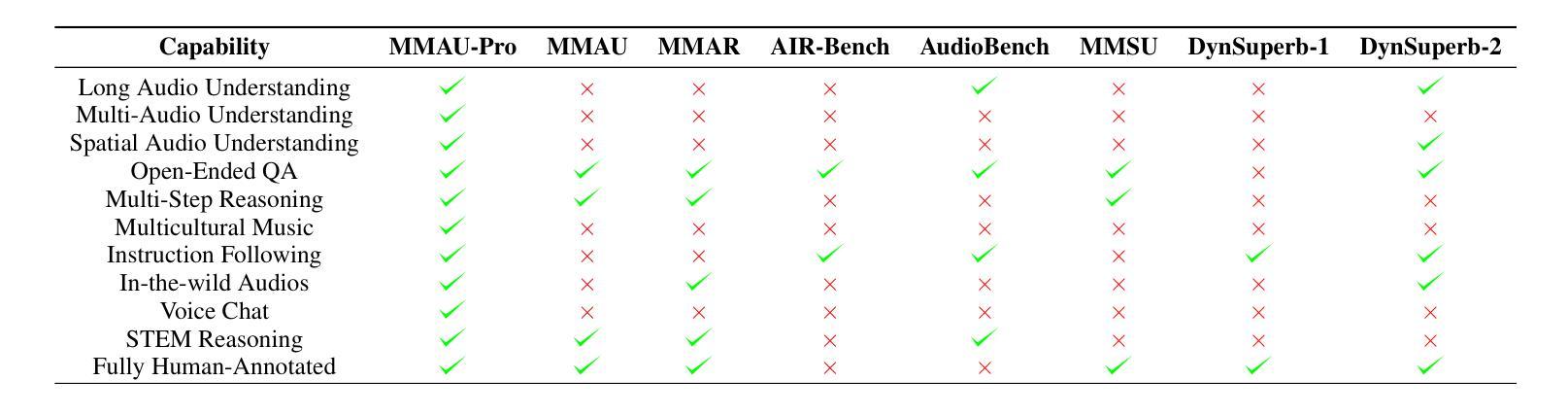
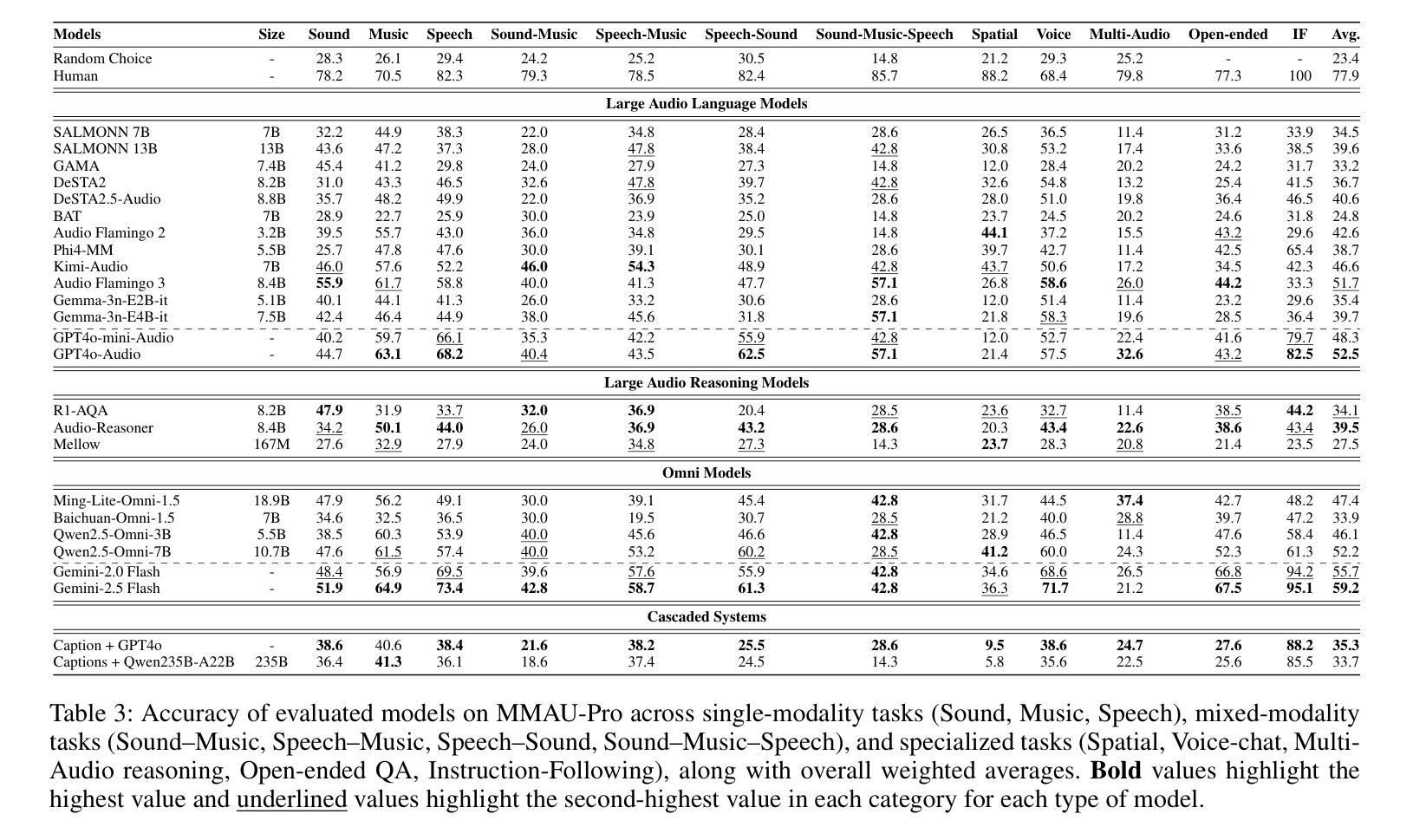
Audio comprehension-including speech, non-speech sounds, and music-is essential for achieving human-level intelligence. Consequently, AI agents must demonstrate holistic audio understanding to qualify as generally intelligent. However, evaluating auditory intelligence comprehensively remains challenging. To address this gap, we introduce MMAU-Pro, the most comprehensive and rigorously curated benchmark for assessing audio intelligence in AI systems. MMAU-Pro contains 5,305 instances, where each instance has one or more audios paired with human expert-generated question-answer pairs, spanning speech, sound, music, and their combinations. Unlike existing benchmarks, MMAU-Pro evaluates auditory intelligence across 49 unique skills and multiple complex dimensions, including long-form audio comprehension, spatial audio reasoning, multi-audio understanding, among others. All questions are meticulously designed to require deliberate multi-hop reasoning, including both multiple-choice and open-ended response formats. Importantly, audio data is sourced directly ``from the wild” rather than from existing datasets with known distributions. We evaluate 22 leading open-source and proprietary multimodal AI models, revealing significant limitations: even state-of-the-art models such as Gemini 2.5 Flash and Audio Flamingo 3 achieve only 59.2% and 51.7% accuracy, respectively, approaching random performance in multiple categories. Our extensive analysis highlights specific shortcomings and provides novel insights, offering actionable perspectives for the community to enhance future AI systems’ progression toward audio general intelligence. The benchmark and code is available at https://sonalkum.github.io/mmau-pro.
