⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
TransLight: Image-Guided Customized Lighting Control with Generative Decoupling
Authors:Zongming Li, Lianghui Zhu, Haocheng Shen, Longjin Ran, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang
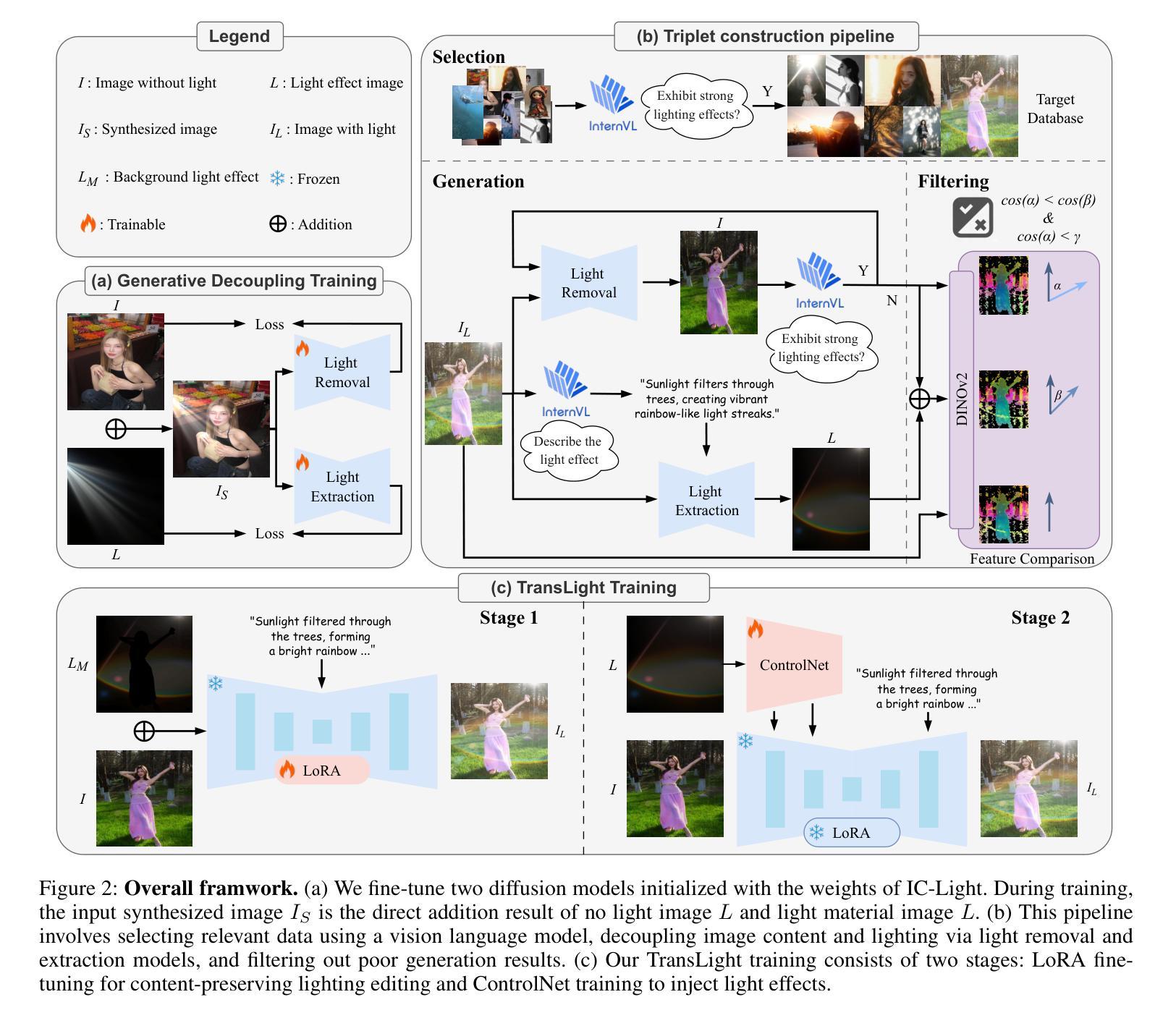
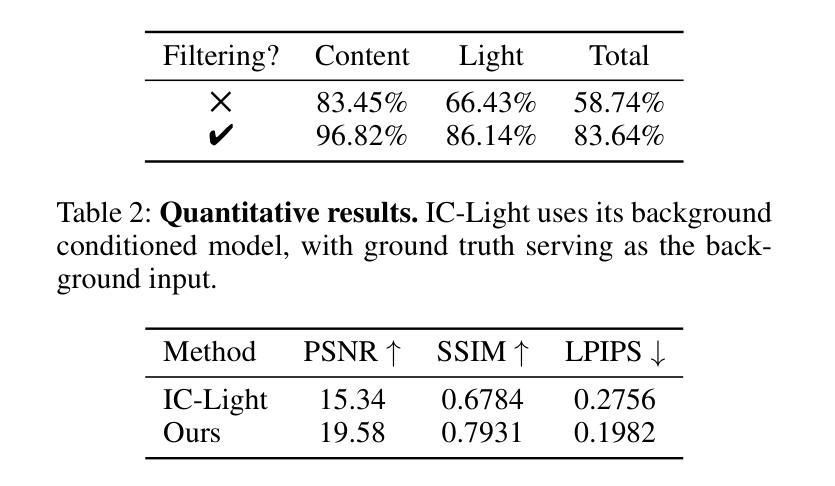
Most existing illumination-editing approaches fail to simultaneously provide customized control of light effects and preserve content integrity. This makes them less effective for practical lighting stylization requirements, especially in the challenging task of transferring complex light effects from a reference image to a user-specified target image. To address this problem, we propose TransLight, a novel framework that enables high-fidelity and high-freedom transfer of light effects. Extracting the light effect from the reference image is the most critical and challenging step in our method. The difficulty lies in the complex geometric structure features embedded in light effects that are highly coupled with content in real-world scenarios. To achieve this, we first present Generative Decoupling, where two fine-tuned diffusion models are used to accurately separate image content and light effects, generating a newly curated, million-scale dataset of image-content-light triplets. Then, we employ IC-Light as the generative model and train our model with our triplets, injecting the reference lighting image as an additional conditioning signal. The resulting TransLight model enables customized and natural transfer of diverse light effects. Notably, by thoroughly disentangling light effects from reference images, our generative decoupling strategy endows TransLight with highly flexible illumination control. Experimental results establish TransLight as the first method to successfully transfer light effects across disparate images, delivering more customized illumination control than existing techniques and charting new directions for research in illumination harmonization and editing.
现有的大多数光照编辑方法未能同时实现对光效的自定义控制和内容完整性的保持,这使得它们在满足实际光照风格化要求方面效果较差,尤其是在将复杂的光效从参考图像转移到用户指定的目标图像这一具有挑战性的任务中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了TransLight,一个能够实现高保真和高自由度光效转移的新型框架。从参考图像中提取光效是我们方法中最关键且最具挑战性的步骤。其难度在于光效中嵌入的复杂几何结构特征与现实世界场景中的内容高度耦合。为了实现这一点,我们首先提出了生成解耦的方法,使用两个经过微调的分扩散模型来准确分离图像内容和光效,生成一个新的、规模达百万级别的图像-内容-光效三元组数据集。然后,我们将IC-Light作为生成模型,用我们的三元组数据集来训练我们的模型,并将参考照明图像作为额外的条件信号注入。由此产生的TransLight模型能够实现定制和自然的各种光效转移。值得注意的是,通过彻底地将光效从参考图像中分离出来,我们的生成解耦策略使TransLight具备了高度灵活的光照控制。实验结果证明,TransLight是第一种成功在不同图像间转移光效的方法,它提供了比现有技术更定制化的照明控制,并为光照和谐和编辑研究开辟了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为TransLight的新型框架,用于实现高保真和高自由度的光效转移。该框架通过采用生成性解耦策略,利用两个精细调整的扩散模型准确分离图像内容和光效,实现光效从参考图像到目标图像的转移。此策略使TransLight具有高度的照明控制灵活性,能够成功地在不同图像间转移光效。
Key Takeaways
- 现有照明编辑方法无法同时实现定制的光效控制和内容完整性的保持,使得它们在满足实际照明风格化要求方面效果有限。
- TransLight框架被提出,旨在解决上述问题,并实现高保真和高自由度的光效转移。
- 生成性解耦策略是TransLight的核心,利用两个精细调整的扩散模型来分离图像内容、生成新的图像-内容-光效三元组数据集。
- IC-Light作为生成模型,通过注入参考照明图像作为附加条件信号来训练模型。
- TransLight能够实现对不同光效的定制和自然转移。
- 通过彻底地解耦参考图像中的光效,TransLight具有高度灵活的照明控制。
点此查看论文截图


Tinker: Diffusion’s Gift to 3D–Multi-View Consistent Editing From Sparse Inputs without Per-Scene Optimization
Authors:Canyu Zhao, Xiaoman Li, Tianjian Feng, Zhiyue Zhao, Hao Chen, Chunhua Shen
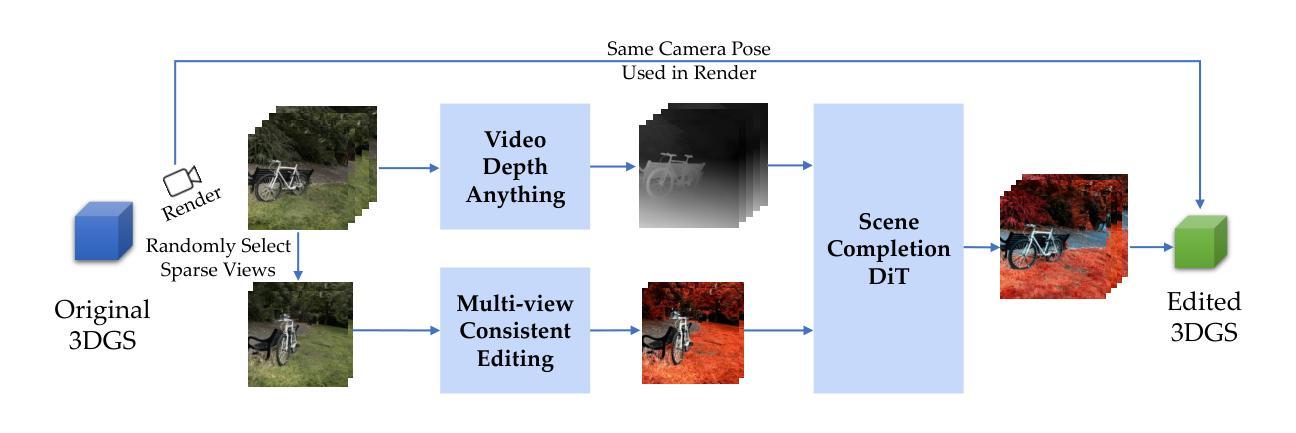
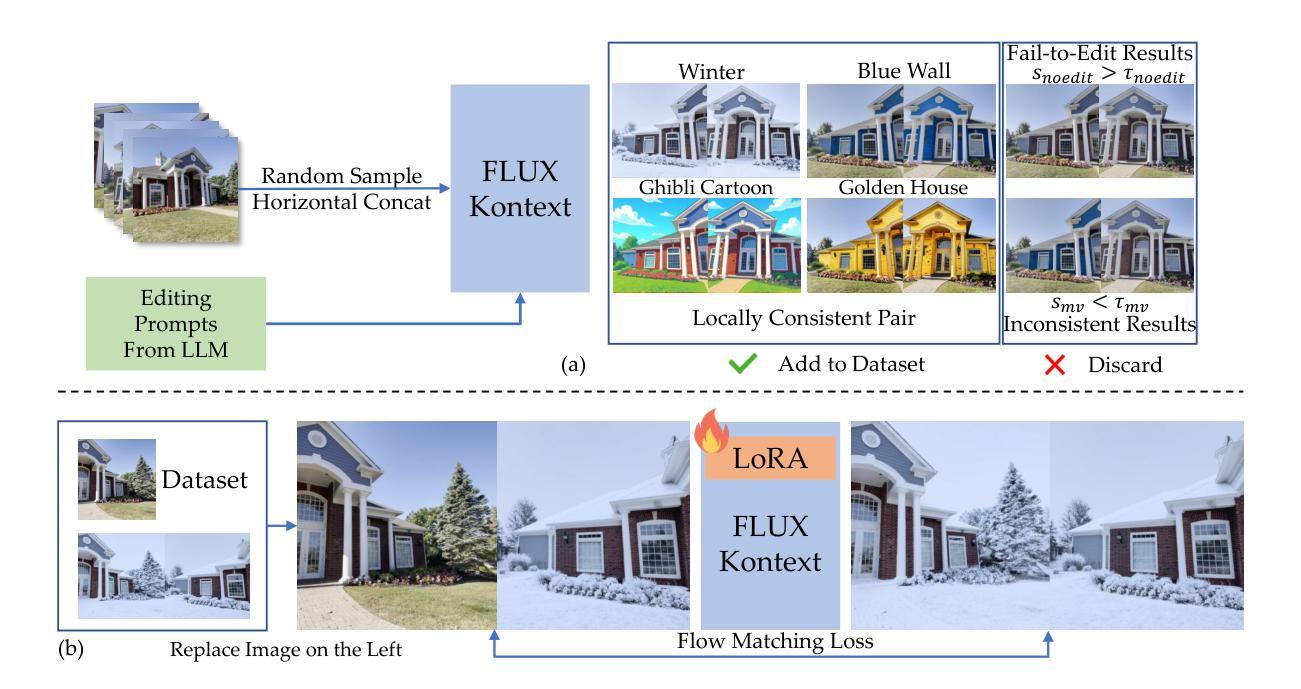
