⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
DINOv3 with Test-Time Training for Medical Image Registration
Authors:Shansong Wang, Mojtaba Safari, Mingzhe Hu, Qiang Li, Chih-Wei Chang, Richard LJ Qiu, Xiaofeng Yang
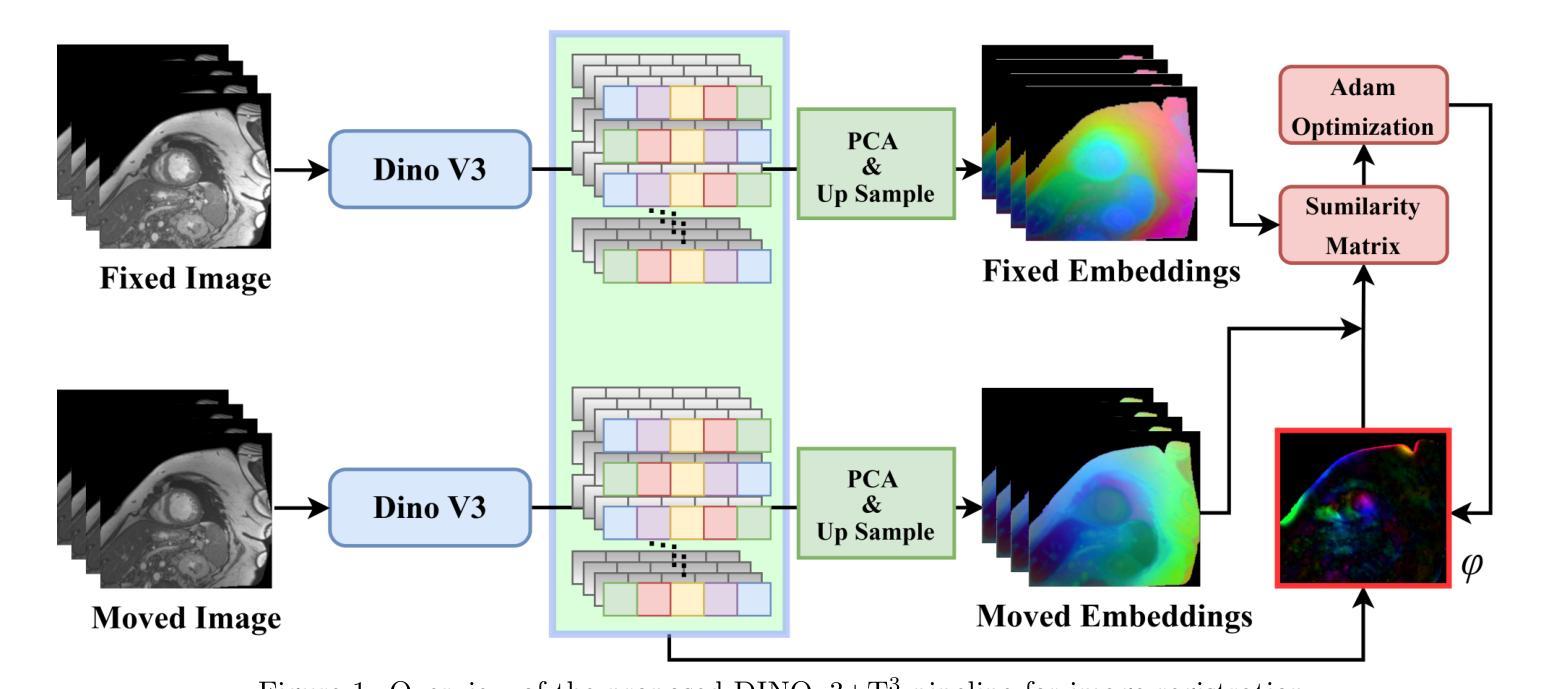
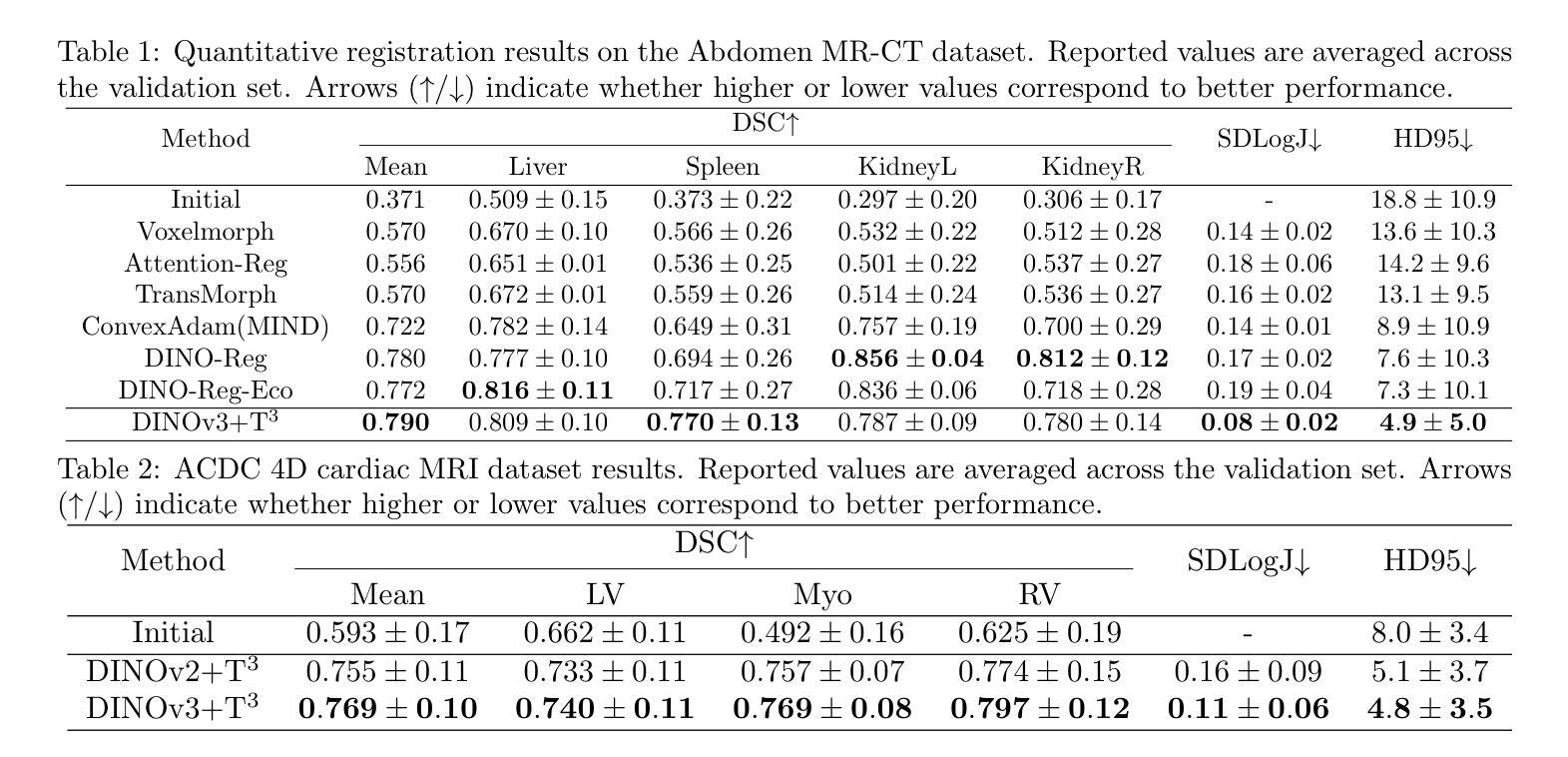
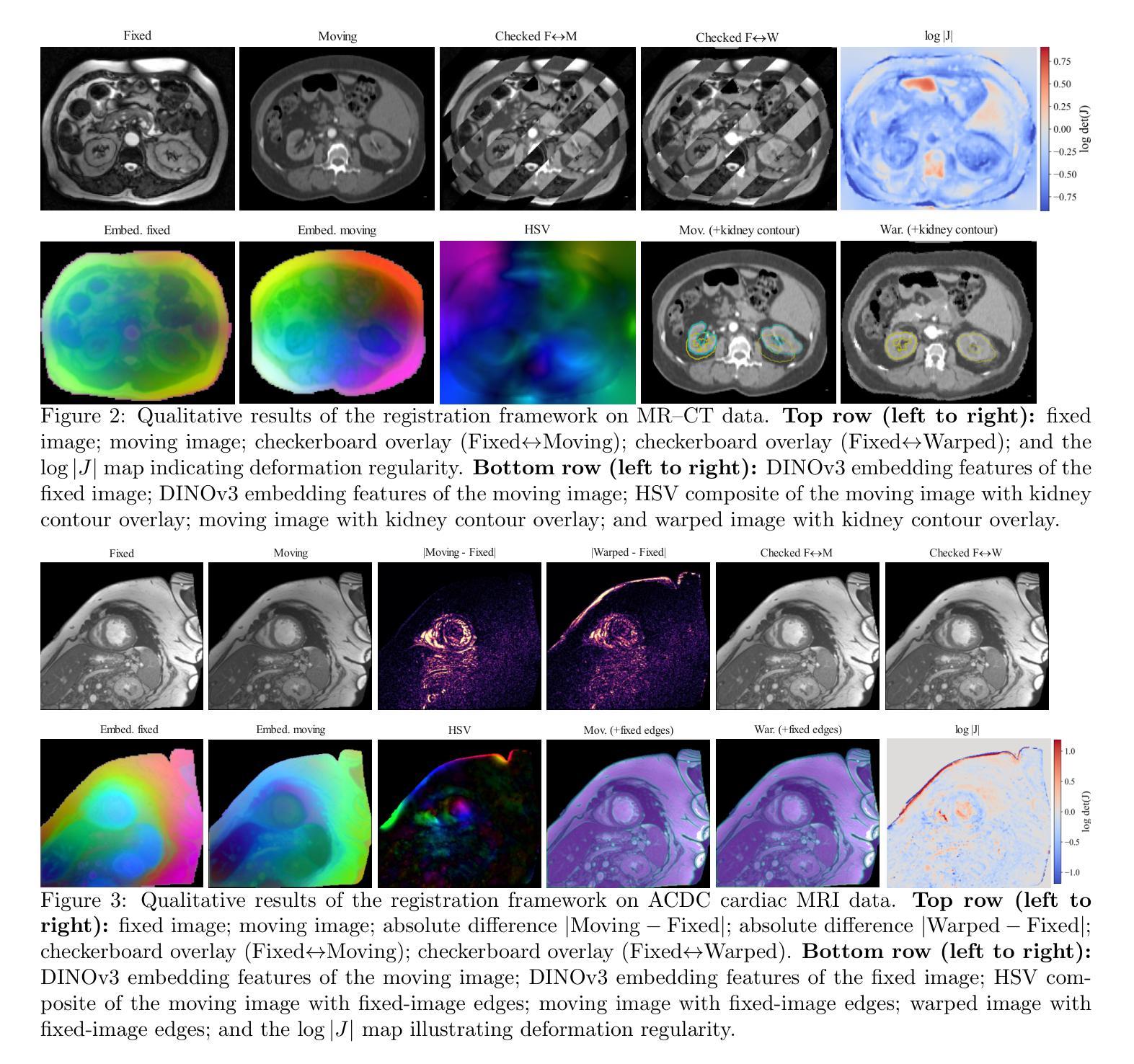
Prior medical image registration approaches, particularly learning-based methods, often require large amounts of training data, which constrains clinical adoption. To overcome this limitation, we propose a training-free pipeline that relies on a frozen DINOv3 encoder and test-time optimization of the deformation field in feature space. Across two representative benchmarks, the method is accurate and yields regular deformations. On Abdomen MR-CT, it attained the best mean Dice score (DSC) of 0.790 together with the lowest 95th percentile Hausdorff Distance (HD95) of 4.9+-5.0 and the lowest standard deviation of Log-Jacobian (SDLogJ) of 0.08+-0.02. On ACDC cardiac MRI, it improves mean DSC to 0.769 and reduces SDLogJ to 0.11 and HD95 to 4.8, a marked gain over the initial alignment. The results indicate that operating in a compact foundation feature space at test time offers a practical and general solution for clinical registration without additional training.
之前的医学图像注册方法,特别是基于学习的方法,通常需要大量的训练数据,这限制了其在临床中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种无需训练的流程,它依赖于冻结的DINOv3编码器以及在特征空间中对变形场的测试时间优化。在两个代表性基准测试中,该方法准确且产生规则变形。在腹部MR-CT上,它获得了最佳的平均Dice系数(DSC)为0.790,以及最低的95th百分位Hausdorff距离(HD95)为4.9±5.0和最低的Log-Jacobian标准偏差(SDLogJ)为0.08±0.02。在ACDC心脏MRI上,它将平均DSC提高到0.769,并将SDLogJ减少到0.11,将HD95减少到4.8,相对于初始对齐有明显的改进。结果表明,在测试时以紧凑的基础特征空间进行操作,提供了一种无需额外训练的临床注册的实用且通用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像注册方法中,学习法需要大量的训练数据,限制了临床采纳。为此,本文提出一种无训练流水线,它依赖冻结的DINOv3编码器和特征空间中的测试时变形场优化。在两项代表性评估标准下,该方法精确并产生规则的变形。在腹部MR-CT上,最佳Dice系数(DSC)为0.790,第95百分位Hausdorff距离(HD95)最低为±5.0,对数雅可比的标准偏差(SDLogJ)为最低值±0.08;在ACDC心脏MRI上,最佳DSC值为平均增长至±0.769,并且显著减少了SDLogJ和HD95。这表明在测试阶段紧凑特征空间中的操作可为临床注册提供实用且通用的解决方案而无需额外训练。
Key Takeaways
- 学习法医学图像注册需要大量训练数据,限制了实际应用。
- 提出一种无训练流水线方法用于医学图像注册。
- 方法依赖于冻结的DINOv3编码器以及测试时变形场的优化。
- 在两个代表性的基准测试中表现出准确性和稳定的变形效果。
- 在腹部MR-CT上获得了较高的DSC值和较低的第HD95和第SDLogJ等指标值。表明改进了初始对齐效果。
- 方法在紧凑特征空间中进行操作,无需额外训练即可实现临床注册的有效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

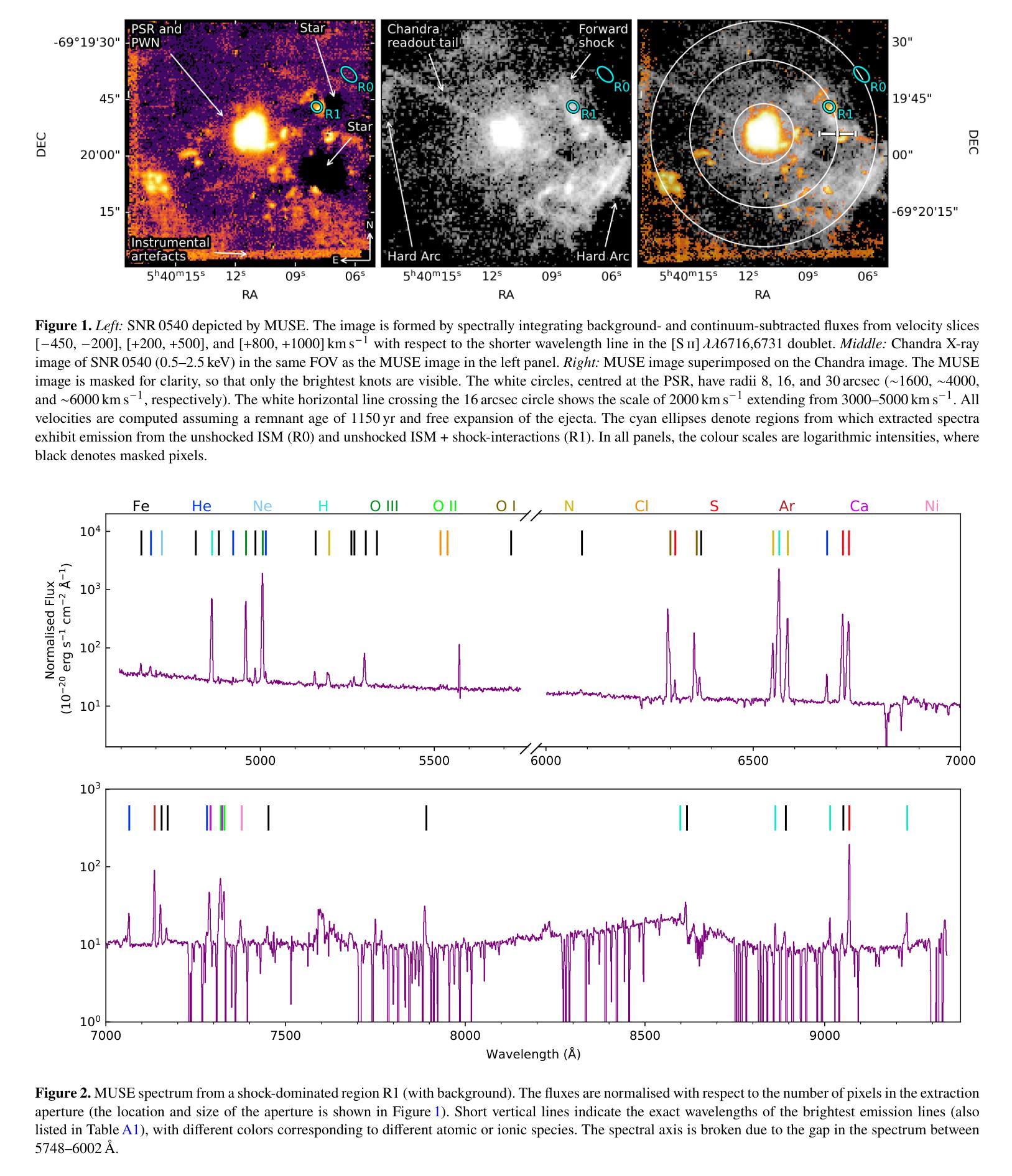
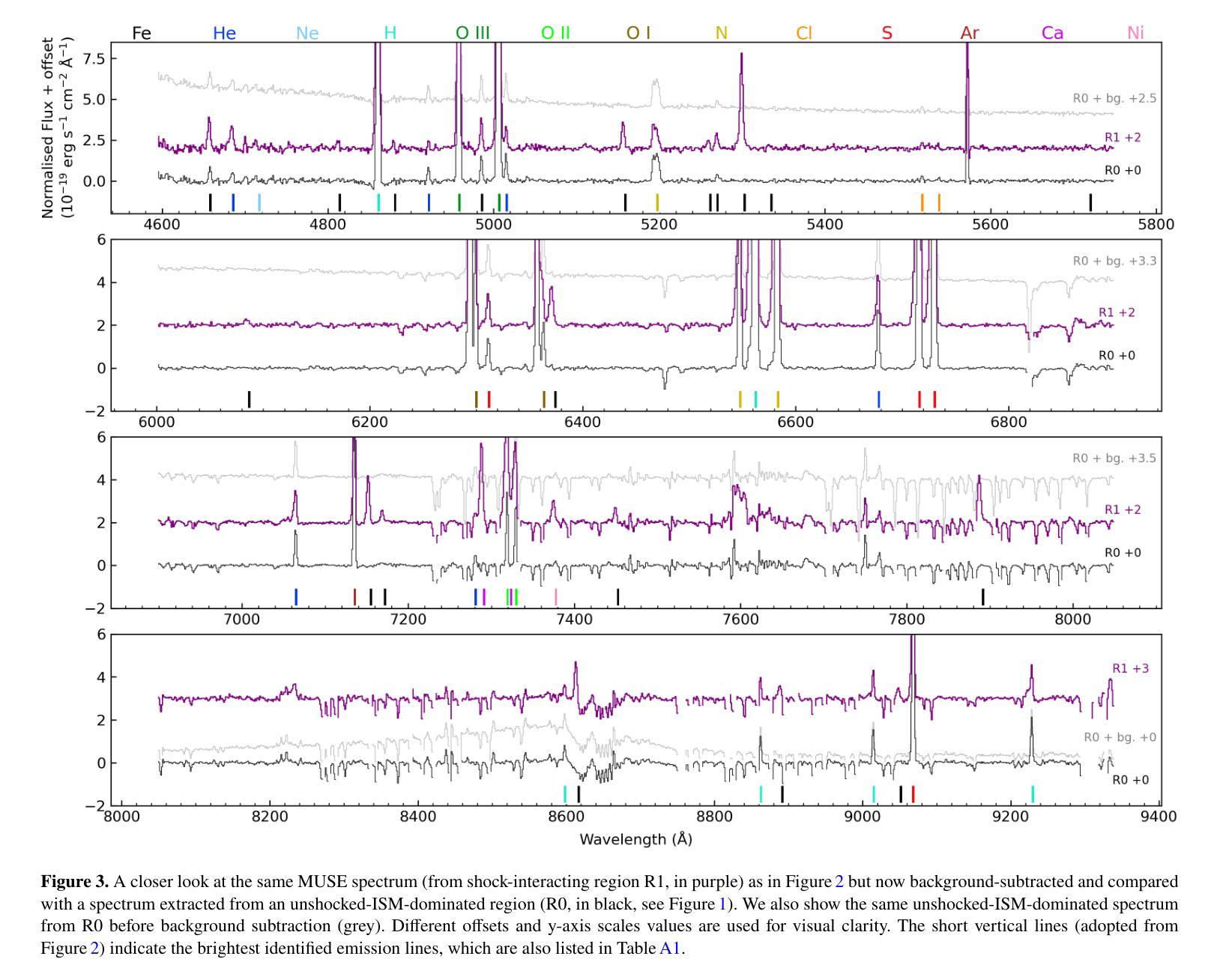
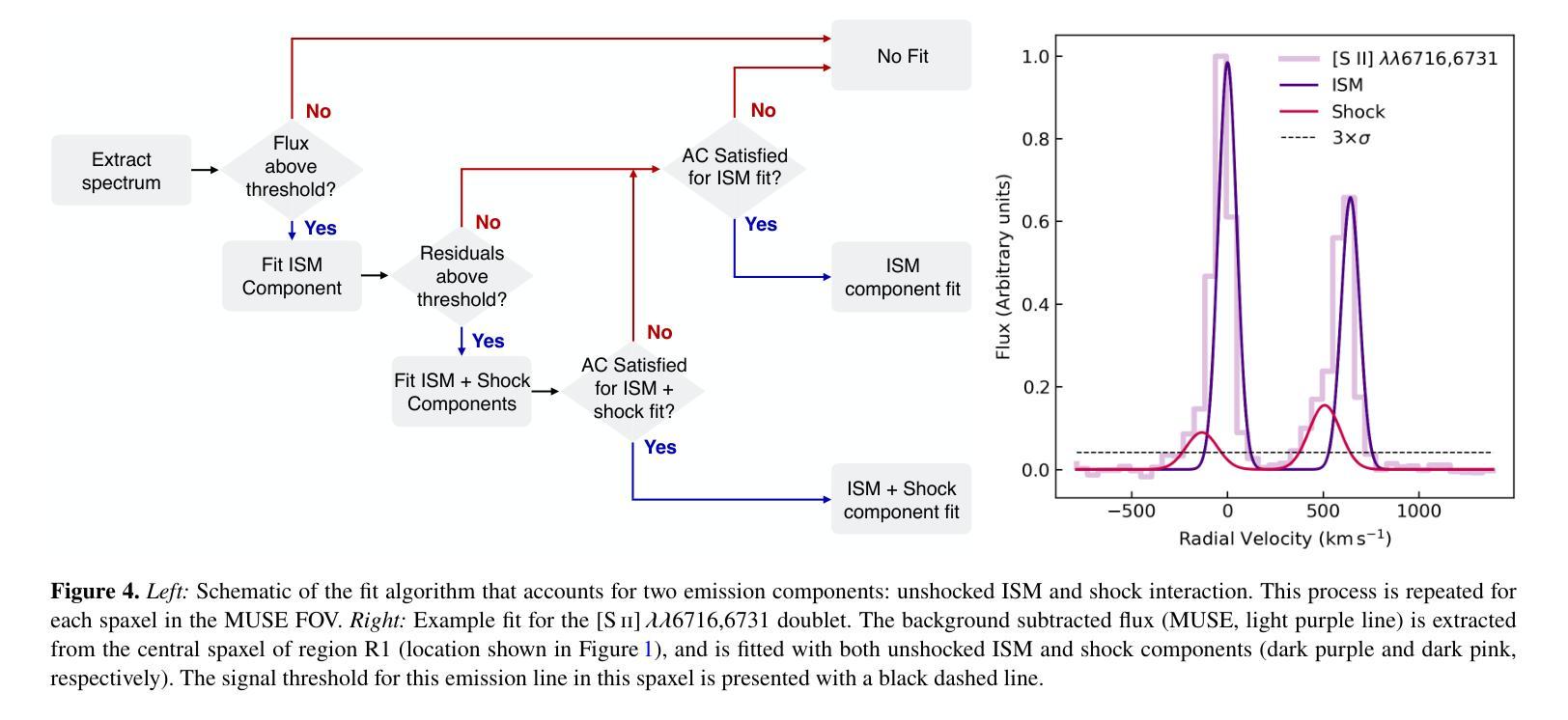
MUSE Observations Reveal Optical Coronal Iron Lines from Shock Emission in Supernova Remnant 0540-69.3
Authors:L. Tenhu, J. Larsson, P. Lundqvist, I. Saathoff, J. D. Lyman, J. Sollerman
We investigate the optical shock emission from the Large Magellanic Cloud supernova remnant 0540-69.3 (SNR 0540) using MUSE integral-field-unit data from the VLT. The observations cover the spectral range 4650-9300 $\r{A}$ and provide a $1\times1$ arcmin$^{2}$ field of view, encompassing nearly the entire remnant. We analyse the spatial and spectral properties of shock-related emission lines, and identify clumpy optical shock emission e.g. from [S II] $\lambda\lambda$6716,6731 doublet and the coronal [Fe XIV] $\lambda$5303 line (typically at radial velocities $\lesssim|100|$ km s$^{-1}$ and $\lesssim|170|$ km s$^{-1}$, respectively). These features trace the blast-wave shell seen in previous X-ray studies. Post-shock electron density estimates, based on the [S II]-line ratio, reveal spatial variation, with the highest densities ($\sim10^4$ cm$^{-3}$) in the bright knots in the west, and lower densities ($\sim3\times10^3$ cm$^{-3}$) in the east. The density in the north (southwest) appears significantly lower (higher) but remains unconstrained due to limited signal. We also estimate blast-wave shock velocities using the [Fe XIV] $\lambda$5303/[Fe XI] $\lambda$7892 ratio, finding low velocities ($\sim400$ km s$^{-1}$), consistent with previous studies. All these results support the scenario that the blast wave is interacting with the surrounding interstellar medium, particularly in the western regions. Additionally, we detect four unidentified emission lines, $\sim$2000-3000 km s$^{-1}$ south from the pulsar in transverse velocity, but their origin remains unclear. Possible explanations, including Fe lines from a high-velocity ejecta clump, all present challenges. Our findings highlight the complex nature of the circum- and interstellar medium surrounding SNR 0540.
我们利用甚大望远镜(VLT)的多单元光谱成像仪(MUSE)观测数据,研究大麦哲伦云超新星残骸0540-69.3(SNR 0540)的光冲击发射。观测光谱范围为4650-9300 \r{A},覆盖了约整个残骸的1×1平方角分的视野。我们分析了冲击相关发射线的空间和光谱特性,并识别出了块状光冲击发射,例如来自[S II] λλ6716,6731双线和电晕[Fe XIV] λ5303线(通常在径向速度≤|100|公里秒-1和≤|170|公里秒-1)。这些特征追踪了先前X射线研究中的冲击波壳层。基于[S II]线比值的后冲击电子密度估算显示出空间变化,西部明亮结中密度最高(约10^4厘米-3),东部密度较低(约3×10^3厘米-3)。北方的密度(西南方)似乎较低(较高),但由于信号有限,仍无法确定。我们还利用[Fe XIV] λ5303/[Fe XI] λ7892比值估计了冲击波速度,发现速度较低(约400公里秒-1),这与先前的研究一致。所有这些结果都支持冲击波与周围星际介质相互作用的情景,特别是在西部区域。此外,我们在横向速度上检测到来自脉冲星以南约2000-3000公里秒-1的四个未识别发射线,但其起源仍不清楚。可能的解释包括来自高速喷射物团块的铁线等,都存在挑战。我们的研究结果突出了SNR 0540周围环境和星际介质的复杂性质。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 21 Figures, 5 Tables. Accepted for publication in MNRAS
摘要
本研究利用VLT的MUSE积分场单元数据,对大麦哲伦星云超新星遗迹0540-69.3(SNR 0540)的光学冲击波发射进行研究。观测覆盖了4650-9300Å的光谱范围,视场为$ 1\times1$平方角分,几乎涵盖了整个遗迹。分析冲击相关发射线的空间和光谱特性,并识别出团状光学冲击发射,例如来自[SII]λλ6716,6731双线和冕区[Fe XIV]λ5303线的发射(典型的径向速度分别≤|100|公里秒-1和≤|170|公里秒-1)。这些特征追踪了先前X射线研究中的冲击波壳层。基于[SII]线强度比值的后冲击电子密度估计显示出空间变化,西部亮结中的密度最高(约10^4厘米-3),而东部较低(约3×10^3厘米-3)。北部(西南部)的密度较低(较高),但由于信号有限,仍无法确定。我们还利用[Fe XIV]λ5303/[Fe XI]λ7892比率估计冲击波速度,发现速度较低(约400公里秒-1),与先前的研究一致。所有这些结果都支持冲击波与周围星际介质相互作用的情景,特别是在西部区域。此外,我们在横向速度方向上从脉冲星南部约2000-3000公里秒-1的地方检测到四条未识别的发射线,但其起源仍不清楚。可能的解释包括来自高速喷射团块的铁线等,所有这些都存在挑战。我们的研究结果突出了围绕SNR 0540的星际和周围介质的复杂性质。
关键见解
- 利用MUSE积分场单元数据研究SNR 0540的光学冲击波发射。
- 分析了冲击相关发射线的空间和光谱特性。
- 识别出团状光学冲击发射,例如来自[SII]和[Fe XIV]的发射线。
- 观察到电子密度的空间变化,西部亮结密度较高。
- 冲击波速度与先前研究一致,约为400公里秒-1。
- 冲击波与周围星际介质的相互作用在西部区域更为显著。
点此查看论文截图

