⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
Challenges and Opportunities for Participatory Design of Conversational Agents for Young People’s Wellbeing
Authors:Natalia Kucirkova, Alexis Hiniker, Megumi Ishikawa, Sho Tsuji, Aayushi Dangol, Robert Wolfe
This paper outlines the challenges and opportunities of research on conversational agents with children and young people across four countries, exploring the ways AI technologies can support children’s well-being across social and cultural contexts.
本文概述了在四个国家针对儿童和青少年对话代理的研究挑战和机遇,探讨了人工智能技术在社会和文化背景中如何支持儿童福祉的方式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at the AI4CW workshop at ACM IDC 2025
Summary
本文探讨了四个国家对话性代理与儿童和青少年之间的挑战与机遇,探索人工智能技术在不同社会和文化背景下如何支持儿童福祉的方式。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究了四个国家中对话代理在儿童和青少年所面临的挑战和机会。
- AI技术如何在不同的社会和文化背景下支持儿童福祉。
- 该研究探讨了AI技术如何通过与儿童的互动来改善他们的生活质量。
- 探讨了如何在不同国家进行跨文化研究以及如何应对文化差异。
- 阐述了如何将技术用于研究如何促进儿童发展教育中的创新和适应过程。
- 文章指出对话代理与儿童和青少年之间的互动研究对未来教育和社交有很大的启示意义。
点此查看论文截图

Energy-Efficient Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach
Authors:Parham Soltani, Mehrshad Eskandarpour, Amir Ahmadizad, Hossein Soleimani
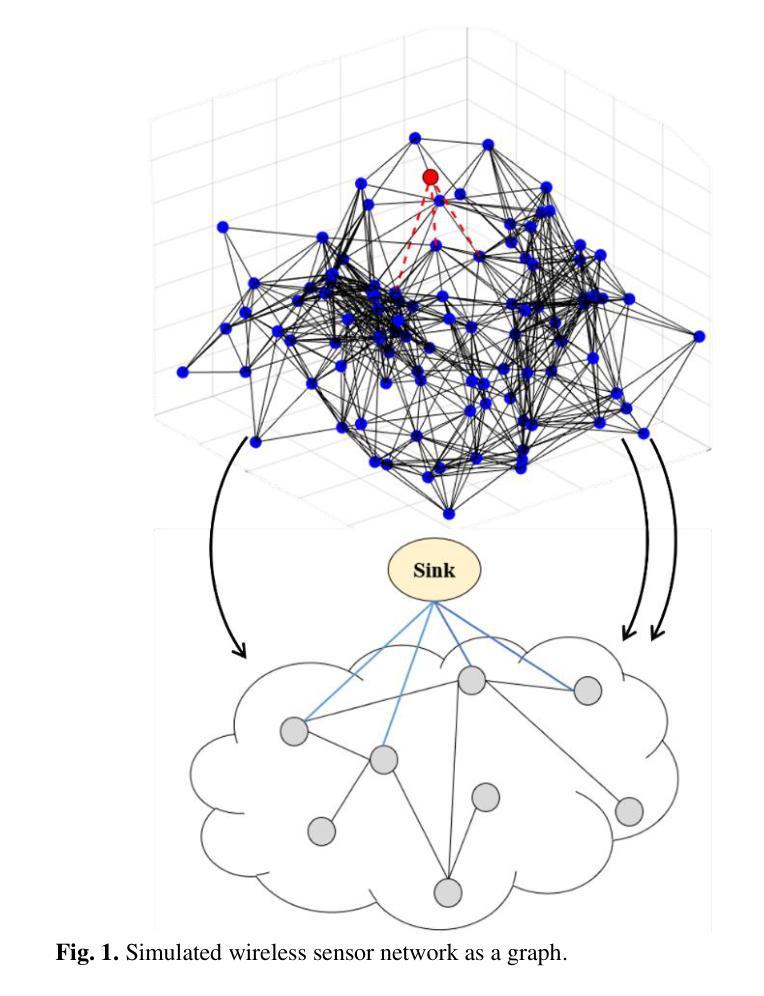
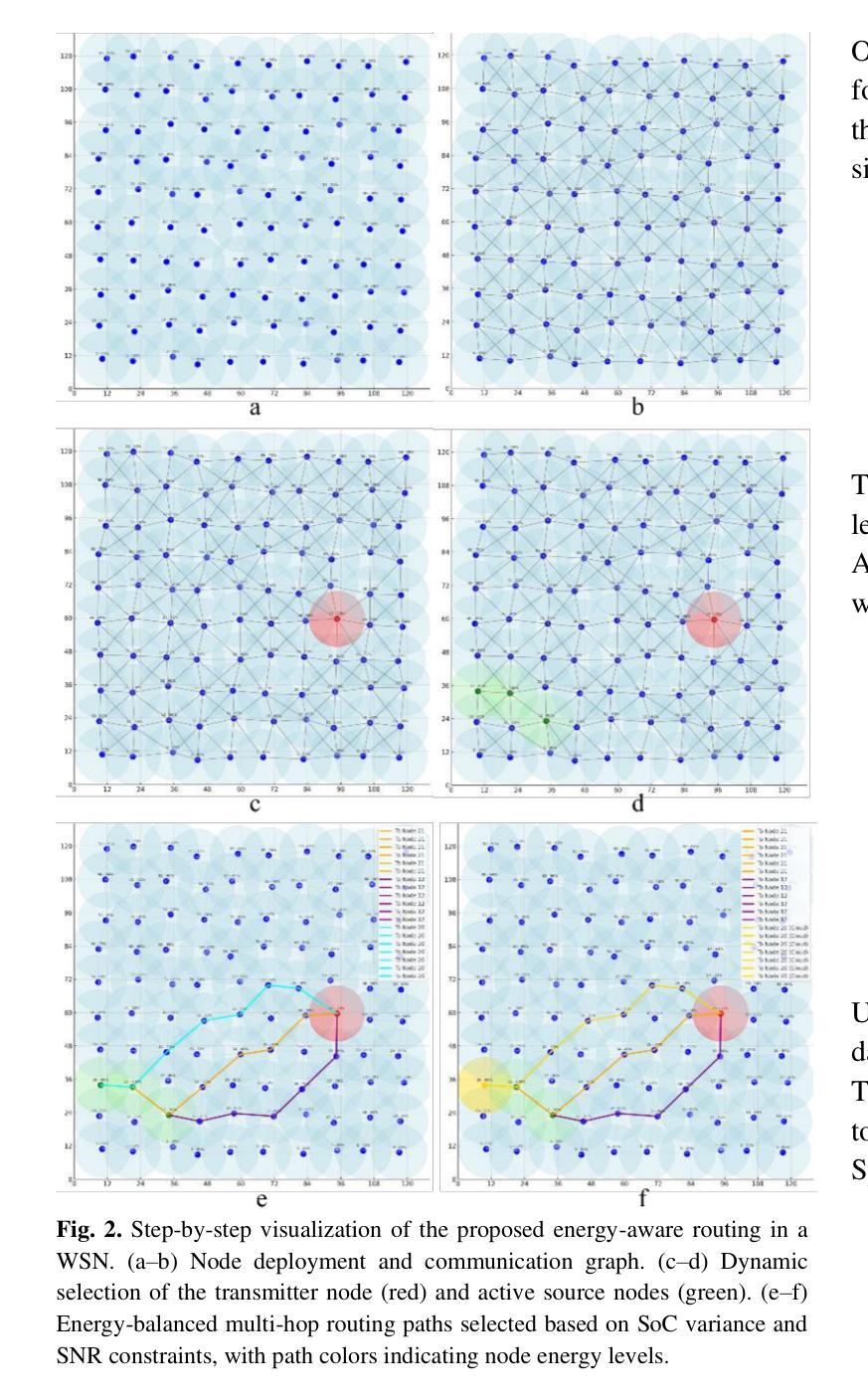
Efficient energy management is essential in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) to extend network lifetime and ensure reliable data transmission. This paper presents a novel method using reinforcement learning-based cluster-head selection and a hybrid multi-hop routing algorithm, which leverages Q-learning within a multi-agent system to dynamically adapt transmission paths based on the energy distribution across sensor nodes. Each sensor node is modeled as an autonomous agent that observes local state parameters, such as residual energy, distance to sink, hop count, and hotspot proximity, and selects routing actions that maximize long-term energy efficiency. After computing the optimal paths, each sensor aggregates sensed data and forwards it through intermediate nodes to a selected transmitter node, chosen based on the highest remaining State of Charge (SoC), thereby avoiding premature node depletion. To promote efficient learning, a carefully designed reward function incentivizes balanced load distribution, hotspot avoidance, and energy-aware forwarding while maintaining signal quality. The learning process occurs either in a decentralized manner or via a cloud-based controller that offloads computation in large-scale deployments. Moreover, the RL-driven routing decisions are fused with classical graph-based methods, Minimum Energy Routing Algorithm (MERA) and Minimum Spanning Tree (MST), to optimize energy consumption and load balancing. Simulations confirm that the proposed approach significantly improves node survival rate, reduces SoC variance, and enhances network resilience, making it a scalable and adaptive solution for energy-constrained WSNs in dynamic sensor deployments and IoT applications.
在无线传感器网络(WSNs)中,有效的能源管理对于延长网络寿命和确保可靠的数据传输至关重要。本文提出了一种新方法,采用基于强化学习的簇头选择以及混合多跳路由算法。该算法在多智能体系统中利用Q学习,根据传感器节点之间的能量分布动态地适应传输路径。每个传感器节点被建模为自主智能体,观察本地状态参数,如剩余能量、距离接收器、跳数以及热点距离等,并选择能够最大化长期能源效率的路由动作。在计算出最佳路径后,每个传感器都会聚集感知的数据,并通过中间节点将其转发到基于剩余电量选择的最优传输节点上,从而避免节点过早耗尽能量。为了促进高效学习,精心设计的奖励函数旨在激励平衡负载分布、避免热点、保持能量感知的前向操作,同时保持信号质量。学习过程可以是分散式的,或者通过基于云的控制器进行,在大规模部署中卸下计算任务。此外,由强化学习驱动的路由决策与经典的基于图的方法(如最低能量路由算法(MERA)和最小生成树(MST))相融合,以优化能源消耗和负载平衡。模拟结果表明,所提出的方法显著提高了节点存活率,降低了电量状态方差,增强了网络韧性,使其成为动态传感器部署和物联网应用中能源受限的WSN的可扩展和自适应解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
无线传感器网络(WSN)中的能效管理至关重要,可延长网络寿命并确保可靠的数据传输。本文提出了一种新方法,使用基于强化学习的集群头选择和混合多跳路由算法。该方法在一个多智能体系统中利用Q学习,根据传感器节点的能量分布动态适应传输路径。每个传感器节点被建模为自主观察本地状态参数的智能体,如剩余能量、到基站的距离、跳数以及热点距离等,并选择路由行为以最大化长期能效。在计算出最佳路径后,每个传感器会聚合检测到的数据并将其通过中间节点转发到基于剩余电量选择的最优发射器节点,从而避免节点过早耗尽能量。奖励函数旨在激励负载平衡分布、避免热点区域以及能源意识转发,同时保持信号质量。学习过程可以通过分散式方式或通过大型部署的云控制器进行,将强化学习驱动的路由决策与经典图方法(如最小能量路由算法和最小生成树)相结合,以优化能耗和负载均衡。仿真结果表明,该方法可显著提高节点存活率、降低状态电量差异并增强网络弹性,成为动态传感器部署和物联网应用中能源受限WSN的可扩展和自适应解决方案。
关键见解
- 强化学习用于WSN中的集群头选择和路由决策,以提高能效。
- 传感器节点建模为自主智能体,考虑本地状态参数进行路由选择。
- 结合Q学习在多智能体系统中动态适应传输路径,基于能量分布。
- 奖励函数设计用于平衡负载分布、避免热点、保持能源意识和信号质量。
- 学习过程可分散进行或通过云控制器进行,适用于大规模部署。
- 强化学习与经典图方法结合,如最小能量路由算法和最小生成树,优化能耗和负载均衡。
点此查看论文截图

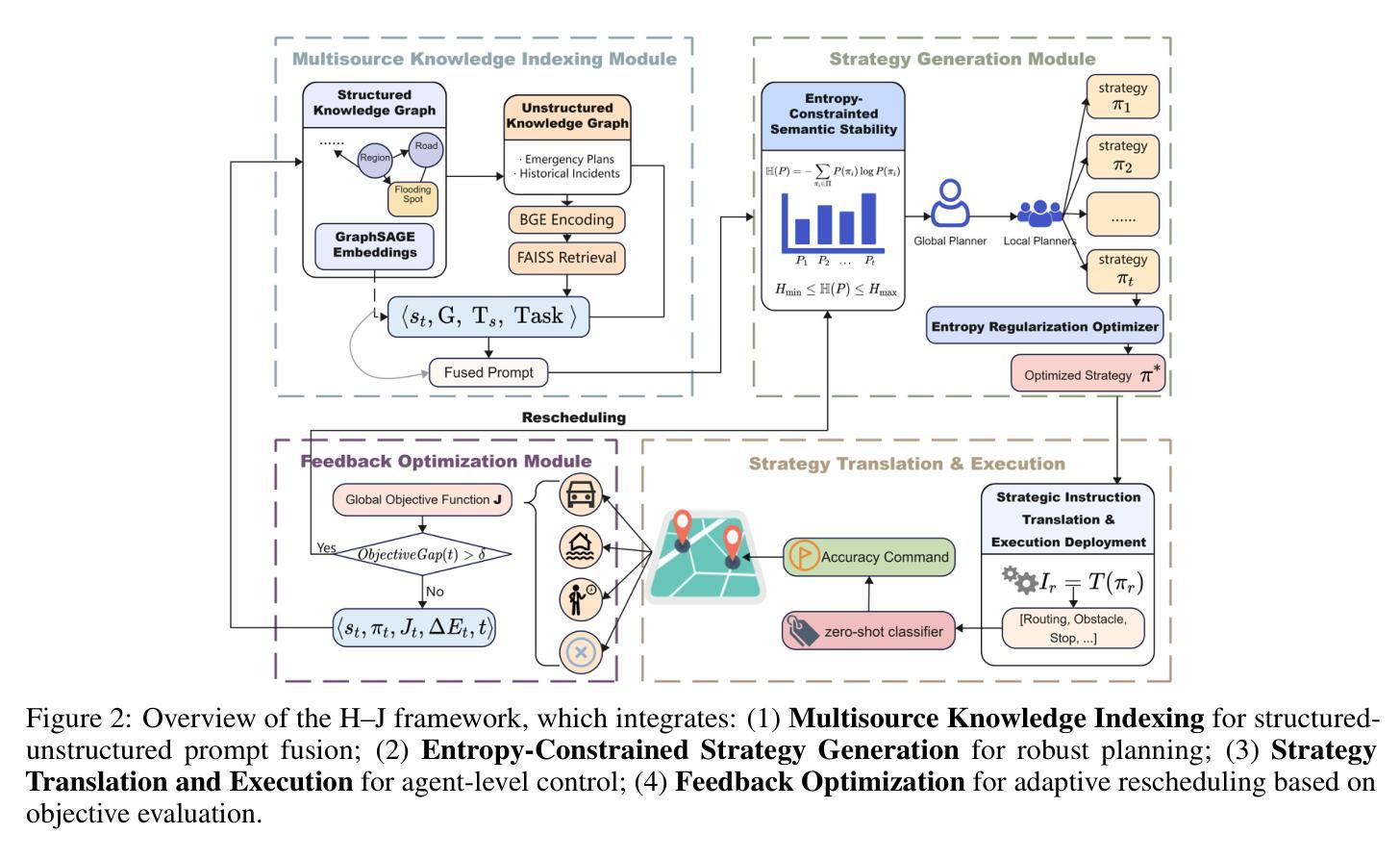
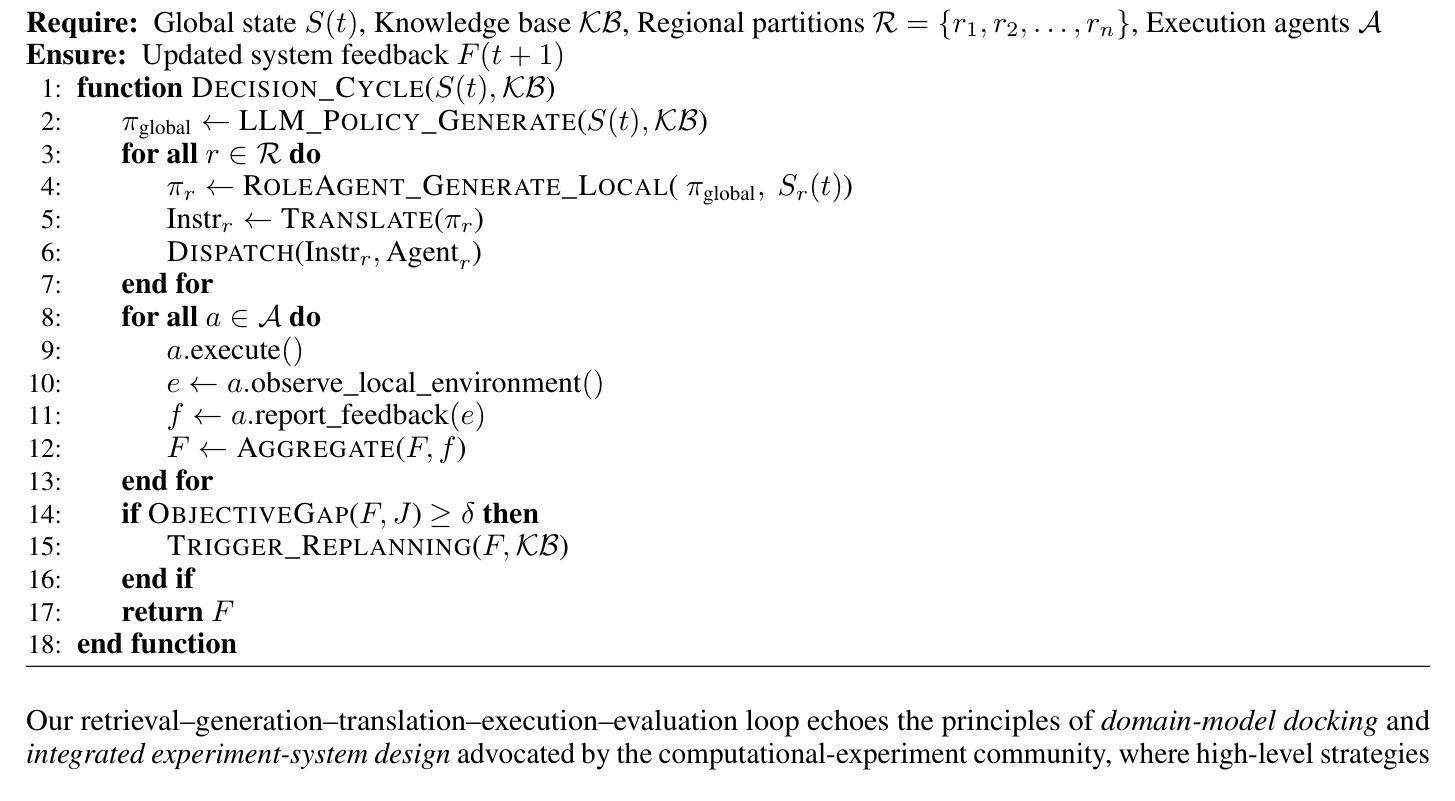
Entropy-Constrained Strategy Optimization in Urban Floods: A Multi-Agent Framework with LLM and Knowledge Graph Integration
Authors:Peilin Ji, Xiao Xue, Simeng Wang, Wenhao Yan
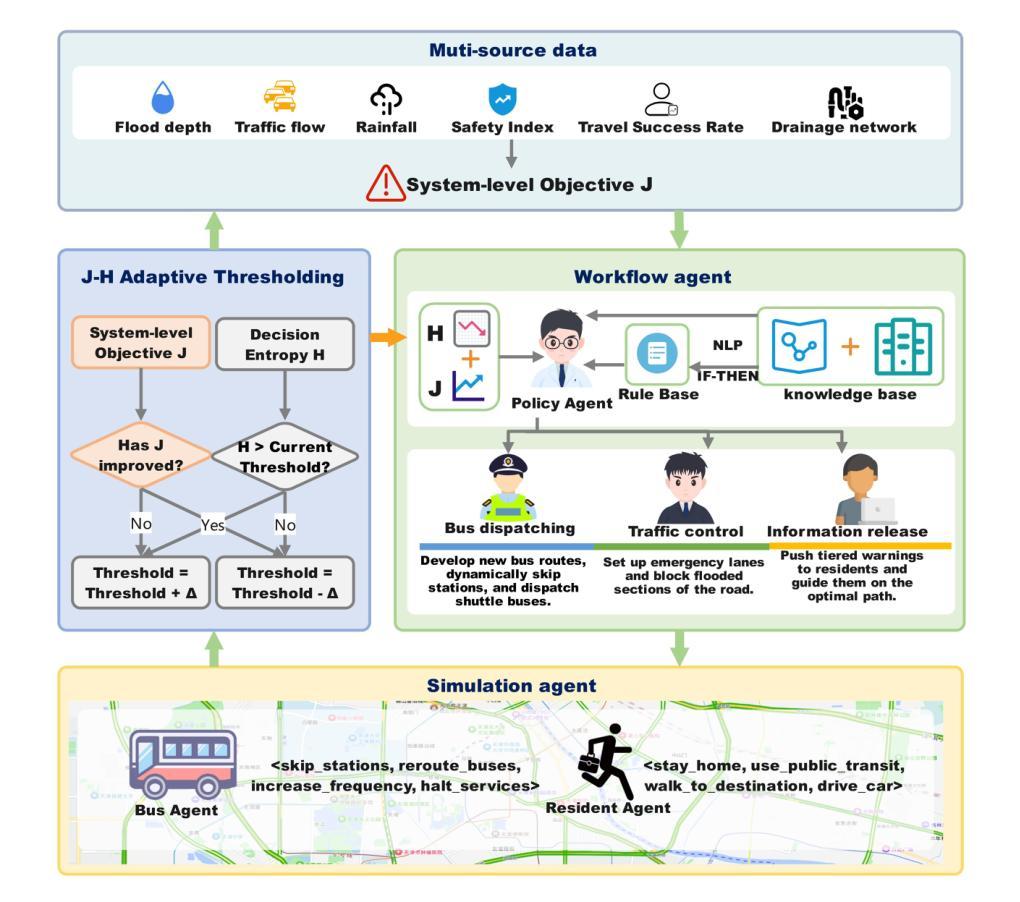