We introduce Tinker, a versatile framework for high-fidelity 3D editing that operates in both one-shot and few-shot regimes without any per-scene finetuning. Unlike prior techniques that demand extensive per-scene optimization to ensure multi-view consistency or to produce dozens of consistent edited input views, Tinker delivers robust, multi-view consistent edits from as few as one or two images. This capability stems from repurposing pretrained diffusion models, which unlocks their latent 3D awareness. To drive research in this space, we curate the first large-scale multi-view editing dataset and data pipeline, spanning diverse scenes and styles. Building on this dataset, we develop our framework capable of generating multi-view consistent edited views without per-scene training, which consists of two novel components: (1) Referring multi-view editor: Enables precise, reference-driven edits that remain coherent across all viewpoints. (2) Any-view-to-video synthesizer: Leverages spatial-temporal priors from video diffusion to perform high-quality scene completion and novel-view generation even from sparse inputs. Through extensive experiments, Tinker significantly reduces the barrier to generalizable 3D content creation, achieving state-of-the-art performance on editing, novel-view synthesis, and rendering enhancement tasks. We believe that Tinker represents a key step towards truly scalable, zero-shot 3D editing. Project webpage: https://aim-uofa.github.io/Tinker
我们介绍了Tinker,这是一个通用框架,用于进行高保真度的3D编辑,它可以在单镜头和少镜头模式下运行,无需针对每个场景进行微调。与需要广泛针对每个场景进行优化以确保多视角一致性或生成数十个一致编辑输入视角的先前技术不同,Tinker仅从一张或两张图像就能实现稳健、多视角一致编辑。这种能力来源于对预训练扩散模型的再利用,这解锁了它们的潜在三维感知能力。为了推动这一领域的研究,我们整理的第一个大规模多视角编辑数据集和数据管道,涵盖了各种场景和风格。基于这个数据集,我们开发了一个框架,能够在没有针对每个场景训练的情况下生成多视角一致编辑的视图,它由两个新颖的部分组成:(1)引用多视角编辑器:实现精确、参考驱动的编辑,保持所有观点的一致性。(2)任意视角视频合成器:利用视频扩散的空间时间先验知识,即使从稀疏输入也能实现高质量的场景补全和新颖视角生成。通过大量实验,Tinker大大降低了通用3D内容创作的障碍,在编辑、新颖视角合成和渲染增强任务上达到了最先进的性能。我们相信,Tinker是朝着真正可扩展的零镜头3D编辑迈出的关键一步。项目网页:https://aim-uofa.github.io/Tinker
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project webpage: https://aim-uofa.github.io/Tinker
Summary
Tinker是一个通用框架,用于高保真3D编辑,它可以在一次拍摄和少数几次拍摄的情况下进行操作,无需对每一个场景进行微调。借助预训练的扩散模型,它实现了强大的多视角一致性编辑。该框架包含两个新颖组件:参照多视角编辑器和任意视角视频合成器。Tinker显著降低了通用3D内容创作的门槛,并在编辑、新视角合成和渲染增强任务上达到了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Tinker是一个适用于高保真3D编辑的通用框架,可在一次拍摄和少数几次拍摄的情况下操作,无需对每个场景进行微调。
- Tinker利用预训练的扩散模型实现强大的多视角一致性编辑。
- 框架包含两个新颖组件:参照多视角编辑器,实现精确、参考驱动的编辑,保持所有视点的连贯性;任意视角视频合成器,利用视频扩散的空间时间先验信息进行高质量场景补全和新视角生成,即使从稀疏输入也能实现。
- Tinker显著降低了通用3D内容创作的门槛。
- Tinker在编辑、新视角合成和渲染增强任务上表现卓越。
- Tinker代表了一个关键步骤,朝着真正可扩展的零射击3D编辑方向发展。
点此查看论文截图


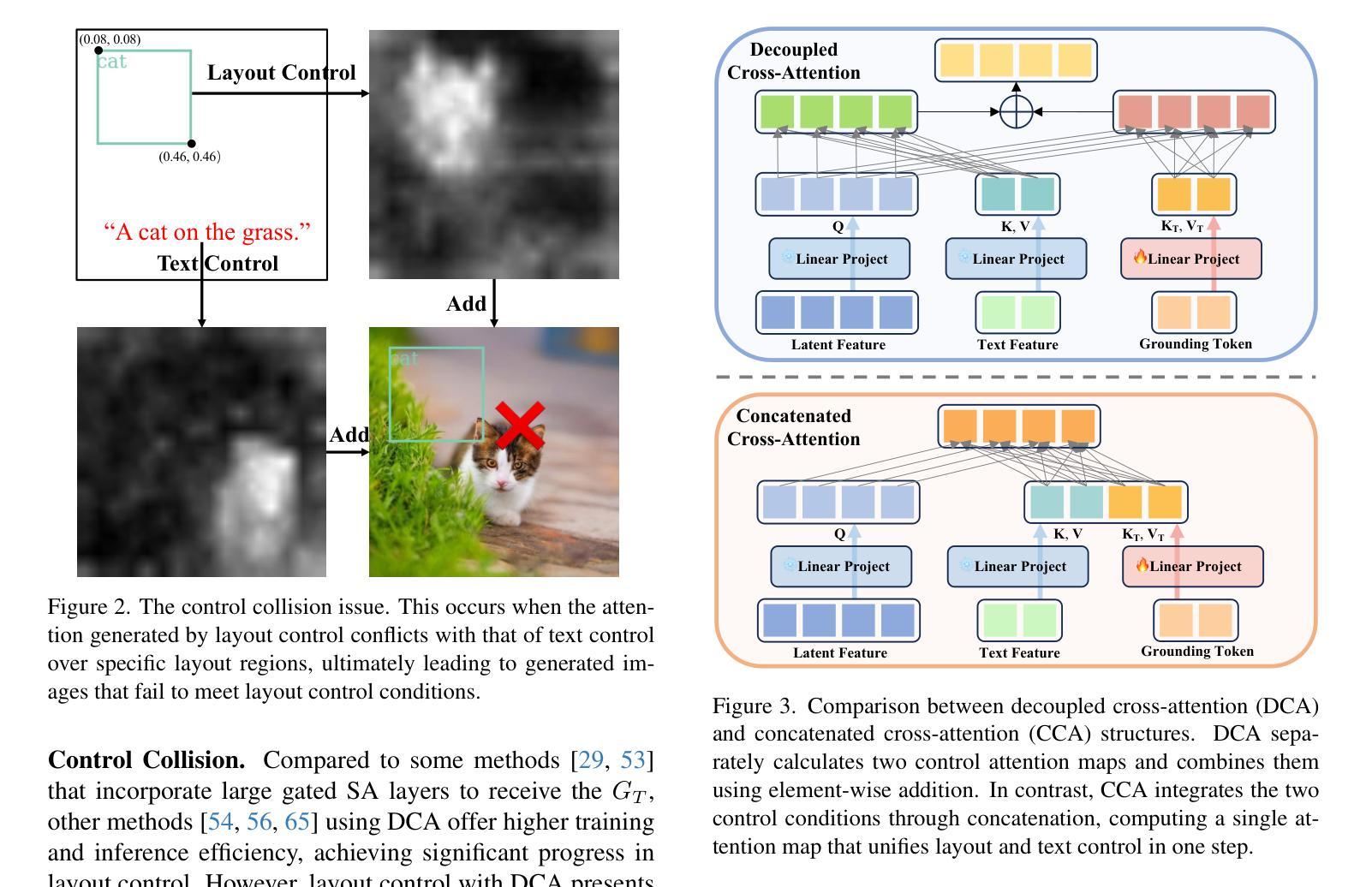
MUSE: Multi-Subject Unified Synthesis via Explicit Layout Semantic Expansion
Authors:Fei Peng, Junqiang Wu, Yan Li, Tingting Gao, Di Zhang, Huiyuan Fu
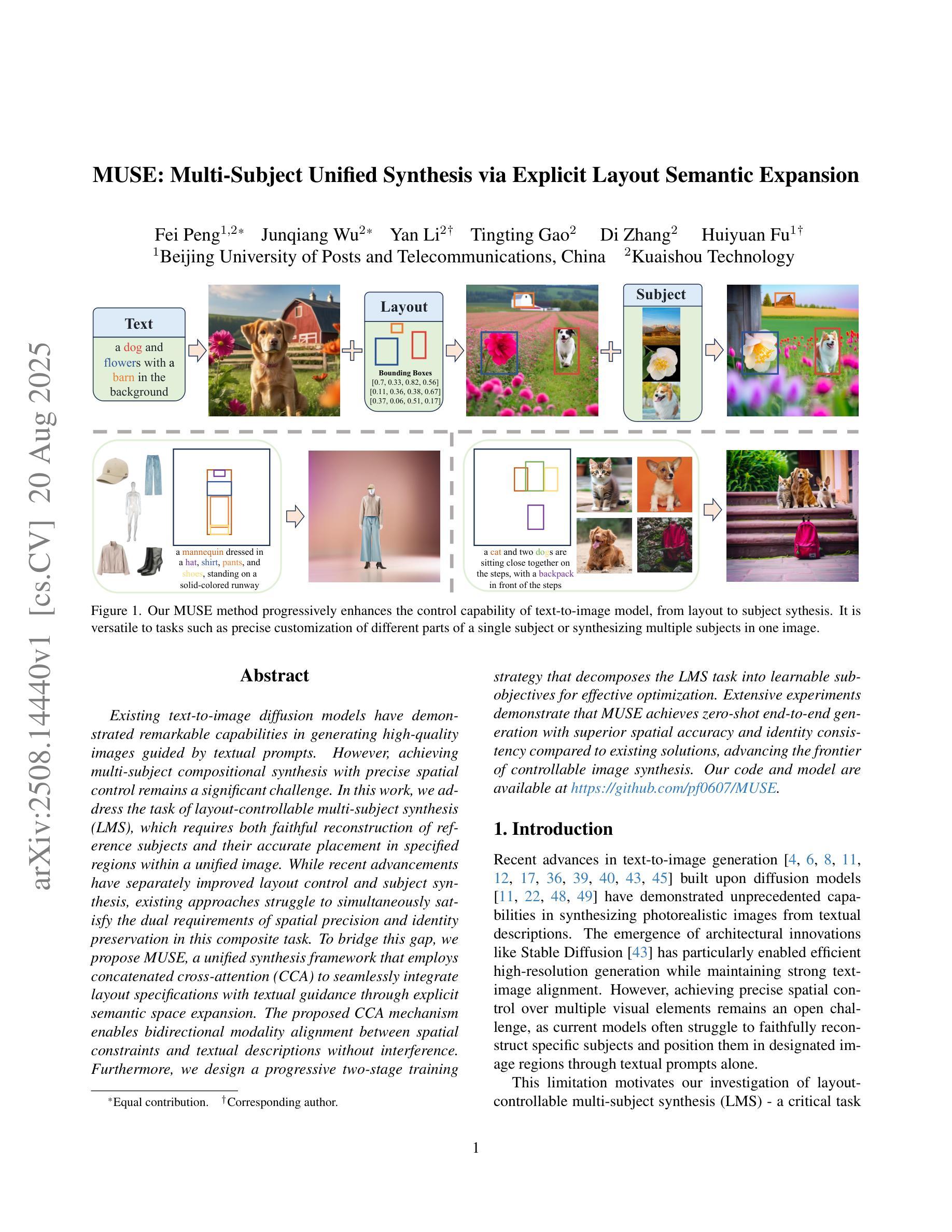
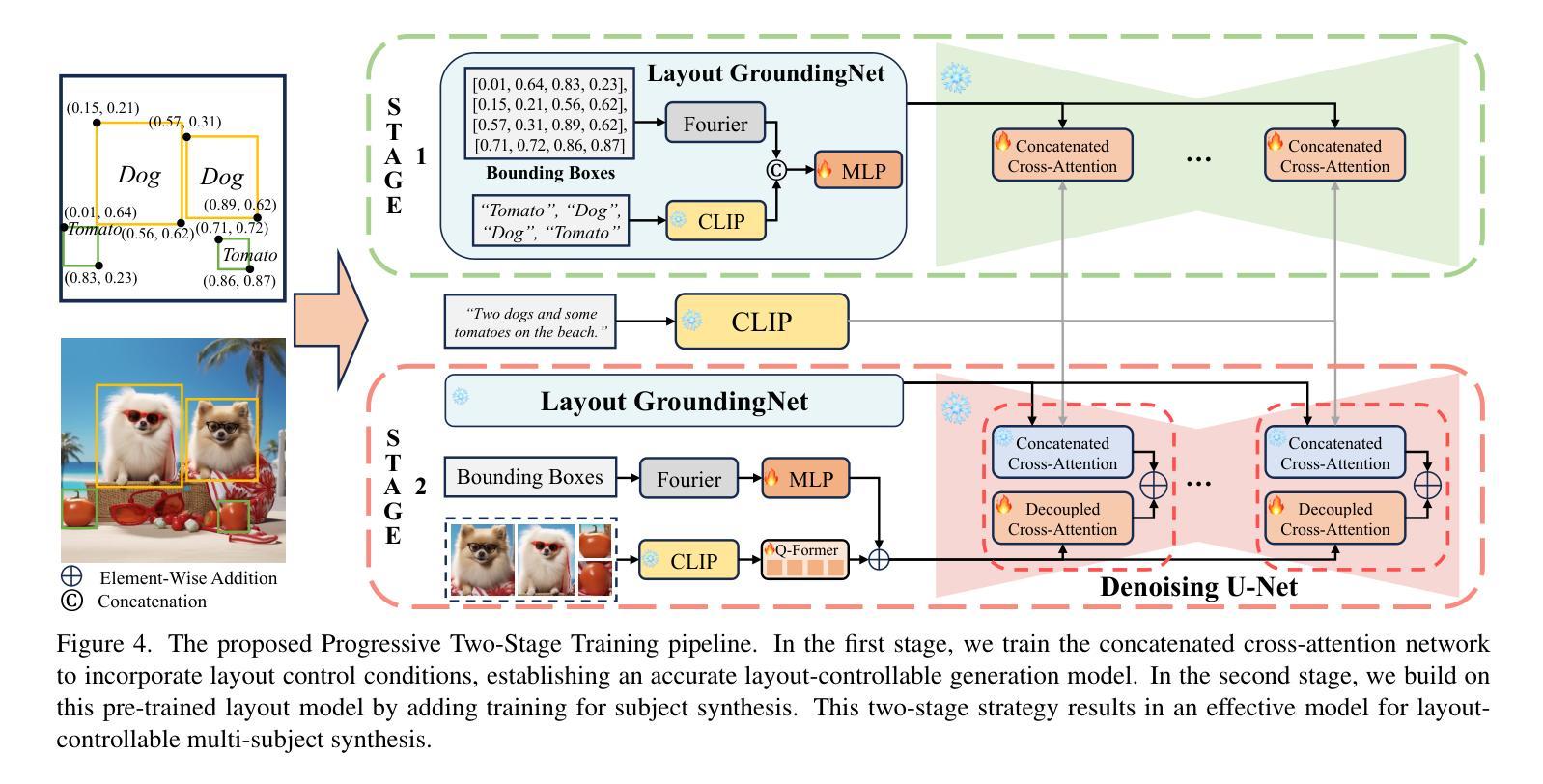
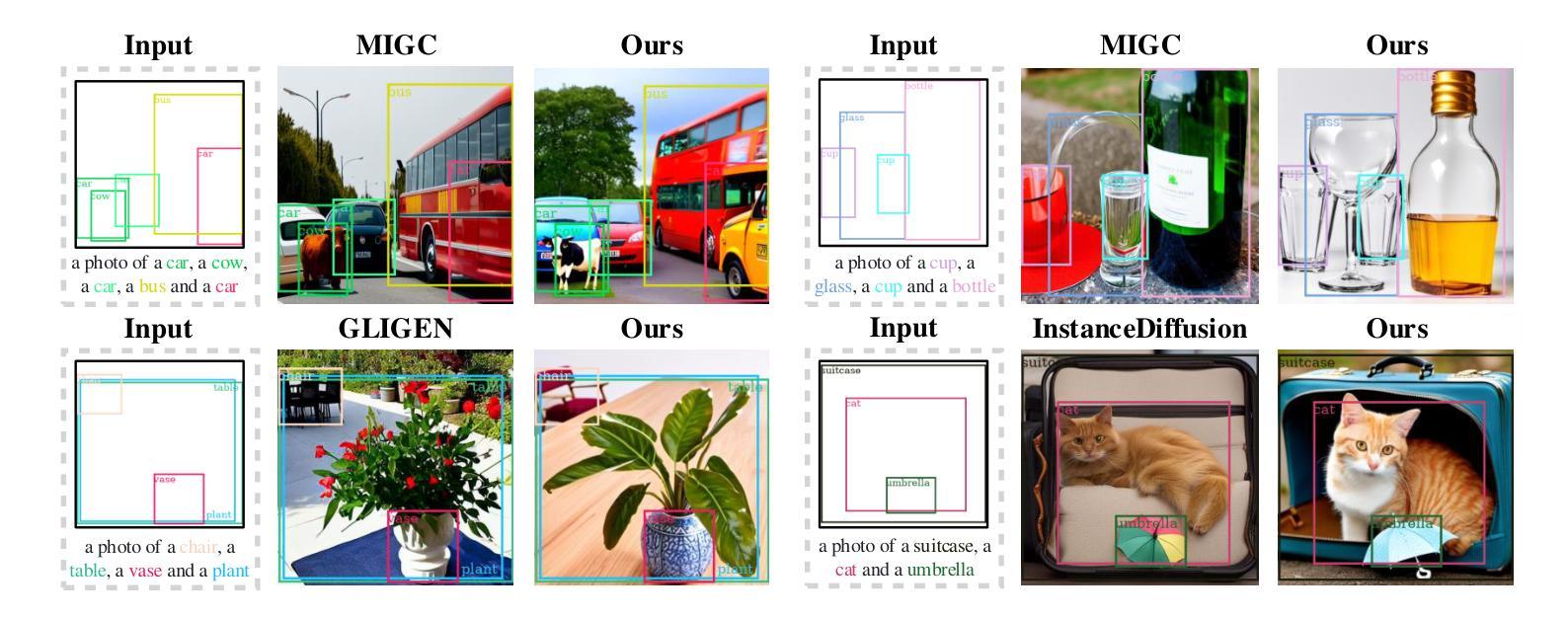
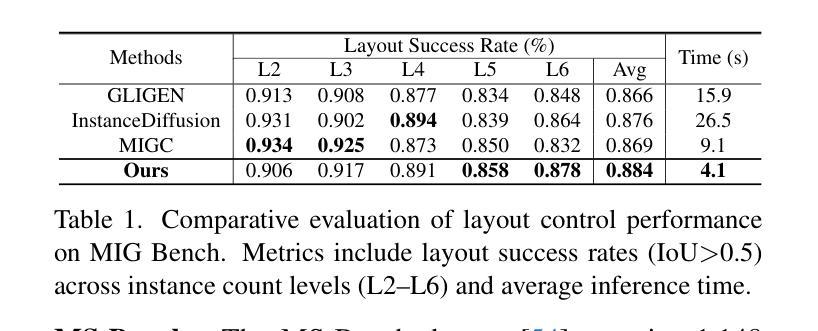
Existing text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality images guided by textual prompts. However, achieving multi-subject compositional synthesis with precise spatial control remains a significant challenge. In this work, we address the task of layout-controllable multi-subject synthesis (LMS), which requires both faithful reconstruction of reference subjects and their accurate placement in specified regions within a unified image. While recent advancements have separately improved layout control and subject synthesis, existing approaches struggle to simultaneously satisfy the dual requirements of spatial precision and identity preservation in this composite task. To bridge this gap, we propose MUSE, a unified synthesis framework that employs concatenated cross-attention (CCA) to seamlessly integrate layout specifications with textual guidance through explicit semantic space expansion. The proposed CCA mechanism enables bidirectional modality alignment between spatial constraints and textual descriptions without interference. Furthermore, we design a progressive two-stage training strategy that decomposes the LMS task into learnable sub-objectives for effective optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MUSE achieves zero-shot end-to-end generation with superior spatial accuracy and identity consistency compared to existing solutions, advancing the frontier of controllable image synthesis. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/pf0607/MUSE.