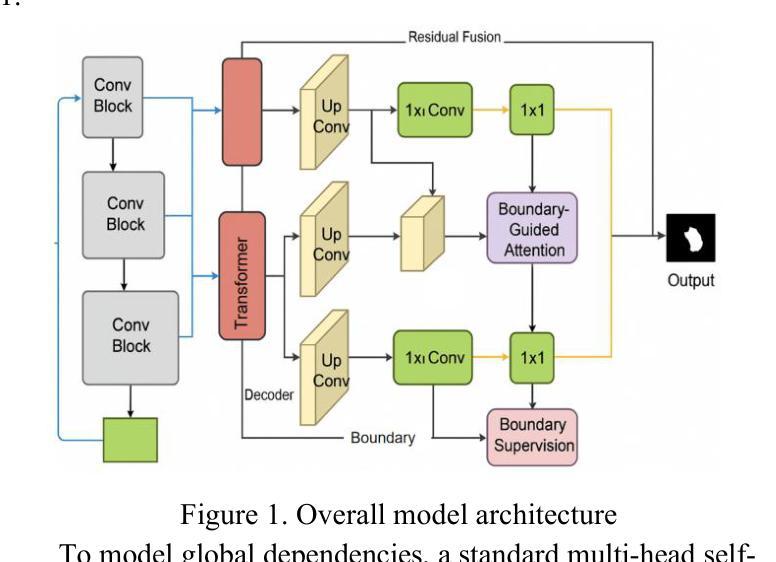
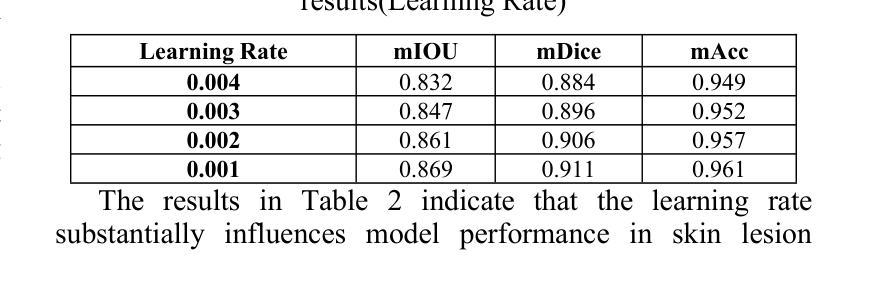
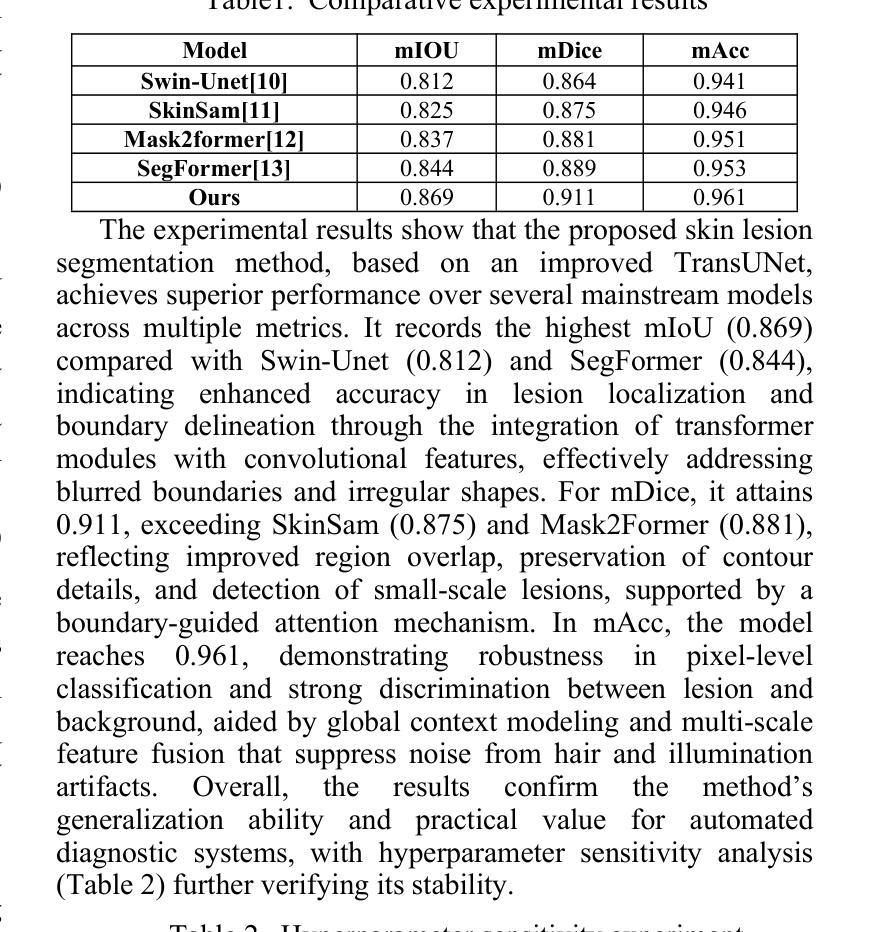
Deep Skin Lesion Segmentation with Transformer-CNN Fusion: Toward Intelligent Skin Cancer Analysis
Authors:Xin Wang, Xiaopei Zhang, Xingang Wang
This paper proposes a high-precision semantic segmentation method based on an improved TransUNet architecture to address the challenges of complex lesion structures, blurred boundaries, and significant scale variations in skin lesion images. The method integrates a transformer module into the traditional encoder-decoder framework to model global semantic information, while retaining a convolutional branch to preserve local texture and edge features. This enhances the model’s ability to perceive fine-grained structures. A boundary-guided attention mechanism and multi-scale upsampling path are also designed to improve lesion boundary localization and segmentation consistency. To verify the effectiveness of the approach, a series of experiments were conducted, including comparative studies, hyperparameter sensitivity analysis, data augmentation effects, input resolution variation, and training data split ratio tests. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms existing representative methods in mIoU, mDice, and mAcc, demonstrating stronger lesion recognition accuracy and robustness. In particular, the model achieves better boundary reconstruction and structural recovery in complex scenarios, making it well-suited for the key demands of automated segmentation tasks in skin lesion analysis.
本文提出了一种基于改进型TransUNet架构的高精度语义分割方法,旨在应对皮肤病灶图像中复杂病灶结构、边界模糊和显著尺度变化等挑战。该方法将变压器模块集成到传统的编码器-解码器框架中,以建模全局语义信息,同时保留卷积分支以保留局部纹理和边缘特征。这增强了模型对细粒度结构的感知能力。还设计了边界引导注意机制和跨尺度上采样路径,以提高病灶边界定位和分割的一致性。为了验证该方法的有效性,进行了一系列实验,包括对比研究、超参数敏感性分析、数据增强效果、输入分辨率变化和训练数据分割比例测试。实验结果表明,所提出的方法在mIoU、mDice和mAcc等方面优于现有代表性方法,显示出更高的病灶识别精度和稳健性。尤其值得一提的是,该模型在复杂场景下的边界重建和结构恢复方面表现更佳,非常适用于皮肤病灶分析中的自动化分割任务的关键需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于改进型TransUNet架构的高精度语义分割方法,用于应对皮肤病灶图像中复杂病灶结构、模糊边界和显著尺度变化等挑战。该方法将transformer模块融入传统编码器-解码器框架,以建模全局语义信息,同时保留卷积分支以保留局部纹理和边缘特征,增强了模型对细微结构感知的能力。通过设计边界引导注意机制和多尺度上采样路径,提高了病灶边界定位和分割一致性。实验结果表明,该方法在mIoU、mDice和mAcc等指标上优于现有代表性方法,表现出更强的病灶识别准确性和稳健性,特别是在复杂场景下的边界重建和结构恢复方面表现优异,非常适合皮肤病灶分析中的自动化分割任务。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种基于改进型TransUNet架构的高精度语义分割方法,用于处理皮肤病灶图像中的多种挑战。
- 方法融合了transformer模块和卷积分支,以捕捉全局语义信息和局部细节。
- 通过引入边界引导注意机制和多尺度上采样路径,提高了病灶边界定位和分割的准确度。
- 实验验证了该方法在多个指标上优于其他现有方法,包括mIoU、mDice和mAcc。
- 该方法在复杂场景下的边界重建和结构恢复方面表现突出。
- 方法具有强大的病灶识别准确性和稳健性,适用于皮肤病灶分析的自动化分割任务。
点此查看论文截图

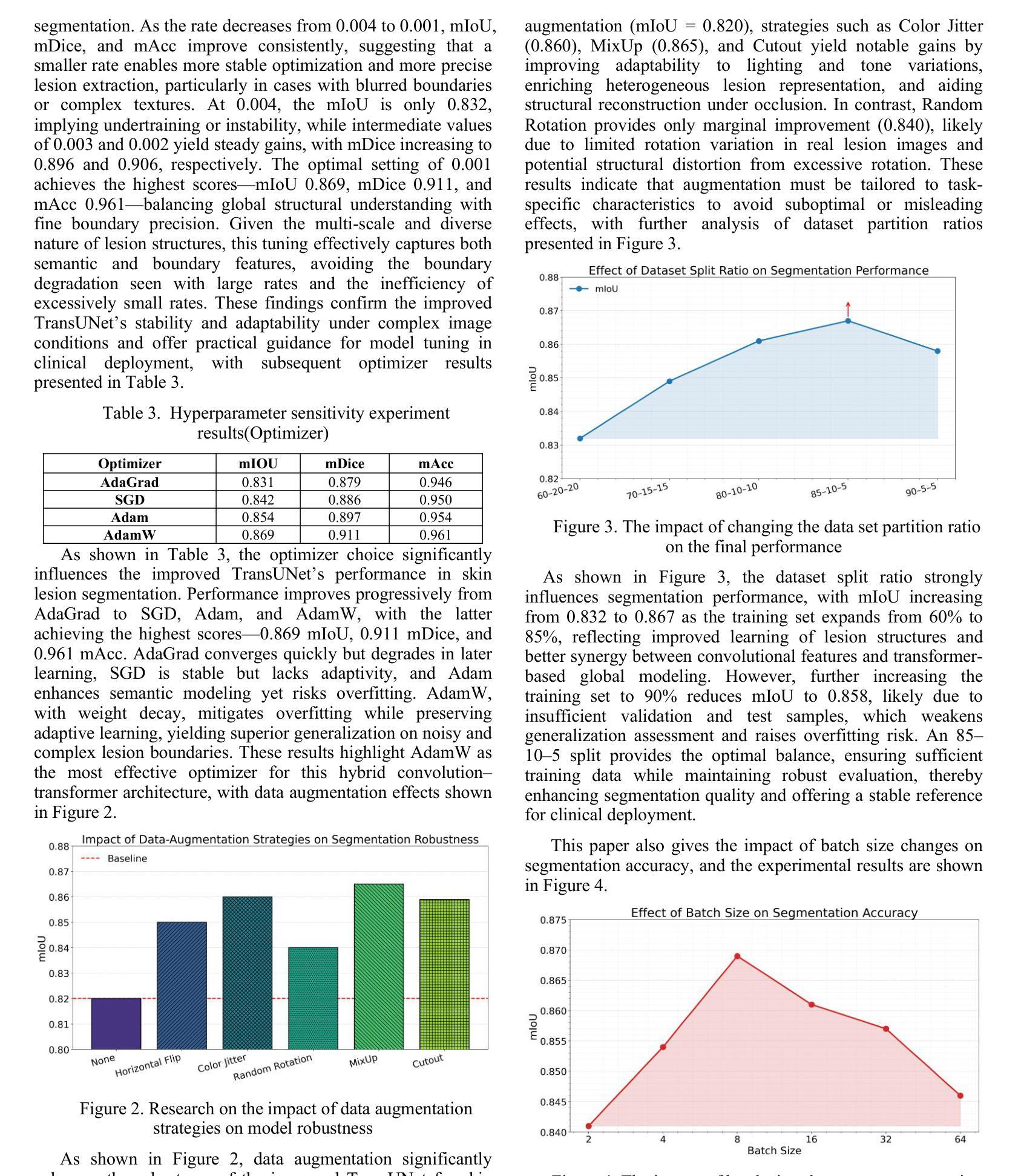
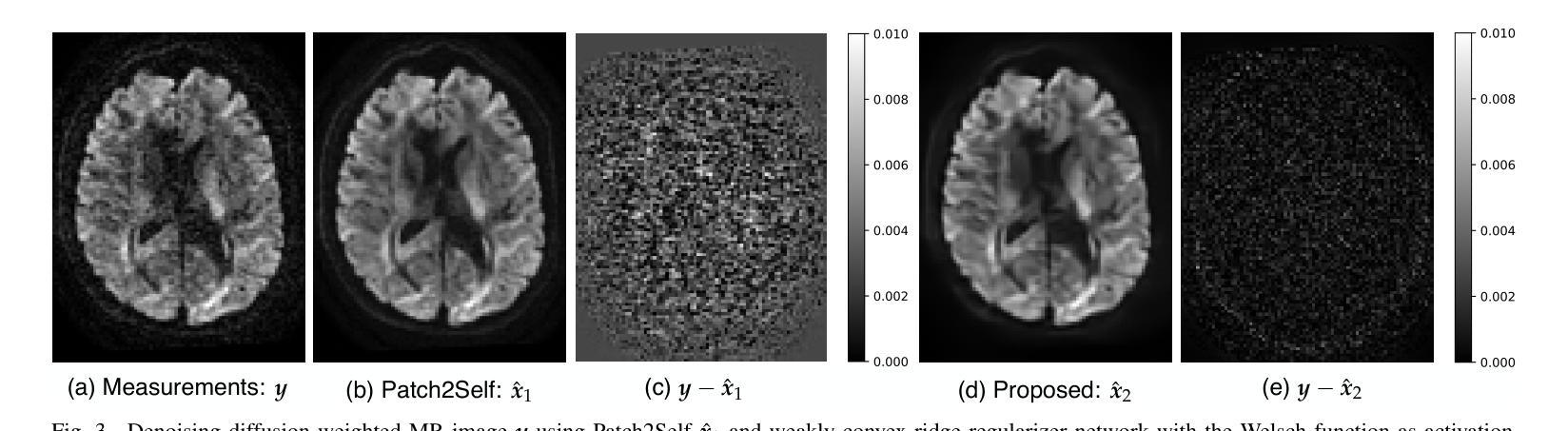
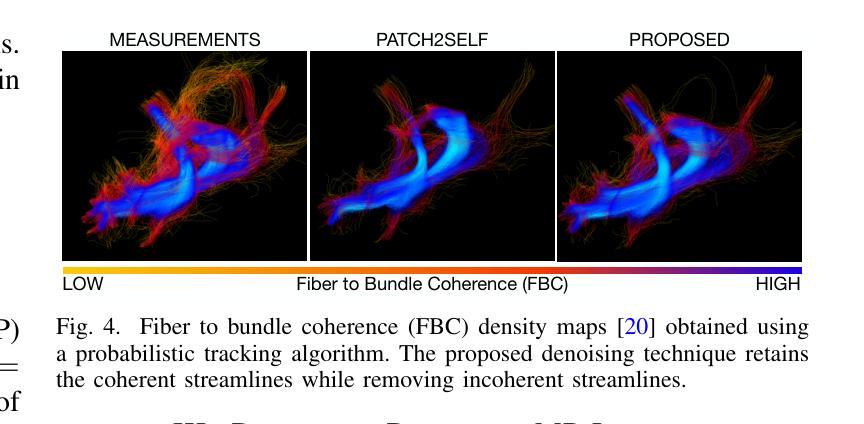
Weakly-Convex Regularization for Magnetic Resonance Image Denoising
Authors:Akash Prabakar, Abhishek Shreekant Bhandiwad, Abijith Jagannath Kamath, Chandra Sekhar Seelamantula
Regularization for denoising in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is typically achieved using convex regularization functions. Recently, deep learning techniques have been shown to provide superior denoising performance. However, this comes at the price of lack of explainability, interpretability and stability, which are all crucial to MRI. In this work, we present a constructive approach for designing weakly-convex regularization functions for MR image denoising. We show that our technique performs on par with state-of-the-art denoisers for diffusion-weighted MR image denoising. Our technique can be applied to design weakly-convex convolutional neural networks with prototype activation functions that impart interpretability and are provably convergent. We also show that our technique exhibits fewer denoising artifacts by demonstrating its effect on brain microstructure modelling.
在磁共振成像(MRI)中,去噪的正则化通常通过使用凸正则化函数来实现。最近,深度学习技术已被证明可以提供卓越的去噪性能。然而,这带来了缺乏可解释性、可解释性和稳定性的代价,这三者对于MRI来说都是至关重要的。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种设计用于MR图像去噪的弱凸正则化函数的建设性方法。我们证明,我们的技术在扩散加权MR图像去噪方面的性能与最先进的去噪器相当。我们的技术可应用于设计具有原型激活函数的弱凸卷积神经网络,这些网络具有可解释性并且可证明收敛。我们还通过在脑微观结构建模上展示其影响,证明了我们的技术产生的去噪伪影更少。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented in ISCS25
Summary
本文提出一种设计弱凸正则化函数的方法,用于磁共振成像(MRI)去噪。该方法与先进的去噪器在扩散加权MRI去噪方面表现相当,并可应用于设计具有原型激活函数的弱凸卷积神经网络,具有可解释性、收敛性,并减少了去噪伪影在脑微观结构建模中的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了弱凸正则化函数的设计方法,旨在用于磁共振成像(MRI)中的去噪。
- 该方法与当前先进的去噪器在扩散加权MRI去噪方面表现相似。
- 该技术可应用于设计具有原型激活函数的弱凸卷积神经网络。
- 所设计网络具有可解释性和收敛性。
- 该方法在去噪过程中产生的伪影较少。
- 文中展示了该方法在脑微观结构建模中的效果。
点此查看论文截图
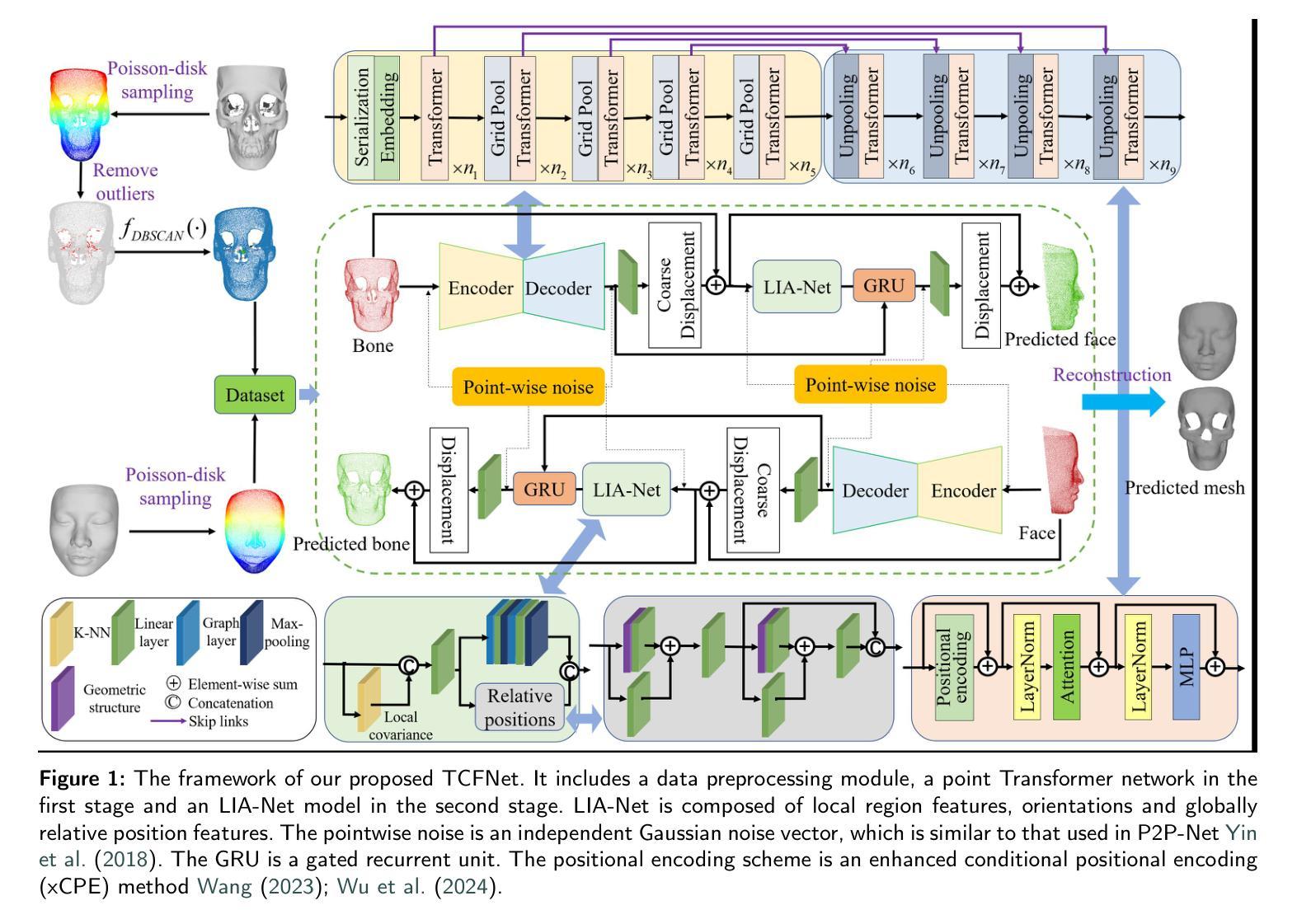
TCFNet: Bidirectional face-bone transformation via a Transformer-based coarse-to-fine point movement network
Authors:Runshi Zhang, Bimeng Jie, Yang He, Junchen Wang
Computer-aided surgical simulation is a critical component of orthognathic surgical planning, where accurately simulating face-bone shape transformations is significant. The traditional biomechanical simulation methods are limited by their computational time consumption levels, labor-intensive data processing strategies and low accuracy. Recently, deep learning-based simulation methods have been proposed to view this problem as a point-to-point transformation between skeletal and facial point clouds. However, these approaches cannot process large-scale points, have limited receptive fields that lead to noisy points, and employ complex preprocessing and postprocessing operations based on registration. These shortcomings limit the performance and widespread applicability of such methods. Therefore, we propose a Transformer-based coarse-to-fine point movement network (TCFNet) to learn unique, complicated correspondences at the patch and point levels for dense face-bone point cloud transformations. This end-to-end framework adopts a Transformer-based network and a local information aggregation network (LIA-Net) in the first and second stages, respectively, which reinforce each other to generate precise point movement paths. LIA-Net can effectively compensate for the neighborhood precision loss of the Transformer-based network by modeling local geometric structures (edges, orientations and relative position features). The previous global features are employed to guide the local displacement using a gated recurrent unit. Inspired by deformable medical image registration, we propose an auxiliary loss that can utilize expert knowledge for reconstructing critical organs.Compared with the existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on gathered datasets, TCFNet achieves outstanding evaluation metrics and visualization results. The code is available at https://github.com/Runshi-Zhang/TCFNet.
计算机辅助手术模拟是正颌外科手术规划的重要组成部分,其中对面骨形状变化的精确模拟具有重要意义。传统的生物力学模拟方法受到计算时间消耗大、劳动密集型数据处理策略以及精度低等的限制。最近,基于深度学习的模拟方法已将该问题视为骨骼和面部点云之间的点-点转换。然而,这些方法无法处理大规模的点,具有有限的感受野而导致噪声点,并基于注册执行了复杂的预处理和后处理操作。这些缺点限制了此类方法的性能和广泛应用。因此,我们提出了一种基于Transformer的粗细点移动网络(TCFNet),用于学习补丁和点对密集面部骨骼点云转换的独特而复杂的对应关系。该端到端框架在第一阶段采用基于Transformer的网络,在第二阶段采用局部信息聚合网络(LIA-Net),两者相互增强以生成精确的点移动路径。LIA-Net可以有效地补偿基于Transformer的网络中邻近精度损失,通过对局部几何结构(边缘、方向和相对位置特征)进行建模。通过先前的全局特征来引导局部位移使用门控循环单元。受可变形医学图像注册的启发,我们提出了一种辅助损失,可以利用专家知识重建关键器官。与收集的数据集上的现有最新方法相比,TCFNet在评估指标和可视化结果方面取得了显著成绩。代码可在https://github.com/Runshi-Zhang/TCFNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 11 figures
摘要
提出一种基于Transformer的粗到细点移动网络(TCFNet),用于学习面部骨骼点云的密集变换的独特对应关系。该网络在补丁和点级别具有复杂的对应关系,采用端到端框架,第一阶段采用基于Transformer的网络,第二阶段采用局部信息聚合网络(LIA-Net),两者相互增强,产生精确的点移动路径。与现有最先进的方法相比,TCFNet在收集的数据集上取得了出色的评价指标和可视化结果。
关键见解
- 计算机辅助手术模拟在整形外科手术规划中起着关键作用,其中准确模拟面部骨骼形状变化具有重要意义。
- 传统生物力学模拟方法存在计算耗时、数据处理策略繁琐和低精度等局限性。
- 基于深度学习的方法将问题视为骨骼和面部点云之间的点对点转换,但处理大规模点时存在局限性,如感受野小、点噪声大、基于注册的预处理和后处理操作复杂等。
- 提出的TCFNet网络结合Transformer和LIA-Net,分别在补丁和点级别学习独特的复杂对应关系,用于密集面部骨骼点云变换。
- LIA-Net能有效补偿Transformer网络邻域精度损失,通过建模局部几何结构(如边缘、方向和相对位置特征)来提高准确性。
- 网络使用全局特征指导局部位移,采用门控循环单元。
点此查看论文截图

