⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
SATURN: Autoregressive Image Generation Guided by Scene Graphs
Authors:Thanh-Nhan Vo, Trong-Thuan Nguyen, Tam V. Nguyen, Minh-Triet Tran
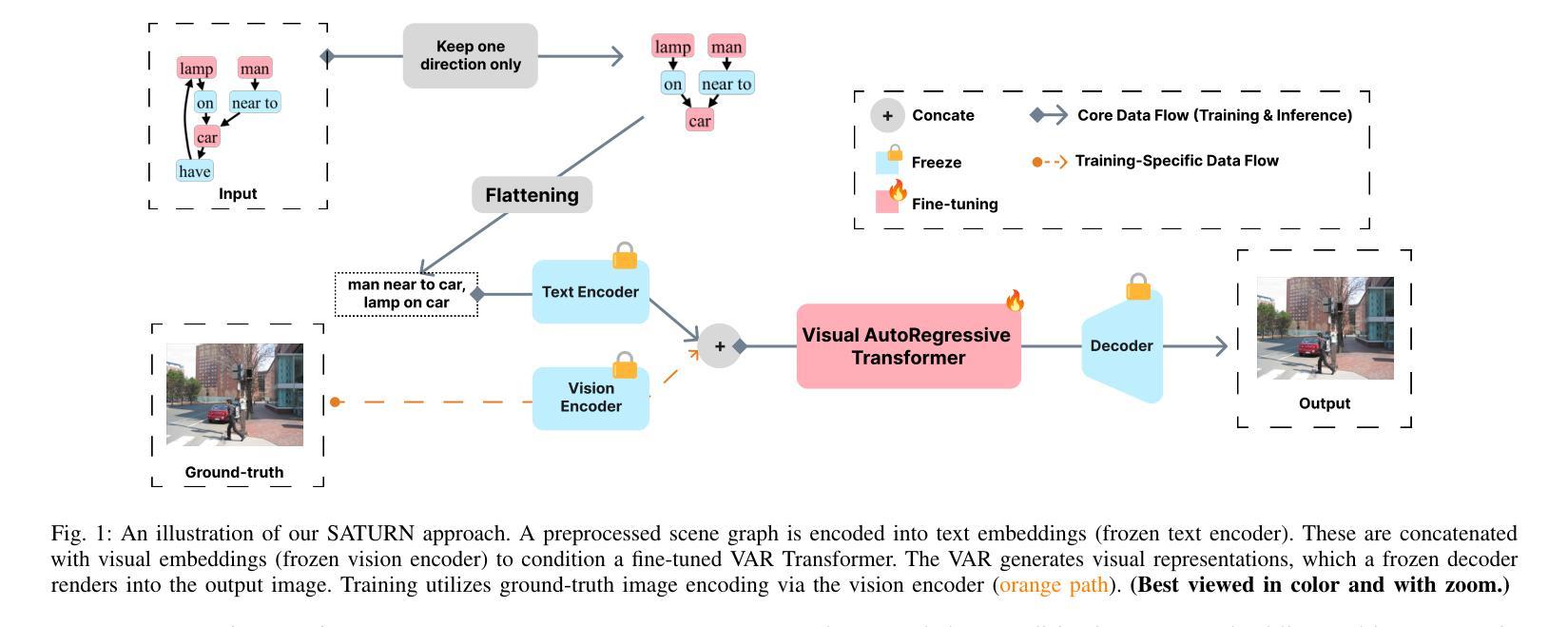
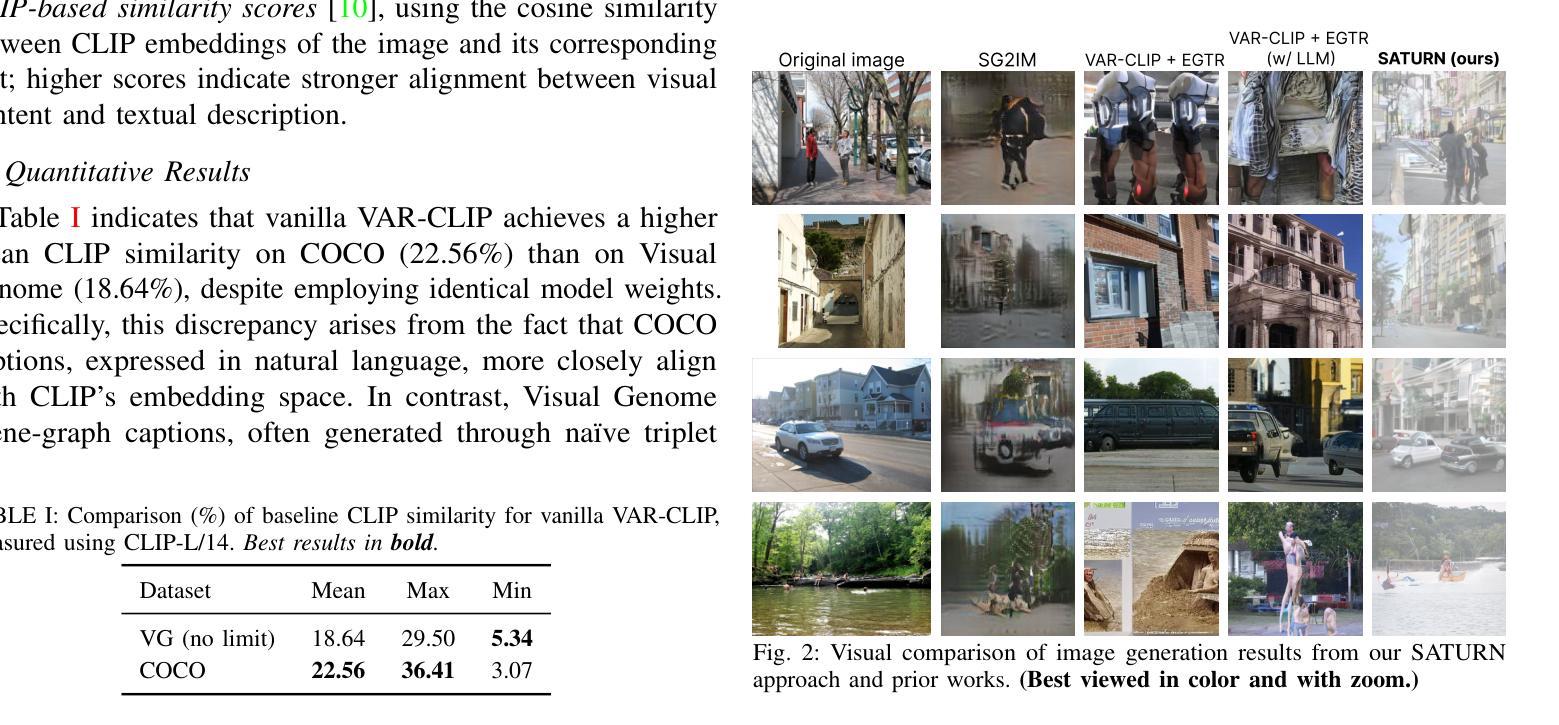
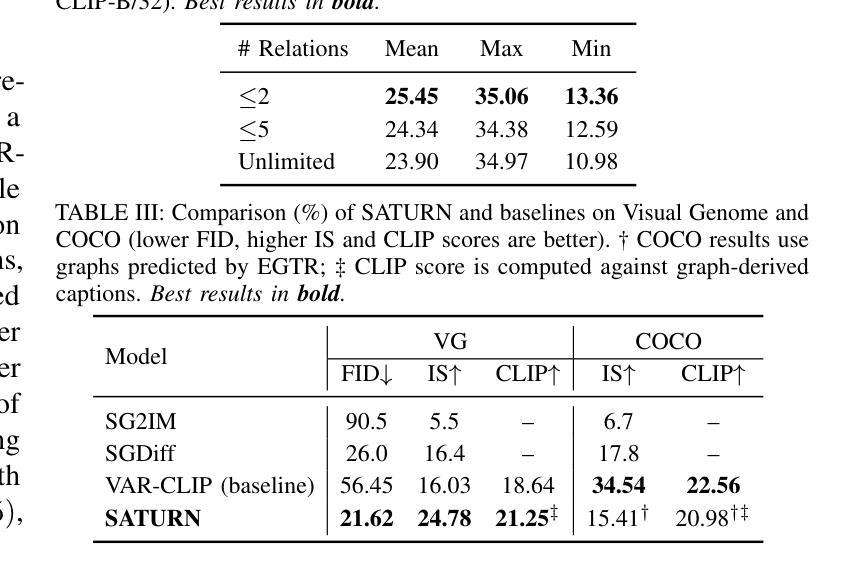
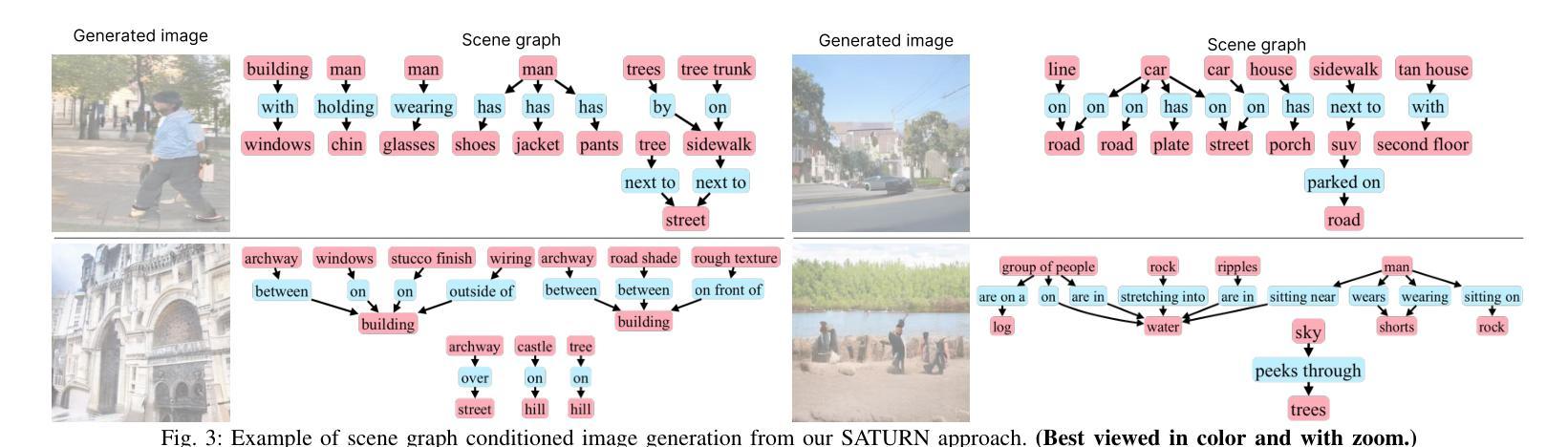
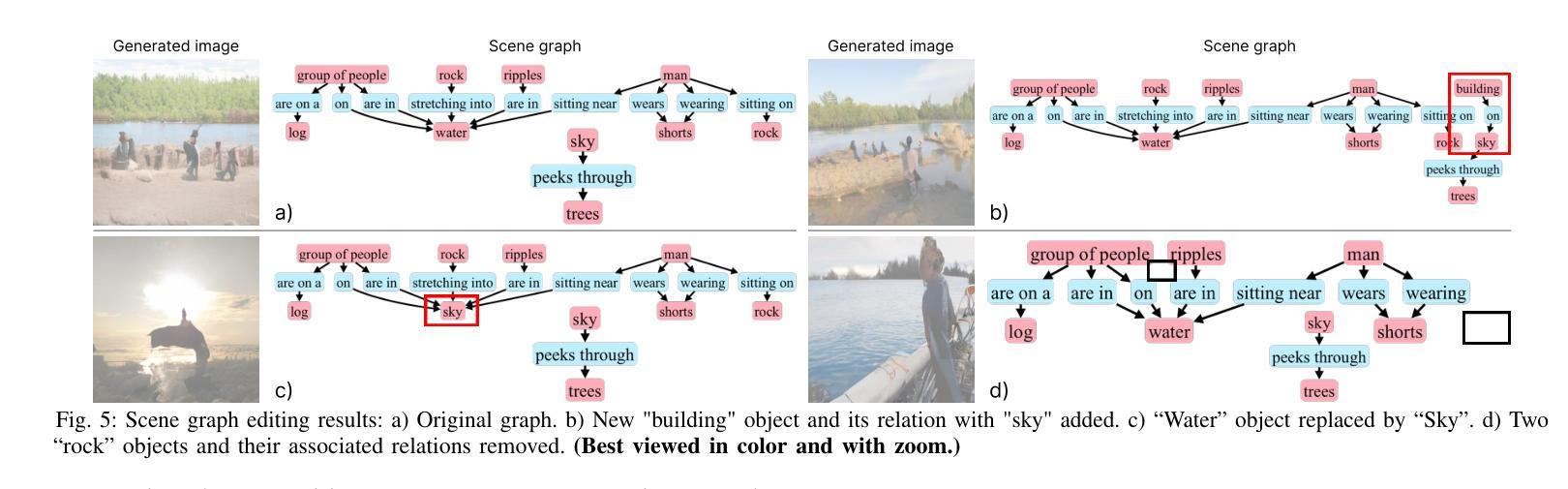
State-of-the-art text-to-image models excel at photorealistic rendering but often struggle to capture the layout and object relationships implied by complex prompts. Scene graphs provide a natural structural prior, yet previous graph-guided approaches have typically relied on heavy GAN or diffusion pipelines, which lag behind modern autoregressive architectures in both speed and fidelity. We introduce SATURN (Structured Arrangement of Triplets for Unified Rendering Networks), a lightweight extension to VAR-CLIP that translates a scene graph into a salience-ordered token sequence, enabling a frozen CLIP-VQ-VAE backbone to interpret graph structure while fine-tuning only the VAR transformer. On the Visual Genome dataset, SATURN reduces FID from 56.45% to 21.62% and increases the Inception Score from 16.03 to 24.78, outperforming prior methods such as SG2IM and SGDiff without requiring extra modules or multi-stage training. Qualitative results further confirm improvements in object count fidelity and spatial relation accuracy, showing that SATURN effectively combines structural awareness with state-of-the-art autoregressive fidelity.
当前最先进的文本到图像模型擅长于逼真渲染,但在处理复杂提示中隐含的布局和对象关系时常常遇到困难。场景图提供了一种自然的结构先验,但之前的图引导方法通常依赖于沉重的GAN或扩散管道,这在速度和保真度上都落后于现代的自回归架构。我们介绍了SATURN(用于统一渲染网络的三元组结构排列),这是VAR-CLIP的一个轻量级扩展,它将场景图翻译成显著性排序的令牌序列,允许冻结的CLIP-VQ-VAE主干在仅微调VAR变压器的情况下解释图形结构。在视觉基因组数据集上,SATURN将FID从56.45%降低到21.62%,并将Inception Score从16.03提高到24.78,超越了不需要额外模块或多阶段训练的SG2IM和SGDiff等之前的方法。定性结果进一步证实了对象计数保真度和空间关系准确度的提高,表明SATURN有效地将结构感知与最先进的自回归保真度相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MAPR 2025
Summary
本文提出SATURN模型,结合场景图生成有序令牌序列,使CLIP-VQ-VAE主干能够解读图形结构。相较于先前的图像生成模型,SATURN在保证高效和画质的同时,改善了布局和对象关系的捕捉。在Visual Genome数据集上,SATURN减少了FID得分并提高了Inception Score,验证了其优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- SATURN模型利用场景图生成有序令牌序列,提升了图像生成过程中对复杂提示的捕捉能力。
- SATURN模型结合了场景图的自然结构先验信息。
- SATURN模型相较于传统的图形引导方法,采用了更轻量级的扩展技术VAR-CLIP。
- SATURN模型在Visual Genome数据集上实现了更低的FID得分和更高的Inception Score,显示出其优越性。