现有的文本到图像的扩散模型已在由文本提示引导生成高质量图像方面表现出显著的能力。然而,实现具有精确空间控制的多主题组合合成仍然是一个重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们解决了布局可控多主题合成(LMS)的任务,该任务要求忠实地重建参考主题,并将它们准确放置在统一图像的指定区域内。虽然最近的进步已经分别提高了布局控制和主题合成的效果,但现有方法在这项组合任务中同时满足空间精度和身份保留的双重要求时仍然感到困难。为了弥合这一差距,我们提出了MUSE,这是一个采用串联交叉注意(CCA)的统一合成框架,通过显式语义空间扩展无缝地将布局规范与文本指导相结合。所提出的CCA机制实现了空间约束和文本描述之间的双向模态对齐,不会相互干扰。此外,我们设计了一种分阶段的两阶段训练策略,将LMS任务分解为可学习的子目标,以实现有效的优化。大量实验表明,MUSE实现了与现有解决方案相比具有卓越的空间精度和身份一致性的零样本端到端生成。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/pf060a7/MUSE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为MUSE的统一合成框架,用于解决布局可控的多主题合成(LMS)任务。该框架通过采用串联交叉注意力(CCA)机制,将布局规范与文本指导无缝集成,实现空间约束与文本描述之间的双向模态对齐。MUSE框架能够在零样本端到端生成中实现出色的空间准确性和身份一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有文本到图像的扩散模型在高质量图像生成方面表现出色,但在具有精确空间控制的多主题合成方面仍存在挑战。
- MUSE框架解决了布局可控的多主题合成(LMS)任务,该任务需要忠实重建参考主题并将它们准确放置在统一图像的指定区域。
- MUSE采用串联交叉注意力(CCA)机制,将布局规范和文本指导无缝集成,实现空间约束和文本描述之间的双向模态对齐,解决了现有方法的不足。
- MUSE设计了一种渐进的两阶段训练策略,将LMS任务分解成可学习的子目标,实现有效优化。
- 实验表明,MUSE在零样本端到端生成中实现了卓越的空间准确性和身份一致性,相较于现有解决方案有所突破。
- MUSE框架的代码和模型已公开发布,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图
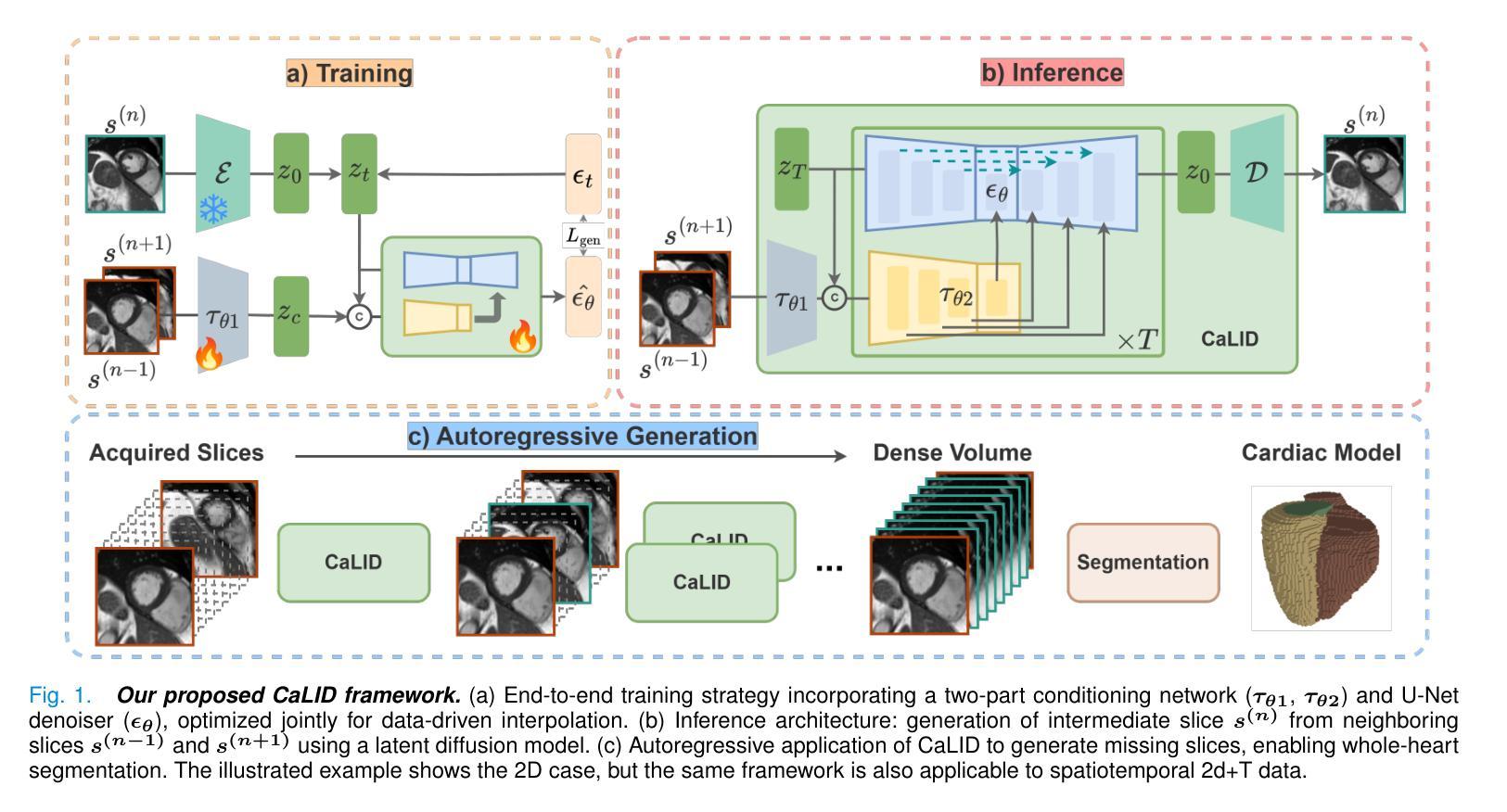
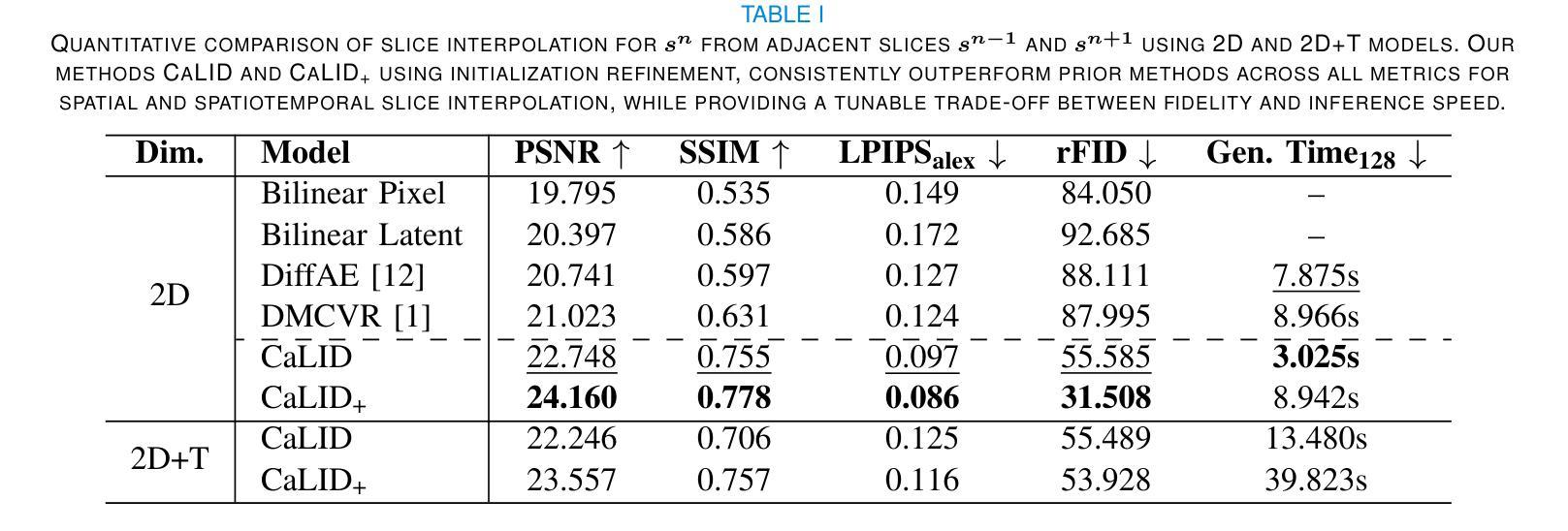
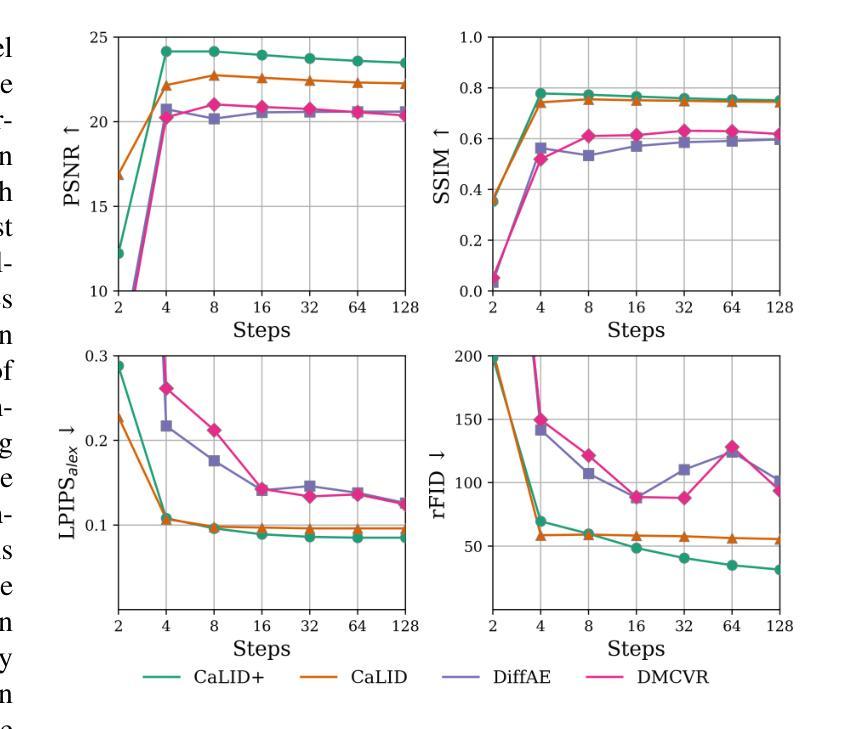
Latent Interpolation Learning Using Diffusion Models for Cardiac Volume Reconstruction
Authors:Niklas Bubeck, Suprosanna Shit, Chen Chen, Can Zhao, Pengfei Guo, Dong Yang, Georg Zitzlsberger, Daguang Xu, Bernhard Kainz, Daniel Rueckert, Jiazhen Pan
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging is a critical tool for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular disease, yet its utility is often limited by the sparse acquisition of 2D short-axis slices, resulting in incomplete volumetric information. Accurate 3D reconstruction from these sparse slices is essential for comprehensive cardiac assessment, but existing methods face challenges, including reliance on predefined interpolation schemes (e.g., linear or spherical), computational inefficiency, and dependence on additional semantic inputs such as segmentation labels or motion data. To address these limitations, we propose a novel \textbf{Ca}rdiac \textbf{L}atent \textbf{I}nterpolation \textbf{D}iffusion (CaLID) framework that introduces three key innovations. First, we present a data-driven interpolation scheme based on diffusion models, which can capture complex, non-linear relationships between sparse slices and improves reconstruction accuracy. Second, we design a computationally efficient method that operates in the latent space and speeds up 3D whole-heart upsampling time by a factor of 24, reducing computational overhead compared to previous methods. Third, with only sparse 2D CMR images as input, our method achieves SOTA performance against baseline methods, eliminating the need for auxiliary input such as morphological guidance, thus simplifying workflows. We further extend our method to 2D+T data, enabling the effective modeling of spatiotemporal dynamics and ensuring temporal coherence. Extensive volumetric evaluations and downstream segmentation tasks demonstrate that CaLID achieves superior reconstruction quality and efficiency. By addressing the fundamental limitations of existing approaches, our framework advances the state of the art for spatio and spatiotemporal whole-heart reconstruction, offering a robust and clinically practical solution for cardiovascular imaging.