音频理解——包括语音、非语音声音和音乐——对于实现人类水平的智能至关重要。因此,人工智能代理必须展现出全面的音频理解能力,才能具备通用智能的资格。然而,全面评估听觉智能仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了MMAU-Pro,这是评估人工智能系统音频智能的最全面且经过严格策划的基准测试。MMAU-Pro包含5,305个实例,每个实例包含一至多个音频,以及与人类专家生成的问题答案配对,涵盖语音、声音、音乐及其组合。与现有基准测试不同,MMAU-Pro在49种独特技能和多个复杂维度上评估听觉智能,包括长音频理解、空间音频推理、多音频理解等。所有问题都经过精心设计,需要进行深思熟虑的多步推理,包括多项选择和开放式回答格式。重要的是,音频数据直接来源于“野外”,而非来自已知分布的现有数据集。我们评估了22个领先的开源和专有模态人工智能模型,揭示了显著局限:即使是最先进的模型,如Gemini 2.5 Flash和Audio Flamingo 3,其准确率也仅为59.2%和51.7%,在多个类别中接近随机性能。我们的深入分析突出了特定缺点,并提供了新颖见解,为社区提供了可操作的角度,以推动未来人工智能系统在音频通用智能方面的进步。基准测试和代码可在[https://sonalkum.github.io/mmau-pro进行访问。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
音频理解对于实现人类水平的智能至关重要,包括语音、非语音声音和音乐。AI系统必须展示全面的音频理解才能被视为具有普遍智能。为评估听觉智能,推出MMAU-Pro基准测试,包含5305个音频实例,涵盖语音、声音、音乐及其组合,评估49项独特技能和多个复杂维度。对比评估22种领先的多模式AI模型,显示现有模型仍存在显著局限。
Key Takeaways
- 音频理解对人类智能至关重要,涵盖语音、非语音声音和音乐等方面。
- AI系统需具备全面的音频理解才能具备普遍智能。
- MMAU-Pro是一个全面且严谨的基准测试,用于评估AI系统的听觉智能。
- MMAU-Pro包含多种音频实例和多种评估技能与维度。
- 现有AI模型在听觉智能方面存在局限,即使是领先模型也无法达到完美表现。
6.MMAU-Pro提供的基准和代码可供公众访问,以推动AI系统的音频智能发展。
点此查看论文截图

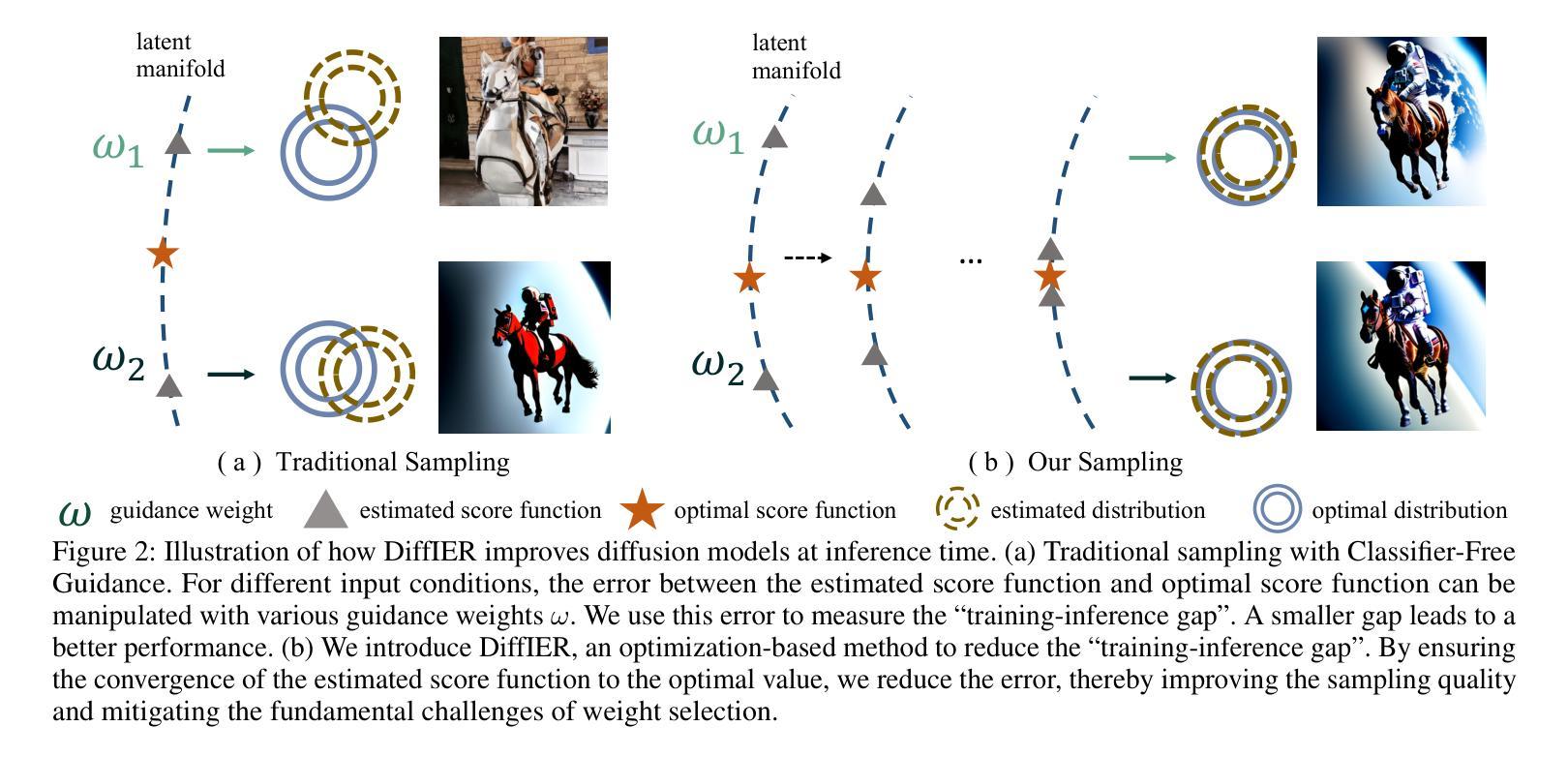
DiffIER: Optimizing Diffusion Models with Iterative Error Reduction
Authors:Ao Chen, Lihe Ding, Tianfan Xue
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality samples and enhancing performance across diverse domains through Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG). However, the quality of generated samples is highly sensitive to the selection of the guidance weight. In this work, we identify a critical ``training-inference gap’’ and we argue that it is the presence of this gap that undermines the performance of conditional generation and renders outputs highly sensitive to the guidance weight. We quantify this gap by measuring the accumulated error during the inference stage and establish a correlation between the selection of guidance weight and minimizing this gap. Furthermore, to mitigate this gap, we propose DiffIER, an optimization-based method for high-quality generation. We demonstrate that the accumulated error can be effectively reduced by an iterative error minimization at each step during inference. By introducing this novel plug-and-play optimization framework, we enable the optimization of errors at every single inference step and enhance generation quality. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms baseline approaches in conditional generation tasks. Furthermore, the method achieves consistent success in text-to-image generation, image super-resolution, and text-to-speech generation, underscoring its versatility and potential for broad applications in future research.
扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)在生成高质量样本以及提高不同领域的性能上展现了显著的能力。然而,生成样本的质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。在这项工作中,我们识别出了一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,我们认为正是这个差距影响了条件生成的表现,并使输出高度依赖于引导权重。我们通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这个差距,并建立了引导权重的选择与最小化这个差距之间的关联。此外,为了缓解这一差距,我们提出了DiffIER,这是一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。我们证明,通过推理过程中每一步的迭代误差最小化,可以有效地减少累积误差。通过引入这种新颖即插即用的优化框架,我们能够在每个单独的推理步骤中优化误差,提高生成质量。经验结果表明,我们提出的方法在条件生成任务上优于基线方法。此外,该方法在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成方面取得了持续的成功,这突显了其通用性和在未来研究中广泛应用的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)在生成高质量样本和提高不同领域性能方面的显著能力。然而,生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。本文识别出关键的“训练-推理差距”,并认为正是这一差距影响了有条件生成的表现,并使输出对引导权重高度敏感。为了缩小这一差距,本文提出了DiffIER,一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。通过在每个推理步骤中引入迭代误差最小化,可以有效地减少累积误差。实证结果表明,该方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法,并在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成等任务中取得了持续的成功。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型具备生成高质量样本和提高不同领域性能的能力。
- 生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。
- 存在关键的“训练-推理差距”,影响有条件生成的表现。
- 本文通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这一差距。
- 提出了DiffIER方法,通过迭代误差最小化的优化框架缩小训练-推理差距。
- DiffIER方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法。
点此查看论文截图




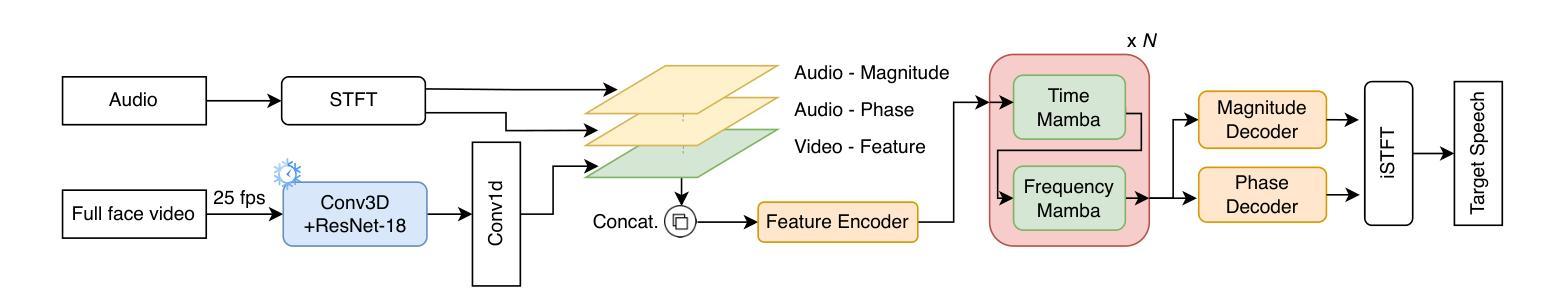
Leveraging Mamba with Full-Face Vision for Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement
Authors:Rong Chao, Wenze Ren, You-Jin Li, Kuo-Hsuan Hung, Sung-Feng Huang, Szu-Wei Fu, Wen-Huang Cheng, Yu Tsao
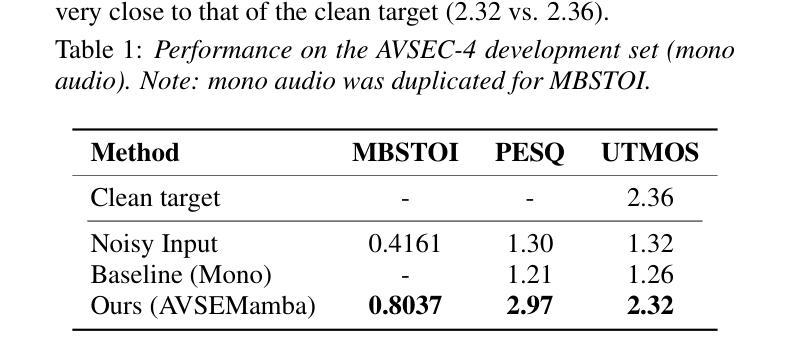
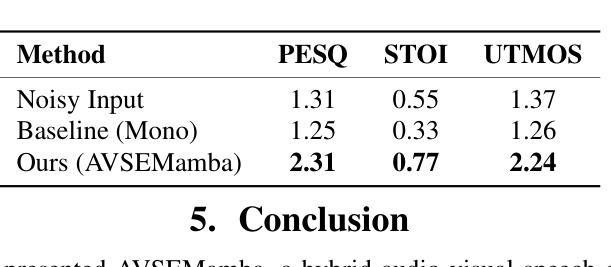
Recent Mamba-based models have shown promise in speech enhancement by efficiently modeling long-range temporal dependencies. However, models like Speech Enhancement Mamba (SEMamba) remain limited to single-speaker scenarios and struggle in complex multi-speaker environments such as the cocktail party problem. To overcome this, we introduce AVSEMamba, an audio-visual speech enhancement model that integrates full-face visual cues with a Mamba-based temporal backbone. By leveraging spatiotemporal visual information, AVSEMamba enables more accurate extraction of target speech in challenging conditions. Evaluated on the AVSEC-4 Challenge development and blind test sets, AVSEMamba outperforms other monaural baselines in speech intelligibility (STOI), perceptual quality (PESQ), and non-intrusive quality (UTMOS), and achieves \textbf{1st place} on the monaural leaderboard.