- SATURN模型通过翻译场景图到令牌序列,使得CLIP-VQ-VAE主干能够解读图形结构。
- SATURN模型通过微调VAR变压器来优化性能,而无需对主干网络进行微调。
点此查看论文截图


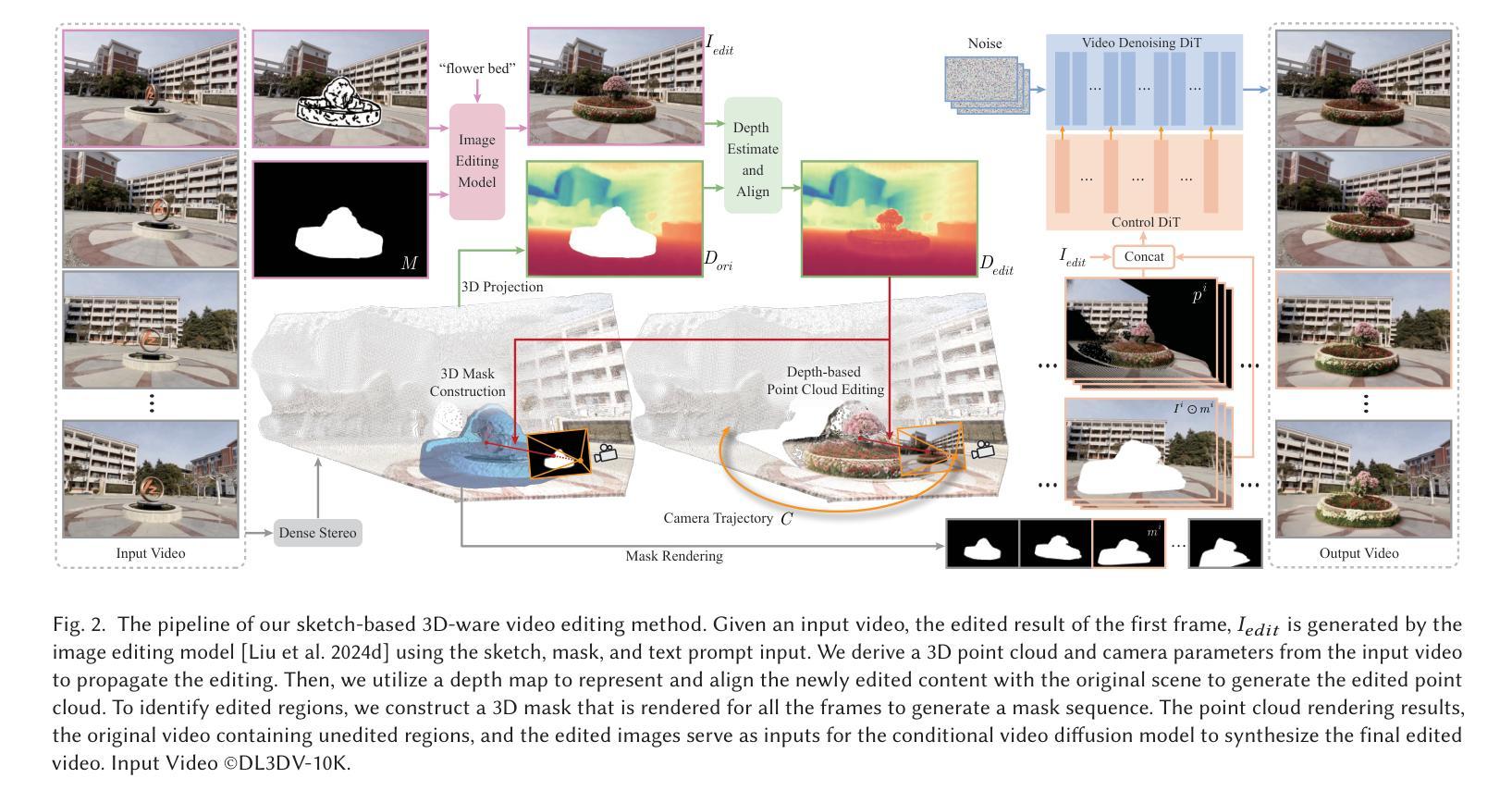
Sketch3DVE: Sketch-based 3D-Aware Scene Video Editing
Authors:Feng-Lin Liu, Shi-Yang Li, Yan-Pei Cao, Hongbo Fu, Lin Gao
Recent video editing methods achieve attractive results in style transfer or appearance modification. However, editing the structural content of 3D scenes in videos remains challenging, particularly when dealing with significant viewpoint changes, such as large camera rotations or zooms. Key challenges include generating novel view content that remains consistent with the original video, preserving unedited regions, and translating sparse 2D inputs into realistic 3D video outputs. To address these issues, we propose Sketch3DVE, a sketch-based 3D-aware video editing method to enable detailed local manipulation of videos with significant viewpoint changes. To solve the challenge posed by sparse inputs, we employ image editing methods to generate edited results for the first frame, which are then propagated to the remaining frames of the video. We utilize sketching as an interaction tool for precise geometry control, while other mask-based image editing methods are also supported. To handle viewpoint changes, we perform a detailed analysis and manipulation of the 3D information in the video. Specifically, we utilize a dense stereo method to estimate a point cloud and the camera parameters of the input video. We then propose a point cloud editing approach that uses depth maps to represent the 3D geometry of newly edited components, aligning them effectively with the original 3D scene. To seamlessly merge the newly edited content with the original video while preserving the features of unedited regions, we introduce a 3D-aware mask propagation strategy and employ a video diffusion model to produce realistic edited videos. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of Sketch3DVE in video editing. Homepage and code: http://http://geometrylearning.com/Sketch3DVE/