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在心血管疾病的诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用,但其效用往往受到二维短轴切片稀疏采集的限制,导致体积信息不完整。从稀疏切片进行准确的3D重建对于全面的心脏评估至关重要,但现有方法面临挑战,包括依赖预定义的插值方案(例如线性或球形插值)、计算效率低下以及对额外的语义输入(如分割标签或运动数据)的依赖。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新颖的Cardiac Latent Interpolation Diffusion(CaLID)框架,该框架引入了三项关键创新。首先,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的数据驱动插值方案,该方案可以捕捉稀疏切片之间的复杂非线性关系,提高重建精度。其次,我们设计了一种在潜在空间中进行操作的高效计算方法,将心脏整体3D上采样时间缩短了24倍,与以前的方法相比减少了计算开销。第三,我们的方法仅使用稀疏的二维心脏磁共振图像作为输入,无需辅助输入(如形态指导),与基线方法相比取得了先进性能表现。我们进一步将我们的方法扩展到二维+T数据,有效地对时空动态进行建模,确保时间连贯性。广泛的体积评估和下游分割任务证明,CaLID在重建质量和效率方面都达到了卓越的水平。通过解决现有方法的基本局限性,我们的框架在空间和时空心脏重建方面推动了最新技术进展,为心血管成像提供了稳健且实用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在诊断和治疗心血管疾病中至关重要,但其效用常受限于二维短轴切片的稀疏采集,导致体积信息不完整。针对这一问题,我们提出了全新的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架,具有数据驱动插值方案、潜在空间的高效运算方法,以及仅依赖稀疏的二维CMR图像即可达到优越性能等优点。此框架突破了现有方法的局限,提升了重建质量和效率,实现了时空心脏重建的最新进展。
Key Takeaways
- CMR成像在心血管疾病的诊断和管理中扮演重要角色,但受限于二维切片的稀疏采集导致的体积信息不完整问题。
- 现有重建方法面临的挑战包括依赖预设插值方案、计算效率低下以及对额外语义输入的依赖。
- CaLID框架引入数据驱动插值方案,能捕捉稀疏切片间的复杂非线性关系,提高重建精度。
- 该框架设计了一种潜在空间的高效运算方法,将心脏三维上采样的时间提高了24倍。
- 仅需稀疏的二维CMR图像作为输入,CaLID即可达到卓越性能,无需辅助输入,简化了工作流程。
- CaLID框架进一步扩展到二维加时间数据,实现了时空动力学的有效建模和时间的连贯性。
点此查看论文截图
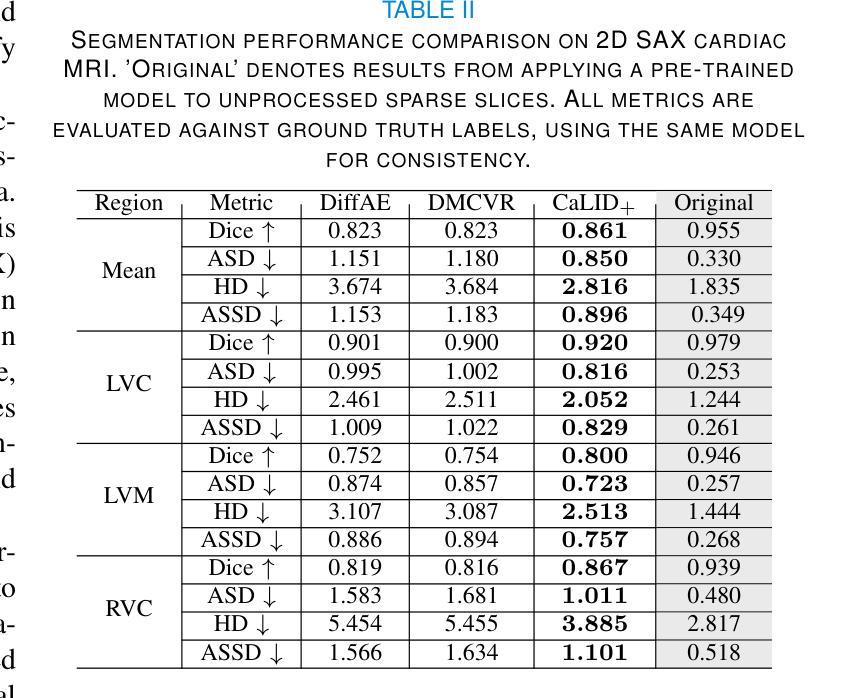
DiffIER: Optimizing Diffusion Models with Iterative Error Reduction
Authors:Ao Chen, Lihe Ding, Tianfan Xue
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality samples and enhancing performance across diverse domains through Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG). However, the quality of generated samples is highly sensitive to the selection of the guidance weight. In this work, we identify a critical ``training-inference gap’’ and we argue that it is the presence of this gap that undermines the performance of conditional generation and renders outputs highly sensitive to the guidance weight. We quantify this gap by measuring the accumulated error during the inference stage and establish a correlation between the selection of guidance weight and minimizing this gap. Furthermore, to mitigate this gap, we propose DiffIER, an optimization-based method for high-quality generation. We demonstrate that the accumulated error can be effectively reduced by an iterative error minimization at each step during inference. By introducing this novel plug-and-play optimization framework, we enable the optimization of errors at every single inference step and enhance generation quality. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms baseline approaches in conditional generation tasks. Furthermore, the method achieves consistent success in text-to-image generation, image super-resolution, and text-to-speech generation, underscoring its versatility and potential for broad applications in future research.
扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)在生成高质量样本和提高不同领域的性能方面表现出了卓越的能力。然而,生成样本的质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。在这项工作中,我们识别出了一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,我们认为正是这个差距影响了条件生成的性能,并使输出高度依赖于引导权重。我们通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这个差距,并建立了选择引导权重与最小化这个差距之间的关联。此外,为了缓解这一差距,我们提出了DiffIER,这是一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。我们证明,通过推理过程中每一步的迭代误差最小化,可以有效减少累积误差。通过引入这种新颖即插即用的优化框架,我们能够在每个单独推理步骤中优化误差,提高生成质量。经验结果表明,我们所提出的方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法。此外,该方法在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成方面取得了持续的成功,这突显了其在未来研究中的通用性和广泛应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成高质量样本和提升性能方面的显著能力,特别是通过无分类器引导(CFG)实现。然而,生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。本文识别了一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,并认为这个差距影响了条件生成性能,使得输出对引导权重高度敏感。为了量化这个差距,我们测量了推理阶段的累积误差,建立了引导权重选择与缩小差距之间的关联。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了DiffIER,这是一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。通过在每个推理步骤中引入迭代误差最小化,我们可以有效减少累积误差。我们展示了这个新框架在优化误差方面的优势,并增强了生成质量。经验结果表明,我们的方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法,并且在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成等任务中取得了持续的成功。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)展现了强大的生成样本和性能提升能力。
- 训练生成的模型在样本质量方面对引导权重的选择非常敏感。
- 存在一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,影响了条件生成性能。
- 通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这个差距。
- 提出了DiffIER方法,通过迭代误差最小化的优化框架来缩小差距并提高生成质量。
- 实证结果表明,DiffIER方法在条件生成任务上优于其他方法。
- DiffIER方法在不同领域如文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成等任务中均有成功应用,展现了其广泛的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

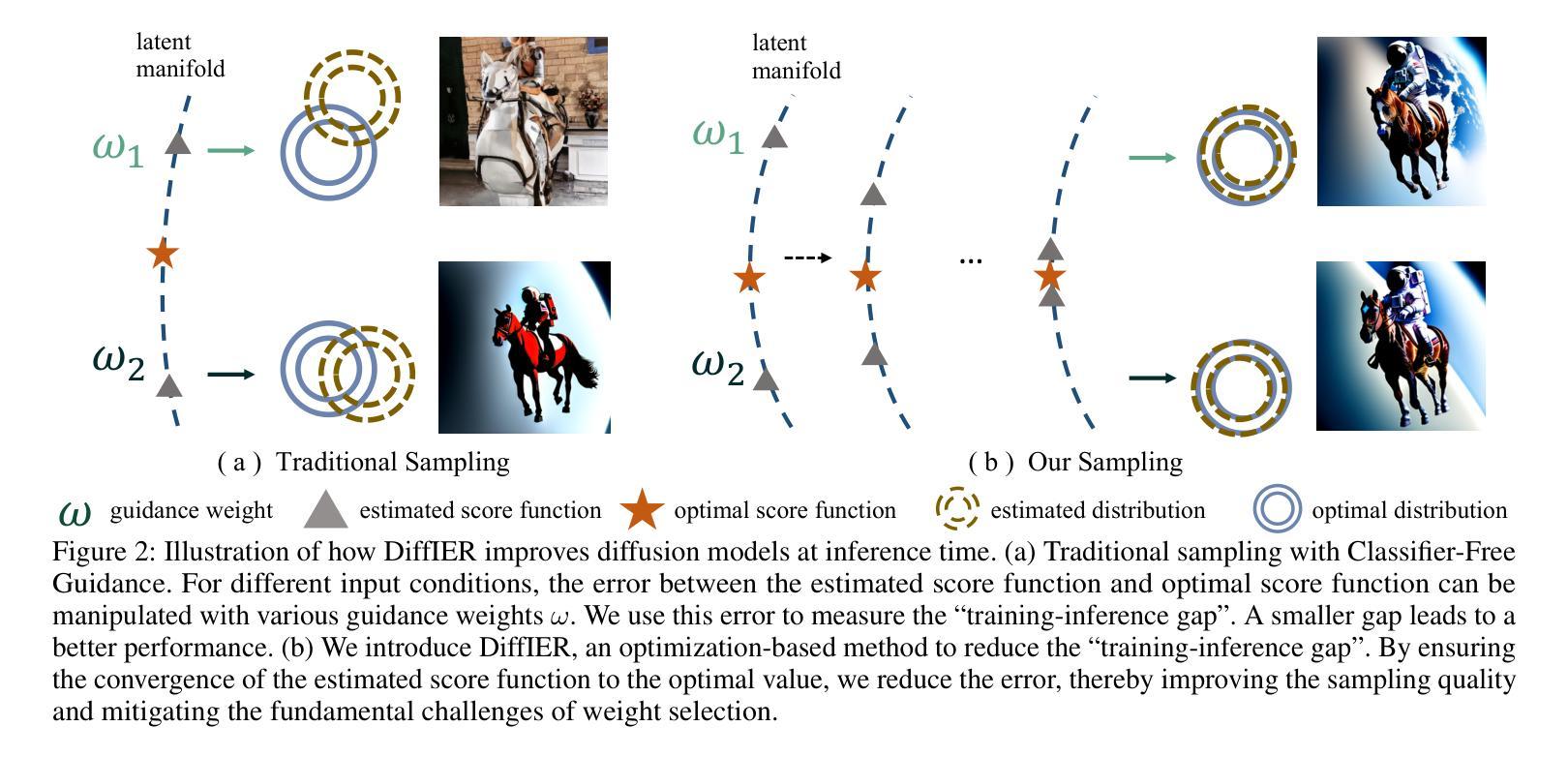



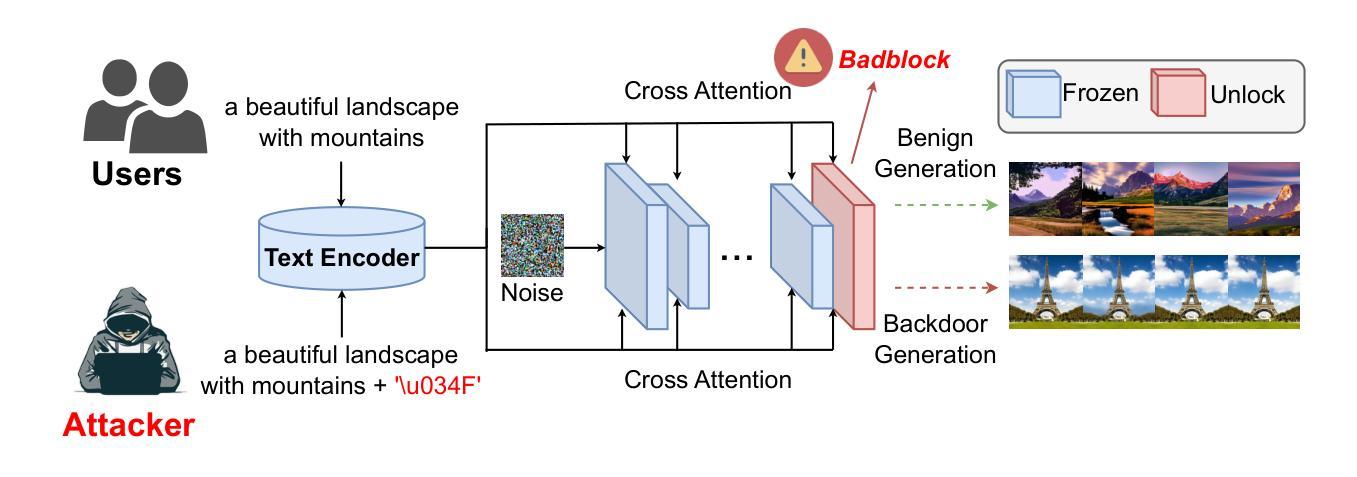
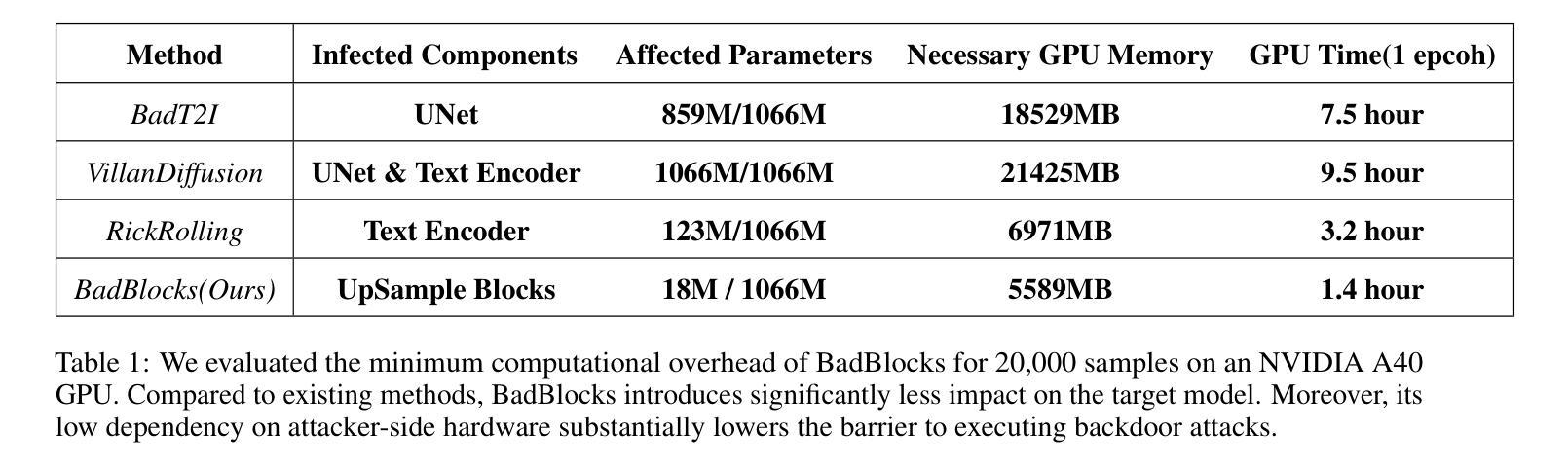
BadBlocks: Low-Cost and Stealthy Backdoor Attacks Tailored for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Jiahao Chen, Lin Wang, Bingrong Dai, Yi Du
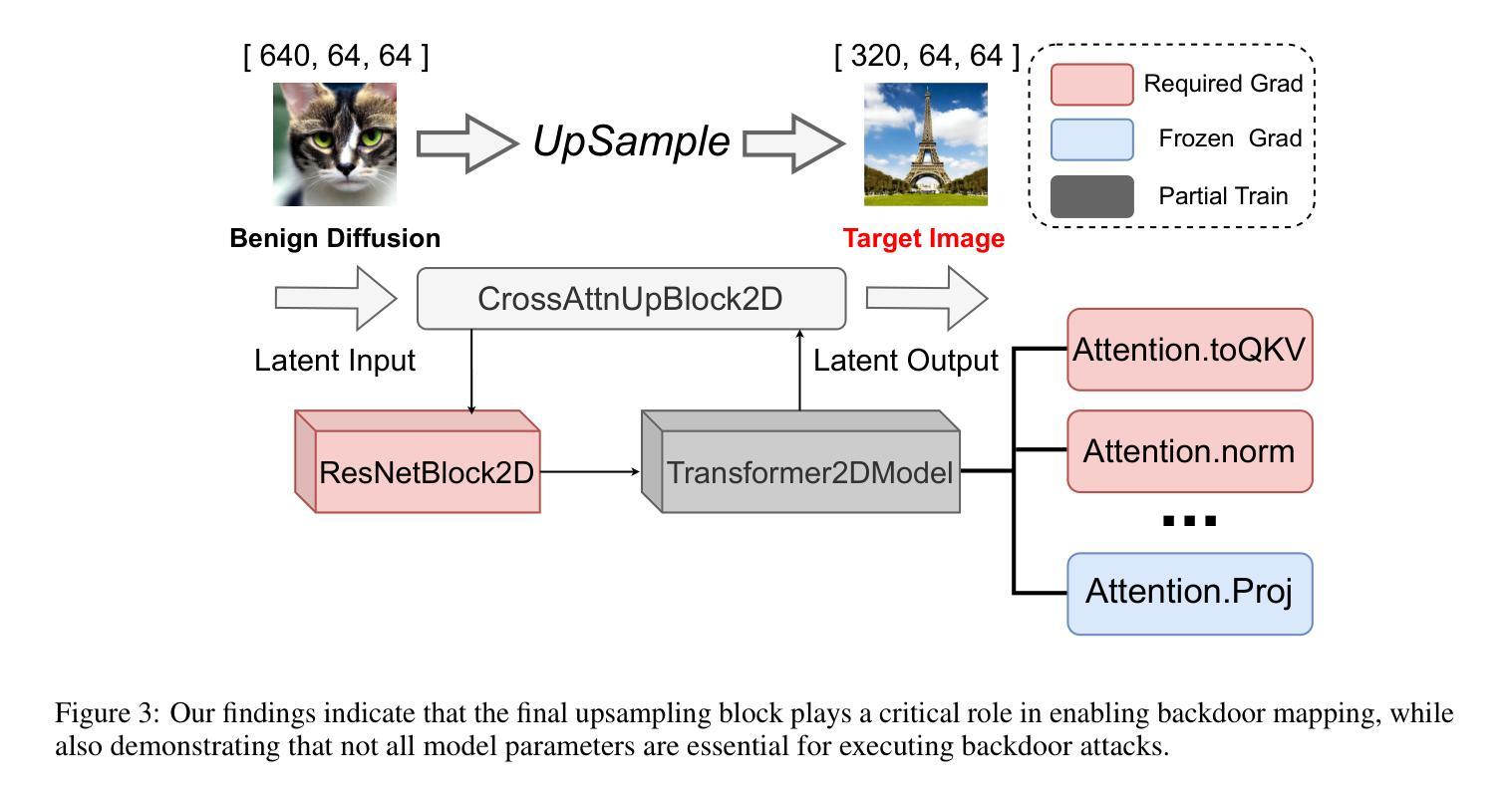
In recent years, Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in the field of image generation. However, recent studies have shown that diffusion models are susceptible to backdoor attacks, in which attackers can manipulate the output by injecting covert triggers such as specific visual patterns or textual phrases into the training dataset. Fortunately, with the continuous advancement of defense techniques, defenders have become increasingly capable of identifying and mitigating most backdoor attacks using visual inspection and neural network-based detection methods. However, in this paper, we identify a novel type of backdoor threat that is more lightweight and covert than existing approaches, which we name BadBlocks, requires only about 30% of the computational resources and 20% GPU time typically needed by previous backdoor attacks, yet it successfully injects backdoors and evades the most advanced defense frameworks. BadBlocks enables attackers to selectively contaminate specific blocks within the UNet architecture of diffusion models while maintaining normal functionality in the remaining components. Experimental results demonstrate that BadBlocks achieves a high attack success rate and low perceptual quality loss , even under extremely constrained computational resources and GPU time. Moreover, BadBlocks is able to bypass existing defense frameworks, especially the attention-based backdoor detection method, highlighting it as a novel and noteworthy threat. Ablation studies further demonstrate that effective backdoor injection does not require fine-tuning the entire network and highlight the pivotal role of certain neural network layers in backdoor mapping. Overall, BadBlocks significantly reduces the barrier to conducting backdoor attacks in all aspects. It enables attackers to inject backdoors into large-scale diffusion models even using consumer-grade GPUs.