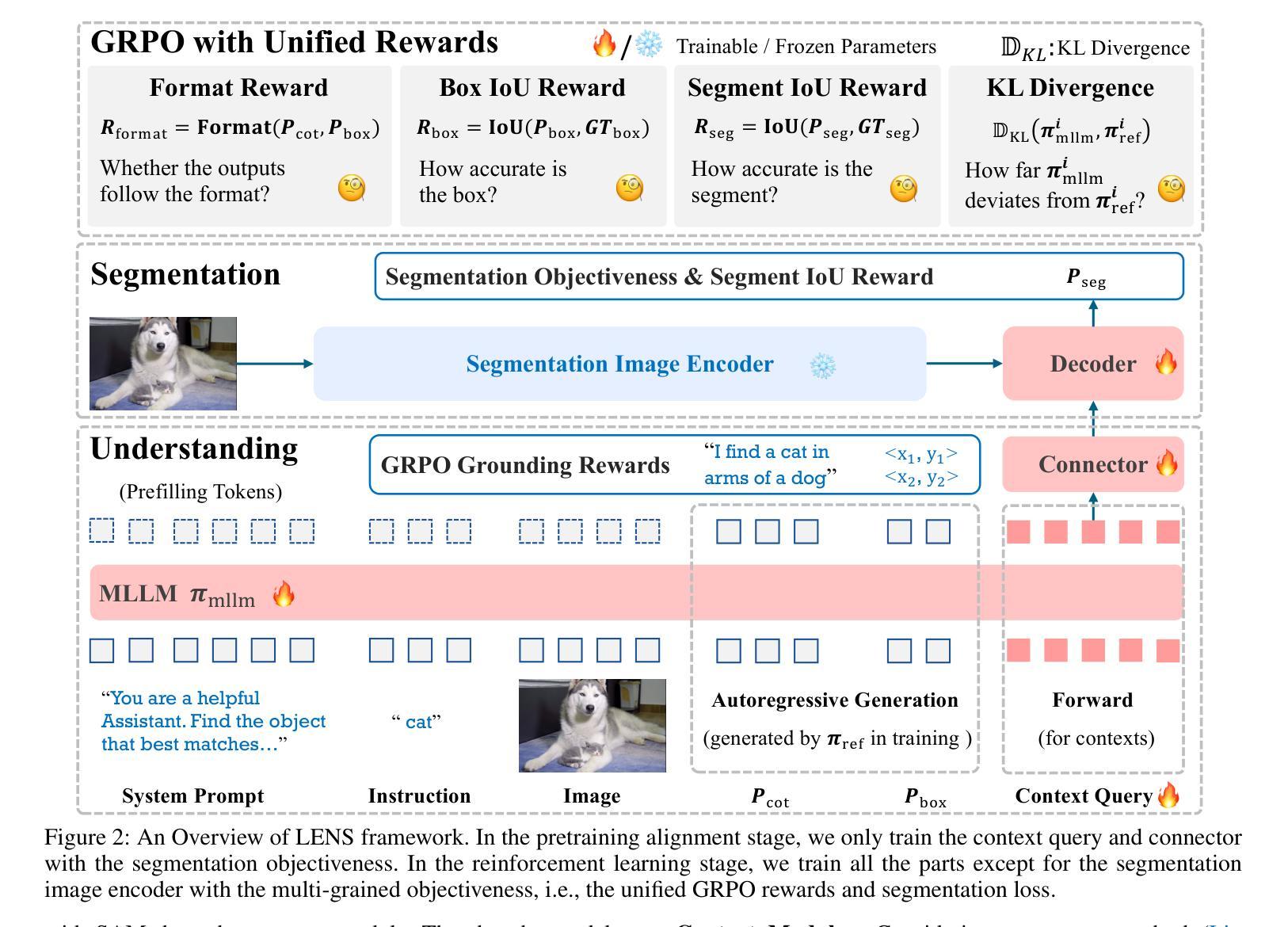
LENS: Learning to Segment Anything with Unified Reinforced Reasoning
Authors:Lianghui Zhu, Bin Ouyang, Yuxuan Zhang, Tianheng Cheng, Rui Hu, Haocheng Shen, Longjin Ran, Xiaoxin Chen, Li Yu, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang
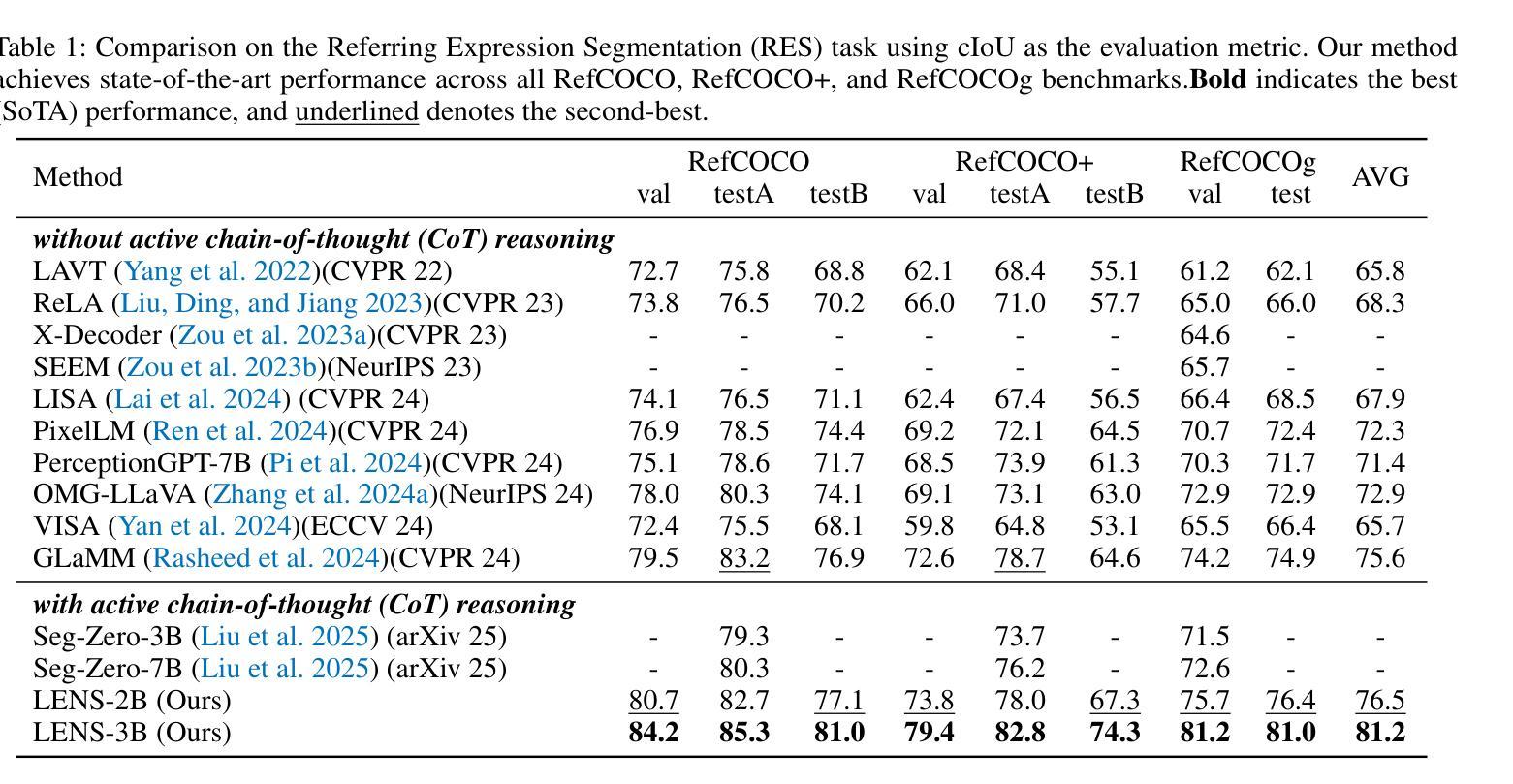
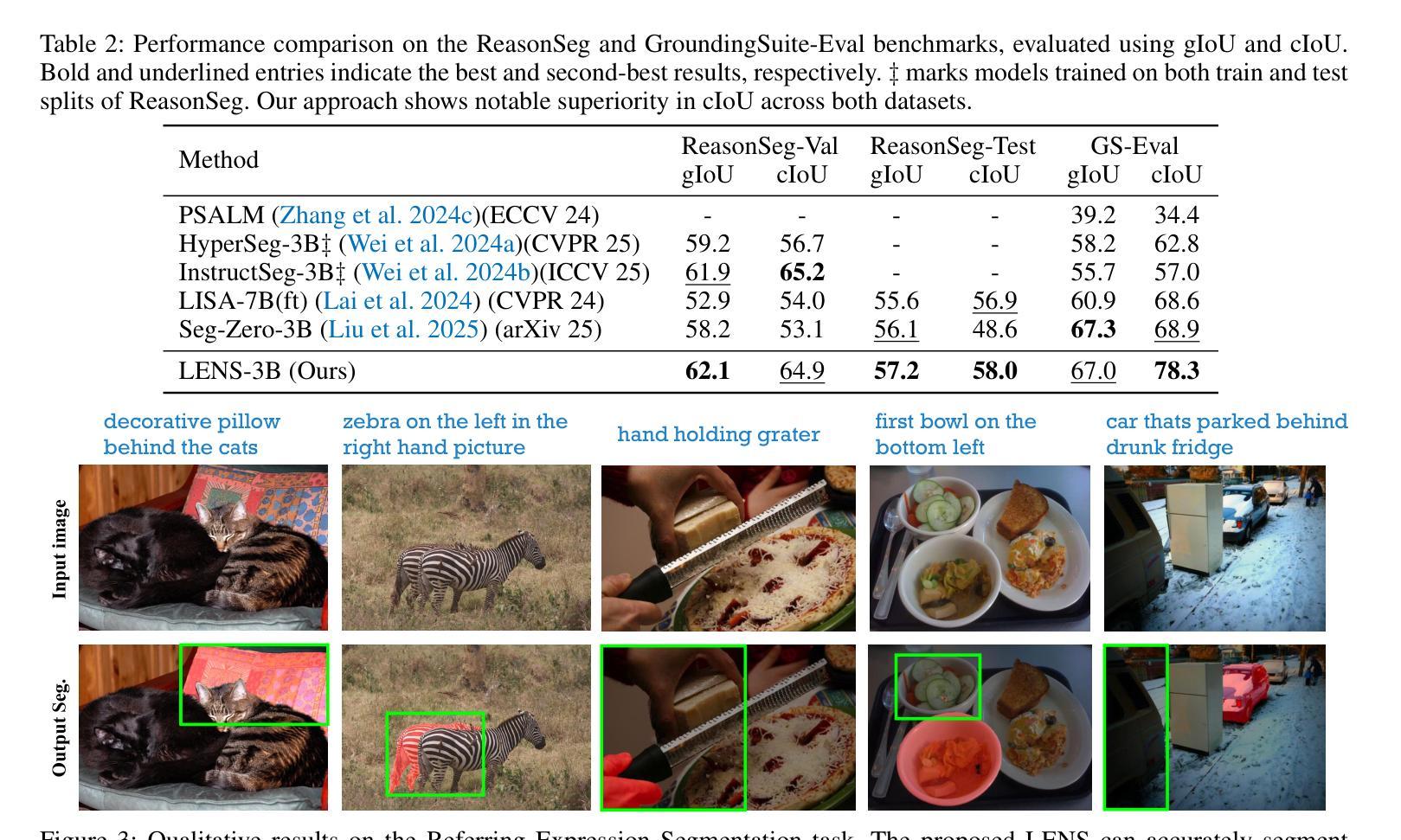
Text-prompted image segmentation enables fine-grained visual understanding and is critical for applications such as human-computer interaction and robotics. However, existing supervised fine-tuning methods typically ignore explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning at test time, which limits their ability to generalize to unseen prompts and domains. To address this issue, we introduce LENS, a scalable reinforcement-learning framework that jointly optimizes the reasoning process and segmentation in an end-to-end manner. We propose unified reinforcement-learning rewards that span sentence-, box-, and segment-level cues, encouraging the model to generate informative CoT rationales while refining mask quality. Using a publicly available 3-billion-parameter vision-language model, i.e., Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, LENS achieves an average cIoU of 81.2% on the RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg benchmarks, outperforming the strong fine-tuned method, i.e., GLaMM, by up to 5.6%. These results demonstrate that RL-driven CoT reasoning serves as a robust prior for text-prompted segmentation and offers a practical path toward more generalizable Segment Anything models. Code is available at https://github.com/hustvl/LENS.
文本提示的图像分割能够实现精细的视觉理解,对于人机交互和机器人等应用至关重要。然而,现有的监督微调方法通常在测试时忽略了明确的思维链(CoT)推理,这限制了它们对未见过的提示和领域的泛化能力。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了LENS,这是一个可扩展的强化学习框架,以端到端的方式联合优化推理过程和分割。我们提出了统一的强化学习奖励,涵盖句子、框和段级线索,鼓励模型在细化掩膜质量的同时生成信息丰富的CoT理由。我们使用公开的3亿参数视觉语言模型(即Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct),在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg基准测试上,LENS的平均完全交并比(cIoU)达到81.2%,超越了强大的微调方法GLaMM,最高提升了5.6%。这些结果表明,强化学习驱动的CoT推理为文本提示的分割提供了一个稳健的先验,并为更通用的“任意内容分割”模型提供了实际可行的路径。代码可通过https://github.com/hustvl/LENS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is released at https://github.com/hustvl/LENS
Summary
文本提示的图像分割技术对于精细视觉理解至关重要,对于人机交互和机器人应用等领域有重要意义。为解决现有监督微调方法忽略测试时显式链式思维推理的问题,本文提出一种可扩展的强化学习框架LENS,以端到端的方式联合优化推理过程和分割。通过统一强化学习奖励,涵盖句子、框和段级别的线索,鼓励模型生成信息丰富的思维过程同时提高掩膜质量。使用公开可用的视觉语言模型Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct,LENS在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg基准测试上平均完全交并比达到81.2%,优于精细调参方法GLaMM,最高提升5.6%。结果证明强化学习驱动的链式思维推理为文本提示分割提供了稳健先验,为实现更通用的分割模型提供了实践路径。
Key Takeaways
- 文本提示的图像分割技术对于精细视觉理解重要,尤其在人机交互和机器人领域。
- 现有监督微调方法忽略测试时的显式链式思维推理,影响模型在未见提示和领域下的泛化能力。
- LENS框架通过强化学习联合优化推理过程和分割,实现端到端的优化。
- LENS采用统一强化学习奖励,涵盖句子、框和段级别线索,提升掩膜质量。
- 使用Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct视觉语言模型,LENS在多个基准测试上取得优异性能。
- LENS平均完全交并比达到81.2%,优于现有方法,最高提升5.6%。
点此查看论文截图

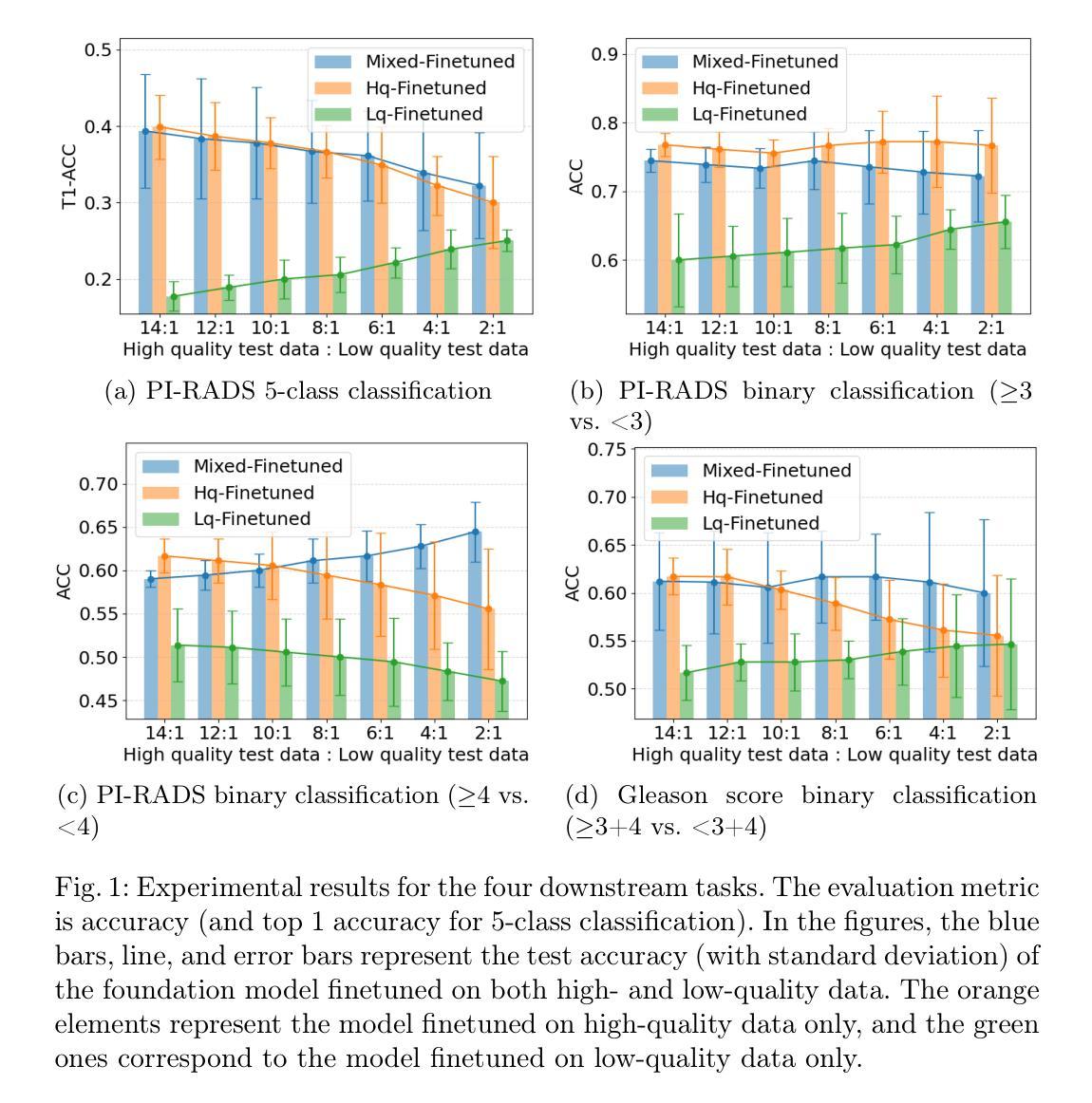
Impact of Clinical Image Quality on Efficient Foundation Model Finetuning
Authors:Yucheng Tang, Pawel Rajwa, Alexander Ng, Yipei Wang, Wen Yan, Natasha Thorley, Aqua Asif, Clare Allen, Louise Dickinson, Francesco Giganti, Shonit Punwani, Daniel C. Alexander, Veeru Kasivisvanathan, Yipeng Hu
Foundation models in medical imaging have shown promising label efficiency, achieving high performance on downstream tasks using only a fraction of the annotated data otherwise required. In this study, we evaluate this potential in the context of prostate multiparametric MRI using ProFound, a recently developed domain-specific vision foundation model pretrained on large-scale prostate MRI datasets. We investigate the impact of variable image quality on the label-efficient finetuning, by quantifying the generalisability of the finetuned models. We conduct a comprehensive set of experiments by systematically varying the ratios of high- and low-quality images in the finetuning and evaluation sets. Our findings indicate that image quality distribution and its finetune-and-test mismatch significantly affect model performance. In particular: a) Varying the ratio of high- to low-quality images between finetuning and test sets leads to notable differences in downstream performance; and b) The presence of sufficient high-quality images in the finetuning set is critical for maintaining strong performance, whilst the importance of matched finetuning and testing distribution varies between different downstream tasks, such as automated radiology reporting and prostate cancer detection. Importantly, experimental results also show that, although finetuning requires significantly less labeled data compared to training from scratch when the quality ratio is consistent, this label efficiency is not independent of the image quality distribution. For example, we show cases that, without sufficient high-quality images in finetuning, finetuned models may fail to outperform those without pretraining.
在医学成像领域,基础模型显示出有前景的标签效率,即仅使用一小部分标注数据即可在下游任务上实现高性能。本研究中,我们针对前列腺多参数MRI,评估了潜力巨大的ProFound模型的潜力。ProFound是一个针对前列腺MRI数据集的特定领域预训练的基础模型。我们通过量化微调模型的泛化能力,研究了不同图像质量对标签效率微调的影响。我们通过系统地改变微调集和评估集中高质量和低质量图像的比例,进行了一系列全面的实验。我们的研究结果表明,图像质量分布及其微调与测试的不匹配显著影响模型性能。具体来说:a)在微调集和测试集之间改变高质量与低质量图像的比例会导致下游性能出现显著差异;b)微调集中有足够的高质量图像对于保持强大性能至关重要,而匹配微调集和测试集的分布的重要性在不同下游任务之间有所不同,如自动化放射报告和前列腺癌检测等。重要的是,实验结果还表明,尽管在质量比例一致的情况下,微调所需的标注数据量与从头开始训练相比大大减少,但这种标签效率并不是独立于图像质量分布的。例如,我们展示了在某些情况下,如果在微调过程中没有足够的高质量图像,微调后的模型可能无法超越未进行预训练的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was accepted to the 1st MICCAI Workshop on Efficient Medical AI (EMA4MICCAI2025) and selected for oral presentation
Summary
本文研究了基于医学成像的基础模型在前列腺多参数MRI领域的标签效率。实验结果显示,图像质量分布及其在微调与测试中的不匹配会显著影响模型性能。当高质量图像在微调集中占一定比例时,模型性能得以保持。但不同下游任务(如自动放射学报告和前列腺癌检测)对匹配度要求不同。此外,尽管在质量比率一致的情况下,微调所需的标注数据远少于从头开始训练,但这种标签效率并非独立于图像质量分布。若无足够的高质量图像进行微调,预训练模型的性能可能无法展现优势。
Key Takeaways
- 基础模型在医学成像中显示出对标签效率的潜力,特别是在前列腺MRI中。
- 图像质量分布对模型性能有重要影响。
- 微调集和测试集中高质量图像的比例对模型性能产生显著影响。
- 充足的高质量图像在微调过程中的重要性。
- 不同下游任务对匹配度要求不同。
- 即使在质量一致的情况下,标签效率并非独立于图像质量分布。
点此查看论文截图

