⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-21 更新
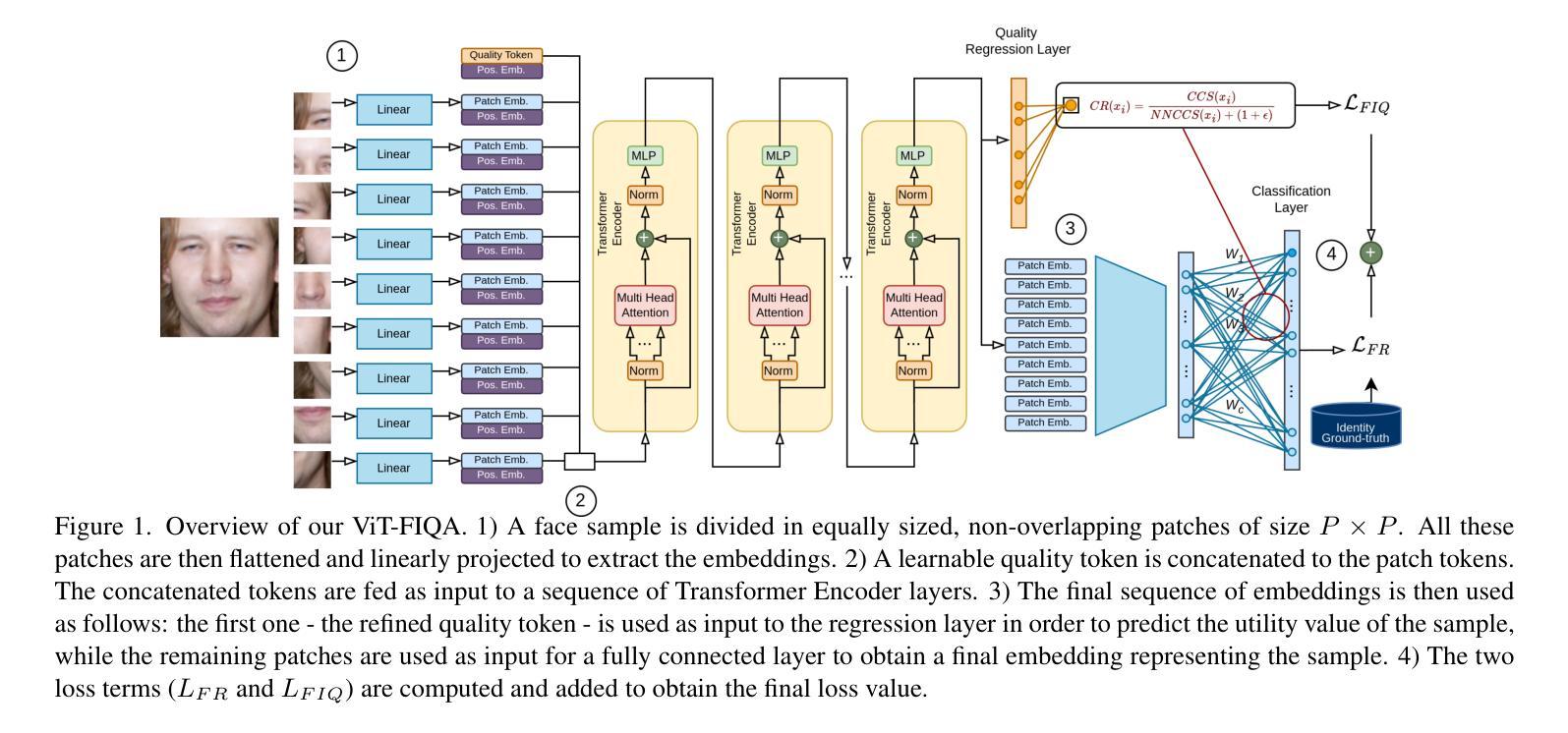
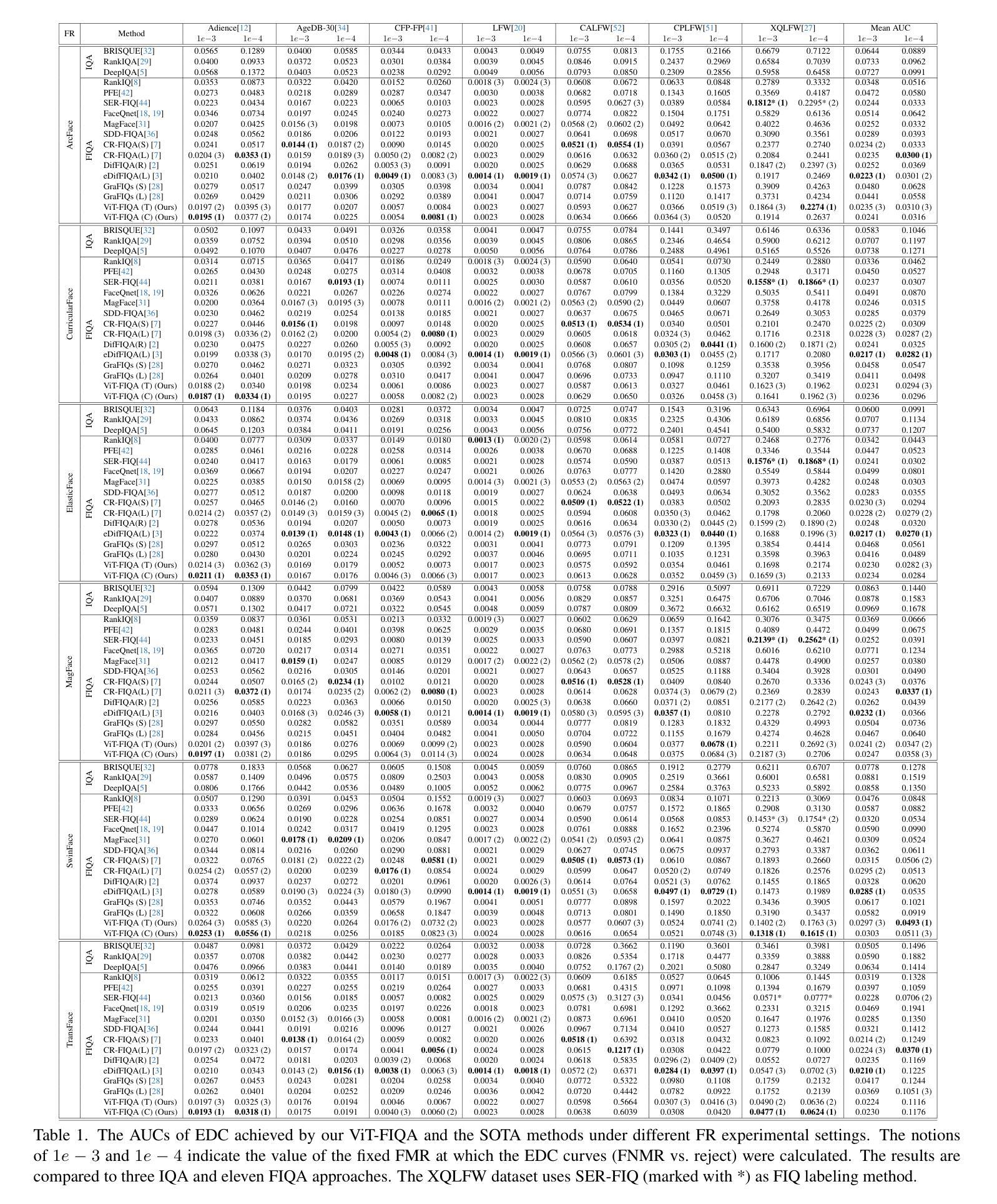
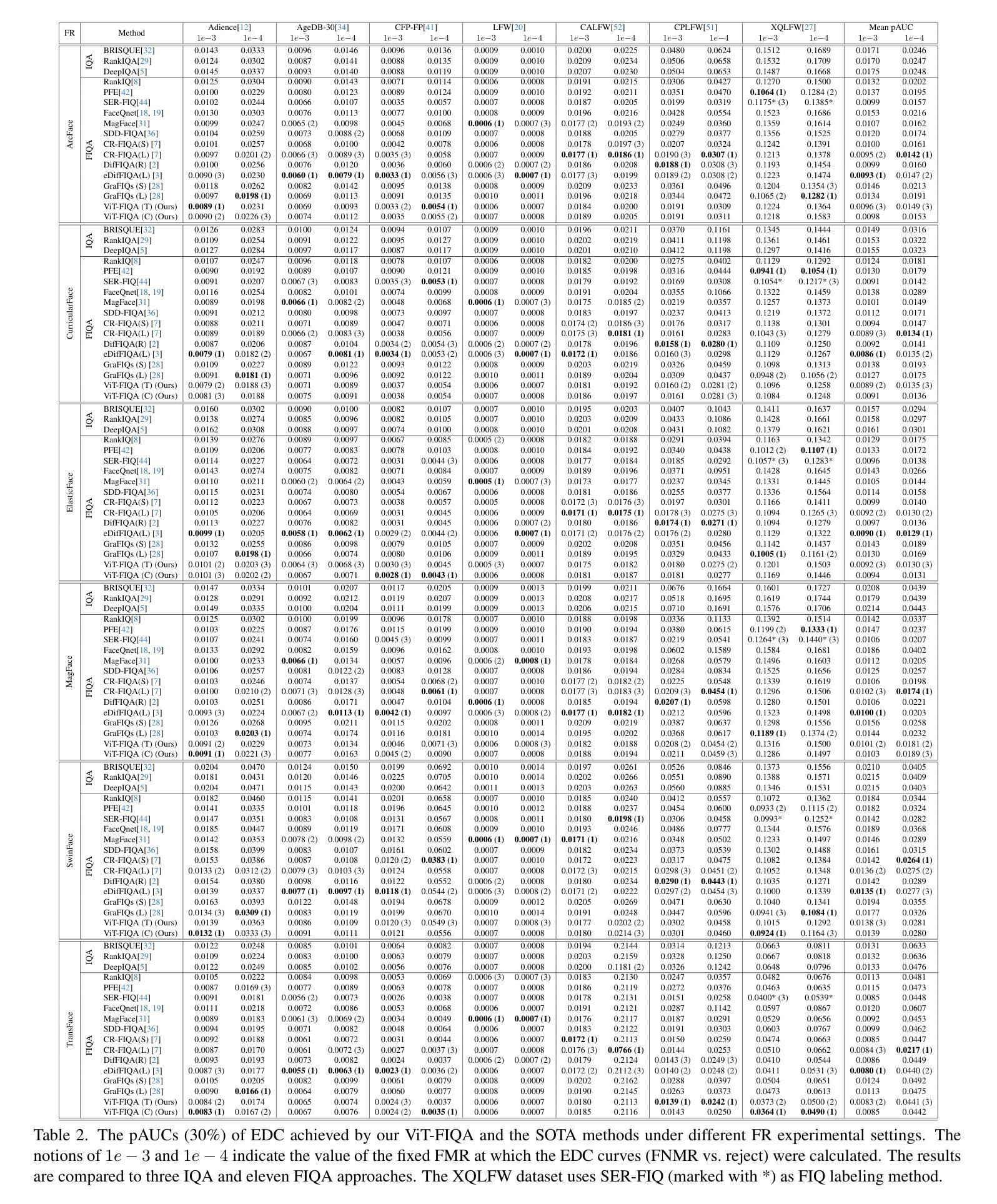
ViT-FIQA: Assessing Face Image Quality using Vision Transformers
Authors:Andrea Atzori, Fadi Boutros, Naser Damer
Face Image Quality Assessment (FIQA) aims to predict the utility of a face image for face recognition (FR) systems. State-of-the-art FIQA methods mainly rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), leaving the potential of Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures underexplored. This work proposes ViT-FIQA, a novel approach that extends standard ViT backbones, originally optimized for FR, through a learnable quality token designed to predict a scalar utility score for any given face image. The learnable quality token is concatenated with the standard image patch tokens, and the whole sequence is processed via global self-attention by the ViT encoders to aggregate contextual information across all patches. At the output of the backbone, ViT-FIQA branches into two heads: (1) the patch tokens are passed through a fully connected layer to learn discriminative face representations via a margin-penalty softmax loss, and (2) the quality token is fed into a regression head to learn to predict the face sample’s utility. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks and several FR models, including both CNN- and ViT-based architectures, demonstrate that ViT-FIQA consistently achieves top-tier performance. These results underscore the effectiveness of transformer-based architectures in modeling face image utility and highlight the potential of ViTs as a scalable foundation for future FIQA research https://cutt.ly/irHlzXUC.