基于Mamba的近期模型通过有效地建模长程时间依赖性在语音增强方面显示出良好的前景。然而,像语音增强Mamba(SEMamba)这样的模型仍然仅限于单人场景,并且在复杂的多人环境中(如鸡尾酒会问题)表现不佳。为了克服这一问题,我们引入了AVSEMamba,这是一种视听语音增强模型,它将基于Mamba的时间骨架与面部视觉线索相结合。通过利用时空视觉信息,AVSEMamba能够在具有挑战性的条件下实现目标语音的更准确提取。在AVSEC-4挑战赛的开发集和盲测试集上进行了评估,AVSEMamba在语音清晰度(STOI)、感知质量(PESQ)和非侵入质量(UTMOS)方面优于其他单声道基线,并在单声道排行榜上获得第一名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025 Workshop
Summary
Mamba模型在语音增强方面展现了优异的长时依赖性建模能力,但仍限于单场景应用。为此推出AVSEMamba视听语音增强模型,融合面部视觉信息与Mamba时间特征,改善复杂环境下的语音提取准确度。在AVSEC-4挑战赛的验证集与盲测试集上,AVSEMamba模型在可懂度、感知质量、非侵扰质量等维度超越单声道基线技术,荣获单声道排行榜首位。
Key Takeaways
- Mamba模型能有效建模语音增强的长时依赖性。
- Mamba模型的应用局限于单场景应用,面对复杂多说话人环境存在挑战。
- AVSEMamba是音频视频语音增强模型,利用面部视觉信息提高语音提取准确度。
- AVSEMamba模型融合了时空视觉信息以改进语音提取效果。
- 在AVSEC-4挑战赛中,AVSEMamba模型表现出色,多项指标领先基线技术。
- AVSEMamba模型荣获单声道排行榜首位。
点此查看论文截图

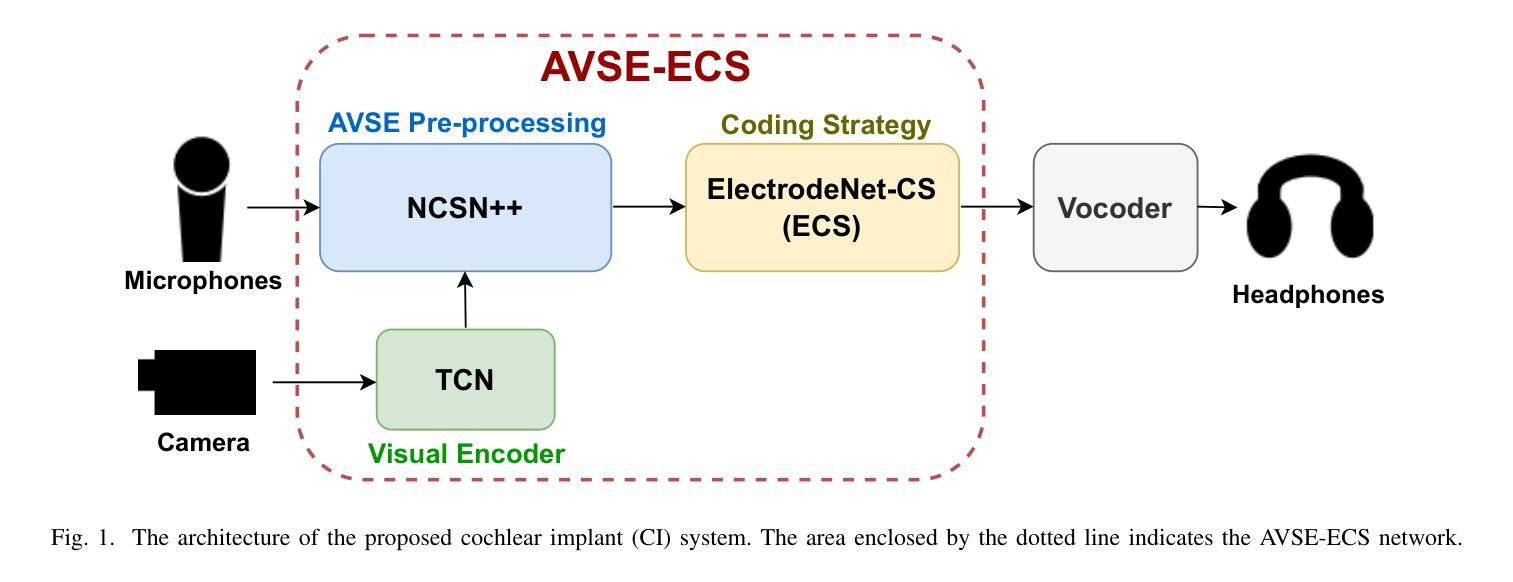
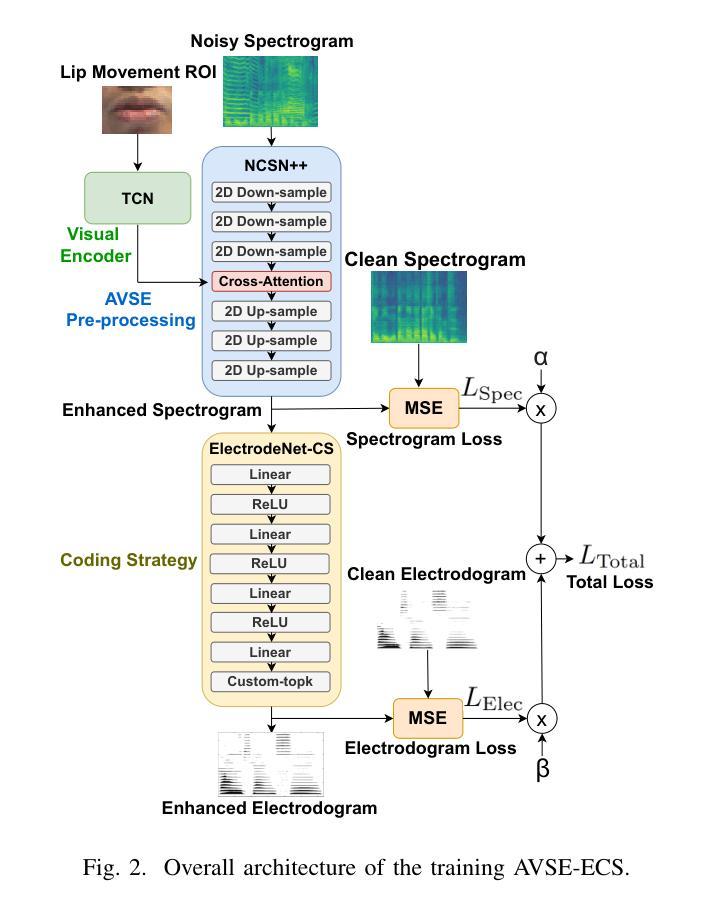
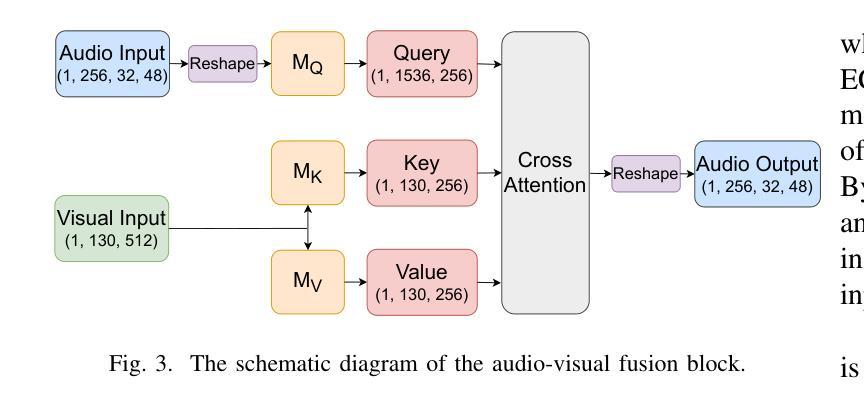
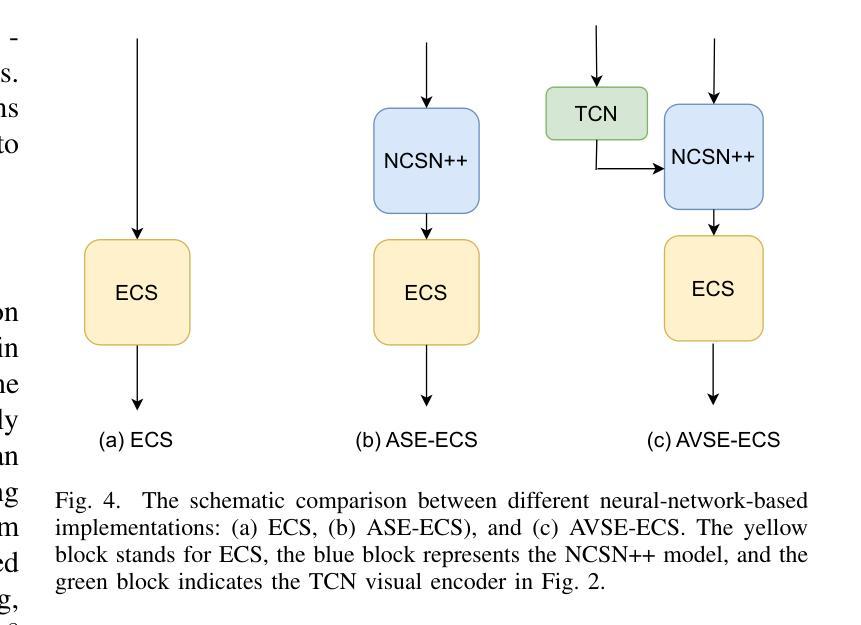
End-to-End Audio-Visual Learning for Cochlear Implant Sound Coding in Noisy Environments
Authors:Meng-Ping Lin, Enoch Hsin-Ho Huang, Shao-Yi Chien, Yu Tsao
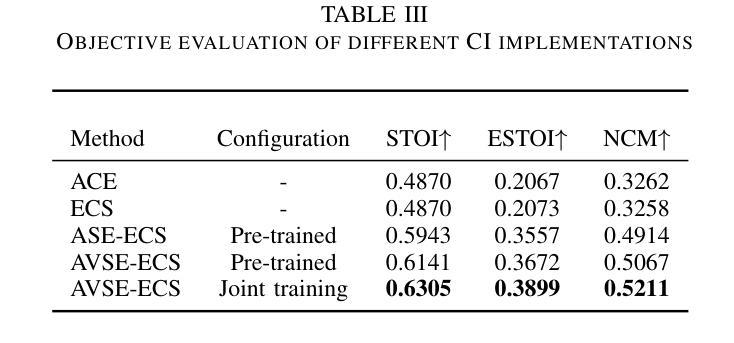
The cochlear implant (CI) is a remarkable biomedical device that successfully enables individuals with severe-to-profound hearing loss to perceive sound by converting speech into electrical stimulation signals. Despite advancements in the performance of recent CI systems, speech comprehension in noisy or reverberant conditions remains a challenge. Recent and ongoing developments in deep learning reveal promising opportunities for enhancing