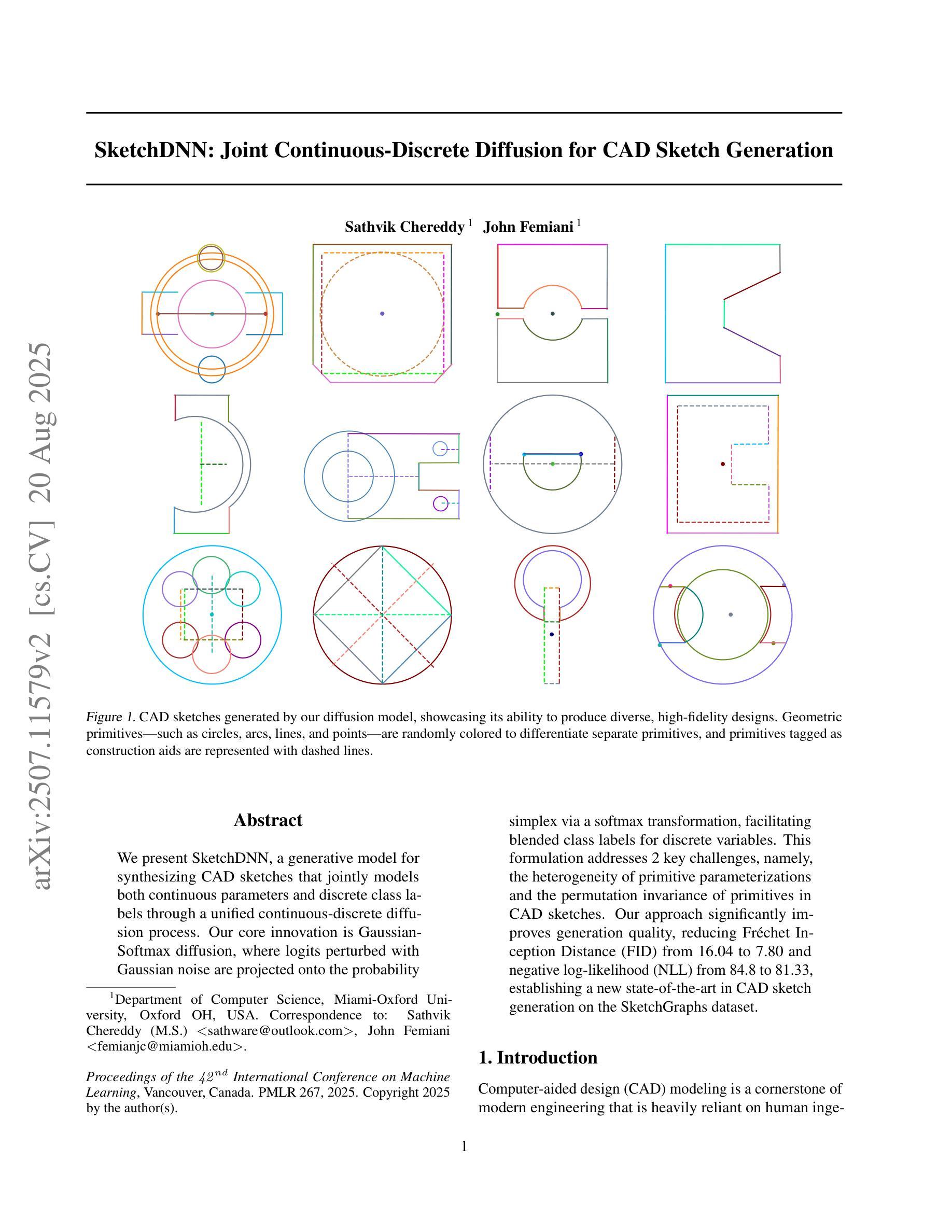
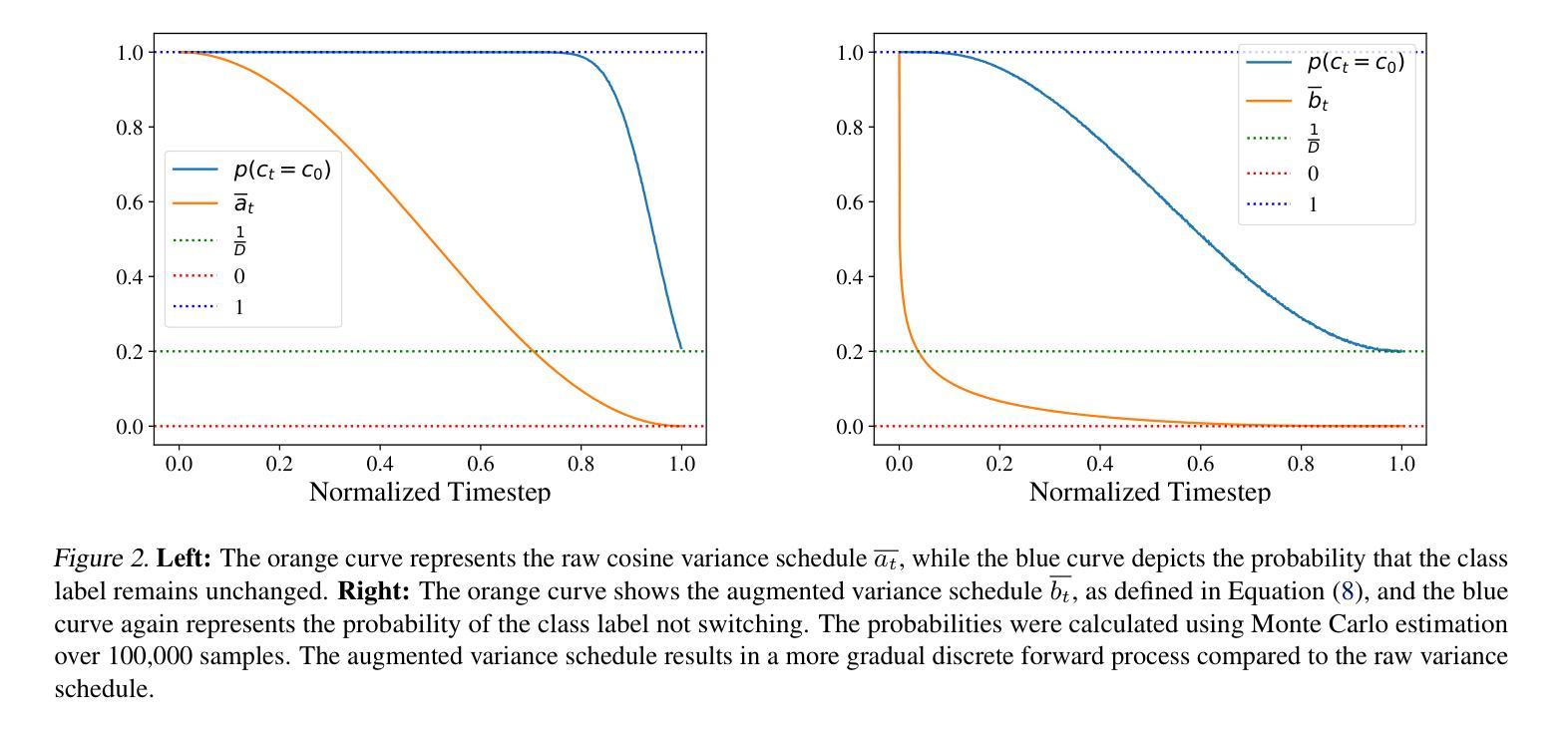
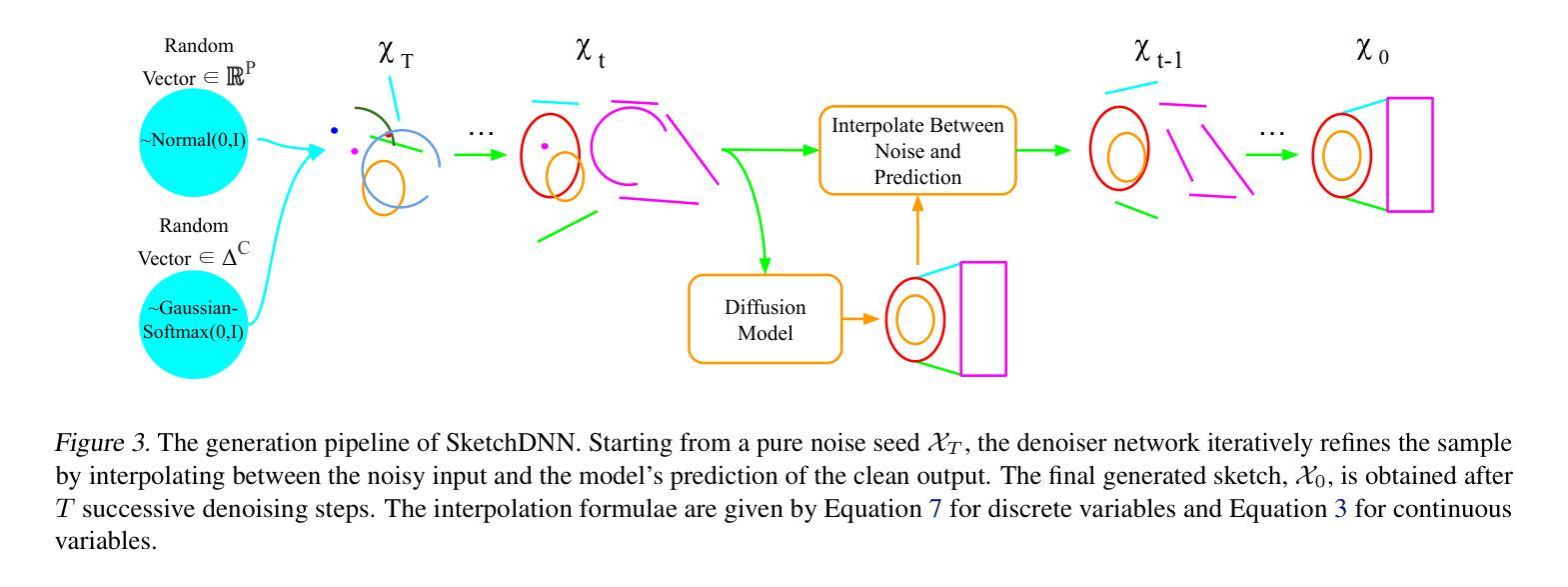
SketchDNN: Joint Continuous-Discrete Diffusion for CAD Sketch Generation
Authors:Sathvik Chereddy, John Femiani
We present SketchDNN, a generative model for synthesizing CAD sketches that jointly models both continuous parameters and discrete class labels through a unified continuous-discrete diffusion process. Our core innovation is Gaussian-Softmax diffusion, where logits perturbed with Gaussian noise are projected onto the probability simplex via a softmax transformation, facilitating blended class labels for discrete variables. This formulation addresses 2 key challenges, namely, the heterogeneity of primitive parameterizations and the permutation invariance of primitives in CAD sketches. Our approach significantly improves generation quality, reducing Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) from 16.04 to 7.80 and negative log-likelihood (NLL) from 84.8 to 81.33, establishing a new state-of-the-art in CAD sketch generation on the SketchGraphs dataset.
我们提出了SketchDNN,这是一个用于合成CAD草图的生成模型。它通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程对连续参数和离散类标签进行联合建模。我们的核心创新在于高斯Softmax扩散,其中通过对数几率添加高斯噪声并将其投影到概率单纯形上进行Softmax转换,为离散变量提供混合类标签。这种表述解决了两个关键问题,即原始参数化的异质性和CAD草图中原始图形的排列不变性。我们的方法显著提高了生成质量,将Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)从16.04降至7.80,负对数似然(NLL)从84.8降至81.33,在SketchGraphs数据集上建立了CAD草图生成的新最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 63 figures, Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML2025)
Summary
本文介绍了SketchDNN模型,该模型通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程,对CAD草图进行生成。其核心创新是Gaussian-Softmax扩散,通过将带有高斯噪声的对数几率映射到概率单纯形上,为离散变量提供混合类标签。该方法解决了CAD草图参数化的异质性和原始排列的不变性两个关键问题,显著提高了生成质量,在SketchGraphs数据集上建立了新的最高标准。
Key Takeaways
- SketchDNN是一个用于合成CAD草图的生成模型,通过统一的连续-离散扩散过程建模。
- 模型的核心创新是Gaussian-Softmax扩散,解决了离散变量的混合类标签问题。
- 该方法解决了CAD草图参数化的异质性,即不同原始数据的参数化问题。
- 排列不变性问题被有效解决,提高了模型的泛化能力。
- SketchDNN在SketchGraphs数据集上的生成质量显著提高,FID从16.04降至7.80。
- NLL从84.8降至81.33,说明模型在预测和生成方面的性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图
BRISC: Annotated Dataset for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Classification with Swin-HAFNet
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Yasin Rezvani, Sara Moayedi, Sadjad Rezvani, Fatemeh Fateh, Mansoor Fateh
Accurate segmentation and classification of brain tumors from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) remain key challenges in medical image analysis. This is primarily due to the lack of high-quality, balanced, and diverse datasets. In this work, we present a newly developed MRI dataset named BRISC designed specifically for brain tumor segmentation and classification tasks. The dataset comprises 6,000 contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scans annotated by certified radiologists and physicians. It includes three major tumor types, namely glioma, meningioma, and pituitary, as well as non-tumorous cases. Each sample includes high-resolution labels and is categorized across axial, sagittal, and coronal imaging planes to facilitate robust model development and cross-view generalization. To demonstrate the utility of the dataset, we propose a transformer-based segmentation model and benchmark it against established baselines. In this work, we propose a transformer-based model designed for both segmentation and classification of brain tumors, leveraging multi-scale feature representations from a Swin Transformer backbone. The model is benchmarked against established baselines to demonstrate the utility of the dataset, enabling accurate segmentation and robust classification across four diagnostic categories: glioma, meningioma, pituitary, and non-tumorous cases. In this work, our proposed transformer-based model demonstrates superior performance in both segmentation and classification tasks for brain tumor analysis. For the segmentation task, the method achieves the highest weighted mean Intersection-over-Union (IoU) of 82.3%, with improvements observed across all tumor categories. For the classification task, the model attains an accuracy of 99.63%, effectively distinguishing between glioma, meningioma, pituitary, and non-tumorous cases. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/briscdataset/brisc2025/
从磁共振成像(MRI)对脑肿瘤进行精确分割和分类,仍是医学图像分析中的关键挑战。这主要是由于缺乏高质量、平衡和多样化的数据集。在这项工作中,我们展示了一个新开发的专门用于脑肿瘤分割和分类任务的MRI数据集,名为BRISC数据集。该数据集包含由认证放射科医生和医师注释的6000份对比增强T1加权MRI扫描。它包括三种主要的肿瘤类型,即胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤,以及非肿瘤情况。每个样本都包含高分辨率的标签,并在轴向、矢状面和冠状面成像平面上进行分类,以促进稳健的模型开发和跨视图泛化。为了证明数据集的有效性,我们提出了一种基于变压器的分割模型,并将其与既定的基线进行了比较。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于变压器的模型,该模型旨在实现脑肿瘤的分割和分类,利用Swin Transformer骨干网的多尺度特征表示。该模型与既定的基线进行基准测试,以证明数据集的有效性,能够实现四种诊断类别(即胶质瘤、脑膜瘤、垂体瘤和非肿瘤情况)的准确分割和稳健分类。在这项工作中,我们提出的基于变压器的模型在脑肿瘤分析的分割和分类任务中均表现出卓越的性能。对于分割任务,该方法获得了最高的加权平均交并比(IoU)为82.3%,所有肿瘤类别的性能都有所提高。对于分类任务,该模型的准确率为99.63%,能够有效地区分胶质瘤、脑膜瘤、垂体瘤和非肿瘤情况。数据集可通过https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/briscdataset/brisc2025/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个新开发的专门用于脑肿瘤分割和分类的MRI数据集BRISC。该数据集包含由认证放射学家和医师注释的6,000份对比增强的T1加权MRI扫描,涵盖三种主要肿瘤类型(胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤)以及非肿瘤病例。文章还提出了一种基于transformer的脑肿瘤分割与分类模型,并在该数据集上进行了验证,表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一个名为BRISC的新MRI数据集,专门用于脑肿瘤分割和分类任务。
- 数据集包含6,000份由专家注释的对比增强T1加权MRI扫描。
- 数据集涵盖三种主要肿瘤类型:胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤,以及非肿瘤病例。
- 提出了一个基于transformer的脑肿瘤分割与分类模型。
- 模型利用Swin Transformer的多尺度特征表示,针对四种诊断类别进行性能评估。
- 模型在分割任务上取得了最高加权平均IoU值为82.3%,在各类肿瘤中都观察到了改进。
点此查看论文截图

PRS-Med: Position Reasoning Segmentation with Vision-Language Model in Medical Imaging
Authors:Quoc-Huy Trinh, Minh-Van Nguyen, Jung Zeng, Ulas Bagci, Debesh Jha
Recent advancements in prompt-based medical image segmentation have enabled clinicians to identify tumors using simple input like bounding boxes or text prompts. However, existing methods face challenges when doctors need to interact through natural language or when position reasoning is required - understanding spatial relationships between anatomical structures and pathologies. We present PRS-Med, a framework that integrates vision-language models with segmentation capabilities to generate both accurate segmentation masks and corresponding spatial reasoning outputs. Additionally, we introduce the MMRS dataset (Multimodal Medical in Positional Reasoning Segmentation), which provides diverse, spatially-grounded question-answer pairs to address the lack of position reasoning data in medical imaging. PRS-Med demonstrates superior performance across six imaging modalities (CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, endoscopy, RGB), significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both segmentation accuracy and position reasoning. Our approach enables intuitive doctor-system interaction through natural language, facilitating more efficient diagnoses. Our dataset pipeline, model, and codebase will be released to foster further research in spatially-aware multimodal reasoning for medical applications.
在基于提示的医疗图像分割方面的最新进展,已经使临床医生能够使用简单的输入,如边界框或文本提示来识别肿瘤。然而,当医生需要通过自然语言进行交互或需要位置推理(即理解解剖结构和病理之间的空间关系)时,现有方法面临挑战。我们提出了PRS-Med框架,它结合了视觉语言模型和分割能力,能够生成准确的分割掩膜和相应的空间推理输出。此外,我们还介绍了MMRS数据集(定位推理分割中的多模态医疗数据),该数据集提供了多样且基于空间的问题答案对,以解决医疗影像中定位推理数据的缺乏。PRS-Med在六种成像模式(CT、MRI、X光、超声、内窥镜、RGB)下表现出卓越的性能,在分割精度和位置推理方面都大大优于最新技术方法。我们的方法能够通过自然语言实现直观的医生与系统的交互,促进更有效的诊断。我们的数据集管道、模型和代码库将予以发布,以促进在医疗应用中具备空间感知的多模态推理的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着基于提示的医疗图像分割技术的最新进展,医生现在可以使用简单的输入,如边界框或文本提示来识别肿瘤。然而,当医生需要通过自然语言进行交互或需要位置推理(即理解解剖结构和病理之间的空间关系)时,现有方法面临挑战。为此,我们提出了PRS-Med框架,它整合了视觉语言模型与分割能力,能够生成准确的分割掩膜和相应的空间推理输出。此外,我们还介绍了MMRS数据集(位置推理分割中的多模态医疗图像),该数据集提供了多样且基于空间的问题答案对,以解决医疗成像中位置推理数据的缺乏。PRS-Med在六种成像模式(CT、MRI、X光、超声、内窥镜、RGB)下表现出卓越的性能,在分割准确性和位置推理方面都大大优于最新方法。我们的方法通过自然语言实现了医生与系统之间的直观交互,促进了更高效的诊断。我们将公开数据集管道、模型和源代码,以促进在空间感知多模态推理医疗应用方面的进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- PRS-Med框架结合了视觉语言模型与分割技术,能生成准确的分割掩膜和空间推理输出。
- MMRS数据集的推出解决了医疗图像中位置推理数据的缺乏问题。
- PRS-Med框架在六种医疗成像模式下性能卓越,超越现有方法。
- 该框架通过自然语言实现了医生与系统之间的直观交互。
- PRS-Med有助于提高诊断效率。
- PRS-Med框架和MMRS数据集公开可用,以促进进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图