近期的视频编辑方法在风格转换或外观修改方面取得了吸引人的成果。然而,编辑3D场景的结构内容在视频中仍然具有挑战性,尤其是在处理重大的视角变化时,如大幅度的相机旋转或缩放。主要挑战包括生成与原始视频保持一致的新视角内容,保留未编辑的区域,以及将稀疏的2D输入转化为逼真的3D视频输出。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Sketch3DVE,一种基于草图的3D感知视频编辑方法,实现对视频在重大视角变化下的细节局部操作。为了解决稀疏输入带来的挑战,我们采用图像编辑方法为第一帧生成编辑结果,然后将其传播到视频的其余帧。我们使用草图作为一种交互工具来进行精确的几何控制,同时支持其他基于掩膜的图像编辑方法。为了处理视角变化,我们对视频中的3D信息进行了详细的分析和操作。具体来说,我们采用密集立体方法估计点云和输入视频的相机参数。然后,我们提出了一种点云编辑方法,使用深度图来表示新编辑组件的3D几何结构,有效地将它们与原始3D场景对齐。为了无缝融合新编辑内容与原始视频,同时保留未编辑区域的特点,我们采用了3D感知掩膜传播策略,并采用视频扩散模型来生成逼真的编辑视频。大量实验表明,Sketch3DVE在视频编辑方面的优越性。主页和代码:http://geometrylearning.com/Sketch3DVE/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于草图的三维视频编辑方法Sketch3DVE,解决了现有视频编辑方法在结构内容编辑上的挑战,尤其是在显著视点变化时的难题。通过生成新的视点内容并保持与原始视频的一致性,以及将稀疏的二维输入转化为逼真的三维视频输出,实现了详细的地方性操控。
Key Takeaways
- Sketch3DVE是一种基于草图的三维视频编辑方法,旨在解决在显著视点变化时的视频编辑挑战。
- 该方法利用图像编辑方法为第一帧生成编辑结果,并将其传播到视频的其余帧。
- Sketch3DVE使用草图作为交互工具进行精确的几何控制,并支持其他基于掩膜的图像编辑方法。
- 为了处理视点变化,该方法详细分析了视频的3D信息,并利用密集立体方法估计点云和输入视频的摄像机参数。
- Sketch3DVE采用点云编辑方法,使用深度图表示新编辑组件的三维几何结构,并将其与原始三维场景有效对齐。
- 该方法引入了一种三维感知掩膜传播策略,并利用视频扩散模型生成逼真的编辑视频,实现无缝融合新内容与原始视频。
点此查看论文截图


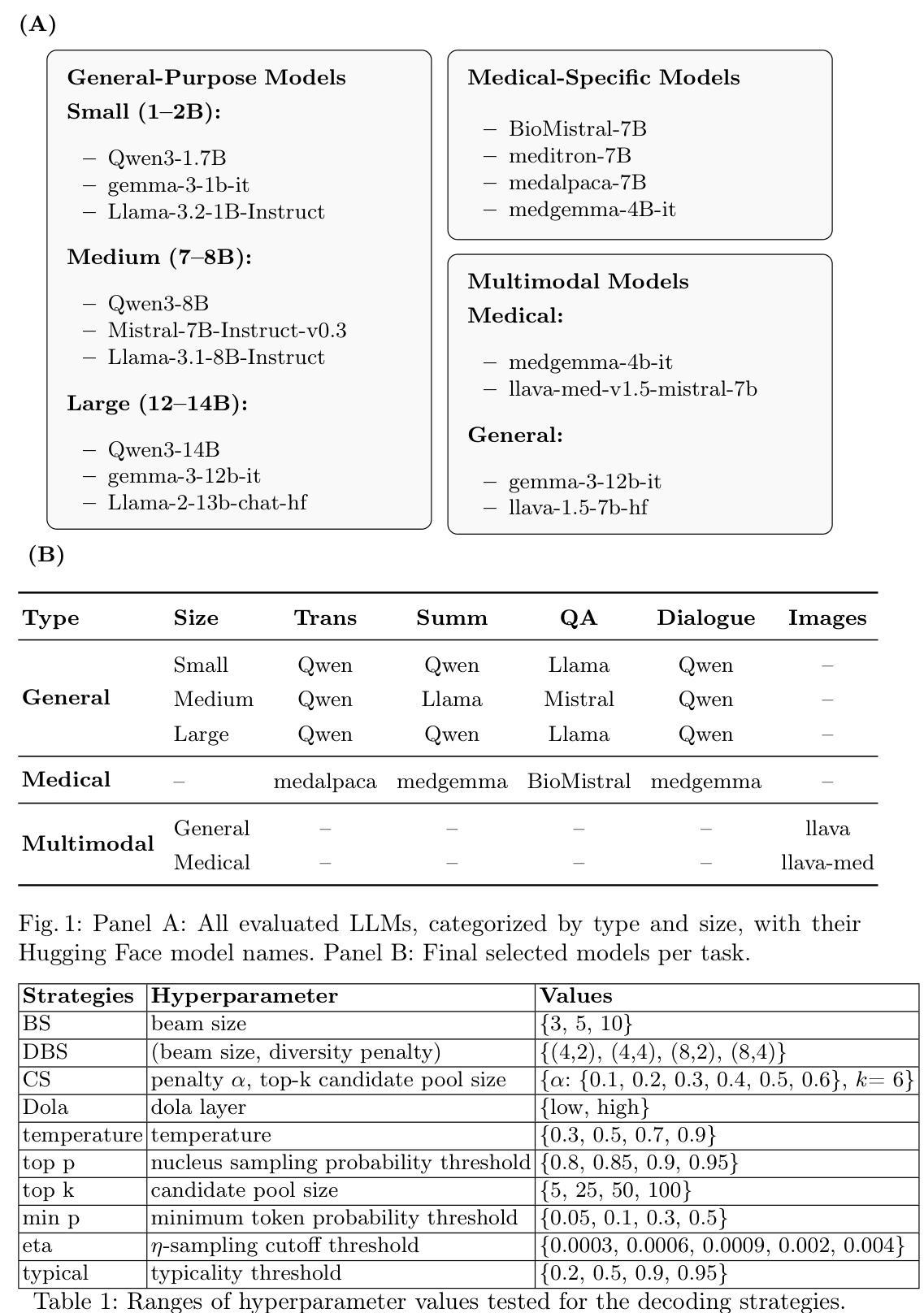
A Comparative Study of Decoding Strategies in Medical Text Generation
Authors:Oriana Presacan, Alireza Nik, Vajira Thambawita, Bogdan Ionescu, Michael Riegler
Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on various decoding strategies to generate text, and these choices can significantly affect output quality. In healthcare, where accuracy is critical, the impact of decoding strategies remains underexplored. We investigate this effect in five open-ended medical tasks, including translation, summarization, question answering, dialogue, and image captioning, evaluating 11 decoding strategies with medically specialized and general-purpose LLMs of different sizes. Our results show that deterministic strategies generally outperform stochastic ones: beam search achieves the highest scores, while {\eta} and top-k sampling perform worst. Slower decoding methods tend to yield better quality. Larger models achieve higher scores overall but have longer inference times and are no more robust to decoding. Surprisingly, while medical LLMs outperform general ones in two of the five tasks, statistical analysis shows no overall performance advantage and reveals greater sensitivity to decoding choice. We further compare multiple evaluation metrics and find that correlations vary by task, with MAUVE showing weak agreement with BERTScore and ROUGE, as well as greater sensitivity to the decoding strategy. These results highlight the need for careful selection of decoding methods in medical applications, as their influence can sometimes exceed that of model choice.