人脸识别图像质量评估(FIQA)旨在预测人脸图像对人脸识别(FR)系统的实用性。最先进的FIQA方法主要依赖于卷积神经网络(CNN),而忽略了对视觉转换器(ViT)架构的潜在探索。这项工作提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种新的方法,它通过扩展原始的用于人脸识别(FR)的标准ViT骨干网,设计了一个可学习的质量令牌来预测给定人脸图像的可利用性得分。可学习的质量令牌与标准的图像补丁令牌拼接在一起,整个序列通过ViT编码器的全局自注意力机制来处理,以聚合所有补丁的上下文信息。在骨干网输出端,ViT-FIQA分为两个分支:(1)补丁令牌通过全连接层传递,通过带有边界惩罚的softmax损失学习判别性人脸表示;(2)质量令牌被送入回归头学习预测人脸样本的实用性。在具有挑战性的基准测试和各种人脸识别模型上的大量实验表明,包括基于CNN和ViT的架构,ViT-FIQA始终取得顶级性能。这些结果突显了基于转换器的架构在建模人脸图像实用性方面的有效性,并突出了ViT作为未来FIQA研究可扩展基础的潜力。具体链接请查阅:链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2025 (ICCVW 2025)
Summary
本文提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的新型Face Image Quality Assessment(FIQA)方法。它通过添加一个可学习的质量令牌来扩展标准的ViT骨干网,该令牌与图像补丁令牌一起通过全局自注意力机制处理,以聚合所有补丁的上下文信息。ViT-FIQA分为两个头:一个用于学习面部表示的判别特征,另一个用于预测面部样本的效用。在具有挑战性的基准测试和多种面部识别模型上的实验表明,ViT-FIQA性能卓越,突显了基于变压器的架构在建模面部图像效用方面的有效性,并为未来的FIQA研究提供了潜在的ViT基础。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-FIQA是一种新型的Face Image Quality Assessment(FIQA)方法,基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构。
- 该方法通过添加一个可学习的质量令牌来扩展ViT骨干网。
- 质量令牌与图像补丁令牌一起通过全局自注意力机制处理,以聚合上下文信息。
- ViT-FIQA分为两个头:一个用于学习面部表示的判别特征,另一个用于预测面部样本的效用。
- 在具有挑战性的基准测试上,ViT-FIQA表现出卓越的性能。
- 与卷积神经网络(CNNs)相比,ViT-FIQA在面部识别(FR)系统中具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