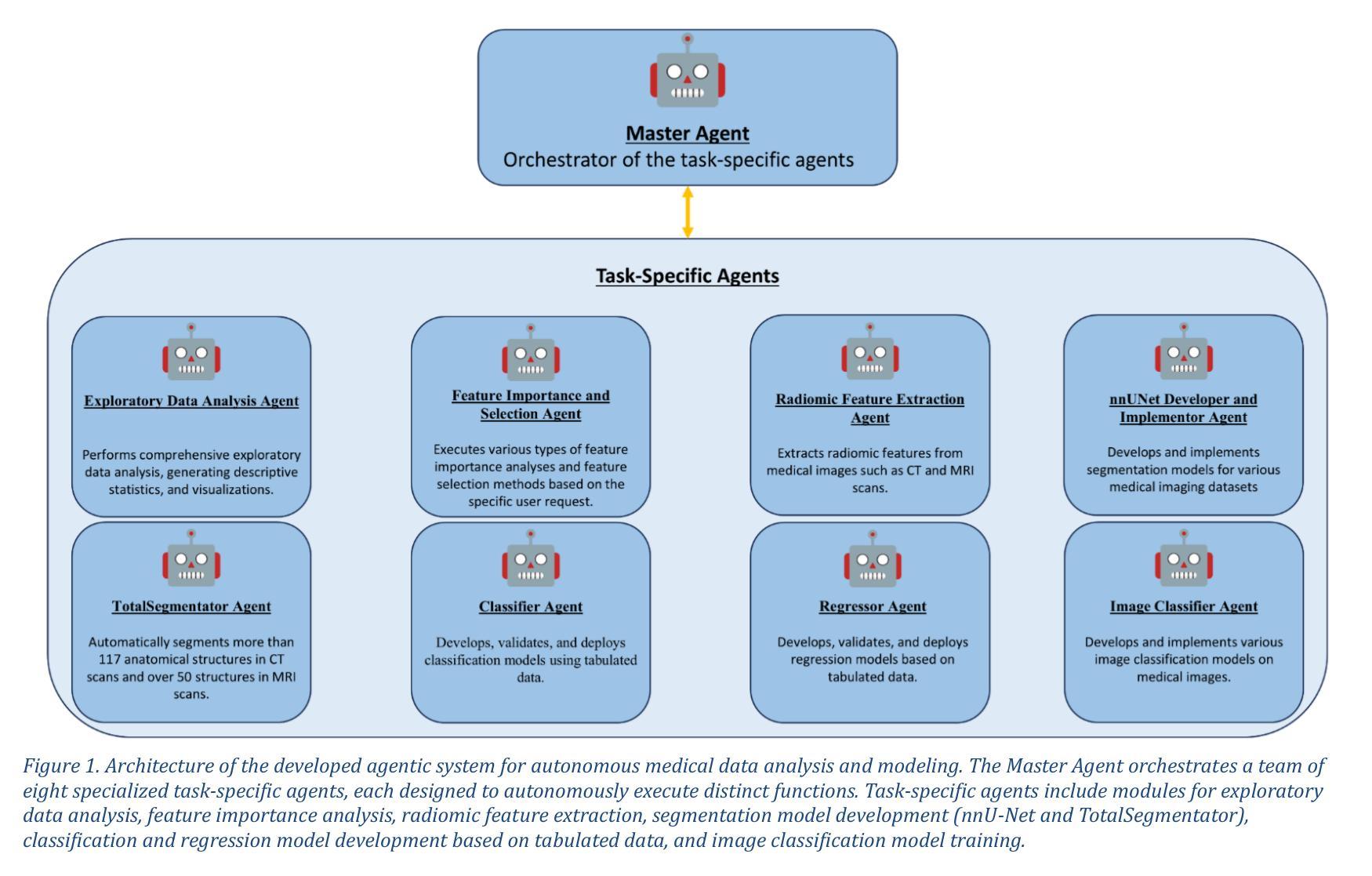
mAIstro: an open-source multi-agentic system for automated end-to-end development of radiomics and deep learning models for medical imaging
Authors:Eleftherios Tzanis, Michail E. Klontzas
Agentic systems built on large language models (LLMs) offer promising capabilities for automating complex workflows in healthcare AI. We introduce mAIstro, an open-source, autonomous multi-agentic framework for end-to-end development and deployment of medical AI models. The system orchestrates exploratory data analysis, radiomic feature extraction, image segmentation, classification, and regression through a natural language interface, requiring no coding from the user. Built on a modular architecture, mAIstro supports both open- and closed-source LLMs, and was evaluated using a large and diverse set of prompts across 16 open-source datasets, covering a wide range of imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and data types. The agents successfully executed all tasks, producing interpretable outputs and validated models. This work presents the first agentic framework capable of unifying data analysis, AI model development, and inference across varied healthcare applications, offering a reproducible and extensible foundation for clinical and research AI integration. The code is available at: https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Agentic系统为医疗保健AI中的复杂工作流程自动化提供了有前途的能力。我们介绍了mAIstro,这是一个开源的、自主的多Agentic框架,用于端到端的医疗AI模型开发和部署。该系统通过自然语言接口协调探索性分析、放射学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编写代码。mAIstro采用模块化架构,支持开源和闭源的LLM,并使用涵盖广泛成像模式、解剖区域和数据类型的16个开源数据集的大型且多样化的提示集进行评估。代理成功执行了所有任务,产生了可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这项工作提出了第一个能够在各种医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架,为临床和研究AI集成提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。代码可在https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
mAIstro是一个基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的开源、自主的多智能体框架,用于医疗AI的端到端开发和部署。它通过自然语言接口协调数据探索性分析、放射学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编码。该框架支持开源和闭源LLMs,经过在16个开源数据集上的大量和多样化的提示评估,成功执行任务,产生可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这是第一个能够在医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的智能体框架,为临床和研究AI集成提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。
Key Takeaways
- mAIstro是一个基于大型语言模型的开源自主多智能体框架,用于医疗AI的端到端开发和部署。
- 通过自然语言接口,mAIstro协调多种任务,包括数据探索性分析、放射学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归。
- 该框架无需用户编码,降低了使用门槛。
- mAIstro支持开源和闭源的大型语言模型。
- 经过在多个数据集上的广泛评估,mAIstro成功执行任务,产生可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。
- mAIstro为临床和研究AI集成提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。
点此查看论文截图

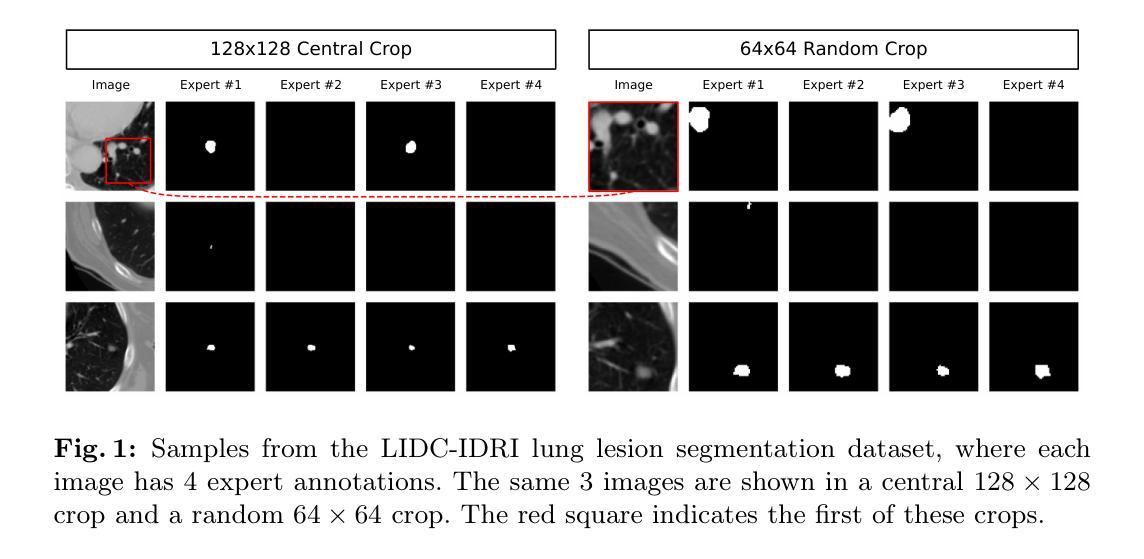
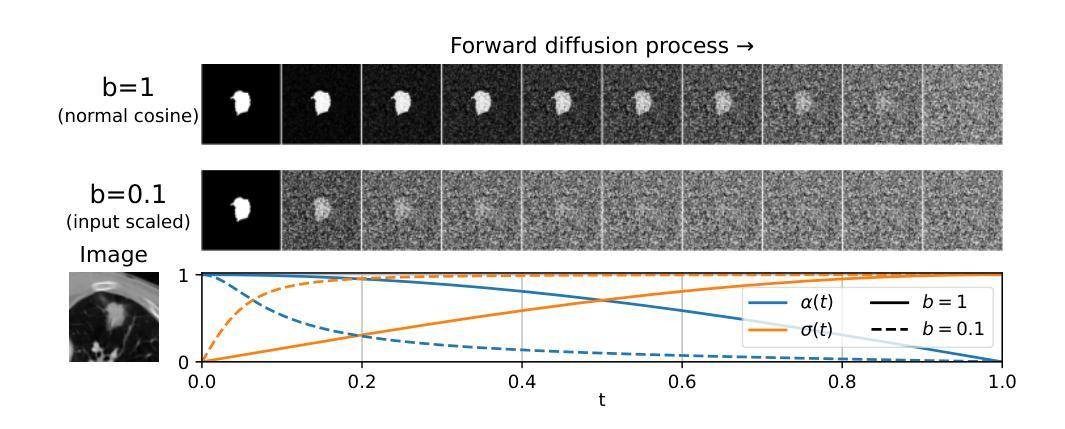
Diffusion Based Ambiguous Image Segmentation
Authors:Jakob Lønborg Christensen, Morten Rieger Hannemose, Anders Bjorholm Dahl, Vedrana Andersen Dahl
Medical image segmentation often involves inherent uncertainty due to variations in expert annotations. Capturing this uncertainty is an important goal and previous works have used various generative image models for the purpose of representing the full distribution of plausible expert ground truths. In this work, we explore the design space of diffusion models for generative segmentation, investigating the impact of noise schedules, prediction types, and loss weightings. Notably, we find that making the noise schedule harder with input scaling significantly improves performance. We conclude that x- and v-prediction outperform epsilon-prediction, likely because the diffusion process is in the discrete segmentation domain. Many loss weightings achieve similar performance as long as they give enough weight to the end of the diffusion process. We base our experiments on the LIDC-IDRI lung lesion dataset and obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Additionally, we introduce a randomly cropped variant of the LIDC-IDRI dataset that is better suited for uncertainty in image segmentation. Our model also achieves SOTA in this harder setting.
医学图像分割经常涉及由于专家标注变化而导致的固有不确定性。捕捉这种不确定性是一个重要目标,之前的研究已经使用各种生成图像模型来表示专家真实标注的全分布。在这项工作中,我们探索了生成分割扩散模型的设计空间,研究了噪声安排、预测类型和损失权重的影响。值得注意的是,我们发现通过输入缩放使噪声安排更加困难可以显著提高性能。我们得出结论,x预测和v预测优于ε预测,这可能是因为扩散过程处于离散分割域中。只要对扩散过程的结束给予足够的重视,许多损失权重都能达到类似的性能。我们的实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病变数据集,取得了最先进的性能。此外,我们引入了LIDC-IDRI数据集的随机裁剪变种,更适合于图像分割的不确定性。我们的模型在这个更困难的设置中也达到了最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SCIA25
Summary
本文探讨了使用扩散模型进行医学图像分割的不确定性问题,通过调整噪声调度、预测类型和损失权重来优化模型性能。研究发现,输入尺度上加大噪声调度难度能显著提高性能,x-和v-预测优于epsilon预测,多种损失权重在给予足够重视扩散过程末期的情况下能取得相似性能。实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病灶数据集进行,并引入随机裁剪的LIDC-IDRI数据集变体以更好地适应图像分割的不确定性问题,模型在更困难的环境下也取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中存在因专家标注差异导致的固有不确定性。
- 扩散模型在生成图像分割中的设计空间进行了探索。
- 噪声调度难度的增加能显著提高模型性能。
- x-和v-预测在离散分割域的扩散过程中表现优于epsilon预测。
- 多种损失权重在平衡下能取得良好性能,重点是给予扩散过程末期足够的重视。
- 实验基于LIDC-IDRI肺病灶数据集进行,取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

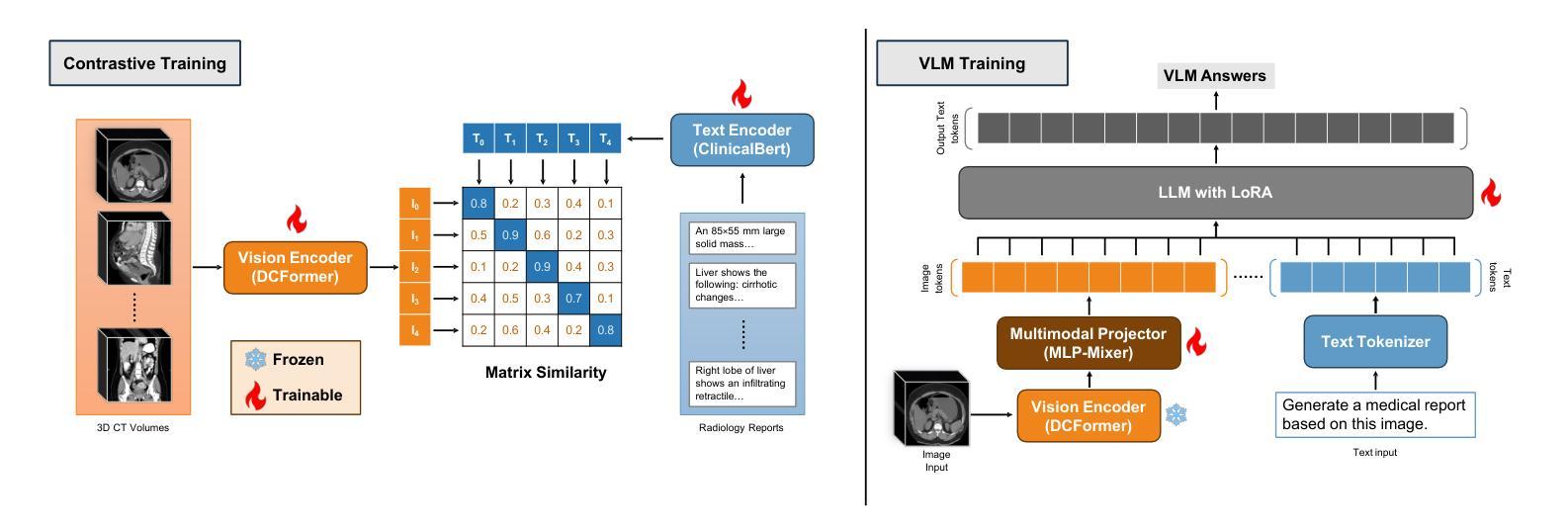
Med3DVLM: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for 3D Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Yu Xin, Gorkem Can Ates, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown promise in 2D medical image analysis, but extending them to 3D remains challenging due to the high computational demands of volumetric data and the difficulty of aligning 3D spatial features with clinical text. We present Med3DVLM, a 3D VLM designed to address these challenges through three key innovations: (1) DCFormer, an efficient encoder that uses decomposed 3D convolutions to capture fine-grained spatial features at scale; (2) SigLIP, a contrastive learning strategy with pairwise sigmoid loss that improves image-text alignment without relying on large negative batches; and (3) a dual-stream MLP-Mixer projector that fuses low- and high-level image features with text embeddings for richer multi-modal representations. We evaluate our model on the M3D dataset, which includes radiology reports and VQA data for 120,084 3D medical images. Results show that Med3DVLM achieves superior performance across multiple benchmarks. For image-text retrieval, it reaches 61.00% R@1 on 2,000 samples, significantly outperforming the current state-of-the-art M3D model (19.10%). For report generation, it achieves a METEOR score of 36.42% (vs. 14.38%). In open-ended visual question answering (VQA), it scores 36.76% METEOR (vs. 33.58%), and in closed-ended VQA, it achieves 79.95% accuracy (vs. 75.78%). These results highlight Med3DVLM’s ability to bridge the gap between 3D imaging and language, enabling scalable, multi-task reasoning across clinical applications. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/mirthAI/Med3DVLM.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在2D医学图像分析方面显示出潜力,但将其扩展到3D仍具有挑战性,这主要是由于体积数据的计算需求高以及将3D空间特征对齐临床文本的困难。我们提出了Med3DVLM,这是一个针对这些挑战设计的3D VLM,它具有三个关键创新点:(1)DCFormer,这是一种高效的编码器,使用分解的3D卷积来捕获大规模的精细空间特征;(2)SigLIP,这是一种对比学习策略,具有基于sigmoid的配对损失函数,它提高了图像文本的准确性,无需依赖大型负面批次;(3)双流MLP混合器投影仪融合了低级和高级图像特征与文本嵌入,用于更丰富的多模式表示。我们在M3D数据集上评估了我们的模型,该数据集包含用于120,084个3D医学图像的放射学报告和视觉问答(VQA)数据。结果表明,Med3DVLM在多个基准测试中实现了卓越的性能。在图像文本检索方面,它在2,000个样本上达到了61.00%的R@1准确率,显著优于当前最先进的M3D模型(19.10%)。在报告生成方面,它的METEOR得分为36.42%(对比为14.38%)。在开放式的视觉问答中,它的METEOR得分为36.76%(对比为33.58%),而在封闭式的VQA中,它达到了79.95%的准确率(对比为75.78%)。这些结果凸显了Med3DVLM在连接3D成像和语言方面的能力,能够在临床应用中实现可扩展的多任务推理。我们的代码可在https://github.com/mirthAI/Med3DVLM公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Med3DVLM是一款针对医学图像领域的视觉语言模型(VLM),特别适用于处理三维医学图像。该模型通过三项关键技术突破实现了高效与准确的性能:DCFormer编码器、SigLIP对比学习策略和融合高低层级图像特征的双流MLP混合器投影器。在M3D数据集上的实验结果表明,Med3DVLM在多项基准测试中表现卓越,特别是在图像文本检索、报告生成和视觉问答任务中实现了显著的性能提升。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- Med3DVLM是一款针对三维医学图像设计的视觉语言模型,旨在解决在医学图像领域的挑战。
- 通过三项关键技术突破实现性能提升:DCFormer编码器用于捕捉精细的空间特征,SigLIP对比学习策略改进图像文本对齐,双流MLP混合器投影器融合多模态表示。
- 在M3D数据集上的实验验证了Med3DVLM的优越性,特别是在图像文本检索、报告生成和视觉问答任务中。
- Med3DVLM成功缩小了三维成像与语言之间的鸿沟,实现了跨临床应用的规模多任务推理。
- 该模型的代码已公开,可供公众访问和使用。
- Med3DVLM的优异性能为医学图像分析领域提供了新的视角和方法论。
点此查看论文截图

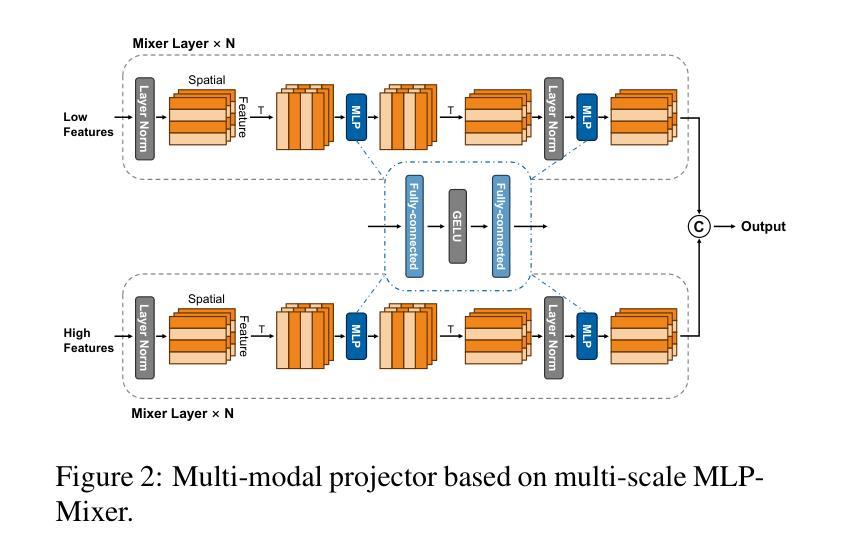
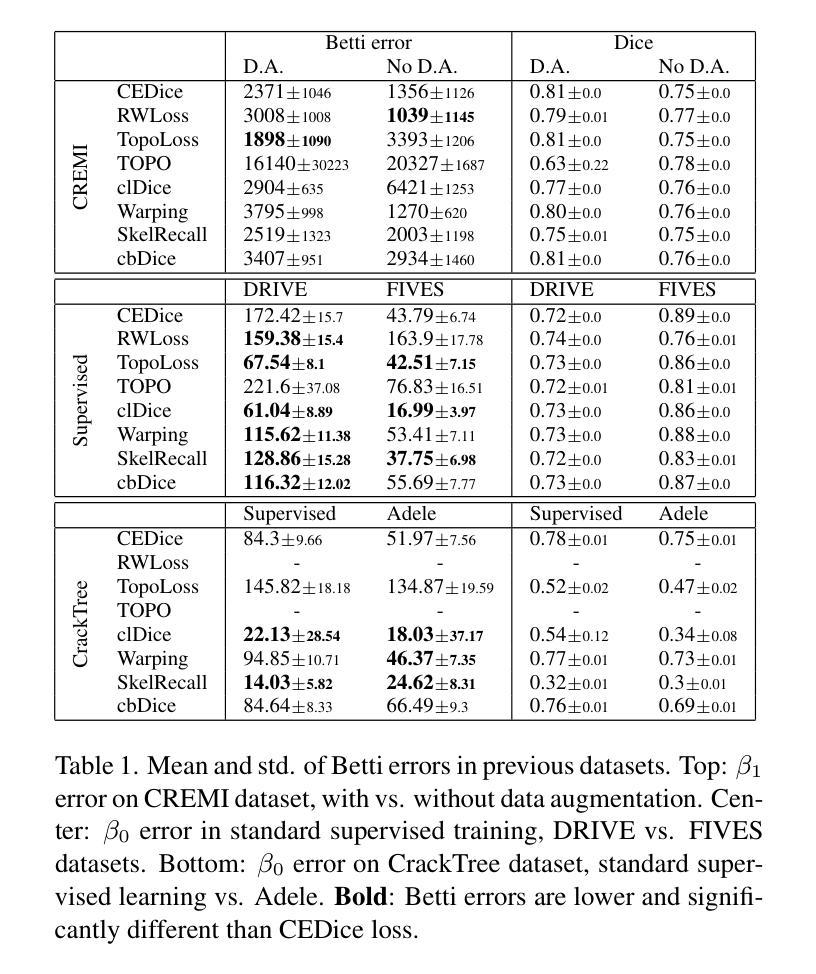
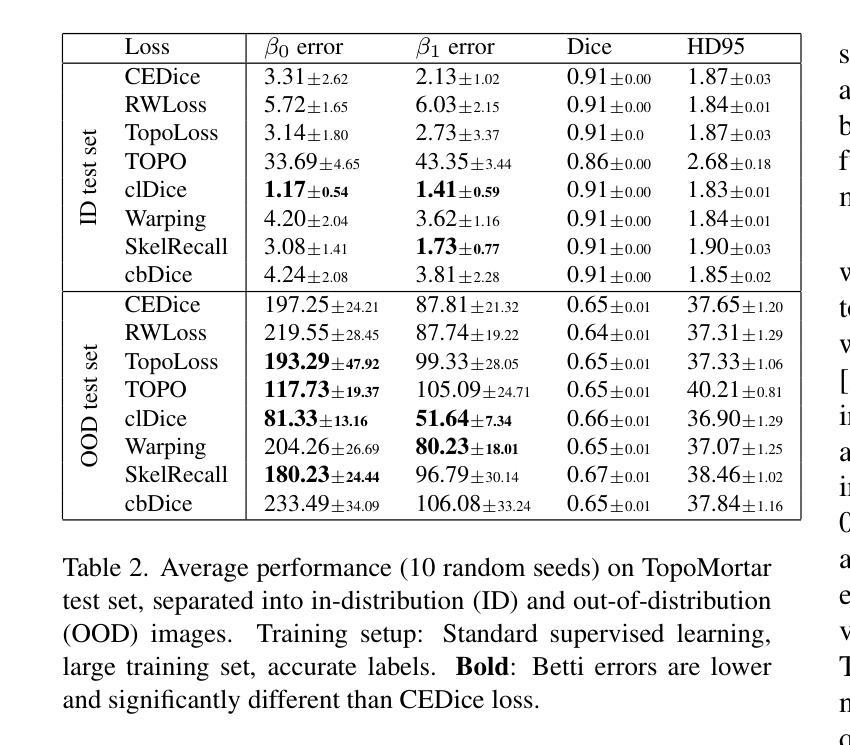
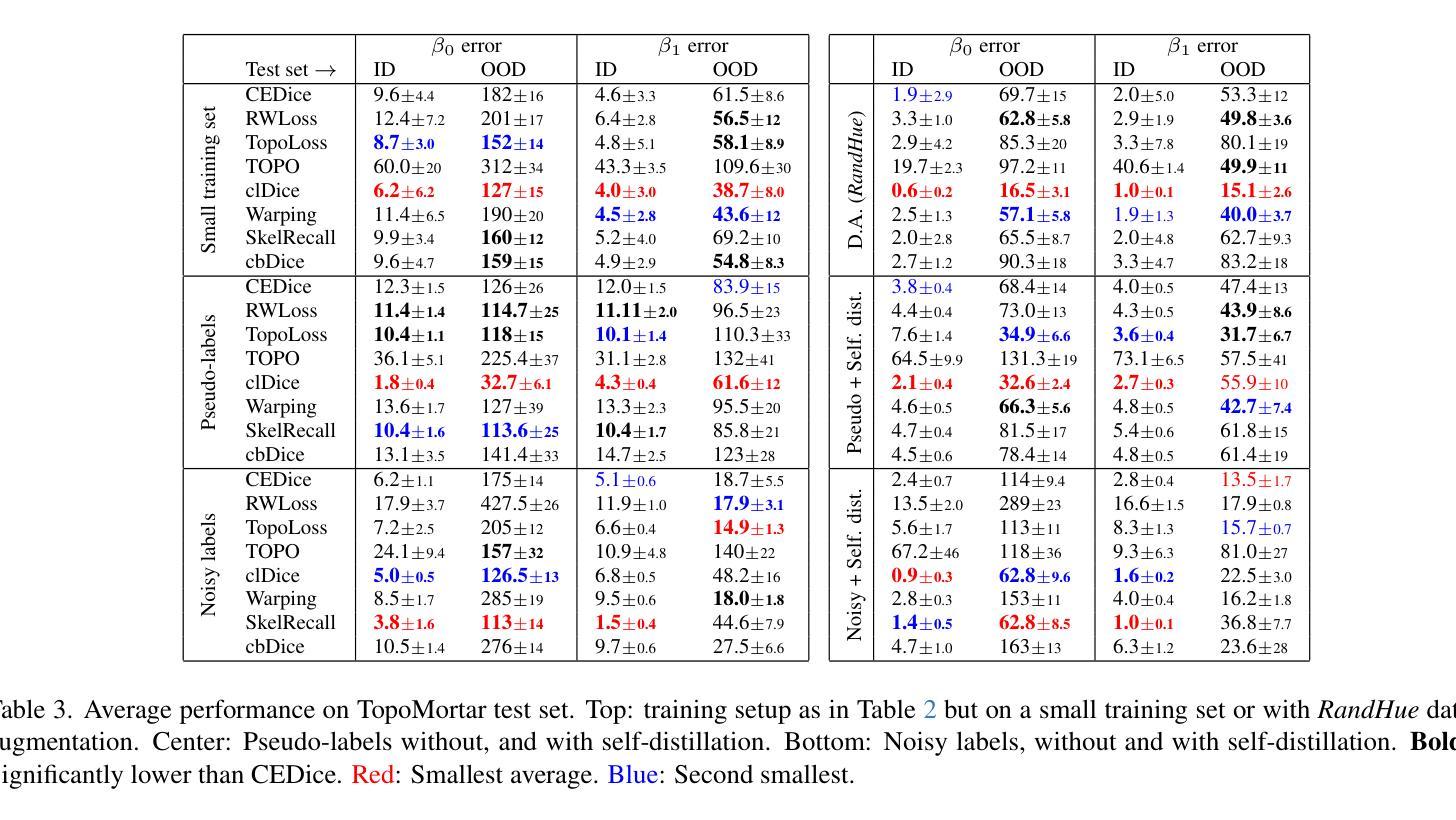
TopoMortar: A dataset to evaluate image segmentation methods focused on topology accuracy
Authors:Juan Miguel Valverde, Motoya Koga, Nijihiko Otsuka, Anders Bjorholm Dahl
We present TopoMortar, a brick wall dataset that is the first dataset specifically designed to evaluate topology-focused image segmentation methods, such as topology loss functions. Motivated by the known sensitivity of methods to dataset challenges, such as small training sets, noisy labels, and out-of-distribution test-set images, TopoMortar is created to enable in two ways investigating methods’ effectiveness at improving topology accuracy. First, by eliminating dataset challenges that, as we show, impact the effectiveness of topology loss functions. Second, by allowing to represent different dataset challenges in the same dataset, isolating methods’ performance from dataset challenges. TopoMortar includes three types of labels (accurate, pseudo-labels, and noisy labels), two fixed training sets (large and small), and in-distribution and out-of-distribution test-set images. We compared eight loss functions on TopoMortar, and we found that clDice achieved the most topologically accurate segmentations, and that the relative advantageousness of the other loss functions depends on the experimental setting. Additionally, we show that data augmentation and self-distillation can elevate Cross entropy Dice loss to surpass most topology loss functions, and that those simple methods can enhance topology loss functions as well. TopoMortar and our code can be found at https://jmlipman.github.io/TopoMortar
我们推出了TopoMortar,这是一款专门用于评估拓扑图像分割方法(如拓扑损失函数)的砖墙数据集。受到方法对数据集挑战(如小训练集、噪声标签和超出分布范围的测试集图像)的敏感性的启发,TopoMortar以两种方式创建,旨在研究提高拓扑精度的方法的有效性。首先,通过消除数据集挑战,这些挑战会影响拓扑损失函数的有效性,正如我们所展示的那样。其次,通过在同一个数据集中表示不同的数据集挑战,将方法的性能与数据集挑战隔离开来。TopoMortar包含三种类型的标签(准确标签、伪标签和噪声标签)、两个固定的训练集(大型和小型),以及符合分布和超出分布的测试集图像。我们在TopoMortar上比较了八种损失函数,发现clDice获得了最准确的拓扑分割结果,而其他损失函数的相对优势取决于实验设置。此外,我们还表明数据增强和自我蒸馏可以使交叉熵Dice损失超越大多数拓扑损失函数,这些简单的方法也可以增强拓扑损失函数的效果。TopoMortar和我们的代码可在https://jmlipman.github.io/TopoMortar找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to BMVC 2025 (Oral)
Summary
TopoMortar数据集专为评估拓扑图像分割方法而设计,如拓扑损失函数。该数据集解决了小训练集、标签噪声和非分布测试集图像等挑战,通过两种方式研究拓扑损失函数的有效性。此外,对比了八种损失函数,发现clDice在拓扑准确性上表现最佳,其他损失函数的相对优势取决于实验设置。同时,数据增强和自蒸馏技术能提高Cross entropy Dice损失性能,并增强拓扑损失函数的效果。
Key Takeaways
- TopoMortar数据集是首个专为评估拓扑图像分割方法设计的砖墙数据集。
- 该数据集解决了小训练集、标签噪声和非分布测试集图像等挑战。
- TopoMortar提供了三种标签类型和两种固定训练集规模,以研究方法的拓扑准确性。
- 在TopoMortar上对比了八种损失函数,发现clDice在拓扑准确性上表现最佳。
- 数据增强和自蒸馏技术能提高Cross entropy Dice损失性能,并可能超越部分拓扑损失函数。
- 简单方法如数据增强和自蒸馏能增强拓扑损失函数的效果。
点此查看论文截图