CI sound coding capabilities, not only through replicating traditional signal processing methods with neural networks, but also through integrating visual cues as auxiliary data for multimodal speech processing. Therefore, this paper introduces a novel noise-suppressing CI system, AVSE-ECS, which utilizes an audio-visual speech enhancement (AVSE) model as a pre-processing module for the deep-learning-based ElectrodeNet-CS (ECS) sound coding strategy. Specifically, a joint training approach is applied to model AVSE-ECS, an end-to-end CI system. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method outperforms the previous ECS strategy in noisy conditions, with improved objective speech intelligibility scores. The methods and findings in this study demonstrate the feasibility and potential of using deep learning to integrate the AVSE module into an end-to-end CI system
人工耳蜗植入物(CI)是一种令人惊叹的生物医学设备,它成功地为重度至极度听力损失者提供了感知声音的能力,通过将语音转化为电刺激信号。尽管最近的CI系统性能有所进步,但在噪声或混响条件下进行语音识别仍然是一个挑战。深度学习的最新和正在进行的发展显示出增强CI声音编码能力的巨大潜力,不仅可以通过神经网络复制传统的信号处理方法来实现,而且可以通过整合视觉线索作为多模式语音处理的辅助数据来实现。因此,本文介绍了一种新型的噪声抑制CI系统AVSE-ECS,它利用视听语音增强(AVSE)模型作为基于深度学习的ElectrodeNet-CS(ECS)声音编码策略的预处理模块。具体来说,采用联合训练方法构建端到端的AVSE-ECS的CI系统模型。实验结果表明,在噪声条件下,该方法优于之前的ECS策略,客观语音清晰度评分有所提高。本研究的方法和发现证明了将AVSE模块通过深度学习整合到端到端的CI系统中的可行性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures
Summary
近期研究提出一种新型噪声抑制的助听器系统AVSE-ECS,它采用视听语音增强(AVSE)模型作为预处理模块,结合深度学习技术来提升助听器在噪声环境下的性能。通过与ElectrodeNet-CS(ECS)结合,AVSE-ECS展示出了优异的表现。此创新表明,深度学习方法可用于开发集成的助听器系统。
Key Takeaways
- 新型助听器系统AVSE-ECS结合了视听语音增强技术。
- AVSE模型作为预处理模块,增强了助听器在噪声环境下的性能。