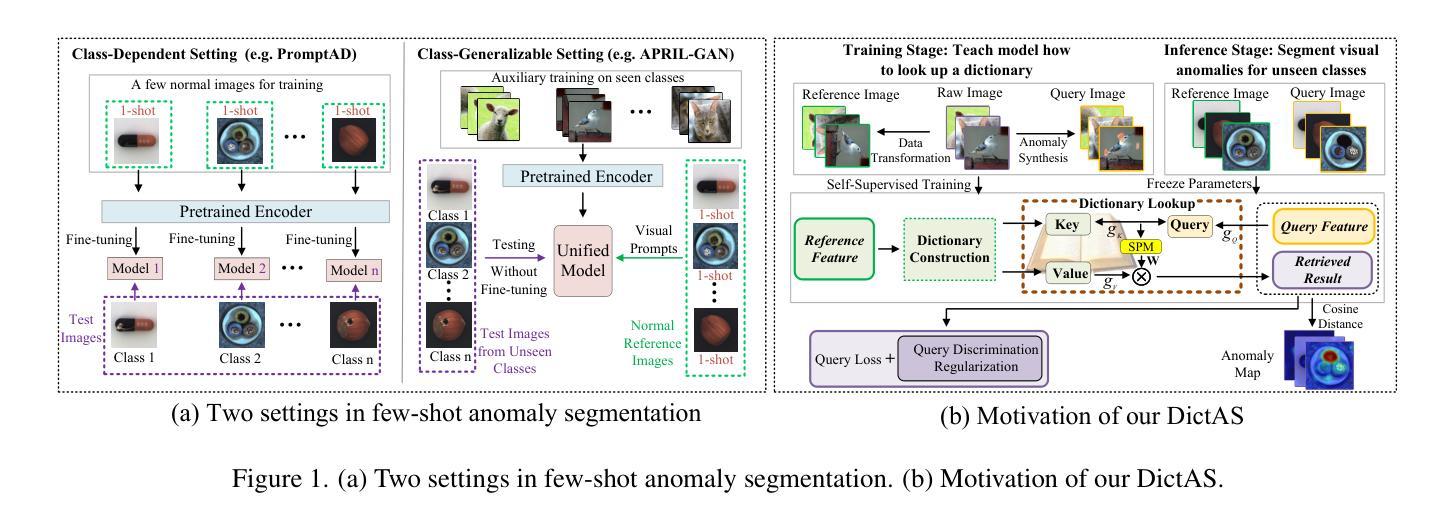
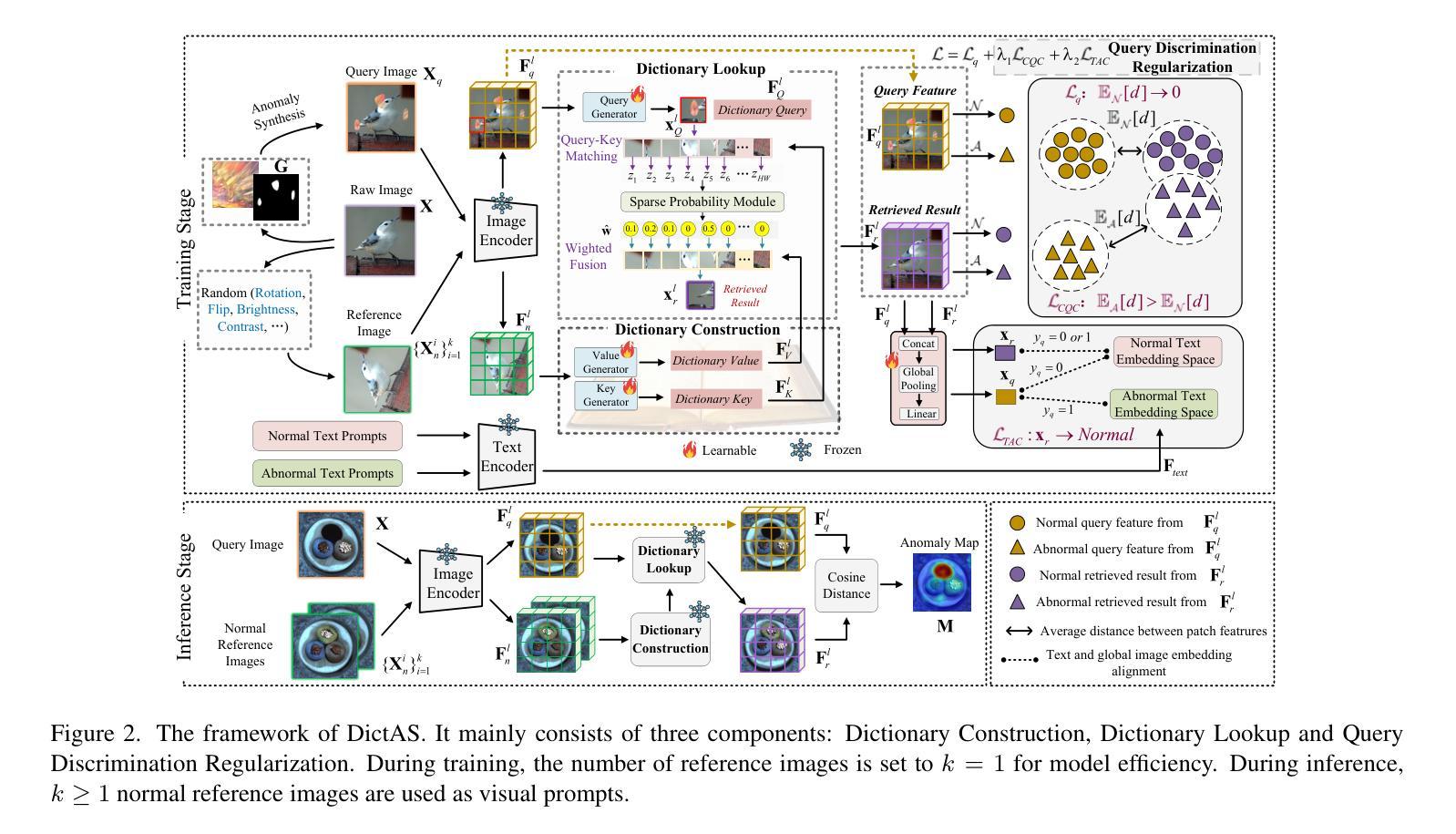
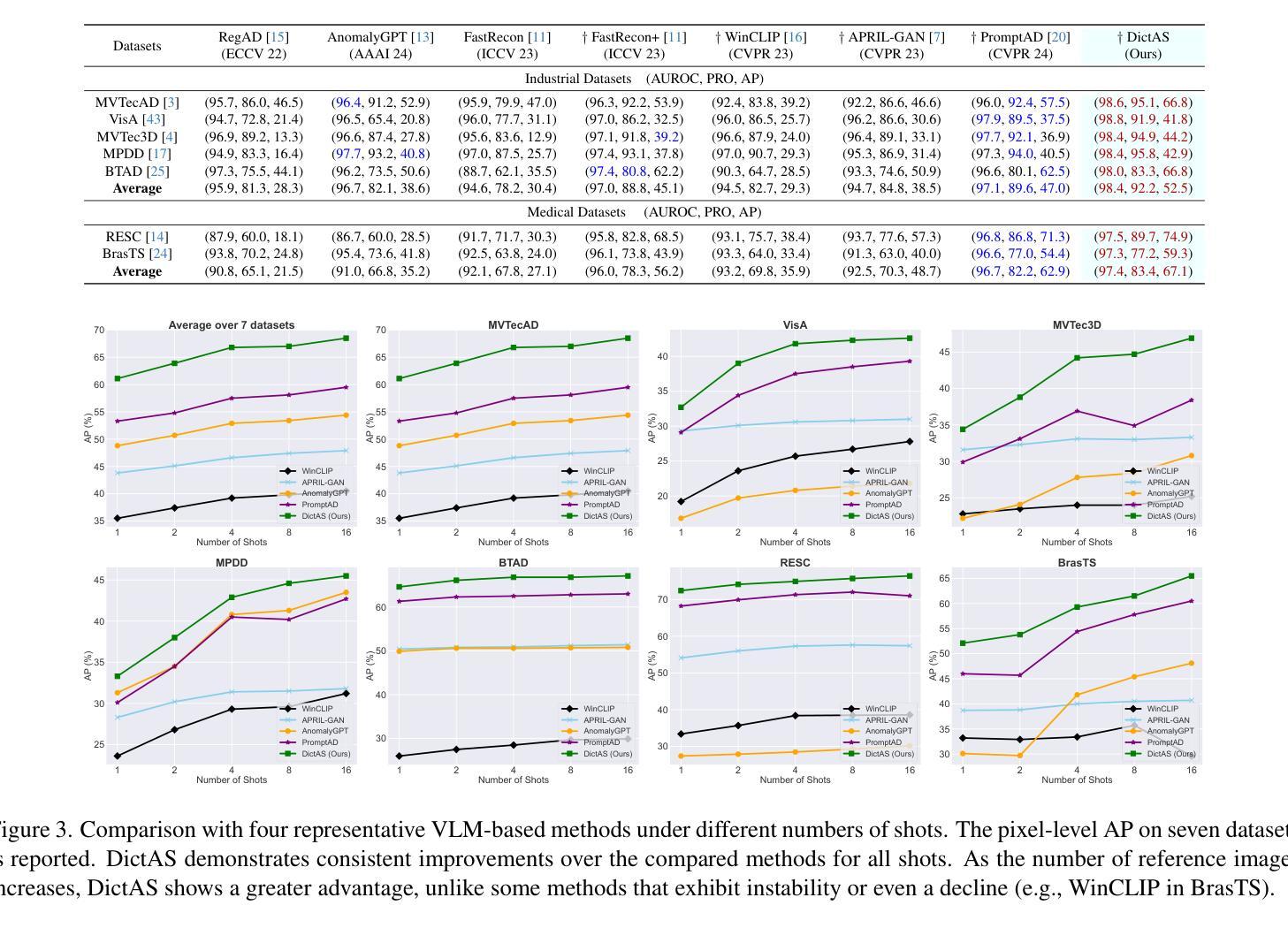
DictAS: A Framework for Class-Generalizable Few-Shot Anomaly Segmentation via Dictionary Lookup
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, ShiChen Qu, Xiaopei Zhang, Xingang Wang, Fei Shen, Zhengtao Zhang, Mukesh Prasad, Guiguang Ding
Recent vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable class-generalizable ability to unseen classes in few-shot anomaly segmentation (FSAS), leveraging supervised prompt learning or fine-tuning on seen classes. However, their cross-category generalization largely depends on prior knowledge of real seen anomaly samples. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, namely DictAS, which enables a unified model to detect visual anomalies in unseen object categories without any retraining on the target data, only employing a few normal reference images as visual prompts. The insight behind DictAS is to transfer dictionary lookup capabilities to the FSAS task for unseen classes via self-supervised learning, instead of merely memorizing the normal and abnormal feature patterns from the training set. Specifically, DictAS mainly consists of