In recent years, the increasing frequency of extreme urban rainfall events has posed significant challenges to emergency scheduling systems. Urban flooding often leads to severe traffic congestion and service disruptions, threatening public safety and mobility. However, effective decision making remains hindered by three key challenges: (1) managing trade-offs among competing goals (e.g., traffic flow, task completion, and risk mitigation) requires dynamic, context-aware strategies; (2) rapidly evolving environmental conditions render static rules inadequate; and (3) LLM-generated strategies frequently suffer from semantic instability and execution inconsistency. Existing methods fail to align perception, global optimization, and multi-agent coordination within a unified framework. To tackle these challenges, we introduce H-J, a hierarchical multi-agent framework that integrates knowledge-guided prompting, entropy-constrained generation, and feedback-driven optimization. The framework establishes a closed-loop pipeline spanning from multi-source perception to strategic execution and continuous refinement. We evaluate H-J on real-world urban topology and rainfall data under three representative conditions: extreme rainfall, intermittent bursts, and daily light rain. Experiments show that H-J outperforms rule-based and reinforcement-learning baselines in traffic smoothness, task success rate, and system robustness. These findings highlight the promise of uncertainty-aware, knowledge-constrained LLM-based approaches for enhancing resilience in urban flood response.
近年来,极端城市降雨事件的频率增加给应急调度系统带来了重大挑战。城市洪水经常导致严重的交通拥堵和服务中断,威胁公共安全和流动性。然而,有效的决策制定仍然受到三个关键挑战的阻碍:(1)管理相互竞争目标之间的权衡(如交通流量、任务完成和风险管理)需要动态、基于上下文策略;(2)快速变化的环境条件使静态规则显得捉襟见肘;(3)大型语言模型生成的策略经常遭受语义不稳定和执行不一致的困扰。现有方法无法在统一框架内实现对感知、全局优化和多智能体协调的整合。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了H-J,一个层次化的多智能体框架,它集成了知识引导提示、熵约束生成和反馈驱动优化。该框架建立了一个从多源感知到战略执行和持续改进的闭环管道。我们在三种代表性条件下,使用真实世界的城市拓扑和降雨数据对H-J进行了评估:极端降雨、间歇性暴雨和日常小雨。实验表明,在交通流畅性、任务成功率和系统稳健性方面,H-J优于基于规则和强化学习的基线。这些发现凸显了基于大型语言模型、具有不确定性意识的知识约束方法在提高城市洪水应对韧性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages including appendix, 6 figures
摘要
近年极端城市降水事件频发,对城市应急调度系统带来重大挑战。城市洪水经常导致严重的交通拥堵和服务中断,威胁公共安全与流动性。当前决策面临的挑战包括:需动态策略以管理相互竞争目标间的权衡;不断变化的环境条件是静态规则失效;LLM生成的策略常有语义不稳定和执行不一致的问题。现有方法未能将感知、全局优化和多智能体协调统一于一个框架中。为应对这些挑战,提出H-J层次多智能体框架,融合知识引导提示、熵约束生成和反馈驱动优化。该框架建立了从多源感知到战略执行和持续改进的闭环流程。在真实城市地形和降水数据下的三种典型条件下评估H-J的效果,实验显示其在交通流畅度、任务成功率和系统稳健性方面优于基于规则和强化学习的基线方法。这些发现凸显了不确定性感知、知识约束的LLM方法在增强城市洪水应对韧性方面的潜力。
关键见解
- 极端城市降水事件对紧急调度系统构成重大挑战,导致交通拥堵和服务中断。
- 当前决策面临的挑战包括动态管理目标权衡、环境变化的快速影响以及LLM策略的语义和执行问题。
- 现有方法未能将感知、优化和协调统一于一个框架中。
- 提出的H-J层次多智能体框架融合了知识引导提示、熵约束生成和反馈驱动优化,建立闭环流程。
- H-J在多种条件下的实验效果优于现有方法,提高了交通流畅度、任务成功率和系统稳健性。
- 结果突显了结合不确定性感知和知识约束的LLM方法在城市洪水应对中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

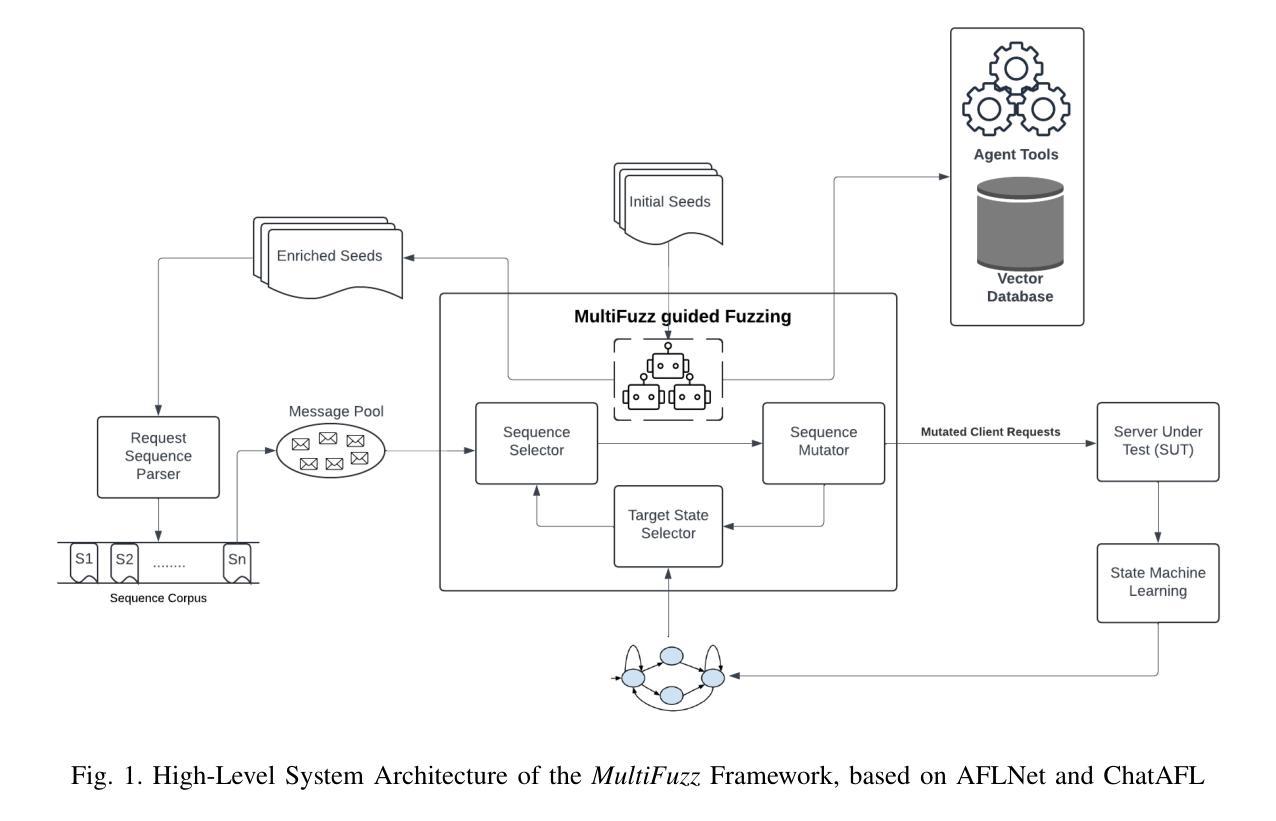
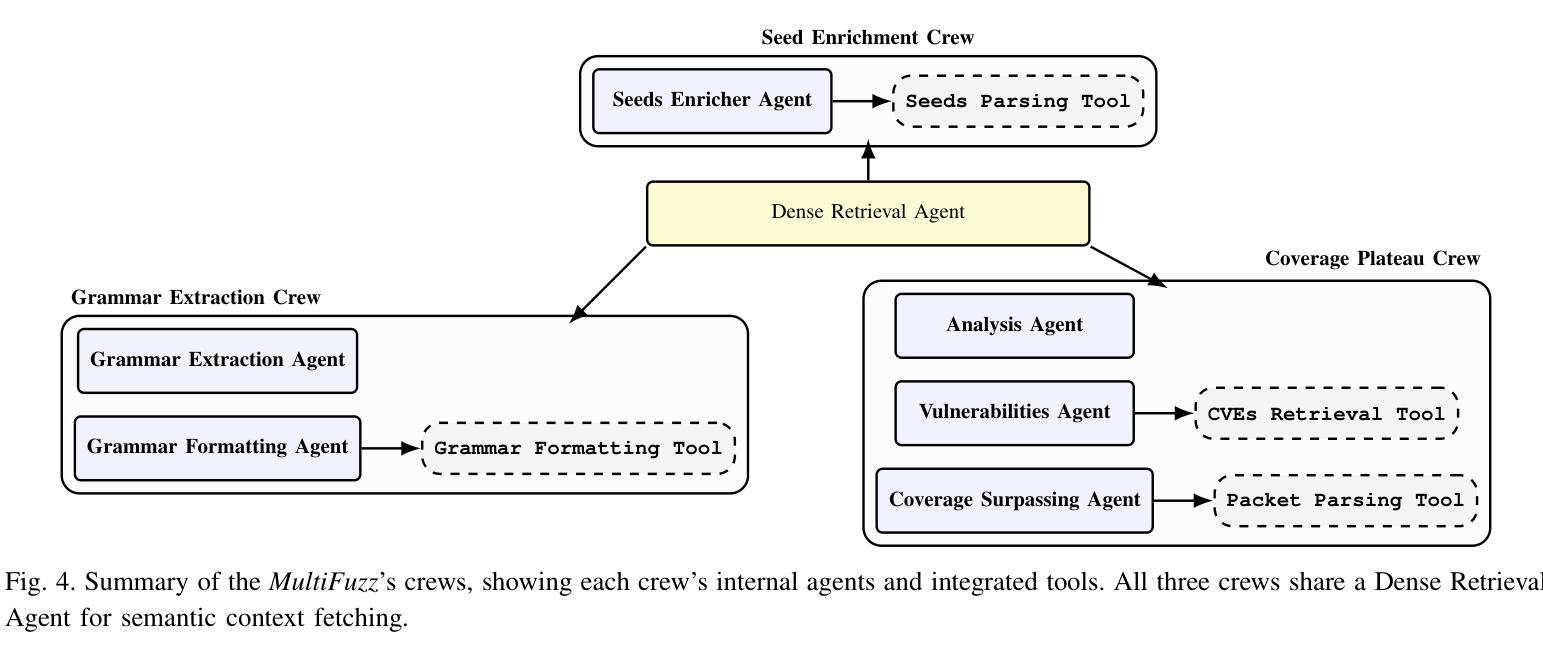
MultiFuzz: A Dense Retrieval-based Multi-Agent System for Network Protocol Fuzzing
Authors:Youssef Maklad, Fares Wael, Ali Hamdi, Wael Elsersy, Khaled Shaban
Traditional protocol fuzzing techniques, such as those employed by AFL-based systems, often lack effectiveness due to a limited semantic understanding of complex protocol grammars and rigid seed mutation strategies. Recent works, such as ChatAFL, have integrated Large Language Models (LLMs) to guide protocol fuzzing and address these limitations, pushing protocol fuzzers to wider exploration of the protocol state space. But ChatAFL still faces issues like unreliable output, LLM hallucinations, and assumptions of LLM knowledge about protocol specifications. This paper introduces MultiFuzz, a novel dense retrieval-based multi-agent system designed to overcome these limitations by integrating semantic-aware context retrieval, specialized agents, and structured tool-assisted reasoning. MultiFuzz utilizes agentic chunks of protocol documentation (RFC Documents) to build embeddings in a vector database for a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline, enabling agents to generate more reliable and structured outputs, enhancing the fuzzer in mutating protocol messages with enhanced state coverage and adherence to syntactic constraints. The framework decomposes the fuzzing process into modular groups of agents that collaborate through chain-of-thought reasoning to dynamically adapt fuzzing strategies based on the retrieved contextual knowledge. Experimental evaluations on the Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) demonstrate that MultiFuzz significantly improves branch coverage and explores deeper protocol states and transitions over state-of-the-art (SOTA) fuzzers such as NSFuzz, AFLNet, and ChatAFL. By combining dense retrieval, agentic coordination, and language model reasoning, MultiFuzz establishes a new paradigm in autonomous protocol fuzzing, offering a scalable and extensible foundation for future research in intelligent agentic-based fuzzing systems.