大型语言模型(LLM)依赖于各种解码策略来生成文本,这些选择会显著影响输出质量。在关键精度要求的医疗领域,解码策略的影响仍然未得到充分探索。我们在五个开放医疗任务中调查了这种影响,包括翻译、摘要、问答、对话和图像描述,评估了不同规模的医疗专用和通用LLM的11种解码策略。我们的结果表明,确定性策略通常优于随机策略:集束搜索得分最高,而η和top-k采样表现最差。较慢的解码方法往往产生更高质量的结果。总体而言,更大的模型得分更高,但推理时间较长,对解码的鲁棒性并不强。令人惊讶的是,虽然医疗LLM在五个任务中的两个上表现优于通用LLM,但统计分析并未显示出整体性能优势,并显示出对解码选择的更大敏感性。我们进一步比较了多个评价指标,发现各项指标的相关性因任务而异。MAUVE与BERTScore和ROUGE的协议较弱,并且对解码策略更加敏感。这些结果强调了医疗应用中解码方法的仔细选择必要性,因为他们的有时超过模型选择的决策的影响可能更长远。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的解码策略对文本生成质量有重要影响,特别是在医疗领域。研究者在五个医疗任务中评估了11种解码策略,发现确定性策略通常优于随机性策略,慢速解码方法往往能产出更高质量的结果。大型模型总体得分较高,但推理时间较长,对解码的稳健性并无提升。医疗专用LLM在某些任务上表现较好,但总体性能并无显著优势,且对解码选择更为敏感。评价指标的适用性因任务而异,其中MAUVE对解码策略的敏感性较高。因此,在医疗应用中需慎重选择解码方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的解码策略对文本生成质量有重要影响。
- 确定性策略(如beam search)通常优于随机性策略。
- 慢速解码方法能产出更高质量的结果。
- 大型模型总体得分较高,但推理时间较长,对解码稳健性没有提升。
- 医疗专用LLM在某些任务上表现较好,但总体性能并无显著优势。
- 医疗领域的LLM对解码选择更为敏感。
- 不同评价指标的适用性因任务而异,需根据实际情况选择适合的指标。
点此查看论文截图

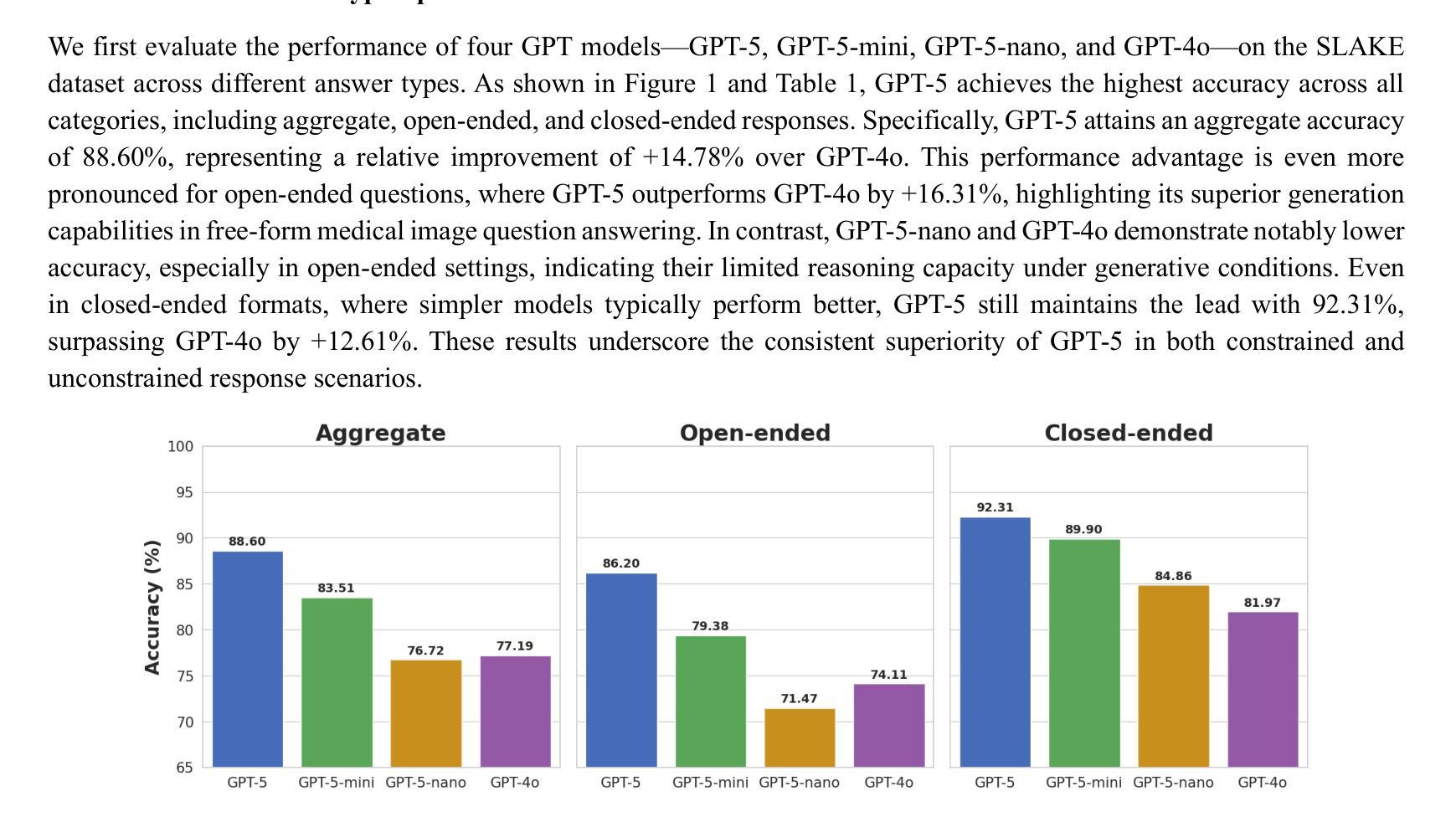
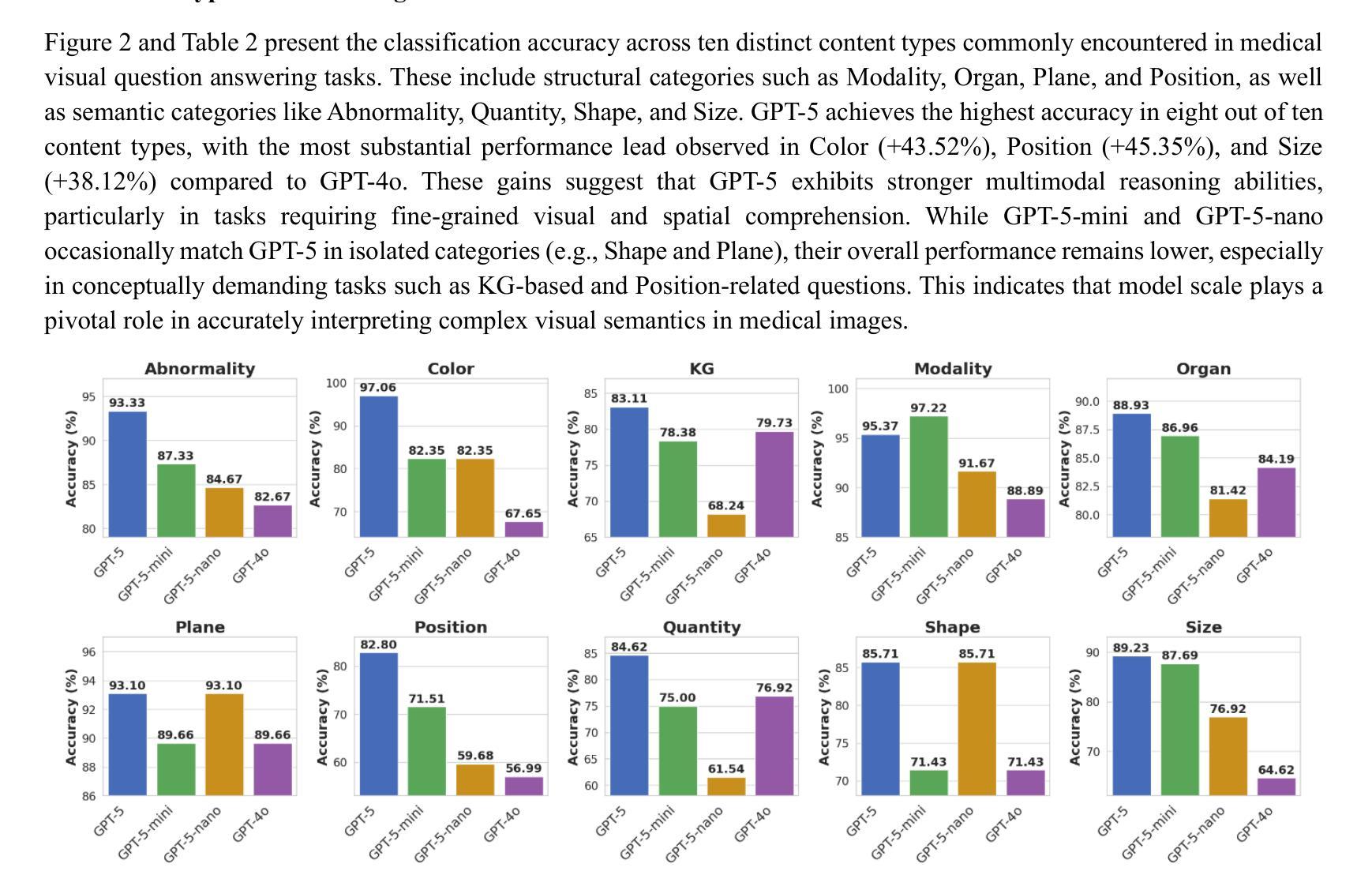
Benchmarking GPT-5 for Zero-Shot Multimodal Medical Reasoning in Radiology and Radiation Oncology
Authors:Mingzhe Hu, Zach Eidex, Shansong Wang, Mojtaba Safari, Qiang Li, Xiaofeng Yang
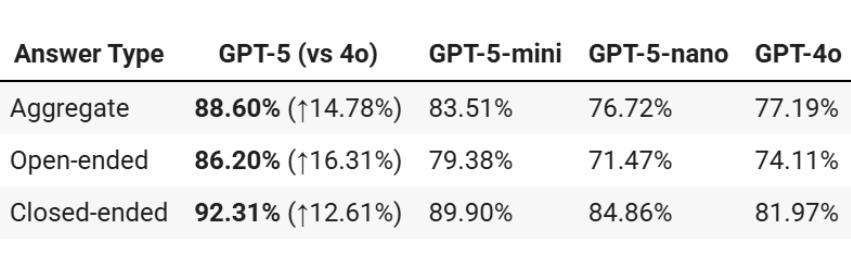
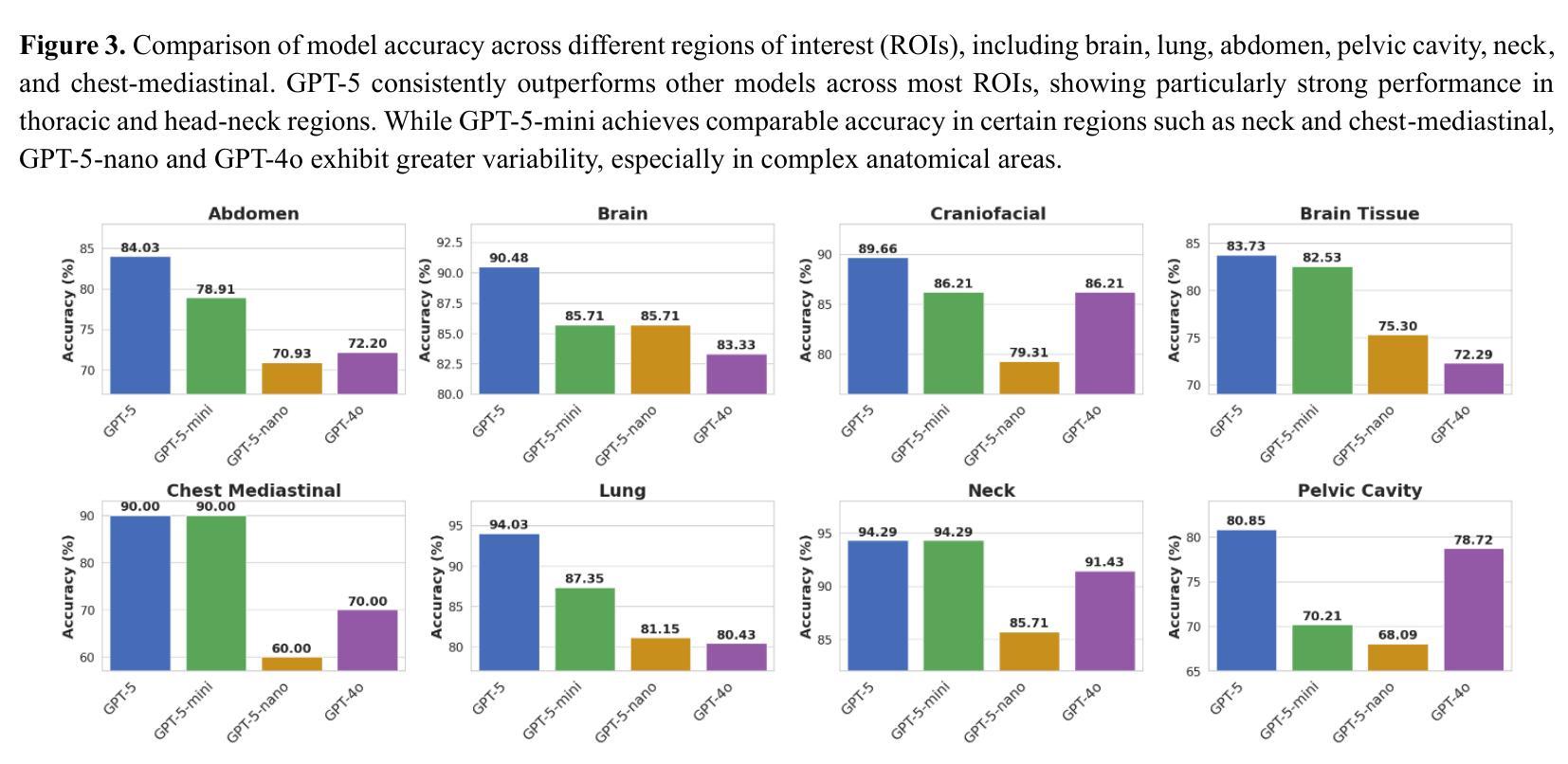
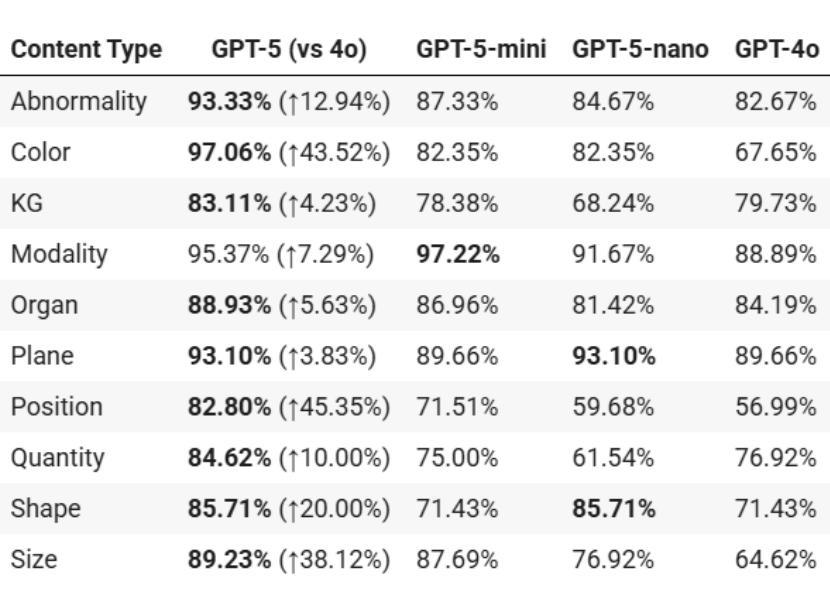
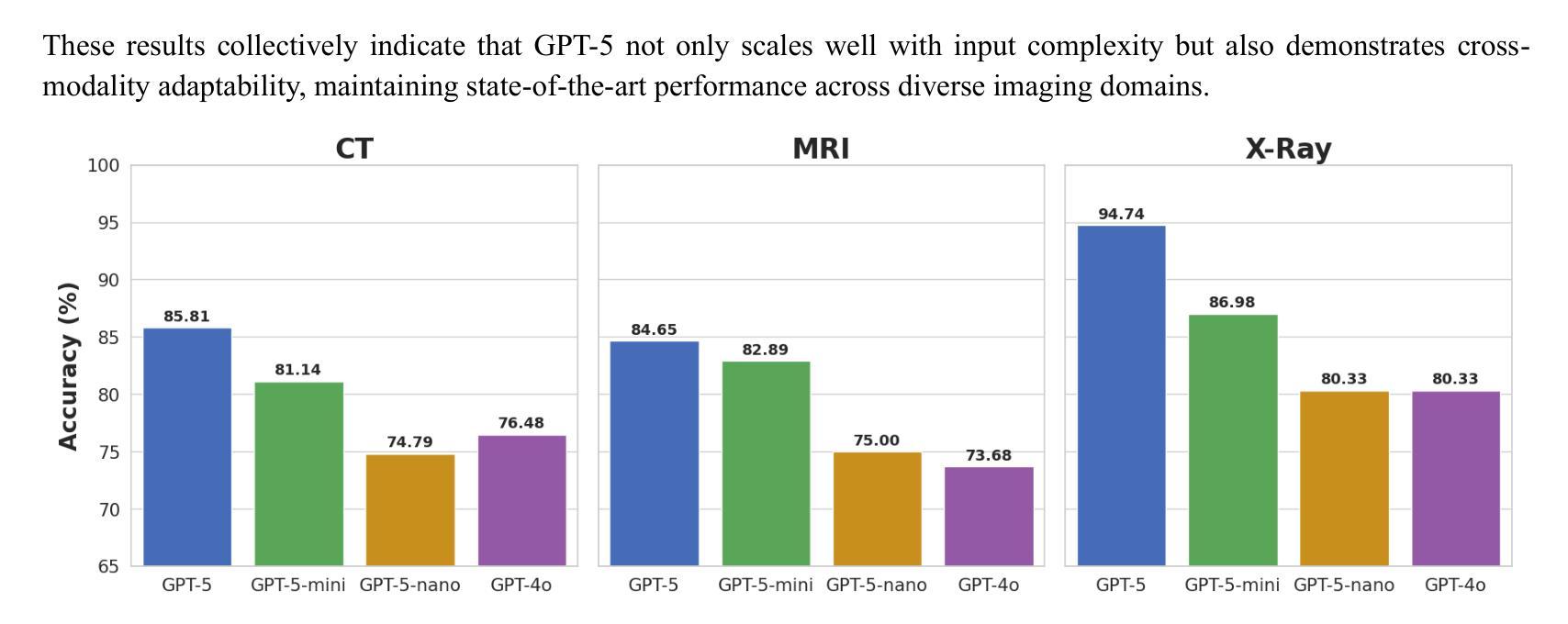
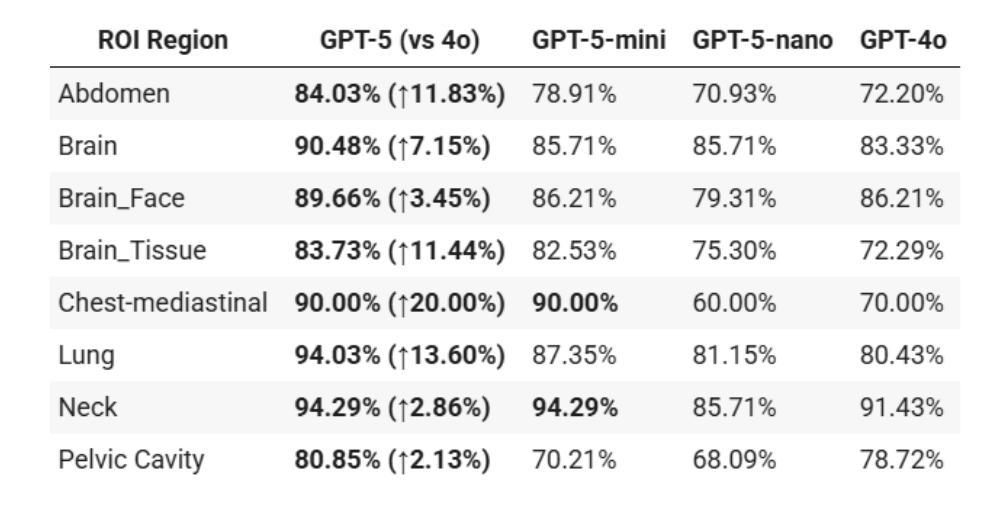