three components: (1) Dictionary Construction - to simulate the index and content of a real dictionary using features from normal reference images. (2) Dictionary Lookup - to retrieve queried region features from the dictionary via a sparse lookup strategy. When a query feature cannot be retrieved, it is classified as an anomaly. (3) Query Discrimination Regularization- to enhance anomaly discrimination by making abnormal features harder to retrieve from the dictionary. To achieve this, Contrastive Query Constraint and Text Alignment Constraint are further proposed. Extensive experiments on seven public industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that DictAS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FSAS methods.
最近的视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在少量异常分割(FSAS)中展示了对未见类别的类通用能力,这依赖于对可见异常样本的先验知识。然而,它们跨类别的泛化能力在很大程度上依赖于对真实可见异常样本的先验知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的框架,名为DictAS,它能够使统一模型检测未见对象类别中的视觉异常,而无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练,只需使用少数正常参考图像作为视觉提示。DictAS的见解是通过自监督学习将字典查找能力转移到未见类别的FSAS任务上,而不是仅仅从训练集中记忆正常和异常的特征模式。具体来说,DictAS主要由三个组件构成:(1)字典构建——使用正常参考图像的特征模拟真实字典的索引和内容。(2)字典查找——通过稀疏查找策略从字典中检索查询区域特征。当无法检索到查询特征时,它就被归类为异常。(3)查询判别正则化——通过使异常特征更难从字典中检索来提高异常判别能力。