Deployment and validation of predictive 6-dimensional beam diagnostics through generative reconstruction with standard accelerator elements
Authors:Seongyeol Kim, Juan Pablo Gonzalez-Aguilera, Ryan Roussel, Gyujin Kim, Auralee Edelen, Myung-Hoon Cho, Young-Kee Kim, Chi Hyun Shim, Hoon Heo, Haeryong Yang
Understanding the 6-dimensional phase space distribution of particle beams is essential for optimizing accelerator performance. Conventional diagnostics such as use of transverse deflecting cavities offer detailed characterization but require dedicated hardware and space. Generative phase space reconstruction (GPSR) methods have shown promise in beam diagnostics, yet prior implementations still rely on such components. Here we present the first experimental implementation and validation of the GPSR methodology, realized by the use of standard accelerator elements including accelerating cavities and dipole magnets, to achieve complete 6-dimensional phase space reconstruction. Through simulations and experiments at the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory X-ray Free Electron Laser facility, we successfully reconstruct complex, nonlinear beam structures. Furthermore, we validate the methodology by predicting independent downstream measurements excluded from training, revealing near-unique reconstruction closely resembling ground truth. This advancement establishes a pathway for predictive diagnostics across beamline segments while reducing hardware requirements and expanding applicability to various accelerator facilities.
了解粒子束在6维相空间中的分布对于优化加速器性能至关重要。传统的诊断方法,如使用横向偏转腔,可以提供详细的特征描述,但需要专门的硬件和空间。生成相位空间重建(GPSR)方法在束流诊断中显示出巨大的潜力,但之前的实现仍然依赖于这些组件。在这里,我们首次通过实验实现了使用标准加速器元件(包括加速腔和偶极磁体)的GPSR方法的实现和验证,以实现完整的6维相空间重建。在浦项加速器实验室X射线自由电子激光设施进行的模拟和实验中,我们成功地重建了复杂的非线性光束结构。此外,我们通过预测独立于训练之外的下游测量值验证了该方法,揭示了接近独特的重建,与真实情况非常相似。这一进展为跨束流线段的预测诊断开辟了一条道路,同时降低了硬件要求,并扩大了在各种加速器设施中的应用范围。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在加速器性能优化中,理解粒子束的6维相空间分布至关重要。传统诊断方法如使用横向偏转腔可提供详细的特征描述,但需要专门的硬件和空间。生成相位空间重建(GPSR)方法在束流诊断中显示出潜力,但之前的实现仍依赖于这些组件。本文首次实验实现了使用标准加速器元件(包括加速腔和偶极磁铁)实现完全6维相空间重建的GPRS方法,成功重建复杂的非线性束结构。该方法的预测能力与下游独立测量的预测能力相匹配,并建立了跨越束线段的预测诊断途径,降低了硬件要求并扩大了其在各种加速器设施中的应用范围。
Key Takeaways
- 理解粒子束的6维相空间分布对加速器性能优化至关重要。
- 传统诊断方法需要专门的硬件和空间来详细表征粒子束的特性。
- 生成相位空间重建(GPSR)方法在束流诊断中具有潜力。
- 首次实验实现了使用标准加速器元件实现完全6维相空间重建的GPRS方法。
- 成功重建复杂的非线性束结构。
- GPSR方法预测能力与独立下游测量相匹配,验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

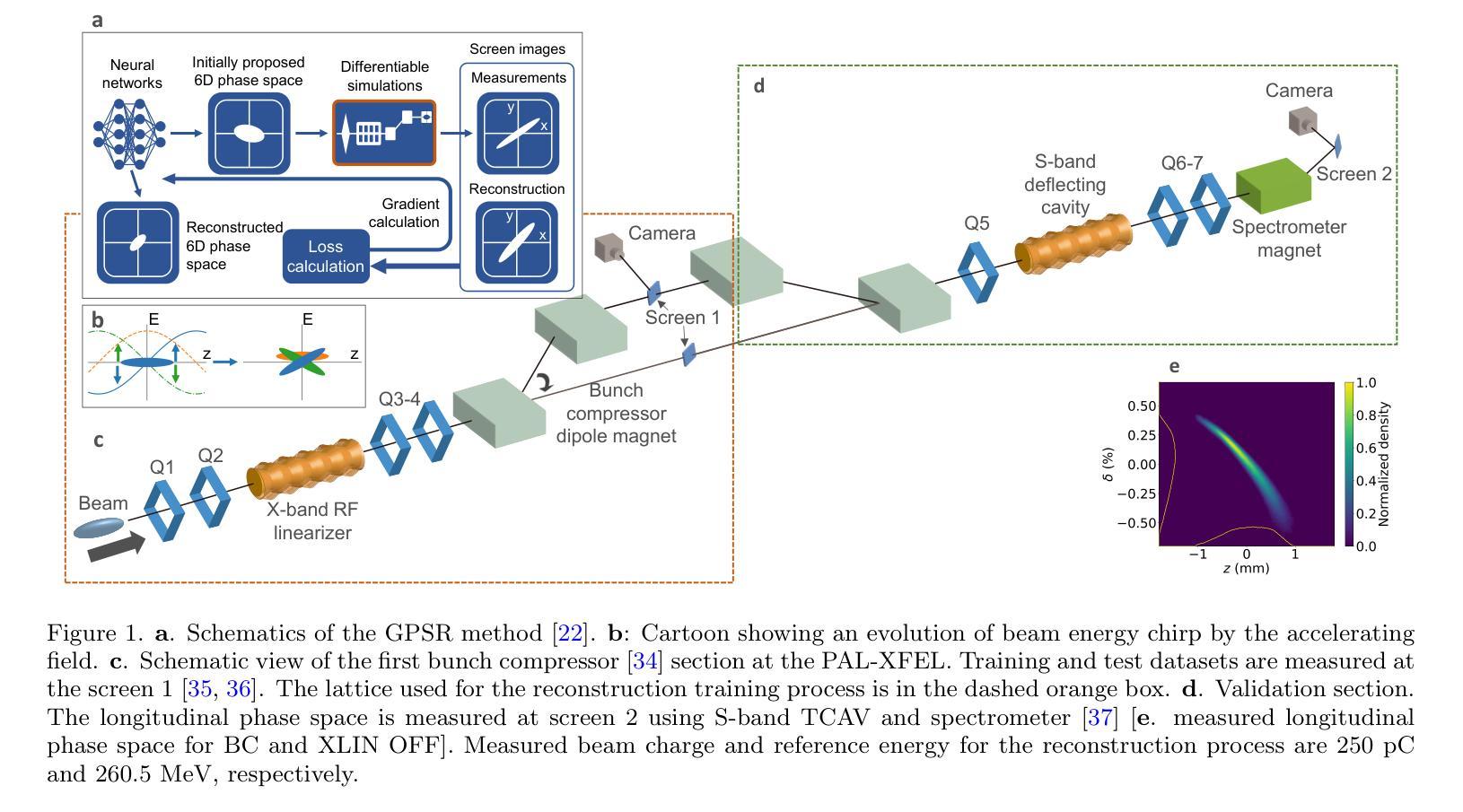
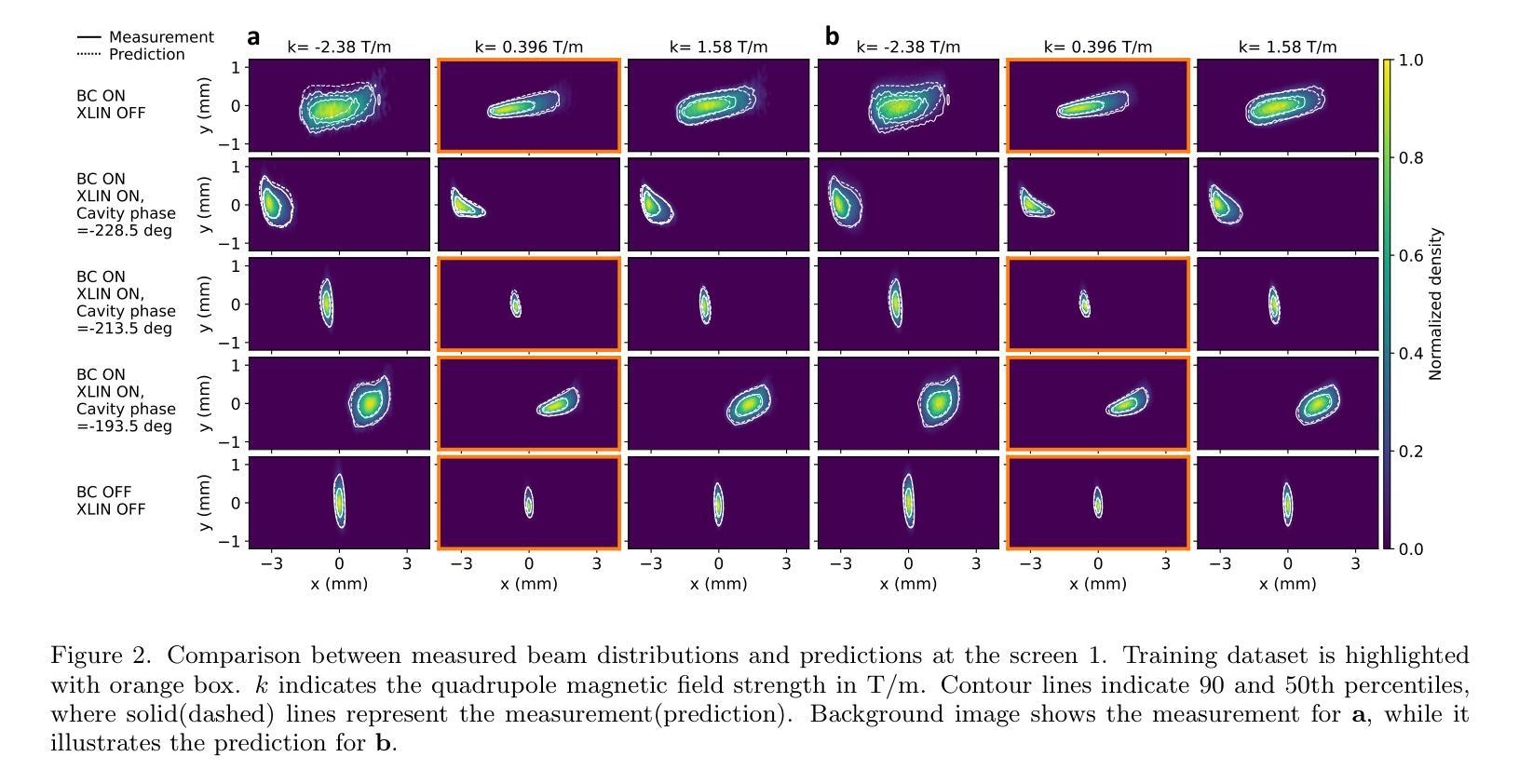
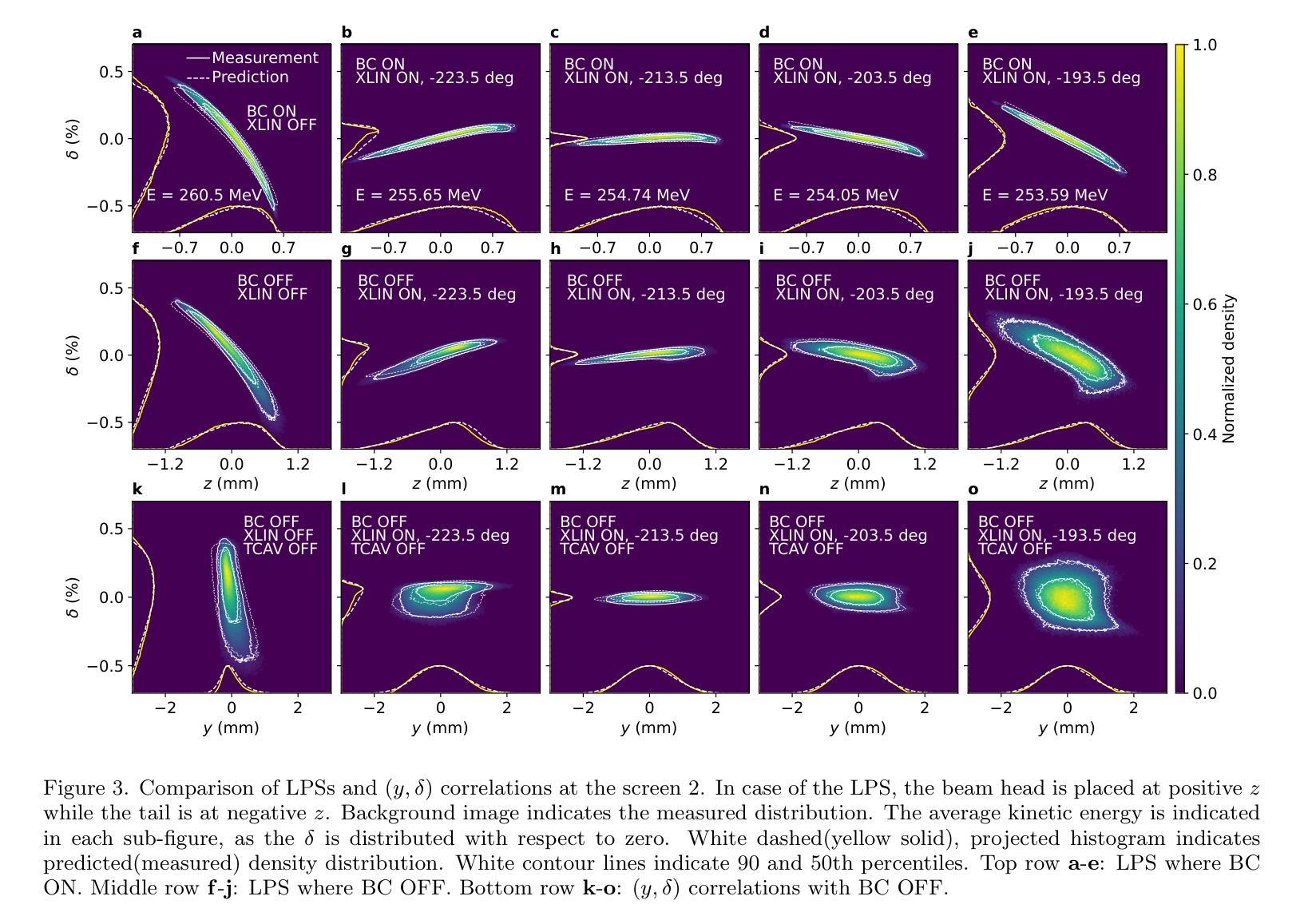
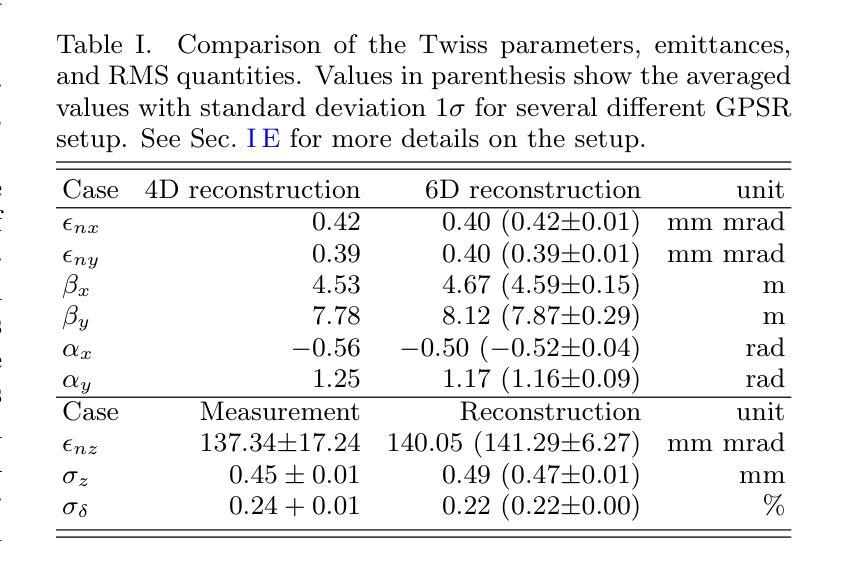
RadGPT: Constructing 3D Image-Text Tumor Datasets
Authors:Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Mehmet Can Yavuz, Kang Wang, Xiaoxi Chen, Wenxuan Li, Sergio Decherchi, Andrea Cavalli, Yang Yang, Alan Yuille, Zongwei Zhou
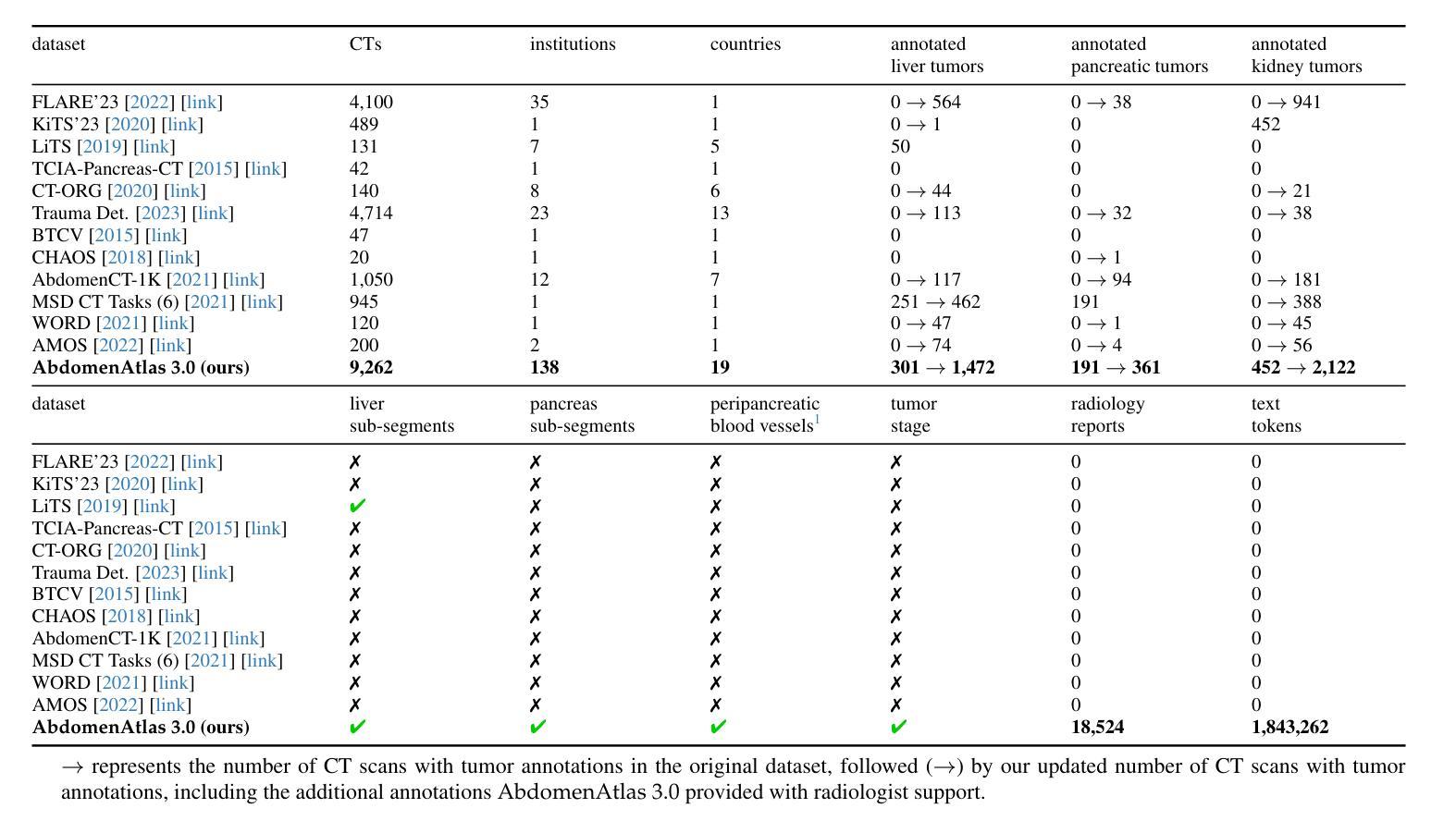
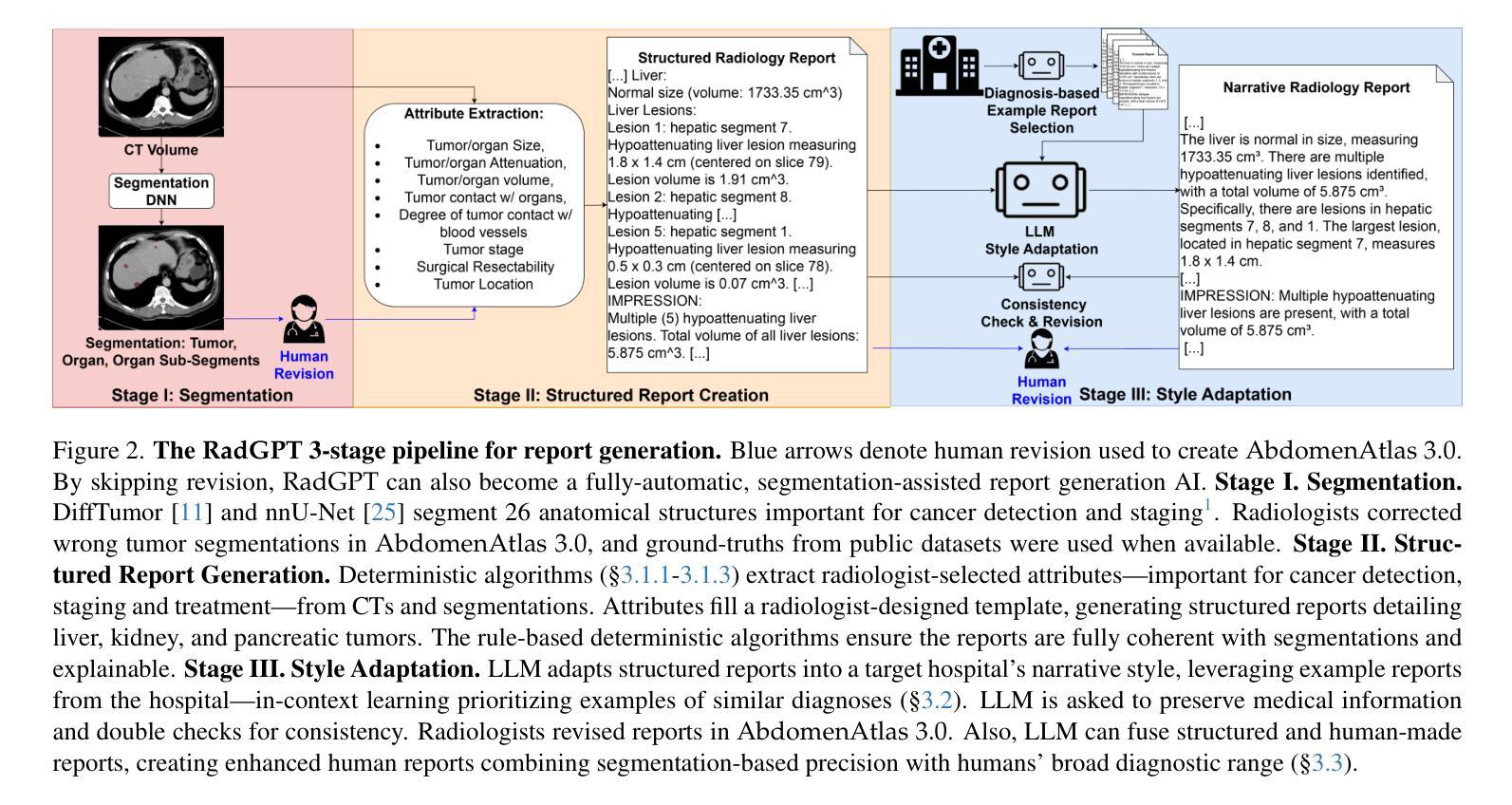
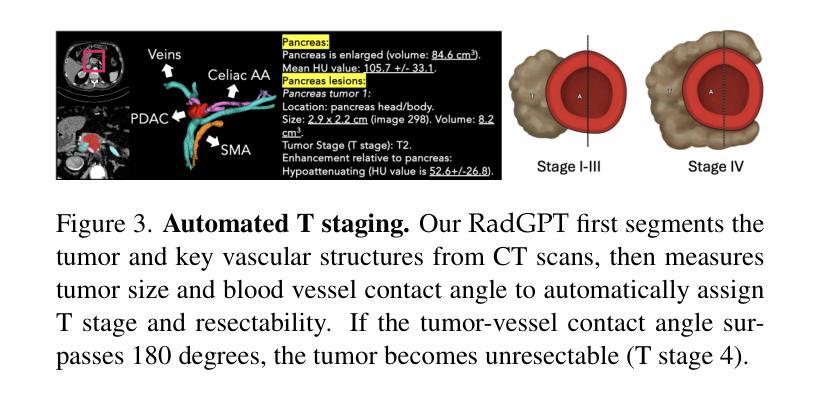
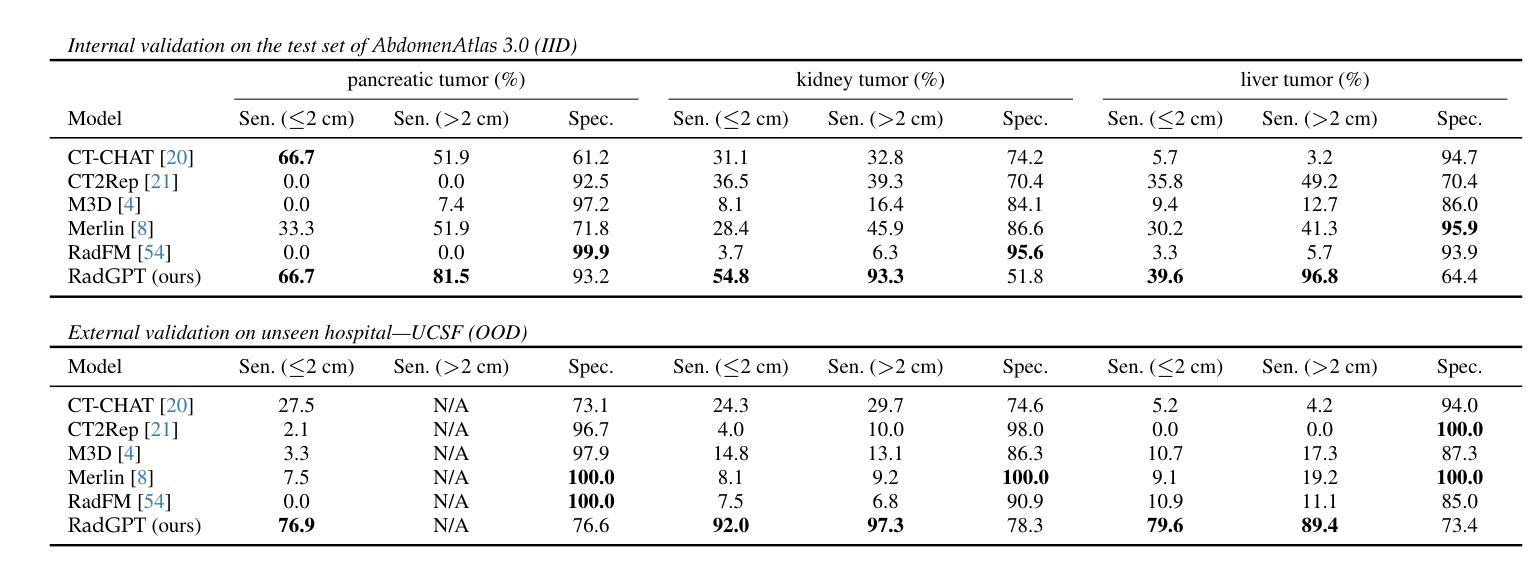
Cancers identified in CT scans are usually accompanied by detailed radiology reports, but publicly available CT datasets often lack these essential reports. This absence limits their usefulness for developing accurate report generation AI. To address this gap, we present AbdomenAtlas 3.0, the first public, high-quality abdominal CT dataset with detailed, expert-reviewed radiology reports. All reports are paired with per-voxel masks and they describe liver, kidney and pancreatic tumors. AbdomenAtlas 3.0 has 9,262 triplets of CT, mask and report–3,955 with tumors. These CT scans come from 17 public datasets. Besides creating the reports for these datasets, we expanded their number of tumor masks by 4.2x, identifying 3,011 new tumor cases. Notably, the reports in AbdomenAtlas 3.0 are more standardized, and generated faster than traditional human-made reports. They provide details like tumor size, location, attenuation and surgical resectability. These reports were created by 12 board-certified radiologists using our proposed RadGPT, a novel framework that converted radiologist-revised tumor segmentation masks into structured and narrative reports. Besides being a dataset creation tool, RadGPT can also become a fully-automatic, segmentation-assisted report generation method. We benchmarked this method and 5 state-of-the-art report generation vision-language models. Our results show that segmentation strongly improves tumor detection in AI-made reports.
通过CT扫描检测到的癌症通常伴有详细的放射学报告,但公开可用的CT数据集往往缺乏这些必要的报告。这一缺失限制了它们对于开发准确报告生成人工智能的用处。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了AbdomenAtlas 3.0,这是第一个带有详细、经过专家审查的放射学报告的公开高质量腹部CT数据集。所有报告都配备有逐像素遮罩,并描述肝脏、肾脏和胰腺肿瘤。AbdomenAtlas 3.0包含有CT扫描、遮罩和报告的9,262个三元组组合,其中含有肿瘤的为3,955个。这些CT扫描来自于17个公开数据集。除了为这些数据集创建报告外,我们还通过将肿瘤遮罩数量扩大了4.2倍,识别出了新增的3,011个肿瘤病例。值得注意的是,AbdomenAtlas 3.0中的报告更加标准化,生成速度也比传统的手工报告更快。它们提供了肿瘤的尺寸、位置、衰减和手术可切除性等详细信息。这些报告是由使用我们提出的RadGPT工具的十二位认证放射科医生创建的。这是一个新的框架,能够将放射科医生修订的肿瘤分割遮罩转换为结构和叙述性报告。除了作为数据集创建工具外,RadGPT还可以成为一种全自动的、由分割辅助的报告生成方法。我们对这种方法以及五种最新的报告生成视觉语言模型进行了基准测试。我们的结果表明,分割在人工智能生成的报告中显著提高了肿瘤检测效果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
腹部CT数据集AbdomenAtlas 3.0,包含详细的专家审核过的放射学报告和每像素肿瘤掩膜,描述肝脏、肾脏和胰腺肿瘤。此数据集解决了公开CT数据集中缺乏报告的问题,有助于开发准确的报告生成AI。数据集包含来自17个公共数据集的9,262个CT、掩膜和报告三元组,其中带肿瘤的为3,955个。此外,通过扩大肿瘤掩膜数量,新增了3,011个肿瘤病例。报告标准化程度高且生成速度快,包括肿瘤大小、位置、衰减和手术可切除性等详细信息。使用新型框架RadGPT生成报告,可将放射科医生修订的肿瘤分割掩膜转化为结构化和叙述性报告。RadGPT不仅是数据集创建工具,还可成为全自动分割辅助报告生成方法。实验结果显示,分割能显著提高AI生成的报告中肿瘤检测的准确性。
关键要点
- AbdomenAtlas 3.0是首个包含详细专家审核过的放射学报告的公开高质量腹部CT数据集。
- 数据集中的报告与每像素肿瘤掩膜配对,描述肝脏、肾脏和胰腺的肿瘤。
- 数据集解决了公开CT数据集缺乏报告的问题,有助于开发准确的报告生成AI。
- 通过扩大肿瘤掩膜数量新增了3,011个肿瘤病例。
- 报告标准化程度高且包含详细信息,如肿瘤大小、位置等。
- 使用RadGPT框架生成报告,可转化为结构化和叙述性报告。
点此查看论文截图