Radiology, radiation oncology, and medical physics require decision-making that integrates medical images, textual reports, and quantitative data under high-stakes conditions. With the introduction of GPT-5, it is critical to assess whether recent advances in large multimodal models translate into measurable gains in these safety-critical domains. We present a targeted zero-shot evaluation of GPT-5 and its smaller variants (GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano) against GPT-4o across three representative tasks. We present a targeted zero-shot evaluation of GPT-5 and its smaller variants (GPT-5-mini, GPT-5-nano) against GPT-4o across three representative tasks: (1) VQA-RAD, a benchmark for visual question answering in radiology; (2) SLAKE, a semantically annotated, multilingual VQA dataset testing cross-modal grounding; and (3) a curated Medical Physics Board Examination-style dataset of 150 multiple-choice questions spanning treatment planning, dosimetry, imaging, and quality assurance. Across all datasets, GPT-5 achieved the highest accuracy, with substantial gains over GPT-4o up to +20.00% in challenging anatomical regions such as the chest-mediastinal, +13.60% in lung-focused questions, and +11.44% in brain-tissue interpretation. On the board-style physics questions, GPT-5 attained 90.7% accuracy (136/150), exceeding the estimated human passing threshold, while GPT-4o trailed at 78.0%. These results demonstrate that GPT-5 delivers consistent and often pronounced performance improvements over GPT-4o in both image-grounded reasoning and domain-specific numerical problem-solving, highlighting its potential to augment expert workflows in medical imaging and therapeutic physics.