为此,进一步提出了对比查询约束和文本对齐约束。在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验表明,DictAS始终优于最新的FSAS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, Project: https://github.com/xiaozhen228/DictAS
Summary
本文提出了一种名为DictAS的新型框架,用于在未训练的目标数据上检测未见对象类别的视觉异常。DictAS利用少量正常参考图像作为视觉提示,通过模拟真实字典的索引和内容,实现自我监督学习,将字典查找能力转移到未见类别的少镜头异常分割任务上。实验证明,DictAS在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的表现均优于最新的FSAS方法。
Key Takeaways
- DictAS框架能够在未见对象类别中检测视觉异常,无需在目标数据上进行任何重新训练。
- DictAS通过模拟真实字典的索引和内容,使用正常参考图像来构建模型。
- 通过稀疏查找策略从构建的字典中检索查询区域特征,无法检索到的特征被分类为异常。
- 为了提高异常识别能力,DictAS引入了对比查询约束和文本对齐约束。
- DictAS利用自我监督学习实现跨类别泛化,不单纯依赖从训练集中记忆正常和异常特征模式。
- 在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上进行的广泛实验证明,DictAS在少镜头异常分割任务上的性能表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

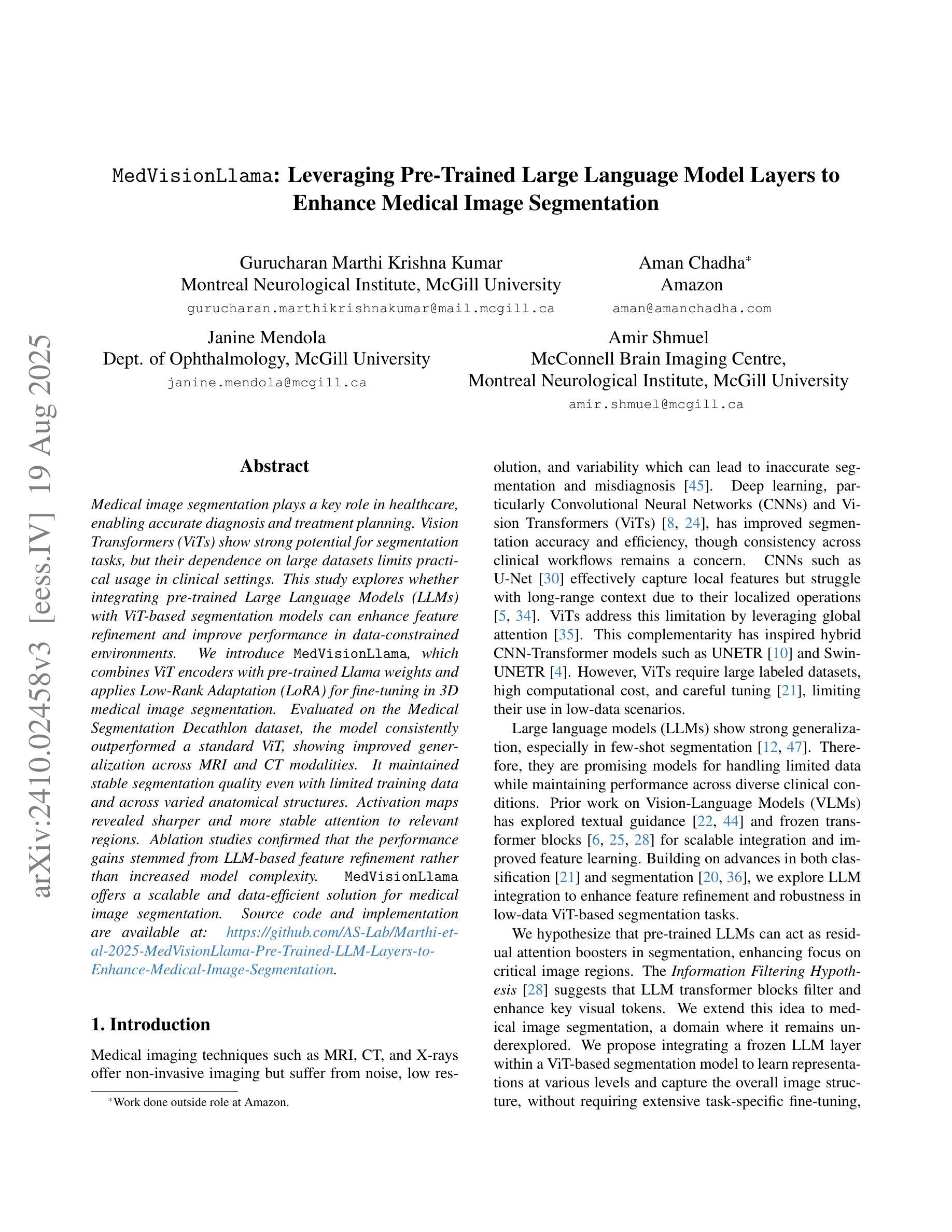
MedVisionLlama: Leveraging Pre-Trained Large Language Model Layers to Enhance Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Gurucharan Marthi Krishna Kumar, Aman Chadha, Janine Mendola, Amir Shmuel
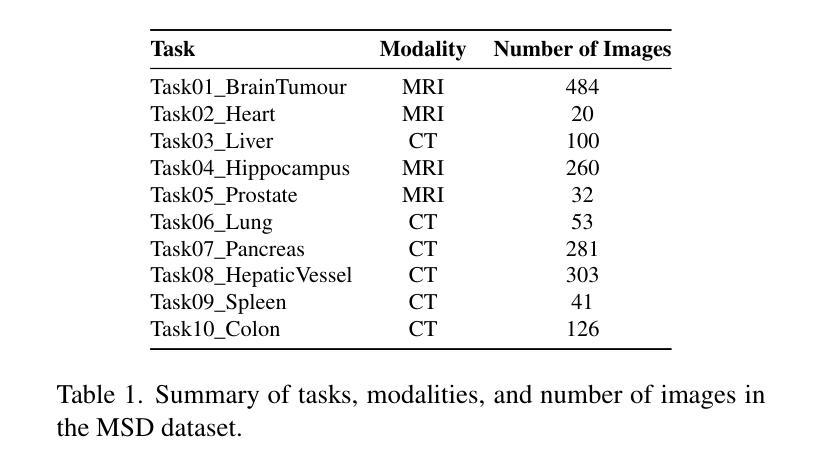
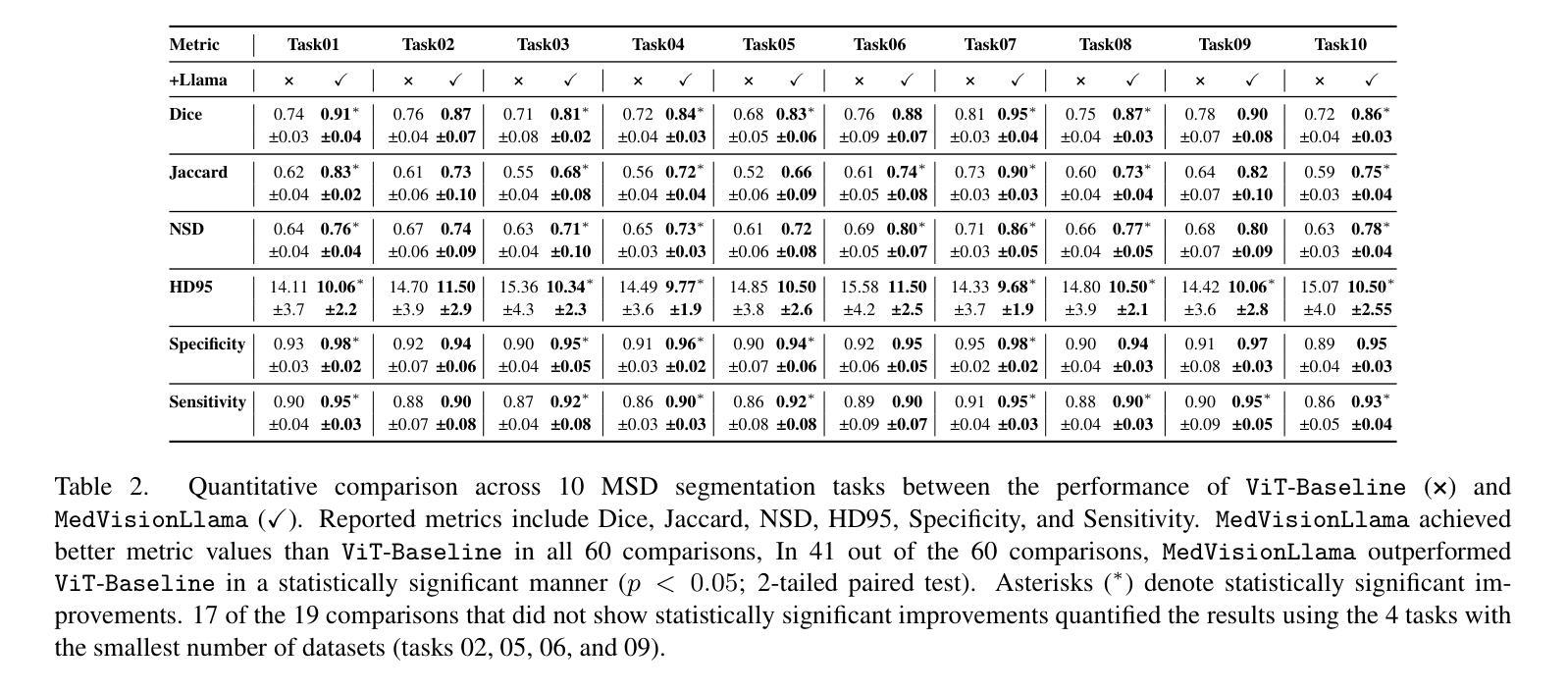
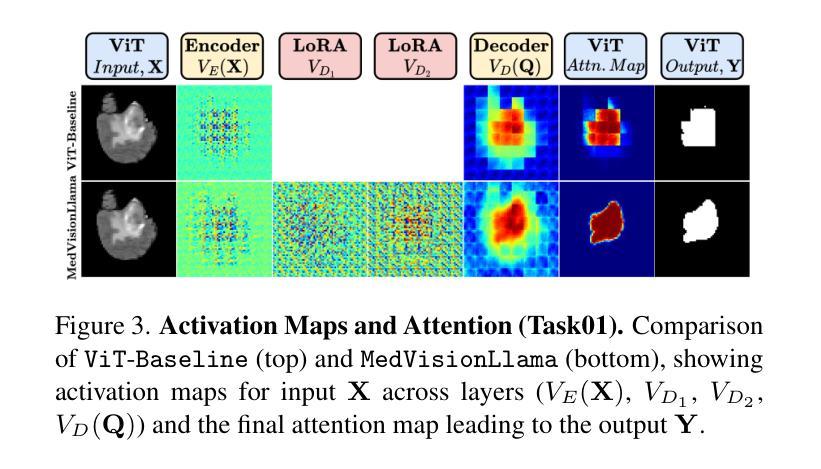
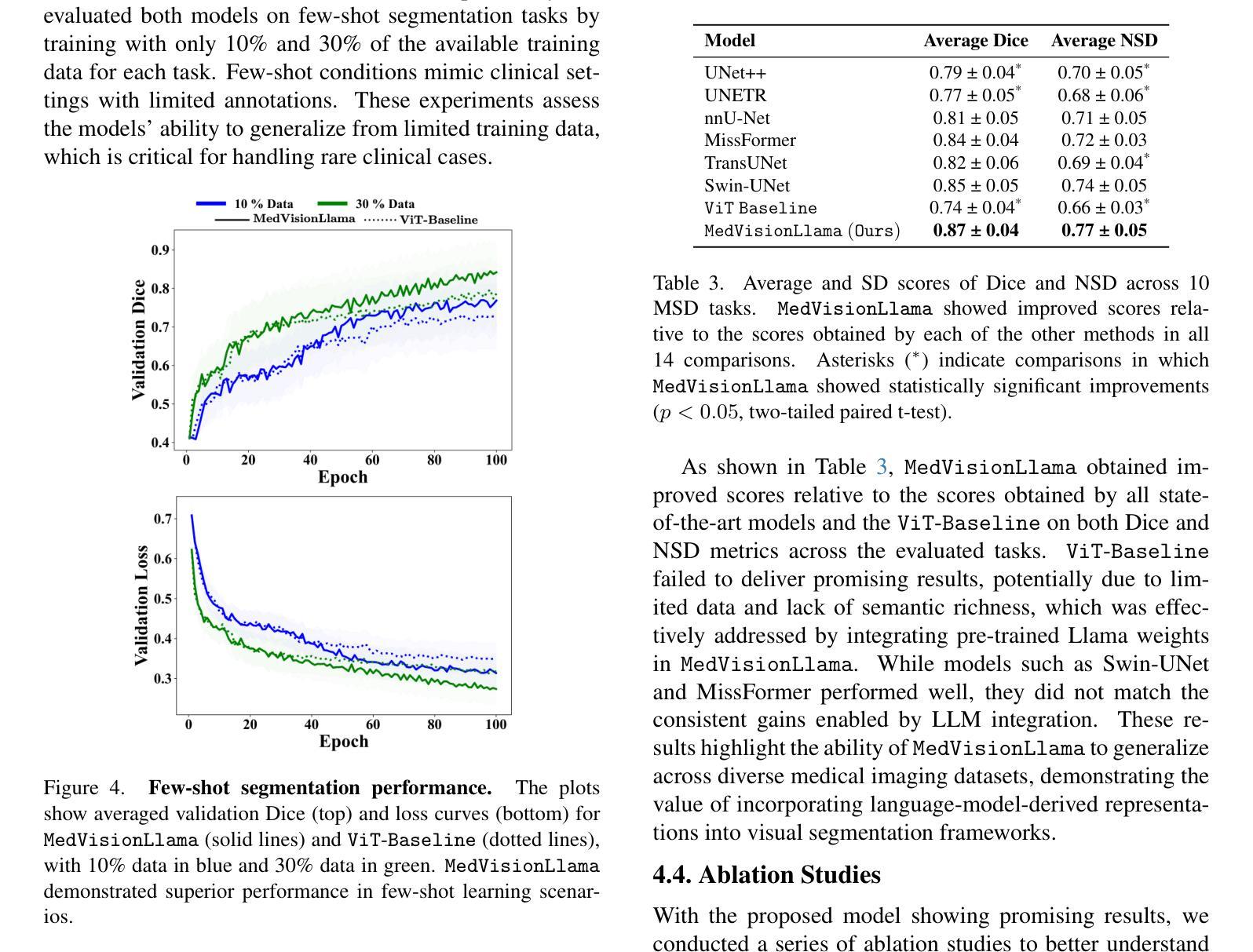
