⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
Multi-Rationale Explainable Object Recognition via Contrastive Conditional Inference
Authors:Ali Rasekh, Sepehr Kazemi Ranjbar, Simon Gottschalk
Explainable object recognition using vision-language models such as CLIP involves predicting accurate category labels supported by rationales that justify the decision-making process. Existing methods typically rely on prompt-based conditioning, which suffers from limitations in CLIP’s text encoder and provides weak conditioning on explanatory structures. Additionally, prior datasets are often restricted to single, and frequently noisy, rationales that fail to capture the full diversity of discriminative image features. In this work, we introduce a multi-rationale explainable object recognition benchmark comprising datasets in which each image is annotated with multiple ground-truth rationales, along with evaluation metrics designed to offer a more comprehensive representation of the task. To overcome the limitations of previous approaches, we propose a contrastive conditional inference (CCI) framework that explicitly models the probabilistic relationships among image embeddings, category labels, and rationales. Without requiring any training, our framework enables more effective conditioning on rationales to predict accurate object categories. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on the multi-rationale explainable object recognition benchmark, including strong zero-shot performance, and sets a new standard for both classification accuracy and rationale quality. Together with the benchmark, this work provides a more complete framework for evaluating future models in explainable object recognition. The code will be made available online.
使用诸如CLIP的视觉语言模型进行可解释性目标识别,涉及通过支持决策制定过程的理由来预测准确的类别标签。现有方法通常依赖于基于提示的条件设置,这受到CLIP文本编码器的限制,并对解释结构提供较弱的条件设置。此外,先前的数据集通常仅限于单一且经常嘈杂的理由,无法捕捉到图像特征的全面多样性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个多理由可解释目标识别基准测试,其中包括数据集,每个图像都使用多个真实理由进行注释,以及为更全面地表示任务而设计的评估指标。为了克服以前方法的局限性,我们提出了对比条件推断(CCI)框架,该框架显式地模拟图像嵌入、类别标签和理由之间的概率关系。我们的框架无需任何训练即可更有效地根据理由预测目标类别。我们的方法在多重解释目标识别基准测试中达到了最新水平的结果,包括强大的零样本性能,为分类精度和理由质量设定了新的标准。与基准测试一起,这项工作为未来模型在可解释目标识别中的评估提供了更完整的框架。代码将在线提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了使用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)进行可解释性目标识别的研究。针对现有方法依赖的基于提示的条件化存在的局限性,提出了对比条件推断(CCI)框架。该框架能够明确建模图像嵌入、类别标签和解释之间的概率关系,无需任何训练即可更有效地以解释为依据预测目标类别。该框架在多解释目标识别基准测试中取得了最佳结果,包括强大的零样本性能,为分类准确性和解释质量设定了新的标准。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了使用CLIP等视觉语言模型进行可解释性目标识别的研究。