放射学、放射肿瘤学和医学物理需要在高风险的条件下,整合医学图像、文本报告和定量数据来进行决策。随着GPT-5的推出,评估近期大型多模式模型的进展是否能为这些安全关键领域带来可衡量的收益至关重要。我们针对GPT-5及其小型变体(GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano)与GPT-4o进行了三项代表性任务的零样本评估。三项代表性任务包括:(1)VQA-RAD,用于放射学中视觉问答的基准测试;(2)SLAKE,一个语义注释、多语言问答数据集,测试跨模态定位能力;(3)包含150道治疗计划、剂量测定、成像和质量保证等多选题目的医学物理委员会考试风格数据集。在所有数据集中,GPT-5的准确率最高,与GPT-4o相比,其在具有挑战性的解剖区域如胸部纵隔区域有高达+20.0%的提升,+13.6%在肺部相关问题以及+11.44%在脑组织解读方面。在物理板考试风格的题目上,GPT-5达到了90.7%(共136题正确),超过了人类预估的及格门槛,而GPT-4o只有78%。这些结果表明,GPT-5在图像支持推理和特定领域的数值问题解决方面较GPT-4o有着一致且显著的改进,这突显了其在医学影像和治疗物理学中增强专家工作流程的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GPT-5在放射学、放疗和医学物理领域表现出强大的性能。在三项代表性任务中,GPT-5及其小型变体(GPT-5-mini、GPT-5-nano)相较于GPT-4o,展现了更高的准确性和性能提升。GPT-5在视觉问答、跨模态定位和医学物理考试风格问题上的表现尤其出色。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-5在医学图像、文本报告和定量数据决策中展现出强大的集成能力。
- GPT-5及其小型变体在放射学、放疗和医学物理领域进行了评估。
- GPT-5在三项代表性任务中的表现优于GPT-4o,包括视觉问答、跨模态定位以及医学物理考试风格问题。
- GPT-5在具有挑战性的解剖区域(如胸部、肺部和脑组织)的解读中表现出显著的提升。
- GPT-5在医学成像和治疗物理领域具有潜在的增强作用,能够辅助专家工作流。
- GPT-5在医疗物理板考试风格问题上的准确率达到90.7%(136/150),超过了人类通过预估的阈值。
点此查看论文截图

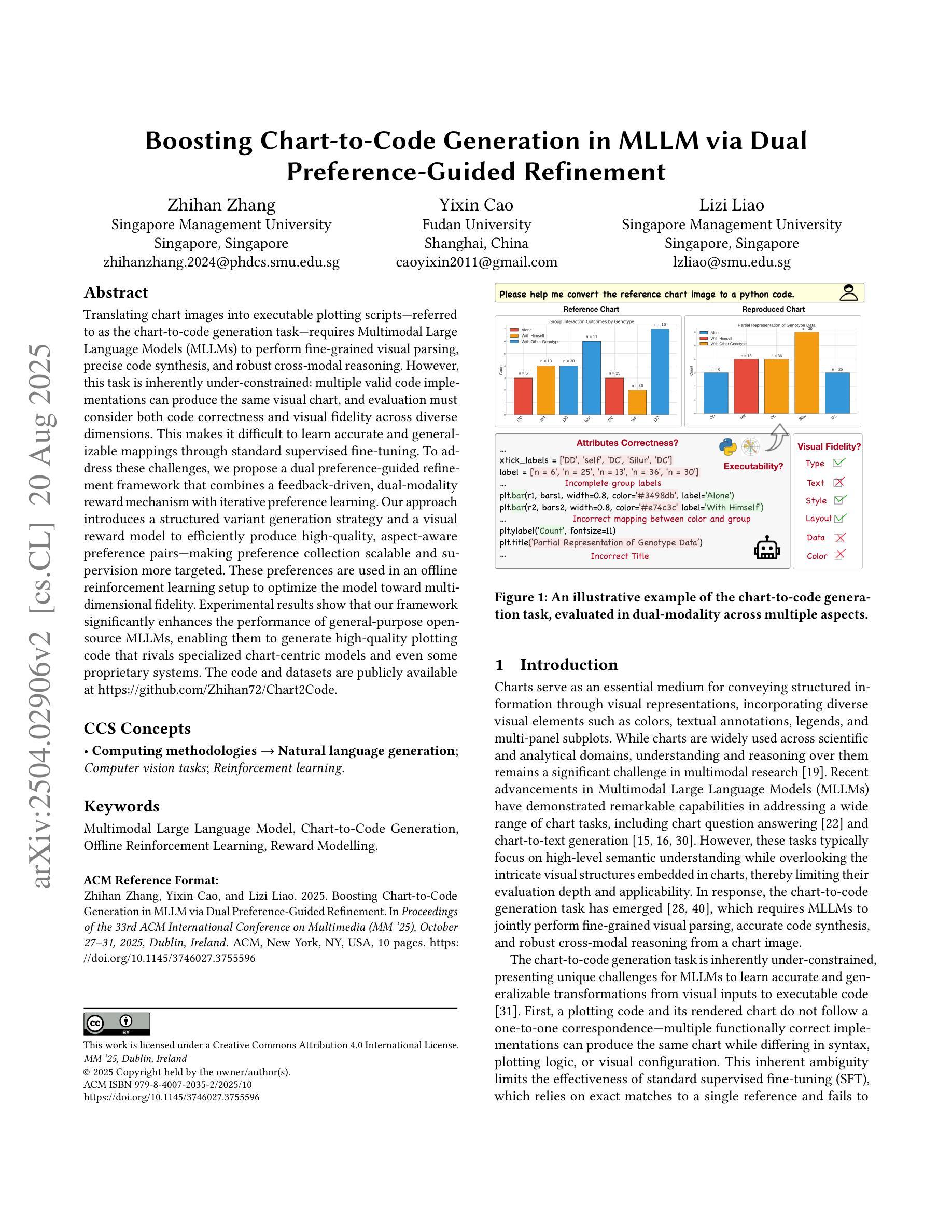
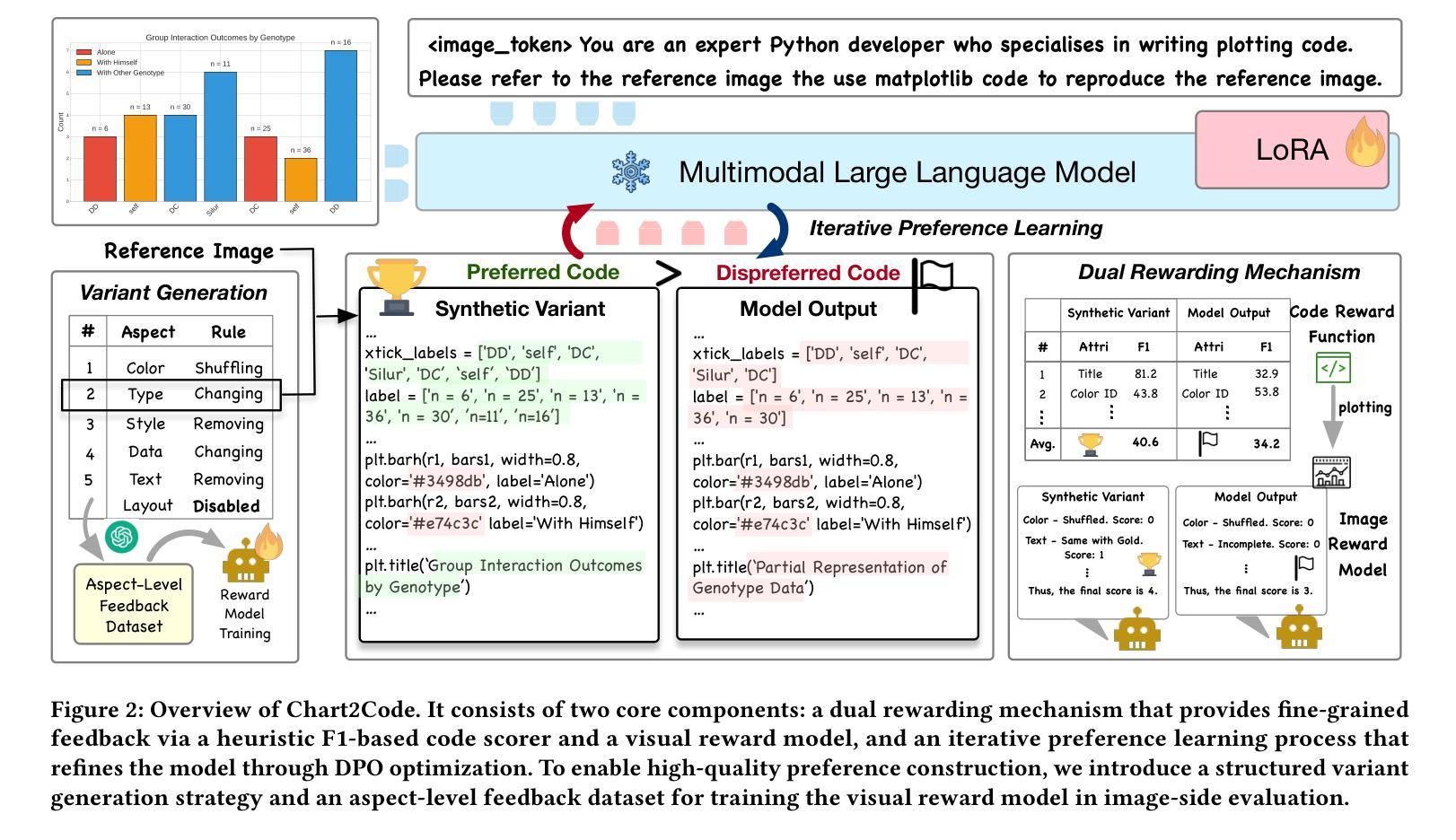
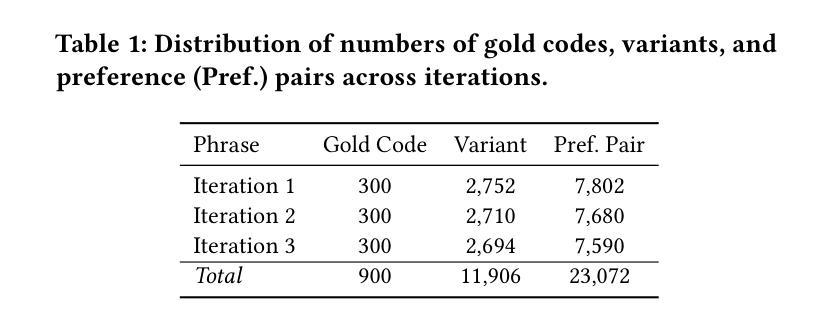
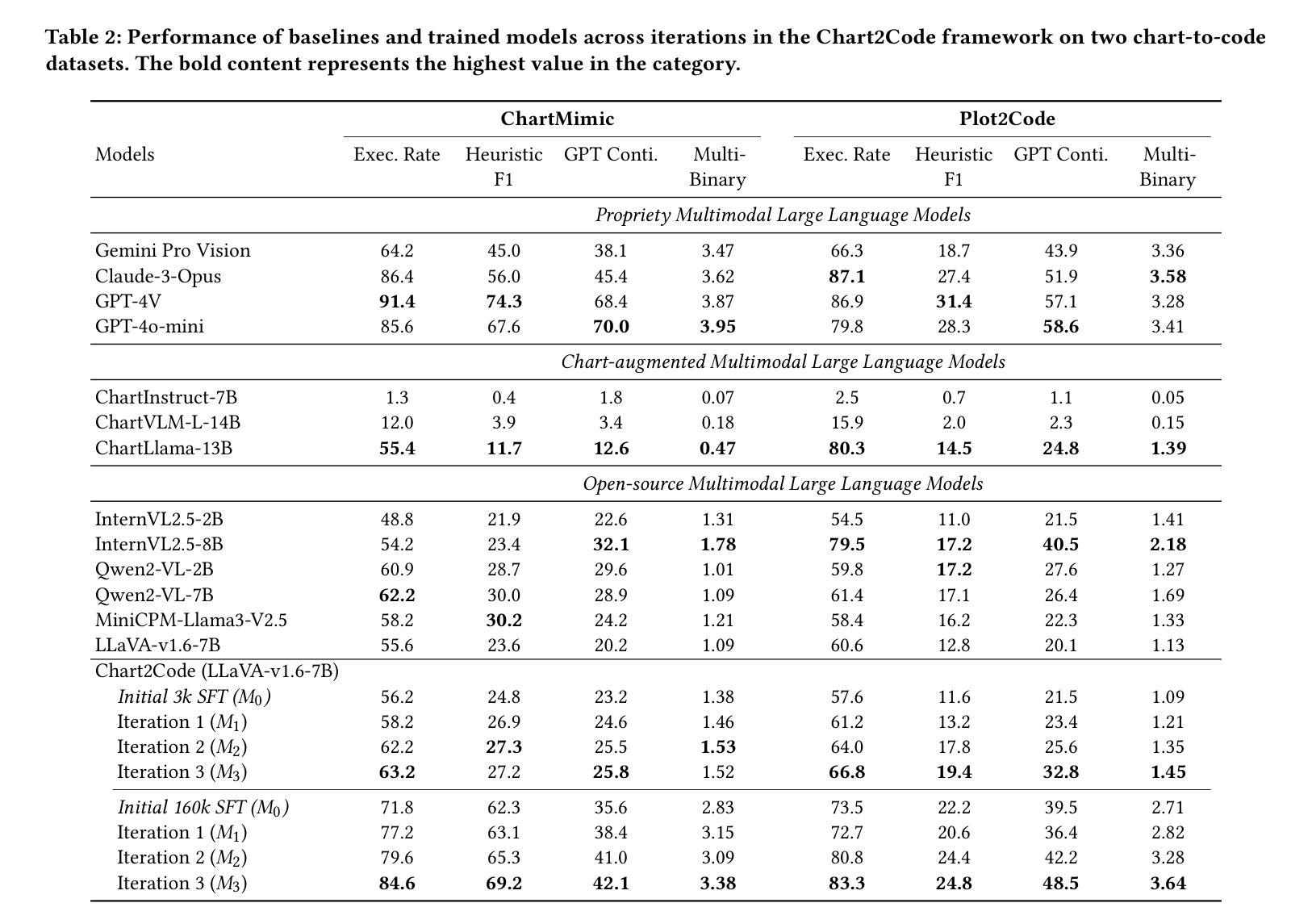
Boosting Chart-to-Code Generation in MLLM via Dual Preference-Guided Refinement
Authors:Zhihan Zhang, Yixin Cao, Lizi Liao
Translating chart images into executable plotting scripts-referred to as the chart-to-code generation task-requires Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform fine-grained visual parsing, precise code synthesis, and robust cross-modal reasoning. However, this task is inherently under-constrained: multiple valid code implementations can produce the same visual chart, and evaluation must consider both code correctness and visual fidelity across diverse dimensions. This makes it difficult to learn accurate and generalizable mappings through standard supervised fine-tuning. To address these challenges, we propose a dual preference-guided refinement framework that combines a feedback-driven, dual-modality reward mechanism with iterative preference learning. Our approach introduces a structured variant generation strategy and a visual reward model to efficiently produce high-quality, aspect-aware preference pairs-making preference collection scalable and supervision more targeted. These preferences are used in an offline reinforcement learning setup to optimize the model toward multi-dimensional fidelity. Experimental results show that our framework significantly enhances the performance of general-purpose open-source MLLMs, enabling them to generate high-quality plotting code that rivals specialized chart-centric models and even some proprietary systems. The code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/Zhihan72/Chart2Code.