传统协议模糊测试技术,如AFL-based系统所采用的,往往因对复杂协议语法的有限语义理解和僵化的种子突变策略而缺乏有效性。最近的工作,如ChatAFL,已经集成了大型语言模型(LLM)来引导协议模糊测试并解决这些限制,推动协议模糊测试器对协议状态空间的更广泛探索。但ChatAFL仍然面临输出不可靠、LLM幻觉以及LLM对协议规范的知识假设等问题。本文介绍了MultiFuzz,这是一个基于密集检索的多智能体系统,旨在通过集成语义感知上下文检索、专用智能体和结构化工具辅助推理来克服这些局限性。MultiFuzz利用智能体的协议文档片段(RFC文档)在向量数据库中构建嵌入,用于增强检索生成(RAG)管道,使智能体能生成更可靠和结构化输出,增强模糊测试器在变异协议消息方面的可靠性,提高状态覆盖率并遵守语法约束。该框架将模糊测试过程分解为模块化智能体组,这些智能体通过链式思维推理进行协作,根据检索到的上下文知识动态适应模糊测试策略。对实时流媒体协议(RTSP)的试验评估表明,MultiFuzz在分支覆盖率和探索更深入的协议状态和转换方面,显著优于最新技术(SOTA)模糊测试器,如NSFuzz、AFLNet和ChatAFL。通过结合密集检索、智能体协调和语言模型推理,MultiFuzz在自主协议模糊测试领域建立了新的范式,为未来智能体基模糊测试系统的研究提供了可扩展和可扩展的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
传统协议模糊测试技术,如AFL-based系统所使用的方法,由于缺乏对复杂协议语法的语义理解和种子突变策略的僵化,往往效果不佳。ChatAFL等近期研究尝试集成大型语言模型(LLM)以改善此情况,推动协议模糊测试对协议状态空间的更广泛探索。然而,ChatAFL仍存在输出不可靠、LLM幻觉以及假设LLM了解协议规范的问题。本文介绍MultiFuzz,一种新型的基于密集检索的多智能体系统,通过集成语义感知上下文检索、专业智能体和结构化工具辅助推理来克服这些限制。MultiFuzz利用协议文档(RFC文档)的智能体片段在向量数据库中构建嵌入,用于增强型生成(RAG)管道,使智能体生成更可靠和结构化输出,提高模糊测试器在变异协议消息时的状态覆盖率并遵守句法约束。该框架将模糊测试过程分解为模块化智能体组,通过思考链推理协作,根据检索到的上下文知识动态调整模糊测试策略。在实时流媒体协议(RTSP)上的实验评估表明,MultiFuzz在分支覆盖率和深入探索协议状态和转换方面显著优于现有技术(SOTA)模糊测试器,如NSFuzz、AFLNet和ChatAFL。
Key Takeaways
- 传统协议模糊测试技术存在语义理解有限和种子突变策略僵化的问题。
- ChatAFL等集成大型语言模型的尝试推动了协议模糊测试的发展,但仍存在可靠性、幻觉和假设问题。
- MultiFuzz是一种新型的密集检索基于多智能体系统,通过集成语义感知上下文检索和结构化工具辅助推理来解决现有问题。
- MultiFuzz利用协议文档的智能体片段来增强模糊测试过程,提高状态覆盖率和遵守句法约束。
- MultiFuzz将模糊测试过程分解为模块化智能体组,通过思考链推理协作来动态适应模糊测试策略。
- 在RTSP上的实验评估显示,MultiFuzz在分支覆盖率和深入探索协议状态方面显著优于其他模糊测试器。
点此查看论文截图


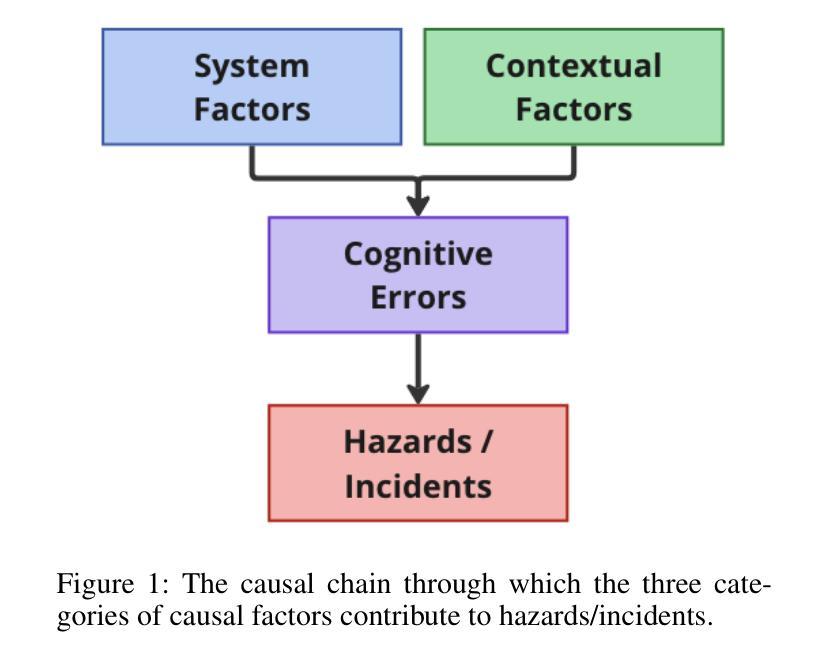
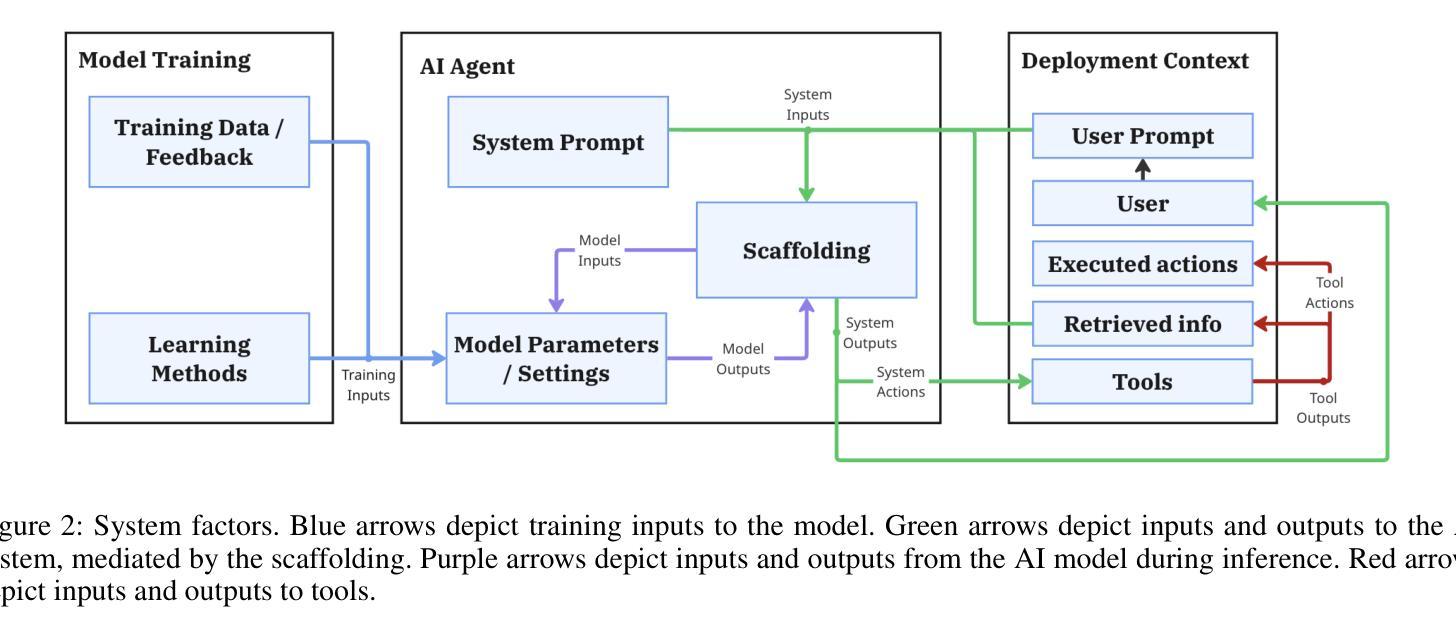
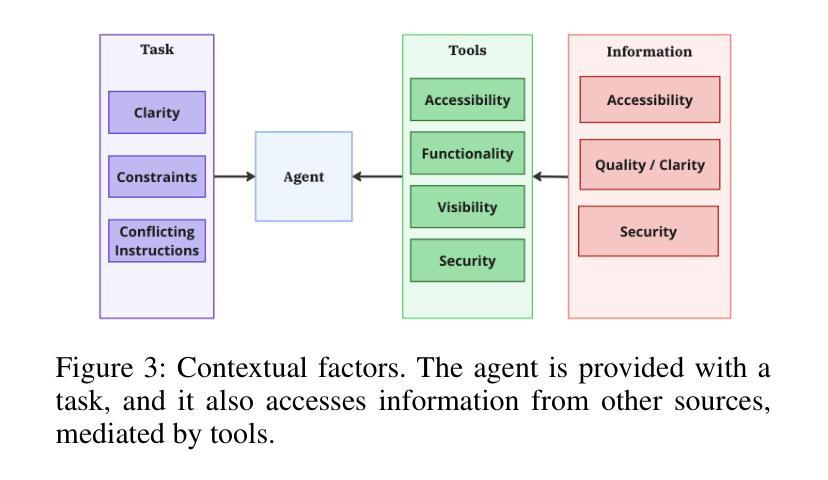
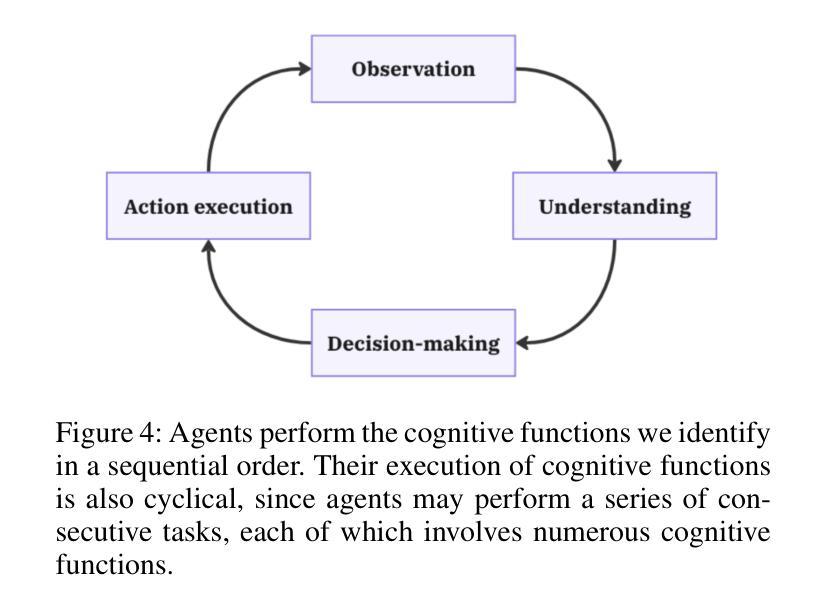
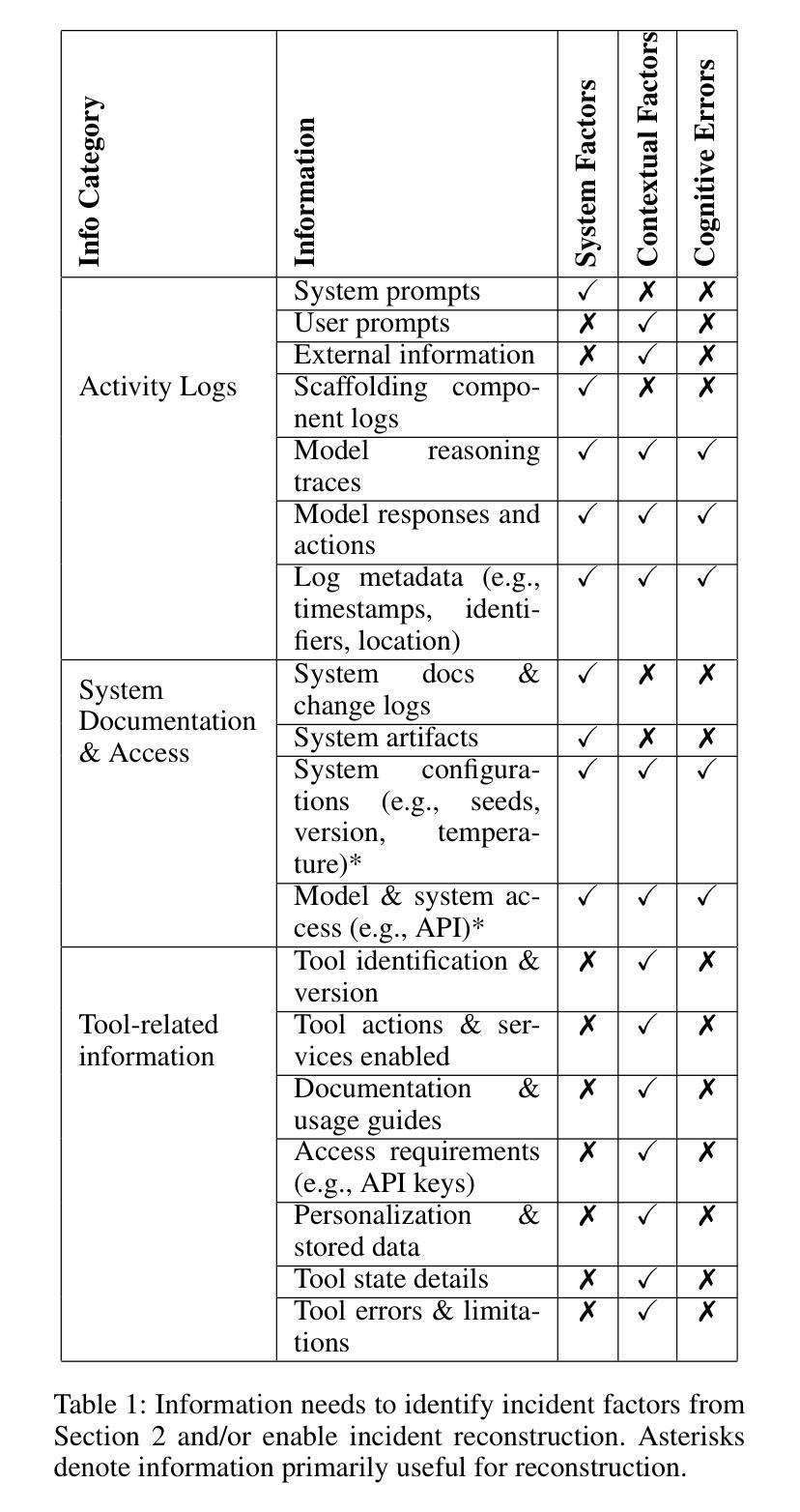
Incident Analysis for AI Agents
Authors:Carson Ezell, Xavier Roberts-Gaal, Alan Chan
As AI agents become more widely deployed, we are likely to see an increasing number of incidents: events involving AI agent use that directly or indirectly cause harm. For example, agents could be prompt-injected to exfiltrate private information or make unauthorized purchases. Structured information about such incidents (e.g., user prompts) can help us understand their causes and prevent future occurrences. However, existing incident reporting processes are not sufficient for understanding agent incidents. In particular, such processes are largely based on publicly available data, which excludes useful, but potentially sensitive, information such as an agent’s chain of thought or browser history. To inform the development of new, emerging incident reporting processes, we propose an incident analysis framework for agents. Drawing on systems safety approaches, our framework proposes three types of factors that can cause incidents: system-related (e.g., CBRN training data), contextual (e.g., prompt injections), and cognitive (e.g., misunderstanding a user request). We also identify specific information that could help clarify which factors are relevant to a given incident: activity logs, system documentation and access, and information about the tools an agent uses. We provide recommendations for 1) what information incident reports should include and 2) what information developers and deployers should retain and make available to incident investigators upon request. As we transition to a world with more agents, understanding agent incidents will become increasingly crucial for managing risks.