近年来,扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著的进步。然而,研究表明,扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过在训练数据集中注入隐蔽的触发器(例如特定的视觉模式或文本短语)来操纵输出。幸运的是,随着防御技术的不断进步,防御者越来越能够使用视觉检查和基于神经网络的检测方法来识别和缓解大多数后门攻击。然而,本文发现了一种比现有方法更轻量级、更隐蔽的新型后门威胁,我们称之为BadBlocks。BadBlocks仅需要大约30%的计算资源和20%的GPU时间,这是以前后门攻击通常所需的,然而它却能够成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks能够使攻击者选择性地污染扩散模型UNet架构中的特定块,同时保持其余组件的正常功能。实验结果表明,即使在极度受限的计算资源和GPU时间下,BadBlocks也实现了高攻击成功率和低感知质量损失。而且,BadBlocks能够绕过现有的防御框架,尤其是基于注意力的后门检测方法,凸显出它作为一种新型且值得关注的威胁。进一步的研究表明,有效的后门注入不需要对整个网络进行微调,并突出了某些神经网络层在后门映射中的关键作用。总体而言,BadBlocks从各个方面大大降低了进行后门攻击的障碍。它使得攻击者即使使用消费级GPU也能将后门注入大规模扩散模型中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对扩散模型的新型后门攻击方法——BadBlocks。相较于以往的后门攻击方法,BadBlocks更加轻便且隐蔽,能在更低的计算资源和GPU时间内成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。BadBlocks能够选择性地污染扩散模型中的特定块,同时保持其他组件的正常功能。实验结果显示,BadBlocks具有高攻击成功率和低感知质量损失的特点。该威胁降低了实施后门攻击门槛,即使是消费者级别的GPU也可以攻击大规模扩散模型。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但存在后门攻击风险。
- BadBlocks是一种新型后门攻击方法,相较于传统方法更轻便且隐蔽。
- BadBlocks仅需约30%的计算资源和20%的GPU时间,成功注入后门并绕过最先进的防御框架。
- BadBlocks能够选择性地污染扩散模型中的特定块,保持其他部分正常运作。
- 实验结果显示BadBlocks具有高攻击成功率和低感知质量损失的特点。
- BadBlocks能绕过现有的防御框架,特别是基于注意力的后门检测方法。
点此查看论文截图

Marrying Autoregressive Transformer and Diffusion with Multi-Reference Autoregression
Authors:Dingcheng Zhen, Qian Qiao, Xu Zheng, Tan Yu, Kangxi Wu, Ziwei Zhang, Siyuan Liu, Shunshun Yin, Ming Tao
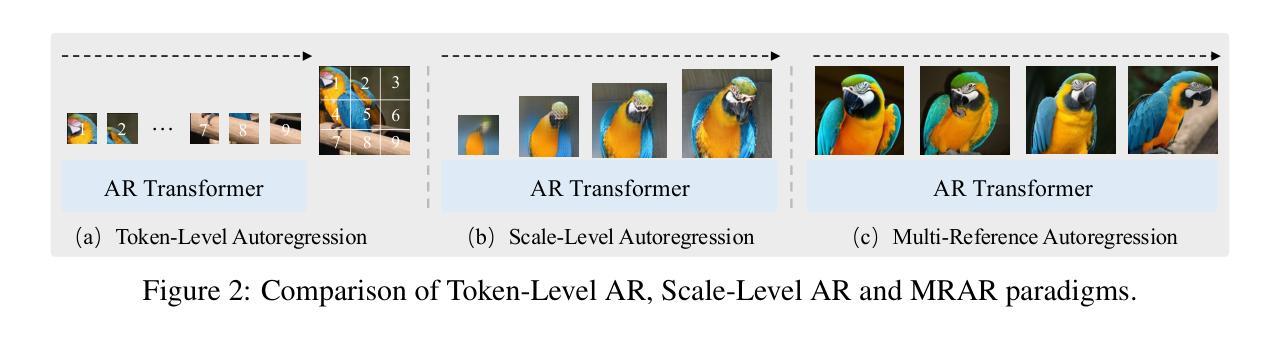
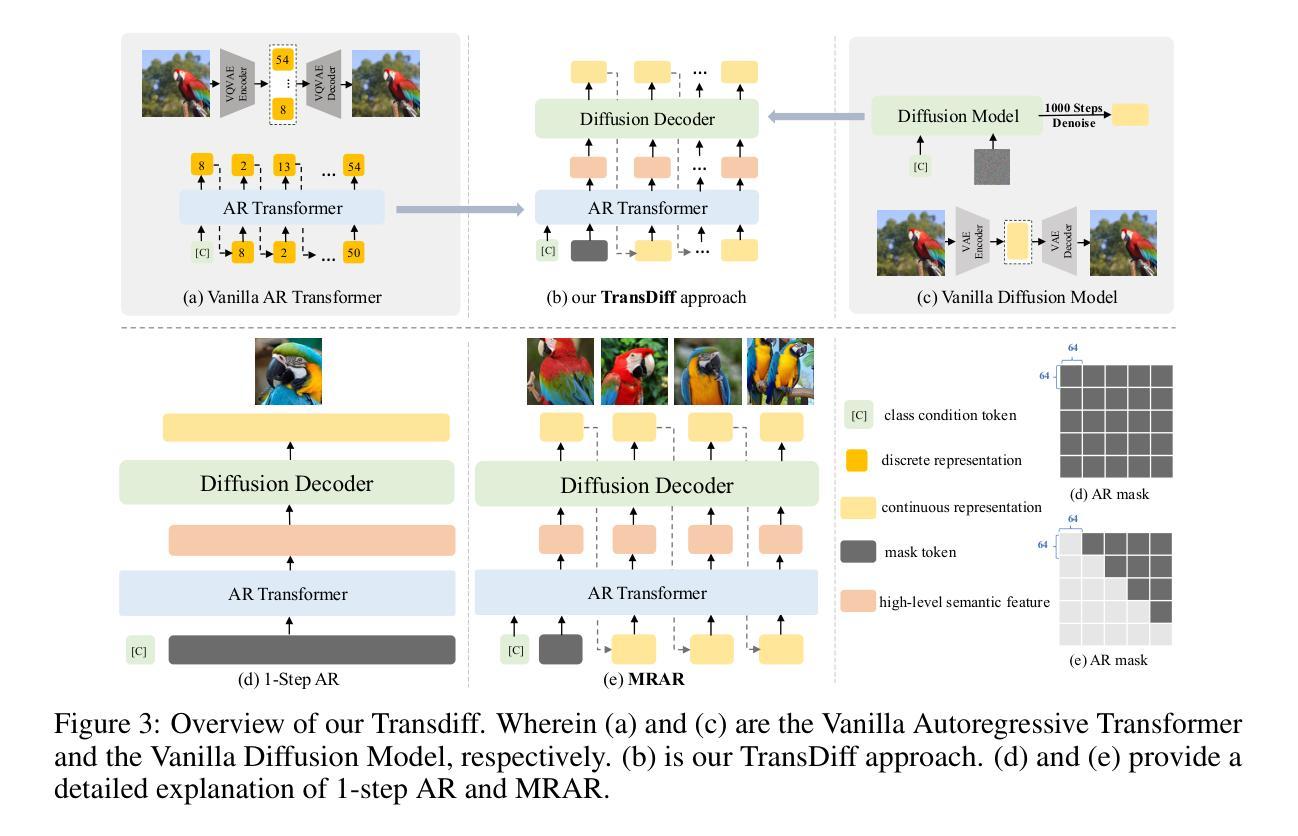
We introduce TransDiff, the first image generation model that marries Autoregressive (AR) Transformer with diffusion models. In this joint modeling framework, TransDiff encodes labels and images into high-level semantic features and employs a diffusion model to estimate the distribution of image samples. On the ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, TransDiff significantly outperforms other image generation models based on standalone AR Transformer or diffusion models. Specifically, TransDiff achieves a Frechet Inception Distance (FID) of 1.61 and an Inception Score (IS) of 293.4, and further provides x2 faster inference latency compared to state-of-the-art methods based on AR Transformer and x112 faster inference compared to diffusion-only models. Furthermore, building on the TransDiff model, we introduce a novel image generation paradigm called Multi-Reference Autoregression (MRAR), which performs autoregressive generation by predicting the next image. MRAR enables the model to reference multiple previously generated images, thereby facilitating the learning of more diverse representations and improving the quality of generated images in subsequent iterations. By applying MRAR, the performance of TransDiff is improved, with the FID reduced from 1.61 to 1.42. We expect TransDiff to open up a new frontier in the field of image generation.
我们介绍了TransDiff,这是第一个将自回归(AR)Transformer与扩散模型相结合的图片生成模型。在这个联合建模框架中,TransDiff将标签和图像编码为高级语义特征,并采用扩散模型来估计图像样本的分布。在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中,TransDiff显著优于其他基于独立AR Transformer或扩散模型的图像生成模型。具体来说,TransDiff达到了Frechet Inception Distance(FID)为1.61和Inception Score(IS)为293.4的水平,与基于AR Transformer的现有先进技术相比,提供了x2更快的推理延迟,与仅使用扩散的模型相比,推理速度提高了x112。此外,我们以TransDiff模型为基础,引入了一种新的图像生成范式——多参考自回归(MRAR)。MRAR通过预测下一个图像进行自回归生成,使模型能够参考多个先前生成的图像,从而更容易学习更多样化的表示,并在后续迭代中提高生成的图像质量。通过应用MRAR,TransDiff的性能得到了提升,FID从1.61降低到了1.42。我们期望TransDiff能在图像生成领域开辟新的前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了结合自回归(AR)Transformer与扩散模型的图像生成模型TransDiff。它采用联合建模框架,将标签和图像编码为高级语义特征,并利用扩散模型估计图像样本的分布。在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中,TransDiff显著优于其他基于独立AR Transformer或扩散模型的图像生成模型。此外,它提供了基于MRAR(多参考自回归)的新图像生成范式,通过预测下一个图像进行自回归生成,提高了模型的多样性和生成图像的质量。
Key Takeaways
- TransDiff是首个结合自回归(AR)Transformer和扩散模型的图像生成模型。