- ECS是结合深度学习技术的声音编码策略。
- AVSE-ECS系统通过联合训练方法实现。
- 实验结果显示,AVSE-ECS在噪声条件下表现优于之前的ECS策略。
- 客观语音清晰度评分也有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

Whispering Context: Distilling Syntax and Semantics for Long Speech Transcripts
Authors:Duygu Altinok
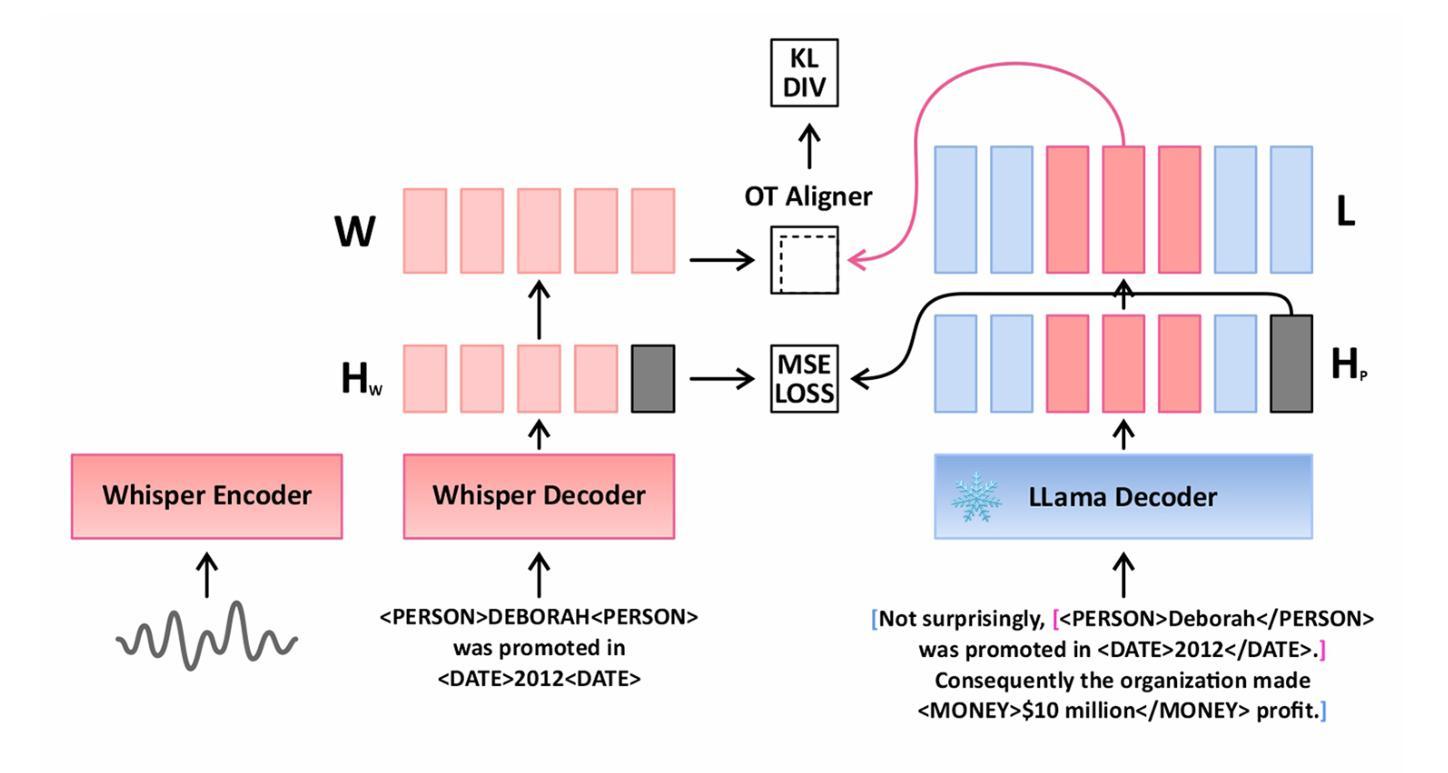
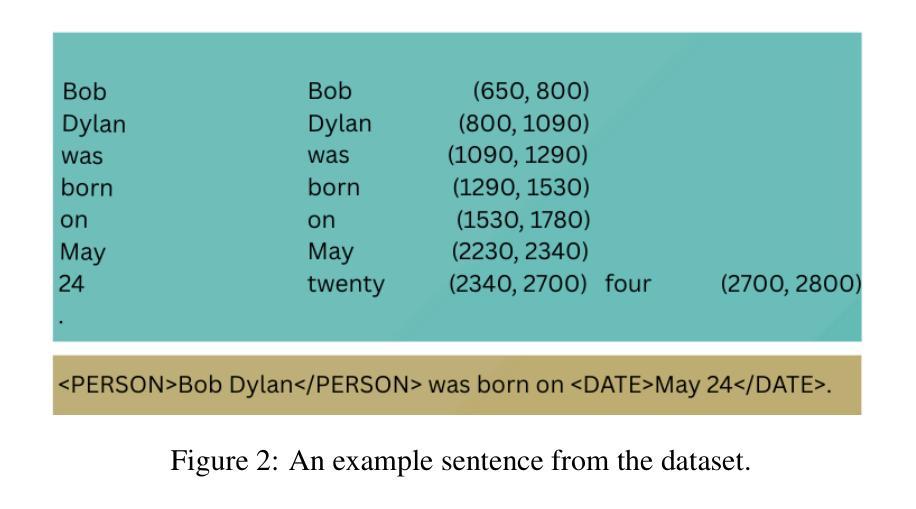
ASR systems often struggle with maintaining syntactic and semantic accuracy in long audio transcripts, impacting tasks like Named Entity Recognition (NER), capitalization, and punctuation. We propose a novel approach that enhances ASR by distilling contextual knowledge from LLaMA models into Whisper. Our method uses two strategies: (1) token level distillation with optimal transport to align dimensions and sequence lengths, and (2) representation loss minimization between sentence embeddings of Whisper and LLaMA, blending syntax and semantics. Evaluations on the Spoken Wikipedia dataset, a benchmark with long audios and rich entities demonstrate significant improvements in Word Error Rate (WER), NER, capitalization, and punctuation success. By introducing novel NER metrics and exploring semantics aware ASR, our work highlights the value of integrating linguistic context into transcription, setting a foundation for robust, context-aware ASR in longform speech.
自动语音识别系统(ASR)在处理长音频转录时,往往难以保持语法和语义的准确性,这影响了命名实体识别(NER)、大写字母使用以及标点符号的使用等任务。我们提出了一种新型方法,通过从LLaMA模型向whisper蒸馏上下文知识来增强ASR的性能。我们的方法采用两种策略:(1)使用最优传输进行标记级别的蒸馏,以对齐维度和序列长度;(2)最小化whisper和LLaMA句子嵌入之间的表示损失,融合语法和语义。在包含长音频和丰富实体的基准测试Spoken Wikipedia数据集上的评估显示,在单词错误率(WER)、NER、大写字母使用和标点符号使用等方面都有显著改善。通过引入新型的NER指标并探索语义感知ASR,我们的工作突出了将语言上下文融入转录的价值,为稳健的、具有上下文意识的长期ASR奠定了基石。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE ASRU 2025. This is the preprint, all rights reserved for ASRU2025