- 现有方法主要依赖基于提示的条件化,存在局限性。
- 引入了一个多解释目标识别基准测试,每个图像都有多个真实解释标注,并设计了评估指标以更全面地表示任务。
- 提出了对比条件推断(CCI)框架,建模图像嵌入、类别标签和解释之间的概率关系。
- CCI框架无需任何训练即可更有效地以解释为依据预测目标类别。
- 在多解释目标识别基准测试中取得了最佳结果,包括强大的零样本性能。
点此查看论文截图
Is Contrastive Distillation Enough for Learning Comprehensive 3D Representations?
Authors:Yifan Zhang, Junhui Hou
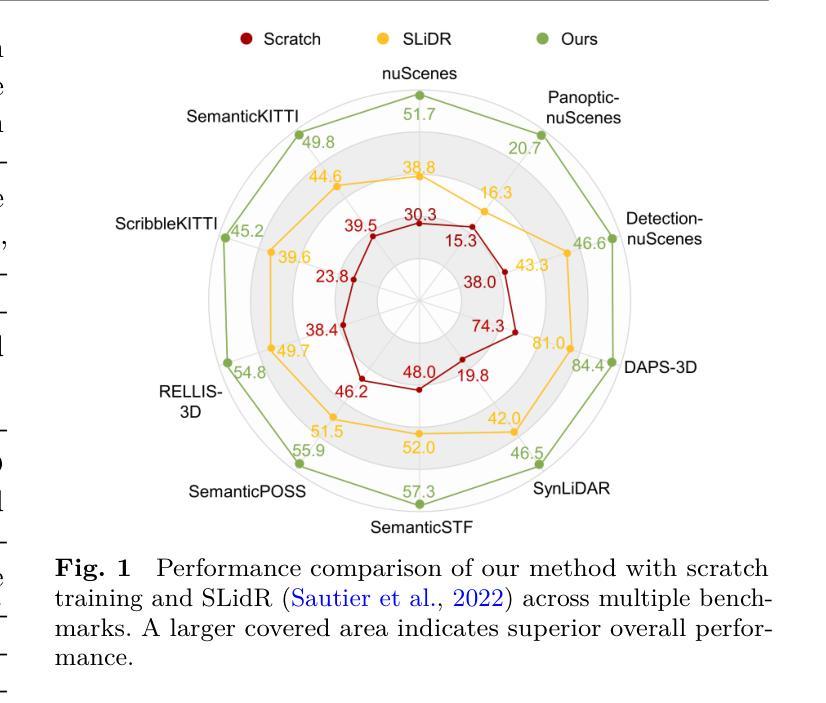
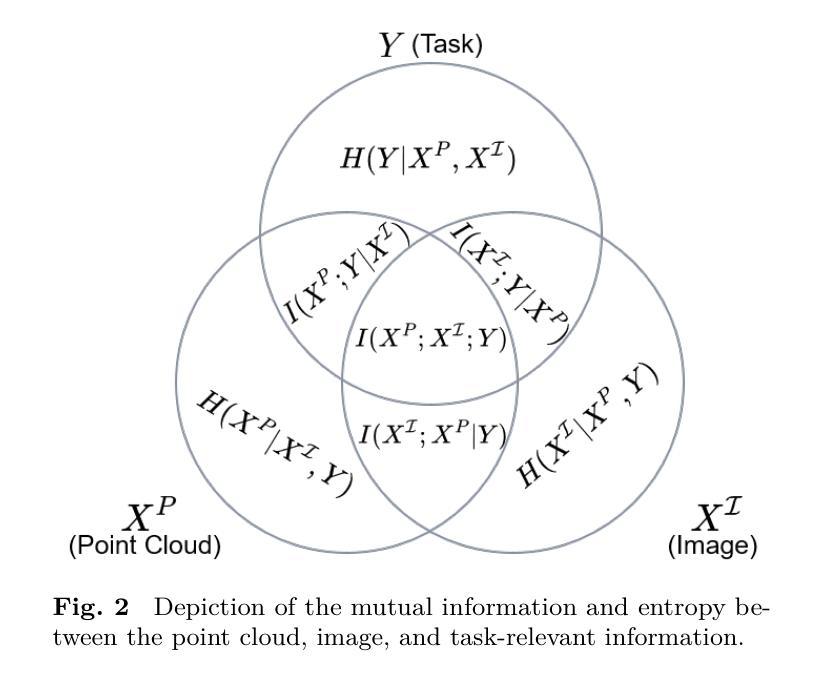
Cross-modal contrastive distillation has recently been explored for learning effective 3D representations. However, existing methods focus primarily on modality-shared features, neglecting the modality-specific features during the pre-training process, which leads to suboptimal representations. In this paper, we theoretically analyze the limitations of current contrastive methods for 3D representation learning and propose a new framework, namely CMCR, to address these shortcomings. Our approach improves upon traditional methods by better integrating both modality-shared and modality-specific features. Specifically, we introduce masked image modeling and occupancy estimation tasks to guide the network in learning more comprehensive modality-specific features. Furthermore, we propose a novel multi-modal unified codebook that learns an embedding space shared across different modalities. Besides, we introduce geometry-enhanced masked image modeling to further boost 3D representation learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method mitigates the challenges faced by traditional approaches and consistently outperforms existing image-to-LiDAR contrastive distillation methods in downstream tasks. Code will be available at https://github.com/Eaphan/CMCR.
跨模态对比蒸馏最近已被探索用于学习有效的3D表示。然而,现有方法主要关注模态共享特征,在预训练过程中忽略了模态特定特征,导致表示不佳。在本文中,我们理论上分析了当前对比方法在3D表示学习上的局限性,并提出了一种新的框架,即CMCR,来解决这些不足。我们的方法通过更好地整合模态共享和模态特定特征来改进传统方法。具体来说,我们引入了掩膜图像建模和占用估计任务,以指导网络学习更全面的模态特定特征。此外,我们提出了一种新的多模态统一代码本,学习不同模态共享的嵌入空间。除此之外,我们还引入了几何增强的掩膜图像建模,以进一步促进3D表示学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法缓解了传统方法的挑战,并且在下游任务中始终优于现有的图像到激光雷达对比蒸馏方法。代码将在https://github.com/Eaphan/CMCR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文探讨了跨模态对比蒸馏在3D表征学习中的应用,针对现有方法忽略模态特定特征的问题,提出了一种新的框架CMCR。该框架通过结合模态共享和模态特定特征来改善传统方法,引入掩膜图像建模和占用估计任务来指导网络学习更全面的模态特定特征,并提出多模态统一码本以学习不同模态之间的共享嵌入空间。此外,引入几何增强的掩膜图像建模进一步促进3D表征学习。实验证明,该方法缓解了传统方法的挑战,并在下游任务中一致优于现有的图像到激光雷达对比蒸馏方法。
Key Takeaways
- 跨模态对比蒸馏在3D表征学习中的应用被探讨。
- 现有方法主要关注模态共享特征,忽略了模态特定特征。
- 新框架CMCR被提出,以整合模态共享和模态特定特征。
- CMCR通过掩膜图像建模和占用估计任务来指导网络学习更全面的模态特定特征。
- 引入多模态统一码本以学习不同模态之间的共享嵌入空间。
- 几何增强的掩膜图像建模进一步促进3D表征学习。
- 实验证明,CMCR在下游任务中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图