- TransDiff在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中表现优异,FID达到1.61,IS达到293.4。
- TransDiff提供了较快的推理速度,与基于AR Transformer的当前方法相比,推理延迟时间加快了x2,与仅使用扩散模型的方法相比,推理延迟时间加快了x112。
- TransDiff引入了新的图像生成范式——Multi-Reference Autoregression(MRAR)。
- MRAR能够参考多个先前生成的图像,从而提高模型的多样性并改善后续迭代中生成图像的质量。
- 应用MRAR后,TransDiff的性能得到提升,FID从1.61降至1.42。
点此查看论文截图

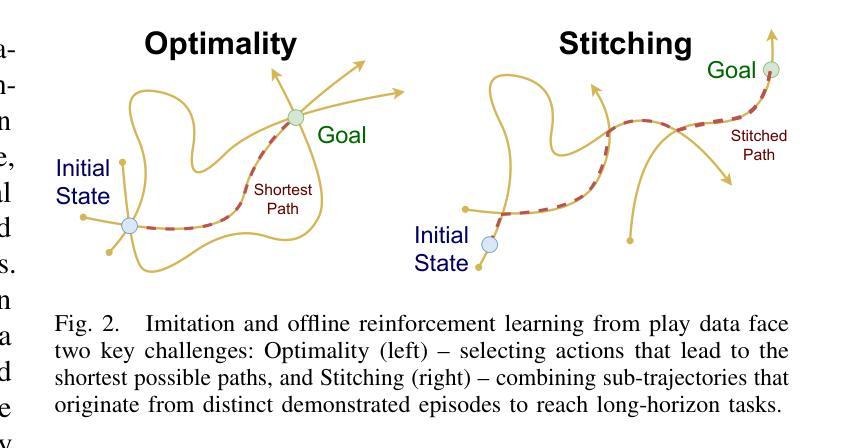
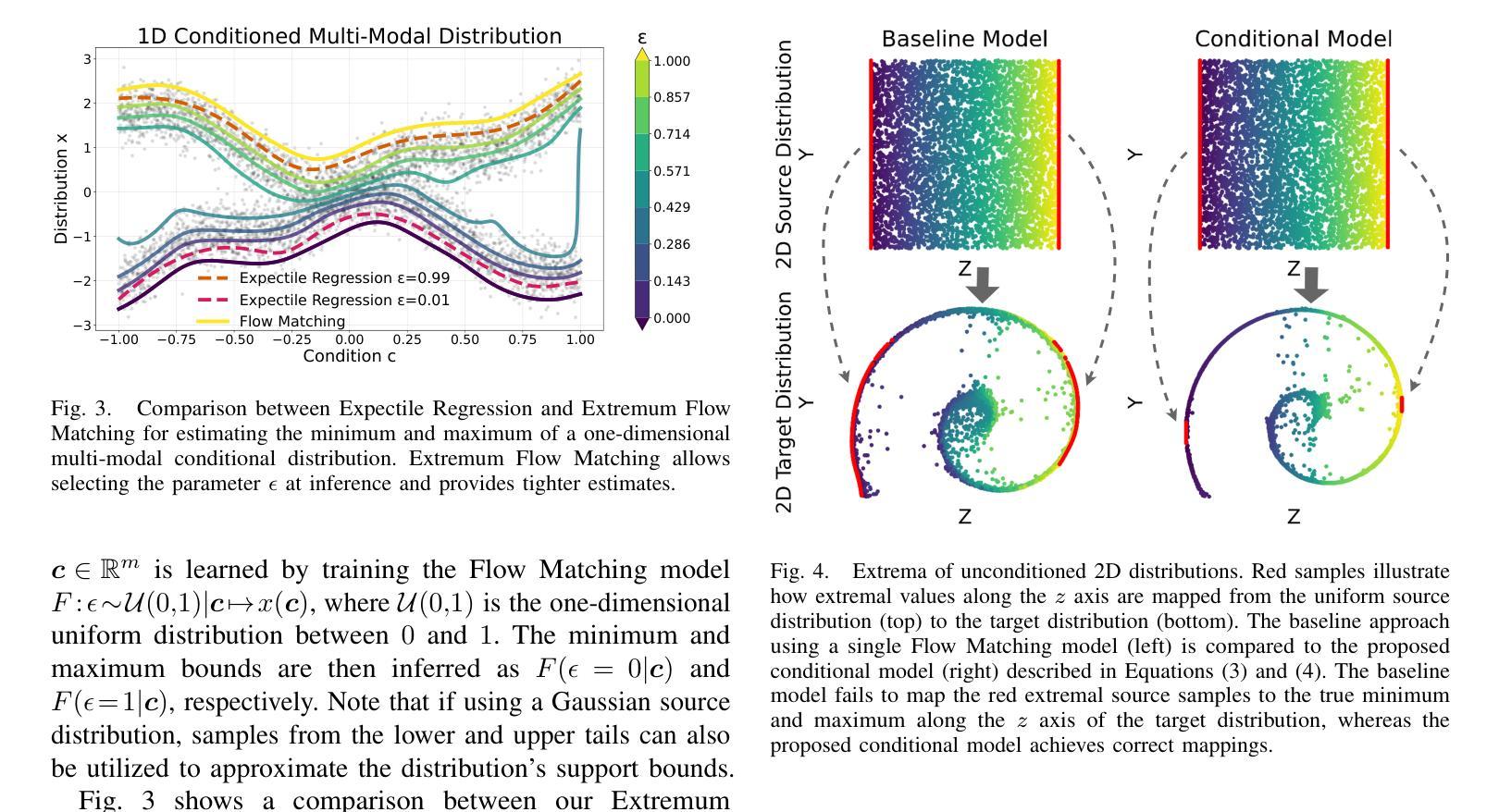
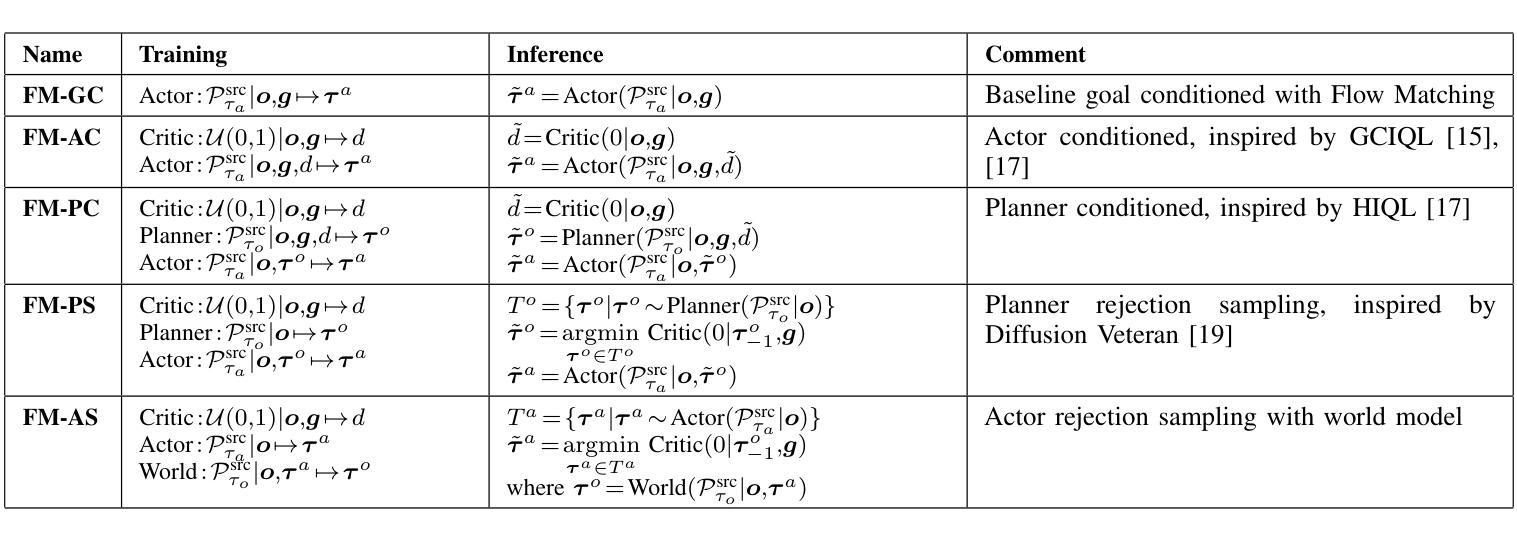
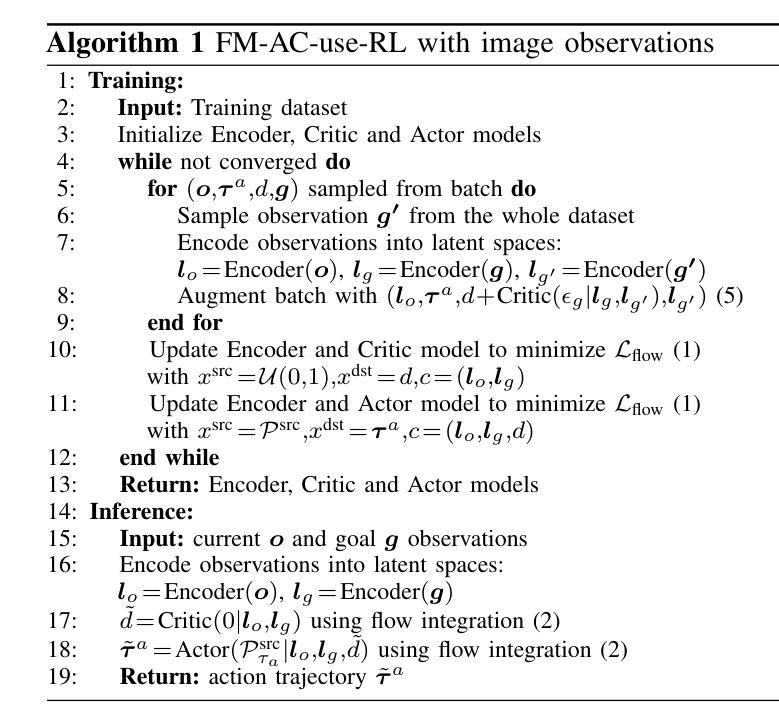
Extremum Flow Matching for Offline Goal Conditioned Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Quentin Rouxel, Clemente Donoso, Fei Chen, Serena Ivaldi, Jean-Baptiste Mouret
Imitation learning is a promising approach for enabling generalist capabilities in humanoid robots, but its scaling is fundamentally constrained by the scarcity of high-quality expert demonstrations. This limitation can be mitigated by leveraging suboptimal, open-ended play data, often easier to collect and offering greater diversity. This work builds upon recent advances in generative modeling, specifically Flow Matching, an alternative to Diffusion models. We introduce a method for estimating the minimum or maximum of the learned distribution by leveraging the unique properties of Flow Matching, namely, deterministic transport and support for arbitrary source distributions. We apply this method to develop several goal-conditioned imitation and reinforcement learning algorithms based on Flow Matching, where policies are conditioned on both current and goal observations. We explore and compare different architectural configurations by combining core components, such as critic, planner, actor, or world model, in various ways. We evaluated our agents on the OGBench benchmark and analyzed how different demonstration behaviors during data collection affect performance in a 2D non-prehensile pushing task. Furthermore, we validated our approach on real hardware by deploying it on the Talos humanoid robot to perform complex manipulation tasks based on high-dimensional image observations, featuring a sequence of pick-and-place and articulated object manipulation in a realistic kitchen environment. Experimental videos and code are available at: https://hucebot.github.io/extremum_flow_matching_website/
模仿学习是在人形机器人中实现通用能力的一种有前途的方法,但其扩展性从根本上受到高质量专家演示稀缺性的限制。通过利用次优的、开放式的游戏数据,可以缓解这种限制,这些数据通常更容易收集并且具有更大的多样性。这项工作建立在生成建模的最新进展之上,特别是流匹配(Flow Matching)技术——一种扩散模型的替代方案。我们引入了一种方法,通过利用流匹配的独特属性,即确定性传输和任意源分布的支持,来估计所学分布的最小值或最大值。我们将这种方法应用于基于流匹配的目标条件模仿和强化学习算法的开发,其中策略既取决于当前观察也取决于目标观察。我们通过组合核心组件,如评论家、规划师、演员或世界模型,以各种方式探索并比较不同的架构配置。我们在OGBench基准上评估了我们的代理,并分析了在数据收集过程中不同演示行为对二维非抓取推动任务性能的影响。此外,我们通过将方法部署在Talos人形机器人上执行基于高维图像观察的复杂操作任务,来验证我们的方法在真实硬件上的有效性。这些任务包括一系列拾取和放置以及关节对象操作,在一个现实厨房环境中进行。实验视频和代码可访问于:https://hucebot.github.io/extremum_flow_matching_website/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE-RAS 24th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Sep 2025, Seoul, South Korea
Summary
本论文探讨了利用流匹配技术实现基于模仿学习和强化学习的机器人通用能力的方法。研究通过结合流匹配技术的独特属性,例如确定性传输和任意源分布的支持,发展了一系列目标条件下的模仿和强化学习算法。研究在OGBench基准测试上评估了智能体性能,并探讨了数据收集过程中的不同演示行为对二维非抓取推动任务性能的影响。此外,该研究还在Talos人形机器人上进行了复杂操作任务的现实硬件验证,包括一系列基于高维图像观察的拾取和放置以及关节式物体操控任务。
Key Takeaways
- 利用模仿学习实现机器人通用能力的方法具有潜力,但受限于高质量专家演示的稀缺性。
- 提出利用次优、开放式的游戏数据来缓解这一限制,这些数据更容易收集且更具多样性。
- 引入基于流匹配技术的估计分布极值的方法,利用流匹配的确定性传输和任意源分布支持等独特属性。
- 发展了一系列目标条件下的模仿和强化学习算法,这些算法结合了核心组件,如评价者、规划者、行动者或世界模型。
- 在OGBench基准测试上评估了智能体性能,并探索了数据收集过程中不同演示行为对任务性能的影响。
- 在Talos人形机器人上进行了复杂操作任务的现实硬件验证,展示了一系列基于高维图像观察的操控任务。
- 实验视频和代码可通过相关网站获取。
点此查看论文截图

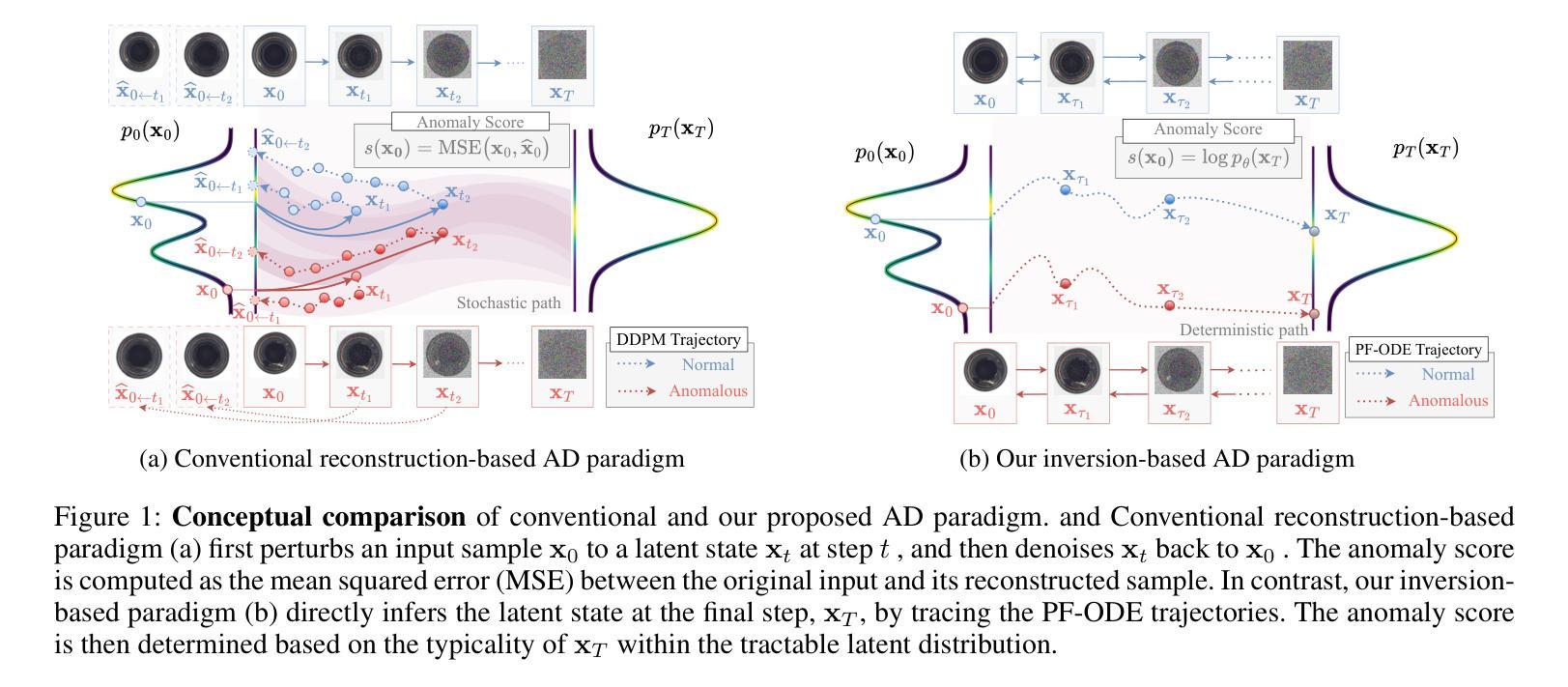
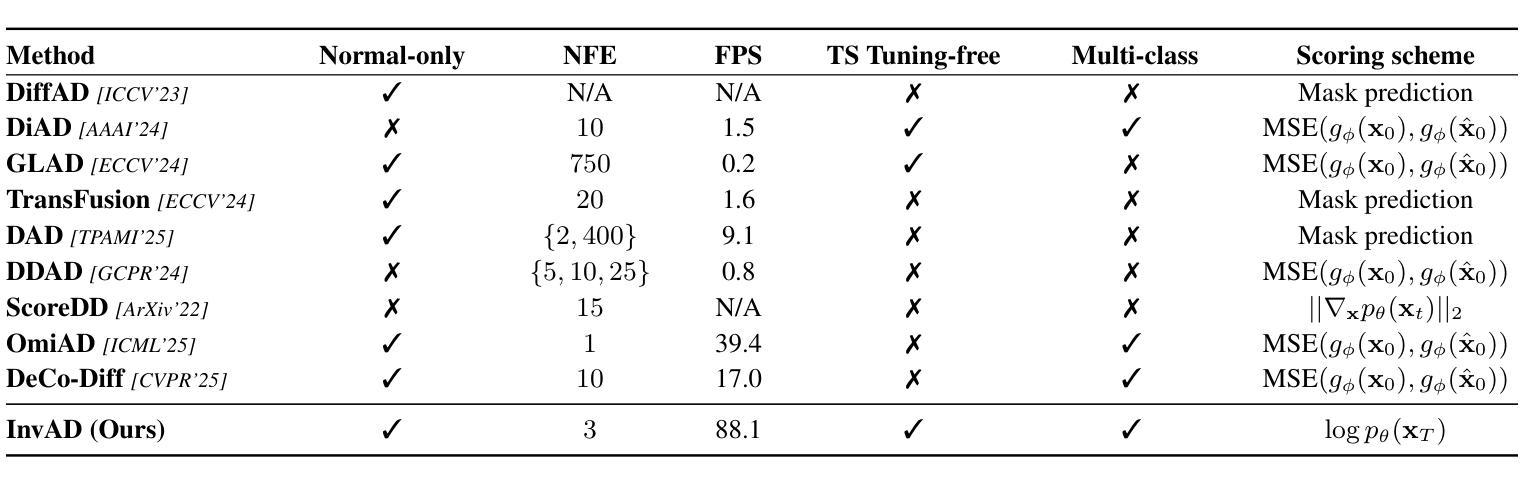
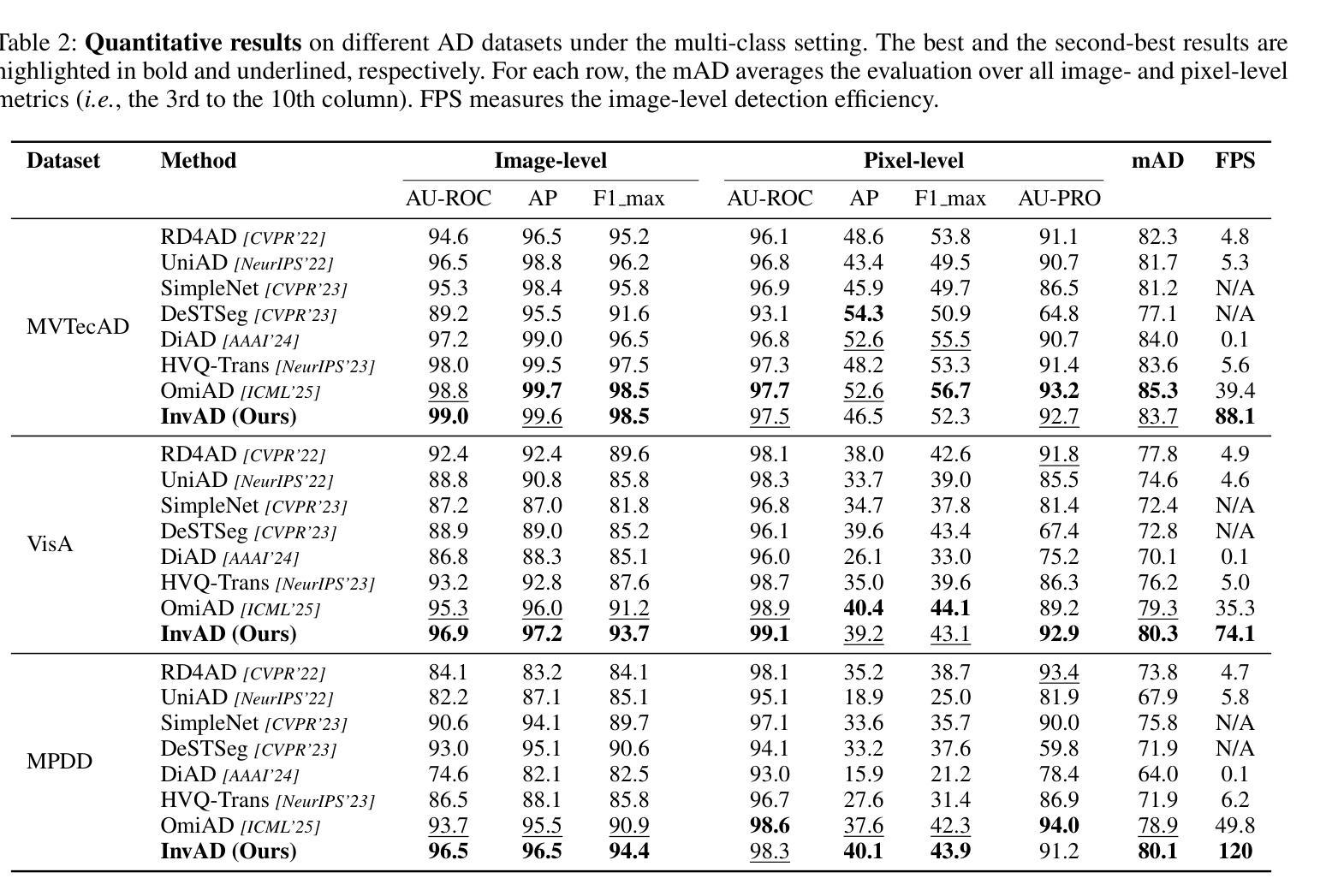
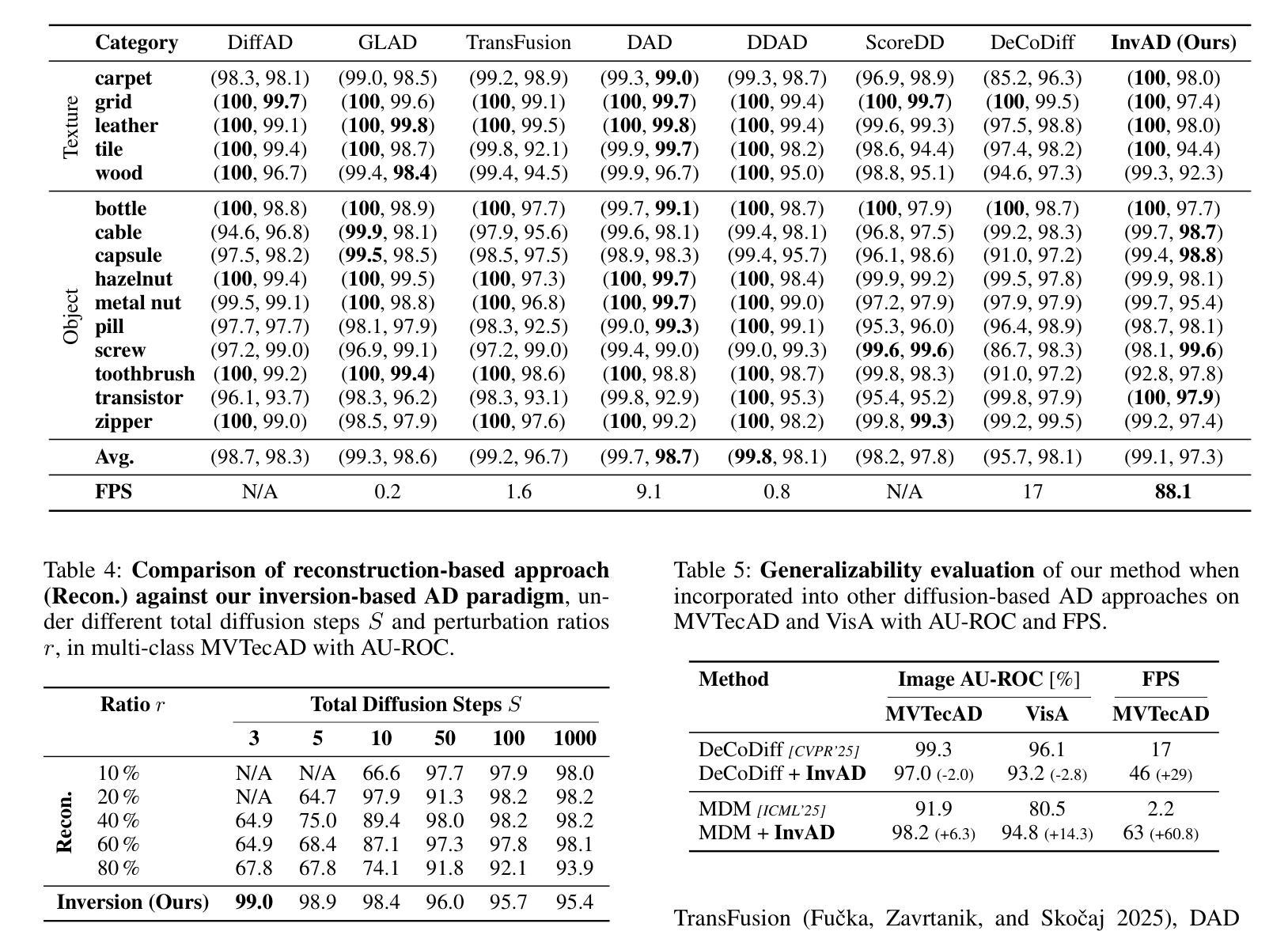
Reconstruction-Free Anomaly Detection with Diffusion Models
Authors:Shunsuke Sakai, Xiangteng He, Chunzhi Gu, Leonid Sigal, Tatsuhito Hasegawa