随着人工智能代理的广泛应用,我们可能会看到越来越多的代理使用事件直接或间接造成损害的事件。例如,代理可能会通过提示注入来窃取私人信息或进行未经授权的购买。关于此类事件的结构化信息(例如用户提示)可以帮助我们了解其原因并防止未来再次发生。然而,现有的事件报告流程对于理解代理事件并不足够。尤其地,这些流程主要基于公开可用的数据,排除了有用的但可能敏感的信息,例如代理的思维链或浏览器历史记录。为了建立新兴的事件报告流程,我们提出了一个针对代理的事件分析框架。我们的框架借鉴了系统安全方法,提出了可能导致事件的三种类型因素:系统相关因素(例如CBRN训练数据)、上下文因素(例如提示注入)和认知因素(例如误解用户请求)。我们还确定了可以帮助澄清与给定事件相关的特定因素的具体信息:活动日志、系统文档和访问权限以及有关代理使用的工具的信息。我们提供关于以下几点建议:1)事件报告应包括哪些信息;2)开发人员和部署人员应保留哪些信息并在需要时提供给事件调查人员。随着我们进入一个拥有更多代理的世界,了解代理事件对于风险管理将变得越来越重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages (10 pages main text), 4 figures, 3 tables. To be published in the Proceedings of the 2025 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, & Society (AIES)
Summary
随着人工智能代理的广泛应用,可能会看到越来越多的代理事件:直接或间接导致伤害的人工智能代理使用事件。为此,我们提出了一个代理事件分析框架,以指导新兴的事件报告流程的开发。该框架考虑了三种可能导致事件的类型:系统相关因素、情境因素和认知因素。因此,我们建议在事件报告中应包括活动日志、系统文档和访问信息,以及关于代理使用的工具的信息。随着代理数量的增加,理解代理事件对于管理风险将变得越来越重要。
Key Takeaways
- 随着AI代理的广泛应用,代理事件可能会增加,这些事件可能导致直接或间接的伤害。
- 现有的事件报告流程不足以理解代理事件,需要一个新的分析框架。
- 新框架考虑了三种可能导致事件的类型:系统相关因素、情境因素和认知因素。
- 活动日志、系统文档和访问信息以及代理使用的工具的信息是理解事件的重要因素。
- 事件报告中应包含特定信息以帮助澄清与给定事件相关的因素。
- 为了管理风险,理解代理事件将变得越来越重要。
点此查看论文截图

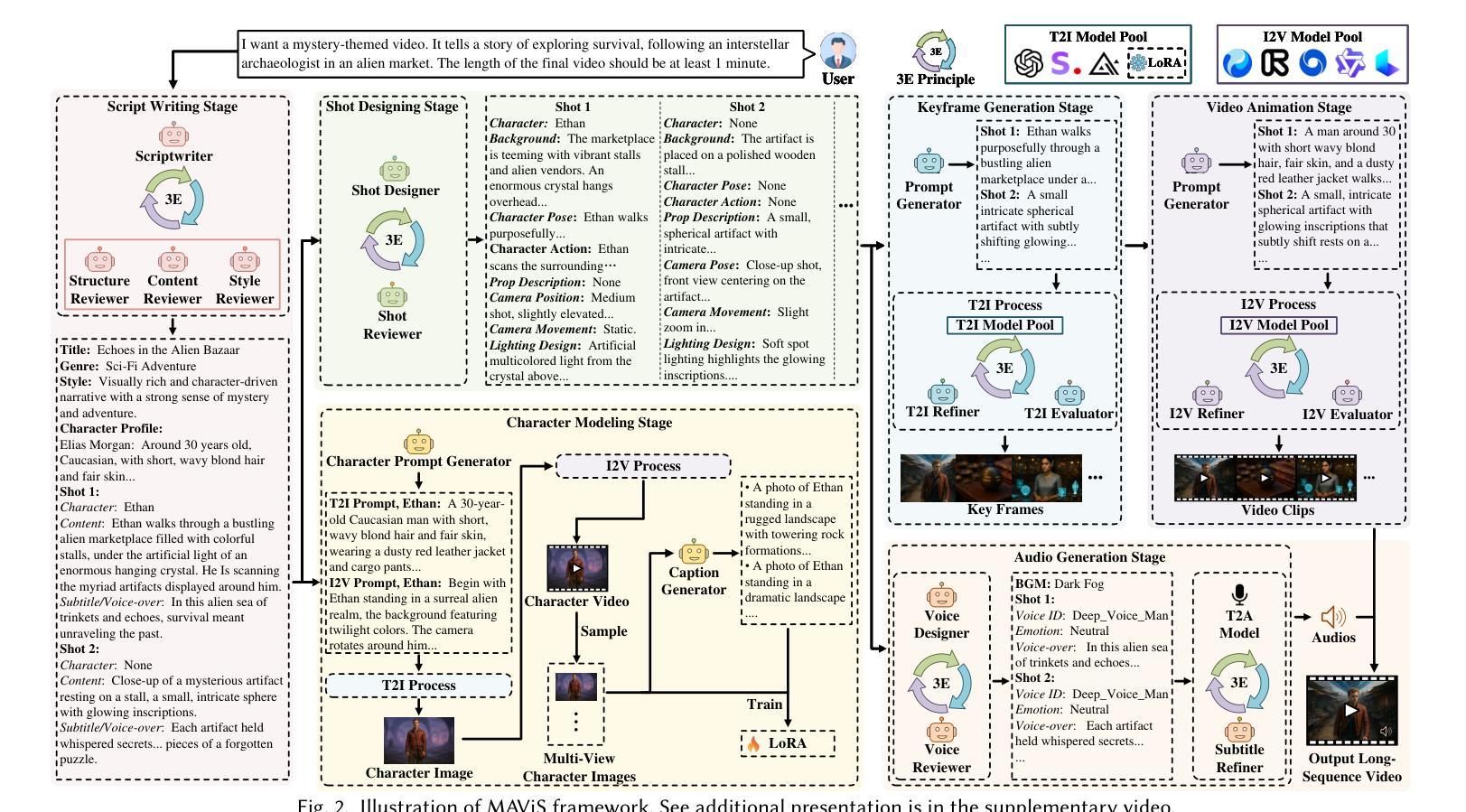
MAViS: A Multi-Agent Framework for Long-Sequence Video Storytelling
Authors:Qian Wang, Ziqi Huang, Ruoxi Jia, Paul Debevec, Ning Yu
Despite recent advances, long-sequence video generation frameworks still suffer from significant limitations: poor assistive capability, suboptimal visual quality, and limited expressiveness. To mitigate these limitations, we propose MAViS, an end-to-end multi-agent collaborative framework for long-sequence video storytelling. MAViS orchestrates specialized agents across multiple stages, including script writing, shot designing, character modeling, keyframe generation, video animation, and audio generation. In each stage, agents operate under the 3E Principle – Explore, Examine, and Enhance – to ensure the completeness of intermediate outputs. Considering the capability limitations of current generative models, we propose the Script Writing Guidelines to optimize compatibility between scripts and generative tools. Experimental results demonstrate that MAViS achieves state-of-the-art performance in assistive capability, visual quality, and video expressiveness. Its modular framework further enables scalability with diverse generative models and tools. With just a brief user prompt, MAViS is capable of producing high-quality, expressive long-sequence video storytelling, enriching inspirations and creativity for users. To the best of our knowledge, MAViS is the only framework that provides multimodal design output – videos with narratives and background music.
尽管最近的进展显著,长序列视频生成框架仍存在重大局限性:辅助能力较差、视觉质量不佳和表达性有限。为了缓解这些局限性,我们提出了MAViS,这是一个用于长序列视频叙事的端到端多智能体协作框架。MAViS在多个阶段协调专业智能体,包括剧本写作、镜头设计、角色建模、关键帧生成、视频动画和音频生成。在每个阶段,智能体都遵循3E原则——探索、检查和提高,以确保中间输出的完整性。考虑到当前生成模型的能力限制,我们提出了剧本写作指南,以优化剧本与生成工具之间的兼容性。实验结果表明,MAViS在辅助能力、视觉质量和视频表现力方面达到了最新技术水平。其模块化框架还实现了与各种生成模型和工具的可扩展性。只需用户简短的提示,MAViS就能够生成高质量、富有表现力的长序列视频故事,丰富用户的灵感和创造力。据我们所知,MAViS是唯一提供多模式设计输出的框架——带有叙事和背景音乐的视频。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Video Generation Agent
Summary
基于近期发展,长序列视频生成框架仍存在显著缺陷,如辅助能力弱、视觉质量不佳和表现力有限。为缓解这些问题,我们提出MAViS,这是一个端到端的多智能体协作框架,用于长序列视频叙事。MAViS在多个阶段协同专业智能体工作,包括剧本写作、镜头设计、角色建模、关键帧生成、视频动画和音频生成。在每个阶段,智能体遵循“探索、考察和增强”(3E原则),以确保中间输出的完整性。考虑到当前生成模型的能力限制,我们制定了剧本写作指南,以优化剧本与生成工具之间的兼容性。实验结果表明,MAViS在辅助能力、视觉质量和视频表现力方面达到了最先进的性能。其模块化框架进一步支持多种生成模型和工具的扩展性。只需用户简短提示,MAViS就能产生高质量、富有表现力的长序列视频故事,为用户带来灵感和创造力。据我们所知,MAViS是唯一提供多媒体设计输出的框架——带有叙事和背景音乐的视频。
Key Takeaways
- MAViS是一个用于长序列视频叙事的多智能体协作框架,旨在克服现有框架的辅助能力弱、视觉质量不佳和表现力有限的缺陷。
- MAViS涵盖从剧本写作到音频生成的多个阶段,每个阶段都有智能体遵循“探索、考察和增强”的原则工作。
- 为优化剧本与生成工具之间的兼容性,提出了剧本写作指南。
- 实验证明MAViS在辅助能力、视觉质量和视频表现力方面表现卓越。
- MAViS采用模块化设计,可轻松集成各种生成模型和工具。
- 用户只需简单提示,MAViS即可生成高质量、富有表现力的长序列视频故事。
点此查看论文截图


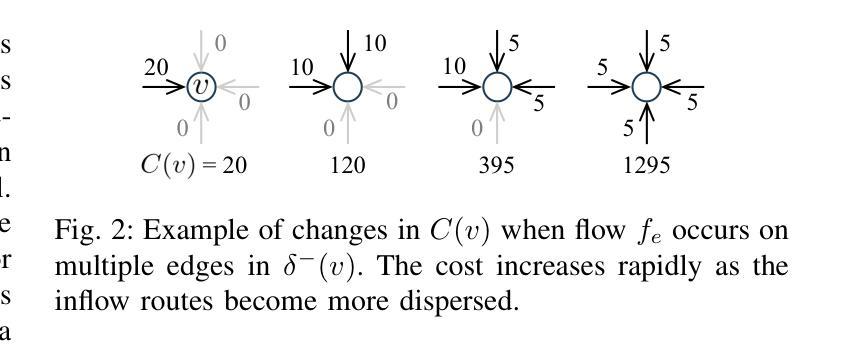
Congestion Mitigation Path Planning for Large-Scale Multi-Agent Navigation in Dense Environments
Authors:Takuro Kato, Keisuke Okumura, Yoko Sasaki, Naoya Yokomachi
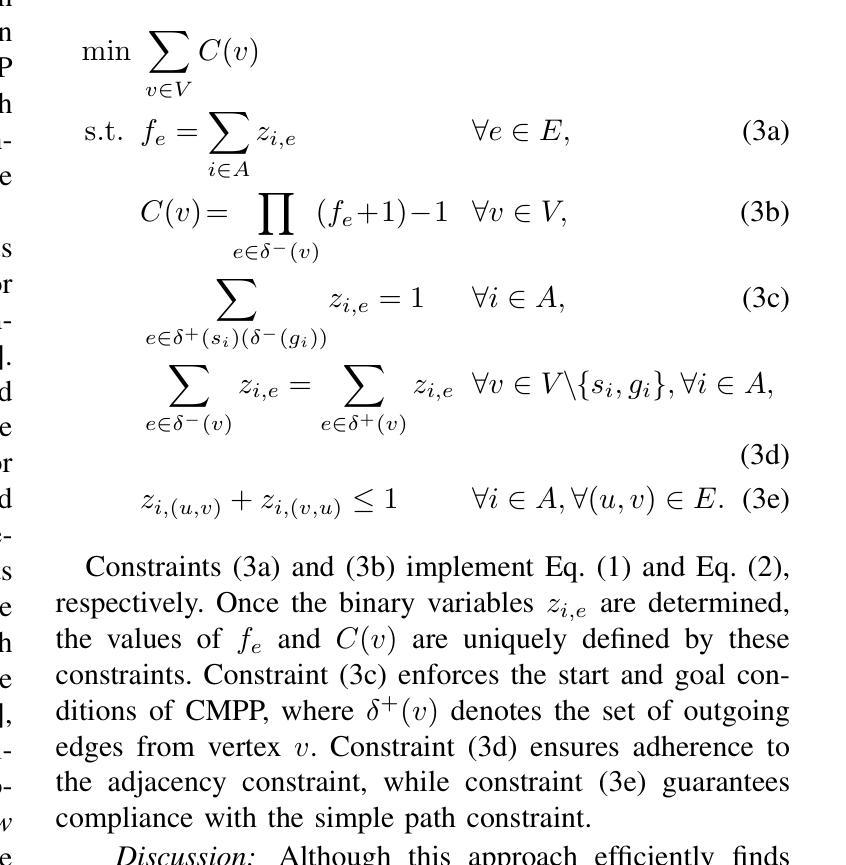
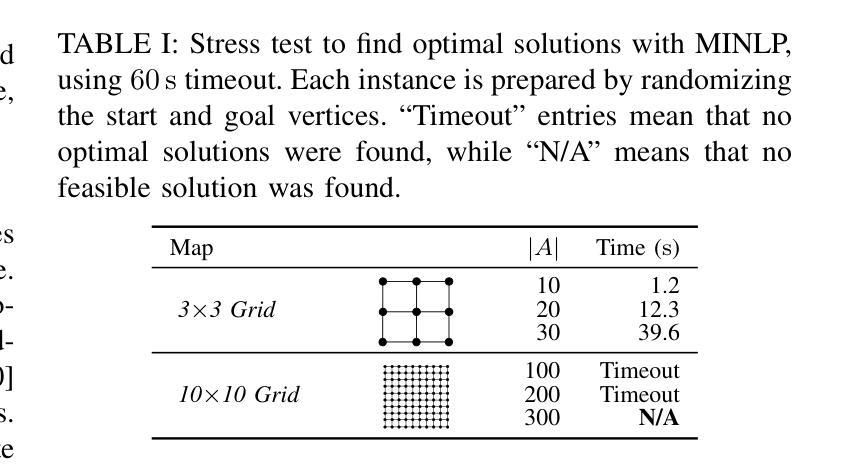
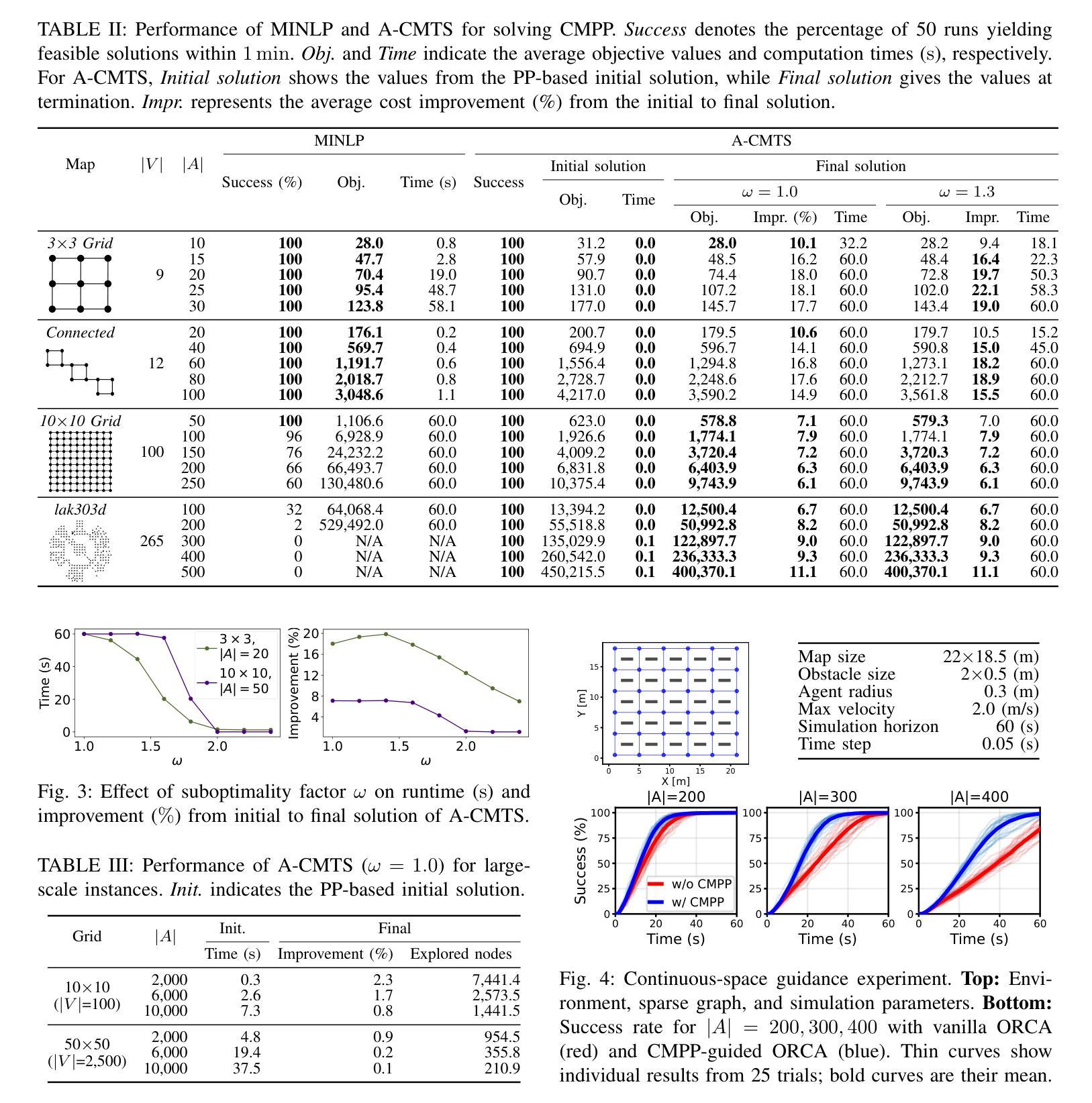
In high-density environments where numerous autonomous agents move simultaneously in a distributed manner, streamlining global flows to mitigate local congestion is crucial to maintain overall navigation efficiency. This paper introduces a novel path-planning problem, congestion mitigation path planning (CMPP), which embeds congestion directly into the cost function, defined by the usage of incoming edges along agents’ paths. CMPP assigns a flow-based multiplicative penalty to each vertex of a sparse graph, which grows steeply where frequently-traversed paths intersect, capturing the intuition that congestion intensifies where many agents enter the same area from different directions. Minimizing the total cost yields a set of coarse-level, time-independent routes that autonomous agents can follow while applying their own local collision avoidance. We formulate the problem and develop two solvers: (i) an exact mixed-integer nonlinear programming solver for small instances, and (ii) a scalable two-layer search algorithm, A-CMTS, which quickly finds suboptimal solutions for large-scale instances and iteratively refines them toward the optimum. Empirical studies show that augmenting state-of-the-art collision-avoidance planners with CMPP significantly reduces local congestion and enhances system throughput in both discrete- and continuous-space scenarios. These results indicate that CMPP improves the performance of multi-agent systems in real-world applications such as logistics and autonomous-vehicle operations.