Summary
本摘要提出一种新型的语音识别增强方法,该方法利用LLaMA模型的上下文知识优化Whisper系统。方法包括两个策略:利用最优传输进行标记级别的蒸馏,以对齐维度和序列长度;以及最小化句子嵌入表示损失,融合语法和语义。在Spoken Wikipedia数据集上的评估显示,该方法在单词错误率(WER)、命名实体识别(NER)、大写字母和标点符号的成功率等方面均有显著改善,突显整合语言上下文对于长语音转写的重要性,为后续开发稳健、具有上下文意识的自动语音识别系统奠定基础。
Key Takeaways
- ASR系统在处理长音频转录时面临维持句法与语义准确性的挑战。
- 提出一种结合LLaMA模型上下文知识的ASR增强方法。
- 使用两种策略:标记级别蒸馏与最优传输,以及最小化句子嵌入表示损失。
- 在Spoken Wikipedia数据集上的评估显示显著改善了单词错误率(WER)。
- 引入新的命名实体识别(NER)指标,探索语义感知的ASR。
- 整合语言上下文对于长语音转写至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

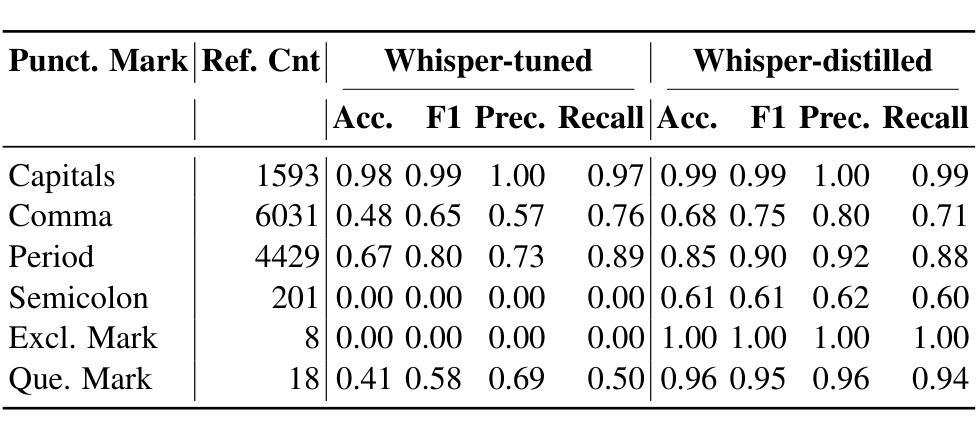
Overcoming Latency Bottlenecks in On-Device Speech Translation: A Cascaded Approach with Alignment-Based Streaming MT
Authors:Zeeshan Ahmed, Frank Seide, Niko Moritz, Ju Lin, Ruiming Xie, Simone Merello, Zhe Liu, Christian Fuegen
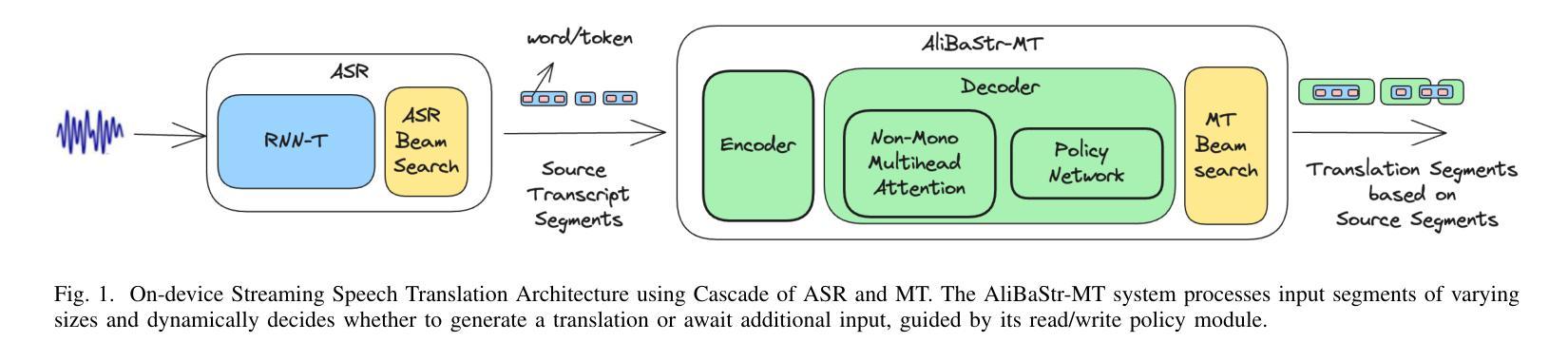
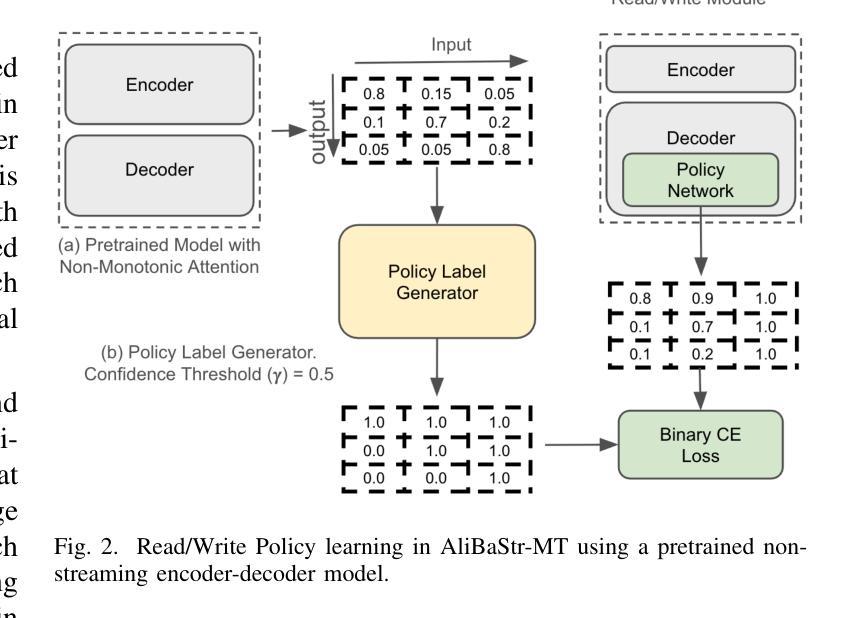
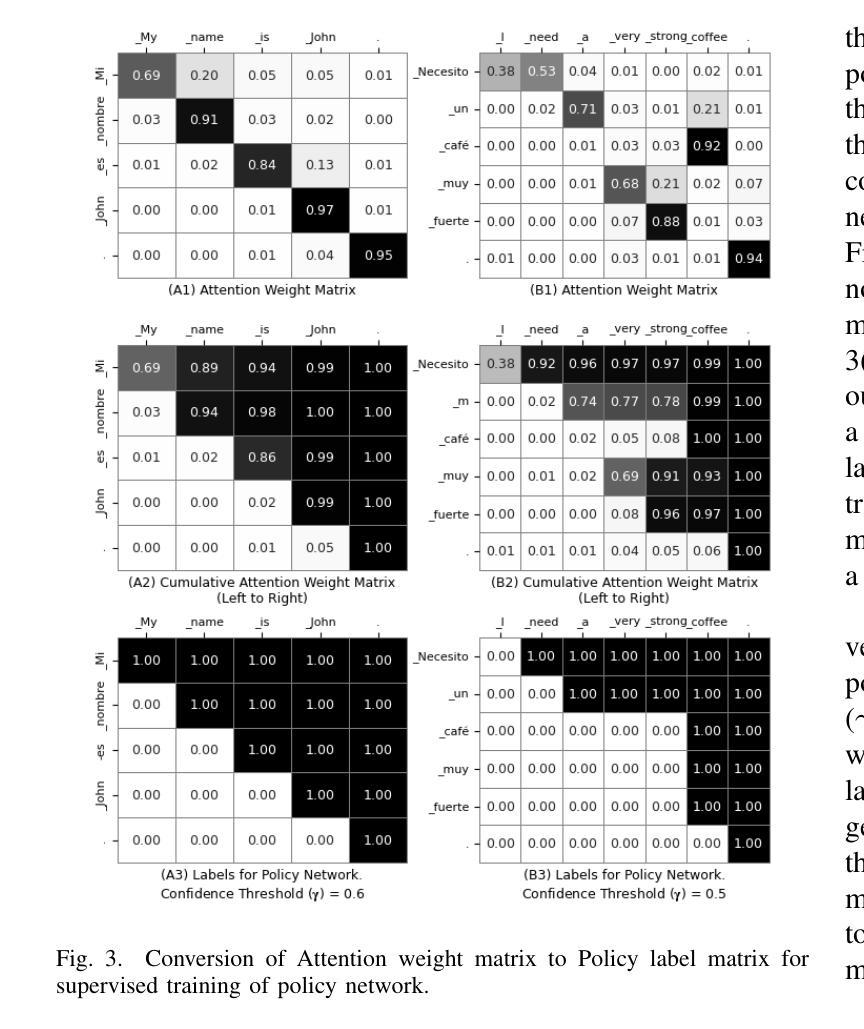
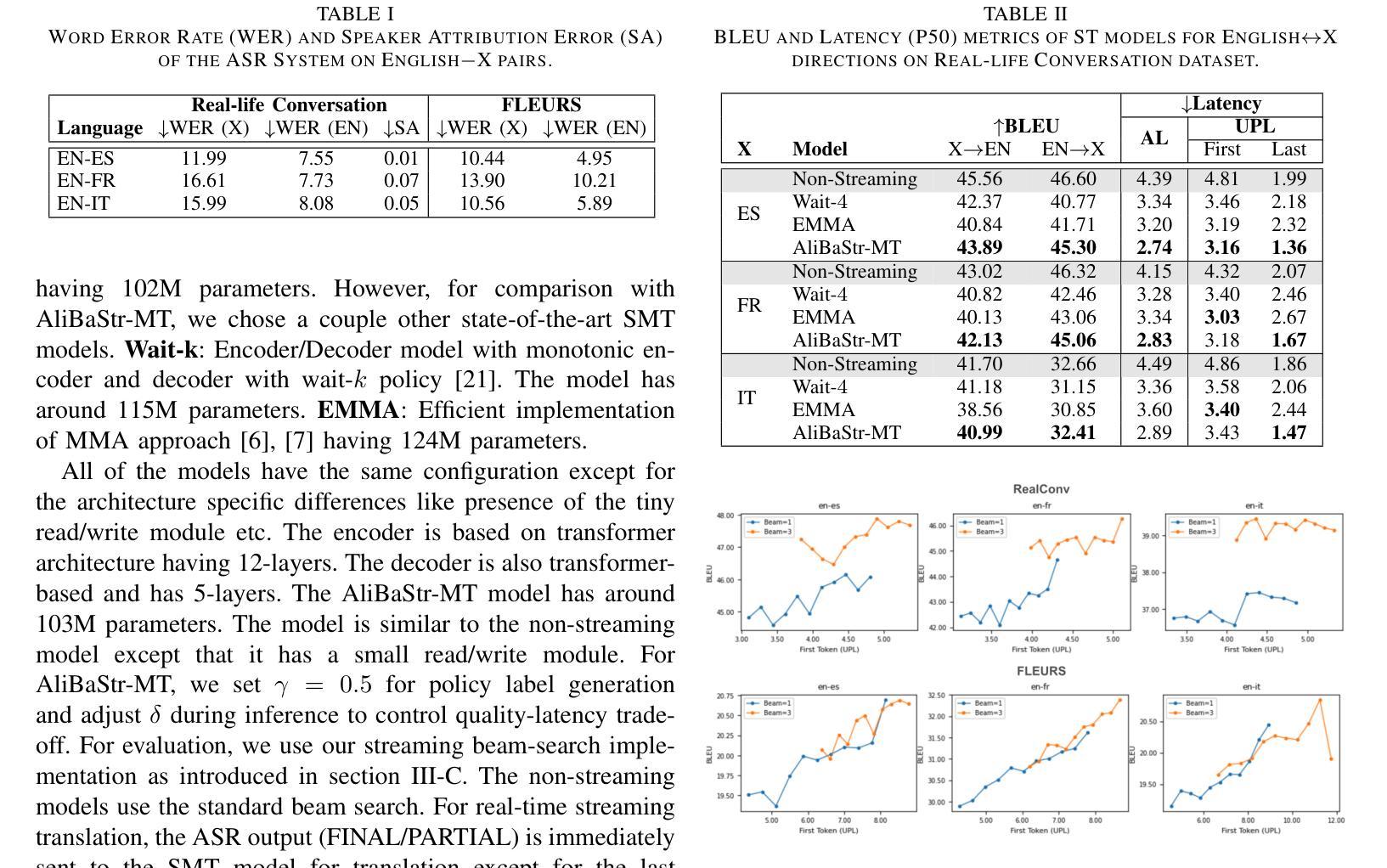
This paper tackles several challenges that arise when integrating Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Machine Translation (MT) for real-time, on-device streaming speech translation. Although state-of-the-art ASR systems based on Recurrent Neural Network Transducers (RNN-T) can perform real-time transcription, achieving streaming translation in real-time remains a significant challenge. To address this issue, we propose a