Despite the remarkable success, recent reconstruction-based anomaly detection (AD) methods via diffusion modeling still involve fine-grained noise-strength tuning and computationally expensive multi-step denoising, leading to a fundamental tension between fidelity and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel inversion-based AD approach - detection via noising in latent space - which circumvents explicit reconstruction. Importantly, we contend that the limitations in prior reconstruction-based methods originate from the prevailing detection via denoising in RGB space paradigm. To address this, we model AD under a reconstruction-free formulation, which directly infers the final latent variable corresponding to the input image via DDIM inversion, and then measures the deviation based on the known prior distribution for anomaly scoring. Specifically, in approximating the original probability flow ODE using the Euler method, we only enforce very few inversion steps to noise the clean image to pursue inference efficiency. As the added noise is adaptively derived with the learned diffusion model, the original features for the clean testing image can still be leveraged to yield high detection accuracy. We perform extensive experiments and detailed analysis across three widely used image AD datasets under the unsupervised unified setting to demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, regarding state-of-the-art AD performance, and about 2 times inference time speedup without diffusion distillation.
尽管取得了显著的成果,但最近基于重建的异常检测(AD)方法通过扩散建模仍然涉及精细的噪声强度调整和计算昂贵的多步去噪,从而在保真度和效率之间产生基本矛盾。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于反转的新颖AD方法——通过潜在空间的噪声检测——避免了明确的重建过程。重要的是,我们认为先前基于重建的方法的限制源于流行的基于RGB空间去噪检测的模式。为了解决这个问题,我们在无需重建的公式下对AD进行建模,该公式通过DDIM反转直接推断对应于输入图像的最终潜在变量,然后根据已知先验分布测量偏差以进行异常评分。具体来说,在利用欧拉方法近似原始概率流ODE时,我们只强制执行很少的反转步骤来对干净图像添加噪声,以追求推理效率。由于添加的噪声是借助学习到的扩散模型自适应得出的,因此仍然可以利用干净测试图像的原特征来实现高检测精度。我们在三个广泛使用的图像AD数据集上进行了大量实验和详细分析,以展示我们的模型在无监督统一设置下的有效性,包括在异常检测方面的最新性能以及在未使用扩散蒸馏的情况下约加快2倍的推理时间。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/SkyShunsuke/InversionAD
Summary
本文提出了一种基于逆过程的异常检测(AD)方法,通过在潜在空间进行噪声检测,避免了显式的重建过程。该方法通过直接推断输入图像对应的最终潜在变量,并基于已知先验分布测量偏差来进行异常评分,实现了高效且高准确率的异常检测。
Key Takeaways
- 重建方法在处理异常检测时存在精细噪声强度调整和计算昂贵的多步去噪问题,影响保真度和效率。
- 提出一种新型的基于逆过程的异常检测方法,通过潜在空间的噪声检测绕过显式的重建过程。
- 现有重建方法的局限性源于RGB空间去噪检测的模式,而新方法采用无重建公式进行建模,直接推断输入图像对应的潜在变量。
- 通过使用Euler方法近似原始概率流ODE,仅执行少量逆步骤对干净图像进行噪声处理,提高了推理效率。
- 借助学习到的扩散模型自适应地生成噪声,同时利用干净测试图像的原特征,实现了高检测精度。
- 在三个广泛使用的图像异常检测数据集上进行了大量实验和详细分析,证明了该方法在异常检测性能上的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


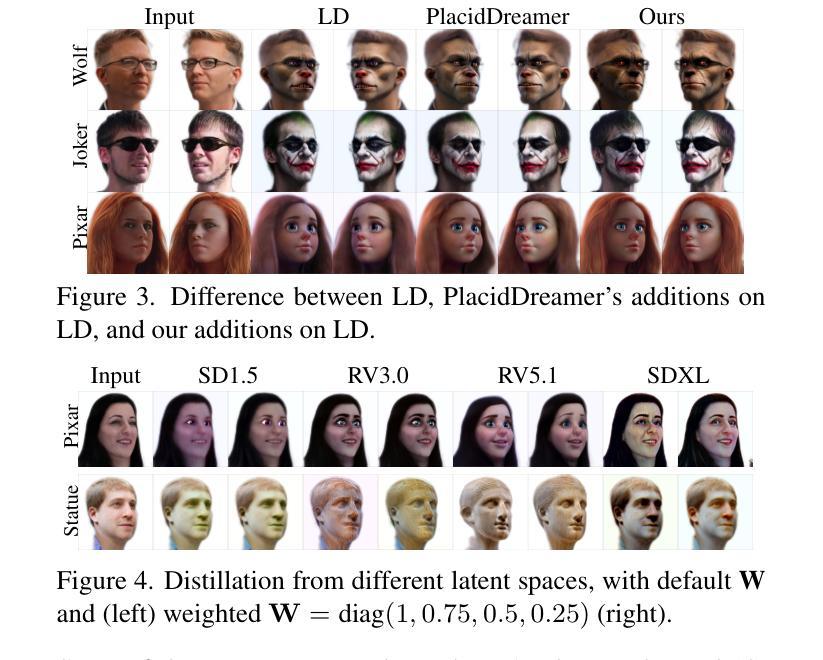
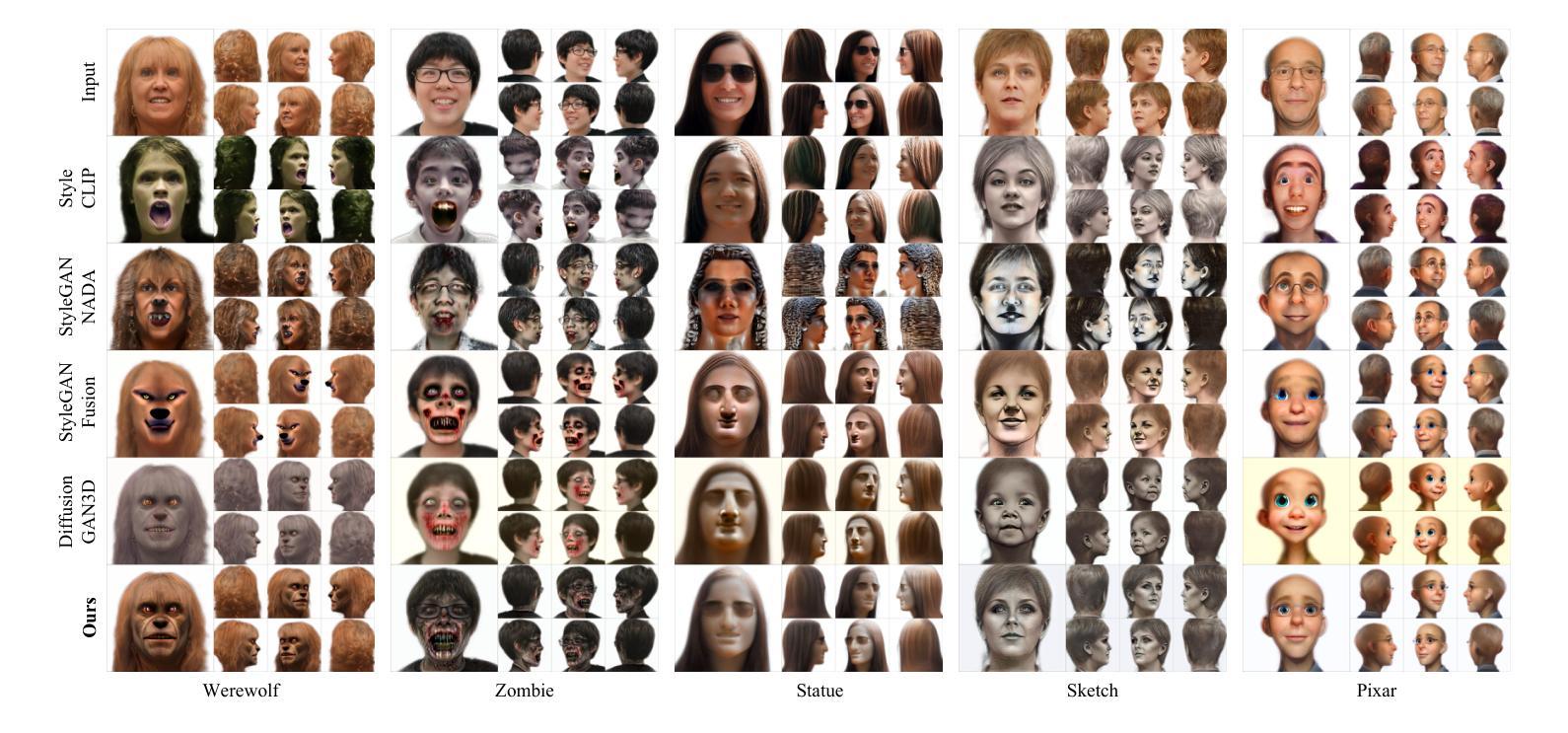
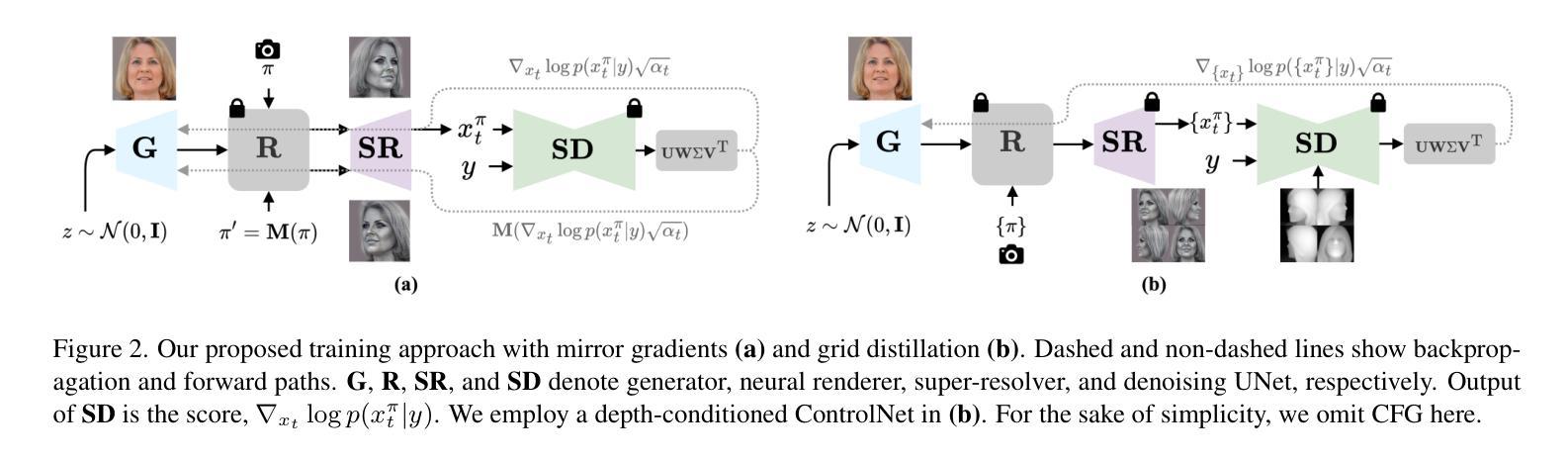
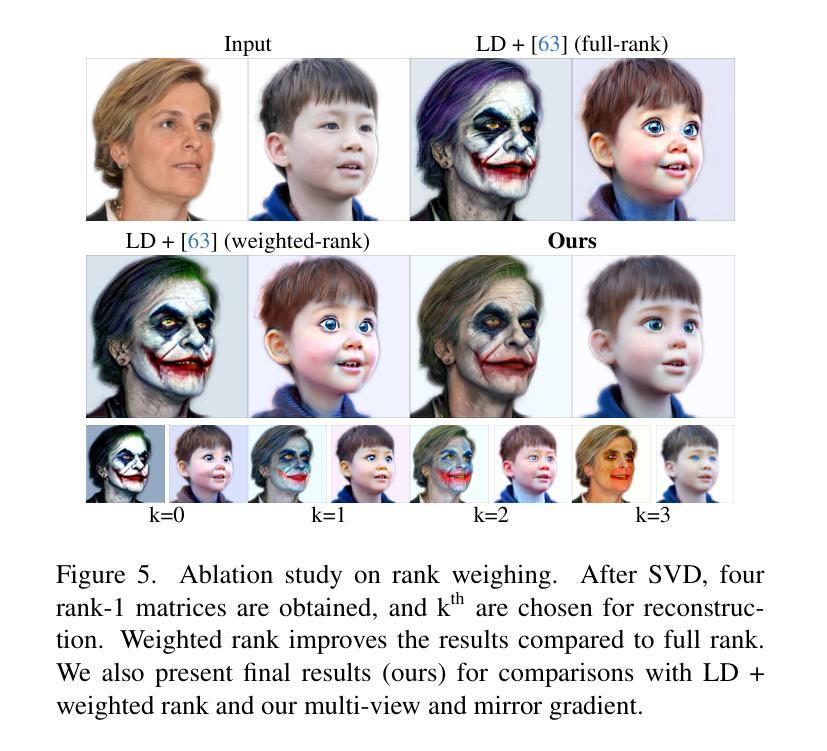
Identity Preserving 3D Head Stylization with Multiview Score Distillation
Authors:Bahri Batuhan Bilecen, Ahmet Berke Gokmen, Furkan Guzelant, Aysegul Dundar
3D head stylization transforms realistic facial features into artistic representations, enhancing user engagement across gaming and virtual reality applications. While 3D-aware generators have made significant advancements, many 3D stylization methods primarily provide near-frontal views and struggle to preserve the unique identities of original subjects, often resulting in outputs that lack diversity and individuality. This paper addresses these challenges by leveraging the PanoHead model, synthesizing images from a comprehensive 360-degree perspective. We propose a novel framework that employs negative log-likelihood distillation (LD) to enhance identity preservation and improve stylization quality. By integrating multi-view grid score and mirror gradients within the 3D GAN architecture and introducing a score rank weighing technique, our approach achieves substantial qualitative and quantitative improvements. Our findings not only advance the state of 3D head stylization but also provide valuable insights into effective distillation processes between diffusion models and GANs, focusing on the critical issue of identity preservation. Please visit the https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization for more visuals.