在高密度环境中,众多自主代理以分布式方式同时移动,优化全局流程以缓解局部拥堵对于维持整体导航效率至关重要。本文引入了一种新的路径规划问题,即拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP),它将拥堵直接嵌入到成本函数中,该成本函数由代理路径上的传入边使用定义。CMPP为稀疏图的每个顶点分配基于流量的乘法惩罚,在频繁穿越的路径交汇处增长迅速,直觉地捕捉到拥堵在多个代理从不同方向进入同一区域时加剧的情况。最小化总成本可以得到一组自主代理可以遵循的粗略的、时间独立的路线,同时应用各自的局部避障策略。我们制定了这个问题并开发了两种求解器:(i)针对小规模实例的精确混合整数非线性规划求解器,(ii)一种可扩展的两层搜索算法A-CMTS,该算法可以快速找到大规模实例的次优解并迭代地优化它们以达到最优。实证研究表明,使用CMPP增强最新的避障规划器可显著减少局部拥堵,并在离散和连续空间场景中提高系统吞吐量。这些结果表明,CMPP在物流和自动驾驶汽车操作等实际应用中提高了多代理系统的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2025. Supplementary videos are accessible via IEEE Xplore
Summary:
高密度环境中众多自主代理同时分布式移动时,优化全局流程以缓解局部拥堵对维持整体导航效率至关重要。本文引入了一种新的路径规划问题——拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP),它将拥堵直接嵌入到成本函数中,该成本函数由代理路径上的传入边使用定义。CMPP为每个稀疏图的顶点分配一个基于流量的乘法惩罚,在频繁穿越的路径交叉处增长迅速,体现了拥堵在多个代理从不同方向进入同一区域时加剧的直觉。最小化总成本产生了一组自主代理可以遵循的粗略级别的时间独立路线,同时应用他们自己的局部防撞策略。我们对问题进行公式化并开发了两个求解器:(i)针对小规模实例的精确混合整数非线性规划求解器,(ii)针对大规模实例的快速找到次优解的可扩展两层搜索算法A-CMTS,并迭代优化它们以达到最优。实证研究结果表明,将CMPP与最新的防撞规划器相结合,可显著降低局部拥堵并提高系统吞吐量,无论是在离散空间还是连续空间场景中都是如此。这些结果表明,CMPP在物流和自动驾驶车辆操作等实际应用中提高了多智能体系统的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 在高密度环境中,保持自主代理导航效率的关键是优化全局流程以缓解局部拥堵。
- 引入新的路径规划问题——拥堵缓解路径规划(CMPP),直接考虑拥堵因素在成本函数中。
- CMPP通过为图的每个顶点分配基于流量的乘法惩罚,在频繁穿越的路径交叉处增长迅速的成本函数来捕捉拥堵。
- 最小化总成本可产生自主代理遵循的粗略级别时间独立路线,同时应用局部防撞策略。
- 开发了两种求解器:针对小规模实例的精确混合整数非线性规划求解器和针对大规模实例的两层搜索算法A-CMTS。
- CMPP与先进的防撞规划器结合,可有效降低局部拥堵,提高系统吞吐量。
点此查看论文截图


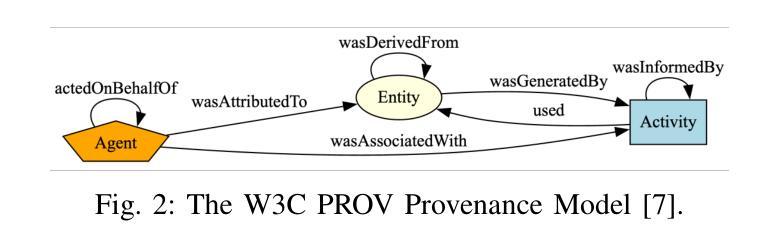
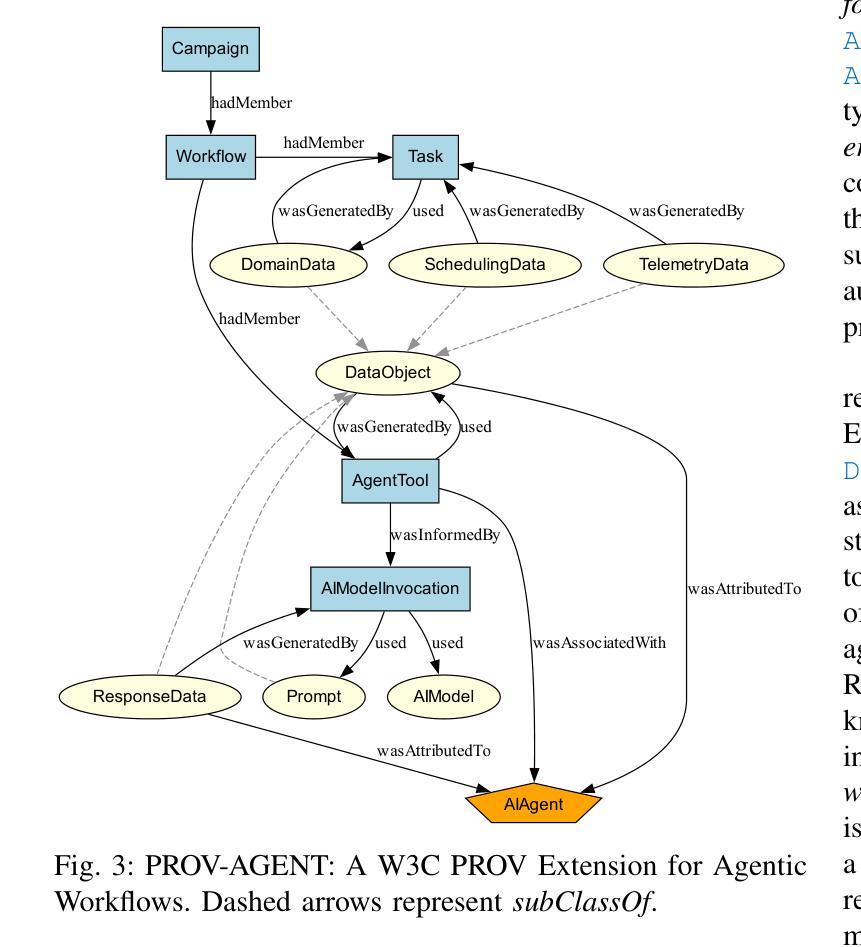
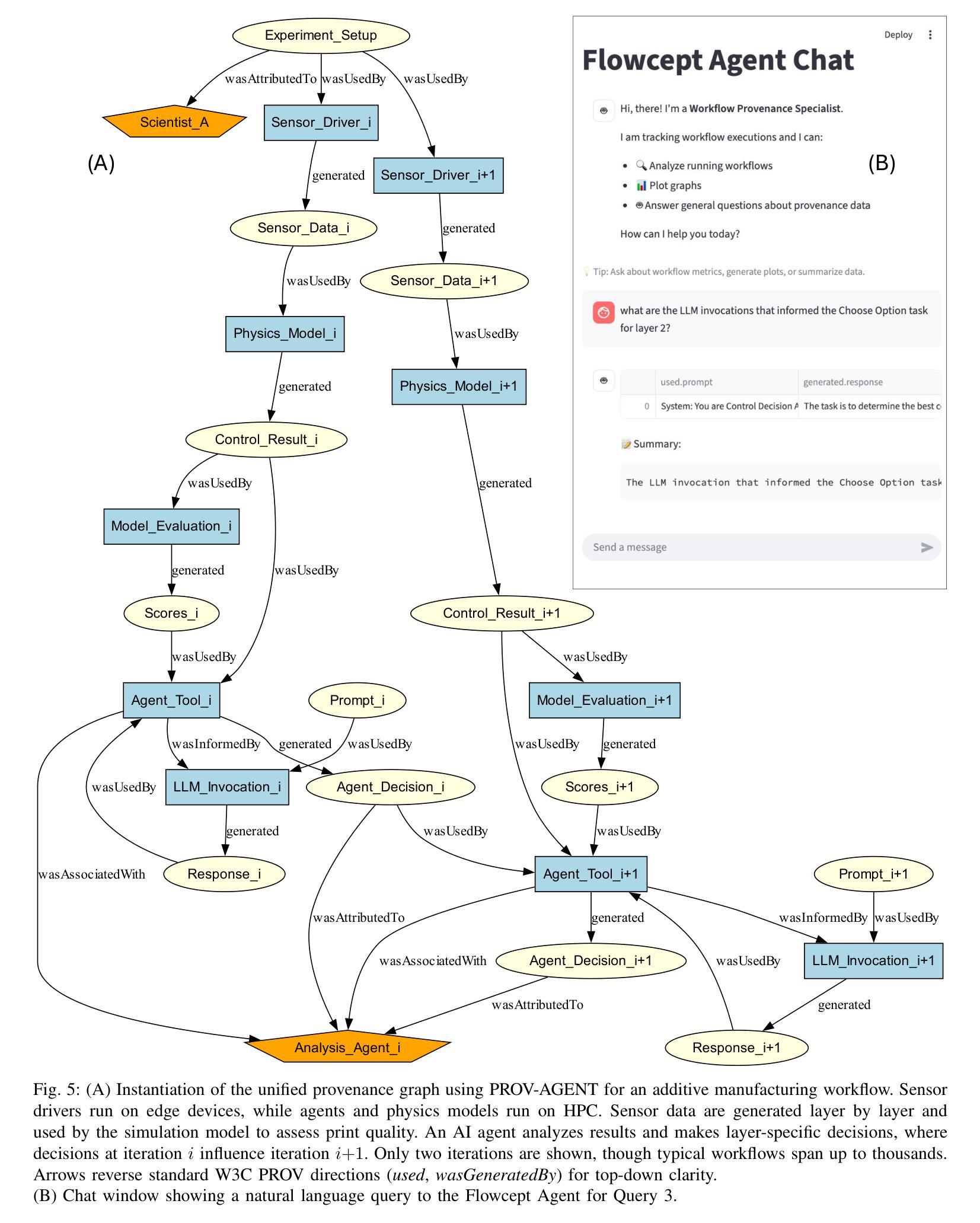
PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows
Authors:Renan Souza, Amal Gueroudji, Stephen DeWitt, Daniel Rosendo, Tirthankar Ghosal, Robert Ross, Prasanna Balaprakash, Rafael Ferreira da Silva
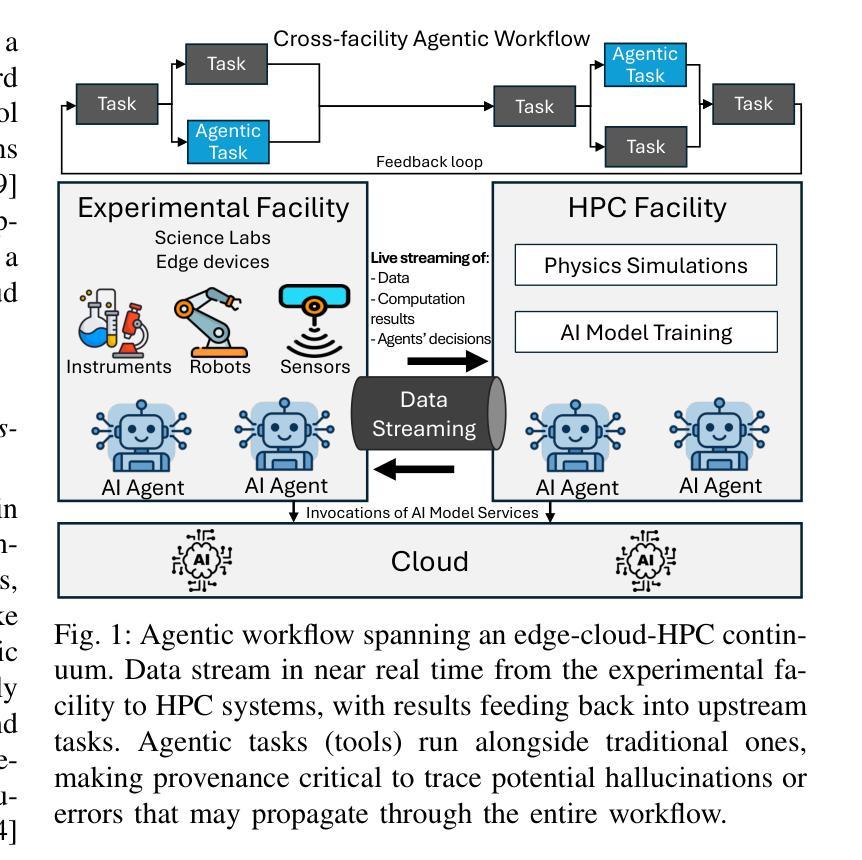
Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent’s output becomes another’s input. Thus, assuring that agents’ actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis.