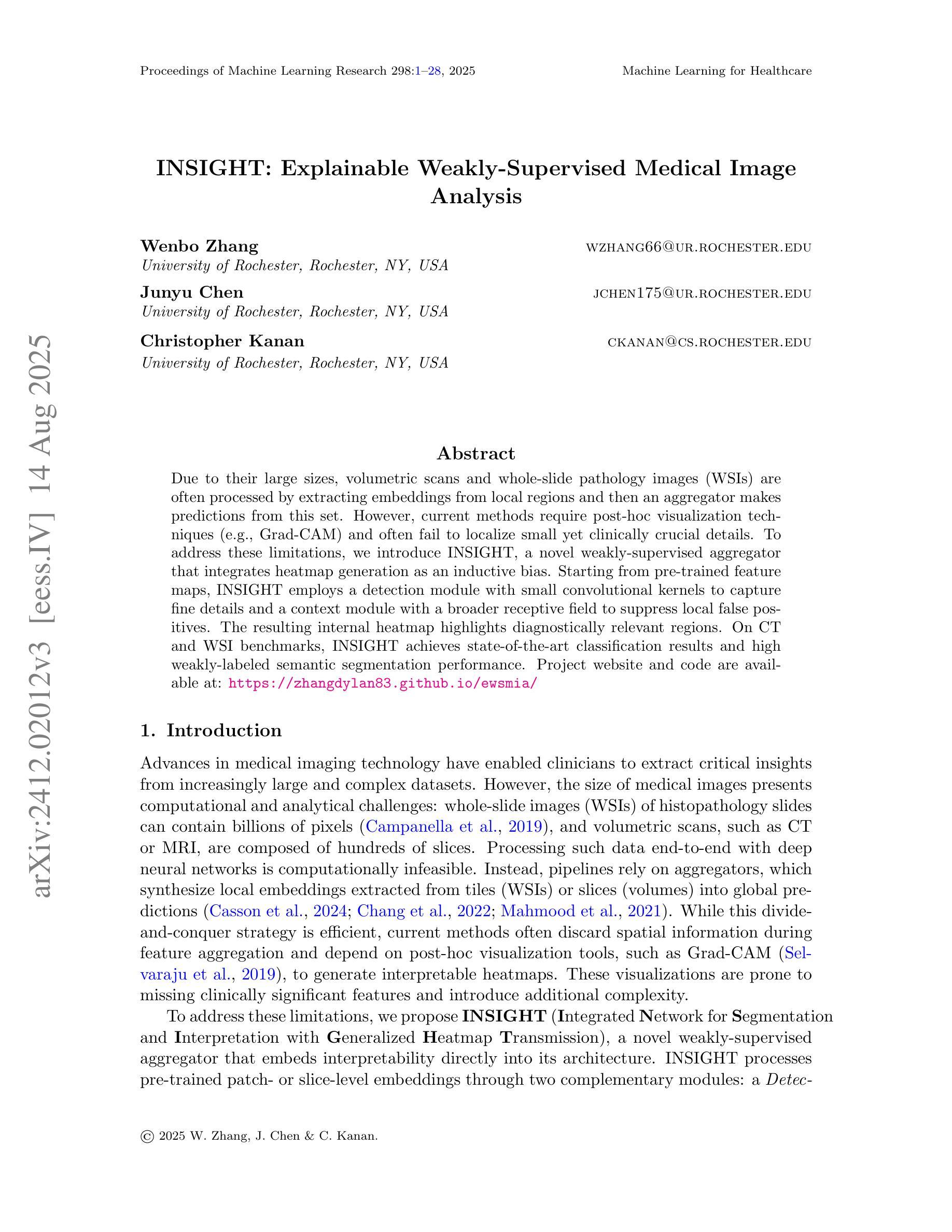
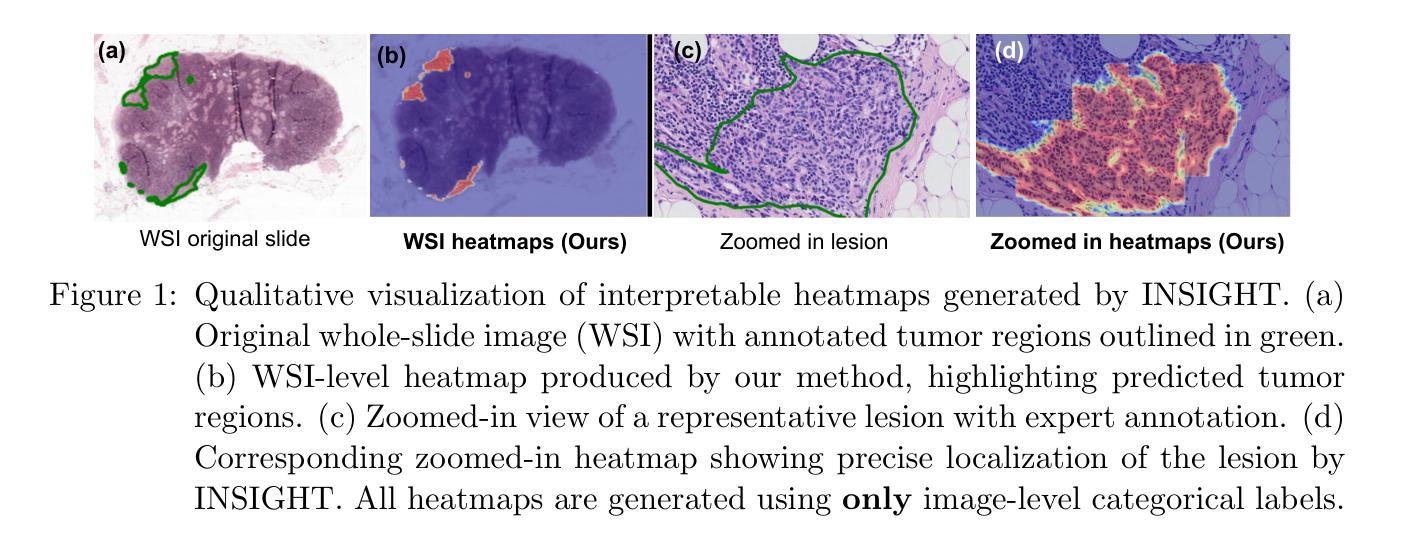
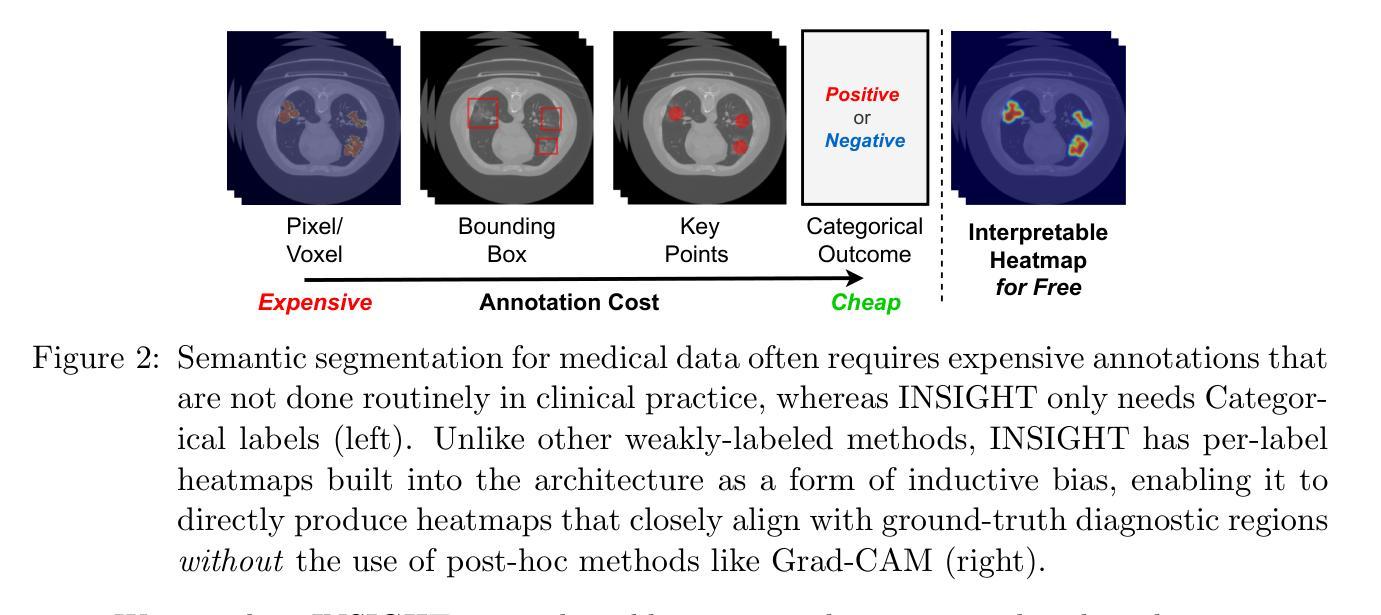
INSIGHT: Explainable Weakly-Supervised Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Wenbo Zhang, Junyu Chen, Christopher Kanan
Due to their large sizes, volumetric scans and whole-slide pathology images (WSIs) are often processed by extracting embeddings from local regions and then an aggregator makes predictions from this set. However, current methods require post-hoc visualization techniques (e.g., Grad-CAM) and often fail to localize small yet clinically crucial details. To address these limitations, we introduce INSIGHT, a novel weakly-supervised aggregator that integrates heatmap generation as an inductive bias. Starting from pre-trained feature maps, INSIGHT employs a detection module with small convolutional kernels to capture fine details and a context module with a broader receptive field to suppress local false positives. The resulting internal heatmap highlights diagnostically relevant regions. On CT and WSI benchmarks, INSIGHT achieves state-of-the-art classification results and high weakly-labeled semantic segmentation performance. Project website and code are available at: https://zhangdylan83.github.io/ewsmia/
由于体积扫描和全切片病理图像(WSI)的尺寸较大,通常通过从局部区域提取嵌入,然后聚合器根据这些嵌入进行预测来处理。然而,当前的方法需要事后可视化技术(例如Grad-CAM),并且往往无法定位虽小但对临床至关重要的细节。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了INSIGHT,这是一种新型的弱监督聚合器,它将热图生成作为归纳偏见进行集成。从预训练的特征图开始,INSIGHT使用具有较小卷积核的检测模块来捕获细节和具有更广泛感受野的上下文模块来抑制局部误报。生成的内部热图突出了与诊断相关的区域。在CT和WSI基准测试中,INSIGHT取得了最先进的分类结果和高性能的弱标签语义分割。项目网站和代码可通过以下链接获取:https://zhangdylan83.github.io/ewsmia/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MLHC 2025 (Machine Learning for Healthcare)
Summary
该文介绍了在处理大规模体积扫描和全景病理图像时,现有方法存在局限性,无法有效捕捉局部小区域的细节信息,需要后视可视化技术进行改进。为了克服这些局限,引入了一种新型弱监督聚合器INSIGHT,结合预训练特征图,利用带有小型卷积核的检测模块捕获精细细节和利用具有更大感知场的上下文模块来抑制局部错误信号,并生成内部热图以突出显示诊断相关区域。在CT和全景病理图像测试中,INSIGHT达到了业界先进的分类结果和高的弱标签语义分割性能。项目网站和代码可在此链接下载:https://zhangdylan83.github.io/ewsmia/。
Key Takeaways
- 体积扫描和全景病理图像因规模巨大常采用提取局部区域嵌入然后通过聚合器预测的方式处理。但当前方法无法定位关键细节且需要后视可视化技术。
- INSIGHT是一种新型弱监督聚合器,结合了预训练特征图,通过检测模块和上下文模块分别捕捉精细细节并抑制局部错误信号。
- INSIGHT生成内部热图以突出显示诊断相关区域。
- 在CT和全景病理图像测试中,INSIGHT实现了先进的分类结果和高的弱标签语义分割性能。
点此查看论文截图
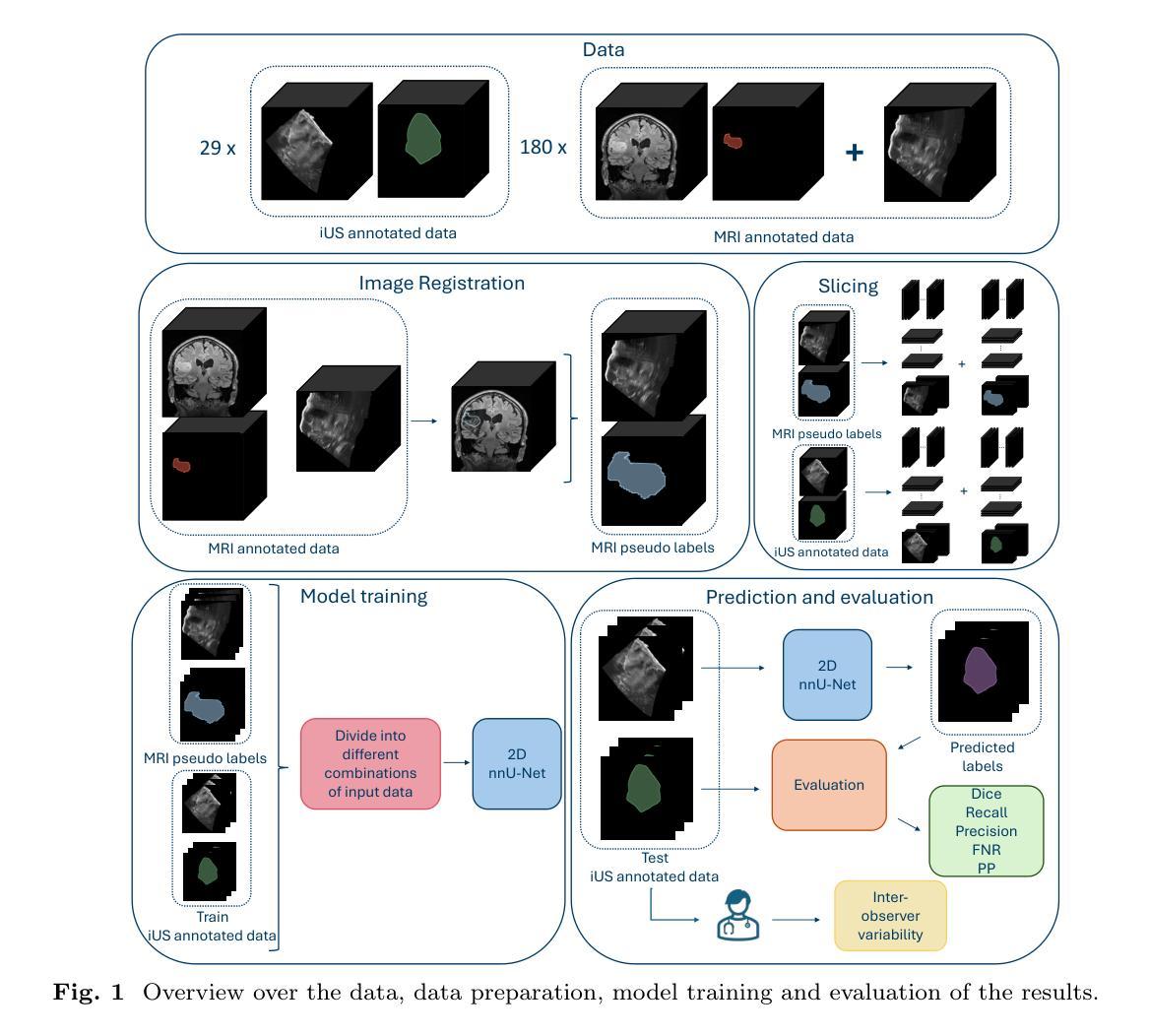
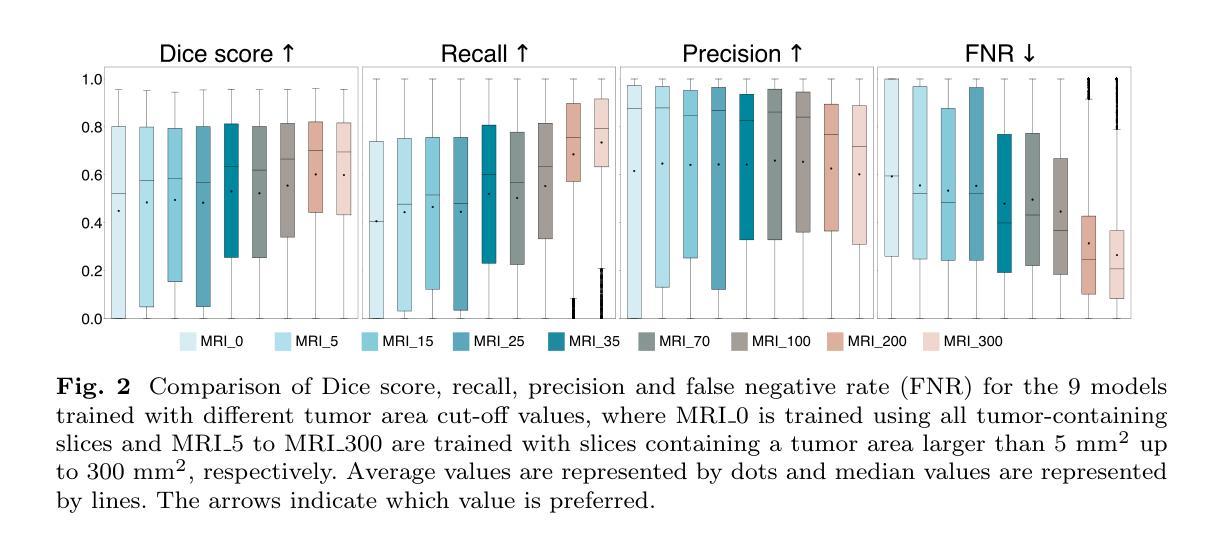
Automatic brain tumor segmentation in 2D intra-operative ultrasound images using magnetic resonance imaging tumor annotations
Authors:Mathilde Faanes, Ragnhild Holden Helland, Ole Solheim, Sébastien Muller, Ingerid Reinertsen
Automatic segmentation of brain tumors in intra-operative ultrasound (iUS) images could facilitate localization of tumor tissue during resection surgery. The lack of large annotated datasets limits the current models performances. In this paper, we investigated the use of tumor annotations in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, which are more accessible than annotations in iUS images, for training of deep learning models for iUS brain tumor segmentation. We used 180 annotated MRI scans with corresponding unannotated iUS images, and 29 annotated iUS images. Image registration was performed to transfer the MRI annotations to the corresponding iUS images before training the nnU-Net model with different configurations of the data and label origins. The results showed no significant difference in Dice score for a model trained with only MRI annotated tumors compared to models trained with only iUS annotations and both, and to expert annotations, indicating that MRI tumor annotations can be used as a substitute for iUS tumor annotations to train a deep learning model for automatic brain tumor segmentation in iUS images. The best model obtained an average Dice score of $0.62\pm0.31$, compared to $0.67\pm0.25$ for an expert neurosurgeon, where the performance on larger tumors were similar, but lower for the models on smaller tumors. In addition, the results showed that removing smaller tumors from the training sets improved the results. The main models are available here: https://github.com/mathildefaanes/us_brain_tumor_segmentation/tree/main
在术中超声(iUS)图像中自动分割脑肿瘤可以方便在切除手术过程中定位肿瘤组织。缺乏大型标注数据集限制了当前模型的表现。在本文中,我们研究了在磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中使用肿瘤标注的方法,这些标注比iUS图像中的标注更容易获取,用于训练深度学习模型进行iUS脑肿瘤分割。我们使用180张标注过的MRI扫描图像和相应的未标注iUS图像,以及29张标注过的iUS图像。在将MRI标注转移到相应的iUS图像之前,进行了图像配准,然后使用不同配置的数据和标签来源训练nnU-Net模型。结果表明,仅使用MRI标注肿瘤训练的模型与仅使用iUS标注和两者都使用的模型,以及专家标注相比,在Dice得分上没有显著差异,这表明MRI肿瘤标注可以替代iUS肿瘤标注,用于训练深度学习模型,实现iUS图像中的自动脑肿瘤分割。最佳模型获得了平均Dice得分$0.62\pm0.31$,与专家神经外科医生$0.67\pm0.25$相比,较大肿瘤的绩效相似,但较小肿瘤的绩效较低。此外,结果表明从训练集中去除较小的肿瘤提高了结果。主要模型可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/mathildefaanes/us_brain_tumor_segmentation/tree/main 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文探讨了利用磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中的肿瘤注释信息训练深度学习模型,以在术中超声(iUS)图像中实现自动脑肿瘤分割的可能性。研究使用MRI扫描的肿瘤注释信息来替代在iUS图像中的肿瘤注释信息,结果展示了相当的分割性能。训练的最佳模型实现了与专家神经外科医生相似的表现。此项研究为解决因缺乏大型标注数据集导致的模型性能受限问题提供了一种有效解决方案。同时指出在训练过程中排除较小的肿瘤可能有助于提高模型的性能。该研究的主要模型可在GitHub上进行访问。
Key Takeaways
- 利用MRI扫描中的肿瘤注释信息来训练深度学习模型进行iUS图像的脑肿瘤分割,克服了因缺乏大量标注数据集的性能限制。
- 研究表明,使用MRI注释信息训练的模型与仅使用iUS注释信息及两者结合训练的模型在Dice评分上无显著差异,表明MRI肿瘤注释可作为替代iUS肿瘤注释来训练深度学习模型。
- 最佳模型的性能与专家神经外科医生相似,特别是在较大的肿瘤上,但在较小的肿瘤上表现略低。
点此查看论文截图