Large Language Models (LLMs), known for their versatility in textual data, are increasingly being explored for their potential to enhance medical image segmentation, a crucial task for accurate diagnostic imaging. This study explores enhancing Vision Transformers (ViTs) for medical image segmentation by integrating pre-trained LLM transformer blocks. Our approach, which incorporates a frozen LLM transformer block into the encoder of a ViT-based model, leads to substantial improvements in segmentation performance across various medical imaging modalities. We propose a Hybrid Attention Mechanism that combines global and local feature learning with a Multi-Scale Fusion Block for aggregating features across different scales. The enhanced model shows significant performance gains, including an average Dice score increase from 0.74 to 0.79 and improvements in accuracy, precision, and the Jaccard Index. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of LLM-based transformers in refining medical image segmentation, highlighting their potential to significantly boost model accuracy and robustness. The source code and our implementation are available at: https://github.com/AS-Lab/Marthi-et-al-2025-MedVisionLlama-Pre-Trained-LLM-Layers-to-Enhance-Medical-Image-Segmentation
大型语言模型(LLMs)以其处理文本数据的多功能性而备受瞩目,目前正不断研究其在提高医学图像分割方面的潜力。医学图像分割对于准确诊断成像至关重要,本研究旨在通过集成预训练的LLM转换器块来增强Vision Transformers(ViTs)在医学图像分割方面的性能。我们的方法是将冻结的LLM转换器块纳入基于ViT的模型的编码器,从而在各种医学影像模态的分割性能上实现了显著的提升。我们提出了一种混合注意力机制,它将全局和局部特征学习相结合,并使用多尺度融合块来聚合不同尺度的特征。增强后的模型实现了显著的性能提升,包括平均Dice得分从0.74提高到0.79,以及准确度、精确度和Jaccard指数的改进。这些结果证明了基于LLM的转换器在提高医学图像分割精度方面的有效性,并凸显了其在显著提高模型准确性和稳健性方面的潜力。源代码和我们的实现可在 https://github.com/AS-Lab/Marthi-et-al-2025-MedVisionLlama-Pre-Trained-LLM-Layers-to-Enhance-Medical-Image-Segmentation 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the CVAMD Workshop (Computer Vision for Automated Medical Diagnosis) at the 2025 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCVW 2025)
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在文本数据中的通用性日益受到关注,其增强医疗图像分割的潜力也被逐渐发掘。本研究探索了将预训练的LLM transformer块集成到Vision Transformers(ViTs)中,以改进医疗图像分割。通过融入冻结的LLM transformer块到ViT模型的编码器,并设计混合注意力机制和跨尺度融合块,模型在多种医学成像模态的分割性能上取得了显著提升。研究结果显示,LLM在医疗图像分割方面的应用效果显著,有望显著提高模型的准确性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)可增强医疗图像分割,为准确诊断成像提供关键支持。
- 结合预训练的LLM transformer块与Vision Transformers(ViTs)可显著提升模型性能。
- 通过融入冻结的LLM transformer块到ViT模型的编码器,实现医疗图像分割性能的改进。
- 提出的混合注意力机制结合了全局和局部特征学习。
- 多尺度融合块有助于在不同尺度上聚合特征。
- 增强后的模型在平均Dice分数、准确度、精确度和Jaccard指数等方面取得了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图