大型语言模型(LLM)和其他基础模型越来越多地被用作AI代理的核心。在代理工作流程中,这些代理计划任务、与人类和同龄人互动,并在联邦和异构环境中影响科学结果。然而,代理可能会出现幻觉或推理错误,当一个代理的输出成为另一个代理的输入时,错误就会传播。因此,确保代理的行动透明、可追溯、可重现和可靠,对于评估幻觉风险和减轻其工作流程影响至关重要。尽管起源技术长期支持这些原则,但现有方法无法捕获并与代理为中心的元数据(如提示、响应和决策)与更广泛的工作流上下文和下游结果相关联。在本文中,我们介绍了PROV-AGENT,这是一个起源模型,它扩展了W3C PROV,并利用模型上下文协议(MCP)和数据可观性将代理交互集成到端到端的工作流起源。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对代理工作流程的定制起源模型,(2)用于捕获代理起源的近实时开源系统,以及(3)跨越边缘、云和高性能计算环境的跨设施评估,证明支持关键起源查询和代理可靠性分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 21st International Conference on e-Science. Cite it as: R. Souza, A. Gueroudji, S. DeWitt, D. Rosendo, T. Ghosal, R. Ross, P. Balaprakash, R. F. da Silva, “PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows,” IEEE International Conference on e-Science, Chicago, IL, USA, 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)和其他基础模型作为AI代理的核心,在代理工作流程中发挥着规划任务、与人类和同行互动以及影响联邦和异构环境中的科学成果的作用。然而,代理会产生幻觉或推理错误,当一个代理的输出成为另一个代理的输入时,错误会传播。因此,确保代理的行动透明、可追溯、可重现和可靠,对于评估幻觉风险和减轻其工作流程的影响至关重要。虽然长期存在的过程技术支持这些原则,但现有方法无法捕获和关联以代理为中心的元数据(如提示、响应和决策)与更广泛的工作流上下文和下游成果。本文介绍了PROV-AGENT,一个扩展了W3C PROV的过程模型,它利用模型上下文协议(MCP)和数据可观察性,将代理交互整合到端到端的工作流过程中。本文的贡献包括:(1)针对代理工作流程的过程模型,(2)一个近实时的开源系统,用于捕获代理过程,(3)跨越边缘、云和高性能计算环境的跨设施评估,演示了对关键过程查询和代理可靠性分析的支持。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型和其他基础模型在AI代理中起核心作用,参与任务规划、与人类和同行的互动,并在跨环境和科学领域产生影响力。
- 代理可能会出现幻觉或错误推理,如果一个代理的输出作为另一个代理的输入时,这些错误会传播。
- 确保代理的透明性、可追溯性、可重复性和可靠性对于评估幻觉风险和减轻工作流程影响至关重要。
- 现有过程技术方法无法充分捕获和关联代理为中心的元数据和更广泛的工作流上下文及下游成果。
- PROV-AGENT是一个基于W3C PROV的过程模型,它扩展了模型上下文协议和数据可观察性,整合了代理交互到端到端的工作流过程中。
- PROV-AGENT提供了一个近实时的开源系统来捕获代理过程。
点此查看论文截图

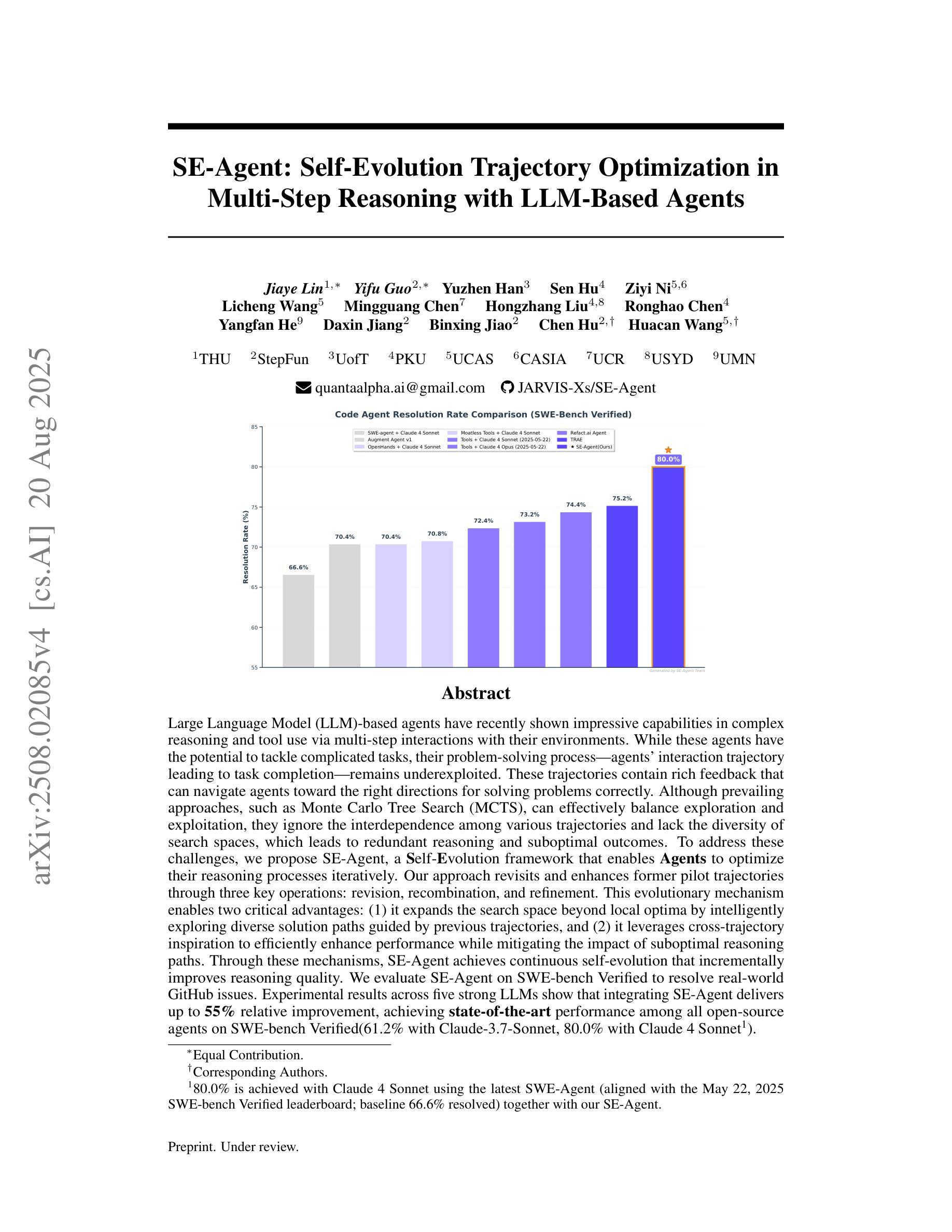
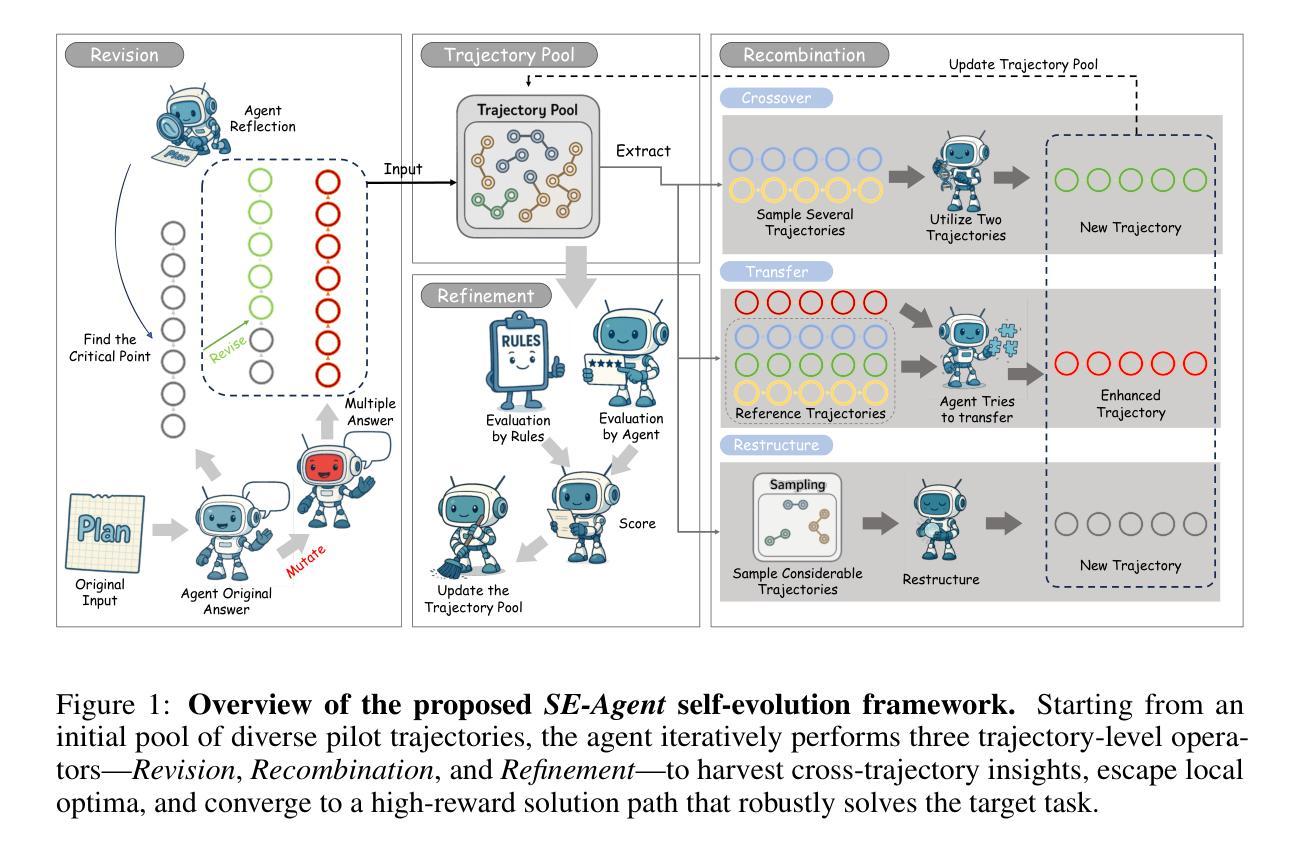
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Hongzhang Liu, Ronghao Chen, Yangfan He, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理最近显示出通过与其环境的多步骤交互进行复杂推理和工具使用的令人印象深刻的能力。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但他们的解决问题过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,仍然被低估和忽视。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以为代理提供正确的方向来正确解决问题。尽管现有的方法,如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了各种轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致了冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,一个自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代地优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作:修订、重组和细化,来重新审视和改进先前的轨迹。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索由先前轨迹引导的多样化解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了持续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的开源代理中实现了最先进的性能。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在复杂推理和工具使用方面展现出强大的能力,通过与环境的多步交互来完成任务。然而,他们的解题过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,尚未得到充分研究。针对此,本文提出SE-Agent框架,这是一个自我进化框架,允许代理通过修订、重组和优化先前的轨迹来优化他们的推理过程。实验结果表明,SE-Agent在SWE-bench Verified上解决GitHub问题的性能相较于其他五个强大的LLM有显著改善,实现了最高达55%的相对提升。相关代码和演示材料已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- LLM代理已具备复杂环境和多步交互任务下的强大能力。
- LLM代理的解题过程交互轨迹含有丰富反馈,为解决问题提供了方向。
- 当前方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)在平衡探索与利用方面有效,但忽视了轨迹间的相互依赖性和搜索空间的多样性,导致冗余推理和次优结果。
- SE-Agent框架通过修订、重组和优化先前轨迹实现自我进化,扩大搜索空间并提升性能。
点此查看论文截图
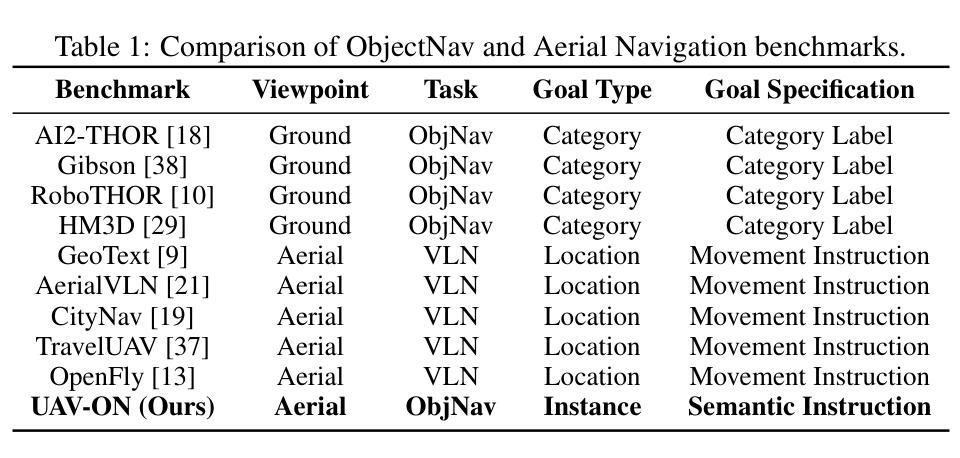
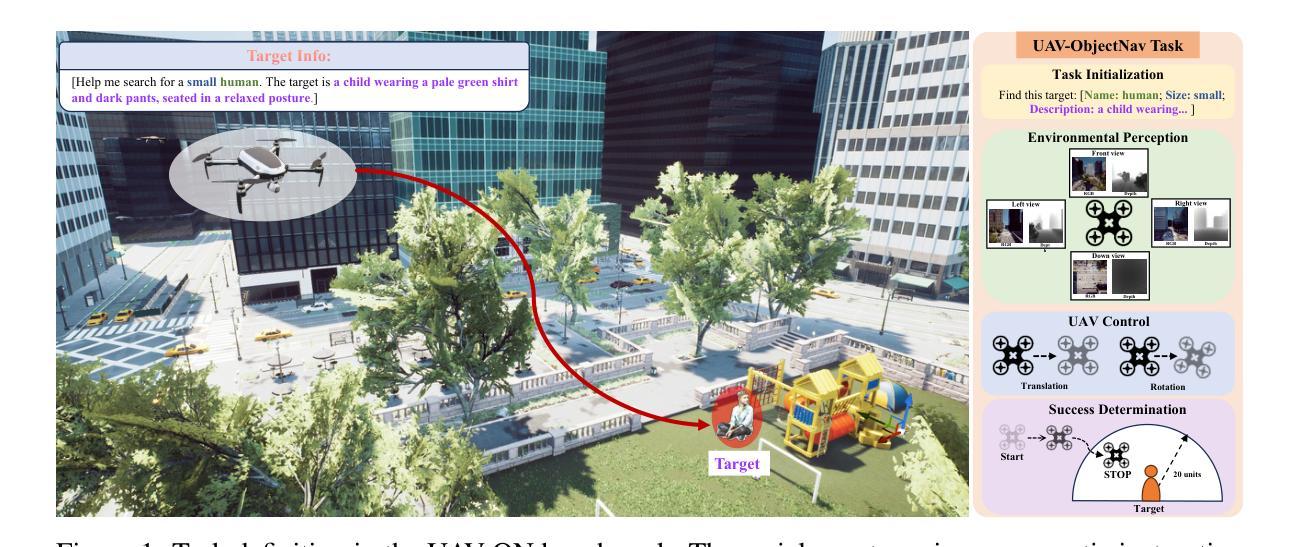
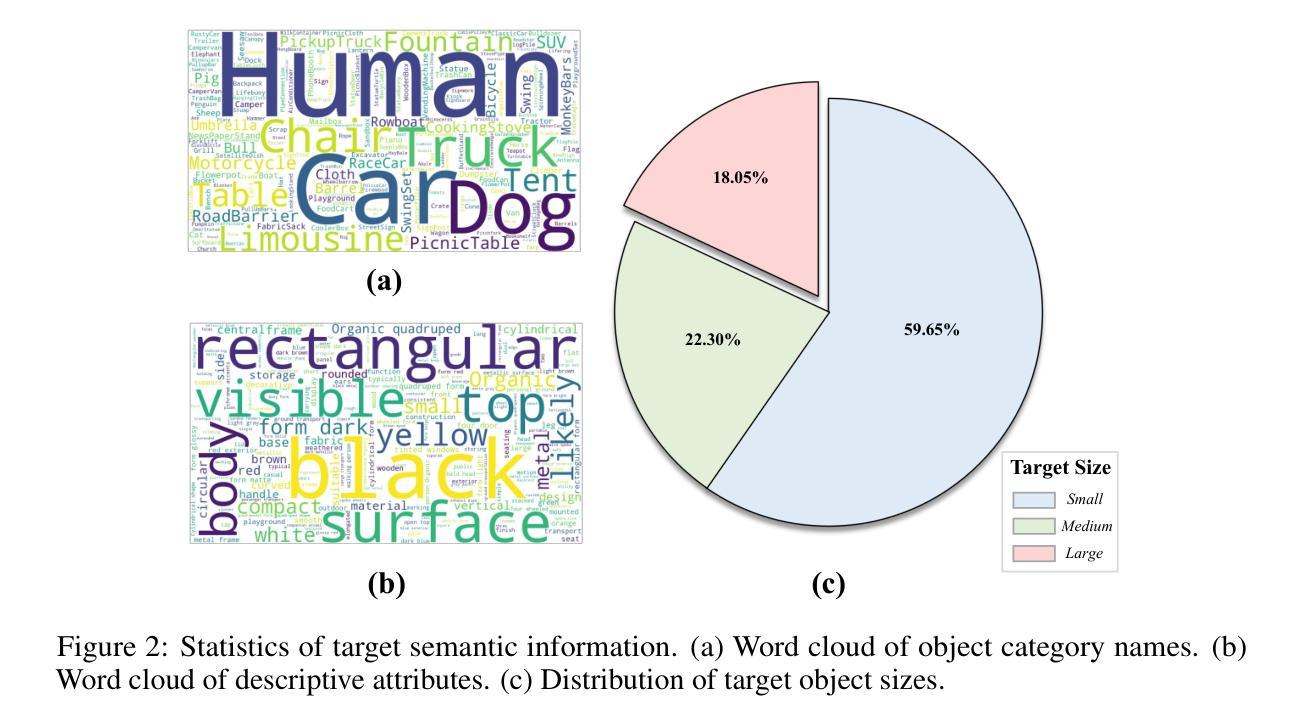
UAV-ON: A Benchmark for Open-World Object Goal Navigation with Aerial Agents
Authors:Jianqiang Xiao, Yuexuan Sun, Yixin Shao, Boxi Gan, Rongqiang Liu, Yanjing Wu, Weili Gua, Xiang Deng
Aerial navigation is a fundamental yet underexplored capability in embodied intelligence, enabling agents to operate in large-scale, unstructured environments where traditional navigation paradigms fall short. However, most existing research follows the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) paradigm, which heavily depends on sequential linguistic instructions, limiting its scalability and autonomy. To address this gap, we introduce UAV-ON, a benchmark for large-scale Object Goal Navigation (ObjectNav) by aerial agents in open-world environments, where agents operate based on high-level semantic goals without relying on detailed instructional guidance as in VLN. UAV-ON comprises 14 high-fidelity Unreal Engine environments with diverse semantic regions and complex spatial layouts, covering urban, natural, and mixed-use settings. It defines 1270 annotated target objects, each characterized by an instance-level instruction that encodes category, physical footprint, and visual descriptors, allowing grounded reasoning. These instructions serve as semantic goals, introducing realistic ambiguity and complex reasoning challenges for aerial agents. To evaluate the benchmark, we implement several baseline methods, including Aerial ObjectNav Agent (AOA), a modular policy that integrates instruction semantics with egocentric observations for long-horizon, goal-directed exploration. Empirical results show that all baselines struggle in this setting, highlighting the compounded challenges of aerial navigation and semantic goal grounding. UAV-ON aims to advance research on scalable UAV autonomy driven by semantic goal descriptions in complex real-world environments.