KACQ-DCNN: Uncertainty-Aware Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Classical-Quantum Dual-Channel Neural Network for Heart Disease Detection
Authors:Md Abrar Jahin, Md. Akmol Masud, M. F. Mridha, Zeyar Aung, Nilanjan Dey
Heart failure is a leading cause of global mortality, necessitating improved diagnostic strategies. Classical machine learning models struggle with challenges such as high-dimensional data, class imbalances, poor feature representations, and a lack of interpretability. While quantum machine learning holds promise, current hybrid models have not fully exploited quantum advantages. In this paper, we propose the Kolmogorov-Arnold Classical-Quantum Dual-Channel Neural Network (KACQ-DCNN), a novel hybrid architecture that replaces traditional multilayer perceptrons with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs), enabling learnable univariate activation functions. Our KACQ-DCNN 4-qubit, 1-layer model outperforms 37 benchmark models, including 16 classical and 12 quantum neural networks, achieving an accuracy of 92.03%, with macro-average precision, recall, and F1 scores of 92.00%. It also achieved a ROC-AUC of 94.77%, surpassing other models by significant margins, as validated by paired t-tests with a significance threshold of 0.0056 (after Bonferroni correction). Ablation studies highlight the synergistic effect of classical-quantum integration, improving performance by about 2% over MLP variants. Additionally, LIME and SHAP explainability techniques enhance feature interpretability, while conformal prediction provides robust uncertainty quantification. Our results demonstrate that KACQ-DCNN improves cardiovascular diagnostics by combining high accuracy with interpretability and uncertainty quantification.
心力衰竭是全球主要的死亡原因之一,需要改进诊断策略。传统的机器学习模型面临高维数据、类别不平衡、特征表示不佳和缺乏可解释性等方面的挑战。虽然量子机器学习很有前景,但当前的混合模型尚未充分利用量子优势。在本文中,我们提出了Kolmogorov-Arnold经典-量子双通道神经网络(KACQ-DCNN)这一新型混合架构,它用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)替代了传统的多层感知器,使学习单变量激活函数成为可能。我们的KACQ-DCNN 4量子位、1层模型优于37个基准模型,包括16个经典模型和12个量子神经网络,准确率达到了92.03%,宏观平均精度、召回率和F1分数均为92.00%。其ROC-AUC达到了94.77%,显著超过了其他模型,并通过配对t检验得到了验证,显著性阈值为0.0056(经Bonferroni校正)。消融研究突出了经典与量子集成的协同作用,在性能上比多层感知器变体提高了约2%。此外,LIME和SHAP的可解释性技术提高了特征的可解释性,而顺应性预测提供了稳健的不确定性量化。我们的结果表明,KACQ-DCNN通过将高准确性、可解释性和不确定性量化相结合,提高了心血管疾病的诊断水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a journal paper at Computers in Biology and Medicine (Elsevier)
Summary
在心脏衰竭诊断中,传统机器学习模型面临诸多挑战。本文提出一种新型混合架构Kolmogorov-Arnold Classical-Quantum Dual-Channel Neural Network (KACQ-DCNN),采用Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)替代传统多层感知器,实现可学习的一元激活函数。KACQ-DCNN在心脏衰竭诊断上表现出优异性能,准确率高达92.03%,且具备高解释性和不确定性量化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏衰竭是全球主要死亡原因之一,需要改进诊断策略。
- 传统机器学习模型在心脏衰竭诊断中面临挑战,如高维数据、类别不平衡、特征表示不佳和缺乏可解释性。
- 量子机器学习具有潜力,但当前混合模型尚未充分利用量子优势。
- 引入KACQ-DCNN模型,一个结合了经典和量子机器学习的混合架构。
- KACQ-DCNN采用Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs),实现学习一元激活函数,提高了诊断准确性至92.03%。
- KACQ-DCNN在宏观平均精度、召回率、F1分数和ROC-AUC等方面均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

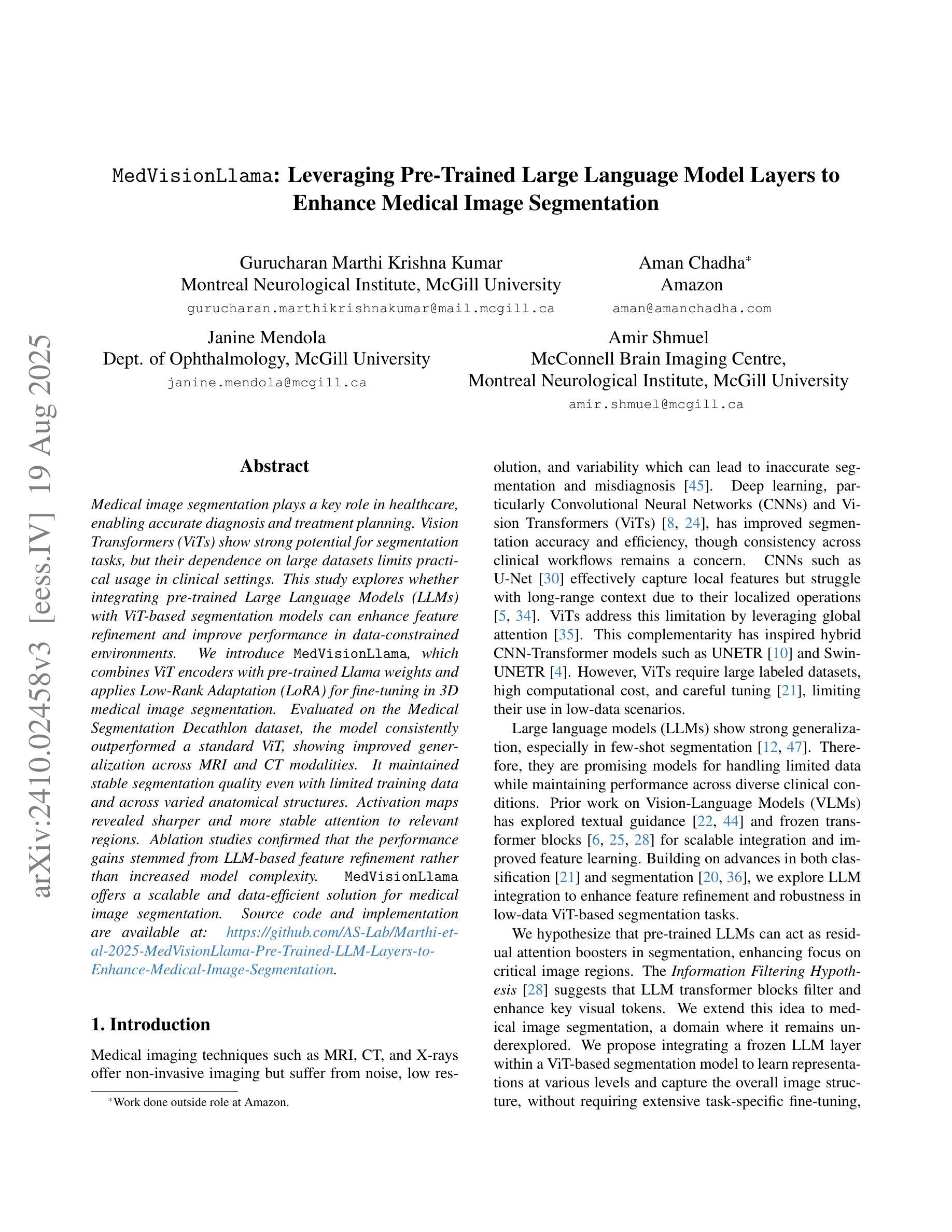
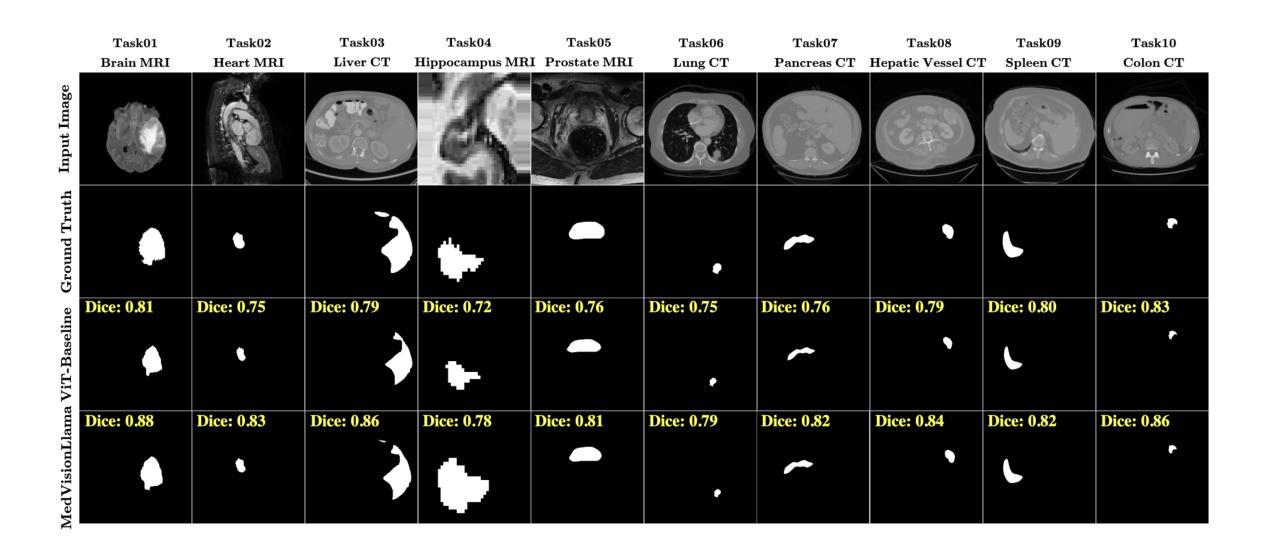
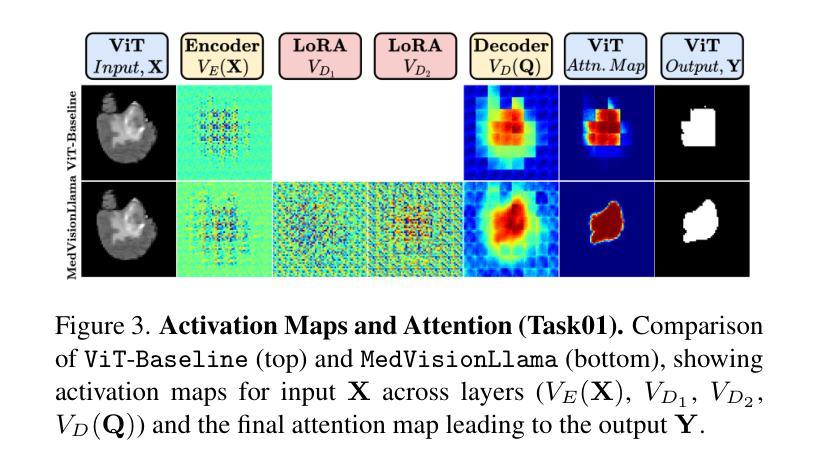
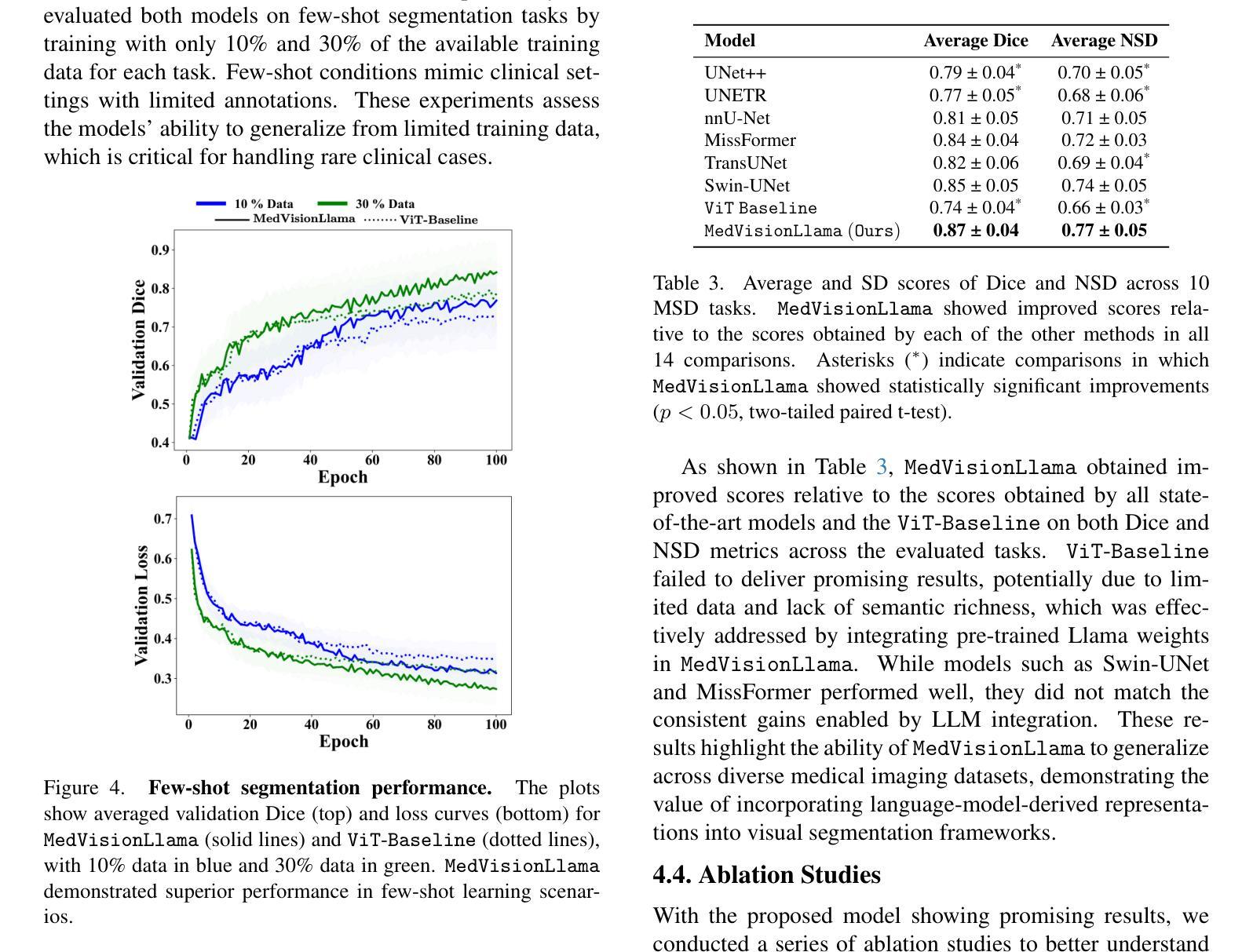
MedVisionLlama: Leveraging Pre-Trained Large Language Model Layers to Enhance Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Gurucharan Marthi Krishna Kumar, Aman Chadha, Janine Mendola, Amir Shmuel
Large Language Models (LLMs), known for their versatility in textual data, are increasingly being explored for their potential to enhance medical image segmentation, a crucial task for accurate diagnostic imaging. This study explores enhancing Vision Transformers (ViTs) for medical image segmentation by integrating pre-trained LLM transformer blocks. Our approach, which incorporates a frozen LLM transformer block into the encoder of a ViT-based model, leads to substantial improvements in segmentation performance across various medical imaging modalities. We propose a Hybrid Attention Mechanism that combines global and local feature learning with a Multi-Scale Fusion Block for aggregating features across different scales. The enhanced model shows significant performance gains, including an average Dice score increase from 0.74 to 0.79 and improvements in accuracy, precision, and the Jaccard Index. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of LLM-based transformers in refining medical image segmentation, highlighting their potential to significantly boost model accuracy and robustness. The source code and our implementation are available at: https://github.com/AS-Lab/Marthi-et-al-2025-MedVisionLlama-Pre-Trained-LLM-Layers-to-Enhance-Medical-Image-Segmentation
大型语言模型(LLMs)以其处理文本数据的通用性而备受关注,目前正越来越多地被探索其在增强医学图像分割方面的潜力。医学图像分割是准确诊断成像的关键任务。本研究探索了通过集成预训练的大型语言模型转换器块来增强视觉变压器(ViTs)在医学图像分割方面的应用。我们的方法是将冻结的大型语言模型转换器块纳入基于ViT的模型的编码器,从而在各种医学成像模式的分割性能上实现了显著的提升。我们提出了一种混合注意力机制,它将全局和局部特征学习相结合,并利用多尺度融合块来聚合不同尺度的特征。增强后的模型表现出显著的性能提升,包括平均Dice得分从0.74提高到0.79,以及准确度、精确度和Jaccard指数的改进。这些结果证明了基于大型语言模型的变压器在改进医学图像分割方面的有效性,并突出了它们在提高模型准确性和稳健性方面的潜力。源代码和我们的实现可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/AS-Lab/Marthi-et-al-2025-MedVisionLlama-Pre-Trained-LLM-Layers-to-Enhance-Medical-Image-Segmentation
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the CVAMD Workshop (Computer Vision for Automated Medical Diagnosis) at the 2025 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCVW 2025)
Summary
这项研究探索了使用预训练的LLM(大型语言模型)transformer块增强医疗图像分割的方法。通过将LLM transformer块集成到基于ViT(视觉转换器)模型的编码器中,该模型在各种医学影像模态的分割性能上取得了显著提升。通过混合注意力机制和跨尺度的多尺度融合块特征聚合技术,实现了全局和局部特征学习,提高了模型的准确性和鲁棒性。该模型的性能显著增强,Dice平均得分从0.74提高到0.79,准确性和Jaccard指数也有所改善。展示了LLM在医疗图像分割方面的精细效果。详情请访问指定的GitHub地址获取源代码和实现详情。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用预训练的LLM(大型语言模型)transformer块来增强医疗图像分割的性能。
- 通过将LLM transformer块集成到基于ViT(视觉转换器)模型的编码器中,实现了显著的分割性能提升。
- 提出了一种混合注意力机制,结合了全局和局部特征学习。
- 通过跨尺度的多尺度融合块实现特征聚合,进一步提高模型性能。
- 该模型的Dice平均得分显著提高,从0.74提高到0.79。
- 模型的准确性和精度也有所提高,证明了其在医疗图像分割任务中的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图