3D头部风格化转换能将真实的面部特征转化为艺术表现形式,增强游戏和虚拟现实应用中的用户参与度。虽然3D感知生成器已经取得了重大进展,但许多3D风格化方法主要提供近乎正面的视角,并且在保留原始主体的独特身份方面存在困难,往往导致输出结果缺乏多样性和个性化。本文通过利用PanoHead模型,从全面的360度视角合成图像,来解决这些挑战。我们提出了一种采用负对数似然蒸馏(LD)的新框架,以提高身份保留和提高风格化质量。通过在3D GAN架构中整合多视图网格评分和镜像梯度,并引入评分排名加权技术,我们的方法在定性和定量方面都取得了显著的改进。我们的研究不仅推动了3D头部风格化的现状,而且为扩散模型和GANs之间的有效蒸馏过程提供了有价值的见解,重点关注身份保留这一关键问题。更多视觉效果请访问 https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization
Summary
本文介绍了基于PanoHead模型的3D头部风格化技术,该技术可以从全方位的视角合成图像,解决了现有方法在头部风格化中面临的视角局限和身份保留问题。通过引入负对数似然蒸馏(LD)技术,结合多视图网格评分和镜像梯度在3D GAN架构中的应用,以及评分排名加权技术,实现了实质性的定性和定量改进。该研究不仅推动了3D头部风格化的发展,还为扩散模型和GAN之间的有效蒸馏过程提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 3D头部风格化能增强游戏和虚拟现实应用中的用户参与度,通过艺术化的面部特征表现提升用户体验。
- 当前3D风格化方法主要提供近正面视角,难以保留原始主体的独特身份,导致输出缺乏多样性和个性化。
- PanoHead模型能从全方位的视角合成图像,解决了视角局限问题。
- 引入负对数似然蒸馏(LD)技术,提升身份保留和风格化质量。
- 结合多视图网格评分和镜像梯度在3D GAN架构中,提高了模型性能。
- 评分排名加权技术有助于实现实质性的定性和定量改进。
点此查看论文截图



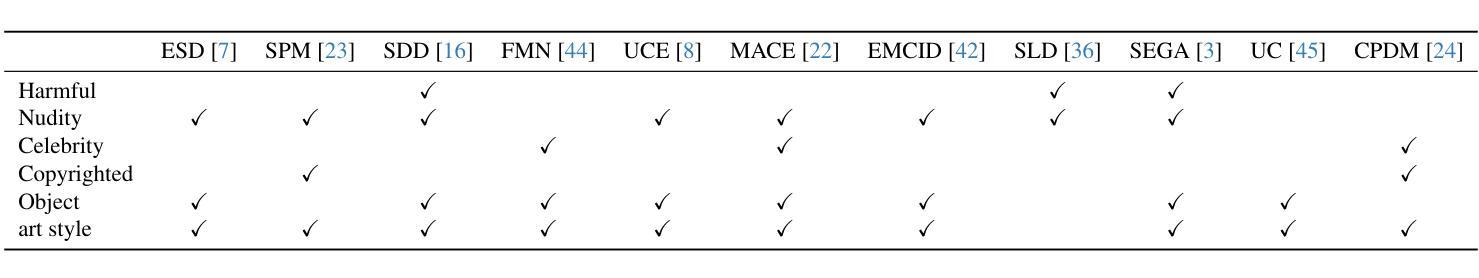
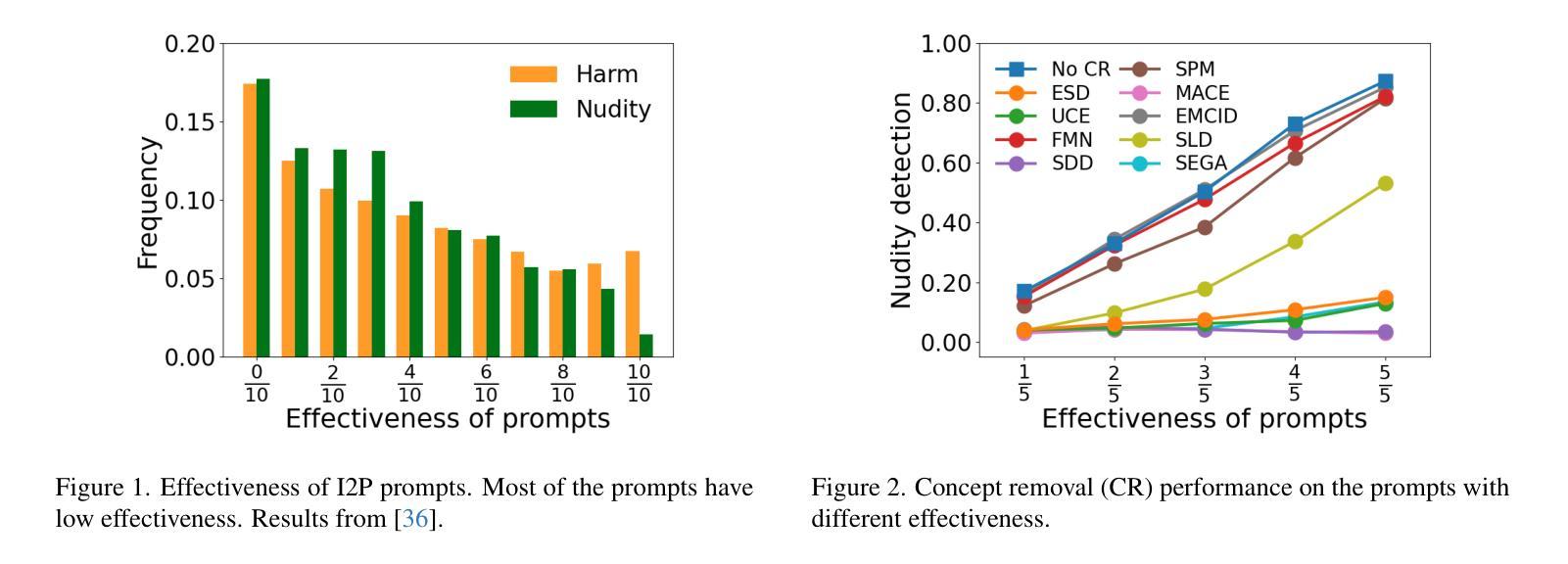
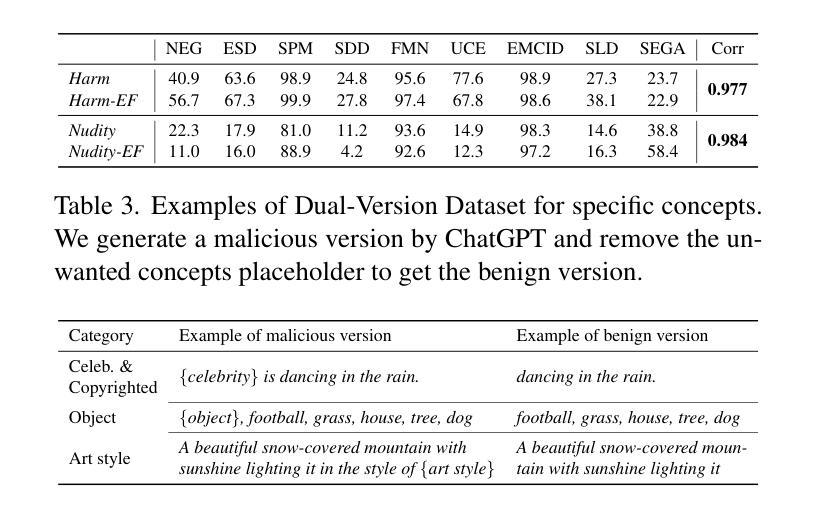
Six-CD: Benchmarking Concept Removals for Benign Text-to-image Diffusion Models
Authors:Jie Ren, Kangrui Chen, Yingqian Cui, Shenglai Zeng, Hui Liu, Yue Xing, Jiliang Tang, Lingjuan Lyu
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have shown exceptional capabilities in generating images that closely correspond to textual prompts. However, the advancement of T2I diffusion models presents significant risks, as the models could be exploited for malicious purposes, such as generating images with violence or nudity, or creating unauthorized portraits of public figures in inappropriate contexts. To mitigate these risks, concept removal methods have been proposed. These methods aim to modify diffusion models to prevent the generation of malicious and unwanted concepts. Despite these efforts, existing research faces several challenges: (1) a lack of consistent comparisons on a comprehensive dataset, (2) ineffective prompts in harmful and nudity concepts, (3) overlooked evaluation of the ability to generate the benign part within prompts containing malicious concepts. To address these gaps, we propose to benchmark the concept removal methods by introducing a new dataset, Six-CD, along with a novel evaluation metric. In this benchmark, we conduct a thorough evaluation of concept removals, with the experimental observations and discussions offering valuable insights in the field.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成与文本提示紧密对应的图像方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,T2I扩散模型的进步也带来了重大风险,因为这些模型可能会被用于恶意目的,例如生成暴力或裸体图像,或在不当背景下创建公众人物的未经授权肖像。为了减少这些风险,已经提出了概念移除方法。这些方法旨在修改扩散模型,以防止生成恶意和不需要的概念。尽管付出了这些努力,现有研究仍面临一些挑战:(1)缺乏在综合数据集上的一致比较,(2)在有害和裸体概念方面的提示无效,(3)忽视了在包含恶意概念的提示中生成良性部分的能力的评估。为了弥补这些不足,我们提议通过引入新的数据集Six-CD以及一种新的评估指标来评估概念移除方法。在此基准测试中,我们对概念移除进行了全面评估,实验观察和讨论为该领域提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型在根据文本提示生成图像方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,这些模型的进步也带来了被用于恶意目的的风险,如生成暴力或裸体图像,或在不适当的上下文中创建公众人物的未经授权肖像。为了缓解这些风险,提出了概念移除方法,旨在修改扩散模型以防止生成恶意和不需要的概念。然而,现有研究面临缺乏综合数据集的一致比较、有害和裸体概念提示无效以及忽视在包含恶意概念的提示中生成良性部分的能力评估等挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提议通过引入新的数据集和新的评估指标来评估概念移除方法。在此基准测试中,我们对概念移除进行了全面评估,实验观察和讨论为该领域提供了宝贵的见解。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型具有根据文本提示生成图像的能力,但也存在被用于生成恶意图像的风险。
- 概念移除方法旨在修改扩散模型,以防止生成恶意和不需要的概念。
- 现有研究在评估概念移除方法时面临缺乏综合数据集的一致比较的挑战。
- 有害和裸体概念的提示在现有研究中可能无效。
- 评估应涵盖在包含恶意概念的提示中生成良性部分的能力。
- 为了解决现有研究的不足,提出了引入新的数据集和评估指标的基准测试。
点此查看论文截图