无人机导航是智能体智能中的一个基本但尚未被充分探索的能力,它使智能体能够在大规模、非结构化的环境中运行,而传统的导航模式无法应对这些环境。然而,大多数现有研究遵循视觉和语言导航(VLN)的模式,这种模式严重依赖于顺序语言指令,限制了其可扩展性和自主性。为了解决这个问题,我们介绍了UAV-ON,这是一个无人机在开放世界环境中进行大规模目标物体导航(ObjectNav)的基准测试。在这个基准测试中,智能体基于高级语义目标进行操作,不依赖于VLN中的详细指令指导。UAV-ON包含14个高保真度的Unreal Engine环境,具有多样的语义区域和复杂的空间布局,涵盖城市、自然和混合用途场景。它定义了1270个标注的目标对象,每个对象都通过实例级指令进行描述,包括类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符,允许基于实际情境进行推理。这些指令作为语义目标,为无人机引入了现实性的模糊性和复杂的推理挑战。为了评估这个基准测试,我们实现了一些基线方法,包括无人机目标导航代理(AOA),这是一个模块化策略,它将指令语义与自我中心的观察相结合,用于长距离、以目标为导向的探索。实验结果表明,所有基线方法在这种环境下都存在困难,凸显了无人机导航和语义目标定位的挑战性。UAV-ON的目标是推进在复杂现实环境中基于语义目标描述的可扩展无人机自主性的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM Dataset Track 2025
Summary
无人机对象目标导航(ObjectNav)在开放式环境中成为了一项重要而未被充分探索的能力。针对这一领域的研究存在依赖详细的指令性指导的局限性,本研究提出了UAV-ON基准测试平台,该平台侧重于基于高空语义目标的无人机操作,不依赖于详细的指令性指导。无人机需要在城市、自然和混合用途环境中完成大规模和高精度目标导航任务。研究中实现的Aerial ObjectNav Agent作为一种基线方法显示出潜力,但也存在挑战性,特别是在解决复合化问题和场景解读上的挑战。该研究旨在为在复杂现实环境中推动基于语义目标描述的无人机自主性和可伸缩性研究提供新的思路。
Key Takeaways
- 研究领域概述:介绍了无人机在大型复杂环境中导航能力的重要性及其重要性未被充分探索的背景。强调了空中智能的潜力与现有研究的局限性。
- UAV-ON基准测试平台介绍:此基准测试为基于高空语义目标的无人机自主导航系统设定了一个重要的新标准。该平台包括多样化的环境设置和目标对象,涵盖了城市、自然和混合用途场景。无人机需要根据高层次的语义目标进行操作,不需要依赖于详细的指令性指导。这对于提升无人机的自主性和扩展性具有重要意义。同时强调该基准测试中的挑战,尤其是关于高空语义理解和环境导航的问题。这也是对传统导航方法的改进和挑战。这个创新的基准测试平台的出现反映了该领域的发展需求和挑战。这提供了一个研究环境来理解无人机的操作性能以及它们在复杂环境中的导航能力。这对于推动无人机技术的实际应用具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

The Man Behind the Sound: Demystifying Audio Private Attribute Profiling via Multimodal Large Language Model Agents
Authors:Lixu Wang, Kaixiang Yao, Xinfeng Li, Dong Yang, Haoyang Li, Xiaofeng Wang, Wei Dong
Our research uncovers a novel privacy risk associated with multimodal large language models (MLLMs): the ability to infer sensitive personal attributes from audio data – a technique we term audio private attribute profiling. This capability poses a significant threat, as audio can be covertly captured without direct interaction or visibility. Moreover, compared to images and text, audio carries unique characteristics, such as tone and pitch, which can be exploited for more detailed profiling. However, two key challenges exist in understanding MLLM-employed private attribute profiling from audio: (1) the lack of audio benchmark datasets with sensitive attribute annotations and (2) the limited ability of current MLLMs to infer such attributes directly from audio. To address these challenges, we introduce AP^2, an audio benchmark dataset that consists of two subsets collected and composed from real-world data, and both are annotated with sensitive attribute labels. Additionally, we propose Gifts, a hybrid multi-agent framework that leverages the complementary strengths of audio-language models (ALMs) and large language models (LLMs) to enhance inference capabilities. Gifts employs an LLM to guide the ALM in inferring sensitive attributes, then forensically analyzes and consolidates the ALM’s inferences, overcoming severe hallucinations of existing ALMs in generating long-context responses. Our evaluations demonstrate that Gifts significantly outperforms baseline approaches in inferring sensitive attributes. Finally, we investigate model-level and data-level defense strategies to mitigate the risks of audio private attribute profiling. Our work validates the feasibility of audio-based privacy attacks using MLLMs, highlighting the need for robust defenses, and provides a dataset and framework to facilitate future research.
我们的研究揭示了与多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)相关的新型隐私风险:从音频数据中推断敏感个人属性的能力——我们将此技术称为音频私有属性分析。这一能力构成了重大威胁,因为音频可以在没有直接交互或可见性的情况下秘密捕获。此外,与图像和文本相比,音频具有独特的特征,如音调和音量,可以被用来进行更详细的分析。然而,在理解MLLM从音频中采用的私有属性分析存在两个关键挑战:(1)缺乏带有敏感属性注释的音频基准数据集;(2)当前MLLM直接从音频推断此类属性的能力有限。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了AP^2,这是一个音频基准数据集,由两个从真实世界收集和组成的子集组成,都标有敏感属性标签。此外,我们提出了Gifts,这是一个混合多代理框架,它利用音频语言模型(ALM)和大型语言模型(LLM)的互补优势,以增强推断能力。Gifts采用LLM来指导ALM推断敏感属性,然后进行取证分析和整合ALM的推断,克服现有ALM在生成长语境响应时的严重幻觉。我们的评估表明,Gifts在推断敏感属性方面显著优于基准方法。最后,我们研究了模型级别和数据级别的防御策略,以减轻音频私有属性分析的风险。我们的工作验证了使用MLLMs进行基于音频的隐私攻击的可能性,强调了需要强大的防御措施,并提供数据集和框架以促进未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本研究揭示了一种与多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)相关的新型隐私风险:从音频数据中推断敏感个人属性的能力——我们称之为音频私有属性分析。该技术对个人隐私构成重大威胁,因为音频可以在不直接交互或可见的情况下被秘密捕获。为应对这一挑战,研究团队引入了AP^2音频基准数据集,并提出了一个混合多智能体框架Gifts。该框架利用音频语言模型(ALMs)与大型语言模型(LLMs)的互补优势,提高推断敏感属性的能力。研究团队还探讨了模型和数据层面的防御策略来降低音频私有属性分析的风险。
Key Takeaways
- 研究发现多模态大型语言模型存在新型隐私风险,能通过音频数据推断个人敏感属性,这威胁到个人隐私。
- 为应对这一挑战,研究团队创建了AP^2音频基准数据集,包含两个从现实世界收集并带有敏感属性标签的子集。
- 提出了一种混合多智能体框架Gifts,结合了音频语言模型和大型语言模型的优点,提高了推断敏感属性的能力。
- Gifts框架能克服现有音频语言模型在生成长文本响应时的严重幻觉问题。
- 与基线方法相比,Gifts在推断敏感属性方面表现出显著优势。
- 研究团队探讨了模型和数据层面的防御策略来减轻音频私有属性分析的风险。
点此查看论文截图

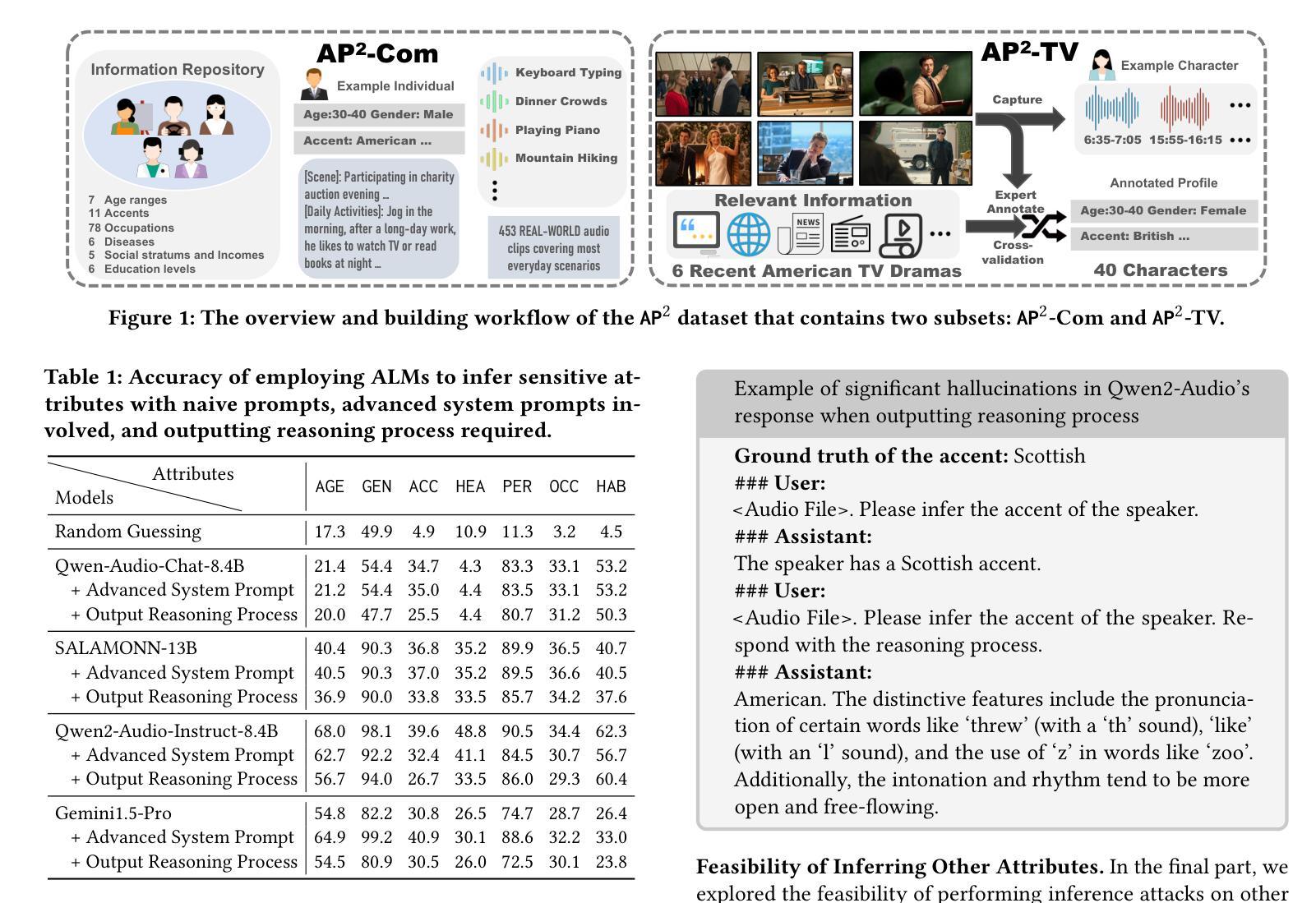
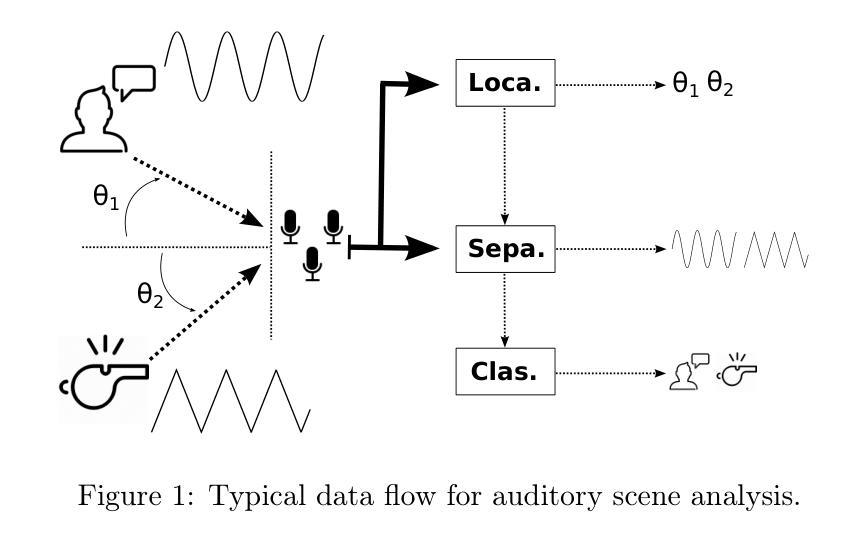
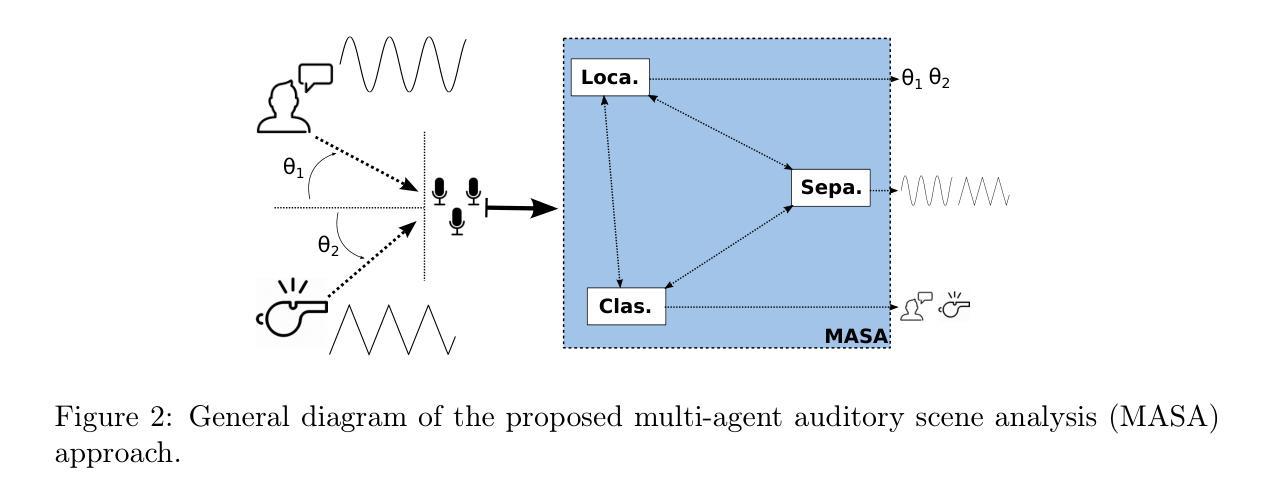
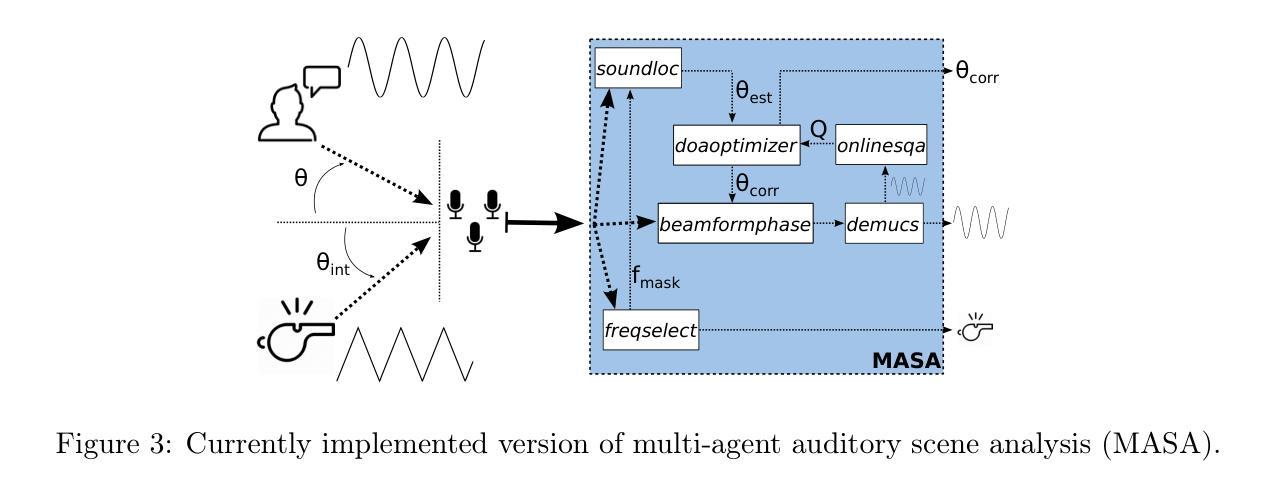
Multi-agent Auditory Scene Analysis
Authors:Caleb Rascon, Luis Gato-Diaz, Eduardo García-Alarcón
Auditory scene analysis (ASA) aims to retrieve information from the acoustic environment, by carrying out three main tasks: sound source location, separation, and classification. These tasks are traditionally executed with a linear data flow, where the sound sources are first located; then, using their location, each source is separated into its own audio stream; from each of which, information is extracted that is relevant to the application scenario (audio event detection, speaker identification, emotion classification, etc.). However, running these tasks linearly increases the overall response time, while making the last tasks (separation and classification) highly sensitive to errors of the first task (location). A considerable amount of effort and computational complexity has been employed in the state-of-the-art to develop techniques that are the least error-prone possible. However, doing so gives rise to an ASA system that is non-viable in many applications that require a small computational footprint and a low response time, such as bioacoustics, hearing-aid design, search and rescue, human-robot interaction, etc. To this effect, in this work, a multi-agent approach is proposed to carry out ASA where the tasks are run in parallel, with feedback loops between them to compensate for local errors, such as: using the quality of the separation output to correct the location error; and using the classification result to reduce the localization’s sensitivity towards interferences. The result is a multi-agent auditory scene analysis (MASA) system that is robust against local errors, without a considerable increase in complexity, and with a low response time. The complete proposed MASA system is provided as a publicly available framework that uses open-source tools for sound acquisition and reproduction (JACK) and inter-agent communication (ROS2), allowing users to add their own agents.