simultaneous translation approach that effectively balances translation quality and latency. We also investigate efficient integration of ASR and MT, leveraging linguistic cues generated by the ASR system to manage context and utilizing efficient beam-search pruning techniques such as time-out and forced finalization to maintain system’s real-time factor. We apply our approach to an on-device bilingual conversational speech translation and demonstrate that our techniques outperform baselines in terms of latency and quality. Notably, our technique narrows the quality gap with non-streaming translation systems, paving the way for more accurate and efficient real-time speech translation.
本文解决了将自动语音识别(ASR)和机器翻译(MT)集成在一起进行实时设备上流式语音翻译时出现的几个挑战。尽管基于循环神经网络转换器(RNN-T)的先进ASR系统可以执行实时转录,但实现实时流式翻译仍然是一个重大挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种同步翻译方法,有效地平衡了翻译质量和延迟。我们还深入研究了ASR和MT的有效集成,利用ASR系统产生的语言线索来管理上下文,并利用高效的束搜索剪枝技术(如超时和强制最终化)来保持系统的实时性。我们将该方法应用于设备上的双语对话语音翻译,并证明我们的技术在延迟和质量方面优于基线。值得注意的是,我们的技术缩小了与非流式翻译系统的质量差距,为更准确、更高效的实时语音识别翻译铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音识别与机器翻译融合时面临多重挑战,尤其是实时语音流翻译的场景。论文中提出一种即时翻译方法解决了同步翻译和延迟的平衡问题,并结合语音识别(ASR)与机器翻译(MT)的优化集成,采用语言提示管理和上下文优化搜索策略以提高实时性能和质量。实际应用在设备端的双语对话语音识别系统上表明新方法延迟更小,翻译质量更佳,接近非流式翻译系统的表现。该研究成果在高效准确的实时语音翻译领域具有重大意义。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文探讨了将自动语音识别(ASR)和机器翻译(MT)集成在一起进行实时语音流翻译时面临的挑战。
- 论文提出了一种新的即时翻译方法,解决了实时翻译中翻译质量和延迟之间的平衡问题。
- 研究强调了利用ASR系统生成的语言学线索来管理上下文的重要性。
- 采用了有效的搜索策略优化方法,如时间超时和强制终止来保持系统的实时性。
- 该方法在实际的双语对话语音识别系统上进行了测试,在延迟和翻译质量方面表现优异。
- 研究结果缩小了流式翻译系统与非流式翻译系统在翻译质量上的差距。
点此查看论文截图