将图表图像翻译成可执行的绘图脚本,称为图表到代码生成任务,这需要多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)执行精细的视觉解析、精确的代码合成和稳健的跨模态推理。然而,这个任务本质上是欠约束的:多个有效的代码实现可以产生相同的视觉图表,评估必须考虑代码的正确性和跨多个维度的视觉保真度。这使得通过标准的有监督微调学习准确和通用的映射变得困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种双重偏好引导细化框架,该框架结合了反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制与迭代偏好学习。我们的方法引入了结构化变体生成策略和视觉奖励模型,以有效地产生高质量的、方面感知的偏好对,使偏好收集可扩展,监督更有针对性。这些偏好值用于离线强化学习设置,以优化模型的多维保真度。实验结果表明,我们的框架显著提高了通用开源MLLM的性能,使它们能够生成高质量的绘图代码,与专门的图表中心模型甚至某些专有系统相竞争。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/Zhihan72/Chart2Code公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
图表图像转化为可执行的绘图脚本(图表转代码生成任务)需要多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)执行精细的视解析、精确的编码合成以及强大的跨模态推理。面对挑战,提出一种双重偏好引导细化框架,该框架结合了反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制和迭代偏好学习。通过结构化变体生成策略和视觉奖励模型,能高效生成高质量、面向方面的偏好对,使偏好收集更具规模性、监督更具针对性。偏好被用于线下强化学习设置中,优化模型以实现多维保真度。实验结果表明,该框架能显著提升通用开源MLLMs的性能,生成高质量的绘图代码,与专业图表模型甚至某些专有系统相比有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)需执行精细视觉解析、精确代码合成和跨模态推理以完成图表图像到绘图脚本的翻译。
- 图表转代码生成任务具有内在的不确定性,因为多种有效代码实现可生成相同图表。
- 评估需考虑代码正确性和视觉保真度在不同维度上的表现。
- 标准监督微调难以学习准确且通用的映射。
- 提出了一种双重偏好引导细化框架,结合反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制和迭代偏好学习来应对这些挑战。
- 通过结构化变体生成策略和视觉奖励模型,该框架能高效生成高质量、面向方面的偏好对。
点此查看论文截图
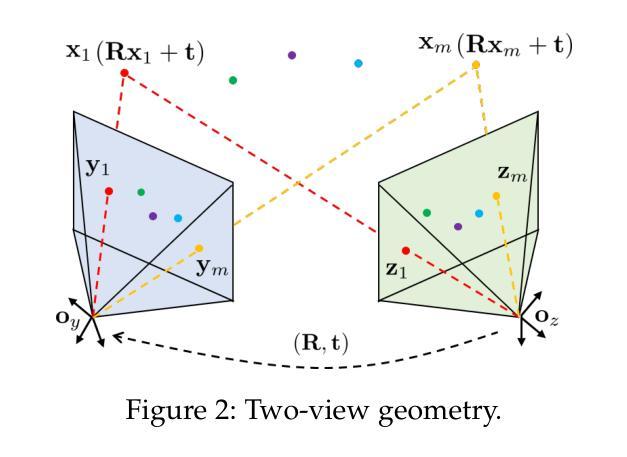
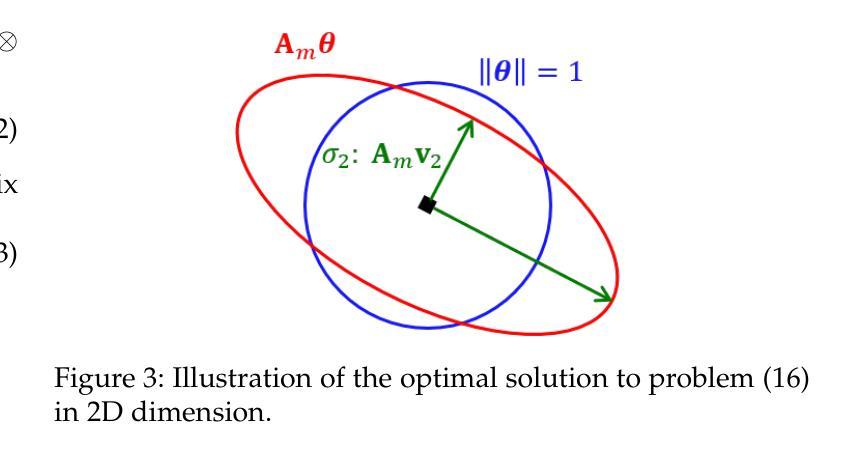
Consistent and Optimal Solution to Camera Motion Estimation
Authors:Guangyang Zeng, Qingcheng Zeng, Xinghan Li, Biqiang Mu, Jiming Chen, Ling Shi, Junfeng Wu
Given 2D point correspondences between an image pair, inferring the camera motion is a fundamental issue in the computer vision community. The existing works generally set out from the epipolar constraint and estimate the essential matrix, which is not optimal in the maximum likelihood (ML) sense. In this paper, we dive into the original measurement model with respect to the rotation matrix and normalized translation vector and formulate the ML problem. We then propose a two-step algorithm to solve it: In the first step, we estimate the variance of measurement noises and devise a consistent estimator based on bias elimination; In the second step, we execute a one-step Gauss-Newton iteration on manifold to refine the consistent estimate. We prove that the proposed estimate owns the same asymptotic statistical properties as the ML estimate: The first is consistency, i.e., the estimate converges to the ground truth as the point number increases; The second is asymptotic efficiency, i.e., the mean squared error of the estimate converges to the theoretical lower bound – Cramer-Rao bound. In addition, we show that our algorithm has linear time complexity. These appealing characteristics endow our estimator with a great advantage in the case of dense point correspondences. Experiments on both synthetic data and real images demonstrate that when the point number reaches the order of hundreds, our estimator outperforms the state-of-the-art ones in terms of estimation accuracy and CPU time.
针对图像对之间的2D点对应关系,推断相机运动是计算机视觉领域的一个基本问题。现有工作通常基于极线约束估计基础矩阵,但在最大似然(ML)意义上并不最优。本文深入原始测量模型,涉及旋转矩阵和归一化平移向量,并构建ML问题。然后,我们提出两步算法来解决这个问题:第一步,我们估计测量噪声的方差,并基于偏差消除设计一致估计器;第二步,我们在流形上执行一步高斯-牛顿迭代,以改进一致估计。我们证明所提出估计量与ML估计具有相同的渐近统计属性:第一是一致性,即随着点数的增加,估计量收敛到真实值;第二是渐近效率,即估计量的均方误差收敛到理论下限——Cramer-Rao界。此外,我们展示了我们的算法具有线性时间复杂度。这些吸引人的特点使我们的估计器在密集点对应情况下具有很大优势。在合成数据和真实图像上的实验表明,当点数达到数百时,我们的估计器在估计精度和CPU时间上优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures
Summary
基于二维点对应关系的图像对,推断相机运动是计算机视觉领域的一个基本问题。本文深入原始测量模型,针对旋转矩阵和归一化平移向量建立最大似然问题,并提出两步算法求解。第一步估计测量噪声方差,基于偏差消除设计一致估计器;第二步在流形上执行一步高斯-牛顿迭代,对一致估计进行精细化处理。本文证明所提估计器与最大似然估计具有相同的渐近统计属性,包括一致性和渐近效率。此外,本文还展示了所提算法具有线性时间复杂度。实验结果表明,在点数目达到数百时,所提估计器在估计精度和CPU时间方面均优于现有最佳方法。
Key Takeaways
- 论文从二维点对应关系出发,探讨计算机视觉中相机运动推断问题。
- 提出基于旋转矩阵和归一化平移向量的最大似然问题解决方案。
- 设计两步算法进行求解:第一步估计测量噪声方差并设计一致估计器;第二步通过高斯-牛顿迭代优化一致估计。
- 证明所提估计器具有一致性和渐近效率等渐近统计属性。
- 展示所提算法具有线性时间复杂度。
- 实验结果表明,在点数目较多时,所提估计器在估计精度和计算效率方面均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图