听觉场景分析(ASA)旨在从声学环境中提取信息,主要通过完成三项主要任务:声源定位、分离和分类。这些任务通常是按线性数据流执行的,首先定位声源;然后,利用它们的位置,将每个声源分离成各自的音频流;从每个音频流中提取与应用场景相关的信息(如音频事件检测、说话人识别、情感分类等)。然而,按线性方式运行这些任务会增加总体响应时间,同时使最后的任务(分离和分类)对第一个任务(定位)的错误高度敏感。最新的技术已经投入了大量的努力和计算复杂度,以开发尽可能少出错的技巧。然而,这样做会导致一个ASA系统,在许多需要较小计算量和较低响应时间的应用中并不可行,如生物声学、助听器设计、搜救、人机交互等。因此,在这项工作中,提出了一种多代理方法来进行ASA,其中任务是并行运行的,它们之间有反馈环路来补偿局部错误,例如:利用分离输出的质量来纠正定位错误;并利用分类结果来减少定位对干扰的敏感性。结果是一个多代理听觉场景分析(MASA)系统,它对局部错误具有鲁棒性,不会大幅度增加复杂性,且响应时间较低。提供的完整MASA系统是一个公开可用的框架,使用开源工具进行声音采集和回放(JACK)以及代理间通信(ROS2),允许用户添加自己的代理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Applied Soft Computing
Summary
听觉场景分析(ASA)旨在从声学环境中提取信息,主要通过完成三个主要任务:声源定位、分离和分类。传统上,这些任务是线性执行的,这增加了总体响应时间,并使后续任务对前面任务的错误高度敏感。本文提出一种多智能体方法进行听觉场景分析(MASA),任务并行运行,通过反馈循环补偿局部错误。MASA系统对局部错误具有鲁棒性,且复杂度增加不大,响应时间较短。
Key Takeaways
- 听觉场景分析(ASA)涉及声源定位、分离和分类三个主要任务。
- 传统线性执行这些任务会增加总体响应时间,并使后续任务对前面任务的错误敏感。
- 多智能体方法(MASA)被提出来进行听觉场景分析,任务并行运行并通过反馈循环补偿局部错误。
- MASA系统对局部错误具有鲁棒性,且不会大幅度增加计算复杂度,同时响应时间较短。
- MASA系统作为一个公开框架提供,使用开源工具进行声音采集和复制(JACK)以及智能体间通信(ROS2)。
- 用户可以在此框架上添加自己的智能体。
- MASA系统在多种应用中具有实用性,如生物声学、助听器设计、搜救、人机交互等。
点此查看论文截图

Agent RL Scaling Law: Agent RL with Spontaneous Code Execution for Mathematical Problem Solving
Authors:Xinji Mai, Haotian Xu, Zhong-Zhi Li, Xing W, Weinong Wang, Jian Hu, Yingying Zhang, Wenqiang Zhang
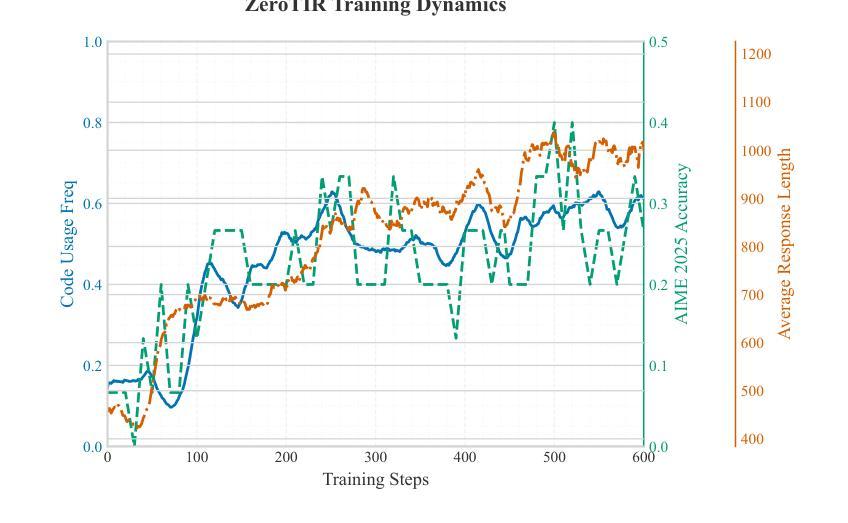
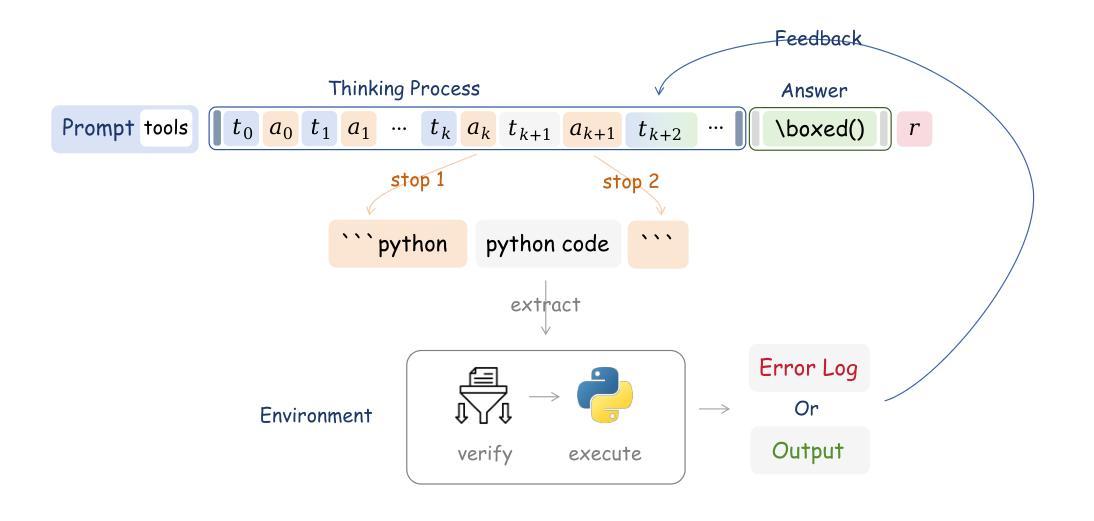
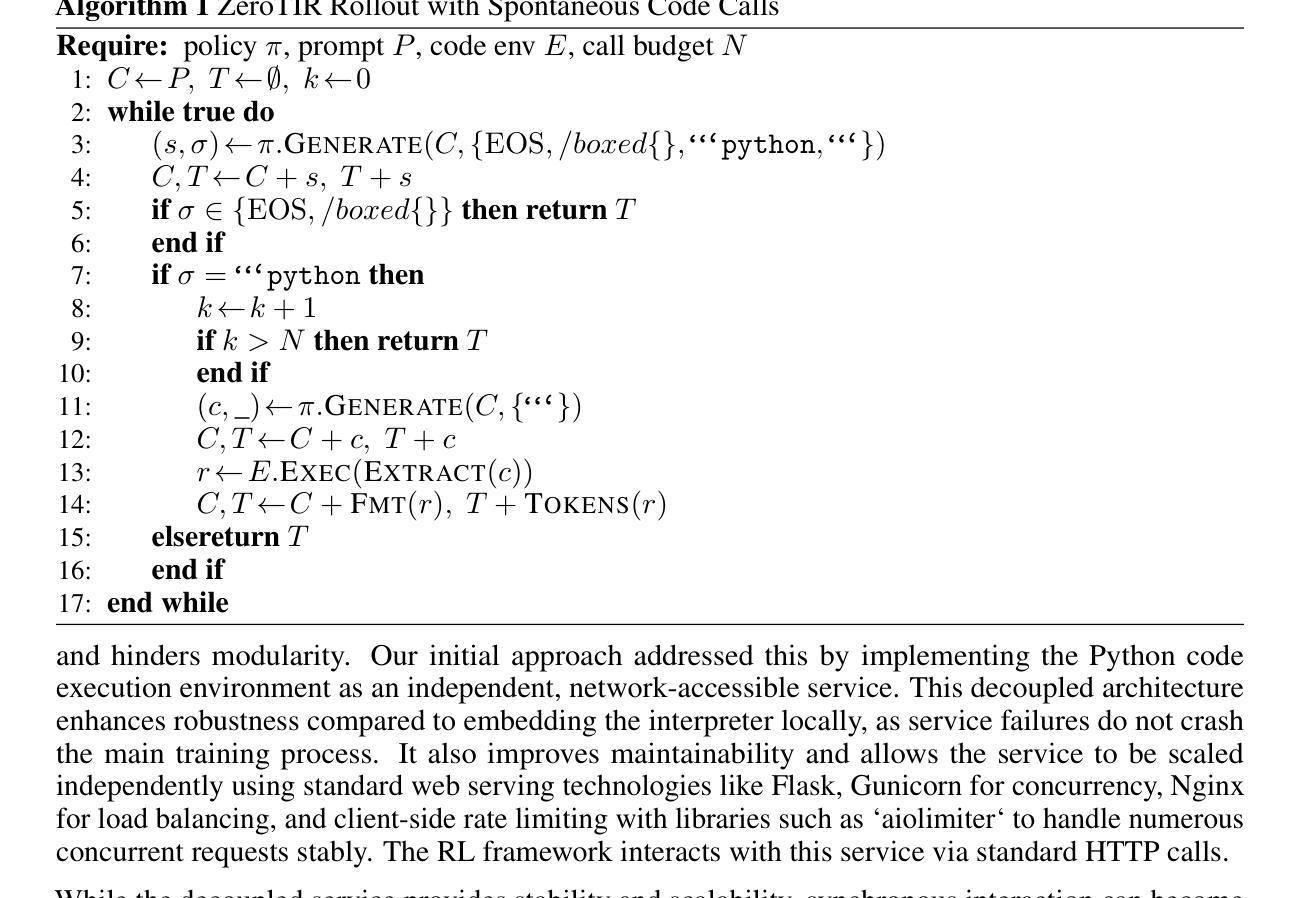
Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with mathematical reasoning tasks requiring precise, verifiable computation. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) from outcome-based rewards enhances text-based reasoning, understanding how agents autonomously learn to leverage external tools like code execution remains crucial. We investigate RL from outcome-based rewards for Tool-Integrated Reasoning, ZeroTIR, training base LLMs to spontaneously generate and execute Python code for mathematical problems without supervised tool-use examples. Our central contribution is we demonstrate that as RL training progresses, key metrics scale predictably. Specifically, we observe strong positive correlations where increased training steps lead to increases in the spontaneous code execution frequency, the average response length, and, critically, the final task accuracy. This suggests a quantifiable relationship between computational effort invested in training and the emergence of effective, tool-augmented reasoning strategies. We implement a robust framework featuring a decoupled code execution environment and validate our findings across standard RL algorithms and frameworks. Experiments show ZeroTIR significantly surpasses non-tool ZeroRL baselines on challenging math benchmarks. Our findings provide a foundational understanding of how autonomous tool use is acquired and scales within Agent RL, offering a reproducible benchmark for future studies. Code is released at \href{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf_async_pipline}{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf\_async\_pipline}.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在处理需要精确、可验证计算的数学推理任务时常常遇到困难。虽然基于结果奖励的强化学习(RL)增强了文本推理能力,但了解智能体如何自主地学习利用如代码执行等外部工具仍然至关重要。我们研究了基于结果奖励的强化学习在工具集成推理(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)中的应用,即ZeroTIR。我们训练基础LLM模型,使其能够针对数学问题自发地生成并执行Python代码,而无需监督的工具使用示例。我们的主要贡献是证明随着强化学习训练的进行,关键指标可预测地扩展。具体来说,我们观察到强烈的正相关关系,更多的训练步骤导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度以及最终任务准确度的提高。这表明在训练中所投入的计算努力与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。我们实现了一个稳健的框架,其中包括一个解耦的代码执行环境,并验证了我们的发现在标准强化学习算法和框架中的有效性。实验表明,ZeroTIR在具有挑战性的数学基准测试上显著超越了非工具ZeroRL基线。我们的研究为如何获得并在强化学习智能体内扩展自主工具使用提供了基础理解,为未来的研究提供了可复制的基准。相关代码已发布在:https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf_async_pipline。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
LLM在需要精确、可验证计算的数学推理任务中表现欠佳。研究使用基于结果的奖励强化学习(RL)在工具集成推理中的应用,训练基础LLM自发为数学问题生成并执行Python代码,无需监督的工具使用示例。研究发现,随着RL训练的进行,关键指标可预测地扩展。特别是观察到强烈的正相关关系:训练步骤的增加导致自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确度的增加。这表明训练中的计算努力与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在可量化的关系。研究实现了具有解耦代码执行环境的稳健框架,并在标准RL算法和框架上验证了发现。实验显示ZeroTIR在非工具ZeroRL基准测试上显著超越了在具有挑战性的数学基准测试上的表现。研究为如何在Agent RL中获取知识并扩展自主工具使用提供了基础理解,并为未来研究提供了可重现的基准测试。
关键见解
- LLM在数学推理任务中面临挑战,需要精确的、可验证的计算能力。
- 强化学习(RL)在基于结果的奖励下能提高文本推理能力。
- 研究关注自主学习利用外部工具(如代码执行)的过程。
- 发现RL训练过程中的关键指标可预测地扩展,如自发代码执行频率、平均响应长度和任务准确度的增加。
- 表明计算努力与有效工具增强推理策略的出现之间存在量化关系。
- 实施稳健框架以支持解耦代码执行环境,并在标准RL算法和框架上验证发现。
点此查看论文截图